Sony DCR-DVD100 User Manual


Introduction
2
2
DVD Handycam TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK

CAMCORDERS: AN INTRODUCTION
Sony led the way in video camcorders. The first consumer cassette
camcorder was developed by Sony. And in 1985, Sony's compact,
®
lightweight 8mm Handycam
video by making memories easy to shoot, play, and share anytime,
anywhere.
Sony also led the way in digital technology. Sony CD and MD recording
raised the standard of excellence in music reproduction. And Sony DV
Handycam models adopted digital video for high-quality recording and
multi-generation editing.
camcorders expanded the world of home
CAMCORDERS: AN INTRODUCTION
Now, Sony takes the next step in digital video: DVD Handycam
®
camcorders. They use DVD discs as their digital recording medium -- so
movies can be shot on disc, stored on disc, edited in the camcorder,
even uploaded to a PC for creative editing and easy sharing.
DVD offers significant advantages over cassette tape. Discs allow instant
access and rapid scene search without fast-forward or rewind. They
record video, audio, even still images. They're more compact and durable
as a storage and playback medium.
Best of all, DVD recordings can be played back on PCs, DVD players,
even PlayStation
2 video game consoles -- for instant compatibility with
®
over 100 million playback devices around the globe.
Sony DVD Handycam camcorders are new and exciting. This handbook
explains basic DVD technology, highlights DVD Handycam camcorder
features, answers common questions, and helps you understand and
appreciate the exciting possibilities of this next step in camcorder
evolution.
DVD Handycam TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK
3
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
CAMCORDERS: AN INTRODUCTION 3
DVD: A BRIEF HISTORY 5
DVD MEDIA TECHNOLOGY 6
DVD VIDEO RECORDING APPLICATIONS 10
THE DVD HANDYCAM CONCEPT 12
DVD HANDYCAM RECORD MODES AND MEDIA 14
DVD HANDYCAM STILL-IMAGE RECORDING 15
DVD HANDYCAM EDITING 16
FAQ (FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS) 18
GLOSSARY 20
4
4
DVD Handycam TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK
DVD: A BRIEF HISTORY
The DVD format was introduced in 1996. Today, DVD is accepted worldwide, in use for a broad range
of applications -- and its next major impact will be felt in the home video recording market.
The development of DVD started 12 years ago. Inspired
by the success of the CD (Digital Audio Compact Disc)
format for music and data recording, manufacturers
began working toward the goal of a new disc format that
would hold two or more hours of high-quality video
recording.
In 1994, two standards were proposed: “MMCD,” from
Sony and Philips, and “SD,” from Toshiba and Pioneer. At
the end of 1995, an agreement was reached on a
common standard. At this point the DVD Consortium was
formed and DVD was ready for marketing. Its first
applications were for prerecorded movies and computer
software (DVD-ROM). Recording standards soon
followed; the DVD-R Book and DVD-RAM Book
standards were defined in 1997.
In 1999, the DVD-RW Book defined a 4.7 GB rewritable
disc format using a short-wavelength red semiconductor
laser. Currently, standardization efforts are underway to
define a next-generation optical disc system using blue
laser technology.
1996 DVD-Video
1997 DVD-R/DVD-RAM/DVD+RW
1998
1999 DVD-RW
2000
2001
2002 DVD+R
Next-generation optical disc
DVD: A BRIEF HISTORY
DVD Advantages
1
DVD is more compact
Because DVD discs are more compact
than videocassettes, they take up less
space inside the camcorder and are
easier to carry, shelve and archive.
3
DVD provides random access
Videotapes must be wound and rewound
on their reels, which takes time and
creates wear. DVD discs never require
rewinding -- and the search process is
virtually instantaneous.
2
DVD is more durable
Videocassette recording requires contact
between videotape and recording head. In
the DVD system, the optical laser pickup
does not touch the disc itself, so there is
far less wear during recording and
playback.
4
DVD recordings can't be
erased
Videotapes can be erased within a VCR or
by exposure to strong magnets. With DVD,
there is no danger that contents may be
accidentally erased.
DVD Handycam TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK
5
DVD MEDIA TECHNOLOGY
DVD MEDIA TECHNOLOGY
Although a 12cm (4-3/4") DVD is the same size as a standard CD, its high-density format allows
more than 7 times more data to be recorded on a single disc.
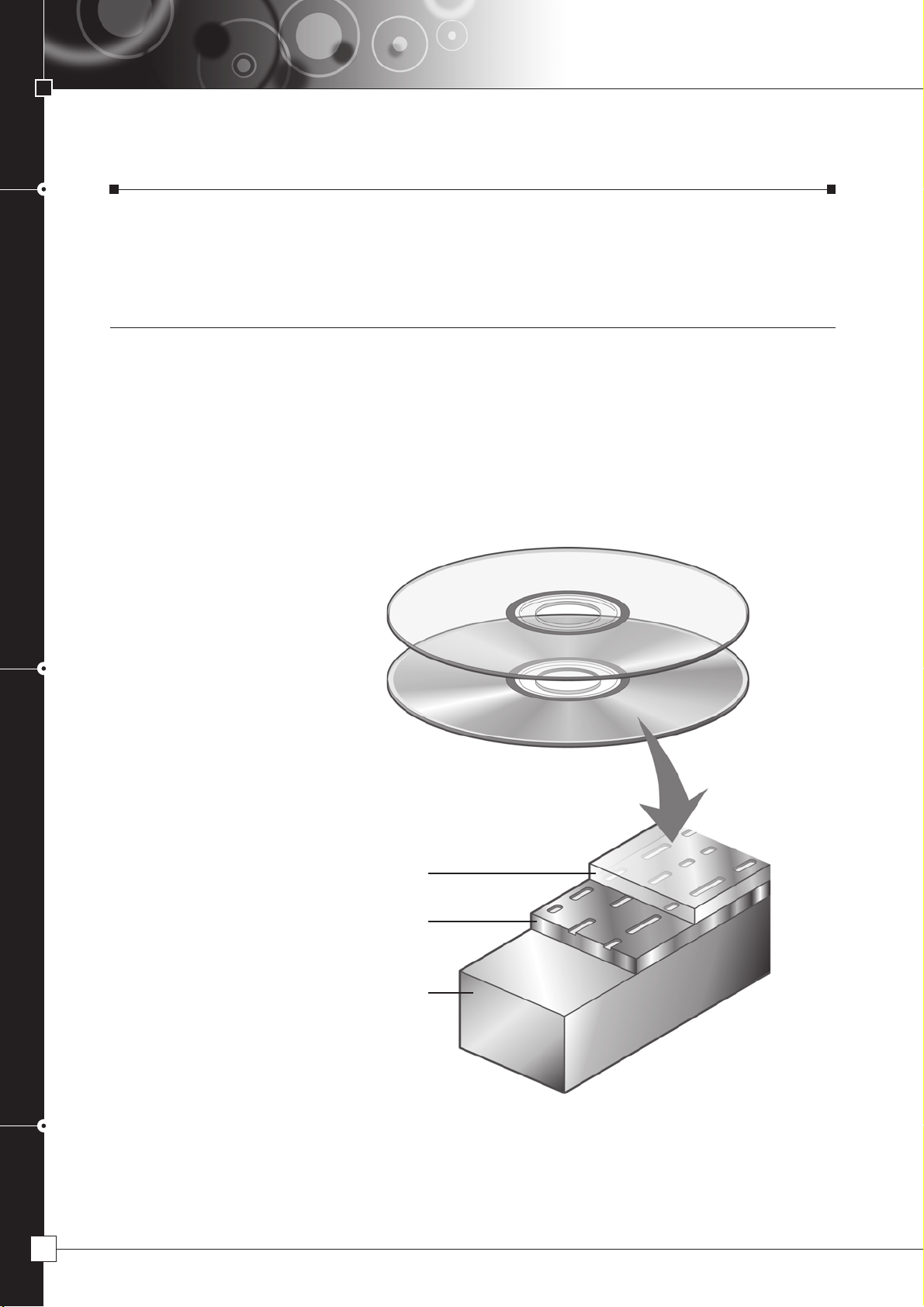
The Basic Structure of a DVD
DVD consists of a dual-layered disc 12cm (4-3/4") or 8cm (3-1/8") in diameter. Each layer has a thickness of 0.6mm
(1/32").
Var ious kinds of DVD suit the needs of various applications, such as DVD-ROM (for playback only), DVD-R (for onetime recording), and DVD-RW (for rewritable recording).
●Structure of DVD-ROM
6
6
DVD Handycam TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK
Protection Layer
Record Layer
Base

DVD-ROM for Playback Only
DVD MEDIA TECHNOLOGY
DVD-ROM discs are for commercial prerecorded movies,
computer software programs, etc. Data is stored in the
form of microscopic “pits” in the record layer of the disc.
These pits are scanned by a laser and then “read” as
minute reflections. These minute changes in reflection
●Record Layer of DVD-ROM
Track pitch
0.74µm
DVD-R for Recording Once
are converted to signals for further processing. There are
four different DVD configurations: single-sided discs with
one or two recordable layers, and double-sided discs
with one or two recordable layers.
Pit
DVD-R discs are for recording only once. Since data
recorded to disc cannot be erased, DVD-R is a good
choice for data that requires long-term storage. Unlike
commercially recorded DVD-ROM discs, DVD-R discs
are recorded by a process of chemical change within the
surface of the disc. After a DVD-R disc is recorded, data
●Record Layer of DVD-R
Track pitch
0.74µm
is read by the optical pickup in a manner similar to the
process of reading a DVD-ROM disc; this similarity
makes DVD-R recordings compatible with DVD playback
units. Recorded (or “written”) areas of a disc are called
“grooves”; unrecorded (or “unwritten”) area is called
“land.”
Groove
Land
DVD Handycam TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK
7

DVD MEDIA TECHNOLOGY
DVD MEDIA TECHNOLOGY
DVD-RW for Repeatable Recording
DVD-RW discs allow repeated recording, erasing, and
re-recording of data. Data is rewritable approximately
1,000 times. This capability makes DVD-RW widely used
in applications that require data editing and future
updating. The recording and playback process is
basically similar to the process of DVD-R recording.
●Record Layer of DVD-RW
Track pitch
0.74µm
DVD Handycam camcorders use both DVD-R and DVD-RW discs. Discs are 8cm (3-1/8") in diameter; they can be
single-sided with one recordable layer, or double-sided with one recordable layer per side.
In the case of DVD-RW, however, the chemical change
that takes place within the surface of the disc during
recording is reversible, allowing data to be erased and
re-recorded. DVD-RW recordings are also compatible
with most DVD players.
Groove
Land
Other DVD Formats
In addition to DVD-ROM, DVD-R and DVD-RW, the following DVD standards also are currently being marketed.
DVD-RAM A rewritable media allowing up to 100,000 reliable rewriting operations. It cannot be played back on
DVD+R A once-only recording media similar in capability to DVD-R.
DVD+RW A rewritable media similar in capability to DVD-RW.
8
8
DVD Handycam TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK
standard DVD players; only players supporting DVD-RAM can be used.
 Loading...
Loading...