STM32F102x8
LQFP48
7 × 7 mm
LQFP64
10 × 10 mm
STM32F102xB
Medium-density USB access line, ARM-based 32-bit MCU with 64/128KB
Flash, USB FS interface, 6 timers, ADC & 8 communication interfaces
Features
■ Core: ARM 32-bit Cortex™-M3
– 48 MHz maximum frequency,
1.25 DMIPS/MHz (Dhrystone 2.1)
performance at 0 WS memory access
– Single-cycle multiplication and hardware
division
■ Memories
– 64 or 128 Kbytes of Flash memory
– 10 or 16 Kbytes of SRAM
■ Clock, reset and supply management
– 2.0 to 3.6 V application supply and I/Os
– POR, PDR and programmable voltage
detector (PVD)
– 4-to-16 MHz crystal oscillator
– Internal 8 MHz factory-trimmed RC
– Internal 40 kHz RC
– PLL for CPU clock
– 32 kHz oscillator for RTC with calibration
■ Low power
– Sleep, Stop and Standby modes
–V
■ Debug mode
supply for RTC and backup registers
BAT
– Serial wire debug (SWD) and JTAG
interfaces
■ DMA
– 7-channel DMA controller
– Peripherals supported: timers, ADC, SPIs,
2
I
Cs and USARTs
■ 1 × 12-bit, 1.2 µs A/D converter (up to 16
channels)
– Conversion range: 0 to 3.6 V
– Temperature sensor
■ Up to 51 fast I/O ports
– 37/51 IOs all mappable on 16 external
interrupt vectors and almost all 5 V-tolerant
CPU
■ Up to 6 timers
– Three 16-bit timers, each with up to 4
IC/OC/PWM or pulse counter
– 2 watchdog timers (Independent and
Window)
– SysTick timer: 24-bit downcounter
■ Up to 8 communication interfaces
– Up to 2 x I
2
C interfaces (SMBus/PMBus)
– Up to 3 USARTs (ISO 7816 interface, LIN,
IrDA capability, modem control)
– Up to 2 SPIs (12 Mbit/s)
– USB 2.0 full speed interface
■ CRC calculation unit, 96-bit unique ID
■ ECOPACK
Table 1. Device summary
Reference Part number
STM32F102x8 STM32F102C8, STM32F102R8
STM32F102xB STM32F102CB, STM32F102RB
®
packages
September 2009 Doc ID 15056 Rev 3 1/69
www.st.com
1

Contents STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB
Contents
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.1 Device overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.2 Full compatibility throughout the family . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.3 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3 Pinouts and pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
4 Memory mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
5 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.1 Parameter conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.1.1 Minimum and maximum values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.1.2 Typical values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.1.3 Typical curves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.1.4 Loading capacitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.1.5 Pin input voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.1.6 Power supply scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
5.1.7 Current consumption measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
5.2 Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
5.3 Operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
5.3.1 General operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
5.3.2 Operating conditions at power-up / power-down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
5.3.3 Embedded reset and power control block characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . 28
5.3.4 Embedded reference voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
5.3.5 Supply current characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
5.3.6 External clock source characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
5.3.7 Internal clock source characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
5.3.8 PLL characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
5.3.9 Memory characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
5.3.10 EMC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
5.3.11 Absolute maximum ratings (electrical sensitivity) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
5.3.12 I/O port characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
2/69 Doc ID 15056 Rev 3

STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB Contents
5.3.13 NRST pin characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
5.3.14 TIM timer characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
5.3.15 Communications interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
5.3.16 12-bit ADC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
5.3.17 Temperature sensor characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
6 Package characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
6.1 Package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
6.2 Thermal characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
6.3 Reference document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
6.3.1 Evaluating the maximum junction temperature for an application . . . . . 66
7 Ordering information scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
8 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Doc ID 15056 Rev 3 3/69

List of tables STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB
List of tables
Table 1. Device summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Table 2. STM32F102x8 and STM32F102xB medium-density USB access line
features and peripheral counts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table 3. STM32F102xx USB access line family . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Table 4. Medium-density STM32F102xx pin definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Table 5. Voltage characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 6. Current characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 7. Thermal characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 8. General operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Table 9. Operating conditions at power-up / power-down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Table 10. Embedded reset and power control block characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Table 11. Embedded internal reference voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Table 12. Maximum current consumption in Run mode, code with data processing
running from Flash . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Table 13. Maximum current consumption in Run mode, code with data processing
running from RAM. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Table 14. Maximum current consumption in Sleep mode, code running from Flash or RAM. . . . . . . 32
Table 15. Typical and maximum current consumptions in Stop and Standby modes . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 16. Typical current consumption in Run mode, code with data processing
running from Flash . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table 17. Typical current consumption in Sleep mode, code running from Flash or RAM. . . . . . . . . 36
Table 18. Peripheral current consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 19. High-speed external user clock characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 20. Low-speed external user clock characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 21. HSE 4-16 MHz oscillator characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 22. LSE oscillator characteristics (f
Table 23. HSI oscillator characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Table 24. LSI oscillator characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table 25. Low-power mode wakeup timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table 26. PLL characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table 27. Flash memory characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Table 28. Flash memory endurance and data retention . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Table 29. EMS characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Table 30. EMI characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Table 31. ESD absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Table 32. Electrical sensitivities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Table 33. I/O static characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Table 34. Output voltage characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Table 35. I/O AC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table 36. NRST pin characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Table 37. TIMx characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Table 38. I
Table 39. SCL frequency (f
Table 40. SPI characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Table 41. USB startup time. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
2
C characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
= 24 MHz, VDD = 3.3 V) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
PCLK1
Table 42. USB DC electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Table 43. USB: Full speed electrical characteristics of the driver. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Table 44. ADC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
= 32.768 kHz) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
LSE
4/69 Doc ID 15056 Rev 3

STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB List of tables
Table 45. R
max for f
AIN
= 12 MHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
ADC
Table 46. ADC accuracy - limited test conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Table 47. ADC accuracy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Table 48. TS characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Table 49. LQFP64 – 10 x 10 mm, 64-pin low-profile quad flat package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . 63
Table 50. LQFP48 – 7 x 7 mm, 48-pin low-profile quad flat package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Table 51. Package thermal characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Table 52. Ordering information scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Table 53. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Doc ID 15056 Rev 3 5/69

List of figures STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB
List of figures
Figure 1. STM32F102xx medium-density USB access line block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 2. Clock tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 3. STM32F102xx medium-density USB access line LQFP48 pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 4. STM32F102xx medium-density USB access line LQFP64 pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 5. Memory map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 6. Pin loading conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 7. Pin input voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 8. Power supply scheme. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 9. Current consumption measurement scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 10. Typical current consumption in Run mode versus temperature (at 3.6 V) -
code with data processing running from RAM, peripherals enabled. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 11. Typical current consumption in Run mode versus temperature (at 3.6 V) -
code with data processing running from RAM, peripherals disabled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 12. Typical current consumption on V
V
values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
BAT
Figure 13. Typical current consumption in Stop mode with regulator in Run mode versus
temperature at V
= 3.3 V and 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
DD
Figure 14. Typical current consumption in Stop mode with regulator in Low-power mode versus
temperature at V
= 3.3 V and 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
DD
Figure 15. Typical current consumption in Standby mode versus temperature at V
3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 16. High-speed external clock source AC timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 17. Low-speed external clock source AC timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 18. Typical application with an 8 MHz crystal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Figure 19. Typical application with a 32.768 kHz crystal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Figure 20. I/O AC characteristics definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Figure 21. Recommended NRST pin protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Figure 22. I
2
C bus AC waveforms and measurement circuit
Figure 23. SPI timing diagram - slave mode and CPHA=0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Figure 24. SPI timing diagram - slave mode and CPHA=1
Figure 25. SPI timing diagram - master mode
Figure 26. USB timings: definition of data signal rise and fall time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Figure 27. ADC accuracy characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Figure 28. Typical connection diagram using the ADC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Figure 29. Power supply and reference decoupling. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Figure 30. LQFP64 – 10 x 10 mm, 64 pin low-profile quad flat package outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Figure 31. Recommended footprint
Figure 32. LQFP48 – 7 x 7 mm, 48-pin low-profile quad flat package outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Figure 33. Recommended footprint
Figure 34. LQFP64 P
max vs. TA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
D
(1)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
(1)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
with RTC on versus temperature at different
BAT
= 3.3 V and
DD
(1)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
(1)
(1)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
6/69 Doc ID 15056 Rev 3

STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB Introduction
1 Introduction
This datasheet provides the ordering information and mechanical device characteristics of
the STM32F102x4 and STM32F102x6 medium-density USB access line microcontrollers.
For more details on the whole STMicroelectronics STM32F102xx family, please refer to
Section 2.2: Full compatibility throughout the family.
The medium-density STM32F102xx datasheet should be read in conjunction with the low-,
medium- and high-density STM32F10xxx reference manual.
For information on programming, erasing and protection of the internal Flash memory
please refer to the STM32F10xxx Flash programming manual.
The reference and Flash programming manuals are both available from the
STMicroelectronics website www.st.com.
For information on the Cortex™-M3 core please refer to the Cortex™-M3 Technical
Reference Manual, available from the www.arm.com website at the following address:
http://infocenter.arm.com/help/index.jsp?topic=/com.arm.doc.ddi0337e/.
Doc ID 15056 Rev 3 7/69

Description STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB
2 Description
The STM32F102xx medium-density USB access line incorporates the high-performance
ARM Cortex™-M3 32-bit RISC core operating at a 48 MHz frequency, high-speed
embedded memories (Flash memory of 64 or 128 Kbytes and SRAM of 10 or 16 Kbytes),
and an extensive range of enhanced peripherals and I/Os connected to two APB buses. All
devices offer standard communication interfaces (two I
USARTs), one 12-bit ADC and three general-purpose 16-bit timers.
The STM32F102xx family operates in the –40 to +85 °C temperature range, from a 2.0 to
3.6 V power supply. A comprehensive set of power-saving mode allows the design of lowpower applications.
The STM32F102xx medium-density USB access line is delivered in the LQFP48 7 × 7 mm
and LQFP64 10 × 10 mm packages.
The STM32F102xx medium-density USB access line microcontrollers are suitable for a
wide range of applications:
● Application control and user interface
● Medical and handheld equipment
● PC peripherals, gaming and GPS platforms
● Industrial applications: PLC, inverters, printers, and scanners
● Alarm systems, Video intercom, and HVAC
2
Cs, two SPIs, one USB and three
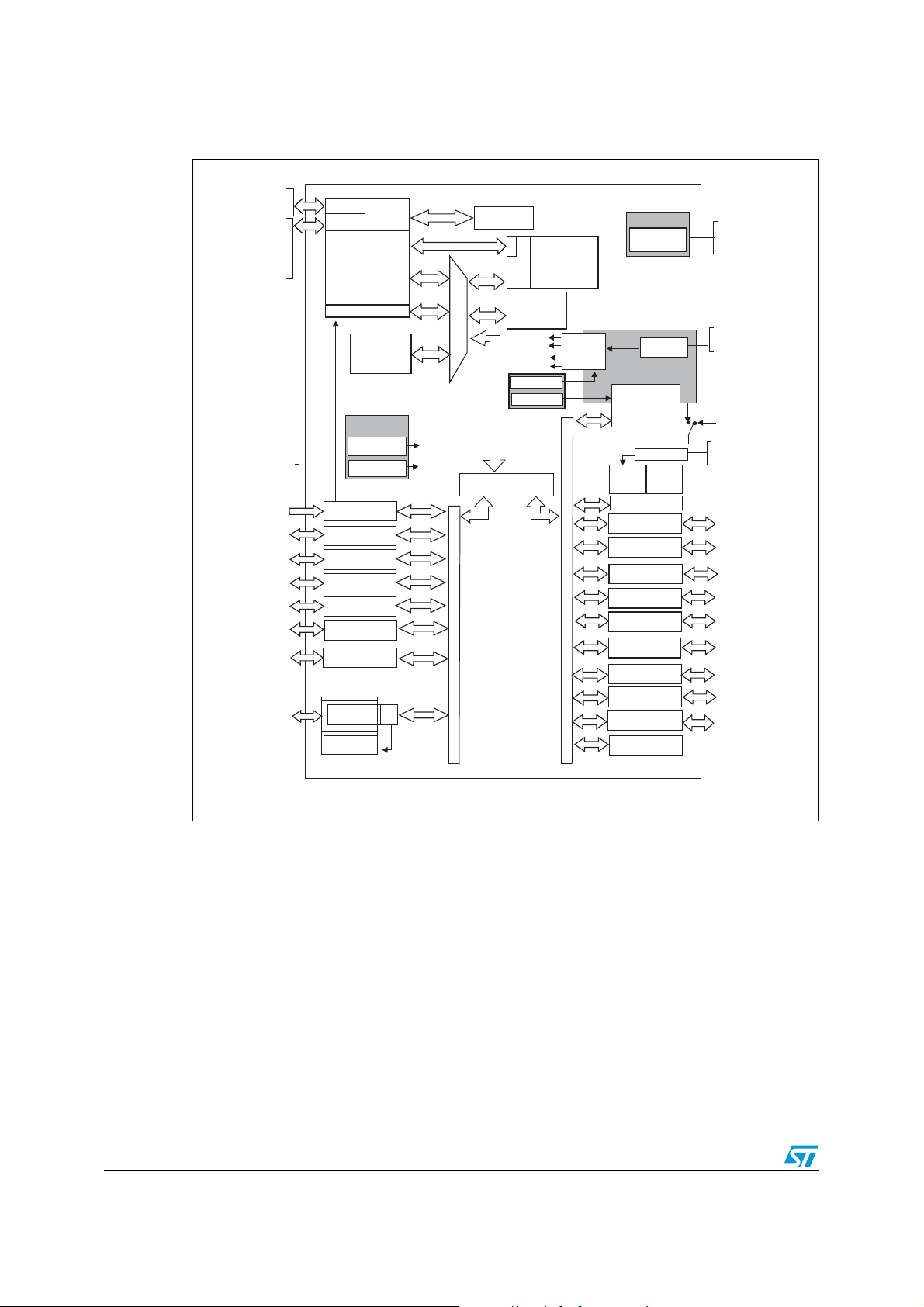
Figure 1 shows the general block diagram of the device family.
8/69 Doc ID 15056 Rev 3
STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB Description
2.1 Device overview
Table 2. STM32F102x8 and STM32F102xB medium-density USB access line
features and peripheral counts
Peripheral
Flash - Kbytes 64 128 64 128
SRAM - Kbytes 10 16 10 16
Timers General-purpose 33 3 3
SPI 22 2 2
2
I
Communication
interfaces
C 22 2 2
USART 33 3 3
USB 11 1 1
STM32F102Cx STM32F102Rx
12-bit synchronized ADC
number of channels
1
10 channels
1
16 channels
GPIOs 37 51
CPU frequency 48 MHz
Operating voltage 2.0 to 3.6 V
Operating temperatures
Ambient temperature: –40 to +85 °C (see Ta bl e 8 )
Junction temperature: –40 to +105 °C (see Ta b le 8 )
Packages LQFP48 LQFP64
Doc ID 15056 Rev 3 9/69
Description STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB
Temp sensor
PA[15: 1]
EXTI
W W D G
NVIC
12bit ADC1
SWD
16 AF
JTDI
JTCK/ SWCLK
JTMS/SWDIO
JNTRST
JTDO
NRST
V
DD
= 2 to 3.6V
51AF
PB[15: 0]
PC[15:0]
AHB2
MOSI,MISO,SCK,NSS
SRAM
x16bit)
WAKEUP
GPIOA
GPIOB
GPIOC
F
max
: 48 MHz
V
SS
SCL,SDA, SMBA
I2C2
GP DMA
TIM2
TIM3
XTAL OSC
4-16 MHz
XTAL 32 kHz
OSC_IN
OSC_OUT
OSC32_OUT
OSC32_IN
PLL &
APB1: F
max
= 24 MHz
PCLK1
HCLK
CLOCK
MANAG T
PCLK 2
as AF
as AF
VOLT. REG.
3.3V TO 1.8V
POWER
Backup interface
as AF
16 KB
RTC
RC 8 MHz
Cortex M3 CPU
USART1
USART2
SPI2
7 channels
Backup
reg
SCL,SDA ,SMBA
I2C1
as AF
RX,TX, CTS, RTS,
USART3
PD[2:0]
GPIOD
AHB: F
max
=48 MHz
4 Chann els
4 Chann els
FCLK
RC 40 kHz
Stand by
IWDG
@VDD
@VBAT
POR / PDR
SUPPLY
@VDDA
VDDA
VSSA
@VDDA
V
BAT
CK, Smartcard as AF
RX,TX, CTS, RTS,
Smart Card as AF
RX,TX, CTS, RTS,
APB2 : F
max
= 48 MHz
NVIC
SPI1
MOSI,MISO,
SCK,NSS as AF
IF
int erface
@VDDA
SUPERVISION
PVD
Rst
Int
@VDD
AHB2
APB2
APB1
AWU
TAMPER-RTC
Flash 128 KB
BusM atrix
64 bit
Interface
Ibus
Dbus
pbus
obl
Flash
Trace
Controlleront
System
TIM4
4 Channels
ai14868f
TRACECLK
TRACED[0:3]
as AS
SW/JTAG
TPIU
Trace/trig
CK, Smartcard as AF
USB 2.0 FS
USBDP, USBDM as AF
Figure 1. STM32F102xx medium-density USB access line block diagram
10/69 Doc ID 15056 Rev 3
1. AF = alternate function on I/O port pin.
= –40 °C to +85 °C (junction temperature up to 105 °C).
2. T
A
STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB Description
HSE OSC
4-16 MHz
OSC_IN
OSC_OUT
OSC32_IN
OSC32_OUT
LSE OSC
32.768 kHz
HSI RC
8 MHz
LSI RC
40 kHz
to Independent Watchdog (IWDG)
PLL
x2, x3, x4
PLLMUL
Legend:
MCO
Clock Output
Main
PLLXTPRE
/2
..., x16
AHB
Prescaler
/1, 2..512
/2
PLLCLK
HSI
HSE
APB1
Prescaler
/1, 2, 4, 8, 16
ADC
Prescaler
/2, 4, 6, 8
ADCCLK
PCLK1
HCLK
PLLCLK
to AHB bus, core,
memory and DMA
USBCLK
to USB interface
to TIM2, 3
and 4
USB
Prescaler
/1, 1.5
to ADC
LSE
LSI
HSI
/128
/2
HSI
HSE
peripherals
to APB1
Peripheral Clock
Enable (13 bits)
Enable (3 bits)
P
eripheral Clock
APB2
Prescaler
/1, 2, 4, 8, 16
PCLK2
peripherals
to APB2
Peripheral Clock
Enable (11 bits)
48 MHz
48 MHz max
48 MHz
48 MHz max
24 MHz max
to RTC
PLLSRC
SW
MCO
CSS
to Cortex System timer
/8
Clock
Enable (3 bits)
SYSCLK
max
RTCCLK
RTCSEL[1:0]
TIMXCLK
IWDGCLK
SYSCLK
FCLK Cortex
free running clock
TIM2,3, 4
If (APB1 prescaler =1) x1
else x2
HSE = high-speed external clock signal
HSI = high-speed internal clock signal
LSI = low-speed internal clock signal
LSE = low-speed external clock signal
ai14994
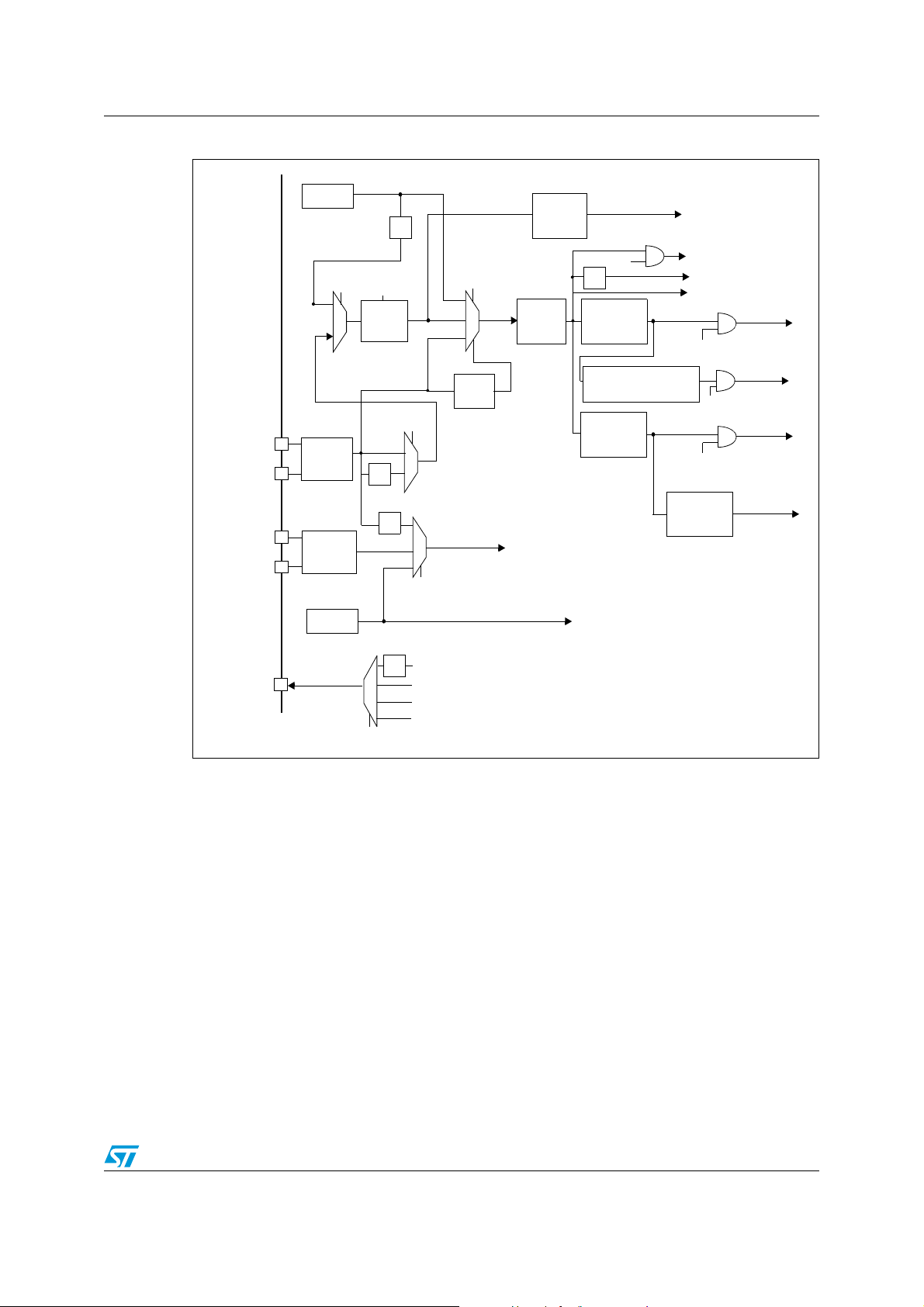
Figure 2. Clock tree
1. For the USB function to be available, both HSE and PLL must be enabled, with the CPU running at
48 MHz.
2. To have an ADC conversion time of 1.2 µs, APB2 must be at 12 MHz, 24 MHz or 48 MHz.
Doc ID 15056 Rev 3 11/69
Description STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB
2.2 Full compatibility throughout the family
The STM32F102xx is a complete family whose members are fully pin-to-pin, software and
feature compatible. In the reference manual, the STM32F102x4 and STM32F102x6 are
referred to as low-density devices and the STM32F102x8 and STM32F102xB are referred to
as medium-density devices.
Low-density devices are an extension of the STM32F102x8/B devices, they are specified in
the STM32F102x4/6 datasheet. Low-density devices feature lower Flash memory and RAM
capacities, a timer and a few communication interfaces less.
The STM32F102x4 and STM32F102x6 are a drop-in replacement for the STM32F102x8/B
medium-density devices, allowing the user to try different memory densities and providing a
greater degree of freedom during the development cycle.
Moreover the STM32F102xx family is fully compatible with all existing STM32F101xx
access line and STM32F103xx performance line devices.
Table 3. STM32F102xx USB access line family
Low-density STM32F102xx devices Medium-density STM32F102xx devices
Pinout
64
48
1. For orderable part numbers that do not show the A internal code after the temperature range code (6), the
reference datasheet for electrical characteristics is that of the STM32F102x8/B medium-density devices.
2.3 Overview
ARM® Cortex™-M3 core with embedded Flash and SRAM
The ARM Cortex™-M3 processor is the latest generation of ARM processors for embedded
systems. It has been developed to provide a low-cost platform that meets the needs of MCU
implementation, with a reduced pin count and low-power consumption, while delivering
outstanding computational performance and an advanced system response to interrupts.
The ARM Cortex™-M3 32-bit RISC processor features exceptional code-efficiency,
delivering the high-performance expected from an ARM core in the memory size usually
associated with 8- and 16-bit devices.
The STM32F102xx medium-density USB access line having an embedded ARM core, is
therefore compatible with all ARM tools and software.
16 KB Flash 32 KB Flash
(1)
64 KB Flash 128 KB Flash
4 KB RAM 6 KB RAM 10 KB RAM 16 KB RAM
2 × USARTs, 2 × 16-bit timers
1 × SPI, 1 × I
2
C, 1 × ADC, 1 × USB
3 × USARTs, 3 × 16-bit timers
2 × SPIs, 2 × I2Cs, 1 × ADC, 1 × USB
Embedded Flash memory
64 or 128 Kbytes of embedded Flash is available for storing programs and data.
12/69 Doc ID 15056 Rev 3

STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB Description
CRC (cyclic redundancy check) calculation unit
The CRC (cyclic redundancy check) calculation unit is used to get a CRC code from a 32-bit
data word and a fixed generator polynomial.
Among other applications, CRC-based techniques are used to verify data transmission or
storage integrity. In the scope of the EN/IEC 60335-1 standard, they offer a means of
verifying the Flash memory integrity. The CRC calculation unit helps compute a signature of
the software during runtime, to be compared with a reference signature generated at linktime and stored at a given memory location.
Embedded SRAM
10 or 16 Kbytes of embedded SRAM accessed (read/write) at CPU clock speed with 0 wait
states.
Nested vectored interrupt controller (NVIC)
The STM32F102xx medium-density USB access line embeds a nested vectored interrupt
controller able to handle up to 36 maskable interrupt channels (not including the 16 interrupt
lines of Cortex™-M3) and 16 priority levels.
● Closely coupled NVIC gives low latency interrupt processing
● Interrupt entry vector table address passed directly to the core
● Closely coupled NVIC core interface
● Allows early processing of interrupts
● Processing of late arriving higher priority interrupts
● Support for tail-chaining
● Processor state automatically saved
● Interrupt entry restored on interrupt exit with no instruction overhead
This hardware block provides flexible interrupt management features with minimal interrupt
latency.
External interrupt/event controller (EXTI)
The external interrupt/event controller consists of 19 edge detectors lines used to generate
interrupt/event requests. Each line can be independently configured to select the trigger
event (rising edge, falling edge, both) and can be masked independently. A pending register
maintains the status of the interrupt requests. The EXTI can detect external line with pulse
width lower than the Internal APB2 clock period. Up to 51 GPIOs are connected to the 16
external interrupt lines.
Clocks and startup
System clock selection is performed on startup, however the internal RC 8 MHz oscillator is
selected as default CPU clock on reset. An external 4-16 MHz clock can be selected, in
which case it is monitored for failure. If failure is detected, the system automatically switches
back to the internal RC oscillator. A software interrupt is generated if enabled. Similarly, full
interrupt management of the PLL clock entry is available when necessary (for example on
failure of an indirectly used external crystal, resonator or oscillator).
Several prescalers allow the configuration of the AHB frequency, the High Speed APB
(APB2) and the low Speed APB (APB1) domains. The maximum frequency of the AHB and
the APB domains is 48 MHz. See Figure 2 for details on the clock tree.
Doc ID 15056 Rev 3 13/69

Description STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB
Boot modes
At startup, boot pins are used to select one of five boot options:
● Boot from User Flash
● Boot from System Memory
● Boot from embedded SRAM
The boot loader is located in System Memory. It is used to reprogram the Flash memory by
using USART1. For further details please refer to AN2606.
Power supply schemes
● V
● V
● V
= 2.0 to 3.6 V: External power supply for I/Os and the internal regulator.
DD
Provided externally through V
, V
SSA
= 2.0 to 3.6 V: External analog power supplies for ADC, Reset blocks, RCs
DDA
and PLL (minimum voltage to be applied to V
V
and V
DDA
= 1.8 to 3.6 V: Power supply for RTC, external clock 32 kHz oscillator and backup
BAT
must be connected to V
SSA
registers (through power switch) when V
DD
pins.
is 2.4 V when the ADC is used).
DDA
and VSS, respectively.
DD
is not present.
DD
For more details on how to connect power pins, refer to Figure 8: Power supply scheme.
Power supply supervisor
The device has an integrated power on reset (POR)/power down reset (PDR) circuitry. It is
always active, and ensures proper operation starting from/down to 2 V. The device remains
in reset mode when V
external reset circuit.
The device features an embedded programmable voltage detector (PVD) that monitors the
V
DD/VDDA
power supply and compares it to the V
generated when V
than the V
threshold. The interrupt service routine can then generate a warning
PVD
message and/or put the MCU into a safe state. The PVD is enabled by software.
Refer to Table 10: Embedded reset and power control block characteristics for the values of
V
POR/PDR
and V
PVD
is below a specified threshold, V
DD
DD/VDDA
drops below the V
.
POR/PDR
threshold. An interrupt can be
PVD
threshold and/or when VDD/V
PVD
, without the need for an
is higher
DDA
Voltage regulator
The regulator has three operation modes: main (MR), low power (LPR) and power down.
● MR is used in the nominal regulation mode (Run)
● LPR is used in the Stop mode
● Power down is used in Standby mode: the regulator output is in high impedance: the
kernel circuitry is powered down, inducing zero consumption (but the contents of the
registers and SRAM are lost)
This regulator is always enabled after reset. It is disabled in Standby mode, providing high
impedance output.
14/69 Doc ID 15056 Rev 3

STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB Description
Low-power modes
The STM32F102xx medium-density USB access line supports three low-power modes to
achieve the best compromise between low power consumption, short startup time and
available wakeup sources:
● Sleep mode
In Sleep mode, only the CPU is stopped. All peripherals continue to operate and can
wake up the CPU when an interrupt/event occurs.
● Stop mode
The Stop mode achieves the lowest power consumption while retaining the content of
SRAM and registers. All clocks in the 1.8 V domain are stopped, the PLL, the HSI RC
and the HSE crystal oscillators are disabled. The voltage regulator can also be put
either in normal or in low power mode.
The device can be woken up from Stop mode by any of the EXTI line. The EXTI line
source can be one of the 16 external lines, the PVD output or the RTC alarm.
● Standby mode
The Standby mode is used to achieve the lowest power consumption. The internal
voltage regulator is switched off so that the entire 1.8 V domain is powered off. The
PLL, the HSI RC and the HSE crystal oscillators are also switched off. After entering
Standby mode, SRAM and registers content are lost except for registers in the Backup
domain and Standby circuitry.
The device exits Standby mode when an external reset (NRST pin), a IWDG reset, a
rising edge on the WKUP pin, or an RTC alarm occurs.
Note: The RTC, the IWDG, and the corresponding clock sources are not stopped by entering Stop
or Standby mode.
DMA
The flexible 7-channel general-purpose DMA is able to manage memory-to-memory,
peripheral-to-memory and memory-to-peripheral transfers. The DMA controller supports
circular buffer management avoiding the generation of interrupts when the controller
reaches the end of the buffer.
Each channel is connected to dedicated hardware DMA requests, with support for software
trigger on each channel. Configuration is made by software and transfer sizes between
source and destination are independent.
The DMA can be used with the main peripherals: SPI, I
2
C, USART, general purpose timers
TIMx and ADC.
RTC (real-time clock) and backup registers
The RTC and the backup registers are supplied through a switch that takes power either on
V
supply when present or through the V
DD
registers used to store 20 bytes of user application data when V
The real-time clock provides a set of continuously running counters which can be used with
suitable software to provide a clock calendar function, and provides an alarm interrupt and a
periodic interrupt. It is clocked by a 32.768 kHz external crystal, resonator or oscillator, the
internal low power RC oscillator or the high-speed external clock divided by 128. The
internal low power RC has a typical frequency of 40 kHz. The RTC can be calibrated using
an external 512 Hz output to compensate for any natural crystal deviation. The RTC
features a 32-bit programmable counter for long term measurement using the Compare
pin. The backup registers are ten 16-bit
BAT
power is not present.
DD
Doc ID 15056 Rev 3 15/69

Description STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB
register to generate an alarm. A 20-bit prescaler is used for the time base clock and is by
default configured to generate a time base of 1 second from a clock at 32.768 kHz.
Independent watchdog
The independent watchdog is based on a 12-bit downcounter and 8-bit prescaler. It is
clocked from an independent 40 kHz internal RC and as it operates independently from the
main clock, it can operate in Stop and Standby modes. It can be used as a watchdog to
reset the device when a problem occurs, or as a free running timer for application timeout
management. It is hardware or software configurable through the option bytes. The counter
can be frozen in debug mode.
Window watchdog
The window watchdog is based on a 7-bit downcounter that can be set as free running. It
can be used as a watchdog to reset the device when a problem occurs. It is clocked from the
main clock. It has an early warning interrupt capability and the counter can be frozen in
debug mode.
SysTick timer
This timer is dedicated for OS, but could also be used as a standard down counter. It
features:
● A 24-bit down counter
● Autoreload capability
● Maskable system interrupt generation when the counter reaches 0.
● Programmable clock source
General-purpose timers (TIMx)
There are 3 synchronizable general-purpose timers embedded in the STM32F102xx
medium-density USB access line devices. These timers are based on a 16-bit auto-reload
up/down counter, a 16-bit prescaler and feature 4 independent channels each for input
capture, output compare, PWM or one-pulse mode output. This gives up to 12 input
captures / output compares / PWMs on the LQFP48 and LQFP64 packages.
The general-purpose timers can work together via the Timer Link feature for synchronization
or event chaining. Their counter can be frozen in debug mode.
Any of the general-purpose timers can be used to generate PWM outputs. They all have
independent DMA request generation.
These timers are capable of handling quadrature (incremental) encoder signals and the
digital outputs from 1 to 3 hall-effect sensors.
I²C bus
Two I²C bus interfaces can operate in multi-master and slave modes. They can support
standard and fast modes. They support dual slave addressing (7-bit only) and both 7/10-bit
addressing in master mode. A hardware CRC generation/verification is embedded.
They can be served by DMA and they support SM Bus 2.0/PM Bus.
16/69 Doc ID 15056 Rev 3

STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB Description
Universal synchronous/asynchronous receiver transmitter (USART)
The available USART interfaces communicate at up to 2.25 Mbit/s. They provide hardware
management of the CTS and RTS signals, support IrDA SIR ENDEC, are ISO 7816
compliant and have LIN Master/Slave capability.
The USART interfaces can be served by the DMA controller.
Serial peripheral interface (SPI)
Two SPIs are able to communicate up to 12 Mbit/s in slave and master modes in full-duplex
and simplex communication modes. The 3-bit prescaler gives 8 master mode frequencies
and the frame is configurable to 8 bits or 16 bits. The hardware CRC generation/verification
supports basic SD Card/MMC modes.
Both SPIs can be served by the DMA controller.
Universal serial bus (USB)
The STM32F102xx medium-density USB access line embeds a USB device peripheral
compatible with the USB Full-speed 12 Mbs. The USB interface implements a full-speed (12
Mbit/s) function interface. It has software configurable endpoint setting and suspend/resume
support. The dedicated 48 MHz clock is generated from the internal main PLL (the clock
source must use a HSE crystal oscillator).
GPIOs (general-purpose inputs/outputs)
Each of the GPIO pins can be configured by software as output (push-pull or open-drain), as
input (with or without pull-up or pull-down) or as peripheral alternate function. Most of the
GPIO pins are shared with digital or analog alternate functions. All GPIOs are high currentcapable except for analog inputs.
The I/Os alternate function configuration can be locked if needed following a specific
sequence in order to avoid spurious writing to the I/Os registers.
ADC (analog to digital converter)
The 12-bit analog to digital converter has up to 16 external channels and performs
conversions in single-shot or scan modes. In scan mode, automatic conversion is performed
on a selected group of analog inputs.
The ADC can be served by the DMA controller.
An analog watchdog feature allows very precise monitoring of the converted voltage of one,
some or all selected channels. An interrupt is generated when the converted voltage is
outside the programmed thresholds.
Temperature sensor
The temperature sensor has to generate a a voltage that varies linearly with temperature.
The conversion range is between 2 V < V
connected to the ADC_IN16 input channel which is used to convert the sensor output
voltage into a digital value.
< 3.6 V. The temperature sensor is internally
DDA
Serial wire JTAG debug port (SWJ-DP)
The ARM SWJ-DP Interface is embedded. and is a combined JTAG and serial wire debug
port that enables either a serial wire debug or a JTAG probe to be connected to the target.
The JTAG TMS and TCK pins are shared respectively with SWDIO and SWCLK and a
specific sequence on the TMS pin is used to switch between JTAG-DP and SW-DP.
Doc ID 15056 Rev 3 17/69

Pinouts and pin description STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB
64 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 29 30 31 3225 26 27 28
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
VBAT
PC14-OSC32_IN
PC15-OSC32_OUT
PD0-OSC_IN
PD1-OSC_OUT
NRST
PC0
PC1
PC2
PC3
VSSA
VDDA
PA 0- W K UP
PA 1
PA 2
VDD_3
VSS_3
PB9
PB8
BOOT0
PB7
PB6
PB5
PB4
PB3
PD2
PC12
PC11
PC10
PA 1 5
PA 14
VDD_2
VSS_2
PA 1 3
PA 1 2
PA 1 1
PA 1 0
PA 9
PA 8
PC9
PC8
PC7
PC6
PB15
PB14
PB13
PB12
PA 3
VSS_4
VDD_4
PA 4
PA 5
PA 6
PA 7
PC4
PC5
PB0
PB1
PB2
PB10
PB11
VSS_1
VDD_1
LQFP64
ai14387c
PC13-TAMPER-RTC
3 Pinouts and pin description
Figure 3. STM32F102xx medium-density USB access line LQFP48 pinout
VDD_3
VSS_3
PB9
PB8
BOOT0
PB7
PB6
PB5
PB4
PB3
PA 1 5
PA 14
PC13-TAMPER-RTC
VBAT
PC14-OSC32_IN
PC15-OSC32_OUT
PD0-OSC_IN
PD1-OSC_OUT
NRST
VSSA
VDDA
PA 0- W K UP
PA 1
PA 2
48 47 46 45
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13 14 15 16 17 18
PA 3
44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37
LQFP48
PA 4
PA 5
PA 6
PA 7
PB0
19 20 21 22
PB1
PB2
PB10
PB11
VDD_2
36
VSS_2
35
PA1 3
34
PA1 2
33
PA1 1
32
PA1 0
31
PA9
30
PA8
29
PB15
28
27
PB14
26
PB13
25
PB12
24
23
VSS_1
VDD_1
ai14378d
Figure 4. STM32F102xx medium-density USB access line LQFP64 pinout
18/69 Doc ID 15056 Rev 3
STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB Pinouts and pin description
Table 4. Medium-density STM32F102xx pin definitions
Pins
Pin name
LQFP48
LQFP64
11 V
BAT
2 2 PC13-TAMPER-RTC
3 3 PC14-OSC32_IN
4 4 PC15-OSC32_OUT
(5)
I/O PC13
(5)
I/O PC14
(5)
I/O PC15
(2)
(1)
Main
function
Typ e
(after reset)
I / O level
SV
BAT
(6)
(6)
(6)
5 5 PD0 I/O FT OSC_IN
6 6 PD1 I/O FT OSC_OUT
(3)
(7)
(7)
Alternate functions
Default Remap
TAMPER-RTC
OSC32_IN
OSC32_OUT
7 7 NRST I/O NRST
- 8 PC0 I/O PC0 ADC_IN10
- 9 PC1 I/O PC1 ADC_IN11
- 10 PC2 I/O PC2 ADC_IN12
- 11 PC3 I/O PC3 ADC_IN13
812 V
913 V
SSA
DDA
SV
SV
SSA
DDA
WKUP/USART2_CTS/
10 14 PA0-WKUP I/O PA0
11 15 PA1 I/O PA1
12 16 PA2 I/O PA2
13 17 PA3 I/O PA3
-18 V
-19 V
SS_4
DD_4
SV
SV
SS_4
DD_4
14 20 PA4 I/O PA4
15 21 PA5 I/O PA5 SPI1_SCK
16 22 PA6 I/O PA6
17 23 PA7 I/O PA7
ADC_IN0/
TIM2_CH1_ETR
USART2_RTS/
ADC_IN1/TIM2_CH2
USART2_TX/
ADC_IN2/TIM2_CH3
USART2_RX/
ADC_IN3/TIM2_CH4
(8)
SPI1_NSS
/ADC_IN4
USART2_CK/
(8)
/ADC_IN5
SPI1_MISO
SPI1_MOSI
(8)
/ADC_IN6/
TIM3_CH1
(8)
/ADC_IN7/
TIM3_CH2
(8)
(8)
(8)
(8)
(8)
(8)
- 24 PC4 I/O PC4 ADC_IN14
- 25 PC5 I/O PC5 ADC_IN15
18 26 PB0 I/O PB0 ADC_IN8/TIM3_CH3
19 27 PB1 I/O PB1 ADC_IN9/TIM3_CH4
(8)
(8)
20 28 PB2 I/O FT PB2/BOOT1
(3) (4)
Doc ID 15056 Rev 3 19/69
Pinouts and pin description STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB
Table 4. Medium-density STM32F102xx pin definitions (continued)
Pins
LQFP48
LQFP64
Pin name
(2)
(1)
Typ e
Main
function
(3)
(after reset)
I / O level
Alternate functions
Default Remap
21 29 PB10 I/O FT PB10 I2C2_SCL/ USART3_TX
22 30 PB11 I/O FT PB11 I2C2_SDA/ USART3_RX
23 31 V
24 32 V
SS_1
DD_1
25 33 PB12 I/O FT PB12
26 34 PB13 I/O FT PB13
27 35 PB14 I/O FT PB14
SV
SV
SS_1
DD_1
SPI2_NSS / I2C2_SMBA/
USART3_CK
SPI2_SCK
(8)
USART3_CTS
SPI2_MISO/
USART3_RTS
(8)
/
28 36 PB15 I/O FT PB15 SPI2_MOSI
- 37 PC6 I/O FT PC6 TIM3_CH1
- 38 PC7 I/O FT PC7 TIM3_CH2
- 39 PC8 I/O FT PC8 TIM3_CH3
- 40 PC9 I/O FT PC9 TIM3_CH4
29 41 PA8 I/O FT PA8 USART1_CK/MCO
30 42 PA9 I/O FT PA9 USART1_TX
31 43 PA10 I/O FT PA10 USART1_RX
(8)
(8)
32 44 PA11 I/O FT PA11 USART1_CTS/USBDM
33 45 PA12 I/O FT PA12 USART1_RTS/USBDP
34 46 PA13 I/O FT JTMS-SWDIO PA13
35 47 V
36 48 V
SS_2
DD_2
SV
SV
SS_2
DD_2
37 49 PA14 I/O FT JTCK/SWCLK PA14
38 50 PA15 I/O FT JTDI
- 51 PC10 I/O FT PC10 USART3_TX
- 52 PC11 I/O FT PC11 USART3_RX
- 53 PC12 I/O FT PC12 USART3_CK
- 54 PD2 I/O FT PD2 TIM3_ETR
39 55 PB3 I/O FT JTDO
40 56 PB4 I/O FT JNTRST
(3) (4)
(8)
TIM2_CH3
(8)
TIM2_CH4
TIM2_CH1_ETR/
PA15 /SPI1_NSS
TIM2_CH2/ PB3/
TRACESWO/
SPI1_SCK
TIM3_CH1 / PB4
SPI1_MISO
20/69 Doc ID 15056 Rev 3
STM32F102x8, STM32F102xB Pinouts and pin description
Table 4. Medium-density STM32F102xx pin definitions (continued)
Pins
LQFP48
LQFP64
Pin name
(2)
(1)
Typ e
Main
function
(3)
(after reset)
I / O level
Alternate functions
Default Remap
41 57 PB5 I/O PB5 I2C1_SMBA
42 58 PB6 I/O FT PB6 I2C1_SCL
43 59 PB7 I/O FT PB7 I2C1_SDA
(8)
/ TIM4_CH1 USART1_TX
(8)
/ TIM4_CH2 USART1_RX
44 60 BOOT0 I BOOT0
45 61 PB8 I/O FT PB8 TIM4_CH3 I2C1_SCL
46 62 PB9 I/O FT PB9 TIM4_CH4 I2C1_SDA
47 63 V
48 64 V
SS_3
DD_3
1. I = input, O = output, S = supply.
2. FT= 5 V tolerant.
3. Function availability depends on the chosen device. For devices having reduced peripheral counts, it is always the lower
number of peripherals that is included. For example, if a device has only one SPI, two USARTs and two timers, they will be
called SPI1, USART1 & USART2 and TIM2 & TIM 3, respectively. Refer to Table 2 on page 9Table 3 on page 12.
4. If several peripherals share the same I/O pin, to avoid conflict between these alternate functions only one peripheral should
be enabled at a time through the peripheral clock enable bit (in the corresponding RCC peripheral clock enable register).
5. PC13, PC14 and PC15 are supplied through the power switch. Since the switch only sinks a limited amount of current (3
mA), the use of GPIOs PC13 to PC15 in output mode is limited: the speed should not exceed 2 MHz with a maximum load
of 30 pF and these IOs must not be used as a current source (e.g. to drive an LED).
6. Main function after the first backup domain power-up. Later on, it depends on the contents of the Backup registers even
after reset (because these registers are not reset by the main reset). For details on how to manage these IOs, refer to the
Battery backup domain and BKP register description sections in the STM32F102xx reference manual, available from the
STMicroelectronics website: www.st.com.
7. The pins number 5 and 6 in the LQFP48 package are configured as OSC_IN/OSC_OUT after reset, however the
functionality of PD0 and PD1 can be remapped by software on these pins. For more details, refer to the Alternate function
I/O and debug configuration section in the STM32F10xxx reference manual.
The use of PD0 and PD1 in output mode is limited as they can only be used at 50 MHz in output mode.
8. This alternate function can be remapped by software to some other port pins (if available on the used package). For more
details, refer to the Alternate function I/O and debug configuration section in the STM32F10xxx reference manual,
available from the STMicroelectronics website: www.st.com.
SV
SV
SS_3
DD_3
(3) (4)
TIM3_CH2 /
SPI1_MOSI
Doc ID 15056 Rev 3 21/69
 Loading...
Loading...