Page 1

Installation Instructions
MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Catalog Numbers MPAI-A2xxxC, MPAI-B2xxxC, MPAI-A3xxxC, MPAI-B3xxxC,
MPAI-A3xxxE, MPAI-B3xxxE, MPAI-A3xxxR, MPAI-B3xxxR, MPAI-A3xxxS, MPAI-B3xxxS,
MPAI-A4xxxC, MPAI-B4xxxC, MPAI-A4xxxE, MPAI-B4xxxE, MPAI-A4xxxR, MPAI-B4xxxR,
MPAI-A4xxxS, MPAI-B4xxxS MPAI-A5xxxC, MPAI-B5xxxC, MPAI-A5xxxE, MPAI-B5xxxE
Topi c Page
Important User Information 2
Catalog Number Explanation 3
About the MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 5
Before You Begin 6
Install the Electric Cylinder 9
Mount the Electric Cylinder 13
Change Connector Orientation 16
Dimensions 17
Connector Data 29
Commissioning 30
Lubricat ion 46
Troubleshooting 51
Accessories 53
Specifications 64
Additional Resources 66
Page 2

2 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
IMPORTANT
Important User Information
Solid state equipment has operational characteristics differing from those of electromechanical equipment. Safety Guidelines for
the Application, Installation and Maintenance of Solid State Controls, publication SGI-1.1
Automation® sales office or online at http://www.rockwellautomation.com/literature
between solid state equipment and hard-wired electromechanical devices. Because of this difference, and also because of the
wide variety of uses for solid state equipment, all persons responsible for applying this equipment must satisfy themselves that
each intended application of this equipment is acceptable.
In no event will Rockwell Automation, Inc. be responsible or li able for indirect or consequential damages resulting from the use or
application of this equipment.
The examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for illustrative purposes. Because of the many variables and
requirements associated with any particular installation, Rockwell Automation, Inc. cannot assume responsibilit y or liability for
actual use based on the examples and diagrams.
No patent liability is assumed by Rockwell Automation, Inc. with respect to use of information, circuits, equipment, or software
described in this manual.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual, in whole or in part, without written permission of Rockwell Automation, Inc., is
prohibited.
Throughout this manual, when necessary, we use notes to make you aware of safety considerations.
WARNIN G: Identifies information about practices or circumstances that can cause an explosion in a
hazardous environment, which may lead to personal injury or death, property damage, or economic loss.
, available from your local Rockwell
describes some important differences
ATT EN TI ON : Identifies information about practices or circumstances that can lead to personal injury or
death, property damage, or economic loss. Attentions help you identify a hazard, avoid a hazard and
recognize the consequences.
SHOCK HAZARD: Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a drive or motor, to alert people
that dangerous voltage may be present.
BURN HAZARD: Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a drive or motor, to alert people
that surfaces may reach dangerous temperatures.
Identifies information that is critical for successful application and understanding of the product.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 3

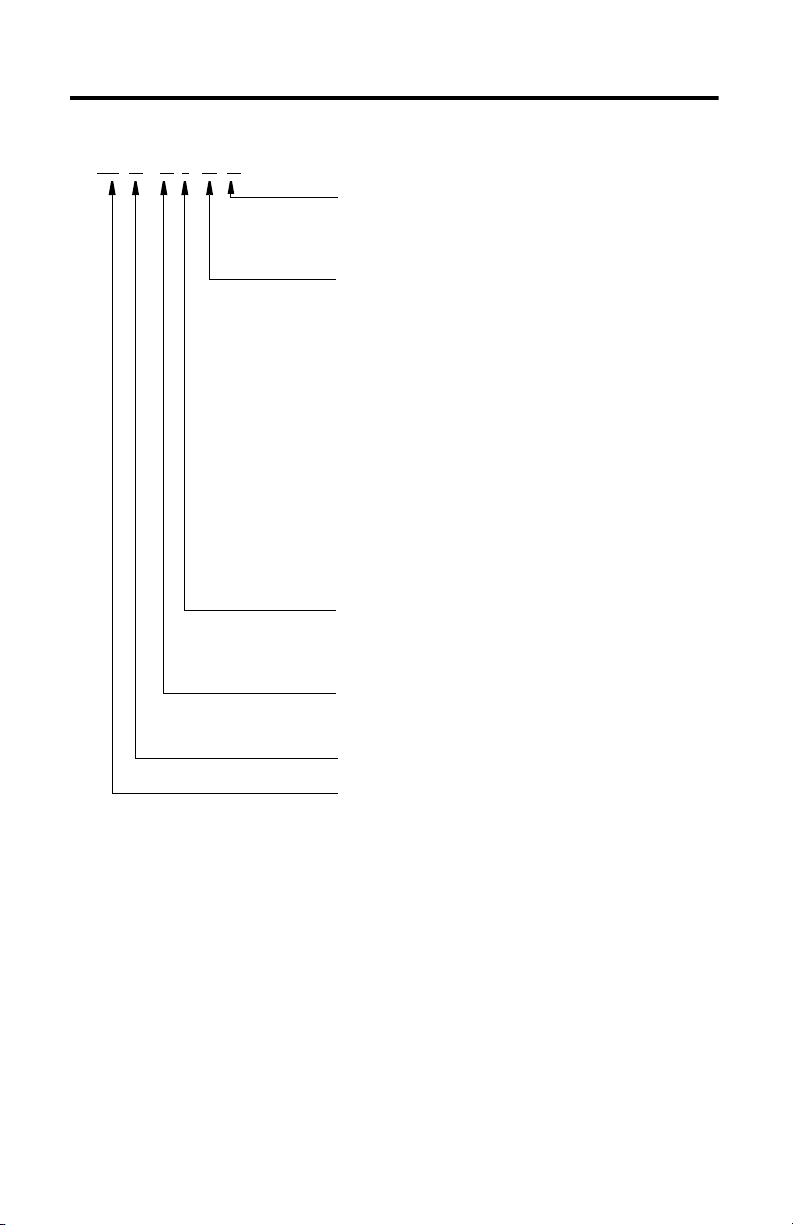
Catalog Number Explanation
Special Feature
(1)
Blank = IP67 is standard
W = Food grade (white paint) stainless steel rod
Actuator Mounting
A = Front face, side front, bottom front and rear tapped mounting holes
B = Front trunnion, no tapped mounting h oles
C = Rear clevis mount, no tapped mounting ho les
(food-grade paint only)
E = Front face mount, front face tapped mounting holes
(food-grade paint only)
Holding Brake
2 = No brake
4 = 24V DC brake
Motor Type
1 = 76 mm (3 in.) stroke length
3 = 150…450 mm (6…18 in.) stroke length
Motor Feedback Type
M = Multi-turn, 1024 sin/cos, absolute encoder, Hiperface protocol
(2)
V = Multi-turn, 128 sin/cos, absolute encoder, Hiperface protocol
Mechanical Drive/Screw Lead, Motor Type
C = 5.0 m m/rev ball s crew (0.197 in./rev )
E = 10.0 mm/rev ball screw (0.394 in./rev)
(2)
R = 5.0 m m/rev roller screw (0.19 7 in./rev)
(2)
S = 10.0 mm/rev roller screw (0.394in./rev)
(2)
Rod Stroke Length
076 = 76.2 mm (3.0 in.)
(3)
150 = 152.4 mm (6.0 in.)
300 = 304.8 mm (12.0 in.)
450 = 457.2 mm (18.0 in.)
(2)
Actuator Frame Size
2 = 64 mm (2.52 in.)
3 = 83 mm (3.27 in.)
4 = 110 mm (4.33 in.)
5 = 144 mm (5.67 in.)
Voltage Class
A = 200V
B = 400V
Actuator Type
AI = Actuator rod
Actuator Series
MP-Series
(1) The Special Feature field is for customer specific coding.
(2) Not available in the 64 mm (2.25 in.) fra me.
(3) 76 mm (3.0 in.) stroke length, is only available in the 64 mm (2.5 in.) and 83 mm (3.27 i n.) frames.
MP AI - x x xxx x x x x x - x
This is the catalog explanation for the MPAI electric cylinders.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 3
Page 4
4 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Stroke Length
(1)
76 = 76.2 mm (3.0 in.)
15 = 152.4 mm (6.0 in.)
30 = 304.8 mm (12.0 in.)
45 = 457.2 mm (18.0 in.)
Versio n Number
01 = If NAx01 = Front flange mount
If NRx01 = Roller screw grease cartridge
If NEx01 = Alignment coupling attachment
21 = NAx21, Front flange mount (stainless steel)
02 = If NAx02 = Front flange mount
If NEx02 = Anti-rotation option
If NRx02 = Ball screw grease cartridge
03 = If NAx03 = Rear clevis mount
If NEx03 = Spherical rod-eye
If NRx03 = Replacement zerk fitting
23 = NEx23, Sphe rical rod-e ye (corrosion res istant)
04 = If NEx04, Rod clevis
If NRx04, Grease plug
24 = NEx24, Rod clevis (stainless steel)
05 = Replacement zerk fitting cap
06 = If NAx06 = Mounting plates kit
If NRx06 = Front wiper seal kit
07 = Front bearing block and wiper kit
Actuator Frame Size
2 = 64 mm (2.52 in.)
3 = 83 mm (3.27 in.)
4 = 110mm (4.33in.)
5 = 144 mm (5.67 in.)
Accessory Type
NA = Accessory mounting
NE = Rod-end accessory
NR = Replacement kit accessory
Actuator Type
AI = Actuator rod
Actuator Series
MP-Series
(1) The Stroke Length field is used only for the anti-rotation guide, catalog number MPAI-NEx02xx.
MP AI - xx x xx xx
This is the catalog explanation for the MPAI electric cylinder accessories.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 5

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 5
IMPORTANT
8
5
6
3
2
1
MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinder
(MPAI-A3150CM32A is shown)
4
7
About the MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
MP-Series™ electric cylinders feature multi-turn high resolution encoders and are available with
24V DC brakes. The MP-Series motor drives a ball screw or roller screw that converts rotary
motion into linear movement. The linear motion extends or retracts the thrust rod within the
electric cylinder housing.
The MP-A/Bxxxxxx2x electric cylinders are non-braking. When there is no input torque, the
thrust rod can be moved freely. To achieve self-locking of your motion system, use an electric
cylinder with an integrated brake (catalog number MPAI-A/Bxxxxxx4x).
The MP-Series electric cylinders have been designed for exact positioning at high speeds.
Item Description
1 Feedback connector
2 Power connector
3 Motor with feedback device
4 Actuator cylinder
5 Threaded mounting holes on front, sides, rear, and bottom sur faces
6 Wrench flats for counteracting torque on thrust rod when installing rod-end accessories
7 Grease fitting (not included on catalog number MPAI-x2xxxC)
8 Thrust rod
(1) Trunnion mount electric cylinders, not shown, have threaded mounting holes only on the rear surface.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
(1)
Page 6

6 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Before You Begin
Remove all packing materials from within and around the item. After unpacking, verify the
nameplate catalog number against the purchase order.
1. Remove the polyethylene foam cushioning.
2. Remove the electric cylinder carefully from its shipping container.
Consider the weight of the electric cylinder. Depending on the design, the electric
cylinder can weigh up to 49 kg (108 lb).
Do not rotate the thrust rod. Rotating the thrust rod will cause the home position to be
lost.
ATT EN TI ON : Elec tric cylinders that exceed 23 kg (51 lb) require a two man lift. Do not lift
the electric cylinder by the thrust rod.
ATT EN TI ON : Do not rotate the thrust rod. Rotating the thrust rod will cause the factory
set home position to be lost and require the electric cylinder be homed before its initial
use.
3. Visually inspect the electric cylinder for damage.
Closely examine the mounting surface, frame, and thrust rod for defects.
4. Notify the carrier of shipping damage immediately.
ATT EN TI ON : Do not attempt to open and modify the electric cylinder beyond changing
motor connector orientation as described on page 16
described on page 12. Only a qualified Allen-Bradley employee can service the internal
working of the electric cylinder.
Failure to observe these safety precautions could result in personal injury or damage to
equipment.
, or installing a rear clevis mount as
Planning Your Installation
Refer to the Kinetix® Motion Control Selection Guide, publication GMC-SG001, for the
specifications and additional products referenced in this section:
• This product can be operated in compliance with the relevant safety regulations, only if
the maximum loading limits are observed.
ATT EN TI ON : The electric cylinder is not intended to be used in applications where
side-loading occurs. Loads must be guided and supported. Aligned load with the
line-of-motion of the thrust rod.
Side loading will reduce the lifetime of the electric cylinder.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 7

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 7
• If you are mounting your electric cylinder in a vertical or sloping position, include safety
measures that will control the work load, should the spindle nut fail.
ATT EN TIO N: Uncontrolled moving masses can cause injury or damage to property.
If there is a spindle nut fracture inside the actuator cylinder due to wear, the working
mass will drop down.
Check whether additional external safety measures are required to prevent damage in
the event of a spindle nut fracture.
• Keep the rod from rotating when in use to achieve consistent linear motion. In most
applications the connection to the load inherently provides anti-rotation. If your work
load is free to rotate when the actuator is attached use the anti-rotate option, catalog
MPAI-NEx02xx, to prevent rotation.
• Corrosive environments reduce the service life of electric cylinders.
• Where possible, install the electric cylinder with the grease fitting facing up. This will
reduce the residual grease from falling or dripping on your application.
• Factory-manufactured feedback and power cables are available in standard cable lengths.
They provide environmental sealing and shield termination. Contact your
Allen-Bradley® sales office or refer to the Kinetix Motion Control Selection Guide,
publication GMC-SG001, for additional information.
Prolonging Electric Cylinder Life
Thoughtful design and proper maintenance can increase the life of an electric cylinder. Follow
these guidelines to maximize the life of a electric cylinder especially within a food processing
environment:
• Always provide a drip loop in each cable to carry liquids away from the connection to the
motor.
• If design requirements permit, provide shields that protect the motor housing, thrust
rod, seals, and their junctions from contamination by foreign matter or fluids.
• Replace the thrust rod seals at or before its expected lifetime of 12-months.
Refer to page
59 for catalog information on thrust rod seals.
• Inspect the seals for damage or wear on a regular basis. If damage or excessive wear is
observed, replace the item.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 8

8 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
IMPORTANT
Electric Cylinders with Brake Option
The brake option on this servo motor is a spring-set holding brake that releases when voltage is
applied to the brake coil. A separate power source is required to disengage the brake. This power
source can be applied by a servo motor controller or manual operator control.
If system main power fails, holding brakes can withstand occasional use as stopping brakes.
However, this creates rotational mechanical backlash that is potentially damaging to the system,
increases brake wear, and reduces brake life.
An unpowered electric cylinder will require a brake to maintain its position if the force on the
actuator exceeds the Back Drive Force listed in Kinetix Linear Motion Specifications Technical
Data, publication GMC-TD002.
A brake can be use with the actuator to keep it from backdriving, typically in vertical
applications. A brake may be used for safety reasons or for energy savings allowing the actuator to
hold position when unpowered.
Holding brakes are not designed to stop rotation of the motor shaft, nor are they intended to be
used as a safety device. They are designed to hold a motor shaft at 0 rpm for up to the rated
brake holding torque.
The recommended method of preventing motor shaft rotation is a four step process: first,
command the servo drive to 0 rpm; second, verify the motor is at 0 rpm; third, engage the
brake; and fourth, disable the drive.
Disabling the drive removes the potential for brake wear caused by a badly-tuned servo system
oscillating the shaft.
Preventing Electrical Noise
Electromagnetic interference (EMI), commonly called electrical noise, can reduce motor
performance. Effective techniques to counter EMI include filtering the AC power, by using
shielded cables, separating signal cables from power wiring, and practicing good grounding
techniques.
Follow these guidelines to avoid the effects of EMI:
• Isolate the power transformers or install line filters on all AC input power lines.
• Physically separate signal cables from motor cabling and power wiring. Do not route
signal cables with motor and power wires, or over the vent openings of servo drives.
• Ground all equipment by using a single-point parallel ground system that employs
ground bus bars or large straps. If necessary, use additional electrical noise reduction
techniques to reduce EMI in noisy environments.
Refer to System Design for Control of Electrical Noise Reference Manual, publication
GMC-RM001
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
, for additional information on reducing the effects of EMI.
Page 9

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 9
Build and Route Cables
Knowledgeable cable routing and careful cable construction improves system electromagnetic
compatibility (EMC).
To build and install cables, perform these steps.
1. Keep wire lengths as short as physically possible.
2. Route signal cables (encoder or serial) away from motor and power wiring.
3. Separate cables by 0.3 m (1 ft) minimum for every 9 m (30 ft) of parallel run.
4. Ground both ends of the encoder cable shield and twist the signal wire pairs to prevent
electromagnetic interference (EMI) from other equipment.
ATTENTION: High voltage can be present on the shield of a power cable, if the shield is not
grounded.
Make sure there is a connection to ground for any power cable shield.
Failure to observe these safety precautions could result in personal injury or damage to equipment.
Install the Electric Cylinder
The installation must comply with all local regulations and use of equipment and installation
practices that promote electromagnetic compatibility and safety.
ATTENTION: Unmounted electric cylinders, disconnected mechanical couplings, and disconnected
cables are dangerous if power is applied.
Appropriately identify (tag-out) disassembled equipment, and restrict (lock-out) access to
electrical power.
Failure to observe these safety precautions could result in personal injury.
Follow these steps to prepare the electric cylinder for installation on the machine.
1. Provide sufficient clearances in the area of the electric cylinder for it to stay within its
specified operating temperature range.
Refer to Specifications
the electric cylinder unless forced air is blown across the electric cylinder for cooling.
Keep other heat producing devices away from the electric cylinder.
2. Make sure the mounting surface supports the electric cylinder evenly so that it is free of
mechanical stress and distortion.
on page 64 for the operating temperature range. Do not enclose
• Evenness of the mounting surface must be within 0.127 mm (0.005 in.).
• The thrust rod must be parallel to the guide within 0.0254 mm (0.010 in.).
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 10

10 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Wrench
Flats
3. Attach mounting accessories, shown on page
53, to the electric cylinder.
ATT EN TI ON : Proper attachment of the rear clevis mount is important to achieving an
IP67 rating. Refer to Installing the Rear Clevis Mounting Kit on page 12.
Failure to observe precautionary steps could result in damage to the electric cylinder
and its components.
Use these torque values to attach mounting accessories to the cylinder.
Frame
Mounting Plates Front Flange
Size
64 MPAI-NA206 MPAI-NA202 MPAI-NA203 13.2 N•m (117 lb•in)
83 MPAI-NA306 MPAI-NA302 MPAI-NA303
110 MPAI-NA406 MPAI-NA402 MPAI-NA403
144 MPAI-NA506 MPAI-NA502 MPAI-NA503 56.5 N•m (41.7 lb•ft)
(1) Rear clevis requires removal of the end cap from the electric cyl inder. If the cylinder is opened, take precautions to avoid
contamination and then reseal the cylinder so an IP67 rating is achieved.
(2) Unless otherwise noted, torque specifications have a ±20% tolerance.
(3) The anti-rotation guide is not included in this step. Refer to page
Rear Clevis
11 for anti-rotation guide torque values.
(1)
Tor que, m ax
39.5 N•m (29.1 lb•ft)
(2) (3)
If desired, you may seal the actuator front flange to the drive equipment by applying a
bead of food grade RTV around the periphery of the join between the actuator and the
machine surface. Use of a gasket or RTV on the mating surface is not recommended, as
this can cause the misalignment of the shaft and result in damage to the actuator and the
driven equipment.
4. Attach rod-end accessories, see on page
54, to the work load as outlined below.
Be sure the work load center of gravity is centric to the thrust rod.
ATTENTION: Damage may occur to the electric cylinder bearings and the feedback
device if sharp impact to the thrust rod is applied during installation. Do not strike the
thrust rod with tools during installation or removal.
Failure to observe these safety precautions could result in damage to the electric cyl inder
and its components.
5. Use these torque values to attach a rod eye or rod clevis to the thrust rod.
Frame
Size
64 M10 x 1.25 22.99 mm (.905 in.) 24.4 N•m (18.0 lb•ft)
83 M16 x 1.5 26.97 mm (1.062 in.) 61.0 N•m (45.0 lb•ft)
110 M20 x 1.5 38.08 mm (1.489 in.) 76.3 N•m (56.3 lb•ft)
114 M27 x 2.0 53.98 mm (2.125 in.) 135.6 N•m (100.0 lb•ft)
(1) Unless otherwise noted, torque specifications have a ±20% tolerance.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Thrust Rod
Thread
Wrench Flats Width Torque, max
(1)
Page 11

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 11
Use two wrenches to attach a rod-end accessory: one wrench to tighten the rod-end
accessory, and the other wrench to counter act the applied torque at the thrust-rod
wrench flats.
ATTENTION: Do not apply torque or rotate the thrust rod itself. Rotating the thrust rod
will cause the home position to be lost.
6. Use these torque values to attach an anti-rotation guide to the cylinder and the thrust
rod.
Frame
Size
64 MPAI-NE202xx 13.2 N•m (117 lb•in) 7.8 N•m (69 lb•in) 7.8 N•m (69 lb•in)
83 MPAI-NE302xx
144 MPAI-NE502xx 56.5 N•m (70.0 lb•ft) 20.3 N•m (15.0 lb•ft)
(1) Torque value applies to mounting screws with standard threads and strength class 8.8. Apply torque to mounting screws evenly.
(2) Torque value applies to the clamp bolt attached to the thrust rod of the electric cylinder .
(3) Torque value applies to the clamp bolt attached to the horizontal guid e shaft of the Anti-rotation guide.
Anti-rotation Guide
Bearing Block
(1)
Screws
39.5 N•m (29.13 lb•ft) 7.8 N•m (5.75 lb•ft)
Thrust Rod
(2)
Clamp
Anti-rotation
(3)
Shaft
13.2 N•m (9.74 lb•ft)110 MPAI-NE402xx
To reduce wear on the horizontal guides of the Anti-rotation kit, adjust the guides at the
work lo ad and the ele ctric cy linder so that they are exa ctly para llel, as described in Mo unt
the Electric Cylinder on page
13.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 12

12 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Installing the Rear Clevis Mounting Kit
Follow this procedure to install a rear clevis mount on an MP-Series electric cylinder.
ATTENTION: Proper attachment of the rear clevis mount is important to achieving an IP67 rating.
Failure to observe this procedure could result in damage to the electric cylinder and its
components.
1. Prepare a contamination-free area in which to work.
2. Remove the four bolts that secure the end cap.
Bolts sizes are shown here.
Frame Size Bolt Size
64 M6 x 1.0 (0.04)
83
110
144 M12 x 1.75 (0.07)
3. Set aside the mounting bolts for reuse.
4. Clean the mounting surface and verify it is undamaged before continuing.
5. Carefully position the rear clevis mount and seal on the mounting surface.
The seal is included in the rear clevis mounting kit.
6. Using an alternating torque pattern, evenly torque each of the four mounting bolts to
value shown on page
M8 x 1.25 (0.05)
10.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 13

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 13
Rod Extended
< 0.254 mm (0.010 in.)
Rod Retracted
< 0.127 mm (0.005 in.)
Load
Guide
Guide
Thrust R od
Electric Cylind er
Mount the Electric Cylinder
Follow these steps to mount the electric cylinder on the machine.
1. Verify the mounting surface flatness.
The mounting surface must be flat or shimmed flat to the mounting surface of the
electric cylinder within 0.127 mm (0.005 in.) to avoid distortion and damage to the
actuator housing.
2. Install and evenly tighten the steel fasteners so the electric cylinder is securely mounted
on the machine before thrust rod alignment is performed.
3. Align the electric cylinder as shown in the diagram and described below.
Align the thrust rod of the electric cylinder parallel to the load supporting bearing
system in both flatness and straightness within these specifications:
• With thrust rod extended <0.254 mm (0.010 in.) parallel to the load guides.
• With thrust rod retracted <0.127 mm (0.005 in.) parallel to the load guides.
Load
4. Torque the steel fasteners evenly to 39.5 N•m (350 lb•in), and then verify the thrust rod
alignment remains within specifications.
ATTENTION: When installed, pinch points with high forces are created that have the potential for
causing physical damage. The risk area surrounding the electric cylinder must be enclosed or
clearly marked, including signage in accordance with national and international requirements.
The risk area must be protected by a safety system that stops the equipment if anyone enters the
risk area. Personnel who enter the risk area must be authorized, trained, and qualified for any task
performed inside the risk area.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 14

14 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
O-ring
Groove reserved for
quick-lock plug.
Backshell Seal Inside
Feedback and Power/Brake
Connector Housing
Verify Connector O-ring and Backshell Seal
An O-ring on the feedback connector, and a backshell seal on the feedback and power/brake
connectors are necessary to achieve the maximum environmental rating. Verify the seal and
O-rings are installed as described.
Location Verify
• An O-ring is mounted on the external surface of the
feedback connector and the power/brake connector.
• The O-ring is undamaged, not twisted, and rests in the
groove near the rear of the connector.
• A backshell seal covers the joint inside the feedback and
power/brake housings. It seals the joint between the
backshell and the housing of the connector.
• The backshell seal is undamaged, and it is fully seated
against the face of the backshell.
Attach Motor Cables
Use this procedure to attach the power and feedback cables after the electric cylinder is mounted.
1. Carefully align each cable connector with the respective motor connector as shown in
the diagram.
ATT EN TI ON : Keyed connectors must be properly aligned and hand-tightened the
recommended number of turns.
Improper connector alignment is indicated by the need for excessive force to seat
connectors. For example, the need to use tools to fully seat connectors.
Failure to observe these safety precautions could result in damage to equipment.
ATT EN TI ON : When installing a threaded DIN cable with an M4 designation, an O-ring
must be installed in the groove immediately adjacent to the body of the motor
connector. This O-ring dampens the effects of vibration at the cable-to-motor
connection.
Cables requiring O-rings include 2090-XXNPMF-xxSxx or 2090-CPxM4DF-xxAFxx power
cables, and 2090-CFBM4DF-CDAFxx feedback cable.
Continuous flex cables with a SpeedTec DIN connector have an M7 designation.
2. Fully seat the feedback connector and the power/brake connector.
• Hand tighten the collar of a threaded (M4) connector five or six turns.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 15

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 15
Flat Surface
with Logo on Top
Top of connector is relative to motor
orientation.
Feedback Connector
Drip Loop
Power Connector
Flat Surface
with Logo on Top
• Hand tighten the collar of a SpeedTec (M7) connector one-quarter turn.
ATTENTION: Make sure cables are installed and restrained to prevent uneven tension or
flexing at the cable connectors. Excessive and uneven lateral force at the cable
connectors may result in the connector’s environmental seal opening and closing as the
cable flexes.
Failure to observe these safety precautions could result in damage to the electric cylinder
motor and its components.
3. Form a drip loop in the cable to keep liquids away from the connectors.
4. Verify the continuity and functionality of the thermal switch signals, TS+ and TS-.
These signals are transmitted through the feedback cable that connects the motor to its
controlling drive.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 16

16 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
180°
90°
270°
As Manufactured
Front
(rod side of actuator)
Front
(rod side of actuator)
Change Connector Orientation
You can rotate the circular DIN connector housings up to 270° in either direction.
ATTENTION: For actuators with food grade white paint, consider rerouting cables instead of
rotating the connectors. Rotation of the connectors interrupts continuity of the white paint across
the rotation joint. This might allow foreign material in and start corrosion. If you must rotate the
connectors, consider applying food grade RTV to the joint to assist in corrosion protection.
ATTENTION: You can rotate the connectors into a fixed position during installation of the electric
cylinder and remain in that position without further adjustment. Strictly limit the applied forces
and the number of times the connector is rotated to be sure that connectors meet the
requirements of IP67 for the motor portion of the electric cylinder.
Failure to observe these safety precautions could result in damage to the motor and its
components.
Follow these steps to rotate the DIN connectors.
1. Mount and fully seat a mating cable on the connector.
2. Grasp the connector and the cable plug by their housings and slowly rotate them to the
outside of the motor.
If necessary, repeat these steps for the other connector (feedback or power/brake).
ATT EN TIO N: Only apply force to the connectors; do not apply force to the cable. Do
not use tools (for example, pliers and vise-grips) to assist with the rotation of the
connector.
Failure to observe these safety precautions could result in personal injury or damage
to equipment.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 17

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 17
HD
AD
S (mounting
bolts) on M
(diameter of bolt
circle)
B
G2
G1
See
Detail A
Dimensions for L7 and ZJ are the
length when the rod is fully retracted.
AM
WH
L3 1.5 (0.06)
L1
L2
L7
ZJ
B
Feedback
Connec tor
T
Mounting Bolts (4x)
TG1
TG2
Power/Brake
Connec tor
Grease Fitting 1/4-28 thread
(not present on MPAI-x2xxx)
Dimensions are in mm (in.)
P
Wrench F lats
See Detail A for size
Detail A
AF
PD
RD
TL
Standard Mount Frame 64, 83, 110, and 144 Electric Cylinders
This is a bottom view, the connectors
are on the opposite side.
Frame
Size
TL (thread length) min
mm (in.)
PD (pilot dia.)
mm (in.)
AF (across flats)
mm (in.)
RD (rod dia.)
mm (in.)
64
M10 x 1.25 x 22.1 (0.049 x 0.87) Ø 47.955…48.000 (1.8880…1.8898) 22.74…22.99 (0.895…0.905) Ø 25.38 (0.999)83M16 x1.5 x 34.3 (0.06 x 1.35) Ø 59.955…60.000 (2.3604…2.3622) 26.72…26.97 (1.052…1.062) Ø 30.13 (1.186)
110
M20 x 1.5 x 41.4 (0.06 x 1.63) Ø 71.955…72.000 (2.8328…2.8346) 34.73…34.98 (1.367…1.377) Ø 38.08 (1.499)
144
M27 x 2.0 x 45.7 (0.08 x 1.80) Ø 99.955…100.000 (3.9352…3.9370) 53.73…53.98 (2.115…2.125) Ø 57.13 (2.249)
Dimensions
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 18

18 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Standard Dimensions (frame 64)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B2076CV12A
MPAI-A/B2150CV32A
MPAI-A/B2300CV32A
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B2076CV12A
MPAI-A/B2150CV32A
MPAI-A/B2300CV32A
(1) If ordering MPAI-A/B2xxxxCV4x-x actuator with brake, add 37.6 mm (1.48 in.) to dimensions G2, L7, and ZJ.
(2) The tolerance for this dimension is +0.0, -0.038 mm (+0.0, -0.0015 in.).
AD
mm
(in.)
72.8
(2.87)
L3
mm
(in.)
1.5
(0.06)
HD
mm
(in.)
104.5
(4.11)
(1)
L7
mm
(in.)
288.1
(11.34)
364.3
(14.34)
516.74
(20.34)
AM
mm
(in.)
41.9
(1.65)
M
mm
(in.)
70.0
(2.76)
B
S
mm
mm
(in.)
(in.)
34.0
M6 x 1.0 x 9.0
(1.34)
(0.04 x 0.35)
(2)
P
T
mm
mm
(in.)
(in.)
63.5
M6 x 1.0 x 9.0
(2.50)
(0.04 x 0.35)
G1
mm
(in.)
28.8
(1.13)
TG1
mm
(in.)
54.0
(2.13)
Standard Dimensions (frame 83)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B3076xM12A
MPAI-A/B3150xM32A
MPAI-A/B3300xM32A
MPAI-A/B3450xM32A
AD
mm
(in.)
82.8
(3.26)
HD
mm
(in.)
124.6
(4.90)
AM
mm
(in.)
54.6
(2.15)
B
mm
(in.)
44.0
(1.73)
S
mm
(in.)
M8 x 1.25 x12
(0.05 x 0.47)
G1
mm
(in.)
31.9
(1.25)
G2
mm
(in.)
106.9
(4.21)
TG2
mm
(in.)
20.0
(0.79)
G2
mm
(in.)
127.5
(5.02)
(1)
L1
L2
mm
mm
(in.)
(in.)
144.0
(5.67)
20.00
220.2
(0.787)
(8.67)
372.6
(14.67)
WH
mm
(in.)
17.3
(0.68)
(1)
L1
mm
(in.)
177.0
(6.97)
253.1
(9.97)
405.5
(15.97)
557.9
(21.97)
(1)
ZJ
mm (in.)
263.5
(10.37)
339.7
(13.37)
492.1
(19.37)
L2
mm
(in.)
21.0
(0.83)
(1)
(2)
P
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B3076xM12A
MPAI-A/B3150xM32A
MPAI-A/B3300xM32A
MPAI-A/B3450xM32A
(1) For MPAI-A/B3xxxxMx4A actuators, add 47.7 mm (1.88 in.) to dimensions G2, L7, and ZJ.
(2) The tolerance for this dimension is +0.0, -0.038 mm (+0.0, -0.0015 in.).
L3
mm
(in.)
1.5
(0.06)
L7
mm
(in.)
337.4
(13.29)
413.6
(16.29)
566.0
(22.29)
718.4
(28.29)
M
mm
(in.)
92.0
(3.62)
mm
(in.)
83.6
(3.29)
T
mm
(in.)
M8 x 1.25 x 8
(0.05 x 0.31)
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
TG1
mm
(in.)
69.0
(2.72)
TG2
mm
(in.)
36.0
(1.42)
WH
mm
(in.)
17.3
(0.68)
(1)
ZJ
mm
(in.)
300.0
(11.81)
376.3
(14.81)
528.7
(20.81)
681.1
(26.81)
Page 19

Standard Dimensions (frame 110)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B4150xM32A
MPAI-A/B4300xM32A
MPAI-A/B4450xM32A
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B4150xM32A
MPAI-A/B4300xM32A
MPAI-A/B4450xM32A
(1) For MPAI-A/B4xxxxM34A actuators, add 46.2 mm (1.88 in.) to dimensions G2, L7, and ZJ.
(2) The tolerance for this dimension is +0.0, -0.038 mm (+0.0, -0.0015 in.).
AD
mm
(in.)
96.3
(3.79)
L3
mm
(in.)
1.5
(0.06)
HD
mm
(in.)
151.5
(5.96)
(1)
L7
mm
(in.)
466.6
(18.37)
619.0
(24.37)
771.4
(30.37)
AM
mm
(in.)
61.3
(2.41)
(2)
M
mm
(in.)
127.0
(5.0)
B
mm
(in.)
50.0
(1.97)
P
mm
(in.)
110.5
(4.35)
S
mm
(in.)
M8 x 1.25 x12
(0.05 x 0.47)
T
mm
(in.)
M8 x 1.25 x 8
(0.05 x 0.31)
Standard Dimensions (frame 144)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B5150xM32A
MPAI-A/B5300xM32A
MPAI-A/B5450xM32A
AD
mm
(in.)
110.1
(4.33)
HD
mm
(in.)
181.9
(7.16)
AM
mm
(in.)
74.9
(2.75)
B
mm
(in.)
85.00
(3.346)
S
mm
(in.)
M12 x 1.75 x 12
(0.07 x 0.81)
MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 19
G2
mm
(in.)
130.7
(5.15)
TG2
mm
(in.)
55.0
(2.17)
G2
mm
(in.)
146.8
(5.78)
(1)
L1
L2
mm
mm
(in.)
(in.)
295.4
(11.63)
25.0
447.8
(0.98)
(17.63)
600.2
(23.63)
WH
mm
(in.)
16.8
(0.66)
(1)
L1
mm
(in.)
343.6
(13.53)
496.0
(19.53)
648.4
(25.53)
(1)
ZJ
mm
(in.)
422.1
(16.62)
574.5
(22.62)
726.9
(28.62)
L2
mm
(in.)
30.00
(1.181)
G1
mm
(in.)
31.9
(1.25)
TG1
mm
(in.)
85.0
(3.35)
G1
mm
(in.)
34.4
(1.35)
(1)
(2)
P
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B5150xM32A
MPAI-A/B5300xM32A
MPAI-A/B5450xM32A
L3
mm
(in.)
1.6
(0.06)
L7
mm
(in.)
553.4
(21.79)
705.8
(27.79)
858.2
(33.79)
M
mm
(in.)
155.0
(6.10)
mm
(in.)
143.6
(5.66)
T
mm
(in.)
M12 x 1.75 x 12
(0.07 x 0.81)
(1) For MPAI-A/B5xxxxMx4A actuators, add 51.5 mm (1.88 in.) to dimensions G2, L7, and ZJ.
(2) The tolerance for this dimension is +0.0, -0.038 mm (+0.0, -0.0015 in.).
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
TG1
mm
(in.)
110.0
(4.33)
TG2
mm
(in.)
65.0
(2.56)
WH
mm
(in.)
24.1
(0.95)
(1)
ZJ
mm
(in.)
502.6
(19.79)
655.0
(25.79)
807.4
(31.79)
Page 20

20 MP-Series Heavy Duty Elec tric Cylinders
HD
AD
G2
G1
See
Detail A
Dimensions for L7 and ZJ are the
length when the rod is fully retracted.
AM
WH
L3
L7
ZJ
Feedback
Connector
T
Mounting Bolts (4x)
TG1
TG2
Power/ Brake
Connector
Grease Fitting 1/4-28 thread
(not present on MPAI-x2xxx)
Dimensions are in mm (in.)
P
Wrench F lats
See Detail A for size
Detail A
AF
PD
RD
TL
These dimensions apply to MPAI-xxxxxxxxxE-W (food-grade paint) configurations.
This is a bottom view, the connectors are on
the opposite side.
Frame
Size
TL (thread length) min
mm (in.)
PD (pilot dia.)
mm (in.)
AF (across flats)
mm (in.)
RD (rod dia.)
mm (in.)
64
M10 x 1.25 x 22.1 (0.049 x 0.87) Ø 47.955…48.000 (1.8880…1.8898) 22.74…22.99 (0.895…0.905) Ø 25.38 (0.999)83M16 x1.5 x 34.3 (0.06 x 1.35) Ø 59.955…60.000 (2.3604…2.3622) 26.72…26.97 (1.052…1.062) Ø 30.13 (1.186)
100
M20 x 1.5 x 41.4 (0.06 x 1.63) Ø 71.955…72.000 (2.8328…2.8346) 34.73…34.98 (1.367…1.377) Ø 38.08 (1.499)
144
M27 x 2.0 x 45.7 (0.08 x 1.80) Ø 99.955…100.000 (3.9352…3.9370) 53.73…53.98 (2.115…2.125) Ø 57.13 (2.249)
Dimensions for Face Mount 64, 83, 110, and 144 Electric Cylinders
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 21

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 21
Face Mount Dimensions (frame 64)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B2076CV12E-W
MPAI-A/B2300CV32E-W 514.4 (20.25)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B2076CV12E-W
MPAI-A/B2150CV32E-W 337.4 (13.28)
MPAI-A/B2300CV32E-W 489.8 (19.28)
(1) For MPAI-A/B2xxxxCV4E-W actuators, add 47.7 mm (1.88 in.) to dimensions G2, L7, and ZJ.
AD
mm (in.)AMmm (in.)G1mm (in.)
72.8 (2.87) 42.1 (1.66) 26.9 (1.06) 104.6 (4.12) 104.5 (4.11)
L3
mm (in.)
1.8 (0.07) 54.0 (2.13) 20.0 (0.79) 17.5 (0.69)
TG1
mm (in.)
TG2
mm (in.)WHmm (in.)
(1)
G2
mm (in.)
HD
mm (in.)
(1)
ZJ
mm (in.)Tmm (in.)
261.2 (10.28)
(1)
L7
mm (in.)Pmm (in.)
285.8 (11.25)
M6x 1.00 x 9
(0.039 x 0.35)
Face Mount Dimensions (frame 83)
(1)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B3076xM12E-W
MPAI-A/B3150xM32E-W 413.9 (16.29)
MPAI-A/B3300xM32E-W 566.3 (22.29)
MPAI-A/B3450xM32E-W 718.7 (28.29)
AD
mm (in.)AMmm (in.)G1mm (in.)
82.8 (3.26) 54.9 (2.16) 30.0 (1.18) 126.0 (5.96) 124.6 (4.90)
G2
mm (in.)
HD
mm (in.)
(1)
L7
mm (in.)Pmm (in.)
337.7 (13.29)
63.5 (2.5)MPAI-A/B2150CV32E-W 362.0 (14.25)
83.6 (3.29)
(1)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B3076xM12E-W
MPAI-A/B3150xM32E-W 376.6 (14.83)
MPAI-A/B3300xM32E-W 529.0 (20.83)
MPAI-A/B3450xM32E-W 681.4 (26.83)
(1) For MPAI-A/B3xxxxMx4E-W actuators, add 47.7 mm (1.88 in.) to dimensions G2, L7, and ZJ.
L3
mm (in.)
1.8 (0.07 69.0 (2.72) 36.0 (1.42) 17.6 (0.69)
TG1
mm (in.)
TG2
mm (in.)WHmm (in.)
ZJ
mm (in.)Tmm (in.)
300.4 (11.83)
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
M8 x 1.25 x 8
(0.05 x 0.31)
Page 22

22 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Face Mount Dimensions (frame 110)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B4150xM32E-W
MPAI-A/B4450xM32E-W 771.6 (30.38)
AD
mm (in.)AMmm (in.)G1mm (in.)
96.3 (3.79) 61.5 (2.42) 30.0 (1.18) 130.8 (5.15) 151.5 (5.96)
(1)
G2
mm (in.)
HD
mm (in.)
(1)
L7
mm (in.)Pmm (in.)
466.8 (18.38)
110.5 (4.35)MPAI-A/B4300xM32E-W 619.2 (24.38)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B4150xM32E-W
MPAI-A/B4300xM32E-W 574.7 (22.62)
MPAI-A/B4450xM32E-W 727.1 (28.62)
(1) For MPAI-A/B4xxxxM34E-W actuators, add 46.2 mm (1.81 in.) to dimensions G2, L7, and ZJ.
L3
mm (in.)
1.8 (0.07) 85.0 (3.35) 55.0 (2.17) 16.8 (0.66)
TG1
mm (in.)
TG2
mm (in.)WHmm (in.)
(1)
ZJ
mm (in.)Tmm (in.)
422.3 (16.62)
M8 x 1.25 x 8
(0.05 x 0.31)
Face Mount Dimensions (frame 144)
(1)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B5150xM32E-W
MPAI-A/B5450xM32E-W 857.4 (33.76)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B5150xM32E-W
MPAI-A/B5300xM32E-W 654.2 (25.76)
MPAI-A/B5450xM32E-W 806.6 (31.76)
(1) For MPAI-A/B5xxxxMx4E-W actuators, add 51.6 mm (2.03 in.) to dimensions G2, L7, and ZJ.
AD
mm (in.)AMmm (in.)G1mm (in.)
110.1 (4.33) 75.2 (2.96) 34.0 (1.34) 146.0 (5.75) 181.9 (7.16)
L3
mm (in.)
1.7 (0.07) 110.0 (4.33) 65.0 (2.56) 24.4 (0.96)
TG1
mm (in.)
TG2
mm (in.)WHmm (in.)
G2
mm (in.)
HD
mm (in.)
(1)
ZJ
mm (in.)Tmm (in.)
501.8 (19.76)
(1)
L7
mm (in.)
552.6 (21.76)
M12x 1.75 x 12
(0.07 x 0.47)
P
mm (in.)
143.6 (5.66)MPAI-A/B5300xM32E-W 705.0 (27.76)
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 23

23 MP-Series Heavy Duty Elec tric Cylinders
Dimension for Trunnion Mount Frame 64, 83, 110, and 144 Electric Cylinders
HD
AD
P
G2
G1
See
Detail A
Dimensions for L7 and ZJ are the
length when the rod is fully retracted.
Wrenc h Flat s
See Detail A for size
AM
WH
L3
1.5 (0.06)
L7
ZJ
Feedback
Connec tor
TB1
Power/ Brake
Connec tor
Grease Fitting 1/4-28 thread
(not present on MPAI-x2xxx)
TB2
MD
L1
Dimensions are in mm (in.)
S (diameter of
holes) on M
(diameter of bo lt
circle)
TD
Detail A
AF
PD
RD
TL
MD
Frame
Size
TL (thread length) min
mm (in.)
PD (pilot dia.)
mm (in.)
AF (across flats)
mm (in.)
RD (rod dia.)
mm (in.)
TD (trunnion dia.)
mm (in.)
64 M10 x 1.25 x 22.1 (0.049 x 0.87) Ø 47.955…48.000 (1.8880…1.8898) 22.74…22.99 (0.895…0.905) Ø 25.38 (0.999) Ø 11.97…11.98 (0.471…0.472)
83 M16 x1.5 x 34.3 (0.06 x 1.35) Ø 59.955…60.000 (2.3604…2.3622) 26.72…26.97 (1.052…1.062) Ø 30.13 (1.186) Ø 15.96…15.98 (0.983…0.984)
110 M20 x 1.5 x 41.4 (0.06 x 1.63) Ø 71.955…72.000 (2.8328…2.8346) 34.73…34.98 (1.367…1.377) Ø 38.08 (1.499) Ø 24.97…24.99 (0.983…0.984)
144 M27 x 2.0 x 45.7 (0.08 x 1.80) Ø 99.955…100.000 (3.9352…3.9370) 53.73…53.98 (2.115…2.125) Ø 57.13 (2.2 49) Ø 24.97…24.99 (0.983…0.984)
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 24

24 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Trunnion Mount Dimensions (frame 64)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B2150CV32B
MPAI-A/B2300CV32B
MPAI-A/B2450CV32B
AD
mm (in.)AMmm (in.)G1mm (in.)
72.8
41.9
(2.87)
(1.65)
28.8
(1.13)
(1)
G2
mm (in.)
106.9
(4.21)
HD
mm (in.)
104.5
(4.11)
(1)
L7
mm (in.)
288.0
(11.34)
364.2
(14.34)
516.64
(20.34)
(2)
M
mm (in.)
70.00
(2.756)
L1
mm (in.)
15.00
(0.591)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
L3
mm (in.)MDmm (in.)Pmm (in.)Smm (in.)
TB1
mm (in.)
MPAI-A/B2150CV32B
MPAI-A/B2300CV32B
1.5 (0.06)
9.5
(0.38)
63.5
(2.50)
M6 x 1.0 x 9
(0.04 x 0.35)
8.7
(0.34)
MPAI-A/B2450CV32B
(1) If ordering MPAI-A/B2xxxCV34B actuator with brake, add 37.6 mm (1.48 in.) to dimensions G2, L7, and ZJ.
(2) The tolerance for this dimension is +0.0, -0.038 mm (+0.0, -0.0015 in.).
Trunnion Mount Dimensions (frame 83)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
AD
mm (in.)AMmm (in.)G1mm (in.)
(1)
G2
mm (in.)
MPAI-A/B3150xM32B
MPAI-A/B3300xM32B
82.8
(3.26)
54.6
(2.15)
30.4
(1.20)
127.5
(5.02)
MPAI-A/B3450xM32B
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
L3
mm (in.)MDmm (in.)Pmm (in.)Smm (in.)
MPAI-A/B3150xM32B
MPAI-A/B3300xM32B
1.5
(0.06)
16.8
(0.66)
83.6
(3.29)
M8 x 1.25 x12
(0.05 x 0.47)
MPAI-A/B3450xM32B
(1) For MPAI-A/B3xxxxM34B actuator, add 47.7 mm (1.88 in.) to dimensions G2, L7, and ZJ.
(2) The tolerance for this dimension is +0.0, -0.038 mm (+0.0, -0.0015 in.).
HD
mm (in.)
124.6
(4.90)
TB1
mm (in.)
16.0
(0.63)
TB2
mm (in.)WHmm (in.)
2.3
(0.09)
17.3
(0.68)
(1)
L7
mm (in.)
413.6
(16.29)
566.0
(22.29)
718.4
(28.29)
TB2
mm (in.)WHmm (in.)
3.2
(0.13)
(2)
M
mm (in.)
92.0
(3.622)
17.3
(0.68)
(1)
ZJ
mm (in.)
263.5
(10.37)
339.7
(13.37)
492.1
(19.37)
L1
mm (in.)
15.0
(0.59)
(1)
ZJ
mm (in.)
376.3
(14.81)
528.7
(20.81)
681.1
(26.81)
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 25

Trunnion Mount Dimensions (frame 110)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B4150xM32B
MPAI-A/B4300xM32B
MPAI-A/B4450xM32B
AD
mm (in.)AMmm (in.)G1mm (in.)
96.3
(3.79)
61.3
(2.41)
30.4
(1.20)
(1)
G2
mm (in.)
130.7
(5.15)
MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 25
(1)
HD
mm (in.)
151.5
(5.96)
L7
mm (in.)
466.6
(18.37)
619.0
(24.37)
771.4
(30.37)
(2)
M
mm (in.)
127.0
(5.0)
L1
mm (in.)
21.0
(0.83)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
L3
mm (in.)MDmm (in.)Pmm (in.)Smm (in.)
MPAI-A/B4150xM32B
MPAI-A/B4300xM32B
1.5
(0.06)
22.2
(0.87)
110.5
(4.35)
M8 x 1.25 x12
(0.05 x 0.47)
MPAI-A/B4450xM32B
(1) For MPAI-A/B4xxxxM34B actuator, add 46.2 mm (1.88 in.) to dimensions G2, L7, and ZJ.
(2) The tolerance for this dimension is +0.0, -0.038 mm (+0.0, -0.0015 in.).
Trunnion Mount Dimensions (frame 144)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
AD
mm (in.)AMmm (in.)G1mm (in.)
MPAI-A/B5150xM32B
110.1
74.9
MPAI-A/B5300xM32B
(4.33)
(2.95)
34.4
(1.35)
MPAI-A/B5450xM32B
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
L3
mm (in.)MDmm (in.)Pmm (in.)Smm (in.)
MPAI-A/B5150xM32B
1.4
22.2
MPAI-A/B5300xM32B
(0.06)
(0.88)
143.6
(5.66)
MPAI-A/B5450xM32B
(1) For MPAI-A/B5xxxxM34B actuator, add 51.5 mm (2.03 in.) to dimensions G2, L7, and ZJ.
(2) The tolerance for this dimension is +0.0, -0.038 mm (+0.0, -0.0015 in.).
(1)
G2
mm (in.)
146.8
(5.78)
M12 x 1.75 x 12
(0.07 x 0.47)
TB1
mm (in.)
20.05
(0.79)
HD
mm (in.)
181.9
(7.16)
TB1
mm (in.)
24.9
(0.98)
TB2
mm (in.)WHmm (in.)
6.25
(0.25)
16.8
(0.66)
(1)
L7
mm (in.)
553.4
(21.79)
705.8
(27.79)
858.2
(33.79)
TB2
mm (in.)WHmm (in.)
8.2
(0.32)
(2)
M
mm (in.)
155.00
(6.10)
24.1
(0.95)
(1)
ZJ
mm (in.)
422.1
(16.62)
574.5
(22.62)
726.9
(28.62)
L1
mm (in.)
28.0
(1.10)
(1)
ZJ
mm (in.)
502.6
(19.79)
655.0
(25.79)
807.4
(31.79)
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 26

26 MP-Series Heavy Duty Elec tric Cylinders
These dimensions apply to MPAI-xxxxxxxxxC-W (food-grade paint) configurations.
Flat for Wrench
See Detail A
Grease Fitting 1/4-28 thread
(not present on MPAI-x2xxx)
Feedback
Connector
Power/ Brake
Connector
Clevis Mount Frame 64, 83, 110, and 144 Electric Cylinders
See
Detail A
Detail A
TL
RD
AF
P
OT
IN
HD
AD
Ø D
H
G1
G2
AM
WH
ZJ
L7
Dimensions for L7 and ZJ are the length
when piston rod is fully retracted.
Frame
Size
TL (thread length) min
mm (in.)
PD
mm (in.)
AF (across flats)
mm (in.)
RD (rod dia.)
mm (in.)
64
M10 x 1.25 x 22.1 (0.049 x 0.87) Ø 48.0 (1.89) 22.74…22.99 (0.895…0.905) Ø 25.38 (0.999)83M16 x1.5 x 34.3 (0.06 x 1.35) Ø 60.0 (2.36) 26.72…26.97 (1.052…1.062) Ø 30.13 (1.186)
110
M20 x 1.5 x 41.4 (0.06 x 1.63) Ø 72.0 (2.83) 34.73…34 .98 (1.367…1.377) Ø 38.08 (1.499)
144
M27 x 2.0 x 45.7 (0.08 x 1.80) 100.0 (3.94) 53. 73…53.98 (2.115…2.125) Ø 57.13 (2.249)
PD
L3
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 27

Clevis Mount Dimensions (frame 64)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B2076CV12C-W
MPAI-A/B2300CV32C-W
AD
mm (in.)AMmm (in.)ØDmm (in.)
72.8 (2.87) 41.9 (1.65)
10.01
(0.394
…10.02
…0.395)
MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 27
(1)
G1
mm (in.)
G2
mm (in.)
26.9 (1.06) 104.6(4.12)
H
mm (in.)HDmm (in.)
13.00
(0.512)
104.5 (4.11)MPAI-A/B2150CV32C-W
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
L3
mm (in.)INmm (in.)
MPAI-A/B2076CV12C-W
MPAI-A/B2150CV32C-W 362.0 (14.25) 337.4 (13.28
1.5 (0.06) 26.3 (1.03)
(1)
L7
mm (in.)
285.8 (11.25)
OT
mm (in.)Pmm (in.)WHmm (in.)
46.25 (1.821) 63.5 (2.50) 17.3 (0.68)
(1)
ZJ
mm (in.)
261.2 (10.28)
MPAI-A/B2300CV32C-W 514.4 (20.25) 489.8 (19.28)
(1) If ordering MPAI-A/B2xxxxCV4C-W actuator with brake, add 37.6 mm (1.48 in.) to dimensions G2, L7, and ZJ.
Clevis Mount Dimensions (frame 83)
(1)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
AD
mm (in.)AMmm (in.)ØDmm (in.)
G1
mm (in.)
G2
mm (in.)
MPAI-A/B3076xM12C-W
MPAI-A/B3150xM32C-W
MPAI-A/B3300xM32C-W
82.8 (3.26) 54.6 (2.15) 12.01 (0.473) 30.0 (1.18) 127.5 (5.02) 16.0 (0.630) 124.6 (4.90)
MPAI-A/B3450xM32C-W
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
L3
mm (in.)INmm (in.)
MPAI-A/B3076xM12C-W
MPAI-A/B3150xM32C-W 413.6 (16.29) 376.3 (14.81)
MPAI-A/B3300xM32C-W 566.0 (22.29) 528.7 (20.81)
1.5 (0.06) 32.3 (1.27)
(1)
L7
mm (in.)
337.4 (13.28)
OT
mm (in.)Pmm (in.)WHmm (in.)
64.3 (2.53) 83.6 (3.29) 17.3 (0.68)
MPAI-A/B3450xM32C-W 718.4 (28.29) 681.1 (26.81)
(1) For MPAI-A/B3xxxxMx4C-W actuator, add 47.7 mm (1.88 in.) to dimensions G2, L7, and ZJ.
H
mm (in.)HDmm (in.)
(1)
ZJ
mm (in.)
300.1 (11.81)
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 28

28 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Clevis Mount Dimensions (frame 110)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B4150xM32C-W
MPAI-A/B4450xM32C-W
AD
mm (in.)AMmm (in.)ØDmm (in.)
96.3 (3.79) 61.3 (2.41) 16.01 (0.630) 30.0 (1.18) 130.7 (5.15) 22.0 (0.866) 151.5 (5.96)MPAI-A/B4300xM32C-W
G1
mm (in.)
(1)
G2
mm (in.)
H
mm (in.)HDmm (in.)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B4150xM32C-W
MPAI-A/B4300xM32C-W 619.0 (24.37) 574.5 (22.62)
MPAI-A/B4450xM32C-W 771.4 (30.37) 726.9 (28.62)
(1) For MPAI-A/B4xxxxM34C-W actuator, add 46.2 mm (1.82 in.) to dimensions G2, L7, and ZJ.
L3
mm (in.)INmm (in.)
1.5
(0.06)
50.3 (1.98)
(1)
L7
mm (in.)
466.6 (18.37)
OT
mm (in.)Pmm (in.)WHmm (in.)
94.3 (3.71) 110.5 (4.35) 16.8 (0.66)
(1)
ZJ
mm (in.)
422.1 (16.62)
Clevis Mount Dimensions (frame 144)
(1)
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B5150xM32C-W
MPAI-A/B5450xM32C-W
Electric Cylinder
Cat. No.
MPAI-A/B5150xM32C-W
MPAI-A/B5300xM32C-W 705.0 (27.76) 654.2 (25.76)
MPAI-A/B5450xM32C-W 857.4 (33.76) 806.6 (31.76)
(1) For MPAI-A/B5xxxxM34C-W actuator, add 51.6 mm (1.82 in.) to dimensions G2, L7, and ZJ.
AD
mm (in.)AMmm (in.)ØDmm (in.)
110.1 (4.33) 74.9 (2.95)
L3
mm (in.)INmm (in.)
1.4 (0.06)
60.33
(2.375)
20.02…20.04
(0.788…0.789)
(1)
L7
mm (in.)
552.6 (21.76)
G1
mm (in.)
34.0 (1.34) 146.0 (5.75) 27.0 (1.06) 181.9 (7.16)MPAI-A/B5300xM32C-W
OT
mm (in.)Pmm (in.)WHmm (in.)
114.30
(4.500)
G2
mm (in.)
143.6 (5.66) 24.1 (0.95)
H
mm (in.)HDmm (in.)
(1)
ZJ
mm (in.)
501.8 (19.76)
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 29

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 29
ACBD
E
H
L
F
G
Intercontec P/N
BEDC091NN00000202000
Intercontec P/N
AEDC113NN00000202000
Connector Data
This table lists the signal descriptions for connector pins on the electric cylinder.
Feedback Power and Brake
Pin Signal Name
MPAI-Axxxxx
(230V)
1Sin+ Sin+ A
2Sin- Sin- B
3 Cos+ Cos+ C
4 Cos- Cos- D
5Data+ Data+ E
6Data- Data- F
7 Reserved Reserved G
8HReserved
9+5VDC L
10 Common Case Ca ble Shield and GND
11 Reserved +9V DC
12 Common
13 TS+
14 TS-
(1)
(1)
15 Reserved Reserved
16
17
Case Shield Shield
(1) The normally closed thermal switch opens at 100 °C (212 °F).
(2) Power pins A, B, C, and D may be labeled as U, V, W, and GND respec tively.
Brake pins F and G brake may be labeled as + and - respectively.
Reserved pins E and H may be numbered 1 or 2 .
(3) Brake signals (MBRK+ and MBRK-) are available only on electric cy linders with a brake.
Signal Name
MPAI-Bxxxxx
(460V)
(1)
TS+
(1)
TS-
Pin Signal Name
(2)
Phase U
(2)
Phase V
(2)
Phase W
(2)
Ground
(2)
Reserved
(2)
(2)
MBRK+
MBRK-
10
9
(3)
(3)
11
12
13
16
17
1415
8
6
7
5
1
2
3
4
ATTENTION: Be sure that cables are installed and restrained to prevent uneven tension or
flexing at the cable connectors. Excessive and uneven lateral force at the cable connector may
result in damage to the housing and contacts as the cable flexes.
Failure to observe these safety precautions could result in damage to the motor and its
components.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 30

30 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Commissioning
This section provides guidelines for using RSLogix™ 5000 and MotionView OnBoard software
to configure your electric cylinder servo drive system.
Required Files
Firmware revisions and software versions required to support the electric cylinders include the
following:
• RSLogix 5000 software, version 16.00 or later
• Kinetix 2000, Kinetix 6000 multi-axis drives or Ultra™ 3000 drives with SERCOS
– Firmware revision 1.96 or later
– For RSLogix 5000 software, version 16.xx,
use Motion Database file, version 4.25.0 or later
– For RSLogix 5000 software, version 17.xx or later,
use Motion Database file, version 5.18.0 or later
– For RSLogix 5000 software, version 18.xx and 19.xx,
use MPAI_5_19_11.cmf or later
• Kinetix 6200 multi-axis drives
– Firmware revision 1.30 or later
– For RSLogix 5000 software, version 17.xx,
use MPAI_5_19_11.cmf or later
• Kinetix 6500 multi-axis drives
– Firmware revision 1.11 or later
– For RSLogix 5000 software, version 18.xx,
use MPAI_5_19_11.cmf or later
• Kinetix 300 single-axis drives
– For RSLogix 5000 software, version 17.xx or later,
use Kinetix 300 drive MotionView OnBoard web interface
• Kinetix 350 single-axis Ethernet drives
– For RSLogix 5000 software, version 20.xx or later
– Firmware revision 1.30 or later
• Ultra3000 drives with Ultraware software
– Firmware revision 1.52 or later
– Motion Database (.mdb) file, dated May 2011 or later
• Motion Analyzer software, version 4.8 or later
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 31

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 31
IMPORTANT
Download these files from http://www.rockwellautomation.com/support
. Contact Rockwell
Automation Technical Support at (440) 646-5800 for assistance.
Configure Your Electric Cylinder
Configure the electric cylinder by using the basic parameter settings described in this section.
Use the procedure appropriate for your motion axis.
Drive Refer to:
Kinetix 350
Kinetix 2000
Kinetix 6000
Kinetix 6200
Kinetix 6500
Ultra3000 Configure Your Ser vo Drive with Ultraware Software
Kinetix 300 Configure Your Kinetix 300 Servo Drive with MotionView OnBoard
Configure Your Servo Drive with RSLogix 5000 Software
Cylinder with RSLogix 5000 Software on page 36.
ATTENTION: Moving parts can cause injuries. Before running the electric cylinder, make sure all
components are secure and safe guards are in place to prevent access to the path of moving
machinery.
Safeguards should prevent access to the electric cylinder until all motion has stopped.
Check that the electric cylinder is clear of foreign matter and tools. Objects hit by the moving thrust
rod can become projectiles that can cause personal injury or damage to the equipment.
You are responsible to verify that the servo control system safely controls the electric cylinder
with regard to maximum force, acceleration, and speed.
immediately below, and Tune Your Electric
on page 40.
on page 42
Configure Your Servo Drive with RSLogix 5000 Software
Use the following procedure to configure the drive for your electric cylinder.
The procedure assumes the electric cylinder and the Kinetix 350, Kinetix 2000, Kinetix 6000,
Kinetix 6200, or Kinetix 6500 servo drive are installed and wired as one axis of the motion
system.
ATTENTION: Incorrect parameter settings may result in uncontrolled motion, with the potential
for damage to the electric cylinder.
Initiating a motion command on an electric cylinder with an incorrect Position mode setting may
result in damage to the electric cylinder, and the machine in which it is installed.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 32

32 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
1. Enter these parameters in the Axis Properties tab of RSLogix 5000 software for your
electric cylinder.
Axis Properties
Tab
Drive/Motor Motor Catalog Number Choose one from the
Conversion Positioning Mode Linear
Parameter Entry/Selection
pull-down menu.
MPAI-A2xxxCV1xx
MPAI-A2xxxCV3xx
MPAI-A3xxxCM1xx
MPAI-A3xxxEM1xx
MPAI-A3xxxRM1xx
MPAI-A3xxxSM1xx
MPAI-A3xxxCM3xx
MPAI-A3xxxEM3xx
MPAI-A3xxxRM3xx
MPAI-A3xxxSM3xx
MPAI-A4xxxCM3xx
MPAI-A4xxxEM3xx
MPAI-A4xxxRM3xx
MPAI-A4xxxSM3xx
MPAI-A5xxxCM3xx
MPAI-A5xxxEM3xx
Drive Resolution 200,000
Drive Counts per Motor Rev
Setting the Positioning Mode to Rotary can cause damage to
the electric cylinder or the machine due to incorrec t
positioning.
Conversion Constant 20,000 drive cnts/1.0 mm
Conversion Constant 40,000 drive cnts/1.0 mm
for
MPAI-x3xxxEM1xx
MPAI-x3xxxEM3xx
MPAI-x3xxxSM1xx
MPAI-x3xxxSM3xx
MPAI-x4xxxEM3xx
xSM3xx
MPAI-x4xx
MPAI-x5xxxEM3xx
for
MPAI-x2xxxCM1xx
MPAI-x2xxxCM3xx
MPAI-x3xxxCM1xx
MPAI-x3xxxCM3xx
MPAI-x3xxxRM1xx
MPAI-x3xxxRM3xx
MPAI-x4xxxCM3xx
MPAI-x4xxxRM3xx
MPAI-x5xxxCM3xx
MPAI-B2xxxCV1xx
MPAI-B2xxxCV3xx
MPAI-B3xxxCM1xx
MPAI-B3xxxEM1xx
MPAI-B3xxxRM
AI-B3xxxSM1xx
MP
MPAI-B3xxxCM3xx
MPAI-B3xxxEM3xx
MPAI-B3xxxRM3xx
MPAI-B3xxxSM3xx
MPAI-B4xxxCM3xx
MPAI-B4xxxEM3xx
MPAI-B4xxxRM3xx
MPAI-B4xxxSM3xx
MPAI-B5xxxCM3xx
MPAI-B5xxxEM3xx
508,000 drive cnts/1.0 in. for
1,016,000 drive cnts/1.0 in. for
1xx
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 33

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 33
Axis Properties Tab Parameter Cat. No. Entry/Selection, with applicable distance unit settings
Metric Value mm/s English Valuein/s
Dynamics Maximum Speed MPAI-x2076CM1xx 304 12.0
MPAI-x2150CM3xx 304 12.0
MPAI-x2300CM3xx 304 12.0
MPAI-x3076CM1xx 305 12.0
MPAI-x3076EM1xx 620 25.2
MPAI-x3076RM1xx 305 12.0
MPAI-x3076SM1xx 610 25.2
MPAI-x3150CM3xx 279 11.0
MPAI-x3150EM3xx 559 22.0
MPAI-x3150RM3xx 279 11.0
MPAI-x3150SM3xx 559 22.0
MPAI-x3300CM3xx 279 11.0
MPAI-x3300EM3xx 559 22.0
MPAI-x3300RM3xx 279 11.0
MPAI-x3300SM3xx 559 22.0
MPAI-x3450CM3xx 188 7.4
MPAI-x3450EM3xx 376 14.8
MPAI-x3450RM3xx 176 6.9
MPAI-x3450SM3xx 353 13.9
MPAI-x4150CM3xx 279 11.0
MPAI-x4150EM3xx 559 22.0
MPAI-x4150RM3xx 279 11.0
MPAI-x4150SM3xx 559 22.0
MPAI-x4300CM3xx 279 11.0
MPAI-x4300EM3xx 559 22.0
MPAI-x4300RM3xx 279 11.0
MPAI-x4300SM3xx 559 22.0
MPAI-x4450CM3xx 245 9.6
MPAI-x4450EM3xx 491 19.3
MPAI-x4450RM3xx 196 7.7
MPAI-x4450SM3xx 393 13.3
MPAI-x5150CM3xx 200 7.9
MPAI-x5150EM3xx 400 15.7
MPAI-x5300CM3xx 200 7.9
MPAI-x5300EM3xx 400 15.7
MPAI-x5450CM3xx 200 7.9
MPAI-x5450EM3xx 400 15.7
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 34

34 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
2. Click the Homing tab.
3. Set parameters for either absolute homing or torque level-to-marker homing as shown in
the table.
Parameter Absolute Homing Torque Level-to-Marker Homing
Value Value
Mode Absolute Active
Position 0, typical 0, typical
Offset N/A 0 mm
Sequence Immediate Torque Level-to-Marker
Direction N/A Reverse Bi-directional
Tor que L eve l N/ A 30 %, min
Speed N/A 10 mm /s (1.97 in/s)
Return Speed N/A 10 mm/s (0.39 i n/s)
(1) Torque Level-to-Marker is not available with the Kinetix 6500 drive.
Greater if the system friction, force, or weight exceeds 30% of
the Continuous Force Rating at any point in the range of
motion
(1)
ATT EN TI ON : Avoid excessive force while homing the electric cylinder. Do not exceed
10 mm/s (0.4 in/s) during a home routine.
Speeds greater than 10 mm/s (0.4 in/s) may damage the electric cylinder when the
thrust rod reaches the end of travel.
4. Complete these steps for absolute homing.
a. Use motion direct commands to slowly jog your axis to the home location for your
application, being sure to not exceed 10 mm/s (0.4 in/s).
b. Issue the Motion Direct Command (MAH) to set the home position on your axis.
5. Click the Limits tab.
6. Enter these parameters.
Parameter Entry/Selection, with Applicable Distance Unit Settings
Hard Travel Limits Check if hardware limits are in use. Use the Motion Analyzer
Soft Travel Limits Check if software limits are in use. Use the Motion Analyzer
Maximum Posit ive Enter a value t hat is within the thrust rod mechanical travel.
Maximum Negative Enter a value that is within the thrust rod mechanical travel.
maximum stopping distance in your application to set negative and positive limits.
maximum stopping distance in your application to set negative and positive limits.
software to determine t he
software to determine t he
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 35

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 35
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
7. Set overtravel limits according to the maximum speed of the servo drive system and the
payload of the application.
Set travel limits and direction of tuning moves in ref erence to thrus t rod starti ng
position. Leave adequate travel for the thrust rod to complete its moves while
tuning.
ATTENTION: Software overtravel must be set prior to initiating the tuning process.
Check the starting position of the thrust rod and allow for adequate travel.
Insufficient travel while auto tuning will cause the software overtravel to trigger an
end-stop impact.
ATTENTION: Care should be taken to not exceed the physical travel limits of the electric
cylinder. Doing so will cause the electric cylinder to reach the mechanical end-of-stroke.
Although protected by the end-of-stroke bumpers, frequently impacting the internal
end-of-stroke bumper can physically damage the screw and internal components of the
electric cylinder.
You can determine the deceleration distance before the thrust rod contacts the end of
travel based on the deceleration rate of the load, and the peak force available from the
motor/screw combination. Use Motion Analyzer
deceleration distance at the maximum speed of your application.
A positive-direction move command denotes a rod extend operation: a
negative-direction move command denotes a retract operation. This is when Drive
Polarity is positive, which is the default setting in RSLogix 5000 software.
software to calculate the minimum
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 36

36 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
TIP
IMPORTANT
Tune Your Electric Cylinder with RSLogix 5000 Software
This section shows the steps to tune electric cylinders with RSLogix 5000 software. Refer
to Required Files on page
• Tuning your electric cylinder requires you to calculate and configure the loop gain based
on the actual measured inertia.
• By setting travel limits, your application minimum deceleration is defined.
• Maximum acceleration is determined automatically during the tuning process.
Follow these steps to tune your electric cylinder.
1. In the Axis Properties dialog box, click the Fault Actions tab.
2. Click Set Custom StopAction.
3. In the Custom Stop Action Attributes dialog box, set the Brake Engage and the Brake
Release delay times to the values listed in Specifications
4. Reduce the default Stopping Time Limit from 10 seconds to 0.5 seconds.
30 for the version number:
These parameter settings work best if the electric cylinder is installed in a horizontal
(table top) or a wall mount (vertical) orientation.
on page 65.
To prevent the rod from moving or falling when installed in a vertical orientation,
the Stopping Time Limit must be set to 0.99 seconds or less.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 37

5. Click the Tune tab and enter these parameters:
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
• Travel Limit - Set to within software limits
• Speed (velocity)
• Torque/Force
Set travel limits and the direction of tuning moves in reference to the thrust rod
starting position. Leave adequate travel for the thrust rod to complete its moves
while tuning.
ATTENTION: Software overtravel must be set prior to initiating the tuning process.
Check the thrust rod starting position and allow for adequate travel.
Insufficient travel while auto tuning will cause the software overtravel to trigger an
end-stop impact.
Only check Torque Offset, as shown below, if the electric cylinder is installed in a
non-horizontal mount position.
MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 37
6. Click Start Tuning to access the Initiate Motion dialog box.
ATTENTION: Motion occurs immediately after clicking Yes in the Motion Initiation dialog
box.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 38

38 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
7. Click Yes to begin tuning the electric cylinder.
Tuning is complete when the Tune Servo dialog
box opens.
8. Click OK to exit Tuning.
The Tune Results dialog box opens.
9. Click OK if you are satisfied with the tuning results; otherwise, continue with Calculate
and Configure the Loop Gain.
Calculate and Configure the Loop Gain
Calculate a position loop bandwidth based on the actual measured inertia values from the Tune
Results dialog box.
In this example, the Tune Results dialog box shows a default Position Loop Bandwidth of
45.14153 Hz, and a Load Inertia Ratio of 6.8707952.
1. Calculate the Corrected Position Bandwidth.
Corrected Position Loop Bandwidth = (Initial Position Loop Bandwidth Result/(Initial
Load Inertia Ratio Result +1)
For example, 5.73532 = 45.14153/7.8707952
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 39

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 39
2. Enter the Corrected Position Bandwidth value 5.73532 as the Position Loop
Bandwidth.
3. Click OK.
4. Answer the remaining dialog boxes to apply the values.
The proper Position Bandwidth results in a stable starting point, from which you can adjust the
gains to fit your application requirements.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 40

40 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Configure Your Servo Drive with Ultraware Software
These steps assume an electric cylinder and Ultra3000 drive are installed and wired as one axis of
a motion system.
For help using Ultraware software as it applies to setting up your electric cylinder, refer to
Additional Resources
software.
1. Connect a serial cable, catalog number 2090-DAPC-D09xx, to the CN3 connector on
your Ultra3000 drive.
2. Apply AC input power to the Ultra3000 drive.
When communication with the Ultra3000 drive is established, the Ultra3000 motor
database dialog box opens.
3. Click Cancel.
Ultraware software begins scanning for online drives. When a drive is found, an Online
Drive icon opens in the Workspace.
4. Double-click the Online Drive icon to view the main Drive setup dialog box.
5. Verify the data in the Model Field is correct for your electric cylinder.
6. From the Displayed Units pull-down menu, choose User.
This programs Ultraware software to make distance moves in User Units (mm or in.).
on page 66. This procedure assumes you are familiar with Ultraware
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 41

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 41
7. Expand the Motor Encoder Units menu and enter the appropriate values from this table.
Velocity, position, and acceleration counts per unit are based on the selected User Units
(mm or in.).
Cat. No. Screw
mm/rev (in./rev)
MPAI-x2xxxC5.0
MPAI-x3xxxC5.0
MPAI-x3xxxE 10.0
MPAI-x3xxxR5.0
MPAI-x3xxxS 10.0
MPAI-x4xxxC5.0
MPAI-x4xxxE 10.0
MPAI-x4xxxR5.0
MPAI-x4xxxS 10.0
MPAI-x5xxxC5.0
MPAI-x5xxxE 10.0
(0.19685)
(0.19685)
(0.3937)
(0.19685)
(0.3937)
(0.19685)
(0.3937)
(0.19685)
(0.3937)
(0.19685)
(0.3937)
Encoder
periods/rev
128 26214.40
1024 209715.20
1024 104857.60
1024 209715.20
1024 104857.60
1024 209715.20
1024 104857.60
1024 209715.20
1024
1024 209715.20
1024 104857.60
Veloc ity Sc ale
mm/s (in/s)
(665845.76)
(2663383.04)
(2663383.04)
(2663383.04)
(2663383.04)
(2663383.04)
(2663383.04)
(2663383.04)
10
4857.60
(2663383.04)
(2663383.04)
(2663383.04)
Posit ion Scal e
mm (in.)
26214.40
(665845.76)
209715.20
(2663383.04)
104857.60
(2663383.04)
209715.20
(2663383.04)
104857.60
(2663383.04)
209715.20
(2663383.04)
104857.60
(2663383.04)
209715.20
(2663383.04)
104857.60
(2663383.04)
209715.20
(2663383.04)
104857.60
(2663383.04)
Acceleration Scale
mm/s/s (in/s/s)
26214.40
(665845.76)
209715.20
(2663383.04)
104857.60
(2663383.04)
209715.20
(2663383.04)
104857.60
(2663383.04)
209715.20
(2663383.04)
104857.60
(2663383.04)
209715.20
(2663383.04)
104857.60
(2663383.04)
209715.20
(2663383.04)
104857.60
(2663383.04)
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 42

42 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Configure Your Kinetix 300 Servo Drive with MotionView OnBoard
Use this procedure to configure your Bulletin MPAI electric cylinder with a Kinetix 300 servo
drive. Refer to the Kinetix 300 EtherNet/IP Indexing Servo Drive User Manual,
publication 2097-UM001
These steps assume an electric cylinder and Kinetix 300 drive are installed and wired as one axis
of a motion system.
1. Establish a connection to the Kinetix 300 servo drive via MotionView OnBoard
software.
2. From the Drive Organizer, select Motor.
3. Click Change Motor.
The motor model will automatically update to the correct model number.
, for details on using the MotionView OnBoard software.
4. Click Yes twice.
5. Verify the motor model matches the electric cylinder model connected to the drive.
6. From the Drive Organizer, select General.
7. Set User Units by entering values for your model from this table.
Cat. No. Lead mm/rev (in./rev) Rev/unit
MPAI-xxxxCxxx, MPAS-xxxxRMxx 5.0 (0.197) 0.2
MPAI-xxxxEMxx, MPAS-xxxxSMxx 10.0 (0.394) 0.1
8. Home the axis.
See Kinetix 300 Single-axis Servo Drives User Manual, publication 2097-UM001
need guidance.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
, if you
Page 43

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 43
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
9. Set overtravel limits according to the maximum speed of the servo drive system and the
payload of the application.
Set travel limits and direction of tuning moves in ref erence to thrus t rod starti ng
position. Leave adequate travel for the thrust rod to complete its moves while
tuning.
ATTENTION: Software overtravel must be set prior to initiating the tuning process.
Check the starting position of the thrust rod and allow for adequate travel.
Insufficient travel while auto tuning will cause the software overtravel to trigger an
end-stop impact.
ATTENTION: Care should be taken to not exceed the physical travel limits of the electric
cylinder. Doing so will cause the electric cylinder to reach the mechanical end-of-stroke.
Although protected by the end-of-stroke bumpers, frequently impacting the internal
end-of-stroke bumper can physically damage the screw and internal components of the
electric cylinder.
You can determine the deceleration distance before the thrust rod contacts the end of
travel based on the deceleration rate of the load, and the peak force available from the
motor/screw combination. Use Motion Analyzer
deceleration distance at the maximum speed of your application.
A positive-direction move command denotes a rod extend operation, a
negative-direction move command denotes a retract operation.
software to calculate the minimum
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 44

44 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Tune Your Electric Cylinder with MotionView OnBoard Software
1. From the Drive Organizer, select General.
2. From the Drive Mode pull-down menu, choose Autotune.
3. Enable the motor.
4. From the Drive Organizer, select Dynamics.
5. Click Autotune.
The Autotune dialog box opens with the default set to Velocity Tuning.
6. Check Velocity Tuning or Position Tuning or both.
7. Follow the instructions in the dialog box.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 45

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 45
Maintenance
Follow these steps to maintain your electric cylinder.
1. Remove power to the electric cylinder.
Lock-out and tag-out the electric cylinder at the power source.
2. Check the axial play of the thrust rod for wear of the spindle nut.
Increased noise is one indicator of wear.
ATTENTION: If a worn spindle nut breaks on a vertically or diagonally mounted electric
cylinder, the work load will fall. Uncontrolled moving mass can cause personal injury or
damage to equipment.
3. Clean the electric cylinder with a soft cloth and, if needed, non-abrasive cleaning
solution.
4. Lightly dampen a soft cloth with isopropyl alcohol and wipe the thrust rod and seal.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 46

46 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
TIP
IMPORTANT
Lubrication
Your electric cylinder has been lubricated at the factory and is ready for installation. Use the
appropriate lubrication interval calculations listed below for schedule estimates or use Rockwell
Motion Analyzer software to calculate the recommenced re-grease schedule for the electric
cylinder. Lubrication kits are shown on page 59
ATTENTION: Overfilling of the lubricant reser voir reduces performance, and may lead to heat
build-up and premature failure of the electric cylinder.
A grease gun typically delivers one gram of lubricant for one pump of the gun.
The type of lubricant and the appropriate maintenance interval is dependent on the type of
electric cylinder and one or more usage factors:
• Ball screw catalog number MPAI-x2xxxC does not require lubrication.
• Ball screw (catalog number MPAI-xxxxxC or MPAI-xxxxxE) electric cylinders use
Mobilith SHC220 lubricant. A maximum case temperature above or below 50 °C
(125 °F) during operation determines the lubrication interval.
• Roller screw (catalog number MPAI-xxxxxR or MPAI-xxxxxS) electric cylinders require
lubrication at an interval that must be calculated. Factors in the calculation include
severity of use, screw lead pitch, and frame size.
.
Ball Screw Lubrication
Lubrication is recommended at these intervals:
• Light to moderate - The case temperature does not exceed 50 °C (125 °F), and does not
require additional lubrication.
• Severe duty - The case temperature exceeds 50 °C (125 °F), and requires refilling of the
lubricant reservoir through the grease fitting at 1000 hours of use.
The maximum lubricant fill capacity for ball screw drives is the following:
• 3.0 g of Mobilith SHC220 for frame size 83
• 5.0 g of Mobilith SHC220 for frame size 110
• 6.0 g of Mobilith SHC220 for frame size 144
Use Mobilith SHC220 to lubricate the ball screw. Set your browser to http://www.mobil.com
view the Mobilith SHC220 product information.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
to
Page 47

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 47
IMPORTANT
100,000
10,000
1000
100
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Cycle RMS Velocity (in/s)
Lubrication Interval (hr)
Basic Lubrication Interval (tbl)
Roller Screw Lubrication
The lubrication interval (tl) of a roller screw actuator must be calculated. Factors that influence
the lubrication interval include the following:
• Frame Size - 83 or 110 mm (3.27 or 4.33 in.)
• Screw Lead - 5.0 or 10 mm/rev (0.197 or 0.394 in./rev)
• Basic lubrication interval (t
• Load correction factor (K) based on the actuator peak force (F
maximum commanded force (F
Use only the lubricant the factory recommends for your roller screw application.
Lubrication Interval Calculation
Use these steps to calculate the lubrication interval (tl) in hours for your roller screw electric
cylinder.
) based on RMS velocity (V
bl
)
Xn
rms
)
Xpeak
) and application
1. Select the basic lubrication interval (t
tbl = 4500 x (V
The basic lubrication interval (t
2. Determine the load correction factor (K) based on the ratio of actuator peak force
) to the application maximum commanded force (FXn).
(F
Xpeak
) based on the RMS velocity (V
bl
-1.57
)
, hr
rms
) should fall within the range of this graph.
bl
rms
).
Load Correction (K) must not be greater than one (<1).
Frame Size 83, 5 mm Roller Screw Load Correction
K
MPAI-x3xxxSM3xx
= 0.24 (F
Xpeak/FXn
)-0.15
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 48

48 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
IMPORTANT
Frame Size 83, 10 mm Roller Screw Load Correction
K
MPAI-x3xxxSM3xx
= 0.44 (F
Xpeak/FXn
)-0.15
Frame Size 110, 5 mm Roller Screw Load Correction
K
MPAI-x4xxxSM3xx
= 0.26 (F
Xpeak/FXn
)-0.15
Frame Size 110, 10 mm Roller Screw Load Correction
K
MPAI-x4xxxSM3xx
3. Calculate the lubrication interval (t
Use the basic lubrication interval (t
= 0.40 (F
) in hours.
l
= tbl x K, h
t
1
) and the load correction factor (K) from step 1 and
bl
Xpeak/FXn
)-0.15
step 2.
4. When the calculated lubrication interval elapses, refill the lubricant reservoir through
the grease fitting.
The maximum lubricant fill capacity for a roller screw drive is the following:
• 3.0 g of factory recommended lubricant for frame size 83
• 5.0 g of factory recommended lubricant for frame size 110
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 49

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 49
EXAMPLE
Lubrication Calculation Example
The following is and example of lubrication interval calculation for MPAI-x3xxxRMxx electric
cylinder.
Operators
Variable Description
F
xpeak
F
xn
K Load correction factor
S
co
t
bl
V
rms
Screw Static Load Factors
Actuator peak force
Application maximum command force
Screw static load factor
Basic lubrication interval
RMS velocity
Cat. No. S
MPAI-x3xxxRM3xx 0.24
MPAI-x3xxxSM3xx 0.44
MPAI-x4xxxRM3xx 0.26
MPAI-x4xxxSM3xx 0.40
Product MPAI-x3xxxRM3xx
V
rms
F
xpeak
F
xn
t
bl
K
MPAI-x3xxxRM3xx
= 2030 x (0.87) = 1766 hr
t
l
1.66 in/s
1700 lbf
400 lbf
= 4500 x (1.66 in/s)-1.57 = 2030 hr
co
= 0.24 (1700 lbf/400 lbf)
-0.15
= 0.87
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 50

50 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Storage
Store your electric cylinder for a minimal amount of time in a clean and dry location within the
Environmental Specifications on page
Observe these conditions when storing the electric cylinder:
• Be sure the equipment is in good working order before storing. Perform repairs,
maintenance, and inspections before storing equipment.
• Store the equipment in a suitable storage position (horizontal) that will prevent damage
to the connectors and electronics.
• After 6 months of storage, cycle the equipment two complete strokes to redistribute the
internal lubricants.
• After storage for a period longer than 2 years without use, lubricant replacement is
recommended through Rockwell Automation Technical Support.
65.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 51

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 51
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Electric Cylinders
Description Possible cause Corrective action
Axial play too large. Wear
Squeaking noises or vibrations. Distortions
Tuning is necessary. Modify control parameters.
Running noises at the spindle
support of an electric cylinder with a
300 mm (11.81 in.) stroke and high
positioning speeds.
Thrust rod does not move. Jamming in mechanical end
No response from electric cylinder. Controller/drive not enabled. Enable controller/drive.
Electric cylinder is enabled but not
operating or is operating erratically.
position, after traveling at excessive
speed or into end position.
Load is too large.
Ambient temperature too low
(increased breakaway torque in
initial run due to increasing viscosity
of the lubricants in the spindle
system).
Controller/drive faulted. Reset the controller/drive.
Improper/failed wiring. Check the wiring.
Feedback cable may be damaged. Test the feedback cable.
Feedback wiring may be incorrect. Verify correct feedback wiring.
• Replace actuator cylinder.
• Send to Rockwell Automation for repair.
• Verify the electric cylinder is free of stress
and evenly supported 0.2 mm
(0.008 in.).
• Lubricate thrust rod. See Configure Your
Kinetix 300 Servo Drive with MotionView
OnBoard on page
• Modify positioning speed.
Normal, no impairment of function.
• Loosen jamming manually.
1. Switch off power supply.
2. Remove motor and coupling housing.
3. Turn drive shaft.
• Reduce speed for reference travel.
• Provide software end positions, at least
0.25 mm (0.01 in.) from the mechanical
end positions (stops).
• Reduce load mass.
• Reduce positioning speed.
• Return for repairs.
• Reduce load mass.
• Reduce positioning speed.
• If necessary, allow higher current with
servo motors (see operating instructions for
the motor).
• Increase ambient temperature.
42.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 52

52 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Troubleshooting Electric Cylinders (cont.)
Description Possible cause Corrective action
Electric cylinder is operating but is not
up to rated speeds/forces.
Electric cylinder cannot move load. Force is too large for the capacity of
Electric cylinder moves or vibrates
when thrust rod is in motion.
Actuator is overheating. Duty cycle is higher than actuator
Motor phases are wired incorrectly
or in incorrect order.
Amplifier may be improperly tuned. Verify gain settings.
Amplifier may be set up improperly
for electric cylinder used.
the electric cylinder or too much
friction is present.
Misalignment of thrust rod to load. Verify load alignment.
Amplifier has too low of current
capacity or is limited to too low of
current capacity.
Loose mounting. Verify actuator mounting.
Amplifier is improperly tuned or
gain setting is wrong.
rating.
Actuator operated outside of
continuous rating.
Amplifier is poorly tuned, requiring
excessive current be applied to the
motor.
Verify correct motor power wiring.
Verify amplifier setting for number of poles,
voltage, current, resistance, inductance,
inertia, and other motor settings.
Verify force requirements.
Verify correct amplifier and settings.
Tun e a mpl ifi er.
Verify load forces and electric cylinder rating.
Adjust operation to be within continuous
operation rating.
Verify gain settings.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 53

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 53
Electric Cylinder
MPAI-A/BxxxxxM3xA
and Accessories
Trunnion-mount Electric Cylinder
MPAI-A/BxxxxxM3xB
and Accessories
3
4
6
5
6
5
1
Trunnion Mount (x2)
2
7
Accessories
This diagram depicts the accessories available for the electric cylinders. Tables list the catalog
number and weight for each accessory. Refer to the Kinetix Motion Control Selection Guide,
publication GMC-SG001
Mounting Accessories
Accessory Item
1Mounting
plates
2 Rear c levis
mount
64 MPAI-NA206 500 (17.6) 3 Front flange mount 64 MPAI-NA201 490 (17.3)
83 MPAI-NA306 920 (32.5) 83 MPAI-NA301 1070 (37.7)
110 MPAI-NA406 1150 (40.6) 110 MPAI-NA401 1740 (61.4)
144 MPAI-NA506 3080 (108.6) 144 MPAI-NA501 4170 (147.1)
64 MPAI-NA203 310 (10.9) 3 Front flange mount
83 MPAI-NA303 700 (24.7) 83 MPAI-NA321 1090 (38.4)
110 MPAI-NA403 1430 (12.3) 110 MPAI-NA421 1770 (62.4)
144 MPAI-NA503 3010 (106.2) 144 MPAI-NA521 4250 (149.9)
, for dimensions.
Cat. No. Weight,
Frame
approx
g (oz)
Accessory Item
(stainless steel)
Cat. No. Weight,
approx
Frame
64 MPAI-NA221 500 (17.6)
g (oz)
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 54

54 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Anti-rotation Guide Accessory
Accessory Item
4Anti-rotation
guide
Rod-end Accessories
Cat. No. Weight,
Frame
64 MPAI-NE20276 330 (11.6) 4 Anti-rotation guide 110 MPAI-NE40215 820 (28.9)
MPAI-NE20215 370 (13.1) MPAI-NE40230 980 (34.6)
MPAI-NE20230 450 (15.9) MPAI-NE40245 1130 (39.8)
83 MPAI-NE30276 660 (23.3) 144 MPAI-NE50215 2330 (82.2)
MPAI-NE30215 740 (26.1) MPAI-NE50230 2660 (93.8)
MPAI-NE30230 890 (31.4) MPAI-NE50245 3000 (106.0)
MPAI-NE30245 1040 (36.7)
approx
g (oz)
Accessory Item
Cat. No. Weight,
Frame
approx
g (oz)
Accessory Item
5 Rod clevis 64 MPAI-NE204 100 (3.5) 5 Rod clevis
6 Rod eye 64 M PAI-NE203 90 (3.2) 6 Rod eye
7Alignment
coupler
Cat. No. Weight,
Frame
83 MPAI-NE304 350 (12.3) 83 MPAI-NE324 390 (13.7)
110 MPAI-NE404 710 (25.0) 110 MPAI-NE424 800 (28.2)
144 MPAI-NE504 2030 (71.6) 144 MPAI-NE524 1900 (67.0)
83 MPAI-NE303 255 (9.0) 83 MPAI-NE323 210 (7.4)
110 MPAI-NE403 497 (17.5) 110 MPAI-NE423 380 (13.4)
144 MPAI-NE503 1330 (46.9) 144 MPAI-NE523 1300 (45.8)
64 MPAI-N201 220 (7.8)
83 MPAI-NE301 660 (23.3)
110 MPAI-NE401 730 (25.7)
144 MPAI-NE501 2200 (77.6)
approx
g (oz)
Accessory Item
(stainless steel)
(corrosion
resistant)
Cat. No. Weight,
Frame
64 MPAI-NE224 110 (3.9)
64 MPAI-NE223 70 (2.5)
approx
g (oz)
Anti-rotation Option
The design of the Bulletin MPAI electric cylinder allows the extending rod to rotate. This
provides simple setup of the actuator because you can rotate the rod and thread it in and out of
the actuator for mechanical attachment or system testing. This feature also requires that the rod
be kept from rotating when used in its dedicated application to be sure of proper linear motion.
In most applications, such as those where the load is coupled to linear bearings, or some other
support device, the load cannot rotate, and thus provides anti-rotation for the extending rod of
the actuator.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 55

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 55
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
For applications in which the load is free to rotate, Rockwell Automation offers the anti-rotation
systems shown below.
ATTENTION: The anti-rotation option is not a guide or support mechanism. It is intended only as
an anti-rotation device.
Anti-rotation Option
Item Description Item Description
1 Anti-rotation shaft fastener 6 Bearing block
2 Anti-rotation clamp 7 Washers
3 Thrust rod fastener 8 Bearing block fasteners
4 Grease zerk 9 Anti-rotat ion shaft
5Rodend
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 56

56 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Install the Anti-rotation Option
These are the recommended tools: 4, 5, 6, and 10 mm hex keys (Allen wrenches), small dead
blow hammer.
ATTENTION: Improper alignment of the Anti-rotation shaft may result in binding and or side
loading, which may reduce the life of the actuator.
ATTENTION: Take precautions to not cause damage to the actuator’s grease zerk throughout the
following process.
ATTENTION: This procedure requires you to rotate the thrust rod. Rotating the thrust rod will cause
the factory set home position to be lost and require the electric cylinder be homed before its initial
use.
1. Assemble the anti-rotation shaft fastener into the anti-rotation clamp finger-tight, then
back off one turn.
2. Assemble the anti-rotation clamp on to the rod end, orientated such that the shallow
counterbore faces the non-working end of the actuator and the clamp’s opening straddles
the grease zerk.
3. Engage the flats of the anti-rotation clamp with the flats of the rod end.
Light tapping with a dead-blow hammer may be necessary to seat the anti-rotation clamp
against the thrust tube.
4. Torque the anti-rotation shaft fastener to 7.8 N•m (5.8 lb•ft) while making sure the
anti-rotate clamp does not shift.
5. Apply medium strength thread-locker to the two bearing block fasteners.
6. Assemble the bearing block on to the actuator finger-tight only by using the two
fasteners and two washers, oriented such that the bearing block does not breech the face
of the actuator.
7. Insert the anti-rotation shaft through the bearing block, orientated with the shaft’s
tapped hole facing the working end of the actuator.
8. Light tapping with the dead-blow hammer may be necessary to get the anti-rotation
shaft through the oil wick of the bearing block.
9. Manually rotate the thrust rod to retract the actuator as far as the application allows
without mechanically stopping or striking any mounting means.
10. Verify that the bearing block fasteners are just finger-tight allowing the bearing block to
float.
11. Align the shallow counterbore of the anti-rotation clamp with the anti-rotation shaft,
engage the shaft into the counterbore.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 57

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 57
12. Apply medium strength thread-locker to the anti-rotate shaft fastener and assemble
through the anti-rotate clamp and into the anti-rotate shaft; torque to the value shown
on the table.
Frame Size Torque
64
7.8N•m (5.75lb•ft)83
110
144 20.3 N•m (15.0 lb•ft)
13. Torque the two bearing block fasteners as shown in the table.
Frame Size Torque
64 13.2 N•m (9.7 lb•ft)
83
110
144 56.5 N•m (70.0 lb•ft)
39.5 N•m (29.13 lb•ft)
14. Use the procedure in Configure Your Servo Drive with RSLogix 5000 Software on
page 31 to re-establish home.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 58

58 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
O-ring
Air Fitting
Tor x Scr e w
M3 x 10 mm Flat Head
Feedback connector attaches to a rotary or linea r
motion device that is not shown.
MP-Series Sealing Air Pressure Kit
A sealing air pressure kit (catalog number MPF-7-AIR-PURGE) is available for field installation
on an M23 feedback connector. Positive air pressure supplied through the kit provides an
additional level of protection against the ingress of foreign substances and moisture.
The kit replaces the M23 feedback connector cap, provides a replacement O-ring, and includes
installation instructions. You must supply 4 mm (5/32 in.) OD Teflon FEP tubing, and an
external air supply that does exceed 0.1 bar (1.45 psi).
Air Pressure Kit Installation on an M23 Feedback Connector
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 59

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 59
Replacement Parts and
Maintenance Kits
1
2
3
4
1
Item Cat. No. Description
MPAI-NR206 Viton rod wiper seal kit(64 frame)
MPAI-NR306 Viton rod wiper seal kit (83 frame)
1
2 MPAI-NR004 Grease plug, five per package
3 MPAI-NR003 Zerk fitting, five per package
4 MPAI-NR005 Zerk fitting replacement cap, five per package
N/A MPAI-NR001 Roller screw grease kit, contains one 414 ml (14 oz.) tube
N/A MPAI-NR002 Ball screw grease kit, contains one 414 ml (14 oz.) tube
(1) All MPAI electric cylinders have been standardized on the Series B construction NR06 front wiper seal kits. MPAI-x3 and MPAI-x4 made prior to mid
2012 have a front bearing block NR07 (Series A) in their construction. Check your MPAI-x3 and MPAI-x4 actuator nameplate for Series A or Series B
before specifying replacem ent front wiper seal kits.
(2) Fits a standard grease gun with 52 mm (2.0 in.) piston.
MPAI-NR406 Viton rod wiper seal kit (110 frame)
MPAI-NR506 Viton rod wiper seal kit (144 frame)
MPAI-NR307 Front bearing and wiper seal kit for Series A non-food grade white paint (83 frame)
MPAI-NR407 Front bearing and wiper seal kit for Series A non-food grade white paint (110 frame)
(1)
(1)
(2)
(2)
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 60

60 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
BR+
BR-
D
C
B
A
F
G
W
V
U
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
SIN+
SIN-
COS+
COS-
DATA+
DATA-
+5VDC
ECOM
Green
WHT/Green
Gray
WHT/Gray
Black
WHT/Black
Red
WHT/Red
3
4
5
6
1
2
9
10
1
2
3
4
5
10
14
6
14
12
+9VDC
TS+
Orange
WHT/Orange
11
13
7
11
4
3
2
1
6
5
4
3
2
1
Green/Yellow
Blue
Black
Brown
Black
White
GND
Shield
W
V
U
MBRK -
MBRK +
COM
PWR
DBRK -
DBRK +
BR+
BR-
TS-
COM
BLUE
2090-CPxM7DF-16AAxx, or
2090-CPxM7DF-16AFxx
Power Cable
2090-K6CK-D15M
Low Profile Connector
MP-Series Electric Cylinder
2090-CFBM7DF-CDAFxx, or
2090-CFBM7DF-CEAAxx Feedback
Cable
User Supplied
24V DC
Motor
Feedback
Thermostat
Brake
Resistive Brake
Connections
Motor Power (MP)
Connector
Motor Feedback (MF)
Connector
Motor/Resistive
Brake (BC)
Connec tor
Bulletin 2094
IAM (inverter) or AM
Module
Cable Shield
Clamp
2090-CPxM7DF-16AAxx, or
2090-CPxM7DF-16AFx x
Power Cabl e
2090-K2CK-D15M
Low Profile Connector
MP-Series Electric Cylinder
2090-CFBM7DF-CDAFxx, or
2090-CFBM7DF-CEAAxx Feedback
Cable
User Supplied
24V DC
Motor
Feedback
Thermostat
Brake
Three-Phase
Motor Power
Motor
Power ( MP)
Connector
Motor Feedback
(MF) Connector
Motor
Brake (BC)
Connec tor
Cable Shield
Clamp
Kinetix 2000
IAM (inverter) or AM
Module
Interconnect Diagrams
These wiring examples are for an electric cylinder, specifically Allen-Bradley servo drives.
Wiring Example of MP-Series Electric Cylinders to Kinetix 6000, Kinetix 6200, and Kinetix 6500
Drives
Wiring Example of MP-Series Electric Cylinders to Kinetix 2000 Drives
Shield
Green/Yellow
Blue
Black
Brown
Black
White
D
C
B
A
G
F
BR-
BR+
W
GND
V
U
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
W
V
U
MBRK +
MBRK -
PWR
COM
4
3
2
1
2
3
1
4
1
Black
WHT/Black
2
3
4
5
6
9
10
11
13
14
12
Red
WHT/Red
Green
WHT/Green
Gray
WHT/Gray
Orange
WHT/Orange
Blue
SIN+
SIN-
COS+
COS-
DATA+
DATA+5V DC
ECOM
+9V DC
TS+
TS-
COM
1
2
3
4
5
10
14
6
7
11
Page 61

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 61
D
C
B
A
BR+
BR-
F
G
W
V
U
3
4
5
6
1
2
9
10
14
12
11
13
GND
SIN+
SIN-
COS+
COS-
DATA+
DATA-
Green
WHT/Green
Gray
WHT/Gray
Black
WHT/Black
RED
WHT/Red
1
2
3
4
5
10
14
6
+9VDC
TS+
Orange
WHT/Orange
7
11
+5VDC
ECOM
TS-
COM
Blue
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Green/Yellow
Blue
Black
Brown
Shield
W
V
U
Black
White
CR1
OUT4-E
OUT4-C
24V DC
24V DC COM
Motor Brake
MP-Series
Electric Cylinder
Motor Feedback
(MF) Connector
Thermostat
User Supplied
24V DC
2090-K2CK-D15M
Connector Kit
2090-CFBM7DF-CDAFxx, or
2090-CFBM7DF-CEAAxx
Feedba ck Cable
2090-CPxM7DF-16AAxx, or
2090-CPxM7DF-16AFxx
Power C able
I/O (IOD)
Connec tor
Cable Shiel d
Clamp
Kinetix 300 Drive
Motor
Feedba ck
Motor Power
(MP) Connector
Three-phase
Motor Power
D
C
B
A
BR+
BR-
F
G
W
V
U
3
4
5
6
1
2
9
10
14
12
11
13
GND
SIN+
SIN-
COS+
COS-
DATA+
DATA-
GREEN
WHT/GREEN
GRAY
WHT/GRAY
BLACK
WHT/BLACK
RED
WHT/RED
1
2
3
4
5
10
14
6
+9VDC
TS+
ORANGE
WHT/ORANGE
7
11
+5VDC
ECOM
TS-
COM
BLUE
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Green/Yellow
Blue
Black
Brown
Shield
W
V
U
Black
White
CR1
MTR_BRAKE MTR_BRAKE +
24V DC
24V DC COM
44
43
Motor Brake
Motor Power
(MP) Connector
Motor Feedback
(MF) Connector
Three-phase
Motor Power
Motor
Feedback
Thermostat
User Supplied
24V DC
2090-K2CK-D15M
Connector Kit
Kinetix 350 Drive
I/O (IOD)
Connector
Cable Shield
Clamp
MP-Series
Electric Cylinder
2090-CPxM7DF-16AAxx, or
2090-CPxM7DF-16AFxx
Power Cabl e
2090-CFBM7DF-CDAFxx, or
2090-CFBM7DF-CEAAxx
Feedback Cable
Wiring Example of MP-Series Electric Cylinders to Kinetix 300 Drives
Wiring Example of MP-Series Electric Cylinders to Kinetix 350 Drives
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 62

62 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
1
2
3
4
5
10
14
6
7
11
D
C
B
A
BR+
BR-
F
G
W
V
U
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
SIN+
SIN-
COS+
COS-
DATA+
DATA-
+5V DC
ECOM
Green
WHT/Green
Gray
WHT/Gray
Black
WHT/Black
Red
WHT/Red
3
4
5
6
1
2
9
10
14
12
+9V DC
TS+
Orange
WHT/Orange
11
13
Green/Yellow
Blue
Black
Brown
Black
White
GND
Shield
W
V
U
TS-
COM
Blue
BRK -
BRK+
43
44
+24VCOM
2090-CPxM7DF-16AAxx, or
2090-CPxM7DF-16AFxx
Power C able
Motor Brake
Motor Power
Connector
MP-Series
Electric Cylinder
Motor Feedback
(CN2) Connector
Three-phase
Motor Power
Thermostat
User Supplied
24V DC
2090-UXBB-DM15 Drive
Mounted
Connector
Ultra3000 Drives
2090-CFBM7DF-CDAFxx,Allen-Bradley
, ControlLogix, CompactLogix, Kinetix,
MP-Series, Rockwell So ftware,
Control Interface
(CN1) Connector
Cable Shield
Ground Clamp
Motor
Feedba ck
Wiring Example of MP-Series Electric Cylinders to Ultra3000 Drives
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 63

Grounding Techniques for Feedback Cable Shield
Clamp
Expose shield secured under clamp.
Clamp Screw (2)
Turn clamp over to hold small cable
secure.
Cable Tie
Exposed shield secured under
clamp.
Use 2090-K2CK-D15M connector
with these drives:
Kinetix 300
Kinetix 2000
Use 2090-K6CK-D15M connector
with these drives:
Kinetix 6000
Kinetix 6200
Kinetix 6500
Use 2090-UXBB-DM15 connector
with Ultra3000 drives.
MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 63
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 64

64 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Specifications
Electric Cylinder Weights
Electric Cylinder
(frame 64) Cat. No.
MPAI-x2076CV12x 3.2 (7.1) MPAI-x3076xM12x 6.2 (13.7)
MPAI-x2150CV32x 4.7 (10.4) MPAI-x3150xM32x 8.3 (18.3)
MPAI-x2300CV32x 5.8 (12.8) MPAI-x3300xM32x 10.1 (22.2)
N/A MPAI-x3450xM32x 11.9 (26.2)
MPAI-x2076CV14x 3.7 (8.2) MPAI-x3076xM14x 7.2 (15.9)
MPAI-x2150CV34x 5.2 (11.5) MPAI-x3150xM34x 9.3 (20.5)
MPAI-x2300CV34x 6.3 (13.9) MPAI-x3300xM34x 11.1 (24.4)
N/A MPAI-x3450xM34x 12.9 (28.4)
(1) For MPAI-x2xxxCVxx-W (rear clevis mount) cylinders, add 0.2 kg (0.44 lb).
Electric Cylinder
(frame 110) Cat. No.
MPAI-x4150xM32x 15.8 (34.8) MPAI-x5150xM32x 32.1 (70.7)
MPAI-x4300xM32x 18.8 (41.4) MPAI-x5300xM32x 37.8 (83.3)
MPAI-x4450xM32x 21.8 (48.0) MPAI-x5450xM32x 43.6 (96.1)
MPAI-x4150xM34x 17.3 (38.1) MPAI-x5150xM34x 34.4 (75.8)
MPAI-x4300xM34x 20.3 (44.7) MPAI-x5300xM34x 40.2 (88.6)
MPAI-x4450xM34x 23.3 (51.4) MPAI-x5450xM34x 45.9 (101.2)
(1) Includes MPAI-x5xxxxM3xA and MPAI-x5xxxxM3xE-W (front face mount) cylinders.
(2) For MPAI-x5xxxxM3xB (front trunnion mount) cylinders, add 0.5 kg (1.1 lb).
(3) For MPAI-x5xxxxM3xC-W (rear clevis mount) cylinders, add 2.1 kg (4.6 lb).
(1)
Weight,
approx
kg (lb)
Weigh t,
approx
kg (lb)
Electric Cylinder
(frame 83) Cat. No.
Electric Cylinder
(frame 144) Cat. No.
(1)
Weigh t,
approx
kg (lb)
Weigh t,
approx
kg (lb)
(2) (3)
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 65

MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 65
Environmental Specifications
Attribute Value
Temperature, operating ambient 0…40 °C (32…104 °F)
Temperature, storage ambient -25…60 °C (-13…140 °F)
Humidity, relative (noncondensing) 5…95%
Liquid/dust protection IP67 - dust tight, effects of immersion
(2)
Shock, max 20 g peak, 6 ms duration
Vibrat ion, max
(1) Tested for one hour per Rockwell Automation specification 10000056670. Contact your distributor for a copy of this specification.
(2) The use of environmentally sealed (Bulletin 2090) cables are required to achieve this International Protection (IP) rating for the complete
(1)
unit.
2.5 g peak @ 30…2000 Hz
Brake Specifications
Cat. No. Static Torque Coil Current
at 24V DC
MPAI-A/B2xxxxVx4x 1.6 N•m (14.0 lb•in) 0.35 A
MPAI-A/B3xxxxM34x 4.0 N•m (35.4 lb•in) 0.43 A
MPAI-A/B4xxxxM34x 10.0 N•m (88.5 lb•in) 0.67 A
MPAI-A/B5xxxxM34x 16.4 N•m (145 lb•in) 0.66 A
(1) Brake engage time delay with voltage removed and a metal oxide varistor (MOV ) used for arc suppression.
Use of a diode array for arc suppression will approximately double (x2) the engage time delay.
(2) Brake release time delay with voltage applied.
peak
peak
peak
peak
Brake Response Time
(1)
Engage
75 ms 20 ms
40 ms 50 ms
25 ms 35 ms
15 ms 25 ms
Cat. No. Estimated Brake Holding Force
MPAI-A/Bxxxx Cxxx
N (lb)
MPAI-A/B2xxxxV34x 2300 (517) N/A N/A N/A
MPAI-A/B3xxxxM34x 5818 (1308) 2909 (654) 6423 (1444) 3211 (722)
MPAI-A/B4xxxxM34x 14550 (3271) 7272 (1635) 16062 (3611) 8029 (1805)
MPAI-A/B5xxxxM34x 23838 (5359) 11921 (2680) N/A N/A
(1) MPAI-A/BxxxxCxxx and MPAI-A/BxxxxExxx have ball screw actuators of 5 mm and 10 mm respectively.
(2) MPAI-A/BxxxxRxxx and MPAI-A/BxxxxSxxx have roller screw actuators of 5 mm and 10 mm respectively.
(1)
MPAI-A/Bxxxx Exxx
N (lb)
(1)
MPAI-A/Bxxxx Rxxx
N (lb)
(2)
MPAI-A/Bxxxx Sxxx
N (lb)
Release
(2)
(2)
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 66

66 MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders
Additional Resources
These documents contain additional information concerning related products from Rockwell
Automation.
Resource Description
Kinetix 300 EtherNet/IP Indexing Servo Drives User Manual,
publication 2 097-UM001
Kinetix 350 Single-axis EtherNet/IP Ser vo Drives User Manual,
publication 2 097-UM002
Kinetix 2000 Multi-axis Servo Drives User Manual,
publication 2093-UM001
Kinetix 6000 Multi-axis Servo Drives User Manual,
publication 2094-UM001
Kinetix 6200 and Kinetix 6500 Modular Multi-axis Ser vo Drives
User Manu al, publicati on 2094-UM002
Ultra3000 Digital Servo Drives Installation Manual,
publication 2098-IN003
Ultra3000 Digital Servo Drives Integration Manual,
publication 2098-IN005
Motion Analyzer software, download at
http;//www.rockwellautomation.com/en/e-tools
SERCOS and Analog Motion Configuration User Manual,
publication MOTION-UM001
System Design for Control of Electrical Noise Reference Manual,
publication GMC-RM001
Kinetix Motion Control Selection Guide, publication GMC-SG001
How to install, set up, and troubleshoot a servo-drive
system.
Drive and motor sizing with application analysis software.
Information on configuring and troubleshooting your
ControlLogix® and CompactLogix™ SERCOS interface
modules, and using the home to torque-level sequence.
Information, examples, and techniques designed to
minimize system failures caused by electrical noise.
Specifications, motor/servo-drive system combinations,
and accessories for Kinetix Motion Control products.
You can view or download publications at http://www.rockwellautomation.com/literature. To
order paper copies of technical documentation, contact your local Allen-Bradley distributor or
Rockwell Automation sales representative.
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 67

Notes:
MP-Series Heavy Duty Electric Cylinders 67
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Page 68

Rockwell Automation Support
Rockwell Automation provides tec hnical information on the Web to assist you in using its products.
At http://www.rockwellautomation.com/support
links to software service packs, and a MySupport feature that you can customize to make the best use of these tools. You can also visit
our Knowledgebase at http://www.rockwellautomation.com/knowledgebase
forums, software updates, and to sign up for product notification updates.
For an additional level of technical phone support for installation, configuration and troubleshooting, we offer TechConnect
programs. For more information, contact your local distributor or Rockwell Automation representative, or visit
http://www.rockwellautomation.com/support/
Installation Assistance
If you experience a problem within the first 24 hours of installation, please review the information that's contained in this manual.
You can also contact a special Customer Support number for initial help in getting your product up and running.
United States or Canada 1.440.646.3434
Outside United States or
Canada
Use the Wor ldwi de Loc ator
http://www.rockwellautomation.com/support/americas/phone_en.html
Rockwell Automation representative.
New Product Satisfaction Return
Rockwell Automation tests all o f its products to ensure that they are fully operational when shipped from the manufacturing facility.
However, if your product is not functioning and needs to be returned, follow these procedures.
, you can find technical manuals, technical and application notes, sample code and
for FAQs, technical information, support chat and
sm
support
.
at
, or contact your local
United States
Outside United States Please contact your local Rockwell Automation representative for the return procedure.
Contact your distributor. You must provide a Customer Support case number (call the phone number
above to obtain one) to your distributor to complete the return process.
Documentation Feedback
Your comments will help us serve your documentation needs better. If you have any suggestions on how to improve this document,
complete this form, publication RA-DU002
Allen-Bradley, ControlLogix, CompactLogix, Kinetix, MP-Series, Rockwell Software, RSLogix, Rockwell Automation, TechConnect, and Ultra
are trademarks of Rockwell Automation, In c.
Rockwell Otomasyon Ticaret A.Ş., Kar Plaza İş Merkezi E Blok Kat:6 34752 İçerenköy, İstanbul, Tel: +90 (216) 5698400
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAI-IN001E-EN-P - March 2012
Supersedes Publication MPAI-IN001D-EN-P - November 2011 Copyright © 2012 Rockwell Automation, Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A.
, available at http://www.rockwellautomation.com/literature/.
 Loading...
Loading...