Page 1

CHAPTER 1 SPECIFICATIONS
1.1 OVERVIEW.................................................................................................................................1
1.2 PRODUCT NAME AND MODEL ................................................................................................1
1.2.1 Name......................................................................................................................................1
1.2.2 Name for sales .......................................................................................................................1
1.2.3 Name for export .....................................................................................................................1
1.2.4 Models....................................................................................................................................1
1.2.5 Product Structure Code (PS code) and goods item code ......................................................1
1.3 CLASSIFICATION.......................................................................................................................2
1.4 TERMINOLOGY .........................................................................................................................2
1.5 SYSTEM ORGANIZATION .........................................................................................................2
1.5.1 Configuration and expandabilities to systems ........................................................................2
1.5.1.1 Configuration ................................................................................................................2
1.5.1.2 Expandability for system (peripheral equipment) .........................................................2
1.5.1.3 Expandability for system(software)...............................................................................3
1.5.2 Electrical Rating .....................................................................................................................3
1.5.3 Dimensions and Weight .........................................................................................................3
1.5.4 Measurement Principle(Process flow, detection principle).....................................................4
1.6 SPECIFICATIONS AND FUNCTIONS........................................................................................5
1.6.1 Intended Use..........................................................................................................................5
1.6.2 Specification ...........................................................................................................................5
1.6.2.1 Analysis Parameter and Display ..................................................................................5
1.6.2.2 Analysis and Display Range.........................................................................................6
1.6.2.3 Reproducibility..............................................................................................................7
1.6.2.4 Accuracy.......................................................................................................................8
1.6.2.5 Linearity........................................................................................................................9
1.6.2.6 Carryover......................................................................................................................9
1.6.2.7 Stability.........................................................................................................................9
1.6.2.8 Throughput .................................................................................................................11
1.6.2.9 Required Sample and Reagent volume .....................................................................12
1.6.3 Functions..............................................................................................................................13
1.6.3.1 Select Function...........................................................................................................13
1.6.3.2 Input ...........................................................................................................................13
1.6.3.3 Display Function.........................................................................................................13
1.6.3.4 Data storage............................................................................................................
1.6.3.5 Timer (Sleep) function ................................................................................................14
1.6.3.6 Biohazard function......................................................................................................14
1.6.3.7 Printer (Built-in Printer)...............................................................................................15
1.6.3.8 Serial Interface ...........................................................................................................15
1.6.3.9 Calendar and Clock....................................................................................................15
...14
XP series S/M
April 2013
Page 2

1.6.3.10 Histogram Analysis.....................................................................................................15
1.6.3.11 Quality Control............................................................................................................15
1.6.3.12 Calibration ..................................................................................................................16
1.6.3.13 Abnormality Detection Function .................................................................................16
1.6.3.14 START-UP ..................................................................................................................17
1.6.3.15 SHUT DOWN .............................................................................................................17
1.6.3.16 Service Maintenance..................................................................................................17
1.6.3.17 Safety Protection........................................................................................................18
1.6.3.18 Reagent Control (exclude XP-100 for China market) .................................................19
1.7 TRACEABILITY ........................................................................................................................19
1.8 REQUIREMENTS .....................................................................................................................19
1.8.1 Environmental Requirements...............................................................................................19
1.8.2 Electric Source .....................................................................................................................20
1.8.3 Reagents..............................................................................................................................20
1.9 OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE .........................................................................................20
1.9.1 Operation .............................................................................................................................20
1.9.2 Supply ..................................................................................................................................20
1.9.3 Maintenance.........................................................................................................................21
1.10 PACKAGING .............................................................................................................................21
1.11 ATTACHMENTS........................................................................................................................21
1.11.1Accessories..........................................................................................................................21
1.12 REQUIRED CONDITIONS .......................................................................................................21
1.12.1Environmental Conditions....................................................................................................21
1.13 ACOUSTIC NOISE ...................................................................................................................22
1.14 EXPECTED LIFE TIME ............................................................................................................22
XP series S/M
April 2013
Page 3
CHAPTER 1 SPECIFICATIONS
1.1 OVERVIEW
Automated Hematology Analyzer XP series is succession machine of KX-21 that more than 10 years have
passed since its introduction to the market. The purpose of XP series development is to expand business
relations in developing nations. Only essential changes implemented from KX-21/KX-21N to XP series, and
its hardware, sequence software and appearance are designed based on KX-21N, and basic software is
designed based on pocH-100i and silent design.
While XP series inherited the basic performance and functions of KX-21N and pocH-100i, its specification
has been enhanced with changes as follows.
- Increase the number of stored data (40,000 items (XP-300))
- Adopt color touchpad display
- Expand SNCS functionality
- Add PCT (Platelet count) to analysis items
- Add reagent management function (Unique barcode)
- Increase available languages (Russian, Indonesian and Korean)
1.2 PRODUCT NAME AND MODEL
1.2.1 Name
Automated Hematology Analyzer (JMDN Code: 35476000)
1.2.2 Name for sales
Automated Hematology Analyzer XP series
1.2.3 Name for export
Automated Hematology Analyzer XP series
1.2.4 Models
XP-100/XP-300
1.2.5 Product Structure Code (PS code) and goods item code
PS code Name JAN Code UPC code
AP807129 XP-300 COMPLETE(EU/230V) 4987562429172 636090429171
AJ213506 XP-300 COMPLETE(UK/240V) 4987562429189 636090429188
BG491812 XP-300 COMPLETE(CHN/220V) 4987562429196 636090429195
BL783052 XP-300 COMPLETE(JP/100V) 4987562429202 636090429201
AR408878 XP-300 COMPLETE(EXP/120V) 4987562429219 636090429218
BS649542 XP-100 COMPLETE(EU/230V) 4987562429226 636090429225
AQ088754 XP-100 COMPLETE(UK/240V) 4987562429233 636090429232
BN167486 XP-100 COMPLETE(CHN/220V) 4987562429240 636090429249
1-1 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 4

1.3 CLASSIFICATION
Classification Class: Class Ⅰ
1.4 TERMINOLOGY
Whole blood mode : mode that measures sample blood without dilution.
Pre-dilute mode : mode that measures sample blood that dilute by 26 times.
Service data : data that is used for production, technical service and scientific activities, but
not provided to users.
Service function : function that is used for production, technical services and scientific activities,
and not used by users.
1.5 SYSTEM ORGANIZATION
1.5.1 Configuration and expandabilities to systems
1.5.1.1 Configuration
(1) Units
Main unit (with data processing function, compressor, built-in lyse container)
* A common program that is used for XP-100 and XP-300 has installed on the main unit.
(2) Reagent
Diluent CELLPACK
Lyse reagent STROMATOLYSER-WH
Detergent CELLCLEAN
(3) Control blood and Calibrator
Control blood EIGHTCHECK-3WP, EIGHTCHECK 3WP X-TRA
Calibrator SCS-1000
(4) Reagent for gain adjustment
WBC, RBC CELLCHECK-400
PLT PLT Latex Calibrator(E)
1.5.1.2 Expandability for system (peripheral equipment)
(1) Handy barcode reader (Option)
(2) GP(Graphic print)/LP(Listed print)
(3) RS-232C-LAN adaptor (for SNCS)
313B059
1-2 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 5

1.5.1.3 Expandability for system(software)
(1) SNCS
Main functionalities
Online QC, Real time error log, Emergency Error Notification, Screen Capture(Available to save 5
captures at maximum on SNCS server), Failure Prediction(Pressure 0.05Mpa/ Vacuum -
0.0333Mpa / Draining time of drain chamber, HGB Blank, Clogs ), Parameter Backup, Opera-
tion Cycle Count log, Maintenance log
* As to failure prediction, data needs to be collected for verifications.
1.5.2 Electrical Rating
1) Rated Voltage
100V/120V/220V/230V/240V
2) AC/DC
AC
3) Frequency
50Hz or 60Hz
4) Maximum Rated Power
200VA
5) Protection Type
Class Ⅰ equipment
1.5.3 Dimensions and Weight
1) Dimensions
Width 420mm
Height 480mm
Depth 355mm
2) Weight
Approx. 30kg
1-3 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 6

1.5.4 Measurement Principle(Process flow, detection principle)
1) Blood Quantative Method
Quantify with sampling valve(SRV).
2) Whole Blood Mode Dilution and Lysis
Aspirate approx. 50 μL of blood with anti-coagulant and quantify with SRV. Prepare WBC/HGB
sample and RBC/PLT sample by diluting with diluent and lyse agent by approx. 500 times and
approx. 25000 times, respectively.
WBC/HGB sample (Approx. 500 times)
First dilution: 6.012μL blood + 2.0 mL Diluent + 1.0 mL lyse
RBC/PLT sample ( Approx. 25000 times = 500x50)
First dilution: 4.008μL blood + 2.0mL diluent
Second dilution: 40.82μL First sample + 2.0 mL diluent
3) Pre-diluted Mode dilution
Aspirate approx. 200 μL of pre-diluted sample that diluted with diluent by 26 times. Quantify the
pre-diluted sample with sampling valve and prepare WBC/HGB sample and RBC/PLT sample by
diluting by approx. 1000 times and approx. 25000, respectively. In Pre-diluted Mode, use a pore
that is not used in Whole Blood Mode and the RBC/PLT sample dilution should be done at first
dilution only.
WBC/HGB sample (Approx. 1000 times = 26x38.46)
First dilution: 26 times; 80.08μL PD sample + 2.0 mL diluent + 1.0 mL lyse
RBC/PLT sample (Approx. 25000 times = 26x961.5)
First dilution: 26 times; 2.082 μL PD sample + 2.0 mL diluent
4) WBC measurement
Aspirate WBC/HGB sample 0.50mL through φ100μm pore and measure with DC detection
method. Diaphragm pump is used to aspirate and quantify.
5) RBC/PLT measurement
Aspirate 0.25mL of RBC/PLT sample through φ75μm pore and measure with DC detection
method. Diaphragm pump is used to aspirate and quantify. Analysis result is obtained by autodiscriment of histograms.
6) HGB measurement
Measure absorption value of transmitted light at 555nm for diluent every measurement, and
calculate HGB values that is determined by deducting the absorption value of transmitted light at
555nm for diluent from that for HGB sample(Colorimeteric Method). LED and photodiode are used
as a light source and a photo detector, respectively. Measurement method is SLS-Hb method.
1-4 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 7

1.6 SPECIFICATIONS AND FUNCTIONS
1.6.1 Intended Use
1) Purpose
The XP series is intended for in vitro diagnostic use, analyzing 20 parameters in anti-coagulated
human blood. The Anti-coagulants are EDTA-2K, EDTA-3K and EDTA-2Na. The anti-coagulants
volume conforms to CLSI standards.
Note: EDTA-2Na is not intended for North American markets.
2) Workload
Expected workload is 60 samples/day.
1.6.2 Specification
1.6.2.1 Analysis Parameter and Display
(1) Analysis Mode
Whole Blood Mode
Pre-diluted Mode
(2) Measurement Parameters
White Blood corpuscle (WBC), Red Blood corpuscle (RBC), Hemoglobin (HGB), Hematocrit
(HCT), Mean Red Blood Corpuscular Volume (MCV), Mean Corpusclar Hemoglobin (MCH),
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC), Platelet count (PLT)
(3) Analysis Parameters
WBC Small Cell Ratio (W-SCR), WBC Middle Cell Ratio (W-MCR), WBC Large Cell Ratio
(W-LCR), WBC Small Cell Count (W-SCC), WBC Middle Cell Count (W-MCC), WBC Large
Cell Count (W-LCC), RBC Distribution Width (RDW-SD, RDW-CV), Platelet Distribution
Width (PDW), Mean Platelet Volume (MPV), Platelet Large Cell Ratio (P-LCR), Platelet Crit
(PCT)
For N.A market, PDW, P-LCR and PCT are not output.
(4) Research Parameters
ResearchW, ResearchS, ResearchM, ResearchL
(5) Histograms
WBC/RBC/PLT
(6) Flags
Possible sample abnormalities are as follows.
1)WL, RL, PL : Relative height at Lower Discriminator exceeds the preset limit.
2)WU, RU, PU : Relative height at Upper Discriminator exceeds the preset limit.
3)DW : The RBC histogram does not cross the 20% height level twice.
4)MP : Two or more peaks exist in RBC or PLT histogram.
5)T1 : The trough discriminator cannot be set between SCR and MCR populations.
6)T2 : The trough discriminator cannot be set between MCR and LCR populations.
7)F1, F2, F3 : Relative height at the trough discriminator exceeds the preset limit.
8)AG : Too many cells exist at WBC Lower Discriminator and lower 2 channels.
313B059
1-5 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 8
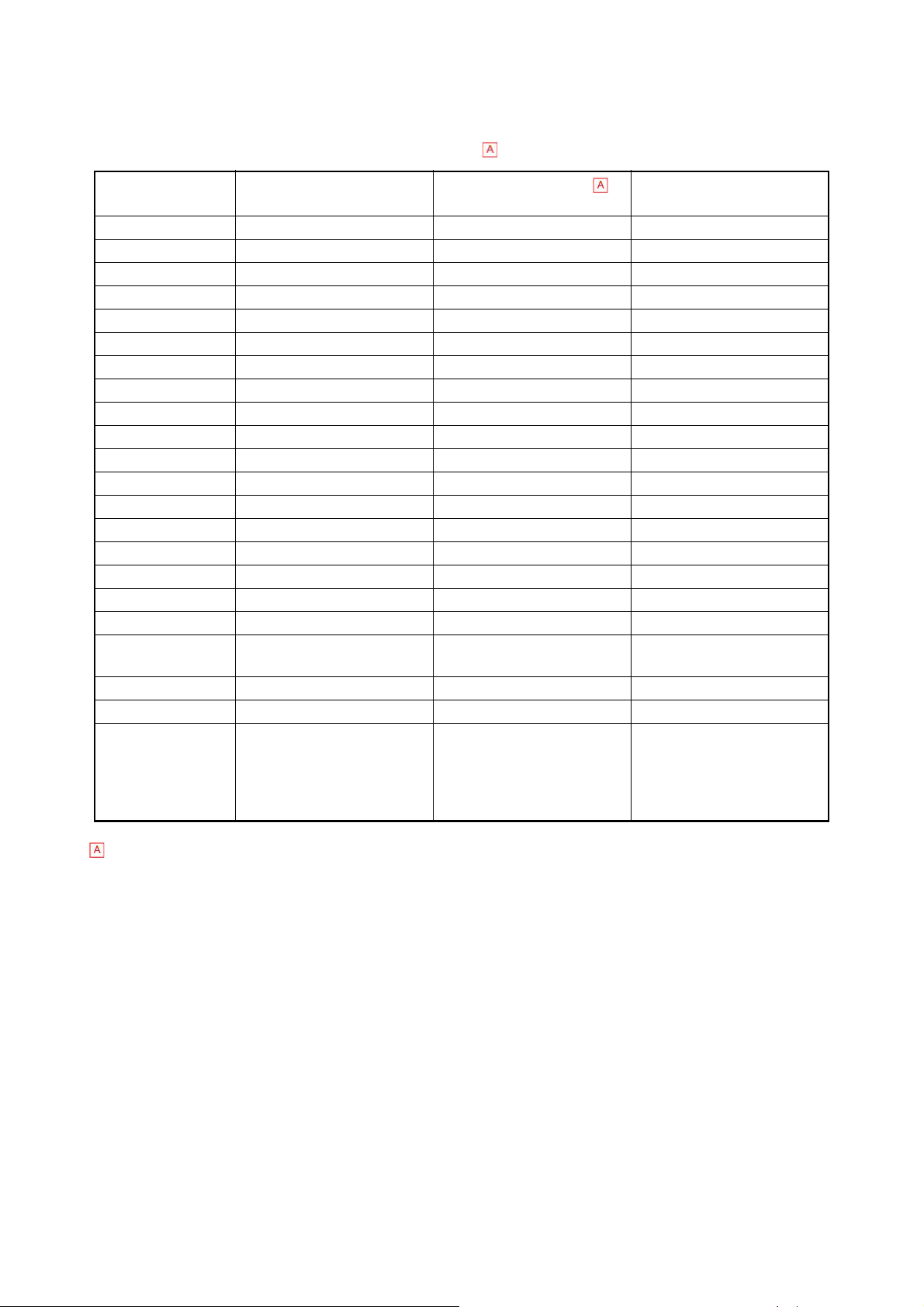
1.6.2.2 Analysis and Display Range
Analysis and display range is shown in the table as follows. Note that Reportable Range in
the table is intended for US markets only.
Parameter Analysis Range
Reportable Range Display Range
(Linearity Range)
WBC 10 - 999 x 102/μL 10 - 999 x 102/μL 0 - 2999 x102/μL
RBC 30 - 700 x104/μL 30 - 700 x104/μL 0 - 1999 x104/μL
HGB 0.1 - 25.0 g/dL 0.1 - 25.0 g/dL 0.0 - 25.0 g/dL
HCT 10.0- 60.0 % 10.0- 60.0 0.0 - 99.9 %
MCV ────── ────── 0.0 - 299.9fL
MCH ────── ────── 0.0 - 99.9 pg/dL
MCHC ────── ────── 0.0 - 99.9 g/dL
PLT 1.0 - 99.9 x104/μL 1.0 - 99.9 0.0 - 199.9 x104/μL
W-SCR ────── 0.1 - 99.8 0.0 - 100.0 %
W-MCR ────── 0.1 - 99.8 0.0 - 100.0 %
W-LCR ────── 0.1 - 99.8 0.0 - 100.0 %
W-SCC ────── 10 - 999 0 - 2999 x 102/μL
W-MCC ────── 10 - 999 0 - 2999 x 102/μL
W-LCC ────── 10 - 999 0 - 2999 x 102/μL
RDW-CV ────── ────── 0.0 - 100.0 %
RDW-SD ────── ────── 0.0 - 250.0 fL
PDW ────── ────── 0.0 - 40.0 fL
MPV ────── ────── 0.0 - 40.0 fL
P-LCR
PCT
WBC Histogram ────── ────── 0 - 300 fL
RBC Histogram ────── ────── 0 - 250 fL
PLT Histogram
ResearchW
ResearchS
ResearchM
ResearchL
──────
──────
──────
──────
──────
──────
──────
──────
──────
──────
──────
──────
──────
──────
0.0 - 100.0 %
0.00 - 99.99 %
0 - 40 fL
0.00 - 2999.99 x10
0.00 - 2999.99 x10
0.00 - 2999.99 x10
0.00 - 2999.99 x10
2
2
2
2
/μL
/μL
/μL
/μL
313B059
1-6 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 9
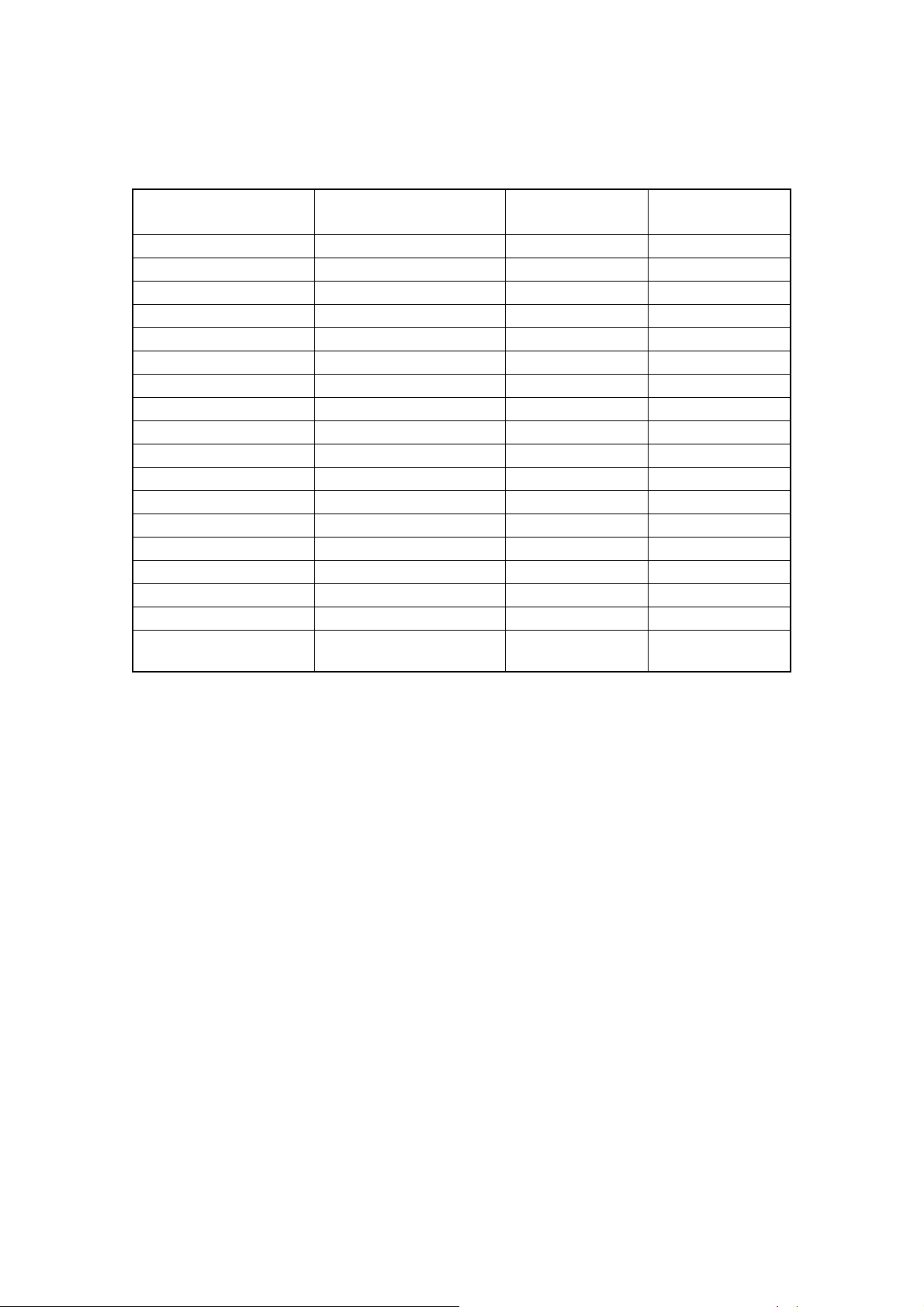
1.6.2.3 Reproducibility
When fresh normal blood or control blood is analyzed in Whole Blood Mode 10 times con-
secutively, the variation of coefficient under 95% confidence interval should be within the fol-
lowing range:
Parameter Condition Whole Blood
Mode
WBC 40x102/μL or more 3.5% or lower 6.0% or lower
RBC 400 x104/μL or more 2.0% or lower 3.0% or lower
HGB 1.5% or lower 2.5% or lower
HCT 2.0% or lower 3.0% or lower
MCV 2.0% or lower 3.0% or lower
MCH 2.0% or lower 3.0% or lower
MCHC 2.0% or lower 3.0% or lower
PLT 10x104/μL or more 6.0% or lower 9.0% or lower
W-SCR 15.0% or lower 25.0% or lower
W-MCR W-MCR rate 12% or more 30.0% or lower 45.0% or lower
W-LCR 15.0% or lower 25.0% or lower
W-SCC 15.0% or lower 25.0% or lower
W-MCC 10x102/μL or more 30.0% or lower 45.0% or lower
W-LCC 15.0% or lower 25.0% or lower
RDW-CV, RDW-SD 4.0% or lower 6.0% or lower
PDW 12.0% or lower 18.0% or lower
MPV 5.0% or lower 7.5% or lower
P-LCR
PCT
20.0% or lower
9.0% or lower
Pre-diluted
Mode
30.0% or lower
13.5% or lower
1-7 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 10
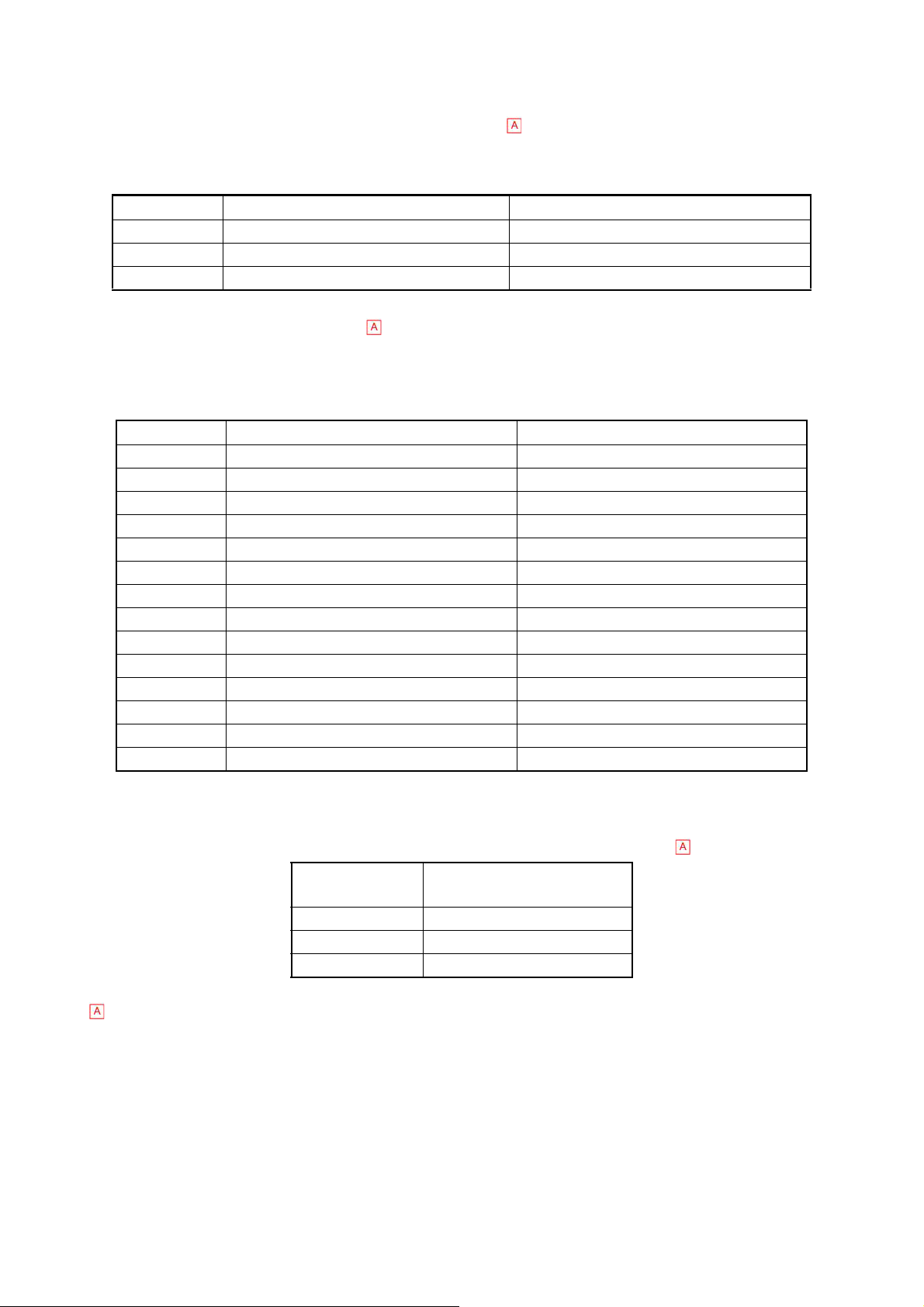
1.6.2.4 Accuracy
(1 ) For markets excluding North American markets
When calibrator is analyzed 10 times consecutively, the mean difference from the value
obtained on the standard instrument should be within the following range:
Parameter Whole Blood Mode Pre-diluted Mode
WBC Within ±3% or ±2 x102/μL Within ±5 % or ±3 x102/μL
RBC Within ±2% or ±3 x104/μL Within ±3 % or ±5 x104/μL
PLT Within ±5% or ±1.0 x104/μL Within ±8 % or ±1.5 x104/μL
(2) For North American markets
When the instrument is calibtrated and 100 fresh blood samples or more are analyzed on
the same day, the mean difference should be within the following range compared to the
value obtained on calibrated KX-21 or KX21N instrument.
Parameter Whole Blood Mode Pre-diluted Mode
WBC Within ±3% or ±2 ×10?/μL ±5 % or ±3 ×10?/μL
RBC Within ±2% or ±3 ×10?/μL ±3 % or ±5 ×10?/μL
HGB Within ±2% or ±0.2 g/dL ──────
HCT Within ±3% or ±1.0 HCT% ──────
MCV Within ±5% ──────
MCH Within ±10% ──────
MCHC ±10% ──────
PLT Within ±5% or ±1.0 ×10?/μL ±8 % or ±1.5 ×10?/μL
W-SCR Within ±5.0 W-SCR% ──────
W-MCR Within ±3.0 W-MCR% ──────
W-LCR Within ±5.0 W-LCR% ──────
RDW-CV Within ±10% ──────
RDW-SD Within ±10% ──────
MPV Within ±10% ──────
In regards to W-SCR, W-MCR and W-LCR, when the instrument is calibtrated and 100 fresh blood
samples or more are analyzed on the same day, the correlation coefficient should be in the following
range compared to the value obtained on calibrated KX-21 or KX21N instrument.
Parameter Whole Blood Mode
Correlation Coefficient
W-SCR r ≧ 0.90
W-MCR r ≧ 0.70
W-LCR r ≧ 0.90
313B059
1-8 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 11
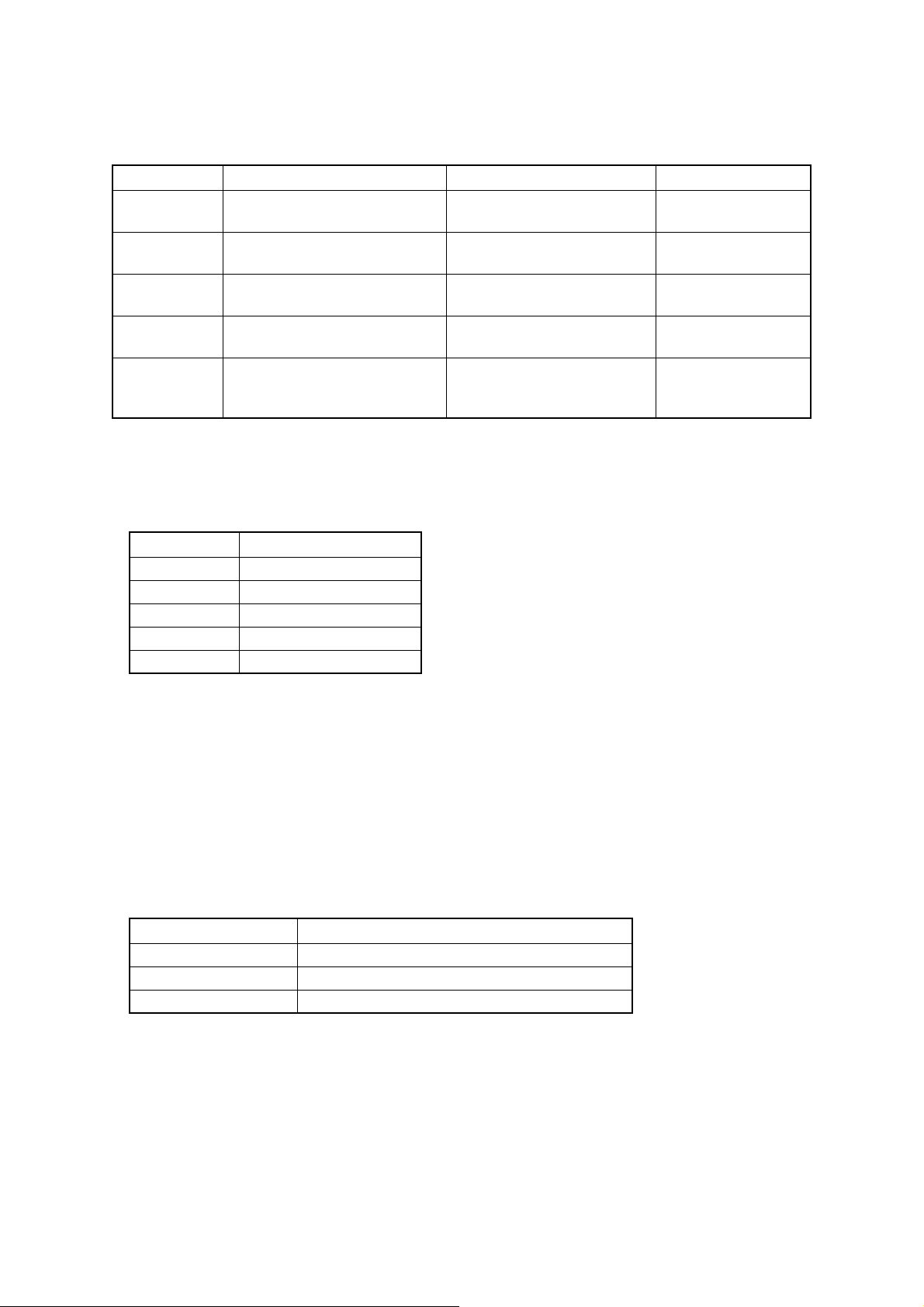
1.6.2.5 Linearity
When the Whole Blood Manual Mode analysis is executed, the difference from the theoreti-
cal value should be within the following range:
Parameter Concentration Difference Difference rate
WBC 10 - 99 x102/μL
100 - 999 x10
RBC 30 - 99 x104/μL
100 - 700 x10
HGB 0.1 - 9.9 g/dL
10.0 - 25.0 g/dL
HCT 10.0 - 33.3 %
33.4 - 60.0 %
PLT 1.0 - 19.9 x104/μL
20.0 - 99.9 x10
(RBC<700 x10
2
4
/μL
/μL
4
4
/μL
/μL)
Within ±3 x102/μL
────────
Within ±3 x104/μL
────────
Within ±0.2 g/dL
────────
Within ±1.0 HCT%
────────
Within ±1.0 x104/μL
────────
────
Within ±3 %
────
Within ±3 %
────
Within ±2 %
────
Within ±3 %
────
Within ±5 %
1.6.2.6 Carryover
When control blood is analyzed in Whole Blood Mode, the carryover rate should be within the
following range:
Parameter Carryover rate
WBC 3 % or less
RBC 1.5% or less
HGB 1.5% or less
HCT 1.5% or less
PLT 5 % or less
1.6.2.7 Stability
When the Whole Blood Mode is executed, the stability should be within the following range:
(1) Stability relative to Temperature
In fresh normal blood or control blood analysis, the data fluctuation while the ambient temper-
ature changes from 15°C to 30°C should be within the following range:
The following data are based on the assumption that the sample is analyzed within 12 hours
after collection, and that any change in the sample should be executed from the fluctuation
ratio.
Parameter Fluctuation rate
WBC Within 10% or 5.0x102/μL
RBC, HGB, HCT Within 5%
PLT Within 15% or 3.0x104/μL
1-9 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 12
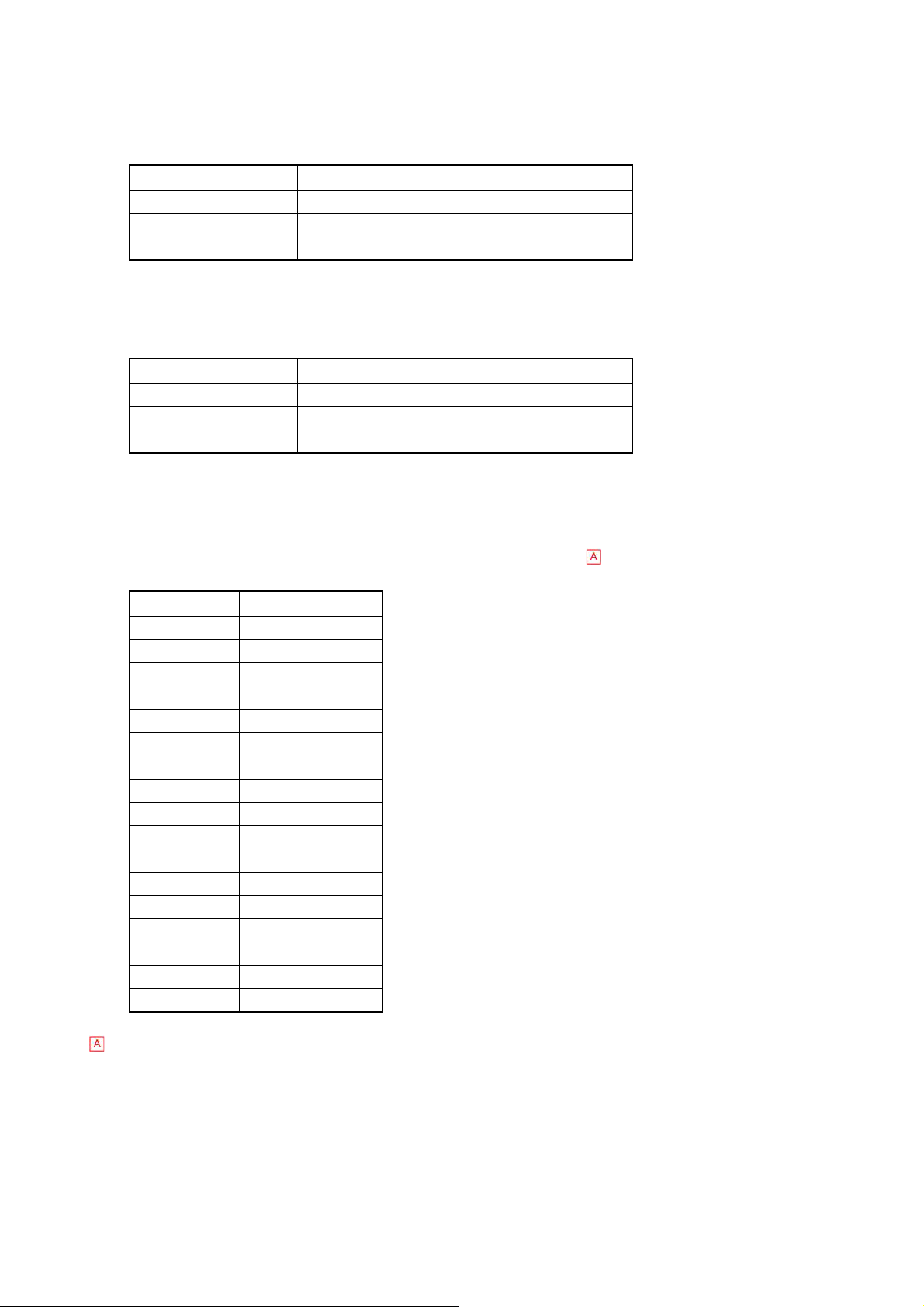
(2) Within-a-Day Stability
In control blood analysis of 5°C or less ambient temperature change, the data fluctuation for
24 hours after startup should be within the following range:
Parameter Change rate
WBC Within 10%
RBC, HGB, HCT Within 5%
PLT Within 15% or 3.0x104/μL
(3) Day-to-Day Stability
In control blood analysis of 5°C or less ambient temperature change, the data fluctuation for
ten days should be within following range:
Parameter Change rate
WBC Within 10%
RBC, HGB, HCT Within 5%
PLT Within 15% or 3.0x104/μL
For North American markets, when control blood is analyzed in the whole blood mode in
accordance with CLSI Document EP05-A2. Evaluation of Precision Performance of Quantita-
tive Measurement Methods; Approved Guideline. 2004,Total Imprecision change rate calcu-
lated from data obtained should be in the following range.
Parameter Change rate
WBC Within 6.0%
RBC Within 3.0%
HGB Within 2.5%
HCT Within 3.0%
MCV Within 3.0%
MCH Within 3.0%
MCHC Within 3.0%
PLT Within 9.0%
W-SCR Within 25.0%
W-MCR Within 45.0%
W-LCR Within 25.0%
W-SCC Within 25.0%
W-MCC Within 45.0%
W-LCC Within 25.0%
RDW-CV Within 6.0%
RDW-SD Within 6.0%
MPV Within 7.5%
313B059
1-10 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 13
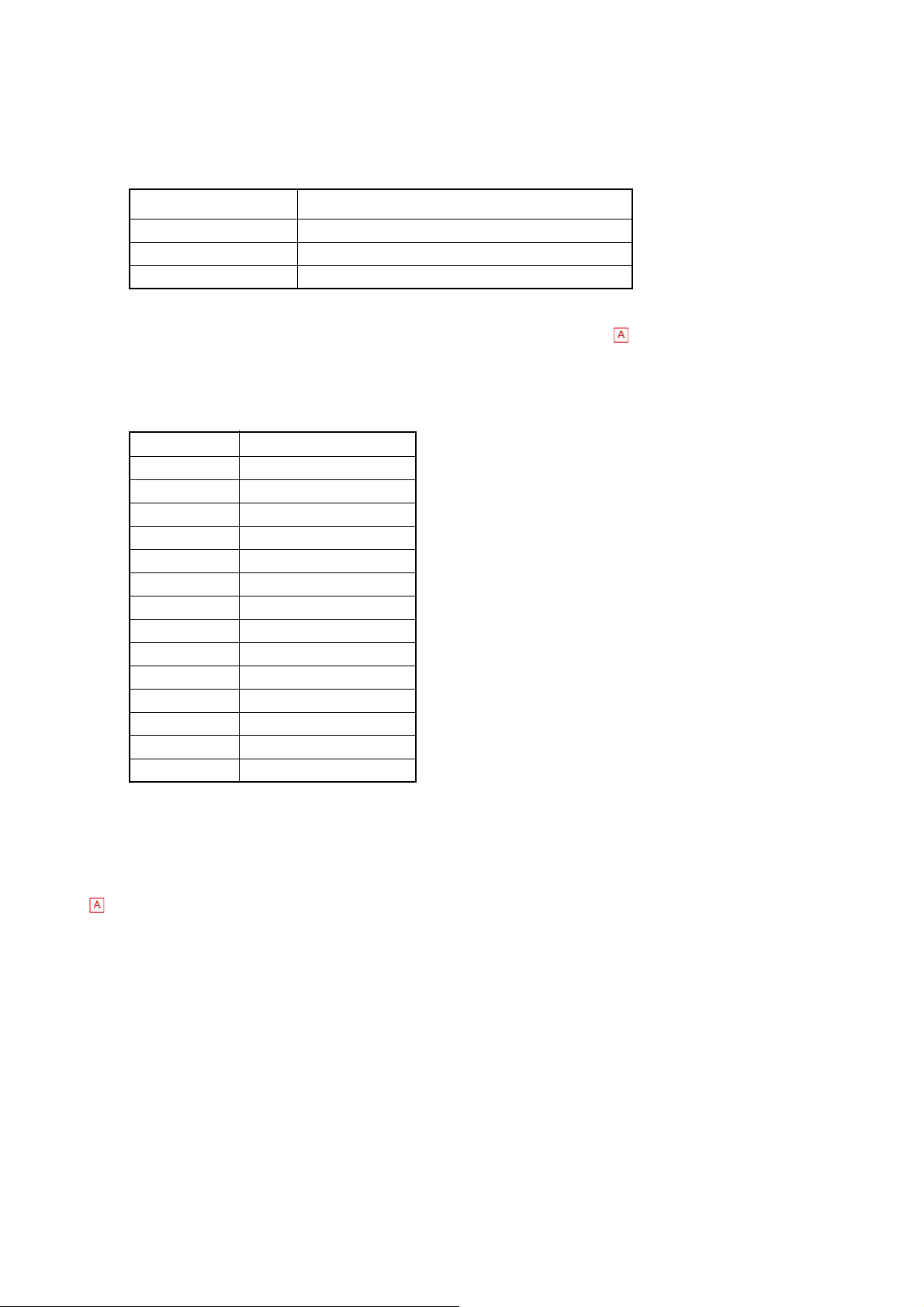
(4) Stability relative to Power Supply Voltage
In control blood analysis of 5°C or less ambient temperature change, the data fluctuation while
the power supply voltage changes ±10% from the rated voltage should be within the following
range:
Parameter Change rate
WBC Within 10%
RBC, HGB, HCT Within 5%
PLT Within 15% or 3.0x104/μL
(5) Sample Day-to-Day Stability (for North American markets only)
In human blood analysis of 5°C or less ambient temperature change, the data fluctuation in 12
hours (human blood stored in room temperature (18-26 °C)) or 24 hours (human blood stored
in cold storage (2-8 °C) ) from blood sampling should be within the following range:
Parameter Change rate
WBC Within 10.0%
RBC Within 5.0%
HGB Within 5.0%
HCT Within 5.0%
MCV Within 10.0%
MCH Within 10.0%
MCHC Within 10.0%
PLT Within 15.0%
W-SCR Within 10 W-SCR%
W-MCR Within 5 W-MCR%
W-LCR Within 10 W-MCR%
RDW-CV Within 15.0%
RDW-SD Within 15.0%
MPV Within 15.0%
1.6.2.8 Throughput
(1) Time per sample : Approx. 60 seconds/sample
(2) Throughput per hour : Approx. 60 samples/hour
313B059
1-11 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 14
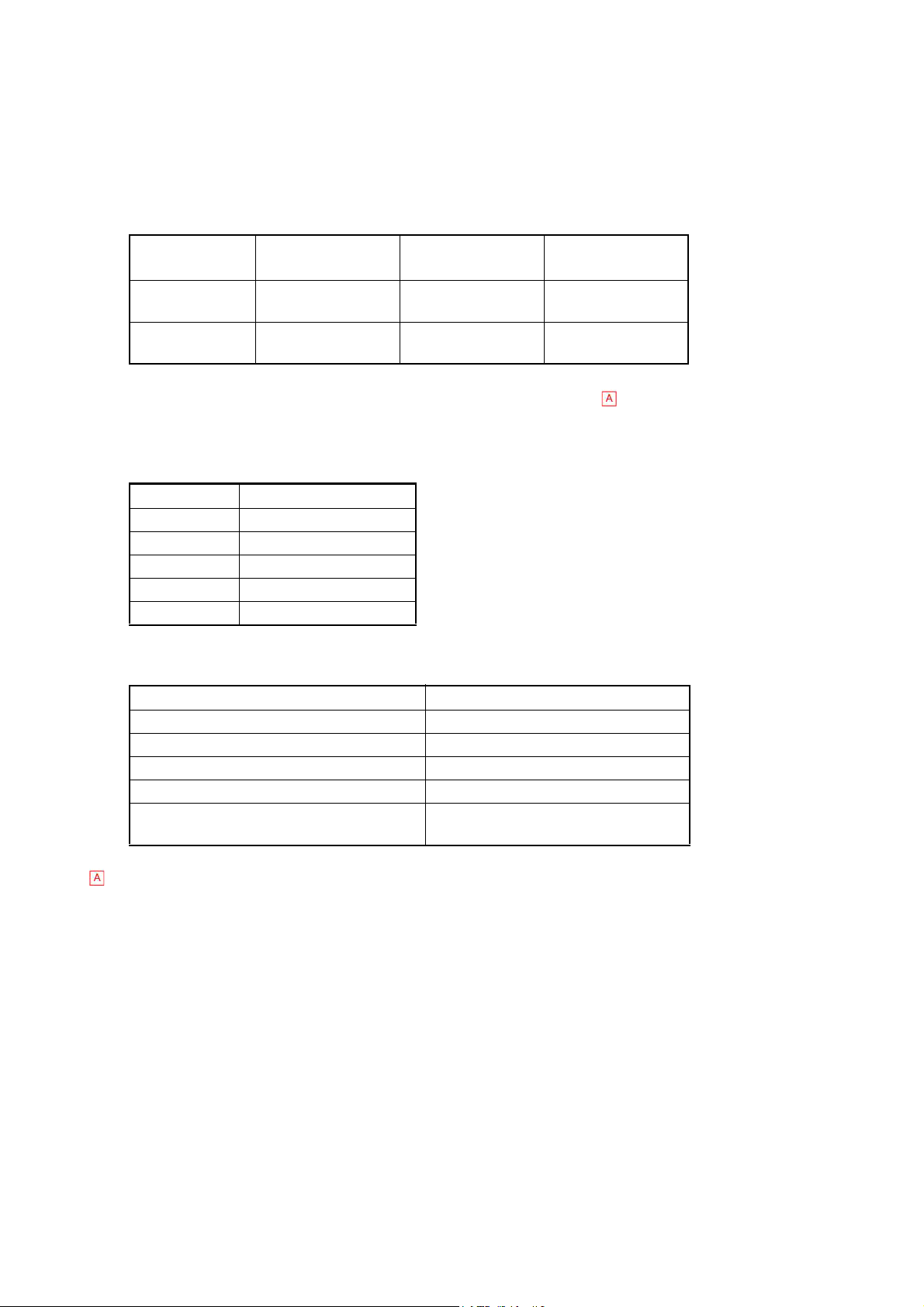
1.6.2.9 Required Sample and Reagent volume
(1) Required Sample Volume
Whole Blood Mode : Approx. 50μL
Pre-diluted Mode : Approx. 20μL
(2) Required reagent volume
Total reagent
Diluent sample Lyse reagent
volume sample
Whole Blood
Mode
Pre-diluted
Mode
Approx. 35 mL Approx. 34 mL Approx. 1 mL
Approx. 35 mL Approx. 34 mL Approx. 1 mL
1.6.2.10 Influence by inhibitor (for North American markets only)
The data fluctuation as a result of influence by inhibitor (Whole blood mode) should be in the
following range (in accordance with CLSI document H26-A2).
Parameter Change rate
WBC Within 10.9%
RBC Within 3.2%
HGB Within 2.8%
HCT Within 2.8%
PLT Within 9.1%
The density of inhibitor which satisfies the fluctuation above is as follows:
sample
313B059
Inhibitor Density
Bilibrubin C (Conjugated) Within 41.2 mg/dl
Bilirubin F (Free or Unconjugated) Within 36.6 mg/dl
Hemolytic Hemoglobin Within 974 mg/dl
Chyle Within 2840 FTU
Intralipid HGB: Within 2.9 OD(660nm)
Other: Within 4 OD(660nm)
1-12 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 15

1.6.3 Functions
1.6.3.1 Select Function
Under standby mode, following processes can be executed from the select functions.
(1) Stored data
(2) Exchange reagent
(3) Maintenance
(4) Calibration
(5) Setting
(6) Gain adjustment
(7) Service
(8) Paper feed
1.6.3.2 Input
(1) Power switch
Turn on and off electrical power source
(2) Start switch
Aspirate from the whole blood pipette and start analysis.
(3) LCD touchpad
Pressing power switch, analysis start screen is displayed on LCD. Each operation can be
selected on the LCD.
1) Sample ID
i) Manual input
Sample ID can be input before measurement execution.
ii) Auto input by barcode reader
Handy barcode reader is used to read barcode of sample ID that attached on sample
tube automatically.
iii) Auto-increment
Sample ID is automatically incremented. This function can be disabled by setting.
2) Operator ID
Operator ID can be input before analysis start. This data can be set to disable.
(4) Handy Barcode Reader
Barcode Reader is used to read sample ID, reagent barcode and values of control blood.
1.6.3.3 Display Function
(1) Graphic LCD
Panel Specification
i) Display system : STN Colour
ii) Display dot : 320x240 dots(dot pitch: 0.36x0.36 mm)
iii) Backlight : YES(CCFT)
iv) Display Area : 115.17x86.37mm
1-13 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 16
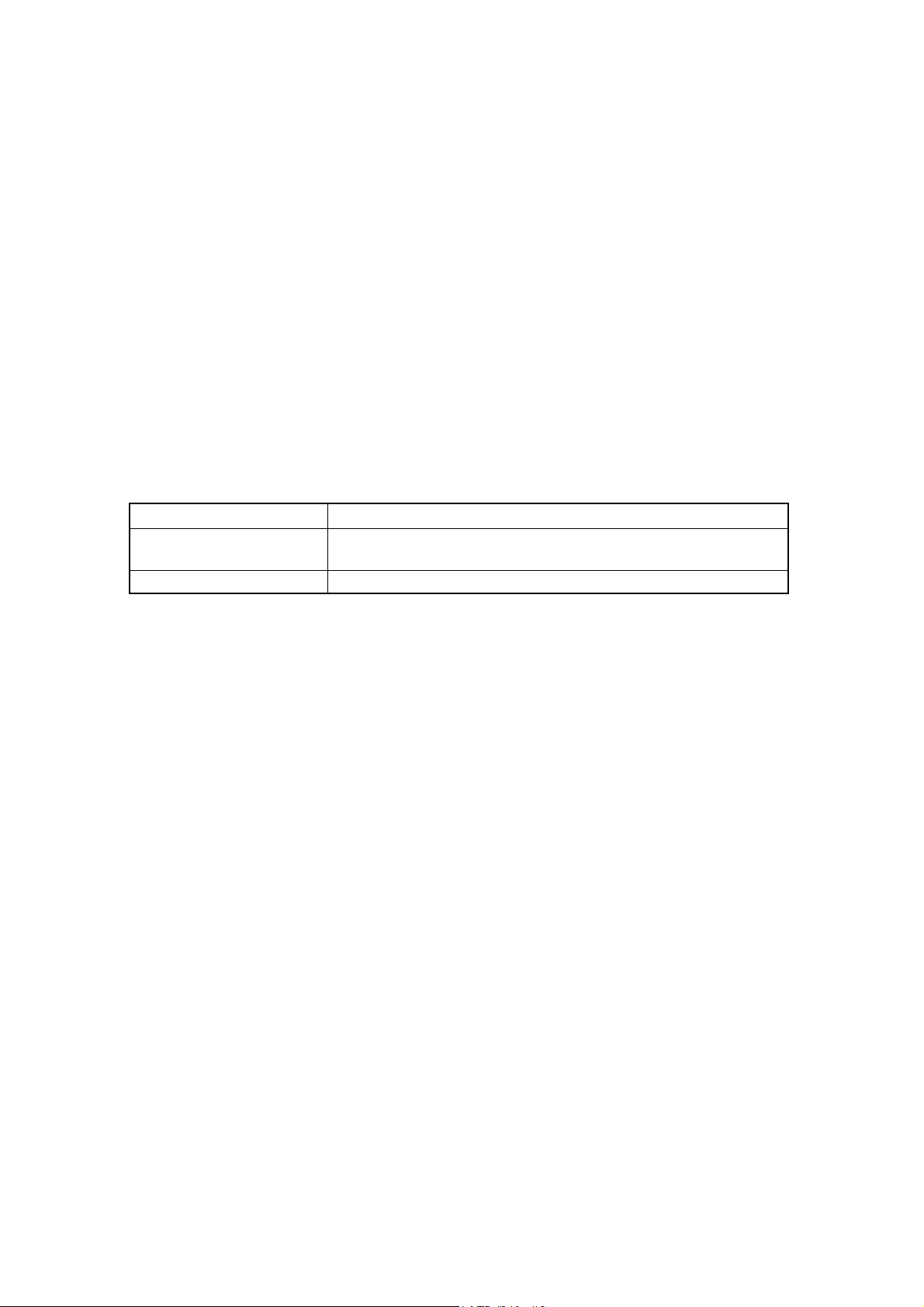
Display Items
i) Measurement results
- Date/Time
- Sample ID(Max: 15 digit)
- Operator ID
- Analysis results(Include flags and histograms)
* Analysis parameter display setting: for service purpose only
- Measurement mode menu
- Service data
ii) System status
- Error messages(Display numerical data in case of pressure errors.)
- Instrument status
iii) User operation
- Menu (Maintenance, Settings, Adjustment...etc)
(2) Used Languages
Display Languages
LCD Display Japanese, English, Spanish, Portuguese, Russian, Mandarin, German,
Italian, Indonesian and Korean
Printer Display English
1.6.3.4 Data storage
(1) Analysis Results 35,000 or more (Include histograms) (XP-100)
40,000 samples(Include histograms)(XP-300)
* Analysis Results Display Setting: for service purpose only
(2) Quality Control Data 60points(in 6 files)
(3) Setting Values
(4) Maintenance data
i) Instrument Operation Cycle Count
ii) Unit Operation Cycle
- Stores the number of operations after the replacement or maintenance of user maintenance
units.
- Not store the data on other units.
iii) Error history
- Can be output to host computer, but not displayed on LCD.
1.6.3.5 Timer (Sleep) function
Stop compressor 15 minutes after completion of its operation
1.6.3.6 Biohazard function
Aspiration pipette wiping
1-14 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 17

1.6.3.7 Printer (Built-in Printer)
(1) Specifications
i) Print method : Thermal printer
ii) Paper : 58mm Thermal paper (57.5mm width)
(2) Printed Items
i) Date/Time
ii) Sample ID
iii) Operator ID
iv) Analysis results (Including flag and histogram)
* Analysis Result Display Setting: for service purpose only
v) Histograms
vi) Quality Control data
vii) Setting values
viii) Service data
1.6.3.8 Serial Interface
RS-232C, LAN(Ethernet)
i) Latest sample analysis results
Analysis results, Flags, Histograms)
ii) Stored data
Analysis results, Flags, Histograms
iii) QC data
Analysis results, Flags, Histograms
iv) SNCS relative data
Realtime online QC, Realtime log output, Image capture output, Failure prediction,
Backup parameter settings, Instrument log output including reagent exchange history etc...
1.6.3.9 Calendar and Clock
1.6.3.10 Histogram Analysis
Discriminator position on the latest analysis can be manually changed.
1.6.3.11 Quality Control
X-Bar Control or L-J Control
Up to 60 points of control data can be stored for 6 type of samples(in 6 files)
Up to 22 control parameters can be selected.
* 20 parameters for measurement and analysis + 2 sensitivity parameters(W-SMV, W-LMV)
For North America market, up to 17 parameters.
* Parameters for measurement and analysis excluding PDW,P-LCR,PCT
Judgement of control limit is executed based on control limit values that are set by manually
or barcode.
Sample for quality control
: EIGHTCHECK-3WP, EIGHTCHECK-3WPEXTRA, EIGHTCHECK-C
1-15 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 18

1.6.3.12 Calibration
(1) Customer Calibration
i) Calibration Method : Auto-calibration, Manual calibration and Calibrator calibration
ii) Calibration Mode : Whole Blood Mode
iii) Calibration Parameters: HGB, HCT only in case of Auto-calibration, Manual calibration
WBC, RBC, HGB, HCT, PLT for Calibrator calibration
iv) Calibration Samples : Fresh normal blood samples for auto-calibration and manual
calibration. SCS-1000 for Calibrator calibration
(2) Service/Production calibration
i) Calibration Method : Manual calibration
ii) Calibration Mode : Whole Blood Mode, Pre-diluted Mode
iii) Calibration Parameters: WBC, RBC, HGB, HCT, PLT
iv) Calibration Samples : SCS-1000 for Service calibration
1.6.3.13 Abnormality Detection Function
(1) Error Alerting Function
Details of this function are described in Abnormal process specifications.
The following abnormalities are monitored. An error message and alarm will occur when an abnormality
is detected. An error recovery program is also provided.
i) Hydraulic System and Mechanical System
a) Reagent level in the internal reservoir chambers
b) Fluid level in the waste chambers
c) Pressure and vacuum
d) Rinse cup operation
e) Others
ii) Analysis Condition
a) Sampling data
b) HGB detection
c) Temperature
d) Clog
iii) Electricity
a) Sub-processor operation
b) External device connection
c) Built-in printer connection
d) Built-in printer paper
iv) Others
a) Calibration
b) Quality Control
1-16 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 19

(2) Histogram Abnormality
Monitors the abnormalities in the histograms, and adds flag to abnormal data.
i) WL, RL, PL : Relative height at Lower Discriminator exceeds the preset limit.
ii) WU, RU, PU : Relative height at Upper Discriminator exceeds the preset limit.
iii) DW : The RBC histogram does not cross the 20% height level twice.
iv) MP : Two or more peaks exist in RBC or PLT histogram.
v) T1 : The trough discriminator cannot be set between SCR and MCR populations.
vi) T2 : The trough discriminator cannot be set between MCR and LCR populations.
vii) F1, F2, F3 : Relative height at the trough discriminator exceeds the preset limit.
viii) AG : Too many cells exist at WBC Lower Level Discriminator and lower 2 channels.
(3) Analysis Results Abnormality
Monitors the abnormalities in the analysis results, and adds flag to abnormal data.
i) abnormal value
:
Analysis results exceed the preset Lower or Upper level of limits.
ii) Out of linearity range : Analysis results become beyond the linearity range
1.6.3.14 START-UP
When main power switch is turned on, the following start-up processes are automatically executed:
(1) System Check including initialization of mechanical parts.
(2) Auto Rinse
(3) Background Check
The background check limit is as follows (The background check can be repeated up to three
times.):
WBC : 3x102/μL or lower
4
RBC : 2x10
/μL or lower
HGB : 0.1g/dL or lower
4
PLT : 1.0x10
/μL or lower
1.6.3.15 SHUT DOWN
The hydraulic system is cleaned with diluted CELLCLEAN aspirated from the whole blood pipette.
To shut down the system, press the [Shutdown] key.
1.6.3.16 Service Maintenance
The details of special sequence for services and test process are defined in Service Maintenance
Specification manual.
(1) Customer Maintenance
i) Detector Rinse sequence with clog removal process
ii) Auto rinse with background check sequence
iii) Waste Chamber Cleaning sequence
iv) Shutdown
v) Parameter change/Print
vi) Transducer drain
vii) Reagent Replacement Sequence
viii) Built-in Printer paper feeding
1-17 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 20

ix) Status Display
- HGB convert value (Realtime display)
- Pressure value (Realtime display
- Instrument and unit operation cycle count
* Temperature and sampling data is displayed on Service data view.
(2) Service Sequences (Service purpose only)
i) Instrument installation sequence
ii) Service data Printing
iii) Gain adjustment
iv) Initialize/Change/Print setting values
v) Stop sequence
vi) Initialize all settings
vii) Shipment sequence
viii) Continuous mode
ix) Control blood analysis mode
x) Clog removal
(3) Test Processing (Service purpose only)
i) Diaphragm test operation
ii) Solenoid valve operation
iii) Compressor operation
iv) Built-in Printer output test
)
(4) Service Information Display/Print (Service Purpose Only)
i) Temperature
ii) Operation status
iii) Sampling data
iv) Service data
(5) Program supply
i) Version up program by Compact Flash
1.6.3.17 Safety Protection
(1) Main Unit Power Supply: Fuse
1-18 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 21
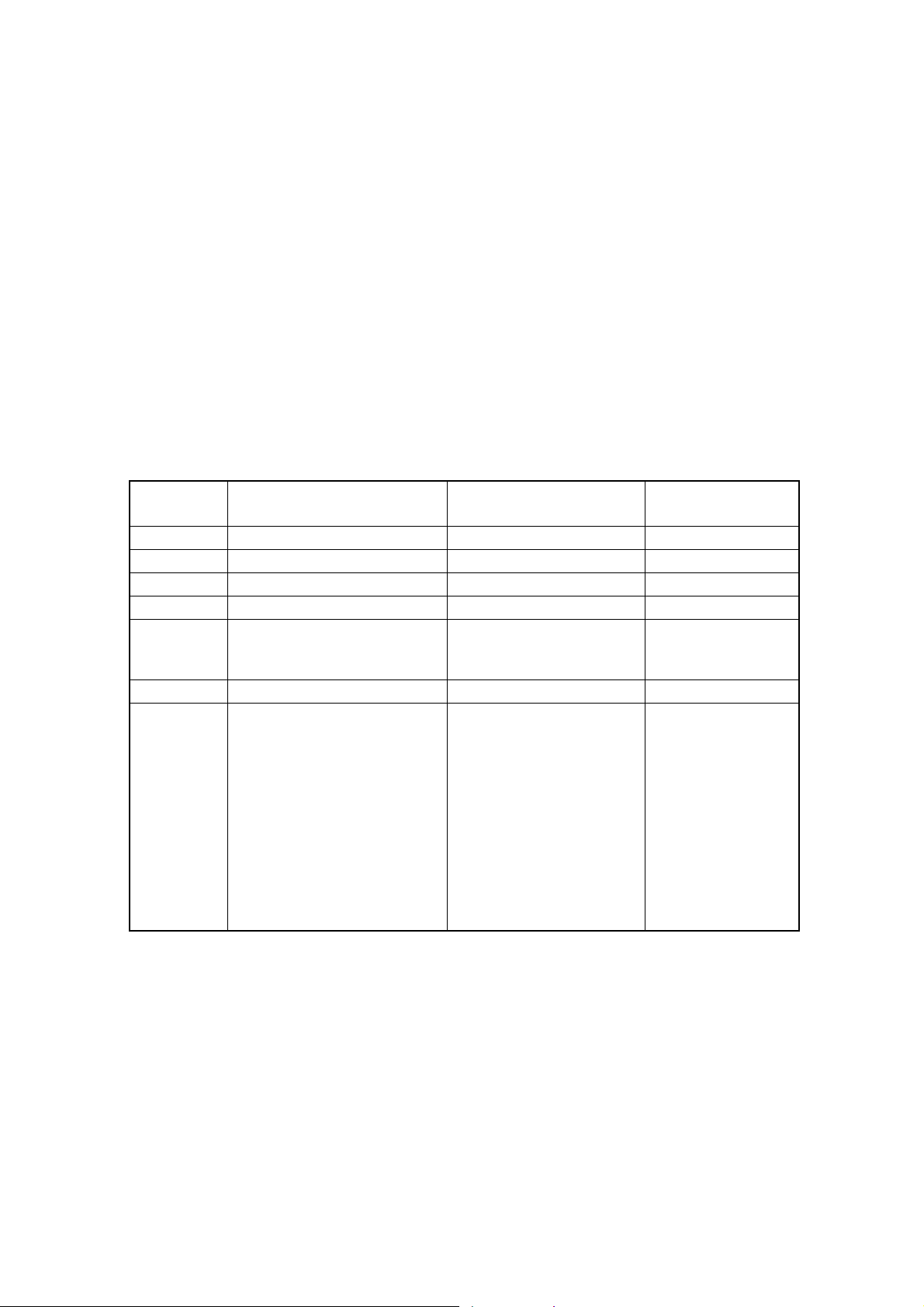
1.6.3.18 Reagent Control (exclude XP-100 for China market)
Scan the unique barcode on the reagent container so that the following data can be read by bar-
code reader on reagent replacement.
(1) Reagent Name
(2) Replacement Date/Time
(3) Lot Number
(4) Serial Number
(5) Expiration Date of reagent
(6) Expiration date of reagent after opening
(7) Products Code *In case of genuine products, the field is null.
(8) Manufacturer(Seller) *In case of genuine products, the field is null
(9) Manufacturer(Seller) *In case of genuine products, the field is null
1.7 TRACEABILITY
Items Traceability guaranty Calibration standard
Reason for null
material
WBC ICSH Reference method SCS - 1000 -
RBC ICSH Reference method SCS - 1000 -
HGB ICSH Reference method SCS - 1000 -
HCT ICSH Reference method SCS - 1000 -
MCV
MCH
MCHC
PLT ICSH Reference method SCS - 1000 -
W-SCR
W-MCR
W-LCR
W-SCC
W-MCC
W-LCC
RDW-CV
RDW-SD
PDW
MPV
P-LCR
PCT
- - Due to calculated
item.
- - Due to analyzed and
calculated items
from histogram of
WBC, RBC and PLT
1.8 REQUIREMENTS
1.8.1 Environmental Requirements
(1) Ambient temperature : 15 - 30°C(The reagent temperature should also be within this range.)
(2) Relative Humidity : 30 - 85%
(3) Atmospheric Pressure : 70 - 106kPa
(4) Installation Condition : Avoid installation in a place where the instrument may be exposed to
direct sunlight, dust, vibration or acid
(5) Electromagnetic Environment
EMC conformity standard : IEC61326-2-6: 2005
EMI(emission) test : Class A
1-19 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 22

1.8.2 Electric Source
(1) Voltage : 100, 120, 220, 230, 240V/AC
(2) Frequency : 50/60Hz
1.8.3 Reagents
(1) Diluent : CELLPACK
(2) Lyse reagent : STROMATOLYSER-WH
(3) Detergent : CELLCLEAN
1.9 OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE
1.9.1 Operation
(1) Applicable Sample Collection Tube
Length : 80 mm or shorter (Excluding lid)
(2) Preparation
i) Reagent check and replacement
Check the volume of reagent and replace when needed.
ii) Turn on power
iii) Check instruments
Instruments starts self-check process automatically, when power is turned on.
iv) Quality Control
Check data with control blood or other QC method.
(3) Measurement
Press [Start] switch to aspirate sample with pipette and measure.
(4) Analysis results
Analysis results is displayed after measurement. The result can be printed and output to a computer.
(5) Post-analysis operation
i) Cleaning is executed automatically during shutdown process.
ii) Turn off the instrument
(6) Preventive Maintenance
To keep reliability of analysis results, carry out PM by control blood and other method, and to keep the
instruments stable, carry out defined maintenance items periodically.
1.9.2 Supply
(1) Reagent
Diluent, Lyse reagent, CELLCLEAN
(2) Consumables
i) Replacement parts : Fuse
ii) Filling parts : Paper for printing
iii) Additional parts : Brush, Pipette
1-20 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 23
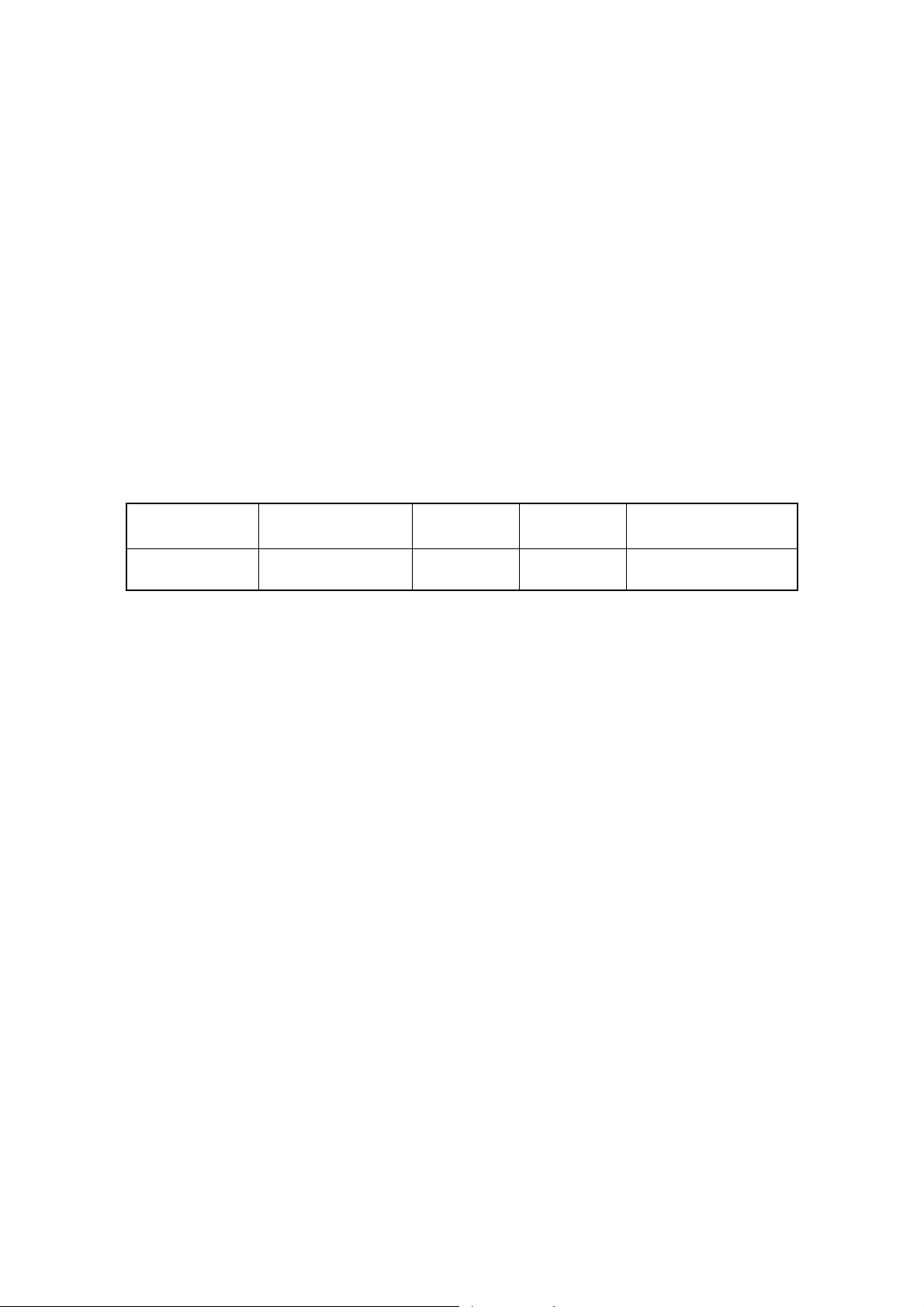
1.9.3 Maintenance
(1) Customer Maintenance
Customer maintenance and service should be executed from the front or side faces.
i) Shutdown : Once/day
ii) Clean SRV : Once/3 months or when operation cycle count becomes 4,500 cycles
iii) Clean detector : Once/Month or when operation cycle count becomes 1,500 cycles
iv) Clean waste chamber: Once/Month or when operation cycle count becomes 1,500 cycles
v) Replace reagent : As needed
(2) User Maintenance Item
User maintenance should be executed from the front or side.
i) Clean detector
ii) Pressure adjustment
(3) Regular Maintenance Item by FSR
None
1.10 PACKAGING
Package Unit Dimention(mm) Total
Main body and
accessories
505Dx595Wx593H Approx. 35kg Approx.
1.11 ATTACHMENTS
1.11.1 Accessories
(1) Service Manual
(2) Power cord
(3) Dispensing set
(4) Tray
(5) Tubes
(6) Syringe
(7) Brush
(8) Fuse
(9) Clamp
(10) Paper for printing (Roll sheet)
1.12 REQUIRED CONDITIONS
Weight
Weight of
packages
4.4kg
Corrugated board
NO
1.12.1 Environmental Conditions
(1) Ambient Temperature : 15 - 30°C
(2) Relative Humidity : 30 - 85%, No dew condensation
(3) Atmospheric Pressure : 70 - 106kPa
Avoid an installation location where the instrument may be exposed to direct sunlight.
1-21 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 24

1.13 ACOUSTIC NOISE
The noise level should be 55dB or less in conformity with SYSMEX internal testing method.
1.14 EXPECTED LIFE TIME
(1) Service life : 5 years
(2) Number of standard sample processing : 60 samples/day
(3) Designed life time : 60 samples/day x 300 days/year x 5 years = 90,000 samples
1-22 April 2013XP series S/M
Page 25

CHAPTER 2 HYDRAULICS AND MECHANICAL SYSTEM
2.1 HYDRAULIC SYSTEM BLOCK DIAGRAM................................................................1
2.1.1 Block Diagram (Whole Blood Mode) ...................................................................1
2.1.2 Block Diagram (Pre-diluted Mode)......................................................................1
2.2 ANALYSIS FLOW.......................................................................................................2
2.2.1 WBC/HGB Analysis Flow....................................................................................2
2.2.2 RBC/PLT Analysis Flow......................................................................................2
2.3 SAMPLE FLOW IN SRV.............................................................................................3
2.3.1 Sample Path........................................................................................................3
2.3.2 Sample Path (Whole Blood Mode)......................................................................4
2.3.3 Sample Path (Pre-diluted Mode).........................................................................4
2.4 SOLENOID VALVE LOCATION.................................................................................5
2.5 DIAPHRAGM PUMP LOCATION...............................................................................6
2.6 MASTER VALVE LOCATION.....................................................................................7
2.6.1 Valve Unit A........................................................................................................7
2.6.2 Valve Unit B........................................................................................................8
2.7 PNEUMATIC SYSTEM...............................................................................................9
2.7.1 Sample Aspiration System..................................................................................9
2.7.2 Vacuum System................................................................................................10
2.7.3 Pressure System...............................................................................................10
2.8 WASTE CHAMBER TUBING ...................................................................................11
2.9 RINSE CUP..............................................................................................................11
2.10 RBC DETECTOR UNIT..........................................................................................12
2.11 WBC DETECTOR UNIT.........................................................................................12
2.12 SRV UNIT...............................................................................................................13
2.13 HYDRAULIC FLOW DESCRIPTION......................................................................14
2.13.1 Whole Blood Mode..........................................................................................14
2.13.1.1) Sample Aspiration...................................................................................14
2.13.1.2) HGB Blank Analysis................................................................................15
2.13.1.3) Creating samples for RBC and WBC analysis........................................16
2.13.1.4) HGB Analysis..........................................................................................19
2.13.1.5) RBC/WBC analysis.................................................................................20
2.13.2 Pre-diluted Mode.............................................................................................21
2.13.2.1) Sample Aspiration...................................................................................21
2.13.2.2) HGB blank analysis.................................................................................21
2.13.2.3) Preparing samples for RBC/WBC analysis.............................................22
2.13.2.4) HGB Analysis..........................................................................................22
2.13.2.5) RBC/WBC Analysis.................................................................................22
2.14 PNEUMATIC & HYDRAULIC PARTS ....................................................................23
November 2012XP series S/M
Page 26

CHAPTER 2 HYDRAULICS AND MECHANICAL SYSTEM
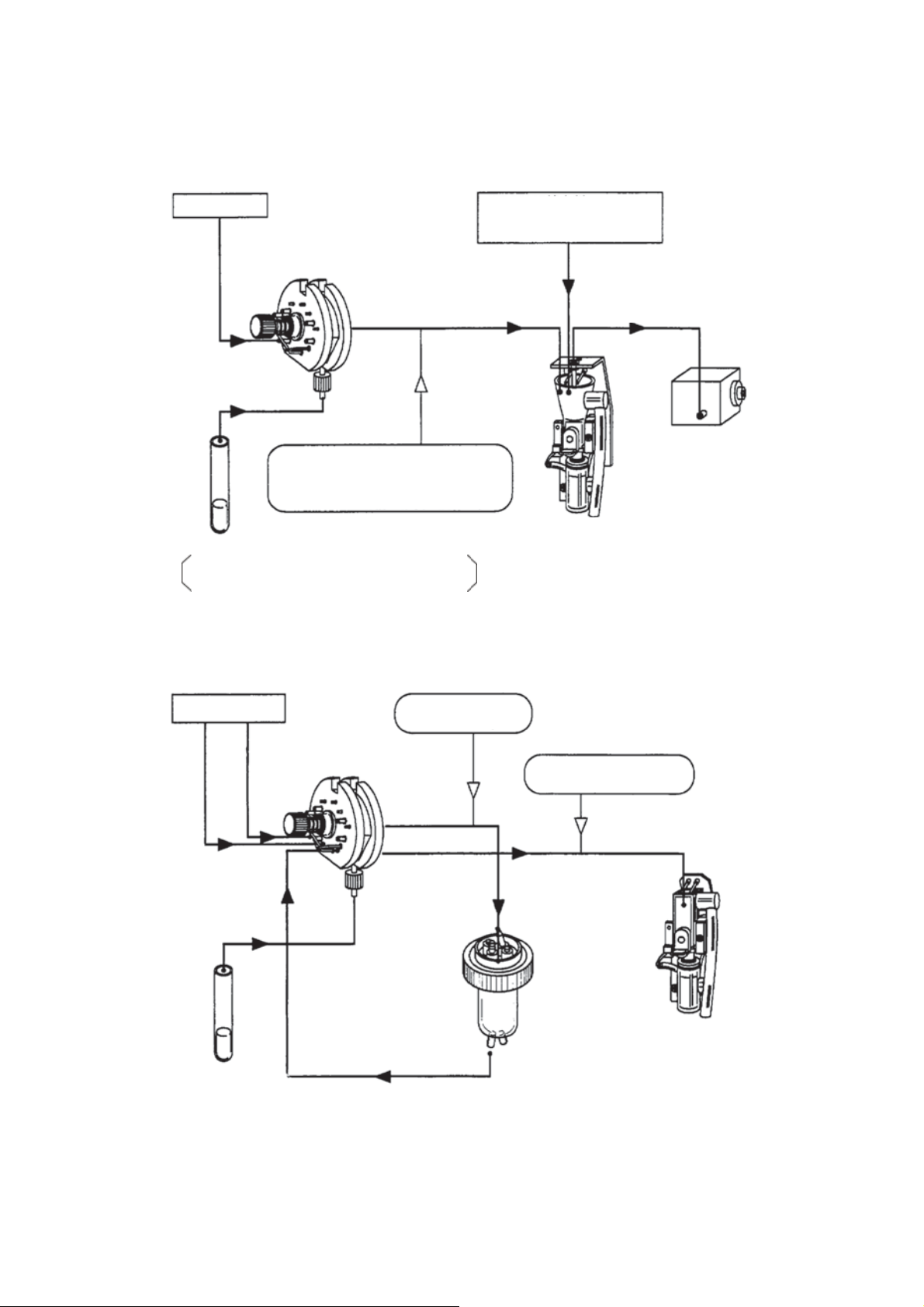
2.1 HYDRAULIC SYSTEM BLOCK DIAGRAM
2.1.1 Block Diagram (Whole Blood Mode)
Figure 2-1-1: Whole Blood Mode Block Diagram
2.1.2 Block Diagram (Pre-diluted Mode)
Figure 2-1-2: Pre-diluted Mode Block Diagram
2-1 April 27, 2012XP series S/M
Page 27
2.2 ANALYSIS FLOW
㻰㼕㼘㼡㼑㼚㼠㻌㻦㻌㻞㻚㻜㼙㻸
㻿㼍㼙㼜㼘㼕㼚㼓㻌㼂㼍㼘㼢㼑
㼃㼔㼛㼘㼑㻌㻮㼘㼛㼛㼐㻌㻹㼛㼐㼑㻌㻦㻌㻌㻌㻰㼕㼘㼡㼑㼚㼠㻌㻌㻌㻌㻝㻚㻥㻥㻠㼙㻸
㻮㼘㼛㼛㼐㻌㻌㻌㻌㻌㻌㻌㻌㻌㻢䃛㻸
㻼㼞㼑㻙㼐㼕㼘㼡㼠㼑㼐㻌㻹㼛㼐㼑㻌㻦㻌㻌㻌㻌㻌㻰㼕㼘㼡㼑㼚㼠㻌㻌㻌㻌㻝㻚㻥㻞㻞㼙㻸
㻝㻦㻞㻢㻌㻰㼕㼘㼡㼠㼑㼐㻌㻿㼍㼙㼜㼘㼑㻌㻌㻌㻣㻤䃛㻸
㼀㼡㼎㼑㻌㼛㼞㻌㻹㼕㼏㼞㼛㼠㼡㼎㼑
㼃㼔㼛㼘㼑㻌㻮㼘㼛㼛㼐㻌㻹㼛㼐㼑㻌㻦㻌㻮㼘㼛㼛㼐㻌㻡㻜䃛㻸
㻼㼞㼑㻙㼐㼕㼘㼡㼠㼑㼐㻌㻹㼛㼐㼑㻌㻦㻌㻝㻦㻞㻢㻌㻰㼕㼘㼡㼠㼑㼐㻌㻿㼍㼙㼜㼘㼑㻌㻞㻜㻜䃛㻸
㼃㻮㻯㻌㼀㼞㼍㼚㼟㼐㼡㼏㼑㼞
㻴㻳㻮㻌㻲㼘㼛㼣㻌㻯㼑㼘㼘
㼃㼔㼛㼘㼑㻌㻮㼘㼛㼛㼐㻌㻹㼛㼐㼑㻌㻌㻝㼙㻸㻌
㻼㼞㼑㻙㼐㼕㼘㼡㼠㼑㼐㻌㻹㼛㼐㼑㻌㻌㻝㼙㻸
㼃㻮㻯㻛㻴㻳㻮㻌㻸㼥㼟㼑㻌㻦
㼃㼔㼛㼘㼑㻌㻮㼘㼛㼛㼐㻌㻹㼛㼐㼑㻌㻌㻝㻚㻜㼙㻸
㻼㼞㼑㻙㼐㼕㼘㼡㼠㼑㼐㻌㻹㼛㼐㼑㻌㻌㻝㻚㻜㼙㻸㻌
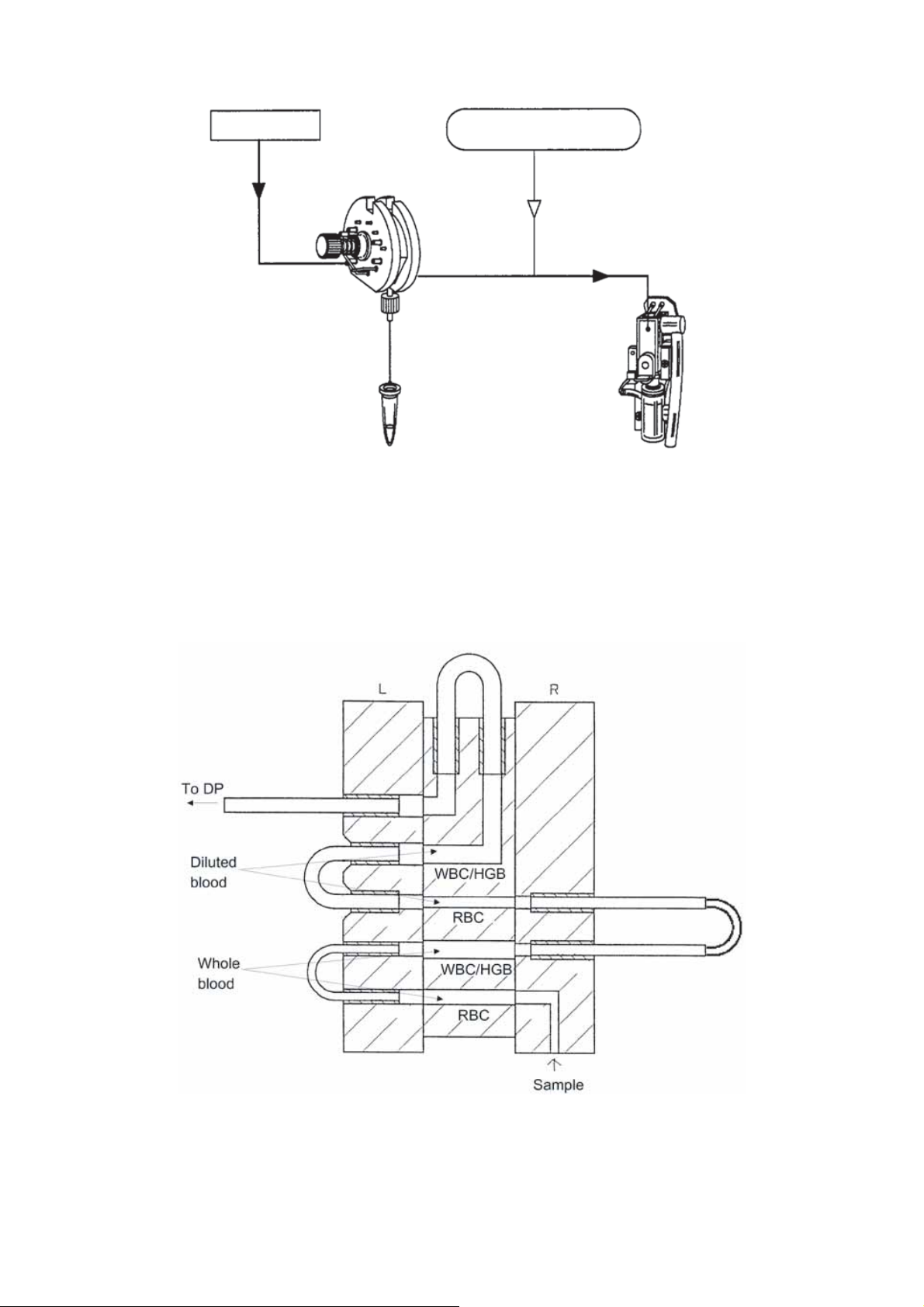
2.2.1 WBC/HGB Analysis Flow
Figure 2-2-1: WBC/HGB Analysis Flow
2.2.2 RBC/PLT Analysis Flow
㻰㼕㼘㼡㼑㼚㼠㻌㻦㻌㻞㻚㻜㼙㻸
㻿㼍㼙㼜㼘㼕㼚㼓㻌㼂㼍㼘㼢㼑
㼀㼡㼎㼑
㻔㻮㼘㼛㼛㼐㻌㻦㻌㻡㻜䃛㻸䠅
㻔㻝㻦㻡㻜㻜㻌㻰㼕㼘㼡㼠㼕㼛㼚㻌㻿㼍㼙㼜㼘㼑㻌㻦㻌㻠㻜䃛㻸㻕
㻰㼕㼘㼡㼑㼚㼠㻌㻦㻌㻝㻚㻥㻥㻢㼙㻸
㼃㼔㼛㼘㼑㻌㻮㼘㼛㼛㼐㻌㻦㻌㻠䃛㻸
㻹㼕㼤㼕㼚㼓㻌㻯㼔㼍㼙㼎㼑㼞
㻝㻦㻡㻜㻜㻌㻰㼕㼘㼡㼠㼕㼛㼚㻌㻿㼍㼙㼜㼘㼑㻌㻦㻌㻠㻜䃛㻸
㻰㼕㼘㼡㼑㼚㼠㻌㻦㻌㻝㻚㻥㻢㻜㼙㻸
㻾㻮㻯㻛㻼㻸㼀㻌㻌㼀㼞㼍㼚㼟㼐㼡㼏㼑㼞
Figure 2-2-2: RBC/PLT Analysis Flow (Whole Blood Mode)
2-2 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 28
㻰㼕㼘㼡㼑㼚㼠㻌㻦㻌㻞㻚㻜㼙㻸
㻰㼕㼘㼡㼑㼚㼠㻌㻌㻌㻌㻌㻌㻌㻌㻌㻝㻚㻥㻥㻣㻥㻞㼙㻸
㻝㻦㻞㻢㻌㻰㼕㼘㼡㼠㼑㼐㻌㻿㼍㼙㼜㼘㼑㻌㻌㻌㻞㻚㻜㻤䃛㻸
㻿㼍㼙㼜㼘㼕㼚㼓㻌㼂㼍㼘㼢㼑
㻔㻝㻦㻞㻢㻌㻰㼕㼘㼡㼠㼑㼐㻌㻿㼍㼙㼜㼘㼑㻌㻦㻌㻞㻜㻜䃛㻸㻕
㻹㼕㼏㼞㼛㼠㼡㼎㼑
Figure 2-2-3: RBC/PLT Analysis Flow (Pre-diluted Mode)
2.3 SAMPLE FLOW IN SRV
2.3.1 Sample Path
㻾㻮㻯㻛㻼㻸㼀㻌㻌㼀㼞㼍㼚㼟㼐㼡㼏㼑㼞
Figure 2-3-1: Sample Flow in SRV
2-3 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 29
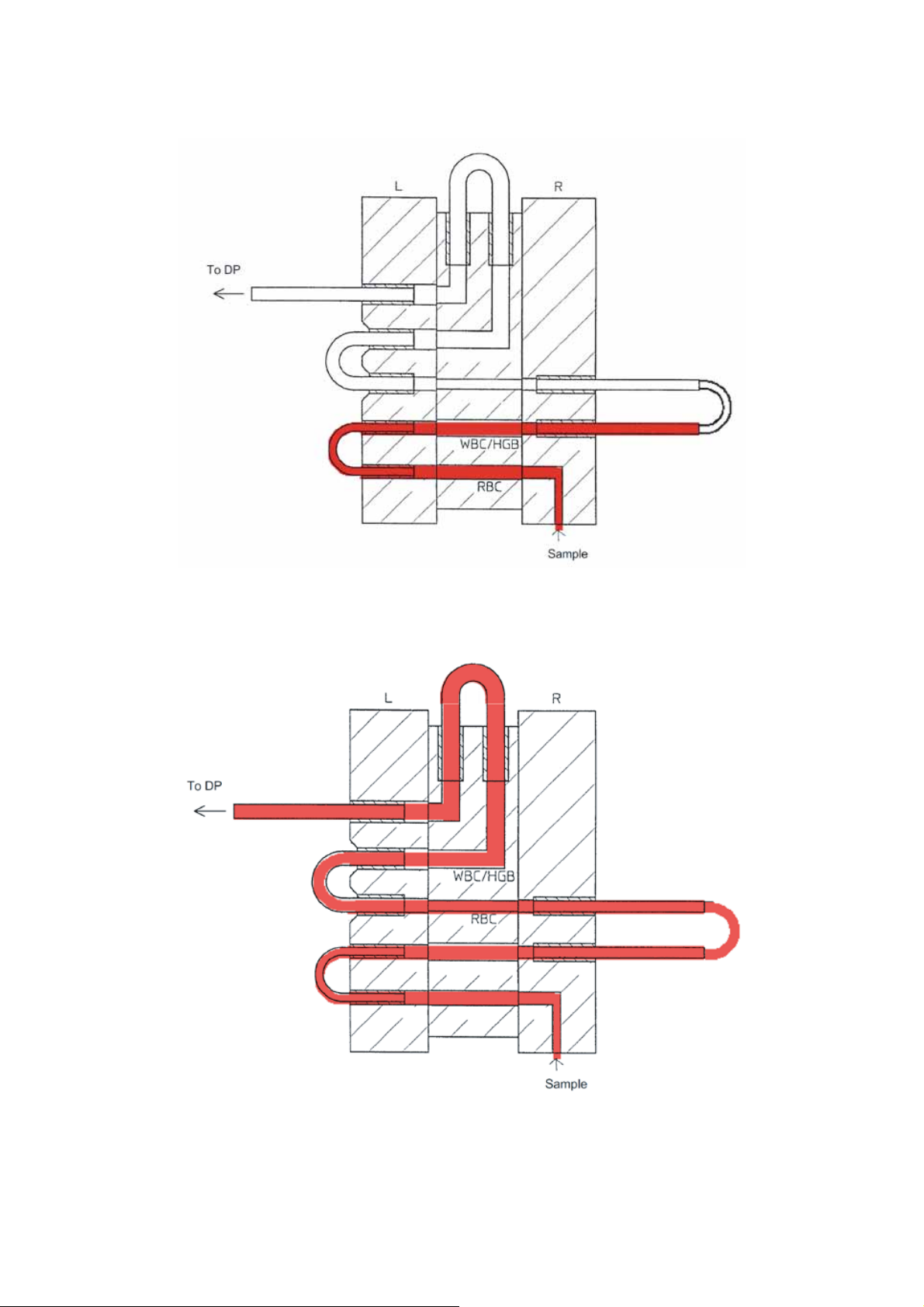
2.3.2 Sample Path (Whole Blood Mode)
Figure 2-3-2: Sample Flow in SRV (Whole Blood Mode)
2.3.3 Sample Path (Pre-diluted Mode)
Figure 2-3-3: Sample Flow in SRV (Pre-diluted Mode)
2-4 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 30
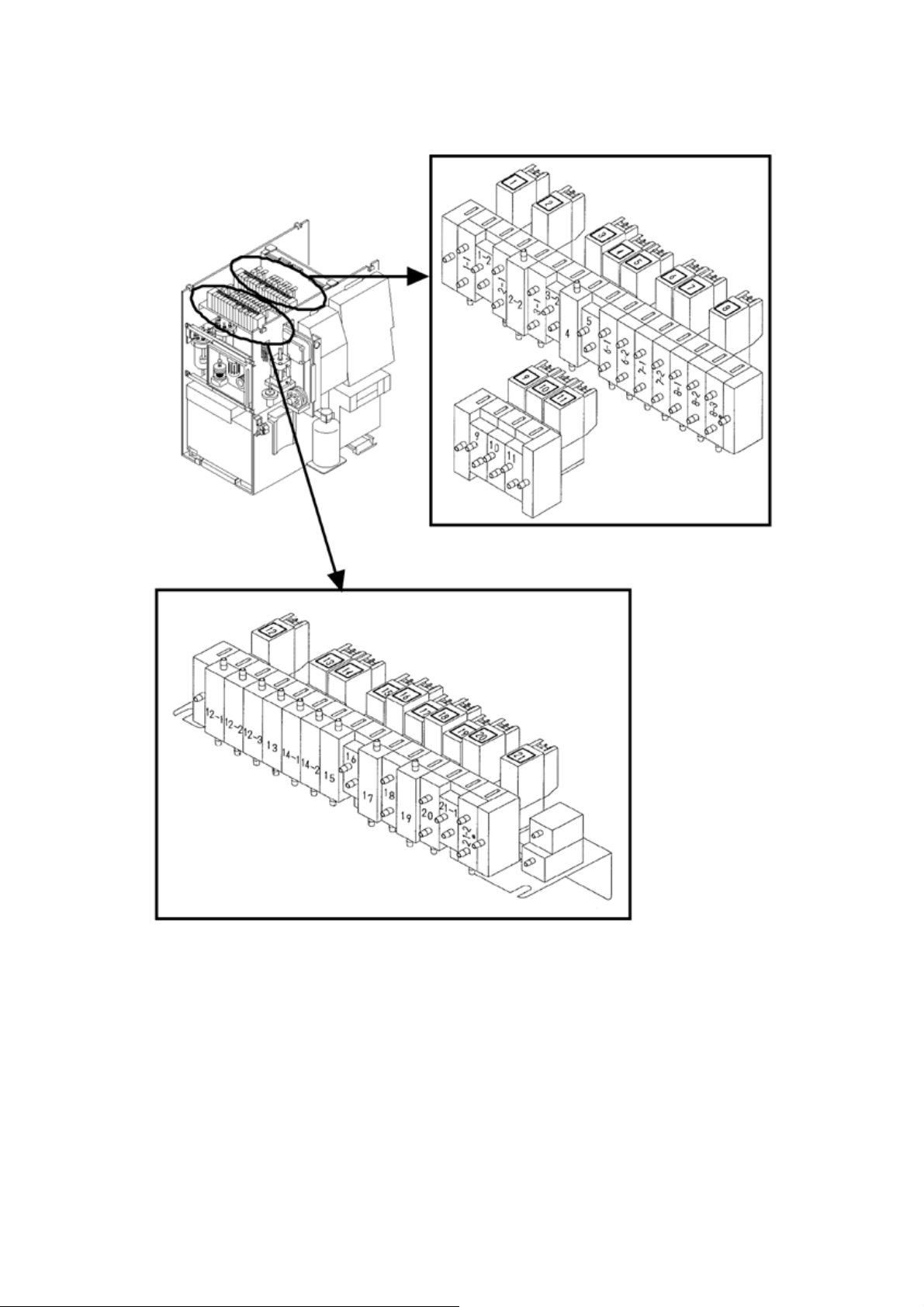
2.4 SOLENOID VALVE LOCATION
Figure 2-4-1: Valve Location
2-5 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 31

2.5 DIAPHRAGM PUMP LOCATION
Figure 2-5-1: Diaphragm Pump Location
2-6 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 32

2.6 MASTER VALVE LOCATION
0.20MPa
2.6.1 Valve Unit A
MV No. Function MV No. Function
1-1 Waste drain, switch pressure/vacuum 6-1 RBC diluent DP fill/dispense switch
1-2 Waste drain, drive Pinch Valve 6-2 RBC diluent DP drive
2-1 Diluent fill, switch pressure/vacuum 7-1 RBC diluent line switch
2-2 Diluent fill, connect diluent line 7-2 WBC/Hgb diluent line switch
3-1 Diluent chamber pressure relief 8-1 WBC/Hgb diluent DP/lyse DP drive
3-2 Rinse cup drain, drive Pinch Valve 8-2 WBC/Hgb diluent DP switch
4 STR-WH (lyse) dispense control 8-3 WBC/Hgb lyse DP switch
5 Fill Detector Block Master Valve Assy
Figure 2-6-1: Valve Unit A-1 Tubing
Figure 2-6-2: Valve Unit A-2 Tubing
201297
2-7 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 33

2.6.2 Valve Unit B
0.20MPa
-0.0333
MPa
MV No. Function MV No. Function
12-1 Fill Rinse Cup 16 SRV rotation
12-2 SRV vacuum cut 17 RBC charging
12-3 SRV outer rinse 18 PD mode sample aspiration DP drive
13 Mixing Chamber drain 19 Supply rinse into sample aspiration line
14-1 RBC Transducer drain 20 WB mode sample aspiration DP drive
14-2 WBC Transducer drain 21-1 Air gap generation
15 Hgb Flow Cell drain 21-2 Detector DP drive for counting
Figure 2-6-3: Valve Unit B Tubing
2-8 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 34

2.7 PNEUMATIC SYSTEM
Pressure is only monitored for 0.05MPa. (Pressure at the source is not monitored.)
Vacuum is only monitored for -0.0333MPa. (Vacuum source is not monitored.)
2.7.1 Sample Aspiration System
Aspiration speed is adjusted to Whole Blood mode. Tube Teflon is inserted betwee n Whole Blood
DP and Diluted Blood DP for adjusting aspiration speed.
201297
Figure 2-7-1: Sample Aspiration System
2-9 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 35

2.7.2 V acuum System
XP series has no tank for Vacuum system therefore Polyurethane tubing is inserted between bellows and pressure switch for stabilizing the vacuum.
-0.0333MPa
-0.0333MPa
Figure 2-7-2: Vacuum System
2.7.3 Pressure System
XP series has no tank for pressure system therefore Teflon tubing is inserted between compressor
and 0.05MPa regulator for stabilizing the pressure.
0.05MPa
0.05MPa
Figure 2-7-3: Pressure System
2-10 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 36

2.8 WASTE CHAMBER TUBING
-0.0333MPa
Figure 2-8-1: Waste Chamber Tubing
2.9 RINSE CUP
Rinsing solution is injected while the rinse cup is going down and any blood adhering to the pipette
exterior is aspirated into the waste chamber. (Left in Figure 2-9-1 below.)
To clean the whole blood line, rinsing solution (containing whole blood) is discharged from the
pipette tip and aspirated into the waste chamber when the rinse cup reache s the lower end point.
When the rinse cup goes up, rinsing solution will not be discharged nor aspirated into the pipette.
(Right in Figure 2-9-1 below.)
(-0.0333MPa)
Figure 2-9-1: Rinse Cup
2-11 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 37

2.10 RBC DETECTOR UNIT
Figure 2-10-1: RBC Detector Unit
2.11 WBC DETECTOR UNIT
Figure 2-11-1: WBC Detector Unit
2-12 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 38

2.12 SRV UNIT
Figure 2-12-1: SRV Unit
2-13 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 39

2.13 HYDRAULIC FLOW DESCRIPTION
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪧
㪪㪭㪊
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪉㪇
㪪㪭㪈㪊
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪈㪌㪇
㱂㪈㪅㪏㬍㪣㪈㪋㪇㪇
㱂㪇㪅㪏㬍㪣㪎㪇㪇
㪪㪭㪈
㪪㪭㪋
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪇
㪌㪇㱘㫃
㪉㪇㪇㱘㫃
㪉㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪭㪸㪺
㪉㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪌
㪈㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪌㪇㪇㱘㪣㪉㪌㪇㱘㪣
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪛㫀㫃
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪛㫀㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪋㪇
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪭㪸㪺
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪧㪪
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪤
㪧
㪭
㪧㪪
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪧
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪛㫀㫃
㪭㪸㪺
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪪㪭㪉
㪤㪭㪉㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪉㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪄㪈
㪪㪭㪈㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪍
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪊
㪪㪭㪈㪎
㪪㪭㪈㪋
㪤㪭㪈㪋㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪋㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪌
㪪㪭㪉㪈
㪤㪭㪉㪈㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪐
㪪㪭㪈㪌
㪪㪭㪏
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪊
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪍㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪍㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪍
㪪㪭㪈㪐
㪪㪭㪈㪏
㪤㪭㪉㪈㪄㪈
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪈
㪪㪭㪎
㪤㪭㪎㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪎㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪊㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪌
㪤㪭㪋
㪤㪭㪈㪎
㪤㪭㪈㪊
㪤㪭㪈㪐
㪤㪭㪈㪏
㪤㪭㪉㪇
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪊㪇
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪚
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪘
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪙
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪛
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪌
WB Mode WB Asp. DP
WBC/HGB DP
RBC DP
STROMATOLYSER WH DP
Dilution Mode Dilution ASP. DP
RBC
Transducer
WBC
Transducer
HGB Cell
Compressor
CELLPACK
Chamber
Waste
CELLPACK
Trap
Chamber
Waste
Chamber
Mixing
Chamber
Rince Cup
ASP
Pipette
STROMATOLYSER
WH Bottle
Regulator Section
Transducer
Chamber Unit
Sample Aspiration
Vacuum
2.13.1 Whole Blood Mode
2.13.1.1) Sample Aspiration
1) Samples are aspirated into SRV using Whole Blood Mode Aspiration Diaphragm Pump.
2-14 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 40

2.13.1.2) HGB Blank Analysis
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪧
㪪㪭㪊
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪉㪇
㪪㪭㪈㪊
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪈㪌㪇
㱂㪈㪅㪏㬍㪣㪈㪋㪇㪇
㱂㪇㪅㪏㬍㪣㪎㪇㪇
㪪㪭㪈
㪪㪭㪋
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪇
㪌㪇㱘㫃
㪉㪇㪇㱘㫃
㪉㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪭㪸㪺
㪉㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪌
㪈㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪌㪇㪇㱘㪣㪉㪌㪇㱘㪣
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪛㫀㫃
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪛㫀㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪋㪇
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪭㪸㪺
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪧㪪
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪤
㪧
㪭
㪧㪪
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪧
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪛㫀㫃
㪭㪸㪺
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪪㪭㪉
㪤㪭㪉㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪉㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪄㪈
㪪㪭㪈㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪍
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪊
㪪㪭㪈㪎
㪪㪭㪈㪋
㪤㪭㪈㪋㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪋㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪌
㪪㪭㪉㪈
㪤㪭㪉㪈㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪐
㪪㪭㪈㪌
㪪㪭㪏
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪊
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪍㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪍㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪍
㪪㪭㪈㪐
㪪㪭㪈㪏
㪤㪭㪉㪈㪄㪈
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪈
㪪㪭㪎
㪤㪭㪎㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪎㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪊㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪌
㪤㪭㪋
㪤㪭㪈㪎
㪤㪭㪈㪊
㪤㪭㪈㪐
㪤㪭㪈㪏
㪤㪭㪉㪇
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪊㪇
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪚
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪘
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪙
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪛
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪌
WB Mode WB Asp. DP
WBC/HGB DP
RBC DP
STROMATOLYSER WH DP
Dilution Mode Dilution ASP. DP
RBC
Transducer
WBC
Transducer
HGB Cell
Compressor
CELLPACK
Chamber
Waste
CELLPACK
Trap
Chamber
Waste
Chamber
Mixing
Chamber
Rince Cup
ASP
Pipette
STROMATOLYSER
WH Bottle
Regulator Section
Transducer
Chamber Unit
HGB blank sample aspiration
Vacuum
1) Samples (diluent and lyse) in WBC Detector Unit are aspirated into HGB Flow Cell to perform HGB blank analysis.
2-15 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 41

2.13.1.3) Creating samples for RBC and WBC analysis
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪧
㪪㪭㪊
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪉㪇
㪪㪭㪈㪊
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪈㪌㪇
㱂㪈㪅㪏㬍㪣㪈㪋㪇㪇
㱂㪇㪅㪏㬍㪣㪎㪇㪇
㪪㪭㪈
㪪㪭㪋
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪇
㪌㪇㱘㫃
㪉㪇㪇㱘㫃
㪉㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪭㪸㪺
㪉㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪌
㪈㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪌㪇㪇㱘㪣㪉㪌㪇㱘㪣
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪛㫀㫃
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪛㫀㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪋㪇
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪭㪸㪺
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪧㪪
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪤
㪧
㪭
㪧㪪
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪧
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪛㫀㫃
㪭㪸㪺
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪪㪭㪉
㪤㪭㪉㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪉㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪄㪈
㪪㪭㪈㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪍
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪊
㪪㪭㪈㪎
㪪㪭㪈㪋
㪤㪭㪈㪋㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪋㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪌
㪪㪭㪉㪈
㪤㪭㪉㪈㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪐
㪪㪭㪈㪌
㪪㪭㪏
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪊
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪍㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪍㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪍
㪪㪭㪈㪐
㪪㪭㪈㪏
㪤㪭㪉㪈㪄㪈
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪈
㪪㪭㪎
㪤㪭㪎㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪎㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪊㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪌
㪤㪭㪋
㪤㪭㪈㪎
㪤㪭㪈㪊
㪤㪭㪈㪐
㪤㪭㪈㪏
㪤㪭㪉㪇
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪊㪇
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪚
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪘
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪙
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪛
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪌
WB Mode WB Asp. DP
WBC/HGB DP
RBC DP
STROMATOLYSER WH DP
Dilution Mode Dilution ASP. DP
RBC
Transducer
WBC
Transducer
HGB Cell
Compressor
CELLPACK
Chamber
Waste
CELLPACK
Trap
Chamber
Waste
Chamber
Mixing
Chamber
Rince Cup
ASP
Pipette
STROMATOLYSER
WH Bottle
Regulator Section
Transducer
Chamber Unit
RBC 1st dilution
Vacuum
1) SRV rotates.
2) Samples within SRV and diluent are dispensed into Mixing Chamber to create RBC 1st
dilution samples.
3) RBC 1st dilution samples are mixed in Mixing Chamber by bubbles.
2-16 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 42

4) RBC 1st dilution samples are within SRV.
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪧
㪪㪭㪊
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪉㪇
㪪㪭㪈㪊
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪈㪌㪇
㱂㪈㪅㪏㬍㪣㪈㪋㪇㪇
㱂㪇㪅㪏㬍㪣㪎㪇㪇
㪪㪭㪈
㪪㪭㪋
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪇
㪌㪇㱘㫃
㪉㪇㪇㱘㫃
㪉㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪭㪸㪺
㪉㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪌
㪈㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪌㪇㪇㱘㪣㪉㪌㪇㱘㪣
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪛㫀㫃
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪛㫀㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪋㪇
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪭㪸㪺
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪧㪪
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪤
㪧
㪭
㪧㪪
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪧
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪛㫀㫃
㪭㪸㪺
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪪㪭㪉
㪤㪭㪉㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪉㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪄㪈
㪪㪭㪈㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪍
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪊
㪪㪭㪈㪎
㪪㪭㪈㪋
㪤㪭㪈㪋㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪋㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪌
㪪㪭㪉㪈
㪤㪭㪉㪈㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪐
㪪㪭㪈㪌
㪪㪭㪏
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪊
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪍㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪍㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪍
㪪㪭㪈㪐
㪪㪭㪈㪏
㪤㪭㪉㪈㪄㪈
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪈
㪪㪭㪎
㪤㪭㪎㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪎㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪊㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪌
㪤㪭㪋
㪤㪭㪈㪎
㪤㪭㪈㪊
㪤㪭㪈㪐
㪤㪭㪈㪏
㪤㪭㪉㪇
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪊㪇
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪚
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪘
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪙
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪛
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪌
WB Mode WB Asp. DP
WBC/HGB DP
RBC DP
STROMATOLYSER WH DP
Dilution Mode Dilution ASP. DP
RBC
Transducer
WBC
Transducer
HGB Cell
Compressor
CELLPACK
Chamber
Waste
CELLPACK
Trap
Chamber
Waste
Chamber
Mixing
Chamber
Rince Cup
ASP
Pipette
STROMATOLYSER
WH Bottle
Regulator Section
Transducer
Chamber Unit
Sample Aspiration for RBC 1st Dilution
Vacuum
2-17 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 43

5) SRV rotates.
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪧
㪪㪭㪊
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪉㪇
㪪㪭㪈㪊
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪈㪌㪇
㱂㪈㪅㪏㬍㪣㪈㪋㪇㪇
㱂㪇㪅㪏㬍㪣㪎㪇㪇
㪪㪭㪈
㪪㪭㪋
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪇
㪌㪇㱘㫃
㪉㪇㪇㱘㫃
㪉㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪭㪸㪺
㪉㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪌
㪈㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪌㪇㪇㱘㪣㪉㪌㪇㱘㪣
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪛㫀㫃
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪛㫀㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪋㪇
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪭㪸㪺
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪧㪪
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪤
㪧
㪭
㪧㪪
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪧
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪛㫀㫃
㪭㪸㪺
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪪㪭㪉
㪤㪭㪉㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪉㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪄㪈
㪪㪭㪈㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪍
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪊
㪪㪭㪈㪎
㪪㪭㪈㪋
㪤㪭㪈㪋㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪋㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪌
㪪㪭㪉㪈
㪤㪭㪉㪈㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪐
㪪㪭㪈㪌
㪪㪭㪏
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪊
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪍㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪍㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪍
㪪㪭㪈㪐
㪪㪭㪈㪏
㪤㪭㪉㪈㪄㪈
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪈
㪪㪭㪎
㪤㪭㪎㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪎㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪊㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪌
㪤㪭㪋
㪤㪭㪈㪎
㪤㪭㪈㪊
㪤㪭㪈㪐
㪤㪭㪈㪏
㪤㪭㪉㪇
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪊㪇
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪚
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪘
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪙
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪛
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪌
WB Mode WB Asp. DP
WBC/HGB DP
RBC DP
STROMATOLYSER WH DP
Dilution Mode Dilution ASP. DP
RBC
Transducer
WBC
Transducer
HGB Cell
Compressor
CELLPACK
Chamber
Waste
CELLPACK
Trap
Chamber
Waste
Chamber
Mixing
Chamber
Rince Cup
ASP
Pipette
STROMATOLYSER
WH Bottle
Regulator Section
Transducer
Chamber Unit
RBC 2nd Dilution
WBC Dilution
WBC/HGB Lyse
Pressure
6) RBC 1st dilution samples within SRV and diluent are dispensed into RBC Detector Unit
to create samples for RBC analysis.
7) Samples within SRV, diluent and lyse are dispensed into WBC Detector Unit to create
samples for WBC/HGB analysis.
8) Samples for RBC/WBC analysis are mixed by bubbles in the applicable detector units.
2-18 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 44

2.13.1.4) HGB Analysis
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪧
㪪㪭㪊
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪉㪇
㪪㪭㪈㪊
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪈㪌㪇
㱂㪈㪅㪏㬍㪣㪈㪋㪇㪇
㱂㪇㪅㪏㬍㪣㪎㪇㪇
㪪㪭㪈
㪪㪭㪋
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪇
㪌㪇㱘㫃
㪉㪇㪇㱘㫃
㪉㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪭㪸㪺
㪉㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪌
㪈㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪌㪇㪇㱘㪣㪉㪌㪇㱘㪣
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪛㫀㫃
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪛㫀㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪋㪇
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪭㪸㪺
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪧㪪
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪤
㪧
㪭
㪧㪪
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪧
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪛㫀㫃
㪭㪸㪺
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪪㪭㪉
㪤㪭㪉㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪉㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪄㪈
㪪㪭㪈㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪍
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪊
㪪㪭㪈㪎
㪪㪭㪈㪋
㪤㪭㪈㪋㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪋㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪌
㪪㪭㪉㪈
㪤㪭㪉㪈㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪐
㪪㪭㪈㪌
㪪㪭㪏
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪊
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪍㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪍㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪍
㪪㪭㪈㪐
㪪㪭㪈㪏
㪤㪭㪉㪈㪄㪈
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪈
㪪㪭㪎
㪤㪭㪎㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪎㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪊㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪌
㪤㪭㪋
㪤㪭㪈㪎
㪤㪭㪈㪊
㪤㪭㪈㪐
㪤㪭㪈㪏
㪤㪭㪉㪇
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪊㪇
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪚
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪘
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪙
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪛
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪌
WB Mode WB Asp. DP
WBC/HGB DP
RBC DP
STROMATOLYSER WH DP
Dilution Mode Dilution ASP. DP
RBC
Transducer
WBC
Transducer
HGB Cell
Compressor
CELLPACK
Chamber
Waste
CELLPACK
Trap
Chamber
Waste
Chamber
Mixing
Chamber
Rince Cup
ASP
Pipette
STROMATOLYSER
WH Bottle
Regulator Section
Transducer
Chamber Unit
HGB Sample Aspiration
Vacuum
1) Samples in WBC Detector Unit are aspirated into HGB Flow Cell to p erform HGB analysis.
2-19 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 45

2.13.1.5) RBC/WBC analysis
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪧
㪪㪭㪊
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪉㪇
㪪㪭㪈㪊
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪈㪌㪇
㱂㪈㪅㪏㬍㪣㪈㪋㪇㪇
㱂㪇㪅㪏㬍㪣㪎㪇㪇
㪪㪭㪈
㪪㪭㪋
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪇
㪌㪇㱘㫃
㪉㪇㪇㱘㫃
㪉㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪭㪸㪺
㪉㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪌
㪈㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪌㪇㪇㱘㪣㪉㪌㪇㱘㪣
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪛㫀㫃
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪛㫀㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪋㪇
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪭㪸㪺
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪧㪪
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪤
㪧
㪭
㪧㪪
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪧
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪛㫀㫃
㪭㪸㪺
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪪㪭㪉
㪤㪭㪉㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪉㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪄㪈
㪪㪭㪈㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪍
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪊
㪪㪭㪈㪎
㪪㪭㪈㪋
㪤㪭㪈㪋㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪋㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪌
㪪㪭㪉㪈
㪤㪭㪉㪈㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪐
㪪㪭㪈㪌
㪪㪭㪏
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪊
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪍㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪍㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪍
㪪㪭㪈㪐
㪪㪭㪈㪏
㪤㪭㪉㪈㪄㪈
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪈
㪪㪭㪎
㪤㪭㪎㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪎㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪊㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪌
㪤㪭㪋
㪤㪭㪈㪎
㪤㪭㪈㪊
㪤㪭㪈㪐
㪤㪭㪈㪏
㪤㪭㪉㪇
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪊㪇
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪚
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪘
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪙
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪛
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪌
WB Mode WB Asp. DP
WBC/HGB DP
RBC DP
STROMATOLYSER WH DP
Dilution Mode Dilution ASP. DP
RBC
Transducer
WBC
Transducer
HGB Cell
Compressor
CELLPACK
Chamber
Waste
CELLPACK
Trap
Chamber
Waste
Chamber
Mixing
Chamber
Rince Cup
ASP
Pipette
STROMATOLYSER
WH Bottle
Regulator Section
Transducer
Chamber Unit
WBC Analysis
Pressure
Vacuum
RBC Analysis
1) RBC/WBC samples are aspirated to perform analysis.
2-20 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 46
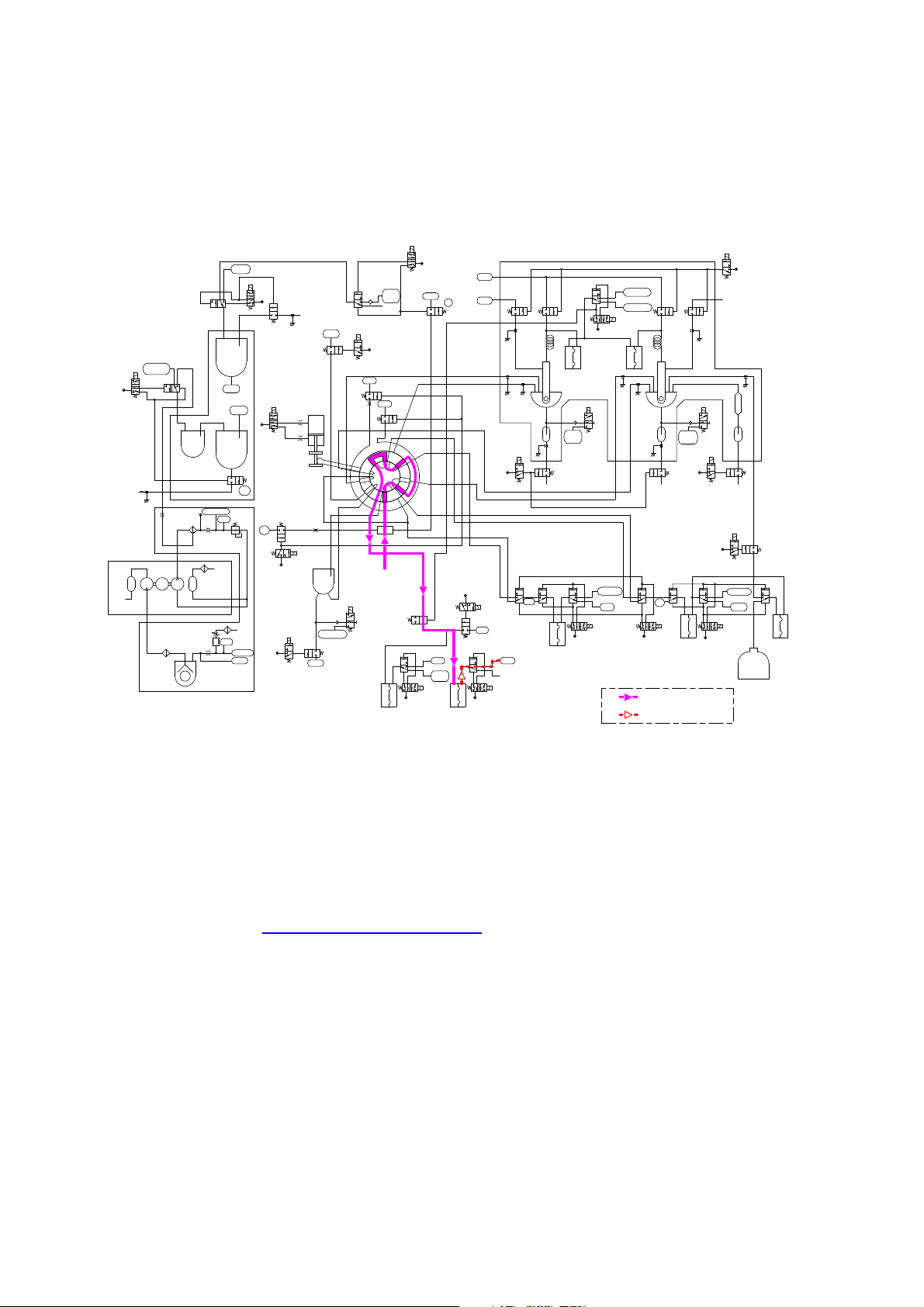
2.13.2 Pre-diluted Mode
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪧
㪪㪭㪊
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪉㪇
㪪㪭㪈㪊
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪈㪌㪇
㱂㪈㪅㪏㬍㪣㪈㪋㪇㪇
㱂㪇㪅㪏㬍㪣㪎㪇㪇
㪪㪭㪈
㪪㪭㪋
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪇
㪌㪇㱘㫃
㪉㪇㪇㱘㫃
㪉㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪭㪸㪺
㪉㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪌
㪈㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪌㪇㪇㱘㪣㪉㪌㪇㱘㪣
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪛㫀㫃
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪛㫀㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪋㪇
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪭㪸㪺
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪧㪪
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪤
㪧
㪭
㪧㪪
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪧
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪛㫀㫃
㪭㪸㪺
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪪㪭㪉
㪤㪭㪉㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪉㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪄㪈
㪪㪭㪈㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪍
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪊
㪪㪭㪈㪎
㪪㪭㪈㪋
㪤㪭㪈㪋㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪋㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪌
㪪㪭㪉㪈
㪤㪭㪉㪈㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪐
㪪㪭㪈㪌
㪪㪭㪏
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪊
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪍㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪍㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪍
㪪㪭㪈㪐
㪪㪭㪈㪏
㪤㪭㪉㪈㪄㪈
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪈
㪪㪭㪎
㪤㪭㪎㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪎㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪊㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪌
㪤㪭㪋
㪤㪭㪈㪎
㪤㪭㪈㪊
㪤㪭㪈㪐
㪤㪭㪈㪏
㪤㪭㪉㪇
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪊㪇
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪚
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪘
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪙
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪛
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪌
WB Mode WB Asp. DP
WBC/HGB DP
RBC DP
STROMATOLYSER WH DP
Dilution Mode Dilution ASP. DP
RBC
Transducer
WBC
Transducer
HGB Cell
Compressor
CELLPACK
Chamber
Waste
CELLPACK
Trap
Chamber
Waste
Chamber
Mixing
Chamber
Rince Cup
ASP
Pipette
STROMATOLYSER
WH Bottle
Regulator Section
Transducer
Chamber Unit
㪮㪿㫆㫃㪼㩷㪙㫃㫆㫆㪻 㪘㫊㫇㫀㫉㪸㫋㫀㫆㫅
㪭㪸㪺㫌㫌㫄
2.13.2.1) Sample Aspiration
1) Samples diluted 26-fold are aspirated into SRV using Pre-diluted Mode Aspiration Diaphragm Pump.
2.13.2.2) HGB blank analysis
1) Refer to 2.13.1.2) HGB Blank Analysis.
2-21 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 47

2.13.2.3) Preparing samples for RBC/WBC analysis
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪧
㪪㪭㪊
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪉㪇
㪪㪭㪈㪊
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪈㪌㪇
㱂㪈㪅㪏㬍㪣㪈㪋㪇㪇
㱂㪇㪅㪏㬍㪣㪎㪇㪇
㪪㪭㪈
㪪㪭㪋
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪇
㪌㪇㱘㫃
㪉㪇㪇㱘㫃
㪉㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪭㪸㪺
㪉㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪌
㪈㪅㪇㫄㫃
㪌㪇㪇㱘㪣㪉㪌㪇㱘㪣
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾
㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪛㫀㫃
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪭㪸㪺
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪛㫀㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪛㫀㫃
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪋㪇
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪭㪸㪺
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪧㪪
㪦㪧㪜㪥
㪤
㪧
㪭
㪧㪪
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪧
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪮㪅㪚㪅
㪛㫀㫃
㪭㪸㪺
㪉㪌㪇㫄㫄㪟㪾
㪪㪭㪉
㪤㪭㪉㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪉㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪄㪈
㪪㪭㪈㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪍
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪊
㪪㪭㪈㪎
㪪㪭㪈㪋
㪤㪭㪈㪋㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪋㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪌
㪪㪭㪉㪈
㪤㪭㪉㪈㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪐
㪪㪭㪈㪌
㪪㪭㪏
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪊
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪏㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪍㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪍㪄㪉
㪪㪭㪍
㪪㪭㪈㪐
㪪㪭㪈㪏
㪤㪭㪉㪈㪄㪈
㪇㪅㪌㫂㪾㪆㪺㫄㪉
㪪㪭㪈㪈
㪪㪭㪎
㪤㪭㪎㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪎㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪉㪄㪉
㪤㪭㪊㪄㪈
㪤㪭㪈㪌
㪤㪭㪋
㪤㪭㪈㪎
㪤㪭㪈㪊
㪤㪭㪈㪐
㪤㪭㪈㪏
㪤㪭㪉㪇
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪊㪇
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪚
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪘
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪙
㪤㪭㪌㪄㪛
㱂㪇㪅㪌㬍㪣㪌
WB Mode WB Asp. DP
WBC/HGB DP
RBC DP
STROMATOLYSER WH DP
Dilution Mode Dilution ASP. DP
RBC
Transducer
WBC
Transducer
HGB Cell
Compressor
CELLPACK
Chamber
Waste
CELLPACK
Trap
Chamber
Waste
Chamber
Mixing
Chamber
Rince Cup
ASP
Pipette
STROMATOLYSER
WH Bottle
Regulator Section
Transducer
Chamber Unit
RBC Dilution
WBC Dilution
WBC/HGB Lyse
Pressure
1) SRV rotates.
2) Samples within SRV and diluent are dispensed into RBC Detector Unit.
3) Samples within SRV, diluent and lyse are dispensed into WBC Detector Unit.
4) Samples for RBC/WBC analysis are mixed by bubbles in the applicable detector units.
2.13.2.4) HGB Analysis
1) Refer to 2.13.1.4) HGB Analysis.
2.13.2.5) RBC/WBC Analysis
1) Refer to 2.13.1.5) RBC/WBC analysis.
2-22 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 48

2.14 PNEUMATIC & HYDRAULIC PARTS
Pneumatic Controls are used to regulate the air-flow, and to change the direction of flow.
Name & Symbol Figures Used for
Regulator Regulator is used to regulate
airflow rate, which is adjusted by
turning the Adjustment Knob. Only
on regulator, which is shown in left
figure, is used in the XP series.
This regulator is used to regulate
0.20MPa air pressure into
0.05MPa pressure with an air filter
and auto draining mechanism.
Non-Return Valve The Non-return Valve perm its
hydraulic flow in only one direction
from A to B.
No hydraulic flow will occur from B
to A.
Orifice An orifice controls the rate of
airflow or the volume of air with
respect to time. These orifices are
identical to those used in the
pneumatic and hydraulic system.
There are several kinds of orifice
each of which permits a different
flow rate.
Table 2-1 Pneumatic and Hydraulic Parts (1)
2-23 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 49

Name & Symbol Figures Used for
Bellows The bellows unit in the XP series is
used to regulate the vacuum (-
0.0640MPa or more) into -
0.0333MPa. This unit consists of
bellows and small air tank. If the
inner vacuum exceeds the
mechanical pressure of bellows,
vacuum is released from its top
port. If the mechanical pressure
exceeds the inner vacuum of
bellows, vacuum increases after
the top port is closed by the needle
valve. (See below figures.)
Two types of Solenoid valves (3port and 5-port type) are used in
the hydraulic system.
Solenoid Valves are driven by
applying 12 VDC which are
controlled by computer program,
and are used to control the
pneumatic pressure to drive Master
valves, Air cylinder, or Air Bubble
Mixing.
Solenoid valve symbol has two
boxes in its drawing. Arrows in
these boxes indicate the status of
connection. Status (1) or (2) shown
in “Name & Symbol” column will be
switched by the activation of
solenoid valve by the activation or
deactivation of solenoid valve
respectively.
Table 2-1 Pneumatic and Hydraulic Parts (2)
2-24 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 50

Name & Symbol Figures Used for
Master valves in XP series are
used to switch Hydraulic lines
(liquid, 0.05MPa pressure, and -
0.0640MPa/-0.0333MPa vacuum).
Two types of Master Valve (2-port
and 3-port type) are used in the
hydraulic system. Master Valves
are driven by 0.20MPa air pressure
controlled by Solenoid valves.
Master valve symbols has also two
boxes in its drawing. Arrows and
lines in these boxes indicates
hydraulic ways. Status (1) or (2)
shown in “Name & Symbol” column
will be switched by the activation or
deactivation of master valve,
respectively.
Sample Rotor Valve
&
Air Cylinder
Sample Rotor Valve Mechanism is
driven by the air cylinder.
The air cylinder is provided with
two (A and B) ports, (A) for
pneumatic activation to rotate the
SRV counter clockwise and the
other (B) for pneumatic
deactivation to reset the SRV.
The 0.20MPa pressure for these
action are supplied by a 3-port type
solenoid valve.
Table 2-1 Pneumatic and Hydraulic Parts (3)
2-25 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 51

Name & Symbol Figures Used for
Diaphragm Pump Seven Diaphragm Pumps are used
in the hydraulic system. Diaphragm
Pumps are driven by 0.05MPa air
pressure and -0.0640MPa vacuum
controlled by Master valves, and
dispenses or aspirates constant
volume of liquid. Diaphragm
Pumps are drawn by left symbols
in sequence flow charts.
Diaphragm Pump has two nipples
on it. One is to connect to
pneumatic system (0.05MPa
pressure or -0.0640MPa vacuum),
and the other is to hydraulic
system. Either of pressure or
vacuum is always supplied to the
pneumatic side nipple. If the
vacuum is supplied to pneumatic
side nipple, the fixed volume of
liquid is aspirated into the
diaphragm pump. If the pressure
supplied, the fixed volume of liquid
is dispensed from the diaphragm
pump.
Manometer Ball float manometers are located
in detector blocks, and are used to
detect constant volume of diluted
sample, which are aspirated
through the transducer aperture.
Isolation Chamber These Isolation Chambers are
used to isolate the liquid in detector
block from the remaining hydraulic
line in the system in order not to be
influenced by the external noise
through the hydraulic line.
Table 2-1 Pneumatic and Hydraulic Parts (4)
2-26 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 52

Name & Symbol Figures Used for
Transducer Cha m b e r Diluted samples of WBC or RBC
are dispensed into each transducer
chamber, mixed by air bubbles,
and constant volume of the sample
is aspirated through the aperture.
Pressure Gauge Four pressure gauges are used in
the system to check the following
pressures or vacuums.
Pneumatic unit
1: 0.20MPa
2: -0.0640MPa vacuum
Main unit
3: 0.05MPa
4: -0.0333MPa vacuum
0.20MPa pressure source 0.20MPa pressure is used to drive
the master valves and SRV air
cylinder. To make simple the
hydraulic flow chart, the symbol in
the “Name & Symbol” column is
used.
Glass Chamber Glass chambers with float switch
are used as Waste Chamber,
Diluent Chamber, and lyse reagent
chamber. 480mmHg or -
0.0333MPa vacuum is applied into
these chambers to aspirate or
prime liquid. When exhausting the
waste liquid in Waste Chamber,
0.05MPa is applied instead of
vacuum. Float switch is provided
with these chambers to prevent
overflow of these chambers.
Relief Valve The Relief Valve releases air
pressure if the supplied air
pressure exceed the preset value.
This valve is adjusted by turning
the knurled knob.
Table 2-1 Pneumatic and Hydraulic Parts (5)
2-27 November 2012XP series S/M
Page 53

CHAPTER 3 ELECTRONICS
3.1 PCB LOCATION .............................................................................................................................1
3.2 BLOCK DIAGRAM..........................................................................................................................2
3.2.1 Hardware Configuration..........................................................................................................3
3.3 PCB NO. 6374 (CPU board)...........................................................................................................4
3.3.1 Function ..................................................................................................................................4
3.3.2 Block Diagram ........................................................................................................................5
3.3.3 Cable Connection ...................................................................................................................6
3.3.4 Restoring setting values after CPU board is replaced ............................................................7
3.4 PCB NO.30012.............................................................................................................................10
3.4.1 Function ................................................................................................................................10
3.4.1.1 Intended use .................................................................................................................10
3.4.1.2 Specification..................................................................................................................10
3.4.2 Detailed function ...................................................................................................................11
3.4.2.1 Analog Data Logger ......................................................................................................11
3.4.2.2 Driver and Sensor .........................................................................................................12
3.4.3 PCB NO.30012 Cable Connection .......................................................................................13
3.4.4 Driver and Sensor map.........................................................................................................14
3.4.5 Assignment of connector pin ................................................................................................15
3.5 PCB NO.20034/PCB NO.2135 .....................................................................................................18
3.5.1 Function ................................................................................................................................18
3.5.2 Description............................................................................................................................18
3.5.3 Block Diagram ......................................................................................................................19
3.5.4 Assignment of Connector Pin ...............................................................................................20
3.6 PCB NO.9301...............................................................................................................................22
3.6.1 Function ................................................................................................................................22
3.6.2 Descriptions ..........................................................................................................................22
3.6.3 Cable Connection .........................................................................................................
3.6.4 Assignment of connector pin ................................................................................................23
3.7 PCB NO.90043.............................................................................................................................25
3.7.1 Function ................................................................................................................................25
3.7.1.1 Intended Use.................................................................................................................25
3.7.1.2 Description ....................................................................................................................25
3.7.2 Detail Specifications..............................................................................................................26
3.7.3 PCB NO.90043 Cable Connection .......................................................................................27
3.7.4 Assignment of connector pin ................................................................................................28
........22
3.8 Power Supply Unit (PCB NO.4087T1)..........................................................................................29
3.8.1 Function ................................................................................................................................29
3.8.2 Description............................................................................................................................30
3.8.3 Block Diagram ......................................................................................................................32
June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 54

CHAPTER 3 ELECTRONICS
3.1 PCB LOCATION
ECR 312J003: PCB NO.20034 (XP/KX) has been added.
3-1 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 55

3.2 BLOCK DIAGRAM
3-2 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 56

3.2.1 Hardware Configuration
Microcomputer Board (PCB No.6374T8)
- CPU : SH7709A(SH3), 133MHz
- FlashROM : 4MByte
- SDRAM : 16Mbyte
- BBU RAM : 512kByte
- Touch Panel : Analog Type
- Color LCD : 256 color, 320x240dot
- Serial : 5ch (1ch : connected to PCB No.90043 for SNCS mail sending)
- Parallel : 2ch
- SV/Sensor
-Buzzer
Analog/Driver board (PCB No.30012)
- Histogram Counter (128 division x 3ch)
- HGB Counter
- Stepping Motor: 1ch
- SV: 24ch
3-3 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 57

3.3 PCB NO. 6374 (CPU board)
NOTE:
PCB NO.6374 is commonly used on RU-20 and XP series, however, the improved version
of PCB NO.6374 is used on XP series.
A white mark is put on the improved version to distinguish between the original version or
improved version.
When replacing PCB NO.6374 for XP series, confirm whether there is the white mark on
PCB NO.6374 or not.
(The original and improved version can be used for RU-20.)
3.3.1 Function
This PCB has the SH-3RISC core CPU and LINUX-OS with 16 MB work memory(SDRAM) on board to
cope with the network communication system.
CPU
The SH-3 core 32 bit RISC CPU and the 16 MB work memory (SDRAM). Internal 133 MHz, Exter-
nal 33MHz clock.
BBURAM
512KB (4MB SRAMx1)
Lithium battery 3.0 V-3.6 V, 1000mAh is used. 15-year backup at power OFF status is expected.
Work Memory
16MB(64MB SDRAMx2)
Program Memory
14MB (16MB flash memory x2)
PCMCIA
1 slot of compact flash connector is provided.
Calendar and Clock
Epson RTC7301SF RTC64613. For Year 2000 through 2099.
LCD
320x240 pixels, 256 colors. Controller(SED1375) with 80KB VRAM
3-4 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 58
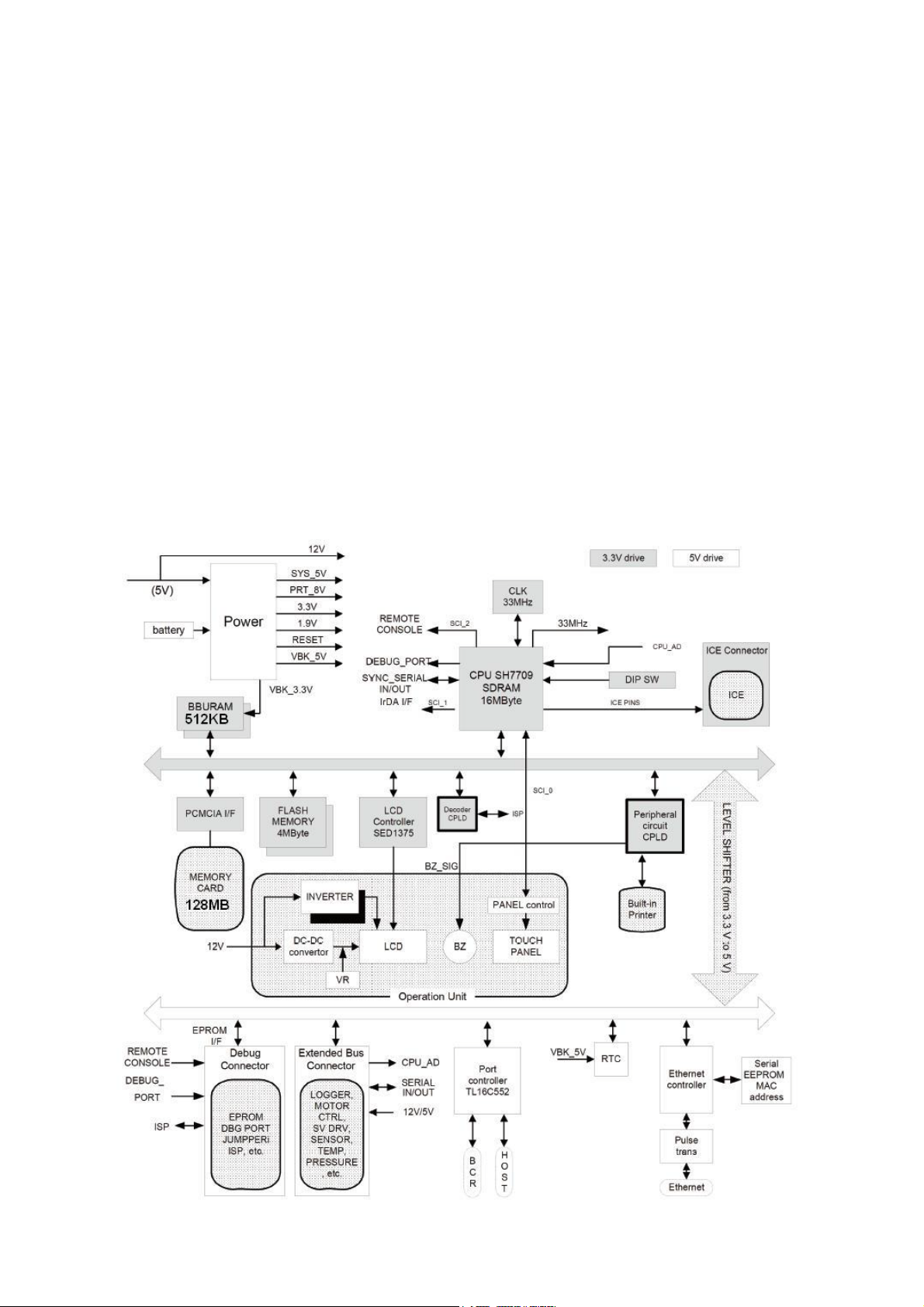
Buzzer Controller motor
Buzzer is mounted on PCB No. 9301(relay board)
Serial Interface
RS232C port for host computer (*D-sub 9-pin (male) connector)
RS232C port for barcode reader (*DIN 8-pin round connector. 5 V is supplied to pin NO.8.)
Parallel Interface
Centronics for built-in printer (*5V for login and 8V for head motor drive are supplied.)
Centronics for external printer(*D-sub 25-pin (female) connector (Pin No.26 is not used.))
TCP/IP
Ethernet(10BASE-T) x 1
Power Supply
12 VDC is input from Switching Regulator. DC-DC converter generates 5 VDC, 500 mA for logic, and 8
VDC for built-in printer. From the 5 VDC, then 3.3VDC (15mA) is generated for pull up purpose only,
and also 1.9 VDC is generated for CPU internal power supply. The power consumption is approx. 1 A.
3.3.2 Block Diagram
3-5 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 59

3.3.3 Cable Connection
3-6 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 60

3.3.4 Restoring setting values after CPU board is replaced
1. Print out setting values and back up BBU. (Refer to Chapter 5 Service Program: 5.7 BBU Backup
and 5.8 BBU Restore.)
2. Replace PCB.
3. Turn ON the power to the instrument.
4. Press [Init.] button to initialize setting values.
5. Press [Execute] button to initialize.
TB201377: Added “Restoring setting values after CPU board is replaced”.
3-7 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 61

6. Turn OFF the power. Then, turn ON the power once again.
7. After the instrument is started, press [BBU Restore] button.
8. Press [OK] button.
TB201377: Added “Restoring setting values after CPU board is replaced”.
3-8 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 62

9. Turn OFF the power.
10. Turn ON the power.
11. Print out and check setting values.
TB201377: Added “Restoring setting values after CPU board is replaced”.
3-9 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 63

3.4 PCB NO.30012
3.4.1 Function
This PCB is analog, logger and driver board for XP series, and connect to PCB No.6374, that is CPU
board, and PCB NO.20034 (XP/KX) [P/N: AG620580]/PCB No.2135, that is waveform processing board.
( Data logger, solenoid valve/stepping motor driver and sensor)
3.4.1.1 Intended use
This board is used as analog/driver board for XP series.
While its analog board has the function as data logger and sensor for XP series, its driver board
also has sensor of solenoid valve driver, stepping motor driver and float switch.
3.4.1.2 Specification
(1) Resistance Detection
Digitalize pulse height of RBC, PLT, WBC and store the data into memory.
(2) Hgb (Hemoglobin) measurement
Digitalize pulse duration of count gate signal and store the data into memory.
(3) Sensor
Relay signals of pressure, temperature and clog from PCB NO.20034 (XP/KX) [P/N: AG620580]/
PCB No.2135 to PCB NO.6374.
Monitor Start Switch and Float Switch.
(4) SV Driver
Receive serial signal from CPU and drive solenoid valve, relay control, pneumatic control relay and
pneumatic fan (24ch)
(5) Stepping Motor
Constant voltage drive(1ch)
312J003
3-10 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 64

3.4.2 Detailed function
3.4.2.1 Analog Data Logger
(1) Control Circuit for resistance detector
Output control signals of WBC, RBC detective current and clog removal relay toward PCB
NO.20034 (XP/KX) [P/N: AG620580]/PCB NO.2135.
(2) Detection Circuit of RBC, PLT and WBC
Receive peak hold signal of RBC, PLT, WBC and AD Start signal from PCB NO.20034 (XP/KX)
[P/N: AG620580]/PCB NO.2135 and send A/D converted signal to data logger.
(3) Hgb Circuit
Receive PCB count gate signal from PCB NO.20034 (XP/KX) [P/N: AG620580]/PCB NO.2135
and convert to pulse.
(4) Electron volume
Transmit the setting signal of electron volume(AD8403AR) for WBC, RBC gain adjustment of
PCB NO.20034 (XP/KX) [P/N: AG620580]/PCB NO.2135 with FPGA.
312J003
Electron Volume
AD8403AR10
(10 kΩ)
(10kΩ)
Address Data
A1 A0 D7 D0
0 0 ―――
0 1 ―――
1 0 R_GAIN
1 1 W_GAIN
MSB → LSB
Application
RBC pre-amplify gain adjustment
RBC pre-amplify gain adjustment
3-11 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 65

3.4.2.2 Driver and Sensor
(1) Stepping Motor Driver
When receiving signal from Motor controller of FPGA at driver IC, Stepping Motor is driven.
Power supply for motor drive : Constant voltage + 12 Vdc
Motor Driver IC
STM 1 : SSM5H12TU (TOSHIBA) Current : 1.9 A ( at 25°C)
(2) Serial Driver
When receiving serial signal from M - I/O, convert it from serial to parallel and control each ports.
Serial - Parallel conversion IC
a) Shift resistor IC74VHC595 ( 8bit, 3-state)
b) Create shift resistor within FPGA
Driver IC
SSM5H12TU (TOSHIBA) : Output withstand voltage : 30V, Current 1.9 A
Control ports
Solenoid valve
Pneumatic fan on/off Relay
Relay for clog removal power
Pneumatic on/off relay
(Stepping motor excitation)
Detector clog monitoring switch
21ch
:
1ch
:
1ch
:
1ch
:
1ch (Shift Resistor in FPGA)
:
1ch (Shift Register in FPGA)
:
(3) Sensor
(4) Serial Input
Convert signal from each sensor from parallel to serial and send CPU board.
Control ports 8ch
Micro switch : 1ch (Start SW)
Float switch : 3 ch (diluent, waste fluid, external3 WP reagent)
DIP switch : 3 ch (Not mounted)
Spare : 4 ch
3-12 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 66

3.4.3 PCB NO.30012 Cable Connection
* Through J4, power supply volume is 12 V only. 5V and ±15V are supplied through J5 from PCB
NO. 6374 and J6 from PCB NO.20034 (XP/KX) [P/N: AG620580]/PCB NO.2135, respectively.
312J003
3-13 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 67

3.4.4 Driver and Sensor map
(1) Stepping motor
No Application Movement
Direction
Limit SW
[ logic at ON]
CW
STM1 Sampling Unit Top CCW (down)
[low]
(2) Control map for serial output
No Data bit
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1 SV8 SV7 SV6 SV5 SV4 SV3 SV2 SV1
2 SV16 SV15 SV14 SV13 SV12 SV11 SV10 SV9
3 SV24
pnuema
tic
4
SV23
Clog
removal
SV22
pnuema
tic FAN
SV21 SV20 SV19 SV18 SV17
CLOG
switch
STM
excitation
3-14 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 68

3.4.5 Assignment of connector pin
<J1>(S.V Output 1)
Connector : DF11 - 32DP - 2DSA (HIROSE)
Pin No. Signal Pin No. Signal
1 + 12 V 2 SV1 - S
3 + 12 V 4 SV2 - S
5 + 12 V 6 SV3 - S
7 + 12 V 8 SV4 - S
9 + 12 V 10 SV5 - S
11 + 12 V 12 SV6 - S
13 + 12 V 14 SV7 - S
15 + 12 V 16 SV8 - S
17 + 12 V 18 SV9 - S
19 + 12 V 20 SV10 - S
21 + 12 V 22 SV11 - S
23 + 12 V 24 SV12 - S
25 + 12 V 26 SV13 - S
27 + 12 V 28 SV14 - S
29 + 12 V 30 SV15 - S
31 + 12 V 32 SV16 - S
<J2>(S.V Output 2)
Connector : DF11 - 16DP - 2DSA(HIROSE)
Pin No. Signal Pin No. Signal
1 + 12 V 2 SV17 - S
3 + 12 V 4 SV18 - S
5 + 12 V 6 SV19- S
7 + 12 V 8 SV20 - S
9 + 12 V 10 SV21 - S
11 + 12 V 12 SV22 - S
13 + 12 V 14 SV23 - S
15 + 12 V 16 SV24 - S
<J3>(Motor control output/Sensor input)
Connector : DF11 - 22DP - 2DSA(HIROSE)
Pin No. Signal Pin No. Signal
1 + 12 V 2 + 12 V
3 STM - A 4 STM - B
5 STM - #A 6 STM - #B
7 GND 8 FSW1
9 GND 10 FSW1
11 GND 12 CCW_LIM
13 GND 14 CW_LIM
15 GND 16 START_SW
17 GND 18 SW6
19 GND 20 SW6
21 VCC 22 VCC
3-15 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 69

<J4>(Power Supply)
Connector :
Pin No. Signal Pin No. Signal
1 + 12 V 2 (5V)
3 GND 4 GND
<J5>Bus Connector
Pin No. Signal Pin No. Signal
1 GND 51 GND
2 CKIO 52 GND
3 GND 53 GND
4 DB0 54 DB1
5 DB2 55 DB3
6 DB4 56 DB5
7 DB6 57 DB7
8 DB8 58 DB9
9 DB10 59 DB11
10 DB12 60 DB13
11 DB14 61 DB15
12 5V 62 5V
13 5V 63 5V
14 5V 64 5V
15 AB0 65 AB1
16 AB2 66 AB3
17 AB4 67 AB5
18 AB6 68 AB7
19 AB8 69 AB9
20 --- 70 ---
21 --- 71 ---
22 --- 72 ---
23 GND 73 GND
24 --- 74 ---
25 --- 75 ---
26 --- 76 ---
27 --- 77 AB23
28 AB24 78 GND
29 EX8CSb 79 EX16CSb
30 --- 80 ---
31 GND 81 GND
32 --- 82 ---
33 RDb 83 ---
34 WE0b 84 ---
35 --- 85 ---
36 --- 86 ---
37 --- 87 ---
38 --- 88 GND
39 GND 89 GND
3-16 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 70

Pin No. Signal Pin No. Signal
40 SERCLK 90 SERSVLTCH
41 SERISENS 91 SERSV
42 SERSENSLTCHb 92 SERENb
43 5V 93 5V
44 3.3V 94 3.3V
45 GND 95 GND
46 RESET/ 96 GND
47 GND 97 GND
48 ANA0 98 ANA1
49 ANA2 99 GND
50 GND 100 GND
<J6>(Analog I/F)
Connector : PCN10C - 44S - 2. 54DSA(HIROSE)
Pin No. Signal Pin No. Signal
1 (1A) A + 5V 23 (1B) A + 15 V
2 (2A) AGND 24 (2B) A - 15 V
3 (3A) AGND 25 (3B) P - PLS (A)
4 (4A) AGND 26 (4B) R - PLS (A)
5 (5A) AGND 27 (5B) W - PLS (A)
6 (6A) AGND 28 (6B) *P - ADSTART
7 (7A) AGND 29 (7B) *R - ADSTART
8 (8A) AGND 30 (8B) *W - ADSTART
9 (9A) BOADSEL 31 (9B) *HGB_COUNT
10 (10A) VCC 32 (10B) *HGB_START - S
11 ( 11A) *W_TDON-S 33 (11B) *R_TDON - S
12 (12A) VCC 34 (12B) VCC
13 (13A) *CLN-S 35 (13B) AGND
14 (14A) AGND 36 (14B) VCC
15 (15A) PS_0.5 37 (15B) PS_250
16 (16A) R.CLOG 38 (16B) TEMP
17 (17A) AGND 39 (17B) W.CLOG
18 (18A) AGND 40 (18B) AGND
19 (19A) *PDATEST 41 (19B) AGND
20 (20A) VCC 42 (20B) *PM - SDI - S
21 (21A) N.C. 43 (21B) *PM - CLK - S
22 (22A) N.C. 44 (22B) *PM - CS - S
3-17 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 71

3.5 PCB NO.20034/PCB NO.2135
3.5.1 Function
PCB NO.20034 (XP/KX) [P/N: AG620580]/PCB NO.2135 is the analog main board.
3.5.2 Description
(1) RBC/PLT Detection Circuit
Amplifies the blood signal transmitted from the RBC detector, discriminates it into RBC and PLT
signals, and then sends the peak hold signal to the digital board. The RBC/PLT circuit also
internally generates an A/D START signal for each signal and sends it to the digital board. The
peak hold and A/D START signals are transmitted as they are generated. The start and end of
counting are controlled on the digital board in accordance with the predetermined sequence.
(2) WBC Detection Circuit
Amplifies the blood signal from the WBC detector and sends the peak hold signal to the digital
board.The WBC circuit also internally generates an A/D START signal sends it to the digital board.
The peak hold and A/D START signal are transmitted as they as generated.
* Blood cell signal amplification method
The analog main board uses a current-responsive amplifier to detect the blood cell signal. Below is
an overview of this method.
E serves as constant power supply within the blood cell signal band, according to the operation of
C.
2
I = I0 -
=
~
=
E
RTD + 2R RTD + 2R
I02R
RTD+2R
I02R
RTD
= I0 -
∴RTD >>2R
∴ 2R = K1ρ(T)υ
RTD = K2ρ(T)
2
V= -R f KυI0=K′υ
(3) HGB Detection Circuit
Firstly converts the photodiode current signal transmitted from the HGB unit into a voltage signal
and then into a time signal. The digital board then converts the time signal into pulses.The
constant-current circuit for the LED(555nm), light source for HGB measurement, is also included in
the configuration.
(4) Temperature Monitoring Circuit
Measures the ambient temperature in the vicinity of detectors. The thermistor temperature (TEMP)
is transmitted as an analog signal, which is then converted to a digital signal on the digital board.
I0RTD
(5) Clog Detection Circuit
Measures the DC voltage in detectors. The DC voltage level is transmitted as analog signal, which
is them converted to a digital signal on the digital board.
312J003
3-18 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 72

(6) Pressure Detection
Two pressure sensing (monitoring) systems, 0.5kg/cm2, 250mmHg, are adopted, using
adjustment-free pressure sensors, The sensor outputs are converted to pressure values by the
formulas below.
-0.049 MPa
P = (X - 0.2)/4.41 [MPa]
- 0.0333 MPa
V = (X - 0.2)/0.006 [MPa]
* Here, C represents sensor output(V).
3.5.3 Block Diagram
312J003
PCB NO.20034/PCB NO.2135 Block Diagram
3-19 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 73

3.5.4 Assignment of Connector Pin
(1) J1 (±15V, DC100V : B6PS - VH)
Pin NO. Signal Pin NO. Signal
1 DC100V 4 + 15V
2 GND (DC100V) 5 GND
3 A.GND 6 - 15V
(2) J2(AC100V : B3PS - VH)
Pin NO. Signal
1 AC100V(H)
2 AC100V(C)
3 A.GND
(3) J3 (RBC : FFC - 04LAMEP1)
Pin NO. Signal Pin NO. Signal
1 Used to prevent disconnection 3 RBC.TD (+)
2 A.GND (Shield) 4 RBC.TD (-)
(4) J4 (WBC : FFC - 04LAMEP1)
Pin NO. Signal Pin NO. Signal
1 A.GND (Shield) 3 WBC.TD (+)
2 Used to prevent misconnection 4 WBC.TD (-)
(5) J5 (HGB : FFC - 06LBMEP1)
Pin NO. Signal Pin NO. Signal
1 HGB.SIG 4 -
2 HGB.GND 5 A.GND
3 HGB.LED 6 A.GND
(6) J6 (Thermistor : FFC - 04LAMEP1)
Pin NO. Signal Pin NO. Signal
1 TH 3 NC
2 NC 4 TH(GND)
3-20 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 74

(7) J7 (Digital PC : PCN10HA - 44PA - 2.54DSA)
Pin NO. Signal Pin NO. Signal
1A + 5V 1B + 15V
2A GND 2B - 15V
3A GND 3B P. S I G
4A GND 4B R.SIG
5A GND 5B W.S IG
6A GND 6B P.A/D.START/
7A GND 7B R.A/D.START/
8A GND 8B W.A/D.START/
9A NC 9B HGB.COUNT (SIG)/
10A HGB.START (+ 5V) 10B HGB.START (SIG)/
11A W.TD.ON (SIG)/ 11 B R.TD.ON (SIG)/
12A W.T D.ON ( + 5V) 12B R.TD.ON (+ 5V)
13A CLN (SIG)/ 13B GND
14A GND 14B CLN (+ 5V)
15A PS.0.5 15B PS.250
16A R.GLOG 16B TEMP
17A GND 17B W.GLOG
18A GND 18B GND
19A NC 19B GND
20A DVR (5V) 20B D.SDI
21A NC 21B D.CLK
22A NC 22B D.CS/
(8) J8 (FFC-6BMEPI), J9 (DIC-252) are not used. * PCB NO.20034 only.
(However, check that J9 is connected to the point between Pin No.3 and Pin No. 4 of J8.)
312J003
3-21 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 75

3.6 PCB NO.9301
3.6.1 Function
This board is LCD relay board. Touch panel controller and buzzer are mounted on this board.
3.6.2 Descriptions
(1) Touch Panel Control
Has the interface with the analog touch panel.
(2) LCD Control signal Relay
Relays the signal from the CPU board to LCD.
(3) LCD Power supply
DC-DC Converter generates the power for the LCD(VEE). The voltage can be adjusted by VR for
contrast adjustment.
(4) Buzzer
Buzzer level is adjusted to 4 level by digital signals from CPU.
(5) CFL
Supplies +12V to the inverter (for LCD backlight). Backlight amount is adjusted by the signal from
CPU.
3.6.3 Cable Connection
3-22 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 76

3.6.4 Assignment of connector pin
(1) J1 : CFL
Pin NO. Function
1 12V
2 GND (12V)
3 12V
4 CFLDOWN
5 GND (12V)
(2) J2 : CPU
Pin NO. Function Pin NO. Function
1 GND (5V) 16 D0
2 GND (5V) 17 GND (5V)
3 5V 18 GND (5V)
4 5V 19 CFLDOWNb
5 FRAME 20 BZSIG
6 LOAD 21 BZCTR[1]
7 CP 22 BZCTR[0]
8 DISPOFFb 23 TxD
9 D7 24 RxD
10 D6 25 RESETb
11 D5 26 GND (12V)
12 D4 27 12V
13 D3 28 12V
14 D2 29 GND (12V)
15 D1 30 GND (12V)
(3) J3 : Touch panel (Unused)
Pin NO. Function
1 YL
2 YLref
3 YUewd
4 YU
5 XR
6 XL
7 Xlref
8 XRref
(4) J4 : Touch panel
Pin NO. Function
1 YU
2 XR
3 YL
4 XL
3-23 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 77

(5) J5 : LCD
Pin NO. Function
1 FRAME
2 LOAD
3 CP
4 DISPOFFb
5 VCC
6 GND
7 VEE
8 D7
9 D6
10 D5
11 D4
12 D3
13 D2
14 D1
15 D0
(6) J6 : External buzzer
Pin NO. Function
1 12V
2 BZ
3 GND (12V)
4 GND (12V)
(7) J7 : External volume (LCD brightness)
Pin NO. Function
1 CONT - A
2 GND
3 CONT - B
4 GND
3-24 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 78

3.7 PCB NO.90043
3.7.1 Function
This board is transmission board of SNCS for XP series and connect with PCB NO.6374, that is CPU
board.
3.7.1.1 Intended Use
This board is used as transmission board of SNCS mail for XP series.
Serial data that is sent from PCB NO.6374 is converted to mail form and transmitted to network.
3.7.1.2 Description
- Transmit a message to mail server by instructions from serial instruments.
- Set the XPort04R network and destination settings by instructions from serial instruments.
- Get IP address using DHCP server
- Name resolution using DNS server
- Update firmware
3-25 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 79

3.7.2 Detail Specifications
- XPORT04R
Device : LANTRONIX XP1001000-04R
OS : μITORON
Architecture CPU DSTni-EX (16bit,48MHz)
SRAM 256 kbyte
FlashROM 512 kbyte
Farmware Can be upgraded via TFTP and serial port
Serial I/F Interface CMOS, Asynchronous Communication
Transmission Speed 300 - 921kbps at 88MHz
Parity odd/even/none
Bit Length 7, 8 bit / 1, 2 stop bit
Control signal DTR/DCD, CTS/RTS
Flow control Hardware, software
Programmable
I/O(PIO)
Network I/F Connector RJ - 45
Interface 100BASE - TX/10BASE - T automatic recognition
Protocol TCP/IP, UDP/IP.ARP, ICMP, SNMP, TFTP,
Communication transposition Ethernet : Version 2.0 / IEEE 802.3
LED display 100BASE - TX/10BASE - T,
Management SNMP(Read only), Telnet, Serial,
Built-in WEB server Available to store HTML, Java applet
Power supply Input Voltage DC3.3V
Current
Consumption
Ambient
Temperature
Size
Under operation - 40 - 85°C(Operate at 48 MHz)
Under standby - 40 - 85°C
3 GPIOPin (Available software setting)
Telnet, DHCP, BOOTP, HTTP, AutoIP, SMTP
Link/Activity (Full Duplex, Half Duplex)
Built-in WEB server, Exclusive utility
Storage volume : 384KB
Approx. 230 mA (Operate at 48 MHz)
Weight
TB201284
9g
3-26 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 80

3.7.3 PCB NO.90043 Cable Connection
3-27 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 81

3.7.4 Assignment of connector pin
<J1> (Solenoid valve 1)
Connector : Connector : FX8C-100P-SV6 (HIROSE)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 GND 51 GND
2 3.3 V 52 3.3 V
3 5 V 53 5 V
4 TXD2 54 RXD2
5 RTS2 55 CTS2
6 --- 56 GND
7 --- 57 --8 --- 58 ---
9 --- 59 --10 --- 60 --11 --- 61 --12 --- 62 --13 --- 63 --14 GND 64 GND
15 --- 65 --16 --- 66 --17 --- 67 --18 --- 68 --19 --- 69 --20 --- 70 --21 GND 71 GND
22 --- 72 --23 --- 73 --24 --- 74 --25 --- 75 --26 --- 76 --27 GND 77 GND
28 --- 78 --29 --- 79 --30 --- 80 --31 --- 81 --32 --- 82 --33 --- 83 --34 --- 84 --35 --- 85 --36 GND 86 GND
37 --- 87 --38 --- 88 --39 --- 89 --40 --- 90 --41 --- 91 --42 --- 92 --43 --- 93 --44 --- 94 --45 GND 95 GND
46 --- 96 --47 --- 97 --48 5 V 98 5 V
49 3.3 V 99 3.3 V
50 GND 100 GND
3-28 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 82

3.8 Power Supply Unit (PCB NO.4087T1)
3.8.1 Function
The unit has two type of power supplies for 100-V and 200-V groups of AC lines for different global
markets. As the connector on the primary side of the transformer can be used as voltage selector, select
appropriate voltage level in conformity with specification of each market.
Configuration of Power Supply Unit is as follows.
- AC Inlet
- Fuse holder
- Power switch
- Noise filter
- Power trans
- Power supply board (PCB NO.4087T1)
- Switching Regulators (LFA100F-12-J1Y)
AY086732 POWERSUPPLY_ASSY NO.115(JPN/100V)
CD136144 NOISEFILTER_ASSY NO.2(100V)
26650113 FUSE 250V4A ST4-4A-N1 (N.AMER)
26637021 FUSE HOLDER 4303-2901 (N.AMER)
CA878955 TRANSFORMER POWER PT-114
BU291768 POWERSUPPLY_ASSY NO.115(EXP/120V)
BN671730 NOISEFILTER_ASSY NO.2(120V)
26650113 FUSE 250V4A ST4-4A-N1 (N.AMER)
26637021 FUSE HOLDER 4303-2901 (N.AMER)
CA878955 TRANSFORMER POWER PT-114
AJ787188 POWERSUPPLY_ASSY NO.115(CHN/220V)
CC069195 NOISEFILTER_ASSY NO.2(220V)
AX880901 FUSE 50T032H
26637017 FUSE HOLDER 4303-2401 (EURO+UK)
CS177111 TRANSFORMER POWER PT-115
CF438275 POWERSUPPLY_ASSY NO.115(EU/230V)
CR905019 NOISEFILTER_ASSY NO.2(230V)
AX880901 FUSE 50T032H
26637017 FUSE HOLDER 4303-2401 (EURO+UK)
CS177111 TRANSFORMER POWER PT-115
AH239055 POWERSUPPLY_ASSY NO.115(UK/240V)
BS442303 NOISEFILTER_ASSY NO.2(240V)
AX880901 FUSE 50T032H
26637017 FUSE HOLDER 4303-2401 (EURO+UK)
CS177111 TRANSFORMER POWER PT-115
3-29 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 83

3.8.2 Description
(1) Power Input
Input Voltage 100-V group: 100 V, 120 V
200-V group: 220 V, 230 V, 240 V
Frequency 50 Hz/60 Hz
(2) Power Consumption
Max : 200 VA
(3) Power Output
Rated
Voltage
+ 15VDC
- 15VDC
100VDC 10 mA 20 mA Constant-current supply
100VAC 10 mA 20 mA Clog removal
+ 12DCV 2.0 A 2.8 A Solenoid valve, motor, LCD backlight
100VAC 1.2 A 1.2 A Pneumatic unit drive
Average
Current
0.5 A
0.4 A
* Output specification above are guaranteed at an ambient temperature below 60°C.
(4) Power supply type and Performance
Voltage Type Constant
+ 15 VDC Series ±0.75 V 2 % 15 mV max.
- 15 VDC Series ±0.75 V 2 % 15 mV max.
100 VDC Series ±3 V 2 % 10 mV max.
+ 12 VDC Switching ±0.2 V 2 % 150 mV max.
100 VAC Transformer output - - -
(5) Dimensions and weight
Dimensions W x D x H = 215 x 235 x 120
Weight Approx. 5.2kg
Peak Current Application
0.7 A
0.5 A
Voltage
Accuracy
Analog circuits and analog V
Analog circuits
Load
Regulati
Ripple
Voltage
on
(6) Power Transformer
Primary side input
voltage
Secondary side
input voltage
Capacity 150 VA
Insulation Type A
Dimension W x D x H = 140 x 115 x 75
Weight Approx. 3.8 kg
AC100 V, 120 V, 220 V, 230 V, 240 V
AC108 V, 100V, 102 V, 16.5 V - 0 - 16.5 V
3-30 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 84

(7) Fuses
PCB NO. 4087T1
Circuit Symbol PS code Part Name
F1 AF208615 FUSE 37405000410 0.5A
F2, 3 BF752335 FUSE 37411600410 1.6A
F5 AY775445 FUSE 37400500410 0.05A
F6 BU624205 FUSE 37414000410 4A
AC inlet
Circuit Symbol PS code Part Name
100/200 V groups 26636757 AC INLET KD14.1101.151
(8) Voltage Selection
Connect the Wiring Cord NO.2370 as below according to the required voltage.
1) 120 V
Pin 1 (light blue) and Pin 3 (brown)
2) 220 V
Pin 1 (light blue) and Pin 4 (brown)
3) 230 V
Pin 1 (light blue) and Pin 5 (brown)
4) 240 V
Pin 1 (light blue) and Pin 6 (brown)
Wiring at Connector J1
201297
3-31 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 85

3.8.3 Block Diagram
Power Supply Unit (for 100V-Group) Block Diagram
3-32 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 86

Power Supply Unit (for 200V-Group) Block Diagram
3-33 June 2013XP Series S/M
Page 87

CHAPTER 4 ADJUSTMENT
4.1 STANDARD SENSITIVITY ADJUSTMENT .........................................................................................1
4.1.1 WBC and RBC Sensitivity Adjustment...............................................................................1
4.1.2 PLT Sensitivity Adjustment ................................................................................................7
4.2 HGB ADJUSTMENT..........................................................................................................................10
4.3 CLOG LEVEL ADJUSTMENT ...........................................................................................................12
4.4 PCB CHECKING AND ADJUSTMENT .............................................................................................14
4.4.1 PCB NO.20034/PCB No. 2135 ........................................................................................14
4.4.2 PCB No. 6374 (CPU) .......................................................................................................14
4.4.3 PCB No. 4087 (Power Supply) ........................................................................................16
4.5 Mechanical Parts Adjustment ............................................................................................................17
4.5.1 SRV Position Adjustment.................................................................................................17
4.5.2 Rinse Cup Position Adjustment .......................................................................................19
March 2013 XP Series S/M
Page 88

CHAPTER 4 ADJUSTMENT
4.1 STANDARD SENSITIVITY ADJUSTMENT
<NOTE>
Do not disconnect J3 (Wiring Cord No.2363) and J4 (Wiring Cord No.2364) while performing Standard
Sensitivi
When disconnecting the connection of the wiring cords to confirm the connection status, turn off the
instrument first.
ty Adjustment). If the wiring cord is disconnected while the power on, the PCB will be damaged.
4.1.1 WBC and RBC Sensitivity Adjustment
Required reagent CELLCHECK-400 (P/N: 814-0012-9)
(1) Verify that the temperature of CELLPACK and the r
30°C.
(2) Enter the Service mode. (Enter C, 9,
enter the service mode.)
(3) Press the Start Switch and verify WBC and RBC ba
WBC background value 0.30 x 10
RBC background value 0.30 x 10
-, 0 into the sample number input box.) Hot start is also can be
3
/μL
4
/μL
oom temperature is within the range of 15 -
ckground counts fall into the ranges below:
XP series S/M
4-1
March 2013
Page 89

(4) Select menu > Service > Service Seq. > Gain Adjustment > WBC/RBC.
(5) Pre-process for automatic sensitivity adjustment sequence starts.
Figure 4-1-1:WBC/RBC Gain Adjustment Display
(6) After completing pre-sequence, Gain Adjustment screen appears.
XP series S/M
4-2
March 2013
Page 90

TARGET Area for entering the target value
1, 2, 3 Area that displays the 3 analysis values
MAX-MIN Area that displays the difference between the maximum and minimum of
the 3 analysis values.
RATIO(%) Area that displays the calculated compensation ratio Area that displays
the analysis values after they are compensated
(7) Enter the TARGET values using the numeric and decimal keys.
When the Gain Adjustment screen appears, W-MFV target box will be reversed. Enter the target
value.
Parameter Target value CELLCHECK-400 Lot
No.
W-MFV 188.0 +/- 2.0 fL A1003 - A3005
W-MFV 180.5 +/- 2.0 fL A TB201379 A3006 and thereafter
R-MCV 1.26 x (Assay value MCV of
CELLCHECK-400/CC-108)
-
(8) Open the Detector Cover by loosening the fixing screw.
(9) Mix CELLCHECK-400 ampules vigorously, and pour it into the DB-1 sample beaker.
XP series S/M
4-3
June 2013
Page 91

(10) Pour approx. 3.5 mL of CELLCHECK-400 into the WBC transducer chamber and approx. 2.5 mL
into the RBC transducer chamber.
(11) Close the Detector Cover, and press the Start Switch.
(12) The recount analysis sequence will be performed automatically three times and the three analysis
values (1 to 3), difference between the maximum and minimum (MAX-MIN), and compensation
ratio (RATIO%) will be calculated. (For approximately 2 minutes.)
XP series S/M
4-4
March 2013
Page 92

FIgure 4-1-3 WBC/RBC Gain Adjustment Display
(13) Analysis is performed once again and displays the analysis values (RESULT).
Verify that the followings are all satisfied. (W-MFV, R-MCV)
[W-MFV] A TB201379
MAX-MIN
≤4[fl]
RATIO(%)=100 ±50
RESULT=Target±2[fl]
[R-MCV]
MAX-MIN≤4[fl]
RATIO(%)=100 ±50
RESULT=Target ±2[fl]
(14) Click [OK] when the analysis values (RESULT) satisfy the standard values. The gain adjustment
value will be updated and the system will return to the Ready Screen.
(15) If the result is not satisfied with target +/- 2 fL, calculate new target value as follows.
New Target value = (TARGET) ^ 2 / Result (Round off below decimal)
XP series S/M
4-5
June 2013
Page 93

(16) Click Cancel enter the new target value in target M-MFV or R-MCV and perform sensitivity adjust-
ment again.
(17) After completing adjustment, "Confirm Result?" appears, click OK.
XP series S/M
4-6
March 2013
Page 94

4.1.2 PLT Sensitivity Adjustment
Required reagent LATEX CALIBRATOR PLT (E); Part No. 951-0222-1 (Or diluted in 1: 55 with
CELLSHEATH 8LTX4203A_3.0MICRONS/15ML_3.063 P/N: 66645267 with assay value.)
(1) Verify that the temperature of CELLPACK and the r
30°C.
oom temperature is within the range of 15 -
(2) Remove the Top Cover Remove the Shield Cover N
(SUS).
o. 224 by loosening four fixing screw M3x8
(3) Enter the Service mode. (Enter C, 9, -, 0 into the sample number input box.) Hot start is also can be
enter the service mode.)
(4) Press the Start Switch and verify PLT backgro
PLT background value
XP series S/M
≤ 0.30 x 104/μL
und counts fall into the ranges below.
4-7
March 2013
Page 95

(5) elect menu > Service > Service Seq. > Gain Adjustment > PLT.
Fiigure 4-1-4: PLT Gain Adjustment Display
(6) Mix the PLT Latex Calibrator by gently swirling vial. Set the Latex Calibrator at the aspiration
pipette and press the Start Switch to aspirate it.
(7) When the analysis is completed, the P-MFV re
sult will be displayed.
Figure 4-1-5: Displayed the 1st Result of P-MFV
(8) Adjust the VR5 on PCB NO.20034 (XP/KX) [P/N: AG620580]/ PCB No. 2135 (KX-21)/No. 2150
1N) so that the P-MFV falls within the acceptable range below.
(KX-2
Turning the VR clockwise will increase the value.
P-MFV = (Target MFV value provided for each LATEX CALIBRATOR PLT (PM/C2)) ±
0.
2.
312J003
XP series S/M
4-8
March 2013
Page 96

Figure 4-1-6: VR5 on PCB NO.20034/PCB No. 2135
(9) Press the Start Switch to recount the Latex Calibrator.
Run the recount sequence and VR adjustment three times in total.
(10) After the 4th analysis (recounting) is completed
, press [Cont] key to continue the Latex analyses
again.
(11) Repeat the steps (7) through (9) above until
(12) After the adjustment is completed, obtain three
the P-MFV falls into the acceptable range.
P-MFV results by analyzing or recounting Latex
Calibrator.
(13) Calculate the average of the three results and verify that the
average falls within the acceptable
range. If the result is not satisfied the acceptable range, adjustment should be performed again/
Acceptable range=Target MFV value provided for
each LATEX CALIBRATOR PLT (PM/C2)) ± 0.2
(14) Press [OK] key to exit the adjustment program.
(15) Refit the Shield Cover No. 224 and the Top Cover.
312J003
XP series S/M
4-9
March 2013
Page 97

4.2 HGB ADJUSTMENT
(1) Confirm that 30 minutes past after turning on the main unit.
(2) Select Menu > (Maintenance) > (Status Display) to display status display.
Figure 4-2-1: Status Display
(3) Adjust the VR1 on the PCB NO.20034 (XP/KX) [P/N: AG620580]/ PCB No. 2135 (KX-21) so that
HGB CONVERT value falls within the range 2000±200.
the
Figure 4-2-2: VRs for HGB Adjustment
(4) Press “Run” key on the LCD to aspirate the fresh Sysmex
Level).
201297 312J003
XP series S/M
4-10
control blood EIGHTCHECK (Normal
March 2013
Page 98

(5) Press [Stop] key to stop the sequence at Sequence 7.
Figure 4-2-3: Sequence Stop at Sequence 7
(6) Adjust the VR2 on the PCB NO.200
34 (XP/KX) [P/N: AG620580]/PCB No. 2135 (KX-21) so that
the HGB CONVERT value falls within the following range:
HGB CONVERT = (HGB Assay Value for EIGHTCHECK) ± 0.5 [g/dL]
(7) Press [Resume] key to resume the sequence.
(8) Confirm that the HGB Convert value is within the rang
e below after screen turns to ready status. If
the value is out of the range, adjust the VR1 on PCB NO.20034 (XP/KX) [P/N: AG620580]/PCB No.
2135 so that HGB Convert value is within the range below.
HGB Convert Value =2000±200
312J003
XP series S/M
4-11
March 2013
Page 99

4.3 CLOG LEVEL ADJUSTMENT
(1) Select menu > Service > Service Seq. > Clog Adjustment. Select WBC.
(2) When below screen appears, Adjust the VR6 on the PCB NO.20034 (XP/KX) [P/N: AG620580]/
PCB No. 2135 (KX-21) so that the WBC clog level falls within the following range.
WBC Clog value:100.0±1.0
The system returns to the Ready screen in 30 second
s. If the adjustment has not been completed
when the system returns to Ready status, select WBC again.
312J003
XP series S/M
Figure 4-3-1: Clog Adjustment Screen
4-12
March 2013
Page 100

(3) In the same manner, adjust the VR7 on the PCB NO.20034 (XP/KX) [P/N: AG620580]/PCB No.
2135 (KX-21) so that the RBC clog level falls within the following range.
RBC Clog:100.0±1.0
Figure 4-3-2: CLOG LEVEL ADJUSTMENT
(4) The system returns to the Ready screen in 30 seconds.
If the adjustment has not been completed
when the system returns to Ready status, select RBC
again.
312J003
XP series S/M
4-13
March 2013
 Loading...
Loading...