Page 1

RLXIB-IHA
802.11a
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial
Hotspot
July 24, 2013
USER MANUAL
Page 2

Your Feedback Please
We always want you to feel that you made the right decision to use our products. If you have suggestions, comments,
compliments or complaints about our products, documentation, or support, please write or call us.
ProSoft Technology
5201 Truxtun Ave., 3rd Floor
Bakersfield, CA 93309
+1 (661) 716-5100
+1 (661) 716-5101 (Fax)
www.prosoft-technology.com
support@prosoft-technology.com
Copyright © 2013 ProSoft Technology, Inc., all rights reserved.
RLXIB-IHA User Manual
July 24, 2013
ProSoft Technology ®, ProLinx ®, inRAx ®, ProTalk ®, and RadioLinx ® are Registered Trademarks of ProSoft
Technology, Inc. All other brand or product names are or may be trademarks of, and are used to identify products
and services of, their respective owners.
In an effort to conserve paper, ProSoft Technology no longer includes printed manuals with our product shipments.
User Manuals, Datasheets, Sample Ladder Files, and Configuration Files are provided on the enclosed DVD and are
available at no charge from our web site: http://www.prosoft-technology.com
Important Safety Information
The following Information and warnings pertaining to the radio module must be heeded.
WARNING – EXPLOSION HAZARD – DO NOT REPLACE ANTENNAS UNLESS POWER HAS BEEN SWITCHED
OFF OR THE AREA IS KNOWN TO BE NON-HAZARDOUS.
"THIS DEVICE CONTAINS A TRANSMITTER MODULE, FCC ID: . PLEASE SEE FCC ID LABEL ON BACK OF
DEVICE."
"THIS DEVICE USES AN INTERNAL COMPACT FLASH RADIO MODULE AS THE PRIMARY RADIO
COMPONENT. THE COMPACT FLASH RADIO MODULE DOES NOT HAVE AN FCC ID LABEL. THE COMPACT
FLASH RADIO MODULE HAS NO USER SERVICEABLE PARTS."
"THIS DEVICE COMPLIES WITH PART 15 OF THE FCC RULES. OPERATION IS SUBJECT TO THE FOLLOWING
TWO CONDITIONS: (1) THIS DEVICE MAY NOT CAUSE HARMFUL INTERFERENCE, AND (2) THIS DEVICE
MUST ACCEPT ANY INTERFERENCE RECEIVED, INCLUDING INTERFERENCE THAT MAY CAUSE
UNDESIRED OPERATION."
"CHANGES OR MODIFICATIONS NOT EXPRESSLY APPROVED BY THE PARTY RESPONSIBLE FOR
COMPLIANCE COULD VOID THE USER’s AUTHORITY TO OPERATE THE EQUIPMENT."
Industry Canada Requirements
"THIS DEVICE HAS BEEN DESIGNED TO OPERATE WITH AN ANTENNA HAVING A MAXIMUM GAIN OF 24 dB.
AN ANTENNA HAVING A HIGHER GAIN IS STRICTLY PROHIBITED PER REGULATIONS OF INDUSTRY
CANADA. THE REQUIRED ANTENNA IMPEDANCE IS 50 OHMS."
"TO REDUCE POTENTIAL RADIO INTERFERENCE TO OTHER USERS, THE ANTENNA TYPE AND ITS GAIN
SHOULD BE CHOSEN SUCH THAT THE EQUIVALENT ISOTROPICALLY RADIATED POWER (EIRP) IS NOT
MORE THAN THAT REQUIRED FOR SUCCESSFUL COMMUNICATION."
"THE INSTALLER OF THIS RADIO EQUIPMENT MUST INSURE THAT THE ANTENNA IS LOCATED OR
POINTED SUCH THAT IT DOES NOT EMIT RF FIELD IN EXCESS OF HEALTH CANADA LIMITS FOR THE
GENERAL POPULATION; CONSULT SAFETY CODE 6, OBTAINABLE FROM HEALTH CANADA."
Page 3

A2502S-OA
A5812NJ-OC
A5829NJ-DB
A2508NJ-DP
A5019NJ-DP
A0524NJ-DP
Recommended Antennas
Other Antennas with similar specifications may be substituted.
Antenna spacing requirements for user safety
It is important to keep the radio's antenna a safe distance from the user. To meet the requirements of FCC part
2.1091 for radio frequency radiation exposure, this radio must be used in such a way as to guarantee at least 20 cm
between the antenna and users. Greater distances are required for high-gain antennas. The FCC requires a
minimum distance of 1 mW *cm2 power density from the user (or 20 cm, whichever is greater).
If a specific application requires proximity of less than 20 cm, the application must be approved through the FCC for
compliance to part 2.1093.
RLXIB: CSA C22.2 213-M1987 and N. American Standard ANSI/ISA 12.12.01 listing
In accordance with Canadian Standard CSA C22.2 213-M1987 and ANSI Standard ISA 12.12.01, the RLXIB series
radios have been UL listed for operation in Class I, Division 2, Groups A, B, C, and D Locations.
This equipment is suitable for use in Class I, Division 2, Groups A, B, C and D OR non-hazardous locations only.
WARNING – EXPLOSION HAZARD – Do not disconnect equipment unless power has been removed or the area is
known to be non-hazardous.
WARNING – EXPLOSION HAZARD - Substitution of any components may impair suitability for Class I, Division 2.
Power must be provided from a Limited Power Source.
AVERRTISSEMENT - RISQUE D'EXPLOSION - LA SUBSTITUTION DE COMPOSANTS PEUT RENDRE CE
MATERIEL INACCEPTABLE POUR LES EMPLACEMENTS DE CLASSE I, DIVISION 2.
AVERRTISSEMENT - RISQUE D'EXPLOSION - AVANT DE DECONNECTER L'EQUIPEMENT, COUPER LE
COURANT OU S'ASSURER QUE L'EMPLACEMENT EST DESIGNE NON DANGERUEX.
The following label is applied to the radio to indicate that it is listed under ANSI/ISA standard 12.12.01 and CSA
standard C22.2 213-M1987.
This Device contains a Radio Transmitter Module
FCC ID: Canada IC:
Conforms to ANSI/ISA Std. 12.12.01 – Certified to CSA Std. C22.2 No. 213-M1987
Class I Division 2 10-24 Volts dc 6 Watts
48 Volts dc using the PoE Injector
Groups A, B, C & D
Max. Ambient: 60ºC
RLXIB-IHA and RLXIB-IHG: ATEX Approval
II 3 G
Ex nA nL IIC X
-40C° <= Ta <=75°C
ProSoft Technology, Inc., Bakersfield, CA USA
Model: RLXIB-IHA and RLXIB-IHG
S/N: XXXXXXXXXX
Caution:
Read instructions before operating in Hazardous Areas
N. America
The Radio must be installed inside an IP54 enclosure which requires a special tool for access.
Page 4

AUS B DK
FIN
F D GR
IRE
I
LUX
NL P E S UK
Product name: RLXIB-IHA, RLXIB-IHG
Safety Warning Statements
Explosive Atmosphere
Power, Input, and Output (I/O) wiring must be in accordance with the authority having jurisdiction
A Warning – Explosion Hazard – Do not make or break connections in an explosive atmosphere.
B Caution – Use only approved recommended power supply.
C Warning - Power supply should be installed in a non-hazardous area.
D Warning – DO NOT OPEN WHEN ENERGIZED.
E These products are intended to be mounted in an IP54 enclosure. The devices shall provide external means to
prevent the rated voltage being exceeded by transient disturbances of more than 40%. This device must be used
only with ATEX certified backplanes.
United States FCC & Industry Canada rules
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to
Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful
interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
CAUTION: Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the manufacturer could void the user’s authority to
operate the equipment.
European CE certification
The radio modem has been approved for operation under the RTT&E directive, passing the following tests: ETS300826 (EMC), ETS300-328 (Functionality), and EN60950 (Safety).
The following is the appropriate label that is applied to the radio modem product line to indicate the unit is approved
to operate with CE certification:
The following is the appropriate label that is applied to the radio modem product line shipping package to indicate the
unit is approved to operate with CE certification:
Note: Member states in the EU with restrictive use for this device are crossed out. This device is also authorized for
use in all EFTA member states (CH, ICE, LI, and NOR).
Page 5

EU Requirements
1. For outdoor use, France has a frequency restriction of 2.4 GHz to 2.454 GHz for an output power greater than 10
mW and below 100 mW.
2. For outdoor use in France, the output power is restricted to 10 mW in the frequency range of 2.454 GHz to 2.4835
GHz.
3. 5.15 GHz to 5.35 GHz is restricted to 200 mW EIRP throughout the European Union.
Power Supply and Accessories Warning
The certifications listed in this document apply to only the radio mentioned herein. These certifications do not extend
to any other items, including accessories or any external means of supplying power to the radio. Accessories and
power supplies shipped with the radio have not been tested and are not covered by these certifications. Any noncertified items added to the radio, including any means of supplying power, must be located in an area known to be
non-hazardous. All wiring to and from the Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) injector supplied with the radio must be routed
and installed inside the building or plant and never routed or installed outside of the building or plant.
Location and Use
The Industrial HotSpot radios, such as the RLXIB-IHA are used by professionals in Industrial
Applications/installations only and not used by the general consumer. These industrial radios are used for industrial
applications such as, water treatment facilities, power plants, factories, railroads, remote oil/gas pipelines, refineries,
cargo ships, refueling ships etc….and used for wireless high speed data transmission. All radios are installed and
used by professionals in restricted areas.
Page 6

Page 7

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Contents
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
Contents
Your Feedback Please ........................................................................................................................ 2
Important Safety Information ............................................................................................................... 2
Recommended Antennas ................................................................................................................... 3
Antenna spacing requirements for user safety ................................................................................... 3
RLXIB: CSA C22.2 213-M1987 and N. American Standard ANSI/ISA 12.12.01 listing ..................... 3
RLXIB-IHA and RLXIB-IHG: ATEX Approval ...................................................................................... 3
United States FCC & Industry Canada rules ...................................................................................... 4
European CE certification ................................................................................................................... 4
EU Requirements ................................................................................................................................ 5
Power Supply and Accessories Warning ............................................................................................ 5
Location and Use ................................................................................................................................ 5
1 Start Here 11
1.1 About the RadioLinx® 802.11a High Power Industrial Hotspot™ ............................ 11
1.1.1 Specifications .......................................................................................................... 11
1.1.2 Regulatory Approvals .............................................................................................. 12
1.2 Package Contents ................................................................................................... 12
1.3 System Requirements ............................................................................................. 13
1.4 Install the IH Browser Configuration Tool ................................................................ 13
1.5 Install ProSoft Wireless Designer ............................................................................ 14
1.6 Planning the Network .............................................................................................. 14
1.6.1 Installation Questions .............................................................................................. 15
1.6.2 ProSoft Wireless Designer ...................................................................................... 15
1.6.3 Planning the Physical Installation ............................................................................ 16
1.7 Configuring the Radios ............................................................................................ 16
1.7.1 Start IH Browser ...................................................................................................... 18
1.7.2 Plug In the Cables ................................................................................................... 19
1.7.3 Detecting the Radio ................................................................................................. 20
1.7.4 Assign a Temporary IP Address ............................................................................. 20
1.7.5 Set Up the Master Radio ......................................................................................... 21
1.7.6 Save the Radio Configuration ................................................................................. 23
1.7.7 Set Up a Repeater ................................................................................................... 24
1.7.8 Set Up a Client ........................................................................................................ 25
1.8 Verify Communication ............................................................................................. 25
2 Installing the Radios 27
2.1 Connecting antennas .............................................................................................. 28
2.2 Testing the Network Installation Plan ...................................................................... 28
3 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting 31
3.1 Diagnostics .............................................................................................................. 31
3.2 Check the Ethernet cable ........................................................................................ 32
3.3 LED display ............................................................................................................. 32
3.4 Retrieve the default password ................................................................................. 33
3.5 Troubleshoot IH Browser error messages .............................................................. 34
3.6 Troubleshoot missing radios ................................................................................... 34
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 7 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 8

Contents RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
3.7 Improving Signal Quality ......................................................................................... 35
4 Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility 37
4.1 Radio Status ........................................................................................................... 41
4.1.1 Available Parents .................................................................................................... 42
4.1.2 Address table .......................................................................................................... 43
4.1.3 Port status ............................................................................................................... 44
4.2 Radio Network settings ........................................................................................... 46
4.2.1 Parent Link Settings ................................................................................................ 48
4.2.2 IGMP Settings ......................................................................................................... 51
4.2.3 Rapid Spanning Tree Functionality......................................................................... 52
4.2.4 Spanning Tree Settings .......................................................................................... 54
4.2.5 Advanced Settings .................................................................................................. 56
4.2.6 Serial Port Settings ................................................................................................. 57
4.3 Security settings...................................................................................................... 59
4.3.1 Encryption type ....................................................................................................... 60
4.3.2 WPA phrase ............................................................................................................ 60
4.3.3 WEP key ................................................................................................................. 61
4.3.4 MAC filter ................................................................................................................ 61
4.3.5 Hide Network SSID ................................................................................................. 62
4.4 Radio access settings ............................................................................................. 62
4.4.1 SNMP Agent settings .............................................................................................. 63
4.4.2 Change password ................................................................................................... 64
4.5 Apply Changes........................................................................................................ 65
4.6 Cancel Changes ..................................................................................................... 65
4.7 Factory Defaults ...................................................................................................... 65
5 RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser 67
5.1 Primary radio functions ........................................................................................... 68
5.2 File Menu ................................................................................................................ 69
5.2.1 Scan Setup ............................................................................................................. 69
5.2.2 Scan ........................................................................................................................ 70
5.2.3 Clear ....................................................................................................................... 70
5.2.4 Import ...................................................................................................................... 70
5.2.5 Export ...................................................................................................................... 70
5.2.6 Freeze ..................................................................................................................... 71
5.2.7 Print ......................................................................................................................... 71
5.2.8 Print Preview ........................................................................................................... 71
5.2.9 Print Setup .............................................................................................................. 71
5.2.10 Exit .......................................................................................................................... 71
5.3 Operations Menu .................................................................................................... 71
5.3.1 Connect ................................................................................................................... 72
5.3.2 Assign IP ................................................................................................................. 72
5.3.3 Update Firmware .................................................................................................... 73
5.3.4 Start Ping Session .................................................................................................. 74
5.4 Dialogs Menu .......................................................................................................... 75
5.4.1 Wireless Clients ...................................................................................................... 75
5.4.2 Ethernet Nodes ....................................................................................................... 76
5.4.3 Scan List ................................................................................................................. 77
5.4.4 Port Table ............................................................................................................... 78
5.4.5 Event Log ................................................................................................................ 78
Page 8 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 9

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Contents
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
5.4.6 Properties ................................................................................................................ 79
5.5 View Menu ............................................................................................................... 81
5.5.1 Tool Bar ................................................................................................................... 81
5.5.2 Status Bar ................................................................................................................ 82
5.5.3 List View .................................................................................................................. 82
5.5.4 Topology View ......................................................................................................... 82
5.5.5 Zoom In ................................................................................................................... 84
5.5.6 Zoom Out ................................................................................................................ 85
5.5.7 Zoom to Fit .............................................................................................................. 85
5.5.8 Show Ping Stations ................................................................................................. 86
5.5.9 Show Parents .......................................................................................................... 86
5.5.10 Print Area ................................................................................................................ 87
5.5.11 Reset Columns ........................................................................................................ 87
5.6 Help Menu ............................................................................................................... 87
5.6.1 Help Topics ............................................................................................................. 88
5.6.2 About RLX-IH Browser ............................................................................................ 88
6 Reference 89
6.1 Product Overview .................................................................................................... 89
6.2 Radio hardware ....................................................................................................... 90
6.2.1 Radio power requirements ...................................................................................... 90
6.2.2 Ethernet Cable Specifications ................................................................................. 91
6.2.3 Ethernet Cable Configuration .................................................................................. 92
6.3 Antennas ................................................................................................................. 92
6.3.1 Antenna Pattern ...................................................................................................... 92
6.3.2 Antenna Gain .......................................................................................................... 93
6.3.3 Antenna Polarity ...................................................................................................... 93
6.3.4 Whip antennas ........................................................................................................ 94
6.3.5 Collinear array antennas ......................................................................................... 94
6.3.6 Yagi Array Antenna ................................................................................................. 95
6.3.7 Parabolic reflector antennas ................................................................................... 95
6.3.8 Antenna location, spacing, and mounting ............................................................... 96
7 Support, Service & Warranty 97
Contacting Technical Support ........................................................................................................... 97
7.1 Return Material Authorization (RMA) Policies and Conditions................................ 98
7.1.1 Returning Any Product ............................................................................................ 98
7.1.2 Returning Units Under Warranty ............................................................................. 99
7.1.3 Returning Units Out of Warranty ............................................................................. 99
7.2 LIMITED WARRANTY ........................................................................................... 100
7.2.1 What Is Covered By This Warranty ....................................................................... 101
7.2.2 What Is Not Covered By This Warranty ................................................................ 102
7.2.3 Disclaimer Regarding High Risk Activities ............................................................ 103
7.2.4 Intellectual Property Indemnity .............................................................................. 104
7.2.5 Disclaimer of all Other Warranties ........................................................................ 105
7.2.6 Limitation of Remedies ** ...................................................................................... 105
7.2.7 Time Limit for Bringing Suit ................................................................................... 106
7.2.8 No Other Warranties ............................................................................................. 106
7.2.9 Allocation of Risks ................................................................................................. 106
7.2.10 Controlling Law and Severability ........................................................................... 106
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 9 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 10

Contents RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
8 Glossary of Terms 107
Index 121
Page 10 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 11

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Start Here
In This Chapter
About the RadioLinx® 802.11a High Power Industrial Hotspot™ ........... 11
Package Contents ................................................................................. 12
System Requirements ........................................................................... 13
Install the IH Browser Configuration Tool .............................................. 13
Install ProSoft Wireless Designer .......................................................... 14
Planning the Network ............................................................................ 14
Configuring the Radios .......................................................................... 16
Verify Communication ........................................................................... 25
Frequency Band
(Varies by country)
802.11a
5.150 GHz to 5.250 GHz (FCC/ETSI)
5.725 GHz to 5.850 GHz (FCC)
Wireless Standards
802.11a, 802.11i
Transmit Power (Programmable)
(varies by country)
24 dBm (250 mW) at 6 Mbps
24 dBm (250 mW) at 24 Mbps
21 dBm (125 mW) at 54 Mbps
Channel data rates (Modulation)
802.11a: 54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9, 6 Mbps (OFDM)
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
1 Start Here
For most applications, the installation and configuration steps described in the
following topics will work without additional programming. ProSoft Technology
strongly recommends that you complete the steps in this chapter before
developing a custom application.
1.1 About the RadioLinx® 802.11a High Power Industrial Hotspot™
The RadioLinx® 802.11a High Power Industrial Hotspot™ (RLXIB-IHA) is a high-
speed wireless Ethernet radio, with PoE and Serial Encapsulation. The RLXIBIHA operates at speeds up to 54 Mbps, using the IEEE 802.11a (5 GHz band)
standard. In addition to transmit power up to 250 mW, the RLXIB-IHA offers
many Industrial features including hazardous location certifications, IGMP
Snooping, OFDM for noise immunity, simultaneous bridge / repeater / access
point mode, OPC server diagnostics, extended operating temperature, high
vibration/shock resistance and DIN-rail mounting.
1.1.1 Specifications
Radio
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 11 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 12

Start Here RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
Receiver Sensitivity (Typical)
-92 dBm at 6 Mbps
-84 dBm at 24 Mbps
-72 dBm at 54 Mbps
Channel Selection
36, 40, 44, 48, 149, 153, 157, 161, 165
Security
WPA2 - 802.11i with 128 bit AES-CCM
Legacy WPA TKIP, WEP support
MAC ID filter
Admin password
Enclosure
Extruded aluminum with DIN and panel mount
Size
115 x 117 x 45 mm (W x H x D)
4.5 x 4.6 x 1.75 inches
Vibration
IEC 60068 2-6 (20g, 3-Axis)
Shock
IEC 60068 2-27 (5g, 10 Hz to 150 Hz)
Ethernet Ports
One 10/100 Base-T connector, shielded RJ45
IEEE 802.3, 802.3u, 802.3x
Antenna Port
(1) RP-SMA connector
Weight
1.1 lbs (499g)
Operating Temperature
-40°C to +75°C
Humidity
Up to 100% RH, with no condensation
External Power
PoE Injector
10 Vdc to 24 Vdc
802.3af PoE Powered Device
Average Power
<9W
UL
ANSI/ISA 12.12.01 Class I, Division 2, Groups A, B, C, D
cULus
C22.2 No. 213-M1987
CSA/UL
ANSI/EN60950-1
ATEX
EN60079-0/-15 Zone 2 Category 3
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
Physical
Environmental
1.1.2 Regulatory Approvals
Wireless Approvals
Visit our web site at www.prosoft-technology.com for current wireless approval information.
Hazardous Locations
1.2 Package Contents
The following components are included with your RLXIB-IHA radio, and are all
required for installation and configuration.
Important: Before beginning the installation, please verify that all of the following items are
present.
Page 12 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 13

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Start Here
Qty.
Part Name
Part Number
Part Description
1
RLXIB-IHA Radio
RLXIB-IHA
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
1
Cable
085-1007
6 foot RS232 serial cable
1
Cable
RL-CBL025
5 foot Ethernet Straight-Thru Cable (Gray)
1
Antenna
A2502S-OA
2 dBi Omni RP-SMA articulating, 2.4/5GHz
1
Power Supply
RL-PS005-2
AC Power Adapter, 12V1.25A w/2 pin & 4
plug Set
1
ProSoft Solutions CD
Contains sample programs, utilities and
documentation for the RLXIB-IHA module.
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
If any of these components are missing, please contact ProSoft Technology
Support for replacement parts.
1.3 System Requirements
The RadioLinx IH Browser is designed for Microsoft Windows XP, 2000, and
2003. Minimum hardware requirements are:
Pentium® II 450 MHz minimum. Pentium III 733 MHz (or better)
recommended
Supported operating systems:
o Microsoft Windows XP Professional with Service Pack 1 or 2
o Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional with Service Pack 1, 2, or 3
o Microsoft Windows Server 2003
o Microsoft Windows Vista
128 Mbytes of RAM minimum, 256 Mbytes of RAM recommended
CD-ROM drive
100 MB available hard drive space
Available RS-232 serial port and null modem cable
256-color VGA graphics adapter, 800 x 600 minimum resolution (True Color
1024 x 768 recommended)
Ethernet hub with standard RJ45 Ethernet cable
or
Ethernet port with RJ45 crossover cable for direct connection to module
A web browser, for example Microsoft Internet Explorer or Firefox.
In addition, you will need
A connection to an existing wired or wireless Ethernet network, with a Static
or Dynamic IP address for your computer
Static IP address, Subnet Mask and Gateway address for each RadioLinx
device you plan to install. Obtain this information from your system
administrator
1.4 Install the IH Browser Configuration Tool
1 Insert the ProSoft Solutions CD in your CD-ROM drive. On most computers,
a menu screen will open automatically. If you do not see a menu within a few
seconds, follow these steps:
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 13 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 14

Start Here RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
a Click the START button, and then choose RUN.
b In the Run dialog box, click the BROWSE button.
c In the Browse dialog box, click MY COMPUTER. In the list of drives, choose
the CD-ROM drive where you inserted the ProSoft Solutions CD.
d Select the file PROSOFT.EXE, and then click OPEN.
e On the Run dialog box, click OK.
2 On the CD-ROM menu, select IH BROWSER FOR THE RLX-IHX AND RLXIB-X
PRODUCTS. This action opens the Setup Wizard for IH Browser.
3 Follow the instructions on the installation wizard to install the program with its
default location and settings.
4 When the installation finishes, you may be prompted to restart your computer
if certain files were in use during installation. The updated files will be
installed during the restart process.
1.5 Install ProSoft Wireless Designer
1 On the CD-ROM, navigate to the folder containing ProSoft Wireless
Designer, and then double-click the file SETUP.EXE. This action starts the
installation wizard.
2 Follow the instructions on the installation wizard to install the program.
3 Click FINISH to complete the installation. If you are prompted to restart your
computer, save your work in any applications that are running, close the
applications, and allow the computer to restart.
1.6 Planning the Network
Before you configure and install the network, you should create a plan for it. The
following points assume that you are creating a bridge network of masters and
repeaters, but you can also set up clients to work with devices on existing
wireless LANs. For information, see Set up a Client (page 25).
The simplest way to design the physical network of radios, antennas, connectors,
cables, amplifiers and other accessories, is to use ProSoft Wireless Designer
(page 15). This application determines your hardware needs based on your
answers to a few questions, and then generates a Bill of Materials specifying all
the components you will need for your installation.
To begin, determine where you need radios and then choose locations for
them accordingly. For example, you might decide to install your master radio
near a PC in a central plant location (You can use the PC to configure the
radios through the Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility). If the plant is an
oil refinery, for example, you might decide to install radios near the oil tanks.
The next important issue is how to link the radios. Unless the radios are very
close together, you must make sure that each pair of radio antennas in the
network has a line of sight between them. In other words, you must be able to
see from one antenna to another, either with the naked eye, or with
binoculars.
Page 14 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 15

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Start Here
How many radios in your network?
Master ID
Repeater ID
Client ID
Locations
Is there a Line of Sight between them?
Selected the appropriate antennas for
your network?
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
If a line of sight does not exist between antennas, you must choose a site for
installing a repeater radio, which will create a bridge between the radio
antennas.
Choose the appropriate antennas for the network. If an antenna will be
connected to the radio by a long cable, you might need to purchase a power
amplifier, which is available from ProSoft Technology. The more distance
between an antenna and its radio, the more signal loss the radio will have.
Consider drawing up your network plans on paper. As part of the drawing,
you should assign a logical name to each radio. You can use these names
later when configuring the radios in the Radio Configuration / Diagnostic
Utility.
As part of your planning, you might want to conduct a site survey. ProSoft
Technology can perform this survey, you can do it yourself, or you can hire a
surveyor.
Protect radios from direct exposure to weather, and provide an adequate,
stable power source. Make sure that your plan complies with the radio’s
power requirements and cable specifications.
Important: Radios and antennas must be located at least 8 inches (20 cm) away from personnel.
1.6.1 Installation Questions
Answer the following questions to make your installation easier and to familiarize
yourself with your system and what you want to do.
1.6.2 ProSoft Wireless Designer
ProSoft Wireless Designer simplifies the task of specifying a ProSoft Wireless
installation, and provides a variety of views containing an accurate description of
each site in a wireless network, including:
Visual diagram of site layout
Location (latitude/longitude, based on GPS coordinates)
Radio type, frequency range, and country-specific channel and power
requirements
Length, type and estimated signal loss for cables
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 15 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 16

Start Here RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
Required accessories, including lightning protection, cable adaptors and
antennas
Complete parts list
Use ProSoft Wireless Designer when conducting a site audit for a customer, and
then provide the customer with a complete list of components and a detailed
description for each site and link. Customers can use this information to
understand and visualize their network, and provide necessary information for
technical support and maintenance.
Functional Specifications:
Contains a database of all currently available RadioLinx radios, antennas,
cables, connectors and accessories
Exports Parts List, Site and Link Details, and Wizard settings into a variety of
common file formats, for import into applications such as spreadsheets,
databases and word processors
Checks wireless link feasibility based on path length and recommended
accessories
Predicts signal strength based on distance, local regulations and hardware
choices
Fully documents your ProSoft Wireless network plan
1.6.3 Planning the Physical Installation
A network's performance is affected by attributes specific to the installation site.
Consider the following cautions, where possible, to optimize your network
installation:
Design the network to use less than 2048 radios (per network)
Place radios within the specified 15 miles of each other
Add repeater to extend distance or where line of sight is limited
Radios or antennas CANNOT be placed within 8 inches (20 cm) of where
people will be
Though radio frequency communication is reliable, sometimes its performance
can be affected by intangibles. A good network installation plan includes time
and resources for performance testing and installation changes.
Test the installation plan (page 28) before the network installation is complete.
1.7 Configuring the Radios
To configure the network radios, follow these steps.
Use the RLX-IH Browser to display all radios on the network, and then use a
Web browser or SNMP manager to view and change radio settings. The radio
package includes the program CD, power supply, Ethernet cable, and a small
antenna. You must install the antenna later, but it is not needed to get started.
IMPORTANT: If possible, you should configure all the radios side by side in an office setting and
make sure they link before you try to install them in the field.
To configure the radios in a network:
Page 16 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 17

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Start Here
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
1 Start the IH Browser (page 18) configuration application.
The PC must have a wired or wireless Ethernet connection configured with a
static or dynamic IP address.
2 Plug in the power cable and Ethernet cable (page 19) to the RLXIB-IHA radio,
wait a moment for the radio to power up, and then examine the radio's LED
display to make sure the radio is working properly.
3 Assign a temporary IP address: (page 20, page 72) Double-click the radio
listing in the RLX-IH Browser. In the next window, click OK to accept the
temporary IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
4 Double-click the radio listing again in the RLX-IH Browser to open the Radio
Configuration / Diagnostic Utility in your web browser. Enter "password"
(lower case, no quotes) in the next window and then click Login.
If necessary, you can enter your own password later. For information, see
Change Password (page 64).
5 Set up the master radio first, using the Radio Settings window in the Radio
Configuration / Diagnostic Utility.
6 Click Apply Changes to save the master radio settings.
To cancel the settings and start over, click the Cancel Changes button before
you click Apply Changes. After they are configured, master radios are
preceded by an "M" in the utility window list.
Note: The text shown in yellow at the bottom of the window indicates the status of changes you
have made to the configuration.
If the text shows "Changes not saved", click Apply Changes to save your settings.
If the text shows "Changes not saved; Will disrupt X s", you can click Apply Changes, however
the network will be disrupted temporarily while the changes are applied. The value of "X"
indicates the number of seconds the network will be offline.
7 Unplug the Ethernet cable from the radio and plug it into the next radio to be
configured.
8 Set Up a Repeater. (page 24) Return to the RLX-IH Browser. To be sure that
you are seeing the latest status of the radio(s), go to the toolbar (page 81)
and click the "Clear" icon (eraser) followed by the "Scan" icon (binoculars).
Double-click the listing of the next radio to be configured, and configure it as
a repeater radio.
9 Save the Radio Configuration. (page 23) Save the repeater radio settings by
clicking Apply Changes at the bottom of the Radio Settings screen. Repeat
steps 7 through 9 to configure each repeater in the network.
10 After configuring the network and its radios, physically label each radio.
Labeling eliminates confusion about which radios correspond with which
radio configurations in the software. You should identify the radio's name,
network SSID, and IP address, if set.
11 Install the radios and antennas (page 26).
The remainder of the topics in this section describe each of these steps in more
detail.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 17 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 18
Start Here RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
1.7.1 Start IH Browser
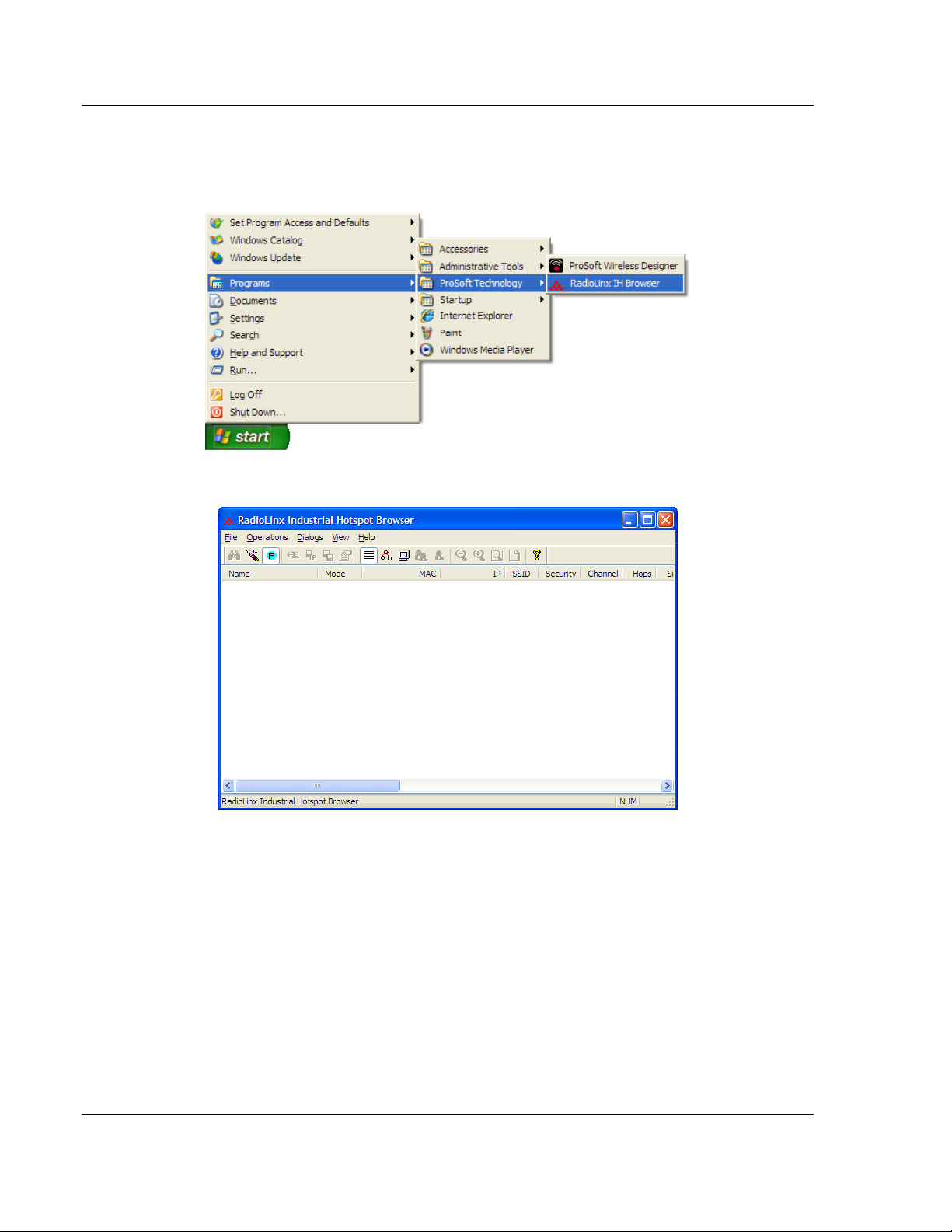
1 Click the START button, and then navigate to PROGRAMS / PROSOFT
TECHNOLOGY
2 Click to start RADIOLINX IH BROWSER.
The window lists all the radios your computer can access. The MAC ID number is
essentially the serial number of the radio; this number is also printed on the side
of the radio. If a radio listing does not appear in the window, select Scan from the
File menu. If you still do not see a radio listing, see Troubleshooting.
Page 18 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 19

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Start Here
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
1.7.2 Plug In the Cables
You can configure the RLXIB-IHA using the Ethernet port on the radio. On the
underside are three ports; Ethernet, Serial and Power (10 to 24 VDC 6 W).
From left to right: Power connector, Serial port and Ethernet port.
Use the Ethernet cable to configure the radio for the first time.
Note: After you plug in the power cable and Ethernet cable, the radio performs a startup procedure
that includes a self-test, loading the main program, and initializing the radio. The front panel LEDs
will illuminate after approximately two seconds. The entire startup procedure can take up to 90
seconds.
After the startup procedure has completed successfully, the Power LED should
be green, meaning that the radio has power. The Ethernet LED should also be
green, meaning that the Ethernet connection is working. The RF Transmit and
RF Receive LEDs should blink.
For information on making connections, see Radio Power Requirements and
Cable Specifications (page 92, page 91).
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 19 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 20
Start Here RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
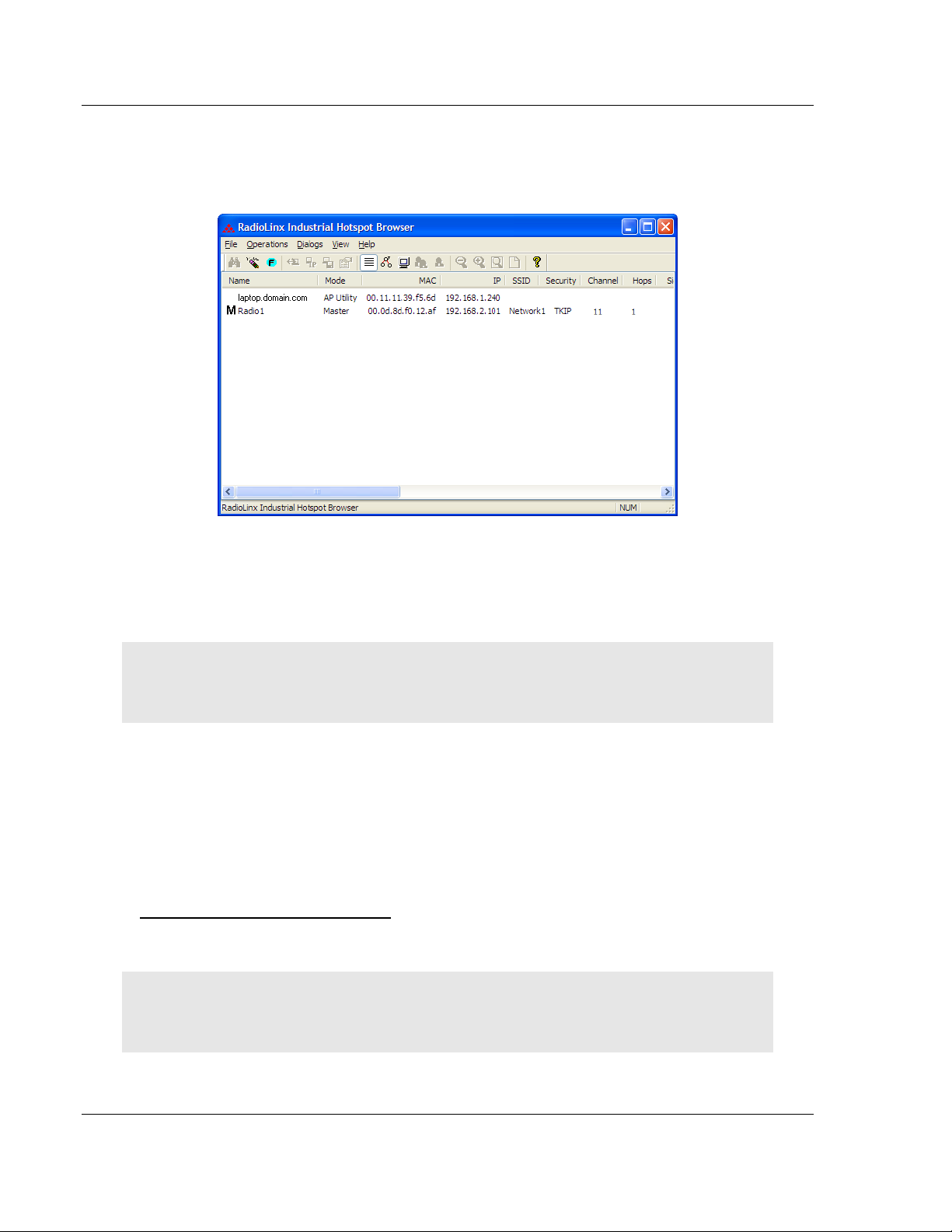
1.7.3 Detecting the Radio
After the radio has completed its startup procedure, the radio will appear in the IH
Browser window.
The window lists all the radios your computer can access. The MAC ID number is
essentially the serial number of the radio; this number is also printed on the side
of the radio. If a radio listing does not appear in the window, select Scan from the
File menu.
Tip: If a radio listing does not appear in the window, open the File menu and choose Scan. If you
still do not see a radio listing, refer to Diagnostics and Troubleshooting in the RLXIB-IHA User
Manual.
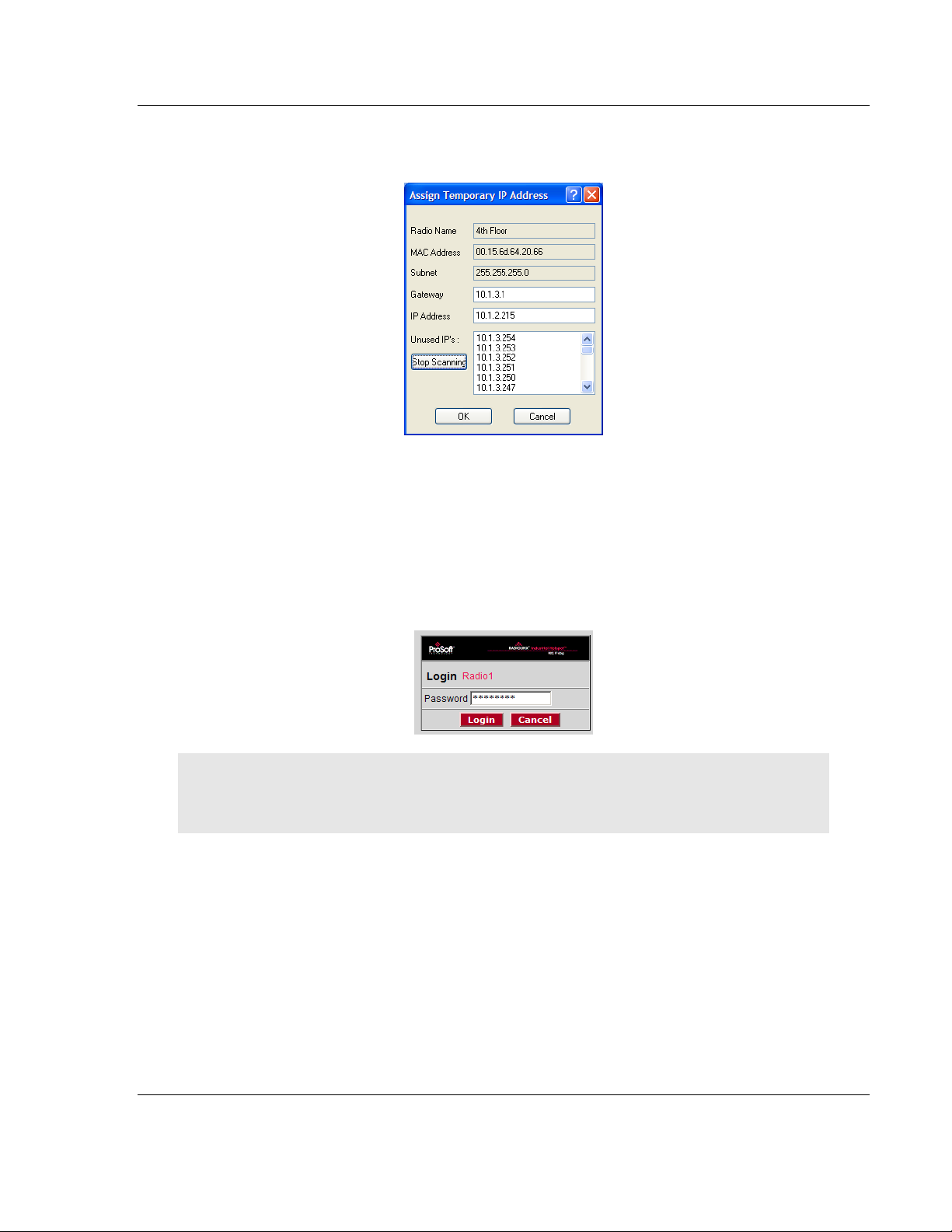
1.7.4 Assign a Temporary IP Address
You need the IP address to log into the Radio Configuration/Diagnostic Utility
and configure the radio settings. If the radio is connected to a network with a
DHCP server, the radio may already have an IP address assigned to it.
If a DHCP server is not available, or if you prefer to assign a static IP address,
you can enter a temporary IP here. You will use the Radio Configuration /
Diagnostic Utility (page 36) to assign a permanent IP address.
To assign a temporary IP Address
1 In IH Browser, click to select the radio.
Tip: If a radio listing does not appear in the window, open the File menu and choose Scan. If you
still do not see a radio listing, refer to Diagnostics and troubleshooting in the RLXIB-IHA User
Manual.
Page 20 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 21
RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Start Here
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
1 Open the Operations menu, and choose Assign IP. This action opens the
Assign Temporary IP Address dialog box.
2 Select one of the unused IP addresses, and then click OK.
For information, see Radio Access settings (page 62).
1.7.5 Set Up the Master Radio
To configure the radio, double click on the radio (Radio1) in the IH Browser
window. This action opens a web browser (for example Microsoft Internet
Explorer or Firefox) and loads the IH Radio’s web configuration interface.
Important: The radio configuration is protected by a login password. The default password for the
radio is "password" (lower case, no quotes). To prevent unauthorized access to the radio
configuration, you should change the password when you have finished the initial configuration.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 21 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 22
Start Here RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
Note: The master is the "root" or top-level radio in a network. You must have at least one master
radio per network. For redundancy, you can assign more than one master to a network.
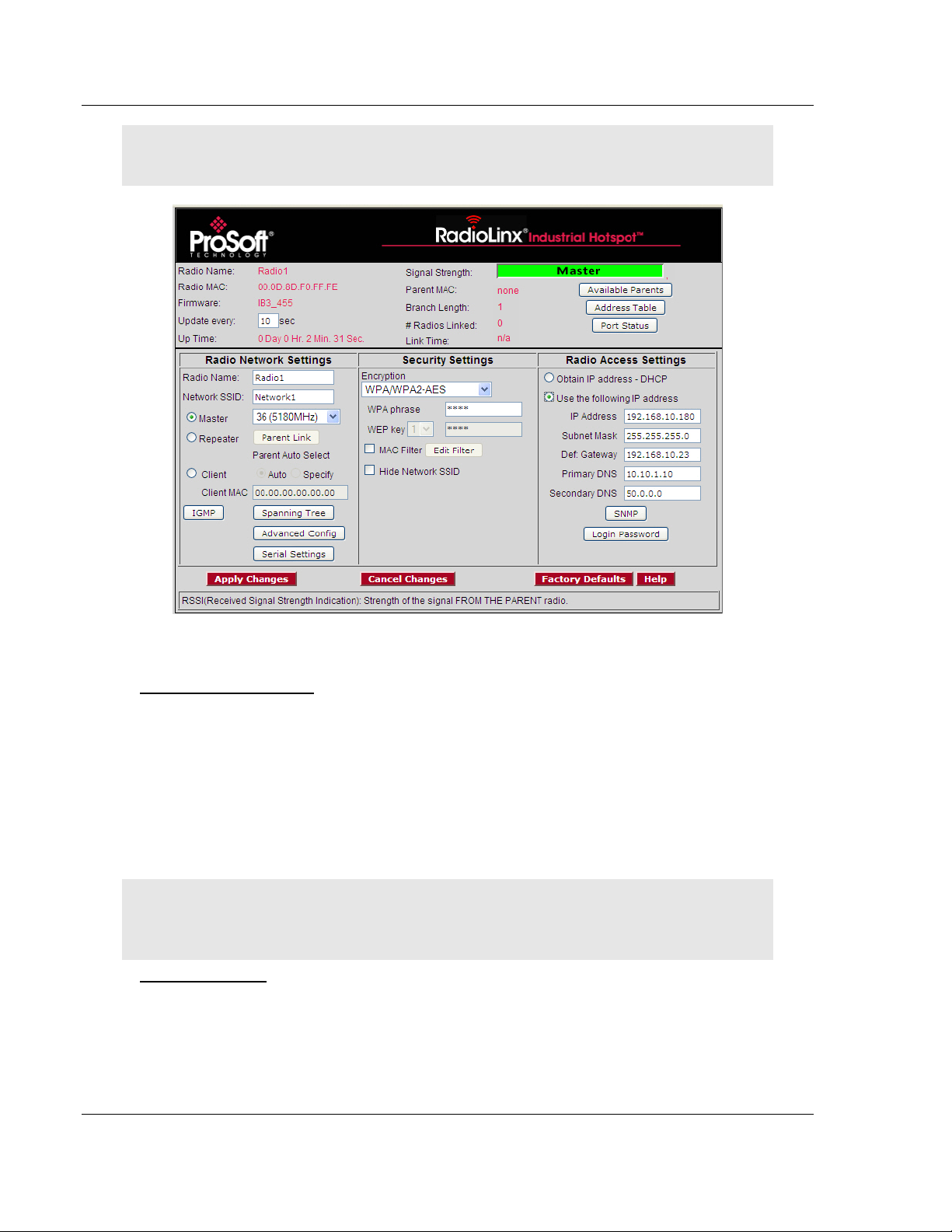
To configure a Master radio, make the following changes to the web
configuration form:
Radio Network Settings
Radio Name: Enter a unique name for the radio.
Select Master as the radio mode.
Network SSID: Assign a network name (SSID) of up to 32 characters. The
radio uses this name in all network references. All radios in a network must
have the same SSID.
Channel: Select a channel and frequency range for the network or accept the
default value. Network channels allow radios to avoid sharing a frequency
with other networks in the same location. The channel list indicates the
channel number as well as the frequency.
Important: The RLXIB-IHA radio is supplied with a dual-band antenna that supports both
frequency ranges. If you use a different antenna with the RLXIB-IHA radio, you must choose a
channel and frequency range supported by the antenna.
Security Settings
Encryption Type: Encryption scrambles data so that only intended viewers
can decipher and understand it. Although "none" is an available encryption
type, ProSoft Technology strongly recommends encrypting all data sent and
received from every radio on your network, to help prevent your data from
being intercepted and decoded.
Page 22 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 23

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Start Here
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
WPA phrase: To use WPA encryption on packets sent between the radios,
select WPA in the Encryption Type field. Next, in the WPA phrase field, enter
a pass phrase of between eight and 63 normal keyboard characters. This
phrase automatically generates an encryption key of 128 hexadecimal
characters. The default pass phrase is "passphrase" (lower case, no quotes).
For more information on encryption, see Security settings (page 59).
Because you must assign the same Network SSID and WPA phrase to the
repeater radios later in this procedure, you should write down the settings.
Note: Network SSID and WPA phrase are both case-sensitive.
Network SSID:_________________
WPA phrase:__________________
Radio Access Settings
If a DHCP (Dynamic Host Control Protocol) server is configured on your local
area network, the DHCP server can assign IP addresses automatically.
If you prefer to assign a Static (Fixed) IP address, select "Use the following IP
address", and then enter the IP Address, Subnet Mask and Default Gateway in
the Radio Access Settings area of the IH Radio web configuration form.
Important: If you intend to assign IP addresses manually, you must not duplicate an IP address
that is already in use on your network. If you are not sure what IP addresses are available, ask
your network administrator for assistance.
1.7.6 Save the Radio Configuration
Before closing the Radio Configuration window, you must apply your changes.
Click APPLY CHANGES to save your configuration and restart the radio.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 23 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 24
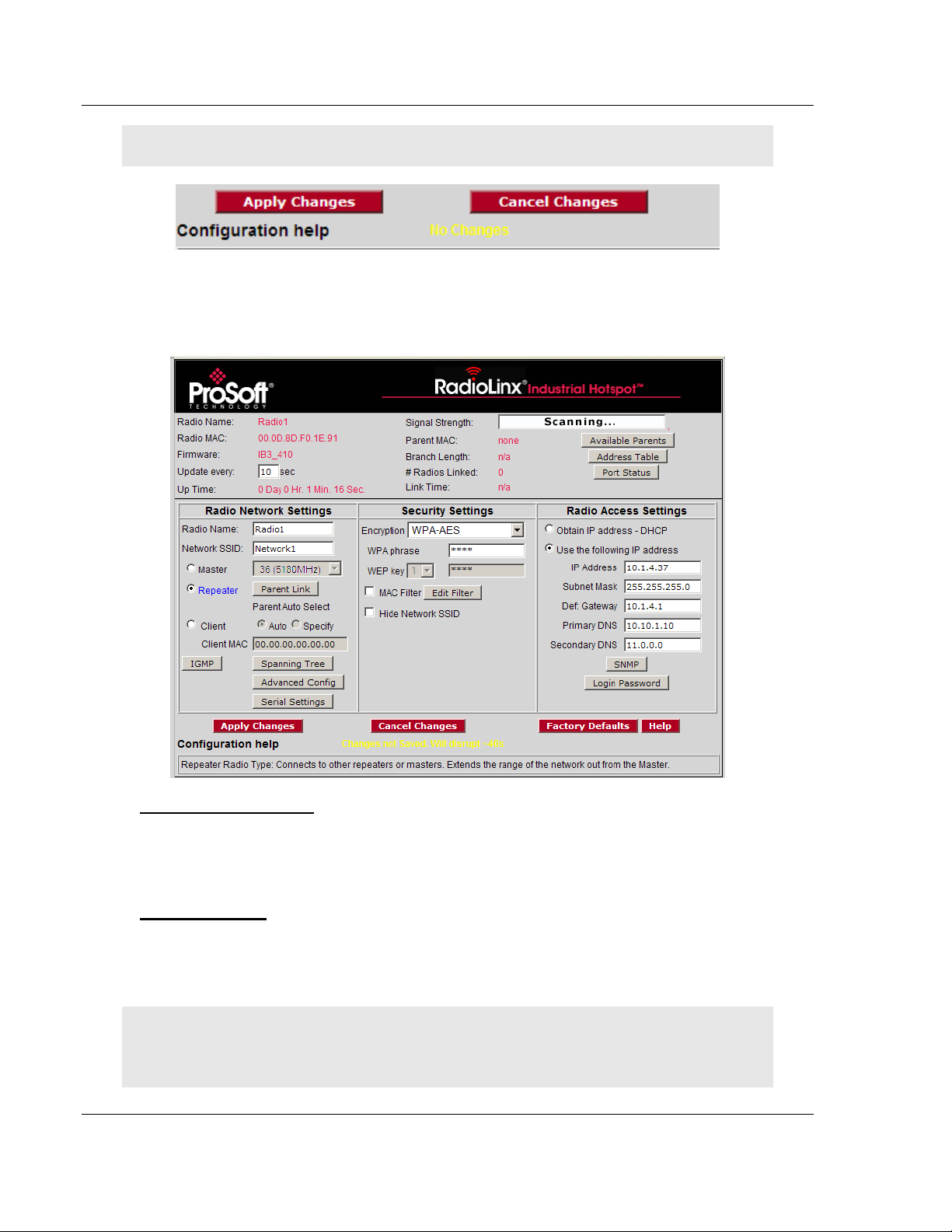
Start Here RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
Note: To discard your changes and start over, click CANCEL CHANGES.
1.7.7 Set Up a Repeater
To configure a radio as a Repeater, make changes to the web configuration form.
Radio Network Settings
Radio Name: Enter a unique name for the radio.
Select Repeater as the radio mode.
Network SSID: Enter the SSID you configured for the Master radio. All radios
in a network must have the same SSID.
Security Settings
Encryption Type: Encryption scrambles data so that only intended viewers
can decipher and understand it. Choose the same encryption type you
configured for the Master radio.
WPA phrase: Enter the pass phrase you configured for the Master radio.
Important: The Network SSID and WPA phrase are case sensitive. Use exactly the same
combination of upper case and lower case letters you entered for the Master radio, otherwise the
Repeater radio will not be able to connect to the Master radio.
Page 24 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 25
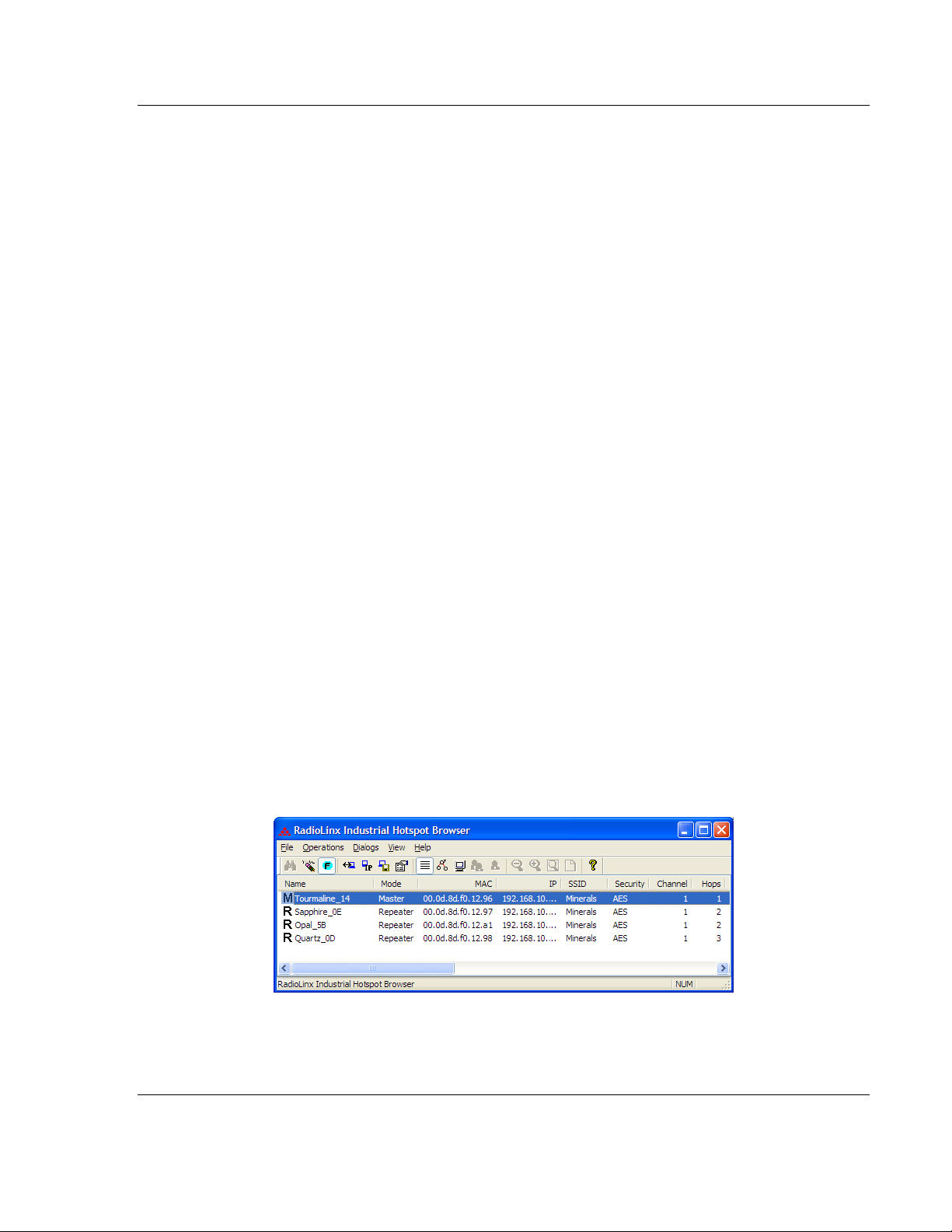
RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Start Here
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
By default, a repeater connects automatically to the best available parent radio
on the network. If necessary, however, you can click the Parent Link button and
specify how repeater radios connect to the network. See Parent Link settings for
information.
1.7.8 Set Up a Client
Client mode is a special mode in the radio that allows a user to connect an
Ethernet device to a wireless network through any 802.11a access point. Any
Ethernet device that has an RJ45 Ethernet port can, in effect, be transformed into
an 802.11a wireless client by attaching the radio. Only a single device can be
connected to the radio in client mode. Do not connect to more than one Ethernet
device (using a switch or hub).
You only use client mode if you need to connect to another brand 802.11a
access point. If you are using RLXIB-IHA radios, you should always use them as
repeaters (and masters).
To connect a device to a radio in client mode, click the Client button for the radio
and try programming the radio’s client mode using the Auto setting. To test
whether the Auto setting will work:
1 Connect the cable between the device and the radio.
2 Turn ON the radio power, or cycle the power if the radio is already on.
3 Turn ON the device. Watch the radio to see if it initializes. The Auto setting
will work if the device advertises its MAC ID to the radio.
If the radio’s RF LEDs do not show consistent activity after a few minutes, then
you may need to modify the radio’s client settings. Click the Specify radio button,
determine the MAC ID of the Ethernet device, and type the ID into the Client
MAC field.
Client radios are preceded by a 'C' in the list of radios in the RLX-IH Browser.
1.8 Verify Communication
When configured, the name of each radio is preceded by an M (for Master), an R
(for Repeater), or a C (for Client) in the IH Browser window.
Look at the LEDs to ensure good link quality, as explained in LED display (page
32). After a repeater is configured, you can unplug the Ethernet cable from it.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 25 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 26

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
Page 26 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 27

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Installing the Radios
In This Chapter
Connecting antennas ............................................................................ 28
Testing the Network Installation Plan .................................................... 28
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
2 Installing the Radios
If possible, you should configure all the radios side by side in an office setting
and make sure they link before you install them in the field. If feasible, it would be
even better if you could set up the entire system in the office and make sure your
equipment communicates properly through the radio network.
Important: If the radios are close enough to each other that their received signal strength is
greater than -40dBm, performance may be degraded. Disconnect antennas from radios during
bench testing, or move the radios further apart from each other.
Tip: To make it easier to physically identify the radios you are configuring, apply a label to each
radio indicating the radio name and IP address.
After you have configured each radio using IH Browser and the web configuration
form, you can install the radios and test their performance. Install the radios in
their proposed permanent locations, then temporarily place each radio’s antenna
near its proposed mounting location. The temporary placement of the antenna
can be by hand; however, with this testing method, one person must hold the
antenna while another monitors the radio’s signal strength.
To see how a radio is linked in the network, make sure that the radio is
connected to a PC, and then select Topology View from the View menu in the
RLX-IH Browser.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 27 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 28

Installing the Radios RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
The Topology view shows a diagram of the network’s wireless connections. Use
this view to see whether all the radios are linked, and that you approve of the
way the radios are linked. A radio that is not linked to a parent will show as a
circle outlined by a flashing dashed red line. It may be near the bottom of the
window, so scroll down to view all available radios. To change how radios link to
the network, see Parent Link settings.
Refer to Improve Signal Quality (page 35) for more information on overcoming
poor connectivity.
2.1 Connecting antennas
Each radio must have an antenna connected to the Main antenna port on the
RLXIB radio; without an antenna for each radio, the network will not function.
All antennas for radios that communicate directly with each other should be
mounted so they have the same antenna polarity. Small antennas with a reversepolarity SMA connector can be mounted directly on the radio. Screw the antenna
onto the antenna port connector until it is snug.
Larger antennas and antennas that do not have a reverse-gender SMA
connector must be mounted separately and connected to the radio using a
coaxial antenna cable. Because the antenna cable attenuates the RF signal, use
an antenna cable length that is no longer than necessary to ensure optimum
performance.
Important: If the radio is to be used in a hazardous location, the radio must be mounted in an
enclosure approved for hazardous locations. The radio requires a separate cable connection to the
SMA connector that leads to an internal antenna.
2.2 Testing the Network Installation Plan
Test proposed installations before finalizing the installation.
After you have configured the network and the radios:
install the Master radio in its proposed permanent location
cable the Configuration PC to the Master radio
place the Remote radios in their proposed locations
temporarily place each radio's antenna near its proposed mounting location.
The temporary placement of the antenna can be by hand, however, with this
testing method, one person must hold the antenna while another monitors the
Remote radio's signal strength as displayed on the Configuration PC.
To improve the signal quality of each Remote's communication:
increase the height of the antenna's placement
use higher-gain antennas
increase the radio's transmission power, cable the radio to the Configuration
PC, and reconfigure it
select a new location for the Remote radio and/or its antenna
decrease the length of antenna cable
Page 28 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 29

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Installing the Radios
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
determine and resolve sources of "electrical" noise which may be interfering
with the radio transmission
add a repeater between the radios that are not communicating, or reconfigure
an existing radio as a repeater if line of sight is available
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 29 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 30

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
Page 30 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 31

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
In This Chapter
Diagnostics ............................................................................................ 31
Check the Ethernet cable ...................................................................... 32
LED display ........................................................................................... 32
Retrieve the default password ............................................................... 33
Troubleshoot IH Browser error messages ............................................. 34
Troubleshoot missing radios .................................................................. 34
Improving Signal Quality........................................................................ 35
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
3 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Use the program’s diagnostic and signal strength settings at the top of the Radio
Settings window to make sure the network is working properly.
Signal Strength graph: This setting graphically shows the radio’s signal
strength. The graph will show the word Master if a master radio is selected.
The graph will show the word Scanning if the radio is scanning to find another
radio to which to connect. If the radio is not connected to a network and not
currently scanning, the graph will show the words Not connected.
Update readings every: If you want to update the diagnostic readings
according to a particular interval, specify the interval (in seconds) in this field.
Read-only fields that appear with the diagnostic settings.
You can perform the following troubleshooting routines:
Check the Ethernet cable (page 32)
Retrieve the default password (page 33)
For more troubleshooting information, go to the ProSoft Technology web site at
www.prosoft-technology.com
3.1 Diagnostics
The Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility (the web configuration form for the
radio) provides information that can help you troubleshoot problems with the
radio.
Use the program’s diagnostic and signal strength settings at the top of the Radio
Settings window to make sure the network is working properly.
Signal Strength graph: This setting graphically shows the radio’s signal
strength.
The graph will show the word Master if a master radio is selected.
The graph will show the word Scanning if the radio is scanning to find
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 31 of 123
July 25, 2013
another radio to which to connect.
Page 32

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
LED
Description
Power
This green LED indicates that the radio has power.
RF Transmit
This yellow LED indicates RF transmission.
RF Receive
This green LED indicates RF reception.
Serial
Reserved for future use.
Ethernet
If this green LED is lit, the Ethernet cable is connected. If this LED is flashing, an
Ethernet packet is being transmitted or received.
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
If the radio is not connected to a network and not currently scanning, the
graph will show the words Not connected.
Update every: If you want to update the diagnostic readings according to a
particular time interval, specify the interval (in seconds) in this field. After entering
the new value, press Enter only if you want to save the new value; press Tab or
click elsewhere to use the new value temporarily.
The following configuration forms in the Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
provide information about current radio operation:
Address table (page 43)
Port status (page 44)
Available Parents (page 42)
Read-only fields (page 40)
The following topics describe troubleshooting routines:
Check the Ethernet cable (page 32)
Retrieve the default password (page 33)
Troubleshoot IH Browser error messages (page 34)
Troubleshoot missing radios in the IH Browser (page 34)
For more troubleshooting information, visit the ProSoft web site at
www.prosoft-technology.com
3.2 Check the Ethernet cable
If you connect a radio and the Ethernet LED does not light on the radio, there
may be a problem with the Ethernet cable. Verify that the cable is plugged into
the radio at one end, and to an Ethernet hub or a 10/100 Base-T Ethernet switch
at the other end. If using the PoE injector, verify that the M12 to RJ45 cable is
connected between the radio and the injector and also that the Ethernet patch
cable is connected between the injector and switch.
Note: The RLXIB-IHA radio auto-detects the Ethernet connection type, and does not require a
crossover cable for direct connection to a PC.
3.3 LED display
The RLXIB-IHA front panel includes a set of LEDs that indicate the radio’s status:
Page 32 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 33

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
LED
Description
Signal Strength
If only one of these three LEDs is lit, then the radio is linked. If two LEDs are lit,
the radio’s signal strength is fair. If all three LEDs are lit, the signal strength is
good.
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
If a radio is configured as a master, the middle light of the three Signal Strength
LEDs will always be on, and the bottom Signal Strength LED will always be off.
The top LED on the master will flash if any radios are linked to this master.
After you first plug in the power cable and Ethernet cable to the radio, the
Power/Status LED should be green, meaning that the radio has power. If the
Ethernet LED is green, then the Ethernet connection is working. The RF Transmit
and RF Receive LEDs should blink.
All three LEDs will blink just after the radio links to the Master’s signal but before
it has been fully authenticated. Normally you will see this last only a few seconds.
If it lasts longer or never turns solid it usually means the encryption keys are not
correct.
3.4 Retrieve the default password
If you forget your password, you will be unable to change the radio settings. You
can retrieve the default password to use the software again, but you will lose all
the settings you programmed before. To retrieve the default password and return
the radio to its default settings, follow these steps:
1 Turn off power to the radio.
2 Locate the reset button hole, located to the left of the power connector.
3 Insert the end of a paperclip or similar device into the hole to press the reset
button.
4 Turn on power to the radio, and hold down the reset button for 30 seconds.
5 The radio will be reset to its default settings, including the password. You
should now be able to log in using the default password, which is "password".
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 33 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 34

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
3.5 Troubleshoot IH Browser error messages
One error message commonly occurs when you use the IH Browser, "Unable to
scan for AP's". You can easily remedy this error.
This error occurs when the IH Browser attempts to scan for radios and no valid
network connection exists on the PC, wired or wireless.
To correct this error, Confirm that your PC has at least one active network (LAN)
connection; it could be a wired Ethernet connection or a wireless 802.11
connection. One way to determine if your network connections are active is to
look in the system tray in the lower-right corner of your desktop. The two-PC icon
indicates a connection and the icon with a red X indicates an inactive connection.
If no connections are visible in the system tray, check Network Connections in
the Control Panel.
Confirm that the network connection has a valid IP address. Your network
connection might need to have a static IP address assigned to it. Check the IP
address of your network connection to determine that one has been assigned.
3.6 Troubleshoot missing radios
If radios are not visible in the IH Browser, try the following:
First, click the SCAN button again. Scans are sent as broadcast messages,
which can be dropped in RF connections, requiring the user to scan again.
Second, disable any software firewall running on your PC (This is most
common in Windows XP and newer). Open the NETWORK CONNECTIONS
folder in your Windows Control Panel, then open the LOCAL AREA
CONNECTION PROPERTIES window and verify that the check box under
INTERNET CONNECTION FIREWALL is not checked.
If the preceding approaches do not help, the PC running the IH Browser and
the radios are probably not connected to the same local network. Verify your
connections.
If you are in topological view, any unlinked radios may be at the bottom of the
window. Scroll down to see all radios. If you still cannot see radios with the IH
Browser, call technical support.
Page 34 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 35

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
3.7 Improving Signal Quality
If you need to improve a radio’s signal quality, try the following steps:
Adjust the direction of the high-gain antennas.
Increase the height of the antenna’s placement.
Use higher-gain antennas or external preamplifiers.
Select a new location for the radio and/or its antenna.
Decrease the length of the antenna cable.
Determine and resolve sources of interfering electrical noise.
Add a repeater between radios that are not communicating.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 35 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 36

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
Page 36 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 37

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
In This Chapter
Radio Status .......................................................................................... 40
Radio Network settings.......................................................................... 46
Security settings .................................................................................... 59
Radio access settings ........................................................................... 62
Apply Changes ...................................................................................... 65
Cancel Changes .................................................................................... 65
Factory Defaults .................................................................................... 65
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
4 Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
The RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot radio has a built-in Radio Configuration /
Diagnostic Utility (radio web configuration form) that allows you to configure the
radio from any computer that can connect to the radio, through a wired Ethernet
connection, or through a Wireless connection.
You can use a web browser such as Microsoft Internet Explorer or Firefox on
your network-enabled desktop computer, laptop or Personal Data Assistant
(PDA) to monitor and change the settings within the RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot
radio.
To open the Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
1 In the RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser, select the radio to configure from
the list view or topography view, and then click the right mouse button to
open a shortcut menu.
2 On the shortcut menu, choose Connect. The Radio Configuration / Diagnostic
Utility will open in your web browser.
Or,
Double-click the selected radio to launch the Radio Configuration / Diagnostic
Utility.
You can also open the Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility directly from your
web browser.
Important: Your desktop computer, laptop, or PDA must be connected to the same network as the
RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot radio.
1 Open your web browser.
2 In the address bar, type "http://", followed by the IP address for the radio,
and then click the "Go" button. For example,
http://192.168.6.10
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 37 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 38

Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
Read-Only fields
Some of the fields on the Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility form are readonly, meaning that the content of the field is provided for information only, and
cannot be directly modified. Notice also that depending on the way the radio is
configured, some fields and buttons may be unavailable because they do not
affect the configuration you have selected. Review the topics in this section for
more information on when and how to use each configuration option.
Configuration Help
Help is available for each item in the Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility.
To view a brief help message about any field on the screen, move your
mouse pointer over the field, or use the [Tab] key, and refer to the text that
appears at the bottom of the screen.
Page 38 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 39

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
To view more help about the selected field, click the field name. This action
opens a help page in a new browser window.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 39 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 40

Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
To view the complete online documentation for your RLXIB-IHA Radio, click
the button. This action opens the online documentation in a new
browser window. Use the Contents, Index and Search tabs in the left frame to
navigate the help system.
Page 40 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 41

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
Field
Description
Radio Name
The name of the selected radio.
Radio MAC
The MAC address of the selected radio. The MAC ID is also printed on
the side of the radio.
Firmware
The version of firmware currently installed. All radios on the network
must have the same firmware versions installed. For more information
on firmware versions, refer to Update firmware (page 73).
Update every
This value in seconds controls how often the web configuration form
automatically refreshes. To change the value temporarily, enter the new
value and press the [Tab] key. To change the value permanently, enter
the new value and press the [Enter] key.
Up Time
The length of time the radio has operated since the last system powerup or last system reset.
Signal Strength
Strength of the signal from the Parent radio.
Parent MAC
The MAC address of the parent radio to which the selected radio is
linked.
Branch Length
The number of RF links from the radio to the master radio.
# Radios Linked
The number of other radios that are linked to this radio.
Link Time
The length of time the radio has been continuously connected to a
parent radio.
Available Parents
Click this button to view the list of Access Points (Parents) from which
this radio can detect beacons. This button is only available when the
radio type is Repeater.
Address Table
Click this button to view a list of MAC addresses for devices entered in
the radio’s address table.
Port Status
Click this button to view spanning tree status of each switch port, for RF
ports and the RJ45 (Ethernet) port.
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
4.1 Radio Status
The general radio status fields appear at the top of the Radio Configuration
window.
Note: Different versions of the RLXIB Radios support different functionality. You may see more or
fewer options on this page, depending on the version of the radio you purchased.
Use the settings in the Radio Status panel to view the current settings for this
radio.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 41 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 42

Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
Field
Description
Only Show Same SSID
Select (check) this box to restrict the list of available parents to those
with the same SSID as the radio you are configuring.
Refresh
Click this button to re-scan the network and update the devices in the
list.
Mac ID
A unique hexadecimal number that identifies any Ethernet device.
SSID
Network Name (Service Set Identifier).
Channel
The radio channel on which the device is transmitting. The channel list
indicates the channel number as well as the frequency (5 gHz).
RSSI
Received Signal Strength Indication.
Security
The encryption type enabled for the device.
Speed
The IEEE 802.11 connection speed.
Cost
Parent selection cost.
Age
The length of time (in seconds) since the radio last saw a packet from
this MAC address
Hops
The number of hops to the Master. A value of 0 (zero) is shown for
non-ProSoft devices.
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
4.1.1 Available Parents
This page opens when you click the Available Parents button on the Radio
Configuration Form.
Note: This form is not available when the radio type is Master.
This page is helpful for viewing:
Possible parents for a repeater. The current parent should normally be the
radio with the lowest cost and a matching SSID.
Other 802.11 networks in the area.
This list contains both 802.11 devices that are part of the same SSID as the
RLXIB-IHA itself (for example, "Minerals") as well as devices that belong to
different SSIDs (for example, "Network1" and "ProSoftInternal"). This list is
updated continuously and can be used for many purposes.
Page 42 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 43

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
Field
Description
Radio MAC
The MAC address of the selected radio. The MAC ID is also printed on
the side of the radio.
Show Addresses for the
Following
Use this dropdown list to filter the address list. Options are:
Devices Out Ethernet Port
Directly Linked Radios/Clients
Devices beyond Direct RF Links
When the table is filtered to show only Directly linked radios/clients, an
additional RSSI column is listed, showing the Received Signal Strength
from each radio or client linked to the radio.
Number of Rows to
Display
Use this field to choose how many MAC addresses to display on this
page. Use the Next and Prev buttons to scroll through the available
MAC addresses.
Index
Position in the list. Each page shows up to 10 devices. Use the Next
and Previous buttons to move up and down through the table.
MAC Address
The MAC address for the device.
Connection
The connection type
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
The IH radio updates this list with each 802.11 packet that is received, whether
from a radio of the same network or one that belongs to another SSID. It can also
see radios from other vendors.
Once per second the IH radio evaluates the link it has to its parent to determine if
this link is the best parent to use. A cost is calculated for each entry and can be
seen in the column labeled "Cost" in the preceding table. The cost calculation is
based not only on the strongest signal, but on several other factors to provide
optimum network communication.
4.1.2 Address table
The Address Table shows the port through which each MAC address is
connected, along with the age in seconds since the radio last saw a packet from
this MAC address.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 43 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 44

Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
Field
Description
Age (s)
The length of time (in seconds) since the radio last saw a packet from
this MAC address
Top
Click the Top button to see the top of the table. The radio will display
updated data in the table entries.
Next / Prev
If the table has more MAC addresses than it can display in the window,
use the Next and Prev buttons to move up and down through the table.
Refresh
Click Refresh to update the table.
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
4.1.3 Port status
This configuration page opens when you click the Port Status button on the
Radio Configuration form.
When you click the Port Status button, you can see information about all the
active ports on the radio. Above the table, you can see information about the
current Spanning Tree (page 54), including the MAC address of the "root" device,
and the timing parameters that are set for the current Spanning Tree. Each radio
can have up to 34 active ports—one Ethernet cable, one parent RF link, and up
to 32 child RF links.
The primary reason for creating a Spanning Tree is that it allows you to create
fully redundant paths. If any single radio in a redundant path loses its connection,
another path still exists, and the connection will be updated and communication
restored.
Page 44 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 45

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
Field
Description
Spanning Tree Protocol:
Wireless Ports
The Spanning Tree Protocol level for the wireless port (Rapid STP or
STP).
Ethernet Port
The Spanning Tree Protocol level for the Ethernet port (Rapid STP or
STP).
Spanning Tree Root MAC
The MAC ID of the root device in the spanning tree.
Priority
The Spanning Tree device with the lowest-priority value is elected the
root of the tree
Max Age
The length of time a port can stay enabled without any new spanning
updates.
Hello Time
The length of time between the transmission of spanning update
packets.
Forward Delay
The length of time a port must listen for spanning information before
being activated.
#
Position in the list. Each page shows up to 10 ports. Use the Next and
Previous buttons to move up and down through the table.
Connection
This field indicates what the port represents: Ethernet, a parent radio, or
a child radio.
State
The current Spanning Tree state of the port. Possible states are
Blocking, Learning, Listening, and Forwarding. Forwarding packets can
be transferred.
Designation
The Spanning Tree designation for the branch off the port. Possible
designations are Root (ports going to the root), Designated (ports going
to a branch), or Normal.
Path Cost
The cumulative cost of all wired and wireless links from the port to the
Spanning Tree root.
Designated Bridge
The next bridge toward the Spanning Tree root for this port.
Top
Click the Top button to see the top of the table.
Next / Prev
If the table has more ports than it can display in the window, use the
Next and Prev buttons to move up and down through the table.
Refresh
Click Refresh to update the table.
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
The following illustration shows the RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser (page
66) application provided with the radios. Notice it shows the radio named
Hermatite_4F, linked to Amethyst_BD. This link is shown with a red dotted line.
Also visible is the level of redundancy in their network. Each of the blue lines
represents an alternate parent. From this view, you can easily tell how much
redundancy exists in their network.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 45 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 46

Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
To display the redundant paths, select the toolbar button denoting two "parents."
To view the redundancy on a per-radio basis, select the single "parent" button,
and then click on the radio to view its available redundancies.
4.2 Radio Network settings
The following fields appear in the Radio Network Settings area at the left side of
the Radio Configuration window.
Note: Different versions of the RLXIB Radios support different functionality. You may see more or
fewer options on this page, depending on the version of the radio you purchased.
Page 46 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 47

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
Field
Description
Radio Name
Assign a unique name to each radio.
Network SSID
Assign a network name (SSID) of up to 32 characters. The radio uses
this name in all network references. All radios in a network must have
the same SSID. SSID names are case-sensitive.
Master
Click this button to configure a radio as a master. The master is the root
radio in a network. You must have at least one master radio per
network. For redundancy, you can assign more than one master to a
network. For information, see Redundancy,
Channel list (master
radio)
The channel list indicates the channel number as well as the frequency
(5 gHz).
Repeater
Click this button to configure a radio as a repeater. The repeater mode
is the normal radio mode for the network, while the master mode is
more of a special setting to establish the network channel and define
the root of the network tree. Repeater radios help extend the range of a
network and help create the signal "bridges" that allow networked
radios to communicate. All RLXIB-IHA radios are capable of repeating.
Parent Link settings
Click this button to specify how a repeater radio connects to the
network. For information, see Parent Link settings.
Client
This is a special mode that allows you to connect an Ethernet device to
any 802.11a access point. You would only use this mode in the special
event that you wanted to connect a device to another brand access
point. For information on setting up a client, see Configuring clients.
Auto / Specify
Only choose "specify" if device does not send out any unsolicited
Ethernet packets. Try Auto first.
Client MAC
The MAC ID of the device connected to the radio, only if the device
does not advertise its MAC address.
IGMP
Click this button to open the IGMP Settings form. Use this form to
enable (default) or disable IGMP, and to configure how the RLXIB-IHA
radio will be have when IGMP is enabled.
Spanning Tree
Click this button to open the Spanning Tree Settings form.
Advanced Config
Click this button to open the Advanced Settings form.
Serial Settings
Click this button to open the Serial Settings form.
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
Use the settings in the Radio Network Settings panel to configure the radios in
your network. For more information on using these settings, see Configuring the
radios (page 16).
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 47 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 48

Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
Field
Description
Parent MAC
The MAC Address of the radio’s Parent node.
Parent Selection Method
Automatically Choose
Best
The Automatic Parent Selection algorithm uses a calculation to create
a cost for each possible parent radio that it detects.
In the calculation the radio includes,
RSSI - Stronger signals receive a better cost.
Hop Count - Fewer hops from the Master radio is given preference
and therefore a lower cost
Choose this setting to allow the radio to determine the best parent to
select.
Parent Branch Length
With the branch length setting the IH will choose its parent strictly by
the number of repeaters between it and the Master radio. If Branch
Length of 1 is chosen, the IH will link only to the Master radio. If Branch
Length of 2 is chosen, the IH will link only to an IH that is linked to the
Master radio, and so on.
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
4.2.1 Parent Link Settings
This configuration page opens when you click the Parent Link button on the
Radio Configuration form.
Page 48 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 49

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
Field
Description
Preferred Parent
With the preferred parent setting the IH radio will select its parent from
a list of possible parents specified by the user. The user can list up to
eight radios to choose from.
Best in List
When Best in List is selected the IH will select its parent using the
"Automatic Parent Selection" algorithm, but it will limit the selection
to the list of radios in the list. Therefore, the radio in the list with
the lowest cost according to the algorithm will be chosen as its
parent.
Follow List Priority
When Follow List Priority is chosen the IH will select its parent
from the list giving preference to the 1st entry followed by the 2nd
entry and so on.
Parent Selection Parameters
Signal Strength Threshold
When the signal from a parent reaches a high enough value, a stronger
signal will not improve the quality of the link any further. For signals
that are above that threshold, only fewer hops from the Master give
preference. You can adjust that threshold here.
Rate to Parent
The default setting is auto which allows the radio to select the best rate
to use to the parent radio, and adapt over time. You might specify a
fixed rate rather than auto for example if the link to the parent has a low
signal strength in which case fixing a lower rate can improve
performance. The actual rate used between this radio and its parent is
the lower value of this setting and the Max Data Rate setting in the
parent (see Max Data Rate). So use these two controls in conjunction if
desired to tailor the rate of each parent link.
Save
Saves your changes and updates the radio configuration.
Cancel
Discards your changes without updating the radio configuration.
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
When you save a selection and return to the Radio Network Settings panel,
notice that your selection is indicated under the Parent Link button.
The Automatic Parent Selection algorithm uses a calculation to create a cost for
each possible parent radio that it detects. The following graph describes how the
cost is calculated when the signal strength threshold is set to -60 dBm.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 49 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 50

Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
Once per second the RLXIB-IHA radio evaluates the link it has to its parent to
determine if this link is the best parent to use. A cost is calculated for each entry
and can be seen in the column labeled "Cost" in the preceding table. The cost
calculation is based not only on the strongest signal, but on several other factors
to provide optimum network communication.
Prioritized Parent Selection
If you need more control than the automatic algorithm allows, you can also define
a priority list of parents for the IH Radio to choose.
Prioritized Parent by Branch Length
With Parent Branch Length, the IH will choose its parent strictly by the number
of repeaters between it and the Master radio. If Branch Length of 1 is chosen, the
IH will link only to the Master radio. If Branch Length of 2 is chosen, the IH will
link only to an IH that is linked to the Master radio, and so on.
Page 50 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 51

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
Prioritized Parent by Preferred Parent List
With Preferred Parent, the IH radio will select its parent from a list of possible
parents that you specify. You can list up to eight radios to choose from.
Best in List
The IH will select its parent using the "Automatic Parent Selection" algorithm
described above but it will limit the selection to the radios in the list. The radio
in the list with the lowest cost according to the algorithm will be chosen as its
parent.
Follow List Priority
The IH will select its parent from the list giving preference to the first entry,
followed by the second entry, and so on.
4.2.2 IGMP Settings
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 51 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 52

Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
Field
Description
IGMP Multicast Filtering
Disabling filtering will cause the radio flood multicast packets to all
ports.
Default Propagation
Action
Determines how to handle multicast addresses that are not in the
radio’s address table.
IGMP Query Generation
Enables or disables query generation from this radio.
IGMP Query Interval
Number of seconds between queries (if not pre-emptied by another
devices queries).
Multicast State Count
Number of queries generated before a device is removed from the
multicast group on this radio if no response is received.
Save
Saves your changes and updates the radio configuration.
Cancel
Discards your changes without updating the radio configuration.
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
RLXIB-IHA radios support IGMP v1 and v2. The default operation of the RLXIBIHA radios is to have IGMP functionality enabled, although the user can disable
IGMP entirely. Additionally, the user can specify settings associated with IGMP
filtering and snooping. Unknown multicast addresses can be sent to all ports
(flood) or to none (filtered) by changing the IGMP Multicast Filtering option. The
user can specify whether the radio will generate IGMP queries, and configure the
query interval time.
By RFC specification, only one device on a network should generate IGMP
queries. As such, RLXIB-IHA radios will only send a query if another device has
not sent a query within its Query Interval setting, even if Query Generation is
enabled.
4.2.3 Rapid Spanning Tree Functionality
The software’s built-in Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP) functionality enables you to
set up full redundancy between radios or other devices. Spanning Tree shuts off
ports as necessary to prevent loops. If loops are created in an Ethernet network,
packets can be circulated endlessly, consuming all the bandwidth and making
the network unusable.
RSTP allows users to create truly redundant connections between any two points
in the network. The radios detect the redundant paths and keep one connection
alive for communications. If the primary connection fails for any reason, the
secondary connection is quickly transitioned to a state to forward packets,
allowing the network to adapt itself to handle problems without customer
intervention.
RSTP uses active communications between network devices to propagate
changes in the network and to cause transitions to occur much more quickly.
Because RSTP is an IEEE standard, IH radios work in conjunction with wired
Ethernet switches to form a redundant network.
Page 52 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 53

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
Each RSTP device (RLXIB-IHA Radio or Ethernet switch) communicates with
other RSTP devices in the network via packets called Bridge Protocol Data Units
(BPDUs). BPDUs are sent out each of the devices ports. In a wired switch this
would be from each of the Ethernet ports. In an RLXIB-IHA Radio, in addition to
the Ethernet port, each wireless link is considered a port. These BPDUs are the
communications means to allow each RSTP device in the network to make sure
that the proper connections still exist.
In the following illustration, this RLXIB-IHA Radio has 4 RSTP "ports":
Ethernet port (1)
A port for its parent connection (2)
A port for each of its two child connections (11 and 12).
BPDUs are sent out the port at a rate called the "Hello Time". The accepted
standard value for this is 2 seconds. If a radio (or any other RSTP device) does
not get a BPDU for 2 Hello Times, it assumes the RSTP device that had been
there is no longer available. It can then open an alternate path if one is available.
This process is much like the STP process. If other devices on the network are
not operating in rapid spanning tree mode, the radio will revert to normal
spanning tree operation on a per-port basis.
RSTP provides a performance enhancement over STP operation. By
comparison, the radio using the STP algorithm would revert its port to the
listening state, and then to the learning state, before returning to the forwarding
state. Each of these states takes at least 15 seconds, during which the STP
devices are listening for BPDUs to re-negotiate the network topology. The
advantage of using the RSTP functionality is that is uses active handshaking
between adjacent RSTP devices to re-negotiate the network topology. This
process takes one to two seconds.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 53 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 54

Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
Field
Description
Enable Spanning Tree
Spanning Tree is enabled when this box is checked. Without spanning
tree, redundant connections might exist if multiple radio links are
created in parallel with each other. Redundant connections are
blocked only if spanning tree is enabled. Additionally, spanning tree is
used to flush the Ethernet switch table when the network topology
changes as described in the section on Automatic Parent Selection.
Firmware versions 2.5xx and above for RLX-IH, and all versions of
RLXIB-IHA radios also support Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP), and will
default to this mode when enabled.
The recommended setting for spanning tree is "Enabled".
Ethernet Edge Port
Because RSTP is an active protocol, it depends on communication
between RSTP devices. If no RSTP device is connected to the radio’s
Ethernet port, the handshake cannot take place. In this case RSTP
reverts to STP. This means that the Ethernet port will be forced to
adhere to the timer based transition protocol of STP.
Therefore on network transitions and power up, communications will
not be allowed over the Ethernet port for 30 to 45 seconds. This
setting is an indication that no redundant connections exist out this
port and communication can immediately be allowed. If for some
reason a BPDU is received on this port, the RSTP protocol will
negotiate properly and handle any possible redundant paths.
The recommended setting for Ethernet Edge Port is "Enabled".
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
Each RLXIB-IHA Radio contains a switch table, which tells it how to forward
Ethernet packets to get them to their proper destination. When the network
topology changes, the RLXIB-IHA Radio flushes its Ethernet switch table
immediately. This allows it to pass traffic immediately over the new network
topology and learn the configuration in the process. Until the learning is
complete, the packets are broadcast to their destination. As each packet is seen
and the switch table rebuilds, the radios return to directing packets to their
destinations.
4.2.4 Spanning Tree Settings
Page 54 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 55

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
Field
Description
Bridge Times
The values in this list configure the timing intervals to use.
Priority
This setting determines who should be the root of the RSTP. The
RSTP device with the lowest priority becomes the root. The accepted
standard value for this is 32768. If wired switches exist in the network
that support RSTP, they should always be allowed to be the root.
Set this value to 32769 to prevent the radio from being the root over a
wired switch. Use this setting when a radio is configured to be a
Master.
Set this value to 32770 when the radio is configured to be a Repeater.
In this way, if only IHs exist in the network, the Master radio will
become the root.
Hello Time
The rate at which BPDUs are sent out. The industry standard is 2
seconds.
Max Age
Measures the age of the received protocol information recorded for a
port and ensures that this information is discarded when its age limit
exceeds the value to the maximum age parameter recorded by the
switch. The timeout value for this timer is the maximum age parameter
of the switches.
Forward Delay
Monitors the time spent by a port in the learning and listening states.
The timeout value is the forward delay parameter of the switches.
Path Costs
The RSTP and STP algorithms use a cost to determine which
connections should be used. The "spanning tree" is formed by
determining the least cost paths from any RSTP device back to the
root.
Wireless
To give preference to a wired connection, set the Wireless cost to 200.
Ethernet
To give preference to a wired Ethernet connection, set the Ethernet
cost to 100.
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
You can define multiple master radios on the same network. Then, if one master
radio goes down, any radios linked to it can switch over to the other master, so
the networked radios remain connected and transmitting. In order to be
redundant, the two masters should typically be on the same segment—in other
words, they should be wired together into the same switch. These two masters
can be assigned different channels to increase network bandwidth, but they must
be assigned the same SSID.
Also, because all radios are repeaters, you can set up each radio to be able to
reach a master radio via multiple repeater paths. Then, if a repeater goes down,
the linked radios can use a different path to get back to a master radio.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 55 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 56

Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
Field
Description
Max Data Rate
The maximum data transmission rate, in megabits per second, for this
radio. Available settings range from 1 to 54.
Max Basic Rate
In addition to the Data Rate setting which controls generic data traffic,
the Basic Rate setting adjusts the rate at which control packets such
as Beacons and Acks are sent at as well as packets that need to go to
the whole network such as Broadcasts. Because these packets are
intended for the whole network, the Max Basic Rate setting of the
Master is advertised to each of the radios in the network through
Beacons. Each radio, other than the Master, then inherits the Max
Basic Rate setting of the Master. Therefore the setting only needs to
be made in the Master radio. The setting in each of the other radios is
disregarded.
Immediate Broadcasting
Forward multicast traffic immediately, rather than waiting for specific
time intervals.
Block General Probe
Requests
Do not respond to general probe requests that are not specific to the
radio's SSID.
Range
The Range setting allows the radios to account for round trip delays.
The Range settings should be the same in all radios in the network
and should be at least large enough to account for the length of any
links. However, increasing the Range beyond what is necessary can
cause a slight decrease in throughput.
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
4.2.5 Advanced Settings
This configuration page opens when you click the Advanced Configuration button
on the Radio Configuration form.
It is important to allow many industrial protocols to communicate properly over
the RLXIB-IHA radios. The standard 802.11 AP operation for transmitting
broadcast messages is to accumulate them and transmit them only on specific
time intervals. This allows clients that are in power-save mode to wake up at the
synchronized time interval and receive the broadcast packets. However, the
power-save mode is rarely used in industrial networks. Additionally, many
industrial protocols utilize multicast traffic, which is sent as broadcast messages
over the wireless network. By enabling immediate broadcasting, these multicast
messages are not delayed by the wait for the next time interval to occur before
they can be transmitted. This results in improved network performance.
The settings on this form also allow you to configure the transmission rate and
broadcast mode to optimize this radio's use on an industrial network.
Page 56 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 57

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
Field
Description
TX Power
This sets the output power of the radio.
Save
Saves your changes and updates the radio configuration.
Cancel
Discards your changes without updating the radio configuration.
Field
Description
Serial Encapsulation Mode
None: No serial data encapsulation.
UDP: In UDP mode, programs on networked computers can be used
to send short messages or Datagrams. Once enabled, the serial port
will be used to transmit and receive packets.
NOTE: In UDP mode if a multicast group address is entered in this
field then packets are sent to that address.
TCP Server: In TCP Server mode, only connections from this address
will be accepted. Once the session is established, the serial port is
enabled to transmit and receive packets.
NOTE: To accept connections from any IP address the field should be
set to 0.0.0.0.
TCP Client: In TCP Client mode, a TCP connection will be established
with this address.
When the session is established, the serial port is enabled to transmit
and receive packets.
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
4.2.6 Serial Port Settings
This configuration page opens when you click the Serial Settings button on the
Radio Configuration form.
Use this page to configure the way serial data packets are encapsulated and
transmitted over an Ethernet network.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 57 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 58

Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
Field
Description
Single IP Address
Enter the IP Address or URL of the radio that should receive
encapsulated serial protocol packets.
Range of IP Addresses
Enter up to 4 IP Address ranges for radios that should receive
encapsulated serial protocol packets.
Remote Port Number
Enter the remote UDP port number to use for encapsulated serial data
transmission.
Local Port Number
Enter the local UDP port number to use for encapsulated serial data
transmission.
Delineation Method
None: All data received between packet delineation events is sent to
the remote node in a single network frame.
Time Gap: The minimum time gap between characters that is to be
interpreted as a delineator for a packet. Configure this value in the
EOL Time Gap field.
Character: The particular character sequence in the stream of
characters that indicates the delineator for the packet. Configure this
value in the EOL Delineator field.
EOL Delineator
This field is available when the selected Delineation Method is
Character. Choose the type of delineator to use from the dropdown
list:
Available delineation types are:
Type
Decimal
Hex
Description
Use Text
Any string of characters
CR
13
0D
Carriage Return
ESC
27
1B
Escape
LF
10
0A
Line Feed (New Line / nl)
Null
00
00
Null
Spacebar
32
20
Space
Tab
09
09
Horizontal Tab
EOL Time Gap
This field is available when the selected Delineation Method is Time
Gap; This value configures the length of time in milliseconds that must
elapse after a character is received (from the local attached device)
before that character marks the end of a packet.
NOTE: the smallest value this field can be set to will be limited by the
device and is platform dependent.
Packet Rate (milliseconds)
This parameter sets the minimum time gap that will be interpreted as
an inter-packet space. When detected the characters received up to
that point will constitute a single packet and will be sent to the remote
node. Units: microseconds. Values: 1,000 to 500,000.
Baud Rate
Select the baud rate from the dropdown list. The baud rate on the
radio must match the baud rate on the connected serial device.
Data Bits
Select the number of data bits (5, 6, 7 or 8) from the dropdown list.
The data bits on the radio must match the data bits on the connected
serial device.
Parity
Select the parity (None, Even, Odd, 1 or 0) from the dropdown list. The
parity on the radio must match the parity on the connected serial
device.
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
Page 58 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 59

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
Field
Description
Flow Control
Select the flow control (handshaking) mode (None or Hardware) from
the dropdown list. The handshaking mode on the radio must match the
handshaking mode on the connected serial device.
Stop Bits
Select the number of stop bits (1 or 2) from the dropdown list. The stop
bits on the radio must match the stop bits on the connected serial
device.
Save
Saves your changes and updates the radio configuration.
Cancel
Discards your changes without updating the radio configuration.
Field
Description
Encryption type (page 60)
WPA-AES is the preferred encryption method. It contains the latest
updates to the 802.11 standards for best security. However, some
legacy devices do not yet support these updates. Therefore, you can
choose combinations of legacy methods.
Available encryption types are:
None (not recommended)
WPA-AES - Latest security setting using WPA (pre-shared key)
authentication and AES encryption.
WPA-TKIP - Security setting using WPA (pre-shared key)
authentication and TKIP encryption.
WEP128 - Legacy security setting using a 128-bit key and WEP
encryption.
WEP64 - Legacy security setting using a 64-bit key and WEP
encryption.
WPA phrase (page 60)
Enter a WPA pass phrase of between eight and 63 normal keyboard
characters.
WEP key (page 61)
Enter five normal text characters in the WEP key field
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
4.3 Security settings
Note: Different versions of the RLXIB Radios support different functionality. You may see more or
fewer options on this page, depending on the version of the radio you purchased.
You can assign the following security settings:
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 59 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 60

Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
Field
Description
MAC Filter (page 61)
Check (select) this field to restrict connections by MAC address.
Edit Filter
Opens the MAC filter (page 61) form, allowing you to specify the MAC
addresses of devices to allow in the network.
Hide Network SSID (page
62)
Hides the Network SSID (Network Name) from other 802.11 users.
You can still connect clients to the "hidden" network by typing the
Network SSID.
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
The following topics describe each security setting in more detail.
4.3.1 Encryption type
The preferred encryption type is WPA (WiFi Protected Access). You should only
select WEP (wired equivalency protocol) for use with an older client radio that
only has WEP encryption. For compatibility with clients that do not support WPA,
you can select WPA+WEP128 (bits) or WPA+WEP64 (bits) as the encryption
type. Then the older clients can connect to an access point using the WEP
setting, but new clients will use WPA and the RLXIB-IHA radios will still use WPA
among themselves.
IMPORTANT: If WPA+WEP is selected, some clients using WPA might not be able to connect
unless you use a WEP key other than number 1, due to limitations in these clients. In such cases,
you should set a WEP key other than key 1 and set this same key in all clients that are using WEP.
See WEP key (page 61).
WEP is the original security protocol used by 802.11 networks, but WPA offers
better protection against attacks, for several reasons: WPA distances the
encryption key from the actual data by performing several algorithms to the key
before generating the encrypted data, it performs dynamic key management by
changing keys frequently, and it performs message integrity checks to prevent
forgery and replay.
You can also select WEP 128, WEP 64, or None (no encryption) as the
encryption type, but none of these settings are recommended.
Note: If an RLXIB-IHA is set to use WPA+WEP, it will connect to other radios set to WPA only or
WPA+WEP, but it will not communicate with radios set to WEP only. Likewise, an RLXIB-IHA in
client mode with WPA+WEP selected will not connect to an access point with WEP only selected.
4.3.2 WPA phrase
To use WPA encryption on packets sent between the radios, enter a WPA pass
phrase of between eight and 63 normal keyboard characters. This phrase
automatically generates an encryption key of 128 hexadecimal characters. This
field is only available if you select WPA as the encryption type.
The default WPA-AES Phrase when a module ships is 'passphrase'.
Page 60 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 61

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
Field
Description
Add MAC
Enter the MAC address to add. The address will appear in the list after
you click the Add MAC button.
Delete
Click this button to delete the selected MAC address from the list.
Address
This list contains all the MAC addresses you have added.
Top
Click the Top button to see the top of the list.
Next / Prev
Click the Next and Prev buttons to move up and down through the
address list.
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
4.3.3 WEP key
A key is a set of hexadecimal (hex) or ASCII characters used to encrypt data.
This field is only available if you select WEP as the encryption type. Write down
your WEP encryption key as you create it, because you must enter the same key
on your client.
To create a 64-bit WEP key, enter five normal text characters in the WEP key
field, which converts the characters automatically to 10 hex digits. Alternatively,
you can enter 10 hex digits (0 to 9, a to f, A to F) directly in the WEP key field. To
create a 128-bit key, enter 13 normal text characters, which convert to 26 hex
digits, or enter 26 hex digits (0 to 9, a to f, A to F) directly.
Note: Clients often support more than one WEP key. Packets received can be decrypted using any
one of the keys if programmed, but packets are always transmitted with the "default" WEP key
number. If you set a transmit key number on the RLXIB-IHA, make sure all other radios and clients
have this key programmed. To set keys other than key 1 on some clients using Windows, you
might have to use the Advanced settings.
Programming more than one key on the RLXIB-IHA requires setting the key
number to the key you want to program, entering the key, and saving your
changes. Repeat these steps for each key you want to program, saving after
each one; finally, change to the desired transmit key number if necessary and
save again (If "****" remains in the key field, the previously programmed key will
not be changed when changes are applied)
4.3.4 MAC filter
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 61 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 62

Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
Field
Description
Upload File
To assign the same list of MAC addresses to several radios
conveniently, open a text editor such as Notepad.exe. Enter addresses
in hexadecimal format, one MAC address per line, including periods.
When you finish, save the document. In the MAC Filter window, click
Browse to select the text file, then click Upload File to upload the list of
MAC addresses.
Browse
Click Browse to navigate to a prepared text file of MAC addresses on
the appropriate drive and folder, and click the Upload File button.
Save
Saves your changes and updates the radio configuration.
Cancel
Discards your changes without updating the radio configuration.
Field
Description
Obtain IP address - DHCP
Select this option to allow the radio to obtain its IP address from a
DHCP server.
Use the following IP
address
Select this option to specify a Static IP address to the radio. Enter the
IP address information in the following fields.
IP Address
Enter an IP address that will not interfere with any other devices on the
network. Request a block of IP addresses you can use from your
Network Administrator.
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
4.3.5 Hide Network SSID
If you want your radio network to be hidden from other 802.11 users, click the
Hide Network SSID check box in each radio you want hidden. With the SSID
hidden, your network does not show up when other clients scan for an access
point. You can still connect clients to the "hidden" network by typing the Network
SSID.
4.4 Radio access settings
The following fields appear in the Security Settings area on the right side of the
Radio Configuration window.
In order to configure or diagnose a radio using its built-in Web server or SNMP
agent, both your computer and the radio must have IP addresses, and these IP
addresses must be on the same subnetwork. An IP address is only needed so
you can configure the radio and view its diagnostic settings. Otherwise, the
address is unnecessary.
Page 62 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 63

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
Field
Description
Subnet Mask
Enter the Subnet Mask provided by your Network Administrator.
Default Gateway
Enter the Default Gateway address provided by your Network
Administrator.
Primary DNS
Enter the Primary DNS address provided by your Network
Administrator.
Secondary DNS
Enter the Secondary DNS address provided by your Network
Administrator.
SNMP button
Click this button to open the SNMP (Simple Network Management
Protocol) Agent settings form. Use this form to configure access to
radio network settings through an SNMP agent.
Login Password button
Click this button to change the Login Password for the radio. The
default password is "password". You should change this password,
and keep a record of it in a safe place, to protect the radio from being
reconfigured by unauthorized users.
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
DHCP (Dynamic Host Control Protocol) is a service provided by a server
(typically a router or a firewall) on a local area network. Devices on a network
that supports DHCP can request and receive an IP address from the DHCP
server. RLXIB-IHA radios support DHCP; by default, they attempt to obtain an IP
address from a DHCP server.
If a DHCP server is not available, the radio will not be able to acquire an IP
address automatically, therefore you must assign an IP address, subnet mask
and default gateway to the radio so that it can communicate on the network.
You can also assign a Static (fixed or permanent) IP address to the radio to
make it easier to identify and configure the radio. Static IP addresses are
particularly useful when configuring radios to serve as Access Points, or for
radios that must be accessible through a firewall.
A detailed discussion of TCP/IP networking is beyond the scope of this manual.
Refer to the following Microsoft knowledgebase article for more information:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/164015
4.4.1 SNMP Agent settings
SNMP is a network management protocol that is often used with TCP/IP and
Ethernet. As an alternative to using the Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility,
you can change radio settings and view diagnostics in an SNMP manager
application, if necessary.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 63 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 64

Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
Field
Description
Enable
Click this button to enable the following SNMP Agent settings.
Allow Any Manager
Select this option to allow any user to change the radio settings from
any computer using SNMP.
Allow IP
Select this setting to restrict access to an SNMP manager with a
particular IP address, then enter the IP address in the Allow IP field.
Community String
Enter a "community string" (essentially a password) that a manager
must use to access the radio’s SNMP agent.
Permission
Select the permission level to assign to this radio.
Read only
An SNMP Agent can view but cannot modify radio settings.
Read/Write
An SNMP Agent can view and modify radio settings.
Save
Saves your changes and updates the radio configuration.
Cancel
Discards your changes without updating the radio configuration.
Field
Description
Old
Enter the current password in this field. The default password is
"password" (lower case, no quotes). This entry must exactly match the
current password, otherwise the change will be rejected.
New
Enter the new password in this field. Passwords are case sensitive.
Repeat
Confirm the new password in this field. This entry must exactly match
the password you entered in the "New" field, otherwise the change will
be rejected.
Save
Saves your changes and updates the radio configuration.
Cancel
Discards your changes without updating the radio configuration.
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
The RLXIB-IHA SNMP agent supports SNMP protocol version 1.4 and 2 MIBs:
RFC12133-MIB (partial; internet.mgmt.MIB-2.system, .interfaces, .snmp)
ROMAP-MIB (included on the CD; internet.private.enterprises.romap)
It also supports a selection of standard SNMP traps, including Cold Start, which
is sent when the radio initializes.
4.4.2 Change password
You can enter any alphanumeric value between one and 31 characters. The
password is case-sensitive.
If you forget your password, you will be unable to change the radio settings. To
get the default password again, see Troubleshooting.
Page 64 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 65

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
4.5 Apply Changes
Click the Apply Changes button to save your changes after editing radio
configuration in order for those changes to take effect. When you apply changes,
the radio will shut down and restart using the new settings.
4.6 Cancel Changes
Click Cancel Changes to discard any settings you made during this session.
Note: This button only applies to changes made in the Radio Configuration / Diagnostic window.
Changes made to individual configuration forms (for example, Spanning Tree, Parent Link, and
SNMP Agent settings) take effect when you click the Save button on each of those forms.
4.7 Factory Defaults
Click the Factory Defaults button to reset the radio to the default settings.
Important: This action discards all your radio configuration settings.
You will be prompted to confirm this action before it takes effect.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 65 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 66

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
Page 66 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 67

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser
In This Chapter
Primary radio functions .......................................................................... 68
File Menu ............................................................................................... 69
Operations Menu ................................................................................... 71
Dialogs Menu ........................................................................................ 75
View Menu ............................................................................................. 81
Help Menu ................................................................ ............................. 87
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
5 RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser
The RLX-IH Browser allows you to find any radios connected to your network,
see some of their basic settings, and change the IP address so you can access
the radio’s Web page. For more information, see Primary radio functions (page
68).
When you run the program, the List view (shown in the illustration) appears with
a list of any radios on the same network as the computer running the RLX-IH
Browser. If you do not see a radio you expect to see, click the Scan (page 70)
button in the tool bar or select Scan from the File menu.
The preceding illustration shows the List View. Refer to Topology view (page 82)
to see alternate views.
To clear all the radios from the list, click the Erase button in the tool bar or select
Clear from the File menu. You can then refresh the list by clicking Scan.
If you have trouble viewing radios in the RLX-IH Browser, see Troubleshoot
missing radios (page 34).
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 67 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 68

RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
5.1 Primary radio functions
You can perform the following primary functions on any radio in the list by rightclicking the radio name.
Connect (page 72): Log in to the Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility to
configure a radio or check diagnostics.
Assign IP (page 20, page 72): Assign a temporary IP address to a radio.
Update Firmware (page 73): Update the version of firmware the radio uses.
Start Ping Session (page 74):
Wireless Clients (page 75): View a list of client radios
Ethernet Nodes (page 76): View a list of wired Ethernet nodes connected to the
network
Scan List (page 77): View a list of all the radios detected on the network
(including those from other vendors)
Port Table (page 78):
Event Log (page 78):
Properties (page 79): View the selected radio’s properties.
In addition, there are more options in the File menu.
You can print either a list of the radios' properties or a topology view.
Change how the RLX-IH Browser scans for radios.
Page 68 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 69

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
5.2 File Menu
The following commands are available on the File menu:
Scan Setup (page 69)
Scan (page 70)
Clear (page 70)
Import (page 70)
Export (page 70)
Freeze (page 71)
Print (page 71)
Print Preview (page 71)
Print Setup (page 71)
Exit (page 71)
5.2.1 Scan Setup
The Scan Setup command allows you to change some settings that govern how
the RLX-IH Browser scans for radios. In the top field of the Scan Setup dialog
box, you can adjust how often the program automatically scans for radios. Enter
a value (in seconds) to have the RLX-IH Browser scan at that rate.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 69 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 70

RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
In the New address/range fields, you can adjust how the program scans for
radios. By default, the program sends a broadcast message to all the radios at
the same time, looking for a response. Broadcasts are limited to a local network,
and will not be passed through a router. If there is a router between the PC
running the RLX-IH Browser and the radio to be scanned, the IP address of the
radio or a range of addresses can be added to the scan list. At each interval
determined by the scan rate, each IP address is individually queried.
5.2.2 Scan
The RLX-IH Browser automatically scans for all active radios on the network at a
regular interval, but you can use the Scan command in the File menu to look for
active radios at any time.
5.2.3 Clear
This command clears (deletes) all entries from the IH Browser window.
5.2.4 Import
This command imports an XML file created by the Export command in the
RadioLinx IH Browser.
5.2.5 Export
This command creates and saves an XML file containing the current
configuration and status of all radios discovered by the RadioLinx IH Browser.
Use this command under the direction of ProSoft Technical Services, for
troubleshooting purposes.
Page 70 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 71

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
5.2.6 Freeze
Use this command to temporarily stop the display from updating. This command
is useful for studying network topology and performance without the distraction of
radios and other devices appearing and disappearing from the screen.
5.2.7 Print
Use this command to print the contents of the RadioLinx IH Browser window.
Depending on the view you selected, you can print either a list of the radios'
properties, or a topology view.
5.2.8 Print Preview
Displays a preview of the contents of the RadioLinx IH Browser window. You can
use this to adjust the placement of elements so that they do not span page
boundaries.
5.2.9 Print Setup
Displays the standard Window Print Setup dialog box.
5.2.10 Exit
Closes RadioLinx IH Browser.
5.3 Operations Menu
The following commands are available on the Operations Menu:
Connect (page 72)
Assign IP (page 20, page 72)
Update Firmware (page 73)
Start Ping Session (page 74)
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 71 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 72

RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
5.3.1 Connect
To connect to the Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility and change radio
settings, double-click the radio listing in the RLX-IH Browser after it has been
assigned an IP address (either manually or with DHCP). Alternatively, you can
select the Connect option in the AP Operations menu. Enter your password to
log in to the radio.
5.3.2 Assign IP
Page 72 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 73

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
If the radio is connected to a network with a DHCP server, the radio may already
have an IP address assigned to it. If no address appears, double-click the radio
listing in the RLX-IH Browser or select Assign IP in the AP Operations menu. In
the next window, click OK to accept the temporary IP address, subnet mask, and
default gateway. If necessary, you can enter a particular IP address (see Radio
Access settings (page 62)). After an IP address is assigned, you can configure
radios through the Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility (page 36).
5.3.3 Update Firmware
"Firmware" is the program that runs in the RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
that allows it to communicate and exchange data between devices, using the
radio as a network connection. Different versions of the firmware communicate
with other radios in different ways, and provide different levels of functionality.
In order for your RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot radio to communicate with other
RLXIB-IHA devices, all radios on the network must use the same firmware
version.
To change the firmware version of the radio:
1 Start RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser.
2 Open the Operations menu, and then choose Update Firmware.
3 Enter the password for the radio. This is the same password you use to log
into the radio from the Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility (page 36).
4 Click the Browse button to locate the Image File (firmware version) to update.
Both versions of firmware are available both on the CD that came with in the
box with the radio, and at our web site at www.prosoft-technology.com
5 Click Update to begin copying the new firmware to the radio. Do not
disconnect the cable or turn off power to the radio during this operation.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 73 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 74

RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
5.3.4 Start Ping Session
A Ping Session allows you to run traffic over the radio network between any two
computers running the IH Browser. With it the user can monitor their network
over time.
To start the ping session, enable "Show Ping Stations" on the View menu, and
then highlight one of the other computers visible in the IH Browser. The session
then starts automatically and the Ping Results dialog box opens.
This dialog box displays statistics on the minimum, maximum and average
latency between two points on the network.
Ping Options dialog box
The Ping Options dialog box opens when you click the Show Options button on
the Ping Results (page 74) dialog box. Use this dialog box to choose ping
parameters, logging options, and response to other stations.
Page 74 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 75

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
5.4 Dialogs Menu
The Dialogs menu contains the following commands:
Wireless Clients (page 75)
Ethernet Nodes (page 76)
Scan List (page 77)
Port Table (page 78)
Event Log (page 78)
Properties (page 79)
5.4.1 Wireless Clients
This dialog box opens when you open the AP Dialogs menu and choose
Wireless Clients.
Use this dialog box to see information about wireless clients attached to the
radio.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 75 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 76

RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
5.4.2 Ethernet Nodes
This dialog box opens when you open the AP Dialogs menu and choose Ethernet
Nodes.
Use this dialog box to see information about Ethernet devices attached to the
radios. The following illustration shows a list of Ethernet devices (by IP address
and MAC ID) attached to the Ethernet port of Tourmaline_14. In addition to the IP
and MAC ID it gives an age for each entry, which is the amount of time since a
packet has been heard from that device.
Page 76 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 77

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
5.4.3 Scan List
This dialog box opens when you open the AP Dialogs menu and choose Scan
List.
The scan list is a list of all the radios that this particular radio "hears" on this
channel (via beacons) even if it is not linked to it (different SSID or encryption).
This list shows the same information as the Available Parents (page 42) list in the
Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility.
List entries marked with a "*" indicate the entry is an alternate path, which can
also be seen if the ‘parents' button is selected in the menu bar (blue lines will link
the radio to its alternate parents).
802.11 Access Point Detector
The RLXIB-IHA Radio can be used as an installation tool to analyze the 802.11
environment and provide the user with information on choosing antenna location
and channel selection.
By using the table in the radio, you can mount an RLXIB-IHA Radio with its
actual antenna and use it to report information on every active 802.11 radio in the
area. It will report
Each 802.11 AP heard including SSID
Actual RSSI from each given in dBm
Channel of each radio
Use this information to help choose a channel that is least utilized, or to select
appropriate antenna types and alignments to minimize interference.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 77 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 78

RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
5.4.4 Port Table
This dialog box opens when you open the AP Dialogs menu and choose Port
Table.
The port table is a list of all the active ports on the radio. This list shows the same
information as the Port status (page 44) list in the Radio Configuration /
Diagnostic Utility. Each radio can have up to 34 active ports—one Ethernet
cable, one parent RF link, and up to 32 child RF links.
5.4.5 Event Log
The event log allows you to extract a log from the selected radio. The log shows
a history of the radio. You can save the event log to a file for troubleshooting
purposes.
Page 78 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 79

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
Event Filter
The Event Filter dialog box allows you to include or exclude specific event types
from the event log.
5.4.6 Properties
This dialog box opens when you select a radio, and then open the AP Dialogs
menu and choose Properties.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 79 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 80

RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
Field
Description
Radio Name
The name of the selected radio.
MAC
The physical media access control address for the network interface.
IP, Mask, and Gateway
The radio’s IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway. For
information, see Radio Access settings (page 62).
IP State
Indicates whether a radio’s IP address has been set—"Uninit(ialized)"
or "OK".
SSID
A name that identifies a wireless network. You assign this name when
you configure the radio. The SSID must be the same for all radios on
the same network.
Mode
Indicates whether you designated the radio as a master, repeater, or
client.
Connection
The status of the wireless connection.
Signal
The signal strength, which in this field is a number from 0 to 15.
Hops
The number of wireless connections a radio is from the closest master
radio.
Master
The MAC address of the selected radio’s master radio.
Associations
The number of network elements to which a radio has a wireless
connection.
Bridges
The number of repeaters to which a radio has a wireless connection.
Tx and Rx
The transmission throughput rate and the received throughput rate.
Both rates are measured in kilobytes per second (KB/s).
Software Version and
Boot Version
The versions of the radio’s firmware and its boot code.
Image
The image type can be Primary or Secondary.
Compression
Indicates whether the radio’s firmware images are compressed or not.
Ethernet
The Ethernet connection status, either Attached or Detached.
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
To see additional properties, click the More button.
Page 80 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 81

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser
Field
Description
Channel
The channel that the radio is using, if connected. The channel list
indicates the channel number as well as the frequency (2.4 gHz or 5
gHz).
Important: The RadioLinx RLXIB radio is not supplied with an antenna.
When choosing an antenna for use with the RLXIB radio, you must
choose one that supports the frequency range set in the configuration
for the radio.
Security
Indicates the encryption setting on the radio. See Security settings
(page 59) for information.
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
5.5 View Menu
The View menu contains the following commands:
Tool Bar (page 81)
Status Bar (page 82)
List View (page 82)
Topology View (page 82)
Zoom In (page 84)
Zoom Out (page 85)
Zoom to Fit (page 85)
Show Ping Stations (page 86)
Show Parents (page 86)
Print Area (page 87)
Reset Columns (page 87)
5.5.1 Tool Bar
The Tool Bar near the top of the IH Browser window contains buttons to access
frequently used commands. Hold the mouse button over each button to view a
brief "Tool Tip" explaining the button’s use.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 81 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 82

RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
5.5.2 Status Bar
The Status Bar at the bottom of the RLX IH Browser displays additional
information about the currently selected menu command or tool bar button. On
the right side of the Status Bar, you can see the status of the Caps Lock and
Num Lock keys on your computer keyboard. Use the corner of the status bar to
drag and resize the RLX-IH Browser window.
5.5.3 List View
List View shows a list of all the connected radios in a grid, arranged similarly to
data in a spreadsheet. Resize the window or scroll across to see all of the
available columns. Click between column headers and drag to the left or right to
resize columns. Click on column headers and drag to the left or right to re-order
columns.
Tip: Use the Reset Columns command to restore the column size and order to their default values.
5.5.4 Topology View
To see how radios are connected together in the network, select Topology View
from the View menu. The Topology view shows a diagram of the network’s
wireless connections. If a radio does not appear in the view, it is not connected to
the network. To change the way a radio is linked to the network, connect to it and
make changes through its Web page. For information on these settings, see
Parent Link settings.
Page 82 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 83

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser
Master; always shown at the top
Radio linked to the network
Radio not linked; no parent
An Ethernet connection exists to the radio; does not
indicate the number of devices on the connection
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
In the topology view, you can double-click a radio to log in to the Radio
Configuration / Diagnostic Utility and change the radio’s settings. To view a
radio’s properties, right-click on a radio representation in the topology view and
then select Properties from the resulting menu.
Refer to Topology View key (page 83) for an explanation of the symbols that
appear in this view.
Topology View key
For information on other options that appear when you right-click a radio
representation, see RLX-IH Browser options (page 66).
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 83 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 84

RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
Wireless clients (PCMCIA cards) are linked to this
radio; the number of clients linked is indicated by the
number of boxes
Signal strength; the width of the line is not calibrated
Alternate parents.
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
5.5.5 Zoom In
Use the ZOOM IN command in Topology View to enlarge the size of the items in
the RadioLinx IH Browser window.
Page 84 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 85

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
5.5.6 Zoom Out
Use the ZOOM OUT command in Topology View to to reduce the size of the items
in the RadioLinx IH-Browser window.
5.5.7 Zoom to Fit
Use the ZOOM TO FIT command in Topology View to change the size of the items
so that the entire network fits within the RadioLinx IH-Browser window.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 85 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 86

RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
5.5.8 Show Ping Stations
Ping Stations are other computers running an instance of RadioLinx IH Browser.
To test latency between points on the network, select a ping station, open the
Operations menu, and then choose Start Ping Session.
5.5.9 Show Parents
The show parents function allows you to display the possible alternate parents
for a repeater graphically in the topology view. The link from the repeater to its
current parent will be shown in red. If the repeater can hear other radios in the
network, links to those radios will be shown in blue. This gives a graphical
representation of the number of alternate paths available to a radio should its
parent link go down. A detailed list of each of the alternates can be seen by rightclicking and selecting ‘Scan List'. This list, though, shows not only radios in the
same network but also 802.11 radios on other networks.
By selecting All, alternate paths for all repeaters in the network will be shown. By
selecting One, alternate paths will be shown only for the one repeater that is
currently selected.
Page 86 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 87

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
5.5.10 Print Area
Use the Print Area command to show the border around the area of the IH
Browser window that you can print using the Print command on the File menu.
5.5.11 Reset Columns
Use the Reset Columns command to restore the column size and order to their
default values. You will be prompted to confirm this action.
5.6 Help Menu
The Help menu contains the following commands:
Help Topics (page 88)
About RLX-IH Browser (page 88)
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 87 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 88

RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
5.6.1 Help Topics
Most of the information needed to help you use the RadioLinx IH Browser is
provided in an online help system that is always available whenever you are
running the application.
To view the online help, start the RadioLinx IH Browser, open the Help menu,
and then choose Help Topics.
The RadioLinx IH Browser Help System
The RadioLinx IH Browser has an online help system that works like a web
browser. Each dialog box has its own page in the help system, which explains
each item on the dialog box.
To view the online help, open the Help menu and choose Help Topics.
Many help pages have links that lead you to more information if you need it.
Links are always underlined. Use your mouse to click the underlined text to
"follow a link" and open a help page with more information.
You can use the Search tab to search for words or phrases inside a help file. The
help system shows you a list of help topics that contain the words you typed in
the Search field. Click a topic from the list to view the help page.
You can also use the Index button to see an index of keywords. You can type the
first few letters of a keyword to jump directly to the part of the index you would
like to view. Each keyword is linked to one or more help topics. Click a keyword
to see a list of topics, and then click a topic from the list to view the help page.
5.6.2 About RLX-IH Browser
Use this command to view version information about the RadioLinx IH Browser.
You may be asked to provide this information if you contact ProSoft Technical
Services.
Page 88 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 89

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Reference
In This Chapter
Product Overview .................................................................................. 89
Radio hardware ..................................................................................... 90
Antennas ............................................................................................... 92
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
6 Reference
6.1 Product Overview
The RLXIB-IHA is an industrial high-speed Ethernet radio. You can use it in place
of Ethernet cables to save money, extend range, and make connections that may
not otherwise be feasible. The radio operates as a wireless Ethernet switch, so
any data that you can send over a wired network can also be sent over the radio.
The RLXIB-IHA is certified for unlicensed operation in the United States, Canada
and Europe at 5 GHz. With an output power of a 250mW (typical) approved highgain antennas, the radios can achieve distances of 5 miles line-of-sight between
them. You can use multiple repeaters to extend this range to far greater
distances.
You can develop a highly reliable wireless network by creating redundant (page
54) wireless paths. Multiple master radios can be installed without any special
programming or control. Repeater radios can connect to any master at any time;
if one master goes down, the repeater connects to another. Likewise, if a
repeater goes down, any repeater that was connected to it can reconnect to a
different repeater, keeping the network intact. You can create large, self-healing
tree-like networks in this fashion. Fully redundant paths are possible because the
Spanning Tree (page 54) protocol in the radios disables and enables paths as
necessary to avoid Ethernet loops, which would otherwise make your network
stop functioning.
In addition to acting as a switch, every master or repeater radio in an RLXIB-IHA
wireless network can simultaneously act as an 802.11a access point. This allows
802.11 WiFi clients to connect and roam between radios for monitoring of the
wireless network or general network access. The RLXIB-IHA has a special client
mode (page 25) that allows connection of any Ethernet device to any existing
802.11a access point, regardless of the brand (An example of an 802.11 client is
a laptop with a WLAN card).
Note: WiFi is a brand name originally issued by the WiFi Alliance, used to describe the underlying
technology of wireless_local area networks (WLAN) based on the IEEE 802.11 specifications.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 89 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 90

Reference RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
Label Connect to...
+ 10 to 24 VDC
— DC Ground
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
A high level of security is inherent with AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
encryption. You also can choose TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol), and if
necessary add WEP128 or WEP64 (Wired Equivalent Protocol) encryption in
addition to AES or TKIP for clients that do not support AES. A simple Media
Access Control (MAC) filter table restricts the radios or clients that can link to a
selected radio according to the MAC IDs you enter in the table.
The radio is designed for industrial applications with a metal enclosure, DIN-rail
mounting, and shock and vibration tested to IEC 60068.
The RLXIB-IHA is easy to use. Use the Radio Configuration / Diagnostic Utility,
which runs in your web browser, to configure the radio; optionally, you can use
an SNMP manager for configuration. The radio comes with a Windows-based
utility called RLX-IH Browser that finds all the radios on the network and lists
information about them. A topology view in the RLX-IH Browser shows how the
wireless network is linked together at any point in time. You can update firmware
at any time from anywhere on the network, even over the wireless link or over the
Internet.
ProSoft Technology radios can easily be installed into new or existing systems.
The software and manuals can be downloaded from the CD or ProSoft
Technology’s web site at www.prosoft-technology.com.
6.2 Radio hardware
The RLXIB-IHA radio consists of the following components:
1 One antenna port) (page 28)
2 LEDs (page 32) that indicate the status of the radio
3 Ethernet and serial cable ports (page 92, page 91)
4 Power connection
6.2.1 Radio power requirements
The RLXIB-IHA radio accepts voltages between 10 and 24 VDC, with an average
power draw of less than 9 watts. A detachable power connector comes with the
radio, as shown. The connector terminals are labeled + (positive DC connection)
and - (DC ground connection). You can use the provided AC-to-DC power supply
adapter that is pre-wired with a power connector, or you can use power from
another source, for example the power supply for the PLC or the networked
devices.
The DC power wires must be less than 3 m to meet regulatory requirements.
Page 90 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 91

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Reference
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
The RLXIB-IHA radio accepts 802.3af PoE, with an average power draw of less
than 9 watts. You can also order an optional DC PoE Injector if AC is not
available. The DC power wires must be less than 3 m to meet regulatory
requirements.
The radio shall be installed by trained personnel only, as outlined to the installation instructions
provided with each radio.
The equipment shall be installed by a qualified installer/electrician. The installer/electrician is
responsible for obtaining a secured ground connection between the lug terminal on the surge
protector to a verified common ground point using a minimum 6 AWG gauge wire. This must be
done when attaching power lines to the radio during installation.
A solid ground connection should be verified using a meter prior to applying
power to the radio. Failing to secure a proper ground could result in serious injury
or death as a result of a lightning strike.
Using Power over Ethernet (PoE) to power remote devices has several
advantages including:
"Carrier Class" Power Over Ethernet System.
Power can be supplied over long distances, up to 300 feet.
Power can be available wherever network access is available.
The power supply can be centrally located where it can be attached to an
uninterruptible power supply.
The user has the ability to easily power on reset the attached equipment from
a remote location.
There is no need to run additional power cabling to the device as power can
be supplied over the CAT5 Ethernet cable.
Used for remote mounted radios to save on cost of coax and reduce RF
losses.
Built-in Ethernet Surge protection to prevent equipment damage.
Overload and Short Circuit protection.
6.2.2 Ethernet Cable Specifications
The recommended cable is Category 5 or better. A Category 5 cable has four
twisted pairs of wires, which are color-coded and cannot be swapped. The
module uses only two of the four pairs.
The Ethernet ports on the module are Auto-Sensing. You can use either a
standard Ethernet straight-through cable or a crossover cable when connecting
the module to an Ethernet hub, a 10/100 Base-T Ethernet switch, or directly to a
PC. The module will detect the cable type and use the appropriate pins to send
and receive Ethernet signals.
Ethernet cabling is like U.S. telephone cables, except that it has eight
conductors. Some hubs have one input that can accept either a straight-through
or crossover cable, depending on a switch position. In this case, you must ensure
that the switch position and cable type agree.
Refer to Ethernet cable configuration (page 92) for a diagram of how to configure
Ethernet cable.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 91 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 92

Reference RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
Crossover cable
Straight- through cable
RJ-45 PIN
RJ-45 PIN
1 Rx+
3 Tx+
2 Rx-
6 Tx-
3 Tx+
1 Rx+
6 Tx-
2 Rx-
RJ-45 PIN
RJ-45 PIN
1 Rx+
1 Tx+
2 Rx-
2 Tx-
3 Tx+
3 Rx+
6 Tx-
6 Rx-
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
6.2.3 Ethernet Cable Configuration
Note: The standard connector view shown is color-coded for a straight-through cable.
6.3 Antennas
When you are ready to connect antennas to the radio, see Connecting antennas
(page 28).
You must also consider three important electrical characteristics when selecting
antennas:
Antenna pattern (page 92)
Antenna gain (page 93)
Antenna polarity (page 93)
Antenna location, spacing, and mounting (page 96)
6.3.1 Antenna Pattern
Information between two wireless devices is transferred via electromagnetic
energy radiated by one antenna and received by another. The radiated power of
most antennas is not uniform in all directions and has varying intensities. The
radiated power in various directions is called the pattern of the antenna. Each
antenna should be mounted so that its direction of strongest radiation intensity
points toward the other antenna or antennas with which it will exchange signals.
Complete antenna patterns are three-dimensional, although often only a twodimensional slice of the pattern is shown when all the antennas of interest are
located in roughly the same horizontal plane, along the ground rather than above
or below one another.
A slice taken in a horizontal plane through the center (or looking down on the
pattern) is called the azimuth pattern. A view from the side reveals a vertical
plane slice called the elevation pattern.
Page 92 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 93

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Reference
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
An antenna pattern with equal or nearly equal intensity in all directions is
omnidirectional. In two dimensions, an omnidirectional pattern appears as a
circle (in three dimensions, an omnidirectional antenna pattern would be a
sphere, but no antenna has true omnidirectional pattern in three dimensions). An
antenna is considered omnidirectional if one of its two dimensional patterns,
either azimuth or elevation pattern, is omnidirectional.
Beamwidth is an angular measurement of how strongly the power is
concentrated in a particular direction. Beamwidth is a three dimensional quantity
but can be broken into two-dimensional slices just like the antenna pattern. The
beamwidth of an omnidirectional pattern is 360 degrees because the power is
equal in all directions.
6.3.2 Antenna Gain
Antenna gain is a measure of how strongly an antenna radiates in its direction of
maximum radiation intensity compared to how strong the radiation would be if the
same power were applied to an antenna that radiated all of its power equally in
all directions. Using the antenna pattern, the gain is the distance to the furthest
point on the pattern from the origin. For an omnidirectional pattern, the gain is 1,
or equivalently 0 dB. The higher the antenna gain is, the narrower the
beamwidth, and vice versa.
The amount of power received by the receiving antenna is proportional to the
transmitter power multiplied by the transmit antenna gain, multiplied by the
receiving antenna gain. Therefore, the antenna gains and transmitting power can
be traded off. For example, doubling one antenna gain has the same effect as
doubling the transmitting power. Doubling both antenna gains has the same
effect as quadrupling the transmitting power.
6.3.3 Antenna Polarity
Antenna polarization refers to the direction in which the electromagnetic field
lines point as energy radiates away from the antenna. In general, the polarization
is elliptical. The simplest and most common form of this elliptical polarization is a
straight line, or linear polarization. Of the transmitted power that reaches the
receiving antenna, only the portion that has the same polarization as the
receiving antenna polarization is actually received. For example, if the
transmitting antenna polarization is pointed in the vertical direction (vertical
polarization, for short), and the receiving antenna also has vertical polarization,
the maximum amount of power possible will be received. On the other hand, if
the transmit antenna has vertical polarization and the receiving antenna has
horizontal polarization, no power should be received. If the two antennas have
linear polarizations oriented at 45° to each other, half of the possible maximum
power will be received.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 93 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 94

Reference RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
6.3.4 Whip antennas
You can use a 1/2 wave straight whip or 1/2 wave articulating whip (2 dBi)
antenna with RLXIB-IHA radios. These antennas are the most common type in
use today. Such antennas are approximately 5 inches long, and are likely to be
connected to a client radio (connected directly to the radio enclosure). These
antennas do not require a ground plane. Articulating antennas and nonarticulating antennas work in the same way. An articulating antenna bends at the
connection.
6.3.5 Collinear array antennas
A collinear array antenna is typically composed of several linear antennas
stacked on top of each other. The more stacked elements it has, the longer it is,
and the more gain it has. It is fed in on one end.
The antenna pattern is torroidal. Its azimuthal beamwidth is 360°
(omnidirectional). Its vertical beamwidth depends on the number of
elements/length, where more elements equal narrower beamwidth. The antenna
gain also depends on the number of elements/length, where more elements
produce higher gain. Typical gain is 5 to 10 dBi.
The antenna polarity is linear, or parallel to the length of the antenna.
Page 94 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 95

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Reference
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
6.3.6 Yagi Array Antenna
A yagi antenna is composed of an array of linear elements, each parallel to one
another and attached perpendicular to and along the length of a metal boom. The
feed is attached to only one of the elements. Elements on one side of the fed
element are longer and act as reflectors; elements on the other side are shorter
and act as directors. This causes the antenna to radiate in a beam out of the end
with the shorter elements. The pattern depends on the overall geometry,
including the number of elements, element spacing, element length, and so on.
Sometimes the antenna is enclosed in a protective tube hiding the actual
antenna geometry.
The antenna pattern (page 92) is a beam pointed along the boom toward the end
with the shorter elements. The beamwidth varies with antenna geometry but
generally is proportional to the length (where longer length produces a narrower
beam).
The antenna gain (page 93) varies with antenna geometry but generally is
proportional to the length (where longer length produces higher gain). Typical
values are 6 to 15dBi.
The antenna polarity is Linear (parallel to the elements, perpendicular to the
boom).
Refer to the Antenna Types overview section for other types of approved
antennas.
6.3.7 Parabolic reflector antennas
A parabolic reflector antenna consists of a parabolic shaped dish and a feed
antenna located in front of the dish. Power is radiated from the feed antenna
toward the reflector. Due to the parabolic shape, the reflector concentrates the
radiation into a narrow pattern, resulting in a high- gain beam.
The antenna pattern is a beam pointed away from the concave side of the dish.
Beamwidth and antenna gain vary with the size of the reflector and the antenna
construction. Typical gain values are 15 to 30 dBi.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 95 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 96

Reference RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
The antenna polarity depends on the feed antenna polarization.
6.3.8 Antenna location, spacing, and mounting
Consider the following points regarding antenna location, spacing, and mounting:
When placing antennas, ensure a clear line of sight between the master
radio's antenna and all of the other radio antennas.
If the site base contains obstructing terrain or structures, mount the antenna
on a tower or rooftop to provide a line-of-sight path. The line-of-sight
consideration becomes more important as the transmission path becomes
longer.
Mount the antennas as high off the ground as is practical. The higher an
antenna is above the ground, the greater its range.
Mount the antennas away from massive structures. Radio signals bounce off
metal walls, for example, which can compromise a clear signal.
Mount antennas to minimize the amount of nearby metal structures in the
antenna pattern.
Mount the antennas and install radios away from sources of RF interference.
Use the shortest possible antenna cable length. Signals lose power over the
cable's distance.
Choose antennas that are appropriate for the network's intended function.
If antennas are on radios on the same network, mount them so they have the
same polarity. If the antennas are on separate networks, mount them so they
have a different antenna polarity—for example, mount one antenna vertically
and the other horizontally.
Space radios at least three feet (one meter) apart so they do not overload
each other. If antennas must be near each other:
o Mount omnidirectional antennas directly above each other.
o Position directional antennas so they do not point at nearby antennas.
Place antennas side by side if they point in the same direction. Place
antennas back to back if they point in opposite directions.
Page 96 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 97

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Support, Service & Warranty
In This Chapter
Contacting Technical Support ............................................................... 97
Return Material Authorization (RMA) Policies and Conditions ............... 98
LIMITED WARRANTY ......................................................................... 100
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
7 Support, Service & Warranty
Contacting Technical Support
ProSoft Technology, Inc. (ProSoft) is committed to providing the most efficient
and effective support possible. Before calling, please gather the following
information to assist in expediting this process:
1 Product Version Number
2 System architecture
3 Network details
If the issue is hardware related, we will also need information regarding:
1 Module configuration and associated ladder files, if any
2 Module operation and any unusual behavior
3 Configuration/Debug status information
4 LED patterns
5 Details about the serial, Ethernet or fieldbus devices interfaced to the module,
if any.
Note: For technical support calls within the United States, an emergency after-hours answering
system allows 24-hour/7-days-a-week pager access to one of our qualified Technical and/or
Application Support Engineers. Detailed contact information for all our worldwide locations is
available on the following page.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 97 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 98

Support, Service & Warranty RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
Internet
Web Site: www.prosoft-technology.com/support
E-mail address: support@prosoft-technology.com
Asia Pacific
(location in Malaysia)
Tel: +603.7724.2080, E-mail: asiapc@prosoft-technology.com
Languages spoken include: Chinese, English
Asia Pacific
(location in China)
Tel: +86.21.5187.7337 x888, E-mail: asiapc@prosoft-technology.com
Languages spoken include: Chinese, English
Europe
(location in Toulouse,
France)
Tel: +33 (0) 5.34.36.87.20,
E-mail: support.EMEA@prosoft-technology.com
Languages spoken include: French, English
Europe
(location in Dubai, UAE)
Tel: +971-4-214-6911,
E-mail: mea@prosoft-technology.com
Languages spoken include: English, Hindi
North America
(location in California)
Tel: +1.661.716.5100,
E-mail: support@prosoft-technology.com
Languages spoken include: English, Spanish
Latin America
(Oficina Regional)
Tel: +1-281-2989109,
E-Mail: latinam@prosoft-technology.com
Languages spoken include: Spanish, English
Latin America
(location in Puebla, Mexico)
Tel: +52-222-3-99-6565,
E-mail: soporte@prosoft-technology.com
Languages spoken include: Spanish
Brasil
(location in Sao Paulo)
Tel: +55-11-5083-3776,
E-mail: brasil@prosoft-technology.com
Languages spoken include: Portuguese, English
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
7.1 Return Material Authorization (RMA) Policies and Conditions
The following Return Material Authorization (RMA) Policies and Conditions
(collectively, "RMA Policies") apply to any returned product. These RMA Policies
are subject to change by ProSoft Technology, Inc., without notice. For warranty
information, see Limited Warranty (page 100). In the event of any inconsistency
between the RMA Policies and the Warranty, the Warranty shall govern.
7.1.1 Returning Any Product
In order to return a Product for repair, exchange or otherwise, the Customer must
obtain a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number from ProSoft and comply
with ProSoft shipping instructions.
In the event that the Customer experiences a problem with the Product for any
reason, Customer should contact ProSoft Technical Support at one of the
telephone numbers listed above in Section A. A Technical Support Engineer will
request that you perform several tests in an attempt to isolate the problem. If
after completing these tests, the Product is found to be the source of the
problem, we will issue an RMA.
Page 98 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
Page 99

RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a Support, Service & Warranty
RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot User Manual
All returned Products must be shipped freight prepaid, in the original shipping
container or equivalent, to the location specified by ProSoft, and be accompanied
by proof of purchase and receipt date. The RMA number is to be prominently
marked on the outside of the shipping box. Customer agrees to insure the
Product or assume the risk of loss or damage in transit. Products shipped to
ProSoft using a shipment method other than that specified by ProSoft, or shipped
without an RMA number will be returned to the Customer, freight collect. Contact
ProSoft Technical Support for further information.
A 10% restocking fee applies to all warranty credit returns whereby a Customer
has an application change, ordered too many, does not need, etc. Returns for
credit require that all accessory parts included in the original box (i.e.; antennas,
cables) be returned. Failure to return these items will result in a deduction from
the total credit due for each missing item.
7.1.2 Returning Units Under Warranty
A Technical Support Engineer must approve the return of Product under
ProSoft’s Warranty:
a. In-Warranty returns will be repaired and returned to the customer within 8
weeks of receipt of product at ProSoft’s designated repair location. If upon
evaluating the product it is deemed to be non-repairable due to manufacturing
defect, a replacement will be sent. Should this be the case, a purchase order will
be required prior to shipment. If returning the product to ProSoft for repair has an
adverse affect on customer’s production, ProSoft encourages the customer
purchase a remanufactured unit, if available at discounted pricing to use as a
spare now and in the future.
b. Credit for a product under warranty will be issued upon ProSoft completing
test and evaluation of product at designated location referenced on the Return
Material Authorization If a defect is found and is determined to be customer
generated, or if the defect is otherwise not covered by ProSoft’s Warranty, there
will be no credit given. Customer will be contacted and can request module be
returned at their expense.
i.
7.1.3 Returning Units Out of Warranty
Customer sends unit in for evaluation to location specified by ProSoft, freight
prepaid.
If no defect is found, Customer will be charged the equivalent of $100 USD, plus
freight charges, duties and taxes as applicable. A new purchase order will be
required.
If unit is repaired, charge to Customer will be 30% of current list price (USD) plus
freight charges, duties and taxes as applicable. A new purchase order will be
required or authorization to use the purchase order submitted for evaluation fee.
ProSoft will attempt to repair Products that have transitioned to End of Life and
will be based on availability of components needed to repair the unit(s).
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 99 of 123
July 25, 2013
Page 100

Support, Service & Warranty RLXIB-IHA ♦ 802.11a
User Manual RadioLinx® 802.11a Industrial Hotspot
The following is a list of non-repairable units:
1500 – All
1550 – Can be repaired, only if defect is the power supply
1560 - Can be repaired, only if defect is the power supply
2100-AGA – Can be evaluated, but no guarantee for repair
3150 – All
3170 - All
3250 – All
3300 – All
3350 – All
3600 – All
3700 – All
3750 – All
3800 – All
3850-DNP
4XXX Series – All
7.2 LIMITED WARRANTY
This Limited Warranty ("Warranty") governs all sales of hardware, software, and
other products (collectively, "Product") manufactured and/or offered for sale by
ProSoft Technology, Incorporated (ProSoft), and all related services provided by
ProSoft, including maintenance, repair, warranty exchange, and service
programs (collectively, "Services"). By purchasing or using the Product or
Services, the individual or entity purchasing or using the Product or Services
("Customer") agrees to all of the terms and provisions (collectively, the "Terms")
of this Limited Warranty. All sales of software or other intellectual property are, in
addition, subject to any license agreement accompanying such software or other
intellectual property.
Page 100 of 123 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
July 25, 2013
 Loading...
Loading...