Page 1

6-01159-04
Scalar Library
Basic SNMP Reference Guide Basic SNMP Reference Guide
Quantum Scalar i2000 / i6000 Library
Quantum Scalar
i
2000 / i6000 Library
Page 2

Scalar i2000 / i6000 Basic SNMP Guide, 6-01159-04, May 2010, Made in USA.
Quantum Corporation provides this publication “as is” without warranty of any kind, either express or implied, including
but not limited to the implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. Quantum Corporation
may revise this publication from time to time without notice.
COPYRIGHT STATEMENT
Copyright 2010 by Quantum Corporation. All rights reserved.
Your right to copy this manual is limited by copyright law. Making copies or adaptations without prior written
authorization of Quantum Corporation is prohibited by law and constitutes a punishable violation of the law.
TRADEMARK STATEMENT
Quantum, DLT, DLTtape, the Quantum logo, and the DLTtape logo are all registered trademarks of Quantum
Corporation.
SDLT and Super DLTtape are trademarks of Quantum Corporation.
Other trademarks may be mentioned herein which belong to other companies
Published: May 2010 Document Number: 6-01159-04 Rev A
Page 3

Contents
1 About This Guide and Your Product 1
Explanation of Symbols and Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Other Documents you Might Need . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Getting More Information or Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2 Description 5
SNMP Functionality Available to External Applications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Accessing SNMP Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
SNMP Traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
SNMP Queries. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
3 Library Identification 7
Product Name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Logical Library Name. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
4 Library Status and Health 9
Drive Online/Offline Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Drive Overall Health . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Physical Library Online/Offline State. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Robotics Readiness. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Library Main Door Status. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Import/Export Station Door Status. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Partition Online/Offline Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Overall Library Health: RAS Subsystem Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5 SNMP Traps 13
ADIC Intelligent Storage MIB. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Trap # 500: startupSequenceCompleted . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Trap # 501: shutdownSequenceInitiated. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Scalar i2000Basic SNMP Reference Guide iii
Page 4
ADIC Management MIB. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Trap # 101: physLibraryOnlineStatusChange. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Trap # 102: physLibraryDoorStatusChange . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Trap # 103: ieStationDoorStatusChange . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Trap # 110: rcuReady . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Trap # 111: rcuNotReady . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Trap # 204: logicalLibraryOnlineStatusChange . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
RAS System Status Change Traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Trap # 400: connectivityGroupStatusChange . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Trap # 401: controlGroupStatusChange . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Trap # 402: coolingGroupStatusChange. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Trap # 403: drivesAndMediaGroupStatusChange . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Trap # 404: powerGroupStatusChange . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Trap # 405: roboticsGroupStatusChange . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
A MIBs Implemented 17
ADIC Intelligent Storage MIB. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
ADIC Management MIB. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
SANMgr Proxy MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Reference MIBs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
B Variables and Traps Quick Reference 19
iv Contents
Page 5

About This Guide and Your Product
WARNING
CAUTION
Note
This reference guide describes the basic usage of the Sim ple Netw or k Ma nag em e nt Pro to co l (SNM P) to
acquire alert information from the Scalar® i2000 / i6000 library. Focus is placed on the most critical
information available through Traps and Management Information Base (MIB) queries. For information
about the Scalar i2000 / i6000 library, itself, refer to the Scalar i6000 User’s Guide. For information on
integrating MIBs into a SNMP management application, contact your software vendor.
The information presented in this document represents the most commonly requested MIB objects and
SNMP Traps needed to monitor the Scalar i2000 / i6000 from a network management tool. For more
information about the Scalar i2000 / i6000 MIBs, contact technical support.
This basic SNMP reference is written for library customers, partners, third party management software
developers, and other parties interested in integrating the Scalar i2000 / i6000 library with commercial
management frameworks.
This document assumes the reader has a working knowledge of SNMP. The reader should be able to
compile a MIB on their specific framework application, perform SNMP GET operations, as well as
understand how to collect Traps and filter them for information.
Explanation of Symbols and Notes
The following symbols appear throughout this document to highlight important information.
INDICATES A POTENTIALLY HAZARDOUS SITUATION WHICH, IF NOT
AVOIDED, COULD RESULT IN DEATH OR BODILY INJURY.
Indicates a situation that may cause possible damage to equipment, loss of
data, or interference with other equipment.
Indicates important information that helps you make better use of your system.
Scalar i2000 / i6000 Basic SNMP Reference Guide 1
Page 6

Other Documents you Might Need
Note
The following documents are also available for this product. These documents can be found on the prod uct
CD or at www.quantum.com/support
• Scalar i6000 User’s Guide (6-00421-xx)
Release Notes are also available for this product. The Relea se Notes describe changes
to your system or firmware since the last release, provide compatibility information, and
discuss any known issues and workarounds. The Release Notes can be fo und in the
product box or at www.quantum.com/support
Getting More Information or Help
More information about this product is available on the Service and Support website at
www.quantum.com/support
including answers to frequently asked questions (FAQs). You can also access software, firmware, and
drivers through this site.
For further assistance, or if training is desired, contact Quantum:
. The Service and Support Website contains a collection of information,
.
Global Call Handling: 1-800-284-5101
For additional contact information: www.quantum.com/support
To open a Service Request: www.quantum.com/osr
For the most updated information on Quantum Global Services, please visit: www.quantum.com/support
2 About This Guide and Your Product
Page 7

Scalar i2000 / i6000 Basic SNMP Reference Guide 3
Page 8

4 About This Guide and Your Product
Page 9

Description
SNMP is a light-weight protocol designed for remote management and monitoring of infrastructure devices.
On the Scalar i2000 / i6000, SNMP support is included for alert monitoring by means of framework
applications. SNMP should be used as an initial check for library events.
In-depth monitoring and alert management are handled using the Library Management Console ( LMC). The
LMC provides access to descriptions of subsystem status and to the RAS ticket system, which gives
administrators the ability to diagnose specific subsystem events.
SNMP Functionality Available to External Applications
The Scalar i2000 / i6000 provides standard SNMP functionality for monitoring library status. This includes
GET queries and unicast Traps (sent only to registered recipients). SET commands are not currently
enabled on the Scalar i2000 / i6000.
The MIB variables described in this document are the only ones supported by Quantum for external
management of the library. All other variables in the MIB are for internal use only.
Specific Scalar i2000 / i6000 SNMP characteristics include:
• Support for SNMP v1 and v2c
• Usage of well known ports for GETs (161)
• Default community read/Trap strings: publicCmtyStr
• Trap Registration interface in the LMC to configure app lication IP addresses and user-con figurable
UDP port numbers to receive Traps
The MIB files can be retreived using the Scalar i2000 / i6000 LMC option Tools > Retrieve MIBs.
Accessing SNMP Information
SNMP information is accessed from the Scalar i2000 / i6000 through Traps and GET queries. Using the
information contained in this guide, an administrator can configure their framework application to receive
Scalar i2000 / i6000 SNMP information and generate alerts.
By default, SNMP information gathered will be an integer value (logical partition names will be string values).
For instance, the return value of Library Main Door might be 2. As outlined in this manual, a retu rn value of
2 would indicate that the library door is closed.
Scalar i2000 / i6000 Basic SNMP Reference Guide 5
Page 10

It is possible to have the framework return a status value and a description of the status . To accomplish this,
CAUTION
Note
the ADIC MIBs must be compiled and integrated with the framework application. In this case, the return
value of Library Main Door might be closed(2). The required MIBs are discussed in MIBs Implemented
page 17 and are available from your Quantum representative.
on
SNMP Traps
Traps are automatically sent to registered hosts when specific events occur. You can only have one
application per port listening for traps, so if you have more than one application , make sure that you specify
a UDP port on which to send traps.
To receive Traps, you must perform two steps:
1 Configure the framework application to collect Traps from the Scalar i2000 / i6000.
2 Using the LMC Trap Registration feature, register the host’s IP address and UPD port numbe r on the
Scalar i2000 / i6000.
Registration informs the Scalar i2000 / i6000 that Traps sh ould be sent to the host. For details on registering
a host with the Scalar i2000 / i6000, see the Scalar i6000 User’s Guide or the LMC online help.
SNMP Queries
GET queries are initiated on a periodic basis by the framework application. By querying the MIB, hosts can
gather status information about specific components of the library. Frequent MIB queries ar e not required,
however, since the SNMP agent is event-driven.
As with any SNMP device, excessive MIB queries can result in
performance degradation for the SNMP daemon, as well as for the
network.
GETs must also include an instance number. This instance ID tells the Scalar i2000 / i6000 what specific
device to provide status information on. For example, to see if the 2nd logical library on a Scalar i2000 /
i6000 was online, you would access the MIB variable for logical library onl ine status and select the instance
for logical library 2.
The format of each instance may vary depending on the subsystem component. This docum ent provides a
listing of the instance format for each MIB variable you may need to query. You will notice that almost every
instance contains 8.0.0.0.0.0.1.0.59. This is the identifier for the Management Control Blade (MCB), the
device that manages the Scalar i2000 / i6000.
Therefore, if you were querying logical library status, you might see the following two instances returned.
Instance Number Description
1 8.0.0.0.0.0.1.0.59.1 the first logical library
2 8.0.0.0.0.0.1.0.59.2 the second logical library
Selecting instance 8.0.0.0.0.0.1.0.59.2 would indicate if the second logical library was online or offline.
All Scalar i2000 / i6000 MCB’s will have the same identifier: 8.0.0.0.0.0.1.0.59
6 Description
Page 11

Library Identification
The two MIB variables below are available in the ADIC Intelligent Storage MIB from the
productAgentInfoGroup. The productAgentInfoGroup is a group of scalar objects that contains information
about the library as a whole. All objects in productAgentInfoGroup have instance ID “.0”. Unless otherwise
noted, all variables are defined in the ADIC Management MIB.
Product Name
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.3764.1.1.10.3
Name: productName (defined in the ADIC Intelligent Storage MIB)
Type: DisplayString
Values: Indicates the type of library.
Instance: There is one instance for this va riable and it is unique for the entire library. Quantum recommends
querying the Product Name so that the framework application will list the type of library being monitored.
Logical Library Name
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.3764.1.1.200.20.90.20.1.3
Name: name
Type: DisplayString
Values: Returns the logical library name. Logical library is another name for a library partition.
Instance: There will be one instance for each partition configured on the library. Query the specific instance
that you need to access.
Logical libraries are listed using the format:
• 8.0.0.0.0.0.1.0.59.1
The final number (1 in this instance) is the partition number.
To determine the number of partitions, query the MIB variable:
• 1.3.6.1.4.1.3764.1.1.200.20.90.10.1.2
Query Logical Library Name so that the framework application will list the specific partition that is
monitored.
Scalar i2000 / i6000 Basic SNMP Reference Guide 7
Page 12

8 Library Identification
Page 13

Library Status and Health
You can poll the variables below to get library status and health information.
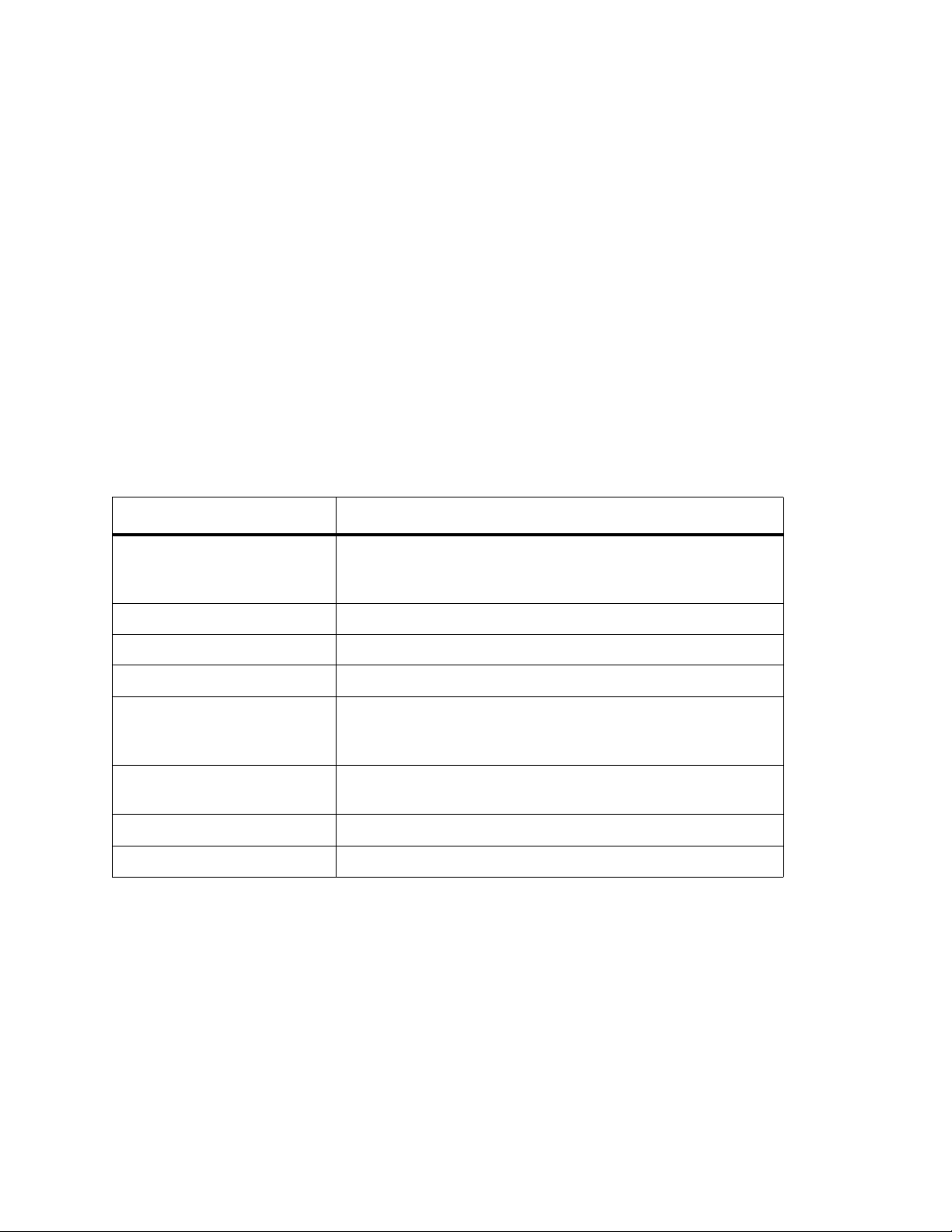
Drive Online/Offline Status
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.3764.1.1.200.20.80.110.1.29
Name: phDriveOnlineStatus
Type: INTEGER
Values: online(1), offline(2), shutdown(3). Currently the drive object never returns shutdown(3)
Description: This variable indicates whether a drive is varied on or varied off.
Instance: There will be one instance for every physical drive in the library. Query the specific instance that
you need to access. Drives are listed in sequential order.
See Table 1
Table 1 Drive Instance ID Format
Instance Information Description
8.0.0.0.0.0.1.0.59--------Identifies the library MCB
for details on interpreting the format of a drive instance ID.
8.0.0.0.0.0.1.0.59.4.2.0.0.0.3.0.0 If this is the full instance name...
4-------Media domain
-2------Media type
--0-----Aisle
---0----Frame
----0---Rack
-----3--Section
------0-Column
-------0Row
Scalar i2000 / i6000 Basic SNMP Reference Guide 9
Page 14

The numbers associated with the aisle, frame, rack, section, column, and row combine to form a location
coordinate. For more about the library locat ion coo rdi na te s an d ho w they ca n tell yo u wher e a dr ive is
located in the physical library, refer to the Scalar i6000 User’s Guide.
Alerted by Trap: 403
Drive Overall Health
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.3764.1.1.200.20.80.110.1.31
Name: phDriveRasStatus
Type: INTEGER
Values: good(1), failed(2), degraded(3), warn ing (4 ), info rm at ion a l(5 ), un kn own(6), invalid(7)
Description: The overall health of the drive is indicated by the phDriveRasStatus object.
Instance: There will be one instance for every physical drive in the library. Query the specific instance that
you need to access. Drives are listed in sequential order. See Table 1
interpreting the format of a drive instance ID.
Alerted by Trap: 403
on the previous page for details on
Physical Library Online/Offline State
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.3764.1.1.200.20.80.10.1.5
Name: onlineStatus
Type: INTEGER
Values: online(1), offline(2), shutdown(3)
Description: The online/offline state of the entire library is returned by the onlineStatus object.
Instance: There will be one instance for the Scalar i2000 / i6000, 8.0.0.0.0.0.1.0.59.
Alerted by Trap: 101
Robotics Readiness
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.3764.1.1.200.20.80.10.1.6
Name: readiness
Type: INTEGER
Values: ready(1) or notReady(2).
Description: The readiness state of the library robotics is returned by the readiness object.
Instance: There will be one instance for the Scalar i2000 / i6000, 8.0.0.0.0.0.1.0.59.
Alerted by Traps: 110, 111
10 Library Status and Health
Page 15

Library Main Door Status
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.3764.1.1.200.20.80.10.1.16
Name: physLibDoorStatus
Type: INTEGER
Values: open(1), closed(2), closedAndLocked(3), closedAndUnlocked(4), controllerFailed(5).
Description: The state of the library’s main door is returned by the physLibDoorStatus object.
Instance: There will be one instance for the Scalar i2000 / i6000, 8.0.0.0.0.0.1.0.59. This refers to a front
door on any module.
Alerted by Trap: 102
Import/Export Station Door Status
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.3764.1.1.200.20.80.75.1.2
Name: physLibIeStationDoorStatus
Type: INTEGER
Values: open(1), closed(2), closedAndLocked(3), closedAndUnlocked(4), controllerFailed(5).
Description: The state of the Import/Export station door is re turned by the phIeStationDoorStatus object.
Instance: There will be one instance for each frame of the library containing an I/E station. You will need to
query for the instance. It will be of the format: 8.0.0.0.0.0.1.0.59.1.1.1.1
See Table 2
Alerted by Trap: 103
Table 2 I/E Station Instance ID Format
Instance Information Description
8.0.0.0.0.0.1.0.59----Identifies the library MCB
for details on interpreting the format of an I/E station instance ID.
8.0.0.0.0.0.1.0.59.1.1.1.1 If this is the full instance name...
1---Aisle coordinate
- 1 - - Frame coordinate
- - 1 - Rack coordinate
---1I/E station ID number
Scalar i2000 / i6000 Basic SNMP Reference Guide 11
Page 16

Partition Online/Offline Status
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.3764.1.1.200.20.90.20.1.12
Values: online(1), offline(2)
Instance: There will be one instance for every logical partition defined on the library. Query the specific
instance that you need to access. Partitions are listed using the format: 8.0.0.0.0.0.1.0.59.1
Where the final number (1 in this instance) is the partition nu m ber. To de te rm in e the nu mb e r of partitions,
query the MIB variable: 1.3.6.1.4.1.3764.1.1.200.20.90.10.1.2. Names of the partitions can be found using
OID 1.3.6.1.4.1.3764.1.1.200.20.90.20.1.3. Refer to Logical Library Name
Alerted by Trap: 204
on page 7 for more information.
Overall Library Health: RAS Subsystem Status
The Reliability, Availability and Serviceability (RAS) system status table provides a concise way to assess
the health of the library's subsystems. The library functionality is divided into six sta tus groups: connectivity,
control, cooling, drives and media, power, and robotics.
Querying this variable will give the status of the last state transition (i.e. a subsystem has changed its status
to good.) Determining the precise reason for a status setting other than "go od" can be accomp lished using
the LMC and accessing the subsystem RAS tickets.
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.3764.1.1.200.20.100.10.1.2
Values: good(1), failed(2), degraded(3), warn ing (4 ), info rm at ion a l(5 ), un kn own(6), invalid(7)
Instance: There will be one instance for each of the 6 key subsystems monitored by the library. Query the
specific instance that you need to access. Subsystem instances are listed using the format:
8.0.0.0.0.0.1.0.59.1
Where the final number (1 in this example) is the subsystem. connectivity(1), control(2), cooling(3), drives
and media(4), power(5), robotics(6)
Alerted by Traps: 400, 401, 402, 403, 404, 405
12 Library Status and Health
Page 17

SNMP T rap s
This section describes the basic set of SNMP system status traps issued by the Scalar i2000 / i6000. These
traps present the physical library point of view, not that of a particular partition.
ADIC Intelligent Storage MIB
Traps defined in the Intelligent Storage MIB are issued with enterprise OID “intelligent”, which resolves to
1.3.6.1.4.1.3764.1.1.
Trap # 500: startupSequenceCompleted
This trap indicates that the library has completed its boot sequence.
Trap # 501: shutdownSequenceInitiated
This trap indicates that the library has started its shutdown sequence, which includes reboot and shutdown.
ADIC Management MIB
These informational traps are defined in the ADIC Management MIB. Each is issued with enterprise OID
“management”, which resolves to 1.3.6.1.4.1.3764.1.1.200.20.
Trap # 101: physLibraryOnlineStatusChange
This trap is issued when the physical library is brought online or taken offline.
Trap # 102: physLibraryDoorStatusChange
This trap is issued when the physical library door has been opened, closed, closed and locked, closed and
unlocked, or when the controller has failed.
Trap # 103: ieStationDoorStatusChange
This trap is issued when an I/E station door has been opened, closed, locked or unlocked.
Scalar i2000 / i6000 Basic SNMP Reference Guide 13
Page 18
Trap # 110: rcuReady
This trap is issued whenever the i2000 / i6000 robotics transitions from the “not re ady” state to the “read y”
state.
Trap # 111: rcuNotReady
This trap is issued whenever the i2000 / i6000 robotics transitions from the “rea dy” sta te to the “ not r eady”
state. For example, this trap will be issued if the front door is opened or the robotics are disabled.
Trap # 204: logicalLibraryOnlineStatusChange
This trap is issued when a logical library, also known as a partition, is brought online or taken offline.
RAS System Status Change Traps
The i2000 / i6000 issues a trap whenever the aggregate state of one o f the six RAS status groups changes.
Listening for these traps is the preferred method of monito ring the health of the Scalar i2000 / i6000. The
payload of each of these traps is very similar; it is summarized in the table below.
Table 3 RAS System Status Change Trap Payload Description
Payload Element Description
componentId Identifies the management control blade which is hosting the
RAS system. For i2000 / i6000, the varbind value is al ways set
to 8.0.0.0.0.0.1.0.59.
trapSequenceNumber This integer uniquely identifies the Trap.
trapSeverity Not Used
trapSummaryText Not Used
rasStatusGroupIndex RAS group whose status has changed; connectivity(1),
control(2), cooling(3), drivesAndMedia(4), power(5), and
robotics(6)
rasStatusGroupStatus New state; good(1), failed(2), degraded(3), warning(4),
informational(5), unknown(6), or invalid(7)
rasTicketId This is beyond the scope of this document.
rasReportId This is beyond the scope of this document.
Trap # 400: connectivityGroupStatusChange
The state of the connectivity hardware/so ftw ar e ha s cha n ge d .
Trap # 401: controlGroupStatusChange
The state of the control hardware/software has changed.
Trap # 402: coolingGroupStatusChange
The state of the cooling hardware/software has changed.
14 SNMP Traps
Page 19

Trap # 403: drivesAndMediaGroupStatusChange
The state of the drives and media hardware/software has changed.
Trap # 404: powerGroupStatusChange
The state of the power hardware/software has changed.
Trap # 405: roboticsGroupStatusChange
The state of the robotics hardware/software has changed.
Scalar i2000 / i6000 Basic SNMP Reference Guide 15
Page 20

16 SNMP Traps
Page 21

MIBs Implemented
The MIBs implemented with the Scalar i2000 / i6000 library include the ADIC Intelligent Storage MIB, ADIC
Management MIB, and the SANMgr Proxy MIB.
ADIC Intelligent Storage MIB
The ADIC Intelligent Storage MIB presents the following generic information that is applicable to almost any
product:
• System identification (product name and serial number)
• Composition: a list of system components with identification and status for each
• Traps for a changed configuration (added and removed components)
• Library startup and shutdown traps
ADIC Management MIB
The ADIC Management MIB contains the management details of the Scalar i2000 / i6000 tape library,
including:
• Library online and offline status
• Library composition
• Storage (cartridge capacity)
• Drives
•Media
• Library partitioning
• Advanced status information: Reliability, Availability and Serviceability (RAS) functionality
SANMgr Proxy MIB
The SANMgr Proxy MIB is beyond the scope of this document, and so is not covered here.
• Connectivity blade information
Scalar i2000 / i6000 Basic SNMP Reference Guide 17
Page 22

Reference MIBs
The Scalar i2000 / i6000 MIBs reference the following SNMP standard MIBs:
• RFC 1155-SMI
• RFC 1212
• RFC 1213-MIB
• RFC 1215
These MIBs are necessary for accurate compilation of the Scalar i2000 / i6000 MIBs, and should be
included with your framework application.
18 MIBs Implemented
Page 23

Variables and Trap s Quick Reference
Use the two tables in this appendix to quickly see the MIB variables and Traps descri bed in this document.
Table 4 Status MIB Variables
Because the front portion of the MIB variable object ID (OID), 1.3.6.1.4.1.3764.1.1, is the same for all
variables defined in the ADIC MIBs, it is omitted in the OID column to save space. For example, the actual
OID of the Drive Online/Offline Status variable is: 1.3.6.1.4.1.3764.1.1.200.20.80.110.1.29.
Event OID Description
Drive Online / Offline
Status
Drive Overall Health ...200.20.80.110.1.31 Indicates the overall status of the drive. If the
Physical Library Online /
Offline Status
Robotic Readiness ...200.20.80.10.1.6 Indicates the status of the library robotics. Make
Library Main Door ...200.20.80.10.1.16 Indicates if the front door(s) of the library
IE Station Door Status ...200.20.80.75.1.2 Indicates if a specific IE station door is closed
Logical Partition Online /
Offline Status
...200.20.80.110.1.29 Indicates if the drive is online or offline. Use the
LMC to confirm the drive is varied on. Also,
check power.
drive has a health status other than good, use
the LMC to determine what RAS tickets have
been generated for the drive.
...200.20.80.10.1.5 Indicates if the library is online or offline. Use
the LMC to confirm the library is online and not
being configured.
sure the module door(s) are closed and the
robotics are online.
modules(s) are closed and locked.
and locked.
...200.20.90.20.1.12 Indicates if a specific partition is online or
offline. Use the LMC to confirm the partition is
online and not being configured.
RAS Subsystem Status ...200.20.100.10.1.2 Indicates the status of a particular su bsystem of
the library. If the value returned is anything but
good, use the LMC to determine what events
have been logged in the RAS ticket system.
Scalar i2000 / i6000 Basic SNMP Reference Guide 19
Page 24
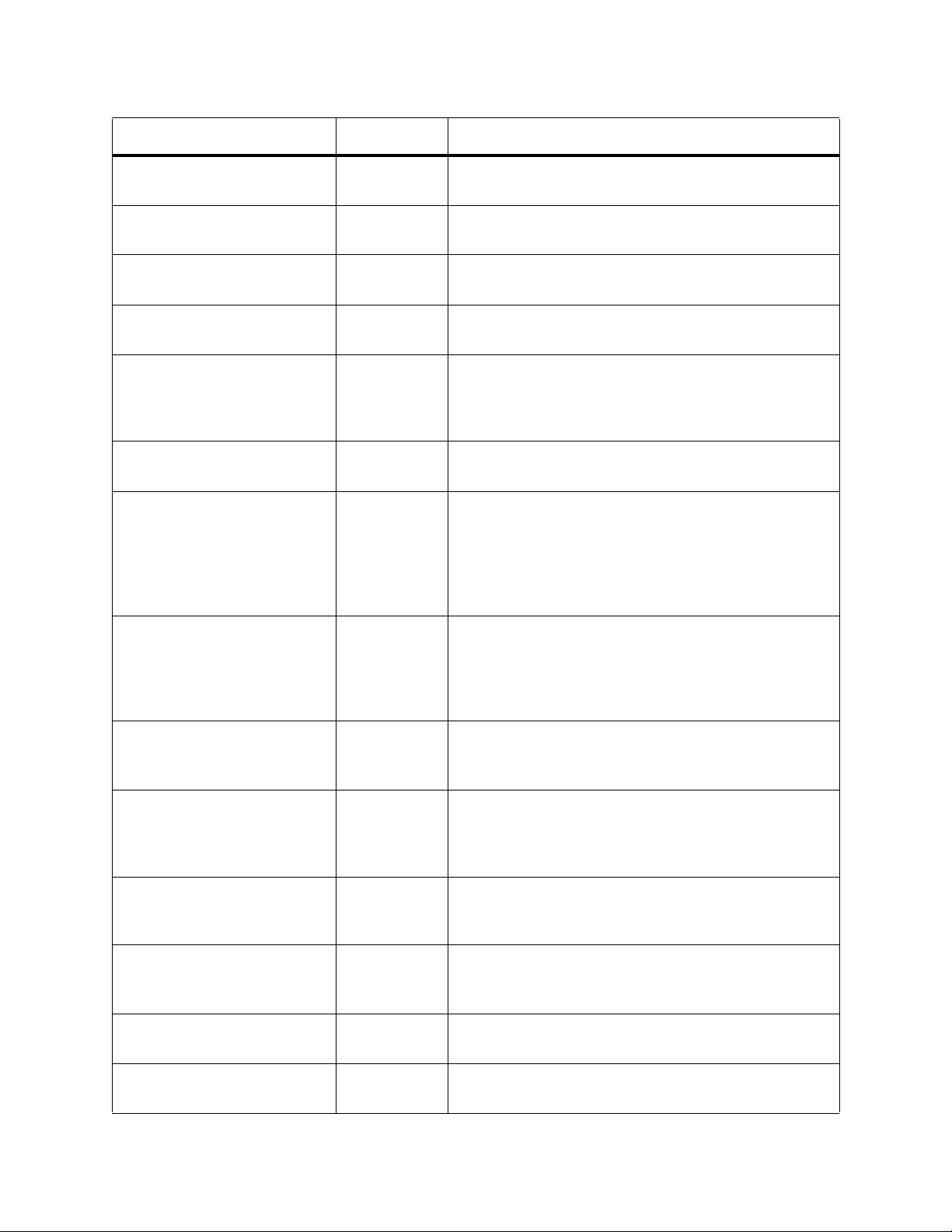
Table 5 Status Traps
Event Trap ID Description
Physical Library Online
Status Change
Physical Library Door
Status Change
I/E Station Door Status
Change
101 Issued when the physical library is brought online or
taken offline.
102 Issued when the physical library door has been
opened, closed, locked, or unlocked.
103 Issued when a partition has been brought online or
taken offline.
RCU Ready 110 Issued when the robotics go from “not ready” to
“ready” state.
RCU Not Ready 111 Issued when the robotics go from “ready” to “not
ready” state. T raps 110 and 1 11 may occur as part of a
startup or shutdown procedure. If seen at another
time, it may indicate that the front door is open.
Logical Library Online
Status Change
RAS Status Change:
Connectivity
204 Issued when a logical library, also known as a
partition, is brought online or taken offline.
400 Issued when the status of the connectivity subsystem
changes, which includes the I/O management unit , I/O
blades, and other components. This may indicate a
change to “good” status, so check the return value for
required action. If the return value shows an issue, use
the LMC to determine the corrective actions.
RAS Status Change:
Control
RAS Status Change:
Cooling
RAS Status Change:
Drives and Media
RAS Status Change:
Power
RAS Status Change:
Robotics
Startup Sequence
Completed
Shutdown Sequence
Completed
401 Issued when the status of the control subsystem
changes, which includes system firmware, the
operator panel, and the MCB, RCU, and other control
blades. If the return value shows an issue, use the
LMC to determine the corrective actions.
402 Issued when the status of the cooling subsystem
changes. If the return value shows an issue, use the
LMC to determine the corrective actions.
403 Issued when the status of the drives and/or me dia
(including drive brick firmware) changes. If the return
value shows an issue, use the LMC to determine th e
corrective actions.
404 Issued when the status of the power subsystem
changes. If the return value shows an issue, use the
LMC to determine the corrective actions.
405 Issued when the status of the robotics subsystem
changes. If the return value shows an issue, use the
LMC to determine the corrective actions.
500 Indicates the library startup sequence has completed.
501 Indicates the library shutdown sequence has
completed.
20 Variables and Traps Quick Reference
Page 25

Index
C
connectivityGroupStatusChange . . . . . . . . . . . .14
contacting
Quantum
controlGroupStatusChange
coolingGroupStatusChange
Customer Service Center
website
documents
additional
latest versions
release notes
driveAndMediaGroupStatusChange
framework applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5, 18
GET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5, 6, 7
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
D
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
. . . . . . . . . .15
F
G
H
drive online/offline status
drive overall health
I/E station door status
library main door status
partition online/offline status
physical library online/offline state
RAS sub-system status
robotics readiness
logicalLibraryOnlineStatusChange
MCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
physLibraryDoorStatusChange . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
physLibraryOnlineStatusChange
powerGroupStatusChange
productAgentInfoGroup
Quantum
contacting
Quantum Intelligent Storage MIB
Quantum Management MIB
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
. . . . . . . . . . . . .12
. . . . . . . .10
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
. . . . . . . . . . .14
M
P
. . . . . . . . . . . .13
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Q
. . . . . . .7, 13, 17
. . . . . . . . . . . . .13, 17
help
contacting Quantum
Customer Service Center
Service Requests
ieStationDoorStatusChange . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
library identification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
logical library name
product name
Library Management Console (LMC)
library status and health
Scalar i2000 / i6000 Basic SNMP Reference Guide 21
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
I
L
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
. . . . 5, 6, 20
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
RAS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12, 14, 20
rcuNotReady
rcuReady
Reference MIBs
release notes
location
roboticsGroupStatusChange
safety
symbols and notes
SANMgr Proxy MIB
Service Requests
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
R
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
S
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Page 26

opening . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
SET
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
shutdownSequenceInitiated
startupSequenceCompleted
symbols and notes
explained
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
T
training
contact Quantum
Trap 101
Trap 102
Trap 103
Trap 110
Trap 111
Trap 400
Trap 401
Trap 402
Trap 403
Trap 404
Trap 405
Trap 500
Trap 501
Trap registration
Traps
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5, 6
website
Customer Service Center
W
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
22 Index
 Loading...
Loading...