Potter Fire Alarm Systems User Manual

Fire Alarm Systems
Training Manual
Manual #8700055 - REV F
4/10
Fire Alarm Training • 8700055 • Rev F • 4/10
Foreword
ThehistoryoffiredetectionandalarmintheUnitedStatedatesbacktothe1800swiththefirststandards.Sincethenthescienceand technology behind fire detection and alarm continues to improve. The primary purpose for fire detection and alarm is the reduction of loss of life and property from fire.
The modern fire alarm is constantly evolving as the technology around detection and notification expands. However, the basic functions of the fire alarm system remain unchanged. There are two key pieces to every fire alarm system; detection, local notification. Most fire alarm systems also provide off premises reporting to either the fire department or a monitoring company that reports the alarm to the local fire department.
This manual will give a brief overview to the pieces of the fire detection and alarm system. These parts include the symbols used for drafting plans, types of detection, control panels and types of notification. In addition, this manual will discuss the required documentation that is required for the permit, installation and maintenance process.
The core pieces of every fire alarm system are the same. The systems can become quite complex with multiple panels networked together over an entire campus. However the basic parts that make up the most complex system are the same as the most simple. Therefore, by learning the basics it can be built upon to assemble the parts and pieces through training for the large addressable networked systems.
1
|
Fire Alarm Training • 8700055 • Rev F • 4/10 |
Table of Contents |
|
Page |
|
3.................................................................................. |
Definitions and Symbols |
11............................................................................... |
Organizations, Codes & Standards |
11................................................................................ |
Determining FireAlarm Requirements |
12................................................................................ |
FireAlarm Signals |
12................................................................................ |
Types of Systems |
14................................................................................ |
Circuit Types |
14................................................................................ |
Smoke Detector Placement |
18................................................................................ |
Residential Smoke Detectors |
20................................................................................ |
Heat Detectors |
21................................................................................ |
ManualAlarm Stations |
22................................................................................ |
Audible & Visual NotificationAppliances |
27................................................................................ |
Notification Voltage Drop |
27................................................................................ |
Battery Standby Calculations |
29................................................................................ |
Required Documentation |
30................................................................................ |
System Installation & Troubleshooting Tips |
2
Fire Alarm Training • 8700055 • Rev F • 4/10
Glossary/Definitions
Addressable Device: Afire alarm system component with discreet identification that can have its status individually identified, or that is used to individually control other functions.
Air Sampling-Type Detector: Adetector that consists of a piping or tubing distribution network from the detector to the areas being protected.Afan in the detector housing draws air from the protected area back to the detector. The air is analyzed for products of combustion
Alarm Signal: Asignal indicating an emergency requiring immediate action, such as a signal indicative of a fire.
Alarm Verification: Afeature of some automatic fire detection and alarm systems to reduce unwanted alarms. Smoke detectors must report alarm conditions for a minimum period of time, or confirm alarm conditions within a given time period after being reset, to be accepted as a valid alarm initiating signal.
Analog Initiating Device: An initiating device that transmits a signal indicating varying degrees of condition, such as smoke obscuration levels.As contrasted with a conventional initiating device which can only indicate an “on/off” condition
Annunciator: Aunit containing two or more indicator lamps, alphanumeric displays, or other equivalent means in which each indication provides status information about a circuit, condition, or location.
Approved: Acceptable to the “authority having jurisdiction”.
Note: The National Fire ProtectionAssociation does not approve, inspect or certify any installations, procedures, equipment, or materials, nor does it approve or evaluate testing laboratories.
Authority Having Jurisdiction:Organization, office or individual responsible for “approving” equipment, an installation or a procedure.
Automatic Extinguishing System Operation Detector: Adevice that detects the operation of an extinguishing system by means appropriate to the system employed. Including but not limited to water flow devices.
Automatic Extinguishing System Supervision: Devices that respond to abnormal conditions that could affect the proper operation of an automatic sprinkler system or other fire extinguishing system. Including but not limited to control valves, pressure levels, room temperature, etc.
Automatic Fire Detectors: Adevice designed to detect the presence of fire or the products of combustion. Including but not limited to heat detectors, flame detectors, smoke detectors.
Auxiliary Fire Alarm System: Asystem connected to a municipal fire alarm system for transmitting an alarm of fire to the public fire service communication center. Fire alarms from an auxiliary system are received at the public fire service communication center on the same equipment and by the same methods as alarms transmitted manually from municipal fire alarm boxes located on streets.
Breakglass Fire Alarm Box: Afire alarm box in which it is necessary to break a special element in order to operate the box.
Ceiling: The upper surface of a space, regardless of height.Areas with a suspended ceiling would have two ceilings, one visible from the floor and one above the suspended ceiling.
Ceiling Height: The height from the continuous floor of a room to the continuous ceiling of a room or space.
Ceiling Surfaces: Ceiling surfaces referred to in conjunction with the locations of initiating devices are as follows:
A} Beam Construction: Ceilings having solid nonstructural members projecting down from the ceiling surface more than 4 in. and spaced more than 3 ft., center to center.
B} Girders: Girders support beams or joists and run at right angles to the beams or joists. When the top of girders are within 4 in. of the ceiling, they are a factor in determining the number of detectors and are to be considered as beams. When the top of the girder is more than 4 in. from the ceiling, it is not a factor in detector location.
Central Station: Asupervising station that is listed for central station service.
Central Station Fire Alarm System: Asystem or group of systems in which the operations of circuits and devices are transmitted automatically to, recorded in, maintained by, and supervised from a listed central station.
ClassACircuit: ClassArefers to an arrangement of monitored initiating device, signaling line, or notification appliance circuits, which would permit a single open or ground on the installation wiring of these circuits from causing loss of the systems intended function.
Class B Circuit: Class B refers to an arrangement of monitored initiating device, signaling line, or notification appliance circuits, which would permit a single open or ground on the installation wiring of these circuits to cause loss of the systems intended function.
Combination Detector: Adevice that either responds to more than one fire phenomenon or employees more than one operating principle to sense one of these phenomenon. Typical examples are combination smoke/heat detectors or a combination rate of rise and fixed temperature heat detector.
3
Fire Alarm Training • 8700055 • Rev F • 4/10
Compatibility Listed: Aspecific listing process that applies only to two wire devices [such as smoke detectors] designed to operate with certain control equipment.
Digital Alarm Communicator Receiver [DACR]: Asystem component that will accept and display signals from digital alarm communicator transmitters [DACT] sent over public switched telephone network.
Digital Alarm Communicator System [DACS]: Asystem in which signals are transmitted from a digital alarm communicator transmitter [DACT] located at the protected premises through the public switched telephone network to a DACR.
Digital Alarm Communicator Transmitter [DACT]: Asystem component at the protected premises to which initiating devices are connected. The DACT will seize the connected telephone line, dial a pre-selected telephone number to connect to a DACR, and transmit signals indicating a status change of the initiating device.
Display: The visual representation of output data other than printed copy.
Evacuation: The withdrawal of occupants from a building.
Note: Evacuation does not include relocation of occupants within a building.
End Of Line Device: Adevice such as a resistor or diode placed at the end of a class B circuit to maintain supervision.
End Of Line Relay: Adevice used to supervise power [usually for 4-wire smoke detectors] and installed within or near the last device on an initiating circuit.
Evacuation Signal: Distinctive signal intended to be recognized by the occupants as requiring evacuation of the building. Exit Plan: Plan for the emergency evacuation of the premises.
Fire Alarm Control Unit [Panel]: Asystem component that receives inputs from automatic and manual fire alarm devices and may supply power to detection devices and transponders or
off-premises transmitters. The control unit may also provide transfer of power to the notification appliances and transfer condition of relays or devices connected to the control unit. The fire alarm control unit can be a local unit or a master control unit.
Fire Rating: The classifications indicating in time [hours] the ability of a structure or component to withstand fire conditions. Fire Safety Functions: Building and fire control functions that are intended to increase the level of life safety for occupants or to control the spread of harmful effects of fire.
Flame Detector: Adevice that detects the infrared, ultraviolet, or visible radiation caused by fire.
Four Wire Smoke Detector: a smoke detector that has two distinct circuits used in its operation. The first circuit provides resettable power for the detector and the second circuit monitors the contact on the device. These types of devices are not listed for compatibility.
Heat Detector: Adevice that detects abnormally high temperature or rate of temperature rise.
Initiating Device: Asystem component that originates transmission of a change of state condition, such as a smoke detector, water flow switch, etc.
Initiating Device Circuit: Acircuit to which automatic or manual initiating devices are connected.
Ionization Smoke Detector: Asmoke detector that has a small amount of radioactive material which ionizes the air in the sensing chamber, thus rendering it conductive and permitting a current to flow between two charged electrodes. This gives the sensing chamber an effective electrical conductance. When smoke particles enter the sensing chamber they decrease the
conductance of the air by attaching themselves to the ions, causing a reduction in mobility. When conductance is reduced to less than a predetermined level, the detector responds.
Level Ceilings: Those ceilings that are actually level or have a slope of less than 1 1/2 in. per foot.
Light Scattering: Theactionoflightbeingreflectedand/orrefractedoffparticlesofcombustionfordetectionbyaphotoelectricsmokedetector.
Line Type Detector: Adevice in which detection is continuous along a path. Examples include projected beam smoke detectors and heat sensitive cable.
Listed: Equipment or materials included in a list published by an organization acceptable to the “authority having jurisdiction” and concerned with product evaluation, that maintains periodic inspection of production of listed equipment or materials and whose listing states either that the equipment or material meets appropriate standards or has been tested and found suitable for use in a specific manner. Note: The means for identifying listed equipment may vary for each organization concerned with product evaluation, some of which do not recognize as listed unless it is also labeled. The “authority having jurisdiction” should utilize the system employed by the listing organization to identify a listed product.
Local Fire Alarm System: Alocal system sounding an alarm at the protected premises as the result of the operation of automatic or manual initiating devices.
4
Fire Alarm Training • 8700055 • Rev F • 4/10
Manual Station [pull station]: Amanually operated device used to initiate an alarm signal.
National Fire Protection Association [NFPA]: Administers the development of and publishes codes, standards, and other materials concerning all phases of fire safety.
Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL) – a laboratory that is recognized by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration as meeting the necessary qualifications specified in the Code of Federal Regulations. Common NRTLin the United States that deal with fire alarm products are FMApprovals, Intertek Testing Services (ETL) and Underwriters Laboratories Inc. (ULI)
Non restorable Initiating Device: Adevice whose sensing element is designed to be destroyed in the process of operation.
Notification Appliance: Afire alarm system component such as a bell, horn, speaker, strobe, etc. that provides an audible or visible output or both.
Notification Appliance Circuit (NAC): Acircuit directly connected to a notification appliance.
Obscuration: Areduction in the atmospheric transparency caused by smoke. Usually expressed in percent per foot. Particles of Combustion: Substances resulting from the chemical process of a fire.
Photoelectric Smoke Detector: Asmoke detector utilizing a light source and a photosensitive sensor so arranged that the rays from the light do not normally shine on the photosensitive sensor. When smoke enters the light path, some of the light reflects off
the smoke onto the sensor, causing the detector to respond.
Proprietary Fire Alarm System: An installation of fire alarm systems that serve contiguous and noncontiguous properties under one ownership from a proprietary supervising station located at the protected property.
Rate Of Rise Heat Detector: Adevice which will respond when the temperature rises at a rate exceeding a predetermined amount [usually about 15 degrees per minute].
Remote Station Fire Alarm System: Asystem installed in accordance with NFPA72 to transmit alarm, trouble and supervisory from one or more protected premises to a remote location at which appropriate action is taken.
Restorable Initiating Device: Adevice whose sensing element is not ordinarily destroyed in the process of operation. Restoration may be manual or automatic.
Shall: In NFPAliterature indicates a mandatory requirement.
Should: In NFPAliterature indicates a recommendation or that which is requested but not required.
Signaling Line Circuit: Acircuit or path between any combination of circuit interfaces, control units, or transmitters over which multiple system input signals or output signals, or both are carried.
Sloping Ceiling: Ceilings having a slope of more than 1 1/2 in. per foot.
A:Sloping - Peaked Type, Ceilings in which the slope is in two directions from the highest point. Curved or domed ceilings may be considered peaked.
B:Sloping - Shed Type, Ceilings in which the high point is at one side with the slope extending toward the opposite side.
Smooth Ceiling: Asurface uninterrupted by continuous projections such as solid joists, beams or ducts, extending more than 4 in. below the ceiling surface.
Solid Joist Construction: Ceilings having solid structural or nonstructural members projecting down from the ceiling surface a distance of more than 4 in. and spaced at intervals 3 ft. or less, center to center.
Spot Type Detector: Adevice whose detecting element is concentrated at a particular location. Examples include certain smoke and heat detectors.
Stratification: An effect that occurs when air containing smoke particles or products of combustion is heated by burning material, rises until it reaches a level where there is no longer a temperature difference between it and the surrounding air.
Story: the portion of a building included between the upper surface of a floor and the upper surface of a floor or roof next above. Supervision: The ability to detect a fault condition in the installation wiring which would prevent normal operation of the fire alarm system.
Supervisory Signal: Asignal indicating an “off normal” condition on the fire suppression system. Examples include, tamper indication, low air pressure and low building temperature.
Thermal Lag: The difference between the operating temperature of a thermal detector and the actual air temperature.
Two-Wire Smoke Detector:Asmoke detector that initiates an alarm condition on the same pair of wires that supply power to the detector.
5
|
|
|
Fire Alarm Training • 8700055 • Rev F • 4/10 |
Symbols for Control Panels |
|||
|
|
|
|
Symbol |
|
Description |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control panel-basic shape |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fire alarm control panel |
|
FACP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fire systems annunciator alarm |
|
FSA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Annunciator panel-from NECA100, symbol 7.006 |
|
FAA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fire alarm transponder or transmitter |
|
FTR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Elevator status/recall |
|
ESR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fire alarm communicator |
|
FAC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fire system control panel |
|
FSCP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FSCP |
HL |
Halon |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Carbon dioxide |
|
FSCP |
CO2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dry chemical |
|
FSCP |
DC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foam |
|
FSCP |
FO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wet chemical |
|
FSCP |
WC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FSCP |
CA |
Clean agent |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Water mist |
|
FSCP |
WM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FSCP |
DL |
Deluge sprinkler |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control panel for heating, ventilation, air conditioning, exhaust stairwell pressurization, or similar equipment |
|
HVA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Remote MIC for voice evacuation system |
|
MIC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Voice evacuation panel-from NECA100, symbol 7.008 |
|
EVAC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fire alarm terminal cabinet-from NECA100, symbol 7.009 |
|
FATC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fire command system |
|
FCS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fire alarm control unit |
|
FACU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sprinkler alarm panel |
|
SAP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Relay alarm panel |
|
RP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data gathering panel |
|
DGP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amplifier rack |
|
AMP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
6
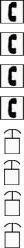
|
|
|
Fire Alarm Training • 8700055 • Rev F • 4/10 |
|
Symbols for Signal Initiating Devices and Switches |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Symbol |
|
Description |
Comments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Manual station |
Basic shape |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HL |
Manual station-Halon |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CO2 |
Manual station-carbon dioxide |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DC |
Manual station-dry chemical |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FO |
Manual station-foam |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WC |
Manual station-wet chemical |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P |
Manual station-pull station |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CA |
Manual station-clean agent |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WM |
Manual station-water mist |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DL |
Manual station-deluge sprinkler |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MB |
Fire alarm master box |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DK |
Drill key |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PRE |
Preaction system |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fire service or emergency telephone station |
Basic shape |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
Fire service or emergency telephone station-accessible |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
J |
Fire service or emergency telephone station |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
Fire service or emergency telephone station-handset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Abort switch |
Basic shape |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HL |
Abort switch-Halon |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CO2 |
Abort switch-carbon dioxide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DC |
Abort switch-dry chemical |
|
|
|
|
|
|
7

Fire Alarm Training • 8700055 • Rev F • 4/10
Symbols for Signal Initiating Devices and Switches
Symbol |
Description |
Comments |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
FO |
Abort switch-foam |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
WC |
Abort switch-wet |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
CA |
Abort switch-clean agent |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
WM |
Abort switch-water mist |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
DL |
Abort switch-deluge sprinkler |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
PRE |
Abort switch-preaction system |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
EPO |
Abort switch-emergency power off |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Automatic detection and supervisory devices |
Basic shape |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Heat detector (thermal detector) |
Symbol orientation not to be changed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
R/F |
Heat detector-combination rate-of-rise and fixed temperature |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
R/C |
Heat detector-rate compensation |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
F |
Heat detector-fixed temperature |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
R |
Heat detector-rate-of-rise only |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Heat detector-line-type detector (heat sensitive cable) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R |
Smoke/heat detector |
|
* Symbols are copied from the National Fire ProtectionAssociation Standard 170, Standard for Fire Safety and Emergency Symbols
8

Fire Alarm Training • 8700055 • Rev F • 4/10
Symbols for Signal Initiating Devices and Switches
Symbol |
|
Description |
Comments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Smoke detector |
Symbol orientation not to be changed |
|
|
|
|
|
P |
Smoke detector-photoelectric products of combustion detector |
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
Smoke detector-ionization products of combustion detector |
|
|
|
|
|
|
BT |
Smoke detector-beam transmitter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
BR |
Smoke detector-beam receiver |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ASD |
Smoke detector-air sampling |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Smoke detector for duct |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gas detector |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indicate ultraviolet (UV), infrared |
|
|
Flame detector |
(IR), ultraviolet/infrared (UV/IR), or |
|
|
visible radiation-type detectors; symbol |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
orientation not to be changed |
|
F |
Flame |
|
|
|
|
|
|
UV |
Ultraviolet |
|
|
|
|
|
|
IR |
Infrared |
|
|
|
|
|
|
UV/IR |
Combination ultraviolet/infrared |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VR |
Visible radiation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Flow detector/switch |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Specify type-water, low air, high air, and |
|
|
Pressure detector/switch |
so forth; symbol orientation not to be |
|
|
|
changed |
|
|
Lever detector/switch |
Symbol orientation not to be changed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tamper detector |
Alternate term-tamper switch |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Valve with tamper detector/switch |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VR |
Output relay |
|
|
|
|
|
|
HT |
Temperature switch-high temperature |
|
|
|
|
|
|
LT |
Temperature switch-low temperature |
|
|
|
|
* Symbols are copied from the National Fire ProtectionAssociation Standard 170, Standard for Fire Safety and Emergency Symbols
9
 Loading...
Loading...