Samsung SonoAce X4 Service manual

.,.~~:~
o 1-1
Safety
Signs
o
1-2
Electrical
c)
1-3
Mechanical
1-4
Biological
1-5
Probe
Precautions
1-6
Environmental
Safety
Safety
Safety
Protection
,
5
7
15
17
27
28
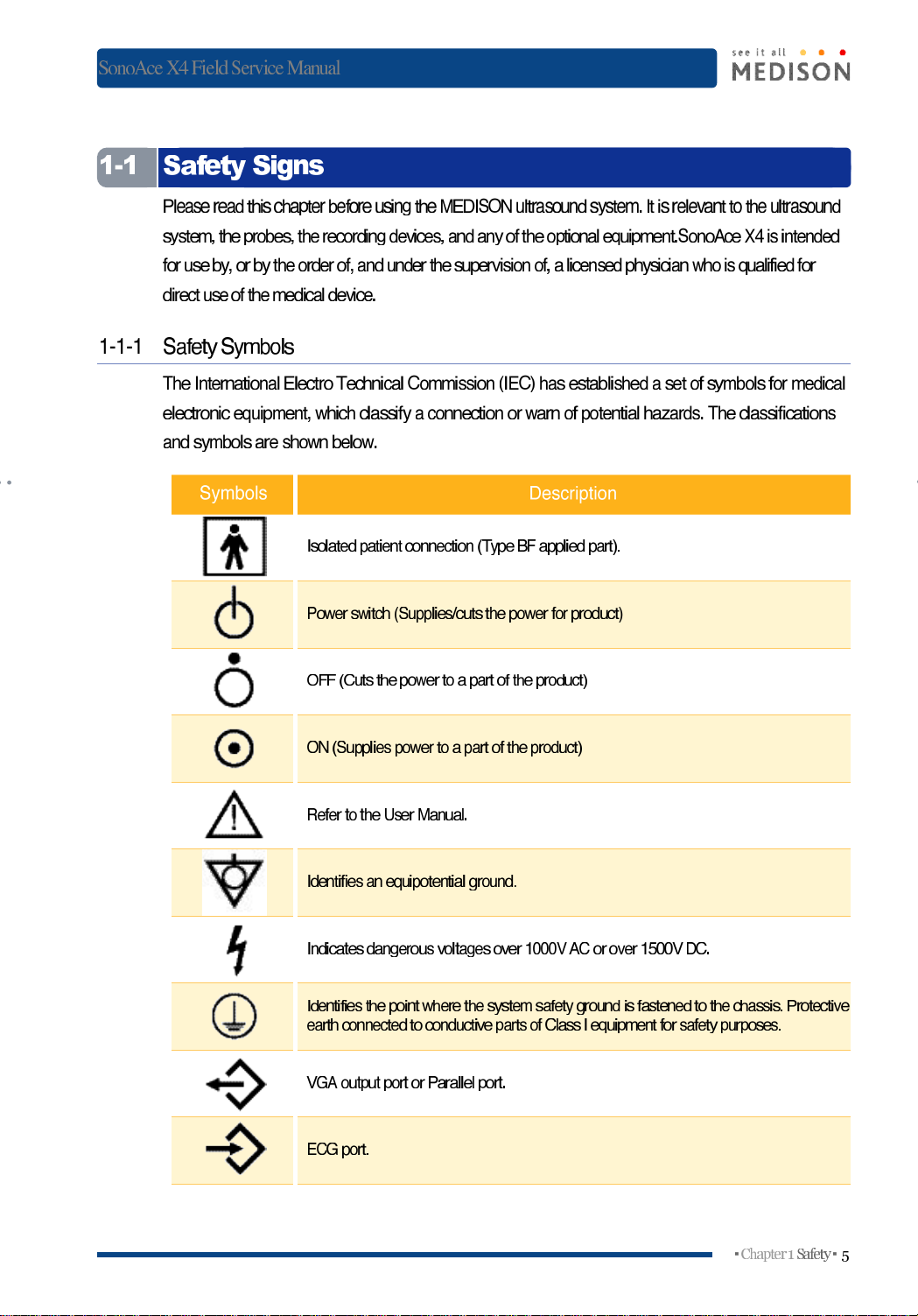
Safety Signs
Please
read
this
chapter
system,
for
direct
use
by,orby
useofthe
the
probes,
the
medical
the
order
before
using
recording
of,
and
device.
the
devices,
under
the
MEDISON
and
anyofthe
supervision
ultrasound
optional
of,alicensed
See
MEDISON
system.Itis
equipment.SonoAceX4is
relevanttothe
physician
whoisqualified
it
all
ultrasound
intended
for
,.
1-1-1
Safety
The
International
electronic
and
symbols
[I]
C:>
o
o
A
Symbols
equipment,
are
••
•
Electro
which
shown
Isolated
Power
OFF
ON
Refertothe
Technical
below.
switch
(Cuts
(Supplies
Commission
classifyaconnectionorwarnofpotential
patient
connection
(Supplies/cuts
the
powertoa
powertoa
User
Manual.
(lEG)
has
Description
(TypeSFapplied
the
power
partofthe
partofthe
product)
product)
establishedasetofsymbols
for
product)
part).
hazards.
The
classifications
for
medical
V
~
tT\.'
'.
~
€>
-t>'
Identifiesanequipotential
Indicates
Identifies
earth
VGA
ECG
dangerous
the
connectedtoconductive
output
portorParallel
port.
point
voltages
where
ground.
over
1000VACor
the
system
safety
groundisfastenedtothe
partsofClassIequipment
port.
over
1500V
for
DC.
safety
chassis.
purposes.
•Chapter 1 Safety· 5
Protective
See
it
all
_.
MEDISON
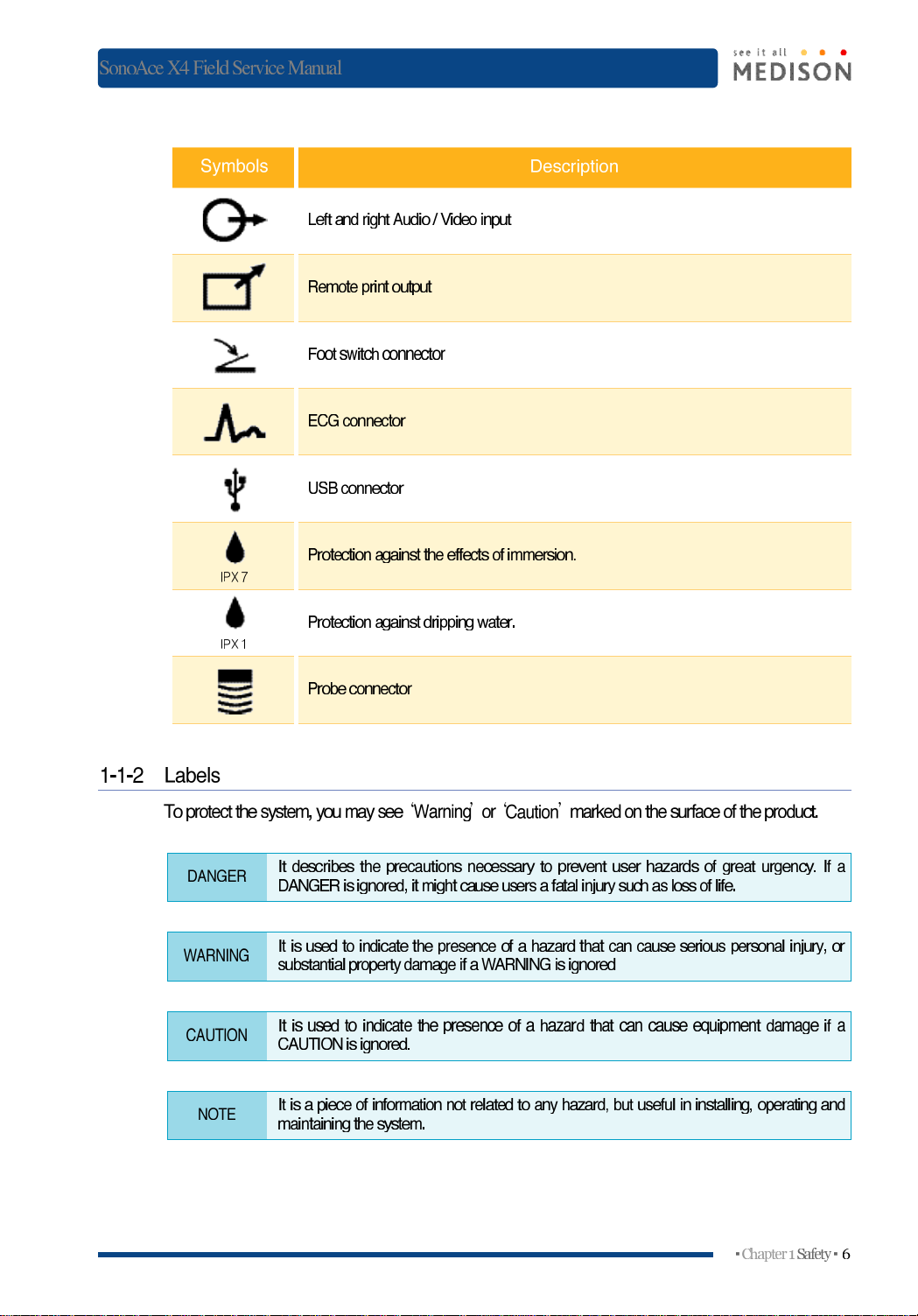
Symbols
IPX
7
IPX
1
Left
and
Remote
Foot
switch
ECG
connector
USB
connector
Protection
Protection
right
Audio/Video
print
output
connector
against
against
input
the
effectsofimmersion.
dripping
water.
Description
1-1-2
Labels
To
protect
DANGER
WARNING
CAUTION
NOTE
-'
=
--
the
Probe
connector
system,
you
may
see
It
describes
DANGERisignored,itmight
Itisusedtoindicate
substantial
Itisusedtoindicate
CAUTIONisignored.
Itisa
maintaining
the
precautions necessarytoprevent
property
pieceofinformation
the
damageifa
system.
'Warning'or'Caution'
cause
usersafatal
the
presenceofa
the
presenceofa
not
relatedtoany
hazard
WARNINGisignored
hazard
markedonthe
user
injury
suchaslossoflife.
that
can
cause
that
can
hazard,
but
usefulininstalling,
surfaceofthe
hazardsofgreat
serious
personal
cause
equipment
product.
urgency.Ifa
injury,
damageifa
operating
and
or
•Chapter 1 Safety· 6
Electrical Safety
This
equipment
has
been
verifiedasa
Class1device
with
TypeSFapplied
parts.
See
it
all
_.
MEDISON
1-2-1
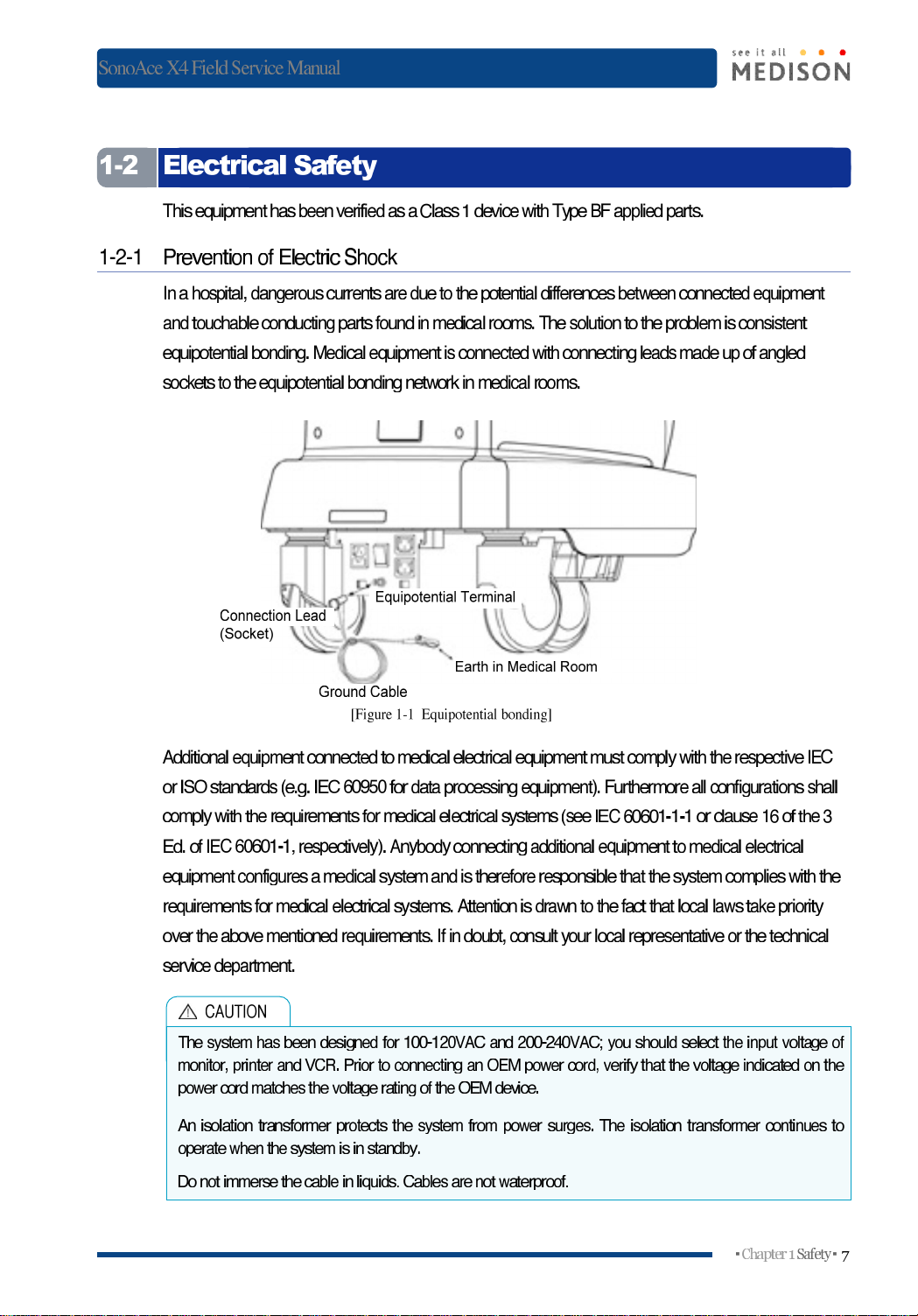
PreventionofElectric
Inahospital,
and
touchable
equipotential
socketstothe
Additional
dangerous
conducting
bonding.
equipotential
equipment
Medical
Ground Cable
connectedtomedical
Shock
currents
are
duetothe
parts
foundinmedical
equipmentisconnected
bonding
[Figure
networkinmedical
1-1
Equipotential bonding]
potential
rooms.
differences
The
with
rooms.
'<
EarthinMedical Room
electrical
equipment
between
solutiontothe
connecting
must
comply
connected
problemisconsistent
leads
madeupof
with
the
respectiveIEC
equipment
angled
or
ISO
standards
comply
with
Ed.ofIEC
equipment
requirements
over
the
above
service
department.
Lt.
CAUTION
The
system
monitor,
power
cord
An
isolation transformer protects
operate
when
Do
not
immerse
(e.g.
the
requirements
60601-1,
configuresamedical
for
medical
mentioned
I
has
been
printer
and
matches
the
systemisin
the
IEC
60950
for
data
for
medical
respectively).
Anybody
system
electrical
systems.
requirements.Ifin
designed
VCR.
the
cableinliquids.
for
1QQ-12QVAC
PriortoconnectinganGEM
vo~age
ratingofthe
the
stand
by.
Cables
processing
electrical
equipment).
systems
connecting
andistherefore
Attentionisdrawntothe
doubt,
consult
and
2QQ-24QVAC;
GEM
device.
system
from
power
are
not
waterproof.
(see
additional
responsible
your
power
cord,
surges.
Furthermore
IEC
60601-1-1orclause16of
all
configurations
equipmenttomedical
that
the
system
fact
that
local
laws
local
representativeorthe
you
should
select
verify
that
the
voltage
The
isolation
transformer continues
shall
the
electrical
complies
take
with
priority
technical
the
input
voltage
indicatedonthe
•Chapter 1 Safety· 7
3
the
of
to

&
WARNING
Electric
shock
monitoring
Do
not
remove
in
place
while
MEDISON
Check
the
housingisdamaged,
Always
disconnect
All
patient
applicationofa
Do
not
touch
the
maximum
The
useofflammable
I
may
exist
devices,isnot
the
coversonthe
the
systemisin
Customer
face,
contact
housing,
the
devices,
high
voltage
the
SIP/SOP
allowable
Service
orifthe
system
anesthetic
resultifthis
properly
and
suchasprobes
defibrillation
and
values.
1-2-2 ECG-Related Information
system,
grounded.
system;
use.
Department.
cable
cableisabraded.
from
patient
gasoroxidizing
hazardous
All
internal
before
the
wall
outlet
pulse.
simultaneously.
including
voltages
adjustments
use.Donot
priortocleaning
and
ECG
gases
and
allofits
are
present
and
replacements
use,ifthe
the
leads,
mustberemoved
Doingsomay
(N20)
shouldbeavoided.
externally
faceiscracked,
system.
causealeakage
mounted
inside.
Cabinet
mustbemadebya
from
See
it
all
MEDISON
recording
panels
must
qualified
chipped,ortorn,
the
patient
prior
current
exceeding
_.
and
be
the
to
1-2-3
&
WARNING
This
deviceisnot
meansofindicatinganinoperative
Do
not
use
resu~
in
Do
not
use
Do
not
use
I
ECG
electrodesofHF
bumstothe
ECG
electrodes
ECG
leads
intendedtoprovideaprimary
patient.
and
ESD
Electrostatic
phenomenon.
heatingorair
individuals,
build-up
equipment,
energy
The
ESD
discharge
ESDismost
conditioning.
creating
static
comesincontact
and
even
other
build-up
caution
fromacharged
symbolison
(ESD),
electricity.AnESD
with
electrocardiograph.
surgical
during
cardiac
electrodesinan
commonly
prevalent
During
low
during
humidity
conductive
individuals.
The
individualtoa
the
probe
ECG
equipment.
pacemaker
operating
Any
proceduresorother
room.
referredtoas
conditionsoflow
conditions,
occurs
whenanindividual
objects
suchasmetal
static
shockorESDisa
lesserornon-charged
connector
and
monitoring
astatic
function,
malfunctionsintheHFsurgical
shock,isa
humidity,
electrical
and
electrical
naturally
which
charges
withanelectrical
doorknobs,
dischargeofthe
individualorobject.
the
rear
panel.
therefore
does
equipment
stimulators.
occurring
canbecaused
naturally
file
buildupon
cabinets,
electrical
not
have
may
by
energy
computer
[Figure
1-2
ESD symbol]
•Chapter 1 Safety· 8

Lt.
CAUTION
The
levelofelectrical
significant
The
following
Anti-static
Anti-static
A
ground
I
energy
discharged
enoughtocause
precautions
sprayoncarpetsorlinoleum
mats
wire
connection
damagetothe
can
helptoreduce
between
fromasystem
systemorprobes.
ESD
the
system
and
userorpatienttoan
:
the
patient
tableorbed.
ultrasound
See
it
all
,.
MEDISON
system
can
be
1-2-4
EMI
Although
Interference)
cause
If
this
used,toidentify
electrical
as
cellular
microwave
Lt.
In
1-2-5 EMC
The
the
intemational
adoptedinEuropeasthe
1)
Guidance
This
or
this
system
requirements,
momentary
occurs
often,
possible
devices
phones
transmission
CAUTION
cases
where
EMIiscausing
testing
for
EMC(Electromagnetic
standard
and
manufacturer's
productisintended
the
userofthis
has
been
manufacturedincompliance
useofthis
degradationofthe
MEDISON
suggestsareviewofthe
sourcesofradiated
used
within
the
and
pagers
can
equipment
disturbances,itmaybenecessarytorelocate
for
EMC
European
declaration-electromagnetic
for
useinthe
product
should
systeminthe
ultrasound
emissions.
same
roomoran
cause
these
emissions.
nearby
can
also
Compatibility)ofthis
with
medical
norm
devices
(EN60601-1-2).
electromagnetic
assure
thatitis
with
existing
presenceofan
EMI(Electromagnetic
electromagnetic
image.
environmentinwhich
These
adjacent
room.
The
cause
interference.
system
(IEC60601-1-2).
emissions
existenceofradios,
has
couldbefrom
Communication
this
been
performed
This
emission
environment
specified
usedinsuchanenvironment.
the
systemisbeing
system.
IEC
standard
below.
field
can
other
devices
TVs,
or
according
was
The
customer
such
to
RF
Emission
(Radiation)
CISPR
11
RF
Emission
(Radiation)
CISPR
11
Harmonic
IEC
61000-3-2
Ricker
Emission
IEC
61000-3-3
•
Emission
•
• •
Group
Class
A
Group
Class
A
Class
A
Complies
.
..
-
1
The
Ultrasound
function.
1
likelytocause
The
Ultrasound
establishments,
directly
network
System
Therefore,
connectedtothe
that
itsRFemissions
any
interferenceinnearby
Systemissuitable
including
supplies
building
•
usesRFenergy
domestic
public
low-voltage
used
•
••
only
for
are
very
low
electronic
for
useinall
establish-ments
power
for
domestic
•Chapter 1 Safety· 9
its
intemal
and
are
equipment.
and
supply
purpose.
not
those

2)
Approved
CD
Cables,
Approved
Transducers
Cable
for
and
Accessories
Electromagnetic
for
EMC
Compliance
See
it
all
I.
MEDISON
Cables
lengths
Printer
connectedtothis
listed
below
..
.
VGA
Parallel
RS232C
USB
LAN(RJ45)
S-Video
Foot
Switch
BNJ
Printer
MIC
Remote
table
product
.
may
affect
Twisted
Unshielded
Unshielded
Unshielded
its
Shielded
Shielded
Shielded
Shielded
Shielded
Shielded
Coaxial
emissions;
pair
Use
only
the
cable
Normal
Normal
Normal
Normal
Normal
2.5m
Normal
Any
Any
Any
types
and
@
Approved
The
CID
Approved
Accessories
&
CAUTION
When
connecting
is
the
user's
CISPR
Audio
R.L
VHS
ECG
AUX
input
Transducer
image
transducer
Accessories
used
I
other
responsibilitytoensure
22,
CLASSBcompliant
for
Electromagnetic
used
with
this
for
Electromagnetic
with
this
product
customer-supplied
the
devices.
Shielded
Shielded
Shielded
Compliance
product
may
Compliance
may
effect
its
accessoriestothe
electromagnetic
affect
its
emission.
emissions.
system,
compatibilityofthe
suchasa
system.
Normal
Normal
<3m
remote
Use
printerorVCR,
only
CISPR11or
it
•Chapter1 Safety·
10

Immunity
Electrostatic
discharge
IEC
61000-4-2
test
(ESD)
IEC
Test
±
6KV
Contact
±8KVair
60601
level
Compliance
±6KV
Contact
±8KV
air
level
environment
Floors
shouldbewood,
ceramic
tile.Iffloors
synthetic
shouldbeat
material,
See
it
MEDISON
Electromagnetic
-guidance
concrete
are
covered
the
relative
least
30%.
all
humidity
_.
or
with
Electrical
transientlburst
IEC61000-4-4
Surge
IEC
Voltage
interruptions
voltage
on
input
IEC
fast
61000-4-5
dips,
variations
power
supply
lines
61000-4-11
and
short
±2KV
for
power
supply
lines
±1KVfor ± 1KVfor
input/output
± 1KVdifferential
mode
±2KVcommon
mode
<5%
(>95%
for
0.5cycle
40%
(60%
for5cycle
70%
(30%
for25cycle
<5%
(<95%
for
5s
Ur
Ur
Ur
Ur
dip
dip
dip
dip
lines
in
Ur)
in
Ur
in
Ur)
in
Ur)
)
±2KV
supply
output
lines
±1
KV
mode
±2KV
<5%Ur
(>95%
for
0.5cycle
40%
Ur
(60%
dip
for5cycle
70%
Ur
(30%
dip
for25cycle
<5%Ur
«95%
for
5s
for
power
lines
input/
differential
common
dipinUT)
in
Ur
in
Ur)
dip
in
Ur)
mode
)
Mains
power
quality
typical
commercialorhospital
environment.
Mains
power
quality
typical
commercialorhospital
environment.
Mains
power
quality
typical
commercialorhospital
environment.Ifthe
requires
power
recommended
powered
supplyora
continued
mains
interruptions,itis
that
fromanuninterruptible
battery.
shouldbethatofa
shouldbethatofa
shouldbethatofa
userofthis
operation
this
during
product
product
be
power
Power
frequency
(50/60Hz)
magnetic
IEC
61000-4-8
NOTEUris
field
the
3A/m 3A/m
a.c.
mains
voltage
priortoapplicationofthe
test
Power
beatlevels
locationina
hospital
level.
frequency
environment.
magnetic
characteristicofa
typical
fields
typical
commercial
•Chapter 1 Safety·
should
or
11

See
it
all
,.
MEDISON
Immunity
Conducted
IEC
61000-4-6
RF
test
IEC60601
Test
level
3Vrms
150
kHz
80MHz
• ••
Portable
and
mobileRFcommuni-cations
equipment
partofthe
cables,
distance
applicabletothe
to
0.01V
transmitter.
Recommended
d =
ril
d = [
wherePis
ratingofthe
accordingtothe
anddis
distanceinmeters
shouldbeusednoclosertoany
Ultrasound
than
the
calculated
[3,,5~Jr
VI
3/J
.[ji
=
["ill
~
(JP
the
the
System,
recommended
from
the
frequencyofthe
separation
P
80MHzto800MHZ
BOOMHzto205GHz
maximum
transmitterinwatts
transmitter
recommended
(m).
including
separation
equation
distance
output
power
(W)
manufacturer
separation
Field
Radiated
IEC
61000-4-3
RF
3
V/m
80
MHzto
2.5GHz
3V/m
strengths
transmitters,asdeter-minedbyan
electromagnetic
less
than
frequency
Interference
equipment
symbol:
from
the
compliance
range.
may
marked
fixed
RF
site
survey,ashould
levelineach
b
occurinthe
with
the
vicinity
following
((~))
NOTE
1)At80MHz
NOTE
2)
These
is
a Field strengths from fixed transmitters, such as base stations for radio (cellular/cordless)
telephones
broadcast cannot
environment due
considered.Ifthe measured field strengthinthe locationinwhich the Ultrasound System
is used exceeds the applicable
be
observedtoverify normal operation.Ifabnormal performance is observed, additional
measures may
using a shielded location with a higher
b Over the frequency range 150kHz
and
800MHz,
guidelines
affectedbyabsorption
and
land mobile radios, amateur radio,
be
to
fixedRFtransmitters,anelectromagnetic site survey should
be
necessary, such as re-orienting or relocating the Ultrasound System or
the
higher
may
not
applyinall
and
reflection
predicted theoretically with accuracy.Toassess the electromagnetic
RF
frequency
situations.
compliance level above, the Ultrasound System should
RF
to
80MHz, field strengths shouldbeless than [V,]
range
applies.
Electromagnetic
from
structures,
shielding effectiveness and filter attenuation.
objects
AM
andFMradio broadcast and TV
propagation
and
people.
be
V/m
be
of
.
•Chapter1 Safety·
12

3)
Recommended
and
the
SonoAce
This
productisintended
are
controlled.
by
maintainingaminimum
separation
X4
The
customerorthe
distances
for
useinan
distance
between
portable
electromagnetic
userofthis
between
product
portable
and
mobileRFcommunications
environmentinwhich
can
help
Prevent
and
mobileRFcommunications
radiatedRFdisturbances
electromagnetic
See
it
all
,.
MEDISON
equipment
interference
equipment
(transmitters)
the
communications
...
..
• •
••
0.01
0.1
10
100
For
transmitters
in
meters
(m)
the
maximum
NOTE1)At
NOTE2)These
80MHz
absorption
and
this
productasrecommended
equipment.
• •
ratedata
canbeestimated
output
guidelines
power
and
and
maximum
ratingofthe
800MHz,
may
reflection
...
....
35.00
110.68
350.00
1106.80
3500.00
output
using
the
transmitterinwatts
the
separation
not
applyinall
from
power
equation
situations.
structures,
below,
accordingtothe
•• • • •
not
listed
applicabletothe
(W)
distance
for
Electromagnetic
objects
and
0.11
0.36
1.16
3.68
11.66
above,
the
frequencyofthe
accordingtothe
the
higher
people.
maximum
••
recommended
frequency
propagationisaffected
output
•
separation
transmitter,
transmitter
range
applies.
power
of
0.23
0.73
2.33
7.37
23.33
distanced
where
manufacturer.
by
pis
4)
Electromagnetic
The
Ultrasound
effectiveness
shielded
and,
location
shouldbeless
Itisessential
be
verifiedtoassure
Lt.
CAUTION
If
the
systemisconnectedtoother
remote
electromagnetic
printer,
that
Medison
environment-guidance
System
mustbeused
for
each
cable
from
fixedRFtransmitters,asdeterminedbyan
than3V/m.
the
actual
shielding
that
they
meet
I
customer-supplied
cannot
guarantee
phenomena.
onlyina
that
enters
effectiveness
the
minimum
that
the
the
remote
shielded
location
shielded
and
filter
specification.
equipment,
equipment
withaminimumRFshielding
location.
Field
strengths
electromagnetic
attenuationofthe
suchasa
will
local
work
correctlyinthe
area
outside
site
shielded
network
•Chapter1Safety·
the
survey,
location
(LAN)ora
presence
of
13

5)
Avoiding
A
Electromagnetic
medical
device
can
Interference
either
generateorreceive
electromagnetic
interference.
See
it
MEDISON
The
EMC
standards
all
_.
describe
Medison
An
to
device,
tests
Ultrasound
Ultrasound
interference
information
for
Systemisdesignedtoreceive
generated
sourceofradiated
attempttolocate
•Isthe
interference
•
Does
the
interference
with
several
•Dotwo
•Isthe
The
answerstothese
the
scanning
customer
transducer?
different
interference
environment.
service
both
emitted
and
received
Systemsdonot
byRFenergy
technology
interference
the
source:
products,
canbea
intermittentorconstant?
showuponly
transducer
operatingatthe
presentifthe
questions
After
will
you
department.
interference.
generate
interferenceinexcessofthe
signalsatradio
sources.
difficult
with
Examplesofother
and
radio
task.
one
transducers
same
and
television
Customers
frequency
systemismovedtoa
help
determineifthe
answer
the
question,
frequency
sourceofinterference
transmission
should
operatingatthe
have
different
problem
contact
locationinthe
reside
your
referenced
andistherefore
towers.
consider
the
same
the
same
problem?
facility?
with
the
system
local
MEDISON
standards.
susceptible
are
medical
Tracing
the
followinginan
frequency
or
or
•Chapter1Safety·
14

Mechanical Safety
See
it
all
_.
MEDISON
1-3-1
Moving the Equipment
When
you
move
the
equipment,
canbeseparated
The
adjustable
The
components
may
cause
system.Ifthe
Service
1)
2)
Department.
Lt.
WARNING
The
system
shouldittopple
The
Brakes
The
brakes
You
can
while
scanning.
PrecautionsonRamps
wheels
system
system
can
over.
areonthe
use
the
and
easily
under
are
installed
failure.Onrare
operates
I
weigh
approximately
front
brakestocontrol
you
should
use
removed
the
securely
from
console
and
the
facilitate
can
occasionsacomponent
abnormally
wheelsofthe
after
101kg(202Ib),
console.
the
movementofthe
the
handleatthe
unitifnecessary.
easy
transportingofthe
withstand
considerable
may
repositioning,
depending
Press
the
please
upon
brakes
product
backsideofthe
product.
shock,
become
disconnected
contact
configuration,
with
your
feettolockorrelease
suchasby
console.
but
excessive
the
MEDISON
and
preventing
inside
could
The
monitor
shock
the
Customer
cause
its
movement
injury
them.
Always
Lt.
WARNING
Be
awareofthe
caution
When
even
with
make
sure
that
the
control
panelisfacing
the
directionofmovement.
I
castors,
when
moving
moving
the
the
brakesondependingonthe
[Good example] [Bad example]
especially
the
productupor
product
when
moving
the
down
system.
ramps.
MEDISON
downaramporrestingittemporarilyona
directionofthe
product.Donot
recommends
ramp,
the
rest
that
you
product
the
may
productonramps.
exercise
tilt
over
•Chapter 1Safety·
15

1-3-2 Safety Note
&
CAUTION
Never
attempttomodify
Check
the
operational
Make
sure
Do
not
block
To
prevent
I
safety
that
other
objects,
the
ventilation
damagetothe
the
productinany
when
suchasmetal
slots.
power
way.
using
the
product
pieces,donot
cord,besuretogrip
afteraprolonged
enter
the
the
plug
head?
breakinservice.
system.
not
the
cord-when
See
it
all
_.
MEDISON
unplugging.
Excessive
of
the
Improper
bendingortwistingofcablesonpatient-applied
system.
cleaningorsterilizationofa
1-3-3 Safety Note for Monitor
When
monitor
adjusting
and
the
the
arm.
positionofthe
patient-applied
monitor,becareful
part
may
nottoget
parts
may
cause
your
cause
failureorintermittent
permanent
fingers
caughtinbetween
operation
damage.
the
[Figure
1-3
Safety Note for Monitor]
•Chapter 1 Safety·
16

Biological Safety
Lt.
WARNING
Ultrasound
thereisno
low.
Please
Do
not
use
condition
Customer
Do
not
useasystem
are
indicativeofa
The
system
observes
I
waves
medical
refertothe
the
systemifan
exists.
Service
limits
American
may
have
benefit,
ALARA
Note
the
Department.
that
exhibits
hardware
the
maximum
FDA
regulations.
damaging
minimize
error
failure
effectsoncells
the
exposure
principle.
error
message
code,
erraticorinconsistent
that
contact
appearsonthe
turn
off
shouldbecorrected
temperatureto43
time
the
powertothe
and,
therefore,
and
maintain
updating.
before
degree
maybeharmfultothe
the
ultrasound
video
display
indicating
system,
Discontinuitiesinthe
use.
Celsius,
and
and
the
call
your
ultrasonic
wave
scanning
See
it
all
_.
MEDISON
patient.
output
level
at
thatahazardous
local
MEDISON
sequence
waves
output
If
1-4-1
ALARA
Guidance
(ALARA)
of
dictate
possible,
Since
qualified
the
the
Principle
for
the
useofdiagnostic
principle.
personnel.Nosetofrules
correct
while
threshold
The
response
obtaining
for
responsibilitytocontrol
exposure
time,
the
The
sound
need
that
There
usedtoimplement
bone
timeisan
values
time
with
diagnostic
the
ultrasound
resultsofthe
abilityofthe
not
onlyinthe
for
more
important
system
exam.
usertoabidebythe
and
better
information
areanumberofvariables,
the
relativetothe
focal
especially
over
time
support
decisionasto
for
every
diagnostic
diagnostic
the
total
energy
image
provides
technology
but
informationtoguide
which
ALARA
useful
principle.
point,
attenuationinthe
variable,
the
ALARA
ultrasoundisdefinedbythe
whatisreasonable
canbeformulated
has
that
circumstance.Bykeeping
images,
ultrasound
because
users
can
bioeffectsisundetermined,itis
transmitted
into
quality.Toensure
controls
ALARA
alsointhe
that
canbemanipulated
principleisimportant.
applicationsofthe
the
user.
affect
the
wayinwhich
These
variables
body,
the
user
minimize
the
patient.
diagnostic
The
include
and
controls
principle.
"as
lowasreasonably
been
lefttothe
judgment
wouldbesufficiently
ultrasound
ultrasonic
exposureaslow
bioeffects.
the
The
sonographer
image
quality
during
Advancesindiagnostic
technology,
output
indices
the
mass,
ultrasound
it.
The
are
output
display
body
exposure
abilitytolimit
size,
achievable"
and
insight
complete
to
as
sonographer'
must
and
limit
the
examtooptimize
s
reconcile
exposure
ultra-
have
resultedinthe
designedtoprovide
indices
can
be
locationofthe
time.
Exposure
the
index
1)
Applying
The
imaging
flow.
ALARA
system-imaging
provide
Scanned
anatomical
modes,
mode
like
used
depends
information,
2D-mode
upon
the
while
Doppler
disperseorscatter
information
imaging
the
ultrasonic
needed.
provide
energy
2D-mode
information
overanarea,
•Chapter!Safety·
and
about
M-mode
blood
while
an
17

See
it
all
_.
MEDISON
unscanned
natureofthe
with
operator
The
This
mode,
imaging
informed
judgment.
experience
decisionasto
decision
mustbebasedonthe
like
the
easeordifficultyofobtaining
the
patient
duetoprobe
exposureislimitedtothe
acceptable
Althoughahigh
shouldbetaken
reading.
There
acoustic
ALARA.
2)
Direct
Application
rangesofallowable
intensity
vascular
the
user
and
Output
control
select
output
diagnostic
index
seriously.
Limiting
are
intensity.
These
several
controls
exposure
system
These
Controls
selection
and
intensityoroutput
for
the
applicationisoneofthe
intensity
proper
bears
user-definable
has
levels
range
foraparticular
the
responsibility
settings.
direct
impactonacoustic
canbeusedtoincreaseordecrease
intensity
intensity
levels
consistent
M-modeorDoppler,
mode
being
used
The
probe
frequency,
aid
the
sonographerinmeeting
amountofacoustic
following
diagnostically
surface
lowest
temperatures.
index
results.
reading
does
Every
timeisan
controls
controls
not
effort
effective
that
are
relatedtothe
canbedivided
the
output
intensity
are
not
recommended
procedure,
for
proper
intensity.
less
than
the
defined
with
good
image
concentrates
allows
the
system
output
is,inthe
factors:
useful
information,
Prudent
reading
mean
for
the
thatabioeffectisactually
ultrasonic
sonographertoapply
set-up
the
definitionofthe
final
typeofpatient,
useofthe
shortest
shouldbemadetoreduce
waytoaccomplish
the
operator
into
three
control
basedonyour
first
things
while
clinical
maximum.
use.
Once
the
for
intensity
can
usetoadjust
techniques
categories:
directly
affect
selection.
required
fetal
others
exams.
The
MEDISON
the
during
require
application
output.
Prudent
thatanoperator
quality.
energy.
values,
scanning
analysis,upto
typeofexam,
and
the
potential
system
amountoftime
occurring,ahigh
the
possible
this
goal.
the
image
direct,
indirect,
acoustic
Selecting
Some
manual
any
intensity.
the
exam.
systems
selection.
system
has
been
The
output
use
dictates
Understanding
the
ALARA
principle
techniques,
ALARA
the
principle.
system
operator.
patient
localized
occurs
when
heating
patient
necessarytoachieve
index
effectsofa
quality
and
might
usetoimplement
and
receiver
correct
For
example,
control.
There
are
rangeofacoustic
peripheral
automatically
Ultimately,
provides
both
automatic
established,
control
allows
that
you
select
the
the
and
history,
reading
high
index
limit
different
select
the
the
output
you
to
lowest
of
the
3)
Indirect
The
indirect
imaging
The
choiceofimaging
mode,
onasingle
the
beamisonly
Pulse
periodoftime.
Controls
controls
mode,
Dopplerisa
are
those
pulse
repetition
mode
determines
stationaryorunscanned
location.Amovingorscanned
concentratedona
repetition
frequencyorrate
The
higher
the
that
haveanindirect
frequency,
given
referstothe
pulse
repetition
effectonacoustic
focus
depth,
the
natureofthe
mode.Astationary
ultrasound
area
beam
forafractionofthe
numberofultrasound
frequency,
pulse
length,
ultrasound
disperses
the
more
time
intensity.
and
beam.
u~rasound
the
These
probe
2D-modeisa
beam
energy
overawide
selection.
concentrates
necessaryinunscanned
burstsofenergy
pulsesofenergyina
controls
affect
scanning
energy
area
mode.
overaspecific
given
period
•Chapter1Safety·
and
18

of
time.
Several
depth,
numberoffocal
Focusofthe
different
of
depth
Pulse
the
focus
system
optimization.
improves
lengthisthe
time-average
temperature
pulse
durationinpulsed
Probe
selection
the
probe
operating
operating
the
point,
same
without
frequencies
output
controls
ultrasound
affect
zones,
beam
pulse
and
sector
affects
repetition
requiresavariationinoutput
Different
the
resolutionofthe
time
during
intensity
increase
and
Doppler.
affects
intensity
frequency,
require
intensity,alower
corresponding
exams
structureofinterest.
which
the
value.
The
cavitations.
Increasing
indirectly.
the
greater
higher
output
probe
increasesinimage
frequency:
width
controls.
the
image
resolution.Tomaintainorincrease
over
the
focal
require
different
ultrasonic
greater
Pulse
burstistumed
the
time-average
lengthorburst
the
Doppler
Tissue
attenuation
the
attenuationofthe
intensitytoscanata
frequencyisrequired.
quality,
can
focal
depth,
zone.
This
focal
depths.
on.
intensity,
lengthorpulse
sample
volume
changes
ultrasonic
deeper
Using
mean
thatalower
See
MEDISON
display
depth,
sample
resolutionata
variationofoutputisa
Setting
the
focustothe
The
longer
the
pulse,
the
greater
the
durationisthe
increases
with
frequency.
energy.
depth.Toscan
more
gain
frequency
the
Higher
and
output
probeisneeded.
it
all
volume
function
the
greater
likelihood
output
pulse
The
higher
probe
deeper
beyond
_.
proper
of
length.
at
a
4)
Receiver
Receiver
on
gain,
is
output,
5)
Additional
Ensure
performed.
follow-up,
and,
6)
Output
The
The
three
user
The
The
Each
is
Controls
controls
output.
Receiver
TGC,
dynamic
that
receiver
optimize
Considerations
that
scanning
Never
which
like
any
tool,
Display
system
output
thermal
index
thermal
choice,
depending
mechanical
thermal
probe
index
application
continuously
are
usedbythe
controls
range,
controls
shouldbeoptimized
gaintoimprove
timeiskepttoa
compromise
ultimately
shouldbeused
Features
display
consistsofthe
indices
willbedisplayedatall
upon
indexiscontinuously
consistsofthe
hasadefault
displayed
application,inincrementsof0.1.
The
application-specific
natureofthe
operatortoimprove
only
affect
and
image
image
qualitybyrushing
increases
efficiently
comprises
following
the
applicationathand.
three
over
the
rangeof0.0tomaximum
image
how
the
ultrasound
processing.
before
The
important
increasing
quality.
minimum,
and
ensure
throughanexam.Apoor
the
time.
Diagnostic
and
effectively.
two
basic
indices:amechanical
indices:
displayed
indices,
selection
default
soft
times.
Which
over
the
and
only
thatisappropriate
settingisalsoanimportant
quality.
These
echoisreceived.
thingtoremember,
output.
that
only
ultrasoundisan
tissue
(Tls)
one
depends
For
medically
index
and
bone
upon
controls
example;
exam
important
andathermal
havenoeffect
These
controls
relativetooutput,
before
required
will
require
toolinmedicine,
(Tlb).
Oneofthese
the
system
increasing
scanning
index.
preset
rangeof0.0to1.9,inincrementsof0.1.
oneoftheseisdisplayedatanyone
for
that
output,
combination.
basedonthe
factorofindex
probe
The
TlborTls
and
behavior.
include
is
a
or
time.
A
•Chapter 1Safety·
18

default
system
by
the
settingisa
has
ultrasound
default
system
index
system
orachangeinapplication
The
decisionasto
Appropriate
Some
factors
or
the
flowofblood.Ahighly
zone
heatingtobe
Scanned
heating
modes
tendstobe
deeperinthe
Always
limit
whichofthe
index
for
might
less
versus
focal
zone.
ultrasound
the
application:
create
than
unscanned
near
exposure
control
settings
when
poweristumed
takes
three
artificially
attenuating
the
the
surface;
state
whichispresetbythe
for
the
probe
application.
on,
place.
thermal
Tlsisused
highorlow
indicestodisplay
for
thermal
tissue
thermal
index
displays.
modesofoperation
for
unscanned
time.Donot
rush
new
imaging
path,
the
The
patient
soft
index
for
example,
affect
modes,
exam.
manufacturerorthe
default
settings
dataisentered
are
into
invoked
the
shouldbebasedonthe
tissue;
and
Tlb
forafocusator
readings
the
the
will
thermal
potential
Ensure
e.g.
presenceoffluidorbone,
cause
the
potential
index.
For
for
heating
that
the
indices
See
it
all
_.
MEDISON
operator.
system
scanned
The
automatically
database,
following
criteria:
near
for
local
modes,
tendstobe
are
kepttoa
bone.
minimum
7)
Mechanical
Mechanical
The
varies
and
Index
bioeffects
threshold
with
peak
theMlvalue,
value
that
means
implementing
8)
Thermal
Index
TheTlinforms
within
body
tissue,orat
the
temperature
influencedbyfactors
usedasa
The
ultrasound
bone
guide
thermal
beam
that
exposure
(Ml)
Display
are
threshold
level
varies,
however,
pressure
the
greater
and
the
thatamechanical
the
ALARA
(Tl)
the
Display
user
about
principle.
the
increaseinspecific
suchastissue
for
implementing
index
(Tlb)
has
passed
timeislimited
ultrasound
without
phenomena
with
the
typeoftissue.
frequency.
that
likelihoodofmechanical
effect
will
actually
the
potential
pointoffocusofthe
the
informs
through
body
type,
ALARA
the
soft
tissues.
vascularity,
user
for
temperature
ultrasound
principle.
about
tissueorfluid,
compromising
occur
whenacertain
The
TheMIaccounts
bioeffects
occur.
occurring
TheMIshouldbeusedasa
increase
beamonbone.
The
actual
amountofany
and
modeofoperation
potential
heatingator
for
example,ator
diagnostic
potential
for
these
occuringatthe
sensitivity.
levelofoutputisexceeded.
for
mechanical
two
but
thereisno
TheTIisanestimate
temperature
etc.
near
the
near
secondorthird
bioeffects
factors.
The
specific
guide
body
surface,
rise
TheTIshould
focus
after
higher
MI
for
of
is
be
the
trimester
The
cranial
the
surface,
The
soft
geneous
You
can
is
displayed
fetal
bone
for
tissue
tissue.
select
when
bone.
thermal
example,
thermal
either
you
index
(TIc)
informs
cranial
bone.
index
(Tls)
informs
TlsorTlb
using
the
selectatrans-cranial
the
user
the
user
TlslTlb
selectiononthe
application.
about
about
the
the
potential
potential
Miscellaneous
heatingofboneator
for
heating
within
system
•Chapter! Safety·
soft
homo-
setups.
near
Tic
19

9)
Mechanical
The
and
Mechanical
TheMIandTIdisplay
These
accuracy
output
modeling
The
displayed
the
ALARA
principle
Thermal
and
estimates
errors
values
indices
Display
Thermal
accuracy
Indicesonthe
estimates
are
basedonthe
and
measurement
shouldbeinterpretedasrelative
through
prudent
useofthe
Precision
for
and
system
the
system
variability
Accuracy
are
preciseto0.1
are
giveninthe
rangeofprobes
variability,asdescribed
informationtohelp
system.
The
values
See
MEDISON
units.
Acoustic
and
below.
should
Output
systems,
the
system
inherent
operator
notbeinterpretedasactual
it
all
Tables
_.
manual.
acoustic
achieve
physical
is
ments
Manyofthe
derived
are
values
investigated
from
laboratory
then
put
assumptions
measurements
into
algorithms
usedinthe
tissueororgans.
Over-estimationofactualinsitu
surement
The
and
measured
calculation
water
tank
process.
values
coefficientof0.3dB/cm-MHz.
Conservative
values
conductivity
Steady
made
that
A
numberoffactors
algorithm
isasignificant
impedance
pulse
values
for
tissueorbone
were
state
temperature
the
uttrasound
accuracy
factor.
differences,
voltage
control
for
tissue
absorption
selected.
probeisheld
are
considered
estimation
Probe
and
and
riseisassumedinthe
variability
sensitive
efficiencies
The
basedonthe
for
calculating
processofmeasurement
exposure,
are
characteristics
rates,
For
example:
de-rated
for
the
usingaconservative,
were
blood
perfusion
industry
steadyinone
when
estimating
and
measurement
results
from
lens
focusing
are
alsoacontributortovariability.
initial
data
thatisusedtosupport
AlUM
the
displayed
and
vast
majorityoftissue
selected
for
rates,
standardTImodels,
position
long
the
accuracyofdisplay
variability.
Variability
piezoelectric
parameter
measurement
output
calculation
values.
are
standard.
conservativeinnature.
paths,isbuilt
industry
standard,
useintheTImodels.
blood
heat
capacity,
and
enough
for
steady
values:
among
probes
crystal
efficiencies,
variations.
Differencesinthe
There
the
output
The
into
attenuation
Conservative
and
tissue
the
assumption
statetobe
hardware
and
process-related
are
inherent
display
measure-
the
mea-
thermal
reached.
variations,
systems
system
uncer-
is
taintiesinthe
operating
algorithms
conditions
used
and
differencesinhydrophone
tolerances,
The
and
conservative
variability
assumptionsofthe
throughaO.3dB/cm-MHz
estimate
occurinwater
and
body,
occuraspulse
displayed.
tank
organs
have
and
particularlyinwater
voltages
Neither
measurementsorin
dissimilar
increase.
for
estimating
pulse
voltages.
calibration
among
test
attenuated
linear
propagation,
attenuation
tank
acoustic
output
Inaccuraciesinlaboratory
and
performance,
operators.
output
medium
most
estimation
are
algorithmsoflinear
not
taken
nor
uniform
tissue
pathsinthe
characteristics.Inwater,
measurements,
non-linear
values
over
the
rangeofpossible
measurements
positioning,
alignment
propagation,atall
into
accountincalculationofthe
attenuationatthe
body.Inthe
thereisalmostnoattenuation.Inthe
propagation
are
and
digitization
0.3dB/cm-MHz
body,
different
and
saturation
•Chapter 1 Safety·
system
related
depths,
accuracy
tissues
losses
to
rate,
20

The
display
rent
acoustic
not
basedonerrors
They
are
also
accuracy
output
estimates
modeling
in,orcausedbymeasuring
independentofthe
take
into
account
errors,
and
measurement
effectsofnon-linear
the
variability
variability.
according
lossonthe
rangesofprobes
Display
to,
the
AlUM
measured
See
MEDISON
and
accuracy
measurement
values.
estimates
it
all
systems,
standards.
_.
inhe-
are
10)Control
Control
11)
Power
from
12)
2D-mode
Effects
affecting
As
various
as
the
power
controls
Power
aMI.They
In
combined
addtothe
the
mode
CD
2D-mode
Narrowing
voltage
the
system
controls
controlisadjusted;
the
changeasthe
modes,
total
TI.
One
with
Controls
size
the
sector
maybeautomatically
maximums.Adecreaseinpulse
®Zoom
Increasing
the
zoom
indices
are
system
adjusted,
however,
acoustic
system
theTIandMIvalues
other
output.
Two
respondstoPower
suchassimultaneousMmode
mode
the
largest
angle
magnification
willbethe
peak
may
adjusted
dominant
pressure.
increase
down
voltage
may
the
will
increase
system
controls
real-time
output
adjustments.
andPWDoppler,
contributortothis
frame
rate.
with
software
decrease
MI.
frame
may
change.
will
affect
values
the
total.
This
action
controlstokeep
rate.
This
action
This
willbemost
the
on-screen
areonthe
individual
The
displayedMIwill
will
increase
theTIbelow
will
increase
apparent
output
screen:aTI
modes
each
the
TI.
Pulse
the
system
the
TI.
values.
and
be
The
numberoffocal
MI
since
@
Persistence
A
lower
in
pulse
CD
Focal
no.
More
focal
Lower
frame
intensity.
®
Focus
on
Changing
depthisnear
zones
the
peak
persistence
voltage
will
zones
may
rates
the
focal
the
natural
may
intensity
will
decrease
increase
change
decrease
depth
will
focusofthe
also
can
MI.
both
the
change
increase
occurata
the
TI.
automaticallytoimprove
different
TI.
Pulse
theTIandMIby
MI
displayed
the
MI.
depth.
voltage
changing
will
Generally,
transducer.
resolution.
maybeautomatically
frame
rateorfocal
correspondtothe
zone
higherMIvalues
This
action
may
change
increased.Anincrease
depth
automatically.
with
the
largest
will
occur
when
the
•Chapter 1 Safety· 21
peak
focal

13)
M-mode
CD
Speed
M-mode
changes,TIchanges.
®
Simultaneous
Useofcombination
During
the
dominant
@
Sample
When
A
decreaseinPRF
voltagetoremain
14)
Doppler,
Whenanew
mode
hasacorresponding
simultaneous
for
the
focal
the
system
and
Doppler
and
Doppler
and
simultaneous
pulse
Volume
Doppler
M-mode
sample
and
imaging
modes,
zone
and
will
retumtothe
Controls
sweep
speed
Update
Methods
modes
affects
mode,
theTIis
type.
The
displayedMIwillbefrom
Depth
volume
will
decrease
below
the
system
Imaging
Controls
modeisselected,
pulse
theTIis
mode
with
the
the
previously
adjustments
both
additive.
depthisincreased
the
TI.
will
not
theTIandMIthrough
During
auto-update
the
Doppler
The
system
may
maximum.Adecreaseinpulse
both
repetition
sumofthe
largest
selected
theTIand
frequency
contribution
derated
settings.
theMIwill
and
intensity.Ifa
affect
the
the
the
mode
also
maximum
from
the
modeistumed
MI.
When
M-mode
combinationofpulse
and
duplex,
theTIwill
with
the
largest
PRF
may
automatically
automatically
voltage
decrease
will
changetodefault
intensity
modes
point.Incombined
enabled
off
and
See
it
all
_.
MEDISON
sweep
speed
types.
display
peak
pressure.
decrease.
the
pulse
decrease
settings.
andMIis
then
MI.
Each
or
the
MI
reselected,
15)
Related
CD
®
@
For
AlUM
Bioeffects
Probe
Each
probe
model
frequency.
application,
Defaults
and
Depth
An
increasein2D-mode
decrease
the
TI.
changeoffocal
peak
intensity.
Application
Acoustic
probe,
Guidance
more
Report,
output
application,
Documents
information
January
Considerations
available
are
selected
The
system
depth
may
defaults
and
about
28,
has
unique
initialized
mode.
depth
when
Defau~s
will
may
change
are
set
when
mode.
Defaults
ultrasonic
1993,
"Bioeffects
for
the
SafetyofDiagnostic
specifications
you
selectaprobe.
have
been
automatically
also
automatically
the
MI.
TheMIdisplayedisthatofthe
you
selectanapplication.
have
been
bioeffects
and
and
SafetyofDiagnostic
for
MEDISON
chosen
decrease
contact
below
the
2D-mode
the
area,
factory
FDA
chooseadeeper
MEDISON
chosen
below
the
FDA
related
topics
refertothe
Ultrasound"
Ultrasound,JUltrasound
beam
shape,
defau~s
limits
for
frame
2D-mode
zone
factory
limits
for
following;
Med.,
vary
intended
rate.
This
focal
with
the
defaults
intended
Sept.
and
with
use.
would
depth.
largest
vary
1998:
center
probe,
A
with
use.
Vol.7,No.9Supplement
•Chapter 1 Safety·
22

See
it
all
_.
MEDISON
Acoustic
Acoustic
Second
this
Information
Transducers.
Standard
Ultrasound
WFUMB.
Thermal
and
16)
Acoustic
Since
uttrasound
the
Committee
Sept.
available
Diagnostic
Output
Measurement
Output
Labeling
Editionofthe
AlUM
documentisshipped
for
Manufacturer
FDA.
September
for
Real-Time
Equipment.
Standard
Standard
with
Output
each
Seeking
1997.
for
Diagnostic
Display
system.)
Marketing
FDA.
DisplayofThermal
(Revision1,AlUM,
for
Diagnostic
Standard
and
NEMA.
SymposiumonSafetyofUltrasoundinMedicine:
and
Biology,
Output
the
first
exposure
American
(Bioeffects
1988:
Vo1.7,
dataonpossible
Ultrasound,"
Non-Thermal
1998:
Vol.
and
usageofdiagnostic
InstituteofUltrasoundinMedicine(AIUM)
No.9
Mechanisms
24,
Supplement1.
Measurement
have
been
studiedbyvarious
Considerations
Supplement),
effectsofultrasound
dated
January
for
ultrasound,
for
the
sometimes
28,
1993
Biological
Ultrasound
Ultrasound
Brochure,
Equipment
Dated
ClearanceofDiagnostic
Mechanical
Acoustic
1998)
Conclusions
EffectsofUltrasound,
the
possible
scientific
human
and
medical
ratifiedareport
SafetyofDiagnostic
referredtoas
exposure.
provides
the
Another
moreupto
Equipment.
Output
(AlUM,
(AlUM,
1998)
March
10,
1994.(Acopy
Ultrasound
Systems
IndicesonDiagnostic
and
Recommendations
NEMA.
UltrasoundinMedicine
biological
effects
(bioeffects)
institutions.InOctober
preparedbyits
Bioeffects
Ultrasound,JUltrasound
Stowe
Report,
which
reviewed
report
"Bioeffects
date
information.
and
Safety
1998)
of
and
on
of
1987,
Med.,
of
The
acoustic
December
Medical
surement
17)InSitu,
All
water
The
of
estimated
In
Devices,"
Standard
Derated,
intensity
measurements
true
valueofthe
the
ultrasound
using
Situ=Water
where:InSitu=In
Water=Water
e=2.7183
a=
Tissue
Brain
output
1985
"510(1<)
except
and
parameters
that
the
[
e(02
Attenuation
a(dB/cm-MHz)
for
this
system
Guide
for
that
the
for
Diagnostic
Water
Value
are
measuredinwater.
representaworst
intensityatany
passes
following
3a
1f)]
Situ
through
formula:
Intensity
Value
Intensity
Factor
.53
has
been
Measuring
hydrophone
Ultrasound
Intensities
case
point
dependsonthe
the
tissue.
Value
measured
and
Reporting
meets
Equipment"
Since
value.
Biological
The
and
calculatedinaccordance
Acoustic
the
requirementsof"Acoustic
OutputofDiagnostic
(NEMAUD2-1992)
water
does
not
absorb
tissue
does
amount
intensity
and
typeoftissue
valueinthe
Output
acoustic
absorb
energy,
acoustic
and
tissue,InSitu,
•Chapter 1 Safety·
with
the
Uttrasound
Mea-
these
energy.
the
frequency
has
been
23

See
it
all
_.
MEDISON
I=
skin
f=
Center
Since
tissue,itis
reporting
· W [
I S
n
Itu=ater
Since
The
maximum
condition;
Situ
(derated)
intensitiesinits
shallowest
18)
Acoustic
The
terms
ISPT
ISPPA.3
MI
Pr.3
WO
Fc
ZSP
Heart
Kidney
Liver
Muscle
linetomeasurement
frequencyofthe
the
ultrasonic
path
difficulttoestimate
purpose;
this
valueisnot
therefore,
3
J
e·(O.2
aIf
derated
therefore,
the
formula.
deepest
focal
zones.
Output
and
Measurement
and
symbols
A.3
The
derated
The
derated
valueofIPA.3atthe
of
ISPPA.3ifthe
The
Mechanical
reported
The
giving
The
the
WOisthe
reported
The
with
For
is
The
x-6,y-6
in
insteadofMI
derated
risetothe
ultrasonic
total
time-average
ultrasonic
under
center
frequency
the
transmit
ISPT
A.3,
definedasthe
axial
distanceatwhich
are
respectively
the
x-y
plane
.66
.79
.43
.55
depth
(cm)
transducer/system/mode
combination(MHz)
duringanexaminationislikelytopass
the
theInSitu
]
the
trueInSitu
and
the
maximum
reported
Take
for
exampleamulti-zone
zone:
the
usedinthe
spatial-peak
spatial-peak
positionofglobal
global
Index.
peak
rarefactional
trueInSitu
maximum
same
acoustic
temporal-average
pulse-average
maximumMIis
The
(global
intensity.Anattenuation
value
whichiscommonly
intensity,
the
water
valuesdonot
water
transducer
output
term
and
may
tables
intensity
maximumMI(IPA.3@MI)
reported.
valueofMIatthe
maximum
pressure
value)ifISPPA.3is?190W/cm2
(megapascals)
derated
array
intensity
reportedMIvalue.
power
(milliwatts).
power;.
power
For
For
operating
associated
the
operating
with
conditions
the
ISPPA.3
(MHz).
pattem
for
combined
overall
where
ForMIand
giving
risetothe
modes
rangeofcenter
the
reported
the
in-plane
ZSPisfound
ISPPA.3,Fcis
global
involving
beam
frequenciesofthe
parameterismeasured
(azimuth)
(centimeters).
through
varying
factorof0.3isused
reported
"derated"isused.
always
occuratthe
values
may
transducer
have
are
(watts
that
its
largest
derated
definedinthe
(milliwatts
per
per
square
has
positionofISPPA.3,
associated
condition
giving
subjecttoreporting
transmit
maximum
pattern
the
center
valueofthe
typesofunequal
respective
and
out-of-plane
(elevation)
lengths
and
for
uses
the
formula:
same
operating
notberelatedtothe
maximum
water
intensityinoneifits
following
square
centimeter).
paragraphs.
centimeter).
The
maybereported
(MI@ISPPA.3)
with
the
transmit
risetoISPTA.3,WOis
under
ISPPA.3,
giving
risetothe
frequency
respective
center
transmit
value
associated
parameter.
frequency,
pattems.
(centimeters).
-6?
dimensions
•Chapter1 Safety· 24
types
general
In
value
instead
may
be
pattern
Fc
of

See
it
all
,.
MEDISON
19)
PD
PRF
EBD
EDS
Acoustic
The
Acoustic
PI1.3
(derated
Wo
(acoustic
Pr.3
(derated
Fc
(center
The
pulse
duration
reported
The
reported
The
The
valueofthe
pulse
repetition
valueofthe
entrance
entrance
Measurement
Measurement
pulse
intensity
power)
rarefaction
frequency)
(microseconds)
respective
frequency
respective
beam
dimensions
dimensionsofthe
Precision
and
Precision
integral)
pressure)
associated
parameter.
(Hz)
associated
parameter.
for
the
scan
Uncertainty
and
Acoustic
azimuth
for
the
azimuth
Measurement
3.2%
6.2%
5.4%
<1
%
with
with
and
the
transmit
the
transmit
elevation
and
elevation
Uncertainty
pattern
pattern
planes
••
+21
giving
giving
(centimeters).
planes
(centimeters).
are
described
%to-24%
+/-19 %
+/-15 %
+/-
4.5 %
risetothe
risetothe
below.
Systematic
For
the
the
pulse
analysis
Uncertainties.
intensity
includes
Hydrophone
Hydrophone/Amp
Spatial
averaging.
Alignment
Voltage
The
systematic
through
We
also
87
and
errors.
measurement
•
Oscilloscope
•
Oscilloscope
•
Oscilloscope
•
Oscilloscope
•
Noise.
the
useofcalibrated
refertoa
preparedbyK.
integral,
considerationsofthe
calibration
driftorerrors.
frequency
accuracy,
vertical
offset
clock
accuracy.
Digitization
uncertainties
September
Beissner,asa
derated
response.
accuracy.
accuracy.
rates.
Acoustic
NIST
acoustic
1993
analysis
rarefaction
pressure
effectsonaccuracy
including.
power
measurements
power
donebya
first
supplementtoIEC
sources.
working
Pr.3,
center
frequency
of:
usingaRadiation
groupofthe
publication
IEC
1161.
and
Force
are
technical
pulse
duration,
measured
committee
The
document
includes
analysis
and
discussionofthe
sourcesoferror/measurement
effects
due
to:
•Chapter 1 Safety·
25

See
it
all
_.
MEDISON
Balance
Absorbing
Linearityofthe
system
(or
reflecting)
calibration.
balance
Extrapolationtothe
and
thermal
Target
Absorbing
Target
Ultrasonic
Water
Ultrasonic
drift).
imperfections.
(reflecting)
misalignment.
transducer
temperature.
attenuation
Couplingorshielding
Plane-wave
Environmental
Excitation
Ultrasonic
Effects
assumption.
influences.
voltage
measurement.
transducer
duetononlinear
target
suspension
system.
momentofswitching
target
geometry
misalignment.
and
foil
properties.
acoustic
streaming.
temperature.
propagation
and
mechanisms.
the
ultrasonic
and
finite
saturation
target
loss.
transducer
size.
(compensation
for
ringing
The
overall
frequency
findingsofthe
analysis
rangeof1-10MHz.
givearough
Acoustic
Power
accuracy
figure
of
+/-
10%
for
the
•Chapter1 Safety· 26

Probe Precautions
The
probe
can
easilybedamagedbyimproper
Always
follow
the
instructionsinthe
after
each
use.
Check
for
the
probe
cracks,
and
broken
contact
parts,
the
MEDISON
leaks
user
manualtoinspect
and
sharp
Customer
useorby
contacting
the
probe
edges.Ifthereisany
Support
Department.
certain
cable,
damage,
Using
chemical
case
and
immediately
damaged
See
it
all
_.
MEDISON
substances.
lens
before
and
stop
using
probes
may
1-5-1
resultinelectric
&
CAUTION
Do
not
apply
mechanical
Do
not
place
the
not
apply
excessive
Do
not
immerse
and
hydrogen
Do
not
expose
Use
and
Infection
The
ultrasonographic
in
use.
Dependingonthe
including
The
However,
protective
most
the
ordinary
effective
probes
devices
ordertominimize
shocks
and
other
hazardstothe
patients
I
shocktothe
probe
cableonthe
forcetobendorpull
the
probe
into
peroxide.
the
probetotemperaturesof+50?Corhigher.
Controlofthe
image
scanner
typesofexaminations,
skinorthe
methodtoprevent
may
need
tobere-usedasthey
suchassheaths
the
riskofinfection
probe.
floor
where
the
cable.
any
inappropriate
Probe
uses
ultrasound,
locationofblood
infection
mustbeused,
among
patients.
the
substances
such
among
are
and/or
cable
canberun
suchasalcohol,
anditmakes
contact
transfusion
duringasurgery.
patientsisto
complexindesign
and
the
safety
users.
overbyequipment
bleach,
direct
contact
canbemadetoa
use
each
and
expensive.
instructions
mustbefolowed
ammonium
with
the
wide
varietyoflocations
probe
only
Consequently,
wheels,
patient
once.
carefully
etc.
Do
chloride,
when
in
&
WARNING
No
neurosurgical
disease
sterilizedbyany
&
the
approved
CAUTION
Sufficient
user
(critical
washing
who
detergents
I
treatmentsorexaminations
brain
disease
causedbyvirus).Ifthe
method
whatsoever.
I
and
manages
and
disinfecting
and
sheaths.
mustbecarried
maintains
shouldbecarried
the
disinfection
probe
out
for
procedures
outona
has
been
preventing
patient
with
Creutzfeldt-Jakob
usedonsuchapatient,itcannot
infection.
for
the
Thisisthe
equipment.
responsibility
Always
use
•Chapter 1 Safety·
be
of
legally
27

See
it
all
_.
MEDISON
1-5-2
Electric
The
the
Shocks
probe
uses
patientorthe
Lt.
WARNING
Regularly
immerse
Do
Do
Inspect
and
Do
The
protection
the
The
power
receive
the
not
immerse
not
drop
the
the
housing,
after
each
not
apply
power
protection
circuit
probe
surface
temperatureofthe
output
electrical
user.
I
short-circuit
probe
into
the
probe
probeorapply
strain
use.
excessive
fuse
detects
from
(AP&I)isin
energy.Ifit
examination
liquid.
into
liquid
mechanical
relief,
forcetotwist,
protects
excess
current,itimmediately
overheating
product
for
compliance
touches
shocks.
lens
and
seal
pullorbend
the
probe
andtorestrict
making
withUSFDA
conductive
from
and
contact
Environmental Protection
the
for
damage,
the
probe
the
product
the
ultrasound
with
standards.
materials,
MEDISON
shuts
Customer
and
check
cable.Itmay
from
off
the
power
patientsislimited
there
are
Support
for
any
resultina
excess
current.Ifthe
currenttothe
output.
under
risksofelectric
Department.Do
functional
short
probeinordertoprevent
43°C.The
problem
circuit.
power
shocks
monitoring
ultrasound
to
not
before
Lt.
CAUTION
The
equipment
regulations
The
lithium
The
waste
I
and
accessories
mustbeobserved.
batteryinthePCshouldbereplacedbya
sheaths
aretobe
aretobe
disposedofsafely
disposedofsafely
and
MEDISON
national
after
the
service
regulations
life
spanisexceeded
manoran
mustbeobserved
authorized
.
and
national
dealer.
•Chapter1 Safety· 28

• '•
~.~~~~
.I~.~~~~~~.~
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
o 2-1
What
is
SonoAceX4?
Q
2-2
Specifications
o
2-3
Product
Configuration
s
and
Installation
,
30
31
35

What is SonoAce X4?
The
SonoAceX4isahigh-resolutionBWultrasound
scanner
with
high
penetration
$'"
it
all
MEDISON
andavariety
__
of
2-1-1
measurement
Features
1)
High-end
forming
functions.
and
AdvantagesofSonoAce
Digital
Beam
Forming-The
technology.
2)Avarietyofapplications-The
including
3)
Various
4)3Dimages
5)
Measurement
measurement
The
6)
ReviewofScanned
imagesof4096
7)
SonoView-Thisisa
view
8)
DICOM
transmit
abdomen,
diagnostic
canbeobtained.
and
report
function
and
exchange
(Digitallmaging
and
print
obstetrics,
Modes-2D
Report
functions,
collates
Images-The
lines.
total
documents.
DICOM
Functions-Besides
the
ultrasound
and
X4
SonoAceX4utilizes
SonoAceX4is
gynecology,
Mode,MMode,PWSpectral
SonoAceX4also
measurement
SonoAceX4displays
CommunicationinMedicine)
images
throughanetwork.
image
optimized
vascular,
the
cardiac
basic
provides
data.
management
the
newly
developed
for
useina
distance,
application-specific
system,
varietyofultrasound
and
urology
Doppler
area,
Cine
imagesof512
which
applications.
Mode(optional),
circumference
measurement
frames
allowsausertoarchive,
Function-Thisisusedtoarchive,
Digital
Beam
departments,
etc.
and
volume
functions.
and
loop
9)
Peripheral/Accessory
canbeeasily
--------------------------
Connection-Avarietyofperipheral
connectedtothe
SonoAce
X4.
devices
including
•Chapter 2 ProductIntroduction'
VCRs
and
printers
30

Specifications
sI!I!itall
••
MEDISON
2-2-1
2-2-2
2-2-3
2-2-4
Specifications
:>
Height:
1330mm
:>
Width:
450mm
:>
Depth:
700mm
:>
Weight:
Imaging
:>
2D
:>
Dual2Dreal-time
:>
2DIM-mode
:>
Pulsed-wave
:>
3D-mode
:>
Simultaneous
Gray
:>
256(8bits)
More
modes
real-time
Scale
Focusing
(with
than
63kg
Doppler
monitor)
2-2-5
2-2-6
2-2-7
:>
Dynamic
:>
Digital
Probes
:>
Curved
C3-7ED,
:>
Linear
HL5-9ED,
:>
Endocavity
EC4-9ED,
Probe
:>
2
probe
:>
3
probe
Monitor
:>
12
inch
transmit
dynamic
Linear
C2-5ET,
Array
focusing,
receive
Array
C4-9ED,
L5-9EC,
Curved
EC4-9ES
connections
connectors,
connectors
BM!
monitor
focusing
L5-9EE
Linear
for
option.
maximumofeight
(continuous)
C2-4ES
Array
points
(four
points
simultaneo-usly
selectable)
-------------------------
•Chapter 2 Product Introduction'
31

$'"
it
all
__
MEDISON
2-2-8
2-2-9
2-2-10
2-3-11
Rear
Panel
:>
VHS
and
:>
ECG
:>
Keyboard
:>
Patient
monitor
:>
BM!
printer
:>
VGA
monitor
:>
Parallel
:>
USB
:>
Foot
Front
:>
USB
Image
:>
Cine
:>
Image
port
2.0
2port
Switch
Panel
2.0
2port
Storage
loop
filing
Application
Input
Audio
video
video
Input
memory
system
Connections
and9Vde
and
remote
Connections
(maximum
power
control
512
frames)
2-3-12
2-2-13
:>
General,
Musculoskeletal,
Electrical
:>
100-120V/200-240VAC,
Automatic
Automatic
:>
Obstetricsin2D
:>
Gynecology:Uterus,
Gynecology,
Parameters
Calculation
measurementofvarious
•
Standard
SL,
CM,
•
Volume
Fetal
•
Fetal
Shinozuka1,
•
Estimated
•
User-defined
TID,
NF,
NT,
Flow,
Carotids,
Weight:
Gestational
APTD,
Lat
Campbell,
Shinozuka2
Fetal
tables
Follicles,
Cardiac,
Umbilical
Abdomen,
Neonatal,
8/5A,
and
Age
APTDXTID,
Vent,
FOOT,
Artery,
Fetal
Aorta,
Weight:
Cervix,
Cyst,
OB,
Renal,
Pediatric
50/60Hz
Quantification
parameters
tables:
GS,
HUM,
ULNA,
EAR,
MP
Mid
Cereb
Ductus
Venous,
Hadlock
Brenner,
Mass
Left
and
1-4,
Doubilet,
Right
Urology,
CRL,
VS,
TIB,
Artery,
Fetal
Hansmann,
Osaka,
Ovary,
Left
Vascular,
BPD,
RAD,
Left
and
Heart,
Merz,
Hadlock,
and
OFD,
FIB,
Right
Placenta
Osaka,
Right
Small
Part,
Fetal
Heart,
HC,
APD,
TAD,
MAD,
CLAV,
VERT,
CEREB,
Uterine
Artery,
Left
Artery
Shepard,Tokyo1,Tokyo2,
Tokyo,
Williams
Ovarian
Artery,
Left
Breast,
AC,FTA,
OOD,
and
Right
and
Right
FL,
10D,
------------------------
•Chapter 2 Product Introduction' 32
 Loading...
Loading...