
SONOACE X6 Service Manual
ENGLISH
Document No. CSD-SMEX6
Revision 00
Copyrightⓒ2008 by MEDISON

Safety Requirements
Classifications:
- Type of protection against electrical shock: Class I
- Degree of protection against electrical shock (Patient connection):Type BF equipment
- Degree of protection against harmful ingress of water: Ordinary equipment
- Degree of safety of application in the presence of a flammable anesthetic material with air
or with oxygen or nitrous oxide: Equipment not suitable for use in the presence of a
flammable anesthetic mixture with air or with oxygen or nitrous oxide.
- Mode of operation: Continuous operation
Electromechanical safety standards met:
- IEC/EN 60601-1 Medical Electrical Eqiupment, Part 1General Requirements for Safety.
- IEC/EN 60601-1-1 Safety requirements for medicalelectrical systems.
- IEC/EN 60601-1-2 Electromagnetic compatibility -Requirements and tests.
- IEC/EN 60601-2-37 Particular requirements for the safety of ultrasonic medical diagnostic
and monitoring equipment.
- IEC 61157 Declaration of acoustic output parameters.
- ISO 10993-1 Biological evaluation of medical devices.
- UL 2601-1 Medical Electrical Equipment, Part 1 General Requirements for Safety.
- CSA 22.2, 601.1 Medical Electrical Equipment, Part 1 General Requirements for Safety.

Declarations;
0123
This is CSA symbol for Canada and United States of
America
This is manufacturer’s declaration of product
compliance with applicable EEC directive(s) and the
European notified body.
This is manufacturer’s declaration of product
compliance with applicable EEC directive(s).

READ THIS FIRST
Before asking for the product to be repaired, read this service manual thoroughly, learn how to
troubleshoot, and make sure you understand the precautions fully.
The repair of the system and the replacement of parts must be carried out by an authorized
dealer or the customer care department of MEDISON Co., Ltd.
The company shall not be held liable for any injury and damage caused by not following this
warning.
For safe use of this product, you should read ‘Chapter 2. Safety’ in this manual, prior to starting
to useing this system.
DANGER
WARNING
CAUTION
NOTE
Describes precautions necessary to prevent user hazards of great
urgency. Ignoring a DANGER warning will risk life-threatening injury.
Used to indicate the presence of a hazard that can cause serious
personal injury, or substantial property damage.
Indicates the presence of a hazard that can cause equipment damage.
A piece of information useful for installing, operating and maintaining
a system. Not related to any hazard.

`````Contents
Chapter 1. General Information 1-1
1.1 Overview 1-1
1.2 Features and Advantages of SONOACE X6 1-2
1.3 Product Configuration 1-3
1.3.1 Console 1-3
1.3.2 LCD Monitor 1-5
1.3.3 Control Panel 1-6
1.3.4 Probe 1-7
1.4 Specifications 1-8
Chapter 2. Safety 2-1
2.1 Overview 2-1
2.2 Safety – Related Information 2-2
2.2.1 Safety Symbols 2-2
2.2.2 Label 2-4
2.3 Electrical Safety 2-6
2.3.1 Prevention Electric Shock 2-6
2.3.2 ECG - Related Information 2-7
2.3.3 ESD 2-8
2.3.4 EMI 2-8
2.3.5 EMC 2-9
2.4 Mechanical Safety 2-15
2.4.1 Moving the Equipment 2-15
2.4.2Safety Note 2-16
2.5 Biological Safety 2-17
2.5.1 ALARA Principle 2-17
2.6 Environmental Protection 2-29
Contents

Contents
Chapter 3. Installing the Product 3-1
3.1 Overview 3-1
3.2 Transportation 3-3
3.2.1 Precautions for Transportation 3-3
3.2.2 Temperature and Humidity 3-3
3.2.3 Transportation of the Product 3-4
3.3 Unpacking 3-5
3.3.1 Unpacking the Box 3-5
3.3.2 Checking Package Contents 3-6
3.4 Precautions for Installation 3-7
3.4.1 Precautions 3-7
3.4.2 Installation Location 3-8
3.5 Installation Procedure 3-9
3.5.1 Installation Safety 3-9
3.5.2 Connecting the Power Cord 3-10
3.5.3 Connecting the Network Cable 3-11
3.5.4 Connecting the Foot switch 3-11
3.5.5 Connecting the Probe 3-12
3.6 Starting the Product 3-13
3.7 Shutting down the Product 3-15
3.7.1 Power Switch 3-15
3.7.2 Cut-off Switch 3-15
3.8 Connecting the Peripherals 3-16
3.8.1 BW Printer 3-16
3.8.2 Color Printer 3-17
3.8.3 Line Printer 3-18
3.8.4 VCR 3-18
3.8.5 USB Storage Device 3-19
3.9 System Setting 3-20
3.9.1 General System Setup 3-20
3.9.2 Display Setup 3-22
3.9.3 Misc 3-24
3.9.4 Peripherals Setup 3-25
3.9.5 Information 3-26
3.9.6 DICOM Setup (Option) 3-27
3.9.7 Option Setup 3-34
Contents

Contents
Chapter 4. Checking the Product 4-1
4.1Overview 4-1
4.2 Starting the Product 4-2
4.3Monitor 4-6
4.3.1Monitor Display 4-4
4.4 Control Panel 4-6
4.4.1Power On/Off 4-6
4.4.2 Starting and Finishing Exam 4-6
4.4.3 Selecting Diagnosis mode and Gain Control 4-7
4.4.4 Image Adjustment 4-9
4.4.5TGC 4-10
4.4.6 Measurement and Annotation 4-10
4.4.7 Trackball and its related control 4-11
4.4.8 SONOVIEW and Report 4-12
4.4.9 Save and Print 4-12
4.4.10 Alphanumeric keyboard 4-13
4.4.11 Flexible Soft Buttons 4-13
4.4.12 Function Buttons 4-14
4.5 Checking the Performance 4-15
4.5.1 Basic Check 4-15
4.5.2 Detail Check 4-16
Contents

Contents
Chapter 5. Product Structure 5-1
5.1 Overview 5-1
5.2 System Block Diagram 5-3
5.3 Basic Structure of SONOACE X6 5-4
5.3.1 Overview 5-4
5.3.2 Ultrasound System Part 5-5
5.3.3 User Interface Part 5-5
5.3.4 Power Part 5-5
5.4 PSA 5-6
5.5 Front End Board 5-9
5.6 CW Board 5-13
5.7 Back End Board 5-15
5.8 Rear Board 5-22
5.9 Control Panel 5-23
5.10 Power Supply 5-24
Chapter 6. Basic Maintenance 6-1
6.1 Overview 6-1
6.2 System Information 6-2
6.3 Entering Admin Mode 6-3
6.4 Upgrade 6-6
6.4.1 Software Upgrade 6-6
6.4.2 Hardware Upgrade 6-9
6.5 Backup & Restore 6-10
6.5.1 Backup User Setting 6-10
6.5.2 Restore User Setting 6-11
6.6 Adding and Deleting Options 6-13
6.6.1Option type 6-13
6.6.2 Registering Options 6-13
6.6.3 Deleting Options 6-14
6.7 Control Panel Test 6-15
Contents

Contents
Chapter 7. Troubleshooting 7-1
7.1 Overview 7-1
7.2 Power 7-2
7.2.1 Power Failure 7-2
7.2.2 Power cannot be turned off 7-2
7.2.3 Power is automatically turned off 7-3
7.3 Monitor 7-4
7.3.1Blank Screen 7-4
7.3.2 Screen Color is Abnormal 7-4
7.4 Error Messages 7-5
7.4.1 System hangs after an error during booting 7-5
7.4.2 System works even if error occurred 7-5
7.4.3 Error code 7-5
7.5 Image 7-6
7.5.1 No BW Image Echo 7-6
7.5.2 No BW Mode Image Format 7-6
7.5.3 Noise Link Rain over the BW Mode Image (Noise) 7-6
7.5.4 PW Doppler Mode Trouble 7-7
7.5.5 CW Doppler Mode Trouble 7-7
7.5.6 Color Doppler Mode Trouble 7-7
7.5.7 Motion Mode Trouble 7-7
Contents

Contents
Chapter 8. Disassembly and Reassembly 8-1
8.1 Overview 8-1
8.2 Disassembly and Reassembly of the External Case 8-4
8.2.1 Preparations 8-4
8.2.2 Cover Front Lower 8-4
8.2.3 Cover Top Plate 8-5
8.2.4 Cover Rear Lower 8-6
8.3 Disassembly and Reassembly of the LCD Monitor 8-7
8.3.1 Preparations 8-7
8.3.2 LCD Monitor 8-7
8.3.3 LCD Monitor Arm 8-8
8.4 Disassembly and Reassembly of the Ultrasound System PCB Part 8-9
8.4.1 Preparations 8-9
8.4.2 PSA ASSY 8-9
8.4.3 CW Board, FE Board, BE Board 8-10
8.4.4 DC to DC Power Module 8-11
8.5 Disassembly and Reassembly of the HDD & DVD 8-12
8.5.1 Preparations 8-12
8.5.2 HDD & DVD 8-12
8.6 Disassembly and Reassembly of the Rear Panel 8-13
8.6.1 Preparations 8-13
8.6.2 Rear Right Board & Rear Left Board 8-13
8.6.3 Back Fan 8-14
8.7 Disassembly and Reassembly of the Power Supply 8-16
8.7.1 Preparations 8-16
8.7.2 AC to DC Power Module 8-16
8.7.3 DC to DC Power Module 8-16
8.8 Disassembly and Reassembly of the Control Panel 8-17
8.8.1 Preparations 8-17
8.8.2 Control Panel 8-17
8.8.3 Key Matrix Board 8-18
8.8.4 Track Ball 8-19
8.8.5 Alpha Numeric Keyboard 8-20
8.8.6 Speaker 8-20
Contents

Content
Chapter 9. Probe 9-1
9.1 Overview 9-1
9.2 Probe List 9-2
9.3 Thermal Index (TI Table) 9-3
9.4 Ultrasound Transmission Gel 9-4
9.5 Sheaths 9-5
9.6 Probe Precautions 9-5
9.7 Cleaning and Disinfecting the Probe 9-8
Chapter 10. User Maintenance 10-1
10.1 Overview 10-1
10.2 System Maintenance 10-2
10.2.1 Installation Maintenance 10-2
10.2.2 Cleaning and Disinfections 10-3
10.2.3 Fuse Replacement 10-5
10.2.4 Cleaning the Air Filter 10-6
10.2.5 Accuracy Check 10-6
10.3 Administration of Information 10-7
10.3.1 User Setting Back-up 10-7
10.3.2 Patient Information Back-up 10-7
10.3.3 Software 10-7
Chapter 11. Service Part List 11-1
11.1 Overview 11-1
11.2 Cover 11-2
11.3 Ultrasound System Part 11-4
11.4 Rear Plan 11-5
11.5 Power Part 11-6
11.6 LCD Monitor 11-7
11.7 Control Panel 11-9
11.8 Probe 11-10
Contents

1 General Information
1.1 Overview
Chapter 1 contains the information necessary to plan the Troubleshooting of SONOACE X6
1.1 Overview 1-1
1.2 Features and Advantages of SONOACE X6 1-2
1.3 Product Configuration 1-3
1.3.1 Console 1-3
1.3.2 LCD Monitor 1-5
1.3.3 Control Panel 1-6
1.3.4 Probes 1-7
1.4 Specifications 1-8
The SONOACE X6 is a high-resolution color ultrasound system with high penetration
and a variety of measurement functions
Contents General Information
Chapter 1. General Information
1-1

p
1.2 Features and Advantages of SONOACE X6
y High-end Digital Beamforming : The SONOACE X6 utilizes the newly developed
Digital Beam forming technology.
y A variety of applications : The SONOACE X6 is o
timized for use in a variety of
ultrasound departments, including general, abdomen, obstetrics, gynecology,
vascular, extremity, pediatric, cardiac, breast, urology, and etc.
y Various diagnostic Modes : 2D Mode, M Mode, Color Doppler Mode, Power
Doppler Mode, PW Spectral Doppler Mode, CW Spectral Doppler Mode(Option),
etc.
y 3D images can be obtained.
y Measurement and Report Functions : Besides the basic distance, area,
circumference and volume measurement functions, the SONOACE X6 also
provides application-specific measurement functions. The report function
collates measurement data.
y Review of Scanned Images : The SONOACE X6 displays Cine images of 512
frames and loop images of 4096 lines.
y SonoView
TM
: This is a total ultrasound image management system, which
allows a user to archive, view and exchange documents.
y Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) Function : This is
used to archive, transmit and print DICOM images through a network.
y Peripheral/Accessory Connection : A variety of peripheral devices including
VCRs and printers can be easily connected to the SONOACE X6.
Chapter 1. General Information
1-2
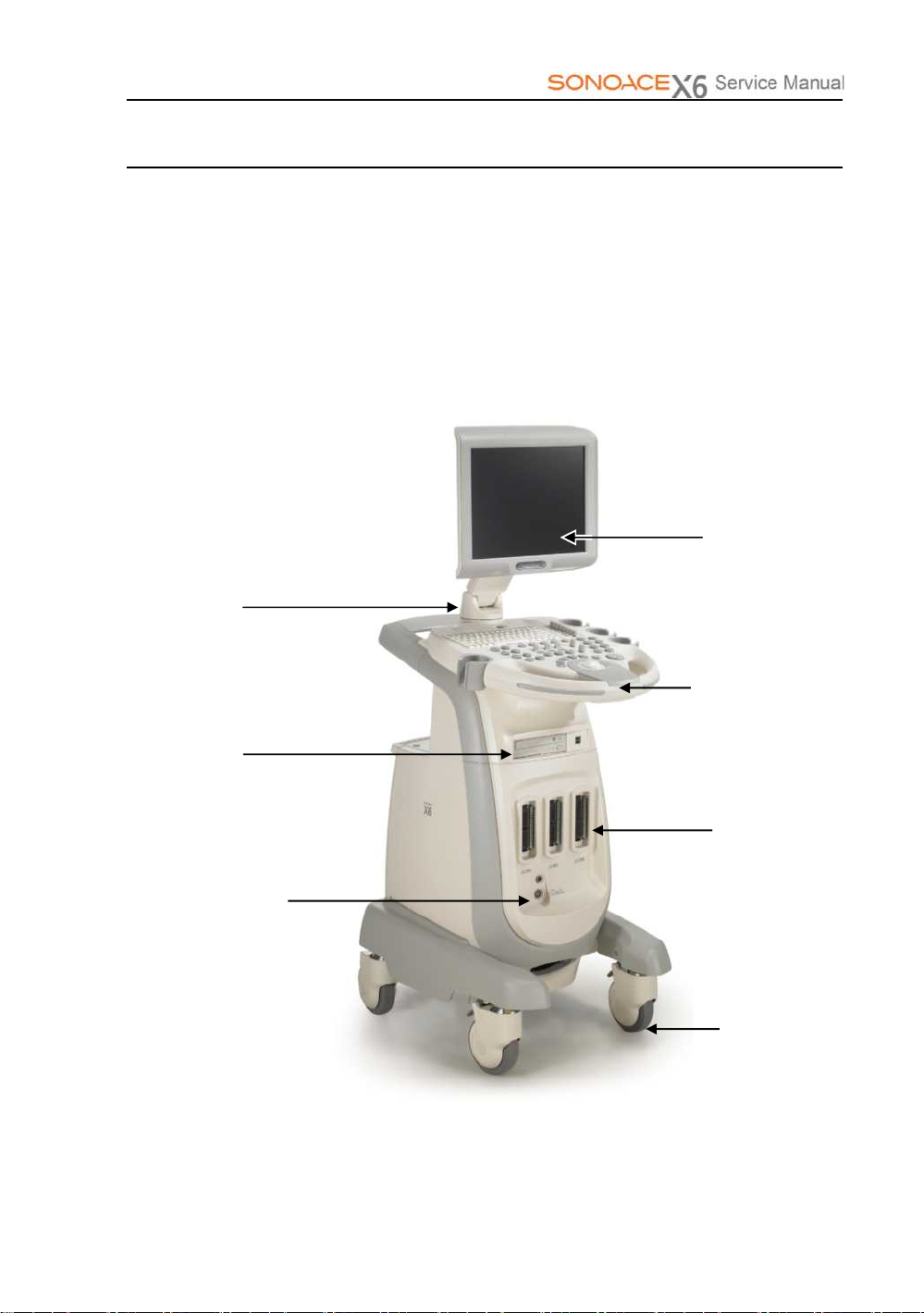
1.3 Product Configuration
This Product consists of the monitor, the control panel, the console and the probes.
1.3.1 Console
The console consists of two parts – the inner unit and the outer unit.
The interior of the console mainly contains devices that produce ultrasound images.
On the exterior of the console is composed of various connectors, probe holders,
storage compartments, handles, wheels, etc.
LCD Arm
DVD-RW Drive
Pencil probe Connector
LCD Monitor
Control Panel
Probe Connector
Wheel
[Figure 1-1] Console of SONOACE X6
Chapter 1. General Information
1-3
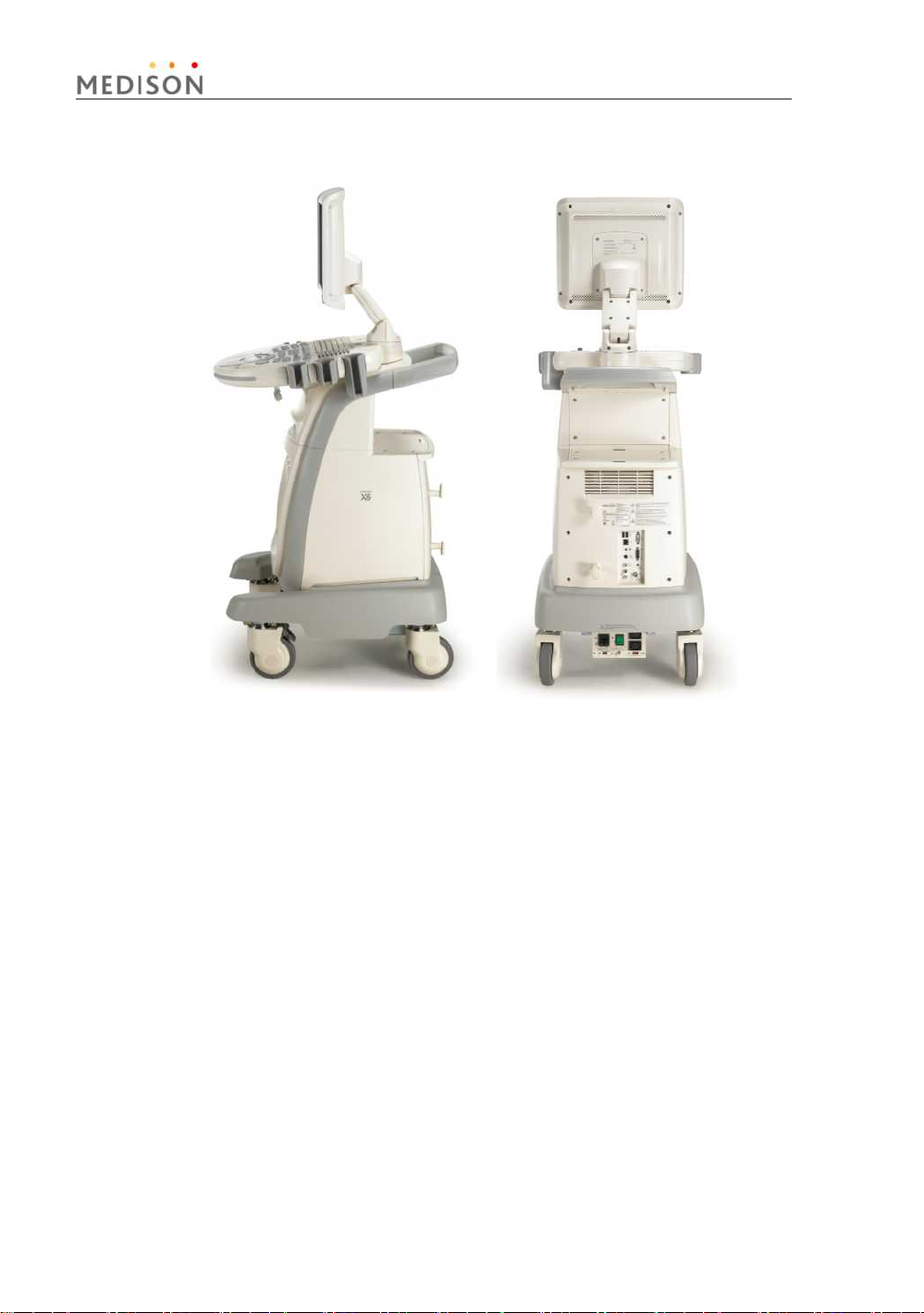
[Figure 1-2] Rear and side of SONOACE X6
Chapter 1. General Information
1-4

p
1.3.2 LCD Monitor
The LCD monitor of this system is a color VGA monitor, which dis
images and additional information. Use the monitor arm to adjust the height or
lays ultrasound
position of the monitor.
[Figure 1-3] LCD Arm
Chapter 1. General Information
1-5

1.3.3 Control Panel
The control panel can be used for controlling the system. It consists of the
following four sections:
Alphanumerics Keyboard
Slide Volume
Button
Dial Button
Track Ball
[Figure 1-4] Control Panel
Chapter 1. General Information
1-6

1.3.4 Probe
Probes are devices that generate ultrasound waves and process reflected wave
data for the purpose of image formation.
NOTE
For more information, refer to `Chapter 9 Probes’.
Chapter 1. General Information
1-7
1.4 Specifications
Height: 1378mm (with monitor)
Physical Dimensions
Monitor 15 inch LCD monitor
Electrical Parameters 100-120V/200-240VAC, 8/5A, 50/60Hz
Width: 483mm
Depth: 691mm
Weight: More than 60.75kg
Pressure Limits
Humidity Limits
Temperature Limits
Imaging modes
Focusing
Operating: 700hPa to 1060hPa
Storage: 700hPa to 1060hPa
Operating: 30% to 75%
Storage & Shipping: 20% to 90%
O
Operating: 10
Storage & Shipping: -25
C ~ 35OC
O
C ~ 60OC
2D imaging mode
Dual 2D imaging mode
M imaging mode
2D/M imaging mode
Color Doppler Imaging (CDI) mode
Power Doppler Imaging (PDI) mode
Pulse Wave (PW) Spectral Doppler imaging mode
Continuous Wave (CW) Spectral Doppler imaging mode
3D imaging mode (Freehand)
Simultaneous mode
Transmit focusing, maximum of eight points (four points
simultaneously selectable)
Digital dynamic receive focusing (continuous)
General, Gynecology, Abdomen, OB, Renal, Urology, Vascular,
Application
Small Part, Fetal Heart, Breast, Musculoskeletal, Pediatric, Cardiac,
TCD, Neonatal
Chapter 1. General Information
1-8
Trackball operation of multiple cursors
2D: Linear measurements and area measurements using elliptical
Measurement
Packages
approximation or trace
M-mode: Continuous readout of distance, time, and slope rate
Doppler: Velocity and trace
Maximum 512 frames for CINE memory
Image Storage
Maximum 4096 Lines for LOOP memory
Image filing system
Gray Scale 256 (8 bits)
TGC control
Mode-independent gain control
Acoustic power control (adjustable)
Dynamic aperture
Dynamic apodization
Dynamic range control (adjustable)
Signal processing
(Pre-processing)
Image view area control
M-mode sweep speed control
HD zoom
Frame average
Gamma-scale windowing
Image orientation (left/right and up/down)
White on black/black on white
Probes
Curved Linear Array
C3-7EP
C4-9ED
Linear Array
HL5-12ED
L5-12/50EP
Endocavity Curved Linear Array
NER4-9ES
NEV4-9ES
Phased Array
P2-4AH
CW
CW2.0
CW4.0
Chapter 1. General Information
1-9
Probe connections
Rear Panel
Input / Output
Connections
Auxiliary
Three probe connectors
Four probe connectors for option
※ Including one CW probe connector.
VHS and S-VHS VCR left and right audio
ECG
Microphone
Patient monitor video and 9V dc power
B/W printer video and remote control
VGA monitor
Parallel port
USB
Black-and white printer
Color printer
VCR
Monitor
Foot switch
Chapter 1. General Information
1-10

2 Safety
2.1 Overview
2.1 Overview 2-1
2.2 Safety – Related Information 2-2
2.2.1 Safety Symbols 2-2
2.2.2 Label 2-4
2.3 Electrical Safety 2-6
2.3.1 Prevention Electric Shock 2-6
2.3.2 ECG - Related Information 2-7
2.3.3 ESD 2-8
2.3.4 EMI 2-8
2.3.5 EMC 2-9
2.4 Mechanical Safety 2-15
2.4.1 Moving the Equipment 2-15
2.4.2Safety Note 2-16
2.5 Biological Safety 2-17
2.5.1 ALARA Principle 2-17
2.6 Environmental Protection 2-29
Chapter 2 contains the information necessary to Safety.
Contents Safety
Ch apt e r 2. Safety
2-1
2.2 Safety - Related Information
2.2.1
Safety Symbols
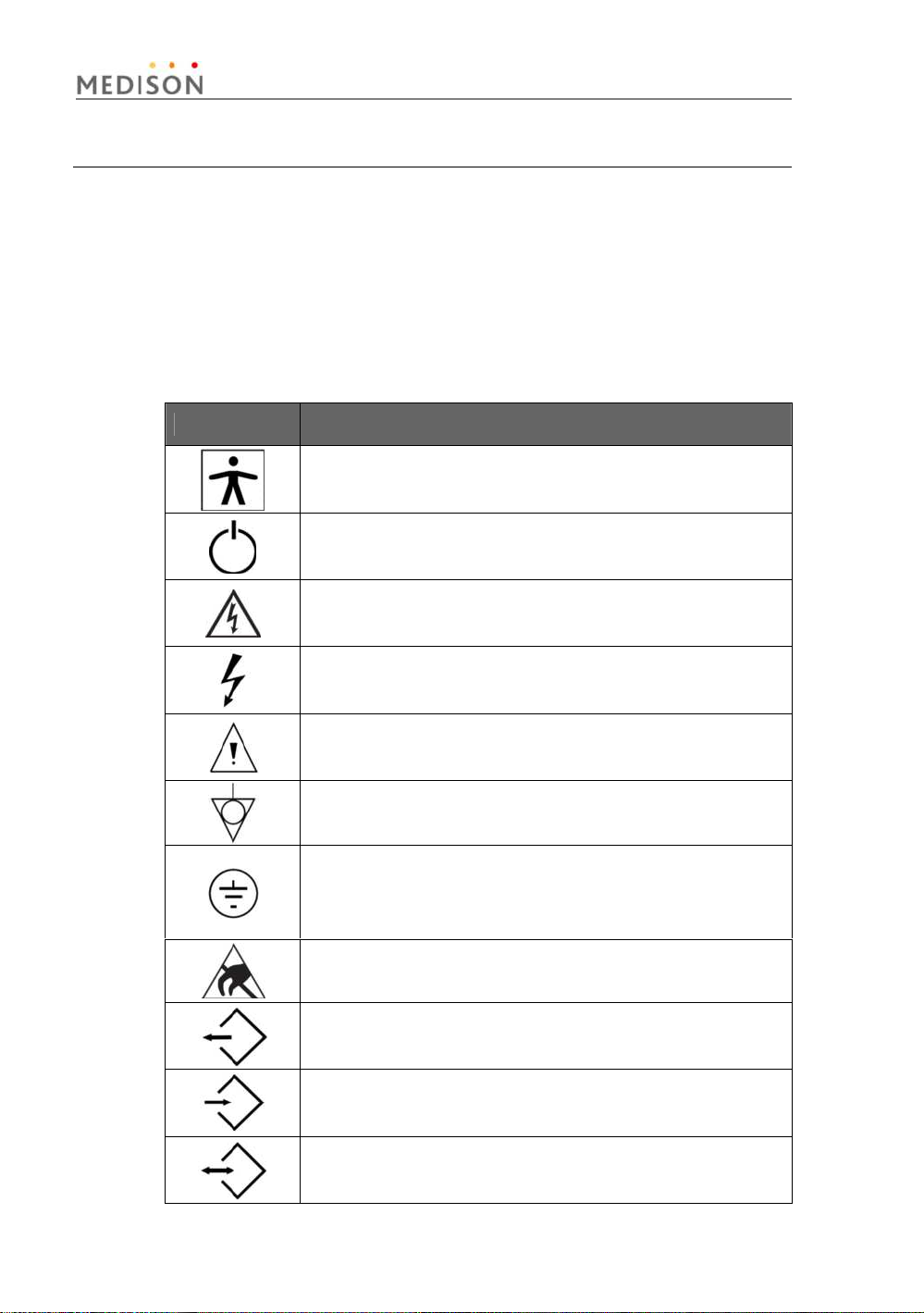
The International Electro Technical Commission (IEC) has established a
set of symbols for medical electronic equipment, which classifies a
connection or warn of potential hazards. The classifications and symbols
are shown below.
Symbols Description
Isolated patient connection (Type BF applied part).
Power switch (Supplies/cuts the power for product)
Indicates a caution for risk of electric shock.
Indicates dangerous voltages over 1000V AC or over
1500V DC.
Chapter 2. Safety
2-2
Warning, Caution
Identifies an equipotential ground.
Identifies the point where the system safety ground is
fastened to the chassis. Protective earth connected to
conductive parts of Class I equipment for safety
purposes.
Electrostatic discharge
Data Output port
Data Input port
Data Input/Output port
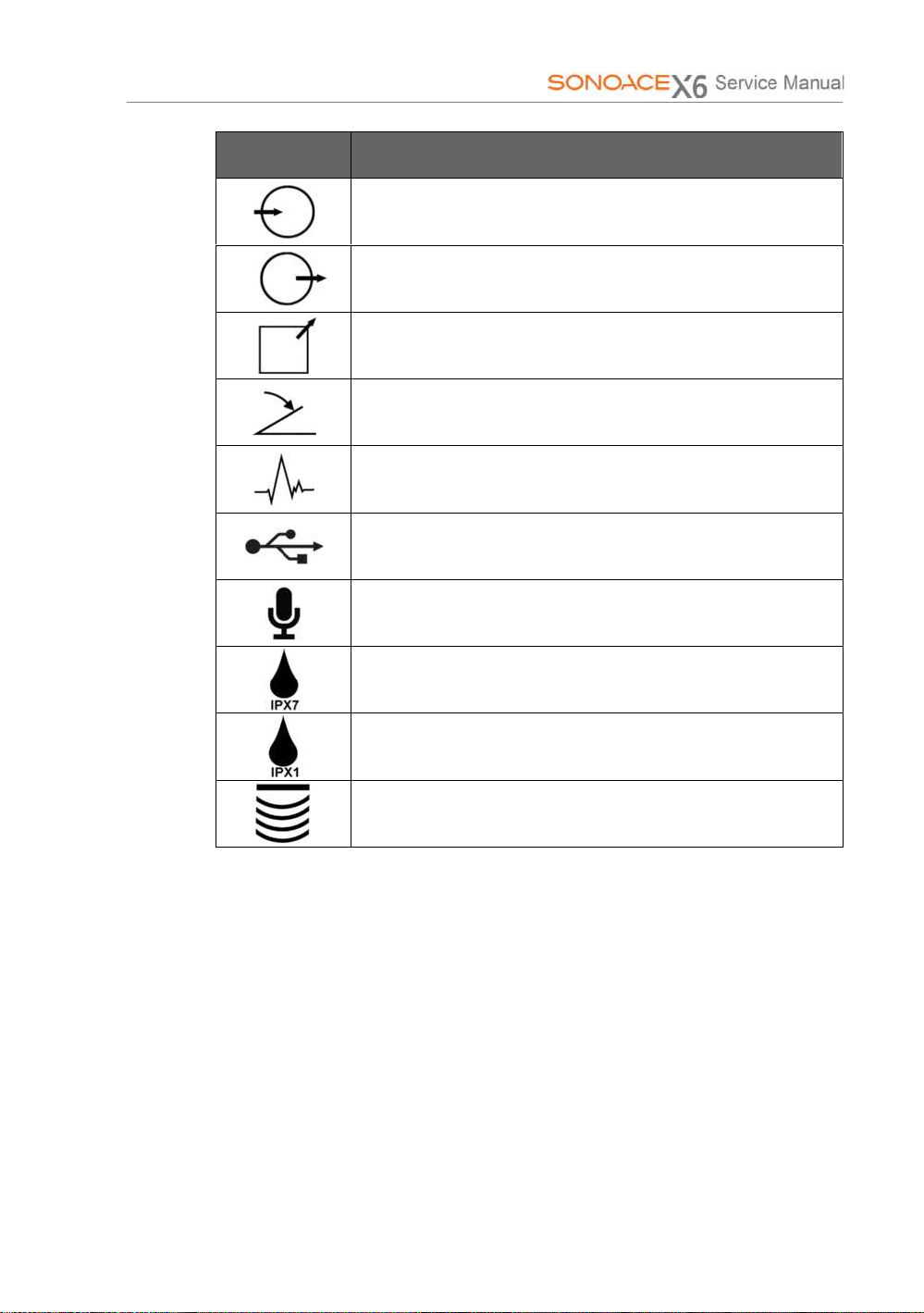
Symbols Description
Left and right Audio / Video input
Left and right Audio / Video output
Print remote output
Foot switch connector
ECG connector
USB connector
Microphone connector
Protection against the effects of immersion.
Protection against dripping water.
Probe connector
Ch apt e r 2. Safety
2-3

2.2.2 Labels
To protect the system, you may see ‘Warning’ or ‘Caution’ marked on the surface
of the product
1) Front
[Figure 2-1] Labels of Front
Chapter 2. Safety
2-4
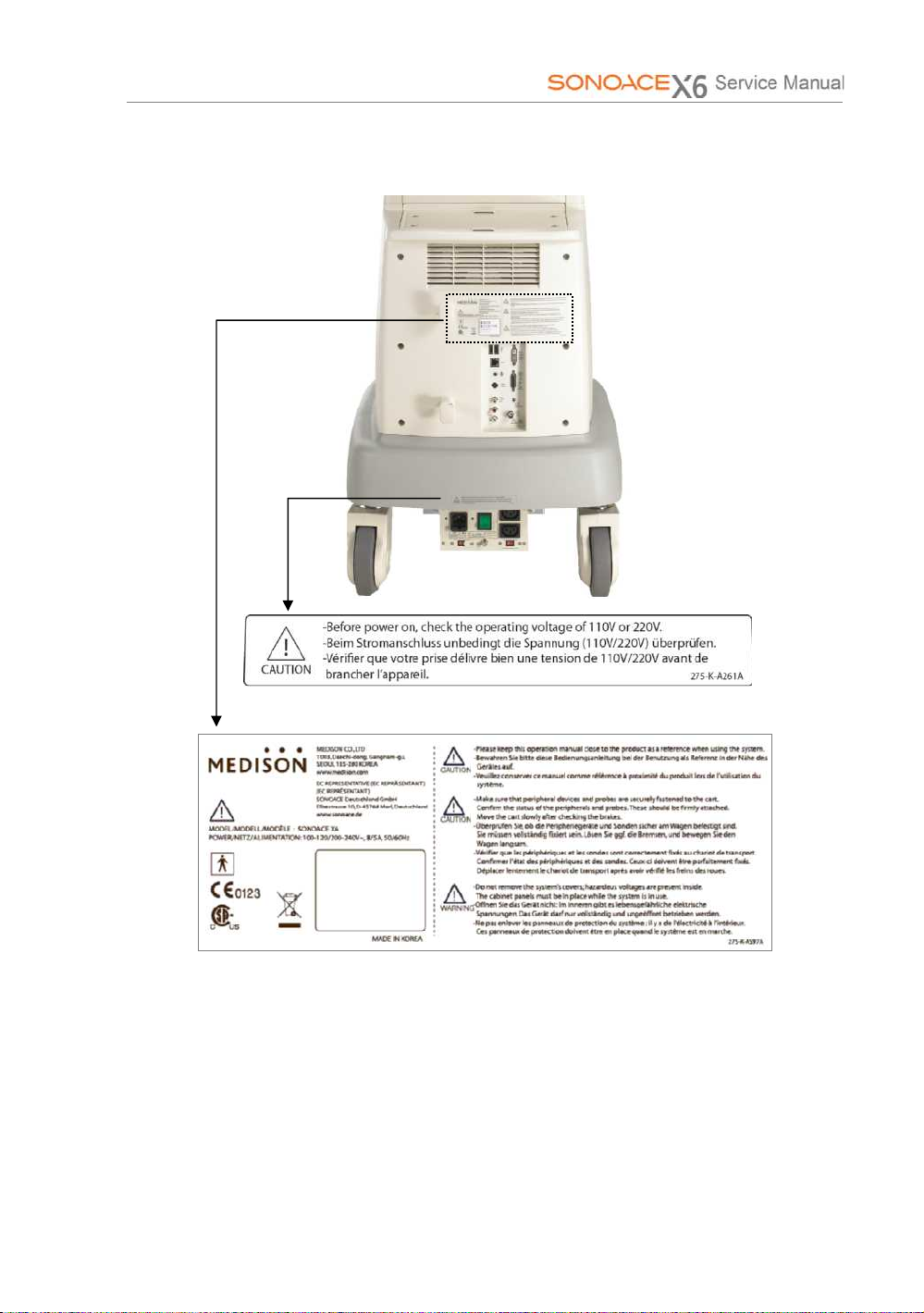
2) Rear
[ Figure 2-2] Labels of Rear
Ch apt e r 2. Safety
2-5

p
p
p
2.3 Electrical Safety
This equipment has been verified as a Class I device with Type BF applied parts.
2.3.1 Prevention of Electric Shock
In a hospital, dangerous currents are due to the potential differences between
connected equipment and touchable conducting parts found in medical rooms.
The solution to the
is connected with connecting leads made u
roblem is consistent equipotential bonding. Medical equipment
of angled sockets to the equipotential
bonding network in medical rooms.
[Figure 2-3] Equipotential bonding
Additional equipment connected to medical electrical equipment must comply
with the respective IEC or ISO standards (e.g. IEC 60950 for data processing
equipment). Furthermore all configurations shall comply with the requirements
for medical electrical systems (see IEC 60601-1-1 or clause 16 of the 3 Ed. of
IEC 60601-1, respectively). Anybody connecting additional equipment to
medical electrical equipment configures a medical system and is therefore
responsible that the system com
lies with the requirements for medical electrical
systems. Attention is drawn to the fact that local laws take priority over the
above-mentioned requirements. If in doubt, consult your local distributor or the
technical service department.
Chapter 2. Safety
2-6
WARNING
CAUTION
y Electric shock may exist result if this system, including and all of its
externally mounted recording and monitoring devices, is not properly
grounded.
y Do not remove the covers on the system; hazardous voltages are present
inside. Cabinet panels must be in place while the system is in use. All
internal adjustments and replacements must be made by a qualified
MEDISON Customer Service Department.
y Check the face, housing, and cable before use. Do not use, if the face is
cracked, chipped, or torn, the housing is damaged, or if the cable is
abraded.
y Always disconnect the system from the wall outlet prior to cleaning the
system.
y All patient contact devices, such as probes and ECG leads, must be
removed from the patient prior to application of a high voltage defibrillation
pulse.
y The use of flammable anesthetic gas or oxidizing gases (N20) should be
avoided.
y The system has been designed for 100-120VAC and 200-240VAC; you
should select the input voltage of monitor, printer and VCR. Prior to
connecting an OEM power cord, verify that the voltage indicated on the
power cord matches the voltage rating of the OEM device.
y An isolation transformer protects the system from power surges. The
isolation transformer continues to operate when the system is in standby.
y Do not immerse the cable in liquids. Cables are not waterproof.
y The operator does not contact the parts (SIP/SOP) and the patient
simultaneously
2.3.2 ECG-Related Information
WARNING
y This device is not intended to provide a primary ECG monitoring function,
and therefore does not have means of indicating an inoperative
electrocardiograph.
y Do not use ECG electrodes of HF surgical equipment. Any malfunctions in
the HF surgical equipment may result in burns to the patient.
y Do not use ECG electrodes during cardiac pacemaker procedures or other
electrical stimulators.
y Do not use ECG leads and electrodes in an operating room.
Ch apt e r 2. Safety
2-7

2.3.3
CAUTION
ESD
Electrostatic discharge (ESD), commonly referred to as a static shock, is a naturally
occurring phenomenon. ESD is most prevalent during conditions of low humidity,
which can be caused by heating or air conditioning. During low humidity
conditions, electrical charges naturally build up on individuals, creating static
electricity. An ESD occurs when an individual with an electrical energy build-up
comes in contact with conductive objects such as metal doorknobs, file cabinets,
computer equipment, and even other individuals. The static shock or ESD is a
discharge of the electrical energy build-up from a charged individual to a lesser or
non-charged individual or object.
The ESD caution symbol is on the probe connector and the rear panel.
[Figure 2-4] ESD symbol
y The level of electrical energy discharged from a system user or
patient to an ultrasound system can be significant enough to cause
damage to the system or probes.
2.3.4 EMI
Although this system has been manufactured in compliance with existing EMI
(Electromagnetic Interference) requirements, use of this system in the presence of
an electromagnetic field can cause momentary degradation of the ultrasound
image.
If this occurs often, MEDISON suggests a review of the environment in which the
system is being used, to identify possible sources of radiated emissions. These
emissions could be from other electrical devices used within the same room or an
adjacent room. Communication devices such as cellular phones and pagers can
cause these emissions. The existence of radios, TVs, or microwave transmission
equipment nearby can also cause interference.
Chapter 2. Safety
y The following precautions can help to reduce ESD:
- Anti-static sprays on carpets or linoleum
- Anti-static mats
- A ground wire connection between the system and the patient
table or bed.
2-8
CAUTION
In cases where EMI is causing disturbances, it may be necessary to relocate
this system.
2.3.5 EMC
The testing for EMC(Electromagnetic Compatibility) of this system has been
performed according to the international standard for EMC with medical devices
(IEC60601-1-2). This IEC standard was adopted in Europe as the European norm
(EN60601-1-2).
2.3.5.1 Guidance and manufacturer’s declaration - electromagnetic emission
This product is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified
below. The customer or the user of this product should assure that it is used in
such an environment.
Emission test Compliance Electromagnetic environment -guidance
RF Emission
(Radiation)
CISPR 11
RF Emission
(Radiation)
CISPR 11
Harmonic Emission
IEC 61000-3-2
Group 1
Class B
Group 1
Class B
Class A
The Ultrasound System uses RF energy only
for its internal function. Therefore, its RF
emissions are very low and are not likely to
cause any interference in nearby electronic
equipment.
The Ultrasound System is suitable for use in
all establishments, including domestic
establishments and those directly connected
to the public low-voltage power supply
Flicker Emission
IEC 61000-3-3
Complies
network that supplies building used for
domestic purpose.
Ch apt e r 2. Safety
2-9
 Loading...
Loading...