Page 1

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
Internet Telephony PBX System
IPX-2000
User’s Manual
1 of 51
Page 2

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
FCC Notice
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant
to Part 15 of FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates,
uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed in accordance with the instruction
manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communication. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct
the interference at the user’s own expense.
Disclaimer
PLANET Technology does not warrant that the hardware will work properly in all environments and
applications, and makes no warranty and representation, either implied or expressed, with respect to the
quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for a particular purpose.
PLANET has made every effort to ensure that this User’s Manual is accurate; PLANET disclaims liability
for any inaccuracies or omissions that may have occurred.
Information in this User’s Manual is subject to change without notice and does not represent a
commitment on the part of PLANET. PLANET assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be
contained in this User’s Manual. PLANET makes no commitment to update or keep current the
information in this User’s Manual, and reserves the right to make improvements to this User’s Manual
and/or to the products described in this User’s Manual, at any time without notice. If you find information
in this manual that is incorrect, misleading, or incomplete, we would appreciate your comments and
suggestions.
CE Declaration of conformity
This equipment complies with the requirements relating to electromagnetic compatibility, EN 55022 class
A for ITE and EN 50082-1. This meets the essential protection requirements of the European Council
Directive 89/336/EEC on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to electromagnetic
compatibility.
Trademarks
All brand, company and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
companies.
WEEE Warning
To avoid the potential effects on the environment and human health as a result of the presence
of hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, end users of electrical and
electronic equipment should understand the meaning of the crossed-out wheeled bin symbol.
Do not dispose of WEEE as unsorted municipal waste and have to collect such WEEE
separately.
Revision
PLAENT IPX-2000 User’s Manual
Revision: 1.1 (Jan. 2006)
Part No. EM-IPX2000V1_1
2 of 51
Page 3

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION.......................................................................................................................................5
1.1 OVERVIEW ...........................................................................................................................................5
1.2 INSTALLATION......................................................................................................................................5
2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION...................................................................................................................7
2.1 TIME SETUP..........................................................................................................................................7
2.1.1 Time Zone Setup..............................................................................................................................7
2.1.2 Date Setup.......................................................................................................................................7
2.2 WAN SETUP.........................................................................................................................................7
2.2.1 Static...............................................................................................................................................8
2.2.2 DHCP.............................................................................................................................................8
2.2.3 PPPoE............................................................................................................................................8
2.2.4 Lan only..........................................................................................................................................8
2.3 LAN SETUP ..........................................................................................................................................9
2.4 LAN ROUTING .....................................................................................................................................9
2.5 DYNDNS SETUP ...................................................................................................................................9
2.5.1 Enable DynDNS............................................................................................................................10
2.5.2 Disable DynDNS...........................................................................................................................10
2.6 QOS SETUP.........................................................................................................................................10
2.6.1 Enable QoS...................................................................................................................................10
2.6.2 Disable QoS..................................................................................................................................10
2.7 VIRTUAL SERVER................................................................................................................................11
2.8 MAINTENANCE...................................................................................................................................11
2.8.1 SIP registration status...................................................................................................................11
2.8.2 Call Detail Record.........................................................................................................................11
2.8.3 System event log............................................................................................................................12
2.8.4 System storage usage.....................................................................................................................12
2.8.5 System storage backup...................................................................................................................12
2.9 FIRMWARE UPGRADE ..........................................................................................................................12
2.10 LOGOUT .............................................................................................................................................12
2.11 SHUTDOWN ........................................................................................................................................12
3 SERVICE CONFIGURATION................................................................................................................13
3.1 NTP SERVICE .....................................................................................................................................13
3.1.1 Enable NTP service.......................................................................................................................13
3.1.2 Disable NTP service......................................................................................................................13
3.2 SNMP SERVICE ..................................................................................................................................13
3.2.1 Enable SNMP service....................................................................................................................13
3.2.2 Disable SNMP service...................................................................................................................13
3.3 STUN SERVICE...................................................................................................................................14
3.3.1 Enable STUN service.....................................................................................................................14
3.3.2 Disable STUN service....................................................................................................................14
3.4 TFTP SERVICE....................................................................................................................................14
3.4.1 Enable TFTP service.....................................................................................................................14
3.4.2 Disable TFTP service....................................................................................................................15
3.5 DHCP SERVICE ..................................................................................................................................16
3.5.1 Enable DHCP service....................................................................................................................16
3.5.2 Disable DHCP service...................................................................................................................17
3.6 IP PBX SERVICE.................................................................................................................................17
3.6.1 IP PBX global parameters.............................................................................................................17
3.6.2 Reload IP PBX configuration.........................................................................................................18
3.6.3 Backup IP PBX configuration........................................................................................................18
3.6.4 Restore IP PBX configuration........................................................................................................18
3.6.5 Restart IP PBX service..................................................................................................................18
3.6.6 Revert IP PBX configuration..........................................................................................................18
3 of 51
Page 4

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
3.7 STACKABLE MANAGEMENT.................................................................................................................19
3.7.1 Operation modes...........................................................................................................................19
3.7.2 Consolidated management.............................................................................................................19
3.7.3 Configuration................................................................................................................................19
IP PBX CONFIGURATION..............................................................................................................................22
3.8 USERGROUP CONFIGURATION .............................................................................................................22
3.8.1 Add Usergroup..............................................................................................................................22
3.8.2 Edit Usergroup..............................................................................................................................23
3.8.3 Delete Usergroup..........................................................................................................................23
3.9 USER CONFIGURATION .......................................................................................................................24
3.9.1 Add User.......................................................................................................................................24
3.9.2 Edit User.......................................................................................................................................24
3.9.3 Delete User...................................................................................................................................24
3.10 DEVICE CONFIGURATION ....................................................................................................................25
3.10.1 IP Phone...................................................................................................................................26
4.3.1.1 Add Device.........................................................................................................................................26
4.3.1.2 Edit Device.........................................................................................................................................26
4.3.1.3 Delete Device......................................................................................................................................26
3.10.2 Analog Phone...........................................................................................................................29
3.11 ROUTE CONFIGURATION .....................................................................................................................30
3.11.1 Add Route.................................................................................................................................31
3.11.2 Edit Route.................................................................................................................................31
3.11.3 Delete Route.............................................................................................................................31
3.12 ROUTEGROUP CONFIGURATION ...........................................................................................................32
3.12.1 Add Routegroup........................................................................................................................32
3.12.2 Edit Routegroup........................................................................................................................32
3.12.3 Delete Routegroup....................................................................................................................32
3.13 SIP TRUNK CONFIGURATION...............................................................................................................33
3.13.1 Add SIP Trunk..........................................................................................................................33
3.13.2 Edit SIP Trunk..........................................................................................................................33
3.13.3 Delete SIP Trunk.......................................................................................................................33
3.14 PSTN TRUNK CONFIGURATION ...........................................................................................................35
3.14.1 Add PSTN Trunk.......................................................................................................................36
3.14.2 Edit PSTN Trunk.......................................................................................................................36
3.14.3 Delete PSTN Trunk...................................................................................................................36
3.15 TRUNK TERMINAL ..............................................................................................................................37
3.15.1 Add Trunk Terminal..................................................................................................................38
3.15.2 Edit Trunk Terminal..................................................................................................................38
3.15.3 Delete Trunk Terminal..............................................................................................................38
3.16 POTS SETUP.......................................................................................................................................39
3.17 FEATURE CONFIGURATION..................................................................................................................39
3.17.1 Auto attendant..........................................................................................................................40
3.17.2 Call park..................................................................................................................................40
3.17.3 Life line....................................................................................................................................41
3.17.4 Meet-me conference..................................................................................................................42
3.17.5 Music on hold...........................................................................................................................43
3.17.6 Voicemail.................................................................................................................................44
3.17.7 Auto-attendant prompts.............................................................................................................45
3.17.8 Meet-me prompts......................................................................................................................46
3.17.9 Voicemail prompts....................................................................................................................46
4 EXAMPLE PROVISIONING..................................................................................................................48
4.1 INTERNAL EXTENSION CONFIGURATION..............................................................................................48
4.2 CASE I: SINGLE-SITE CONFIGURATION ................................................................................................48
4.3 CASE II: TWO-SITE CONFIGURATION...................................................................................................49
4 of 51
Page 5

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
1. AC Power
2. FXO port 1
3. USB port
4. WAN
5. LAN
Slot
1 Slot
0 FXO port 5
1 Introduction
1.1 Overview
The IP PBX Administration Guide provides instructions for administering the IP PBX system. IP
PBX is an embedded call-processing server communicating with client stations with Session
Initiation Protocol (SIP). It migrates the telephony network and the data network of a small-tomedium business (SMB) company into a manageable converged network. IP PBX works with
various IP phones (desktop, WiFi, Bluetooth, and DECT), voice-over-IP (VoIP) gateways, and
analog telephone adapters to route calls among client phones, analog phones, and PSTN network.
Additional voice features such as conferencing, auto attendant, and voicemail are seamlessly
enabled to all phones. IP PBX also provides Internet access to all LAN devices through Network
Address Translation (NAT).
IP PBX provides call control and media relay services to SIP clients and applications. It performs
the following primary functions:
• SIP Registrar
• SIP Outbound Proxy with media relay
• SIP Gateway (FXO)
• SIP PBX for extension calls
• Auto attendant IVR
• Voice mail IVR
• Meet-me conference
IP PBX has a built-in suite of voice applications for supplementary services and therefore no
special-purpose hardware is required. This means the total cost of ownership of a converged
network enabled by IP PBX is lower than building separated infrastructures for legacy telephony
network and data network. Besides, it comes with a web-browsable interface to the data network
configuration and voice service provisioning, which brings the manageability of both networks
together to facilitate administration locally or remotely.
1.2 Installation
5 of 51
Page 6
PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
1. AC Power 110/220 Volt, 60 Hz
2. FXO ports 4 ports per daughter card, numbered from right to the left.
The rightmost port at slot 0 is port 1 and the leftmost port at
slot 1 (if installed) is port 8. FXO ports are to be connected
to FXS jacks on wall or analog PBX using RJ-11 cables.
3. USB ports 2 external ports with compliance to USB 1.1/2.0. Plug in a
USB hard drive for CDR/voicemail backup from the internal
storage.
4. WAN Connect to a broadband modem or a WAN router.
5. LAN Connect to a LAN switch.
6 of 51
Page 7
PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
2 System Configuration
This section describes how to configure system parameters used by IP PBX. The factory default
of LAN IP address is 192.168.1.1. Connect to LAN port and the configuration Web interface
could be reached at https://192.168.1.1/. Once connected, the browser will warn about accepting
a certificate. Please accept it. Then, give default administrator ID and password (both are admin)
to log in for administration. The administrator password could be changed in the User
Management page under user ID admin.
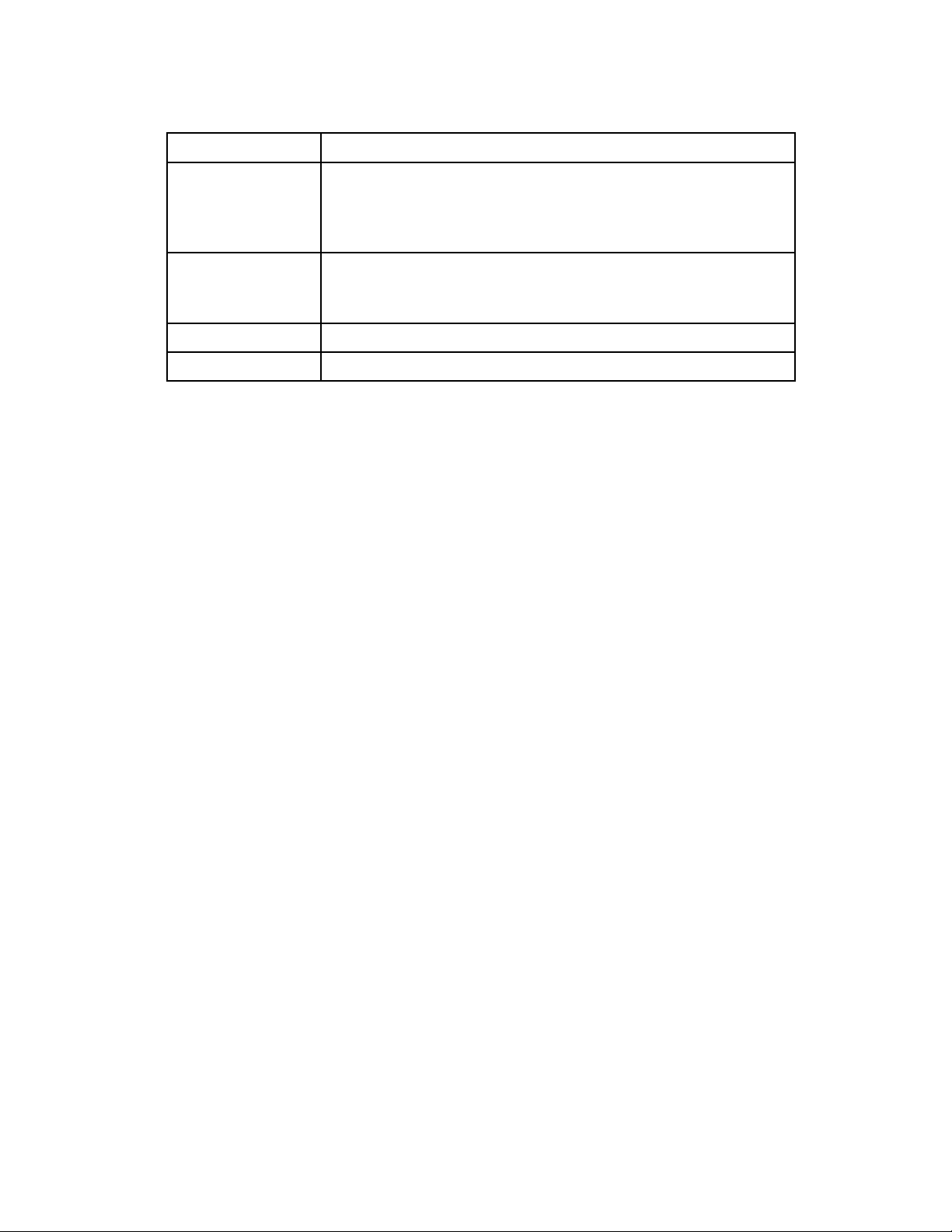
2.1 Time setup
The Time Setup page allows administrator to configure time zone and date for IP PBX. Select
System -> Time setup, current setting of time zone and date is displayed.
2.1.1 Time Zone Setup
Choose time zone in drop-down list, then click Set button.
2.1.2 Date Setup
Choose year, month, day, hour, minute, and sec in drop-down lists respectively, then click Set
button.
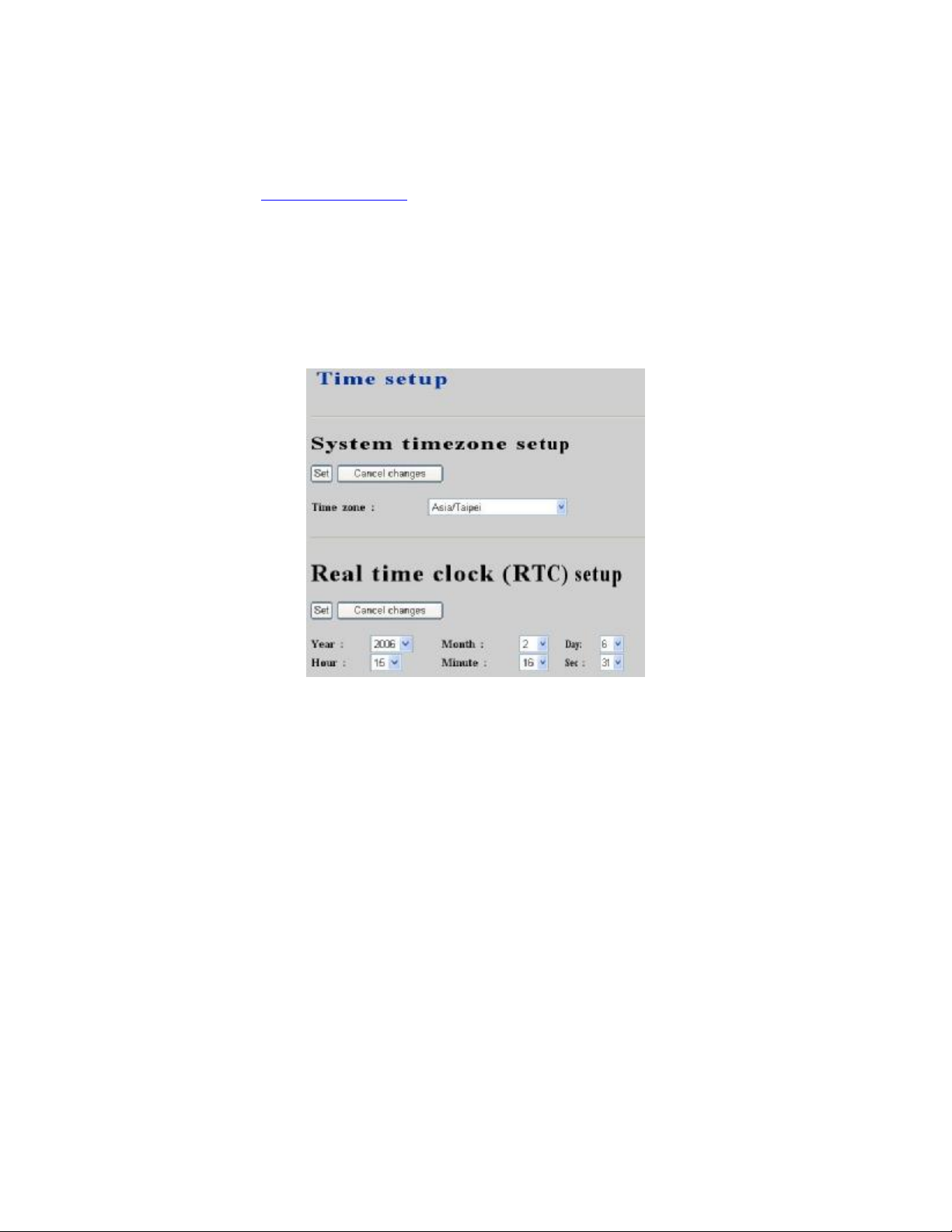
2.2 WAN setup
The WAN Setup page allows administrator to configure WAN network interface for IP PBX.
Select System -> WAN setup, current setting of WAN network interface is displayed, e.g. type,
IP address etc. Unless LAN only checkbox is checked, you can choose one of the three options
for your configuration, Static, DHCP, and PPPoE.
7 of 51
Page 8
PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
2.2.1 Static
You can choose Static IP in Type drop-down list, and manually configure the following
information:
• IP address
• Network mask
• Default gateway IP address
• Primary and secondary DNS servers
And, click Save button to submit.
2.2.2 DHCP
Simply choose DHCP in Type drop-down list, and then click Save button. The acquired IP
address, network mask, and default gateway information will be displayed when revisit this page
later.
2.2.3 PPPoE
Choose PPPoE in Type drop-down list, enter username and password, and then click Save
button. The PPPoE dialing will start right away. When there is an active connection, the page
will show the acquired IP address, network mask, and default gateway information. There will
also be a Disconnect button to disconnect connection when desired.
2.2.4 Lan only
Check Lan only to disable WAN IP setting but allow the configuration of default gateway and
primary/secondary DNS servers.
8 of 51
Page 9

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
2.3 LAN setup
The LAN Setup page allows administrator to configure LAN network interface for IP PBX.
Select System -> LAN setup, current settings of LAN network interface are displayed. You can
modify them by entering new IP address and network mask followed by clicking Save button.
Note that by default IP PBX grants IP addresses to LAN devices via DHCP and translates those
addresses into its WAN IP address for access beyond the LAN subnet. As a result, modifying the
system LAN IP subnet must also change DHCP pool and LAN Routing (if any) accordingly.
Besides, IP PBX service must be restarted.
2.4 LAN Routing
To enable static routing among LAN subnets, enter network info and the IP address of the
corresponding gateway in IP PBX’s LAN. It is important to assure that the given gateway IP
address sits in the IP PBX’s LAN. Each subnet requires an entry even multiple subnets share the
same gateway, unless masking does the same. Examples are adding IP Route IDs net1 and net2
with parameters 192.168.128.0/255.255.255.0, 192.168.129.0/255.255.255.0, shared gateway
192.168.1.254 respectively. Or, IP Route ID net1n2 with 192.168.128.0/255.255.254.0 and
gateway 192.168.1.254 would do the same. Added routes enable routing immediately after
clicking Save button, however, IP PBX service needs to be restarted to regard calls from
designated LAN subnets as LAN traffic.
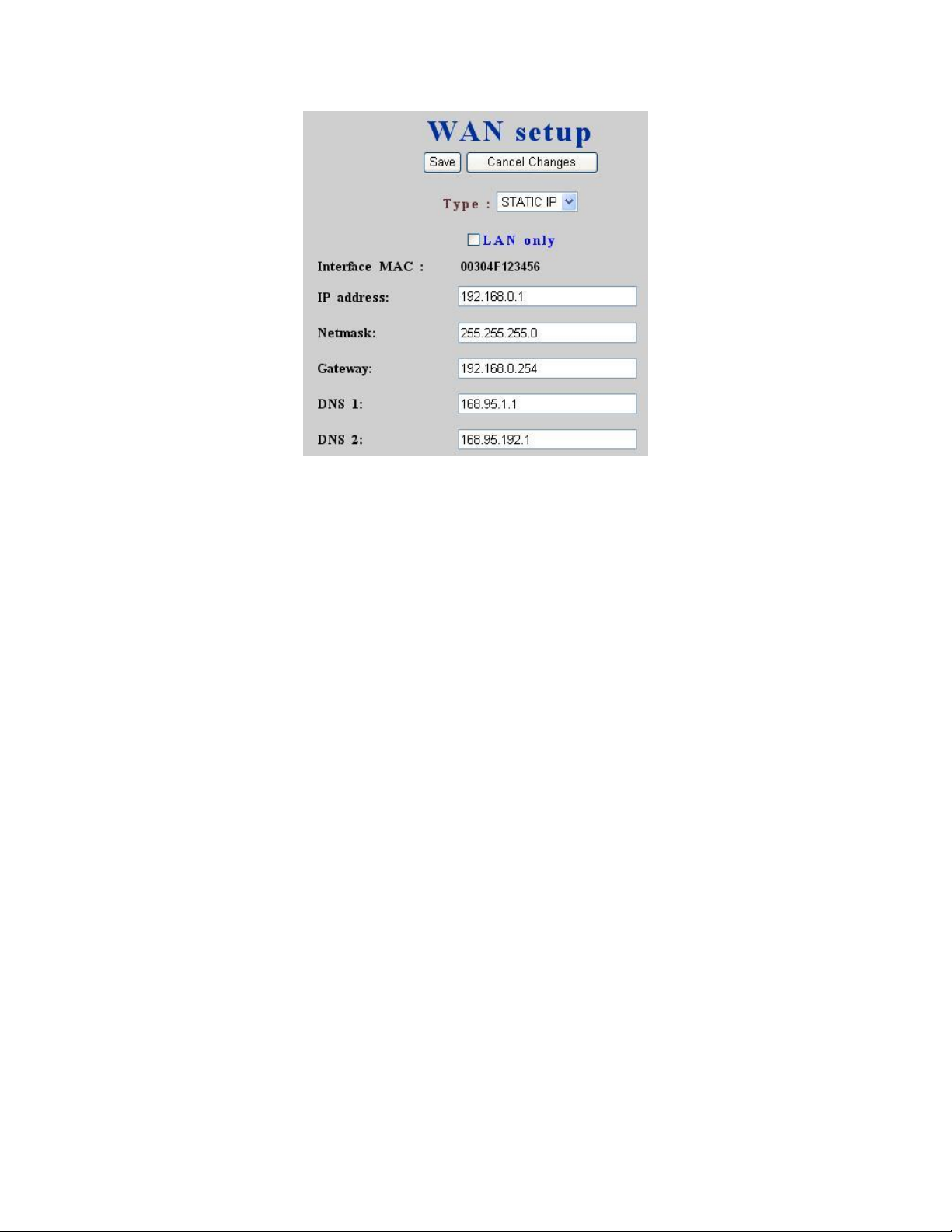
2.5 DynDNS setup
Dynamic WAN IP address causes difficulty for inbound connections from remote clients or IP
PBX systems. A popular work-around is to adopt domain names provided by DynDNS and run a
client on or behind the gateway router (or IP PBX). It is required to apply an account and create a
hostname in the account before configuration. Select Enable and give account info and refresh
interval to activate a DynDNS client. The client then uses Username and Password to access its
account and update the Hostname with the latest WAN IP address at DynDNS in Interval
seconds periodically.
9 of 51
Page 10
PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
2.5.1 Enable DynDNS
Select Enable radio button, enter the Username, Password, Hostname, and Interval, and then
click Save button. Typical hostname has a form of <hostname>.dyndns.org. The refresh interval
is usually between 60 – 600 seconds depending on the volatility of WAN IP assignment.
2.5.2 Disable DynDNS
Select Disable radio button, and then click Save button.
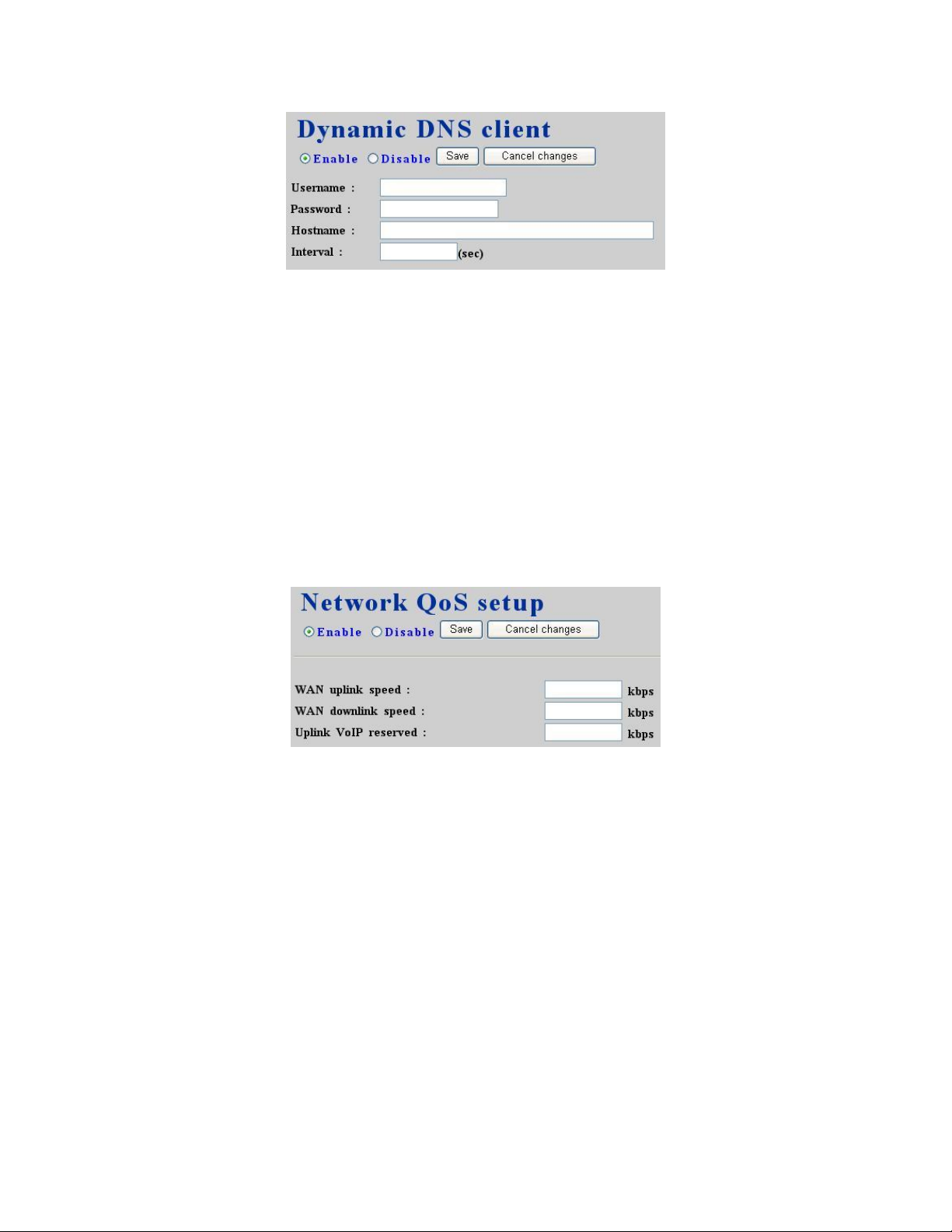
2.6 QoS setup
To assure the bandwidth reserved for the outgoing VoIP traffic over regular data traffic from
LAN, QoS Setup page offers three parameters to characterize the WAN link. By default QoS is
disabled since these parameters must be correctly given according to the actual WAN speed.
2.6.1 Enable QoS
Select Enable radio button, enter the WAN uplink speed, WAN downlink speed, and Uplink
VoIP reserved (bandwidth), and then click Save button. For a popular 2M/256K ADSL program,
the WAN uplink speed would be 256 and the WAN downlink speed would be 2048 since the
unit is in kbps. The Uplink VoIP reserved could be, say, 192 out of the total 256 kbps to allow 2
concurrent G.711 calls.
2.6.2 Disable QoS
Select Disable radio button, and then click Save button.
10 of 51
Page 11

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
2.7 Virtual server
To enable access servers in LAN from a machine beyond WAN, select System -> Virtual
server to configure port mappings. Service ID names the service. Protocol and Port specify the
TCP/UDP port number on WAN IP to be forwarded to the Forward to port of Forward to IP
in LAN. Say 192.168.1.5 is a Mail Server to be seen from outside, one should configure TCP
port 25 to be forwarded to 192.168.1.5 port 25.
2.8 Maintenance
This page includes maintenance functions of IP PBX, from status display to storage backup, etc.
2.8.1 SIP registration status
This Display button lists registration status of each client and remote IP PBX and the IP/Port
from where they register. SIP trunk registrations, if any, are also shown in the end of the list.
Column Dynamic stands for whether the listed IP address is dynamic or specified. Reg.
Progress is the response code and message if registration has been attempted but not successful
so far. Slave Registrar column is used only under the stackable mode. It indicates with which
slave box a SIP client is registered. Blank means a client is registered with the master box.
2.8.2 Call Detail Record
CDR details each call record including calling and called numbers, channel (trunk if outbound)
in use, epochs when the call was made, answered, and ended, which yield the total and billable
durations. The last column denotes the disposition of a call like answered or not.
11 of 51
Page 12

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
2.8.3 System event log
Event log includes reported events from following system services: NTP, DNS, DHCP, and
PPPoE.
2.8.4 System storage usage
This displays the size and utilization percentage of the internal main system storage.
2.8.5 System storage backup
To back up internal main storage, click the Backup button and follow instructions to insert the
USB connector of an external USB drive. Options include whether to keep or remove CDR
and/or voicemails after backup. After a confirmation of the insertion, back starts a few seconds
later if the external USB drive is accessible and found enough available space. On a successful
backup, the name of the new folder created on the external drive will be displayed. Either the
backup is successful or failed, a user must remove the USB connector of the external drive.
2.9 Firmware upgrade
The version of the running PBX firmware could be found in System -> PBX firmware. To
upgrade current firmware, locate a release file obtained from the vendor, and click Upgrade.
Note that the filename of firmware should not be changed, otherwise system will refuse to
upgrade with it.
2.10 Logout
Log out administrator and close browser windows.
2.11 Shutdown
By selecting System -> Shutdown, you can shutdown or reboot the machine after clicking the
Yes button in this page. In case such software reboot fails, press and release the hardware reset
button quickly will do the same.
12 of 51
Page 13

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
3 Service Configuration
This section describes details to configure various services built in the IP PBX.
3.1 NTP service
Select Service -> NTP service to specify a NTP server for network time synchronization. You
can enable or disable NTP service at any time.
3.1.1 Enable NTP service
Select Enable radio button, enter the fully qualified domain name or the IP address of a NTP
server, and then click Save button.
3.1.2 Disable NTP service
Select Disable radio button, and then click Save button.
3.2 SNMP service
Select Service -> SNMP service to specify Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
parameters for networking status retrieval. You can enable or disable SNMP service at any time.
3.2.1 Enable SNMP service
Select Enable radio button, enter System Location, Administrator Contact, read-only
community, and then click Save button. Example settings are Taipei Office, John Doe
admin@foobar.com, and public for the three fields.
3.2.2 Disable SNMP service
Select Disable radio button, and then click Save button.
13 of 51
Page 14
PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
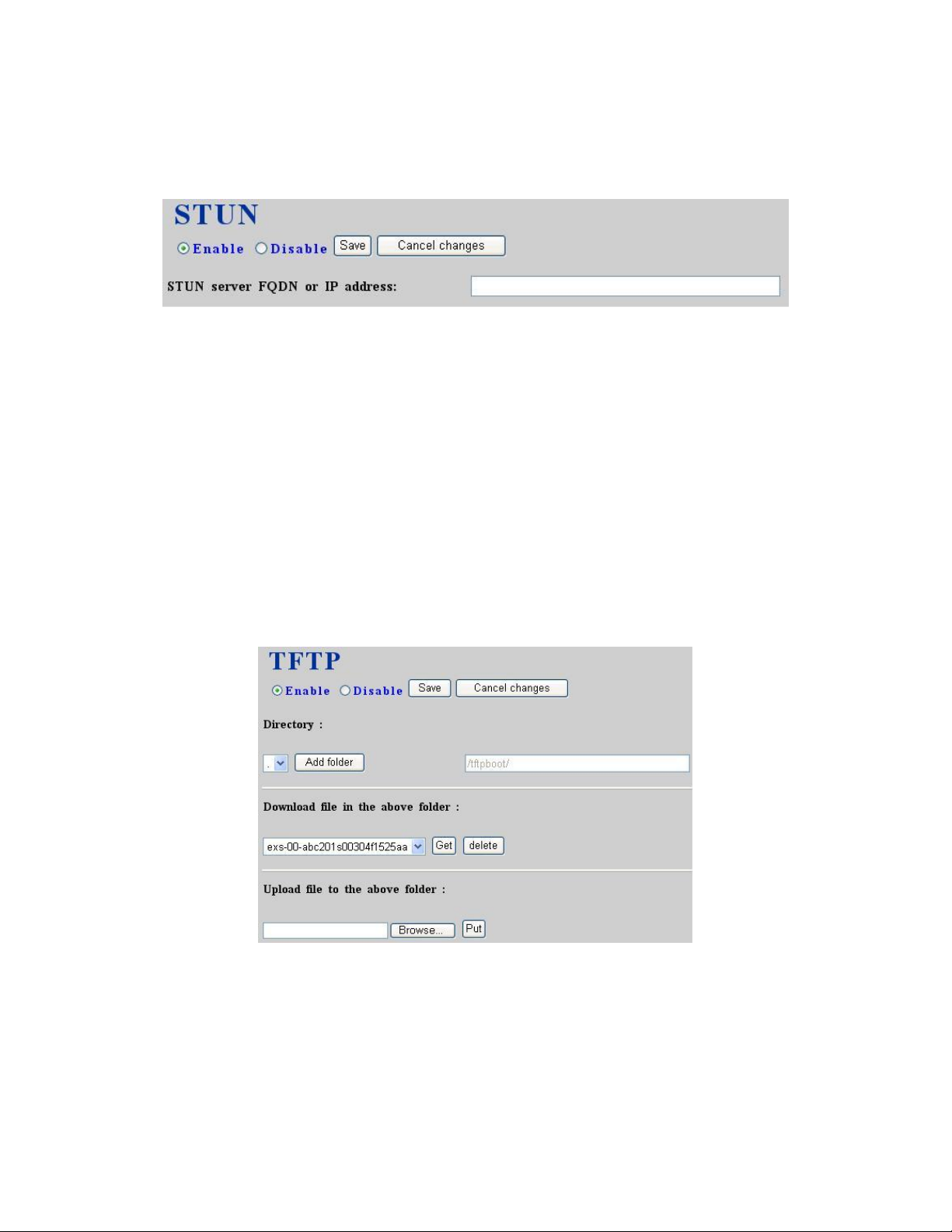
3.3 STUN service
Select Service -> STUN service to specify a Simple Traversal of UDP through NATs (STUN)
server for NAT traversal. You can enable or disable STUN service at any time.
3.3.1 Enable STUN service
Select Enable radio button, enter the fully qualified domain name or the IP address of a STUN
server, and then click Save button. IP PBX service needs to be reloaded to reflect the change.
3.3.2 Disable STUN service
Select Disable radio button, enter the fully qualified domain name or the static IP address of the
external WAN interface and then click Save button. Usually this address refers to the static
WAN IP address if there is a NAT device between the IP PBX and the Internet. If the WAN port
of IP PBX directly connects to Internet or it is unused, leave the address blank.
3.4 TFTP service
Select Service -> TFTP service, this page indicates current status of TFTP service. You can
enable or disable TFTP service at any time.
3.4.1 Enable TFTP service
Select Enable radio button, then click Save button. Afterwards, you are able to do file
management, e.g. upload and download files to and from IP PBX through TFTP service.
3.4.1.1 Change Directory
• Choose directory in Directory drop-down list.
14 of 51
Page 15

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
By default, the root directory is /tftpboot. Initially, you might not be able to change
directory, since there is no folder created under /tftpboot yet.
F Current directory is shown in the gray field on the right side, for instance, it is /tftpboot
at the beginning.
3.4.1.2 Add Folder
• Choose a directory under which you want to add a new folder.
• Click Add folder button.
• Enter name of the new folder in the pop-up window, e.g. myfolder.
• Click OK button.
The new folder is then created accordingly, e.g. /tftpboot/myfolder.
3.4.1.3 Delete Folder
• Choose a directory you would like to delete.
• Click Delete folder button.
The folder you just deleted shall disappear from the Directory drop-down list.
3.4.1.4 Download File
• Choose a directory where you would like to download a file.
• Choose a file from the drop-down list.
• Click Get button.
3.4.1.5 Delete File
• Choose a directory where you would like to delete a file.
• Choose a file from the drop-down list.
• Click Delete button.
3.4.1.6 Upload File
• Choose a directory where you would like to upload a file.
• Click Browse button to locate a file in the local storage.
• Choose a file in the File Upload menu.
• Click Open button to confirm selection.
• Click Put button.
• Enter the destination filename in the pop-up window.
• Click OK button.
Now, the file you just uploaded should appear in current directory and is displayed in the
Download drop-down list.
3.4.2 Disable TFTP service
Select Disable radio button, and then click Save button.
15 of 51
Page 16
PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
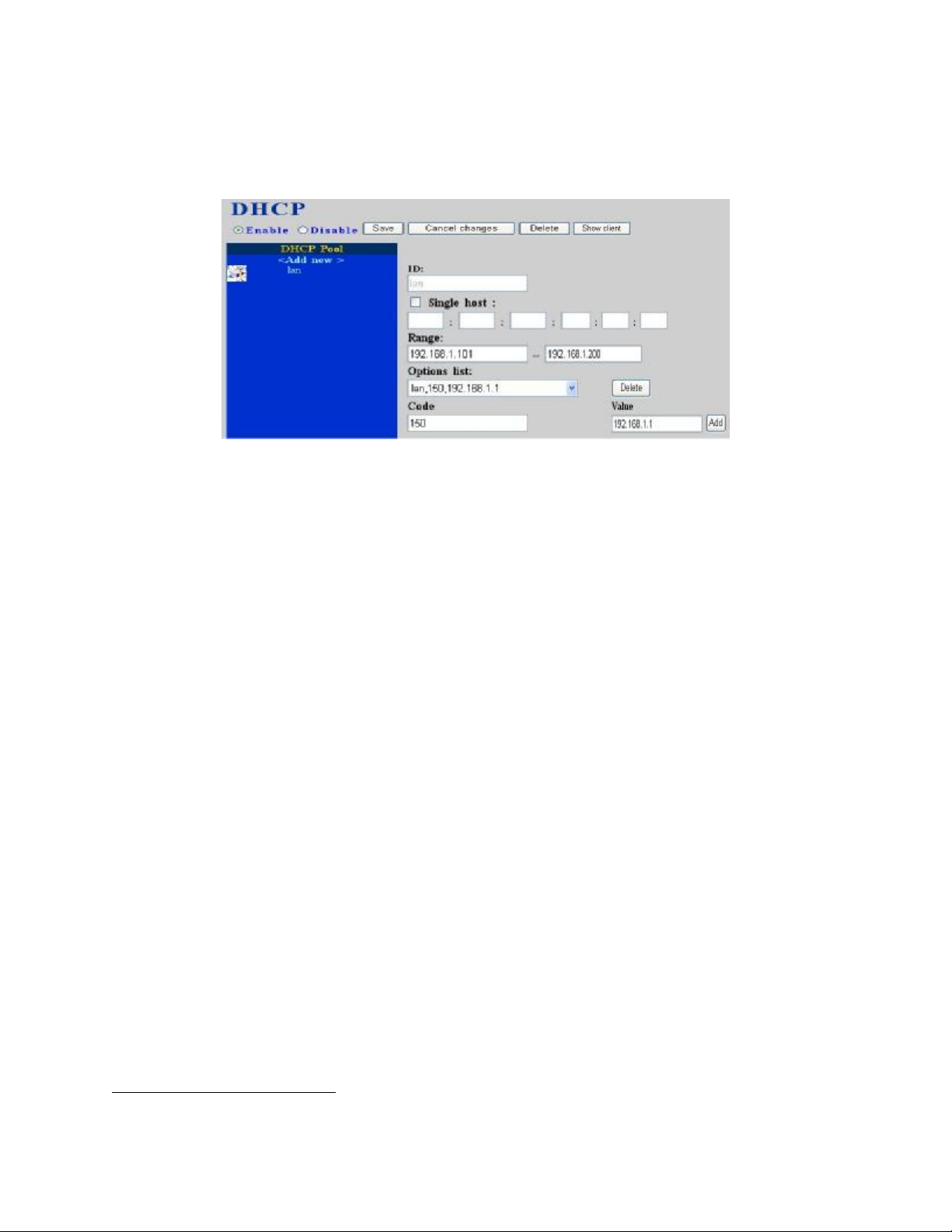
3.5 DHCP service
Select Service -> DHCP service, this page indicates current status of DHCP service. You can
enable or disable DHCP service at any time.
3.5.1 Enable DHCP service
Select Enable radio button, and then click Save button. Afterwards, you can configure DHCP
settings in details in this page.
3.5.1.1 Add DHCP Range
• Click <Add new> button from the left panel.
• Specify a pool ID (must have an alphabet initial) in the Name field.
• Check Single host if the binding is intended for a specific host only. Then give the
MAC address of the host right below the checkbox.
• Enter a DHCP range of addresses available for lease in Range. If checked Single host
the end address will be grayed out.
• Optionally, DHCP options
1
could be configured by entering an option code in Code
and the option value in Value field and click Add button. The DHCP option just added
shall be displayed in the Options list drop-down list. Follow the same steps to add more
DHCP options. To delete an option, choose it from the Options list drop-down list and
click Delete button.
• Click Save button to commit changes.
You should be able to see the newly added DHCP pool displayed in the DHCP Pool panel
on the left side.
3.5.1.2 Edit DHCP Range
• Click the link of the pool ID to edit from the DHCP Pool panel.
• Edit settings shown on the right side.
• Click Save button.
3.5.1.3 Delete DHCP Range
• Click the link of the pool ID to delete from the DHCP Pool panel.
• Click Delete button.
1
Refer to RFC 2132 for the details of available DHCP options.
16 of 51
Page 17

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
The DHCP pool you just deleted shall disappear from the DHCP Pool panel.
3.5.1.4 Show Clients
Click the Show client button to list all leased LAN IP addresses and client details in a
separated window.
3.5.2 Disable DHCP service
Select Disable radio button, and then click Save button.
3.6 IP PBX service
In Service -> IP PBX service, you can specify IP PBX global parameters and reload, backup,
restore, or revert IP PBX configuration. You can also restart IP PBX service in this page.
3.6.1 IP PBX global parameters
Global SIP settings, call records, and status of clients could be found in the first half of the page.
PBX SIP port specifies the UDP port where the SIP service listens on. RTP port range limits
the UDP ports used by the IP PBX for media transport. Max and default expiration time guard
and advertise SIP registration respectively. PBX Caller ID is the default Caller ID if that of an
incoming call is unknown. Check the Enable video codec checkbox if there will be video clients
registering to the system. Checking Support devices multiplex Call-ID forces discrimination of
SIP tags. Do this only when there is such a client device in the system and other devices
17 of 51
Page 18

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
supporting the same. Otherwise, one may find the special device only got registered with this
option but other clients or even SIP trunks fail due to such change. Max active users is for
registration admission control to limit the maximum number of actively registered clients. Max
active calls is for call admission control to limit the maximum number of concurrent calls, while
Max wireless calls limits the calls made by explicitly specified wireless extensions. IP PBX
service must be reloaded to activate changes.
3.6.2 Reload IP PBX configuration
By clicking Reload button, IP PBX will reload configuration as soon as possible until there is no
active call. Current active calls will be retained up to 3 minutes. This is the most frequently used
function in this page since any IP PBX configuration change has to be reloaded to take effect.
3.6.3 Backup IP PBX configuration
By clicking Backup button, IP PBX archives and encrypts current configuration into a timestamped backup file under /tftpboot. To secure configuration files, it is suggested to download
them to a local host through the Get function in Service -> TFTP service once a while. Note
that the filename of a configuration file should not be changed; otherwise, it will be rejected by
the Restore function.
3.6.4 Restore IP PBX configuration
Select a configuration backup file and click Restore button, and IP PBX will restore the
configuration as current setup. One has to choose the Reload function to activate settings.
3.6.5 Restart IP PBX service
Click Restart button, and the IP PBX service will be restarted completely. Currently active calls
will be disconnected immediately. This function should be rarely required unless the LAN
setting has been changed or the service is found operating abnormally without problematic
configuration could be identified.
3.6.6 Revert IP PBX configuration
Click Revert button, and IP PBX will erase current IP PBX settings and revert configuration
back to the factory default. Note the reversion affects IP PBX service only but not rest system
services like DHCP, TFTP, QoS, NTP, STUN, etc. The backup IP PBX configuration files under
TFTP remain intact after reversion, so that one can restore to a specific time if a backup file had
been generated then.
To completely revert the whole system back to the factory default, press the hardware rest button
and hold for 10 seconds before release. Since this will wipe out everything generated by the user,
remember to download configuration files under /tftpboot/ to a local host in case they may be
used later. However, all system interfaces and services must be configured from scratch again.
18 of 51
Page 19

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
3.7 Stackable management
IP PBX is scalable and allows you to enlarge capacity by stacking up to 4 IP PBX boxes to form
a cluster.
3.7.1 Operation modes
There are three different operation modes provided by IP PBX. They are standalone mode,
master mode, and slave mode. The default mode is standalone mode while there is no cluster and
IP PBX box works independently. Once a cluster is formed, there must be only one box running
in master mode, rest of boxes run in slave mode in the cluster. For instance, let us consider fullcapacity case, there would be one master box and 3 slave boxes in a cluster. Select Service ->
Stackable management, you can see current operation mode of each IP PBX box.
3.7.2 Consolidated management
Beside, Stackable management page of master box not only indicates IP addresses of current
slave boxes in a cluster but also allows you to add new slave boxes to cluster and remove slave
boxes from cluster. You would find you can manage a cluster simply by Stackable
management page of master box.
Within a cluster, any update of configuration information on master box would affect all of slave
boxes automatically. As a result, you do not need to configure each box in a cluster. Instead, you
shall only configure the master box to take control over the whole cluster in most cases2.
Meanwhile, all of boxes in the same cluster share the same registration information and thus they
work as one single box.
3.7.3 Configuration
The following examples illustrate how to configure a stack.
3.7.3.1 Case I: Stack multiple boxes at a time
• Ensure all of boxes have factory default setting before being stacked.
• Ensure all of boxes have TCP routing to each other via LAN interfaces if they are in
different local networks.
• Select one of them to be the master box. Others are slave boxes consequently.
2
However, for SIP and PSTN trunks and Meet-me conferences, you need to configure them respectively on each
box in stack. It is similar to how you configure them in standalone mode.
19 of 51
Page 20

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
• Go to Service -> Stackable management page on master box. Select Enable Master
mode checkbox, enter IP address and port of each slave box then click Add slave
button, one by one for each of them.
• Enable Registration Load Balance if clients support 305 or 302 response.
• After adding all of slave boxes, click Save button.
• On slave boxes, specify master’s IP address.
• Finally, go to IP PBX Service page, click Restart button.
Now, all of boxes are stacked and a cluster is formed. You can start to configure extensions etc.
on master box to make internal calls possible. You can also configure SIP and PSTN trunks on
each box to enable inbound and outbound calls2. Please note that after you make any changes of
configuration in stack, remember to click Reload button on IP PBX service page of master box.
Once a Meet-me conference is configured on any one box in a cluster, it can be shared with all of
other boxes. However, in order to share SIP and PSTN trunks with other boxes, you need to do
following settings. For instance, there is a PSTN trunk (with a route pattern) configured on box
A and assigned to some usergroups already. You would like to share this PSTN trunk with box B.
• On box B, configure a route with pattern equal to the one associated with this PSTN
trunk, and then assign this route to the routegroup associated with the intra trunk from
box B toward box A.
• Click Reload button on IP PBX service page of master box.
To explain step one more clearly, for example, box A is 192.168.1.100 and box B is
192.168.1.101. There is a PSTN trunk “pstn1” with a route pattern “9./1”3 configured on box A.
In order to share this PSTN trunk among box A and B, on box B we can configure a route
“BoxA-pstn1” with pattern “9./0”4 and assign it to the routegroup
“_192168001101_192168001100” which associates with the intra trunk
“_192168001101_192168001100”5.
3.7.3.2 Case II: Stack a new box with a running old box
This case means that there is a standalone box up running for a while. Now you would like to
add a new box to form a cluster. Therefore, the old box will become master box later.
• Ensure the new box has factory default setting before being stacked.
• Ensure the new box has TCP routing to the old box via LAN interface if they are in
different local networks.
• Now, backup IP PBX configuration on the old box. Then restore this configuration to
the new box6.
3
9./1 means pattern is 9. and number of stripped digits is 1.
4
Here, please note that we always use 0 for number of stripped digits.
5
You probably notice IP addresses of two boxes meshed by an intra trunk determine name of the intra trunk. In this
case, the name of intra trunk from box B (192.168.1.101) toward box A (192.168.1.100) is
_192168001101_192168001100. Meanwhile, the routegroup associated with this intra trunk has the same name.
6
Please always ensure the initial operation mode of new box is standalone after it being restored with IP PBX
20 of 51
Page 21

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
• On new box, remove all of trunk configuration including routes and routegroups.
• Go to Service -> Stackable management page on old box. Select Enable Master
mode checkbox, enter IP address of new box then click Add slave button.
• Click Save button.
• Finally, go to IP PBX Service page on old box, click Restart button.
Now, the old box turns to be master box and the new box is slave box in cluster.
3.7.3.3 Case III: Add new slave boxes to an existing stack
Similarly to previous case, you can also add more slave boxes to an existing cluster.
3.7.3.4 Remove slave boxes from stack
• Go to Service -> Stackable management page on master box. Select IP address of
slave box you would like to remove in Slaves drop-down menu, then click Remove
button. You can also click Remove all button to remove all of slave boxes at a time.
• Click Save button
• Finally, go to IP PBX Service page on master box, click Restart button.
7
.
From now on, the cluster no longer owns the removed box. The removed box gets off the cluster
and would turn back to be standalone once you click Restart button on IP PBX service page on
it. Moreover, the master box would turn back to be standalone as well if all of slave boxes are
removed and the cluster does not exist any more.
configuration.
7
Please deselect Enable Master mode checkbox before clicking Save button if there is no more slave box.
21 of 51
Page 22

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
IP PBX Configuration
This section introduces steps to provision the IP telephony part of the IP PBX. Please note that
reloading configuration is required in order to make new configuration effective8.
3.8 Usergroup Configuration
A usergroup is a logically grouping of users and their privileges. For instance, one could have
couple of usergroups in an IP telephony network, e.g. Sales, Marketing, Administration,
Accounting, and Engineering, etc. Each usergroup associates with a set of PBX features and call
routing scopes. In other words, all users in the same usergroup share the same reachability of
PBX features and final destinations.
The User Group Management page allows the administrator to manage usergroups. By selecting
User -> Usergroup, one can add, edit, or delete usergroups. IP PBX service must be reloaded to
activate changes.
3.8.1 Add Usergroup
• Click <Add new> button from the left panel
• Enter settings shown in Table 4-1.
• Click Save button.
8
Please refer to 3.6.2 for details.
22 of 51
Page 23

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
Now, you should be able to see the newly added usergroup displayed in the Groups panel
on the left side.
3.8.2 Edit Usergroup
• Click the usergroup link in Groups panel.
• Edit settings shown on the right side.
• Click Save button.
3.8.3 Delete Usergroup
• Click the usergroup link in Groups panel.
• Click Delete button.
The usergroup just deleted shall disappear from the Groups panel.
Table 4-1 Usergroup Configuration Settings
Field Description
Group ID A unique group name containing alphabets,
numbers, and underscore only without spaces;
32 characters maximum.
Description Arbitrary description info.
Associated trunks9 Select outbound SIP trunks and PSTN trunks
accessible by this usergroup. Note the order
matters the hunting sequence in run-time.
F There is no SIP trunk and PSTN trunks
initially. Come back later to revise selection
once trunks have been created.
Reachable usergroups Select other usergroups reachable from this
usergroup. By default, only users in the same
usergroup can be reached one another.
F There is no usergroup initially. Come
back later to revise selection once more
usergroups have been created.
Associated PBX features10 Select PBX features enabled to this usergroup.
Here vm stands for Voice Mail, mm for Meet-
me Conference, parkedcalls for Call Parking,
operator for operator service.
F Most features have to be configured to
function correctly. Remember to examine the
settings of selected features before activating
current configuration.
9
Please refer to 3.13 and 3.14 for details.
10
Please refer to 3.17 for details.
23 of 51
Page 24

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
3.9 User Configuration
A user is a logical entity in IP telephony which associates extensions with a usergroup. It also
propagates its attributes such as e-mail and voicemail PIN to extensions. Usually a user refers to
a real person who has a name and e-mail; however, one can always create virtual users to
associate with public extensions. For example, extensions in reception, break room, and lab areas.
The User Management page allows the administrator to manage users in the IP telephony
network. Select User -> User, one can add, edit, and delete users. IP PBX service must be
reloaded to activate changes.
3.9.1 Add User
• Click <Add new> button from the left panel.
• Enter settings shown in Table 4-2.
• Click Save button.
The newly added user should be displayed in the Users panel on the left side.
3.9.2 Edit User
• Click the link of the user to edit from the Users panel.
• Edit settings shown on the right side.
• Click Save button.
3.9.3 Delete User
• Click the link of the user to delete from the Users panel.
• Click Delete button to confirm deletion.
The deleted user shall disappear from the Users panel.
F A user can be deleted only when no extension is associated with it.
Table 4-2 User Configuration Settings
24 of 51
Page 25

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
Field Description
Login ID A unique ID containing alphabets, numbers,
and underscore only without spaces; 32
characters maximum. This is the ID for
personal configuration through IP PBX Web
management.
Password Password for the user to access IP PBX Web
management.
Name Name of the user, either a real or a virtual one,
e.g. Alice Lee or Conference Room.
Description Arbitrary description info.
E-mail address E-mail address of the user for voicemail
notification.
attach voicemail in e-mail notification Check to enclose the message received in the
notification e-mail as an attachment.
Associated usergroup11 Select the usergroup this user belongs to.
F There is no usergroup initially. Come
back later to revise selection if no appropriate
usergroup could be chosen for now.
3.10 Device Configuration
A device could be an IP phone, gateway, analog telephone adapter, or even another IP PBX, etc.
It has one or more extensions to be registered to the IP PBX.
The Device Management page lets the administrator to create accounts for device extensions.
Before a device can be reached from the IP PBX, the same account information has to be
programmed into it through the configuration interface enabled by the device. Select Device ->
IP Phone, one can add, edit, and delete devices. IP PBX service must be reloaded to activate
changes.
11
Please refer to 3.8 for details.
25 of 51
Page 26

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
3.10.1 IP Phone
4.3.1.1 Add Device
• Click <Add new> button from the left panel.
• Enter settings shown in Table 4-3-1.
• Click Save button.
The newly added device should be displayed in Devices panel on the left side. Following
shows steps to add extensions for the new device.
• Click link of the device shown in the Devices panel.
• Click Show extensions button to switch to the extension management page.
• Click <Add new> button from the left panel.
• Enter settings shown in Table 4-3-2.
• Click Save button.
The newly added extension of this device should be displayed in Extensions panel on the
left side. More extensions could be added by repeating the last 3 steps above.
4.3.1.2 Edit Device
• Click device link in Devices panel.
• Edit settings shown on the right side.
• Click Save button.
Extensions associated with this device could be modified by following steps.
• Click Show extensions button.
• Click extension link in Extensions panel.
• Edit settings shown on the right side.
• Click Save button.
4.3.1.3 Delete Device
To delete one or more extensions associated with a certain device, follow steps below.
• Click device link in Devices panel.
• Click Show extensions button.
• Click extension link in Extensions panel.
• Click Delete button.
The deleted extension shall disappear from the Extensions panel.
Once a device has no extension, it can be deleted.
• Click device link in Devices panel.
• Click Delete button.
The deleted device shall disappear from the Devices panel.
26 of 51
Page 27

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
Table 4-3-1 Device Configuration Settings
Field Description
Device ID A unique ID containing alphabets, numbers,
and underscore only without spaces; 32
characters maximum.
Device administration URL (Optional) Administration URL of the device.
Enable Automatic Client Configuration
(Optional) For phones support auto-config,
check to specify the MAC address and audio
preferences of the phone. Each field is
explained as followings. Note that for phones
using HTTP for auto-config, DHCP setting
needs a new option 151 with a value of
http://<IP PBX LAN IP>/tftpboot/. No extra
setting if the phone uses TFTP for auto-config.
Vendor prefix Specify if provided by phone
MAC address MAC address of the device
Supplementary
Specify if provided by phone
configuration
Codec
preference
Preference order of
supported codecs and packet
times by phone
Enable VAD VAD on phone
DTMF mode DTMF mode used by phone
Table 4-3-2 Device Extension Configuration Settings
Field Description
Extension number A unique line number composed of digits
only, e.g. 101; 32 digits maximum. This is the
login ID on the device configuration side.
Password Password of this extension. Same password
must be configured on the device side as well.
Pickup group The pickup group the extension belongs to.
Extensions in the same pickup group can call
*8 to pick up a call in ringing state.
Unavailable timeout Timeout for ringing before a call is answered.
Line type Specify the type of connection, wired or
wireless, of the client with the extension.
User12 Select the user this extension associates with.
F There may not be appropriate users to
select initially. One can come back later once
the expected user has been added.
Voicemail Select enable to allocate voicemail account for
the extension.
12
Please refer to 3.9 for details.
27 of 51
Page 28

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
Voicemail PIN PIN to access voicemails. This is mandatory if
above voicemail option is enabled.
Language Preferred language for system instructions
heard from the extension.
Allow LAN use only Check to reject registration and calls from
WAN in a SIP ID same as the extension
number. I.e., this extension must be on LAN.
DTMF Mode Choose preferred DTMF mode for this
extension. Currently supported types include
RFC2833, SIP INFO, and in-band tone. It
must match configuration on the device side.
Try peer-to-peer RTP If checked, IP PBX will attempt to notify the
two peers in a conversation to try peer-to-peer
RTP transmission. This is suggested as long
as phones support INVITE or UPDATE
method during a connected call to save the
resource of IP PBX. However, only SIP INFO
DTMF mode phones should enable this since
other DTMF modes require IP PBX being
RTP relay server to support in-line transfer.
Unconditional call forward (Optional) Check voicemail as default
destination or enter a number to which
incoming calls are forwarded unconditionally.
The number could be an extension or a PSTN
number with appropriate outbound prefix.
Unavailable call forward (Optional) Enter a number to which incoming
calls are forwarded when not answered. The
number could be an extension or a PSTN
number with appropriate outbound prefix.
Line in use forward (Optional) Enter a number to which incoming
calls are forwarded when the extension is
busy. The number could be an extension or a
PSTN number with appropriate outbound
prefix.
Selective call blocking (Optional) Check Block anonymous calls to
block all calls without a Caller ID; one could
also explicitly list numbers to block by
entering one or more calling numbers and
click Add button. Use Remove button and
Remove all button to cancel blockings.
Selective call forward (Optional) Unconditional call forwarding
according to the calling number. Enter one or
more calling numbers and a forwarding
number, and click Add button. E.g., forward
only calls from 101 and 102 to a cellular
number, while let the rest enter the voice mail
by default. Note that extensions must be
28 of 51
Page 29

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
separated by commas. Use Remove button
and Remove all button accordingly when
some forwardings are no longer required.
3.10.2 Analog Phone
Connect an analog phone to a FXS port and configure the properties of the port as detailed in
Table 4-3-3.
Table 4-3-3 FXS Extension Configuration Settings
Field Description
POTS port FXS port index
Extension number A unique line number composed of digits
only, e.g. 101; 32 digits maximum.
Pickup group The pickup group the extension belongs to.
Unavailable timeout Timeout for ringing before a call is answered.
User13 Select the user this extension associates with.
F There may not be appropriate users to
select initially. One can come back later once
the expected user has been added.
Voicemail Select enable to allocate voicemail account for
the extension.
Voicemail PIN PIN to access voicemails. This is mandatory if
above voicemail option is enabled.
Language Preferred language for system instructions
heard from the extension.
Input/Output gain Voice amplification or attenuation in dB scale
to adjust input/output volume.
Unconditional call forward (Optional) Check voicemail as default
destination or enter a number to which
incoming calls are forwarded unconditionally.
The number could be an extension or a PSTN
number with appropriate outbound prefix.
Unavailable call forward (Optional) Enter a number to which incoming
calls are forwarded when not answered. The
number could be an extension or a PSTN
number with appropriate outbound prefix.
Line in use forward (Optional) Enter a number to which incoming
calls are forwarded when the extension is
busy. The number could be an extension or a
PSTN number with appropriate outbound
prefix.
13
Please refer to 3.9 for details.
29 of 51
Page 30

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
Selective call blocking (Optional) Check Block anonymous calls to
block all calls without a Caller ID; one could
also explicitly list numbers to block by
entering one or more calling numbers and
click Add button. Use Remove button and
Remove all button to cancel blockings.
Selective call forward (Optional) Unconditional call forwarding
according to the calling number. Enter one or
more calling numbers and a forwarding
number, and click Add button. E.g., forward
only calls from 101 and 102 to a cellular
number, while let the rest enter the voice mail
by default. Note that extensions must be
separated by commas. Use Remove button
and Remove all button accordingly when
some forwardings are no longer required.
3.11 Route Configuration
A route is a destination number pattern for outbound call matching. A pattern consists of digits
0-9, “*”, “#”, digit set, and wildcard characters like “.”, “X”, “Z”, and “N”. Table 4-4-1 explains
digit set and wildcard characters.
Table 4-4-1 Digit Set and Wildcard Characters for Route Patterns
Expression Description
[<digits>] Match any single digit listed explicitly. E.g.,
digit set [13579] match odd digits.
. (dot) Match any digit in any length. Usually given
in the end of a pattern to include all numbers
matched a specific prefix.
X Match any single digit from 0 to 9.
Z Match any single digit from 1 to 9.
N Match any single digit from 2 to 9.
By selecting Route -> Route, the administrator can add, edit, and delete routes in the Route
30 of 51
Page 31

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
Management page. IP PBX service must be reloaded to activate changes.
3.11.1 Add Route
• Click <Add new> button from the left panel.
• Enter settings shown in Table 4-4-2.
• Click Save button.
The newly added route should be displayed in Routes panel on the left side.
3.11.2 Edit Route
• Click the link of the route to edit from the Routes panel.
• Edit settings shown on the right side.
• Click Save button.
3.11.3 Delete Route
• Click the link of the route to delete from the Routes panel.
• Click Delete button.
The deleted route shall disappear from the Routes panel.
Table 4-4-2 Route Configuration Settings
Field Description
Route ID A unique ID containing alphabets, numbers,
and underscore only without spaces; 32
characters maximum.
Description Arbitrary description info.
Destination number pattern A destination number pattern consisting of
digits, digit set, and wildcard characters, e.g.
9NXXXXXX matches any 7-digit called
number starting from a digit larger or equal to
2 and with an extra prefix digit 9.
Number of stripped digits Number of leading digits to be stripped from
the original dialed number when matches this
route. Using 9NXXXXXX as an example
route pattern with number of stripped digits
equal to 1, dialing 95270001 will be stripped
to be 5270001 when it actually got dialed out.
Prefix A sequence of digits to be prefixed to the final
dialed number after stripping. Using
9NXXXXXX as an example route pattern
with number of stripped digits equal to 1 and
prefix 1408, dialing 95270001 will be
14085270001 when it actually got dialed out.
A special prefix character “w” could be used
for PSTN trunks to pause 0.5 second during
31 of 51
Page 32

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
dialing. Say, 4 leading consecutive “w” result
in 2 seconds delay before dialing.
3.12 Routegroup Configuration
A routegroup groups routes into a logical superset of route patterns. Such abbreviation simplifies
the association of multiple routes with a trunk, say, a PSTN line. A route could be included in
various routegroups and a routegroup could contain one single route only.
By select Route -> Routegroup, the administrator can add, edit, and delete routegroups in the
Routegroup Management page. IP PBX service must be reloaded to activate changes.
3.12.1 Add Routegroup
• Click <Add new> button from the left panel.
• Enter settings shown in Table 4-5.
• Click Save button.
The newly added routegroup should be displayed in Groups panel on the left side.
3.12.2 Edit Routegroup
• Click the link of the routegroup to edit from the Groups panel.
• Edit settings shown on the right side.
• Click Save button.
3.12.3 Delete Routegroup
• Click the link of the routegroup to delete from the Groups panel.
• Click Delete button.
The deleted routegroup shall disappear from the Groups panel.
32 of 51
Page 33

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
Table 4-5 Routegroup Configuration Settings
Field Description
Group ID A unique ID containing alphabets, numbers,
and underscore only without spaces; 32
characters maximum.
Description Arbitrary description info.
Associated routes14 Select routes belonged to this routegroup.
Click arrow icons to add or remove a route
to/from the routegroup. The right box lists
currently selected routes. Note the order of
selected routes is important since it decides
which route would be matched first for an
outgoing call.
F There may not be appropriate routes to
select initially. One can come back later to
revise it once the expected routes are added.
3.13 SIP Trunk Configuration
A SIP trunk refers to a SIP account on a remote call routing or gateway device. A practical
example is an account at an Internet Telephony Service Provider (ITSP) where a call is routed to
a SIP client or off-ramped to an analog subscriber via PSTN. One could also build SIP trunk to a
remote IP PBX to reach its extensions and PSTN ports.
The SIP Trunk Management page allows the administrator to configure SIP trunks used by IP
PBX. Select Trunk -> SIP Trunk, and one can add, edit, and delete SIP trunks. IP PBX service
must be reloaded to activate changes.
3.13.1 Add SIP Trunk
• Click <Add new> button from the left panel.
• Enter settings shown in Table 4-6.
• Click Save button.
The newly added SIP trunk shall be displayed in Trunks panel on the left side.
3.13.2 Edit SIP Trunk
• Click the link of the SIP trunk to edit from the Trunks panel.
• Edit settings shown on the right side.
• Click Save button.
3.13.3 Delete SIP Trunk
• Click the link of the SIP trunk to delete from the Trunks panel.
14
Please refer to 3.11 for details.
33 of 51
Page 34

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
Preferred language for system instruct
ions
• Click Delete button.
The deleted SIP trunk shall disappear from the Trunks panel.
Table 4-6 SIP Trunk Configuration Settings
Field Description
Trunk identifier A unique number consisting of digits only.
Usually give the phone number issued by the
ITSP for consistency.
Description Arbitrary description info.
Dynamic peer Check if the trunk is a passive trunk which
means the registration will be from a dynamic
remote peer. Typical application is to accept
registration from an IP PBX at a remote site
with dynamic IP address. Once the remote IP
PBX registers, calls from local to remote can
be made reversely over the trunk.
SIP proxy IP or FQDN
SIP proxy port
Specify IP address (or fully qualified domain
name) and UDP port of the remote SIP proxy,
which usually refer to the SIP server on the
ITSP side.
SIP registrar IP or FQDN
SIP registrar port
Specify IP address (or fully qualified domain
name) and UDP port of the remote SIP
registrar, which usually refer to the SIP server
on the ITSP side (same as proxy).
Registration required Check if registration to a registrar is required
to activate the trunk. This is true for a remote
IP PBX or an ITSP account, however, may be
not required in case of a SIP gateway.
Trunk password Give password used for authentication on the
remote SIP proxy or registrar. Usually this is
given by the ITSP.
Outbound routegroup15 Select a routegroup to associate routes with
this trunk. Outbound calls match included
route patterns could employ this trunk to hop
onto a remote SIP domain.
DID of extension When enabled DID, choose an extension to be
Language
15
Please refer to 3.12 for details.
34 of 51
F There may not be appropriate routegroup
to select initially. One can come back later to
revise it once the expected routegroup has
been added.
an unconditional destination for incoming
calls to this trunk. The number of the SIP
trunk is therefore regarded as the direct line
number of the extension.
Page 35

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
heard from the trunk.
Usergroup16 of privilege When disabled DID, select a usergroup whose
reachability to other usergroups and trunks
will be used as the privilege of inbound calls
from this trunk.
F There may not be appropriate usergroups
to select initially. One can come back later
once the expected usergroup has been added.
DTMF Mode Choose preferred DTMF mode for this trunk.
Currently supported types include RFC2833,
SIP INFO, and in-band tone. It must match
configuration on the server side.
Try peer-to-peer RTP If checked, IP PBX will attempt to notify the
two peers in a conversation to try peer-to-peer
RTP transmission. This is suggested as long
as phone and ITSP side support INVITE or
UPDATE method during a connected call to
save the resource of IP PBX. However, only
SIP INFO DTMF mode should enable this
since other DTMF modes require IP PBX
being RTP relay server to support in-line
transfer.
Bandwidth sensitive Indicate the trunk is over a bandwidth-
sensitive link, e.g. across Internet. If checked,
a limit must be specified for call admission.
3.14 PSTN Trunk Configuration
A PSTN trunk group is a logical group of one or more PSTN subscriber lines connecting to FXO
ports on IP PBX.
The PSTN Trunk Management page allows the administrator to configure PSTN trunks. By
selecting Trunk -> PSTN Trunk, one can add, edit, and delete PSTN trunks. IP PBX service
must be reloaded to activate changes.
16
Please refer to 3.8 for details.
35 of 51
Page 36

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
3.14.1 Add PSTN Trunk
• Click <Add new> button from the left panel.
• Enter settings shown in Table 4-7.
• Click Save button.
The newly added PSTN trunk shall be displayed in Trunks panel on the left side.
3.14.2 Edit PSTN Trunk
• Click the link of trunk to edit from the Trunks panel.
• Edit settings shown on the right side.
• Click Save button.
3.14.3 Delete PSTN Trunk
• Click the link of trunk to delete from the Trunks panel.
• Click Delete button.
The deleted PSTN trunk shall disappear from the Trunks panel.
Table 4-7 PSTN Trunk Configuration Settings
Field Description
Trunk group ID number of this PSTN trunk group. A valid
number ranges from 1 to 31.
Description Arbitrary description info.
Trunk ports FXO port indices grouped by this PSTN
trunk, such as 1 or 1,2 or 1-3, etc. Maximum
port index depends on the number of physical
ports available.
36 of 51
Page 37

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
Port selection Order to hunt for an available port in the
group. Besides Ascending and Descending
options, one could check Rotating to force
ports being selected by turns to even cost.
Outbound routegroup17 Select a routegroup to associate routes with
this trunk. Outbound calls match included
route patterns could employ this trunk to
access PSTN.
F There may not be appropriate routegroup
to select initially. One can come back later to
revise it once the expected routegroup is
added.
DID of extension When enabled DID, choose an extension to be
an unconditional destination for incoming
calls to this trunk. The PSTN numbers of the
included ports are therefore regarded as the
direct line numbers of the extension.
Language Preferred language for system instructions
heard from the trunk.
Usergroup18 of privilege When disabled DID, select a usergroup whose
reachability to other usergroups and trunks
will be used as the privilege of inbound calls
from this trunk.
F There may not be appropriate usergroups
to select initially. One can come back later to
revise it once the expected usergroups are
added.
Input/Output gain Voice amplification or attenuation in dB scale
to adjust input/output volume of a PSTN line.
Minimum disconnection tone Minimum volume level of the disconnection
tone. If a PSTN trunk is found to have
disconnection problem and voice sounds low,
choose a lower dB.
Delay before/after answering Delay in seconds before and after answering a
call from PSTN trunk.
3.15 Trunk Terminal
A SIP trunk terminal refers to a SIP account for a remote SIP trunk to register with. It terminates
SIP registration and invitation from a remote IP PBX and relay calls to local clients, PSTN
trunks, or further SIP trunks. In a site-to-site SIP trunking application, a SIP trunk on one side
usually pairs with a trunk terminal on the other side to form a unidirectional call hand-off path.
To allow trunking in the other direction, the two sides swap roles and form another pair. Since a
trunk terminal is the account for a SIP trunk to authenticate with, exact the same identifier and
17
Please refer to 3.12 for details.
18
Please refer to 3.8 for details.
37 of 51
Page 38

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
password must be used for both.
The Terminal Management page allows the administrator to configure trunk terminals used by IP
PBX. Select Trunk -> Trunk terminal and one can add, edit, and delete terminals. IP PBX
service must be reloaded to activate changes.
3.15.1 Add Trunk Terminal
• Click <Add new> button from the left panel.
• Enter settings shown in Table 4-8.
• Click Save button.
The newly added terminal shall be displayed in Terminals panel on the left side.
3.15.2 Edit Trunk Terminal
• Click the link of the terminal to edit from the Terminals panel.
• Edit settings shown on the right side.
• Click Save button.
3.15.3 Delete Trunk Terminal
• Click the link of the terminal to delete from the Terminals panel.
• Click Delete button.
The deleted terminal shall disappear from the Terminals panel.
Table 4-8 Trunk Terminal Configuration Settings
Field Description
Terminal identifier A unique number consisting of digits only.
This is the trunk identifier configured on the
other IP PBX.
Description Arbitrary description info.
38 of 51
Page 39

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
Terminal password Password of SIP trunk given on the other IP
PBX for authentication.
DID of extension When enabled DID, choose an extension to be
an unconditional destination for incoming
calls to this terminal. The number of the
terminal is therefore regarded as the direct line
number of the extension.
Language Preferred language for system instructions
heard from the terminal.
Usergroup19 of privilege When disabled DID, select a usergroup whose
reachability to other usergroups and trunks
will be used as the privilege of inbound calls
from this terminal.
F There may not be appropriate usergroups
to select initially. One can come back later
once the expected usergroup has been added.
Bandwidth sensitive Indicate the trunk is over a bandwidth-
sensitive link, e.g. across Internet. If checked,
a limit must be specified for call admission.
3.16 POTS setup
This page allows selection of country-based progress tones and/or impedance of POTS ports. IP
PBX service needs to be restarted before new setting takes effect.
3.17 Feature Configuration
A feature is a logical entity presenting a function module of IP PBX, e.g. meet-me conference,
auto attendant, voice mail, etc. IP PBX service must be reloaded to activate changes.
19
Please refer to 3.8 for details.
39 of 51
Page 40

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
3.17.1 Auto attendant
Auto attendant is an Interactive Voice Response (IVR) subsystem which answers incoming calls
to a trunk and prompt voice menu to guide the caller to reach his expected extension. Usually the
caller input the expected extension by pressing digits from the touch-tone pad on his/her phone,
and the auto attendant to make the transfer. In some case, the caller may not know the extension
of the party he/she is looking for so that there should be a key, say 0, to call the operator for help.
Or, if the caller stays on the line for some time without giving a valid extension, IP PBX will
transfer the call to the operator as well. Select Feature -> Auto attendant to configure auto
attendant feature.
• Enter settings shown in Table 3.17-1
• Click Save button.
Table 3.17-1 Auto Attendant Configuration Settings
Field Description
Key for reaching operator Select key for reaching operator if this option
is checked, e.g. 0.
Operator extension The designated extension number of the
operator.
Response timeout action Select an action to be taken if the caller does
not respond to the Auto Attendant for a
certain period of time. Option “disconnect”
means to hang up calls when timeout, while
option “operator” transfers calls to operator
when timeout.
Digit input timeout Enter timeout for digit collection, e.g. 5 sec.
User response timeout Enter timeout for caller response, e.g. 15 sec.
3.17.2 Call park
During a call, the callee may want to continue the conversation using another phone. The call
park feature enables so by letting the callee transfer the call to the call park base extension and IP
PBX will respond an available park line from the pool of call park numbers. After that the callee
hangs up current phone, moves to another phone, and dials the park line number told by IP PBX
to resume conversation with the caller. If the callee does not call the given park line number to
40 of 51
Page 41

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
resume conversation in 45 seconds, IP PBX will ring the original extension where the callee
answered the call. To configure Call Park feature, select Feature -> Call park, enter settings
shown in
Table 3.17-2, and then click Save button.
Table 3.17-2 Call Park Configuration Settings
Field Description
Call park pilot number A unique extension number for call parking,
e.g. 700.
Available parking lines Extension pool available for call parking, e.g.
701-720 forms a pool available for system to
park calls.
Parking timeout Timeout waiting for picking up the parked call
3.17.3 Life line
Life line feature allows specification of emergency number patterns to seize a PSTN line with
absolute priority. For example, someone dials an emergency call while all PSTN lines are in use.
In such case, if the called number matches any specified pattern, the PSTN line with longest talk
time so far will be disconnected right away to allow the connection of the emergency call.
Select Feature -> Life line to configure life-line feature.
3.17.3.1 Add Life-line pattern
• Click <Add new> button from the left panel to add a new pattern.
• Enter settings shown in Table 3.17-3.
• Click Save button.
The newly added pattern should be displayed in Life line panel on the left side.
3.17.3.2 Delete Life-line pattern
• Click link to the pattern to delete from the Life line panel.
• Click Delete button.
The deleted pattern shall disappear from the Life line panel.
41 of 51
Page 42

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
Table 3.17-3 Life line Configuration Settings
Field Description
Number pattern Pattern for emergency numbers. Note: this is
the pattern after digit stripping. For example,
configure 911 here even if users dial 9911 to
reach the 911 service over PSTN when the
PSTN trunk has an outbound dialplan of “9.”.
Description Arbitrary description info.
3.17.4 Meet-me conference
Meet-me conference enables conferencing of multiple parties from various sources. A party
could dial in a conference from an internal IP phone, an external IP phone on Internet, an analog
phone via PSTN, or an IP phone in a remote site. IP PBX allows multiple conference rooms
going concurrently using different room numbers. Before entering a meeting room, the caller has
to give the correct PIN of the room number.
Select Feature -> Meet-me conference to configure meet-me conference feature.
3.17.4.1 Add Meet-me Conference
• Click <Add new> button from the left panel to add a new conference room.
• Enter settings shown in Table 3.17-4.
• Click Save button.
The newly added room should be displayed in Meet-me rooms panel on the left side.
3.17.4.2 Edit Meet-me Conference
• Click the link of the room to edit from the Meet-me rooms panel.
• Edit settings shown on the right side.
• Click Save button.
3.17.4.3 Delete Meet-me Conference
• Click link to the room to delete from the Meet-me rooms panel.
• Click Delete button.
The deleted conference room shall disappear from the Meet-me rooms panel.
Table 3.17-4 Meet-me Conference Configuration Settings
42 of 51
Page 43

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
Field Description
Room number Meeting room number, e.g. 8000.
Description Arbitrary description info.
PIN to join PIN for normal users to join the conference.
During a conference, a normal user has
following options:
- # to quit conference
- *1 to mute/unmute
- *9 to log in as the administrator if
there is no administrator in yet.
Administrator PIN PIN for the administrator of the conference.
During a conference, the administrator has
following options:
- # to quit conference
- *1 to mute/unmute
- *2 to lock/unlock the conference
- *3 to invite a user into the conference
- *4 to drop a user from the conference
- *5 to drop all users in the conderence
3.17.5 Music on hold
Music-on-hold (MOH) is used in several occasions for a single purpose—to comfort the waiting
party with music. One could upload some candidate music files and pick one as the default one.
Select Feature -> Music on hold to manage MOH files.
3.17.5.1 Add MOH file
• Click <Add new> button from the left panel to add a new MOH file.
• Enter settings shown in Table 3.17-5.
• Click Save button.
The newly added file should be displayed in MOH files panel on the left side.
3.17.5.2 Edit MOH file
• Click the link of the file to edit from the MOH files panel.
43 of 51
Page 44

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
• Edit settings shown on the right side.
• Click Save button.
3.17.5.3 Delete MOH file
• Click link to the file to delete from the MOH files panel.
• Click Delete button.
The deleted MOH file shall disappear from the MOH files panel.
Table 3.17-5 MOH file Configuration Settings
Field Description
MOH ID A unique ID containing alphabets, numbers,
and underscore only without spaces; 32
characters maximum.
Media file Candidate music files in the repository. To
upload a new music file, click Browse to
locate a Windows PCM (8000 Hz, 16-bit) file
from local host and press Upload. On
successful uploading, the filename will appear
in the pull-down menu of media files.
Similarly, click Remove to remove selected
MOH file from the candidate list.
Default MOH Check to use this music file for system default
MOH globally.
3.17.6 Voicemail
IP PBX has a built-in voice mail subsystem with a sophisticated IVR. A call to an extension in
use or no answer could be configured to enter voice mail recording procedure. After leaving a
message, a notification e-mail will be sent to the user owns the extension with or without the
message in the form of an attached .wav file. The Message Waiting Indicator (MWI) on phone
(if any) will be lit. The user could then dial the voicemail pilot number to enter voice mail
system to manage messages such as playback, delete, or move them from inbox to different
folders. To configure Voicemail feature, select Feature -> Voicemail from the top menu, enter
settings shown in Table 3.17-6, and then click Save button.
44 of 51
Page 45

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
Table 3.17-6 Voice Mail Configuration Settings
Field Description
Voicemail pilot number Number to access voice mail system IVR.
Minimum message time Message less than this duration will be
discarded. E.g., 3 (sec).
Maximum message time Maximum duration allowed for a single
message. E.g., 60 (sec).
Maximum messages per account Maximum number of messages allowed per
extension.
SMTP server Hostname or IP address of the SMTP server
for voicemail notification.
E-mail from address Most SMTP servers require a valid from
address to accept a mailing request.
SMTP server account Specify account ID if the SMTP server
requires authentication for outgoing mails.
SMTP server password Specify account password if the SMTP server
requires authentication for outgoing mails.
3.17.7 Auto-attendant prompts
This page allows replacing built-in AA prompts with user recordings. Choose a language and
browse a corresponding recording from local storage. Then, click Upload to complete the
replacement. To reset a prompt back to default, leave browsed file blank and directly click the
Upload button. Note that the replacement is done for the selected language only. Currently only
following prompts could be replaced. The recording format must be 8000 Hz, 16 bit, Windows
PCM .wav file.
45 of 51
Page 46

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
Table 3.17-7 Replaceable Auto-attendant Prompts
Prompt Description
Greeting Welcome to ${company}, please dial an
extension or press ${key} for the operator.
Invalid I am sorry, that is not a valid extension. Please
try again.
Extension Extension
Unavailable is not available
Busy is on the phone
3.17.8 Meet-me prompts
This page allows replacing built-in meet-me conference prompts with user recordings. Choose a
language and browse a corresponding recording from local storage. Then, click Upload to
complete the replacement. To reset a prompt back to default, leave browsed file blank and
directly click the Upload button. Note that the replacement is done for the selected language
only. Currently only following prompts could be replaced.
Table 3.17-8 Replaceable Meet-me Prompts
Prompt Description
Get PIN number Please enter the conference pin number.
Invalid PIN That pin is invalid for this conference.
Only person You are currently the only person in this
conference.
3.17.9 Voicemail prompts
This page allows replacing built-in voicemail system prompts with user recordings. Choose a
language and browse a corresponding recording from local storage. Then, click Upload to
complete the replacement. To reset a prompt back to default, leave browsed file blank and
directly click the Upload button. Note that the replacement is done for the selected language
only. Currently only following prompts could be replaced.
46 of 51
Page 47

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
Table 3.17-9 Replaceable Voicemail System Prompts
Prompt Description
Login Welcome to voice mail system, please enter
your mailbox.
Password Password?
Incorrect mailbox Login incorrect, mailbox?
Good-bye Good-bye.
Prerec-intro Press star(*) to cancel recording and return to
the main menu. Or, press pound(#) to start
recording right away.
Intro Please leave your message after the tone.
When done, hang up or press the pound(#)
key.
47 of 51
Page 48

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
LAN
Internet
modem
PS
TN
4 Example Provisioning
This chapter introduces several practical configuration examples of IP PBX deployment. The
configuration of IP PBX is very flexible and the expressiveness of usergroups, routegroups, and
trunks are scalable enough to support various network architectures. Users could reference these
examples and build a larger network involving multiple sites and advanced services.
4.1 Internal Extension Configuration
The procedure introduced below is recommended as the first step of a configuration task. The
configuration only enables internal extension calls, but it serves as a good practice for
administration.
• Configure a usergroup named ALL (refer to 4.1).
• Configure users and assign every user to usergroup ALL (refer to 4.2).
• Configure devices and an extension for each device (refer to 4.3).
• Assign each extension to a corresponding user (refer to 4.3).
• Configure each client phone with respect to the extension number and password in its IP
PBX extension configuration accordingly.
• Reload IP PBX service (refer to 3.4.1).
Up to this point all configured phones should register with the IP PBX with a usable extension.
Since these phones are all belonged to the same usergroup ALL, they can call one another
without limitation.
4.2 Case I: Single-Site Configuration
This case describes the typical settings of a single-site configuration; say Company A. Assume
Company A has a DSL connection for Internet access and 2 PSTN subscriber lines as shown in
Figure 5-1. The provisioning tasks include:
Figure 5-1
• There are staff phones in cubes and offices and utility phones in public areas.
48 of 51
Page 49

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
• Each phone has one extension and it can call any extension without limitation.
• Only staff phones can call out to PSTN with a prefix 9.
• Incoming PSTN calls are answered by auto attendant and could be transferred to any
extension.
Configuration steps:
1. Create usergroups staff, utility, and ext-all.
2. Include staff and utility in the Reachable usergroup of ext-all.
3. Create a user account for each staff and assign it to usergroup staff.
4. Create an additional user account public and assign it to usergroup utility.
5. Create a device for each physical phone and designate an extension.
6. Assign extensions of staff phones to corresponding users.
7. Assign all extensions of utility phones to share the same user public.
8. Create a route pstn with pattern 9. with number of digits stripped 1, no prefix.
9. Create a routegroup pstn-out containing route pstn only.
10. Create a PSTN trunk with ID 1, port 1-2, choose pstn-out as Outbound routegroup,
leave DID unchecked, and select ext-all as the Usergroup of privilege.
11. Return to usergroup configuration. For usergroup staff, include PSTN trunk pstn1
and Reachable usergroup utility; while for usergroup utility, include Reachable
usergroup staff only.
12. Reload IP PBX Service.
4.3 Case II: Two-Site Configuration
This case describes the typical settings of a two-site configuration; say Company B headquarters
B-HQ and its branch B-BR in another country. Assume each site has a DSL connection for
Internet access. B-HQ has 4 PSTN subscriber lines and B-BR has 2 lines as shown in Figure 5-2.
The provisioning tasks include:
• Both sites have staff phones in cubes and offices and utility phones in public areas.
• Each phone has one extension. A utility phones can call extensions within the site it is
in only, while the staff phones can call any extension in both sites without limitation. BHQ has extensions 1XX and B-BR has extensions 2XX.
• Calls between B-HQ and B-BR use private SIP trunks across Internet. IP PBX at B-HQ
has a static IP address 64.1.0.1 and IP PBX at B-BR has a static IP address 222.44.0.1.
• Only staff phones can call out to PSTN with a prefix 9.
• B-HQ staff phones call out starting with 90118621 will relay to B-BR through the SIP
trunk and then hop off to PSTN in B-BR. Similarly, B-BR staff phones call out starting
with 9001408 will relay to B-HQ for PSTN hop-off.
• Incoming PSTN calls are answered by auto attendant and could be transferred to any
extension.
49 of 51
Page 50

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
LAN
Internet
modem
PSTN
LAN
modem
PSTN
B-HQ
Configuration steps in B-HQ:
1. Create usergroups staff, utility, and ext-all.
2. Include staff and utility in the Reachable usergroup of ext-all.
3. Create a user account for each staff and assign it to usergroup staff.
4. Create an additional user account public and assign it to usergroup utility.
5. Create a device for each physical phone and designate an extension.
6. Assign extensions of staff phones to corresponding users.
7. Assign all extensions of utility phones to share the same user public.
8. Create a route pstn with pattern 9Z. with number of digits stripped 1, no prefix.
9. Create a route pstn-br with pattern 90118621. with number of digits stripped 8,
prefix 9.
10. Create a route ext-br with pattern 2XX and number of digits stripped 0, no prefix.
11. Create a routegroup pstn-out containing route pstn only.
12. Create a routegroup to-br containing routes pstn-br and ext-br.
13. Create a PSTN trunk with ID 1, port 1-4, choose pstn-out as Outbound routegroup,
leave DID unchecked, and select ext-all as the Usergroup of privilege.
14. Create a dynamic peer SIP trunk with ID 100; password hq-secret; choose to-br as
Outbound routegroup, leave DID unchecked, and select staff as the Usergroup of
privilege.
15. Return to usergroup configuration. For usergroup staff, include SIP trunk 100, PSTN
B-BR
Figure 5-2
50 of 51
Page 51

PLANET IPX-2000 user’s manual
trunk pstn1 and Reachable usergroup utility; while for usergroup utility, include
Reachable usergroup staff only.
16. Reload IP PBX Service.
Configuration steps in B-BR:
1. Create usergroups staff, utility, and ext-all.
2. Include staff and utility in the Reachable usergroup of ext-all.
3. Create a user account for each staff and assign it to usergroup staff.
4. Create an additional user account public and assign it to usergroup utility.
5. Create a device for each physical phone and designate an extension.
6. Assign extensions of staff phones to corresponding users.
7. Assign all extensions of utility phones to share the same user public.
8. Create a route pstn with pattern 9Z. with number of digits stripped 1, no prefix.
9. Create a route pstn-hq with pattern 9001408. with number of digits stripped 7, prefix
9.
10. Create a route ext-hq with pattern 1XX and number of digits stripped 0, no prefix.
11. Create a routegroup pstn-out containing route pstn only.
12. Create a routegroup to-hq containing routes pstn-hq and ext-hq.
13. Create a PSTN trunk with ID 1, port 1-2, choose pstn-out as Outbound routegroup,
leave DID unchecked, and select ext-all as the Usergroup of privilege.
14. Create a SIP trunk with ID 100 pointing to 64.1.0.1 port 5060; password hq-secret;
choose to-hq as Outbound routegroup, leave DID unchecked, and select staff as the
Usergroup of privilege.
15. Return to usergroup configuration. For usergroup staff, include SIP trunk 100, PSTN
trunk pstn1 and Reachable usergroup utility; while for usergroup utility, include
Reachable usergroup staff only.
16. Reload IP PBX Service.
51 of 51
 Loading...
Loading...