Richtek RT8009-10GJ5, RT8009-10PJ5, RT8009-12GB, RT8009-12GJ5, RT8009-12PB Schematic [ru]
...
1.25MHz, 600mA, High Efficiency PWM Step-Down
DC/DC Converter
RT8009
General Description
The RT8009 is a high-efficiency pulse-width-modulated
(PWM) step-down DC/DC converter. Capable of delivering
600mA output current over a wide input voltage range from
2.5 to 5.5V, the RT8009 is ideally suited for portable
electronic devices that are powered from 1-cell Li-ion
battery or from other power sources within the range such
as cellular phones, PDAs and handy-terminals.
Internal synchronous rectifier with low R
DS(ON)
dramatically
reduces conduction loss at PWM mode. No external
Schottky diode is required in practical application. The
RT8009 automatically turns off the synchronous rectifier
while the inductor current is low and enters discontinuous
PWM mode. This can increase efficiency at light load
condition.
The RT8009 enters Low-Dropout mode when normal PWM
cannot provide regulated output voltage by continuously
turning on the upper P-MOSFET. RT8009 enter shutdown
mode and consumes less than 0.1μA when EN pin is pulled
low.
The switching ripple is easily smoothed-out by small
package filtering elements due to a fixed operation
frequency of 1.25MHz. This along with small SOT-23-5
and TSOT-23-5 package provides small PCB area
application. Other features include soft start, lower internal
reference voltage with 2% accuracy, over temperature
protection, and over current protection.
Pin Configurations
(TOP VIEW)
LX
FB/VOUT
5
VIN
SOT-23-5/TSOT-23-5
4
23
GND EN
Marking Information
Features
2.5V to 5.5V Input Range
Adjustable Output From 0.5V to V
1.0V, 1.2V, 1.3V, 1.5V, 1.8V, 2.5V and 3.3V Fixed/
IN
Adjustable Output Voltage
600mA Output Current
95% Efficiency
No Schottky Diode Required
1.25MHz Fixed Frequency PWM Operation
Small SOT-23-5 and TSOT-23-5 Package
RoHS Compliant and 100% Lead (Pb)-Free
Applications
Cellular Telephones
Personal Information Appliances
Wireless and DSL Modems
MP3 Players
Portable Instruments
Ordering Information
RT8009(- )
Package Type
B : SOT-23-5
J5 : TSOT-23-5
Lead Plating System
P : Pb Free
G : Green (Halogen Free and Pb Free)
Output Voltage
Default : Adjustable
10 : 1.0V
12 : 1.2V
13 : 1.3V
15 : 1.5V
18 : 1.8V
25 : 2.5V
33 : 3.3V
Note :
Richtek products are :
` RoHS compliant and compatible with the current require-
ments of IPC/JEDEC J-STD-020.
` Suitable for use in SnPb or Pb-free soldering processes.
For marking information, contact our sales representative
directly or through a Richtek distributor located in your
area.
DS8009-07 March 2011 www.richtek.com
1
RT8009
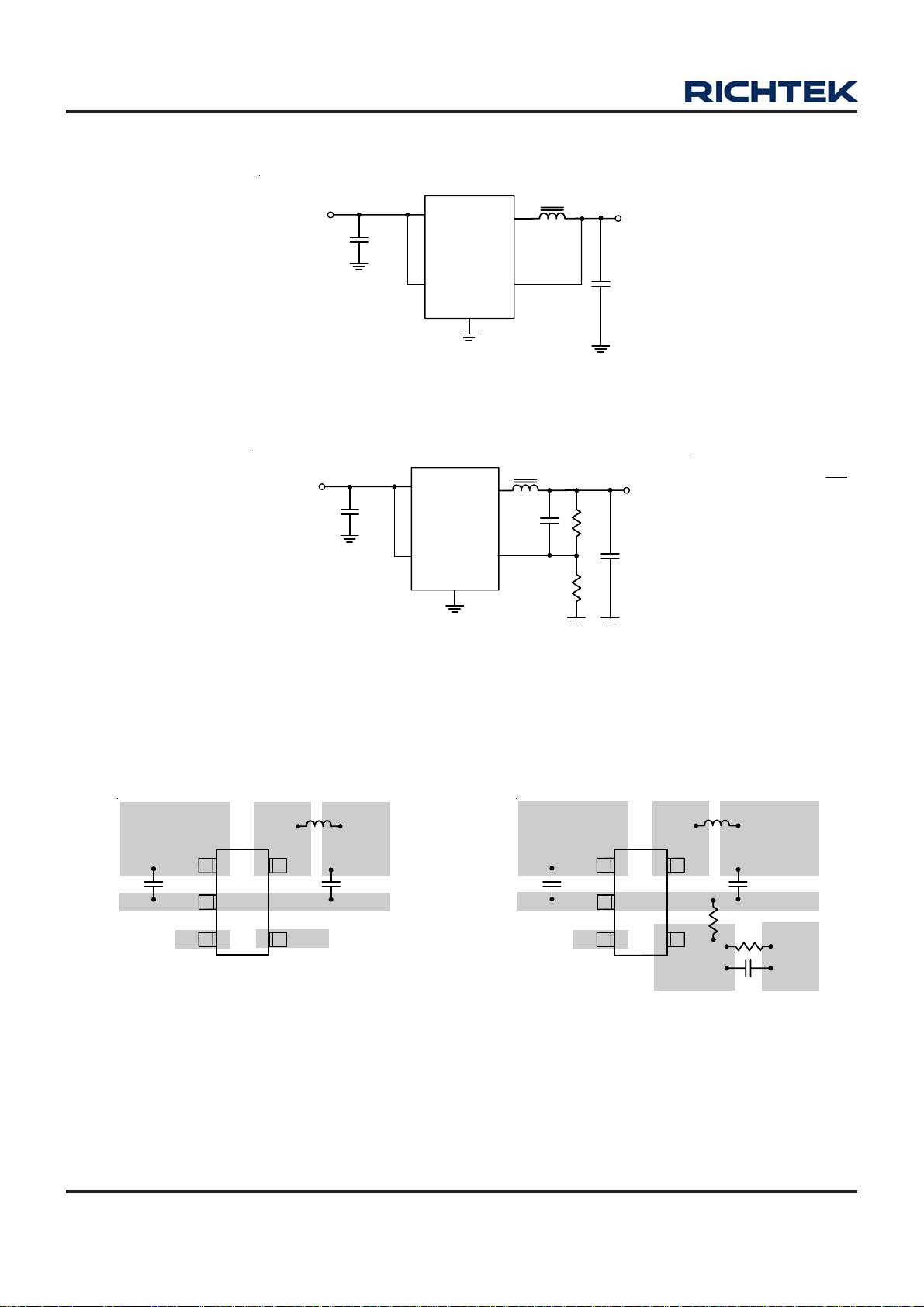
Typical Application Circuit
V
IN
2.5V to 5.5V
L
C
IN
4.7µF
1
3
VIN
EN
RT8009
VOUT
GND
2
LX
5
4
4.7µH
Figure 1. Fixed Voltage Regulator
V
C
OUT
10µF
OUT
Layout Guide
V
IN
C
IN
VIN
GND
EN
1
2
354
V
IN
2.5V to 5.5V
L
LX
VOUT
L
C
IN
4.7µF
1
3
VIN
RT8009
EN
GND
2
LX
FB
4.7µH
5
4
C1
Figure 2. Adjustable Voltage Regulator
C
V
OUT
GND
OUT
V
IN
VIN
C
IN
GND
EN
R1
R2
V
OUT
C
OUT
10µF
1
2
354
REF(Typ.)
L
LX
R2
FB
R1
C
REFOUT
=
OUT
0.5VV
⎛
⎜
⎝
V
OUT
GND
V
OUT
R1
⎞
1 x VV
+=
⎟
R2
⎠
and 1MR2R1 with
Ω≤+
Layout note:
1. The distance that C
2. C
should be placed near RT8009.
OUT
2
Figure 3
connects to VIN is as close as possible (Under 2mm).
IN
C1
DS8009-07 March 2011www.richtek.com
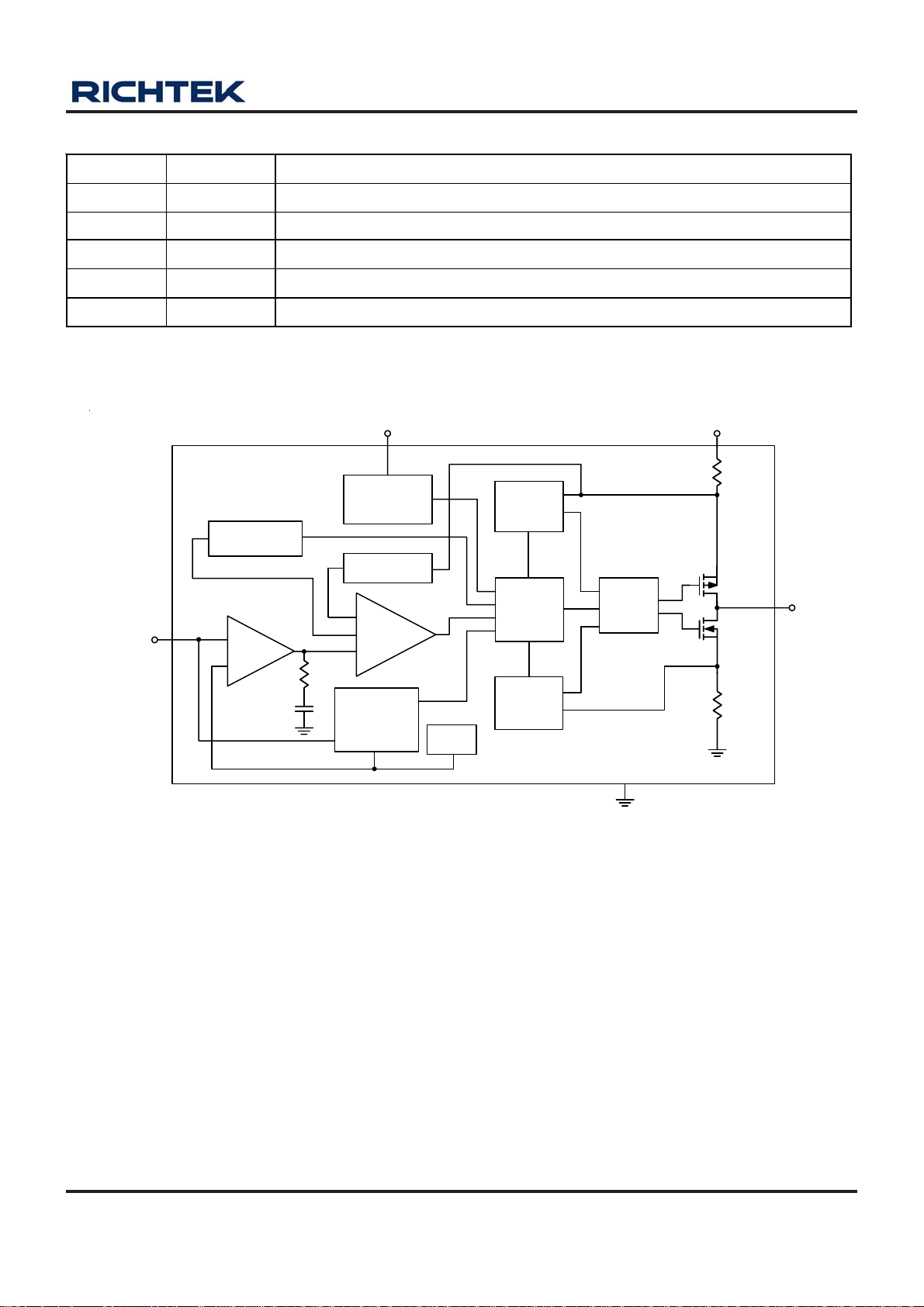
Functional Pin Description
Pin Number Pin Name Pin Function
1 VIN Power Input.
2 GND Ground.
3 EN Chip Enab le (Active H igh, do not leave EN pin floating, and VEN < VIN + 0. 6V).
4 FB/VOUT Feed back Inp ut P in.
5 LX Pin for Switching.
Function Block Diagram
RT8009
FB/VOUT
Slope
Compensation
Error
Amplifier
RC
COMP
EN
OSC &
Shutdown
Control
Current
Sense
PWM
Comparator
UVLO &
Power Good
Detector
V
REF
Current
Limit
Detector
Control
Logic
Zero
Detector
Driver
GND
VIN
RS1
LX
RS2
DS8009-07 March 2011 www.richtek.com
3
RT8009
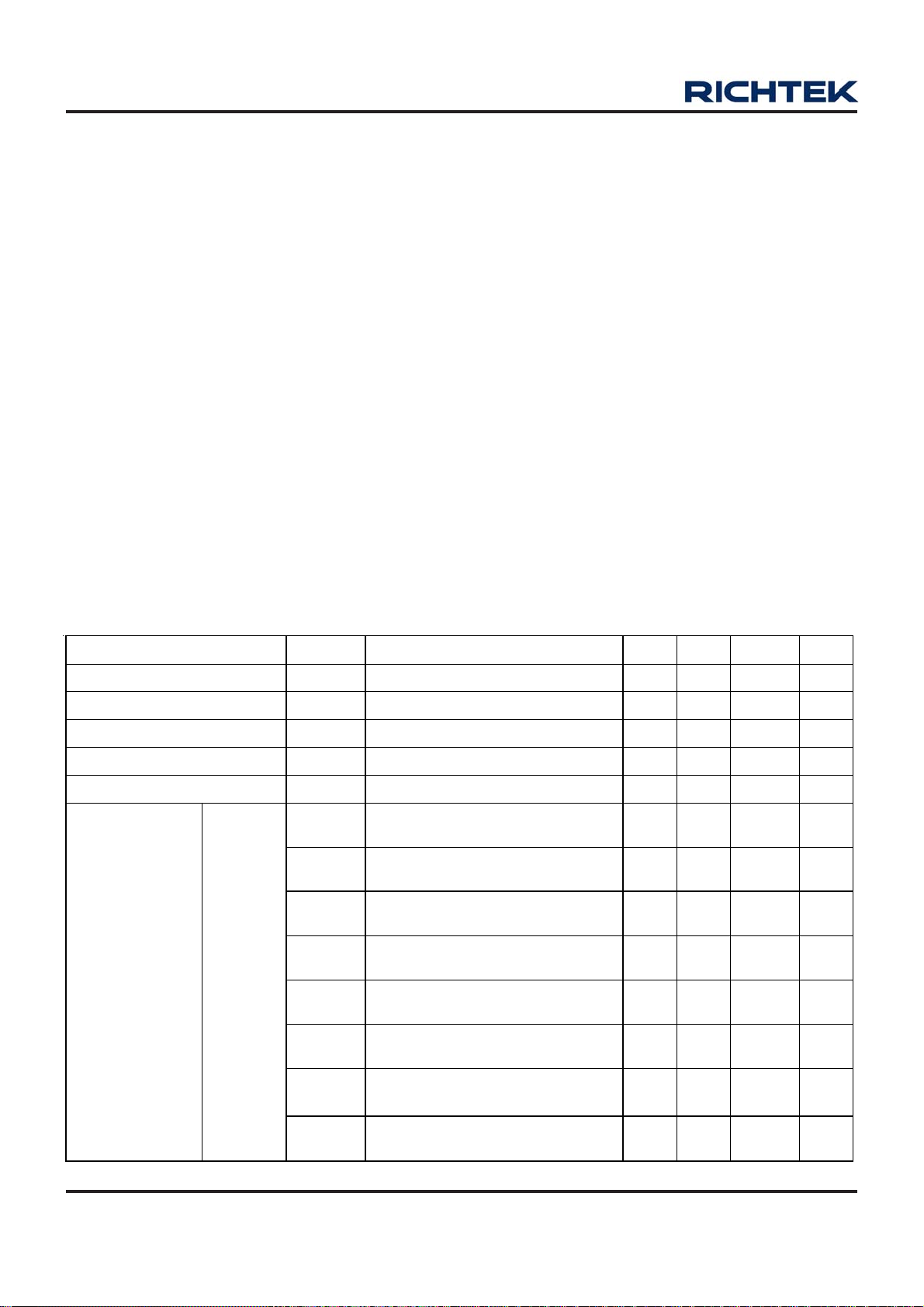
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
Supply Input Voltage ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 6.5V
Enable, FB Voltage ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- V
Power Dissipation, P
@ TA = 25°C
D
SOT-23-5, TSOT-23-5 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.4W
Package Thermal Resistance (Note 2)
SOT-23-5, TSOT-23-5, θJA----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 250°C/W
SOT-23-5, TSOT-23-5, θJC----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 130°C/W
Junction Temperature Range -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 150°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec.)------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 260°C
Storage Temperature Range -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- −65°C to 150°C
ESD Susceptibility (Note 3)
HBM (Human Body Mode) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2kV
MM (Machine Mode) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 200V
Recommended Operating Conditions (Note 4)
Supply Input Voltage ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 2.5V to 5.5V
Junction Temperature Range -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- −40°C to 125°C
Ambient Temperature Range -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- −40°C to 85°C
+ 0.6V
IN
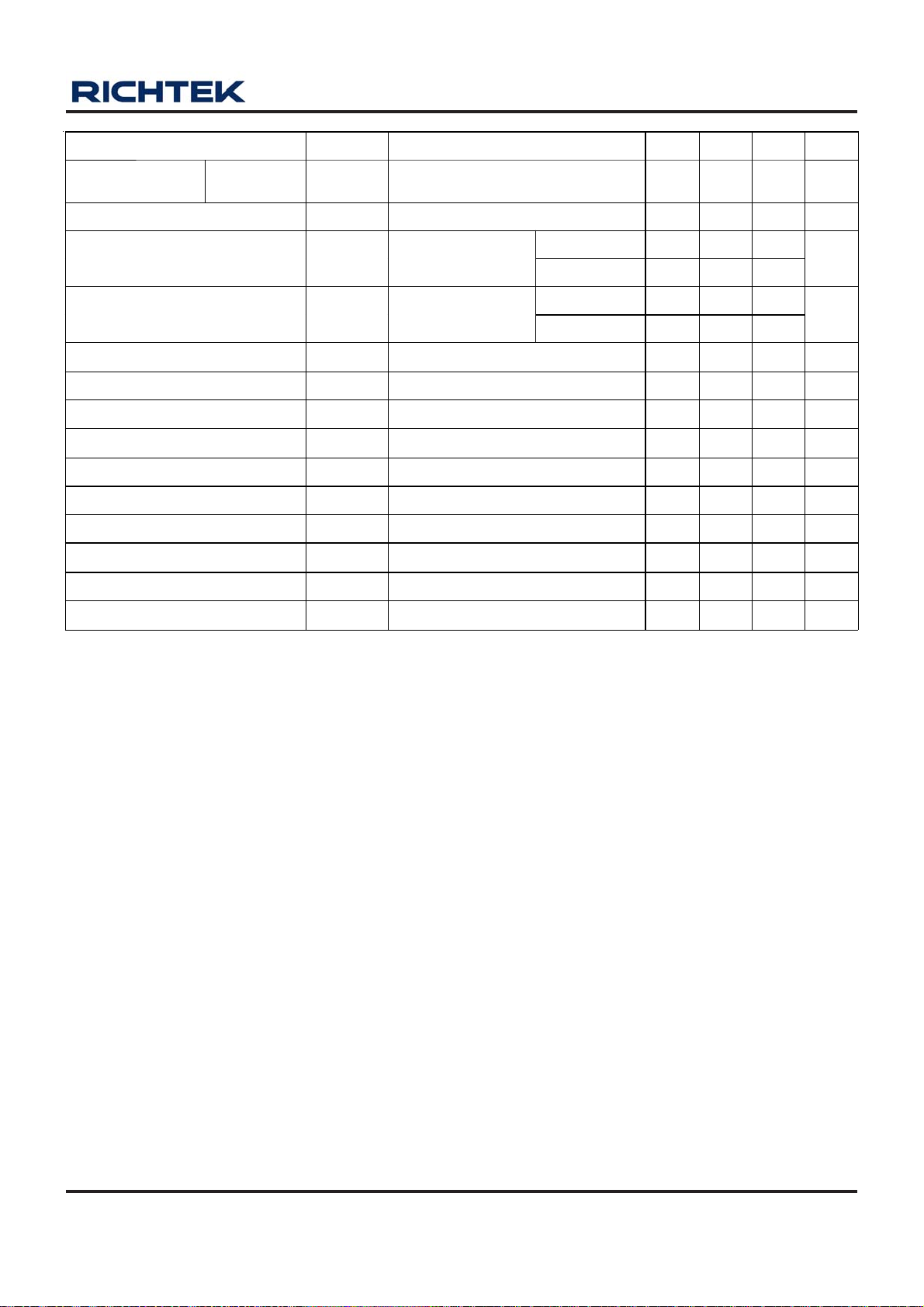
Electrical Characteristics
(V
= 3.6V, V
IN
Input Voltage Range
Quiescent Current
Shutdown Cur rent
Reference Voltage
Adjustable Output Range
Output Voltage
Accuracy
OUT
= 2.5V, V
= 0.5V, L = 4.7μH, C
REF
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
V
IN
I
I
Q
I
SHDN
V
REF
V
OUT
ΔV
OUT
ΔV
OUT
ΔV
OUT
ΔV
OUT
Fix
ΔV
OUT
ΔV
OUT
ΔV
OUT
ΔV
OUT
= 4.7μF, C
IN
OUT
= 10μF, T
= 25°C, I
A
= 600mA unless otherwise specified)
MAX
2.5 -- 5.5 V
= 0mA, VFB = V
OUT
EN = GND -- 0.1 1 μA
For adjustable output voltage 0.49 0.5 0.51 V
= 2. 5 to 5. 5V , V
V
IN
0A < I
V
IN
0A < I
V
IN
0A < I
V
IN
0A < I
V
IN
0A < I
V
IN
V
OUT
V
IN
V
OUT
V
IN
0A < I
< 600mA
OUT
= 2. 5 to 5. 5V , V
< 600mA
OUT
= 2. 5 to 5. 5V , V
< 600mA
OUT
= 2. 5 to 5. 5V , V
< 600mA
OUT
= 2. 5 to 5. 5V , V
< 600mA
OUT
= V
+ ΔV to 5.5V (Note 5)
OUT
= 2.5V, 0A < I
= V
+ ΔV to 5.5V (Note 5)
OUT
= 3.3V, 0A < I
= V
+ 0.2V to 5.5V
OUT
< 600mA
OUT
+ 5%
REF
= 1.0V
OUT
= 1.2V
OUT
= 1.3V
OUT
= 1.5V
OUT
= 1.8V
OUT
< 600mA
OU T
< 600mA
OU T
-- 50 100
V
REF
--
V
− 0.2
IN
−3 -- 3 %
−3
−3
−3
−3
−3
−3
−3
-- 3 %
-- 3 %
-- 3 %
-- 3 %
-- 3 %
-- 3 %
-- 3 %
To be continued
μA
V
DS8009-07 March 2011www.richtek.com
4
RT8009
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Output Voltage
Accuracy
Adjustable
FB Input Current
R
R
of P- Channel MO SFET R
DS(ON)
of N-Channel MOSFET R
DS(ON)
P-Channel Current Limit
EN High-Level Input Voltage
EN Low-Level Input Voltage
ΔV
OU T
I
V
FB
DS(ON)_P
DS(ON)_N
I
LIM_P
V
EN_H
V
EN_L
V
I
I
V
= V
IN
0A < I
= VIN −50
FB
OUT
OUT
= 2.5V to 5.5 V
IN
+ ΔV to 5.5V (Note 5)
OUT
< 600mA
OUT
= 200mA
= 200mA
VIN = 2.5V to 5.5V
VIN = 2.5V to 5.5V
V
IN
V
IN
V
IN
V
IN
= 3.6V
= 2.5V
= 3.6V
= 2.5V
−3
-- 3 %
-- 50 nA
-- 0.3 0.65
Ω
-- 0.4 0.80
-- 0.25 0.55
Ω
-- 0.35 0.65
1 -- 1.8 A
1.5 -- -- V
-- -- 0.4 V
Under Voltage Lockout Threshold -- 1.8 -- V
Hysteresis -- 0.1 -- V
Oscillator Frequency
Thermal Shutdown Temperature
f
V
OSC
T
SD
= 3.6V, I
IN
OUT
= 100mA
-- 160 -- °C
0.8 1.25 1.85 MHz
Min. On Time -- 50 -- ns
Max. Duty Cycle 100 -- -- %
LX Leakage Current
V
IN
= 3.6V, V
= 0V or V
LX
= 3.6V −1
LX
-- 1
μA
Note 1. Stresses listed as the above “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are for
stress ratings. Functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the
operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended
periods may remain possibility to affect device reliability.
Note 2. θ
Note 3. Devices are ESD sensitive. Handling precaution recommended.
Note 4. The device is not guaranteed to function outside its operating conditions.
Note 5. ΔV = I
is measured in the natural convection at TA = 25°C on a low effective thermal conductivity test board of
JA
JEDEC 51-3 thermal measurement standard.
x R
OUT
DS(ON)_P
DS8009-07 March 2011 www.richtek.com
5
RT8009
)
)
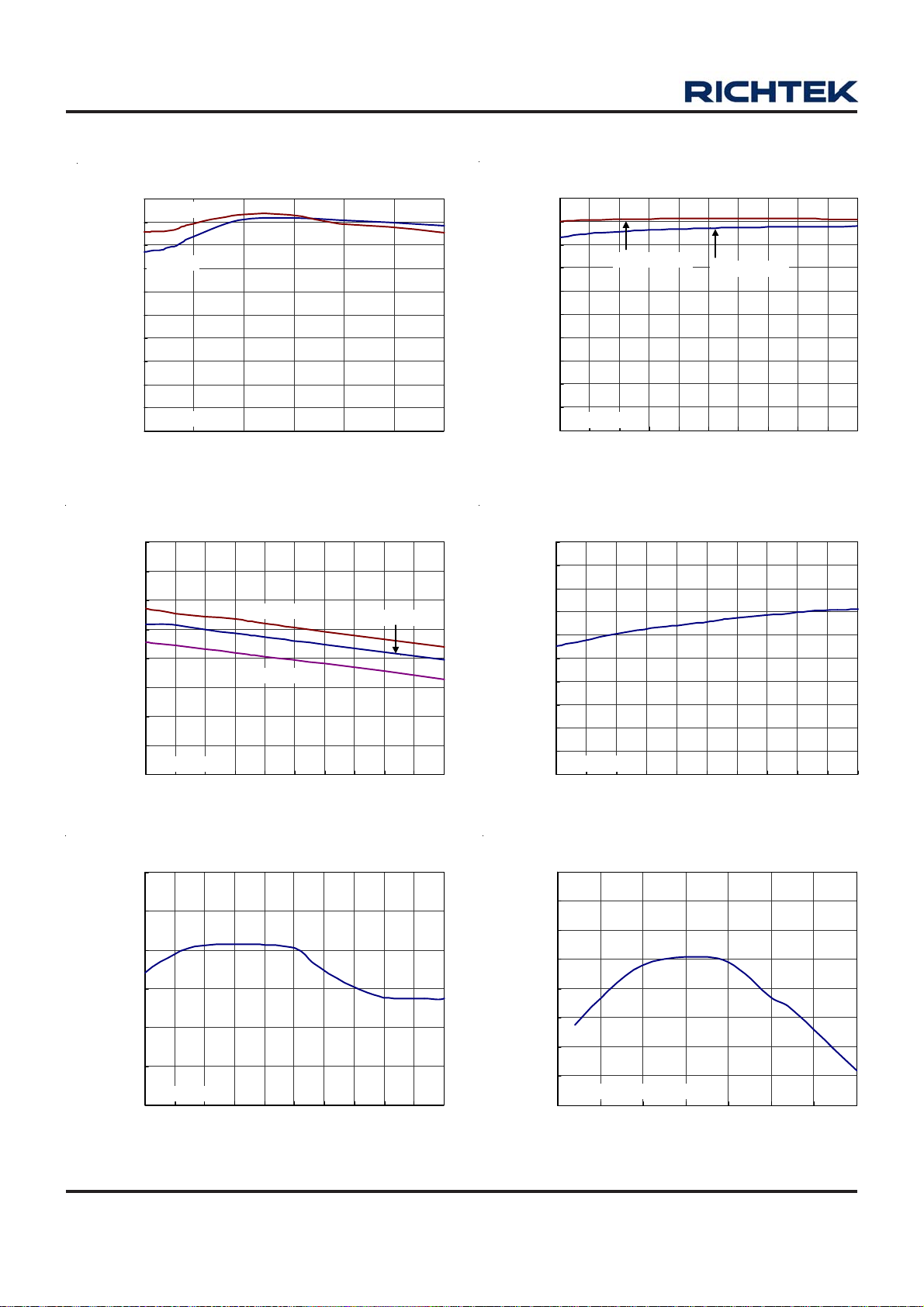
Typical Operating Characteristics
Efficiency vs . Loa d Current
100
VIN = 3.3V
90
80
VIN = 5V
70
60
50
40
Efficiency (%)
30
20
10
V
= 1.8V
OUT
0
0.01 0.11 0.21 0.31 0.41 0.51 0.61
Load Current (A)
Load Regulation
1.810
1.805
1.800
1.795
1.790
1.785
1.780
Load Regulation (V
1.775
V
= 1.8V
1.770
OUT
0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5 0.55 0.6
VIN = 5.5V
VIN = 2.5V
Load Current (A)
VIN = 3.3V
Efficiency v s . Input Voltage
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
Efficiency (%)
30
20
10
V
0
2.5 2.8 3.1 3.4 3.7 4 4.3 4.6 4.9 5.2 5.5
OUT
I
OUT
= 1.8V
= 300mA
I
OUT
= 600mA
Input Voltage (V)
Current Limit vs. Input Voltage
2.50
2.25
2.00
1.75
1.50
1.25
1.00
0.75
Current Limit (A)
0.50
0.25
V
= 1.8V
0.00
OUT
2.5 2.8 3.1 3.4 3.7 4 4.3 4.6 4.9 5.2 5.5
Input Voltage (V)
Frequency vs. Input Voltage
1.26
1.24
1.22
1.20
1.18
Frequency (MHz
1.16
V
= 1.8V
1.14
OUT
2.5 2.8 3.1 3.4 3.7 4 4.3 4.6 4.9 5.2 5.5
Input Voltage (V)
1.26
1.24
1.22
1.20
1.18
1.16
Frequency (MHz) 1
1.14
1.12
1.10
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Frequency vs. Temperature
VIN = 3.3V, V
= 1.8V
OUT
Temperature (°C)
DS8009-07 March 2011www.richtek.com
6

RT8009
0.60
0.58
0.56
0.54
0.52
0.50
0.48
Reference (V)
0.46
0.44
0.42
0.40
V
OUT
(20mV/Div)
Reference vs. Input Voltag e
V
= 1.8V
OUT
2.5 2.8 3.1 3.4 3.7 4 4.3 4.6 4.9 5.2 5.5
Input Voltage (V)
Load Transient Response
VIN = 3.3V, V
= 1.8V, I
OUT
= 150mA to 600mA
OUT
0.510
0.508
0.505
0.503
0.500
0.498
Reference (V)
0.495
0.493
0.490
V
OUT
(20mV/Div)
Reference vs. Temperature
VIN = 3.3V, V
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
= 1.8V
OUT
Temperature (°C)
Load Transient Response
VIN = 3.3V, V
= 1.8V, I
OUT
= 300mA to 600mA
OUT
I
OUT
(500mA/Div)
V
OUT
(2mV/Div)
V
LX
(5V/Div)
I
LX
(500mA/Div)
VIN = 3.3V, V
Time (100μs/Div)
Output Ripple
= 1.8V, I
OUT
Time (500ns/Div)
OUT
= 600mA
I
OUT
(500mA/Div)
V
EN
(2V/Div)
V
OUT
(1V/Div)
I
IN
(200mA/Div)
VIN = 3.3V, V
Time (100μs/Div)
Power On
= 1.8V, I
OUT
Time (100μs/Div)
OUT
= 600mA
DS8009-07 March 2011 www.richtek.com
7

RT8009
Applications Information
The basic RT8009 application circuit is shown in Typical
Application Circuit. External component selection is
determined by the maximum load current and begins with
the selection of the inductor value and operating frequency
followed by CIN and C
OUT
.
Inductor Selection
For a given input and output voltage, the inductor value
and operating frequency determine the ripple current. The
ripple current ΔIL increases with higher VIN and decreases
with higher inductance.
ΔI
V
⎡
=
L
⎢
Lf
×
⎣
V
⎡
⎤
1
−
⎢
⎥
⎣
⎦
⎤
OUTOUT
⎥
V
IN
⎦
Having a lower ripple current reduces the ESR losses in
the output capacitors and the output voltage ripple. Highest
efficiency operation is achieved at low frequency with small
ripple current. This, however, requires a large inductor.
A reasonable starting point for selecting the ripple current
is ΔIL = 0.4(I
). The largest ripple current occurs at the
MAX
highest VIN. To guarantee that the ripple current stays
below a specified maximum, the inductor value should be
chosen according to the following equation :
⎡
V
⎡
L
=
OUT
⎢
L(MAX)
If
Δ×
⎣
V
⎤
1
−
⎢
⎥
V
⎦
⎢
IN(MAX)
⎣
OUT
⎤
⎥
⎥
⎦
Inductor Core Selection
Once the value for L is known, the type of inductor must
be selected. High efficiency converters generally cannot
afford the core loss found in low cost powdered iron cores,
forcing the use of more expensive ferrite or mollypermalloy
cores. Actual core loss is independent of core size for a
fixed inductor value but it is very dependent on the
inductance selected. As the inductance increases, core
losses decrease. Unfortunately, increased inductance
requires more turns of wire and therefore copper losses
will increase.
Ferrite designs have very low core losses and are preferred
at high switching frequencies, so design goals can
concentrate on copper loss and preventing saturation.
Ferrite core material saturates “hard”, which means that
inductance collapses abruptly when the peak design
current is exceeded. This results in an abrupt increase in
inductor ripple current and consequent output voltage ripple.
Do not allow the core to saturate!
Different core materials and shapes will change the size/
current and price/current relationship of an inductor.
Toroid or shielded pot cores in ferrite or permalloy materials
are small and don’t radiate energy but generally cost
more than powdered iron core inductors with similar
characteristics. The choice of which style inductor to use
mainly depends on the price vs size requirements and
any radiated field/EMI requirements.
CIN and C
Selection
OUT
The input capacitance, CIN, is needed to filter the
trapezoidal current at the source of the top MOSFET. To
prevent large ripple voltage, a low ESR input capacitor
sized for the maximum RMS current should be used. RMS
current is given by :
V
II
OUT(MAX)RMS
OUT
V
This formula has a maximum at VIN = 2V
= I
/2. This simple worst-case condition is commonly
OUT
V
IN
1
−=
V
OUT
IN
, where I
OUT
RMS
used for design because even significant deviations do
not offer much relief. Note that ripple current ratings from
capacitor manufacturers are often based on only 2000
hours of life which makes it advisable to further derate the
capacitor, or choose a capacitor rated at a higher
temperature than required. Several capacitors may also
be paralleled to meet size or height requirements in the
design.
The selection of C
is determined by the effective series
OUT
resistance (ESR) that is required to minimize voltage ripple
and load step transients, as well as the amount of bulk
capacitance that is necessary to ensure that the control
loop is stable. Loop stability can be checked by viewing
the load transient response as described in a later section.
The output ripple, ΔV
⎡
ESR ΔIΔV
LOUT
⎢
⎣
, is determined by :
OUT
1
OUT
⎤
⎥
⎦
+≤
8fC
The output ripple is highest at maximum input voltage
since ΔIL increases with input voltage. Multiple capacitors
placed in parallel may be needed to meet the ESR and
RMS current handling requirements. Dry tantalum, special
DS8009-07 March 2011www.richtek.com
8

RT8009
polymer, aluminum electrolytic and ceramic capacitors are
all available in surface mount packages. Special polymer
capacitors offer very low ESR but have lower capacitance
density than other types. Tantalum capacitors have the
highest capacitance density but it is important to only
use types that have been surge tested for use in switching
power supplies. Aluminum electrolytic capacitors have
significantly higher ESR but can be used in cost-sensitive
applications provided that consideration is given to ripple
current ratings and long term reliability. Ceramic capacitors
have excellent low ESR characteristics but can have a
high voltage coefficient and audible piezoelectric effects.
The high Q of ceramic capacitors with trace inductance
can also lead to significant ringing.
Using Ceramic In put and Output Capacitors
Higher values, lower cost ceramic capacitors are now
becoming available in smaller case sizes. Their high ripple
current, high voltage rating and low ESR make them ideal
for switching regulator applications. However, care must
be taken when these capacitors are used at the input and
output. When a ceramic capacitor is used at the input
and the power is supplied by a wall adapter through long
wires, a load step at the output can induce ringing at the
input, VIN. At best, this ringing can couple to the output
and be mistaken as loop instability. At worst, a sudden
inrush of current through the long wires can potentially
cause a voltage spike at VIN large enough to damage the
part.
Output Voltage Programming
The resistive divider allows the VFB pin to sense a fraction
of the output voltage as shown in Figure 4.
V
OUT
Efficiency Considerations
The efficiency of a switching regulator is equal to the output
power divided by the input power times 100%. It is often
useful to analyze individual losses to determine what is
limiting the efficiency and which change would produce
the most improvement. Efficiency can be expressed as :
Efficiency = 100% − (L1+ L2+ L3+ ...)
where L1, L2, etc. are the individual losses as a percentage
of input power. Although all dissipative elements in the
circuit produce losses, two main sources usually account
for most of the losses : VIN quiescent current and I2R
losses. The VIN quiescent current loss dominates the
efficiency loss at very low load currents whereas the I2R
loss dominates the efficiency loss at medium to high load
currents. In a typical efficiency plot, the efficiency curve
at very low load currents can be misleading since the
actual power lost is of no consequence.
1. The VIN quiescent current is due to two components :
the DC bias current as given in the electrical characteristics
and the internal main switch and synchronous switch gate
charge currents. The gate charge current results from
switching the gate capacitance of the internal power
MOSFET switches. Each time the gate is switched from
high to low to high again, a packet of charge ΔQ moves
from VIN to ground.
The resulting ΔQ/Δt is the current out of VIN that is typically
larger than the DC bias current. In continuous mode,
I
GATECHG
= f(QT+QB)
where QT and QB are the gate charges of the internal top
and bottom switches. Both the DC bias and gate charge
losses are proportional to VIN and thus their effects will
be more pronounced at higher supply voltages.
RT8009
R1
VFB
R2
GND
2. I2R losses are calculated from the resistances of the
internal switches, RSW and external inductor RL. In
continuous mode the average output current flowing
through inductor L is “chopped” between the main switch
and the synchronous switch. Thus, the series resistance
Figure 4. Setting the Output Voltage
For adjustable about voltage mode, the output voltage is
set by an external resistive divider according to the following
equation :
where V
DS8009-07 March 2011 www.richtek.com
OUT
is the internal reference voltage (0.5V typ.)
REF
REF
R1
(1VV
)
+=
R2
looking into the LX pin is a function of both top and bottom
MOSFET R
RSW = R
The R
DS(ON)TOP
DS(ON)
and the duty cycle (DC) as follows :
DS(ON)
x DC + R
DS(ON)BOT
x (1−DC)
for both the top and bottom MOSFETs can be
obtained from the Typical Performance Characteristics
9

RT8009
curves. Thus, to obtain I2R losses, simply add RSW to R
and multiply the result by the square of the average output
current.
Other losses including CIN and C
ESR dissipative
OUT
losses and inductor core losses generally account for less
than 2% of the total loss.
Thermal Considerations
The maximum power dissipation depends on the thermal
resistance of IC package, PCB layout, the rate of
surroundings airflow and temperature difference between
junction to ambient. The maximum power dissipation can
be calculated by following formula :
P
Where T
temperature 125°C, T
θ
= ( T
D(MAX)
J(MAX)
is the junction to ambient thermal resistance.
JA
- TA ) / θ
J(MAX)
JA
is the maximum operation junction
is the ambient temperature and the
A
For recommended operating conditions specification of
RT8009 DC/DC converter, where T
is the maximum
J (MAX)
junction temperature of the die (125°C) and TA is the
maximum ambient temperature. The junction to ambient
thermal resistance θJA is layout dependent. For
SOT-23-5/TSOT-23-5 packages, the thermal resistance θ
JA
is 250°C/W on the standard JEDEC 51-3 single-layer
thermal test board. The maximum power dissipation at
TA = 25°C can be calculated by following formula :
P
= ( 125°C - 25°C ) / 250 = 0.4 W for SOT-23-5/
D(MAX)
TSOT-23-5 packages
The maximum power dissipation depends on operating
ambient temperature for fixed T
and thermal
J(MAX)
resistance θJA. For RT8009 packages, the Figure 5 of
derating curves allows the designer to see the effect of
rising ambient temperature on the maximum power
allowed.
The value of junction to case thermal resistance θJC is
popular for users. This thermal parameter is convenient
for users to estimate the internal junction operated
temperature of packages while IC operating. It's
independent of PCB layout, the surroundings airflow effects
and temperature difference between junction to ambient.
The operated junction temperature can be calculated by
following formula :
Where TC is the package case (Pin 2 of package leads)
L
temperature measured by thermal sensor, P
dissipation defined by user's function and the θJC is the
junction to case thermal resistance provided by IC
manufacturer. Therefore it's easy to estimate the junction
temperature by any condition.
450
400
350
300
250
200
150
100
50
Maximum Power Dissipation (mW)
0
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
SOT-23-5, TSOT-23-5 Packages
Ambient Temperature (°C)
Single Layer PCB
Figure 5. Derating Curves for RT8009 Package
Checking Tra n sient Re spon se
The regulator loop response can be checked by looking
at the load transient response. Switching regulators take
several cycles to respond to a step in load current. When
a load step occurs, V
equal to ΔI
resistance of C
discharge C
(ESR), where ESR is the effective series
LOAD
OUT
generating a feedback error signal used
OUT
by the regulator to return V
During this recovery time, V
immediately shifts by an amount
OUT
. ΔI
also begins to charge or
LOAD
to its steady-state value.
OUT
can be monitored for
OUT
overshoot or ringing that would indicate a stability problem.
Layout Considerations
Follow the PCB layout guidelines for optimal performance
of RT8009.
` For the main current paths as indicated in bold lines in
Figure 6 keep their traces short and wide.
` Put the input capacitor as close as possible to the device
pins (VIN and GND).
` LX node is with high frequency voltage swing and should
be kept small area. Keep analog components away from
LX node to prevent stray capacitive noise pick-up.
is the power
D
TJ = TC + PD x θ
10
JC
DS8009-07 March 2011www.richtek.com

` Connect feedback network behind the output capacitors.
Keep the loop area small. Place the feedback
components near the RT8009.
` Connect all analog grounds to a command node and
then connect the command node to the power ground
behind the output capacitors.
` An example of 2-layer PCB layout is shown in Figure 7
and Figure 8 for reference.
RT8009
V
IN
C3
4.7uF
R3
RT8009
1
VIN
3
EN
GND
5
LX
4
FB
2
Figure 6. EVB Schematic
L1
4.7uH
C1
C2
R1
R2
V
OUT
C4
10uF
Figure 7. Top Layer
Figure 8. Bottom Layer
Recommended component selection for Typical Application
Table 1. Inductors
Com ponent Supplie r S er ies Induc tance ( μH) DCR (mΩ) Cur r ent Ra ti ng ( mA ) Dime nsio ns (m m )
TAIYO YUDEN NR 3015 2.2 60 1480 3x3x1.5
TAIYO YUDEN NR 3015 4.7 120 1020 3x3x1.5
Sumida CDRH2D14 2.2 75 1500 4.5x3.2x1.55
Sumida CDRH2D14 4.7 135 1000 4.5x3.2x1.55
GOTREND GTSD32 2.2 58 1500 3.85x3.85x1.8
GOTREND GTSD32 4.7 146 1100 3.85x3. 85x1. 8
Table 2. Capacitors for CIN and C
OUT
Component Sup pl ie r Par t No. Capacitance (μF) Case Size
TDK C1608JB0J475M 4.7 0603
TDK C2012JB0J106M 10 0805
MURAT A GRM188R60J475KE19 4.7 0603
MURAT A GRM219R60J106ME19 10 0805
MURAT A GRM219R60J106KE19 10 0805
TA IYO YUDEN JMK107BJ475RA 4.7 0603
TA IYO YUDEN JMK107BJ106MA 10 0603
TA IYO YUDEN JMK212BJ106RD 10 0805
DS8009-07 March 2011 www.richtek.com
11

RT8009
Outline Dimension
H
D
L
C
b
A
e
Dimensions In Millimeters Dimensions In Inches
Symbol
Min Max Min Max
A 0.889 1.295 0.035 0.051
A1 0.000 0.152 0.000 0.006
B 1.397 1.803 0.055 0.071
b 0.356 0.559 0.014 0.022
C 2.591 2.997 0.102 0.118
D 2.692 3.099 0.106 0.122
B
A1
12
e 0.838 1.041 0.033 0.041
H 0.080 0.254 0.003 0.010
L 0.300 0.610 0.012 0.024
SOT-23-5 Surface Mount Package
DS8009-07 March 2011www.richtek.com

RT8009
H
D
L
C
b
A
e
B
A1
Dimensions In Millimeters Dimensions In Inches
Symbol
Min Max Min Max
A 0.700 1.000 0.028 0.039
A1 0.000 0.100 0.000 0.004
B 1.397 1.803 0.055 0.071
b 0.300 0.559 0.012 0.022
C 2.591 3.000 0.102 0.118
D 2.692 3.099 0.106 0.122
e 0.838 1.041 0.033 0.041
H 0.080 0.254 0.003 0.010
L 0.300 0.610 0.012 0.024
TSOT-23-5 Surface Mount Package
Richtek Technology Corporation
Headquarter
5F, No. 20, Taiyuen Street, Chupei City
Hsinchu, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Tel: (8863)5526789 Fax: (8863)5526611
Information that is provided by Richtek Technology Corporation is believed to be accurate and reliable. Richtek reserves the right to make any change in circuit
design, specification or other related things if necessary without notice at any time. No third party intellectual property infringement of the applications should be
guaranteed by users when integrating Richtek products into any application. No legal responsibility for any said applications is assumed by Richtek.
DS8009-07 March 2011 www.richtek.com
Richtek Technology Corporation
Taipei Office (Marketing)
5F, No. 95, Minchiuan Road, Hsintien City
Taipei County, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Tel: (8862)86672399 Fax: (8862)86672377
Email: marketing@richtek.com
13

 Loading...
Loading...