Features
2
■ I
C interface, slave address: 1001111
■ 7-bit adjustable sink current output
■ 2.25 V to 3.6 V logic supply voltage V
■
AVDD operating voltages
– 4.5 V to 20 V for V
– 4.5 V to 13 V for V
■ EEPROM for storing the optimum V
■ Guaranteed monotonic output over operating
from 2.6 V to 3.6 V
DD
from 2.25 V to 3.6 V
DD
DD
COM
setting
range
■ 400 kHz maximum interface bus speed
■ Operating temperature: –40 °C to 85 °C
■ Available in an 8-pin 3 mm x 3 mm TDFN8 or
3 mm x 3 mm TSSOP8 package
Applications
■ TFT-LCD panels
■ e-paper and e-book displays
Description
The STVM100 is a programmable VCOM
adjustment solution for thin-film transistor (TFT)
liquid-crystal displays (LCDs) to remove “flickers”.
It is also used in e-paper and e-book applications
to avoid the "ghosting" effect (residual pixels after
display refresh). It can replace a mechanical
potentiometer, so that the factory operator can
physically view the front screen when performing
the VCOM adjustment. This significantly reduces
labor costs, increases reliability, and enables
automation.
Table 1. Device summary
STVM100
I2C LCD/e-paper VCOM calibrator
TDFN8 (3 mm x 3 mm) (DC)
TSSOP8 (3 mm x 3 mm) (DS)
The STVM100 provides a digital I
control the sink current output (I
drives an external resistive voltage divider, which
can then be applied to an external V
Three external resistors R
1
mine the highest and lowest value of the V
An increase in the output sink current will lower
the voltage on the external divider so that the
V
can be adjusted by 128 steps within this
COM
range. Once the desired V
COM
achieved, it can be stored in the internal
EEPROM that will be automatically recalled during each power-up.
The STVM100 is available in an 8-pin,
3 mm x 3 mm TDFN8 or 3 mm x 3 mm TSSOP8
package.
2
C interface to
). This output
OUT
COM
, R2, and R
setting is
buffer.
SET
deter-
COM
.
Order code Optimum temperature range Package Packing
STVM100DC6E –40 °C to 85 °C TDFN8 ECOPACK
STVM100DS6F –40 °C to 85 °C TSSOP8 ECOPACK
December 2009 Doc ID 13236 Rev 8 1/27
®
package, tubes
®
package, tape and reel
www.st.com
1

Contents STVM100
Contents
1 Device overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2 Device operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1 2-wire bus characteristics and conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1.1 Bus not busy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1.2 Start data transfer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1.3 Stop data transfer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1.4 Data valid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.1.5 Acknowledge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.2 Read mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.3 Write mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.4 V
power supply ramp-up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
DD
3 Application information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4 Maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
5 DC and AC parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
6 Typical operating characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
7 Package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
8 Part numbering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
9 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
2/27 Doc ID 13236 Rev 8

STVM100 List of tables
List of tables
Table 1. Device summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Table 2. Pin names and functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Table 3. Bit P read and write mode values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Table 4. Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table 5. Operating and AC measurement conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table 6. Capacitances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table 7. DC and AC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Table 8. AC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Table 9. TDFN8 3 x 3 x 0.75 mm, pitch 0.65, package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 10. TSSOP8 – 8-lead, thin shrink small outline, 3 mm x 3 mm, mech. data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 11. Ordering information scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 12. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Doc ID 13236 Rev 8 3/27

List of figures STVM100
List of figures
Figure 1. Logic diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Figure 2. Connections diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 3. Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 4. Hardware hookup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 5. Serial bus data transfer sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 6. Acknowledgement sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure 7. Read/write mode sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 8. R
Figure 9. Bus timing requirements sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Figure 10. V
Figure 11. AV
Figure 12. VDD supply current vs. temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 13. AV
Figure 14. I
Figure 15. Total unadjusted error vs. DAC setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 16. Differential non-linearity vs. DAC setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 17. Integral non-linearity vs. DAC setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 18. AV
Figure 19. Full scale-up response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 20. Full scale-down response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 21. TDFN8 3 x 3 x 0.75 mm, pitch 0.65, package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 22. TSSOP8 – 8-lead, thin shrink small outline, 3 mm x 3 mm, mech. data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
, R2, and R
1
supply current vs. V
DD
supply current vs. AV
DD
supply current vs. temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
DD
error vs. temperature (STVM100 at middle scale) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
OUT
power-up response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
DD
connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
SET
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
DD
DD. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
4/27 Doc ID 13236 Rev 8
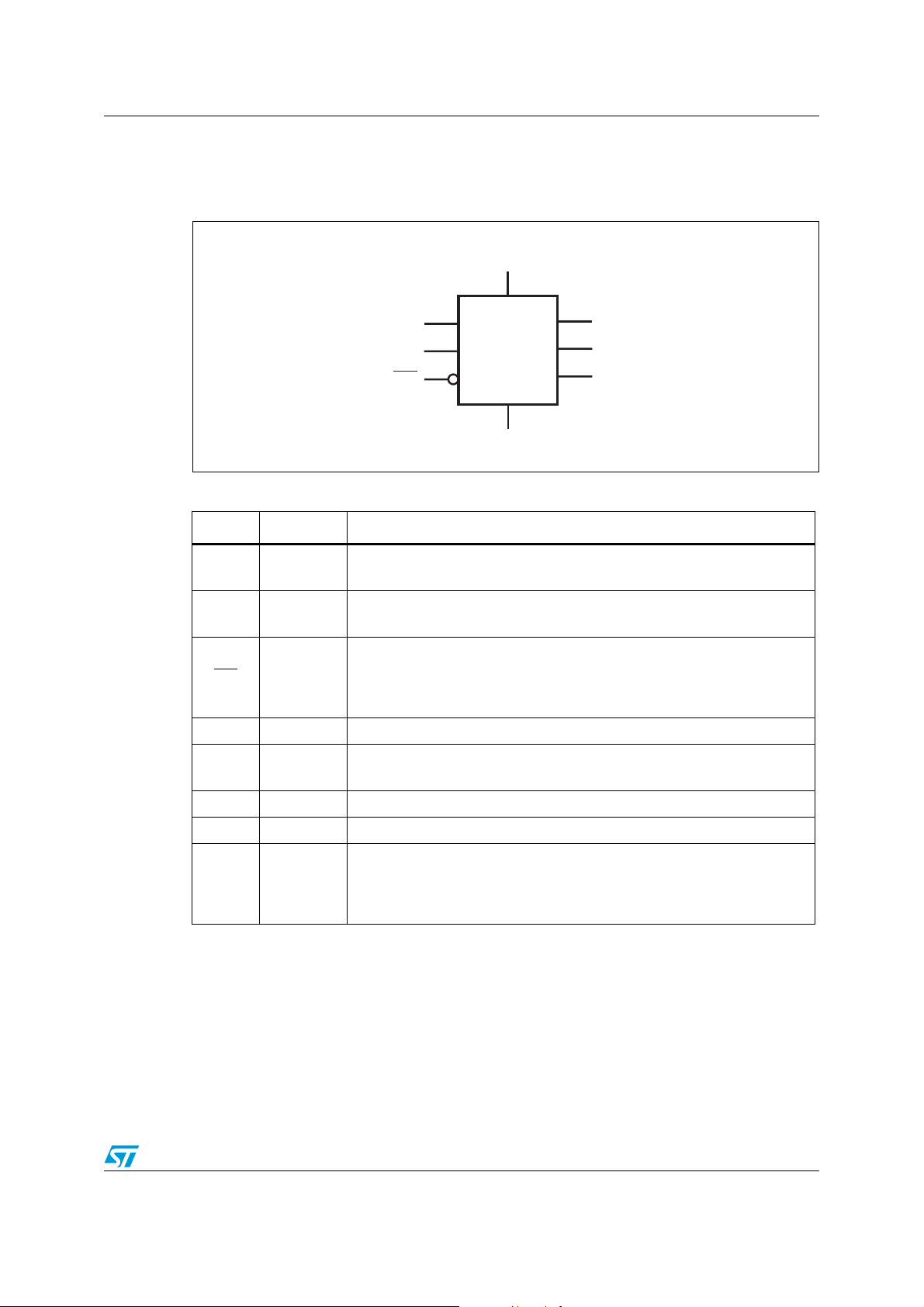
STVM100 Device overview
1 Device overview
Figure 1. Logic diagram
V
DD
SDA
SCL
STVM100
WP
GND
Table 2. Pin names and functions
Name Type Function
(1)
OUT Analog
AV
DD
Supply
Adjustable sink current output pin.
See Section 3: Application information on page 11.
High-voltage analog supply.
Bypass to GND with a 0.1 µF capacitor.
WRITE protectection.
WP Input
Active-low. To enable write operations to the DAC or to the EEPROM
writing, connect to 0.7 VDD or greater. Internally pulled down by a 130 kΩ
resistor.
GND Supply ground.
V
DD
Supply
SDA Input/Output I
SCL Input I
System power supply input.
Bypass to GND with a 0.1 µF capacitor.
2
C serial data input/output.
2
C serial clock input.
AV
OUT
SET
DD
AI12272
Maximum sink current adjustment point.
SET Analog
1. See SET pin function in this table for the maximum adjustable sink current setting.
Connect a resistor from SET to GND to set the maximum adjustable sink
current of the OUT pin. The maximum adjustable sink current is equal to
AVDD /20 divided by R
(see Figure 4 on page 6).
SET
Doc ID 13236 Rev 8 5/27
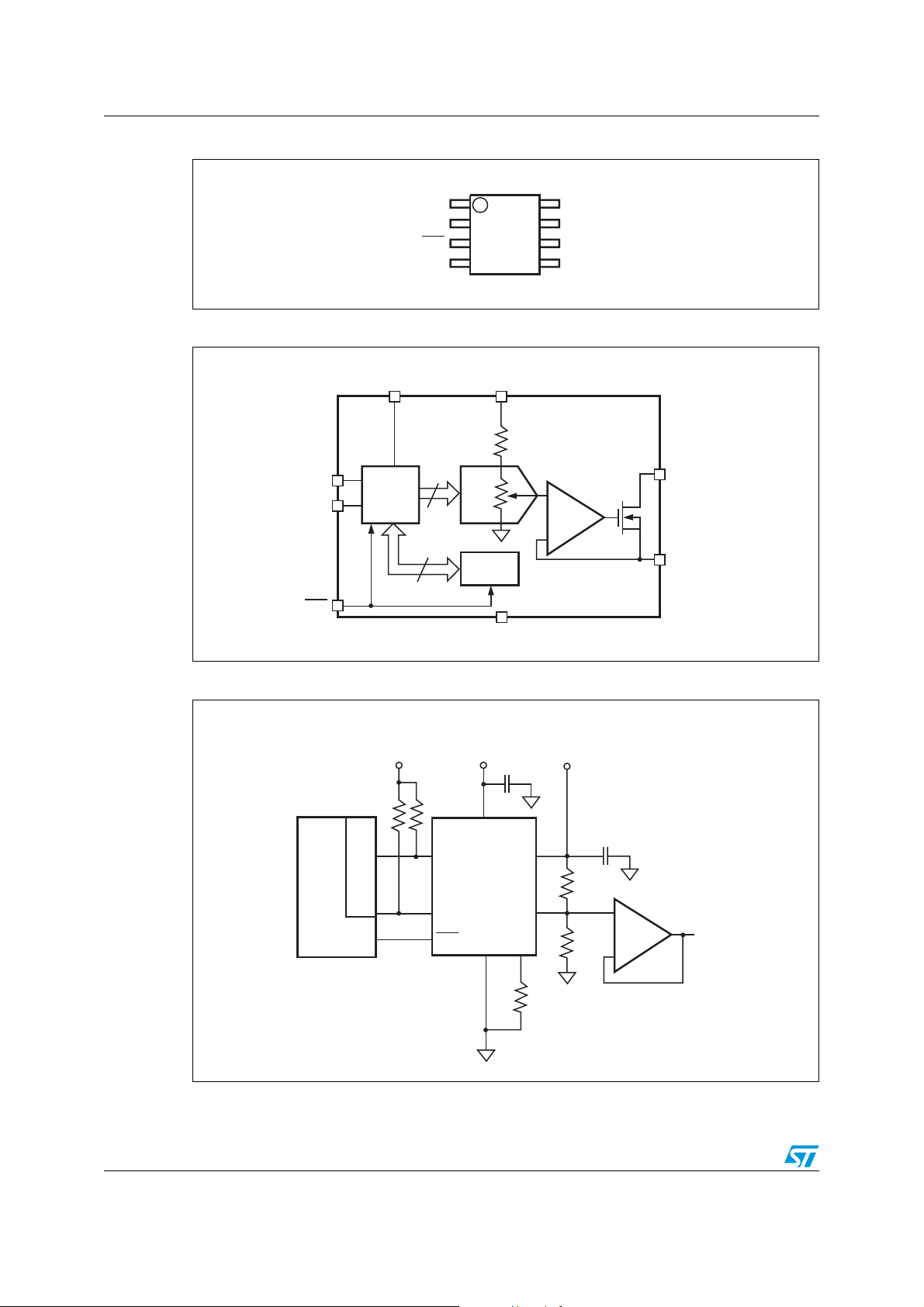
Device overview STVM100
Figure 2. Connections diagram
Figure 3. Block diagram
SDA
SCL
WP
Interface
V
I2C
DD
OUT
AV
GND
DD
WP
7
7
1
2
3
4
AV
DD
DAC
EEPROM
Block
GND
19R
R
SET
8
SCL
7
SDA
6
V
5
DD
AI12273
OUT
+
–
SET
AI12274
Figure 4. Hardware hookup
3.3V
MCU
2
C Interface
I
SDA
STVM100
SCL
WP
V
DD
V
DD
GND
0.1µF
AV
OUT
SET
DD
R
AV
SET
DD
0.1µF
R
1
+
R
2
–
VCOM
AI12275
6/27 Doc ID 13236 Rev 8

STVM100 Device operation
2 Device operation
The STVM100 operates as a slave device on the serial bus. Access is obtained by
implementing a start condition, followed by the 7-bit slave address (1001111), and the
eighth bit for READ/WRITE identification. The volatile DAC register and non-volatile
EEPROM values can be read out or written in.
2.1 2-wire bus characteristics and conditions
This bus is intended for communication between different ICs. It consists of two lines:
● a bi-directional data signal (SDA).
● a clock signal (SCL).
The SDA and SCL lines must be connected to a positive supply voltage via a pull-up
resistor. The following protocols have been defined:
● Data transfer may be initiated only when the bus is not busy.
● During data transfer, the data line must remain stable whenever the clock line is high.
● Changes in the data line while the clock line is high will be interpreted as control
signals.
2.1.1 Bus not busy
Both data and clock lines remain high.
2.1.2 Start data transfer
A change in the data line state from high-to-low while the clock is high indicate the start
condition.
2.1.3 Stop data transfer
A change in the data line state from low-to-high while the clock is high indicates the stop
condition.
Doc ID 13236 Rev 8 7/27
Device operation STVM100
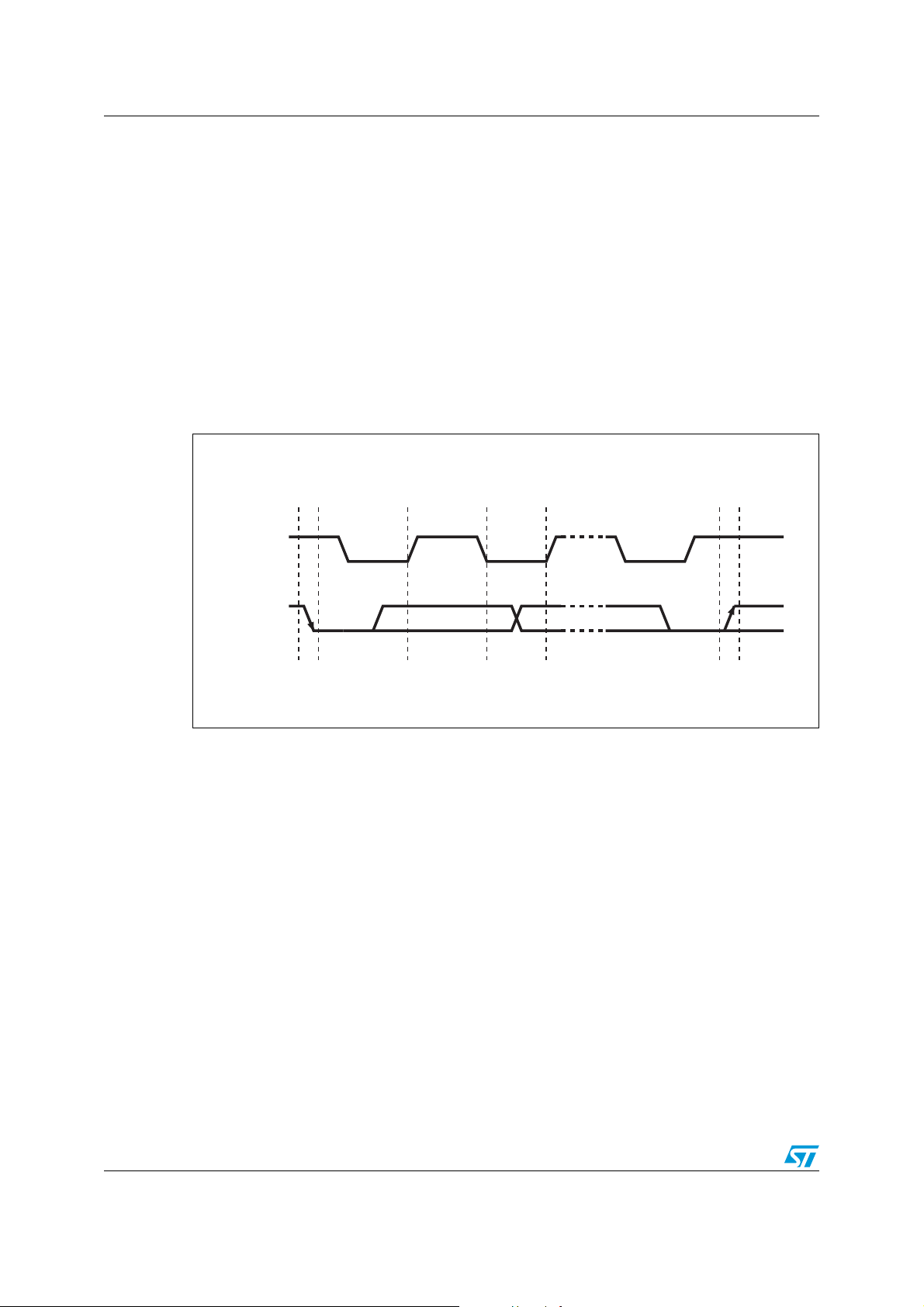
2.1.4 Data valid
The data on the SDA line must be stable during the high period of the clock. The high or low
state of the data line can only change when the clock signal on the SCL line is low (see
Figure 5). The data on the line may be changed during the clock signal low period. There is
one clock pulse per bit of data.
Each data transfer is initiated with a start condition and terminated with a stop condition.
The number of data bytes transferred between the start and stop conditions is not limited.
The information is transmitted byte-wide and each receiver acknowledges transmission with
a ninth bit.
By definition, the device that gives out a message is called “transmitter”, the device that gets
the message is called “receiver”. The device that controls the message is called the
“master”. The devices controlled by the master are called “slave” devices.
Figure 5. Serial bus data transfer sequence
DATA LINE
STABLE
DATA VALID
CLOCK
DATA
START
CONDITION
CHANGE OF
DATA ALLOWED
STOP
CONDITION
AI00587
8/27 Doc ID 13236 Rev 8
STVM100 Device operation
2.1.5 Acknowledge
Each byte of eight bits is followed by one acknowledge bit. This acknowledge bit is a low
level signal put on the bus by the receiver, whereas the master generates an extra
acknowledge-related clock pulse (see Figure 6). A slave receiver which is addressed is
obliged to generate an acknowledge signal after the reception of each byte that has been
clocked out of the slave transmitter.
The device that acknowledges transmissions has to pull down the SDA line during the
acknowledge clock pulse in such a way, that the SDA line is a stable low during the high
period of the acknowledge-related clock pulse. The setup and hold times must be taken into
account. A master receiver must signal an end of transmitted data to the slave transmitter
by not generating an acknowledge on the last byte that has been clocked out of the slave. In
this case, the transmitter must leave the data line high to enable the master to generate the
stop condition.
Figure 6. Acknowledgement sequence
CLOCK PULSE FOR
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
SCL FROM
MASTER
START
12 89
DATA OUTPUT
BY TRANSMITTER
DATA OUTPUT
BY RECEIVER
MSB LSB
AI00601
Doc ID 13236 Rev 8 9/27

Device operation STVM100
2.2 Read mode
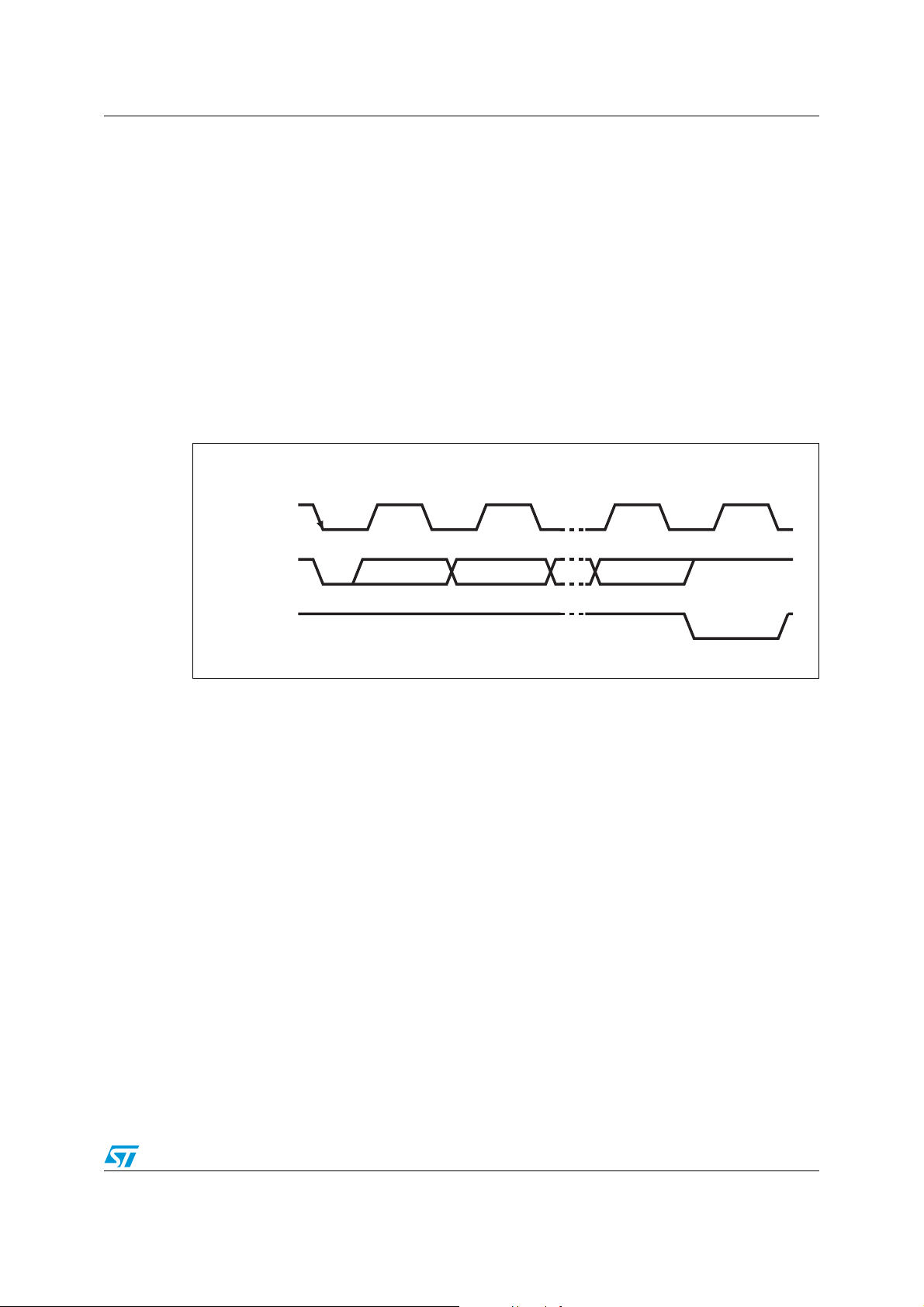
In READ mode, after the start condition, the master sets the slave address (see Figure 7).
Followed by the READ/WRITE mode control bit (R/W
=1) and the acknowledge bit, the value
in DAC register will be transmitted and the master receiver will send an acknowledge bit to
the slave transmitter. Finally the stop condition will terminate the READ operation. In READ
mode, the valid data is the first 7 bits and the P bit (the eight bit) is don’t care.
2.3 Write mode
In WRITE mode the master transmits to the STVM100 slave receiver. The bus protocol is
shown in Figure 7. Following the start condition and slave address, a logic '0' (R/W
placed on the bus to identify a WRITE operation. After the acknowledgement by the slave,
the data will be transmitted to the slave with the 7-bit which indicates the data is valid as well
as the eighth bit “P” for the register’s identification. When P = 1, the DAC register is written
to, and when P = 0, the EEPROM is written to (Programming). After receiving the data, the
slave will generate an acknowledge signal, then a stop condition will terminate the WRITE
operation. STVM100 is pre-programmed with 80H in the EEPROM after manufacturing.
= 0) is
A period of t
(see Table 8) is needed for EEPROM programming. During this period, the
W
slave will not acknowledge any WRITE operation.
The bit P values in both READ and WRITE modes are shown in Table 3.
Figure 7. Read/write mode sequence
STA RT SLAVE ADDRESS
1001111
SCL
SDA
Table 3. Bit P read and write mode values
1
001111
STA RT STOP
Operation P-bit value Description
READ X Don’t care
WRITE
R/W
6543 210P
R/W AA6543 210P
A STOP
A
1 DAC register WRITE
0
EEPROM WRITE
(programming)
AI12276_b
2.4 VDD power supply ramp-up
The ramp-up from 10% VDD to 90% VDD level should be achieved in less than or equal to
10ms to ensure that the EEPROM and power-on reset circuits are synchronized, and the
correct value is read from the EEPROM.
10/27 Doc ID 13236 Rev 8

STVM100 Application information
3 Application information
The STVM100 is a programmable V
avoid the “ghosting effect” (residual pixels during refresh) in e-paper and e-books. It
provides a digital I
2
C interface to control the sink current output. This output drives an
external resistive voltage divider, which can then be applied to an external V
The highest and lowest V
value is determined by three resistors, R1, R2, and R
COM
calibrator to remove flickers in TFT-LCDs or to
COM
COM
buffer.
SET
. The
connection is shown in Figure 8.
The sink current from the STVM100 OUT pin is given in Equation 1. This current then flows
through R
Figure 8. R
. This current must be less than 120 µA (see I
SET
, R2, and R
1
connection
SET
AV
DD
AV
DD
STVM100
OUT
SET
R
SET
I
OUT
AV
DD
R1
R2
value in Table 7 on page 15).
SET
+
V
COM
–
AI12933
Note: In order to choose an appropriate device to buffer the output of STVM100, please see our
operational amplifier product portfolio available at:
http://www.st.com/stonline/products/families/amplifiers_comparators/amplifiers_comparators.htm
Equation 1
I
OUT
D1+
-------------128
AV
DD
--------------------------
⋅=
20 R
()
SET
Note: “D” is a user-selected value, an integer ranging from 0 to 127.
The V
value can be obtained in Equation 2.
COM
Equation 2
V
COM
R
2
-------------------R1R2+
⋅=
D1+
⎛⎞
--------------
AV
1
DD
⎝⎠
128
R
1
--------------------------
⋅–
20 R
()
SET
Doc ID 13236 Rev 8 11/27

Application information STVM100
If the user-selected value is 0 (zero scale), the minimum current is sunk. The maximum
V
value is obtained in Equation 3.
COM
Equation 3
V
COM max()
R
2
-------------------R1R2+
⋅=
1
⎛⎞
----------
AV
1
DD
⎝⎠
128
R
1
--------------------------
⋅–
20 R
()
SET
If the user-selected value is 127 (full scale), the maximum current is sunk and the minimum
V
value is obtained in Equation 4.
COM
Equation 4
R
During operation, the V
V
COM min()
COM(max)
-------------------R1R2+
and V
2
⋅=
COM(min)
⎛⎞
AV
1
DD
⎝⎠
range is set, based on different TFT-LCD
processes.The R1 value is given based on the acceptable power loss from the AV
rail. Using Equation 3 and Equation 4, the R
put into Equation 1 on page 11 and maximum I
and R
2
SET
≥ 120 µA, then R1 should be increased.
OUT
R
–
1
-------------------------20 R
()
SET
DD
values can be calculated. If R
supply
is
SET
12/27 Doc ID 13236 Rev 8

STVM100 Maximum ratings
4 Maximum ratings
Stressing the device above the ratings listed in the absolute maximum ratings table may
cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operating sections of
this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for
extended periods may affect device reliability. Refer also to the STMicroelectronics SURE
Program and other relevant quality documents.
Table 4. Absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
T
STG
T
SLD
T
V
OUT
V
AV
V
SET
Storage temperature (VDD off, AVDD off) –55 to 150 °C
(1)
Lead solder temperature for 10 seconds 260 °C
Maximum junction temperature (plastic package) 150 °C
J
Output voltage (OUT pin to GND) –0.3 to 20 V
VDD to GND +5.5 V
DD
AVDD input voltage to GND –0.3 to 20 V
DD
Output voltage (SET pin to GND) –0.3 to 5.5 V
TDFN8 2.66 W
P
DIS
1. Reflow at peak temperature of 260 °C. The time above 255 °C must not exceed 30 seconds.
Power dissipation
TSSOP8 0.53 W
Doc ID 13236 Rev 8 13/27

DC and AC parameters STVM100
5 DC and AC parameters
This section summarizes the operating measurement conditions, and the dc and ac
characteristics of the device. The parameters in the DC and AC characteristics tables that
follow, are derived from tests performed under the measurement conditions summarized in
Table 5. Designers should check that the operating conditions in their circuit match the
operating conditions when relying on the quoted parameters.
Table 5. Operating and AC measurement conditions
Parameter Conditions Unit
V
supply voltage 2.25 to 3.6 V
DD
EEPROM programming supply voltage 2.25 to 3.6 V
V
DD
AV
reference voltage 4.5 to 20 V
DD
Ambient operating temperature (T
Table 6. Capacitances
Symbol Parameter
) –40 to 85 °C
A
(1)(2)
Min Max Unit
C
b
C
SDA
Bus capacitive load 400 pF
Capacitance on SDA 10 pF
WP = 0 10 pF
C
S
1. Effective capacitance measured with power supply at 3 V. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
2. At 25 °C, f = 1 MHz.
Capacitance on SCL
WP = 1 22 pF
14/27 Doc ID 13236 Rev 8

STVM100 DC and AC parameters
Table 7. DC and AC characteristics
Sym Description Test condition
Supply voltage 2.25 3.6 V
V
EEPROM
DD
programming supply
voltage
(2)
I
DD
AV
I
AVD D
SET
SET
SET
SET
I
SET
SET
AV
SET
OUT
V
SET
V
I
IL(WPN)
V
1. Valid for ambient operating temperature: TA = –40 to 85 °C; VDD = 3 V; AVDD = 10 V; typical TA = 25 °C;
OUT = 1/2AV
2. Simulated maximum current draw when Programming EEPROM is 23 mA; should be considered when
designing a power supply.
3. Tested at AVDD = 20 V.
4. A typical Current of 20 µA is calculated using AVDD = 10 V and R
SET current should be 120 µA.
5. Simulated and determined via design and NOT directly tested.
VDD supply current 50 µA
= 2.6 V to 3.6 V 4.5 20 V
V
Analog supply voltage
DD
(3)
AVDD supply current 25 µA
SET voltage resolution 7 Bits
VR
SET differential
DN
nonlinearity
SET zero scale error ±2 LSB
ZSE
SET full scale error ±8 LSB
FSE
(4)
SET current Through R
SET external
ER
resistance
to
AVDD to SET voltage
DD
attenuation
OUT settling time 8 µs
ST
OUT voltage
OUT
SET voltage drift
VD
SDA, SCL, WP input
IH
logic high
SDA, SCL, WP input
V
IL
logic low
SDA, SCL
hysteresis
(5)
(5)
(5)
DD
V
= 2.25 V to 3.6 V 4.5 13 V
DD
Monotonic over
temperature
To GND, AV
To G ND, AV
T = 25 °C to 55 °C <10 mV
WPN input current 15 25 35 µA
SDA, SCL output logic
OL(s)
low
DD
; R
= 24.9 kΩ (except where noted).
SET
At 3 mA 0.4 V
(1)
Min Typ Max Unit
2.25 3.6 V
±1 LSB
SET
= 20 V 10 200 kΩ
DD
= 4.5 V 2.25 45 kΩ
DD
120 µA
20 V/V
V
+
SET
0.5V
0.7 V
DD
0.22 V
DD
= 24.9 kΩ. The maximum suggested
SET
13 V
0.3V
DD
V
V
V
Doc ID 13236 Rev 8 15/27

DC and AC parameters STVM100
Figure 9. Bus timing requirements sequence
SDA
tHD:STAtBUF
tR
SCL
SP
Table 8. AC characteristics
tF
tHIGH
tLOW
Sym Description Test Condition
f
t
LOW
t
HIGH
t
SU:DAT
t
HD:DAT
SCL clock frequency 0 400 kHz
SCL
Clock low period 1.3 µs
Clock high period 0.6 µs
Data setup time 100 ns
Data hold time 0 900 ns
t
SDA and SCL rise time
R
t
SDA and SCL fall time 300 ns
F
Dependent on load (see
Table 6 on page 14)
tSU:DAT
tHD:DAT
(1)
SR
Min T yp Max Unit
tHD:STA
20 +
0.1 C
b
Bus free time before
t
new transmission can
BUF
1.3 µs
start
t
DSP
t
SU:STA
t
HD:STA
t
SU:STO
1. Valid for ambient operating temperature: TA = –40 to 85 °C; VDD = 3.0 V to 3.6 V; AVDD = 10 V;
OUT = 1/2AVDD; R
I2C spike rejection filter
pulse width
Repeated start
condition setup time
Repeated start
condition hold time
Stop condition setup
time
t
WRITE cycle time 100 ms
W
= 24.9 kΩ (except where noted, see Figure 9).
SET
050ns
0.6 µs
0.6 µs
0.6 µs
tSU:STOtSU:STA
P
AI00589
300 ns
16/27 Doc ID 13236 Rev 8

STVM100 Typical operating characteristics
6 Typical operating characteristics
Typical operating characteristics for the STVM100 are TA = 25 °C, VDD = 3 V, AVDD = 10 V,
OUT = 1/2AV
, and R
DD
= 24.9 kΩ except where noted.
SET
Figure 10. V
Figure 11. AV
(µA)
AVDD
I
supply current vs. V
DD
27. 5
27
26.5
26
(µA)
DD
I
25.5
25
24.5
24
.2. 2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2 3.4 3.6
supply current vs. AV
DD
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
4.5 6 7.5 9 10.5 12 13.5 15 16.5 18 19.5
DD
V
DD
DD
(V)
AI13362
AVDD (V)
AI13363
Doc ID 13236 Rev 8 17/27

Typical operating characteristics STVM100
Figure 12. VDD supply current vs. temperature
35
30
(µA)
25
DD
I
20
15
-40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
Figure 13. AV
Temperature°C
supply current vs. temperature
DD
4.95
4.9
4.85
4.8
(µA)
4.75
4.7
AVDD
I
4.65
4.6
4.55
4.5
-40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
Temperature°C
AI13364
AI13365
18/27 Doc ID 13236 Rev 8

STVM100 Typical operating characteristics
Figure 14. I
error vs. temperature (STVM100 at middle scale)
OUT
0.06
0.05
0.04
0.03
error (LSB)
0.02
OUT
I
0.01
0
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80
Temperature°C
Figure 15. Total unadjusted error vs. DAC setting
0.022474
AI13366
0.020395
0.018316
0.016237
0.014158
0.012079
Total unadjusted error (LSB)
0.01
1 173349 658197113
DAC setting (decimal)
AI13367
Doc ID 13236 Rev 8 19/27

Typical operating characteristics STVM100
Figure 16. Differential non-linearity vs. DAC setting
0.2
0.15
0.1
0.05
0
-0.05
-0.1
Differential non-linearity (LSB)
-0.15
-0.2
1 17334965 8197113
DAC setting (decimal)
AI13368
Figure 17. Integral non-linearity vs. DAC setting
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
-0.1
-0.2
Integral non-linearity (LSB)
-0.3
1 173349658197113
DAC setting (decimal)
AI13369
20/27 Doc ID 13236 Rev 8

STVM100 Typical operating characteristics
Figure 18. AVDD power-up response
AV
: 5V/DIV, VDD: 5V/DIV, V
DD
Figure 19. Full scale-up response
5ms/DIV
OUT
: 1V/DIV, V
SET
: 1V/DIV
20µs/DIV
SCL: 5V/DIV, SDA: 5V/DIV, V
Doc ID 13236 Rev 8 21/27
: 1V/DIV, V
OUT
SET
: 1V/DIV

Typical operating characteristics STVM100
Figure 20. Full scale-down response
20µs/DIV
SCL: 5V/DIV, SDA: 5V/DIV, V
: 1V/DIV, V
OUT
SET
: 1V/DIV
22/27 Doc ID 13236 Rev 8

STVM100 Package mechanical data
7 Package mechanical data
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in different grades of
ECOPACK
specifications, grade definitions and product status are available at: www.st.com.
ECOPACK
®
packages, depending on their level of environmental compliance. ECOPACK®
®
is an ST trademark.
Figure 21. TDFN8 3 x 3 x 0.75 mm, pitch 0.65, package mechanical data
Note: Drawing is not to scale.
Table 9. TDFN8 3 x 3 x 0.75 mm, pitch 0.65, package mechanical data
A
E2
E
A3 A1
D
D2
1
8
e
L
b
0.08
EZ_ME
mm inches
Sym
Typ Min Max Typ Min Max
A 0.75 0.70 0.80 0.0295 0.0276 0.0315
A1 0.02 0.00 0.05 0.0008 0.0000 0.0020
A3 0.20 0.0079
b 0.30 0.25 0.35 0.0118 0.0098 0.0138
D 3.00 0.1181
D2 2.38 2.23 2.48 0.0937 0.0878 0.0976
E 3.00 0.1181
E2 1.64 1.49 1.74 0.0646 0.0587 0.0685
e0.65– –0.0256– –
L 0.40 0.30 0.50 0.0157 0.0118 0.0197
Doc ID 13236 Rev 8 23/27

Package mechanical data STVM100
Figure 22. TSSOP8 – 8-lead, thin shrink small outline, 3 mm x 3 mm, mech. data
D
CP
Note: Drawing is not to scale.
Table 10. TSSOP8 – 8-lead, thin shrink small outline, 3 mm x 3 mm, mech. data
Sym
Typ Min Max Typ Min Max
A 1.100 0.0433
A1 0.050 0.150 0.0020 0.0059
A2 0.850 0.750 0.950 0.0335 0.0295 0.0374
b 0.250 0.400 0.0098 0.0157
c 0.130 0.230 0.0051 0.0091
8
1
5
EE1
4
A2A
A1
eb
L
L1
c
TSSOP8BM
mm inches
CP 0.100 0.0039
D 3.000 2.900 3.100 0.1181 0.1142 0.1220
e 0.650 – – 0.0256 – –
E 4.900 4.6500 5.150 0.1929 0.1831 0.2028
E1 3.000 2.900 3.100 0.1181 0.1142 0.1220
L 0.550 0.400 0.700 0.0217 0.0157 0.0276
L1 0.950 0.0374
α 0° 6° 0° 6°
N8 8
24/27 Doc ID 13236 Rev 8

STVM100 Part numbering
8 Part numbering
Table 11. Ordering information scheme
Example: STVM100 DC 6 F
Device type
STVM100, V
Package
DC = TDFN8
DS = TSSOP8
Temperature range
6 = –40 to 85°C
calibrator with 7-bit DAC and I2C interface
COM
Shipping method
E = ECOPACK
F = ECOPACK
®
package, tubes
®
package, tape & reel
For other options, or for more information on any aspect of this device, please contact the
ST sales office nearest you.
Doc ID 13236 Rev 8 25/27

Revision history STVM100
9 Revision history
Table 12. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
09-May-2006 1 Initial release.
14-Jul-2006 2 Graphical and textual updates
Document status upgraded to Preliminary Data; changed the
wording of Input function to include ‘WRITE operations’ instead of
‘programming’ in Table 2: Pin names and functions; deleted some
bracketed text and modified the P bit function in Section 2.2: Read
08-Nov-2006 3
12-Feb-2007 4
20-Apr-2007 5 Value added in Section 2.3: Write mode.
24-Jul-2007 6 Document status upgraded to full datasheet.
mode; ensured that all of Equation 2 and Equation 3 were visible;
amalgamated 2 cells containing the same information (VDD) in
Table 7: DC and AC characteristics; deleted footnotes 2 and 3 of
Table 8: AC characteristics; updated package mechanical
information in Figure 21, Table 9, and Table 10.
Reformatted inside cover page according to new template; renamed
section 1 Device overview and section 2 Device operation; deleted
Signal names table; moved and renamed Table 2: Pin names and
functions, addedSection 6: Typical operating characteristics and
Figure 10 to Figure 20.
04-Nov-2009 7
09-Dec-2009 8
Added “Note” to Figure 8; updated footnote of Table 4; minor textual
changes.
Updated title of datasheet, Applications, Description, and Section 3:
Application information.
26/27 Doc ID 13236 Rev 8

STVM100
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICUL AR PURPOS E (AND THEIR E QUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJ URY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2009 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
Doc ID 13236 Rev 8 27/27
 Loading...
Loading...