Ransburg LECU5004 User Manual
SERVICE MANUAL
LN-9218-00.13
(REPLACES: LN-9218-00.12)
February - 2013
Ransburg
TM
MICROPAK
MODEL: LECU5004
IMPORTANT: Before using this equipment,
carefully read SAFETY PRECAUTIONS, starting
on page 1, and all instructions in this manual.
Keep this Service Manual for future reference.
Service Manual Price: $50.00 (U.S.)

MicroPak
NOTE: This manual has been changed from revision LN-9218-00.12 to revision LN-9218-00.13.
Reasons for this change are noted under “Manual Change Summary” inside the back cover
of this manual.
Ransburg
LN-9218-00.13

Ransburg
MicroPak - Contents
CONTENTS
SAFETY: 1-5
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS ......................................................................................................1
HAZARDS / SAFEGUARDS ..................................................................................................2-5
INTRODUCTION: 6-7
GENERAL DESCRIPTION ....................................................................................................6
SAFETY FEATURES .............................................................................................................6
DISPLAYS .............................................................................................................................6
SPECIFICATIONS .................................................................................................................6-7
INSTALLATION: 8-12
CONNECTIONS ....................................................................................................................8-12
OPERATION: 13-28
PAGE
OPERATOR CONTROL ........................................................................................................13
MODES OF OPERATION / CONFIGURATION ....................................................................13-17
VERSION 3.8 SOFTWARE ...................................................................................................17
VERSION 3.9 SOFTWARE ...................................................................................................17
SWITCH SETTINGS .............................................................................................................18
SWITCH CONFIGURATION .................................................................................................19
INPUT / OUTPUT SIGNALS .................................................................................................20-23
MICROPAK NODE ADAPTER PLC I/O .................................................................................23-27
DIAGNOSTICS ......................................................................................................................28
MAINTENANCE: 29-31
TROUBLESHOOTING ..........................................................................................................29
OHM METER MEASUREMENTS / CASCADE .....................................................................30
OHM METER MEASUREMENTS FOR RANSPAK 1000 CASCADE ...................................31
PARTS IDENTIFICATION: 32-33
MICROPAK APPLICATION TABLE ...................................................................................... 32
MICROPAK PARTS LIST ..................................................................................................... 33
WARRANTY POLICIES: 34
LIMITED WARRANTY ...........................................................................................................34
LN-9218-00.13
MicroPak - Safety
SAFETY
Ransburg
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Before operating, maintaining or servicing any
Ransburg electrostatic coating system, read and
understand all of the technical and safety literature for your Ransburg products. This manual
contains information that is important for you to
know and understand. This information relates to
USER SAFETY and PREVENTING EQUIPMENT
PROBLEMS. To help you recognize this information, we use the following symbols. Please pay
particular attention to these sections.
A WARNING! states information to alert you
to a situation that might cause serious injury
if instructions are not followed.
A CAUTION! states information that tells how
to prevent damage to equipment or how to
avoid a situation that might cause minor injury.
A NOTE is information relevant to the procedure in progress.
W A R N I N G
!
The user MUST read and be familiar with
the Safety Section in this manual and the
Ransburg safety literature therein identied.
This manual MUST be read and thor-
oughly understood by ALL personnel who
operate, clean or maintain this equipment!
Special care should be taken to ensure that
the WARNINGS and safety requirements for
operating and servicing the equipment are
followed. The user should be aware of and
adhere to ALL local building and re codes
and ordinances as well as NFPA-33 SAFETY STANDARD, LATEST EDITION, prior
to installing, operating, and/or servicing this
equipment.
W A R N I N G
!
While this manual lists standard specications
and service procedures, some minor deviations
may be found between this literature and your
equipment. Differences in local codes and plant
requirements, material delivery requirements,
etc., make such variations inevitable. Compare
this manual with your system installation drawings and appropriate Ransburg equipment manuals to reconcile such differences.
Careful study and continued use of this manual will
provide a better understanding of the equipment
and process, resulting in more efcient operation,
longer trouble-free service and faster, easier
troubleshooting. If you do not have the manuals
and safety literature for your Ransburg system,
contact your local Ransburg representative or
Ransburg.
The hazards shown on the following pag-
es may occur during the normal use of this
equipment. Please read the hazard chart beginning on page 2.
1
LN-9218-00.13
Ransburg
MicroPak - Safety
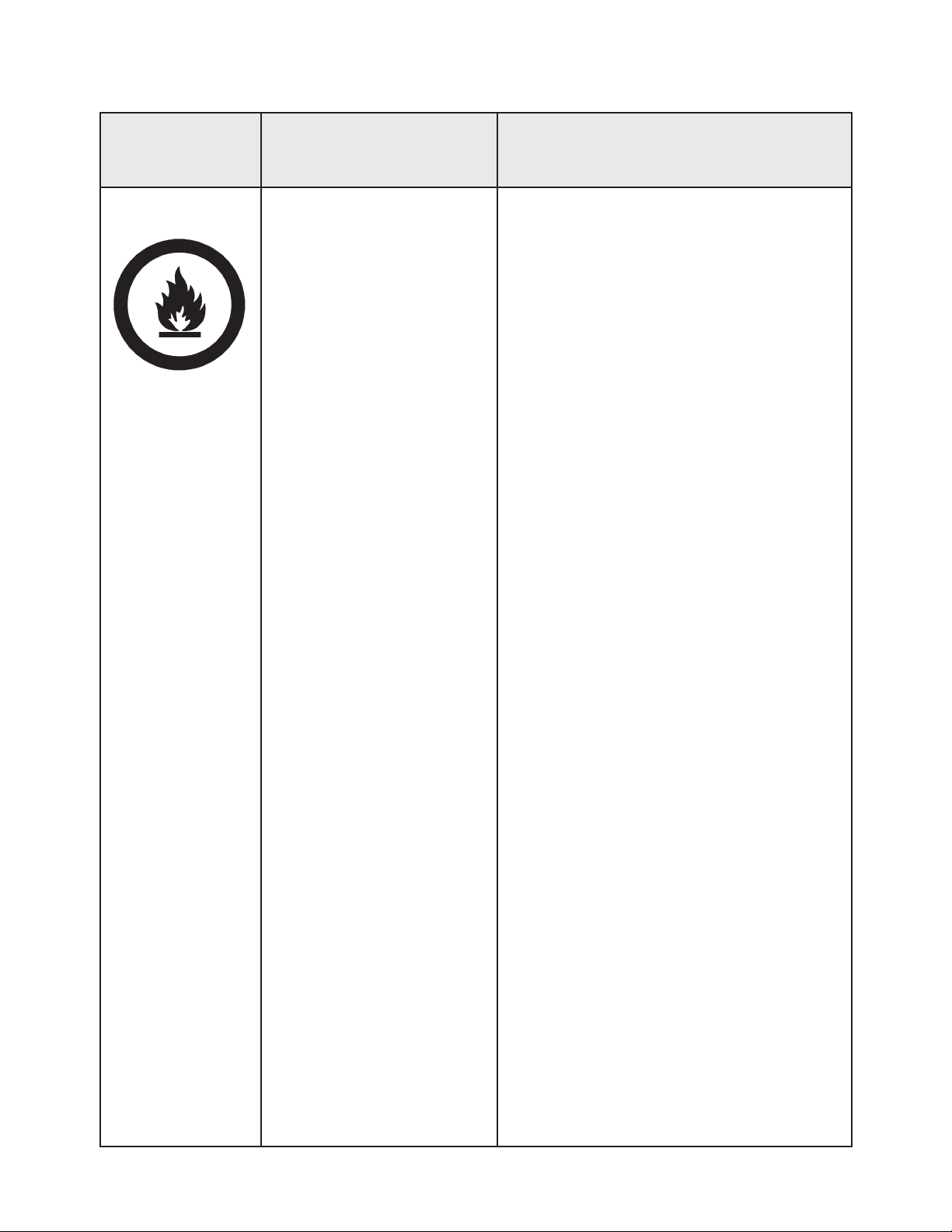
AREA
Tells where hazards
may occur.
Spray Area
HAZARD
Tells what the hazard is.
Fire Hazard
Improper or inadequate
operation and maintenance
procedures will cause a re
hazard.
Protection against inadvertent arcing that is capable of
causing re or explosion is
lost if any safety interlocks
are disabled during operation. Frequent Power Supply
or Controller shutdown indicates a problem in the system
requiring correction.
SAFEGUARDS
Tells how to avoid the hazard.
Fire extinguishing equipment must be present in
the spray area and tested periodically.
Spray areas must be kept clean to prevent the
accumulation of combustible residues.
Smoking must never be allowed in the spray
area.
The high voltage supplied to the atomizer must
be turned off prior to cleaning, ushing or maintenance.
When using solvents for cleaning:
• Those used for equipment ushing should
have ash points equal to or higher than
those of the coating material.
• Those used for general cleaning must have
ash points above 100°F (37.8°C).
Spray booth ventilation must be kept at the rates
required by NFPA-33, OSHA, country, and local
codes. In addition, ventilation must be maintained during cleaning operations using ammable or combustible solvents.
Electrostatic arcing must be prevented. Safe
sparking distance must be maintained between
the parts being coated and the applicator. A distance of 1 inch for every 10KV of output voltage
is required at all times.
Test only in areas free of combustible material.
Testing may require high voltage to be on, but
only as instructed.
Non-factory replacement parts or unautho-
rized equipment modications may cause re or
injury.
If used, the key switch bypass is intended for
use only during setup operations. Production
should never be done with safety interlocks disabled.
Never use equipment intended for use in waterborne installations to spray solvent based materials.
The paint process and equipment should be
set up and operated in accordance with NFPA33, NEC, OSHA, local, country, and European
Health and Safety Norms.
LN-9218-00.13
2
MicroPak - Safety
Ransburg
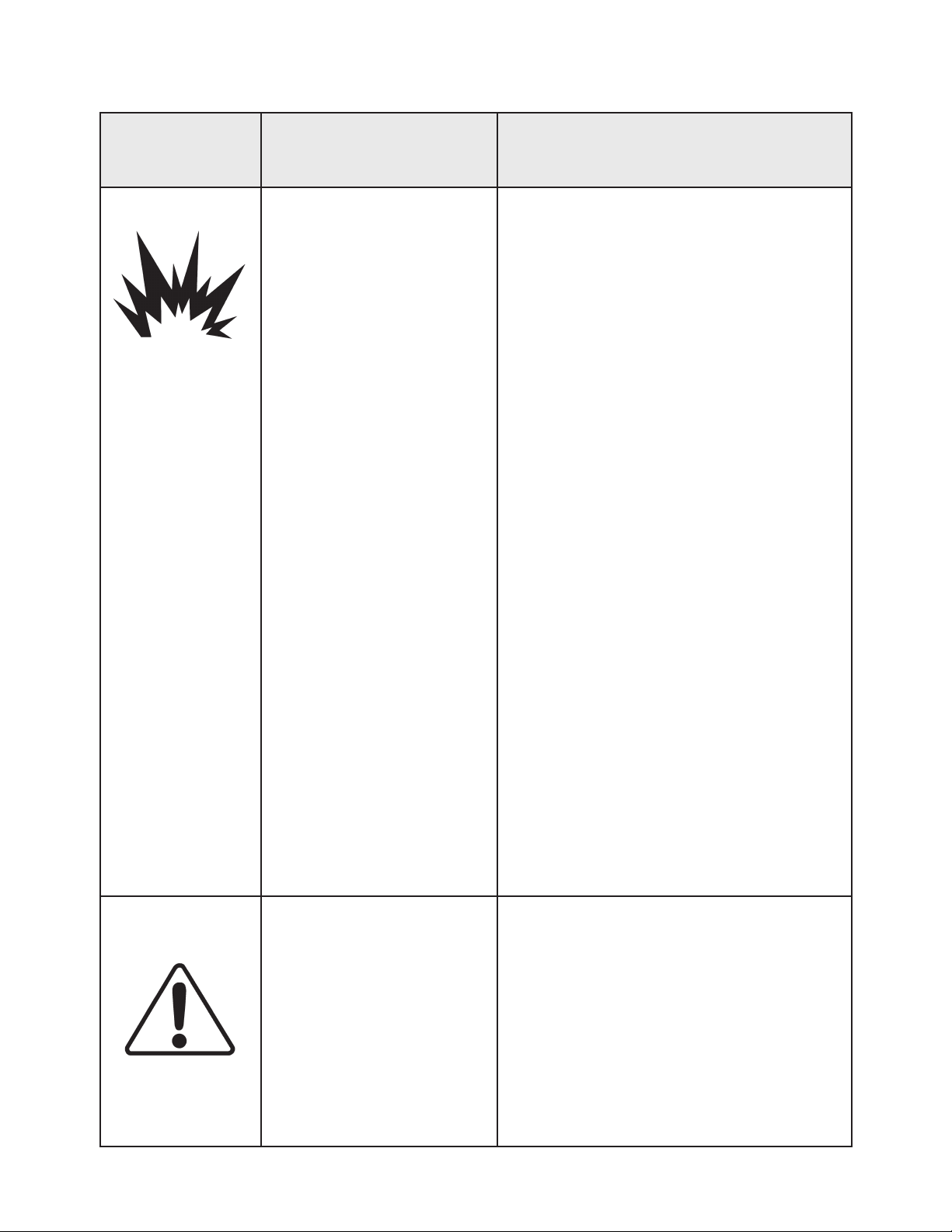
AREA
Tells where hazards
may occur.
Spray Area
HAZARD
Tells what the hazard is.
Explosion Hazard
Improper or inadequate operation and maintenance proce-
dures will cause a re hazard.
Protection against inadvertent
arcing that is capable of caus-
ing re or explosion is lost if
any safety interlocks are disabled during operation.
Frequent Power Supply or
Controller shutdown indicates
a problem in the system requiring correction.
SAFEGUARDS
Tells how to avoid the hazard.
Electrostatic arcing must be prevented. Safe
sparking distance must be maintained between
the parts being coated and the applicator. A distance of 1 inch for every 10KV of output voltage
is required at all times.
Unless specically approved for use in hazardous locations, all electrical equipment must be
located outside Class I or II, Division 1 or 2
hazardous areas, in accordance with NFPA-33.
Test only in areas free of ammable or combustible materials.
The current overload sensitivity (if equipped)
MUST be set as described in the corresponding section of the equipment manual. Protection against inadvertent arcing that is capable
of causing re or explosion is lost if the current
overload sensitivity is not properly set. Frequent power supply shutdown indicates a problem in the system which requires correction.
General Use and
Maintenance
Improper operation or maintenance may create a hazard.
Personnel must be properly
trained in the use of this equipment.
Always turn the control panel power off prior to
ushing, cleaning, or working on spray system
equipment.
Before turning high voltage on, make sure no
objects are within the safe sparking distance.
Ensure that the control panel is interlocked with
the ventilation system and conveyor in accordance with NFPA-33, EN 50176.
Have re extinguishing equipment readily available and tested periodically.
Personnel must be given training in accordance
with the requirements of NFPA-33, EN 60079-0.
Instructions and safety precautions must be
read and understood prior to using this equipment.
Comply with appropriate local, state, and national codes governing ventilation, re protection, operation maintenance, and housekeeping. Reference OSHA, NFPA-33, EN Norms
and your insurance company requirements.
3
LN-9218-00.13
Ransburg
MicroPak - Safety
AREA
Tells where hazards
may occur.
Spray Area /
High Voltage
Equipment
HAZARD
Tells what the hazard is.
Electrical Discharge
There is a high voltage device
that can induce an electrical
charge on ungrounded objects
which is capable of igniting
coating materials.
Inadequate grounding will
cause a spark hazard. A
spark can ignite many coating
materials and cause a re or
explosion.
SAFEGUARDS
Tells how to avoid the hazard.
Parts being sprayed and operators in the spray
area must be properly grounded.
Parts being sprayed must be supported on conveyors or hangers that are properly grounded. The resistance between the part and earth
ground must not exceed 1 meg ohm. (Refer to
NFPA-33.)
Operators must be grounded. Rubber soled insulating shoes should not be worn. Grounding
straps on wrists or legs may be used to assure
adequate ground contact.
Operators must not be wearing or carrying any
ungrounded metal objects.
When using an electrostatic handgun, operators
must assure contact with the handle of the applicator via conductive gloves or gloves with the
palm section cut out.
NOTE: REFER TO NFPA-33 OR SPECIFIC
COUNTRY SAFETY CODES REGARDING
PROPER OPERATOR GROUNDING.
All electrically conductive objects in the spray
area, with the exception of those objects required by the process to be at high voltage, must
be grounded. Grounded conductive ooring
must be provided in the spray area.
Always turn off the power supply prior to ushing, cleaning, or working on spray system equipment.
Unless specically approved for use in hazardous locations, all electrical equipment must be
located outside Class I or II, Division 1 or 2 hazardous areas, in accordance with NFPA-33.
LN-9218-00.13
4
MicroPak - Safety
Ransburg
AREA
Tells where hazards
may occur.
Electrical
Equipment
HAZARD
Tells what the hazard is.
Electrical Discharge
High voltage equipment is utilized in the process. Arcing
in the vicinity of ammable or
combustible materials may oc-
cur. Personnel are exposed to
high voltage during operation
and maintenance.
Protection against inadvertent
arcing that may cause a re or
explosion is lost if safety circuits
are disabled during operation.
Frequent power supply shutdown indicates a problem in the
system which requires correction.
An electrical arc can ignite coat-
ing materials and cause a re or
explosion.
SAFEGUARDS
Tells how to avoid the hazard.
Unless specically approved for use in hazardous locations, the power supply, control cabinet,
and all other electrical equipment must be located outside Class I or II, Division 1 and 2 hazardous areas in accordance with NFPA-33 and EN
50176.
Turn the power supply OFF before working on
the equipment.
Test only in areas free of ammable or combustible material.
Testing may require high voltage to be on, but
only as instructed.
Production should never be done with the safety
circuits disabled.
Before turning the high voltage on, make sure no
objects are within the sparking distance.
Toxic Substances
Spray Area
Certain material may be harmful
if inhaled, or if there is contact
with the skin.
Explosion Hazard –
Incompatible Materials
Halogenated hydrocarbon sol-
vents for example: methylene
chloride and 1,1,1,-Trichloroethane are not chemically
compatible with the aluminum
that might be used in many system components. The chemical
reaction caused by these solvents reacting with aluminum
can become violent and lead to
an equipment explosion.
Follow the requirements of the Material Safety
Data Sheet supplied by coating material manufacturer.
Adequate exhaust must be provided to keep the
air free of accumulations of toxic materials.
Use a mask or respirator whenever there is a
chance of inhaling sprayed materials. The mask
must be compatible with the material being
sprayed and its concentration. Equipment must
be as prescribed by an industrial hygienist or
safety expert, and be NIOSH approved.
Aluminum is widely used in other spray application equipment - such as material pumps,
regulators, triggering valves, etc. Halogenated
hydrocarbon solvents must never be used with
aluminum equipment during spraying, ushing,
or cleaning. Read the label or data sheet for the
material you intend to spray. If in doubt as to
whether or not a coating or cleaning material is
compatible, contact your coating supplier. Any
other type of solvent may be used with aluminum
equipment.
5
LN-9218-00.13

Ransburg
INTRODUCTION
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
MicroPak - Introduction
The MicroPakTM Controller, in conjunction with
an appropriate cascade, is used to provide high
voltage for electrostatic application equipment.
The controller is packaged in a single, 3.2 inch
wide Eurocard module, and thus consumes less
than 1/4 of the available space in a 19 inch rack.
The MicroPak uses a combination of proven high
voltage generation technology including microprocessor-based control with diagnostic and communication functions. The processor circuitry provides
the maximum in applicator transfer efciency, while
maintaining the maximum safety when used in
conjunction with FM listed applicators.
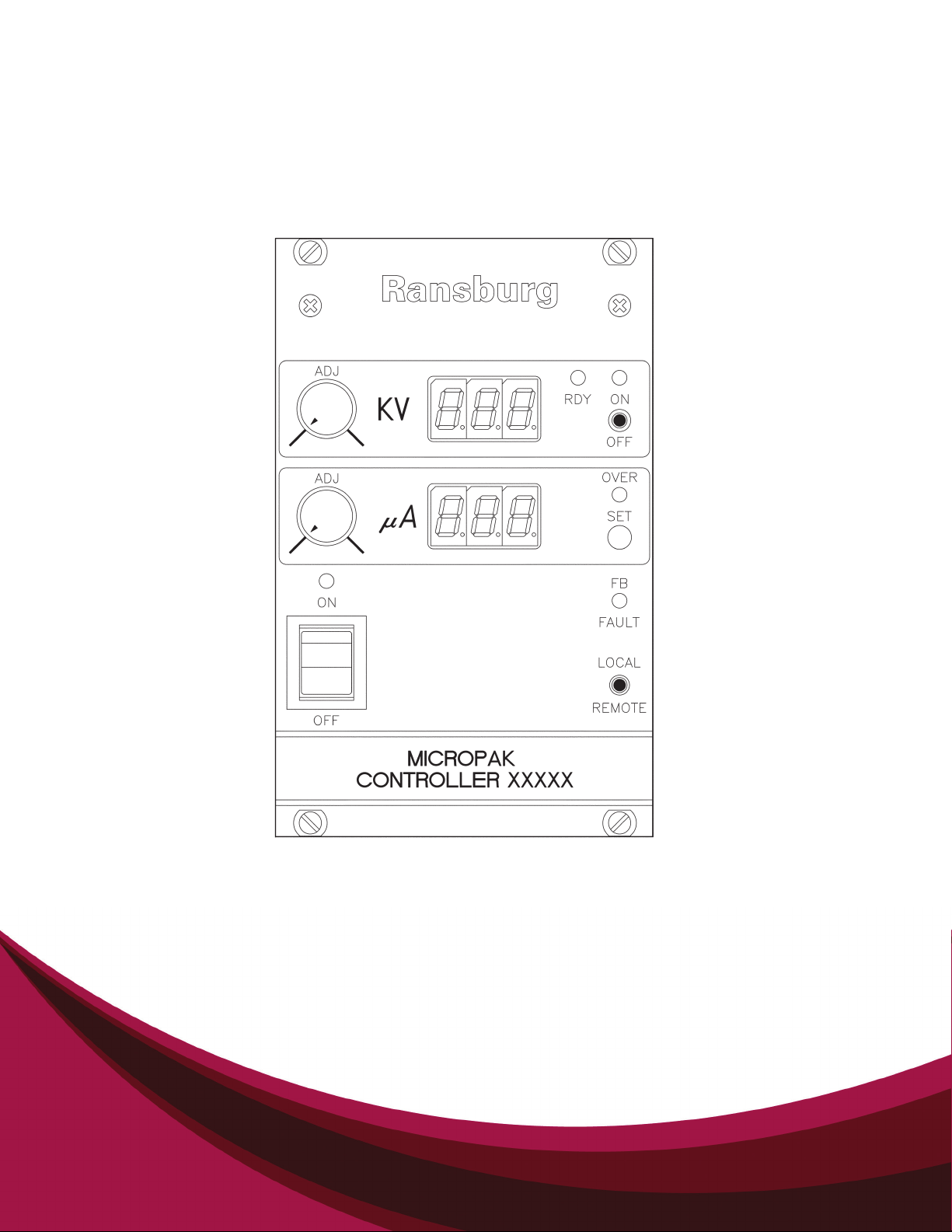
SAFETY FEATURES
When used with FM listed applicators, the MicroPak provides the ultimate in operational safety.
The microprocessor circuits allow the use of output
load curve control, which limits the high voltage
output to safe levels, even with the controls set at
maximum levels, and does so without a hard shut
down. The Over current set point, which can be
monitored on the µa Display by pressing the SET
push-button and holding for one second, does pro-
vide a hard shutdown if the output current exceeds
the set point. The kV set point is also displayed
on the kV display when the SET push-button is
pressed for one second.
DISPLAYS
The front panel displays for output voltage and
current indicate the outputs from the cascade of
direct charge applicators or the probe tip voltage
in the case of indirect charge applicators. They are
derived from feedback signals in the low voltage
cable between the controller and the cascade.
In RansPakTM 1000 mode, beginning with software
version 3.2, the signal used for the current (µA)
display is conditioned to subtract out the internal
cascade “bleeder” current and thus display the
actual output current.
SPECIFICATIONS
(At Sea-Level Conditions)
Environmental / Physical
Temp. Operating: (0
Storage: (-40
Humidity: (95% Non-Condensing)
Size: 100 X 160mm
Eurocard module,
total width 3.2 in.
(one module)
Electrical Requirements
Power Required:
(per MicroPak) 24 VDC at 2.5A
(fully loaded output),
HP404, RP404, and
HP505 Cascades
28 VDC at 6A
(fully loaded output),
RansPak 1000 (RP1000)
Cascade
Note: 24 VDC and 28 VDC power supplies must
be regulated and have overcurrent (40%) and
overvoltage (20%) protection.
o
to 55o C)
o
C to 85o C)
LN-9218-00.13
6

MicroPak - Introduction
Ransburg
Electrical
Controls:
1. All communication to Controller by CANBus
2. Direct A-B RIO communication via additional
Node Adapter Module (Part# LECU4012) or
Serial Node Adapter + Module (Part #78553)
(One Node Adapter per rack)
3. Discrete signals available via additional I/O
Module (Part# 76037) in place of Node
Adapter with levels as shown below
Analog In: (0-10 VDC or 4-20 mA DC)
kV Set
Current Set
(Overcurrent Setpoint)
(Di/dt Sensitivity)
Analog Out: (0-10 VDC)
OUTPUT kV
OUTPUT CURRENT
Discrete Out: (Dry Contact)
HV ON
FB FAULT
HV READY
OVER CURRENT FAULT
LOCAL
HV RESET
Discrete In: (24 VDC Source or Sink)
HV OFF
HV ON
FLUID TRIGGER
START
Trigger Out: (24 VDC, 150 mA Maximum)
(For EFM Gun) AIR TRIGGER
AIR TRIGGER / SEQUENCER
MicroPak with HP404 / RP404 Cascades
Output: 100 kV @ 0 µA
125 µA @ 0 kV
Cascade Size: HP404 1.50” X 1.56” x 7.0”
RP404 4” X 4” X 12”
MicroPak With RP1000 Cascade
Output: 100 kV, 1000 µA
(75% Duty Cycle)
Cascade Size: 4” X 4” X 12”
MicroPak With LEPS5002 Cascade
Output: 100 kV, 1000 µA
(75% Duty Cycle)
Cascade Size: 14” X 12” X 12”
MicroPak With HP404 FM Cascade
Output: 100 kV, 0 µA
(85 µA Max.)
Cascade Size: 1.50” X 1.56” X 7.0”
MicroPak With HP505 Cascade
Output: 100 kV @ 0 µA
240 µA @ 0 kV
Cascade Size: 1.50” X 1.56” X 7.0”
7
LN-9218-00.13
Ransburg
INSTALLATION
MicroPak - Installation
CONNECTIONS
- For MicroPak with HP404, RP404
& HP505-+24 VDC
- For MicroPak with RP1000 - +28 VDC
Input Power
This must be supplied from a regulated power
supply. Connection is made at J2 for +24/28 V,
24/28 VRET, and Factory Ground. The 24/28
VDC supply is protected against excessive current
draw by an automatically resetting fuse internal to
the MicroPak. In case of a current draw over 6 A,
the fuse will open circuit and automatically reset
when 24/28 VDC power is removed.
C A U T I O N
!
The 24VRET must be connected to Fac-
tory Ground at the +24 VDC power supply
(see Figures 1 and 2).
Node Adapter / Discrete I/O Power
When a Node Adapter or Discrete I/O Module is
used, power must be supplied to it via J10. Connect +24 VDC to J10-1, and 24 VRET to J10-2
(see Figures 1 and 2).
The two wire braids must be connected to a dedicated HV power supply ground bus. This bus must
be isolated from the system ground bus except at
the termination point to earth ground.
W A R N I N G
!
If these connections are not made in this
manner, damage will result to system electronic components, and system safety may
be compromised.
Remote I/O
If applicable, connect Remote I/O Blue to J5-B,
Shield to J5-S, and Clear to J5-C.
CANBus
Provide a jumper from the MicroPak mother board
connector J8 (CAN) to pneumatic mother board
connector J4. This should be done with a short
section of shielded pair cable while observing the
(+) and to (+) convention. See Figure 3.
In Node Adapter applications, provide additional
jumper wires from pneumatic mother board to the
next pneumatic mother board, up to a maximum
of four (4) mother boards.
.
Output To Cascade
HP404, HP505 & RP404
Make connections to J3 per Figure 1. Use the
appropriate cable assemblies for HP404 / HP505
(see MicroPak parts list at back of this manual).
Use only the A12971 cable assembly for RP404.
RP1000
Make connections to J3 per Figure 2. Use only
the 74947 cable assembly.
LN-9218-00.13
Interlock
Terminal strip J6 provides a connection point for
system interlock to prevent generation of high
voltage. Terminal J6-1 must be connected to J6-2
by jumper or voltage free contact in order to make
the High Voltage Ready (HVRDY) mode. If this
connection is momentarily broken, HVRDY must
be reset. Make no connection to J6-3 before
reading “HV On Control” in the “Operation” section
of this manual.
8

MicroPak - Installation
Ransburg
MicroPak Grounding
1. The Power Supply must be referenced to true
earth ground at only one point. (Refer to Figures
1, 2, and 3 for Grounding Connections.)
C A U T I O N
!
Separate ground connections MUST be
used for grounding the part and the Power
Supply.
2. Shields from the low voltage cable must be
connected to a bus isolated from panel ground,
then by a 3/4” braid to the building steel or ground
grid if available.
3. The 24 or 28 VDC power supply common should
be connected to the factory ground input for safety,
even though they are connected to the isolated
bus via the MicroPak motherboard.
2. The feedback signals for kV and µA are developed with respect to the cascade ground. If the
cascade ground were routed only to earth ground
via the above mentioned shields, the feedback
conditioning circuitry would have to depend on
the panel ground or power supply common to
get a ground reference for the feedback signals.
This means the low level return current for these
signals would have to ow to earth ground and
back to the controller via factory ground or power
supply common. This adds large amounts of noise
to these low voltage signals.
3. A great deal of testing under high voltage corona
conditions has conrmed that this cascade ground
should be connected directly at a single point to the
signal ground plane of the MicroPak power supply
controller. This single point method maintains a
“clean” feedback signal while limiting the amount
of high frequency noise that is dumped onto the
signal ground and therefore other grounds in the
overall system, such as the PLC.
MicroPak Grounding Theory
1. The low voltage cable has a large amount of high
frequency noise on the shields and grounds from
being in proximity to the high voltage generator.
Taking these grounds directly to earth ground or a
ground grid through good high frequency conductors (braid) keeps this high frequency noise from
interfering with the low voltage control circuitry.
This is why they are isolated from panel ground.
This is consistent with standard practice for lightning protection. (See NFPA-70 and NFPA -780.)
9
LN-9218-00.13
 Loading...
Loading...