SGS Thomson Microelectronics TMBYV10-40FILM Datasheet

®
SMALL SIGNAL SCHOTTKY DIODES
DESCRIPTION
Metal to silicon rectifier diodes in glass case featuring very low forward voltage drop and fast r ecovery
time, intended for low voltage switching mode
power supply, polarity protection and high frequency circuits.
TMBYV 10-40
MELF
(Glass)
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RA TINGS
(limiting values)
Symbol Parameter Val ue Unit
V
RRM
I
F (AV)
I
FSM
T
stg
T
T
L
Repetitive Peak Reverse Voltage 40 V
Average Forward Current
Surge non Repetitive Forward Current
Storage and Junction Temperature
Range
j
= 60 °C
T
i
= 25 °C
T
i
= 10ms
t
p
= 25 °C
T
i
t
= 300µs
p
Sinusoïdal Pulse
Rectangular Pulse
1A
25
50
- 65 to 150
- 65 to 125
Maximum Lead Temperature for Soldering during 15s 260
THERMAL RESISTANCE
Symbol Parameter Value Uni t
A
C
°
C
°
C
°
R
th (j - l)
* Pulse test: t
August 1999 Ed: 1A
Junction-leads 1 10
300µs δ < 2%
≤
p
C/W
°
.
1/4
TMBYV10-40
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
STATIC CHARACTERISTICS
Synbol T est Conditions Min. T yp. Max. Unit
I
*
R
*I
V
F
I
* * Pulse test: t
= 25°C
T
j
T
= 100°C
j
= 1A
F
= 3A 0.85
F
300µs δ < 2%
≤
p
.
V
= V
R
= 25°C
T
j
RRM
0.5
10
0.55
DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS
Symbol Test Conditions M in. Typ. Max. Unit
C
= 25°C VR = 0
T
j
Forward current flow in a Schottky rectifier is due
to majority carrier conduction. S o r everse recovery
is not affected by s torage charge as in conventional
PN junction diodes.
Nevertheless, when the device switches from forward biased condition to reverse blocking state,
This current depends only of diode capacitance and
external circuit impedance. Satisfactory circuit behaviour analysis may be performed assuming that
Schottky rectifier consists of an ideal diode in parallel with a variable capacitance equal to the junction capacitance (see fig. 5 page 4/4).
220 pF
current is required to charge the depletion capacitance of the diode.
mA
V
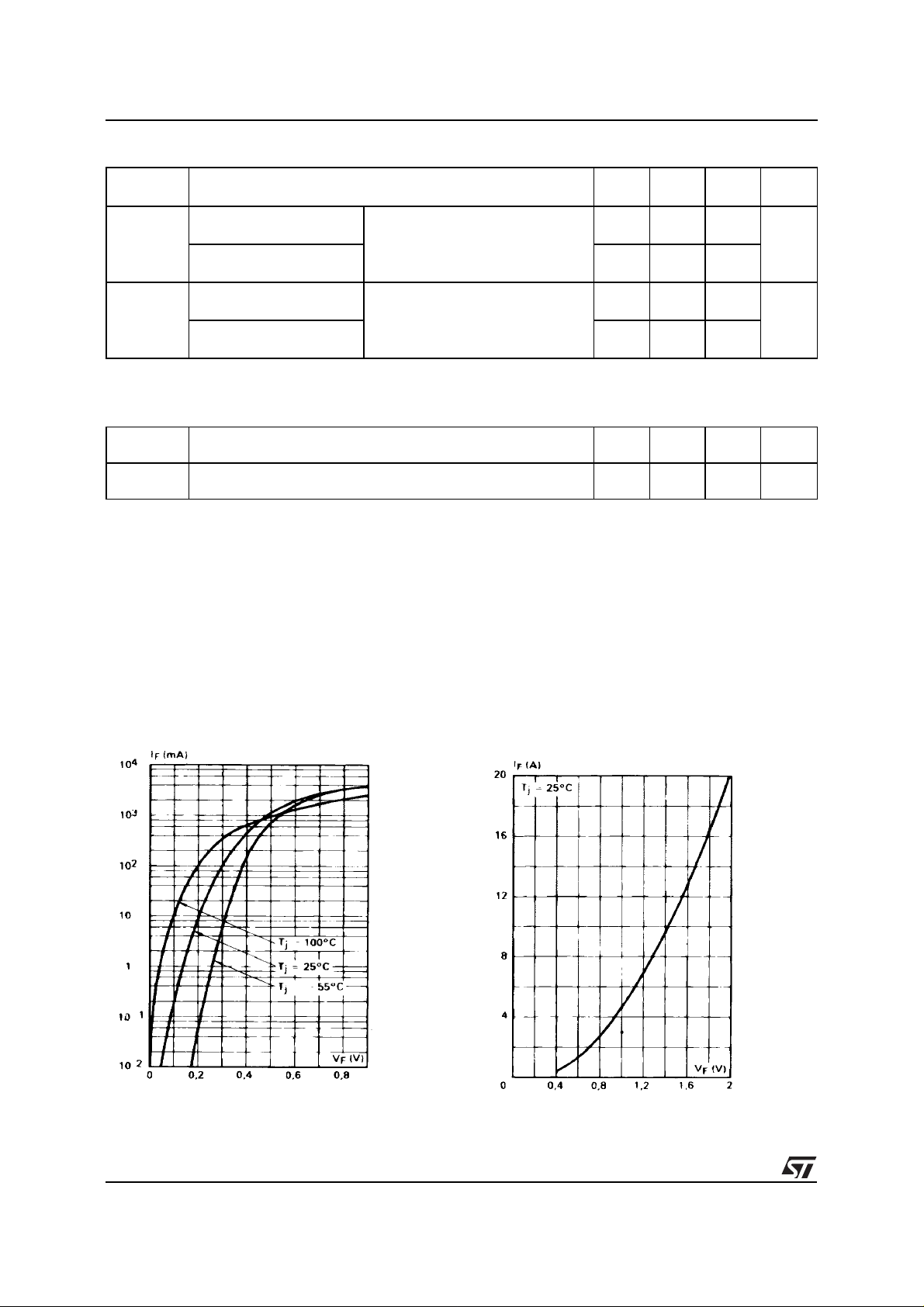
Fig. 1 :
Forward current versus forward voltage
at low level (typical values).
Fig. 2 :
Forward current versus forward voltage
at high level (typical values).
2/4
 Loading...
Loading...