Page 1

3170-PDP
FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
User Manual
August 23, 2007
Page 2
Please Read This Notice
Successful application of this module requires a reasonable working knowledge of the Rockwell
Automation hardware, the 3170-PDP Module and the application in which the combination is to be
used. For this reason, it is important that those responsible for implementation satisfy themselves
that the combination will meet the needs of the application without exposing personnel or
equipment to unsafe or inappropriate working conditions.
This manual is provided to assist the user. Every attempt has been made to assure that the
information provided is accurate and a true reflection of the product's installation requirements. In
order to assure a complete understanding of the operation of the product, the user should read all
applicable Rockwell Automation documentation on the operation of the Rockwell Automation
hardware.
Under no conditions will ProSoft Technology be responsible or liable for indirect or consequential
damages resulting from the use or application of the product.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual, in whole or in part, without written permission from
ProSoft Technology is prohibited.
Information in this manual is subject to change without notice and does not represent a
commitment on the part of ProSoft Technology Improvements and/or changes in this manual or the
product may be made at any time. These changes will be made periodically to correct technical
inaccuracies or typographical errors.
Solid state equipment has operational characteristics differing from those of electromechanical
equipment. "Safety Guidelines for the Application, Installation and Maintenance of Solid State
Controls" (Publication SGI-1.1) describes some important differences between solid state
equipment and hard-wired electromechanical devices. Because of this difference, and also
because of the wide variety of uses for solid state equipment, all persons responsible for applying
this equipment must satisfy themselves that each intended application of this equipment is
acceptable.
The examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for illustrative purposes. Because of
the many variables and requirements associated with any particular installation, ProSoft
Technology, Inc. cannot assume responsibility or liability for actual use based on the examples and
diagrams.
No patent liability is assumed by ProSoft Technology, Inc. with respect to use of information,
circuits, equipment, or software described in this manual.
Throughout this manual we use notes to make you aware of safety considerations.
ATTENTION: Identifies information about practices or
circumstances that can lead to personal injury or death,
property damage, or economic loss.
Attentions help you:
identify a hazard
avoid the hazard
recognize the consequences
Important: Identifies information that is especially important for successful application and
understanding of the product.
Microsoft is a registered trademark of the Microsoft Corporation.
Windows is a trademark of the Microsoft Corporation.
FLEX I/O and PLC-5 are trademarks of the Rockwell Automation Company, Inc.
PROFIBUS is a trademark of the PROFIBUS User Organization
Page 3

Your Feedback Please
We always want you to feel that you made the right decision to use our products. If you have
suggestions, comments, compliments or complaints about the product, documentation or support,
please write or call us.
ProSoft Technology
1675 Chester Avenue, Fourth Floor
Bakersfield, CA 93301
+1 (661) 716-5100
+1 (661) 716-5101 (Fax)
http://www.prosoft-technology.com
Copyright © ProSoft Technology, Inc. 2000 - 2007. All Rights Reserved.
3170-PDP User Manual
August 23, 2007
PSFT.PDP.3170.UM.07.08.23
ProSoft Technology ®, ProLinx ®, inRAx ®, ProTalk® and RadioLinx ® are Registered Trademarks
of ProSoft Technology, Inc.
Page 4

Page 5

Contents 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Contents
PLEASE READ THIS NOTICE.............................................................................................................................. 2
Your Feedback Please ...................................................................................................................................... 3
1 ABOUT THIS USER MANUAL..................................................................................................................... 9
1.1 Purpose ................................................................................................................................................... 9
1.2 Vocabulary............................................................................................................................................... 9
1.3 Publication references ............................................................................................................................. 9
1.4 Related Publications ................................................................................................................................ 9
1.5 Compliance to European Union Directives .............................................................................................10
1.5.1 EMC Directive ...............................................................................................................................10
2 OVERVIEW OF FLEX I/O AND YOUR PROFIBUS ADAPTER MODULE..................................................11
2.1 The FLEX I/O System.............................................................................................................................11
2.2 Mount and Remove your System Easily .................................................................................................12
2.3 Optional Accessories..............................................................................................................................13
2.3.1 Extender Cables (1794-CE1 or -CE3)...........................................................................................13
2.3.2 Mounting Kit (1794-NM1) ..............................................................................................................14
2.3.3 Mounting Dimensions and Spacing Requirements........................................................................15
2.4 Purpose of the 3170-PDP.......................................................................................................................16
2.5 PROFIBUS Adapter Components...........................................................................................................17
2.5.1 Diagnostic Indicators.....................................................................................................................17
2.5.2 Network Connector........................................................................................................................17
2.5.3 Setting the Node Address Switches ..............................................................................................18
2.5.4 Power Wiring.................................................................................................................................18
3 HOW COMMUNICATION TAKES PLACE AND I/O IMAGE TABLE MAPPING........................................19
3.1 Polled I/O Structure.................................................................................................................................20
3.1.1 Adapter Input Status Word ............................................................................................................20
3.2 Mapping Data into the Image Table........................................................................................................22
3.2.1 1794-IB16 – 16-point Discrete Input Module Image Table Mapping..............................................23
3.2.2 1794-OB16 – 16-point Discrete Output Module Image Table Mapping .........................................24
3.2.3 1794-IB8S – 8-point Discrete Sensor Input Module Image Table Mapping...................................25
3.2.4 1794-IA8 – 8-point Discrete Input Module Image Table Mapping .................................................26
3.2.5 1794-OA8 – 8-point Discrete Output Module Image Table Mapping .............................................27
3.2.6 1794-OW8 – 8-point Discrete Relay Output Module Image Table Mapping..................................27
3.2.7 1794-IE8 – 8 Input Analog Module................................................................................................28
3.2.8 1794-OE4 – 4 Output Analog Module Image Table Mapping........................................................30
3.2.9 1794-IE4XOE2 – Analog Combo Module Image Table Mapping ..................................................33
3.2.10 1794-IR8 – RTD Input Analog Module Image Table Mapping .......................................................35
3.2.11 1794-IT8 – Thermocouple Input Module Image Table Mapping....................................................38
3.2.12 1203-FM1 – SCANport Module Image Table Mapping..................................................................41
3.3 Connection Status Word Definition.........................................................................................................42
3.4 Logic Status/Analog Feedback Definition ...............................................................................................42
3.5 Connection Enable Word Definition........................................................................................................42
3.6 Logic Command/Analog Reference Definition........................................................................................42
3.7 Defaults...................................................................................................................................................43
4 CONNECT THE ADAPTER TO THE PROFIBUS DP NETWORK..............................................................45
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 5 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 6

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Contents
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
4.1 The DP Physical Layer ...........................................................................................................................45
4.2 Cabling and Equipment Required for Line A Type..................................................................................46
4.2.1 Cables...........................................................................................................................................46
4.2.2 T-junction Connectors ...................................................................................................................46
4.2.3 Termination Blocks........................................................................................................................46
4.2.4 Bus Connector ..............................................................................................................................46
4.3 Cabling and Equipment Required for Line B Type..................................................................................47
4.3.1 Cables...........................................................................................................................................47
4.3.2 T-junction Connectors ...................................................................................................................47
4.3.3 Termination Blocks........................................................................................................................47
4.3.4 Bus Connector ..............................................................................................................................47
4.4 Connect the Adapter to the Network.......................................................................................................48
4.4.1 Connect to the Adapter .................................................................................................................48
4.5 Terminate the Network ...........................................................................................................................49
4.5.1 Terminate at the Adapter Using Line A .........................................................................................49
4.5.2 Terminate at the Adapter Using Line B .........................................................................................49
5 CONFIGURE THE ADAPTER FOR MASTER/SLAVE COMMUNICATION................................................51
5.1 How Master/Slave Communication Takes Place....................................................................................51
5.2 Entering User Parameter Data ...............................................................................................................52
5.2.1 User Parameter Data ....................................................................................................................52
5.2.2 Auto Configure Format..................................................................................................................53
5.2.3 Condensed Format .......................................................................................................................54
5.2.4 Entering Check Configuration Data...............................................................................................58
5.3 Read Configuration Response Data .......................................................................................................60
5.4 Configuration Example Using PROFIBUS Manager Software................................................................61
6 TROUBLESHOOTING.................................................................................................................................65
6.1 What this Chapter Contains....................................................................................................................65
6.2 Troubleshooting with the Indicators........................................................................................................65
6.3 Configuration differences between 1794-APB and 3170-PDP................................................................67
6.3.1 User parameter data for 1794-APB:..............................................................................................68
6.3.2 User parameter data for 3170-PDP:..............................................................................................68
7 REFERENCE...............................................................................................................................................69
7.1 Product Specifications ............................................................................................................................69
7.2 Device Data Base File ............................................................................................................................70
8 GLOSSARY...............................................................................................................................................131
9 PROSOFT TECHNOLOGY, INC., SUPPORT, SERVICE & WARRANTY................................................141
9.1 How to Contact Us: Sales and Support ................................................................................................142
9.2 Return Material Authorization (RMA) Policies and Conditions..............................................................143
9.2.1 All Product Returns .....................................................................................................................143
9.3 Procedures for Return of Units Under Warranty...................................................................................143
9.4 Procedures for Return of Units Out of Warranty...................................................................................144
9.4.1 Un-repairable Units .....................................................................................................................144
9.4.2 Purchasing Warranty Extension..................................................................................................145
9.5 LIMITED WARRANTY..........................................................................................................................145
9.5.1 What Is Covered By This Warranty.............................................................................................145
9.5.2 What Is Not Covered By This Warranty ......................................................................................146
9.5.3 DISCLAIMER REGARDING HIGH RISK ACTIVITIES................................................................147
Page 6 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 7

Contents 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
9.5.4 DISCLAIMER OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES...........................................................................147
9.5.5 LIMITATION OF REMEDIES**....................................................................................................147
9.5.6 Time Limit for Bringing Suit .........................................................................................................147
9.5.7 No Other Warranties ...................................................................................................................148
9.5.8 Intellectual Property.....................................................................................................................148
9.5.9 Additional Restrictions Relating To Software And Other Intellectual Property.............................148
9.5.10 Allocation of risks ........................................................................................................................148
9.5.11 Controlling Law and Severability .................................................................................................149
INDEX.................................................................................................................................................................151
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 7 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 8

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Contents
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Page 8 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 9

About this User Manual 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
1 About this User Manual
In This Chapter
¾ Purpose.................................................................................... 9
¾ Vocabulary ............................................................................... 9
¾ Publication references.............................................................. 9
¾ Related Publications ................................................................ 9
¾ Compliance to European Union Directives............................. 10
1.1 Purpose
Use this manual to install and configure your FLEX I/OTM PROFIBUS Adapter,
cat. no. 3170-PDP.
1.2 Vocabulary
In this manual, we refer to:
the FLEX I/O PROFIBUS adapter module as the "adapter"
the programmable controller as the "processor"
1.3 Publication references
All publications this document refers to are Rockwell Automation publications.
1.4 Related Publications
For additional information on planning and installing your PROFIBUS system
using FLEX I/O modules, refer to the following publications:
Catalog
Number
3170-PDP 24V dc PROFIBUS Adapter Installation Instructions 801.09
1794-TB2
1794-TB3
1794-TBN Terminal Base Unit Installation Instructions 1794-5.16
1794-TBNF Fused Terminal Base Unit Installation Instructions 1794-5.17
1794-PS1 Power Supply Installation Instructions 1794-5.35
1794-IB16 24V dc 16 Input Module Installation Instructions 1794-5.4
Description
2-wire Terminal Base
3-wire Terminal Base
Related Publications
Pub. Type Pub. Number
Installation Instructions 1794-5.2
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 9 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 10

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform About this User Manual
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Catalog
Number
1794-OB16 24V dc 16 Output Module Installation Instructions 1794-5.3
1794-IR8
1794-IT8
1794-IE8
1794-OE4
1794IE4XOE2
1794-IB8S 24V dc Sensor Input Module Installation Instructions 1794-5.7
1794-IA8 120V ac 8 Input Module Installation Instructions 1794-5.9
1794-OA8 120V ac 8 Output Module Installation Instructions 1794-5.10
1794-OW8 24V dc 8 Relay Output Module Installation Instructions 1794-5.19
1794-CE1 Extender Cable Installation Instructions 1794-5.12
1794-NM1 Mounting Kit Installation Instructions 1794-5.13
Description
24V dc RTD Analog 8 Input
Module
24V dc Thermocouple Analog 8
Input Module
24V dc Selectable Analog 8 Input
Module
24V dc Selectable Analog 4
Output Module
24V dc 4 Input/2 Output Analog
Combo Module
Related Publications
Pub. Type Pub. Number
Installation Instructions
User Manual
Installation Instructions
User Manual
Installation Instructions
User Manual
Installation Instructions
User Manual
Installation Instructions
User Manual
1794-5.22
1794-6.5.4
1794-5.21
1794-6.5.7
1794-5.6
1794-6.5.2
1794-5.5
1794-6.5.2
1794-5.15
1794-6.5.2
To order these publications, contact your local Rockwell Automation
representative.
1.5 Compliance to European Union Directives
If this product has the CE mark it is approved for installation within the European
Union and EEA regions. It has been designed and tested to meet the following
directives.
1.5.1 EMC Directive
This product is tested to meet Council Directive 89/336/EEC Electromagnetic
Compatibility (EMC) and the following standards, in whole or in part, documented
in a technical construction file:
EN 50081-2EMC – Generic Emission Standard, Part 2 – Industrial
Environment
EN 50082-2EMC – Generic Immunity Standard, Part 2 – Industrial
Environment
This product is intended for use in an industrial environment.
Page 10 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 11
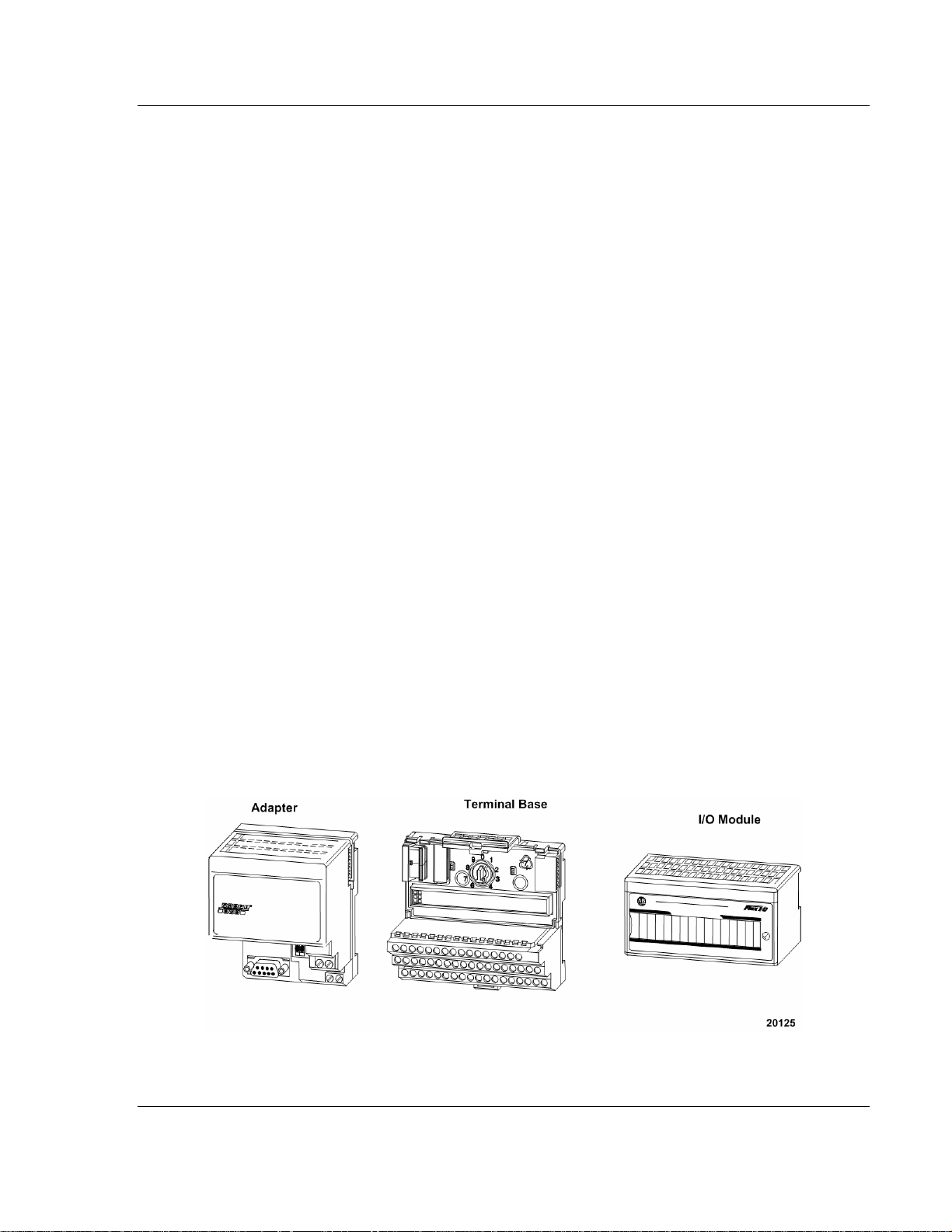
Overview of FLEX I/O and Your PROFIBUS Adapter Module 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
2 Overview of FLEX I/O and Your PROFIBUS
Adapter Module
In This Chapter
¾ The FLEX I/O System ............................................................ 11
¾ Mount and Remove your System Easily ................................ 12
¾ Optional Accessories ............................................................. 13
¾ Purpose of the 3170-PDP ......................................................16
¾ PROFIBUS Adapter Components.......................................... 17
This chapter describes
what the FLEX I/O system is and what it contains
how to mount and remove your system easily
optional accessories
mounting dimensions and spacing requirements
3170-PDP
adapter components
how to connect power wiring
2.1 The FLEX I/O System
FLEX I/O is a small, modular I/O system for distributed applications that performs
all of the functions of rack-based I/O. The FLEX I/O system contains the following
components:
PROFIBUS adapter/power supply - powers the internal logic for as many as
eight I/O modules
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 11 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 12
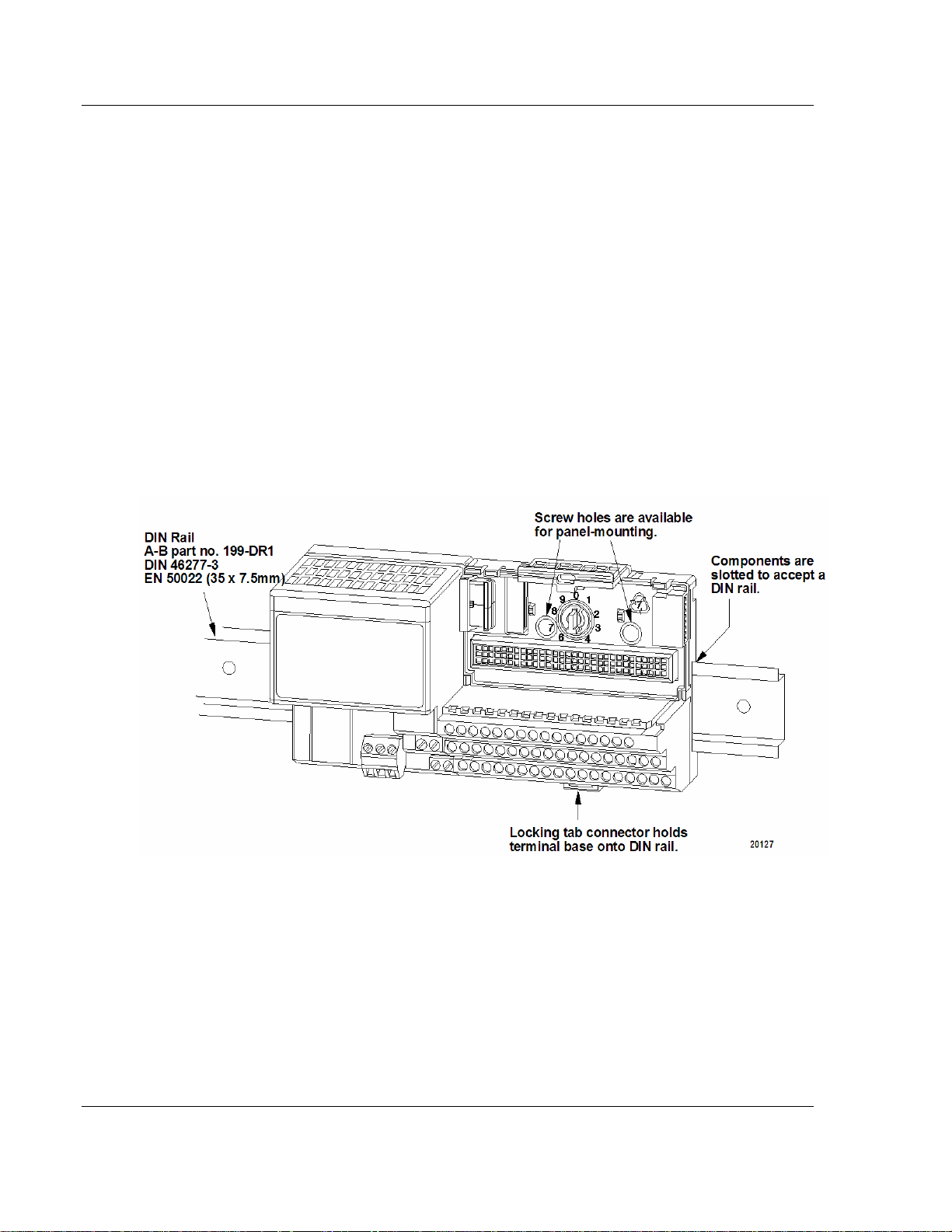
3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Overview of FLEX I/O and Your PROFIBUS Adapter Module
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
terminal base - contains a terminal strip to terminate wiring for two- or three-
wire devices
I/O module - contains the bus interface and circuitry needed to perform
specific functions related to your application
For information on how communication occurs over the FLEX I/O system
backplane, refer to Chapter 2.
You can horizontally or vertically mount the FLEX I/O system on a standard DIN
rail. The adapter and terminal base easily snap on the DIN rail by hand. Refer to
the installation instructions shipped with these components.
2.2 Mount and Remove your System Easily
Screw holes are also provided to horizontally or vertically panel-mount your
system in an enclosure. To panel-mount your FLEX I/O system, use the optional
mounting kit (1794-NM1).
An example of a DIN-rail mounted system is shown below.
Page 12 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 13
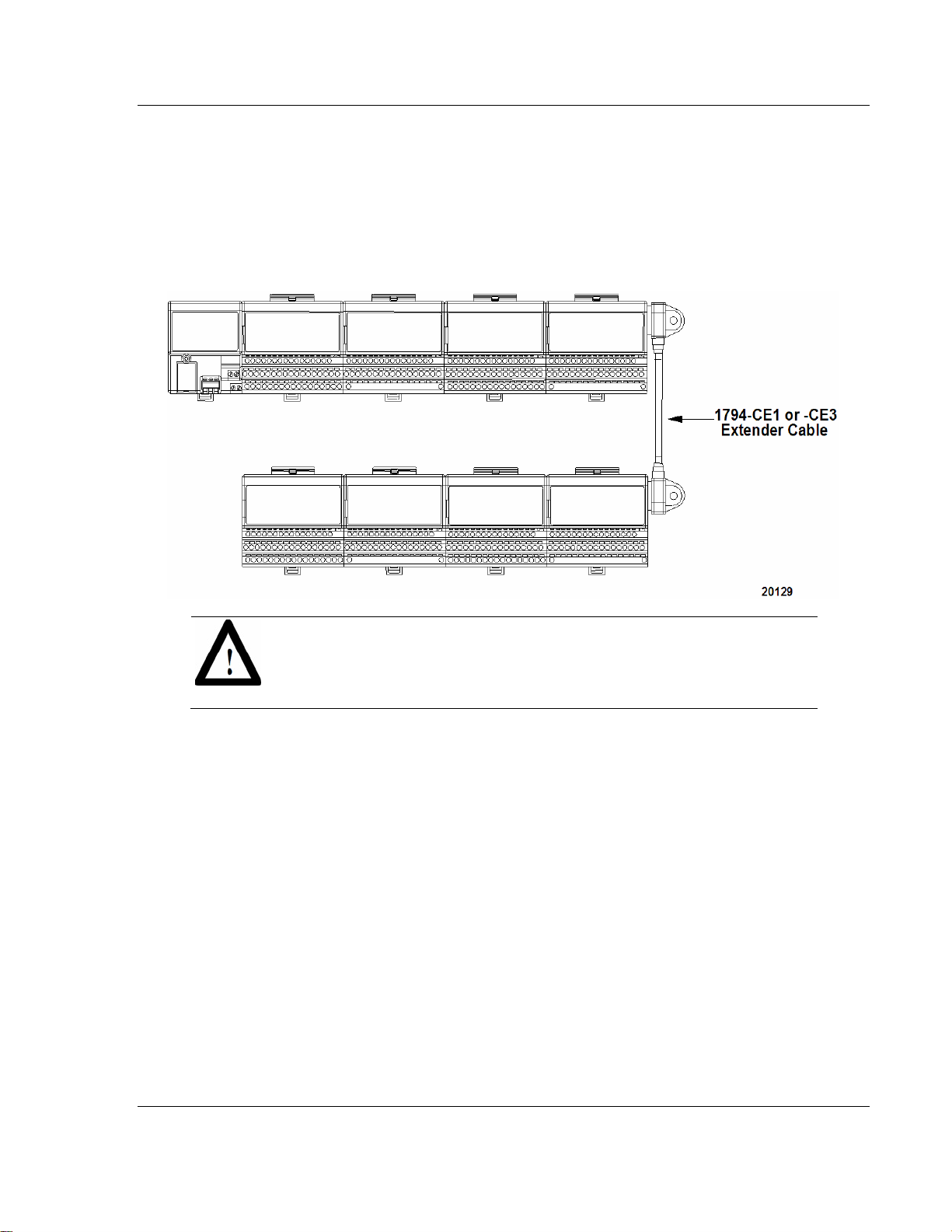
Overview of FLEX I/O and Your PROFIBUS Adapter Module 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
2.3 Optional Accessories
2.3.1 Extender Cables (1794-CE1 or -CE3)
Use the optional 1794-CE1 (0.3m) or -CE3 (0.9m) extender cable (one per
system) to arrange your system in two rows or split your system into horizontal
and vertical orientation.
ATTENTION: This cable can only be used between I/O modules. Do not use
between the adapter and I/O modules. Do not use more than one cable per
system.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 13 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 14
3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Overview of FLEX I/O and Your PROFIBUS Adapter Module
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
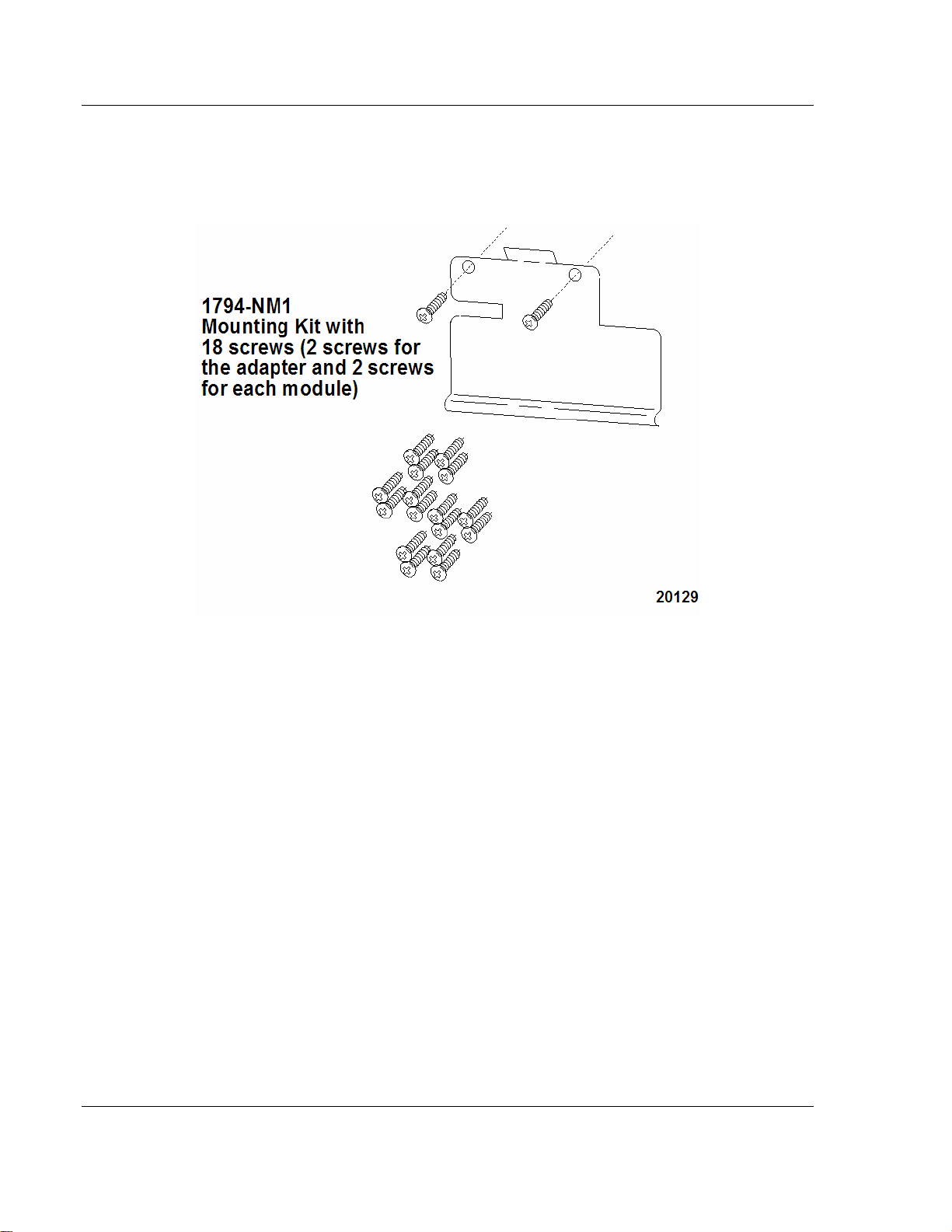
2.3.2 Mounting Kit (1794-NM1)
Use the optional 1794-NM1 mounting kit to mount your system on a panel or wall
without a DIN rail.
Page 14 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 15
Overview of FLEX I/O and Your PROFIBUS Adapter Module 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
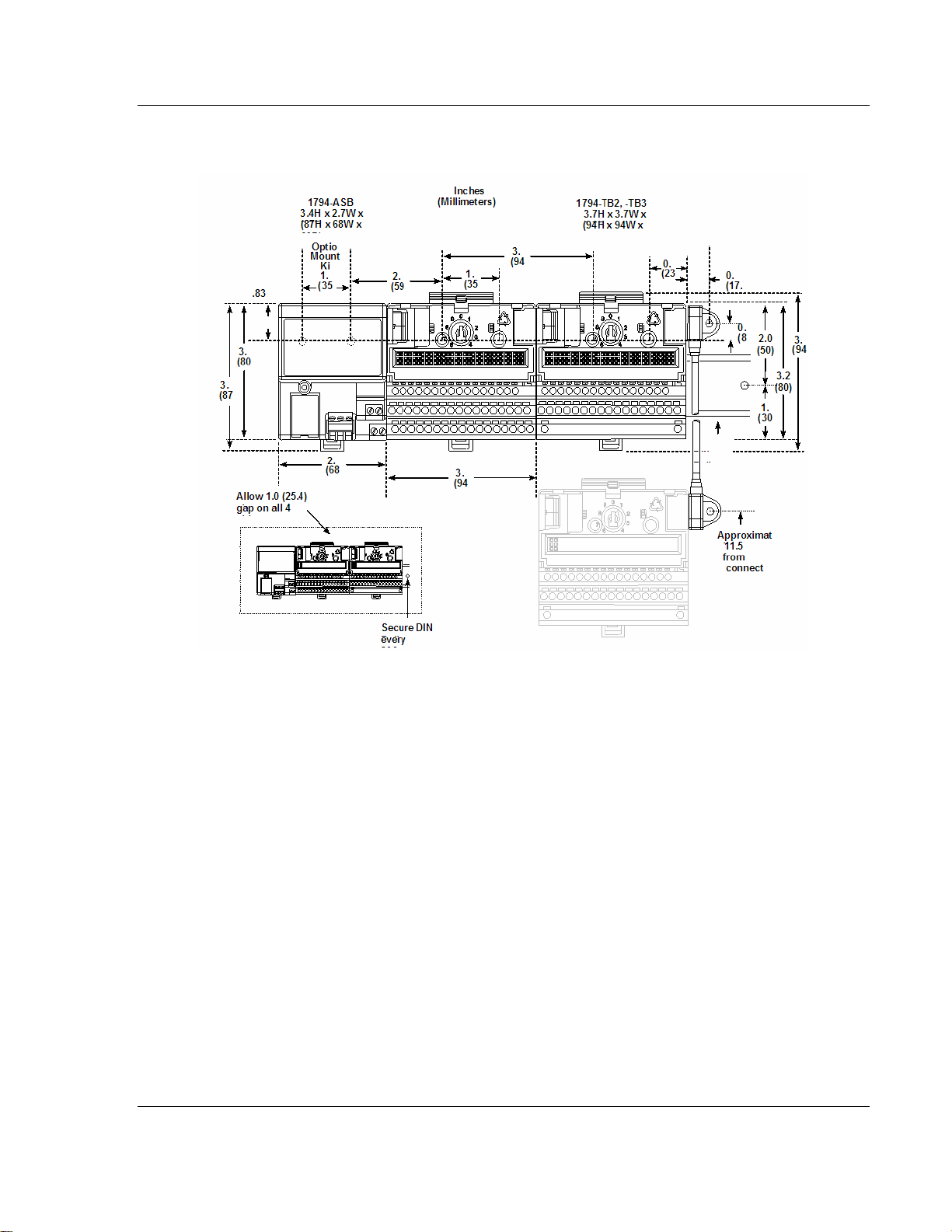
2.3.3 Mounting Dimensions and Spacing Requirements
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 15 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 16
3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Overview of FLEX I/O and Your PROFIBUS Adapter Module
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
2.4 Purpose of the 3170-PDP
The 3170-PDP is a FLEX I/O adapter that interacts with the FLEX I/O backplane
and any PROFIBUS DP master/scanner controller on a PROFIBUS DP network.
The 3170-PDP module is a slave device to the DP master/scanner, and is a
master controller of the FLEX I/O system where it is installed.
The I/O data exchange occurs as follows: Output data is sent from the DP
master/scanner controller across the PROFIBUS DP network to the 3170-PDP
adapter. The adapter then automatically transfers the data across the FLEX I/O
backplane to the output modules. Inputs from the input modules are collected by
the FLEX I/O adapter via the backplane and sent across the PROFIBUS DP
network to the DP master/scanner controller.
Page 16 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 17
Overview of FLEX I/O and Your PROFIBUS Adapter Module 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
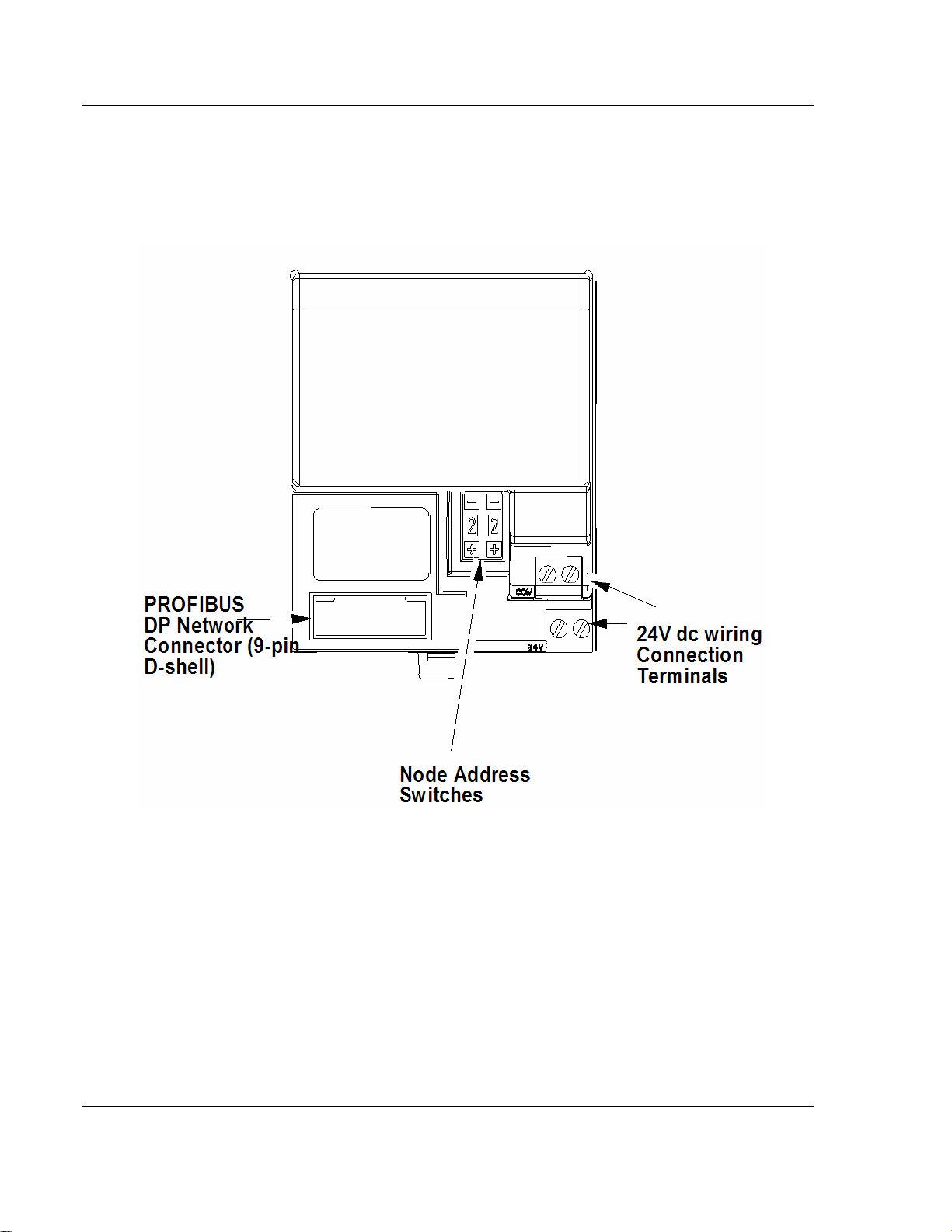
2.5 PROFIBUS Adapter Components
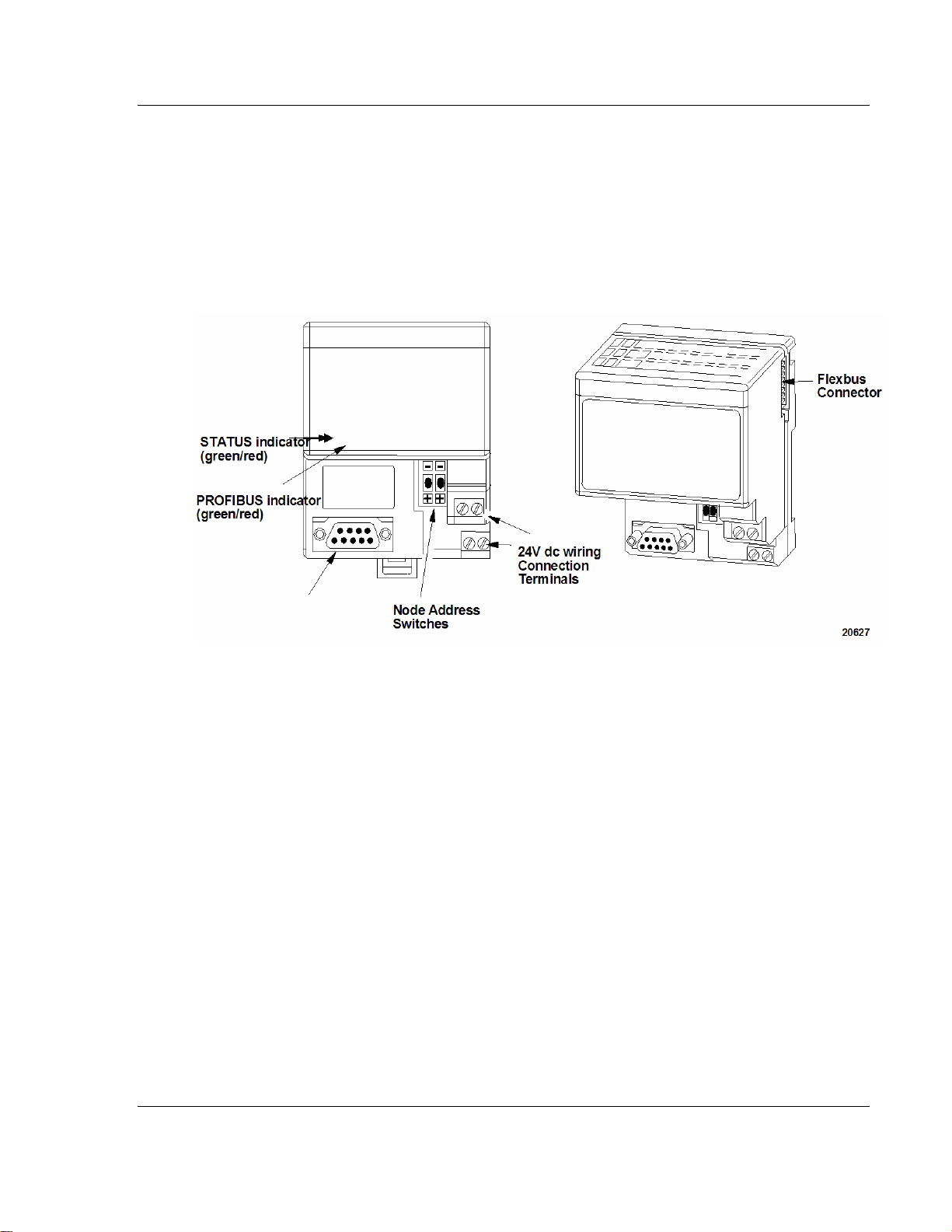
The adapter module consists of the following components:
two diagnostic indicators
PROFIBUS DP network connector
24V dc power wiring connection terminals
two node address switches
2.5.1 Diagnostic Indicators
Diagnostic indicators are located on the front panel of the adapter module. They
show both normal operation and error conditions in your FLEX I/O system. The
indicators are:
Device status (STATUS)
Communication link status (PROFIBUS)
Upon power-up, the adapter goes to an initialization state and performs a selftest (memory check, data memory clear. The indicators also go through a selftest sequence. If a failure occurs, the adapter transitions to a faulted state and
waits for reset (cycle power). Otherwise, the adapter begins monitoring the
network (run state) for messages.
Chapter 5 describes the diagnostic indicators and how to use them for
troubleshooting.
2.5.2 Network Connector
Use the 9-pin D-shell connector to connect your adapter to the PROFIBUS
network.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 17 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 18
3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Overview of FLEX I/O and Your PROFIBUS Adapter Module
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
2.5.3 Setting the Node Address Switches
Set the node address using the 2-position thumbwheel switch. Valid settings
range from 01 to 99. Use a pen to press either the + or - buttons to change the
number.
2.5.4 Power Wiring
Connections are provided for connecting the required 24V dc power to the front
of the module. The power wiring can be daisy-chained to the terminal base unit
located next to the adapter to supply power to the module installed in that base
unit.
Refer to the Installation Instructions (pub. no. 801.09) you received with your
adapter to learn how to install and wire the adapter.
Page 18 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 19
How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
3 How Communication Takes Place and I/O
Image Table Mapping
In This Chapter
¾ Polled I/O Structure................................................................ 20
¾ Mapping Data into the Image Table .......................................22
¾ Connection Status Word Definition ........................................42
¾ Logic Status/Analog Feedback Definition............................... 42
¾ Connection Enable Word Definition .......................................42
¾ Logic Command/Analog Reference Definition ....................... 42
¾ Defaults.................................................................................. 43
In this chapter, you will learn about:
communication over the FLEX I/O backplane (between the PROFIBUS
adapter and the I/O modules)
how data is mapped into the I/O image table
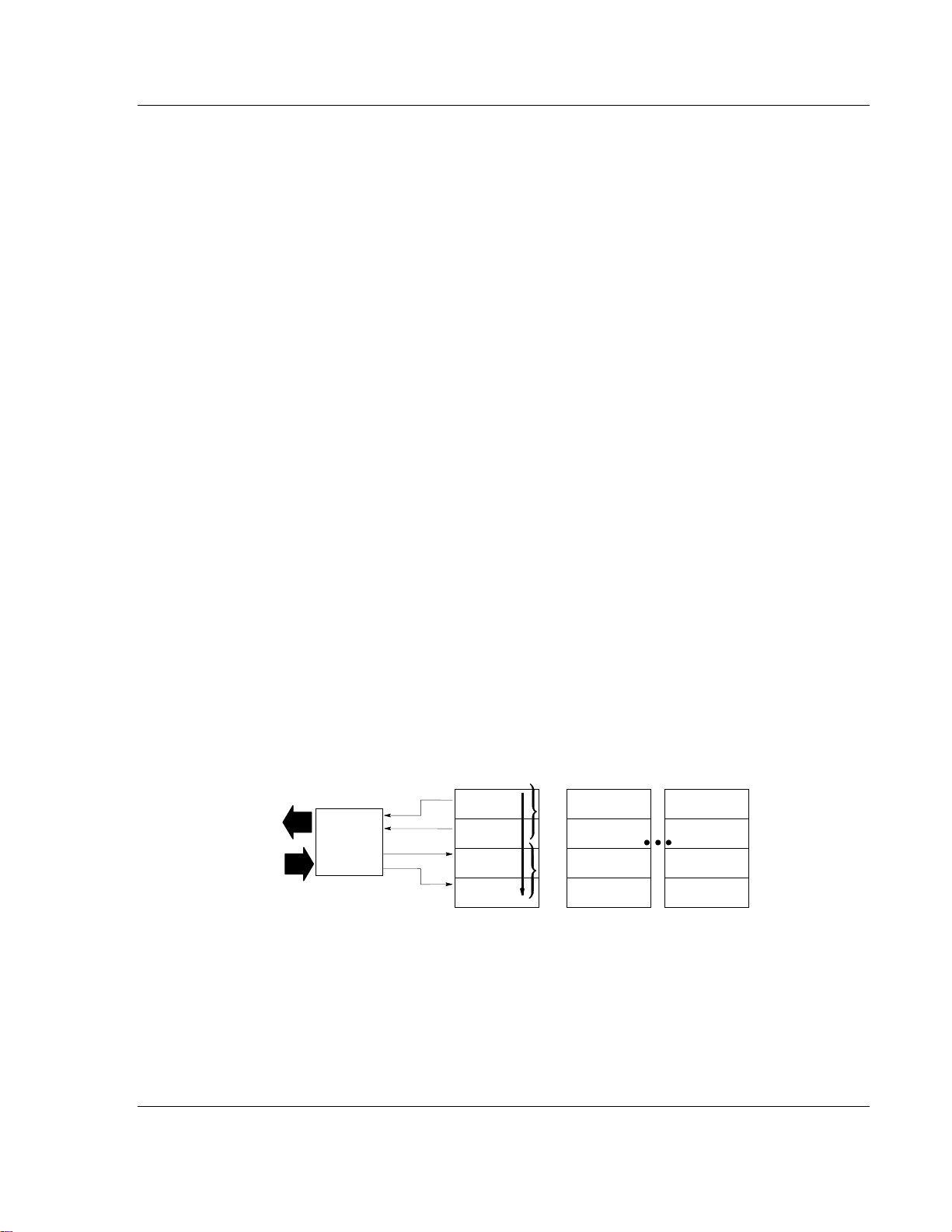
One 3170-PDP PROFIBUS adapter can interface with up to eight terminal base
units with installed FLEX I/O modules, forming a FLEX I/O system of up to eight
slots. The adapter communicates to other network system components over the
PROFIBUS network. The adapter communicates with its I/O modules over the
backplane.
Network
PROFIBUS
Adapter
I/O Module
Inputs
Read
Write
Status
Outputs
Configuration
Slot 1
0
Write
Words
1
Read
Words
I/O Module
Inputs
Status
Outputs
Configuration
Slot 2
I/O Module
Inputs
Status
Outputs
Configuration
Slot 8
The I/O map for a module is divided into read words and write words. Read
words consist of input and status words, and write words consist of output and
configuration words. The number of read words or write words can be 0 or more.
The length of each I/O module's read words and write words vary in size
depending on module complexity. Each I/O module will support at least 1 input
word or 1 output word. Status and configuration are optional, depending on the
module.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 19 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 20
3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
For example, a 16 point discrete input module will have up to 2 read words and 1
write word.
16-point Discrete Input Module
Refer to the I/O map for each module for the exact mapping.
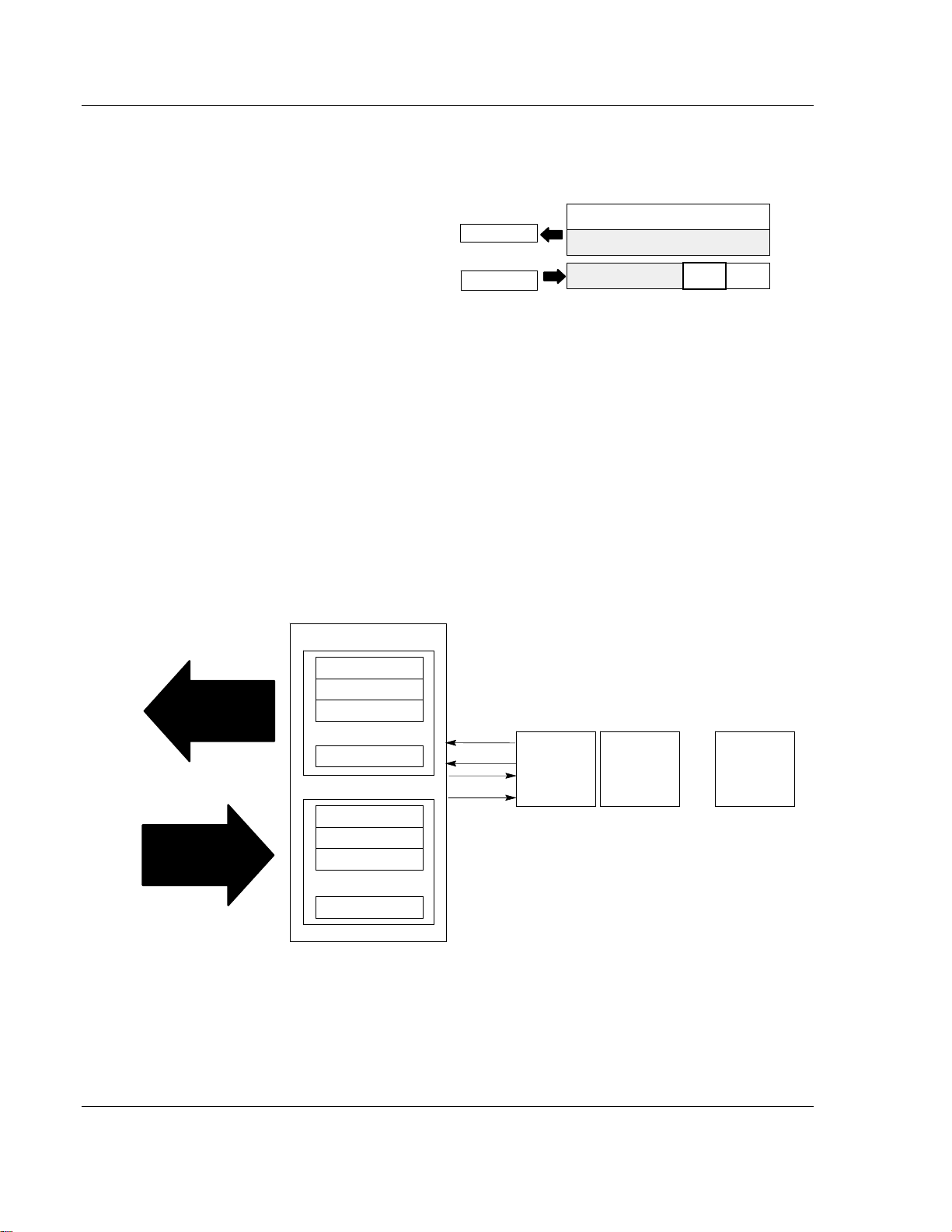
3.1 Polled I/O Structure
The first word of output data sent by the adapter is the Adapter Status Word.
Output data is received by the adapter in the order of the installed I/O modules.
The Output data for Slot 1 is received first, followed by the Output data for Slot 2,
and so on up to slot 8. All bits in the output status word are reserved
The first word of input data sent by the adapter is the Adapter Status Word. This
is followed by the input data from each slot, in the order of the installed I/O
modules. The Input data from Slot 1 is first after the status word, followed by
Input data from Slot 2, and so on up to slot 8.
PROFIBUS Adapter
Adapter Status
Slot 1 Input Data
Network READ
Slot 2 Input Data
... ...
Slot 8 Input Data
Read Data
Write Data
I/O Image
Input Size
1 or 2 Words
Output Size
0 or 1 Word
Module Image
Inputs
Not used
Not used
Delay
Time
Delay
Time
Read
Write
I/O Module
Slot 1
I/O Module
Slot 2
...
I/O Module
Slot 8
Adapter Status
Slot 1 Output Data
Network WRITE
Slot 2 Output Data
...
...
Slot 8 Output Data
3.1.1 Adapter Input Status Word
The input status word consists of:
I/O module fault bits – 1 status bit for each slot
Page 20 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 21

How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
node address changed – 1 bit
The adapter input status word bit descriptions are shown in the following table.
Bit Description Bit Explanation
I/O Module
Fault
9 This bit is set (1) when an error is detected in slot position 2.
10 This bit is set (1) when an error is detected in slot position 3.
11 This bit is set (1) when an error is detected in slot position 4.
12 This bit is set (1) when an error is detected in slot position 5.
13 This bit is set (1) when an error is detected in slot position 6.
14 This bit is set (1) when an error is detected in slot position 7.
15 This bit is set (1) when an error is detected in slot position 8.
Reserved 1 to 7 Reserved
Node Address
Changed
8 This bit is set (1) when an error is detected in slot position 1.
0
This bit is set (1) when the node address switch setting has been
changed since power up.
Possible causes for an I/O module fault are:
transmission errors on the FLEX I/O backplane
a failed module
a module removed from its terminal base
incorrect module inserted in a slot position
the slot is empty
The node address changed bit is set when the node address switch setting has
been changed since power up. The new node address does not take affect until
the adapter has been powered down and then powered back up. Until this power
cycling occurs, the node address switches will not match the actual node
address.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 21 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 22

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
3.2 Mapping Data into the Image Table
All FLEX I/O modules in the following table are supported by the PROFIBUS
adapter. Presently, these consist of:
Module Description Catalog Number
AC Modules 1794-IA8
1794-IA8I
1794-IA16
1794-OA8
1794-OA8I
1794-OA16
1794-IM8
1794-OM8
DC Modules 1794-IB8
1794-IB8S
1794-IB16
1793-IB16/A, S/A
1794-IV16
1793-IV16/A, S/A
1794-OB8
1794-OB16
1794-OB16P
1793-OB16P/A, S/A
1794-OV16
1794-OV16P
1793-OV16P/A, S/A
1794-OB8EP
1794-IB10XOB6
1794-IC16
1794-OC16
1793-IB4(S)
1793-OB4P(S)
1793-IB2XOB2P(S)
1794-IB32/A
1794-OB32P
1794-IB16XOB16P
Analog Modules 1794-IE8
1794-OE4
1794-IE4XOE2
1793-IE4(S)
1793-OE2(S)
1793-IE2XOE1(S)
Page 22 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 23
How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
W
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Module Description Catalog Number
Isolated Analog Modules 1794-IF4I
1794-OF4I
1794-IF2XOF2I
Relay Modules 1794-OW8
1793-OW4(S)
Special Modules 1794-IR8
1794-IRT8
1794-IT8
1794-IJ2
1794-ID2
1794-IP4
1203-FM1
Bentley Nevada Autoc BN 1701-15 Rad Vib Mon
BN 1701-15 Thrust Mon
BN 1701-25 Vel In Mon
BN 1701-25 Acc In Mon
The following topics show typical examples from Rockwell Automation product
literature.
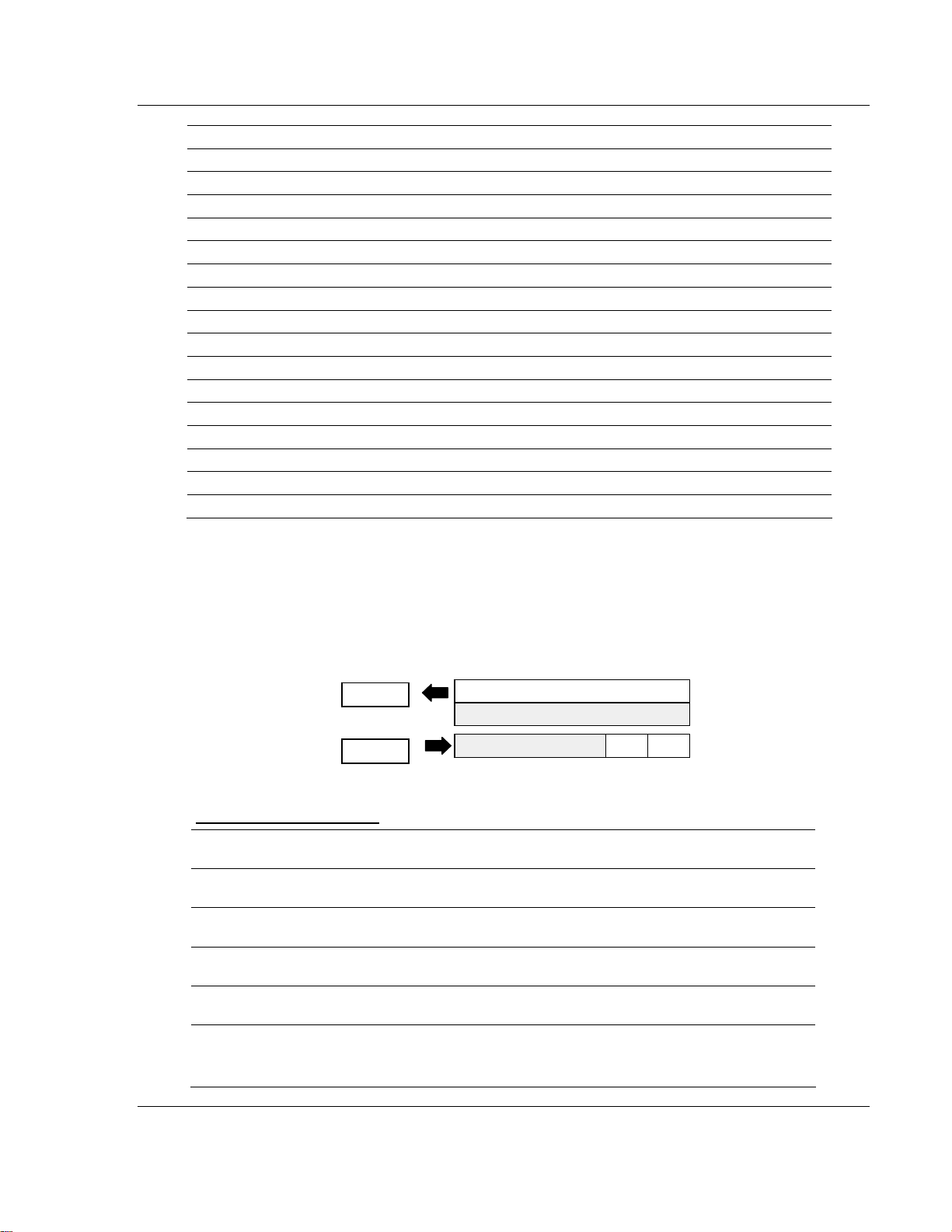
3.2.1 1794-IB16 – 16-point Discrete Input Module Image Table
Mapping
I/O Image
Input Size
1 or 2 Words
Read
Output Size
0 or 1 Word
rite
1794-IB16 Memory Map
Decimal
Bit
Octal Bit 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 Read
Where D = Input Data (D0 corresponds to input 0, D1 corresponds to input 1, etc.
DT = Input Delay Time (DT 00 to 11 corresponds to inputs 0 thru 11; DT 12 to 15 corresponds to
inputs 12 thru 15)
15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 Size
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 Read
Not used Read
Not used DT 12 to
Module Image
Inputs
Not used
Not used
Delay
Time
15
Delay
Time
DT 00 to 11 Write
Words
Word 1
Word 2
Word 1
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 23 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 24
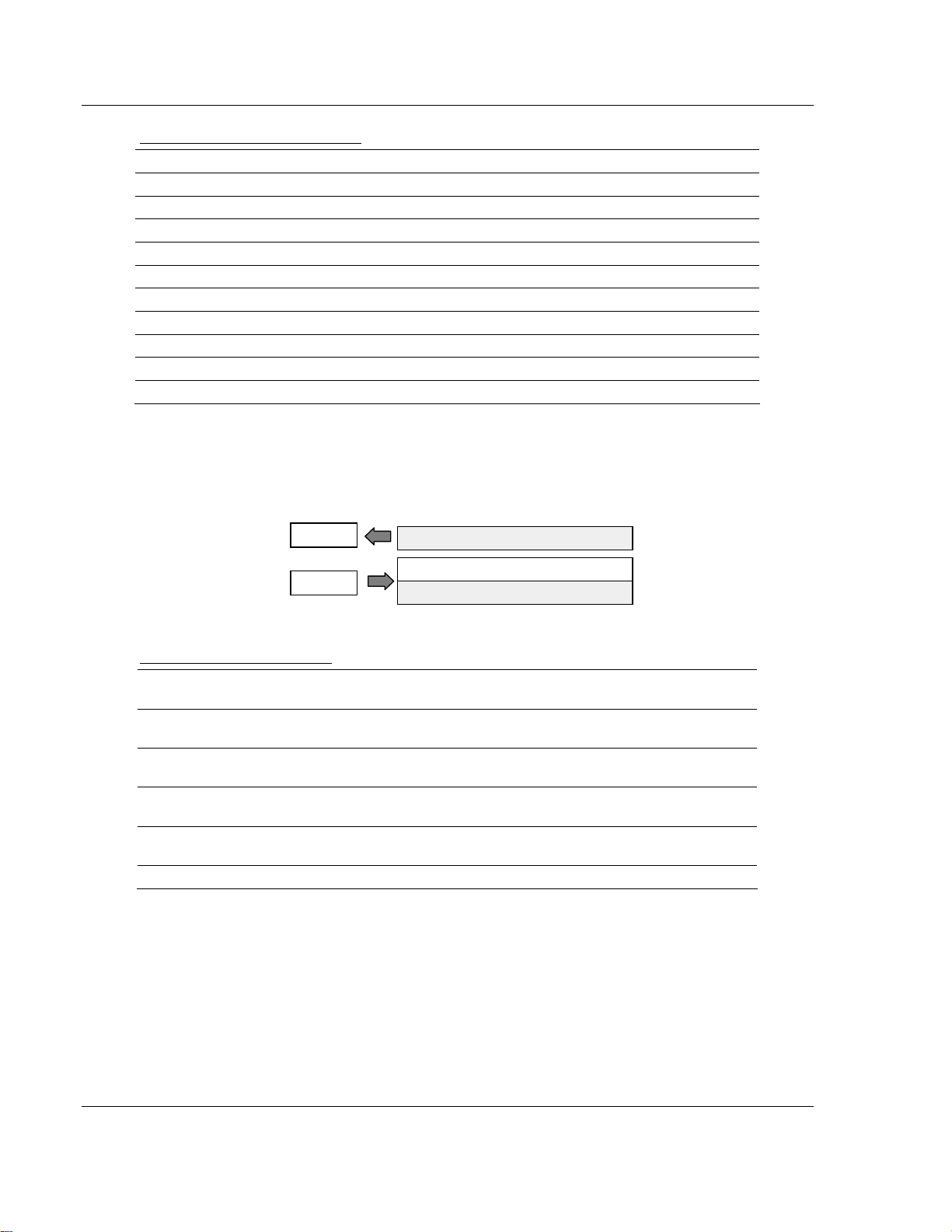
3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
1794-IB16 Input Delay Times
Bits Description Selected Delay Time
02 01 00 Delay Time for Inputs 00 to 11
05 04 03 Delay Time for Inputs 12 to 15
0 0 0 Delay Time 0 (default) 512µs
0 0 1 Delay Time 1 1ms
0 1 0 Delay Time 2 2ms
0 1 1 Delay Time 3 4ms
1 0 0 Delay Time 4 8ms
1 0 1 Delay Time 5 16ms
1 1 0 Delay Time 6 32ms
1 1 1 Delay Time 7 64ms
3.2.2 1794-OB16 – 16-point Discrete Output Module Image Table
Mapping
I/O Image
Input Size
0 or 1 Word
Read
1 or 2 Words
Write
Output Size
Module Image
Not used
Outputs
Not used
1794-OB16 Memory Map
Decimal
Bit
Octal. Bit 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 Read
Where O = Output value (O0 corresponds to output 0, O1 corresponds to output 1, etc.)
15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 Size
Words
Not used Read
Word 1
O15 O14 O13 O12 O11 O10 O9 O8 O7 O6 O5 O4 O3 O2 O1 O0 Write
Word 1
Not used Write
Word 2
Page 24 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 25
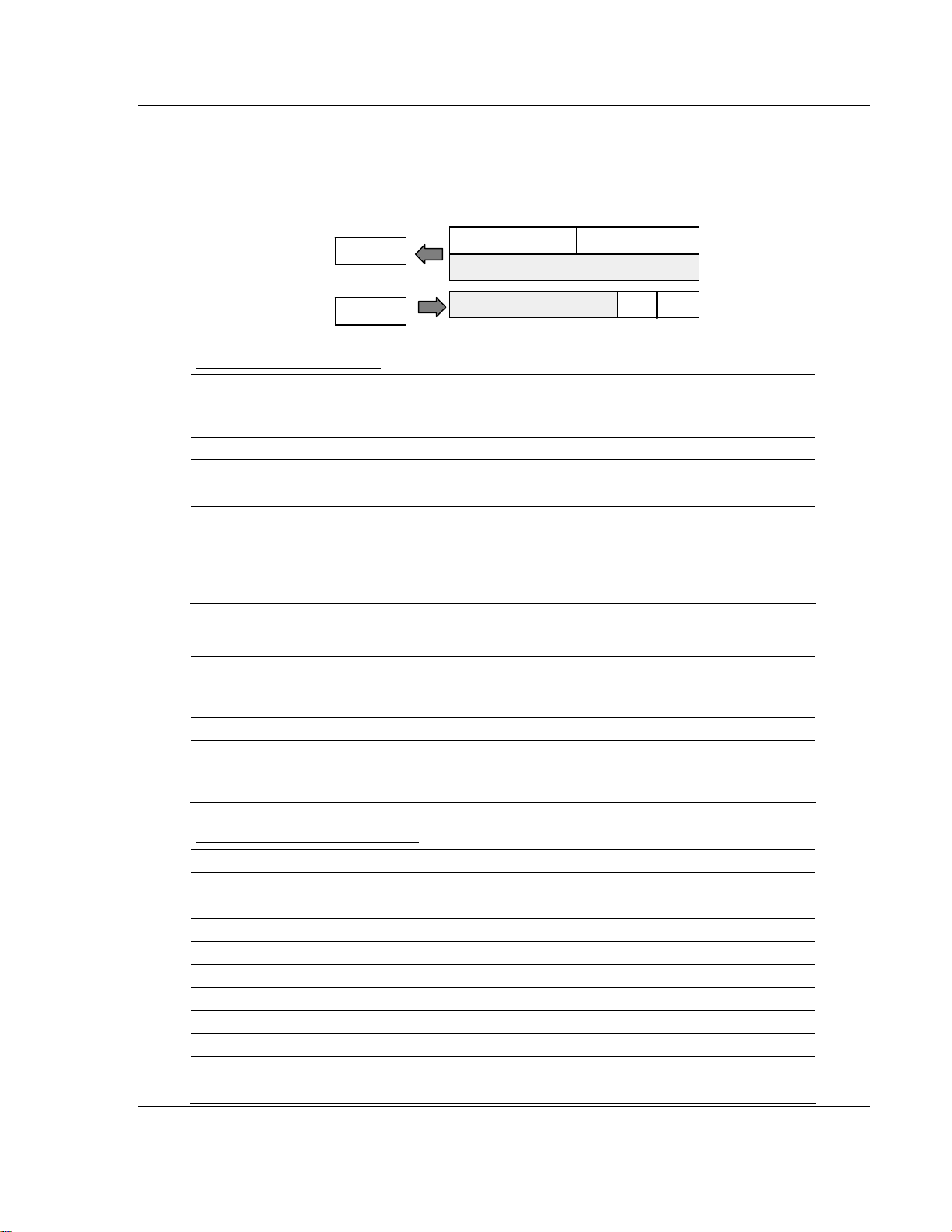
How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
3.2.3 1794-IB8S – 8-point Discrete Sensor Input Module Image Table
Mapping
I/O Image
Input Size
Read
1 or 2 Words
Output Size
Write
0 or 1 Word
Status
1794-IB8S Memory Map
Decimal
Bit
Octal Bit 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 Read Words
Where S = Status of input (where S1 corresponds to the diagnostic bit for input 1, S2 corresponds
to the diagnostic bit for input 2, etc.)
D = Input Data (where D0 corresponds to input 0, D1 corresponds to input 1, etc.
DT = Input Delay Time (where DT 00 to 11 corresponds to inputs 0 thru 11; DT 12 to 15
corresponds to inputs 12 thru 15.
The delay time for 00 to 11 must be the same as the delay time for 12 to 15.
15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 Size
S7 S6 S5 S4 S3 S2 S1 S0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 Read Word 1
Not used Read Word 2
Not used DT 12 to 15 DT 00 to 11 Write Word 1
Smart Sensor
Bits
08 to 15
Standard Sensor
Bits
08 to 15
S = Diagnostic data – 1 = Fault present
(Smart)
0 = Normal (no errors)
S = Diagnostic data – 1 = Diagnostics not
disabled
0 = Normal (Disabled)
Module Image
Not used
Not used
Bits
00 to
07
Bits
00 to
07
Inputs
Delay
Time
Delay
Time
D = Input data 1 = Sensor on
0 = Sensor off
D = Input data 1 = Sensor on
0 = Sensor off
1794-IB8S Input Delay Times
Bits Description Selected Delay Time
02 01 00 Delay Time for Inputs 00 to 11
05 04 03 Delay Time for Inputs 12 to 15
0 0 0 Delay Time 0 (default) 512µs
0 0 1 Delay Time 1 1ms
0 1 0 Delay Time 2 2ms
0 1 1 Delay Time 3 4ms
1 0 0 Delay Time 4 8ms
1 0 1 Delay Time 5 16ms
1 1 0 Delay Time 6 32ms
1 1 1 Delay Time 7 64ms
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 25 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 26
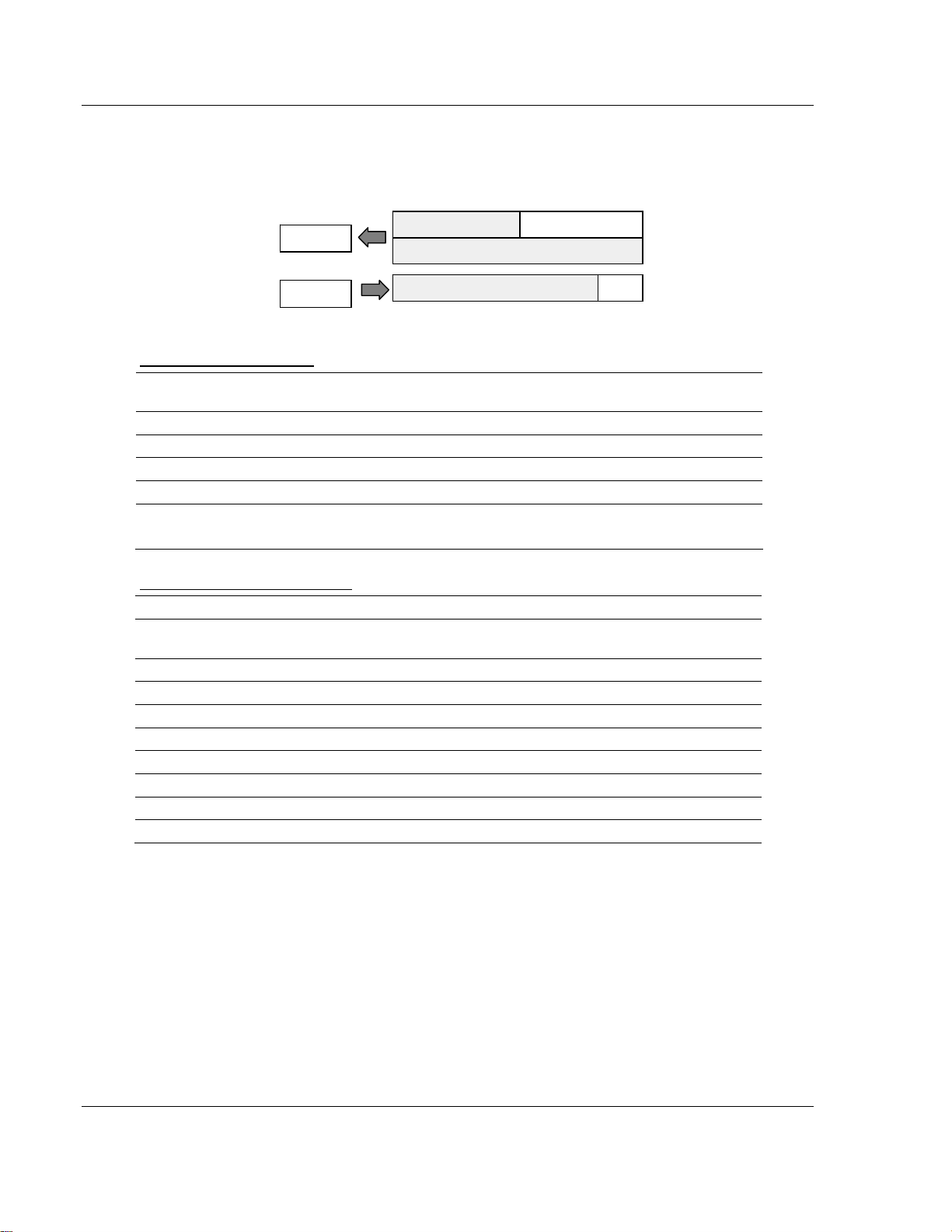
3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping
W
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
3.2.4 1794-IA8 – 8-point Discrete Input Module Image Table Mapping
I/O Image
Input Size
Read
1 or 2 Words
Output Size
0 or 1 Word
rite
Not used
1794-IA8 Memory Map
Decimal
Bit
Octal Bit 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 Read Words
Where D = Input Data (where D0 corresponds to input 0, D1 corresponds to input 1, etc.
DT = Input Delay Time (where DT 00 to 07 corresponds to inputs 0 thru 7)
15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 Size
Not used D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 Read Word 1
Not used Read Word 2
Not used Write Word 1
Module Image
Not used
Not used
Inputs
Delay
Time
1794-IA8 Input Delay Times
Bits Description Maximum Delay Time
02 01 00
0 0 0 Delay Time 0 (default) 8.6ms 26.6ms
0 0 1 Delay Time 1 9ms 27ms
0 1 0 Delay Time 2 10ms 28ms
0 1 1 Delay Time 3 12ms 30ms
1 0 0 Delay Time 4 17ms 35ms
1 0 1 Delay Time 5 26ms 44ms
1 1 0 Delay Time 6 43ms 61ms
1 1 1 Delay Time 7 78ms 96ms
Delay Time for Inputs 00
to 07
Off to On On to Off
Page 26 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 27
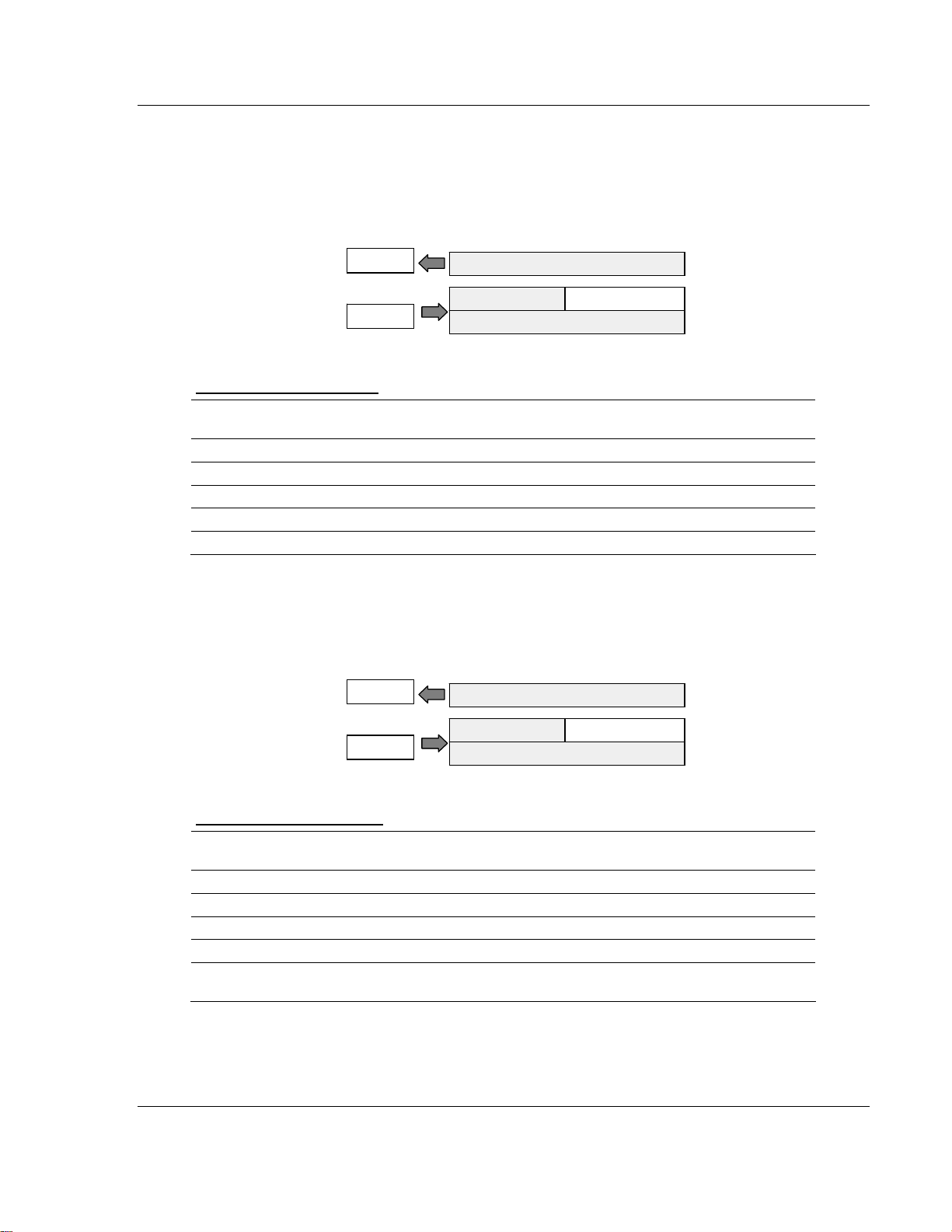
How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
W
W
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
3.2.5 1794-OA8 – 8-point Discrete Output Module Image Table
Mapping
I/O Image
Input Size
Read
0 or 1 Word
Output Size
rite
1 or 2 Words
1794-OA8 Memory Map
Decimal
Bit
Oct. Bit 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 Read Words
Where O = Output value (where O0 corresponds to output 0, O1 corresponds to output 1, etc.)
15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 Size
Not used Read Word 1 Read Word 1
Not used 07 06 O5 O4 O3 O2 O1 O0 Write Word 1
Not used Write Word 2 Write Word 2
Not used
Module Image
Not used
Not used
Outputs
3.2.6 1794-OW8 – 8-point Discrete Relay Output Module Image Table
Mapping
I/O Image
Input Size
Read
0 or 1 Word
Output Size
rite
1 or 2 Words
1794-OW8 Memory Map
Decimal
Bit
Oct. Bit 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 Read Words
Where O = Output value: where O0 corresponds to output 0, O1 corresponds to output 1, etc., and
when bit = 0, the output is off; when bit = 1, the output is on.
15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 Size
Not used Read word 1 Read Word 1
Not used 07 06 O5 O4 O3 O2 O1 O0 Write Word 1
Not used Write word 2 Write Word 2
Not used
Module Image
Not used
Not used
Outputs
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 27 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 28
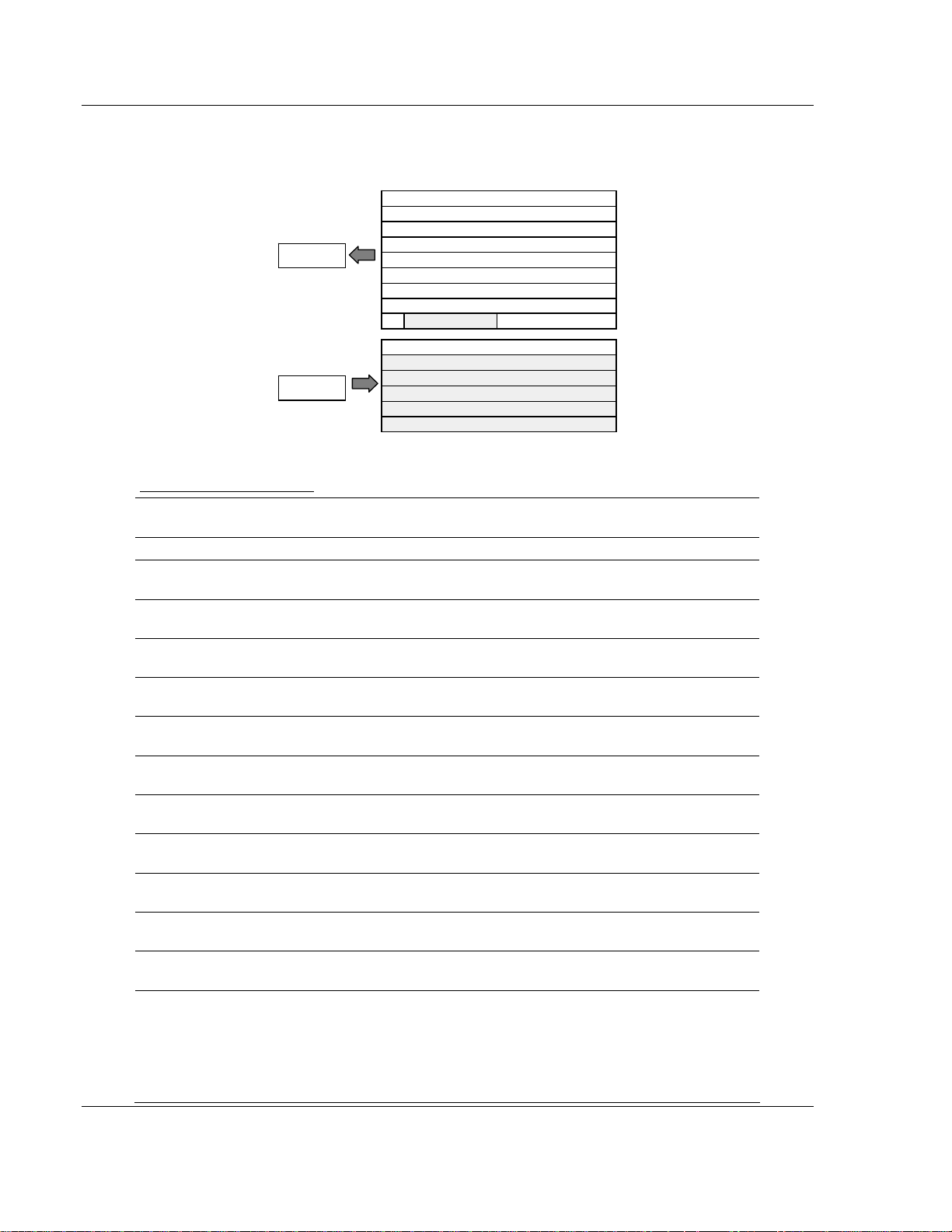
3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
3.2.7 1794-IE8 – 8 Input Analog Module
I/O Image
Input Size
1 to 9 Words
0 or 1 Word
PU
Output
Module
Input Data Channel 0
Input Data Channel 1
Input Data Channel 2
Input Data Channel 3
Input Data Channel 4
Input Data Channel 5
Input Data Channel 6
Input Data Channel 7
Underrange
Configure select
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
1794-IE8 Memory Map
Decimal
Bit
Oct. Bit 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 Read Words
Where: PU = Power up bit – included in series B modules only.
U = Underrange bits for 4 to 20mA inputs
C = Configure select bit
F = Full range bit
S = sign bit (in 2's complement)
15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 Size
S Analog Value Channel 0 Read Word 1 Read Word
1
S Analog Value Channel 1 Read Word 2 Read Word
2
S Analog Value Channel 2 Read Word 3 Read Word
3
S Analog Value Channel 3 Read Word 4 Read Word
4
S Analog Value Channel 4 Read Word 5 Read Word
5
S Analog Value Channel 5 Read Word 6 Read Word
6
S Analog Value Channel 6 Read Word 7 Read Word
7
S Analog Value Channel 7 Read Word 8 Read Word
8
PU Not used – set to zero U7 U6 U5 U4 U3 U2 U1 U0 Read Word
9
C7 C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0 F7 F6 F5 F4 F3 F2 F1 F0 Write Word
1
Not used – set to 0 Write Word
2 thru 6
Page 28 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 29

How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
1794-IE8 Range Selection Bits
Channel
No.
Decimal Bit 00 08 01 09 02 10 03 11 04 12 05 13 06 14 07 15
0 to 10V dc/0
to 20mA
4 to 20mA 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
–10 to +10V
dc
Do Not Use1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
C = Configure select bit
F = Full range bit
1 Do not use this configuration. Individual channels revert to 4 to 20mA if bit selection is all zeroes.
Channel 0 Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 3 Channel 4 Channel 5 Channel 6 Channel
7
F0 C0 F1 C1 F2 C2 F3 C3 F4 C4 F5 C5 F6 C6 F7 C7
1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1794-IE8 Word/Bit Descriptions
Word Decimal Bit Definition
Read Word 1 Bits 00 to 14
Bits 15 Channel 0 analog data sign bit.
Read Word 2 Bits 00 to 14
Bits 15 Channel 1 analog data sign bit.
Read Word 3 Bits 00 to 14
Bits 15 Channel 2 analog data sign bit.
Read Word 4 Bits 00 to 14
Bits 15 Channel 3 analog data sign bit.
Read Word 5 Bits 00 to 14
Bits 15 Channel 4 analog data sign bit.
Read Word 6 Bits 00 to 14
Bits 15 Channel 5 analog data sign bit.
Read Word 7 Bits 00 to 14
Bits 15 Channel 6 analog data sign bit.
Channel 0 analog data – 12-bit left justified two's
complement number; unused lower bits are zero; 4 to 20mA
uses all 16 bits.
Channel 1 analog data – 12-bit left justified two's
complement number; unused lower bits are zero; 4 to 20mA
uses all 16 bits.
Channel 2 analog data – 12-bit left justified two's
complement number; unused lower bits are zero; 4 to 20mA
uses all 16 bits.
Channel 3 analog data – 12-bit left justified two's
complement number; unused lower bits are zero; 4 to 20mA
uses all 16 bits.
Channel 4 analog data – 12-bit left justified two's
complement number; unused lower bits are zero; 4 to 20mA
uses all 16 bits.
Channel 5 analog data – 12-bit left justified two's
complement number; unused lower bits are zero; 4 to 20mA
uses all 16 bits.
Channel 6 analog data – 12-bit left justified two's
complement number; unused lower bits are zero; 4 to 20mA
uses all 16 bits.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 29 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 30
3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping
W
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Word Decimal Bit Definition
Read Word 8 Bits 00 to 14
Bits 15 Channel 7 analog data sign bit.
Read Word 9 Bits 00 to 07
Bits 08 to 14 Not used – set to 0.
Bit 15
Write Word 1 Bits 00 to 07
Bits 08 to 15
Write Word 2 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 3 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 4 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 5 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 6 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Channel 7 analog data – 12-bit left justified two's
complement number; unused lower bits are zero; 4 to 20mA
uses all 16 bits.
Underrange bits (U) for individual channels (4 to 20mA
current input only)- Bit 00 corresponds to input channel 0, bit
01 corresponds to input channel 1, and so on. When set (1),
indicates either a broken or open input wire, or input current
below 4 to 20mA.
Power Up bit – included in series B modules only. This bit is
0 in series A modules. This bit is set to 1 when all bits in the
configuration register are 0 (unconfigured state). The
configuration register can be cleared by either of the reset
inputs, or by the user writing all zeroes to it.
Full range bits (F) for individual channels – Bit 00
corresponds to input channel 0, bit 01 corresponds to input
channel 1, and so on. Refer to range selection above.
Configure select bits (C) for individual channels – Bit 08
corresponds to input channel 0, bit 09 corresponds to input
channel 1, and so on. Refer to range selection above.
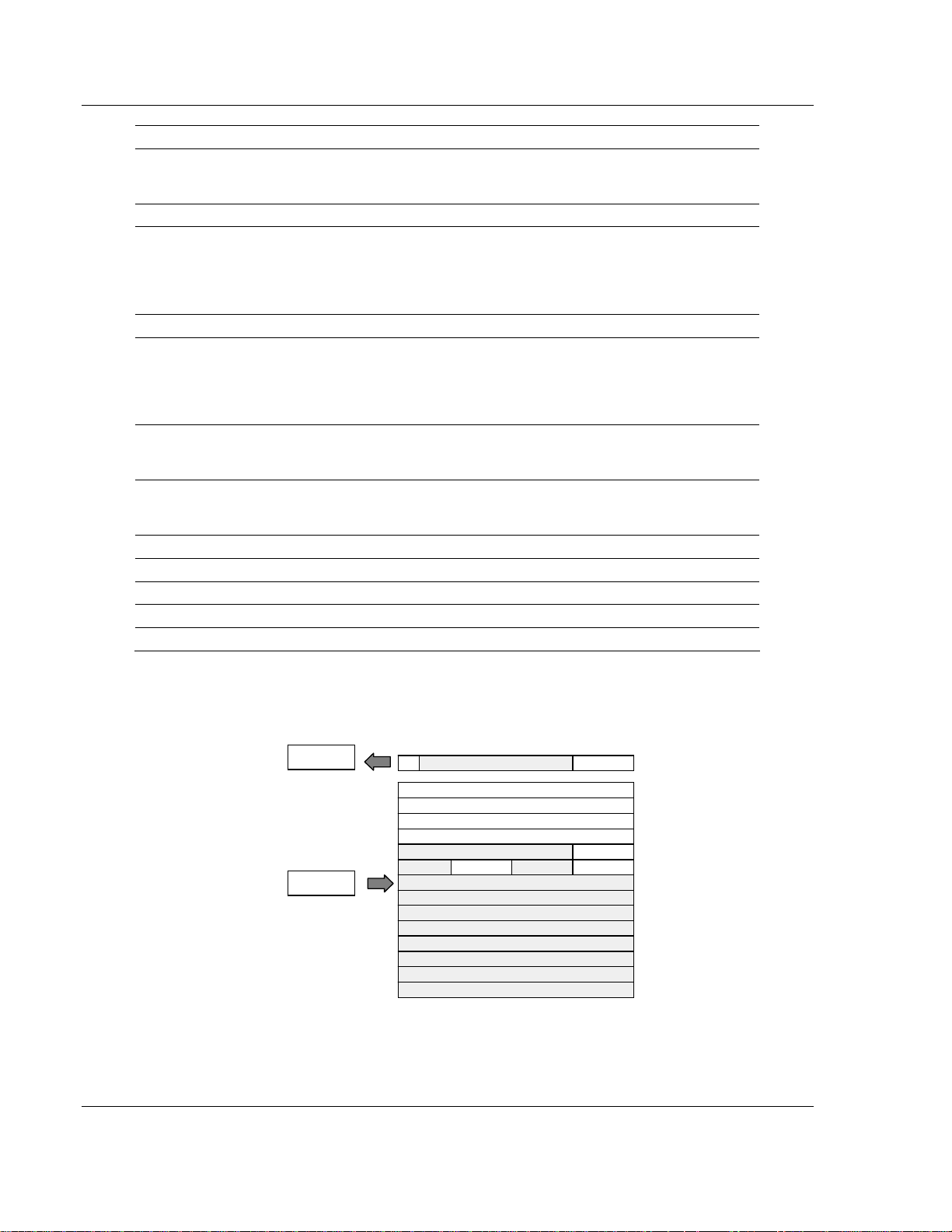
3.2.8 1794-OE4 – 4 Output Analog Module Image Table Mapping
I/O Image
Input Size
0 or 1 Word
Read
1 or 6 Words
rite
Output
PU
Not used Not used
Page 30 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
Module Image
Not used
Analog Data Channel 0
Analog Data Channel 1
Analog Data Channel 2
Analog Data Channel 3
Not used
Config. Select
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Diagnostics
OE
Full Range
August 23, 2007
Page 31

How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
1794-OE4 Memory Map
Decimal
Bit
Oct. Bit 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 Read Words
Where: PU = Power up bit – included in series B modules only.
W = Diagnostic bits for current output wire broken or load resistance high. (Not used on voltage
outputs.)
S = Sign bit (in 2's complement)
OE = Output enable bits (bit 00 corresponds to output 0, bit 01 corresponds to output 1 and so on.
ATTENTION: These bits must be
set to 1.
C = Configure select bit
F = Full range bit
15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 Size
PU Not used – set to 0 W3 W2 W1 W0 Read Word 1
S Analog Data – Channel 0 Write Word 1
S Analog Data – Channel 1 Write Word 2
S Analog Data – Channel 2 Write Word 3
S Analog Data – Channel 3 Write Word 4
Not used – set to 0 OE3 OE2 OE1 OE0 Write Word 5
Not used – set to 0 C3 C2 C1 C0 Not used – set to 0 F3 F2 F1 F0 Write Word 6
Not used – set to 0 Write Words 7
thru 14
1794-OE4 Range Selection Bits (Write Word 6)
Channel No. Channel 0 Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 3
Decimal Bit 00 08 01 09 02 10 03 11
4 to 20mA 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
0 to 10V dc/0 to 20mA 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
to 10 to +10V dc 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Off1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
C = Configure select bit
F = Full range bit
1 When configured to off, individual channels will return 0V.
F0 C0 F1 C1 F2 C2 F3 C3
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 31 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 32

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
1794-OE4 Word/Bit Descriptions
Word Decimal Bit Definition
Read Word 1 Bits 00 to 03
Bits 04 to 14 Not used – set to 0.
Bit 15
Write Word 1 Bits 00 to 14
Bits 15 Channel 0 analog data sign bit.
Write Word 2 Bits 00 to 14
Bits 15 Channel 1 analog data sign bit.
Write Word 3 Bits 00 to 14
Bits 15 Channel 2 analog data sign bit.
Write Word 4 Bits 00 to 14
Bits 15 Channel 3 analog data sign bit.
Write Word 5 Bits 00 to 03
Bits 04 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 6 Bits 00 to 03
Bits 04 to 07 Not used – set to 0.
Bits 08 to 11
Bits 12 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 7 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 8 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 9 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 10 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 11 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 12 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 13 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 14 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Current outputs only – When set (1), the wire on the output is
broken or the load resistance is too high. Bit 00 corresponds to
channel 0, bit 01 corresponds to channel 2, and so on.
Power Up bit – included in series B modules only. This bit is 0 in
series A modules. This bit is set to 1 when all bits in the
configuration register are 0 (unconfigured state). The configuration
register can be cleared by either of the reset inputs, or by the user
writing all zeroes to it.
Channel 0 analog data – 12-bit left justified two's complement
number; unused lower bits are zero; 4 to 20mA uses all 16 bits.
Channel 1 analog data – 12-bit left justified two's complement
number; unused lower bits are zero; 4 to 20mA uses all 16 bits.
Channel 2 analog data – 12-bit left justified two's complement
number; unused lower bits are zero; 4 to 20mA uses all 16 bits.
Channel 3 analog data – 12-bit left justified two's complement
number; unused lower bits are zero; 4 to 20mA uses all 16 bits.
Output Enable bits. Bit 00 corresponds to input 0, bit 01
corresponds to input 1, bit 02 corresponds to input 2, and bit 03
corresponds to input 3. These bits must be set to 1.
Full range bits (F) for individual channels – Bit 00 corresponds to
output channel 0, bit 01 corresponds to output channel 1, and so
on. Refer to range selection above.
Configure select bits (C) for individual channels – Bit 08
corresponds to output channel 0, bit 09 corresponds to output
channel 1, and so on. Refer to range selection above.
Page 32 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 33

How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
W
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
3.2.9 1794-IE4XOE2 – Analog Combo Module Image Table Mapping
I/O Image
Input Size
0 to 5 Words
Read
PU
Output
rite
0 to 4 Words
Not used Full Range and Configure Select
Module Image
Input Data Channel 0
Input Data Channel 1
Input Data Channel 2
Input Data Channel 3
Underrange & Diag.
Output Data Channel 0
Output Data Channel 1
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
Not used
OE
1794-IE4XOE2 Memory Map
Decimal
Bit
Oct. Bit 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 Read Words
Where: PU = Power up bit – included in series B modules only.
W = Diagnostic bits for current output wire broken or load resistance high. (Not used on voltage
outputs.)
U = Underrange bits for 4 to 20mA inputs
OE = Output enable bits (bit 00 corresponds to output 0, bit 01 corresponds to output 1).
ATTENTION: These bits must be set to 1.
S = Sign bit (in 2's complement)
C = Configure select bit
F = Full range bit
15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00 Size
S Analog Value Input Channel 0 Read Word 1
S Analog Value Input Channel 1 Read Word 2
S Analog Value Input Channel 2 Read Word 3
S Analog Value Input Channel 3 Read Word 4
PU Not used – set to 0 W1 W0 U3 U2 U1 U0 Read Word 5
S Analog Data – Output Channel 0 Write Word 1
S Analog Data – Output Channel 1 Write Word 2
Not used – set to 0 OE1 OE0 Write Word 3
Not used C5 C4 C3 C2 C1 C0 0 0 F5 F4 F3 F2 F1 F0 Write Word 4
Not used – set to 0 Write Word 5
thru 10
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 33 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 34

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
1794-IE4XOE2 Range Selection Bits
Channel
No.
Decimal Bit 00 08 01 09 02 10 03 11 04 12 05 13
4 to 20mA 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
0 to 10V dc/0
to 20mA
to 10 to +10V
dc
Off1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
C = Configure select bit
F = Full range bit
1When configured to off, individual channels will return either 0V or 0mA.
Input
Channel 0
F0 C0 F1 C1 F2 C2 F3 C3 F4 C4 F5 C5
1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Input
Channel 1
Input
Channel 2
Input
Channel 3
Output
Channel 0
Output
Channel 1
1794-IE4XOE2 Word/Bit Descriptions
Word Decimal Bit Definition
Read Word 1 Bits 00 to 14 Channel 0 analog data – 12-bit left justified two's complement number; unused
lower bits are zero; 4 to 20mA uses all 16 bits.
Bits 15 Channel 0 analog data sign bit.
Read Word 2 Bits 00 to 14 Channel 1 analog data – 12-bit left justified two's complement number; unused
lower bits are zero; 4 to 20mA uses all 16 bits.
Bits 15 Channel 1 analog data sign bit.
Read Word 3 Bits 00 to 14 Channel 2 analog data – 12-bit left justified two's complement number; unused
lower bits are zero; 4 to 20mA uses all 16 bits.
Bits 15 Channel 2 analog data sign bit.
Read Word 4 Bits 00 to 14 Channel 3 analog data – 12-bit left justified two's complement number; unused
lower bits are zero; 4 to 20mA uses all 16 bits.
Bits 15 Channel 3 analog data sign bit.
Read Word 5 Bits 00 to 03 Underrange bits (U) for individual channels (4 to 20mA current inputs only) – Bit 00
corresponds to input channel 0, bit 01 corresponds to input channel 1, and so on.
Bits 04 to 05 Wire Off bits (W) – Current outputs only – When set (1), the wire on the current
output is broken or the load resistance is too high. Bit 00 corresponds to channel 0,
bit 01 corresponds to channel 2, and so on.
Bits 06 to 14 Not used – set to 0.
Bit 15 Power Up bit – included in series B modules only. This bit is 0 in series A modules.
This bit is set to 1 when all bits in the configuration register are 0 (unconfigured
state). The configuration register can be cleared by either of the reset inputs, or by
the user writing all zeroes to it.
Write Word 1 Bits 00 to 14 Channel 0 analog data – 12-bit left justified two's complement number; unused
lower bits are zero; 4 to 20mA uses all 16 bits.
Bits 15 Channel 0 analog data sign bit.
Write Word 2 Bits 00 to 14 Channel 1 analog data – 12-bit left justified two's complement number; unused
lower bits are zero; 4 to 20mA uses all 16 bits.
Bits 15 Channel 1 analog data sign bit.
Write Word 3 Bits 00 to 01 Output Enable bits. Bit 00 corresponds to output 0, bit 01 corresponds to output 1.
These bits must be set to 1.
Page 34 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 35

How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Word Decimal Bit Definition
Bits 02 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 4 Bits 00 to 05 Full range bits (F) for individual channels – Bit 00 corresponds to input channel 0,
bit 01 corresponds to input channel 1, bit 02 corresponds to input channel 3, bit 03
corresponds to input channel 3, bit 04 corresponds to output channel 1, and bit 05
corresponds to output channel 2. Refer to range selection above.
Bits 06 to 07 Not used – set to 0.
Bits 08 to 13 Configure select bits (C) for individual channels – Bit 08 corresponds to input
channel 0, bit 09 (11) corresponds to input channel 1, bit 10 (12) corresponds to
input channel 2, bit 11 (13) corresponds to input channel 3, bit 12 (14) corresponds
to output channel 0, and bit 13 (15) corresponds to output channel 1. Refer to range
selection above.
Bits 14 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 5 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 6 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 7 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 8 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 9 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
Write Word 10 Bits 00 to 15 Not used – set to 0.
3.2.10 1794-IR8 – RTD Input Analog Module Image Table Mapping
I/O Image
Input Size
1 to 11 Words
Overrange
Output Size
0 to 3 Words
Calibration Mask
1794-IR8 Read
Dec. Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
Oct. Bit 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
Read Word 1 Reserved
Read Word 2 Channel 0 Input Data
Read Word 3 Channel 1 Input Data
Read Word 4 Channel 2 Input Data
Read Word 5 Channel 3 Input Data
Read Word 6 Channel 4 Input Data
Module Image
Reserved
Input Data Channel 0
Input Data Channel 1
Input Data Channel 2
Input Data Channel 3
Input Data Channel 4
Input Data Channel 5
Input Data Channel 6
Input Data Channel 7
Underrange
Calibration Status
Configuration
RTD Type
RTD Type
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 35 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 36

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Dec. Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
Read Word 7 Channel 5 Input Data
Read Word 8 Channel 6 Input Data
Read Word 9 Channel 7 Input Data
Read Word 10 Overrange Bits Underrange Bits
Read Word 11 0 0 0 0 0 Bad
Cal
Cal
Done
Cal
0 Diagnostic Status
Range
Bits
Pwr
0 0 0
Up
1794-IR8 Write
Dec. Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
Oct. Bit 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
Write Word 1 8-bit Calibration Mask Cal
Write Word 2 RTD 3 Type RTD 2 Type RTD 1 Type RTD 0 Type
Write Word 3 RTD 7 Type RTD 6 Type RTD 5 Type RTD 4 Type
Where: Enh = Enhanced
MDT = Module Data Type
Clk
Cal Hi
Filter Cutoff Enh MDT
Cal Lo
1794-IR8 Word/Bit Descriptions
Word
Read Word 1 00 to 15 (00 to 17) Reserved
Read Word 2 00 to 15 (00 to 17) Channel 0 Input data
Read Word 3 00 to 15 (00 to 17) Channel 1 Input data
Read Word 4 00 to 15 (00 to 17) Channel 2 Input data
Read Word 5 00 to 15 (00 to 17) Channel 3 Input data
Read Word 6 00 to 15 (00 to 17) Channel 4 Input data
Read Word 7 00 to 15 (00 to 17) Channel 5 Input data
Read Word 8 00 to 15 (00 to 17) Channel 6 Input data
Read Word 9 00 to 15 (00 to 17) Channel 7 Input data
Read Word 10 00 to 07
08 to 15 (10 to 17)
Read Word 11 00 to 01 Not used – set to 0
02 Reserved
03
04 to 06
07 Unused – set to 0
Dec. Bits (Octal
Bits)
Description
Underrange bits – these bits are set if the input signal is
below the input channel's minimum range.
Overrange bits – these bits are set if 1), the input signal is
above the input channel's maximum range, or 2), an open
detector is detected.
Powerup bit – this bit is set (1) until configuration data is
received by the module.
Critical Error bits – If these bits are anything other than all
zeroes, return the module to the factory for repair
Page 36 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 37

How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Word
08 (10)
09 (11)
10 (12)
11 to 15 (13 to 17) Unused – set to 0
Write word 1 00 to 01 Module Data Type
Bit 01 00
0 0 °C (default)
0 1 °F
1 0
1 1
02
03 to 05 A/D Filter First Notch Frequency
Bit 05 04 03 Definition
0 0 0 10Hz (default)
0 0 1 25Hz
0 1 0 50Hz
0 1 1 60Hz
1 0 0 100Hz
1 0 1 250Hz
1 1 0 500Hz
1 1 1 1000hZ
06
07
08 to 15
Write Word 2 00 to 03 Channel 0 RTD Type
Bit 03 02 01 00 RTD Type – Range
0 0 0 0 Resistance (default)
0 0 0 1 No sensor connected – do not scan
0 0 1 0
0 0 1 1
0 1 0 0
Dec. Bits (Octal
Bits)
Description
Calibration Range bit – set to 1 if a reference signal is out of
range during calibration
Calibration Done bit – set to 1 after an initiated calibration
cycle is complete.
Calibration Bad bit – set to 1 if the channel has not had a
valid calibration.
Bipolar counts scaled between –32768 and
+32767
Unipolar counts scaled between 0 and
65535
Enhanced mode select – measures voltage drop across a
precision resistor in the module to compare with the
unknown input.
Calibration High/Low bit – This bit is set during gain
calibration; reset during offset calibration.
Calibration clock – this bit must be set to 1 to prepare for a
calibration cycle; then reset to 0 to initiate calibration.
Calibration mask – The channel, or channels, to be
calibrated will have the correct mask bit set. Bit 0
corresponds to channel 0, bit 1 to channel 1, and so on.
100 ohm Pt = 0.00385 Euro (–200 to
+870°C)
100 ohm Pt = 0.003916 U.S. (–200
to +630°C)
200 ohm Pt = 0.00385 (–200 to
+630°C)
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 37 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 38

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Word
Dec. Bits (Octal
Bits)
0 1 0 1
0 1 1 0 Reserved
0 1 1 1 10 ohm Copper (–200 to +260°C)
1 0 0 0 120 ohm Nickel (–60 to +250°C)
1 0 0 1 100 ohm Nickel (–60 to +250°C)
1 0 1 0 200 ohm Nickel (–60 to +250°C)
1 0 1 1 500 ohm Nickel (–60 to +250°C)
1 1 0 0 Module data time stamp
1101 to 1111 – Reserved
04 to 07 Channel 1 RTD Type (see bits 00 to 03)
08 to 11 Channel 2 RTD Type (see bits 00 to 03)
12 to 15 Channel 3 RTD Type (see bits 00 to 03)
Write Word 3 00 to 03 Channel 4 RTD Type (see write word 2, bits 00 to 03)
04 to 07 Channel 5 RTD Type (see write word 2, bits 00 to 03)
08 to 11 Channel 6 RTD Type (see write word 2, bits 00 to 03)
12 to 15 Channel 7 RTD Type (see write word 2, bits 00 to 03)
Description
500 ohm Pt = 0.00385 (–200 to
+630°C)
3.2.11 1794-IT8 – Thermocouple Input Module Image Table Mapping
Module Image
Reserved
Input Data Channel 0
I/O Image
Input Size
1 to 11 Words
Output Size
0 to 3 Words
Calibration Mask
1794-IT8 Read
Dec. Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
Octal Bit 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
Read Word 1 Reserved
Read Word 2 Channel 0 Input Data
Read Word 3 Channel 1 Input Data
Read Word 4 Channel 2 Input Data
Read Word 5 Channel 3 Input Data
Input Data Channel 1
Input Data Channel 2
Input Data Channel 3
Input Data Channel 4
Input Data Channel 5
Input Data Channel 6
Input Data Channel 7
Overrange
Calibration Status
Underrange
Configuration
Thermocouple Type
Thermocouple Type
Page 38 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 39

How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Dec. Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
Octal Bit 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
Read Word 6 Channel 4 Input Data
Read Word 7 Channel 5 Input Data
Read Word 8 Channel 6 Input Data
Read Word 9 Channel 7 Input Data
Read Word
Overrange Bits Underrange Bits
10
Read Word
11
0 0 0 0 0 Bad
Cal
Cal
Done
Cal
0 Diagnostics Pwr
Range
Up
Bad
Structure
CJC
over
CJC
Under
1794-IT8 Write
Dec. Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
Octal Bit 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
Write Word 1 8-Bit Calibration Mask Cal
Write Word 2 Thermocouple 3 Ty pe Thermocouple 2 Type Thermocouple 1 Type Thermocouple 0 Type
Write Word 3 Thermocouple 7 Ty pe Thermocouple 6 Type Thermocouple 5 Type Thermocouple 4 Type
Where: FDF = fixed digital filter bit
Clk
Cal hi
Filter Cutoff FDF Data Type
Cal lo
1794-IT8 Word/Bit Descriptions
Word Decimal Bit
(Octal Bit)
Read Word 1 00 to 15 (00 to 17) Reserved
Read Word 2 00 to 15 (00 to 17) Channel 0 Input data
Read Word 3 00 to 15 (00 to 17) Channel 1 Input data
Read Word 4 00 to 15 (00 to 17) Channel 2 Input data
Read Word 5 00 to 15 (00 to 17) Channel 3 Input data
Read Word 6 00 to 15 (00 to 17) Channel 4 Input data
Read Word 7 00 to 15 (00 to 17) Channel 5 Input data
Read Word 8 00 to 15 (00 to 17) Channel 6 Input data
Read Word 9 00 to 15 (00 to 17) Channel 7 Input data
Read Word 10 00 to 07 (00 to 07)
08 to 15 (10 to 17)
Read Word 11 00 (00)
01 (01)
02 (02)
Description
Underrange bits – these bits are set if the input signal is below
the input channel's minimum range.
Overrange bits – these bits are set if 1), the input signal is
above the input channel's maximum range, or 2), an open
detector is detected.
Cold Junction sensor underrange bit. – this bit is set if the cold
junction temperature is below 0°C.
Cold Junction sensor overrange bit. – this bit is set if the cold
junction temperature is above 70°C.
Bad Structure – this bit is set if there is an invalid
thermocouple type selected.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 39 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 40

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Word Decimal Bit
(Octal Bit)
03 (03)
04 to 06 (04 to 06)
07 (07) Unused – set to 0
08 (10)
09 (11)
10 (12)
11 to 15 (13 to 17) Unused – set to 0
Write Word 1 00 to 01 (00 to 01) Module Data Type
Bit 01 00 Definition
0 0 °C (default)
0 1 °F
1 0 Bipolar counts scaled between –32768 and +32767
1 1 Unipolar counts scaled between 0 and 65535
Bit 02 (02)
03 to 05 (03 to 05) A/D Filter First Notch Frequency
Bit 05 04 03 Definition
0 0 0 10Hz (default)
0 0 1 25Hz
0 1 0 50Hz
0 1 1 60Hz
1 0 0 100Hz
1 0 1 250Hz
1 1 0 500Hz
1 1 1 1000hZ
06 (06)
07 (07)
08 to 15 (10 to 17)
Write Word 2 00 to 03 (00 to 03) Channel 0 Thermocouple Type
Bit 03 02 01 00 Thermocouple Type – Range
0 0 0 0 Millivolts (default)
0 0 0 1 300 to 1800°C (572 to 3272°F)
0 0 1 0 –270 to 1000°C (–454 to 1832°F)
Description
Powerup bit – this bit is set (1) until configuration data is
received by the module.
Critical Fault bits – If these bits are anything other than zero,
return the module to the factory for repair.
Calibration Range bit – set to 1 if a reference signal is out of
range during calibration
Calibration Done bit – set to 1 after an initiated calibration
cycle is complete.
Calibration Bad bit – set to 1 if the channel has not had a valid
calibration.
Fixed Digital Filter – When this bit is set (1), a software digital
filter is enabled. This filter settles to 100% of a Full Scale step
input in 60 scans.
Calibration High/Low bit – This bit is set during gain
calibration; reset during offset calibration.
Calibration clock – this bit must be set to 1 to prepare for a
calibration cycle; then reset to 0 to initiate calibration.
Calibration mask – The channel, or channels, to be calibrated
will have the correct mask bit set. Bit 8 corresponds to
channel 0, bit 9 to channel 1, and so on.
Page 40 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 41

How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Word Decimal Bit
(Octal Bit)
0 0 1 1 –210 to 1200°C (–346 to 2192°F)
0 1 0 0 –71 to 1372°C (–95 to 2502°F)
0 1 0 1 –50 to 1768°C (–58 to 3214°F)
0 1 1 0 –50 to 1768°C (–58 to 3214°F)
0 1 1 1 –73 to 400°C (–99 to 752°F)
1 0 0 0 0 to 2315°C (32 to 4199°F)
1 0 0 1 –270 to 1300°C (–450 to 2372°F)
1 0 1 0 Reserved
1 0 1 1 Reserved
1 1 0 0
1 1 0 1
1 1 1 0 Reserved
1 1 1 1 No sensor connected (do not scan)
04 to 07 (04 to 07) Channel 1 Thermocouple Type (see bits 00 to 03)
08 to 11 (10 to 13) Channel 2 Thermocouple Type (see bits 00 to 03)
12 to 15 (14 to 17) Channel 3 Thermocouple Type (see bits 00 to 03)
Write Word 3 00 to 03 (00 to 03) Channel 4 Thermocouple Type (see word 13, bits 00 to 03)
04 to 07 (04 to 07) Channel 5 Thermocouple Type (see word 13, bits 00 to 03)
08 to 11 (10 to 13) Channel 6 Thermocouple Type (see word 13, bits 00 to 03)
12 to 15 (14 to 17) Channel 7 Thermocouple Type (see word 13, bits 00 to 03)
Description
Module reports cold junction temperature
for channels 00 to 03
Module reports cold junction temperature
for channels 04 to 07
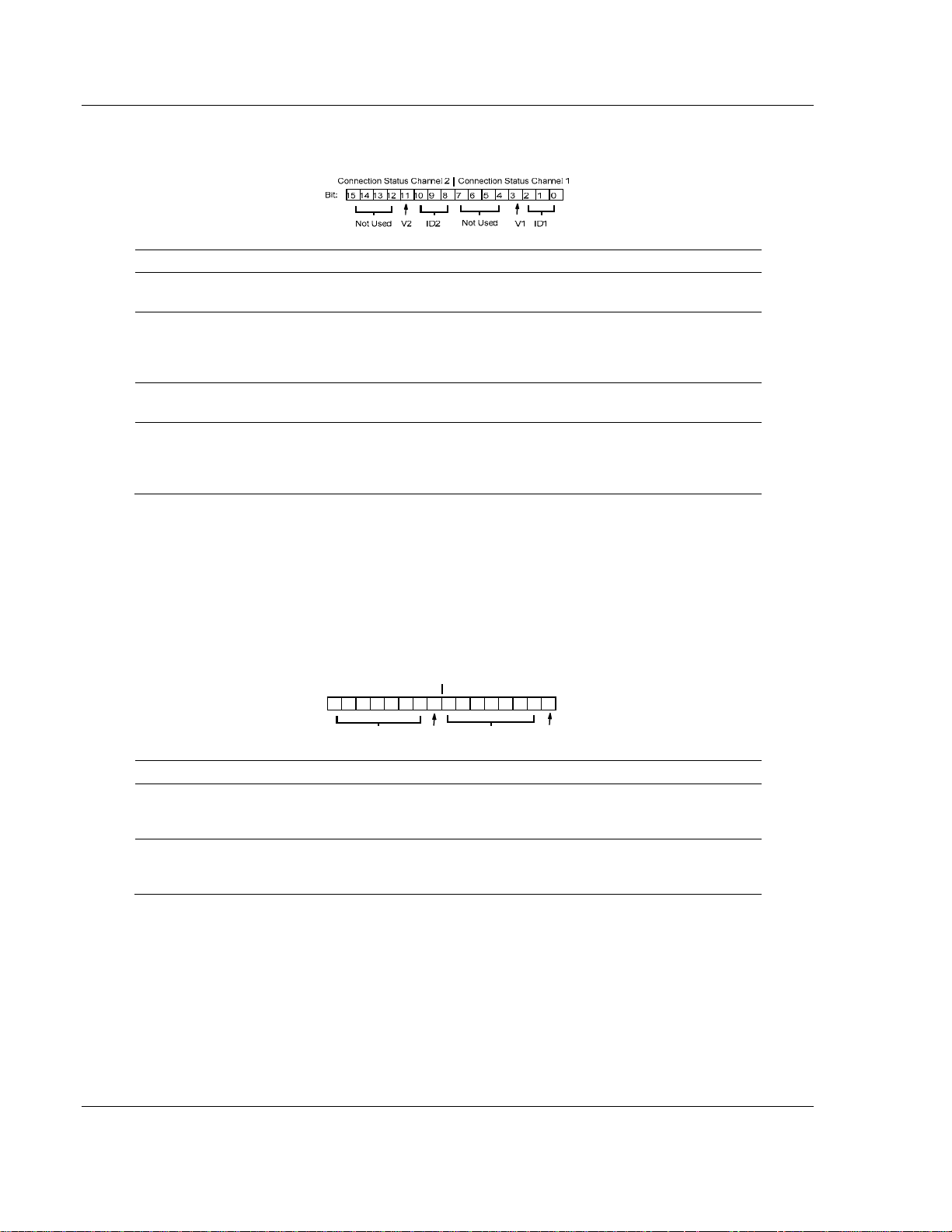
3.2.12 1203-FM1 – SCANport Module Image Table Mapping
I/O Image
Connection StatusChannel 2
Read
6 Words
Connection Enable Channel 2
Write
5 Words
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 41 of 152
August 23, 2007
Module Image
0
Connection Status Channel 1
Logic Status Channel 1
Analog Feedback Channel 1
Logic Status Channel 2
Analog Feedback Channel 2
1 Word
Connection Enable Channel 1
Logic Command Channel 1
Analog Reference Channel 1
Logic Command Channel 2
Analog Reference Channel 2
Not Used
Page 42
3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
3.3 Connection Status Word Definition
Description
SCANport channel 1 valid data bit. When high (1), the Logic Status and Analog Feedback
V1
values are valid and can be used. When low (0), the values should not be used.
SCANport channel 1 connected peripheral port ID number. This three bit field contains the
ID1
port number that channel 1 is connected to on the SCANport device. It should contain a
value between 1 and 7. If this field is 7, then the channel is not connected to the SCANport
device, or the SCANport device may not be powered.
SCANport channel 2 valid data bit. When high (1), the Logic Status and Analog Feedback
V2
values are valid and can be used. When low (0), the values should not be used.
SCANport channel 2 connected peripheral port ID number. This three bit field contains the
ID2
port number that channel 2 is connected to on the SCANport device. It should contain a
value between 1 and 7. If this field is 7, then the channel is not connected to the SCANport
device, or the SCANport device may not be powered.
3.4 Logic Status/Analog Feedback Definition
The Logic Status and Analog Feedback values are defined within the product
manuals of the connected SCANport device(s).
3.5 Connection Enable Word Definition
Connection Enable Channel 2 Connection Enable Channel 1
Bit:
15
14 13 12
11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Not Used E2 Not Used E1
Description
SCANport channel 1 enable bit. When set to 1, the module will attempt to connect to the
E1
SCANport device. When reset to 0, the module stops communicating with the connected
SCANport device. This usually causes the device to fault.
SCANport channel 2 enable bit. When set to 1, the module will attempt to connect to the
E2
SCANport device. When reset to 0, the module stops communicating with the connected
SCANport device. This usually causes the device to fault.
3.6 Logic Command/Analog Reference Definition
The Logic Command and Analog Reference values are defined within the
product manuals of the connected SCANport device(s).
Each I/O module has default values associated with it. At default, each module
will generate inputs/status and expect outputs/configuration.
Page 42 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 43

How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
3.7 Defaults
Module Defaults for: Adapter Defaults Optimal Sizes
Catalog
Number
1794-IB16 16-pt 24V dc Sink Input 1 1 1 0
1794-OB16
1794-IA8 8-pt 120V ac Input 1 1 1 0
1794-OA8 8-pt 120V ac Output 1 1 0 1
1794-IB8S 8-pt 24V dc Sensor Input 1 1 1 0
1794-OW8 8-pt Relay Output 1 1 0 1
1794-IE8 8-pt Analog Input 9 6 8 0
1794-OE4 4-pt Analog Output 1 14 0 4
1794-
IE4XOE2
1794-IR8 8-pt RTD Analog Input 11 4 10 0
1794-IT8 8-pt Thermocouple Input 11 4 10 0
1203-FM1 SCANport Module 6 5 4 3
Description
16-pt 24V dc Source
Output
4 in/2 out Analog Combo 5 10 4 2
Input
Default
1 1 0 1
Output
Default
Input
Default
Output
Default
The default values reflect the maximum number of read/write words.
You can change the I/O data size for a module by reducing the number of words
mapped into the adapter module, as shown in optimal sizes.
Optimal sizes are the settings that provide optimal data to and from the I/O
module. You need a software configuration tool to change
the size. If you are using the Rockwell Automation 1785-PFB/B coprocessor as a
master, you must use the Rockwell Automation PROFIBUS Manager Software
configuration tool. Because the FLEX I/O adapter is compatible with any master,
you can use any comparable configuration tool available on the market.
The optimal settings provide the fastest network time by only mapping read and
write words used by the I/O modules. If you reduce your data sizes to only
include optimal data, you can only change your configuration data with a
software tool. If you must change configuration information on an optimal basis,
your data size must be large enough to include the necessary words.
If you are using PROFIBUS Manager Software to configure your adapter, refer to
your PROFIBUS Manager Software User Manual, publication 1785-6.5.20 for
more information.
For additional information on FLEX I/O modules, refer to the following
publications.
Module Description Catalog Number
16 Sink Input Module 1794-IB16 1794-5.4
16 Source Output Module 1794-OB16 1794-5.3
8 Sensor Input Module 1794-IB8S 1794-5.7
8 Input Module 1794-IA8 1794-5.9
Installation
Instructions
User Manual
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 43 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 44

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform How Communication Takes Place and I/O Image Table Mapping
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Module Description Catalog Number
Installation
Instructions
8 Output Module 1794-OA8 1794-5.10
8 Relay Output Module 1794-OW8 1794-5.19
8 Input Analog Module 1794-IE8 1794-5.6 1794-6.5.2
4 Output Analog Module 1794-OE4 1794-5.5
4 in/2 out Analog Combo
1794-IE4XOE2 1794-5.15
Module
8 RTD Input Analog Module 1794-IR8 1794-5.22 1794-6.5.4
8 Thermocouple Input Module 1794-IT8 1794-5.21 1794-6.5.7
SCANport Module 1203-FM1 1203-5.8
User Manual
Page 44 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 45

Connect the Adapter to the PROFIBUS DP Network 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
4 Connect the Adapter to the PROFIBUS DP
Network
In This Chapter
¾ The DP Physical Layer........................................................... 45
¾ Cabling and Equipment Required for Line A Type .................46
¾ Cabling and Equipment Required for Line B Type .................47
¾ Connect the Adapter to the Network ...................................... 48
¾ Terminate the Network........................................................... 49
4.1 The DP Physical Layer
The PROFIBUS network media is a balanced transmission line corresponding to
the standard EIA RS-485, terminated at both ends. Both line A and line B types
are available, depending on your system requirements.
Specifications and guidelines for DP media:
linear bus, terminated at both ends
drop cables (preferably no longer than .30m), no branches
shielded twisted pair
max. line length between 100 and 1200m (depending on baudrate and cable
type)
number of stations: 32
DP baudrates 3, 6 and 12 M bit/s
Use the following table to determine what line type will best meet your needs.
Characteristic Bus Segments and Drop Cables
Line A Requirements Line B Requirements Total Capacity of
Impedance
Capacity t30 pF/m t60 pF/m
Resistance t110 W/km -
Wire Gauge u0.64 mm u0.53 mm
Conductor Area u0.34 mm2 u0.22 mm2
135-165 W (3 to 29
MHz)
100 to 130 W (fu100
kHz)
all Drop Cables
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 45 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 46

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Connect the Adapter to the PROFIBUS DP Network
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Characteristic Bus Segments and Drop Cables
Maximum
Length1
with a Baud
Rate (bits/s) of:
93.75k 1200 m2 1200 m2 <=3nF
187.5k 1000 m2 600 m2 <=1nF
500k 400 m2 200 m2 <=0.6nF
1.5M 200 m2 NA <=0.2nF
12 M 100 m2 NA
NA = Not Applicable
1 If using a combination of both line types, divide the lengths shown by two. 2 This is the sum of all
bus segment and drop cable lengths.
Line A cabling can support baudrates as high as 12 M bits/s.
<=19.2k 1200 m2 1200 m2 <=15nF
4.2 Cabling and Equipment Required for Line A Type
4.2.1 Cables
You need a shielded twisted pair cable for your cabling (bus segments or drop
cables). Any line A cable available on the market can be used to connect your
adapter to a PROFIBUS network.
4.2.2 T-junction Connectors
You need t-junction connectors to connect your droplines to bus segments. You
can use any t-junctions available on the market.
4.2.3 Termination Blocks
Termination blocks are only needed if the devices on the end of the network do
not have built-in terminating resistors. If you need termination blocks, you can
use any termination blocks available on the market.
4.2.4 Bus Connector
Connect your adapter to the PROFIBUS DP network by attaching a bus
connector to the female 9 pin D-Sub connector on the front of the module.
Important:For detailed information on the topology and cabling for line A, refer to the
PROFIBUS Standard (DIN 19245 Parts 1 & 3, Issue 1994).
Line B cabling can support baudrates as high as 500k bits/s.
Page 46 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 47

Connect the Adapter to the PROFIBUS DP Network 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
4.3 Cabling and Equipment Required for Line B Type
4.3.1 Cables
You need a shielded twisted pair cable for your cabling (bus segments or drop
cables). Any shielded twisted pair cables available on the market can be used to
connect your adapter to a PROFIBUS network, however, bus segment cables
must contain wire for data ground and a cable braid shield. We recommend
Sprecher+Schuh cable as shown in the following table.
4.3.2 T-junction Connectors
You need t-junction connectors to connect your droplines to bus segments. You
can use any t-junctions available on the market, however, we recommend
Sprecher+Schuh connectors as shown in the following table.
4.3.3 Termination Blocks
Termination blocks are only needed if the devices on the end of the network do
not have built-in terminating resistors. If you must use termination blocks, any
termination blocks available on the market can be used, however, we
recommend Sprecher+Schuh termination blocks as shown in the following table.
4.3.4 Bus Connector
Connect your adapter to the PROFIBUS DP network by attaching a bus
connector to the female 9 pin D-Sub connector on the front of the module.
Important: For detailed information on the topology and cabling for line B, refer to the
PROFIBUS Standard (DIN 19245 Parts 1 & 3, Issue 1994).
Equipment Type Catalog Number Part Number
Drop cable Sprecher + Schuh PTL-2, PTL-4, or PDC-10 87.890.282-10
T-junction connector Sprecher + Schuh PTS-0 87.890.276-01
Bus segment cable Sprecher + Schuh none 299.257.001
Bus segment 1m Sprecher + Schuh PCB-10 87.890.281-10
Connector Sprecher + Schuh none 87.890.283-01
Termination Block Sprecher + Schuh PCE-0 87.890.284-01
For line A or B connections, use bus segments with t-junctions and termination
blocks to form the PROFIBUS media (trunk cable). Use termination blocks to
terminate the line at each end of the trunk cable. Use drop cables to connect
devices to the network.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 47 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 48

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Connect the Adapter to the PROFIBUS DP Network
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
4.4 Connect the Adapter to the Network
The maximum number of stations on the same network is 32.
4.4.1 Connect to the Adapter
Connect your drop cable (using either line A or B) to the adapter as shown
below:
1 Connect the cable shield to the housing of the DSUB. The shield is
connected to the FLEX I/O chassis ground.
2 Connect the data signal pins on both ends (Signal + Pin #3 and Signal –
Pin#8).
Page 48 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 49
Connect the Adapter to the PROFIBUS DP Network 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
3 Insert the wired connector into the mating connector on the PROFIBUS
adapter.
RTS (Pin 4) Optional pin. Not used in a standard RS455 PROFIBUS – DP
installation.
4.5 Terminate the Network
You must use termination blocks only if your devices on the end of the network
do not have built-in terminating resistors.
Terminate the PROFIBUS media (trunk cable) at both ends of the network. If you
are not using a connector with built-in resistors, terminate the cable at the
adapter connector as shown below.
4.5.1 Terminate at the Adapter Using Line A
Since Line A has a higher line impedance, you must use the following termination
resistors:
PROFIBUS DP ADAPTER
+ 5 V 6
Signal +
3
8
Signal -
Data Ground
5
9
.
.
6
390 W (2%, 1/4 W)
220 W (2%, 1/4 W)
390 W (2%, 1/4 W)
4.5.2 Terminate at the Adapter Using Line B
Use the following termination resistors with line B:
PROFIBUS DP ADAPTER
+ 5 V 6
Signal +
Signal -
Data Ground
3
8
5
9
.
.
6
390 W (2%, 1/4 W)
150 W (2%, 1/4 W)
390 W (2%, 1/4 W)
5
.
.
1
CABLE
5
.
.
1
CABLE
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 49 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 50

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Connect the Adapter to the PROFIBUS DP Network
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Page 50 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 51

Configure the Adapter for Master/Slave Communication 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
5 Configure the Adapter for Master/Slave
Communication
In This Chapter
¾ How Master/Slave Communication Takes Place.................... 51
¾ Entering User Parameter Data............................................... 52
¾ Read Configuration Response Data....................................... 60
¾ Configuration Example Using PROFIBUS Manager Software61
In this chapter, we describe:
how master/slave communication takes place entering user parameter data entering check configuration data read configuration response data a programming configuration example using Rockwell Automation
PROFIBUS manager software
A data exchange between the master and slave cannot be performed until check
configuration and send parameter data are issued. Each time you power-up the
network, the master sends check configuration and send parameter data to the
slave (FLEX I/O adapter).
5.1 How Master/Slave Communication Takes Place
Check configuration data determines or checks the number of input and output
words used by each FLEX I/O module.
Send parameter data contains device-specific parameters you define for each
FLEX I/O module.
You need a software configuration tool to set the values associated with these
parameters. If you are using the Rockwell Automation 1785-PFB/B coprocessor
as a master, you must use the Rockwell Automation PROFIBUS Manager
Software configuration tool. Since the FLEX I/O adapter is compatible with any
master, you can use any configuration tool available on the market.
The device database (GSD) file is included on the software diskette you
received with your shipment of the FLEX I/O adapter. The PSFT0882.GSD file is
used by your configuration tool to help you set up your system. Your
configuration tool automatically reads the PSFT0882.GSD file and extracts
defaults used in the data exchange.
The file is in ASCII format and you can view it with any text editor. A printed copy
of your PSFT0882.GSD file appears in the Reference chapter.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 51 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 52

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Configure the Adapter for Master/Slave Communication
Y
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
The user parameter data fields are not defined in the PSFT0882.GSD file.
Depending on the format you choose, you may have to manually edit these
values with your configuration tool.
For more information on how you define and enter these user parameter values,
refer to the documentation associated with your master and software
configuration tool. If you are using the Rockwell Automation 1785-PFB/B
Coprocessor master, refer to publications 1785-6.5.15 and 1785-6.5.20.
Send parameter data is comprised of a string of octets that contains 244 bytes of
data:
5.2 Entering User Parameter Data
octets 1 to 7 contain data specific to the:
PROFIBUS standard
defaults contained in the database (PSFT0882.GSD) file
octets 8 to 244 are user configurable and contain user parameter data. User
parameter data consists of these formats:
o auto configure
o condensed
o full
The following illustration shows the structure of the send parameter data table.
Delay
Octets 5 & 6
Ident.
Number
Octet 7
Group
Ident.
Octets 8 -24 4
User P a rameter D at a
ou configure these values using your
software configuration tool.
Octet 1 Octet 2 Octet 3 Octet 4
Station
Status
Watchdog
Control
These values are defined by the PROFIBUS
standard. The defaults are provided by
Watchdog
Control
Minimum
Station
the GSD file.
5.2.1 User Parameter Data
The first byte of the user parameter data is reserved for the SPC3 ASIC. This
byte should always be set to 00h
The second byte of the user parameter data is the flags byte. This byte selects
the appropriate format and also specifies adapter behavior. The flags byte is
defined in the following table:
Send Parameter Data Flags Byte
Bit Position Name Description
0 to 1
Format
Selection
00 = Auto Configure
01 = Reserved
10 = Condensed
11 = Full
Page 52 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 53

Configure the Adapter for Master/Slave Communication 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Send Parameter Data Flags Byte
Bit Position Name Description
2 to 3
4
5 to 7 Reserved Reserved bits must be zero
Fault
Action
Format
Selection
00 = Reset to zero
01 = Hold Last State
10 = Use Safe State
11 = Reserved
0 = Reset inputs to zero
1 = Hold Last Value
If the send parameter data is received with no user parameter data, the flags
byte is set to zero which selects:
auto configure
reset outputs to zero on fault
reset inputs to zero on fault
The reserved bits must be set to zero to prevent undesired firmware update
behavior. This is the default behavior of the module as defined in the
PSFT0882.GSD file.
The descriptions in this chapter use the following example FLEX I/O
configuration to explain the information required for each of these functions:
5.2.2 Auto Configure Format
The Auto Configure format allows you to change modules without affecting the
User Parameter or Check Configuration data. This format provides no keying
from the master on the I/O modules installed in the FLEX I/O system. The
installed module at power-up is taken as the key.
If you change a module while it is being controlled by a master, a minor
recoverable fault will occur. To recover from this fault, you must replace the
module with an identical module type.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 53 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 54

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Configure the Adapter for Master/Slave Communication
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
User Parameter Example
User Parameter Message, Auto Configure Format
Name Value Description
Octet 8: 00h Reserved.
Octet 9: 00h Auto Configure Format, Reset to Zero on Fault
Octet10 to 244 00h Not used
5.2.3 Condensed Format
The condensed format consists of the flags byte and the module key parameter
for each of the eight slots. This parameter dictates which I/O module must be
installed. If at any time the actual module ID does not match this module key, the
slot will be considered in fault and the following occurs:
STATUS LED flashes red/off
an error bit in the poll response data is set
a diagnostic bit in the Ext_Diag_Data field returned in the Read DP-Slave
Diagnostic Information message response is set
All eight slots must be configured. The condensed format structure must be
repeated for each of the eight slots.
Data format for Condensed Format
Name Size Description
Module Key WORD Module ID # that must be installed1
1 Only bits 0 to 12 are used. Bits 13 to 15 must be zero except when keying an empty slot where
0FFFFh is used.
The following table shows the identification numbers for current FLEX I/O
modules.
FLEX I/O Module Catalog Number Module Identification Number (module key)
Four-word Modules
1794-IB16 0281h
1794-OB16 0191h
1794-IA8 0285h
1794IA8I 0280h
1794-OA8 0195h
1794-IB8S 0289h
1794-OW8 0199h
1794IA16 0209h
1794OA8I 019Ch
1794OA16 010Dh
1794IM8 0205h
1794OM8 0105h
1794IB8 0180h
1794IV16 0204h
1794OB8 0190h
Page 54 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 55

Configure the Adapter for Master/Slave Communication 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
FLEX I/O Module Catalog Number Module Identification Number (module key)
Four-word Modules
1794OB16P 0108h
1794OV16 0104h
1794OV16P 0109h
1794OB8EP 019Dh
1794IBIOXOB6 0100h
1794IC16 0208h
1794OC16 010Ch
1793IB4 020Ch
1793OB4P 0110h
1793IB2X0B2P 0111h
1793OW4 0115h
Sixteen-word Modules
1794-IE8/A 1920h
1794-OE4/A 1121h
1794- IE4XOE2/A 1522h
1794-IT8 1B00h
1794-IR8 1B01h
1794-IE8/B 1924h
1794-OE4/B 1125h
1794-IE4XOE2/B 1526h
1293-FM1 1600h
1794IF4I 1720h
1794OF4I 1621h
1794IF2XOF2I 1722h
1794IRT8 1B03h
1794IJ2 1701h
1794ID2 1800h
1794IP4 1A00h
1793IE4 1960h
1793OE2 1161h
1793IE2XOE1 1562h
When you use the condensed format, no safe state data can be defined, thus the
safe state data is left at the power up default of all zeroes. Setting the Fault
Action in the byte to Use Safe State with this format is the equivalent of setting
Reset to Zero.
User Parameter Example
User Parameter Message, Condensed Format
Name Value Description
Octet 8: 00h Reserved
Octet 9: 02h Condensed Format, Reset to Zero on Fault, Rest Inputs to Zero
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 55 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 56

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Configure the Adapter for Master/Slave Communication
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
User Parameter Example
Octet 10 to 11: 0281h 1794-IB16 16-point discrete input module
Octet 12 to 13: 0191h 1794-OB16 16-point discrete output module
Octet 14 to 15: 1920h 1794-IE8 8-point analog input module
Octet 16 to 17: 1121h 1794-OE4 4-point analog output module
Octet 18 to 19: 0FFFFh Empty
Octet 20 to 21: 0FFFFh Empty
Octet 22 to 23: 0FFFFh Empty
Octet 24 to 25: 0FFFFh Empty
Octet 26 to 244 00h Not used
Refer to the configuration example to understand how and where to enter this
data.
Full Format
The full format consists of the flags byte and four parameters for each of the
eight slots. The module key parameter is the same for the full format as defined
by the condensed format, but adds three more parameters for each slot.
Use the full format to:
provide Safe State values for output points
send FLEX I/O module configurations once (when you send parameters)
instead of every poll
configure data sizes to reduce the size of data required during run mode You
must configure all eight slots.
Data format for Full Format
Name Size Description
Module Key WORD Module ID that must be installed1
Module Data Sizes2 BYTE Bits 0 to 3 Safe State Size (in words)
Bits 4 to 7 Config Size (in words)
Safe State Data ARRAY Output Safe States. Word array of size Safe State Size.
Module Configuration
Data
1 Only bits 0 to 12 are used. Bits 13 to 15 must be zero except when keying an
empty slot where 0FFFFh is used.
2 Each of the two sizes can range from 0 to 15 words but when combined cannot
exceed 15 words total.
ARRAY Flex Module Configuration. Word array of size Config Size.
There are some possible configurations of FLEX I/O modules that would exceed
the user parameter area of 237 bytes. Be aware of the totals of the words and
modules you are using.
User Parameter Example
User Parameter Message, Full Format
Name Value Description
Octet 8: 00h Reserved
Page 56 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 57

Configure the Adapter for Master/Slave Communication 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
User Parameter Message, Full Format
Name Value Description
Octet 9: OBh Full Format, Use Safestate
Octet 10 to 11: 0281h Slot 1 Module Key 1794-IB16 16-point discrete input module
Octet 12 to 13 10h Slot 1 config size 1 word, safe state size 0 words
Octet 13 to 14: 0000h 1 config word, input delay times
Octet 15 to 16: 0191h Slot 2 Module Key 1794-OB16 16-point discrete output module
Octet 17: 01h Slot 2 config size 0 words, safe state size 1 word
Octet 18 to 19: 0000h 1 safe state data word, safe state value for output points
Octet 20 to 21: 1920h Slot 3 Module Key 1794-IE8 8-point analog input module
Octet 22: 10h Slot 3 config size 1 word, safe state size 0 words
Octet 23 to 24: 0000h 1 config word, channel selection
Octet 25 to 26: 5121h Slot 4 Module Key 1794-OE4 4-point analog output module
Octet 27: 24h Slot 4 config size 2 words, safe state size 4 words
Octet 28 to 29: 0000h 4 safe state data words – safe state value for output point 1
output point 2
output point 3
output point 4
Octet 30 to 31: 0000h
Octet 32 to 33: 0000h
Octet 34 to 35: 0000h
Octet 36 to 37: 0000h 2 config words – channel selection and
output enable
Octet 38 to 39: 0000h
Octet 40 to 41: 0FFFFh Slot 5 empty
Octet 42: 00h Slot 5 all sizes zero
Octet 43 to 44: 0FFFFh Slot 6 empty
Octet 45: 00h Slot 6 all sizes zero
Octet 46 to 47: 0FFFFh Slot 7 empty
Octet 48: 00h Slot 7 all sizes zero
Octet 49 to 50: 0FFFFh Slot 8 Empty
Octet 51: 00h Slot 8 all sizes zero
Octet 52 to 244 00h Not Used
Refer to the configuration example to understand how and where to enter this
data. On a PROFIBUS DP network, the I/O data exchanged between the
PROFIBUS DP master and a DP slave is encapsulated into logical modules.
The total I/O data exchanged between a PROFIBUS DP master and a DP slave
device comprises a set of logical modules which is defined in the check
configuration data.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 57 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 58

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Configure the Adapter for Master/Slave Communication
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
5.2.4 Entering Check Configuration Data
Each physical slot of the FLEX I/O system is represented by two logical modules
(one input and one output). When the FLEX I/O adapter is powered-up, the
check configuration message configures the module format (input and output
words) and defines the size of the modules within the device. When the sizes are
configured, the I/O data can be optimized to remove unused data from the data
stream.
Both input and output sizes can be configured. If a slot is empty, or if either the
input or output module is zero length, the specific identifier for an empty module
(free place) must be used.
If the end of the identifiers is reached before all slots have been configured, the
remaining slots are configured as empty.
The first two modules allocated are for the adapter itself, and must always be a 1
word input module and a 1 word output module, regardless of what parameter
format you choose. The adapter uses these words for adapter status information.
Modules for each of the individual slots (FLEX I/O modules) must also follow
these word assignments.
The format of the adapter status word is defined in the following table:
Adapter Status Word
Input Status Word
Bit Position Name Description
0 Address Change
1 to 7 Reserved Sent as zeroes.
8 to 15 I/O Module Fault1
Output Status Word
Bit Position Name Description
0 to 15 Reserved Sent as zeroes.
1 I/O Module Faults are caused by:
• transmission errors on the FLEX I/O backplane
• bad module
• removed module
• incorrect module inserted
This bit is set when the Node Address switch is changed
since power up.
This bit is set when an error is detected in a slot position
(bits 0 to 7 refer to slots 1 to 8)
The adapter expects the identifier area for each of the eight FLEX I/O slots to be
2 bytes. The DP input/output identifier and all specific DP identifiers (except the
empty module) are not supported.
Page 58 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 59

Configure the Adapter for Master/Slave Communication 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
e
.
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
The identifier byte and its format are described in the following illustration. This
byte is defined in Part 3 of the PROFIBUS standard.
1 When transferring words, PROFIBUS DP transfers the high byte first, followed by the low byte. If word structure is enter
in the column format the DP master has the possibility to swap the bytes within the word, if required by the target system
Most Significant Bit Least Significant Bit
Bit Number
concistency over
0 byte or word
1 whole length
length format1
0 byte byte structure
1 word word structure
7
5
6
3
4
input/output
00 specific identifier formats
01 input
10 output
11 input-output
1
2
0
Length of data
00 1 byte resp. 1 word
w
w
w
15 16 byte resp. 16 words
The maximum size of this identifier area is 17 bytes. If no FLEX I/O modules are
installed in the upper slots, the length may be less. Consistency must be over a
word.
Check Configuration Example
Check Configuration Message when used with Send Parameter Auto Configure or
Condensed Format (Length 10 bytes)
Name Identifier Byte Description
Octet 1: 50h Input Status Word (input – 1 word)
Octet 2: 60h Output Status Word (output – 1 word)
Octet 3: 50h Slot 1, input module 1 word
Octet 4: 60h Slot 1, output module 1 word
Octet 5: 00h Slot 2, input module empty
Octet 6: 60h Slot 2, output module 1 word
Octet 7: 58h Slot 3, input module 9 words
Octet 8: 60h Slot 3, output module 1 word
Octet 9: 50h Slot 4, input module empty
Octet 10: 65h Slot 4, output module 6 words
I/O sizes configured: 22 input bytes, 20 output bytes
Refer to the configuration example to understand how and where to enter this
data.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 59 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 60

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Configure the Adapter for Master/Slave Communication
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Check Configuration Example
Check Configuration Message when used with Send Parameter Fu ll Format (Length 10
bytes)
Name Identifier Byte Description
Octet 1: 50h Status Word (input – 1 word)
Octet 2: 60h Output Status Word (output – 1 word)
Octet 3: 50h Slot 1, input module 1 word
Octet 4: 00h Slot 1, output module empty
Octet 5: 00h Slot 2, input module empty
Octet 6: 60h Slot 2, output module 1 word
Octet 7: 58h Slot 3, input module 9 words
Octet 8: 00h Slot 3, output module empty
Octet 9: 50h Slot 4, input module 1 word
Octet 10: 63h Slot 4, output module 4 words
I/O sizes configured: 24 input bytes, 12 output bytes
The read configuration message response returns the current configuration data.
At power up, the configuration is the maximum read and write sizes supported by
each FLEX I/O module.
5.3 Read Configuration Response Data
A valid check configuration message updates the internal configuration. The
updated internal configuration is then returned in the message response.
Power Up Configuration Example
Read Configuration Message response at Power Up (Length 10 bytes)
Name Identifier Byte Description
Octet 1: 50h Status Word (input - 1 word)
Octet 2: 60h Output Status Word (output - 1 word)
Octet 3: 51h Slot 1, input module 2 words
Octet 4: 60h Slot 1, output module 1 word
Octet 5: 50h Slot 2, input module 1 word
Octet 6: 61h Slot 2, output module 2 words
Octet 7: 58h Slot 3, input module 9 words
Octet 8: 65h Slot 3, output module 6 word
Octet 9: 50h Slot 4, input module 1 word
Octet 10: 60h Slot 4, output module 14 words
Refer to the configuration example to understand how and where to enter this
data. If you are using the Rockwell Automation PROFIBUS Manager
configuration software, follow this example to understand how to access and
enter data. This example is a User Parameter Message, Full Format.
Page 60 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 61

Configure the Adapter for Master/Slave Communication 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
5.4 Configuration Example Using PROFIBUS Manager Software
For more detailed information on configuring your network, refer to your
PROFIBUS Manager User Manual, publication 1785-6.5.20.
If you are using another configuration tool, how you access and enter data is
similar, however, refer to the user documentation supplied with that tool.
The directions in this example assume you have the software installed and have
constructed a DP network containing at least one 3170-PDP FLEX I/O
PROFIBUS adapter module.
User Parameter Example
User Parameter Message, Full Format
Name Value Description
Octet 8: 00h Reserved
Octet 9: OBh Full Format, Use safe state
Octet 10 to 11: 0281h Slot 1 Module Key 1794-IB16 16-point discrete input module
Octet 12: 10h Slot 1 config size 1 word, safe state size 0 words
Octet 13 to 14: 0000h 1 config word, input delay times
Octet 15 to 16: 0191h Slot 2 Module Key 1794-OB16 16-point discrete output module
Octet 17: 01h Slot 2 config size 0 words, safe state size 1 word
Octet 18 to 19: 0000h 1 safe state data word, safe state value for output points
Octet 20 to 21: 1920h Slot 3 Module Key 1794-IE8 8-point analog input module
Octet 22: 10h Slot 3 config size 1 word, safe state size 0 words
Octet 23 to 24: 0000h 1 config word, channel selection
Octet 25 to 26: 5121h Slot 4 Module Key 1794-OE4 4-point analog output module
Octet 27: 24h Slot 4 config size 2 words, safe state size 4 words
Octet 28 to 29: 0000h 4 safe state data words – safe state value for output point 1
output point 2
output point 3
output point 4
Octet 30 to 31: 0000h
Octet 32 to 33: 0000h
Octet 34 to 35: 0000h
Octet 36 to 37: 0000h 2 config words – channel selection and
output enable
Octet 38 to 39: 0000h
Octet 40 to 41: 0FFFFh Slot 5 empty
Octet 42: 00h Slot 5 all sizes zero
Octet 43 to 44: 0FFFFh Slot 6 empty
Octet 45: 00h Slot 6 all sizes zero
Octet 46 to 47: 0FFFFh Slot 7 empty
Octet 48: 00h Slot 7 all sizes zero
Octet 49 to 50: 0FFFFh Slot 8 Empty
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 61 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 62

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Configure the Adapter for Master/Slave Communication
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
User Parameter Message, Full Format
Name Value Description
Octet 51: 00h Slot 8 all sizes zero
Octet 52 to 244: 00h Not used
1 In your network, double-click on the slave icon.
You see the 3170-PDP Device Parameters screen
Double-click on
You see the User Parameter Data screen:
2 Enter the Full Format data values as shown in the User Parameter example:
User Parameter Example
User Parameter Message, Full Format (Length 43 bytes)
Name Value Description
Octet 8 00h Reserved
Octet 9: 0Bh Full Format, Use safe state
Octet 10 to 11: 0281h Slot 1 Module Key 1794-IB16 16-point discrete input module
Octet 12: 10h Slot 1 config size 1 word, safe state size 0 words
Octet 13 to 14: 0000h 1 config word, input delay times
Octet 15 to 16: 0191h
Octet 17: 01h Slot 2 config size 0 words, safe state size 1 word
Octet 18 to 19: 0000h 1 safe state data word, safe state value for output points
Octet 20 to 21: 1920h Slot 3 Module Key 1794-IE8 8-point analog input module
Octet 22: 10h Slot 3 config size 1 word, safe state size 0 words
Octet 23 to 24: 0000h 1 config word, channel selection
Octet 25 to 26: 5121h Slot 4 Module Key 1794-OE4 4-point analog output module
Octet 27: 24h Slot 4 config size 2 words, safe state size 4 words
Octet 28 to 29: 0000h 2 config words – channel selection and
Octet 30 to 31: 0000h
Slot 2 Module Key 1794-OB16 16-point discrete output
module
output enable
Page 62 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 63

Configure the Adapter for Master/Slave Communication 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
User Parameter Message, Full Format (Length 43 bytes)
Name Value Description
Octet 32 to 33: 0000h 4 safe state data words – safe state value for output point 1
output point 2
output point 3
output point 4
Octet 34 to 35: 0000h
Octet 36 to 37: 0000h
Octet 38 to 39: 0000h
Octet 40 to 41: 0FFFFh Slot 5 empty
Octet 42: 00h Slot 5 all sizes zero
Octet 43 to 44: 0FFFFh Slot 6 empty
Octet 45: 00h Slot 6 all sizes zero
Octet 46 to 47: 0FFFFh Slot 7 empty
Octet 48: 00h Slot 7 all sizes zero
Octet 49 to 50: 0FFFFh Slot 8 Empty
Octet 51: 00h Slot 8 all sizes zero
Octet 52 to 244 00h Not Used
After you enter all octet values, click
In the 3170-PDP Device Parameters screen, click
You see the Modules Information screen:
Select each of the possible modules in the Possible Modules column, then click
on
. Repeat this for the four FLEX I/O modules in the example. Also
add 3170-PDP Status (counts as one module) and three Flex I/O empty slot
modules. All eight slots must be accounted for.
Notice as you add each module, the Module Configuration status appears:
If you want to edit the configuration of a module, select the module and click on
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 63 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 64

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Configure the Adapter for Master/Slave Communication
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
After you account for all module slots in the example, the Modules Information
screen should look similar to this:
This picture is
unavailable at this time.
For more detailed information on configuring your network, refer to your
PROFIBUS Manager User Manual, publication 1785-6.5.20.
Page 64 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 65

Troubleshooting 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
6 Troubleshooting
In This Chapter
¾ What this Chapter Contains ................................................... 65
¾ Troubleshooting with the Indicators........................................ 65
¾ Configuration differences between 1794-APB and 3170-PDP.67
6.1 What this Chapter Contains
In this chapter, we describe how to use the adapter's indicators for
troubleshooting.
It also describes some issues that has to be taken in consideration when
replacing the Rockwell Automation 1794-APB with a 3170-PDP adapter.
Locate the two bi-color indicators on the front panel of the adapter. They show
both normal operation and fault conditions in your Flex I/O PROFIBUS system.
The indicators are:
6.2 Troubleshooting with the Indicators
STATUS - this indicator provides device status
PROFIBUS - this indicator provides communication link status Use the following
table to determine the indicator conditions and status.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 65 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 66

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Troubleshooting
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
STATUS Indicator
Indication Status
OFF No power
Solid Green Normal operation
Flashing Red/OFF Recoverable fault
- Flex I/O module bad
- Incorrect Flex I/O module installed
- Node address changed since
power up
Solid Red Unrecoverable fault
PROFIBUS Indicator
Indication Status
OFF No power or no communication
Solid Green Data is being transmitted and received
Flashing Red/OFF Recoverable fault
- Invalid Send Parameter data1
- Invalid Check Configuration data 2
Solid Red Unrecoverable fault
- Unable to communicate
1 If invalid send Parameter is received, check that:
o The Flag byte (octet 9) contains a Valid mode selection (00h, 10h or 11h).
o The spc3 related byte (octet 8) equals 00h.
2
If invalid Check Configuration data is received, check that the number of
models in the slave configuration data equals nine. (one adapter status
module + one module for each slot)
You can use read diagnostics to view status using the master's configuration
software. The adapter returns identification in response to the Read DP-Slave
Diagnostic Information message.
Viewing Status from the Master's Configuration Software Read DP-Slave
Diagnostics Information
Message
Ext_Diag_Data field (Length 9 bytes)
Octet Description
7 Device Related diagnostic header byte (05h)
8 Revision - Minor
9 Revision - Major
10 Adapter Status
Bit 0 - Node Address Changed
Bits 1 to 7 - Reserved
11 Node Address switch setting
12 Identifier Related diagnostic header byte (44h)
13 to 15 Identifier diagnostic bits1
Page 66 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 67

Troubleshooting 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Message
1 One identifier bit for each logical module (adapter and each slot use two identifier bits). The bits
set indicate a module fault. For example down below.
Example: If the modules in slot 3 and 6 are faulty, byte 13 to 15 will look like this.
Byte 13 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1
Description slot 3 slot 2 slot 1 Adapter
Byte 14 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0
Description slot 7 slot 6 slot 5 slot 4
Byte 15 x x x x x x 0 0
Description not used not used not used slot 8
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit2 Bit 1 Bit 0
6.3 Configuration differences between 1794-APB and 3170-PDP.
There are two things that must be taken in consideration when replacing the AB
adapter with HMS adapter. These items are further described in this document.
1 PSFT0882.GSD file:
The 1794-APB has a Rockwell GSD file with a Rockwell "PROFIBUS Ident
Number" (stating Rockwell as manufactor among other things).
The 3170-PDP has a PSFT0882.GSD file with a "PROFIBUS Ident Number"
(stating PROSOFT TECHNOLOGY, INC. as manufacturer among other
things).
For a new customer this does not make any difference, he just use the
PSFT0882.GSD file instead of the old Rockwell GSD file when installing the
unit.
For a customer already using 1794-APB and need a replacement unit, this
will generate some extra work for that user. The adapter is fully replaceable,
but if a replacement of the adapter is done, the PROFIBUS Master is still
configured with the Rockwell GSD file. The 3170-PDP only responds to the
PSFT0882.GSD file, which means that the Rockwell GSD file must also be
replaced, otherwise network communication will not start.
You must start up the PROFIBUS Configurator and replace the Rockwell
GSD file with the PSFT0882.GSD file.
2 User parameter data:
One extra byte of user parameter data has to be added to the
parameterization string. This extra byte is needed for the 12Mbit ASIC on
board. The user has to add this extra byte in the first position of the user
parameter data string. An example of the adapter configured in Full Format
for the different adapters are shown below. Figure 1 shows the configuration
for 1794-APB, figure 2 shows the same configuration, but for 3170-PDP.
Note that one byte(00h) has to be placed before the Flag byte when 3170PDP is used!
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 67 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 68

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Troubleshooting
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
6.3.1 User parameter data for 1794-APB:
6.3.2 User parameter data for 3170-PDP:
Page 68 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 69

Reference 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
7 Reference
In This Chapter
¾ Product Specifications............................................................ 69
¾ Device Data Base File............................................................ 70
7.1 Product Specifications
3170-PDP Flex I/O PROFIBUS Adapter Specifications
I/O Capacity 8 modules
Input Voltage Rating 24V dc nominal
Input Voltage Range 19.2V to 31.2V dc (includes 5% ac ripple)
Communication Rate All rates up to 12 Mbit/s
Indicators STATUS LED - red/grn
Flexbus Output Current 640mA maximum @ 5V dc
Power Consumption 400mA maximum from external 24V dc supply
Power Dissipation 7.68W maximum @ 19.2V dc
Environmental Conditions
Operational Temperature
Storage Temperature
PROFIBUS Connector 9-pin D-shell
PROFIBUS Drop Cable Standard Drop Cable
Power Conductors
Wire Size
Category
Agency Certification
(when product or packaging is marked)
1 Use this conductor category information for planning conductor routing. Refer to publication 1770-4.1,
"Industrial Automation Wiring and Grounding Guidelines."
PROFIBUS LED - red/grn
0 to 55°C (32 to 122°F)
–40 to 85°C (–40 to 185°F)
12 gauge (4mm2) stranded maximum
3/64 inch (1.2mm) insulation max.
21
• PNO
• CE marked for all applicable directives
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 69 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 70

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Reference
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
7.2 Device Data Base File
This chapter contains an example of the device data base (PSFT0882.GSD) file
for the 3170-PDP.
This file is included on the software diskette you received with your shipment of
the FLEX I/O adapter. The PSFT0882.GSD file is used by your configuration tool
to help you set up your system. Your configuration tool automatically reads the
PSFT0882.GSD file and extracts defaults used in the data exchange.
The file is in ASCII format and you can view it with any text editor. A printed copy
of your PSFT0882.GSD file appears below.
This device data base file changes when new FLEX I/O modules are introduced.
When you add new modules to your system, contact your local Rockwell
Automation representative for the latest version of this file.
;============================================================
; Profibus Device Database of:
; ProSoft Technology Inc. DP slave
; Model: 3170-PDP
; Description: Flex I/O Profibus adapter
; Language: English
; Date: 10 April 2007
; Author: ProSoft Technology Inc.
;============================================================
#Profibus_DP
GSD_Revision = 2
; Device identification
Vendor_Name = " ProSoft Technology Inc "
Model_Name = " 3170-PDP "
Revision = " Version 2.2 "
Ident_Number = 0x0882
Protocol_Ident = 0 ; DP protocol
Station_Type = 0 ; Slave device
FMS_supp = 0 ; FMS not supported
Hardware_Release = " Series A "
Software_Release = " Rev. >= 1.6 "
; Supported baudrates
9.6_supp = 1
19.2_supp = 1
45.45_supp = 1
93.75_supp = 1
187.5_supp = 1
500_supp = 1
1.5M_supp = 1
3M_supp = 1
6M_supp = 1
12M_supp = 1
; Maximum responder time for supported baudrates
MaxTsdr_9.6 = 60
MaxTsdr_19.2 = 60
MaxTsdr_45.45 = 250
Page 70 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 71

Reference 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
MaxTsdr_93.75 = 60
MaxTsdr_187.5 = 60
MaxTsdr_500 = 100
MaxTsdr_1.5M = 150
MaxTsdr_3M = 250
MaxTsdr_6M = 450
MaxTsdr_12M = 800
; Supported hardware features
Redundancy = 0 ; not supported
Repeater_Ctrl_Sig = 2 ; TTL
24V_Pins = 0 ; not connected
Implementation_Type = "SPC3"
; Supported DP features
Freeze_Mode_supp = 1 ; supported
Sync_Mode_supp = 1 ; supported
Auto_Baud_supp = 1 ; supported
Set_Slave_Add_supp = 0 ; not supported
; Max Length of User Parameter
Max_User_Prm_Data_Len = 237
; Maximum polling frequency
Min_Slave_Intervall = 1 ;100 µs
; Maximum supported sizes
Modular_Station = 1 ; modular
Max_Module = 9 ; physical modules = slots
Max_Input_Len = 244
Max_Output_Len = 244
Max_Data_Len = 488
Modul_Offset = 1
Slave_Family = 3
Max_Diag_Data_Len = 15
; Meaning of "device diagnostic" field
;The first two bytes (corresponding to Unit_Diag_Area = 0-15)
;contains information about the actual firmware version.
;The third byte (corresponding to Unit_Diag_Area = 16-23)
;indicates if the address switch has been altered.
Unit_Diag_Bit (16) = "Node address changed"
;The fourth byte (corresponding to Unit_Diag_Area = 24-31) contains ;the current
setting of the node address switch.
;Please look at the user manual (section "Troubleshooting") for a detailed
;explanation about the meaning of these bytes.
;--------------------------------;Prm-Text-Def-List: The Flag byte
;---------------------------------
;Format selection
PrmText = 1
Text(0) = "Auto Configure format"
Text(2) = "Condensed format"
Text(3) = "Full format"
EndPrmText
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 71 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 72

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Reference
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
;Output Fault action
PrmText = 2
Text(0) = "Reset to zero"
Text(1) = "Hold Last State"
Text(2) = "Use Safe State"
EndPrmText
;Input fault action
PrmText = 3
Text(0) = "Reset to zeros"
Text(1) = "Hold Last State"
EndPrmText
;Module specific
PrmText = 4
Text(0) = "8.6 ms / 26.6 ms"
Text(1) = " 9 ms / 27 ms"
Text(2) = "10 ms / 28 ms"
Text(3) = "12 ms / 30 ms"
Text(4) = "17 ms / 35 ms"
Text(5) = "26 ms / 44 ms"
Text(6) = "43 ms / 61 ms"
Text(7) = "78 ms / 96 ms"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 5
Text(0) = "512 us"
Text(1) = "1 ms"
Text(2) = "2 ms"
Text(3) = "4 ms"
Text(4) = "8 ms"
Text(5) = "16 ms"
Text(6) = "32 ms"
Text(7) = "64 ms"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 6
Text(0) = "Disable"
Text(1) = "Enable"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 7
Text(0) = "Degree Celsius"
Text(1) = "Degree Fahrenheit"
Text(2) = "Bipolar"
Text(3) = "Unipolar"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 8
Text(0) = "No enhanced mode"
Text(1) = "Enhanced mode"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 9
Text(0) = "10 Hz"
Page 72 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 73

Reference 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Text(1) = "25 Hz"
Text(2) = "50 Hz"
Text(3) = "60 Hz"
Text(4) = "100 Hz"
Text(5) = "250 Hz"
Text(6) = "500 Hz"
Text(7) = "1000 Hz"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 10
Text(0) = "Resistance"
Text(1) = "No sensor connected"
Text(2) = "100 ohm Pt a = 0.00385 Euro"
Text(3) = "100 ohm Pt a = 0.003916 US"
Text(4) = "200 ohm Pt a = 0.00385"
Text(5) = "500 ohm Pt a = 0.00385"
Text(7) = "10 ohm copper"
Text(8) = "120 ohm nickel"
Text(9) = "100 ohm nickel"
Text(10) = "200 ohm nickel"
Text(11) = "500 ohm nickel"
Text(12) = "Module data time stamp"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 11
Text(0) = "Software digital filter disabled"
Text(1) = "Software digital filter enabled"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 12
Text(0) = "Millivolts"
Text(1) = "B 300 to 1800 C"
Text(2) = "E -270 to 1000 C"
Text(3) = "J -210 to 1200 C"
Text(4) = "K -71 to 1372 C"
Text(5) = "R -50 to 1768 C"
Text(6) = "S -50 to 1768 C"
Text(7) = "T -73 to 400 C"
Text(8) = "C 0 to 2315 C"
Text(9) = "N -270 to 1300 C"
Text(12) = "Rep cold temp for channels 0-3"
Text(13) = "Rep cold temp for channels 4-7"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 13
Text(0) = "7.5 ms / 26.5 ms"
Text(1) = "8 ms / 27 ms"
Text(2) = "9 ms / 28 ms"
Text(3) = "10 ms / 29 ms"
Text(4) = "12 ms / 31 ms"
Text(5) = "16 ms / 35 ms"
Text(6) = "24.5 ms / 44 ms"
Text(7) = "42 ms / 60.5 ms"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 14
Text(0) = "256 us"
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 73 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 74

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Reference
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Text(1) = "512 us"
Text(2) = "1 ms"
Text(3) = "2 ms"
Text(4) = "4 ms"
Text(5) = "8 ms"
Text(6) = "16 ms"
Text(7) = "32 ms"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 15
Text(0) = "No reset"
Text(1) = "Reset"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 16
Text(0) = "Standard input filtered data"
Text(1) = "Fast input"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 17
Text(0) = "0.25 ms"
Text(1) = "0.5 ms"
Text(2) = "1 ms"
Text(3) = "2 ms"
Text(4) = "4 ms"
Text(5) = "8 ms"
Text(6) = "16 ms"
Text(7) = "32 ms"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 18
Text(0) = "Use word 6"
Text(1) = "Use word 0"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 19
Text(0) = "Disabled"
Text(1) = "Enabled"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 20
Text(0) = "Degree Celsius"
Text(1) = "Degree Fahrenheit"
Text(2) = "Degree Kelvin"
Text(3) = "-32767 to +32767"
Text(4) = "0 to 65536"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 21
Text(0) = "0 C"
Text(1) = "20 C"
Text(2) = "25 C"
Text(3) = "30 C"
Text(4) = "40 C"
Text(5) = "50 C"
Text(6) = "60 C"
Text(7) = "70 C"
Page 74 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 75

Reference 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
EndPrmText
PrmText = 22
Text(0) = "Hardware filtering only"
Text(1) = "25 ms"
Text(2) = "100 ms"
Text(3) = "250 ms"
Text(4) = "500 ms"
Text(5) = "1 s"
Text(6) = "2 s"
Text(7) = "5 s"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 23
Text(0) = "Thermocouple"
Text(1) = "RTD"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 24
Text(0) = "Ext comp/2-wire, no comp"
Text(1) = "Int comp/2-wire, user sel comp"
Text(2) = "No comp/3-wire RTD"
Text(3) = "Diff measure 2 ch/4-wire RTD"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 25
Text(0) = "Resistance/mV"
Text(1) = "100 ohm -200 - 870C/300 - 1800C"
Text(2) = "200 ohm -200 - 400C/-270 - 1000C"
Text(3) = "100 ohm -200 - 630C/-210 - 1200C"
Text(4) = "100 ohm -200 - 400C/-270 - 1372C"
Text(5) = "100 ohm nickel/-200 - 800C"
Text(6) = "200 ohm nickel/-270 - 1300C"
Text(7) = "120 ohm nickel/-50 - 1768C"
Text(8) = "10 ohm copper/-50 - 1768C"
Text(9) = "--/-270 - 400C"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 26
Text(0) = "0 ohm"
Text(1) = "5 ohm"
Text(2) = "10 ohm"
Text(3) = "15 ohm"
EndPrmText
Prmtext = 27
Text(0) = "1 - 32767"
Text(1) = "1.0 - 3276.7"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 28
Text(0) = "Use minimum sampling time"
Text(1) = "2"
Text(2) = "4"
Text(3) = "8"
Text(4) = "16"
Text(5) = "32"
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 75 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 76

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Reference
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Text(6) = "64"
Text(7) = "128"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 29
Text(0) = "No multiplier"
Text(1) = "X2"
Text(2) = "X4"
Text(3) = "X32"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 30
Text(0) = "Safe state act by bus comm"
Text(1) = "Safe state act by any failure"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 31
Text(0) = "Reset outputs"
Text(1) = "Hold last state"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 32
Text(0) = "Disabled"
Text(1) = "Alarm only(frequency unchanged)"
Text(2) = "Alarm and force frequency to max"
Text(3) = "Alarm and force frequency to min"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 33
Text(0) = "No multiplier, alarm immediately"
Text(1) = "2 sample periods + 2s delay"
Text(2) = "8 sample periods + 2s delay"
Text(3) = "32 sample periods + 2s delay"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 34
Text(0) = "Frequency alarm"
Text(1) = "Acceleration alarm"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 35
Text(0) = "Rolling average"
Text(1) = "8"
Text(2) = "16"
Text(3) = "32"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 36
Text(0) = "Normal run mode"
Text(1) = "Startup mode"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 37
Text(0) = "2"
Text(1) = "4"
Text(2) = "5"
Text(3) = "10"
Page 76 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 77

Reference 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Text(4) = "20"
Text(5) = "50"
Text(6) = "100"
Text(7) = "200"
Text(8) = "500"
Text(9) = "1000"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 38
Text(0) = "Normal (Active high, 24V=On)"
Text(1) = "Invert input (Active low, 0V=On)"
EndPrmtext
PrmText = 39
Text(0) = "Count on rising edge"
Text(1) = "Quadrature encoder X1"
Text(2) = "Quadrature encoder X2"
Text(3) = "Quadrature encoder X4"
Text(4) = "Count up sig A, down sig B"
Text(5) = "No count"
Text(6) = "No count"
Text(7) = "No count"
EndPrmtext
PrmText = 40
Text(0) = "No gate func on input G"
Text(1) = "Counting if G is high"
Text(2) = "Counting if G is low"
Text(3) = "Counter can be cal if G high"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 41
Text(0) = "Save counter on pos edge Z"
Text(1) = "Save counter on pos edge G"
Text(2) = "Save counter on neg edge G"
Text(3) = "Save counter on neg & pos edge G"
EndPrmtext
PrmText = 42
Text(0) = "Pulse counting and period time"
Text(1) = "Period time"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 43
Text(0) = "Period time with 10MHz clock"
Text(1) = "Period time with 1MHz clock"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 44
Text(0) = "1 period"
Text(1) = "2 periods"
Text(2) = "4 periods"
Text(3) = "8 periods"
Text(4) = "16 periods"
Text(5) = "32 periods"
Text(6) = "64 periods"
Text(7) = "128 periods"
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 77 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 78

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Reference
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
EndPrmText
; Bentley Nevada specific
PrmText = 46
Text(0) = "0-3 mils"
Text(1) = "0-5 mils"
Text(2) = "0-10 mils"
Text(3) = "0-15 mils"
Text(4) = "0-20 mils"
Text(5) = "0-100 um"
Text(6) = "0-125 um"
Text(7) = "0-150 um"
Text(8) = "0-200 um"
Text(9) = "0-250 um"
Text(10) = "0-300 um"
Text(11) = "0-400 um"
Text(12) = "0-500 um"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 47
Text(0) = "4 Hz"
Text(1) = "1 Hz"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 48
Text(0) = "4000 Hz"
Text(1) = "600 Hz"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 49
Text(0) = "0.15 s"
Text(1) = "0.20 s"
Text(2) = "0.30 s"
Text(3) = "0.50 s"
Text(4) = "0.60 s"
Text(5) = "1.00 s"
Text(6) = "2.00 s"
Text(7) = "3.00 s"
Text(8) = "5.00 s"
Text(9) = "6.00 s"
Text(10) = "10.00 s"
Text(11) = "20.00 s"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 50
Text(0) = "Normal operation"
Text(1) = "Reset"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 51
Text(0) = "None"
Text(1) = "Internal galvanic isolator"
Text(2) = "External zener barrier"
Text(3) = "External galvanic isolator"
EndPrmText
Page 78 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 79

Reference 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
PrmText = 52
Text(0) = "Monitor will not accept conf"
Text(1) = "Normal operation mode"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 53
Text(0) = "None"
Text(1) = "1.5"
Text(2) = "2.0"
Text(3) = "3.0"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 54
Text(0) = "Not active"
Text(1) = "Active"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 56
Text(0) = "Thrust direction towards probe"
Text(1) = "Thrust direction away from probe"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 58
Text(0) = "0-0.5 in/s pk"
Text(1) = "0-1.0 in/s pk"
Text(2) = "0-2.0 in/s pk"
Text(8) = "0-10 mm/s pk"
Text(9) = "0-20 mm/s pk"
Text(10) = "0-50 mm/s pk"
Text(16) = "0-5 mils pp, integrated vel"
Text(17) = "0-10 mils pp, integrated vel"
Text(18) = "0-20 mils pp, integrated vel"
Text(24) = "0-100 um pp, integrated vel"
Text(25) = "0-200 um pp, integrated vel"
Text(26) = "0-500 um pp, integrated vel"
Text(32) = "0-0.5 in/s rms"
Text(33) = "0-1.0 in/s rms"
Text(34) = "0-2.0 in/s rms"
Text(40) = "0-10 mm/s rms"
Text(41) = "0-20 mm/s rms"
Text(42) = "0-40 mm/s rms"
Text(43) = "0-50 mm/s rms"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 59
Text(0) = "TOK off"
Text(1) = "TOK on"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 60
Text(0) = "3 Hz"
Text(1) = "10 Hz"
Text(2) = "15 Hz"
Text(3) = "18 Hz"
Text(4) = "20 Hz"
Text(5) = "25 Hz"
Text(6) = "30 Hz"
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 79 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 80

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Reference
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Text(7) = "50 Hz"
Text(8) = "60 Hz"
Text(9) = "80 Hz"
Text(10) = "100 Hz"
Text(11) = "120 Hz"
Text(12) = "110 Hz"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 61
Text(0) = "5500 Hz"
Text(1) = "4000 Hz"
Text(2) = "3000 Hz"
Text(3) = "2000 Hz"
Text(4) = "1600 Hz"
Text(5) = "1400 Hz"
Text(6) = "1200 Hz"
Text(7) = "1000 Hz"
Text(8) = "800 Hz"
Text(9) = "600 Hz"
Text(10) = "400 Hz"
Text(11) = "200 Hz"
Text(12) = "120 Hz"
Text(13) = "100 Hz"
Text(14) = "450 Hz"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 63
Text(0) = "0-2 gs pk"
Text(1) = "0-5 gs pk"
Text(2) = "0-10 gs pk"
Text(3) = "0-20 gs pk"
Text(4) = "0-25 gs pk"
Text(5) = "0-40 gs pk"
Text(6) = "0-50 gs pk"
Text(8) = "0-20 m/s2 pk"
Text(9) = "0-50 m/s2 pk"
Text(10) = "0-100 m/s2 pk"
Text(11) = "0-200 m/s2 pk"
Text(12) = "0-250 m/s2 pk"
Text(13) = "0-400 m/s2 pk"
Text(14) = "0-500 m/s2 pk"
Text(16) = "0-1.0 in/s, int acc"
Text(17) = "0-2.0 in/s, int acc"
Text(24) = "0-25 mm/s pk, int acc"
Text(25) = "0-50 mm/s pk, int acc"
Text(26) = "0-100 mm/s pk, int acc"
Text(32) = "0-2 gs rms acc"
Text(33) = "0-5 gs rms acc"
Text(34) = "0-10 gs rms acc"
Text(35) = "0-20 gs rms acc"
Text(36) = "0-25 gs rms acc"
Text(37) = "0-40 gs rms acc"
Text(38) = "0-50 gs rms acc"
Text(40) = "0-20 m/s2 rms acc"
Text(41) = "0-50 m/s2 rms acc"
Text(42) = "0-100 m/s2 rms acc"
Text(43) = "0-200 m/s2 rms acc"
Page 80 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 81

Reference 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Text(44) = "0-250 m/s2 rms acc"
Text(45) = "0-400 m/s2 rms acc"
Text(46) = "0-500 m/s2 rms acc"
Text(48) = "0-1.0 in/s rms, int rms acc"
Text(49) = "0-2.0 in/s rms, int rms acc"
Text(56) = "0-25 mm/s rms, int rms acc"
Text(57) = "0-50 mm/s rms, int rms acc"
Text(58) = "0-100 mm/s rms, int rms acc"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 64
Text(1) = "Dual accel, 14.05 kHz"
Text(2) = "Dual accel, 31.55 kHz"
Text(3) = "Single channel accel, 23.4 kHz"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 65
Text(1) = "01"
EndPrmText
PrmText = 66
Text(0) = "73.5kHz or min 0.007ms pulsewdth"
Text(1) = "37.8kHz or min 0.013ms pulsewdth"
Text(2) = "12.8kHz or min 0.04ms pulsewdth"
Text(3) = "1.2kHz or min 0.4ms pulsewdth"
EndPrmText
;========================================
;End of all the Text string definitions.
ExtUserPrmData = 1 "Format Selection"
BitArea(0-1) 0 0,2,3
Prm_Text_Ref = 1
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 2 "Output Fault Action"
BitArea(2-3) 0 0-2
Prm_Text_Ref = 2
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 3 "Input Fault Action"
Bit(4) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 3
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 4 "Input delay time"
BitArea(0-2) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 4
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 5 "Delay Time for Inputs 00-11"
BitArea(0-2) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 5
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 6 "Delay Time for Inputs 12-15"
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 81 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 82

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Reference
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
BitArea(3-5) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 5
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 7 "Safe state value word 0"
Unsigned16 0 0-65535
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 8 "Safe state value word 1"
Unsigned16 0 0-65535
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 9 "Safe state value word 2"
Unsigned16 0 0-65535
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 10 "Safe state value word 3"
Unsigned16 0 0-65535
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 11 "Range selection"
Unsigned16 0 0-65535
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 12 "Channel 0 output"
Bit(0) 1 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 6
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 13 "Channel 1 output"
Bit(1) 1 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 6
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 14 "Channel 2 output"
Bit(2) 1 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 6
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 15 "Channel 3 output"
Bit(3) 1 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 6
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 16 "Safe state value byte"
Unsigned8 0 0-255
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 17 "Calibration mask"
Unsigned8 0 0-255
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 18 "Module data type"
BitArea(0-1) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 7
EndExtUserPrmData
Page 82 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 83

Reference 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
ExtUserPrmData = 19 "Enhanched mode selct"
Bit(2) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 8
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 20 "A/D filter first notch frequency"
BitArea(3-5) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 9
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 21 "Channel 0 RTD type"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 10
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 22 "Channel 1 RTD type"
BitArea(4-7) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 10
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 23 "Channel 2 RTD type"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 10
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 24 "Channel 3 RTD type"
BitArea(4-7) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 10
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 25 "Channel 4 RTD type"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 10
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 26 "Channel 5 RTD type"
BitArea(4-7) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 10
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 27 "Channel 6 RTD type"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 10
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 28 "Channel 7 RTD type"
BitArea(4-7) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 10
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 29 "Fixed digital filter"
Bit(2) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 11
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 30 "Channel 0 Thermocouple type"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-15
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 83 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 84

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Reference
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Prm_Text_Ref = 12
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 31 "Channel 1 Thermocouple type"
BitArea(4-7) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 12
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 32 "Channel 2 Thermocouple type"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 12
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 33 "Channel 3 Thermocouple type"
BitArea(4-7) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 12
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 34 "Channel 4 Thermocouple type"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 12
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 35 "Channel 5 Thermocouple type"
BitArea(4-7) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 12
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 36 "Channel 6 Thermocouple type"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 12
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 37 "Channel 7 Thermocouple type"
BitArea(4-7) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 12
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 38 "Input delay time"
BitArea(0-2) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 5
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 39 "Delay time input 0-11"
BitArea(0-2) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 13
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 40 "Delay time input 12-15"
BitArea(3-5) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 13
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 41 "Delay time input"
BitArea(0-2) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 13
EndExtUserPrmData
Page 84 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 85

Reference 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
ExtUserPrmData = 42 "Filter time for inputs"
BitArea(0-2) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 14
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 43 "Counter reset"
Bit(4) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 15
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 44 "Counter fast"
Bit(5) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 16
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 45 "Input filter time, 0-9/11"
BitArea(0-2) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 17
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 46 "Input filter time, 12-15"
BitArea(3-5) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 17
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 47 "Delay Time for Inputs 0-3"
BitArea(0-2) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 5
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 48 "Safe state, 4 bits"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-15
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 49 "Safe state, 2 bits"
BitArea(0-1) 0 0-3
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 50 "Delay Time for Inputs 0-1"
BitArea(0-2) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 5
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 51 "Full range bits"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-15
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 52 "Configure select bits"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-15
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmdata = 53 "Multiplex control bits"
BitArea(0-1) 0 0-3
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmdata = 54 "Configure select bits"
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 85 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 86

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Reference
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
BitArea(0-1) 0 0-3
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmdata = 55 "Full range bits"
BitArea(0-1) 0 0-3
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 56 "Multiplex control bit"
Bit(0) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 18
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmdata = 57 "Configure select bits"
BitArea(0-4) 0 0-31
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmdata = 58 "Full range bits"
BitArea(0-4) 0 0-31
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmdata = 59 "Channel 3,2,1,0 filter"
Unsigned16 0 0-65535
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmdata = 60 "Channel 3,2,1,0 configuration"
Unsigned16 0 0-65535
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmdata = 61 "Real time sample interval"
Unsigned16 0 0-32767
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 62 "Initiate configuration"
Bit(7) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 63 "Transparent bit"
Bit(5) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 64 "Interrupt toggle bit"
Bit(4) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 65 "Revert to defaults"
Bit(7) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 66 "Quick calibration"
Bit(6) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
Page 86 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 87

Reference 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
ExtUserPrmData = 67 "Calibration clock"
Bit(5) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 68 "Gain offset select"
Bit(4) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 69 "Channel 0"
Bit(0) 1 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 70 "Channel 1"
Bit(1) 1 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 71 "Channel 2"
Bit(2) 1 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 72 "Channel 3"
Bit(3) 1 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 73 "One"
Bit(6) 1 1-1
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 74 "Outputs to hold, Channel 0"
Bit(0) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 75 "Outputs to hold, Channel 1"
Bit(1) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 76 "Outputs to hold, Channel 2"
Bit(2) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 77 "Outputs to hold, Channel 3"
Bit(3) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 78 "Input channel 1 filter"
BitArea(4-7) 0 0-15
EndExtUserPrmData
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 87 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 88

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Reference
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
ExtUserPrmData = 79 "Input channel 0 filter"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-15
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 80 "Output channel 1 configuration"
BitArea(4-7) 0 0-15
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 81 "Output channel 0 configuration"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-15
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 82 "Input channel 1 configuration"
BitArea(4-7) 0 0-15
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 83 "Input channel 0 configuration"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-15
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 84 "Input Channel 0"
Bit(0) 1 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 85 "Input Channel 1"
Bit(1) 1 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 86 "Output Channel 0"
Bit(2) 1 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 87 "Output Channel 1"
Bit(3) 1 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 88 "Outputs to hold, Channel 1"
Bit(3) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 89 "Outputs to hold, Channel 0"
Bit(2) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 90 "Calibration"
Bit(6) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 91 "Calibration clock"
Page 88 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 89

Reference 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Bit(7) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 92 "Data format for all channels"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-4
Prm_Text_Ref = 20
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 93 "Fault mode channels 4-7"
Bit(7) 1 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 94 "Fault mode channels 0-3"
Bit(6) 1 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 95 "Reference junction selection"
BitArea(3-5) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 21
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 96 "Filter cut-off"
BitArea(0-2) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 22
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 97 "Input type sel ch 4-7"
BitArea(6-7) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 23
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 98 "Input type sel ch 0-3"
BitArea(6-7) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 23
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 99 "Sensor mode ch 4-7 Thermo/RTD"
BitArea(4-5) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 24
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 100 "Sensor mode ch 0-3 Thermo/RTD"
BitArea(4-5) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 24
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 101 "Sensor type ch 4-7 RTD/Thermo"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-9
Prm_Text_Ref = 25
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 102 "Sensor type ch 0-3 RTD/Thermo"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-9
Prm_Text_Ref = 25
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 89 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 90

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Reference
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 103 "RTD offset Channel 7"
BitArea(6-7) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 26
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 104 "RTD offset Channel 6"
BitArea(4-5) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 26
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 105 "RTD offset Channel 5"
BitArea(2-3) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 26
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 106 "RTD offset Channel 4"
BitArea(0-1) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 26
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 107 "RTD offset Channel 3"
BitArea(6-7) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 26
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 108 "RTD offset Channel 2"
BitArea(4-5) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 26
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 109 "RTD offset Channel 1"
BitArea(2-3) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 26
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 110 "RTD offset Channel 0"
BitArea(0-1) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 26
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmdata = 111 "EDT command word"
Unsigned16 0 0-32767
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 112 "Communication fault"
Bit(7) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 113 "Safe state mode"
Bit(6) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 31
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 114 "Frequency range Ch 0"
Page 90 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 91

Reference 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Bit(5) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 27
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 115 "Frequency range Ch 1"
Bit(5) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 27
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 116 "Pulses to terminate sampl, Ch 0"
BitArea(2-4) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 28
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 117 "Pulses to terminate sampl, Ch 1"
BitArea(2-4) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 28
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 118 "Missing pulse multiplier, Ch 0"
BitArea(0-1) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 29
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 119 "Missing pulse multiplier, Ch 1"
BitArea(0-1) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 29
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 120 "Local fault mode"
Bit(6) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 30
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 121 "Maximum frequency Ch 0"
Unsigned16 0 0-32767
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 122 "Maximum frequency Ch 1"
Unsigned16 0 0-32767
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 123 "Freq scaling multiplier Ch 0"
Unsigned8 0 0-255
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 124 "Freq scaling multiplier Ch 1"
Unsigned8 0 0-255
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 125 "Wire off fault sel GI, Ch 0"
Bit(7) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 126 "Wire off fault sel GI, Ch 1"
Bit(7) 0 0-1
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 91 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 92

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Reference
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 127 "Wire off fault sel FI, Ch 0"
Bit(6) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 128 "Wire off fault sel FI, Ch 1"
Bit(6) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 129 "Invert select GI, Ch 0"
Bit(5) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 38
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 130 "Invert select GI, Ch 1"
Bit(5) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 38
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 131 "Invert select FI, Ch 0"
Bit(4) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 38
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 132 "Invert select FI, Ch 1"
Bit(4) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 38
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 133 "Min freq sampling time, Ch 0"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-9
Prm_Text_Ref = 37
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 134 "Min freq sampling time, Ch 1"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-9
Prm_Text_Ref = 37
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 135 "Initiate startup select, Ch 0"
Bit(7) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 36
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 136 "Initiate startup select, Ch 1"
Bit(7) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 36
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 137 "Acceleration calc time, Ch 0"
BitArea(5-6) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 35
EndExtUserPrmData
Page 92 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 93

Reference 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
ExtUserPrmData = 138 "Acceleration calc time, Ch 1"
BitArea(5-6) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 35
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 139 "Freq/Acc alarm select, Ch 0"
Bit(4) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 34
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 140 "Freq/Acc alarm select, Ch 1"
Bit(4) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 34
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 141 "Missing pulse delay mult, Ch 0"
BitArea(2-3) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 33
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 142 "Missing pulse delay mult, Ch 1"
BitArea(2-3) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 33
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 143 "Wire off/Missing pulse, Ch 0"
BitArea(0-1) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 32
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 144 "Wire off/Missing pulse, Ch 1"
BitArea(0-1) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 32
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 145 "Preset reset, CW0"
Bit(7) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 146 "Store reset, CW0"
Bit(6) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 147 "Rollover, CW0"
Bit(5) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 148 "Store control, CW0"
BitArea(3-4) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 41
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 149 "Gate control, CW0"
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 93 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 94

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Reference
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
BitArea(1-2) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 40
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 150 "Cal cntrl, Reset, CW0"
Bit(0) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 151 "Cal cntrl, Direction, CW0"
Bit(7) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 152 "Cal cntrl, Enable, CW0"
Bit(6) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 153 "Count enable, CW0"
Bit(5) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 154 "Enable Z preset, CW0"
Bit(4) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 155 "Preset bit, CW0"
Bit(3) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 156 "Mode selection, CW0"
BitArea(0-2) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 39
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 157 "Preset reset, CW1"
Bit(7) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 158 "Store reset, CW1"
Bit(6) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 159 "Rollover, CW1"
Bit(5) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 160 "Store control, CW1"
BitArea(3-4) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 41
Page 94 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 95

Reference 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 161 "Gate control, CW1"
BitArea(1-2) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 40
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 162 "Cal cntrl, Reset, CW1"
Bit(0) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 163 "Cal cntrl, Direction, CW1"
Bit(7) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 164 "Cal cntrl, Enable, CW1"
Bit(6) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 165 "Count enable, CW1"
Bit(5) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 166 "Enable Z preset, CW1"
Bit(4) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 167 "Preset bit, CW1"
Bit(3) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 168 "Mode selection, CW1"
BitArea(0-2) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 39
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 169 "Channel 0 Preset"
Unsigned16 0 0-65535
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 170 "Channel 1 Preset"
Unsigned16 0 0-65535
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 171 "Pulse/period measurement, Ch 3"
Bit(3) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 42
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 172 "Pulse/period measurement, Ch 2"
Bit(2) 0 0-1
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 95 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 96

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Reference
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
Prm_Text_Ref = 42
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 173 "Pulse/period measurement, Ch 1"
Bit(1) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 42
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 174 "Pulse/period measurement, Ch 0"
Bit(0) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 42
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 175 "Period nr selection, Ch 3"
BitArea(5-7) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 44
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 176 "Clock freq for period time, Ch 3"
Bit(4) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 43
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 177 "Period nr selection, Ch 2"
BitArea(1-3) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 44
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 178 "Clock freq for period time, Ch 2"
Bit(0) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 43
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 179 "Period nr selection, Ch 1"
BitArea(5-7) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 44
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 180 "Clock freq for period time, Ch 1"
Bit(4) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 43
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 181 "Period nr selection, Ch 0"
BitArea(1-3) 0 0-7
Prm_Text_Ref = 44
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 182 "Clock freq for period time, Ch 0"
Bit(0) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 43
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 183 "Start new measurement, Ch 3"
Bit(3) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
Page 96 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 97

Reference 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
ExtUserPrmData = 184 "Start new measurement, Ch 2"
Bit(2) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 185 "Start new measurement, Ch 1"
Bit(1) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 186 "Start new measurement, Ch 0"
Bit(0) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 187 "CHA Transduc type & Scale factor"
Unsigned16 0 0-65535
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 188 "CHB Transduc type & Scale factor"
Unsigned16 0 0-65535
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 191 "CHA Full scale range"
BitArea(4-7) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 46
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 192 "CHB Full scale range"
BitArea(4-7) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 46
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 193 "CHA Over alarm gap setpoint"
BitArea(0-7) 0 0-240
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 194 "CHA Under alarm gap setpoint"
BitArea(0-7) 0 0-240
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 195 "CHB Over alarm gap setpoint"
BitArea(0-7) 0 0-240
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 196 "CHB Under alarm gap setpoint"
BitArea(0-7) 0 0-240
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 197 "CHA Danger setpoint"
BitArea(0-7) 0 0-200
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 198 "CHA Alert setpoint"
BitArea(0-7) 0 0-200
EndExtUserPrmData
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 97 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 98

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Reference
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
ExtUserPrmData = 199 "CHB Danger setpoint"
BitArea(0-7) 0 0-200
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 200 "CHB Alert setpoint"
BitArea(0-7) 0 0-200
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 201 "CHA HP Corner"
BitArea(4-7) 0 0-13
Prm_Text_Ref = 47
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 202 "CHA LP Corner"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-13
Prm_Text_Ref = 48
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 203 "CHB HP Corner"
BitArea(4-7) 0 0-13
Prm_Text_Ref = 47
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 204 "CHB LP Corner"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-13
Prm_Text_Ref = 48
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 205 "CHA Danger time delay"
BitArea(4-7) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 49
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 206 "CHA Alert time delay"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 49
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 207 "CHB Danger time delay"
BitArea(4-7) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 49
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 208 "CHB Alert time delay"
BitArea(0-3) 0 0-15
Prm_Text_Ref = 49
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 209 "Monitor reset"
Bit(7) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 50
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 210 "Barrier Configuration"
BitArea(5-6) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 51
Page 98 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
Page 99

Reference 3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 211 "Set configuration flag"
Bit(4) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 52
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 212 "Channel A"
Bit(1) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 213 "Channel B"
Bit(0) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 214 "CHA Trip multiply"
BitArea(6-7) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 53
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 215 "CHB Trip multiply"
BitArea(4-5) 0 0-3
Prm_Text_Ref = 53
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 216 "CHA trip multiply enable"
Bit(3) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 217 "CHB trip multiply enable"
Bit(2) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 19
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 218 "CHA Inhibit"
Bit(1) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 54
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 219 "CHB Inhibit"
Bit(0) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 54
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 222 "CHA Full scale range & Zero pos"
Unsigned16 0 0-65535
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 223 "CHB Full scale range & Zero pos"
Unsigned16 0 0-65535
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 224 "CHA Direct over danger setpoint"
Unsigned8 0 0-200
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 99 of 152
August 23, 2007
Page 100

3170-PDP ♦ FLEX Platform Reference
FLEX I/O™ PROFIBUS Adapter
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 225 "CHA Direct under danger setpoint"
Unsigned8 0 0-200
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 226 "CHA Direct over alert setpoint"
Unsigned8 0 0-200
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 227 "CHA Direct under alert setpoint"
Unsigned8 0 0-200
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 228 "CHB Direct over Danger setpoint"
Unsigned8 0 0-200
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 229 "CHB Direct under Danger setpoint"
Unsigned8 0 0-200
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 230 "CHB Direct over alert setpoint"
Unsigned8 0 0-200
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 231 "CHB Direct under alert setpoint"
Unsigned8 0 0-200
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 232 "CHA Upscale thrust direction"
Bit(3) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 56
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 233 "CHB Upscale thrust direction"
Bit(2) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 56
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 236 "CHA Full scale range"
BitArea(2-7) 0 0-63
Prm_Text_Ref = 58
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 237 "CHB Full scale range"
BitArea(2-7) 0 0-63
Prm_Text_Ref = 58
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 238 "CHA TOK"
Bit(1) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref = 59
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData = 239 "CHB TOK"
Bit(1) 0 0-1
Page 100 of 152 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
August 23, 2007
 Loading...
Loading...