STPC® CONSUMER-II
X86 Core PC Co mpatibl e Informati on Applia nce System- on-Chip
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 1/93
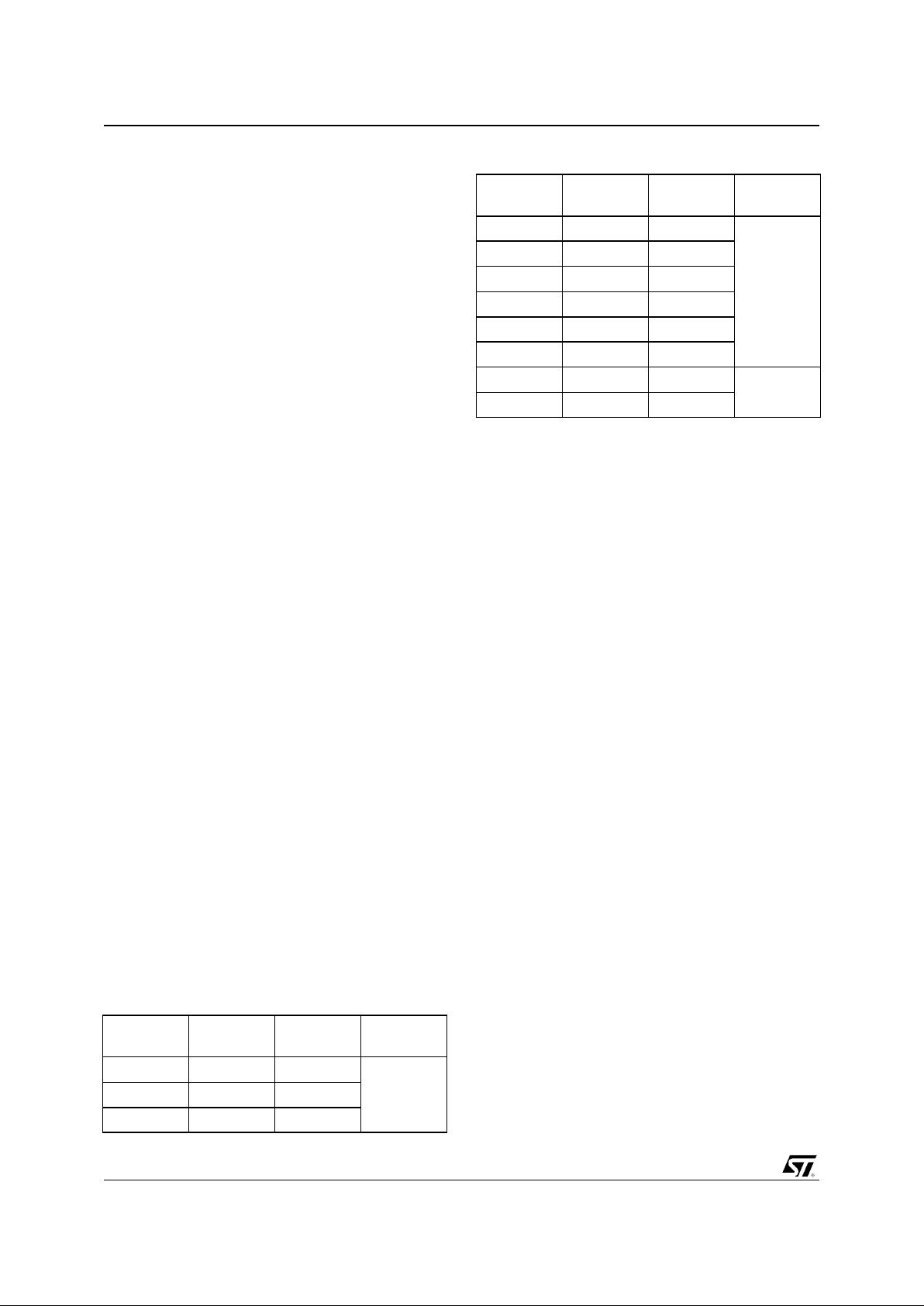
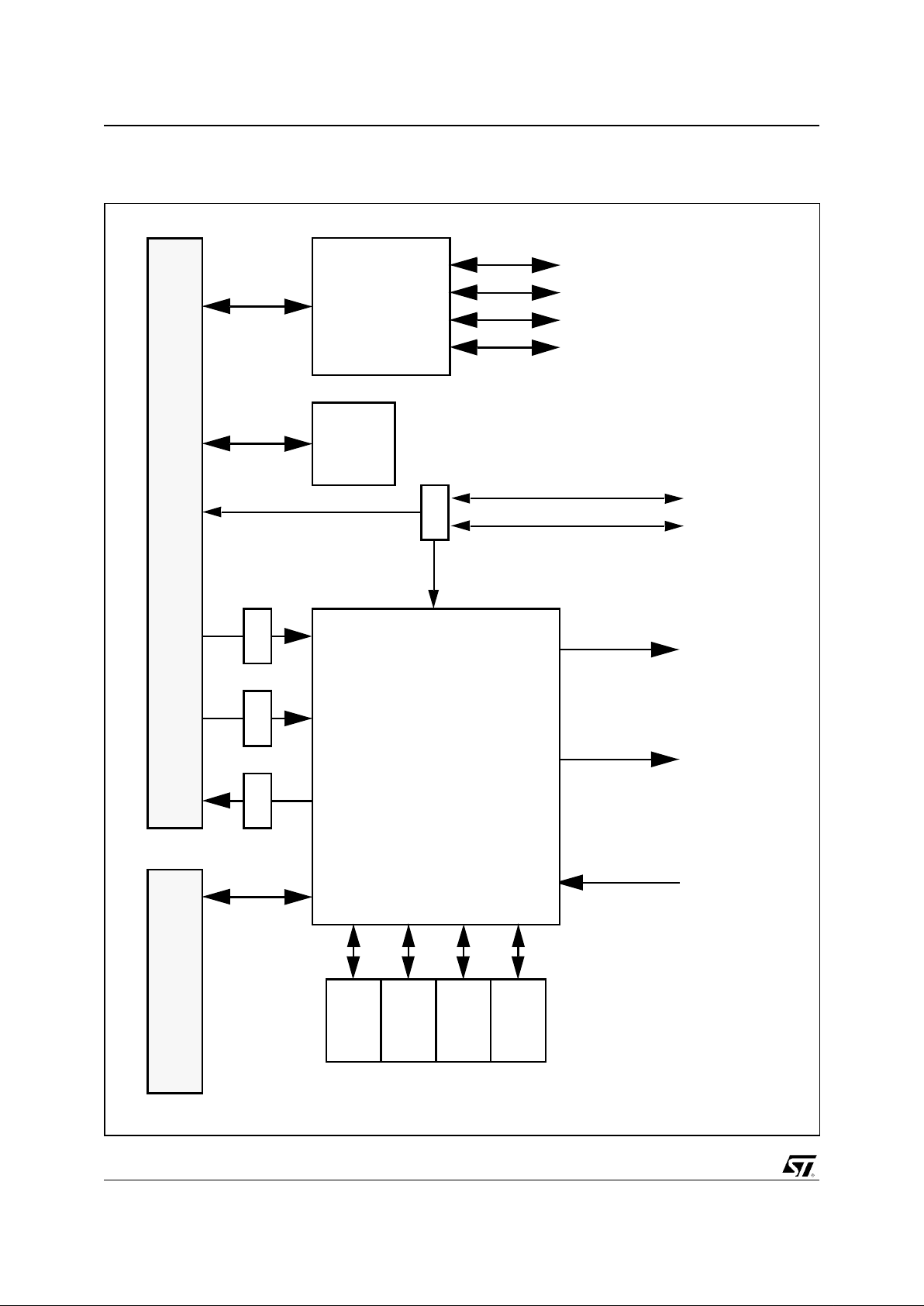
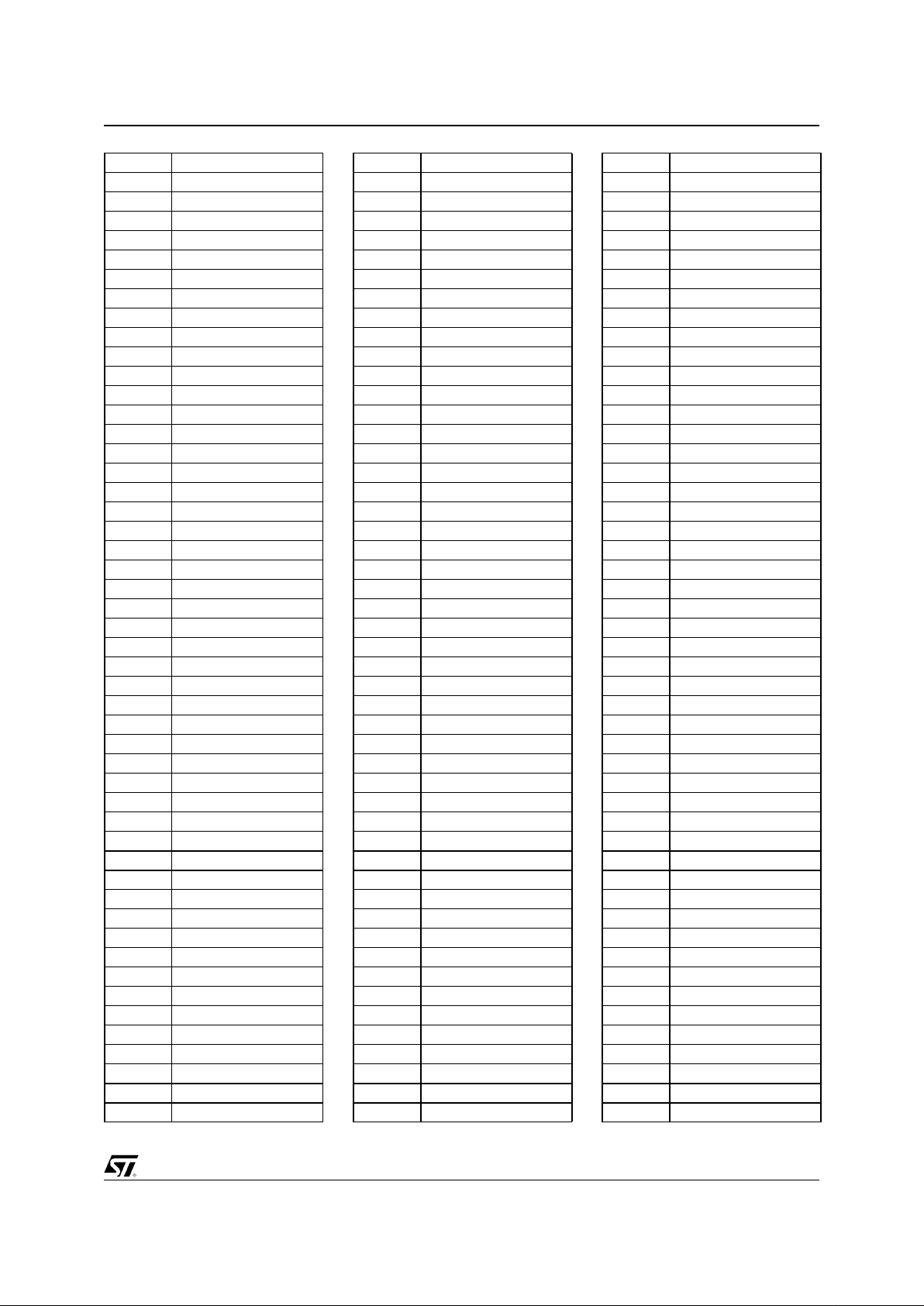
Figure 0-1. Logic Diagram
■
POWERFUL x86 PROCESSOR
■
64-BIT SDRAM UMA CONTROLLER
■
VGA & SVGA CRT CONTROLLER
■
135 MHz RAMDAC
■
2D GRAPHICS ENGINE
■
VIDEO INPUT PORT
■
VIDEO PIPELINE
- UP-SCALER
- VIDEO COLOUR SPACE CONVERTER
- CHROMA & COLOUR KEY SUPPORT
■
TV OUTPUT
- THREE-LINE FLICKER FILTER
- ITU-R 601/656 SCAN CONVERTER
- NTSC / PAL COMPOSITE, RGB, S-VIDEO
■
PCI MASTER / SLAVE / ARBITER
■
ISA M ASTER / SL AVE
■
OPTIONAL 16- BIT LOC AL BU S INTERFACE
■
EIDE CONTROLLER
■
I²C INTERFACE
■
IPC
- DMA CONTROLLER
- INTERRUPT CONTROLLER
- TIMER / COUNTERS
■
POWER MANAGEMENT UNIT
■
JTAG IEEE1149.1
DESCRIPTION
The STPC Consumer-II integrates a standard 5th
generation x86 core, a Synchronous DRAM
controller, a graphics subsystem, a video pipeline,
and support logic including PCI, ISA, and IDE
controllers to provide a single consumer
orientated PC compatible subsystem on a single
device.
The device is based on a t ightly coupled Unified
Memory Architecture (UMA), sharing memory
between the CPU, the graphics and the video.
The STPC Consumer-II is packaged in a 388
Plasti c Ball Grid Array (PBGA).
PBGA388
S
T
P
C
C
o
n
s
u
m
e
r
I
I
x86
Core
Host
I/F
SDRAM
CTRL
SVGA
GE
VIP
PCI
m/s
LB
CTR
PCI Bus
ISA
m/s
IPC
PCI
m/s
ISA Bus
CRTC
Cursor
Monitor
TV
IDE
I/F
PMU
Video
Pipeline
C Key
K Key
LUT
Local Bus
Encoder
TVO
JTAG

STPC® CONSUMER-II
2/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
■
X86 Processor core
■
Fully static 32-bit five-sta
g
e pipeline, x86
processor fully PC compatible .
■
Can access up to 4 GB of external memory .
■
8 Kbyte unified instruction and data cache
with write back and write throu
g
h capability.
■
Parallel processin
g
integral floating point unit,
with automatic power down.
■
Runs up to 100 MHz (x1) or 133 MHz (x2).
■
Fully stat ic de s i
g
n for dynamic clock control.
■
Low power and system mana
g
ement modes.
■
Optimized desi
g
n for 2.5 V operation.
■
SDRAM Controller
■
64-bit data bus.
■
Up to 100 MHz SDRAM clock speed.
■
Inte
g
rated system memory, graphic frame
memory and video frame memory.
■
Supports 2 MB up to 128 MB system
memory.
■
Supports 16-, 64-, and 128-Mbit SDRAMs.
■
Supports 8, 16, 32, 64, and 128 MB DIMMs.
■
Supports buffered, non buffered, and
re
g
istered DIMMs
■
Four-line write buffers for CPU to SDRAM
and PCI to SDRAM cycles.
■
Four-line read prefetch buffers for PCI
masters.
■
Pro
g
rammable latency
■
Pro
g
rammable timing for SDRAM
parameters.
■
Supports -8, -10, -12, -13, -15 memory parts
■
Supports memory hole between 1 MB and
8 MB for PCI/ISA busses.
■
2D Gra
p
hics Controller
■
64-bit windows accelerator.
■
Backward comp atib ilit y to SVG A sta ndards .
■
Hardware acceleration for text, bitblts,
transparent blts and fills.
■
Up to 64 x 64 bit
g
raphics hardware cursor.
■
Up to 4MB lon
g
linear frame buffer.
■
8-, 16-, 24- and 32-bit pixels.
■
Drivers availables for various OSes.
■
CRT Controller
■
Inte
g
rated 135 MHz triple RAMDAC allowing
for 1280 x 1024 x 75 Hz display.
■
Requires external frequency synthesizer and
reference sources.
■
8-bit, 16-bit, 24-bit pixels.
■
Interlaced or non-interlaced output.
■
Requires no external frequency synthesizer.
■
Requires only external reference source.
■
Video In
p
ut port
■
Accepts video inputs in ITU-R 601 mode.
■
Optional 2:1 decimator
■
Stores captured video in off settin
g
area of
the onboard frame buffer.
■
Video pass throu
g
h to the TV output for full
screen video ima
g
es.
■
HSYNC and B/T
g
eneration or lock onto
external video timin
g
source.
■
Video Pi
p
eline
■
Two-tap interpolative horizontal filter.
■
Two-tap interpolative vertical filter.
■
Colour space conversion (RGB to YUV and
YUV to RGB).
■
Pro
g
rammable window size.
■
Chroma and colour keyin
g
for integrated
video overlay.
■
Video Out
p
ut
■
NTSC-M; PAL-B, D, G, H, I, M, N encodin
g
.
■
ITU-R 601 encodin
g
with programmable
colour subcarrier frequencies.
■
ITU-R 656 video output si
g
nal interface.
■
Four analo
g
outputs in two configurations:
- R,G,B + CVBS
- C,YS,CVBS1 + CVBS2
■
Flicker-free interlaced output.
■
Pro
g
rammable two tap filter with gamma
correction or three tap flicker filter.
■
Interlaced or non-interlaced operation mode.
■
Pro
g
ressive to interlaced scan converter.
■
Cross colour reduction by specific trap
filterin
g
on luma within CVBS flow.
■
Power down mode available on each DAC.

STPC® CONSUMER-II
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 3/93
■
PCI Controlle r
■
Fully compliant with PCI 2.1 specification.
■
Integrated PCI arbitration interface. Up to 3
masters can connect directly. External PA L
allows for greater than 3 masters.
■
Translation of PCI cycles to ISA bus.
■
Translation of ISA master init iated cycle to
PCI.
■
Support for burst read/write from PCI master.
■
PCI clock is 1/2, 1/3 or 1/4 cpu bus clock.
■
ISA master /sla ve
■
Generates the ISA clock from either
14.318 MHz oscillator clock or PCI clock
■
Supports programmable extra wait state for
ISA cycles
■
Supports I/O recovery time for back to back
I/O cycles.
■
Fast Gate A20 and Fast reset.
■
Supports the single ROM that C, D, or E.
blocks shares with F block BIOS ROM.
■
Supports flash ROM.
■
Supports ISA hidden refresh.
■
Buffered DMA & ISA master cycles to reduce
bandwidth utilization of the PCI and Host
bus.
■
Local Bus interface
■
Multiplexed with ISA/DMA interface.
■
Low latency asynchronous bus
■
22-bit address bus.
■
16-bit data bus with word steering capability.
■
Programmable timing (Host clock granularity)
■
Two Programmable Flash Chip Select.
■
Four Programmable I/O Chip Select.
■
Supports 32-bit Flash burst.
■
Two-level hardware key protection for Flash
boot block protection.
■
Supports two banks of 16 MB flash devices
with boot block shadowed to 0x000F0000.
■
IDE Interface
■
Supports PIO
■
Transfer Rates to 22 MBytes/sec
■
Supports up to 4 IDE devices
■
Concurrent channel operation (PIO modes) -
4 x 32-Bit Buffer FIFOs per channel
■
Support for PIO mode 3 & 4.
■
Individual drive timing for all four IDE devices
■
Supports both legacy & native IDE modes
■
Supports hard drives larger than 528MB
■
Support for CD-ROM and tape peripherals
■
Backw ar d c o mpatibilit y with IDE (ATA-1).
■
Drivers for Windows and other Operating
Systems
■
Inte
g
rated Peripheral Controller
■
2X8237/AT compatible 7-channel DMA
controller.
■
2X8259/AT compatible interrupt Controller.
16 interrupt inputs - ISA and PCI.
■
Three 8254 compatible Timer/Counters.
■
Co-processor error support logic.
■
Power Mana
g
ement
■
Four power saving modes: On, Doze,
Standby, Suspend.
■
Programmable system activity detector
■
Supports Intel & Cyrix SMM and APM.
■
Supports STOPCLK.
■
Supports IO trap & restart.
■
Independent peripheral time-out timer to
monitor hard disk, serial & parallel port.
■
128K SM_RAM address space from
0xA0000 to 0xB0000
■
JTAG
■
Boundary Scan compatible IEEE1149.1.
■
Scan Chain control.
■
Bypass register compatible IEEE1149.1.
■
ID register compatible IEEE1149.1.
■
RAM BIST control.
The STPC Consumer-II has undergone an errata fix upgrade. The different versions can be differenciated by the part
number. Both versions are pin to pin compatible and there are some software extensions that have been added to the
upgraded parts. The parts labeled STPCC5 are the upgraded parts and the differences are identified in both the Datasheet and Programming Manual. All parts labeled STPCC4 do not support the new features outlined in the documentation.
Where nor C4 nor C5 are specified, the information or feature applies to both versions.

STPC® CONSUMER-II
4/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002

GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 5/93
1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
At the heart of the STPC Consumer-II is an
advanced 64-bit x86 processor block. It includes a
64-bit SDRAM controller, advanced 64-bit
accelerated graphics and video controller, a high
speed PCI local-bus controller and Industry
standard PC chip set functions (Interrupt
controller, DMA Controller, Interval timer and ISA
bus).
The STPC Consumer-II has in addition, an EIDE
Controller, I
2
C Interface, a Local Bus interface and
a JTAG interface.
1.1. ARCHITECTURE
The STPC Consumer-II makes use of a tightly
coupled Unified Memory Architecture (UMA),
where the same mem ory array is used for CPU
main memory and graphics frame-buffer. This
means a reduction in total system memory for
system performances that are equal to that of a
comparable frame buffer and system memory
based system, and generally much better, due to
the higher memory bandwidth allowed by
attaching the graphics engine directly to the 64-bit
processor host interface runni ng at the speed of
the processor bus rather than the traditional PCI
bus. The 64-bit wide mem ory array provides the
system with 528MB/s peak bandwidth. This allows
for higher resolution screens and greater color
depth.
The ‘standard’ PC chipset functions (DMA,
interrupt controller, timers, power management
logic) are integrated together with the x86
processor core; additional functions such as
communications ports are ac ces sed by the S TPC
Consumer-II via internal ISA bus.
The PCI bus is the ma in data comm unication link
to the STPC Consumer-II chip. The STPC
Consumer-II translates appropriate host bus I/O
and Memory cycles onto the PCI bus. It also
supports generation of Configuration cycles on the
PCI bus. The STPC Consumer-II, as a PCI bus
agent (host bridge class), f ully complies with PCI
specification 2.1. The chip-set also implements
the PCI mandatory header registers in Type 0 PCI
configuration space for easy porting of PCI aware
system BIOS. The device contains a PCI
arbitration function for three external PCI devices.
The STPC Consumer-II has two functional blocks
sharing the same balls
: The ISA / IPC / IDE block
and the Local Bus / IDE block (see Ta ble 3). Any
board with the STPC Consumer-II should be built
using only one of these two configurations. The
IDE pins are dynamically multiplexed in each of
the blocks in ISA mode only.
Configuration is done b y ‘stra p option s’. It i s a set
of pull-up or pull-down resistors on the memory
data bus, checked on reset, which auto-configure
the STPC Consumer-II.
1.2. GRAPHICS FEATURES
Graphics functions are controlle d through t he onchip SVGA controller and the monitor display is
produced through the 2D graphics display engine.
This Graphics Engine is tuned to work with the
host CPU to provide a balanced graphics system
with a low silicon area cost. It performs limited
graphics drawing operations which include
hardware acceleration of t ext, bitblts, transparent
blts and fills. The results of these operations
change the contents of the on-screen or offscreen frame buffer areas of SDRAM memory.
The frame buffer can occupy a space up to 4
Mbytes anywhere in the physical main memory.
The graphics resolution supported is a maximum
of 1280x1024 in 16M colors and 16M colors at
75Hz refresh rate, VGA and SVGA compatible.
Horizontal timing fields are V GA com pat ible whi le
the vertical fields are extended by one bit to
accommodate above display resolution.
1.3. VIDEO FUNCTIONS
The STPC Consumer-II provides several
additional functions to handle MPEG or similar
video streams. The Video Input Port accepts an
encoded digital video stream in one of a number of
industry standard formats, decodes it, optionally
decimates it, and deposits it into an off screen
area of the frame buffer. An interrupt request can
be generated when an entire field or frame has
been captured. The video output pipeline
incorporates a video-scaler and color space
converter function and provisions in the CRT
controller to display a video window. While
repainting the screen the CRT controller fetches
both the video as well as the normal non-video
frame buffer in two sepa rate internal FIFOs. The
video stream can be color-space converted
(optionally) and smooth scaled. Smooth
interpolative scaling in both horizontal and vertical
direction are implemented. Color and Chroma key
functions are also implemented to allow mixing
video stream with non-video frame buffer.
The video output passes directly to the RAMDAC
for monitor output or through another optional
color space converter (RGB to 4:2:2 YCrCb) to the
programmable anti-flicker filter. The flicker filter is
configured as either a two line filter with gamma
correction (primarily designed for DOS type text)
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
6/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
or a 3 line flicker filter (primarily designed for
Windows type displays). The fliker filter is optional
and can be software disabled f or use with large
screen area’s of video.
The Video output pipeline of the STPC ConsumerII interfaces directly to the internal digital TV
encoder. It takes a 24 bit RGB non-interlaced pixel
stream and converts to a multiplexed 4:2:2 YCrCb
8 bit output stream, the logic includes a
progressive to interlaced scan converter and logic
to insert appropriate CCIR656 timing reference
codes into the output stream. It facilitates the high
quality display of VGA or full screen video streams
received via the Video input port to standard
NTSC or PAL televisions.
The digital PAL/NTSC encoder outputs interlaced
or non-interlaced video in PAL-B,D,G,H,I PAL-N,
PAL-M or NTSC-M standards and “NTSC- 4.43” is
also possible.
The four frame (for PAL) or 2 frame (for NTSC)
burst sequences are internally generated,
subcarrier generation being performed
numerically with CKREF as reference. Rise and
fall times of synchronisation tips and burst
envelope are internally controlled according to the
relevant ITU-R and SMPTE recommendations.
Video output signals are directed to four analog
output pins through internal D/A converters giving,
simultaneous R,G,B and composite CVBS
outputs.
1.4. MEMORY CONTROLLER
The STPC handles the mem ory data (DATA) bus
directly, controlling from 2 to 128 MBytes. The
SDRAM controller supports accesses to the
Memory Banks to/from the CPU (via the host),
from th e VM I, to/ fro m th e CRT C, to t he V IDEO &
to/from the GE. (Banks 0 to 3) which can be
populated with either single or double sided 72-bit
(4 bit parity) DIMMs. Parity is not supported.
The SDRAM controller only supports 64 bit wide
Memory Banks.
Four Memory Banks (if DIMMS are u sed; Single
sided or two double-sided DIMMs) are supported
in the following configurations (see Table 1-1)
The SDRAM Controller supports buffered or
unbuffered SDRAM but not EDO o r FPM modes.
SDRAMs must support Full Page Mode Type
access.
The STPC Memory Controller provides various
programmable SDRAM parameters to allow the
SDRAM interface to be optimized for different
processor bus speeds SDRAM speed grades and
CAS Latency.
1.5. IDE INTERFACE
An industry standard EIDE (ATA 2) controller is
built into the STPC Consumer-II. The IDE port is
capable of supporting a total of four devices.
1.6. POWER MANAGEMENT
The STPC Consumer-II core is compliant with the
Advanced Power Management (APM)
specification to provide a standard method by
which the BIOS can control the power used by
personal computers. The Power Management
Unit module (PMU) controls the power
consumption providing a comprehensive set of
features that control the power usage and
supports compliance with the United States
Environmental Protection Agency's Energy Star
Computer Program. The PMU provides following
hardware structures to assist the software in
managing the power consumption by the system.
- System Activity Detection.
- Three power down timers.
- Doze timer for detecting lack of system activity
for short durations.
- Stand-by timer for detecting lack of system
activity for medium durations
- Suspend timer for detecting lack of system
activity for long durations.
- House-keeping activity detection.
- House-keeping timer to cope with short bursts
of house-keeping activity while dozing or in standby state.
Table 1-1. Memory configurations
Memory
Bank size
Number
Organisa
tion
Device
Size
1Mx64 4 1Mx16
16Mbits2Mx64 8 2Mx8
4Mx64 16 4Mx4
4Mx64 4 2Mx16x2
64Mbits
8Mx64 8 4Mx8x2
16Mx64 16 8Mx4x2
4Mx64 4 1Mx16x4
8Mx64 8 2Mx8x4
32Mx64 16 4Mx4x4
16Mx64 8 2Mx16x2
128Mbits
32Mx64 16 4Mx8x4
Table 1-1. Memory configurations
Memory
Bank size
Number
Organisa
tion
Device
Size

GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 7/93
- Peripheral activity detection.
- Peripheral timer for detecting l ack of peripheral
activi ty
- SUSP# modulation to adjust the system
performance in various power down state s of the
system including full power on state.
- Power control outputs to disable power from
different planes of the board.
Lack of system activity for progressively longer
period of times is detected by the three power
down timers. These timers can generate SMI
interrupts to CPU so that the SMM software can
put the system in decreasing states of power
consumption. Alternatively, system activity in a
power down state can generate SMI interrupt to
allow the software to bring the system back up to
full power on state. The chip-set supports up to
three power down states: Doze state, Stand-by
state and Suspend mode. These correspond to
decreasing levels of power savings.
Power down puts the STPC Consumer-II into
suspend mode. The processor completes
execution of the cu rrent instruction, any pending
decoded instructions and associated bus cycles.
During the suspend mode, internal clocks are
stopped. Removing power down, the processor
resumes instruction fetching and begins execution
in the instruction stream at the point it had
stopped. Because of the static nature of the core,
no internal data is lost.
1.7. JTAG
JT A G stands for Joint Test Action Group and is the
popular name for IEEE Std. 1149.1, Standard T est
Access Port and Boundary-Scan Architec-ture.
This built-in circuitry is used to assist in the test,
maintenance and support of functional circuit
blocks. The circuitry includes a standard interface
through which instructions and test data are
communicated. A set of test features is defined,
including a boundary-scan registe r so that a
component is able to respond to a minimum set of
test instructions.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
8/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
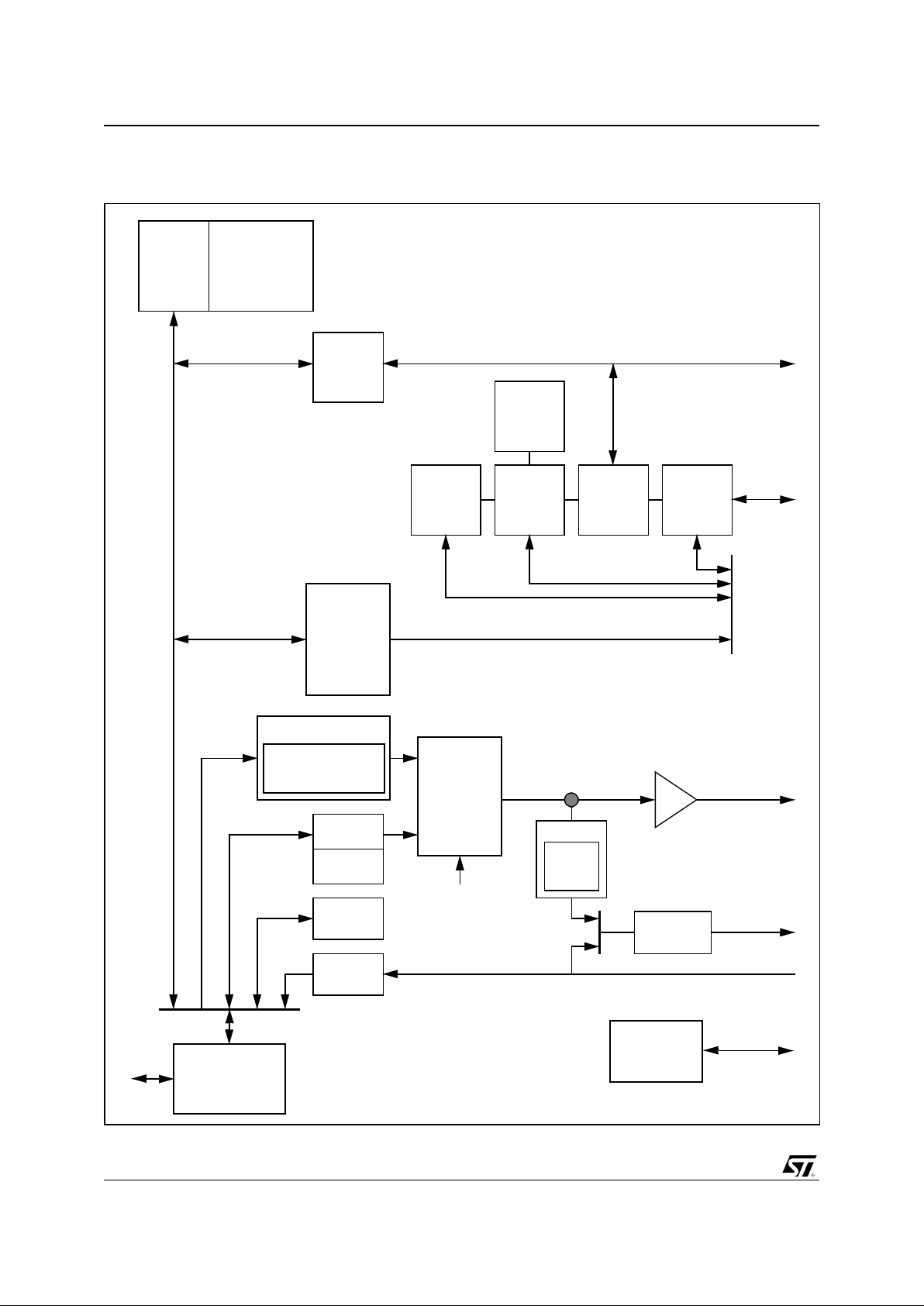
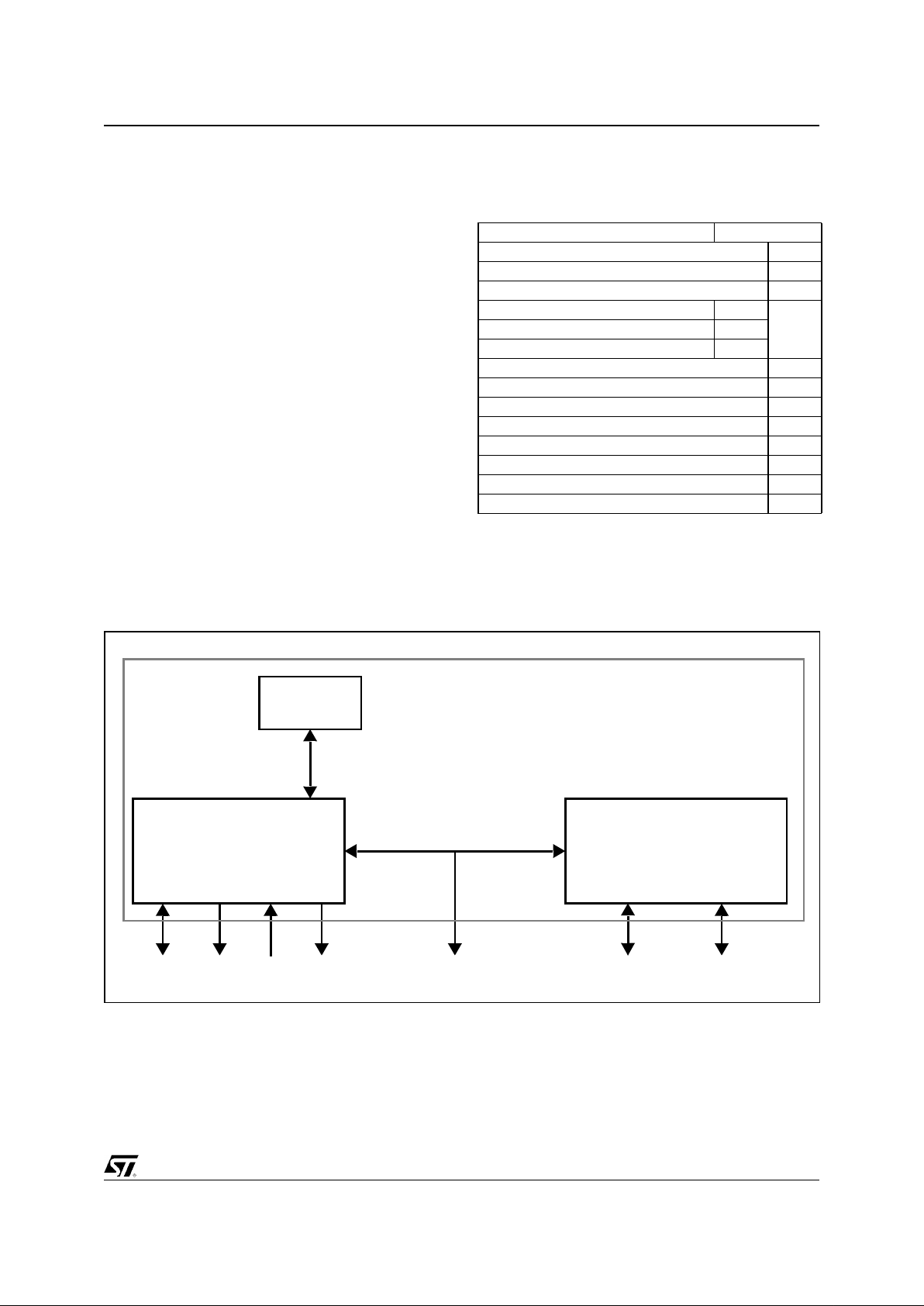
Figure 1-1. Functional description.
x86
Core
Host
I/F
SDRAM
I/F
SVGA
GE
VIP
PCI m/s
Local
Bus I/F
PCI BUS
ISA
m/s
IPC
82C206
PCI m/s
ISA Bus
CRTC
HW Cursor
Monitor
TV
- Pixel fo rm ating
- Scaler
- Colour S pace CVT
IDE
I/F
PMU
Video Pipeline
Colour Key
Chroma Key
LUT
Local Bus
NTSC/PAL
Encoder
TVO
- CSC
- FF
- CCIR
CCIR Input
JTAG
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 9/93
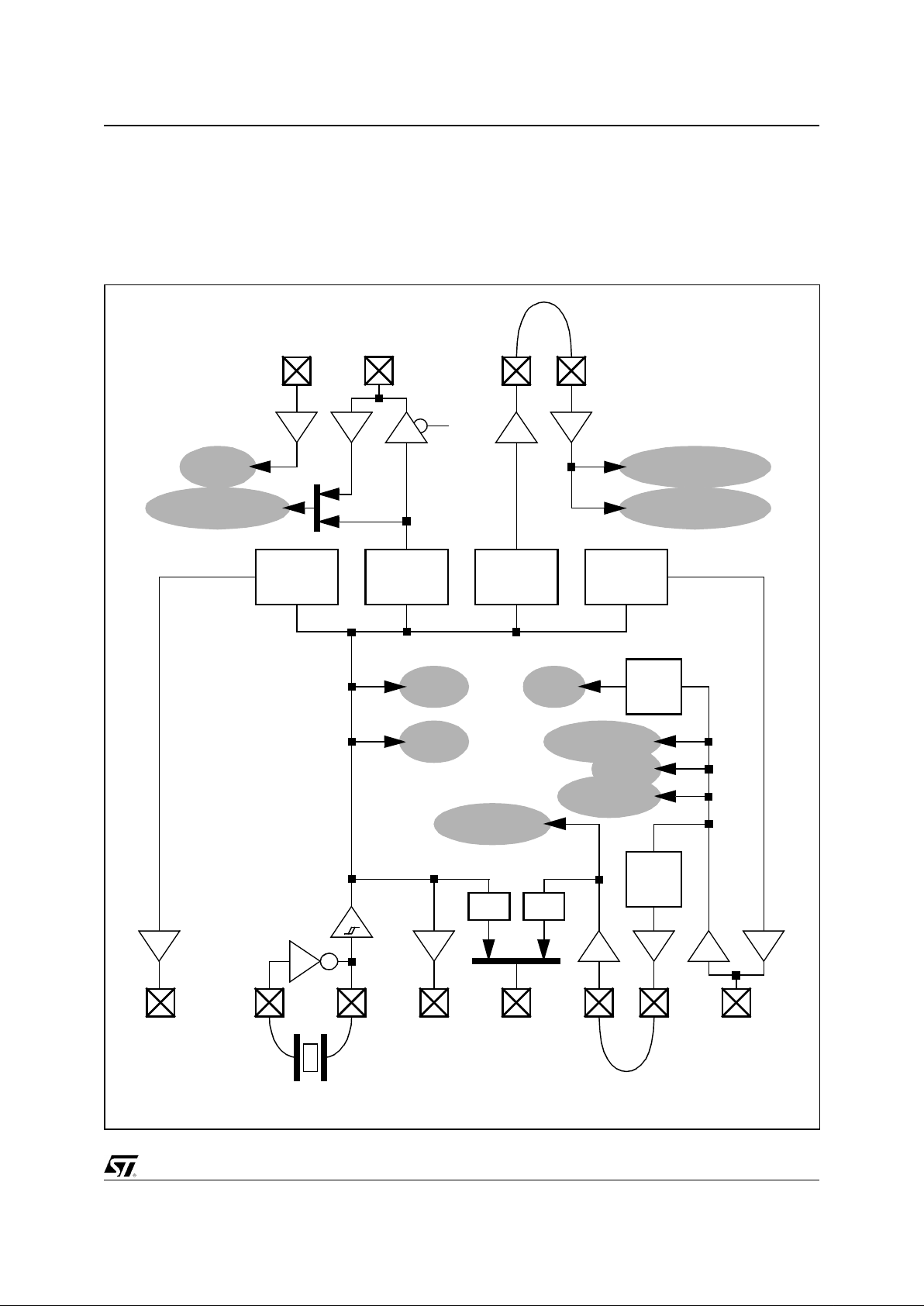
1.8. CLOCK TREE
The STPC Atlas integrates many features and
generates all its clocks from a single 14MHz
oscillator. This results in multiple clock domains as
described in Figure 1-2.
The speed of the PLLs is either fixed (DE VCLK),
either programmable by strap option (HCLK)
either programmable by software (DCLK, MCLK).
When in synchronized mode, MCLK speed is fixed
to HCLKO speed and HCLKI is generated from
MCLKI.
Figure 1-2. STPC Consumer-II clock archit ecture
IPC
SDRAM controller
North Bridge
14.31818 MHz
XTALO XTALI
OSC14M ISACLK
1/4
DEVCLK
DEVCLK
(24MHz)
PLL
(14MHz)
1/2
HCLK
PLL
PCICLKI PCICLKO
South Bridge
1/2
1/3
HCLK
DCLK
PLL
MCLK
PLL
DCLK
MCLKIMCLKO
CRTC,Video,TV
CPU
x1
x2
VCLK
VIP
GE
Local Bus
Host
ISA
HCLKI
HCLKO
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
10/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
Figure 1-3. Typical ISA-based Application.
Monitor
TV
Video
SVGA
CCIR601
CCIR656
S-VHS
RGB
PAL
NTSC
STPC Consumer-II
ISA
PCI
4x 16-bit SDRAMs
Super I/O
2x EIDE
Flash
Keyboard / Mouse
Serial Ports
Parallel Port
Floppy
IRQ
DMA.REQ
DMA.ACK
DMUX
DMUX
MUX
MUX
RTC
PIN DESCRIPTION
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 11/93
2. PIN DESCRIPTION
2.1. INTRODUCTION
The STPC Consumer-II integrates most of the
functionality of the PC architecture. As a result,
many of the traditional interconnections between
the host PC microprocessor and the peripheral
devices are totally internal to the STPC
Consumer-II. This offers improved performance
due to the tight coupling of the processor core and
these peripherals. As a result, many of the
external pin connections are made directly t o the
on-chip peripheral functions.
Figure 2-1 shows the STPC Consum er-II extern al
interfaces. It defines the main buses and their
functions. Table 2-1 describes the physical
implementation, listing signal type and
functionality. Table 2-2 provides a full pin listing
and description of pins. Table 2-7 provides a full
listing of pin locations of the STPC Consum er-II
package by physical connection.
Note: Several interface pins are multiplexed with
other functions, refer to Table 2-4 and Table 2-5
for further details
Table 2-1. Signal Description
Group name Qty
Basic Clocks reset & Xtal (SYS) 7
SDRAM Controller 95
PCI interface 56
ISA 79
89IDE 34
Local Bus 49
Video Input 9
TV Output 12
VGA Monitor interface 8
Grounds 71
V
DD
26
Miscellaneous 9
Unconnected 6
Total Pin Count 388
Figure 2-1. STPC Consumer-II External Interfaces
PCI
x86
SDRAM VGA
VIP TV SYS
ISA/IDE/LB
95 8 9 12 56
7
89
STPC CONSUMER-II
PIN DESCRIPTION
12/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
Table 2-2 . Def i ni t io n of Si gn a l Pin s
Signal Name Dir Buffer Type
2
Description Qty
BASIC CLOCKS AND RESETS
SYSRSETI# I SCHMITT_FT System Power Good Input 1
SYSRSTO# O BD8STRP_FT System Reset Output 1
XTALI I ANA
14.3 MHz Crystal Input- External
Oscillator Input
1
XTALO I/O OSCI13B 14.3 MHz Crystal Output 1
HCLK I/O BD4STRP_FT Host Clock (Test) 1
DEV_CLK O BT8TRP_TC 24 MHz Peripheral Clock (floppy drive) 1
DCLK I/O BD4STRP_FT 27-135 MHz Graphics Dot Clock 1
V
DD
_xxx_PLL
1
VDDCO Power Supply for PLL Clocks
SDRAM CONTROLLER
MCLKI I TLCHT_TC Memory Clock Input 1
MCLKO O BT8TRP_TC Memory Clock Output 1
CS#[1:0] O BD8STRP_TC DIMM Chip Select 2
CS2# / MA11 O BD16STARUQP_TC DIMM Chip Select / Memory Address 1
CS3# / MA12 / BA1 O BD16STARUQP_TC
DIMM Chip Select / Memory Address /
Bank Address
1
BA[0] O BD8STRP_TC Bank Address 1
MA[10:0] O BD16STARUQP_TC Memory Row & Column Address 12
MD[63:49] I/O BD8STRUP_FT Memory Data 15
MD[48:1] I/O BD8TRP_TC Memory Data 48
MD[0] I/O BD8STRUP_FT Memory Data 1
RAS#[1:0] O BD16STARUQP_TC Row Address Strobe 2
CAS#[1:0] O BD16STARUQP_TC Column Address Strobe 2
MWE# O BD16STARUQP_TC Write Enable 1
DQM[7:0] O BD8STRP_TC Data Input/Output Mask 8
PCI CONTROLLER
PCI_CLKI I TLCHT_FT 33 MHz PCI Input Clock 1
PCI_CLKO O BT8TRP_TC 33 MHz PCI O/P Clk (from internal PLL) 1
AD[31:0] I/O BD8PCIARP_FT PCI Address / Data 32
CBE[3:0] I/O BD8PCIARP_FT Bus Commands / Byte Enables 4
FRAME# I/O BD8PCIARP_FT Cycle Frame 1
IRDY# I/O BD8PCIARP_FT Initiator Ready 1
TRDY# I/O BD8PCIARP_FT Target Ready 1
LOCK# I TLCHT_FT PCI Lock 1
DEVSEL# I/O BD8PCIARP_FT Device Select 1
STOP# I/O BD8PCIARP_FT Stop Transaction 1
PAR I/O BD8PCIARP_FT Parity Signal Transactions 1
SERR# O BD8PCIARP_FT System Error 1
PCIREQ#[2:0] I BD8PCIARP_FT PCI Request 3
PCIGNT#[2:0] O BD8PCIARP_FT PCI Grant 3
PCI_INT#[3:0] I BD4STRUP_FT PCI Interrupt Request 4
Note
1
: These pins are must be connected to the 2.5 V power supply. They
must not
be connected to the 3.3 V supply.
Note
2
: See
Table 2-3
for buffer type descriptions
PIN DESCRIPTION
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 13/93
ISA INTERFACE
ISA_CLK O BT8TRP_TC
ISA Clock Output
Multiplexer Select Line For IPC
1
ISA_CLK2X O BT8TRP_TC
ISA Clock x2 Output
Multiplexer Select Line For IPC
1
OSC14M O BD8STRP_FT ISA bus synchronisation clock 1
LA[23:17] O BD8STRUP_FT Unlatched Address 7
SA[19:0] I/O BD8STRUP_FT Latched Address 20
SD[15:0] I/O BD8STRP_FT Data Bus 16
ALE O BD4STRP_FT Address Latch Enable 1
MEMR#, MEMW# I/O BD8STR UP_F T Memory Read and Write 2
SMEMR#, SMEMW# O BD8STRP_FT System MemoryRead and Write 2
IOR#, IOW# I/O BD8STRUP_FT I/O Read and Write 2
MCS16#, IOCS16# I BD4STRUP_FT Memory and I/O ChipSelect16 2
BHE# O BD8STRUP_FT System Bus High Enable 1
ZWS# I BD4STRP_FT Zero Wait State 1
REF# O BD8STRP_FT Refresh Cycle. 1
MASTER# I BD4STRUP_FT Add On Card Owns Bus 1
AEN O BD8STRUP_F T Address Enable 1
IOCHCK# I BD4STRUP_F T I/O Channel Check. 1
IOCHRDY I/O BD8STRUP_FT I/O Channel Read 1
ISAOE# O BD4STRP_FT ISA/IDE Selec tion 1
GPIOCS# I/O BD4STRP_FT General Purpose Chip Select 1
IRQ_MUX[3:0] I BD4STRP_FT Time-Multiplexed Interrupt Request 4
DREQ_MUX[1:0] I BD4STRP_FT Time-Multiplexed DMA Request 2
DACK_ENC[2:0] O BD4STRP_FT Encoded DMA Acknowledge 3
TC O BD4STRP_FT ISA Terminal Count 1
RTCAS O BD4STRP_FT Real Time Clock Address Strobe 1
RMRTCCS# I/O BD4STRP_FT ROM/RTC Chip Select 1
KBCS# I/O BD4STRP_FT Keyboard Chip Select 1
RTCRW# I/O BD4STRP_FT RTC Read/Write 1
RTCDS# I/O BD4STRP_FT RTC Data Strobe 1
LOCAL BUS INTERFACE
PA[23:0] O BD4STRP_FT Address Bus 24
PD[15:0] I/O BD8STRP_FT Data Bus 16
PRD1#,PRD0# O BD4STRUP_FT Peripheral Read Control 2
PWR1#,PWR0# O BD4STRUP_FT Peripheral Write Control 2
PRDY I BD8STRUP_FT Data Ready 1
FCS1#, FCS0# O BD4STRP_FT Flash Chip Select 2
IOCS#[3:0] O BD 8STR UP_F T I/O Chip Select 4
IDE CONTROLLER
DA[2:0] O BD 8STR UP_F T Address Bus 3
DD[15:0] I/O BD8STRUP_FT Data Bus 16
Table 2-2 . Def i ni t io n of Si gn a l Pin s
Signal Name Dir Buffer Type
2
Description Qty
Note
1
: These pins are must be connected to the 2.5 V power supply. They
must not
be connected to the 3.3 V supply.
Note
2
: See
Table 2-3
for buffer type descriptions

PIN DESCRIPTION
14/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
PCS3#,PCS1#,SCS3#,SCS1# O BD8STRUP_FT Primary & Secondary Chip Selects 4
DIORDY O BD8STRUP_FT Data I/O Ready 1
PIRQ, SIRQ I BD4STRP_FT Primary & Secondary Interrupt Request 2
PDRQ, SDRQ I BD4STRP_FT Primary & Secondary DMA Request 2
PDACK#, SDACK# O BD8STRP_FT Primary & Secondary DMA Acknowledge 2
PDIOR#, SDIOR# O BD8STRUP_FT Primary & Secondary I/O Channel Read 2
PDIOW#, SDIOW# O BD8STRUP_FT Primary & Secondary I/O Channel Write 2
VGA CONTROLLER
RED, GREEN, BLUE O VDDCO Analog Red, Green, Blue 3
VSYNC O BD4STRP_FT Vertical Sync 1
HSYNC O BD4STRP_FT Horizontal Sync 1
VREF_DAC
1
I ANA DAC Voltage reference 1
RSET I ANA Resistor Set 1
COMP I ANA Compensation 1
COL_SEL O BD4STRP_FT Colour Select 1
VIDEO INPUT PORT
VCLK I BD8STRP_FT 27-33 MHz Video Input Port Clock 1
VIN[7:0] I BD4STRP_FT CCIR 601 or 656 YUV Video Data Input 8
ANALOG TV OUTPUT PORT
RED_TV, GREEN_TV, BLUE_TV O VDDCO Analog RGB or S-VHS outputs 3
CVBS O VDDCO Analog video composite output 1
IREF1_TV I ANA Reference current of CVBS DAC 1
VREF1_TV I ANA Reference voltage of CVBS DAC 1
IREF2_TV I ANA Reference current of RGB DAC 1
VREF2_TV I ANA Reference voltage of RGB DAC 1
VSSA_TV I Analog Vss for DAC 1
VDDA_TV I
VDDCO
Analog Vdd for DAC 1
VCS I/O BD4STRP_FT
Composite Synchro
Horizontal Line Synchro
1
ODD_EVEN I/O BD4STRP_FT Frame Synchronisation 1
MISCELLANEOUS
SPKRD O BD4STRP_FT Speaker Device Output 1
SCL I/O BD4STRUP_FT
I²C Interface - Clock
Can be used for VGA DDC[1] signal
1
SDA I/O BD4STRUP_FT
I²C Interface - Data
Can be used for VGA DDC[0] signal
1
SCAN_ENABLE I TLCHTD_TC Reserved (Test pin) 1
TCLK I TLCHT_FT Test Clock 1
TDI I TLCHT_FT Test Data Input 1
TMS I TLCHT_FT Test Mode Set 1
TDO O BT8TRP_TC Test Data output 1
Table 2-2 . Def i ni t io n of Si gn a l Pin s
Signal Name Dir Buffer Type
2
Description Qty
Note
1
: These pins are must be connected to the 2.5 V power supply. They
must not
be connected to the 3.3 V supply.
Note
2
: See
Table 2-3
for buffer type descriptions
PIN DESCRIPTION
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 15/93
Table 2-3. Buffer Type Descriptions
Buffer Description
ANA Analog pad buffer
OSCI13B Oscillator, 13 MHz, HCMOS
BT8TRP_TC Tri-State output buffer, 8 mA drive capability, Schmitt trigger with slew rate control and P, TC
BD4STRP_FT LVTTL Bi-Directional, 4 mA drive capability, Schmitt trigger, 5V tolerant
BD4STRUP_FT LVTTL Bi-Directional, 4 mA drive capability, Schmitt trigger, Pull-Up, 5V tolerant
BD8STRP_FT LVTTL Bi-Directional, 8 mA drive capability, Schmitt trigger, 5V tolerant
BD8STRUP_FT LVTTL Bi-Directional, 8 mA drive capability, Schmitt trigger, Pull-Up, 5V tolerant
BD8STRP_TC LVTTL Bi-Directional, 8 mA drive capability, Schmitt trigger
BD8TRP_TC LVTTL Bi-Directional, 8 mA drive capability, Schmitt trigger
BD8PCIARP_FT LVTTL Bi-Directional, 8 mA drive capability, PCI compatible, 5V tolerant
BD16STARUQP_TC LVTTL Bi-Directional, 16 mA drive capability, Schmitt trigger
SCHMITT_FT LVTTL Input, Schmitt trigger, 5V tolerant
TLCHT_FT LVTTL Input, 5V tolerant
TLCHT_TC LVTTL Input
TLCHTD_TC LVTTL Input, Pull-Down
VDDCO
Internal supply for core only power pad

PIN DESCRIPTION
16/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
2.2. SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS
2.2.1. BASIC CLOCKS AND RESETS
SYSRSTI#
System Reset/Power good.
This input
is low when the reset switch is depressed.
Otherwise, it reflects the power supply power
good signal. This input is asynchronous to all
clocks, and acts as a negative active reset. The
reset circuit initiates a hard reset on the rising
edge of this signal.
SYSRSTO#
Rese t Outpu t to System .
This is the
system reset signal and is used to r eset the rest of
the components (not on Host bus) in the system.
The ISA bus reset is an externally inverted
buffered version of this output and the PCI bus
reset is an externally buffered version of this
output.
XTALI
14.3 MHz Crystal Input
XTALO
14.3 MHz Crystal Output.
These pins are
provided for the connection of an external 14.318
MHz crystal to provide the reference clock for the
internal frequency synthesizer, from which all
other clock signals are generated.
The 14.318 MHz series-cut fundamental (not
overtone) mode quartz crystal must have an
Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR, sometimes
referred to as Rm) of less then 50 Ohms (typically
8 Ohms) and a shunt capacitance (Co) of less
than 7 pF. Balance capacitors of 16 pF should
also be added, one connected to each pin.
In the event of an ext ernal o scillat or pr ovidin g the
master clock signal to the STPC Consumer-II
device, the LVTT L signal should b e con nected to
XTAL I.
HCLK
Host Clock.
This clock supplies the CPU
and the host related blocks. This clock can be
doubled inside the CPU and is intended to operate
in the range of 25 M Hz to 1 00 MHz . This clock is
generated internally from a PLL bu t can be driven
directly from the extern a l syst e m.
DEV_CLK
24 MHz Peripheral Clock.
This 24 MHz
signal is provided as a convenience for the system
integration of a Floppy Disk driver function in an
external chip.
DCLK
135 MHz Dot Clock.
This is the dot clock,
which drives graphics display cycles. Its frequency
can go from 8 MHz (us ing inte rnal PLL) up to 135
MHz, and it is required to have a worst case du ty
cycle of 60-40.
This signal is driven either by the internal pll (VGA)
or by an external 27 MHz oscillator (when the
composite video output is enabled ). The direction
can be controlled by a s trap option or an inte rnal
register bit.
2.2.2. SDRAM CONTROLLER
MCLKO
Memory Clock Output.
This clock is
driving the DIMMs on board and is generated from
an internal PLL. The default value is 66 MHz.
MCLKI
Memory Clock Input.
This clock is driving
the SDRAM controller, the graphics engine and
display controller. This input should be a buffered
version of the MCLKO signal with the track lengths
between the buffer and the pin matched with the
track lengths between the buffer and the DIMMs.
CS#[1:0]
Chip S elect
These signals are used to
disable or enable device operation by masking or
enabling all SDRAM inputs except MCLK, CKE,
and DQM.
CS#[2]/MA[11]
Chip Select/Bank Address
This
pin is CS#[2] in the case when 16-Mbit devices are
used. For all other densities, it becomes MA[11].
CS#[3]/MA[12]/BA[1]
Chip Select/Memory
Address/Bank Address
This pin is CS#[3] i n the
case when 16-Mbit devices are used. For all other
densities, it becomes MA[12] when two internal
banks devices are used and BA[1] when four
internal bank devices are used.
MA[10:0]
Memory Address.
Multiplexed row and
column address lines.
BA[0]
Memory Bank Address.
MD[63:0]
Memory Dat a.
This is the 64-bit memory
data bus. MD[40-0] are read by the device strap
option registers during rising edge of SYSRSTI#.
RAS#[1:0]
Row Address Strobe.
There are two
active-low row address strobe output signals. The
RAS# signals drive the memory devices di rectly
without any external buffering.
CAS#[1:0]
Column Address Strobe.
There are
two active-low column address strobe output
signals. The CAS# signals drive the memory
devices directly without any external buffering.
MWE#
Write Enable.
Write enable specifies
whether the memory access is a read (MWE# = H)
or a write (MWE# = L).
DQM#[7:0]
Data Mask.
Makes data output Hi-Z
after the clock and masks the SDRAM outputs.
Blocks SDRAM data input when DQM active.
2.2.3. PCI CONTROLLER
PCI_CLKI
33 MHz PCI Input Clock .
This signal is
the PCI bus clock input and should be driven from
the PCI_CLKO pin.

PIN DESCRIPTION
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 17/93
PCI_CLKO
33 MHz PCI Output Clock .
This is t h e
master PCI bus clock output.
AD[31:0]
PCI Address/Data.
This is the 32-bit
multiplexed address and data bus of the PCI. This
bus is driven by the master during the address
phase and the data phase of wri te transact ions. It
is driven by the target during the data phase of
read transactions.
CBE#[3:0]
Bus Commands/Byte Ena bles.
These
are the multiplexed command and byte enable
signals of the PCI bus. During the address phase
they define the command and during the data
phase they carry the byte enable information.
These pins are inputs when a PCI master other
than the STPC Consumer-II owns the bus and
outputs when the STPC Consumer-II owns the
bus.
FRAME#
Cycle Frame.
This is the frame signal of
the PCI bus. It is an input when a PCI master owns
the bus and is an output when STPC Consumer-II
owns the PCI bus.
IRDY#
Initiator Ready.
This is the initiator ready
signal of the PCI bus. It is used as an output when
the STPC Consum er -II initiates a b us cycl e o n the
PCI bus. It is used as an input during the PCI
cycles targeted to the STPC Consumer-II to
determine when the current PCI master is ready to
complete the current transaction.
TRDY#
Target Ready.
This is the target ready
signal of the PCI bus. It is driven as an output
when the STPC Con sumer-II is the target of the
current bus transaction. It is used as an input
when STPC Consumer-II initiates a cycle on t he
PCI bus.
LOCK#
PCI Lock.
This is the lock signal of the PCI
bus and is used to implement the exclusive bus
operations when acting as a PCI target agent.
DEVSEL#
I/O Device Select.
This signal is used
as an input wh en the STPC Consumer-II initiates
a bus cycle on the PCI bus to determine if a PCI
slave device has decoded itself to be the target of
the current transaction. It is asserted as an output ,
either when the STPC Consumer-II is the target of
the current PCI transaction, or when no other
device asserts DEVSEL# prior to the subtractive
decode phase of the current PCI transaction.
STOP#
Stop Transaction.
Stop is used to
implement the disconnect, retry and abort protocol
of the PCI bus. It is used as an input for the bus
cycles initiated by the STPC Consumer-II and is
used as an output when a PCI master cycle is
targeted to the STPC Consumer-II.
PAR
Parity Signal Transactions.
This is the pa rity
signal of the PCI bus. This signal is used to
guarantee even parity across AD[31:0],
CBE#[3:0], and PAR. Thi s signal is driven by the
master during the address phase and data phase
of write transactions. It is driven by the target
during data phase of read transactions (its
assertion is identical to that of the AD bus delayed
by one PCI clock cycle).
SERR#
System Error.
This is the system error
signal of the PCI bus. It may, if enabled, be
asserted for one PCI clock cycle if target aborts a
STPC Consumer-II initiated PCI transaction. Its
assertion by either the STPC Consumer-II or by
another PCI bus agent w ill tr igge r the a ssert ion of
NMI to the host CPU. This is an open drain output.
PCIREQ#[2:0]
PCI Request.
These are the t hree
external PCI master request pins. They indicates
to the PCI arbiter that external agents desire use
of the bus.
PCIGNT#[2:0]
PCI Grant.
These pins indicate that
the PCI bus has been granted to the master
requesting it on its PCIREQ#.
PCI_INT#[3:0]
PCI Interrupt Request.
These are
the PCI bus interrupt signals.
2.2.4. ISA INTERFACE
ISA_CLK, ISA_CLKX2
ISA Clock x1, x2.
These
pins generate the Clock signal for the ISA bus and
a Doubled Clock signal. They are also used as the
multiplexer control lines for the Interrupt Controller
Interrupt input lines. ISA_CLK is generated from
either PCICLK/4 or OSC14M/ 2.
OSC14M
ISA bus synchronisation clock Output.
This is the buffered 14.318 MHz clock for the ISA
bus.
LA[23:17]
Unlatched Address.
When the ISA bus
is active, these pins are ISA Bus unlatched
address for 16-bit devices. When ISA bus is
accessed by any cycle initiated from PCI bus,
these pins are i n o utput mode. When an ISA bus
master owns the bus, these pins are in input
mode.
SA[19:0]
ISA Address Bus.
System address bus
of ISA on 8-bit slot. These pins are used as an
input when an ISA bus master o wns the bus and
are outputs at all other times.
SD[15:0]
I/O Data Bus.
These pins are the
external data bus to the ISA bus.
ALE
Address Latch En able.
This is the address
latch enable output of the ISA bus and is asserted
by the STPC Consum er-II to indicate that LA2317, SA19-0, AEN and SBHE# signals are valid.
The ALE is driven high during refresh, DMA

PIN DESCRIPTION
18/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
master or an ISA master cycles by the STPC
Consumer-II. ALE is driven low after reset.
MEMR#
Memory Read.
This is the memory read
command signal of the IS A bus. It is used as an
input when an ISA master owns the bus and is an
output at all other times.
The MEMR# signal is active during refresh.
MEMW#
Memory Write.
This is the memory write
command signal of the IS A bus. It is used as an
input when an ISA master owns the bus and is an
output at all other times.
SMEMR#
System Memory Read.
The STPC
Consumer-II generates SMEMR# signal of the
ISA bus only when the address is below one
megabyte or the cycle is a refresh cycle.
SMEMW#
System Memory Write.
The STPC
Consumer-II generates the SMEMW# signal of
the ISA bus only when the address is below one
megabyte.
IOR#
I/O Read.
This is the IO read command
signal of the ISA bus. It is an input when an ISA
master owns the bus an d is an out put at al l other
times .
IOW#
I/O Write.
This is the IO write command
signal of the ISA bus. It is an input when an ISA
master owns the bus an d is an out put at al l other
times .
MCS16#
Memory Chip Select16.
This is the
decode of LA23-17 address pins of the ISA
address bus without any qualification of the
command signal lines. MCS16# is always an
input. The STPC Consumer-I I ignores this signal
during IO and refresh cycles.
IOCS16#
IO Chip Select16.
This signal is the
decode of SA15-0 address pins of the ISA
address bus without any qualification of the
command signals. The STPC Consumer-II does
not drive IOCS16# (similar to PC-AT design). An
ISA master access to an internal register of the
STPC Consumer-II is executed as an extended 8bit IO cycle.
BHE#
System Bus High Enable.
This signal, when
asserted, indicates that a data byte is being
transferred on SD15-8 lines. It is used as an input
when an ISA master owns the bus and is an
output at all other times.
ZWS#
Zero Wait Stat e.
This signal, when asserted by an addressed device, indicates that the current cycle can be shortened.
REF#
Refresh Cycle.
This is the refresh command
signal of the ISA bus. It is driven as an output
when the STPC Consumer-II performs a refresh
cycle on the ISA bu s. It is used as an input when
an ISA master owns the bus and is used to trigger
a refresh cycle.
The STPC Consumer-II performs a pseudo
hidden refresh. It requests the host bus for two
host clocks to drive the refresh address and
capture it in external buffers. The host bus is then
relinquished while the refresh cycle continues on
the ISA bus.
MASTER#
Add On Card Owns Bus.
This signal is
active when an ISA device has been granted bus
ownership.
AEN
Address Enable.
Address Enable is enab led
when the DMA controller is the bus owner to
indicate that a DMA transfer will occur. The
enabling of the signal indicat es to IO devices t o
ignore the IOR#/IOW# signal during DMA
transfers.
IOCHCK#
IO Channel Che ck.
IO Channel Check
is enabled by any ISA device to signal an error
condition that can not be corrected. The NMI
signal becomes active on seeing IOCHCK# active
if the corresponding bit in Port B is enabled.
IOCHRDY
Channel Ready.
IOCHRDY is the IO
channel ready signal of the ISA bus and is driven
as an output in response to an ISA master cycle
targeted to the host bus or an internal register of
the STPC Consumer-II. The STPC Consumer-II
monitors this signal as an input when performing
an ISA cycle on behalf of the host CPU, DMA
master or refresh.
ISA masters which do not monitor IOCHRDY are
not guaranteed to work with the STPC ConsumerII since the access to the system me mory can be
considerably delayed due UMA architecture.
ISAOE#
Bidirectional OE Control.
This signal
controls the OE
signal of the external transceiver
that connects the IDE DD bus and ISA SA bus.
GPIOCS#
I/O General Purpo se Chip Select .
This
output signal is used by the external la tch on ISA
bus to latch the data on the SD[7:0] bus. The latch
can be use by PMU unit to control the external
peripheral devices or any other desired function.
IRQ_MUX[3:0]
Multiplexed Interrupt Request.
These are the ISA bus interrupt signals. They
have to be encoded before connection to the
STPC Consumer-II using ISACLK and I SACLK X 2
as the input selection strobes.
Note that IRQ8B, which by convention is
connected to the RTC, is inverted before being
sent to the interrupt c ontroller, so that it may be
connected directly to the IRQ
pin of the RTC.
DREQ_MUX[1:0]
ISA Bus Multiplexed DMA
Request.
These are the ISA bus DMA request
signals. They are to be encoded before
connection to the STPC Consumer-II using

PIN DESCRIPTION
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 19/93
ISACLK and ISACLKX2 as the input selection
strobes.
DACK_ENC[2:0]
DMA Acknowledge.
These are
the ISA bus DMA ac knowledge sig nals. They are
encoded by the STPC Consum er-II before ou tput
and should be decoded externally using ISACLK
and ISACLKX2 as the control strobes.
TC
ISA Terminal Count.
This is the terminal count
output of the DMA controller and is connected to
the TC line of the ISA bus. It is asserted during the
last DMA transfer, when the byte count expires.
RTCAS
Real time clock address strobe.
This sig-
nal is asserted for any I/O write to port 70H.
RMRTCCS#
ROM/Real Time clock chip select.
This signal is asserted if a ROM access is
decoded during a memory cycle. It should be
combined with MEMR# or MEMW# signals to
properly access the ROM. During a IO cycle, this
signal is asserted if access to the Real Time Clock
(RTC) is decoded. It should be combined with IOR
or IOW# signals to properly acces s the real time
clock.
KBCS#
Keyboard Chip Select.
This signal is
asserted if a keyboard access is decoded during a
I/O cycle.
RTCRW#
Real Time Clock RW.
This pin is a multifunction pin. When ISAOE# is active, this signal is
used as RTCRW#. This signal is asserted for any
I/O write to port 71H.
RTCDS#
Real Time Clock DS
. This pin is a multifunction pin. When ISAOE# is active, this signal is
used as RTCDS#. This signal is asserted for any I/
O read to port 71H. Its polarity complies with the
DS pin of the MT48T86 RTC device when
configured with Intel timings.
Note: RMRTCCS#, KBCS#, RTCRW# and
RTCDS# signals must be ORed externally with
ISAOE# and then connected to the external
device. An LS244 or equivalent function can be
used if OE# is connected to ISAOE# and the
output is provided with a weak pull-up resistor as
shown in Figure 6-10.
2.2.5. LOCAL BUS INTERFACE
PA[23:0]
Address Bus Output.
PD[15:0]
Data Bus.
This is the 16-bit data bus.
D[7:0] is the LSB and PD[15:8] is the MSB.
PRD#[1:0]
Read Control output.
PRD0# is used to
read the LSB and PRD1# to read the MSB.
PWR#[1:0]
Write Control output.
PWR0# is used
to write the LSB and PWR1# to write the MSB.
PRDY
Data Ready input.
This signal is used to
create wait states on the bus. When high, it
completes the current cycle.
FCS#[1:0]
Flash Chip Select output.
These are
the Programmable Chip Select signals for up to
two banks of Flash memory.
IOCS#[3:0]
I/O Chip Select output.
These are the
Programmable Chip Select signals for up to four
external I/O devices.
2.2.6. IDE INTERFACE
SCS1#, SCS3#
Secondary Chip Select.
These
signals are used as the active high secondary
master & slave IDE chip select signals. These
signals must be externally ANDed with the
ISAOE
#
signal before driving the IDE devices to
guarantee it is active only when ISA bus is idle.
DA[2:0]
Address.
These signals are connected to
DA[2:0] of IDE devices directly or through a buffer.
If the toggling of sign als are t o be m asked du ring
ISA bus cycles, they can be externally ORed with
ISAOE# before being connected to the IDE
devices.
DD[15:0]
Databus.
When the IDE bus is active,
they serve as IDE signals D D[11:0]. IDE devices
are connected to SA[19:8] directly and ISA bus is
connected to these pins through two LS245
transceivers as described in Figure 6-10.
PCS1#, PCS3#
Primary Chip Select.
These
signals are used as the active high primary master
& slave IDE chip select signals. These signals
must be externally ANDed with the ISAOE
#
signal
before driving the I DE devices to guarantee it is
active only when ISA bus is idle.
DIORDY
Busy/Ready.
This pin serves as IDE
signal DIORDY.
PIRQ
Primary Interrupt Request.
SIRQ
Secondary Interrupt Request.
Interrupt request from IDE channels.
PDRQ
Primary DMA Request.
SDRQ
Secondary DMA Request.
DMA request from IDE channels.
PDACK#
Primary DMA Acknowledge.
SDACK#
Secondary DMA Acknowledge.
DMA acknowledge to IDE channels.
PDIOR#, PD IOW#
Primary I/O Read & Write.
SDIOR#, SD IOW#
Secondary I/O Read & Write
.
Primary & Secondary channel read & write.

PIN DESCRIPTION
20/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
2.2.7. VGA CONTROLLER
RED, GREEN, BLUE
RGB Video Outputs.
These
are the three analog colour outputs from the
RAMDACs. These signals are sensitive to
interference, therefore they need to be properly
shielded.
VSYNC
Vertical Synchronisation Pulse.
This is
the vertical synchronization signal f rom the VGA
controller.
HSYNC
Horizontal Synchronisation Pulse.
This is
the horizontal synchronization signal from the
VGA controller.
VREF_DAC
DAC Voltage reference.
An external
voltage reference is connected to this pin to bias
the DAC.
RSET
Resistor Current Set.
This reference
current input to the RAMDAC is used to set the
full-scale output of the RAMDAC.
COMP
Compensation.
This is the RAMDAC
compensation pin. Normally, an external capacitor
(typically 10nF) is connected between this pin and
V
DD
to damp oscillations.
2.2.8. VID EO IN PUT PO R T
VCLK
Pixel Clock Input.
This signal is used to
synchronise data being transferred from an
external video device to either the frame buffer, or
alternatively out the TV output in bypass mode.
This pin can be sourced from STP C i f n o exte rnal
VCLK is detected, or can be input from an external
video clock source.
VIN[7:0]
YUV Video Data Input CCIR 601 or 656.
Time multiplexed 4:2:2 luminance and
chrominance data as defined in ITU-R Rec601-2
and Rec656 (except for TTL input levels). This bus
typically carries a stream of Cb,Y,Cr,Y digital
video at VCLK frequency, clocked on the rising
edge (by default) of VCLK.
2.2.9. AN AL OG TV OUTPU T PO RT
RED_TV / C_TV
Analog video outputs
synchronized with CVBS.
This output is currentdriven and must be con nected to analog ground
over a load resistor (R
LOAD
). Following the l oad
resistor, a simple analog low pass filter is
recommended. In S-VHS mode, this is the
Chrominance Output.
GREEN_TV / Y_TV
Analog video outputs
synchronized with CVBS.
This output is currentdriven and must be con nected to analog ground
over a load resistor (R
LOAD
). Following the l oad
resistor, a simple analog low pass filter is
recommended. In S-VHS mode, this is the
Luminance Output.
BLUE_TV / CVBS
Analog video outputs
synchronized with CVBS.
This output is currentdriven and must be con nected to analog ground
over a load resistor (R
LOAD
). Following the l oad
resistor, a simple analog low pass filter is
recommended. In S-VHS mode, this is a second
composite output.
CVBS
Analog video composite output (luminance/
chrominance).
CVBS is current-driven and must
be connected to analog ground over a load
resistor (R
LOAD
). Following the load resistor, a
simple analog low pass filter is recommended.
IREF1_TV
Ref. current
for CVBS 10-bit DAC.
IREF2_TV
Ref er enc e cur re nt
for RGB 10-bit DAC.
VREF1_TV
Ref. voltage
for CVBS 10-bit DAC.
Connect to analog ground.
VREF2_TV
Reference voltage
for RGB 10-bit
DAC. Connect to analog ground.
VSSA_TV
Analog VSS
for DACs.
VDDA_TV
Analog VDD
for DACs.
JTAG Signals
VCS
Line synchronisation Output.
This pin is an
input in ODDEV+HSYNC or VSY NC + HSYN C or
VSYNC slave modes and an output in all other
modes (master/slave)
ODD_EVEN
Frame Synchronisat ion O utput.
This
pin supports the Frame synchronisation s ignal. It
is an input in slave modes, exc ept when sync is
extracted from YCrCbdata, and an output in
master mode and when sync is extracted from
YCrCb data
The signal is synchronous to rising edge of DCLK.
The default polarity for this pin is:
- odd (not-top) field: LOW level
- even (bottom) field: HIGH level
2.2.10. MISCELLANEOUS
SPKRD
Speaker Drive.
This the output to the
speaker. It is an AND of the counter 2 output with
bit 1 of Port 61, and d rives an e xternal speaker
driver. This output should be connected to 7 407
type high voltage driver.
SCL, SDA
I²C Interface
.
These bidirectional pins
are connected to CRTC register 3Fh to implement
DDC capabilities. They conform to I
2
C electrical
specifications, they have open-collector output
drivers which are internally connected to V
DD
through pull-up resistors.

PIN DESCRIPTION
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 21/93
They can be used for the DDC1 (SCL) and DDC0
(SDA) lines of the VGA interface.
SCAN_ENABLE
Reserved
. The pin is reserved
for Test and Miscellaneous functions.
COL_SEL
Colour Select.
Can be used for Picture
in Picture function. Note however that this signal,
brought out from the video pipeline, is not in sync
with the VGA output signals, i.e. the VGA si gnals
run four clock cycles after th e Col_ Sel si gnal .
VDD_CORE
2.5 V Power Supply.
These power
pins are necessary to supply the core with 2.5 V.
TCLK
Test clock
TDI
Test data input
TMS
Test mode input
TDO
Test data output
PIN DESCRIPTION
22/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
..
Table 2-4. ISA / IDE Dynamic Multiplexing
ISA BUS
(ISAOE# = 0)
IDE
(ISAOE# = 1)
RMRTCCS# DD[15]
KBCS# DD[14]
RTCRW# DD[13]
RTCDS# DD[12]
SA[19:8] DD[11:0]
LA[23] SCS3#
LA[22] SCS1#
SA[21] PCS3#
SA[20] PCS1#
LA[19:17] DA[2:0]
IOCHRDY DIORDY
Table 2-5. ISA / Local Bus Pin Sharing
ISA / IPC LOCAL BUS
SD[15:0] PD[15:0]
DREQ_MUX[1:0] PA[21:20]
SMEMR# PA[19]
MEMW# PA[18]
BHE# PA[17]
AEN PA[16]
ALE PA[15]
MEMR# PA[14]
IOR# PA[13]
IOW# PA[12]
REF# PA[11]
IOCHCK# PA[10]
GPIOCS# PA[9]
ZWS# PA[8]
SA[7:4] PA[7:4]
TC, DACK_ENC[2:0] PA[3:0]
SA[3] PRDY
ISAOE#,SA[2:0] IOCS#[3:0]
DEV_CLK, RTCAS FCS#[1:0]
IOCS16#, MASTER# PRD#[1:0]
SMEMW#, MCS16# PWR#[1:0]
Table 2-6. Signal value on Reset
Signal Name SYSRSTI# active
SYSRSTI# inactive
SYSRSTO# active
release of SYSRSTO#
BASIC CLOCKS AND RESETS
XTALO 14MHz
ISA_CLK Low 7MHz
ISA_CLK2X 14MHz
OSC14M 14MHz
DEV_CLK 24MHz
HCLK Oscillating at the speed defined by the strap options.
PCI_CLKO HCLK divided by 2 or 3, depending on the strap options.
DCLK 17MHz
MEMORY CONTROLLER
MCLKO 66MHz if asynchonous mode, HCLK speed if synchronized mode.
CS#[3:1] High
CS#[0] High
SDRAM init sequence:
Write Cycles
MA[10:0], BA[0] 0x00
RAS#[1:0], CAS#[1:0] High
MWE#, DQM[7:0] High
MD[63:0] Input
PCI INTERFACE
AD[31:0] 0x0000
First prefetch cycles
when not in Local Bus mode.
CBE[3:0], PAR Low
FRAME#, TRDY#, IRDY# Input
STOP#, DEVSEL# Input
PERR#, SERR# Input
PIN DESCRIPTION
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 23/93
PCI_GNT#[2:0] High
ISA BUS INTERFACE
ISAOE# High Low
RMRTCCS# Hi-Z
First prefetch cycles
when in ISA or PCMCIA mode.
Address start is 0xFFFFF0
LA[23:17] Unknown 0x00
SA[19:0] 0xFFFXX 0xFFF03
SD[15:0] Unknown 0xFF
BHE#, MEMR# Unknown High
MEMW#, SMEMR#, SMEMW#, IOR#, IOW# Unknown High
REF# Unknown High
ALE, AEN Low
DACK_ENC[2:0] Input 0x04
TC Input Low
GPIOCS# Hi-Z High
RTCDS#, RTCRW#, KBCS# Hi-Z
RTCAS Unknown Low
LOCAL BUS INTERFACE
PA[24:0] Unknown
First prefetch cycles
PD[15:0] Unknown 0xFF
PRD# Unknown High
PBE#[1:0], FCS0#, FCS_0H# High
FCS_0L#, FCS1#, FCS_1H#, FCS_1L# High
PWR#, IOCS#[7:0] High
IDE CONTROLLER
DD[15:0] 0xFF
DA[2:0] Unknown Low
PCS1, PCS3, SCS1, SCS3 Unknown Low
PDACK#, SDACK# High
PDIOR#, PDIOW#, SDIOR#, SDIOW# High
VGA CONTROLLER
RED, GREEN, BLUE Black
VSYNC, HSYNC Lo w
COL_SEL Unknown
TV OUTPUT
RED_TV, GREEN_TV, BLUE_TV Black
CVBS Black
VCS Low
ODD_EVEN Low
I2C INTERFACE
SCL / DDC[1] Input
SDA / DDC[0] Input
JTAG
TDO High
MISCELLANEOUS
SPKRD Low
Table 2-6. Signal value on Reset
Signal Name SYSRSTI# active
SYSRSTI# inactive
SYSRSTO# active
release of SYSRSTO#
PIN DESCRIPTION
24/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
Table 2-7. Pinout.
Pin # Pin name
AF3 SYSRSETI#
AE4 SYSRSETO#
A3 XTALI
C4 XTALO
G23 HCLK
H24 DEV_CLK
AD11 DCLK
AF15 MCLKI
AB23 MCLKO
AE16 MA[0]
AD15 MA[1]
AF16 MA[2]
AE17 MA[3]
AD16 MA[4]
AF17 MA[5]
AE18 MA[6]
AD17 MA[7]
AF18 MA[8]
3
AE19 MA[9]
3
AE20 MA[10]
AC19 MA[11]/BA[0]
AF22 CS#[0]
AD21 CS#[1]
AE24 CS#[2]/MA[11]
AD23 CS#[3]/MA[12]/BA[1]
AF23 RAS#[0]
AD22 RAS#[1]
AE21 CAS#[0]
AC20 CAS#[1]
AF20 DQM#[0]
AD19 DQM#[1]
AF21 DQM#[2]
AD20 DQM#[3]
AE22 DQM#[4]
AE23 DQM#[5]
AF19 DQM#[6]
AD18 DQM#[7]
AC22 MWE#
R1 MD[0]
3
T2 MD[1]
3
R3 MD[2]
T1 MD[3]
R4 MD[4]
U2 MD[5]
T3 MD[6]
U1 MD[7]
U4 MD[8]
V2 MD[9]
U3 MD[10]
V1 MD[11]
W2 MD[12]
V3 MD[13]
Y2 MD[14]
W4 MD[15]
Y1 MD[16]
W3 MD[17]
AA2 MD[18]
Y4 MD[19]
AA1 MD[20]
Y3 MD[21]
AB2 MD[22]
AB1 MD[23]
AA3 MD[24]
AB4 MD[25]
AC1 MD[26]
AB3 MD[27]
AD2 MD[28]
AC3 MD[29]
AD1 MD[30]
AF2 MD[31]
AF24 MD[32]
AE26 MD[33]
AD25 MD[34]
AD26 MD[35]
AC25 MD[36]
AC24 MD[37]
AC26 MD[38]
AB25 MD[39]
AB24 MD[40]
AB26 MD[41]
AA25 MD[42]
Y23 MD[43]
AA24 MD[44]
AA26 MD[45]
Y25 MD[46]
Y26 MD[47]
Y24 MD[48]
W25 MD[49]
3
V23 MD[50]
3
W26 MD[51]
3
W24 MD[52]
3
V25 MD[53]
3
V26 MD[54]
3
U25 MD[55]
3
V24 MD[56]
3
U26 MD[57]
3
U23 MD[58]
3
Pin # Pin name
T25 MD[59]
3
U24 MD[60]
3
T26 MD[61]
3
R25 MD[62]
3
R26 MD[63]
3
F24 PCI_CLKI
D25 PCI_CLKO
B20 AD[0]
C20 AD[1]
B19 AD[2]
A19 AD[3]
C19 AD[4]
B18 AD[5]
A18 AD[6]
B17 AD[7]
C18 AD[8]
A17 AD[9]
D17 AD[10]
B16 AD[11]
C17 AD[12]
B15 AD[13]
A15 AD[14]
C16 AD[15]
B14 AD[16]
D15 AD[17]
A14 AD[18]
B13 AD[19]
D13 AD[20]
A13 AD[21]
C14 AD[22]
B12 AD[23]
C13 AD[24]
A12 AD[25]
C12 AD[26]
A11 AD[27]
D12 AD[28]
B10 AD[29]
C11 AD[30]
A10 AD[31]
D10 CBE[0]
C10 CBE[1]
A9 CBE[2]
B8 CBE[3]
A8 FRAME#
B7 TRDY#
D8 IRDY#
A7 STOP#
C8 DEVSEL#
B6 PAR
Pin # Pin name
PIN DESCRIPTION
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 25/93
D7 SERR#
A6 LOCK#
D20 PCI_REQ#[0]
C21 PCI_REQ#[1]
A21 PCI_REQ#[2]
C22 PCI_GNT#[0]
A22 PCI_GNT#[1]
B21 PCI_GNT#[2]
A5 PCI_INT#[0]
C6 PCI_INT#[1]
B4 PCI_INT#[2]
D5 PCI_INT#[3]
F2 LA[17]/DA[0[
G4 LA[18]/DA[1]
F3 LA[19]/DA[2]
F1 LA[20]/PCS1#
G2 LA[21]/PCS3#
G1 LA[22]/SCS1#
H2 LA[23]/SCS3#
J4 SA[0]
H1 SA[1]
H3 SA[2]
J2 SA[3]
J1 SA[4]
K2 SA[5]
J3 SA[6]
K1 SA[7]
K4 SA[8]
L2 SA[9]
K3 SA[10]
L1 SA[11]
M2 SA[12]
M1 SA[13]
L3 SA[14]
N2 SA[15]
M4 SA[16]
M3 SA[17]
P2 SA[18]
P4 SA[19]
K25 SD[0]
L24 SD[1]
K26 SD[2]
K23 SD[3]
J25 SD[4]
K24 SD[5]
J26 SD[6]
H25 SD[7]
H26 SD[8]
Pin # Pin name
J24 SD[9]
G25 SD[10]
H23 SD[11]
D24 SD[12]
C26 SD[13]
A25 SD[14]
B24 SD[15]
AD4 ISA_CLK
AF4 ISA_CLK2X
C9 OSC14M
P25 ALE
AE8 ZWS#
R23 BHE#
P26 MEMR#
R24 MEMW#
N25 SMEMR#
N23 SMEMW#
N26 IOR#
P24 IOW#
N24 MCS16#
M26 IOCS16#
M25 MASTER#
L25 REF#
M24 AEN
L26 IOCHCK#
T24 IOCHRDY
M23 ISAOE#
A4 RTCAS
P3 RTCDS#
R2 RTCRW#
P1 RMRTCCS#
AE3 GPIOCS#
G26 PA[22]
3
A20 PA[23]
3
B1 PIRQ
C2 SIRQ
C1 PDRQ
D2 SDRQ
D3 PDACK#
D1 SDACK#
E2 PDIOR#
E4 PDIOW#
E3 SDIOR#
E1 SDIOW#
E23 IRQ_MUX[0]
D26 IRQ_MUX[1]
Pin # Pin name
E24 IRQ_MUX[2]
C25 IRQ_MUX[3]
A24 DREQ_MUX[0]
B23 DREQ_MUX[1]
C23 DACK_ENC[0]
A23 DACK_ENC[1]
B22 DACK_ENC[2]
D22 TC
N3 KBCS#
AF9 RED
AE9 GREEN
AD8 BLUE
AC5 VSYNC
AE5 HSYNC
AC10 VREF_DAC
AE10 RSET
AD7 COMP
AE15 VCLK
AD5 VIN[0]
AF7 VIN[1]
AF5 VIN[2]
AE6 VIN[3]
AC7 VIN[4]
AD6 VIN[5]
AF6 VIN[6]
AE7 VIN[7]
AD10 RED_TV
AF11 GREEN_TV
AE12 BLUE_TV
AE13 VCS
AC12 ODD_EVEN
AF14 CVBS
AE11 IREF1_TV
AF12 VREF1_TV
AE14 IREF2_TV
AC14 VREF2_TV
C5 SPKRD
B5 SCL
C7 SDA
B3 SCAN_ENABLE
C15 COL_SEL
G3 TCLK
N1 TMS
W1 TDI
Pin # Pin name
PIN DESCRIPTION
26/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
Note1; These pins must be
connected to the 2.5 V power
supply. They
must not
be
connected to the 3.3 V supply.
AC2 TDO
AD12 VDDA_TV
AF8 VDD_DAC 1
G24 VDD_CPUCLK_PLL
1
AD13 VDD_DCLK_PLL
1
F25 VDD_DEV CLK_PLL
1
AC17 VDD_MCLKI_PLL
1
AC15 VDD_MCLKO_PLL
1
F26 VDD_HCL K_PLL
1
E25 VDD_SKEW_PLL
1
D11 VDD_COR E
1
L23 VDD_CORE
1
T4 VDD_CORE
1
AC6 VDD_COR E
1
D6 VDD
D16 VDD
D21 VDD
F4 VDD
F23 VDD
AC11 VDD
AC16 VDD
AC21 VDD
AA4 VDD
AA23 VDD
T23 VDD
L4 VDD
AF13 VSS A_TV
AC9 VSS_DAC 1
A1:2 VSS
A26 VSS
B2 VSS
B25:26 VSS
C3 VSS
C24 VSS
D4 VSS
D9 VSS
D14 VSS
D19 VSS
D23 VSS
H4 VSS
J23 VSS
L11:16 VSS
M11:16 VSS
N4 VSS
N11:16 VSS
Pin # Pin name
P11:16 VSS
P23 VSS
R11:16 VSS
T11:16 VSS
V4 VSS
W23 VSS
AC4 VSS
AC8 VSS
AC13 VSS
AC18 VSS
AC23 VSS
AD3 VSS
AD14 COMPENSATION_VS
AD24 VSS
AE1:2 VSS
AE25 VSS
AF1 VSS
AF25 VSS
AF26 VSS
A16
Unconnected
B9
Unconnected
B11
Unconnected
D18
Unconnected
E26
Unconnected
AD9
Unconnected
AF10
Unconnected
Pin # Pin name
STRAP OPTIONS
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 27/93
3. STRAP OPTIONS
This chapter defines the STPC Consumer-II Strap
Options and their location. Some strap options are
left programmable for future versions of silicon. .
Table 3-1. Strap Options
Signal Designation Actual Settings
1
Set to ’0’ Set to ’1’
MD1 Reserved Pull up - MD2
HCLK PLL Speed
User defined see
Section 3.1.4.
bit 6
MD3 User defined see
Section 3.1.4.
bit 7
MD4 PCICLKO Division User defined see
Section 3.1.3.
bit 1
MD5 MCLK/HCLK Sync (see
Section 3.1.1.
) User defined Async Sync
MD6 PCICLKO frequency User defined see
Section 3.1.1.
bit 6
MD7
Reserved Pull down - -
MD10
Reserved Pull down - -
MD11
Reserved Pull down - -
MD14
Reserved Pull up - -
MD16
Reserved Pull up - -
MD17 PCI_CLKO Divisor User defined see
Section 3.1.3.
bit 1
MD18
Reserved Pull-up - -
MD19
Reserved Pull-up - MD20 DCLK Pad Direction User defined Input Output
MD21
Reserved Pull up - MD22
Reserved Pull up - MD23
Reserved Pull up - MD24
HCLK PLL Speed
User defined see
Section 3.1.4.
bit 3
MD25 User defined see
Section 3.1.4.
bit 4
MD26 User defined see
Section 3.1.4.
bit 5
MD27
Reserved Pull down - MD28
Reserved Pull down - MD29
Reserved Pull down - MD30
Reserved Pull down - MD40 CPU Mode (see
Section 3.1.3.
) User defined X1 X2
MD41
Reserved Pull down - MD42
Reserved Pull up - MD43
Reserved Pull down - MD44 Bus select (see
Section 3.1.1.
) User defined ISA Local Bus
MD45
Reserved Pull down - MD46
Reserved Pull up - MD47
Reserved Pull down - MD48
Reserved Pull up - -
TC
Reserved Pull up - -
DACK_ENC[2:0]
Reserved Pull up - -
Note
1
: Where a strap is represented by a ’Pull up’ or ’Pull down’, these have to be adhered to. If it is represented as a ’-
’ it can be left unconnected. Where ’User defined’, the strap is set by the user.
STRAP OPTION S
28/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
3.1. POWER-ON STRAP REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS
3.1.1. ADPC STRAP REGISTER 0 CONFIGURATION
Strap0
Access = 0022h/0023h Regoffset = 04Ah
76543210
MD[7] MD[6]
See Table
below
MD[4] Rsv
See Table
below
See Table
below
See Table
belowl
This register defaults to the values sampled on MD[7:4] pins after reset
Bit Number Sampled Mnemonic Description
Bits 7-6 MD[7:6]
PCICLK PLL set-up:
The value sampled on MD[7:6] controls the
PCICLK PLL programming according to PCICL K frequency .
MD7 MD6
0 0 PCICLK frequency between 16 & 32 MHz
0 1 PCICLK frequency between 32 & 64 MHz
1 X Reserved
Bit 5
MD[5] For the parts referenced
STPCC4
, see section
Section 3.1.1.
bit 2.
MD[44]
For the parts referenced
STPCC5
, this s
trap selects betwen Local
Bus or ISA mode.
0 = ISA Mode
1 = Local Bus Mode
This strap is not readable in a register for the
STPCC4
.
Bit 4 M D[4]
PCICLK division: This bit reflects the value sampled on [MD4] and is
used together with MD[17] to select the PCICLK frequency.
MD4 MD17
0 X PCI Clock output = HCLK / 4
1 0 PCI Clock output = HCLK / 3
1 1 PCI Clock output = HCLK / 2
Bits 2
Rsv For the parts referenced
STPCC4
These bits are reserved
MD[5]
Host Memory synchronization. This bit reflects the value sampled on
MD[5] and controls the MCLK/HCLK synchronization.
0: MCLK and HCLK not synchronized
1: MCLK and HCLK synchronized for improved system performance.
Bit 1-0
Rsv For the parts referenced
STPCC4
These bits are reserved
MD[4,17]
For the parts referenced
STPCC5
.
These bits reflect the values sampled on MD[17] pin and
controls the PCI clock output in conjunction with MD[4], as
follows:
MD4 MD17
0 X PCI Clock output = HCLK / 4
1 0 PCI Clock output = HCLK / 3
1 1 PCI Clock output = HCLK / 2

STRAP OPTIONS
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 29/93
3.1.2. ADPC STRAP REGISTER 1 CONFIGURATION
Strap1
Access = 0022h/0023h Regoffset = 04Bh
76543210
Rsv Rsv Rsv Rsv Rsv
This register defaults to the values sampled on MD[13:10] pins after reset
Bit Number Sampled Mnemonic Description
Bits 7-6 Rsv Res erved
Bits 5-2 MD[13:10] Reserved
Bits 1-0 Rsv Res erved

STRAP OPTION S
30/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
3.1.3. ADPC STRAP REGISTER 2 CONFIGURATION
Strap2
Access = 0022h/0023h Regoffset = 04Ch
76543210
See Table
below
Rsv M D[20] MD[19] MD[18]
See Table
below
Rsv
This register defaults to the values sampled on MD pins after reset
Bit Number Sampled Mnemonic Description
Bits 7
Rsv For the parts referenced
STPCC4,
Reserved
MD[40]
For the parts referenced
STPCC5,
this bit reflects the value sampled on
MD[40] is used is used to set the clock multiplication factor of the 486
core, as follows:
MD[40]
0 DX (X1)
1 DX2 (X2)
This strap is not readable in a register for the
STPCC4
.
Bit 6-5 Rsv Reserved
Bits 4 MD[20]
This bit reflects the value sampled on MD[20] pin and controls
the Dot clock (DCLK) source as follows:
0: External. DCLK pin is an input.
1: Internal. DCLK pin is an output and is connected to the
internal frequency synthesizer output. Note this bit is writeable
as well as readable.
Bit 3 Rsv
Reserved
Bit 2 Rsv
Reserved
Bit 1
MD[17] For the parts referenced
STPCC4
, see section
Section 3.1.1.
bits 1:0.
Rsv For the parts referenced
STPCC5
.This bit is reserved and not connected
Bit 0 Rsv Reserved

STRAP OPTIONS
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 31/93
3.1.4. CPC STRAP REGISTER 0 CONFIGURATION
Table 3-1. HCLK Frequency Programming
HCLK_Strap
Access = 0022h/0023h Regoffset = 05Fh
76543210
MD[3} MD[2] MD[26] MD[25] MD[24] Rsv
This register defaults to the values sampled on MD pins after reset
Bit Number Sampled Mnemonic Description
Bits 7-3 MD [3:2] & MD[26:24 ]
These pins reflect the values sampled on MD[3:2] and
MD[26:24] pins respectively and control the Host clock
frequency synthesizer as shown in
Table 3-1
Bits 2-0 Rsv Res erved
MD[3] MD[2] MD[26] MD[25] MD[24] HCLK Speed
00000 25 MHz
00001 50 MHz
00010 60 MHz
00011 66 MHz
01001 75 MHz
10011 90 MHz
11001 100 MHz

STRAP OPTION S
32/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002

ELECTRICAL S PECIFICATIONS
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 33/93
4. ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
4.1. INTRODUCTION
The electrical specifications in this chapter are
valid for the STPC Consumer-II.
4.2. ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
4.2.1. POWER/GROUND CONNECTIONS/
DECOUPLING
Due to the high frequency of operation of the
STPC Consumer-II, it is necessary to install and
test this device using standard high frequency
techniques. The high clock frequencies used in
the STPC Consumer-II and its output buffer
circuits can cause transient power surges when
several output buffers switch output levels
simultaneously. These effects can be minimized
by filtering the DC power leads with lowinductance decoupling capacitors, using low
impedance wiring, and by utilizing all of the VSS
and VDD pins.
4.2.2. U NUS ED I NPU T PINS
No unused input pin should be left unconnected
unless they have an integrated pull-up or pulldown. Connect active-low inputs to VDD through a
20 kΩ (±10%) pull-up resistor and active-high
inputs to VSS. For bi-directionnal active-high
inputs, connect to VSS through a 20 kΩ (±10%)
pull-up resistor to prevent spurious operation.
4.2.3. R ESERVED DESIGNATED PINS
Pins designated as reserved should be left disconnected. Connecting a reserved pin to a pull-up
resistor, pull-down resistor, or an active signal
could cause unexpected results and possible
circuit malfunctions.
4.3. ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
The following table lists the absolute maximum
ratings for the STPC Consumer-II device.
Stresses beyond those listed under Table 4-1
limits may cause permanent damage to the
device. These are stress ratings o nly and do not
imply that operation under any conditions other
than those specified in section "Operating
Conditions".
Exposure to conditions beyond those outlined in
Table 4-1 may (1) reduce device reliability and (2)
result in premature failure even when there is no
immediately apparent sign of failure. Prolonged
exposure to conditions at or near the absolute
maximum rating s (Table 4-1) may also result in
reduced useful life and reliability.
4.3.1. 5V TOLERANCE
The STPC is capable of running with I/O systems
that operate at 5 V such as PCI and ISA devices.
Certain pins of the STPC tolerate inputs up to
5.5 V. Above this limit the compo nent is likely to
sustain permanent damage. .
Note 1:
The figures specified apply to the Tcase of a
STPC device that is s oldered to a board, as detaile d in
the Design Guidelines Section, for Commercial and Industrial temperature ranges.
Table 4-1. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Parameter Minimum Maximum Units
V
DDx
DC Supply Voltage -0.3 4.0 V
V
CORE
DC Supply Voltage for Core -0.3 2.7 V
V
I
, V
O
Digital Input and Output Voltage -0.3 VDD + 0.3 V
V
5T
5Volt Tolerance -0.3 5.5 V
V
ESD
ESD Capacity (Human body mode) - 2000 °C
T
STG
Storage Temperature -40 +150
T
OPER
Operating Temperature (Note 1)
0 +85 °C
-40 +115 °C
P
TOT
Maximum Power Dissipation (package) - 4.8 W

ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
34/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
4.4. DC CHARACTERISTICS
Table 4-2. DC Characteristics
Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min Typ Max Unit
V
DD
Operating Voltage 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
V
CORE
Operating Voltage 2.45 2.5 2.7 V
P
DD
Supply Power 3.0V < VDD < 3.6V 0.18 W
P
CORE
Supply Power 2.45V < V
CORE
< 2.7V 2.90 W
V
IL
Input Low Voltage
Except XTALI -0.3 0.8 V
XTALI -0.3 0.8 V
V
IH
Input High Voltage
Except XTALI 2.1 V
DD
+0.3 V
XTALI 2.35 V
DD
+0.3 V
I
LK
Input Leakage Current Input, I/O -5 5 µA
Integrated Pull up/down 50 KΩ
Table 4-3. PAD buffers DC Characteristics
Buffer Type
I/O
count
V
IH
min
(V)
V
IL
max
(V)
VOH min
(V)
VOL max
(V)
I
OL
min
(mA)
I
OH
max
(mA)
C
load
max
(pF)
Derating
(ps/pF)
1
C
IN
(pF)
ANA 8 2.35 0.9 - - - - - - OSCI13B 1 2.1 0.8 2.4 0.4 2 - 2 50 - BT8TRP_TC 5 - - 2.4 0.4 8 - 8 200 21 6.89
BD4STRP_FT 50 2 0.8 2.4 0.4 4 - 4 100 42 5.97
BD4STRUP_FT 10 2 0.8 2.4 0.4 4 - 4 100 41 5.97
BD8STRP_FT 26 2 0.8 2.4 0.4 8 - 8 200 23 5.96
BD8STRUP_FT 40 2 0.8 2.4 0.4 8 - 8 200 23 5.96
BD8STRP_TC 10 2 0.8 2.4 0.4 8 - 8 200 21 7.02
BD8TRP_TC 60 2 0.8 2.4 0.4 8 - 8 200 21 7.03
BD8PCIARP_FT 49 0.5*V
DD
0.3*VDD0.9*V
DD
0.1*V
DD
1.5 - 0.5 200 15 6.97
BD16STARUQP_TC 19 2 0.8 2.4 0.4 16 -16 400 12 9.34
SCHMITT_FT 1 2 0.8 - - - - - - 5.97
TLCHT_FT 5 2 0.8 - - - - - - 5.97
TLCHT_TC 1 2 0.8 - - - - - - 5.97
TLCHTD_TC 1 2 0.8 - - - - - - 5.97
Note 1: time to output variation depending on the capacitive load.
Table 4-4. RAMDAC DC Specification
Symbol Paramet er Min Max
Vref_dac Voltage Reference 1.00 V 1.24 V
INL Integrated Non Linear Error - 3 LSB
DNL Differentiated Non Linear Error - 1 LSB
BLC Black Level Current 1.0 mA 2.0 mA
WLC White Level Current 15.00 mA 18.50 mA

ELECTRICAL S PECIFICATIONS
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 35/93
Note 1: PCI clock at 33MHz
Table 4-5. VGA RAMDAC Power Consumption
DCLK
(MHz)
DAC mode
(State)
P
Max
(mW)
VDD_DAC
= 2.45V VDD_DAC = 2.7V
- Shutdown 0 0
6.25 - 135 Active 150 180
Table 4-6. 2.5V Power Consumptions (V
CORE
+ VDD_x_PLL + VDD_DAC)
HCLK
(MHz)
CPUCLK
(MHz)
MCLK
(MHz)
Mode
DCLK
(MHz)
PMU
(State)
P
Max
(W)
V
2.5V
=2.45V V
2.5V
=2.7V
66 66 (x1) 66 SYNC
Stopped
Stop Clock 0.6 0.9
Full Speed 1.4 1.8
135
Stop Clock 0.9 1.2
Full Speed 1.7 2.3
100 100 (x1) 100 SYNC
Stopped
Stop Clock 0.8 1.1
Full Speed 1.5 2.0
135
Stop Clock 1.5 1.9
Full Speed 2.1 2.7
66 133 (x2) 66 SYNC
Stopped
Stop Clock 0.7 0.9
Full Speed 1.7 2.1
135
Stop Clock 0.9 1.2
Full Speed 1.9 2.5
66 133 (x2) 100 ASYNC
Stopped
Stop Clock 0.8 1.1
Full Speed 1.6 2.1
135
Stop Clock 1.5 1.9
Full Speed 2.3 2.9
Table 4-7. 3.3V Power Consumptions (VDD)
HCLK
(MHz)
CPUCLK
(MHz)
MCLK
(MHz)
DCLK
(MHz)
PMU
(State)
P
Max
(mW)
66 66 (x1) 66
6.26
Full Speed
90
135 160
100 100 (x1) 100
6.26
Full Speed
115
135 180
66 133 (x2) 66
6.26
Full Speed
100
135 165
66 133 (x2) 100
6.26
Full Speed
115
135 180
Table 4-8 . PLL P ower Consum ptions
PLL name
P
Max
(mW)
VDD_PLL
= 2.45V VDD_PLL = 2.7V
VDD_DCLK_PLL 5 10
VDD_DEVCLK_PLL 5 10
VDD_HCLKI_PLL 5 10
VDD_HCLKO_PLL 5 10
VDD_MCLKI_PLL 5 10
VDD_MCLKO_PLL 5 10
VDD_PCICLK_PLL 5 10

ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
36/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
4.5. AC CHARACTERISTICS
This section lists the AC characteristics of the
STPC interfaces including output delays, input
setup requirements, inp ut hold requirements and
output float delays. These measurements are
based on the measurement points identified in
Figure 4-1 and Figure 4-2. The rising clock edge
reference level VREF and other reference levels
are shown in Table 4-9 below. Input or output
signals must cross these levels during testing.
Figure 4-1 shows output delay (A and B) and input
setup and hold times (C and D). Input setup and
hold times (C and D) are specified minimums,
defining the smallest acceptable sampling window
a synchronous input signal must be stable for
correct operation.
Note : R e fer to F igure 4-1.
Table 4-9. Drive Level and Measurement Points for Switching Characteristics
Symbol Value Units
V
REF
1.5 V
V
IHD
2.5 V
V
ILD
0.0 V
Figure 4-1. Drive Level and Measurement Points for Switching Characteristics
CLK:
V
Ref
V
ILD
V
IHD
Tx
LEGEND: A - Maximum Output Delay Specification
B - Minimum Output Delay Specification
C - Minimum Input Setup Specification
D - Minimum Input Hold Specification
V
Ref
Valid
Valid
Valid
OUTPUTS:
INPUTS:
Output n
Output n+1
Input
MAX
MIN
A
B
CD
V
Ref
V
ILD
V
IHD

ELECTRICAL S PECIFICATIONS
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 37/93
Figure 4-2. CLK Timing Measurement Points
CLK
T5 T4T3
V
Ref
V
IL (MAX)
V
IH (MIN)
T2
T1
LEGEND:
T1 - One Clock Cycle
T2 - Minimum Time at V
IH
T3 - Minimum Time at V
IL
T4 - Clock Fall Time
T5 - Clock Rise Time
NOTE; All sIgnals are sampled on the rising edge of the CLK.

ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
38/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
4.5.1. POWER ON SEQUENCE
Figure 4-3 describes the power-on sequence of
the STPC, also called cold reset.
There is no dependency between the different
power supplies and there is no constraint on their
rising time.
SYSRSTI# as no cons traint on its rising e dge but
must stay active until power supplies are all within
specifications, a margin of 10µs is even
recommended to let the STPC PLLs and strap
options stabilize.
Strap Options are continuously sampled during
SYSRSTI# low and must remain stable. Once
SYSRSTI# is high, they MUST NOT CHANGE
until SYSRSTO# goes high.
Bus activity starts only few clock cycles after the
release of SYSRSTO#. The toggling signals
depend on the STPC configuration.
In ISA mode, activity is visible on PCI prior to the
ISA bus as the controller is part of the south
bridge.
In Local Bus mode, the PCI bus is not accessed
and the Flash Chip Select is the control sig nal to
monito r.
Figure 4-3 . Power-on timing di agram
Strap Options
Power Supplies
SYSRSTI#
SYSRSTO#
14 MH z
1.6 V
VALID CONFIGURATION
> 10 us
HCLK
PCI_CLK
2.3 ms
ISACLK

ELECTRICAL S PECIFICATIONS
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 39/93
4.5.2 RESET SEQUENCE
Figure 4-4 describes the reset sequence of the
STPC, also called warm reset.
The constraints on the strap options and the bus
activities are the same as for the cold reset.
The SYSRSTI# pulse duration must be long
enough to have all the strap options stabilized and
must be adjusted depending on resistor values.
It is mandatory to have a clean reset pulse without
glitches as the STPC could then sample invalid
strap option setting and enter into an umpredictable mode.
While SYSRSTI# is active, the PCI clock P LL runs
in open loop mode at a speed of few 100’s KHz.
Fi
g
ure 4-4. Reset timing diagram
Strap Options
SYSRSTI#
SYSRSTO#
14 M Hz
VALID CONFIGURATION
HCLK
PCI_CLK
2.3 ms
ISACLK
1.6 V
MD[63:0]

ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
40/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
4.5.3. SDRAM INTERFACE
Figure 4-5, Table 4-10 lists the AC character istics
of the SDRAM interface.
For correct operation, the programmable read
clock delay (RDCLK) must be activated for the
CRTC and the delay set to the minimum . This is
done by setting the
Latch_CRTC_Data_In
bit in
the SDRAM Controller register 0 and clear the
bits[3:0] in register 1.
The PC133 memory is recommended to reach
100MHz operation.
Figure 4-5. SDRAM Timing Diagram
MCLKI
STPC.output
STPC.input
MCLKx
T
delay
T
setup
T
hold
T
output (mi n)
T
output (max)
T
cycle
T
high
T
low
Table 4-10. SDRAM Bus AC Timing
Name Parameter Min Typ
Max Unit
Tcycle MCLKI Cycle Time 10 ns
Thigh MCLKI High Time 4 ns
Tlow MCLKI Low Time 4 ns
MCLKI Rising Time 1 ns
MCLKI Falling Time 1 ns
Tdela
y
MCLKx to MCLKI dela
y
-0.9 ns
Toutput
MCLKI to Outputs Valid
5.2 7 ns
MCLKI to DQM[ ] Outputs Valid
6.5 8.8 ns
MCLKI to MD[ ] Outputs Valid
6.5 8.8 ns
Tsetup MD[63:0] setup to MCKLI
3.75 4.0 ns
Thold MD[63:0] hold from MCKLI
1.3 2.5 ns
Note: These timing are for a load of 50pF.

ELECTRICAL S PECIFICATIONS
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 41/93
4.5.4. PCI INTERFACE
Table 4-11 lists the AC characteristics of the PCI
interface.
Table 4-11. PCI Bus AC Timing
Name Parameter
Min Typ Max Unit
HCLK to PCICLKO delay (MD[30:27] = 0000) ns
HCLK to PCICLKI delay 2.9 4.3 5.8 ns
PCICLKO Cycle Time 30 ns
PCICLKO High Time ns
PCICLKO Low Time ns
PCICLKI Cycle Time 30 ns
PCICLKI High Time ns
PCICLKI Low Time ns
PCICLKI Rising Time ns
PCICLKI Falling Time ns
PCICLKI to any output
5.9 - 15.8 ns
PCICLKI to PCI_GNT#[2:0]
6.8 - 16.8 ns
Setup to PCICKLI
2.2 - - ns
FRAME# Setup to PCICKLI
2.9 - - ns
PCI_REQ#[2:0] Setup to PCICKLI
7.2 - - ns
Hold from PCICLKI
4.8 - - ns

ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
42/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
4.5.5 IPC INTERFACE
Table 4-12 lists the AC characteristics of the IPC
interface.
Figure 4-6. IPC timing diagram
ISACLK
IRQ_MUX[3:0]
DREQ_MUX[1:0]
ISACLK2X
T
dly
T
setup
T
setup
Table 4-12. IPC Interface AC Timings
Name Parameter Min Max U nit
T
dly
ISACLK2X to ISACLK delay nS
ISACLK2X to DACK_ENC[2:0] valid nS
ISACLK2X to TC valid nS
T
setup
IRQ_MUX[3:0] Input setup to ISACLK2X 0 - nS
T
setup
DREQ_MUX[1:0] Input setup to ISACLK2X 0 - nS

ELECTRICAL S PECIFICATIONS
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 43/93
4.5.6 ISA INTERFACE AC TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
Table 4-7 and Table 4-13 l ist the AC characteris-
tics of the ISA interface.
Figure 4-7 ISA Cycle (ref
Table 4-13
)
Note 1: Stands for SMEMR#, SMEMW#, MEMR#, MEMW#, IOR# & IOW#.
The clock has not been represented as it is dependent on the ISA Slave mode.
Valid AENx
Valid Address
Valid Address, SBHE*
V.Dat
a
VALID DATA
54
28
26
64
59
58
55
28
23
61
48
47
26
23
57
27
24
42
41
10
11
34
33
3
22
56
29
25
9
18
2
12
38
37
15
14
13
12
ALE
AEN
LA [23:17]
SA [19:0]
CONTROL (Note 1)
IOCS16#
MCS16#
IOCHRDY
READ DATA
WRITE DATA
Table 4-13. ISA Bus AC Timing
Name Parameter Min Max Units
2 LA[23:17] valid before ALE# negated 5T Cycles
3 LA[23:17] valid before MEMR#, MEMW# asserted
3a Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave 5T Cycles
3b Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave 5T Cycles
9 SA[19:0] & SBHE valid before ALE# negated 1T Cycles
10 SA[19:0] & SBHE valid before MEMR#, MEMW# asserted
10a Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave 2T Cycles
10b Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave 2T Cycles
10 SA[19:0] & SHBE valid before SMEMR#, SMEMW# asserted
10c Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave 2T Cycle
Note: The signal numbering refers to
Table 4-7

ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
44/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
10d Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave 2T Cycle
10e SA[19:0] & SBHE valid before IOR#, IOW# asserted 2T Cycles
11 ISACLK2X to IOW# valid
11a Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave - 2BCLK 2T Cycles
11b Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave - Standard 3BCLK 2T Cycles
11c Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave - 4BCLK 2T Cycles
11d Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave - 2BCLK 2T Cycles
11e Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave - Standard 3BCLK 2T Cycles
12 ALE# asserted before ALE# negated 1T Cycles
13 ALE# asserted before MEMR#, MEMW# asserted
13a Memory Access to 16-bit ISA Slave 2T Cycles
13b Memory Access to 8-bit ISA Slave 2T Cycles
13 ALE# asserted before SMEMR#, SMEMW# asserted
13c Memory Access to 16-bit ISA Slave 2T Cycles
13d Memory Access to 8-bit ISA Slave 2T Cycles
13e ALE# asserted before IOR#, IOW# asserted 2T Cycles
14 ALE# asserted before AL[23:17]
14a Non comp resse d 15T Cycles
14b Com press ed 15T Cyc les
15 ALE# asserted before MEMR#, MEMW#, SMEMR#, SMEMW# negated
15a Memory Access to 16-bit ISA Slave- 4 BCLK 11T Cycles
15e Memory Access to 8-bit ISA Slave- Standard Cycle 11T Cycles
18a ALE# negated before LA[23:17] invalid (non compressed) 14T Cycles
18a ALE# negated before LA[23:17] invalid (compressed) 14T Cycles
22 MEMR#, MEMW# asserted before LA[23:17]
22a Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave. 13T Cycles
22b Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave. 13T Cycles
23 MEMR#, MEMW# asserted before MEMR#, MEMW# negated
23b Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 9T Cycles
23e Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 9T Cycles
23 SMEMR#, SMEMW# asserted before SMEMR#, SMEMW# negated
23h Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 9T Cycles
23l Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 9T Cycles
23 IOR#, IOW# asserted before IOR#, IOW# negated
23o Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 9T Cycles
23r Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 9T Cycles
24 MEMR#, MEMW# asserted before SA[19:0]
24b Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 10T Cycles
24d Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave - 3BLCK 10T Cycles
24e Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 10T Cycles
24f Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave - 7BCLK 10T Cycles
24 SMEMR#, SMEMW# asserted before SA[19:0]
24h Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 10T Cycles
24i Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave - 4BCLK 10T Cycles
24k Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave - 3BCLK 10T Cycles
24l Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 10T Cycles
Table 4-13. ISA Bus AC Timing
Name Parameter Min Max Units
Note: The si
g
nal numbering refers to
Table 4-7

ELECTRICAL S PECIFICATIONS
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 45/93
24 IOR#, IOW# asserted before SA[19:0]
24o I/O access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 19T Cycles
24r I/O access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 19T Cycles
25 MEMR#, MEMW# asserted before next ALE# asserted
25b Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 10T Cycles
25d Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 10T Cycles
25 SMEMR#, SMEMW# asserted before next ALE# asserted
25e Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave - 2BCLK 10T Cycles
25f Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 10T Cycles
25h Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 10T Cycles
25 IOR#, IOW# asserted before next ALE# asserted
25i I/O access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 10T Cycles
25k I/O access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 10T Cycles
26 MEMR#, MEMW# asserted before next MEMR#, MEMW# asserted
26b Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 12T Cycles
26d Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 12T Cycles
26 SMEMR#, SMEMW# asserted before next SMEMR#, SMEMW# asserted
26f Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 12T Cycles
26h Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 12T Cycles
26 IOR#, IOW# asserted before next IOR#, IOW# asserted
26i I/O access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 12T Cycles
26k I/O access to 8-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 12T Cycles
28 Any command negated to MEMR#, SMEMR#, MEMR#, SMEMW# asserted
28a Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave 3T Cycles
28b Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave 3T Cycles
28 Any command negated to IOR#, IOW# asserted
28c I/O access to ISA Slave 3T Cycles
29a MEMR#, MEMW# negated before next ALE# asserted 1T Cycles
29b SMEMR#, SMEMW# negated before next ALE# asserted 1T Cycles
29c IOR#, IOW# negated before next ALE# asserted 1T Cycles
33 LA[23:17] valid to IOCHRDY negated
33a Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave - 4 BCLK 8T Cycles
33b Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave - 7 BCLK 14T Cycles
34 LA[23:1 7] valid to read data valid
34b Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 8T Cycles
34e Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 14T Cycles
37 ALE# asserted to IOCHRDY# negated
37a Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave - 4 BCLK 6T Cycles
37b Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave - 7 BCLK 12T Cycles
37c I/O access to 16-bit ISA Slave - 4 BCLK 6T Cycles
37d I/O access to 8-bit ISA Slave - 7 BCLK 12T Cycles
38 ALE# asserted to read data valid
38b Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard Cycle 4T Cycles
38e Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave Standard Cycle 10T Cycles
38h I/O access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard Cycle 4T Cycles
38l I/O access to 8-bit ISA Slave Standard Cycle 10T Cycles
Table 4-13. ISA Bus AC Timing
Name Parameter Min Max Units
Note: The signal numbering refers to
Table 4-7

ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
46/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
41 SA[19:0] SBHE valid to IOCHRDY negated
41a Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave 6T Cycles
41b Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave 12T Cycles
41c I/O access to 16-bit ISA Slave 6T Cycles
41d I/O access to 8-bit ISA Slave 12T Cycles
42 SA[19:0] SBHE valid to read data valid
42b Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 4T Cycles
42e Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 10T Cycles
42h I/O access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 4T Cycles
42l I/O access to 8-bit ISA Slave Standard cycle 10T Cycles
47 MEMR#, MEMW#, SMEMR#, SMEMW#, IOR#, IOW# asserted to IOCHRDY negated
47a Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave 2T Cycles
47b Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave 5T Cycles
47c I/O access to 16-bit ISA Slave 2T Cycles
47d I/O access to 8-bit ISA Slave 5T Cycles
48 MEMR#, SMEMR#, IOR# asserted to read data valid
48b Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard Cycle 2T Cycles
48e Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave Standard Cycle 5T Cycles
48h I/O access to 16-bit ISA Slave Standard Cycle 2T Cycles
48l I/O access to 8-bit ISA Slave Standard Cycle 5T Cycles
54 IOCHRDY asserted to read data valid
54a Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave 1T(R)/2T(W) Cycles
54b Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave 1T(R)/2T(W) Cycles
54c I/O access to 16-bit ISA Slave 1T(R)/2T(W) Cycles
54d I/O access to 8-bit ISA Slave 1T(R)/2T(W) Cycles
55a
IOCHRDY asserted to MEMR#, MEMW#, SMEMR#, SMEMW#,
IOR#, IOW# negated
1T Cycles
55b IOCHRY asserted to MEMR#, SMEMR# negated (refresh) 1T Cycles
56 IOCHRDY asserted to next ALE# asserted 2T Cycles
57 IOCHRDY asserted to SA[19:0], SBHE invalid 2T Cycles
58 MEMR#, IOR#, SMEMR# negated to read data invalid 0T Cycles
59 MEMR#, IOR#, SMEMR# negated to data bus float 0T Cycles
61 Write data before MEMW# asserted
61a Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave 2T Cycles
61b
Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave (Byte copy at end of
start)
2T Cycles
61 Write data before SMEMW# asserted
61c Memory access to 16-bit ISA Slave 2T Cycles
61d Memory access to 8-bit ISA Slave 2T Cycles
61 Write Data valid before IOW# asserted
61e I/O access to 16-bit ISA Slave 2T Cycles
61f I/O access to 8-bit ISA Slave 2T Cycles
64a MEMW# negated to write data invalid - 16-bit 1T Cycles
64b MEMW# negated to write data invalid - 8-bit 1T Cycles
64c SMEMW# negated to write data invalid - 16-bit 1T Cycles
64d SMEMW# negated to write data invalid - 8-bit 1T Cycles
Table 4-13. ISA Bus AC Timing
Name Parameter Min Max Units
Note: The si
g
nal numbering refers to
Table 4-7

ELECTRICAL S PECIFICATIONS
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 47/93
64e IOW# negated to write data invalid 1T Cycles
64f
MEMW# negated to copy data float, 8-bit ISA Slave, odd Byte
by ISA Master
1T Cycles
64g
IOW# negated to copy data float, 8-bit ISA Slave, odd Byte by
ISA Master
1T Cycles
Table 4-13. ISA Bus AC Timing
Name Parameter Min Max Units
Note: The signal numbering refers to
Table 4-7

ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
48/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
4.5.7. LOCAL BUS INTERFACE
Figure 4-3 to Figure 4-11 and Table 4-15 li st the
AC characteristics of the Local Bus interface.
Figure 4-8. Synchronous Read Cycle
PA[ ] bus
CSx#
PRD#[1:0]
PD[15:0]
HCLK
T
setup
T
active
T
hold
Figure 4-9. Asynchronous Read Cycle
PA[ ] bus
CSx#
PRD#[1:0]
PD[15:0]
HCLK
T
setup
T
end
T
hold
PRDY

ELECTRICAL S PECIFICATIONS
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 49/93
Figure 4-1 0. S ynchronous Wri t e Cy c le
PA[ ] bus
CSx#
PWR#[1:0]
PD[15:0]
HCLK
T
setup
T
active
T
hold
Figure 4-11. Asynchronous Write Cycle
PA[ ] bus
CSx#
PWR#[1:0]
PD[15:0]
HCLK
T
setup
T
end
T
hold
PRDY

ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
50/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
The Table 4-14 below refers to Vh, Va, Vs which
are the register value for Setup time, A ctive Time
and Hold time, as described in the P rogramming
Manual.
Table 4-14. Local Bus cycle lenght
Cycle T
setup
T
active
T
hold
T
end
Unit
Memory (FCSx#) 4 + Vh 2 + Va 4 + Vs 4 HCLK
Peripheral (IOCSx#) 8 + Vh 3 + Va 4 + Vs 4 HCLK
Table 4-15. Local Bus Interface AC Timing
Name Parameters Min Max Units
HCLK to PA bus - 15 nS
HCLK to PD bus - 15 nS
HCLK to FCS#[1:0] - 15 nS
HCLK to IOCS#[3:0] - 15 nS
HCLK to PWR#[1:0] - 15 nS
HCLK to PRD#[1:0] - 15 nS
PD[15:0] Input setup to HCLK - 4 nS
PD[15:0] Input hold to HCLK 2 - nS
PRDY Input setup to HCLK - 4 nS
PRDY Input hold to HCLK 2 - nS

ELECTRICAL S PECIFICATIONS
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 51/93
4.5.8 VGA INTERFACE
Table 4-16 lists the AC characteristics of the VGA
interface.
Table 4-16. Graphics Adapter (VGA) AC Timing
Name Parameter Min Max Unit
DCLK (input) Cycle Time ns
DCLK (input) High Time ns
DCLK (input) Low Time ns
DCLK (input) Rising Time ns
DCLK (input) Falling Time ns
DCLK (input) to R,G,B valid ns
DCLK (input) to HSYNC valid ns
DCLK (input) to VSYNC valid ns
DCLK (input) to COL_SEL valid ns
DCLK (output) Cycle Time ns
DCLK (output) High Time ns
DCLK (output) Low Time ns
DCLK (output) to R,G,B valid ns
DCLK (output) to HSYNC valid ns
DCLK (output) to VSYNC valid ns
DCLK (output) to COL_SEL valid ns

ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
52/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
4.5.9 VIDEO INPUT PORT
Table 4-17 lists the AC characteristics of the VIP
interface.
Table 4-17. Video Input AC Timings
Name Parameter Min Max Unit
VCLK Cycle Time ns
VCLK High Time ns
VCLK Low Time ns
VCLK Rising Time ns
VCLK Falling Time ns
VIN[7:0] setup to VCLK ns
VIN[7:0] hold from VCLK ns
ODD_EVEN setup to VCLK ns
ODD_EVEN hold from VCLK ns
VCS setup to VCLK ns
VCS hold from VCLK ns

ELECTRICAL S PECIFICATIONS
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 53/93
4.5.10 IDE INTERFACE
Table 4-18 lists the AC characteristics of the IDE
interface.
4.5.11 JTAG INTERFACE
Figure 4-12 and Table 4-17 list the AC
characteristics of the JTAG interface.
Table 4-18. IDE Interface Timing
Name Parameters Min Max Units
DD[15:0] setup to PIOR#/SIOR# falling 15 - ns
DD[15:0} hold to PIOR#/SIOR# falling 0 - ns
Figure 4-12. JTAG timing diagram
Table 4-19. JTAG AC Timings
Name Parameter Min Max Unit
Treset TRST pulse width 1 Tcycle
Tcycle TCLK period 400 ns
TCLK rising time 20 ns
TCLK falling time 20 ns
TCK
STPC.input
TRST
T
reset
T
cycle
STPC.output
TMS,TDI
TDO
T
jset
T
jhld
T
jout
T
psetTphld
T
pout

ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
54/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
Tjset TMS setup time 200 ns
Tjhld TMS hold time 200 ns
Tjset TDI setup time 200 ns
Tjhld TDI hold time 200 ns
Tjout TCLK to TDO valid 30 ns
Tpset STPC pin setup time 30 ns
Tphld STPC pin hold time 30 ns
Tpout TCLK to STPC pin valid 30 ns
Table 4-19. JTAG AC Timings

ELECTRICAL S PECIFICATIONS
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 55/93
4.5.12 INTENSIONNALY BLANK

ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
56/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002

MECHANICAL DATA
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 57/93
5. MECHAN ICAL DAT A
5.1. 388-PIN PACKAGE DIMENSION
The pin numbering for the ST PC 388-pin Plastic
BGA package is shown in Figure 5-1.
Dimensions are shown in Figure 5-2, Table 5-1
and Figure 5-3, Table 5-2.
Figure 5-1. 388-Pin PBGA Package - Top View
A
B
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
W
Y
AA
AB
AC
AD
AE
AF
C
135791113151719212325
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26
A
B
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
W
Y
AA
AB
AC
AD
AE
AF
C
135791113151719212325
2468101214161820222426

MECHANICAL DATA
58/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
Figure 5-2. 388-pin PBGA Package - PCB Dimensions
Table 5-1. 388-pin PBGA Package - PCB Dimensions
Symbols
mm inches
Min Typ Ma x Min Typ Max
A 34.95 35.00 35.05 1.375 1.378 1.380
B 1.22 1.27 1.32 0.048 0.050 0.052
C 0.58 0.63 0.68 0.023 0.025 0.027
D 1.57 1.62 1.67 0.062 0.064 0.066
E 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.006 0.008 0.001
F 0.05 0.10 0.1 5 0.002 0.004 0.006
G 0.75 0.80 0.8 5 0.030 0.032 0.034
A
A
B
Detail
A1 Ball Pad Corner
D
F
E
G
C

MECHANICAL DATA
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 59/93
Figure 5-3. 388-pin PBGA Package - Dimensions
Table 5-2. 388-pin PBGA Package - Dimensions
Symbols
mm inches
Min Typ Ma x Min Typ Max
A 0.50 0.56 0.62 0.020 0.022 0.024
B 1.12 1.17 1.22 0.044 0.046 0.048
C 0.60 0.76 0.92 0.024 0.030 0.036
D 0.52 0.53 0.54 0.020 0.021 0.022
E 0.63 0.78 0.93 0.025 0.031 0.037
F 0.60 0.63 0.6 6 0.024 0.025 0.026
G 30.0 11.8
A
B
C
Solderball
Solderball after collapse
D
E
F
G

MECHANICAL DATA
60/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
5.2. 388-PIN PACKAGE THERMAL DATA
The 388-pin PBGA package has a Power
Dissipation Capab ility of 4.5W . This increas es to
6W when used with a Heatsink.
The structure in shown in Fi
g
ure 5-4.
Thermal dissipation options are illustrated in
Fi
g
ure 5-5 and Figure 5-6.
Figure 5-4. 388-Pin PBGA structure
Thermal balls
Power & Ground layersSignal layers
Figure 5-5. Thermal Dissipation Without Heatsink
Ambient
Board
Case
Junction
Board
Ambient
Ambient
Case
Junction
Board
Rca
Rjc
Rjb
Rba
66
1258.5
Rja = 13 °C/W
Airflow = 0
Board dimensions:
The PBGA is centred on board
Copper thickness:
- 17µm for internal layers
- 34µm for external layers
- 10.2 cm x 12.7 cm
- 4 layers (2 for signals, 1 GND, 1VCC)
There are no other devices
1 via pad per ground ball (8-mil wire)
40% copper on signal layers
Board temperature taken at the centrecentre b
a

MECHANICAL DATA
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 61/93
Figure 5-6. Thermal Dissipation With Heatsink
Board
Ambient
Case
Junction
Board
Ambient
Ambient
Case
Junction
Board
Rca
Rjc
Rjb
Rba
36
508.5
Rja = 9.5 °C/W
Airflow = 0
Board dimensions:
The PBGA is centred on board
Copper thickness:
- 17µm for internal layers
- 34µm for external layers
- 10.2 cm x 12.7 cm
- 4 layers (2 for signals, 1 GND, 1VCC)
There are no other devices
Heat sink is 11.1°C/W
1 via pad per ground ball (8-mil wire)
40% copper on signal layers
Board temperature taken at the centre balls

MECHANICAL DATA
62/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
5.3. SOLDERING RECOMMENDATIONS
High quality, low defect soldering requires
identifying the
optimum temperature profile
for
reflowing the solder paste, therefore optimizing
the process. The heating and cooling rise rates
must be compatible with the solder paste and
components. A typical profile consists of a
preheat, dryout, reflow and cooling sections.
The most critical parameter in the
preheat
section
is to minimize the rate of temperature rise
to less than 2°C / second, in order to minimize
thermal shock on the semi-conductor
components.
Dryout section
is used primarily to ensure that
the solder paste is fully dried b efore hitting reflow
temperatures.
Solder reflow is accomplished in the
reflow zone
,
where the solder paste is elevated to a
temperature greater than the melting point of the
solder. Melting temperature must be exceeded by
approximately 20°C to ensure quality reflow.
In reality the profile is not a line, but rather
a range
of temperatures
all solder joints must be
exposed. The total temperature deviation from
component thermal mism atch, oven loading and
oven uniformity must be within the band.
Figure 5-7. Reflow soldering temperature rang e
Temperature ( °C )
Time ( s )
PREHEAT DRYOUT REFLOW COOLING
240
0
250
200
150
100
50
0

DESIGN GUIDELINES
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 63/93
6. DESIGN GUIDELINES
6.1. TYPICAL APPLICATIONS
The STPC Consumer-II is well suited for many
applications. Some of the possible
implementations are described below.
6.1.1. WEB BOX
A web box is an analog set top box providing
internet browsing capa bility to a TV s et. It has a
TV output for connecting to the TV set, a modem
for internet connection, a s martcard interface for
the ISP access control, an d an infrared interface
for the remote control or the keyboard.
Figure 6-1. Web Box
STPC
TV OUTPUT
CONSUMER-II
SDRAM
64
FLASH
MODEM
AUDIO
16
PCI
IDE / PCI
SmartCard
R,G,B, CSYNC
S-VHS
CVBS
VIP
STV2310
SCART 1
SCART 2
microphone
Infrared
Printer port
Local Bus
ISA Bus
or
glue logic

DESIGN GUIDELINES
64/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
6.2. STPC CONFIGURATION
The STPC is a very flexible product thanks to
decoupled clock domains and to strap options
enabling a user-optimized configuration.
As some trade off are often necessary, it is
important to do an analysis of the application
needs prior to design a system based on this
product. The applicative constraints are usually
the following:
- CPU performance
- graphics / video performances
- power consumption
- PCI bandwidth
- booting time
- EMC
Some other elements can help to tune the choice:
- Code size of CPU Consuming tasks
- Data size and location
On the STPC side, the configurable parameters
are the following:
- synchronous / asynchronous mode
- HCLK speed
- MCLK speed
- CPU clock ratio (x1, x2)
- Local Bus / ISA bus
6.2.1. LOCAL BUS / ISA BUS
The selection b etwe en the ISA b us and the Local
Bus is relatively simple. The first one is a standard
bus but slow. The Local Bus is fast and
programmable but doesn't su pport any DMA nor
external master mechanisms. The Table 6-1
below summarize the selection:
Before implementing a function requiring DMA
capability on the ISA bus, it is recommended to
check if it exists on PCI, or if it can be
implemented differently, in order to use the local
bus mode.
6.2.2. CLOCK CONFIGURATION
The CPU clock and the memory clock are
independent unless the "synchronous mode"
strap option is set (see the STRAP OPTIONS
chapter). The potential clock configurations are
then relatively limited as listed in Table 6-2.
The advantage of the synchronous mode
compared to the asynchronous mode is a lower
latency when accessing SDRAM from the CPU or
the PCI (saves 4 MCLK cycles for the first access
of the burst). For the same CPU to Memory
transfer performance, MCLK as to be roughly
higher by 20MHz between SYNC and ASYNC
modes (example: 66MHz SYNC = 96MHz
ASYNC).
In all cases, use SDRAM with CAS Latency
equals to 2 (CL2) for the best performances.
The advantage of the asynch ronous mode is the
capability to reprogram the MCLK speed on the
fly. This could help for applications were power
consumption must be optimized.
Regarding PCI bandwidth, the best is to have
HCLK at 100MHz as it gives twice the bandwidth
compared to HCLK at 66MHz.
The last, and more complex, information to
consider is the behaviour of the software. In case
high CPU or FPU computation is needed, it is
sometime better to be in DX2-133/MCLK=66
synchronous mode than DX2-133/MCLK=100
asynchronous mode. This depend s on the locality
of the number crunching code and the amount of
data manipulated.
The Table 6-3 belo w gives some examples. The
right column correspond to the configuration
number as described in Table 6-2:
Obviously, the values for HCLK or MCLK can be
reduced compared to Table 6-2 in case there is no
need to push the device at its limits, or when
avoiding to use specific frequency ranges (FM
radio band for example).
Table 6-1. Bus mode selection
Need Selection
Legacy I/O device (Floppy, ...), Super I/O ISA Bus
DMA capability (Soundblaster) ISA Bus
Flash, SRAM, basic I/O device Local Bus
Fast boot Local Bus
Boot flash of 4MB or more Local Bus
Programmable Chip Select Local Bus
Table 6-2. Main STPC modes
CMode
HCLK
MHz
CPU clock
clock ratio
MCLK
MHz
1 Synchronous 66 133 (x2) 66
2 Asynchronous 66 133 (x2) 100
3 Synchronous 100 100 (x1) 100
Table 6-3. Clock mode selection
Constraints C
Need CPU power
Critical code fits into L1 cache
1
Need CPU power
Code or data does not fit into L1 cache
3
Need high PCI bandwitdh 3
Need flexible SDRAM speed 2

DESIGN GUIDELINES
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 65/93
6.3. ARCHITECTURE RECOMMENDATIONS
This section describes the recommend
implementations for the STPC interfaces. For
more details, download the
Reference
Schematics
from the STPC web site.
6.3.1. POWER DECOUPLING
An appropriate decoupling of the various STPC
power pins is mandatory for optimum behaviou r.
When insufficient, the integrity of the signals is
deteriorated, the stability of the system is reduced
and EMC is increased.
6.3.1.1. PLL decoupling
This is the most important as the STPC clocks are
generated from a single 14MHz stage using
multiple PLLs which are highly sensitive analog
cells. The frequenc ies to filter are the 25-50 KHz
range which correspond to the internal loop
bandwidth of the PLL and the 10 to 100 MHz
frequency of the output. PLL power pins can be
tied together to simplify the board layout.
6.3.1.2. Decoupling of 3.3V and Vcore
A power plane for each of these supplies with one
decoupling capacitance for each power pin is the
minimum. The use of multiple capacitances with
values in decade is the bes t (for example: 10pF,
1nF, 100nF, 10uF), the smallest value, the closest
to the power pin. Connecting the various digital
power planes through capacitances will reduce
furthermore the overall impedance and electrical
noise.
6.3.2. 14MHZ OSCILLATOR STAGE
The 14.31818 MHz oscillator stage can be
implemented using a quartz, which is the
preferred and cheaper solution, or using an
external 3.3V oscillator.
The crystal must be used in its series-cut
fundamental mode and n ot in overtone mode. It
must have an Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR,
sometimes referred to as Rm) of less than 50
Ohms (typically 8 Ohms) and a shunt capacitance
(Co) of less than 7 pF. The ba lance capa citors of
16 pF must be added, one connected to each pin,
as described in Figure 6-3.
In the event of an ext ernal o scillat or pr ovidin g the
master clock signal to the STPC Atlas device, t he
LVTTL signal should be connected to XTALI, as
described in Figure 6-3.
As this clock is the reference for all the other onchip generated clocks, it is
strongly
recommended to shield this stage
, including
the 2 wires going to the STPC balls, in order to
reduce the jitter to the minimum and reach the
optimum system stability.
Figure 6-2. PLL decoup ling
VDD_PLL
VSS_PLL
PWR
100nF 47uF
GND
Connections must be as short as poss i bl e
Figure 6-3. 14.31818 MHz stage
15pF15pF
XTALOXTALI XTALOXTALI
3.3V

DESIGN GUIDELINES
66/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
6.3.3. SDRAM
The STPC provides all the signals for SDRAM
control. Up to 128 MBytes of main memory are
supported. All Banks must be 64 bits wide. Up to 4
memory banks are available when using 16Mbit
devices. Only up to 2 banks can be connected
when using 64Mbit and 128Mbit c omponents due
to the reallocation of CS2# and CS3# signals. This
is described in Table 6-4 and Table 6-5.
Graphics memory resides at the beginning of
Bank 0. Host memory begins at the top of graphics
memory and extends to the top of populated
SDRAM. Bank 0 must always be populated.
Fi
g
ure 6-4, Figure 6-5 and Figure 6-6 show some
typical implementations.
The purpose of the serial resistors is to reduce
signal oscillation and EMI by filtering line
reflections. The capacitance in Fi
g
ure 6-4 has a
filtering effect too, while it is used for propagat ion
delay compensation in the 2 other figures.
Figure 6-4. One Memory Bank with 4 Chips (16-bit)
CS0#
BA[1:0]
MA[12:0]
WE#
RAS0#
DQM[7:0]
MCLKI
MCLKO
DQM[7:6]
Reference Knot
CAS0#
MD[63:48]
DQM[5:4]
MD[47:32]
DQM[3:2]
MD[31:16]
DQM[1:0]
MD[15:0]
MD[63:0]
MCLKA
MCLKBMCLKCMCLKD
10pF
Length(MCLKI) = Length(MCLKy) with y = {A,B,C,D}

DESIGN GUIDELINES
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 67/93
Figure 6-5. One Memory Banks with 8 Chips (8-bit)
Figure 6-6. Two Memory Banks with 8 Chips (8-bit)
CS0#
BA[1:0]
MA[12:0]
WE#
RAS0#
DQM[7:0]
MCLKI
MCLKO
DQM[7]
CAS0#
MD[63:56]
DQM[0]
MD[7:0]
MD[63:0]
A
10pF Length(MCLKI) = Length(MCLKy) with y = {A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H}
DQM[1]
MD[15:8]
BCDEFG
H
CY2305
CS1#
BA[1:0]
MA[12:0]
WE#
RAS0#
DQM[7:0]
MCLKI
MCLKO
DQM[7]
CAS0#
MD[63:56]
DQM[0]
MD[7:0]
MD[63:0]
A
1
22pF
Length(MCLKI) = Length(MCLKy
x
) with
DQM[1]
MD[15:8]
B
1
C
1
D
1
E
1
F
1
G
1
H
1
CS0#
A
0
B
0
C
0
D
0
E
0
F
0
G
0
H
0
x = {0,1}
y = {A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H}
CY2305

DESIGN GUIDELINES
68/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
For other implementations like 32-bit SDRAM
devices, refers to the SDRAM controller signal
multiplexing and address mapping described in
the following Table 6-4 and Table 6-5.
6.3.4. PCI BUS
The PCI bus is always active and the following
control signals must be pulled-up to 3.3V or 5V
through 2K2 resistors even if this bus is not
connected to an external device: FRAME#,
TRDY#, IRDY#, STOP#, DEVSEL#, LOCK#,
SERR#, PCI_REQ#[2:0].
PCI_CLKO must be connected to PCI_CLKI
through a 10 to 33 Ohms resistor. Fi
g
ure 6-7
shows a typical implementation.
For more information on layout constraints, go to
the
place and route recommendations
section.
Table 6-4 . DIM M Pi no ut
SDRAM Density 16 Mbit 64/128 Mbit 64/128 Mbit
STPC I/F
Internal Banks 2 Banks 2 Banks 4 Banks
DIMM Pin Number
... MA[10:0] MA[10:0] MA[10:0] MA[10:0]
123 - MA11 MA11 CS2# (MA11)
126 - MA12 - CS3# (MA12)
39 - - BA1 (MA1 2) CS3 # (BA1)
122 BA0 (MA11) BA0 (MA13) BA0 (MA13) BA0
Table 6-5. Address Mapping
Address Mapping: 16 Mbit - 2 internal banks
STPC I/F BA0 MA10 MA9 MA8 MA7 MA6 MA5 MA4 MA3 MA2 MA1 MA0
RAS Address A11 A22 A21 A2 A19 A18 A17 A16 A15 A14 A13 A12
CAS Address A11 0 A24 A23 A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3
Address Mapping: 64/128 Mbit - 2 internal banks
STPC I/F BA0 MA12 MA11 MA10 MA9 MA8 MA7 MA6 MA5 MA4 MA3 MA2 MA1 MA0
RAS Address A11 A24 A23 A22 A21 A20 A19 A18 A17 A16 A15 A14 A13 A12
CAS AddressA110 0 0 A26A25A10A9A8A7A6A5A4A3
Address Mapping: 64/128 Mbit - 4 internal banks
STPC I/F BA0 BA1 MA11 MA10 MA9 MA8 MA7 MA6 MA5 MA4 MA3 MA2 MA1 MA0
RAS Address A11 A12 A24 A23 A22 A21 A20 A19 A18 A17 A16 A15 A14 A13
CAS Address A11 A12 0 0 A26 A25 A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3
Figure 6-7. Typ ic a l PC I cl ock routing
PCICLKI
PCICLKO
PCICLKA
PCICLKB
PCICLKC
0 - 22
10 - 33
Device A
Device B
Device C
0 - 33pF

DESIGN GUIDELINES
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 69/93
In the case of higher clock load it is recommended
to use a zero-delay clock buf fer as described in
Figure 6 -8. This approach is also recommended
when implementing the delay on PCICLKI
according to the PCI section of the
Electrical
Specifications
chapter.
Figure 6-8. PCI clock routing with zero-delay clock buffer
PCICLKI
PCICLKO
Device A
Device B
Device C
PLL
Device D
PCICLKI
PCICLKO
Device A
Device B
Device C
PLL
Device D
CY2305CY2305
Implementation 1 Implementation 2

DESIGN GUIDELINES
70/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
6.3.5. LOCAL BUS
The local bus has all the signals to conn ect flash
devices or I/O devices with the minimum glue
logic.
Fi
g
ure 6-9 describes how to connect a 16-bit boot
flash (the correspondin
g
strap options must be set
accordin
g
ly).
Figure 6-9. Typical 16-bit boot flash implementation
M58LW064A
STPC
22
DQ[15:0]
A[22:1]
CE
OE
W
RP
B
CLK
RB
LE
R
3V3
GND
RESET#
16
PD[15:0]
FCS0#
PWR0#
SYSRSTI#
PRD0#
PA[22:1]
PRD1#
PWR1#

DESIGN GUIDELINES
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 71/93
6.3.6. IPC
Most of the IPC signals are multiplexed: Interrupt
inputs, DMA Request i nputs, DMA Acknowledge
outputs. The figure below describes a complete
implementation of the IRQ[15:0] time-multiplexing.
When an interrupt line is used internally, the
corresponding input can be grounded. In most of
the embedded des igns, only few i nterrupts lines
are necessary and the glue logic can be simplified.
When the interface is integrated into the STPC,
the corresponding interrupt line can be groun ded
as it is connected internally.
For example, if the integrated IDE controller is
activated, the IRQ[14] and IRQ[ 15] inputs can be
grounded.
Figure 6-10. Typical IRQ multiplexing
74x153
1C0
1Y
1G
IRQ[0]
IRQ_MUX[0]
1C1
1C2
1C3
2C0
2C1
2C2
2C3
A
B
2G
2Y IRQ_MUX[1]
IRQ[1]
IRQ[2]
IRQ[3]
IRQ[4]
IRQ[5]
IRQ[6]
IRQ[7]
74x153
1C0
1Y
1G
IRQ_MUX[2]
1C1
1C2
1C3
2C0
2C1
2C2
2C3
A
B
2G
2Y IRQ_MUX[3]
IRQ[8]
IRQ[9]
IRQ[10]
IRQ[11]
IRQ[12]
IRQ[13]
IRQ[14]
IRQ[15]
ISA_CLK2X
ISA_CLK
Timer 0
Keyboard
Slave PIC
COM2/COM4
COM1/COM3
LPT2
LPT1
RTC
Mouse
FPU
PCI / IDE
PCI / IDE
Floppy
Floppy

DESIGN GUIDELINES
72/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
The figure below describes a complete
implementation of the external glue logic for DMA
Request time-multiplexing and DMA Acknowledge
demultiplexing. Like for the interrupt lines, this
logic can be simplified when only few DMA
channels are used in the application.
This glue logic is not needed in Local bus mode as
it does not support DMA transfers.
Figure 6-11. Typical DMA multiplexing and demultiplexing
74x153
1C0
1Y
1G
DRQ[0]
DREQ_MUX[0]
1C1
1C2
1C3
2C0
2C1
2C2
2C3
A
B
2G
2Y DREQ_MUX[1]
DRQ[1]
DRQ[2]
DRQ[3]
DRQ[4]
DRQ[5]
DRQ[6]
DRQ[7]
74x138
Y0#
A
G2B
DACK0#
Y1#
Y2#
Y3#
Y4#
Y5#
Y6#
Y7#
C
B
G2A
ISA_CLK2X
ISA_CLK
ISA, Refresh
ISA, PIO
ISA, FDC
ISA, PIO
Slave DMAC
ISA
ISA
ISA
G1
DMA_ENC[0]
DMA_ENC[1]
DMA_ENC[2]
DACK1#
DACK2#
DACK3#
DACK5#
DACK6#
DACK7#

DESIGN GUIDELINES
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 73/93
6.3.7. IDE / ISA DYNAMIC DEMULTIPLEXING
Some of the ISA bus signals are dynamically
multiplexed to optimize the pin count. Figure 6-12
describes how to implement the external glue
logic to demultiplex the IDE and ISA interfaces. In
Local Bus mode the two buffers are not needed
and the NAND gates can be simplified to inverters.
6.3.8. BASIC AUDIO USING IDE INTERFACE
When the application requires only basic audio
capabilities, an audio DAC on the IDE interface
can avoid using a PCI-based audio device. This
low cost solution is not CPU cons uming t hanks to
the DMA controller implemented in the IDE
controller and can generat e 16-bit stereo sound.
The clock speed is programmable when using the
speaker output.
Figure 6-12. Typical IDE / ISA Demultiplexing
MASTER#
74xx245
RMRTCCS#
A
B
DIR
OE
ISAOE#
KBCS#
RTCRW#
RTCDS
SA[19:8]
STPC bus / DD[15:0]
LA[24]
LA[25]
LA[22]
LA[23]
SCS1#
SCS3#
PCS1#
PCS3#
Figure 6-13. Basic audio on IDE
74xx74
16
Q
Q
DD[15:0]
D
PR
RST
D[15:0]
CS#PCS1
WR#
A/B
Audio Out
Right
Left
Stereo DAC
PDRQ
SYSRSTO#
Speaker
PDIOW#
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
STPC
Q
QD
PR
RST
Note * : the inverter can be removed when the DAC CS# is directly connected to GND
*

DESIGN GUIDELINES
74/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
6.3.9. VGA INTERFACE
The STPC integrates a voltage reference and
video buffers. The amount of ex ternal devices is
then limited to the minim um as described in the
Fi
g
ure 6-14.
All the resistors and capacitors have to be as
close as possible to the STPC while the circuit
protector DALC112S1 must be close to the V GA
connector.
The DDC[1:0] lines, not represented here, have
also to be protected when they are used on the
VGA connector.
COL_SEL can be used when implementing the
Picture-In-Picture function outside the STPC, for
example when multiplexing an analog video
source. In that case, the CRTC of the STPC has to
be genlocked to this analog source.
DCLK is usually used by the TFT display which
has RGB inputs in order to synchronise the picture
at the level of the pixel.
When the VGA interface is not needed, the signals
R, G, B, HSYNC, VSYNC, COMP, RSET can be
left unconnected, VSS_DAC and VDD_DAC must
then be connected to GND.
Figure 6-14. Typical VGA implementation
143
VDD_DAC
COMP
VREF_DAC
RSET
VSS_DAC
2.5V
10nF
100nF 47uF
AGND
COL_SEL
DCLK
HSYNC
VSYNC
R
G
B
75 1%
DALC112S1
AGND3.3V
100nF
1%

DESIGN GUIDELINES
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 75/93
6.3.10. TV INTERFACE
The STPC integrates a voltage reference and
video DACs. The amount of external devices is
then limited to video buffers as described in the
Figure 6-15.
The connection from IREFx and VREF x up to the
20 ohms resistors must be as s hort as possible.
The constraint is the same for the connection from
VDDA_TV and VSSA_TV up to the decoupling
capacitances.
The resistors and capacitors of the amplifier stage
have to be as close as possible to the video buffer.
When the TV interface is not needed, the signals
RED, GREEN, BLUE, CVBS, IREF1, IREF2 can
be left unconnected, VDDA_TV must then be
connected to GND.
R,G,B,CVBS outputs:
. Iout
max
= 80.704 / R
ref
< 5mA
. R
load
= 274 ohms
. Vout = {10-bit code} x R
load
x 0.079 / R
ref
Fine tuning of the maximum output level must be
done using the gain control registers 0x11 to 0x13
of the integrated Digital Enco der (write the value
0x0B for a gain of 109%).
Figure 6-15. Typical VGA implementation
20 1%
IREF1
VREF1
IREF2
VREF2
VDDA_TV
2.5V
10nF
100nF 22uF
DCLK
CVBS
RED
GREEN
BLUE
316 1%
27MHz
47pF
FBEAD
VSSA_TV
AGND
AGND
AGND
33
GND
3.3V
FBEAD
100nF
GND
same
as for
RED
AGND
15uH
AGND
AGND
AGND
526
1%
326
1%
478 1%
10
1%
AGND
VCCA
To the connector
75 1%
TSH74
5V
100nF 22uF
FBEAD
AGND
FBEAD
GND
VCCA
GND
R
ref
= 20K 1%

DESIGN GUIDELINES
76/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
6.3.11. JTAG INTERFACE
The STPC integrat es a JTAG i nterface for scanchain and on-board testing. The only external
device needed are the pull up resistors. Fi
g
ure 616 describes a typical implementation using these
devices.
Figure 6-16. Typical JTAG implementation
STPC
TCLK
TDO
3V3
Connector
910
12
6
7
34
8
5
TMS
TDI
TRST
3V3 3V3 3V3

DESIGN GUIDELINES
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 77/93
6.4. PLACE AND ROUTE
RECOMMENDATIONS
6.4.1. GENERAL RECOMMENDATIONS
Some STPC Interfaces run at high speed and
need to be carefully routed or even shielded like:
1) Memor y I n t e rface
2) PCI bus
3) Graphics and video interfaces
4) 14 MHz oscillator stage
All clock signals have to be routed first and
shielded for speeds of 27MHz or higher. The h igh
speed signals follow the same constraints, as for
the memory and PCI control signals.
The next interfaces to be routed are Memory, PCI,
and Video/graphics.
All the analog noise-sensitive signals ha ve to be
routed in a separate area and hence can be
routed indepedently.
6.4.2. PLL DEFINITION AND IMPLIMENTATION
PLLs are analog cells which supply the internal
STPC Clocks. To get the cleanest clock, the jitter
on the power supply must be reduced as much as
possible. This will result in a more stable system.
Each of the integrated PLL has a dedicated power
pin so a single power plane for all of these PLLs,
or one wire for each, or any solution in between
which help the layout of the board can be used.
Powering these pins with one Ferrite +
capacitances is enough. We recommend at least
2 capacitances: one 'big' (few uF) for power
storage, and one or 2 smalls (100nF + 1nF) for
noise filtering.
Figure 6-17. Shielding signals
ground ring
ground pad
shielded signal line
ground pad
shielded signal lines

DESIGN GUIDELINES
78/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
6.4.3. MEMORY INTERFACE
6.4.3.1. Introduction
In order to achieve SDRAM memory interfaces
which work at clock frequencies of 100 MHz and
above, careful consideration has to be given to the
timing of the interface with all the various electrical
and physical constraints taken i nto consideration.
The guidelines described below are related to
SDRAM components on DIMM modules. For
applications where the memories are directly
soldered to the motherboard, the PCB should be
laid out such that the trace lengths fit within the
constraints shown here. The traces could be
slightly shorter since the extra routing on the
DIMM PCB is no longer present but it is then up to
the user to verify the timings.
6.4.3.2. SDRAM Clocking Scheme
The SDRAM Clocking Scheme deserves a special
mention here. Basically the memory clock is
generated on-chip through a PLL and goes
directly to the MCLKO output pin of the STPC. The
nominal frequency is 100 MHz. Because of the
high load presented to th e M CLK on t he b oard by
the DIMMs it is recommended to rebuffer the
MCLKO signal on the board and balance the skew
to the clock ports of the different DIMMs and the
MCLKI input pin of STPC.
6.4.3.3. Board Layout Issues
The physical layout of the motherboard PCB
assumed in this presentation is as shown in Figure
6-19. Because all of the memory interface sign al
balls are located in the same region of the STPC
device, it is possible to orientate the device to
reduce the trace lengths. The worst case routing
length to the DIMM1 is estimated to be 100 mm.
Solid power and ground planes are a must in order
to provide good return paths for the signals and to
reduce EMI and noise. Also there should be ample
high frequency decoupling between the power
and ground planes to provide a low impedance
path between the planes for the return paths for
signal routings which change layers. If possible,
the traces should be routed adjacent to the s ame
power or ground plane for the length of the trace.
For the SDRAM interface, the most critical signal
is the clock. Any skew between the clocks at the
SDRAM components and the memory controller
will impact the timing budget . In order to get well
matched clocks at all components it is
recommended that all the DIMM clock pins, STPC
Figure 6-18. Clock Scheme
DIMM1
MCLKI
MCLKO
DIMM2
PLL
register
PLL
MA[ ] + Control
MD[63:0]
SDRAM
CONTROLLER

DESIGN GUIDELINES
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 79/93
memory clock input (MCLKI) and any other
component using the memory clock are
individually driven from a low skew clock driver
with matched routing leng ths. In other words, all
clock line lengths that go from the buffer to the
memory chips (MCLKx) and from the buffer to the
STPC (MCLKI) must be identical.
This is show n in F igure 6-20.
The maximum skew betwe en pins for this part is
250ps. The important factors for the clock buffer
are a consistent drive strength and low skew
between the outputs. The delay through the buffer
is not important so it does not have to be a zero
delay PLL type buffer. The trace lengths from t he
clock driver to the DIMM CKn pins should be
matched exactly. Since the propagation speed
can vary between PCB layers, the clocks should
be routed in a consistent way. The routing to the
STPC memory input should be longer by 75 mm to
compensate for the extra clock routing on the
DIMM. Also a 20 pF capacitor should be placed as
near as possible to the clock input of the STPC t o
compensate for the DIMM’s higher clock load. The
impedance of the t race used for the cl ock routing
should be matched to the DIMM clock trace
impedance (60-75 ohms)
.
To minimise crosstalk
the clocks should be routed with spacing to
adjacent tracks of at least twice the clock trace
width. For designs which use SDRAMs directly
mounted on the motherboard PCB all the clock
trace lengths should be matched exactly.
Figure 6-19. DIMM placement
DIMM2
DIMM1
STPC
35mm
35mm
15mm
10mm
116mm
SDRAM I/F
Figure 6-20. Clock Routing
MCLKO
DIMM CKn input
STPC MCLKI
DIMM CKn input
DIMM CKn input
Low skew clock driver:
L
L+75mm*
20pF
* No additional 75mm when SDRAM directly soldered on board

DESIGN GUIDELINES
80/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
The DIMM sockets shoul d be populated starting
with the furthest DIMM from the STPC device first
(DIMM1). There are two types of DIMM devices;
single-row and dual-row. The dual-row devices
require two chip select signals to select between
the two rows. A STPC device with 4 chip select
control lines could control either 4 single-row
DIMMs or 2 dual-row DIMMs. When only 2 chip
select control lines are activated, only t wo singlerow DIMMs or one dual-row DIMM can be
controlled.
When using DIM M modules, schematics h ave to
be done carefully in order to avoid data buses
completely crossing on the boa rd. This has to be
checked at the library level. In order to achieve the
layout shown in Fi
g
ure 6-21, schematics have t o
implement the crossing desc ribed in Fi
g
ure 6-22.
The DQM signals must be ex changed using the
same order.
6.4.3.4. Summary
For unbuffered DIMMs the address/control signals
will be the m o s t cr iti ca l for ti ming. The simulations
show that for these signals the best way to drive
them is to use a parallel termination. For
applications where speed is not so critical series
termination can be used as this will save power.
Using a low impedance such as 50Ω for these
critical traces is recomm ended as it b oth reduces
the delay and the overshoot.
The other memory interface signals will typically
be not as critical as the address/control signals.
Using lower impedance traces is also beneficial
for the other signals but if their timing is not as
critical as the address/control signal s they could
use the default value. Usin g a lower impedance
implies using wider traces which may have an
impact on the routing of the board.
The layout of this interface can be validated by an
electrical simulation using the IBIS model
available on the STPC web site.
Figure 6-21. Optimum Data Bus Layout for DIMM
Figure 6-22. Schematics for Optimum Data Bus Layout for DIMM
DIMM
STPC
SDRAM I/F
D[15:00] D[31:16]
D[47:32] D[63:48]
MD[31:00]
MD[63:32]
MD[15:00],DQM[1:0]
MD[31:16],DQM[3:2]
MD[47:32],DQM[5:4]
MD[63:48],DQM[7:6]
D[15:00],DQM[1:0]
D[31:16],DQM[3:2]
D[47:32],DQM[5:4]
D[63:48],DQM[7:6]
DIMMSTPC

DESIGN GUIDELINES
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 81/93
6.4.4. PCI INTERFACE
6.4.4.1. Introduction
In order to achieve a PCI interface which work at
clock frequencies up to 33MHz, careful
consideration has to be given to the timing of the
interface with all the various electrical and
physical constraints taken into consideration.
6.4.4.2. PCI Clocking Scheme
The PCI Clocking Scheme deserves a special
mention here. Basically the PCI clock (PCICLKO)
is generated on-chip from HCLK through a
programmable delay line and a clock divider. The
nominal frequency is 33MHz. This clock must be
looped to PCICLKI and goes t o the internal S outh
Bridge through a des kewer. On the contrary, the
internal North Bridge is clocked by HCLK, putting
some additionnal constraints on T
0
and T1.
Figure 6-23. Clock Scheme
HCLK PLL
1/2
1/3
1/4
clock
Strap Options
PCICLKO
T
1
PCICLKI
HCLK
AD[31:0]
South
North
Deskewer
MUX
T
0
T
2
delay
STPC
MD[30:27] MD[17,4]
MD[7:6]
Bridge
Bridge

DESIGN GUIDELINES
82/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
6.4.4.3. Board Layout Issues
The physical layout of the motherboard PCB
assumed in this presentation is as shown in Figure
6-24. For the PCI interface, the most critical signal
is the clock. Any skew between the clocks at the
PCI components and the STPC will impact the
timing budget. In order to get well matched clocks
at all components it is recommended that all the
PCI clocks are individually driven from a serial
resistance with matched routing lengths. In other
words, all clock line lengths that go from the
resistor to the PCI chips (PCICLKx) must be
identical.
The figure below is for PCI devices soldered onboard. In the case o f a PCI slot, the wire length
must be shortened by 2.5" to compensate the
clock layout on the PCI board. The maximum
clock skew between all devices is 2ns according
to PCI specifications.
The Fi
g
ure 6-25 describes a typical clock delay
implementation. The e xact timing constraints are
listed in the PCI section of the
Electrical
Specifications
Chapter.
Figure 6-24. Typical PCI clock rou tin g
Length(PCICLKI) = Length(PCICLKx) with x = {A,B,C}
Note: The value of 22 Ohm s corresponds to tracks with Z0 = 70 Ohms.
PCICLKI
PCICLKO
PCICLKA
PCICLKB
PCICLKC
Device A
Device B
Device C
Figure 6-25. Clocks relationships
PCICLKO
PCICLKI
HCLK
PCICLKx

DESIGN GUIDELINES
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 83/93
6.4.5. THERMAL DISSIPATIO N
6.4.5.1. Power saving
Thermal dissipation of the STPC depends mainly
on supply voltage. When the system does not
need to work at the upper voltage limit, it may
therefore be beneficial to reduce the voltage to the
lower voltage limit, where possible. This could
save a few 100’s of mW.
The second area to look at is unused interfaces
and functions. Depending on the application,
some input signals can be grounded, and some
blocks not powered or shutdown. Clock speed
dynamic adjustment is also a solution t hat can be
used along with the integrated power
management unit.
6.4.5.2. Thermal balls
The standard way to route thermal balls to ground
layer implements only one via pad for each ball
pad, connected using a 8-mil wire.
With such configuration the P lastic BG A package
does 90% of the t hermal dissipation through the
ground balls, and especially the central thermal
balls which are directly connected to the die. The
remaining 10% is dissipated through the case.
Adding a heat sink reduces this value to 85%.
As a result, some basic rules must be followed
when routing the STPC in order to avoid thermal
problems.
As the whole ground layer acts as a heat sink, the
ground balls must be directly connec ted to it, as
illustrated in Figure 6-26. If one ground layer is not
enough, a second ground plane may be added.
When possible, it is important to avoid other
devices on-board using the PCB for heat
dissipation, like linear regulators, as this would
heat the STPC itself and reduce the temperature
range of the whole system, In case these devices
can not use a separate heat sink, they must not be
located just near the STPC
Figure 6-26. G rou nd routing
Pad for ground ball
Thru hole to ground layer
T
o
p
L
a
y
e
r
:
S
i
g
n
a
l
s
P
o
w
e
r
l
a
y
e
r
I
n
t
e
r
n
a
l
l
a
y
e
r
:
s
i
g
n
a
l
s
B
o
t
t
o
m
L
a
y
e
r
:
g
r
o
u
n
d
l
a
y
e
r
Note: For better visibility, ground balls are not all routed.

DESIGN GUIDELINES
84/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
When considering thermal dissipat ion, one of the
most important parts of the layout is the
connection between the ground balls and the
ground layer.
A 1-wire connection is shown in Fi
g
ure 6-27. Th e
use of a 8-mil wire results in a thermal resistance
of 105°C/W assuming copper is used (418 W/
m.°K). This high value is due to the thickness (34
µm) of the copper on the external side of the PCB.
Considering only the central matrix of 36 thermal
balls and one via for each ball, the global thermal
resistance is 2.9°C/W. This can be easily
improved using four 12.5 mil wires to connect to
the four vias around the ground pad link as in
Fi
g
ure 6-28. This gives a total of 49 vias and a
global resistance for the 36 thermal balls of 0.5°C/
W.
The use of a ground plane l ike in Fi
g
ure 6-29 is
even better.
Figure 6-27. R ecom m ended 1-wi re Po wer/Ground P ad Layout
Solder Mask (4 mil)
Pad for ground ball (diameter = 25 mil)
Hole to ground layer (diameter = 12 mil)
Connection Wire (width = 12.5 mil)
Via (diameter = 24 mil)
34.5
mil
1 mil = 0.0254 mm
Figure 6-28. Re commended 4 -wi re Gr ound Pad Layout
4 via pads for each ground ball

DESIGN GUIDELINES
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 85/93
To avoid solder wicking over to t he via pads during
soldering, it is important to have a solder mask of
4 mil around the pad (NSMD pad). This gives a
diameter of 33 mil for a 25 mil ground pad.
To obtain the optimum ground layout, place the
vias directly under the ball pads. In th is case no
local board distortion is tolerated.
6.4.5.3. Heat dissipation
The thickness of the copper on PCB layers is
typically 34 µm for external layers and 17 µm for
internal layers. This means that thermal
dissipation is not good; high board temperat ures
are concentrated around the devices and these
fall quickly with increased distance.
Where possible, place a metal layer inside the
PCB; this improves dramatically the spread of
heat and hence the thermal dissipation of the
board.
The possibility of using the whole system box for
thermal dissipation is very us eful in cases o f high
internal temperatures and low outside
temperatures. Bottom side of the PBGA should be
thermally connected to the metal cha ssis in order
to propagate the heat flow through the metal.
Thermally connecting also the top side will
improve furthermore the heat d issipation. Figure
6-30 illustrate s su c h a n implement a tio n .
Figure 6-29. O pti m um Layout for Centr al Gro und Ball - top laye r
Via to Ground layer
Pad for ground ball
Clearance = 6mil
diameter = 25 mil
hole diameter = 14 mil
Solder mask
diameter = 33 mil
External diameter = 37 mil
connections = 10 mil
Figure 6-30. Use of Metal Plate for Thermal Dissipation
Metal planes Thermal conductor
Board
Die

DESIGN GUIDELINES
86/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
As the PCB acts as a heat sink, the layout of top
and ground layers must be done with care to
maximize the board su rface dissipating the heat.
The only limitation is the risk of losing routing
channels. Fi
g
ure 6-31 and Figure 6-32 show a
routing with a good thermal dissipation thanks to
an optimized placement of power and signal vias.
The ground plane s hould be on bottom layer for
the best heat spreading (thicker layer than internal
ones) and dissipation (direct contact with air). .
Figure 6-31. Layout for Good Thermal Dissipation - top layer
1
A
3.3V ball
2.5V ball (Core / PLLs)
Via
STPC ball
GND ba ll
Not Connected ball

DESIGN GUIDELINES
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 87/93
Figure 6-32. Recommend signal wiring (top & ground layers) with corresponding heat flow
STPC balls
External row
Intern a l row
GND PowerPower

DESIGN GUIDELINES
88/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
6.5. DEBUG METHOD OL OGY
In order to bring a STPC-based board to life with
the best efficiency, it is recommended to follow the
check-list described in this section.
6.5.1. POWER SU PPL IES
In parallel with the assembly process, it is useful to
get a bare PCB to check the potential shortcircuits between the various power and ground
planes. This test is also recomm ended when the
first boards are back from assembly. This will
avoid bad surprises in case of a short-circuit due
to a bad soldering.
When the system is powered, all power supplies,
including the PLL power pins must be checked t o
be sure the right level is present. See Table 4-2 for
the exact supported voltage range:
VDD_CORE: 2.5V
VDD_xxxPLL: 2.5V
VDD: 3.3V
6.5.2. BOOT SEQUENCE
6.5.2.1. Reset input
The checking of the reset sequence is the next
step. The waveform of SYSRSTI# must complies
with the timings described in Fi
g
ure 4-3. This
signal must not have glitches an d must stay low
until the 14.31818MHz outpu t (OSC14 M) is at the
right frequency and the strap options are
stabilized to a valid configuration.
In case this clock is not present, check the 14MHz
oscillator stage (see Fi
g
ure 6 -3).
6.5.2.2. Strap options
The STPC has been d esigned in a way to allow
configurations for test purpose that differs from the
functional configuration. In many cases, the
troubleshootings at this stage of the debug are the
resulting of bad strap options. This is why it is
mandatory to check they are properly setup and
sampled during the boot sequence.
The list of all the strap options is summarized at
the beginning of Section 3.
6.5.2.3. Clocks
Once OSC14M is checked and correct, the next
signals to measure are the Host clock (HCLK),
PCI clocks (PCI_CLKO, PCI_CLKI) and Memory
clock (MCLKO, MCLKI).
HCLK must run at the speed defined by the
corresponding strap options (see Table 3-1) and
must not be more than 100MHz. In x2 CPU c lock
mode, this clock must be limited to 66MHz.
PCI_CLKI and PCI_CLK O m ust be c onnected as
described in Fi
g
ure 6-19 and not be higher than
33MHz. Their speed depends on HCLK and on
the divider ratio defined by the
MD[4] and MD[17]
strap options as described in Section 3.
To ensure a correct behaviour of the device, the
PCI deskewing logic must b e configured properly
by the MD[7:6] strap options according to S ect ion
3. For timings constraints, refers to Section 4.
MCLKI and MCLKO must be connected as
described in Fi
g
ure 6-3 to Figure 6-5 depending
on the SDRAM implementation. The memory
clock must run at HCLK speed when in
synchronous mode and must not be higher than
100MHz in any case.
6.5.2.4. Reset output
If SYSRSTI# and all clocks are correct, then the
SYSRSTO# output signal should behave as
described in Fi
g
ure 4-3
.
6.5.3. ISA MODE
Prior to check the ISA bus control signals,
PCI_CLKI, ISA_CLK, I SA_ C L K2 X, and DEV_CLK
must be running properly. If it is not the case, it is
probably because one of the previou s steps has
not been completed.
6.5.3.1. First code fetches
When booting on the ISA bus, the two key signals
to check at the very beginning are RMRTCCS#
and FRAME#.
The first one is a Chip Select for the boot flash
and is multiplexed with the IDE interface. It should
toggle together with ISAOE# and MEMRD# to
fetch the first 16 bytes of code. This corresponds
to the loading of the first line of the CPU cache.
In case RMRTCCS# does not toggle, it is then
necessary to check the PCI FRAME# signal.
Indeed the ISA controller is part of the South
Bridge and all ISA bus cy cles are visible on the
PCI bus.
If there is no activity on the P CI bus, then one of
the previous steps has not been checked properly.
If the re is activ ity then th ere must be someth ing
conflicting on the ISA bus or on the PCI bus.
6.5.3.2. Boot Flash size
The ISA bus supports 8-bit and 16-bit memory
devices. In case of a 16-bit boot flash, the signal
MEMCS16# must be activated during

DESIGN GUIDELINES
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 89/93
RMRTCCS# cycle to inform the ISA controller of a
16-bit device.
6.5.3.3. POST code
Once the 16 first bytes are fetched and decoded,
the CPU core continue its execution depending on
the content of these first data. Usually, it
corresponds to a JUMP instruction and the code
fetching continues, generating read cycles on the
ISA bus.
Most of the BIOS and boot loaders are reading the
content of the f lash, decompressing it in SDRA M,
and then continue the execution by jumping to the
entry point in RAM. This boot process ends with a
JUMP to the entry point of the OS launcher.
These various steps of the booting sequence are
codified by the so-called POST codes (Power-On
Self-Test). A 8-bit code is written to the port 80H at
the beginning of each stage of the booting process
(I/O write to address 0080H) and can be displayed
on two 7-segment display, enabl ing a fast visual
check of the booting completion level.
Usually, the last POST code is 0x00 and
corresponds to the jump into the OS launcher.
When the execution fails or hangs, the lastest
written code stays visible on that display,
indicating either the piece of code to analyse,
either the area of the hardware not working
properly.
6.5.4. LOCAL BUS MODE
As the Local Bus controller is located into the Host
interface, there is no access to the cycles on the
PCI, reducing the amount of signals to check.
6.5.4.1. First code fetches
When booting on the Local Bu s, the key signal to
check at the very beginning is FCS 0#. This sig nal
is a Chip Select for the boot flash and should
toggle together with PRD# to fetch the first 16
bytes of code. This correspon ds t o the l oading of
the f irst line of the CP U cach e.
In case FCS0# does n ot toggle, then one of the
previous steps has not been done properly, like
HCLK speed and CPU clock multiplier (x1, x2).
6.5.4.2. Boot Flash size
The Local Bus support 16-bit boot memory
devices only.
6.5.4.3. POST code
Like in ISA mode, POST codes can be
implemented on the Loca l Bus. The difference is
that an IOCS# must be programmed at I/O
address 80H prior to writing these code, the POST
display being connected to this IOCS# and to the
lower 8 bits of the bus.
6.5.5. SUMMARY
Here is a check-list for the STPC board debug
from power-on to CPU execution.
For each step, in case of failure, verify first the
corresponding balls of the STPC:
- check if the voltage or activity is correct
- search for potential shortcuts.
For troubleshooting in steps 5 to 10, verify the
related strap options:
- value & connection. Refer to Section 3.
- see Figur e 4-3 for timing constraints
Steps 8a and 9a are for debug in ISA mode while
steps 8b and 9b are for Local Bus mode.
Check: How? Troubleshooting
1
Power
supplies
Verify that voltage is within specs:
- this must include HF & LF noise
- avoid full range sweep
Refer to Table 4-1 for values
Measure voltage near STPC balls:
- use very low GND connection.
Add some decoupling capacitor:
- the smallest, the nearest to STPC balls.
2 14.318 MHz Verify OSC14M speed
The 2 capacitors used with the quartz must
match with the capacitance of the crystal.
Try other values.
3
SYSRSTI#
(Power Good)
Measure SYSRSTI# of STPC
See
Figure 4-3
for waveforms.
Verify reset generation circuit:
- device reference
- components value
5 HCLK
Measure HCLK is at selected frequency
25MHz < HCLK < 100MHz
HCLK wire must be as short as possible

DESIGN GUIDELINES
90/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
6.6.
6 PCI clocks
Measure PCICLKO:
- maximum is 33MHz by standard
- check it is at selected frequency
- it is generated from HCLK by a division
(1/2, 1/3 or 1/4)
Check PCICLKI equals PCICLKO
Verify PCICLKO loops to PCICLKI.
Verify maximum skew between any PCI clock
branch is below 2ns.
In Synchronous mode, check MCLKI.
7
Memory
clocks
Measure MCLKO:
- use a low-capacitance probe
- maximum is 100MHz
- check it is at selected frequency
- In SYNC mode MCLK=HCLK
- in ASYNC mode, default is 66MHz
Check MCLKI equals MCLKO
Verify load on MCLKI.
Verify MCLK programming (BIOS setting).
4 SYSRSTO#
Measure SYSRSTO# of STPC
See
Figure 4-3
for waveforms.
Verify SYSRSTI# duration.
Verify SYSRSTI# has no glitch
Verify clocks are running.
8a PCI cycles
Check PCI signals are toggling:
- FRAME#, IRDY#, TRDY#, DEVSEL#
- these signals are active low.
Check, with a logic analyzer, that first
PCI cycles are the expected ones:
memory read starting at address with
lower bits to 0xFFF0
Verify PCI slots
If the STPC don’t boot
- verify data read from boot memory is OK
- ensure Flash is correctly programmed
- ensure CMOS is cleared.
9a
ISA
cycles
to
boot memory
Check RMRTCCS# & MEMRD#
Check directly on boot memory pin
Verify MEMCS16#:
- must not be asserted for 8-bit memory
Verify IOCHRDY is not be asserted
Verify ISAOE# pin:
- it controls IDE / ISA bus demultiplexing
8b
Local Bus
cycles
to
boot memory
Check FCS0# & PRD#
Check directly on boot memory pin
Verify HCLK speed and CPU clock mode.
9b
Check, with a logic analyzer, that first
Local Bus cycles are the expected one:
memory read starting at the top of boot
memory less 16 bytes
If the STPC don’t boot
- verify data read from boot memory is OK
- ensure Flash is correctly programmed
- ensure CMOS is cleared.
10
The CPU fills its first cache line by fetching 16 bytes from boot memory.
Then, first instructions are executed from the CPU.
Any boot memory access done after the first 16 bytes are due to the instructions executed by the CPU
=> Minimum hardware is correctly set, CPU executes code.
Please have a look to the Bios Writer’s Guide or Programming Manual to go further with your board testing.
Check: How? Troubleshooting

ORDERING DATA
Release 1.5 - January 29, 2002 91/93
7. ORDERING DATA
7.1. ORDERING CODES
ST PC C4 E E B C
STMicroelectronics
Prefix
Product Family
PC: PC Compatible
Product ID
C4: Consumer-II
Core Speed
E: 100 MHz
H: 133 MHz
Memory Interface Speed
D: 90 MHz
E: 100 MHz
Package
B: 388 Overmoulded BGA
Temperature Range
C: Commercial
Case Temperature (Tcase) = 0°C to +85°C
I: Industrial
Case Temperature (Tcase) = -40°C to +115°C

ORDERING DATA
92/93
Release 1.5 - Januar
y
29, 2002
7.2. AVAILABLE PART NUMBERS
7.3. CUSTOMER SERVICE
More information is available on the
STMicroelectronics Internet site
http://
www.st.com/stpc
Part Number
Core Frequency
( MHz )
CPU Mode
( X1 / X2 )
Interface
Speed (MHz)
Tcase Range
( °C )
STPCC4HEBC 133 X2 100 0°C to +85°
STPCC4HEBI 133 X2 100 -40°C to +115°
STPCC5HEBC 133 X2 100 0°C to +85°
STPCC5HEBI 133 X2 100 -40°C to +115°

Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences
of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted
by implic ation or otherwise un der any pat ent or pat ent rights of STMicroe l ectronics. S pecificat i ons mentioned in thi s publicati on are subject
to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. STMicroelectronics products are not
authorized for use as cri t i cal compone nts in life support device s or systems without express written approval of STM i croelectr onics.
© 2000 STMicroelectronics - All Rights Reserved
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMic roelectronics.
All other na m es are the prop erty of their respective owners.
STMicroelectronics GROUP OF COMPANIES
Australia - Brazil - China - France - Germany - Italy - Japan - Korea - Malaysia - Malta - Mexico - Morocco - The Netherlands - Singapore -
Spain - Sweden - Switze rl and - Taiwan - Thailand - United Kingdom - U.S. A.
93
Release 1.5
This is preliminary information on a new product now in development or undergoing evaluation. Details are subject to change without notice.
 Loading...
Loading...