Page 1
CAS Calculators
Sean Surratt
TECM 2700
July 3, 2013
Page 2

Page 3

Table of Contents 3
Table of Contents
Table of Contents ............................................................................ 3
Introduction .................................................................................... 5
Basics ...............................................................................................7
Exact and Approximate Results .................................................. 9
Trig Functions ............................................................................. 9
Shortcut Keys .............................................................................10
Syntax .........................................................................................10
Understanding Variables ........................................................... 11
Storing Variables .................................................................... 11
Deleting Variables .................................................................. 11
Variable Naming Conventions................................................ 11
Symbolic Math ............................................................................... 13
Symbolic Algebra ....................................................................... 15
Solving Equations ................................................................... 15
Factoring Expressions ............................................................ 15
Understanding Units .................................................................. 16
Unit Conventions .................................................................... 16
Unit Operations ...................................................................... 16
Symbolic Calculus ...................................................................... 17
Matrix/Vector/List ........................................................................ 19
Matrix ......................................................................................... 21
Creating a Matrix .................................................................... 21
Manipulating a Matrix ............................................................ 21
Matrix Operations .................................................................. 21
Vector ........................................................................................ 22
Vector Operations .................................................................. 22
Page 4

4 CAS Calculators
Lists ........................................................................................... 22
Creating Lists ......................................................................... 22
Manipulating Lists ................................................................. 23
List Operations ...................................................................... 23
Introduction to Programming ...................................................... 25
Programs Make Life Easier ....................................................... 27
Make a Simple Program ............................................................ 27
Index ............................................................................................. 29
Page 5

Introduction 5
Introduction
This document will focus on the Texas Instruments nspire cx CAS
calculator. The ability to use a Calculator with a Computer Algebra
System is fundamental to be a successful engineering student
today. CAS calculators can solve long equations just by typing
them in and hitting solve. Students unskilled with this tool are at a
significant disadvantage. The best resource to learn about the TI
CAS is the TI nspire guidebook. For some the guidebook has a
steep learning curve. Reading this quick reference manual will
help lower the curve.
To download the guidebook visit the TI website at:
education.ti.com/en/us/guidebook/search/ti-nspire-cas
Page 6

Page 7

Basics
TI-nspire CX CAS 1
Page 8

Page 9
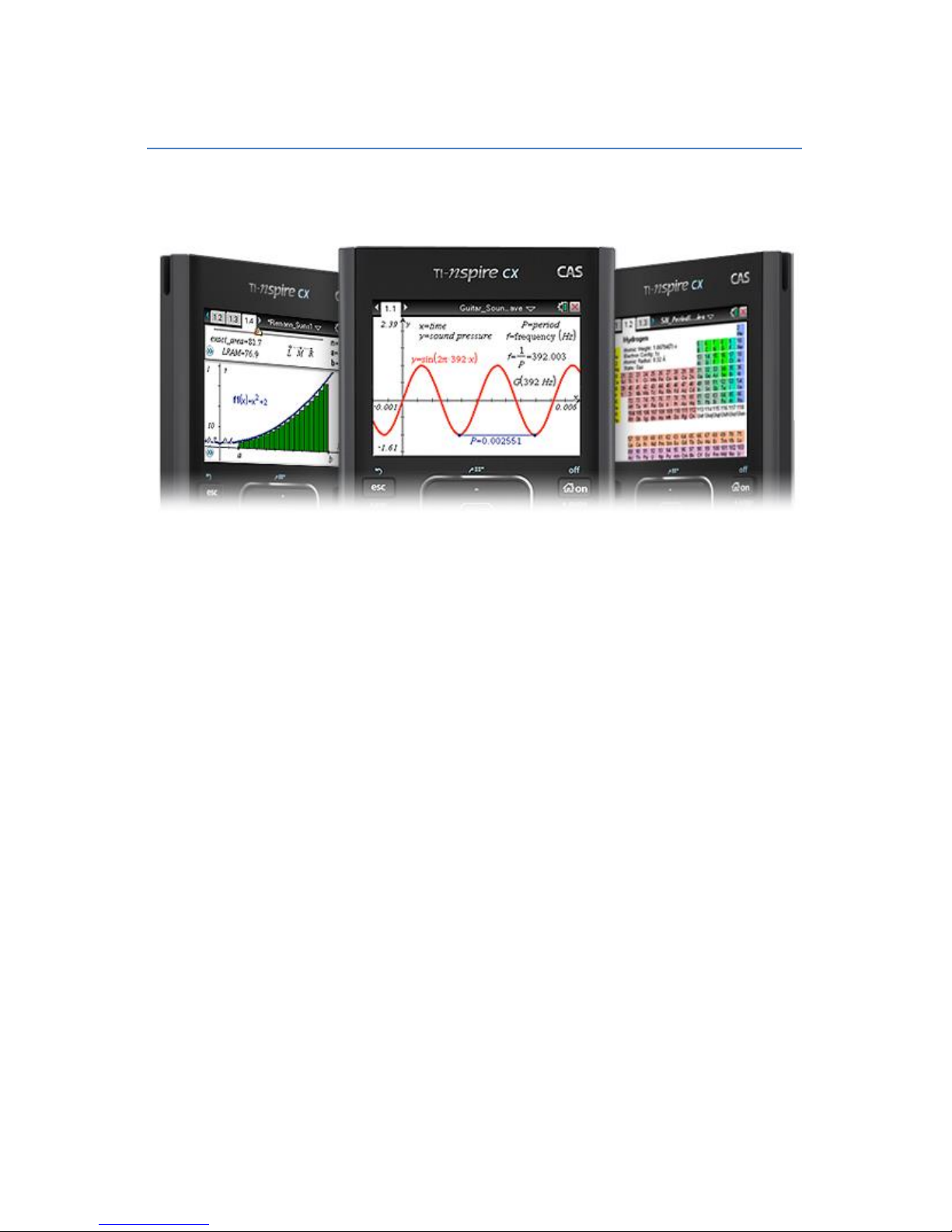
Basics 9
Exact and Approximate Results
Results that are not whole numbers will automatically be shown in
a fractional or symbolic form. An exact result is a fraction and an
approximate result is a decimal.
Nspire Example I
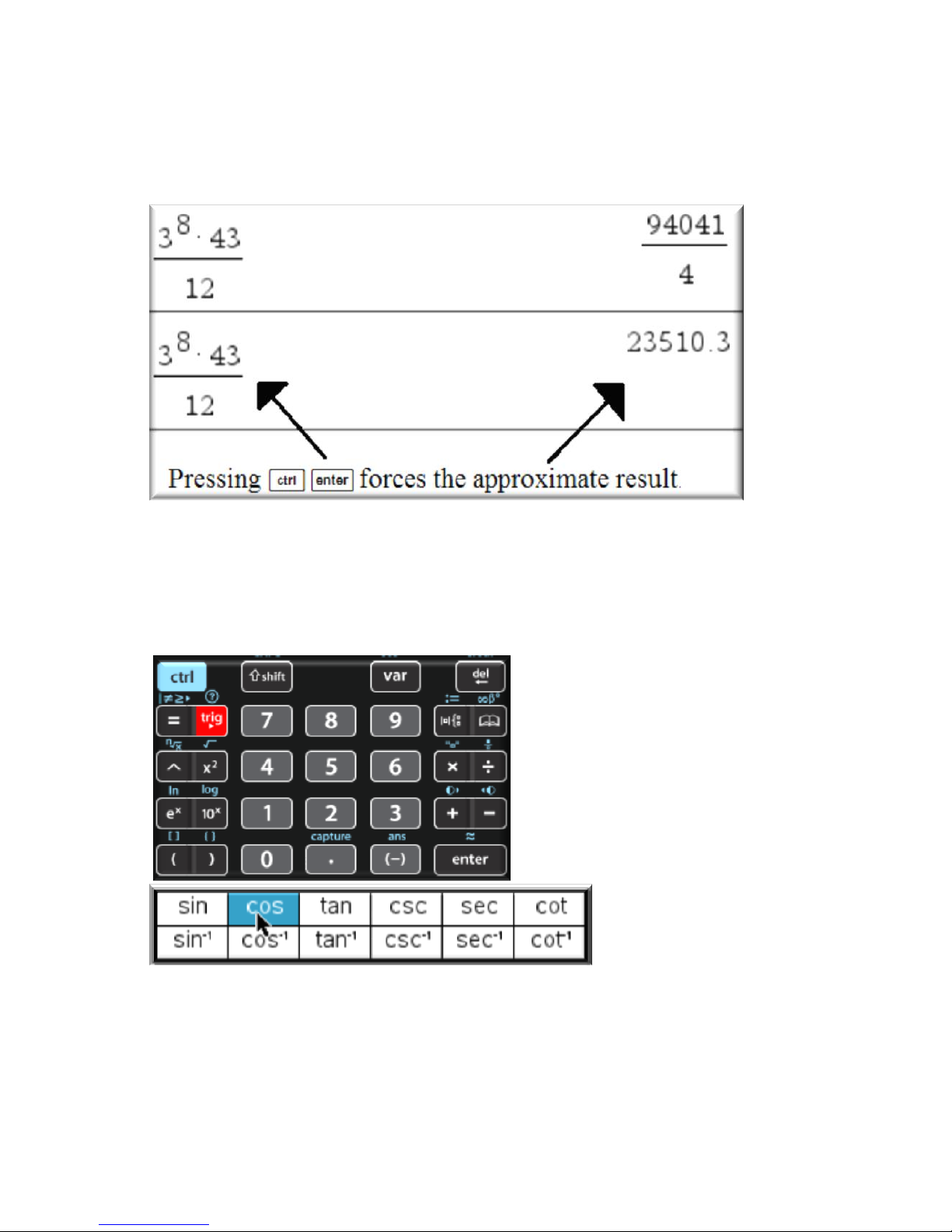
Trig Functions
Press µ to find all the trig functions.
TI-nspire CX CAS 2
Page 10

10 CAS Calculators
Shortcut Keys
There are hidden shortcuts on the keypad that are listed in the
user manual. There are a few shortcuts you should memorize:
Add a column
g@
Add a row
@
Integration template
g+
Derivative template
g-
Fraction template
/p
Underscore
/_
Shortcuts 1
Syntax
Syntax is very important in computational math. Syntax is
basically the set of rules the system uses to communicate. Access
the list of commands from the catalog.
TI-nspire CX CAS 3
Syntax examples appear at the bottom of the screen when scrolling
through the list. Press e · to see more examples of syntax. Use
the expressions template to avoid syntax errors.
TI-nspire CX CAS 4
Page 11

Basics 11
Understanding Variables
Storing Variables
Variables are stored using the define or store commands.
Nspire Example II
Deleting Variables
Delete variables using the Del Var command.
Nspire Example III
Variable Naming Conventions
There are a few ways to name a variable.
single letter (x, y, z)
letter and number (x1,y1,z1)
name (observed, list, expected)
Page 12

Page 13

Symbolic Math
Page 14

Page 15

Symbolic Math 15
Symbolic Algebra
Solving Equations
Use the Solve command to save time working out algebra
problems. Use this command to solve one equation for one
variable or multiple equations for multiple variables
simultaneously
Nspire Example IV
Factoring Expressions
Use the Factor command to return an expression factored with
respect to a variable.
Nspire Example V
Expand expressions by following the same syntax as factoring.
Nspire Example VI
Page 16

16 CAS Calculators
Understanding Units
Units are very similar to variables. A list of measurement units and
constants are built into the catalog. If you don’t see a unit you
want to work with you can create your own. You just follow the
same steps as you would when defining a variable, but with an
underscore in front of the “variable”.
Unit Conventions
When working with units in equations use parentheses to avoid
syntax and order of operations errors.
Unit Operations
To convert units use the Conversion Operator (¢).
Nspire Example VII
CAUTION: Temperature units must be converted using the
Temp Convert command.
TI-nspire CX CAS 5
Page 17

Symbolic Math 17
Symbolic Calculus
The CAS automatically evaluates L’Hopital’s rule, integration by
parts, and countless other methods.
Use the limit, derivative, and integral, templates under the
expressions template button enter values in just as you would on
paper.
Nspire Example VIII
TI-nspire CX CAS 6
Page 18

Page 19

Matrix/Vector/List
Nspire Example IX
Page 20

Page 21

Matrix/Vector/List 21
Matrix
Creating a Matrix
Select the expression template button
Input the dimensions of your matrix and press enter
Fill in the first element and press tab to move to the next.
Manipulating a Matrix
If you need to add more elements to your matrix:
Add a column g@
Add a row @
Matrix Operations
Matrix operations are straight forward. Just make sure you use
the rules for matrix multiplication, addition, etc.
Element Operations are less straight forward.
You must use the “dot multiply” commands.
Nspire Example X
Page 22

22 CAS Calculators
Vector
A vector is a matrix. Create and manipulate vectors as you would a
matrix.
Vector Operations
The built in vector operations include Unit Vector, Cross Product,
Dot Product, and converting to different coordinate systems.
Nspire Example XI
NOTE: The order of the elements of in the Cross Product function
matter! (M=R x F)
Lists
Creating Lists
To create a list you must use the curved brackets. After you create
a list store it as list1 or an appropriate name. Some list operations
require your list to be stored.
Nspire Example XII
Page 23

Matrix/Vector/List 23
Manipulating Lists
You can find everything you need to manipulate a list under the
list operations tab. Manipulating the list is much faster than
retyping the augmented list.
Nspire Example XIII
List Operations
Select the list operations from the list math tab. These commands
are very useful when working in statistics.
TI-nspire CX CAS 7
Page 24

Page 25

Introduction to Programming
Lua Programming Logo 1
Page 26

Page 27

Introduction to Programming 27
Programs Make Life Easier
Find a group of problems in a course that use the same equations.
Make a flow chart of what to do when you encounter different
parameters in this group of problems. Write down the formulas
you would need for each step. That is basically what a program is.
Make a Simple Program
Mohr’s circle is another problem that is simple but takes longer
than needed to work out. Write a program that solves Mohr’s
circle:
Nspire Example XIV
To make a new program open up the program editor and select
new program and name it Mohr.
Page 28

28 CAS Calculators
Copy the code and test it out. Then try writing a program for a
problem in your class.
Define LibPub mohr(x,y,τ,β)=
Prgm
setMode(2,2)
setMode(5,2)
a:=((y+x)/(2))
r:=√((x-a)^(2)+τ^(2))
setMode(1,6)
-y))))/(2))
m:=a+r
n:=a-r
If α=±45 Then
θ:=45
Else
θ:=α
EndIf
φ:=θ+45
t:=r*sin(2*β-2*θ)
If x<y Then
-r*cos(2*β-2*θ)
-2*θ)
Else
-2*θ)
-r*cos(2*β-2*θ)
EndIf
Disp "σ max =",m," σ min =",n
Disp "σ ave =",a," τ max =",r
Disp "θp =",θ,"°"," θs =",φ,"°"
EndPrgm
Page 29

Index 29
Index
approximate, 9
command, 11, 15, 16
commands, 10, 21, 23
constants, 16
convert, 16
curved brackets, 22
Define, 11
Delete, 11
derivative, 16
Element, 21
exact, 9
Expand, 15
expression, 15, 21
Factor, 15
fractional, 9
guidebook, 5
integral, 16
limit, 16
Lists, 4, 22, 23
manipulate, 22, 23
Matrix, 3, 19, 21
operations, 16, 21, 22, 23
program, 4, 27, 28
Shortcut, 3, 10
Solve, 15
symbolic, 9
Syntax, 3, 10
template, 10, 16, 21
trig, 9
Unit, 3, 16, 22
units, 16
Variables, 3, 11
Vector, 3, 4, 19, 22
 Loading...
Loading...