Single phase energy metering IC with pulsed output
Feature summary
■ Ripple free active energy pulsed output
■ Direct stepper counter drivers
■ Shunt, current transformer, Rogowsky coil
sensors
■ Live and neutral monitoring (STPM13/14)
■ Easy and fast digital calibration at only one
load point
■ No-load, negative power and tamper indicators
■ Integrated linear VREGS
■ RC (STPM11/13) or crystal oscillator
(STPM12/14)
■ Support 50÷60 HZ - IEC62052-11, IEC62053-
2X specification
■ Less than 0.1% error
Description
The STPM1x family is designed for effective
measurement of active energy in a power line
system using a Rogowski Coil, Current
Transformer and Shunt sensors. This device is
specifically designed to provide all the necessary
features to implement a single phase energy
meter without any other active component. The
STPM1x device family consists, essentially, of two
parts: the analog part and the digital part. The
former, is composed of a preamplifier and first
order ∑ ∆ A/D converter blocks, band gap
STPM11/12/13/14
and digital calibration
TSSOP20
voltage reference, low drop voltage regulator. The
digital part is composed of a system control,
oscillator, hard wired DSP and interface for
calibration and configuration.
The calibration and configuration are done by
OTP cells, that can be programmed through a
serial interface. The configured bits are used for
testing, configuration and calibration purposes.
From two ∑ ∆ output signals coming from the
analog section, a DSP unit computes the amount
of consumed active energy. The active energy is
available as a pulse frequency output and directly
driven by a stepper counter. In the STPM1X an
output signal with pulse frequency proportional to
energy is generated. This signal is used in the
calibration phase of the energy meter application
allowing a very easy approach. When the device
is fully configured and calibrated, a dedicated bit
of OTP block can be written permanently in order
to prevent accidental entry into test mode or
changing any configuration bit.
Order code
Part number Package Packaging
STPM11ATR TSSOP20 (Tape & reel) 2500 parts per reel
STPM12ATR TSSOP20 (Tape & reel) 2500 parts per reel
STPM13ATR TSSOP20 (Tape & reel) 2500 parts per reel
STPM14ATR TSSOP20 (Tape & reel) 2500 parts per reel
March 2007 Rev. 3 1/43
www.st.com
43

STPM11/12/13/14
Contents
1 Schematic diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2 Pin configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
3 Maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
4 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
5 Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
5.1 Measurement error . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
5.2 ADC Offset error . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
5.3 Gain error . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
5.4 Power supply DC and AC rejection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
5.5 Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
6 Typical performance characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
7 Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
7.1 General operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
7.2 Analog inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
7.3
7.4 Period and line voltage measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
7.5 Single wire meter mode (STPM13/14 with Rogowsky coil sensor) . . . . . 16
7.6 Power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
7.7 Load monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
7.8 Error detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
7.9 Tamper detection module (STPM13/14 only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
7.10 Phase compensation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7.11 Clock generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
∑ ∆ A/D Converters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2/43
7.12 Resetting the STPM1X . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
7.13 Energy to frequency conversion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
7.14 Driving a stepper motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
7.15 Configuring the STPM1X . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
7.16 Mode signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28

STPM11/12/13/14
7.17 CFGI: Configuration interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
8 Energy calculation algorithm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
9 STPM1X Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
10 Schematic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
11 Package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
12 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
3/43
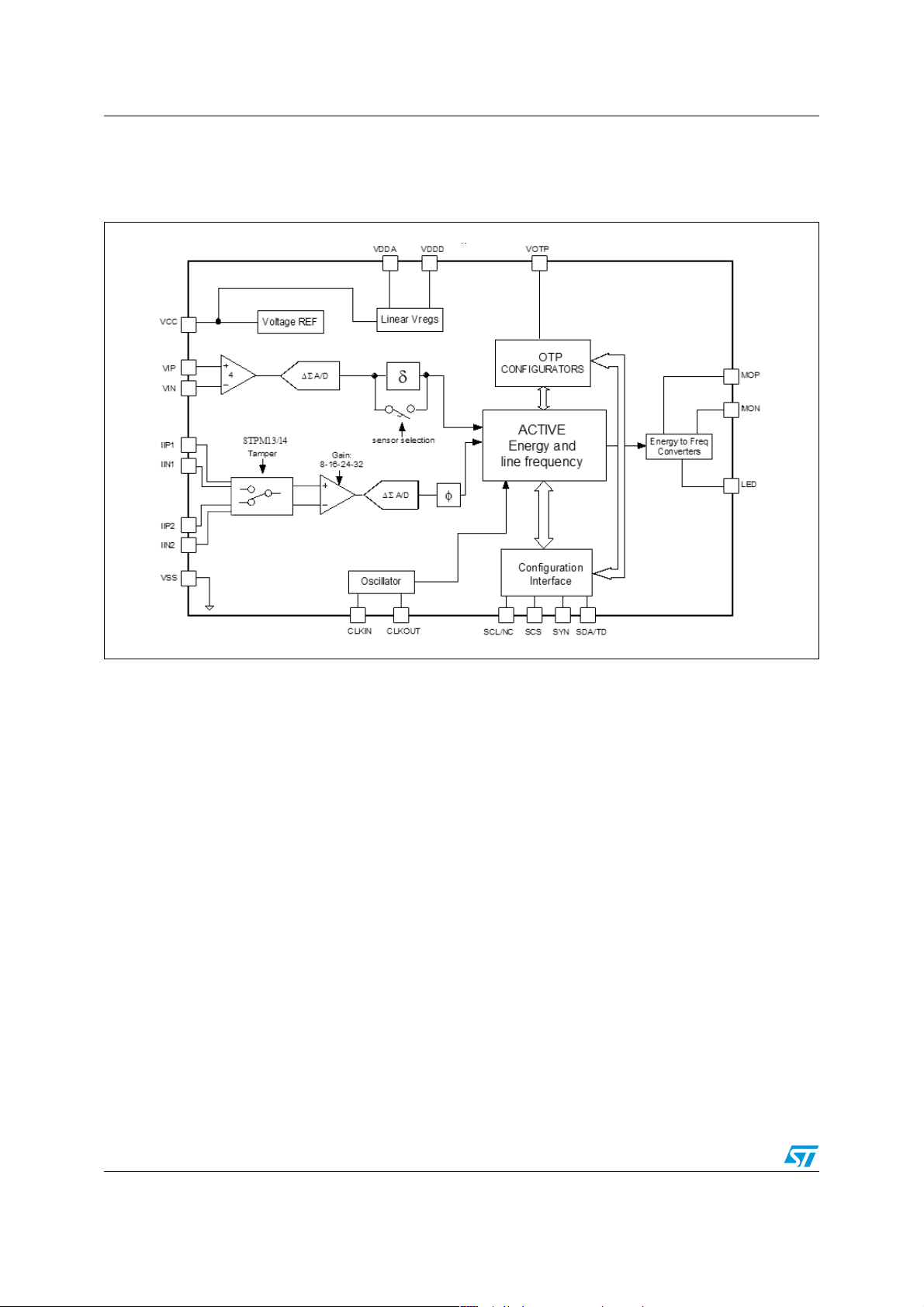
Schematic diagram STPM11/12/13/14
1 Schematic diagram
Figure 1. Block diagram
4/43
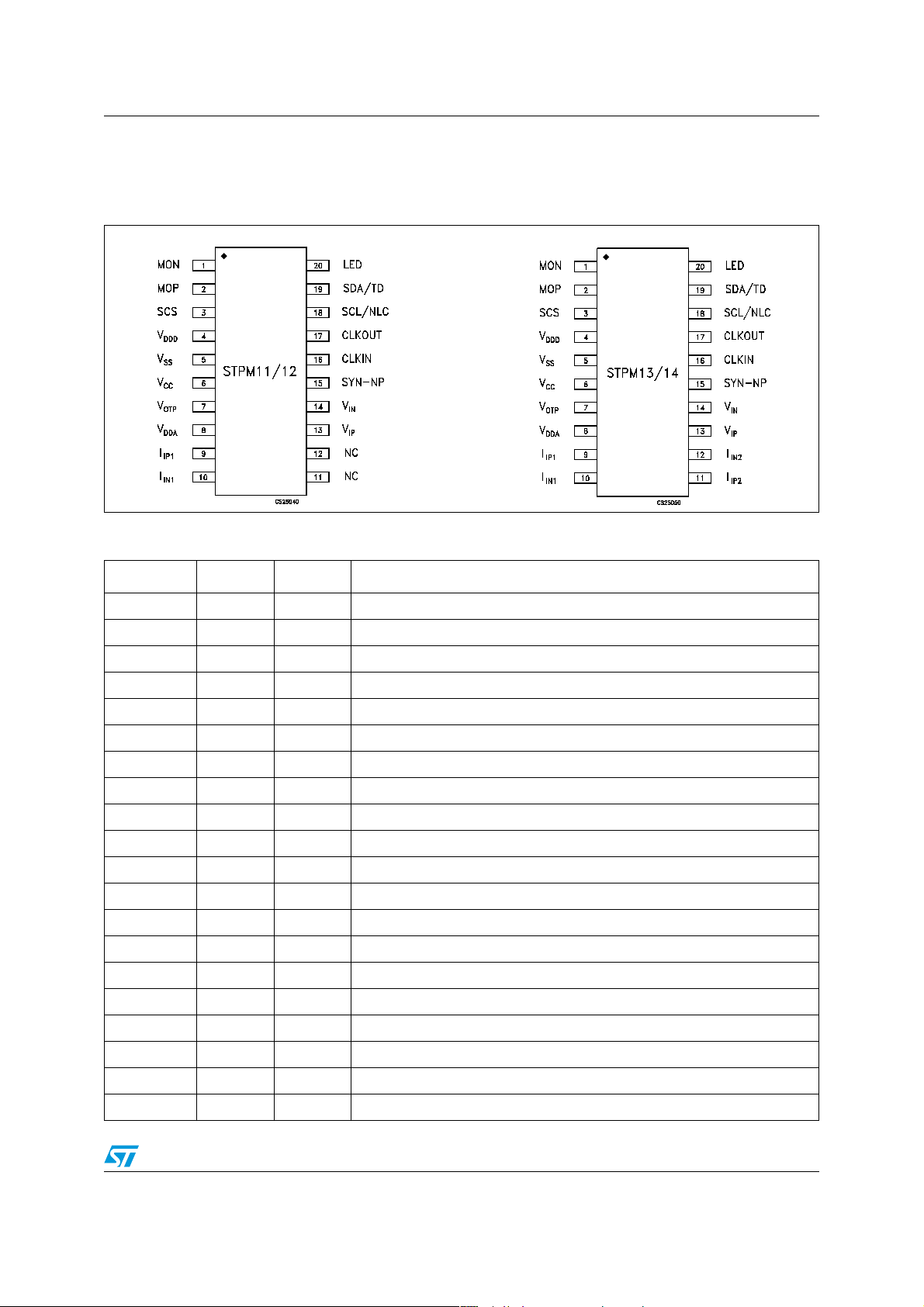
STPM11/12/13/14 Pin configuration
2 Pin configuration
Figure 2. Pin connections (top view)
Table 1. Pin description
Pln N° Symbol Type
(1)
Name and function
1 MON P O Output for Stepper’s node
2 MOP P O Output for Stepper’s node
3 SCS D IN Enable or disable configuration interface for device configuration.
4V
5V
6V
7V
8V
9I
10 I
11 I
12 I
13 V
14 V
DDD
SS
CC
OTP
DDA
IP1
IN1
IP2
IN2
IP
IN
A OUT 1.5V Output of internal low drop regulator which supplies the digital core.
GND Ground.
P IN Supply voltage.
P INr Supply voltage for OTP cells.
A OUT 3V Output of internal low drop regulator which supplies the analog part.
A IN Positive input of primary current channel
A IN Negative input of primary current channel
A IN Positive input of secondary current channel (STPM13/14 only)
A IN Negative input of secondary current channel (STPM13/14 only)
A IN Positive input of voltage channel
A IN Negative input of voltage channel
15 SYN-NP D I/O Negative power indicator. (Configuration interface)
16 CLKIN A IN Crystal oscillator input or resistor connection if RC oscillator is selected
17 CLKOUT A OUT Oscillator output (RC or crystal)
18 SCL/NLC D I/O No-load condition indicator. (Configuration interface)
19 SDATD D I/O Tamper detection indicator. (Configuration interface)
20 LED D O Pulsed output proportional to Active Energy
1. A: Analog, D: Digital, P: Power
5/43

Maximum ratings STPM11/12/13/14
3 Maximum ratings
Table 2. Absolute maximum ratings (See note)
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
DC Input voltage -0.3 to 6 V
Current on any pin (sink/source) ± 150 mA
Input voltage at digital pins (SCS, MOP, MON, SYN, SDATD,
SCLNLC, LED)
Input voltage at analog pins (I
IP1
, I
, I
, I
IN1
, VIP, VIN) -0.7 to 0.7 V
IP2
IN2
-0.3 to V
+0.3 V
CC
Input voltage at OTP pin -0.3 to 25 V
V
V
I
V
V
CC
PIN
ID
IA
OTP
ESD Human body model (all pins) ± 3.5 kV
T
T
T
STG
OP
J
Operating ambient temperature -40 to 85 °C
Junction temperature -40 to 150 °C
Storage temperature range -55 to 150 °C
Note: Absolute Maximum Ratings are those values beyond which damage to the device may
occur. Functional operation under these condition is not implied
Table 3. Thermal Data
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
R
thJA
1. This value is referred to single-layer PCB, JEDEC standard test board.
Thermal resistance junction-ambient 114.5
(1)
°C/W
6/43
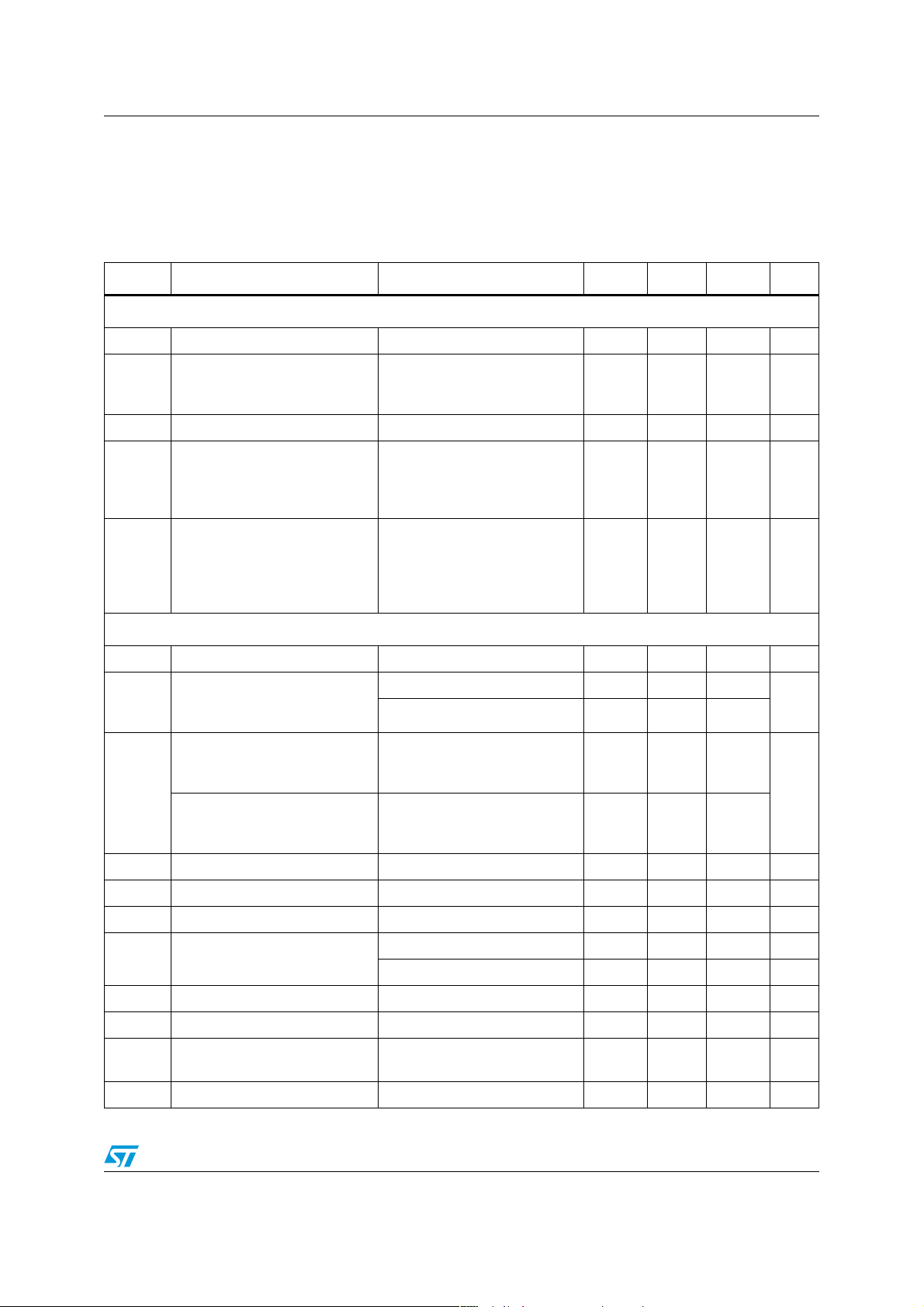
STPM11/12/13/14 Electrical characteristics
4 Electrical characteristics
Table 4. Electrical characteristics
(V
=5V, TA= 25°C, 2.2µF between V
CC
between V
and VSS unless otherwise specified)
CC
Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Energy measurement accuracy
and VSS, 2.2µF between V
DDA
and VSS, 2.2µF
DDD
f
Effective bandwidth Limited by digital filtering 5 400 Hz
BW
Over the dynamic range (5% to
Error Measurement error
1000% of the calibration power
0.1 %
value)
SNR Signal to noise ratio Over the entire bandwidth 52 db
Voltage signal: 200
PSRR
Power supply DC rejection
DC
rms
/50Hz f
mV
rms
V
=3.3V±10%, 5V±10%
CC
CLK
= 4.194 MHz
0.2 %
/50Hz Current signal: 10
mV
Voltage signal: 200
/50Hz Current signal: 10
mV
PSRR
Power supply AC rejection
AC
rms
mV
rms
=3.3V+0.2V
V
CC
=5.0V+0.2V
V
CC
/50Hz f
= 4.194 MHz
CLK
1@100Hz
rms
1@100Hz
rms
0.1 %
General section
V
I
Operating supply voltage 3.0 5.5 V
CC
Supply current configuration
registers cleared or device
CC
locked (TSTD=1)
4 MHz, V
8 MHz, V
= 5V 3.5 4
CC
= 5V 4.7 6
CC
Increase of supply current per
configuration bit, during
4 MHz, V
= 5V 120
CC
programming
∆I
CC
Increase of supply current per
configuration bit with device
4 MHz, V
= 5V 2
CC
locked
mA
µA/bit
POR Power on reset on V
V
V
f
f
LINE
V
I
t
CLK
OTP
OTP
Analog supply voltage 2.85 3.0 3.15 V
DDA
Digital supply voltage 1.425 1.50 1.575 V
DDD
Oscillator clock frequency
Nominal line frequency 45 65 Hz
OTP programming voltage 14 20 V
OTP
OTP programming current per
bit
OTP programming time per bit 100 300 µs
CC
2.5 V
MDIV bit = 0 4.000 4.194 MHz
MDIV bit = 1 8.000 8.192 MHz
2.5 mA
7/43
Electrical characteristics STPM11/12/13/14
Table 4. Electrical characteristics
(V
=5V, TA= 25°C, 2.2µF between V
CC
between V
and VSS unless otherwise specified)
CC
Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
and VSS, 2.2µF between V
DDA
and VSS, 2.2µF
DDD
I
LATCH
Current injection latch-up
immunity
Analog Inputs (I
V
f
ADC
f
V
Z
Z
G
I
I
LEAK
MAX
SPL
OFF
IP
IN
ERR
ILV
Maximum input signal levels
A/D Converter bandwidth 10 KHz
A/D Sampling frequency F
Amplifier offset ±20 mV
VIP, VIN Impedance
V
IP1
Impedance
Current channels gain error ±10 %
Voltage channel leakage current -1 1 µA
Current channel leakage current
, V
IP1
IN1
, I
, V
IN1
IP2
300 mA
, I
, I
, VIP, VIN)
IP2
IN2
Voltage channel -0.3 0.3 V
Gain 8X -0.15 0.15
Current
channels
Gain 16X -0.075 0.075
V
Gain 24X -0.05 0.05
Gain 32X -0.035 0.035
/4 Hz
CLK
, V
IN2
Over the total operating voltage
range
Over the total operating voltage
range
100 400 KΩ
100 KΩ
Channel disabled (PST=0 to 3;
CH2 disabled if C
disabled if C
SEL
=0; CH1
SEL
=1) or device off
-1 1
µA
Input enabled -10 10
Digital I/O Characteristics (SDA-TD, CLKIN, CLKOUT, SCS, SYN-NP, LED)
SDA-TD, SCS, SYN-NP, LED 0.75V
V
Input high voltage
IH
CLKIN 1.5
SDA-TD, SCS, SYN-NP, LED 0.25V
V
V
V
I
t
Input low voltage
IL
Output high voltage IO = -2mA VCC-0.4 V
OH
Output low voltage IO = +2mA 0.4 V
OL
Pull up current 15 µA
UP
Transition time C
TR
CLKIN 0.8
= 50pF 10 ns
LOAD
Power I/O Characteristics (MOP, MON)
V
V
t
Output high voltage IO = -14mA VCC-0.5 V
OH
Output low voltage IO = +14mA 0.5 V
OL
Transition time C
TR
= 50pF 5 10 ns
LOAD
8/43
CC
CC
V
V
STPM11/12/13/14 Electrical characteristics
Table 4. Electrical characteristics
(V
=5V, TA= 25°C, 2.2µF between V
CC
between V
and VSS unless otherwise specified)
CC
Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Crystal oscillator (STPM12/14)
Input current on CLKIN ±1 µA
I
I
R
External resistor 1 4 MΩ
P
C
External capacitors 22 pF
P
f
CLK
Nominal output frequency
RC Oscillator (STPM11/13)
and VSS, 2.2µF between V
DDA
DDD
4 4.194
8 8.192
and VSS, 2.2µF
MHz
I
CLKIN
R
SET
t
JIT
Settling current
f
Settling resistor 12 kΩ
CLK
= 4 MHz
Frequency jitter 1 ns
40 60 µA
On chip reference voltage
Reference voltage 1.23 V
V
REF
Reference accuracy ±1 %
T
Temperature coefficient After calibration 30 50
C
Configuration interface timing
F
SCLKw
t
t
t
SYN
Data write speed 100 KHz
Data setup time 20 ns
DS
Data hold time 0 ns
DH
SYN-NP active width 2/f
CLK
Table 5. Typical external components
Function Component Parameter Value Tolerance Unit
Line voltage
interface
Line current
interface
Resistor divider
R to R ratio V
R to R ratio V
Current shunt
Current to voltage conversion ratio
Rogowsky coil 3 ±12%
=230V 1650 ±1%
RMS
=110V 830 ±1%
RMS
0.2 ±5%
ppm/°
C
s
V/V
mV/ACurrent transformer 30 ±12%
9/43

Terminology STPM11/12/13/14
5 Terminology
5.1 Measurement error
The error associated with the energy measured by STPM1X is defined as:
Percentage Error = [STPM1X (reading) - True Energy] / True Energy
5.2 ADC Offset error
This is the error due to the DC component associated with the analog inputs of the A/D
converters. Due to the internal automatic DC offset cancellation, the STPM1X measurement
is not affected by DC components in voltage and current channel. The DC offset
cancellation is implemented in the DSP.
5.3 Gain error
The gain error is gain due to the signal channel gain amplifiers. This is the difference
between the measured ADC code and the ideal output code. The difference is expressed as
a percentage of the ideal code.
5.4 Power supply DC and AC rejection
This parameter quantifies the STPM1X measurement error as a percentage of the reading
when the power supplies are varied. For the PSRR
nominal supply voltages (3.3 and 5 V) is taken. A second reading is obtained with the same
input signal levels when an ac (200 mV
voltages. Any error introduced by this ac signal is expressed as a percentage of reading.
For the PSRR
taken. A second reading is obtained with the same input signal levels when the supplies are
varied ±10%. Any error introduced is again expressed as a percentage of the reading.
measurement, a reading at two nominal supply voltages (3.3 and 5V) is
DC
/100 Hz) signal is introduced onto the supply
RMS
5.5 Conventions
The lowest analog and digital power supply voltage is named VSS which represents the
system Ground (GND). All voltage specifications for digital input/output pins are referred to
GND.
Positive currents flow into a pin. Sinking current means that the current is flowing into the pin
and is positive. Sourcing current means that the current is flowing out of the pin and is
negative.
The timing specifications of the signal treated by digital control are relative to CLK
signal is provided by from the crystal oscillator of 4.194MHz nominal frequency or by the
internal RC oscillator. An external source of 4.194MHz or 8.192MHz can be used.
measurement, a reading at two
AC
OUT
. This
10/43
The timing specifications of signals of the CFGI interface are relative to the SCL-NLC, there
is no direct relationship between the clock (SCL-NLC) of the CFGI interface and the clock of
the DSP block.
A positive logic convention is used in all equations.
STPM11/12/13/14 Typical performance characteristics
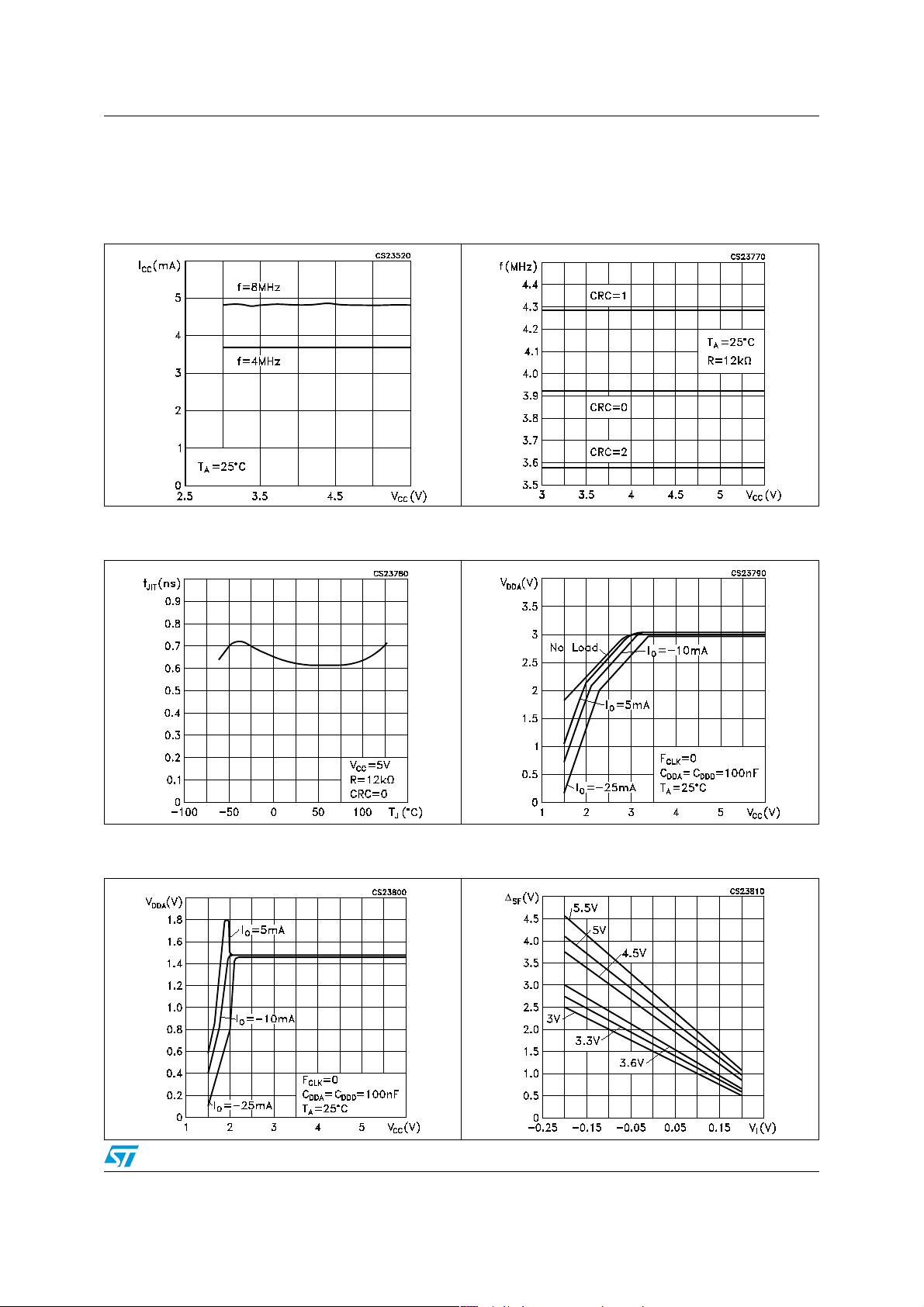
6 Typical performance characteristics
Figure 3. Supply current vs supply voltage,
T
=25°C
A
Figure 5. RC Oscillator: Frequency jitter vs
temperature
Figure 4. RC Oscillator frequency vs V
R=12kΩ, T
=25°C
A
CC
Figure 6. Analog voltage regulator: Line -
load regulation
,
Figure 7. Digital voltage regulator: Line - load
regulation
Figure 8. Voltage channel linearity at
different V
voltages
CC
11/43

Typical performance characteristics STPM11/12/13/14
0
Figure 9. Power supply AC rejection vs V
CC
Figure 11. Error over dynamic range gain
dependence
Figure 10. Power supply DC rejection vs V
CC
Figure 12. Primary current channel linearity at
different V
CC
Figure 13. Gain response of ∆Σ AD Converters Figure 14. Clock frequency vs external
12/43
8
7
6
5
f [MHz]
4
3
2
510152
resistor
CRC=0
CRC=1
CRC=2
R [kΩ]
STPM11/12/13/14 Theory of operation
7 Theory of operation
7.1 General operation
The STPM1X is able to perform active energy measurement (wide band or fundamental) in
single-phase energy meter systems.
Due to the proprietary energy computation algorithm, STPM1X active energy is not affected
by any ripple at twice the line frequency. The calibration is very easy and fast allowing
calibration in only one point over the whole current range which allows saving time during
the calibration phase of the meter. The calibration parameters are permanently stored in the
OTP (one time programmable) cells, preventing calibration tampering.
Several functions are programmable using internal configuration bits accessible through the
configuration interface. The most important configuration bits are two configuration bits
called PST that allow the selection of the sensor and the gain of the input amplifiers.
The STPM1X is able to directly drive a stepper motor with the MOP and MON pins, and
provides information on tamper, no-load and negative power.
Two kinds of active energy can be selected to be brought to the LED pin: the total active
energy that includes all harmonic content up to 50
to the 1
energy.
st
harmonic. This last energy value is obtained by filtering the wide band active
7.2 Analog inputs
Input amplifiers
The STPM1X has one fully differential voltage input channel and one (STPM11/12) or two
(STPM13/14) fully differential current input channels.
The voltage channel consists of a differential amplifier with a gain of 4. The maximum
differential input voltage for the voltage channel is ±0.3V.
In STPM13/14, the two current channels are multiplexed (see tamper section for details) to
provide a single input to a preamplifier with a gain of 4. The output of this preamplifier is
connected to the input of a programmable gain amplifier (PGA) with possible gain selections
of 2,4,6,8. The total gain of the current channels will be then 8, 16, 24, 32. The gain
selections are made by writing to the gain configuration bits PST and it can be different for
the two current channels. The maximum differential input voltage is dependent on the
selected gain according to the
Table 6. Voltage channel
Tab le 6 .
th
harmonic and the active energy limited
:
Voltage channels Current channels
Gain Max Input voltage (V) Gain Max input voltage (V)
8X ±0.15
4 ±0.30
16X ±0.075
24X ±0.05
32X ±0.035
13/43

Theory of operation STPM11/12/13/14
The
Table 7.
and
Table 8.
: below show the gain values according to the configuration bits:
Table 7. Configuration of current sensors
STPM11/12
Current channel Configuration Bits
Gain Sensor PST (2bits) ADDG (1 bit)
8
16 0 1
Rogowsky Coil
24 1 0
32 1 1
8CT2x
32 Shunt 3 x
00
Table 8. Configuration of current sensors
STPM13/14
Primary Secondary Configuration Bits
Gain Sensor Gain Sensor PST (2bits) ADDG (1 bit)
8
16 16 0 1
Rogowsky Coil
24 24 1 0
32 32 1 1
8
CT
32 32 Shunt 3 x
8
Rogowsky Coil
8CT2 x
00
Both the voltage and current channels implement an active offset correction architecture
which has the benefit of avoiding any offset compensation.
The analog voltage and current signals are processed by the ∑ ∆ Analog to digital converters
that feed the hardwired DSP. The DSP implements an automatic digital offset cancellation
that makes possible avoiding any manual offset calibration on the analog inputs.
7.3 ∑ ∆ A/D Converters
The analog to digital conversion in the STPM1X is carried out using two first order ∑ ∆
converters. The device performs A/D conversions of analog signals on two independent
channels in parallel. In STPM13/14, the current channel is multiplexed as primary or
secondary current channel in order to be able to perform a tamper function. The converted
∑ ∆ signals are supplied to the internal hardwired DSP unit, which filters and integrates
those signals in order to boost the resolution and to yield all the necessary signals for
computations.
14/43

STPM11/12/13/14 Theory of operation
A ∑ ∆ modulator converts the input signal into a continuous serial stream of 1s and 0s at a
rate determined by the sampling clock. In the STPM1X, the sampling clock is equal to
f
/4. The 1-bit DAC in the feedback loop is driven by the serial data stream. The DAC
CLK
output is subtracted from the input signal. If the loop gain is high enough, the average value
of the DAC output (and therefore the bit stream) can approach that of the input signal level.
When a large number of samples are averaged, a very precise value of the analog signal is
obtained. This averaging is carried out in the DSP section which implements decimation,
integration and DC offset cancellation of the supplied ∑ ∆ signals. The gain of the decimation
filters is 1.004 for the voltage channel and 0.502 for the current channel. The resulting signal
has a resolution of 11bits for voltage channel and 16 bits for current channel.
Figure 15. First order ∑ ∆ A/D Converter
/4
f
CLK
Integrator
Output digital signal
Input analog signal
+
Σ
∫
-
DAC
7.4 Period and line voltage measurement
The period module measures the period of base frequency of voltage channel and checks if
the voltage signal frequency is in the band from f
produced at every positive peak of the line voltage. If the counted number of pulses between
two trailing edges of this signal is higher than the f
counting is stopped (internal signal is not available), it means that the base frequency is
lower than f
/217 Hz and an internal error flag BFR (Base Frequency Range) is set.
CLK
If the counted number of pulses within one line period is higher than the f
pulses, the base frequency exceeds the limit. In this case, such error must be repeated
three times in a row, in order to set the error flag BFR.
The BFR flag is also set if the value of the RMS voltage drops below a certain value (BFRon) and it is cleared when the RMS voltage goes above BFR-off threshold. The table below
shows the equivalent RMS voltage on the V
IP/VIN
channel calibrator.
/217 to f
CLK
/217 Hz equivalent pulses or if the
CLK
pins according to the value of the voltage
/215. An internal signal is
CLK
/215 equivalent
CLK
15/43

Theory of operation STPM11/12/13/14
The BFR flag is also set if the RMS voltage across VIP-VIN drops below a threshold value
calculated with the following formula:
64
=
BFRIRMS
−
6703
KV⋅
V
(CT/Shunt)
64
=
−
BFRIRMS
(Rogowsky)
6687
KV⋅
V
Where K
The BFR flag is cleared when the V
is the voltage calibrator value ranging from 0.875 to 1.000.
V
value goes above twice V
IRMS
IRMS-BFR
. When the BFR
error is set, the computation of power is suspended and MOP, MON and LED will be held
low.
Table 9. RMS voltage check
BFR-on BFR-off
Rogowsky 0.009571/Kv 0.019142/Kv
CT-Shunt 0.0078/Kv 0.0156/Kv
7.5 Single wire meter mode (STPM13/14 with Rogowsky coil sensor)
STPM1X supports the Single Wire Meter (SWM) operation when working with Rogowsky
Coil current sensors. In SWM mode there is no available voltage information in the voltage
channel. It is possible that someone has disconnected one wire (live or neutral) of the meter
for tampering purposes or in case the line voltage is very stable, it is possible to use a
predefined value for computing the energy without sensing it.
In order to enable the SWM mode, the STPM1X must be configured with PST values of 0 or
1. In this way, if the BFR error is detected, STPM1X enters in SWM. If BFR is cleared, the
energy calculation is performed normally. When BFR is set (no voltage information is
available), the energy computation is carried out using a nominal voltage value according to
the NOM configuration bits.
16/43
Since there is no information on the phase shift between voltage and current, the apparent
rather than active power is used for tamper and energy computation. The calculated
apparent energy will be the product between I
V
that can be calculated as follows:
RMS
V
=VPK*K
RMS
STPM1X and K
, where VPK represents the maximum line voltage reading of the
NOM
is a coefficient that changes according to
NOM
(effectively measured) and an equivalent
RMS
Table 10.
:

STPM11/12/13/14 Theory of operation
Table 10. Nominal voltage values
NOM K
0 0.3594
1 0.3906
2 0.4219
3 0.4531
NOM
For example, if R1 = 783kΩ and R2 = 475Ω are used as resistor divider when the line
voltage is present, the positive voltage present at the input of the voltage channel of
STPM1x is:
R
VI ⋅
2
=
RR
+
21
V
RMS
2
since the maximum voltage value applicable to the voltage channel input of STPM1x is
+0.3V, the equivalent maximum line voltage applicable is:
V
= R1+R2/R2 • 0.3 = 494.82
PK
considering the case of NOM=2, the correspondent RMS values used for energy
computation is:
V
= VPK • 0.4219 = 208.76 [V]
RMS
Usually the supply voltage for the electronic meter is taken from the line voltage. In SWM,
since the line voltage is no longer present, another power source must be used in order to
provide the necessary supply to STPM1x and the other electronic components of the meter.
7.6 Power supply
The main STPM1X supply pin is the VCC pin. From the VCC pin two linear regulators provide
the necessary voltage for the analog part V
V
pin represents the reference point for all the internal signals. The 100nF capacitor
SS
should be connected between V
capacitors must be located very close to the device.
The STPM1X contains a Power-On-Reset (POR) detection circuit. If the V
than 2.5V, then the STPM1X goes into an inactive state, all the functions are blocked
asserting and a reset condition is set. This is useful to ensure that the correct device
operation at power-up and during power-down. The power supply monitor has built-in
hysteresis and filtering, which give a high degree of immunity to false triggering due to noisy
supply voltages.
A BandGap voltage reference (VBG) of 1.23V ±1% is used as reference voltage level source
for the two linear regulators and for the A/D converters. Also, this module produces several
bias currents and voltages for all other analog modules and for the OTP module. The
bandgap voltage temperature behavior can be changed in order to better compensate the
variation of sensor sensitivity with temperature. This task is performed with the BGTC
configuration bits.
and VSS, V
CC
(3V) and for the digital part V
DDA
and VSS, V
DDA
and VSS. All these
DDD
(1.5V). The
DDD
supply is less
CC
17/43

Theory of operation STPM11/12/13/14
Figure 16. Bandgap temperature variation
7.7 Load monitoring
The STPM1X include a no-load condition detection circuit with adjustable threshold. This
circuit monitors the voltage and the current channels and, when the measured power is
below the set threshold, the internal signal BIL becomes high. The information about this
signal is also available in the status bit BIL.
The no load condition occurs when the product between VRMS and IRMS input values is
below a given value. This value can be set with the LTCH configuration bits, and it is also
dependent on the selected current gain (Ai) and the calibration registers constant Kp=Kv*Ki.
Four different no-load threshold values can be chosen according to the two configurations
bits LTCH (see
Tab le 1 1.
).
Table 11. No load detection thresholds
Vrms * Irms (input channel voltages) Vrms * Irms (input channel voltages)
LTCH
Rogowski coil (PST<2) Ct or Shunt (PST>1)
0 0.004488 / (Ai*Kp) 0.003648 / (Ai*Kp)
1 0.008976 / (Ai*Kp) 0.007296 / (Ai*Kp)
2 0.017952 / (Ai*Kp) 0.014592 / (Ai*Kp)
3 0.035904 / (Ai*Kp) 0.029184 / (Ai*Kp)
When a no-load condition occurs (BIL=1), the integration of power is suspended and the
tamper module is disabled.
If a no-load condition is detected, the BIL signal blocks generation of pulses for stepper and
forces the SCLNLC pin to be low.
18/43

STPM11/12/13/14 Theory of operation
7.8 Error detection
In addition to the no-load condition and the line frequency band, the integration of power can
be suspended also due to detected error on the source signals.
There are two kinds of error detection circuits involved. The first checks all the ∑ ∆ signals
from the analog part if any are stacked at 1 or 0 within the 1/128 of f
observation. In case of detected error the corresponding ∑ ∆ signal is replaced with an idle ∑
∆ signal, which represents a constant value 0.
Another error, condition occurs if the MOP, MON and LED pin outputs signals are different
from the internal signals that drive them. This can occur if some of this pin is forced to GND
or to some other imposed voltage value.
period of
CLK
7.9 Tamper detection module (STPM13/14 only)
The STPM13/14 is able to measure the current in both live and neutral wires. This
mechanism has been adapted to implement an anti-tamper function. If this function is
selected (see
between the two measurements is detected, the STPM13/14 enters the Tamper State.
When there is a very small difference between the two channels, the STPM13/14 is in
Normal state.
Table 8.
:), the live and neutral wire currents are monitored. When a difference
In particular, both channels are not constantly observed. A time multiplex mechanism is
used. During the observation time of the selected channel, its active energy is calculated.
The detection of a tamper condition occurs when the absolute value of the difference
between the two active energy values is greater than a certain percentage of the averaged
energy during the activated tamper module. This percentage value can be selected between
two different values (12.5% and 6.25%) according to the value of the configuration bit CRIT.
The tamper condition will be detected when the following formula is satisfied:
EnergyCH1 - EnergyCH2 > K
or 6.25%.
The detection threshold is much higher than the accuracy difference of the current
channels, which should be less than 0.1%. Some margin should be left for a possible
transition effect, due to accidental synchronism between the actual load current change and
the rhythm of taking the energy samples.
The tamper circuit works if the energies associated with the two current channels will be
both positive or both negative. If the two energies have different signs, the tamper remains
on constantly. However, the channel with the associated higher power is selected for the
final computation of energy.
In single wire mode, the Apparent energy rather than active is used for Tamper detection.
(EnergyCH1 + EnergyCH2)/2; where K
CRIT
can be 12.5%
CRIT
Detailed operational description
Normal state
The meter is initially set to normal state, i.e. tamper not detected. In such state, we expect
that the values of both load currents should not differ more than the accuracy difference of
the channels. For this reason, we can use an average value of currents of both channels for
the active energy calculation. The average is implemented with the multiplex ratio of 32:32
periods of line per channel. This means that for 32 periods of line voltage, i.e. 640ms at
50Hz, the current of the primary channel is used for the calculation followed by another 32
19/43

Theory of operation STPM11/12/13/14
periods of line voltage when the current of secondary channel is used instead. Four periods
before the primary to secondary switching point, a tamper detection module is activated. It is
deactivated after eight periods of line have elapsed. This means that energy of four periods
of primary channel immediately followed by energy of four periods of secondary channel is
sampled within the tamper module. We shall call those samples A and B respectively. From
these two samples the criteria of tamper detection is calculated. If four consecutive new
results of criteria happen, i.e. after elapsed 5.12s at 50Hz, the meter will enter into Tamper
State
Tamper State
Within this state the multiplex ratio will change either to 60:4, when primary current is higher
than secondary, or to 4:60 otherwise. Thus, the channel with the higher current is used in
the energy calculation. The energy is not averaged by the mentioned ratio, rather the last
measured higher current is used also during 4 line period gap. The gap is still needed in
order to monitor the samples of the non-selected channel, which should check when the
tamper detected state is changed to either normal or another tamper detected state.
Several cases of transition of the state are shown in the
Figure 17. Tamper conditions
Figure 17.
- below
20/43
The detected tamper condition is stored in the BIT signal. This signal is connected to the
SDA-TD pin. When this pin is low, a tamper condition has been detected.

STPM11/12/13/14 Theory of operation
When internal signals are not good enough to perform the computation, i.e. line period is out
or range or ∑∆ signals from the analog part are stacked at high or low logic level, or no load
condition is activated, the tamper module is disabled and its state is preset to normal.
7.10 Phase compensation
The STPM1X is does not introduce any phase shift between voltage and current channels.
However, the voltage and current signals come from transducers, which could have inherent
phase errors. For example, a phase error of 0.1° to 0.3° is not uncommon for a current
transformer (CT). These phase errors can vary from part to part, and they must be corrected
in order to perform accurate power calculations. The errors associated with phase mismatch
are particularly noticeable at low power factors. The STPM1x provide a means of digitally
calibrating these small phase errors through a introducing delays on the voltage or current
signal. The amount of phase compensation can be set using the 4 bits of the phase
calibration register (CPH).
The default value of this register is at a value of 0 which gives 0° phase compensation. A
CPH value of 15 (1111) introduces a phase compensation of +0.576°. This compensates
the phase shift usually introduced by the current sensor, while the voltage sensor, normally
a resistor divider, does not introduce any delay. The resolution step of the phase
compensation is 0.038°.
7.11 Clock generator
All the internal timing of the STPM1X is based on the CLK
generated by different circuits according to the STPM1x version.
STPM11/13: Internal RC Oscillator. A resistor connected between CLK
will set the RC current. For 4Mhz operation the suggested settling resistor is 12kΩ; The
oscillator frequency can be compensated using the CRC configuration bit (see Table 13
an
Figure 14.
STPM12/14: Quartz Oscillator. The oscillator circuit is designed to support an external
crystal. The suggested circuit is depicted in
external oscillator signal source that must be connected to the CLK
The clock generator is powered from analog supply and is responsible for two tasks. The
first one is to retard the turn-on of some function blocks after POR in order to help smooth
start of external power supply circuitry by keeping all major loads off.
The second task of the clock generator is to provide all necessary clocks for analog and
digital parts. Within this task, the MDIV configuration bit is used to inform the device about
the nominal frequency value of CLK
4.000MHz to 4.194MHz.
)
signal. This signal is
OUT
and Ground
IN
Figure 18.
. The suggested operation frequency range is from
OUT
. These versions support also an
pin.
OUT
21/43

Theory of operation STPM11/12/13/14
Figure 18. Different oscillator circuits (a); (b); (c)
STPM12/14 with quartz
STPM11/13
7.12 Resetting the STPM1X
The STPM1X has no reset pin. The device is automatically reset by the POR circuit when
the V
crosses the 2.5V value. When the reset occurs, all clocks and both DC buffers in the
CC
analog part are kept off for about 30ms and all blocks of the digital part are held in a reset
state for about 125ms after a reset condition.
Resetting the STPM1X causes all the functional modules of STPM1X to be cleared
including the OTP shadow latches (see 7.15 for OTP shadow latches description)
7.13 Energy to frequency conversion
The STPM1X provides energy to frequency conversion both for calibration and energy
readout purposes. In fact, one convenient way to verify the meter calibration is to provide a
pulse train signal with 50% duty cycle whose frequency signal is proportional to the active
energy under steady load conditions. It is convenient to have high frequency pulses during
calibration phase and low frequency for readout purposes; STPM1X supports both cases.
Let's suppose to choose a certain number of pulses on the LED pin (high frequency) that will
corresponds to 1kWh. We will name this value as P.
The Active Energy frequency-based signal is available in the LED pin. The LED is driven
from internal signal AW (Active Energy) whose frequency is proportional to the active
energy. The desired P is achieved acting on the digital calibrators during the calibration
procedure.
STPM12/14 with external source
22/43
The APL configuration bit changes the internal divider that provides the signal on the LED
pin according to
Table 11.
, setting APL=1 the number of pulses are reduced in order to
provide low frequency pulses for readout purposes. The division factor is set according to
KMOT configuration bits. In this case the pulses will have a fixed width of 31.25 ms.

STPM11/12/13/14 Theory of operation
Table 12. Different settings for led signal
APL=0 APL=1
KMOT (2 Bits)
Pulses Pulses
0
1 P/128
2 P/32
3 P/256
Due to the innovative and proprietary power calculation algorithm, the frequency signal is
not affected by any ripple at twice the line frequency. This feature strongly reduces the
calibration time of the meter.
7.14 Driving a stepper motor
The STPM1X is able to directly drive a stepper motor. An internal divider (mono-flop and
decoder) generates stepper driving signals MA and MB from signal AW. The MA and MB
signals are brought to the MOP and MON pins that are able to drive the stepper motor.
Several kinds of selections are possible for the driving signals according to the configuration
bits LVS and KMOT.
The numbers of pulses per kWh (PM) in the MOP and MON outputs are linked with the
number of pulses of the LED P (see previous paragraph - 7.13) pin with the following
relationship.
Table 13. Configuration of Mop and Mon Pins
P/64
P
LVS (1 Bit) KMOT (2 Bits) Pulses length PM
0 0 31.25 ms P/64
0 1 31.25 ms P/128
0 2 31.25 ms P/32
0 3 31.25 ms P/256
1 0 156.25 ms P/640
1 1 156.25 ms P/1280
1 2 156.25 ms P/320
1 3 156.25 ms P/2560
The mono-flop limits the length of the pulses according to the LVS bit value.
The decoder distributes the pulses to MA and MB alternatively, which means that each of
them has only one half of selected frequency.
In case of detected negative power the behavior of MOP and MON depends on the ABS
configuration bit status. If this bit is set, the negative power is computed as it was positive
(absolute value), and the MOP and MON signals maintain the pulse sequence in order to
keep the forward rotation direction of the motor. If ABS is zero, negative power is computed
with its own sign, and the MOP and MON signals invert their logic state in order to make the
backward rotation direction of the motor. See the diagram below.
23/43

Theory of operation STPM11/12/13/14
Figure 19. Positive energy or absolute computation energy (ABS=1) stepper driving signals
Hi
MON
Lo
Hi
MOP
Lo
Figure 20. Negative energy stepper driving signals
Hi
MON
Lo
Hi
Lo
When a no-load condition is detected MOP and MON are held low.
7.15 Configuring the STPM1X
All the configuration bits that control the operation of the device can be written temporarily or
permanently. For temporary writing, the configuration bits value are written in the Shadow
Registers which are simple latches that hold the configuration data. For permanent writing,
the configuration bits are stored in the OTP (one time programmable) cells that keep the
information for an undefined period of time even if the STPM1X is without supply, but, once
written, they cannot be changed. The temporary writing is useful mainly during testing of the
device or during the calibration phase. All the configuration parameters can be changed an
infinite number of times in order to test the device operation.
The shadow registers are cleared whenever a reset condition occurs.
The configuration bits are different for STPM11/12 and for STPM13/14 due to the presence
of the Tamper module. Each of them consists of paired elements, one is latch (the OTP
shadow), and one is the OTP anti-fuse element. When the STPM1X is released in the
market, all anti-fuses represent logic low state but they can be written by the user in order to
configure the STPM1X. This means that STPM1X can retain these bits of information even if
it has been unsupplied for an undefined time. That's why the CFG signals are used to keep
certain configuration and calibration values of the device.
MOP
24/43

STPM11/12/13/14 Theory of operation
The very first CFG bit, called TSTD, is used to disable any change of system signals after it
has been permanently set. During the configuration phase, each bit set to logic level 1
increases the supply current of STPM01 of about 120 µA, until the TSTD bit is set to 1. The
residual increase of supply current is 2µA per each bit set to 1. It is then recommended to
set the TSTD bit to 1 after the configuration procedure in order to keep the supply current as
low as possible.
The STPM1X can work either using the data stored in the OTP cells or the data available in
the shadow latches. This can be chosen according to the value RD Mode signal (see
paragraph 7.16 for description). If the RD is set, the CFG bits originates from corresponding
OTP shadow latches. If the RD is cleared, the CFG bits originates from corresponding OTP
anti-fuses. In this way, it is possible to temporarily set up certain configurations or
calibrations of the device then verify and change, if necessary. This exercise is extensively
used during production tests.
Each configuration bit can be written sending a byte command to STPM1X through its
configuration interface. The procedure to write the configuration bits is described in the
Configuration Interface section (7.17).
After the TSTD bit has been set, no other command can be sent to the STPM1X. This
implies that the shadow latches latches can no longer be used as source of configuration
data.
Table 14. Configuration bits map
Address
N. of
bits
(1)
Name
PST 2
6-BIT
Binary
000000 0 TSTD 1
000001 1 MDIV 1
000011 3 APL 1
000101 5
000110 6
DEC
DESCRIPTION
Test mode and OTP write disable:
- TSTD=0: testing and continuous pre-charge of OTP when in read mode,
- TSTD=1:normal operation and no more writes to OTP
Measurement frequency range selection:
- MDIV=0: 4.000MHz to 4.194MHz,
- MDIV=1: 8.000MHz to 8.192MHz
LED pin frequency output:
- APL=0: P
- APL=1:
KMOT=0
KMOT=1
KMOT=2
KMOT=3
Current channel sensor type, gain and tamper selection:
STPM11/12
- PST=0: primary is Rogowsky coil x8 (x16 if ADDG=1)
- PST=1: primary is Rogowsky coil x24 (x32 if ADDG=1),
- PST=2: primary is CT x8,
- PST=3: primary is shunt x32,
STPM13/14
- PST=0: primary is Rogowsky coil x8 (x16 if ADDG=1), secondary is
Rogowsky coil x8 (x16 if ADDG=1),
- PST=1: primary is Rogowsky coil x24 (x32 if ADDG=1), secondary is
Rogowsky coil x24 (x32 if ADDG=1),
- PST=2: primary is CT x8, secondary is CT x8
- PST=3: primary is CT x8, secondary is shunt x32
→ P/10
→ P/20
→ P/5
→ P/40
(1)
25/43

Theory of operation STPM11/12/13/14
Table 14. Configuration bits map
Address
6-BIT
Binary
001010 10 FUND 1
001011 11 ABS 1
DEC
Name
N. of
bits
DESCRIPTION
This bit swaps the energy type between fundamental or wide band.
- FUND=0: wide band active energy up to 50th harmonic;
- FUND=1: fundamental active energy
Power accumulation type selection:
- ABS=0: signed accumulation,
- ABS=1: absolute accumulation
(1)
001100 12
001101 13
001110 14
001111 15
010010 18
010011 19
010100 20
010101 21
010110 22
010111 23
011000 24
No-load condition constant:
LTCH=0
LT CH 2
(1)
KMOT 2
(1)
BGTC 2 Bandgap temperature compensation bits. See
(1)
CPH 4
(1)
LTCH=1
LTCH=2
LTCH=3
Constant of stepper pulses/kWh (see par. 7.14) selection:
If LVS=0,
KMOT=0
KMOT=1
KMOT=2
KMOT=3
If LVS=1,
KMOT=0 → P/640
KMOT=1
KMOT=2
KMOT=3
4-bit unsigned data for compensation of phase error, 0°+0.576°
16 values are possible with a compensation step of 0.0384°. When CPH=0
the compensation is 0°, when CPH=15 the compensation is 0.576°.
→ 800
→ 1600
→ 3200
→ 6400
→ P/64
→ P/128
→ P/32
→ P/256
→ P/1280
→ P/320
→ P/2560
Figure 16.
for details.
011001 25
011010 26
011011 27
011100 28
011101 29
011110 30
011111 31
26/43
(1)
CHV 8
8-bit unsigned data for voltage channel calibration.
256 values are possible. When CHV is 0 the calibrator is at -12.5% of the
nominal value. When CHV is 255 the calibrator is at +12.5%. The calibration
step is then 0.098%.

STPM11/12/13/14 Theory of operation
Table 14. Configuration bits map
Address
6-BIT
Binary
DEC
100000 32
100001 33
Name
N. of
bits
DESCRIPTION
(1)
100010 34
100011 35
CHP 8
100100 36
100101 37
100110 38
100111 39
(1)
101000 40
101001 41
101010 42
101011 43
CHS 8
101100 44
101101 45
101110 46
101111 47
(1)
110000 48
CRC 2
110001 49
(1)
110010 50
NOM 2
110011 51
(1)
110100 52 ADDG 1
8-bit unsigned data for primary current channel calibration.
256 values are possible. When CHP is 0 the calibrator is at -12.5% of the
nominal value. When CHP is 255 the calibrator is at +12.5%. The calibration
step is then 0.098%.
STPM13/14 only
8-bit unsigned data for secondary current channel calibration.
256 values are possible. When CHS is 0 the calibrator is at -12.5% of the
nominal value. When CHS is 255 the calibrator is at +12.5%. The calibration
step is then 0.098%.
STPM11/13 only
2-bit unsigned data for calibration of RC oscillator. (see Typical characteristics
in)
CRC=0, or CRC=3 cal=0%
CRC=1, cal=+10%;
CRC=2, cal=-10%
2-bit modifier of nominal voltage for Single Wire Meter.
NOM=0: K
NOM=3: K
=0.3594 / NOM=1: K
NOM
=0.4531
NOM
=0.3906 / NOM=2: K
NOM
NOM
=0.4219 /
Selection of additional gain on current channels:
ADDG=0: Gain+=0 / ADDG=1: Gain+=8
STPM13/14 only
110101 53 CRIT 1
Selection of tamper threshold:
CRIT =0: 12,5% / CRIT =1: 6,25%
110110 54 LVS 1
1. IMPORTANT: This Bit represents the MSB of the decimal value indicated in the description column.
Type of stepper selection:
LVS=0: pulse width 31.25 ms, 5V, / LVS=1: pulse width, 156.25 ms, 3V
27/43

Theory of operation STPM11/12/13/14
7.16 Mode signals
The STPM1X includes four Mode signals. These signals change some of the operation of
the STPM1X. The mode signals are not retained when the STPM1X supply is not available
and then they are cleared when a POR occurs.
The mode signals bit can be written using the normal writing procedure of the CFGI
interface (see CFGI par. 7.17)
Table 15. Mode signals description
Signal
Name
PUMP
CSEL
RD
WE
Bit
Val ue
0 MOP and MON operate normally 0111000x 70 or 71
MOP and MON provide the driving signals to implement a
1
charge-pump DC-DC converter
0 Current Channel 1 selected when tamper is disabled 0111100x 78 or 79
1 Channel 2 selected when tamper is disabled 1111100x F8 or F9
0 The 56 Configuration bits originated by OTP anti-fuses 0111101x 7A or 7B
1 The 56 Configuration bits originated by shadow latches 1111101x FA or FB
Any writing in the configuration bits is recorded in the shadow
0
latches
Any writing in the configuration bits is recorded both in the
1
shadow latches and in the OTP anti-fuse elements
Status
Binary
Command
1111000x F0 or F1
0111110x 7C or 7D
1111110x FC or FD
Hex
Command
– RD mode signal has been already described in par. 7.15 (configuring the STPM1X),
but there is another implied function of the signal RD. When it is set, each sense
amplifier is disconnected from corresponding anti-fuse element and this way, its 3V
NMOS gate is protected from the high voltage of V
operation. This means that as long as the V
voltage reads more than 3V, the
OTP
during permanent write
OTP
signal RD should be set.
– PUMP. When set, the PUMP mode signal transforms the MOP and MON pins to act
as driving signals to implement a charge-pump DC-DC converter (see
This feature is useful in order to boost the V
generate the V
voltage (14V to 20V) needed to program the OTP anti-fuse
OTP
supply voltage of the STPM1X to
CC
Figure 23.
elements.
– CSEL (STPM13/14 only). Under normal operating conditions, if anti-tamper module is
not activated (see PST configuration bits) the STPM1X will selects channel 1 as the
source of current information. For debug or calibration purposes, it is possible to
select channel 2 as source of current channel signal when the tamper module is
disabled. This is done by setting CSEL mode bit.
– WE (write Enable): This mode signal is used to permanently write to the OTP anti-
fuse element. When this bit is not set, any writing to the configuration bit is recorded
in the shadow latches. When this bit is set, the writing is recorded both in the shadow
latch and in the OTP anti-fuse element.
).
28/43

STPM11/12/13/14 Theory of operation
7.17 CFGI: Configuration interface
The CFGI interface supports a simple serial protocol, which is implemented in order to
enable the configuration of STPM1x which allows writing the Mode bits and the
configuration bits (temporarily or permanently);
Four pins of the device are dedicated to this purpose: SCS, SYN-NP, SCLNCN, SDATD.
SCS, SYN-NP, SCL-NLC and SDATD are all input pins. A high level signal for these pins
means a voltage level higher than 0.75xV
lower than 0.25xV
The condition in which SCS, SYN-NP and SCL-NLC inputs are set to high level determines
the idle state of the CFGI interface and no data transfer occurs.
– SCS: in the STPM1X, the SYN-NP, SCL-NLC and SDA-TD have the dual task to
provide information on the meter status (see Pin Description table) and to allow CFGI
communication. The SCS pin allows using the above pins for CFGI communication
when it is low and allows the normal operation of SYN-NP, SCL-NLC and SDA-TD
when it is high. In this section, the SYN-NP, SCL-NLC and SDA-TD operation as part
of the CFGI interface is described.
– SYN-NP: this pin allows synchronization of the communication between STPM1x and
the host. See
– SCL-NLC: it is basically the clock pin of the CFGI interface. This pin function is also
controlled by the SCS status. If SCS is low, SCL-NLC is the input of the serial bit
synchronization clock signal. When SCS is high, SCL-NLC is also high which
determines the idle state of the CFGI.
– SDA-TD is the Data pin. SDA-TD is the input of the serial bit data signal.
.
CC
Figure 19.
- for detailed timing of the pin.
, while a low level signal means a voltage value
CC
Any pin above has internal weak pull up device of nominal 15 A. This means that when a pin
is not forced by external signals, the state of the pin is logic high. A high state of any input
pin above is considered as an idle (not active) state. For the CFGI to operate correctly, the
STPM1X must be correctly supplied as described in the Power Supply section. When SCS
is active (low), signal SDA-TD should change its state at trailing edge of signal SCL-NLC
and the signal SDA-TD should be stable at the next leading edge of signal SCL-NLC. The
first valid bit of SDA-TD always starts with the activation of signal SCL-NLC.
Writing procedure
Each writable bit (Configuration and Mode bits) has its own 6-bit absolute address. For the
configuration bits, the 6-bit address value corresponds to its decimal value, while for the
mode bits, the addresses are the ones indicated in the Mode Signal paragraph (7.16).
In order to change the latch state, a byte of data must be sent to STPM1X via CFGI. This
byte consists of 1-bit data to be latched (msb), followed by 6-bit address of destination latch,
followed by 1-bit don't care data (lsb) which totals 8 bits of command byte.
For example, if we would like to set the configuration bit 52 (additional gain of 8) to 1, we
must convert the decimal 52 to its 6-bit binary value: 110100. The byte command will be
then composed like this:
1 bit DATA value+6-bits address+1 bit (0 or 1) as depicted in
binary command will be 11101000 (0xE8) or 11101001 (0xE9).
Figure 19.
-. In this case the
29/43

Theory of operation STPM11/12/13/14
Figure 21. Timing for writing configuration and mode bits
t1 → t2 (>30ns): CFGI out of idle state
t
→ t3 (>30ns): CFGI enabled for write operation
2
t
: data value is placed in SDA
3
t4: SDA value is stable and shifted into the device
t
→ t5 (>10µs): writing Clock period
3
t
→ t5: 1 bit Data value
3
t
→ t6: 6 bits address of the destination latch
5
t
→ t7: 1 bit EXE command
6
t
: end of CFGI writing
8
t
: CFGI enters idle state
9
The same procedure should be applied for the mode signals, but in this case the 6-bits
address must be taken from the
Tab le 1 4 .
.
30/43
The lsb of command is also called EXE bit because instead of data bit value, the
corresponding serial clock pulse is used to generate the necessary latching signal. In this
way the writing mechanism does not need the measurement clock in order to operate, which
makes the operation of CFGI module of STPM1X completely independent from the rest of
the device logic except from the signal POR.
Commands for changing system signals should be sent during active signals SCS and SYNNP as it is shown in the
Figure 19.
-. A string of commands can be send within one period of
active signals SCS and SYN-NP.

STPM11/12/13/14 Theory of operation
Permanent writing of the CFG bits
In order to make a permanent set of some CFG bits, use the following procedure:
1. collect all addresses of CFG bits to be permanently set into a list;
2. clear all OTP shadow latches;
3. set the system signal RD;
4. connect a current source of at least +14V, 1mA to 3mA to VOTP;
5. wait for VOTP voltage to be stable;
6. set one OTP shadow latch from the list;
7. set the system signal WE;
8. wait for 300 s;
9. clear the system signal WE;
10. clear the OTP shadow latch which was set in step 6;
11. until all CFG bits are permanently set as desired, repeat steps 5 to 11;
12. disconnect the current source;
13. wait for VOTP voltage to be less than 3V;
14. clear the system signal RD;
15. verify the correct writing, testing STPM1x operation;
16. if the verification of CFG bits fails, repeat steps 1 to 16.
For steps of set or clear, apply the timing shown in
Figure 19.
- with proper signal on the
SDA-TD.
In order to create a permanent set of the TSTD bit, which does not result in any more writing
to the Configuration bits, the procedure above must be conducted in such a way that steps 6
to 13 are performed in series during a single period of active SCS. The idle state of SCS
would make the signal TSTD immediately effective which in turn, would abort the procedure
and possibly destroy the device due to clearing of system signal RD. This would result in the
connecting of all gates of 3V NMOS sense amplifiers of already permanently set CFG bits to
the V
OTP
source.
31/43

Energy calculation algorithm STPM11/12/13/14
8 Energy calculation algorithm
Inside the STPM1X the computing section of the measured active power uses a completely
new patented signal process approach. This approach allows the device to reach high
performances in terms of accuracy.
The signals, coming from the sensors, for the instantaneous voltage is:
v(t) = V•sin ωt; where V is the peak voltage and ω is related to the line frequency (see[1])
and the instantaneous current is:
i(t) = I • sin (ωt + ϕ); where I is the peak current, ω is related to the line frequency and ϕ is the
phase difference between voltage and current (see[2])
Active power
Figure 22. Active energy computation diagram
32/43
In the STPM1X, after the pre-conditioning and the A/D conversion, the digital voltage signal
(which is dynamically more stable with respect to the current signal) is processed by a
differentiate stage which transforms:
v(t) → v’(t) = dv/dt = V
⋅ ω ⋅ cos tω − [Eq. 1 - see (5) in Figure 6]
The result, together with the pre-processed and digitalized current signal:

STPM11/12/13/14 Energy calculation algorithm
ω
ϕωϕ
+
ϕωϕ
+
ϕ
−
ω
i(t) = I ⋅ sin(tω + ϕ); [Eq. 2 - see (6) in Figure 6 - ]
can then be used to calculate. These digital signals are also used in two additional steps for
integration, obtaining:
dv/dt → v(t) = V
⋅ sin tω; [Eq. 3 - see (7) in
Figure 6.
]
I
i(t) ⋅
[Eq. 4 - see (8) in Figure 6]
Now four signals are available. Combining (pairing) them by two multiplication steps two
results are obtained:
cos
⋅⋅
2
⋅⋅
2
]
cos
−
]
dv
tp
/
1
[Eq. 5 - see (9) in
/
[Eq. 6 - see (10) in
After these two operations, another stage another step involves the subtraction of p1 from
p2 and dividing the result by 2, to obtain the active power:
dt
2
)()(
∫
)()()(
titvtp
−=⋅⋅=
dtti
Figure 6.
=⋅=
Figure 6.
dttitI
∫
⋅⋅
tIVIV
−
2
⋅⋅
)2cos(
tIVIV
2
)cos()()(
ϕω
+⋅−=⋅=
t
)2cos(
tptp
))()((
/
=
tp
)(
/
12
=
2
[Eq. 7 - see (11) in
In this way, the AC part
has been then removed from the instantaneous power.
In the case of current sensors like "Rogowski coils", which provide the rate of the
instantaneous current signal, the initial voltage signal differentiation stage is switched off. In
this case the signals coming from the A/D conversion and their consequent integrations are:
v(t) = V
′
[Eq. 9]
⋅ sin (tω); [Eq. 8]
)(
)(
ti
tdi
dt
Figure 6.
cos
⋅⋅
IV
2
]
⎛
⎜
⎝
)cos(
ϕωω
+⋅⋅−==
tI
2
⎞
+⋅⋅
)2cos(
ϕω
tIV
⎟
⎠
V
dttvtV
∫
t
ω
cos)()( ⋅−=⋅=
33/43

Energy calculation algorithm STPM11/12/13/14
∫
[Eq. 10]
[
)sin()()()(
ϕω
=
′′
[Eq. 11]
The signals process flow is the same as shown in the previous case, and even with the
formulas above, the result is the same.
The absence of any AC component allows a very fast calibration procedure. Averaging the
readings of several line periods is not needed. The active energy measurement is already
stable after one line cycle. Moreover the digital calibration allows saving time and space
compared to the hardware calibration made with resistor strings.
′
+⋅−==⋅
tItidttiti
34/43

STPM11/12/13/14 STPM1X Calibration
9 STPM1X Calibration
Energy meters based on STPM1X devices are calibrated on the frequency of the output
pulse signal.
The devices are comprised of two independent meter channels for line voltage and current
respectively. Each channel includes its own digital calibrator, to adjust the voltage and
current signals coming from the sensors in the range of ±12.5% in 256 steps. A digital filter
is included to remove any signal DC component.
The devices produce an energy output pulse signal whose frequency is proportional to the
measured active energy.
The devices have an embedded memory, 54 bits, used for configuration and calibration
purposes. The value of these bits can be written temporarily or permanently through CFGI
communication channel.
The basic information needed to start the calibration procedure is found in
Table 17.
:
Ta bl e 1 6 .
and
Table 16.
Line RMS voltage Vn (230 V)
Line RMS current In (5 A)
Power sensitivity P (LED: P=128000 pulses/kWh, Stepper Motor: PM=P/64= 2000 pulses/kWh)
Shunt Sensor Si 0,42 mv/A
The following typical STPM01 parameters and constants are also known:
Table 17.
Reference voltage Vbg (1.23 V ± 2%)
Clock fM (223 Hz ± 50ppm)
Amplification of ADC Av, Ai (4 ± 1%, (8, 16, 24, 32) ± 2%))
Gain of voltage and current decimation filters Gp (0.504008)
Calibration data range Cv, Ci (min = 0, ini = 128, max = 255)
AW Bit position that generates LED signal DL (2
11
)
Av is constant. While, Ai is chosen according to the sensor
Gv and Gi are constant
Cv and Ci are 8bits register (CHV, CHP and CHS)
From the values above and for both the given amplification factor and initial calibration data,
the following target values can be calculated:
Considering that Ci=0 generates a correction of 75% and that Ci=128 determines a
correction factor of 87.5%, and the same for Cv, the total correction for the power stands
within Kp = Kv*Ki = (0.75*0.75)=56.25% and 100%, and Cv=Ci=128 gives a correction
factor of Kp= (0.875*0.875) = 76.5625%
Each calibrator value can be changed from a binary form to a decimal correction form, using
the following formula:
35/43

STPM1X Calibration STPM11/12/13/14
Kv=(Cv/128)*0.125 + 0.75 and the same for Ki.
Let us choose as initial value Ai=32
Table 18.
Value of Calibrator Kp = Kv*Ki = 0.765625
Frequency at LED f = P*In*Vn/3600000 = 40.8889 Hz
Voltage divider Sv = (F*DL*Vbg
Voltage divider resistor R1=R2*(1000/Sv-1)
2
)/(fM*Vn*In*Gv*Gi*Kp*Ai*Av*Si)= 0,6324mV/V
From the target power constant C
of the meter and the actual values of V
P
RMS
and I
RMS
,
which are applied to the meter under calibration, the error of power measurement can be
calculated:
err = 100(fx/f -1) [%], where fx is the real frequency read at LED output.
Now, a final unit less power reduction factor can be calculated:
p
= (pD - err)/100
F
This final power reduction factor can be considered as a product of voltage and current
reduction factors which are produced from corresponding calibration constants. So, an
obvious solution to obtain the voltage and current reduction factors is to calculate a common
reduction factor as a square root of pF. This result must fall within the indicated range,
otherwise the device cannot be calibrated:
768 ≤ R = 1024 pF + 0.125 < 1024
In order to obtain the corresponding calibration constants, the reduction factor must be
transformed:
CV = CC = R - 768
By using separately the integer and the fractional part of the common reduction a better fit of
calibration constants can be produced. Simply, let's set one of the two calibration registers
(e.g. CV) to the lowest integer value of R, while the other (CC) should be set to the nearest
integer value of R. Examples:
R-768=128.124; in this case set CV=128; set CC=128
36/43
R-768=127.755; while in this other one set CV=127; set CC=128.

STPM11/12/13/14 Schematic
10 Schematic
Figure 23. Charge pump schematic
37/43

Schematic STPM11/12/13/14
Figure 24. Application schematic
38/43

STPM11/12/13/14 Package mechanical data
11 Package mechanical data
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in ECOPACK®
packages. These packages have a Lead-free second level interconnect. The category of
second Level Interconnect is marked on the package and on the inner box label, in
compliance with JEDEC Standard JESD97. The maximum ratings related to soldering
conditions are also marked on the inner box label. ECOPACK is an ST trademark.
ECOPACK specifications are available at: www.st.com.
39/43

Package mechanical data STPM11/12/13/14
TSSOP20 MECHANICAL DATA
mm. inch
DIM.
MIN. TYP MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
A 1.2 0.047
A1 0.05 0.15 0.002 0.004 0.006
A2 0.8 1 1.05 0.031 0.039 0.041
b 0.19 0.30 0.007 0.012
c 0.09 0.20 0.004 0.0079
D 6.4 6.5 6.6 0.252 0.256 0.260
E 6.2 6.4 6.6 0.244 0.252 0.260
E1 4.3 4.4 4.48 0.169 0.173 0.176
e 0.65 BSC 0.0256 BSC
K0˚ 8˚0˚ 8˚
L 0.45 0.60 0.75 0.018 0.024 0.030
A2
A
A1
b
e
K
c
L
E
D
E1
PIN 1 IDENTIFICATION
40/43
1
0087225C

STPM11/12/13/14 Package mechanical data
Tape & Reel TSSOP20 MECHANICAL DATA
mm. inch
DIM.
MIN. TYP MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
A 330 12.992
C 12.8 13.2 0.504 0.519
D 20.2 0.795
N 60 2.362
T 22.4 0.882
Ao 6.8 7 0.268 0.276
Bo 6.9 7.1 0.272 0.280
Ko 1.7 1.9 0.067 0.075
Po 3.9 4.1 0.153 0.161
P 11.9 12.1 0.468 0.476
41/43

Revision history STPM11/12/13/14
12 Revision history
Table 19. Revision history
Date Revision Changes
30-Jan-2007 1 Initial release.
06-Feb-2007 2 The
20-Mar-2007 3 General description has been updated.
Figure 11.
has been changed.
42/43

STPM11/12/13/14
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2007 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
43/43
 Loading...
Loading...