Page 1

PSSnet SHL Series
Managed Ethernet Switches
Industrial Ethernet Switches – PSSnet S
Redundancy Configuration– Mat - No. 1001653 – EN- 01
Page 2

All rights to this documentation are reserved by Pilz GmbH & Co. KG. Copies may be made
for internal purposes.
Suggestions and comments for improving this documentation will be gratefully received.
Pilz®, PIT®, PMI®, PNOZ®, Primo®, PSEN®, PSS®, PVIS®, SafetyBUS p®, SafetyEYE®,
SafetyNET p®, the spirit of safety® are registered and protected trademarks of
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG in some countries.
Page 3

Content
Content
Content 3
About this Manual 5
Key 7
1 Introduction 9
1.1 Overview of Redundancy Procedure 10
2 Ring Redundancy 11
2.1 Example of HIPER-Ring 13
2.1.1 Setting up and configuring the HIPER-Ring 15
2.2 Example of MRP-Ring 19
3 Ring/Network coupling 25
3.1 Variants of the ring/network coupling 26
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network coupling 28
3.2.1 STAND-BY switch 28
3.2.2 One-Switch coupling 31
3.2.3 Two-Switch coupling 37
3.2.4 Two-Switch coupling with control line 44
4 Rapid Spanning Tree 53
4.1 The Spanning Tree Protocol 55
4.1.1 The tasks of the STP 55
4.1.2 Bridge parameters 56
4.1.3 Bridge Identifier 56
4.1.4 Root Path Costs 57
4.1.5 Port Identifier 58
4.2 Rules for creating the tree structure 59
4.2.1 Bridge information 59
4.2.2 Setting up the tree structure 59
4.3 Example of specifying the root paths 61
4.4 Example of manipulating the root paths 63
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
3
Page 4

Content
4.5 Example of manipulating the tree structure 65
4.6 The Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol 66
4.6.1 Port roles 66
4.6.2 Port states 68
4.6.3 Spanning Tree Priority Vector 69
4.6.4 Fast reconfiguration 69
4.6.5 Configuring the Rapid Spanning Tree 70
4.7 Combination of RSTP and MRP 78
4.7.1 Application example for the combination of RSTP and MRP 79
A Index 83
B Further support 85
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
4
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 5

About this Manual
About this Manual
The “Redundancy Configuration” user manual contains all the information
you need to select a suitable redundancy procedure and configure it.
The “Basic Configuration” user manual contains all the information you need
to start operating the device. It takes you step by step from the first startup
operation through to the basic settings for operation in your environment.
The “Installation” user manual contains a device description, safety instructions, a description of the display, and all the other information that you need
to install the device before you begin with the configuration of the device.
The “Industry Protocols” user manual describes how the device is connected
by means of a communication protocol commonly used in the industry, such
as EtherNet/IP and PROFINET.
The "Web-based Interface" reference manual contains detailed information
on using the Web interface to operate the individual functions of the device.
The "Command Line Interface" reference manual contains detailed information on using the Command Line Interface to operate the individual functions
of the device.
The Network Management Software HiVision/Industrial HiVision provides
you with additional options for smooth configuration and monitoring:
X Configuration of multiple devices simultaneously.
X Graphical interface with network layouts.
X Auto-topology discovery.
X Event log.
X Event handling.
X Client / Server structure.
X Browser interface
X ActiveX control for SCADA integration
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
5
Page 6

About this Manual
X SNMP/OPC gateway
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
6
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 7

Key
Key
The designations used in this manual have the following meanings:
X List
Work step
Link Indicates a cross-reference with a stored link
Note: A note emphasizes an important fact or draws your
Courier ASCII representation in user interface
Symbols used:
Subheading
attention to a dependency.
Execution in the Web-based Interface user interface
Execution in the Command Line Interface user interface
Router with firewall
Switch with firewall
Router
Switch
Bridge
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
7
Page 8
Key
Hub
A random computer
Configuration Computer
Server
PLC Programmable logic
controller
I/O Robot
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
8
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 9

Introduction
1 Introduction
The device contains a range of redundancy functions:
X HIPER-Ring
X MRP-Ring
X Ring/Network Coupling
X Rapid Spanning Tree Algorithm (RSTP)
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
9
Page 10

Introduction
1.1 Overview of
Redundancy Procedure
1.1 Overview of
Redundancy Procedure
Redundancy
procedure
RSTP Random structure typically < 1 s (STP < 30 s), up to < 30 s - depends
HIPER-Ring Ring typically 80 ms, up to < 500 ms - practically indepen-
MRP-Ring Ring typically 80 ms, up to < 500 ms - practically indepen-
Redundant
coupling
Network topology Switching time
heavily on the number of devices
Note: Up to 79 devices possible, depending on topology and configuration. If
the default values are being used, up to 39 devices are possible, depending on
the topology (see page 53).
dently of the number of devices
dently of the number of devices
Note: In combination with RSTP in MRP compatibility mode, up to 39 devices
are possible, depending on the configuration. If the default values for RSTP are
being used, up to 19 devices are possible (see page 53).
Coupling of network
segment/rings via a
main line and a
redundant line
typically 150 ms, up to < 500ms
Table 1: Comparison of the redundancy procedures
10
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 11
Ring Redundancy
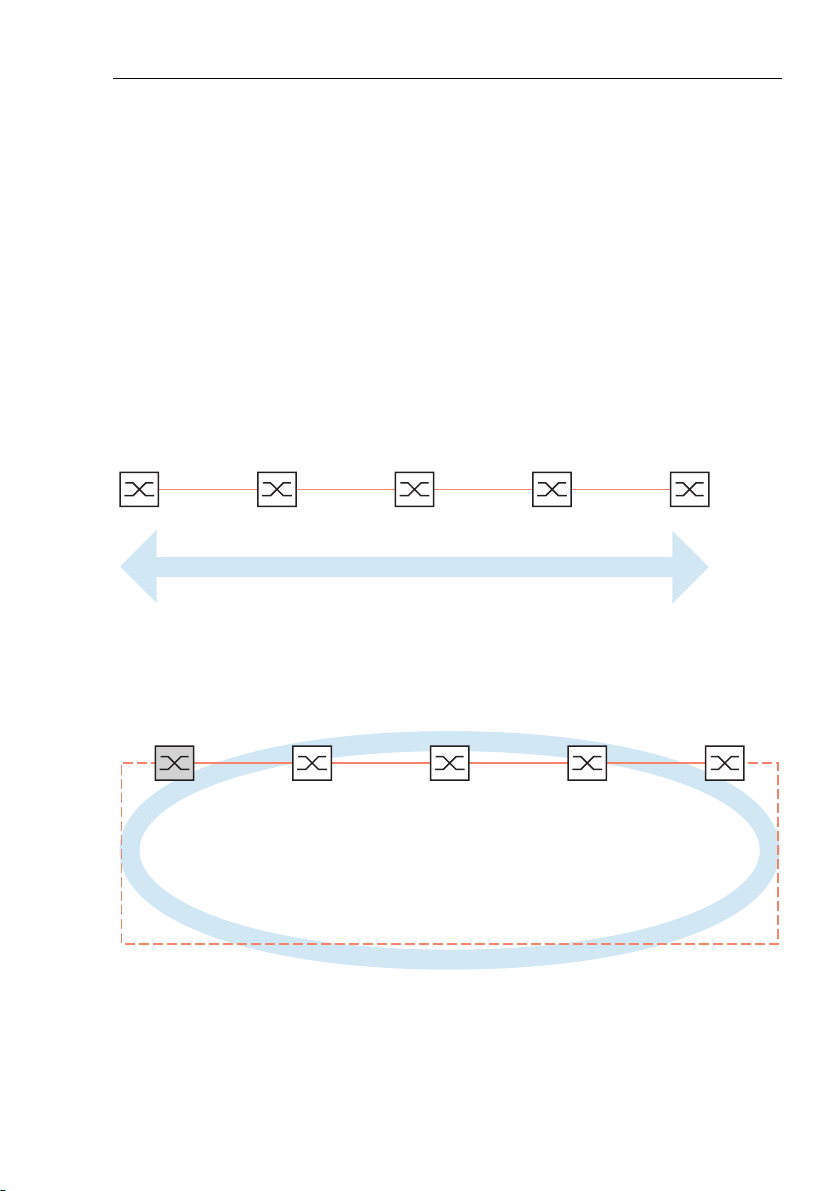
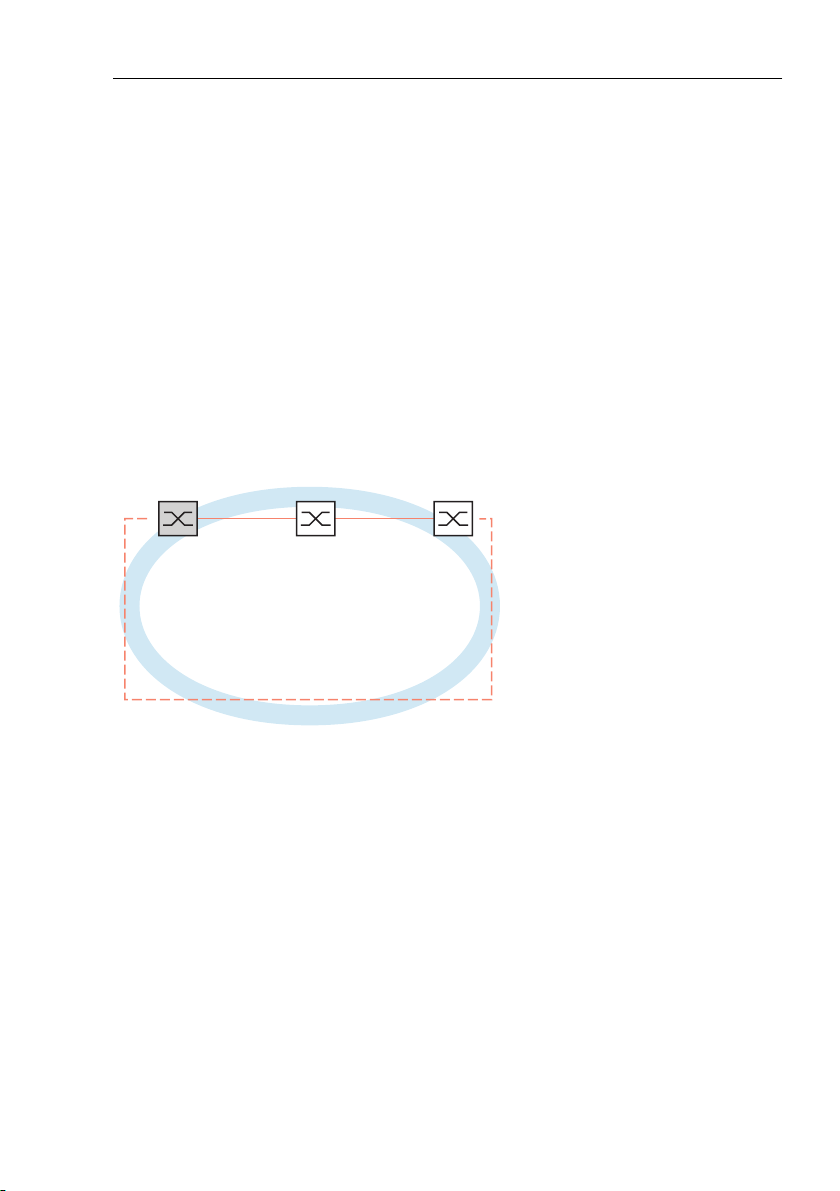
2 Ring Redundancy
The concept of ring redundancy allows the construction of high-availability,
ring-shaped network structures.
With the help of the RM (Ring Manager) function, the two ends of a backbone
in a line structure can be closed to a redundant ring. The ring manager keeps
the redundant line open as long as the line structure is intact. If a segment
fails, the ring manager immediately closes the redundant line, and line
structure is intact again.
Figure 1: Line structure
RM
Figure 2: Redundant ring structure
RM = Ring Manager
—— main line
- - - redundant line
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
11
Page 12

Ring Redundancy
If a section is down, the ring structure of a
X HIPER-(HIGH PERFORMANCE REDUNDANCY) Ring with up to 50 de-
vices typically transforms back to a line structure within 80 ms (setting:
standard/accelerated).
X MRP (Media Redundancy Protocol) Ring (IEC 62439) of up to 50 devices
typically transforms back to a line structure within 80 ms (adjustable to
max. 200 ms/500 ms).
Device requirements for using the HIPER-Ring function:
X Within a HIPER-Ring, you can use any combination of the following
devices:
– PSSnet SHL
X Within an MRP-Ring, you can use devices that support the MRP protocol
based on IEC62439.
Note: Enabled Ring Redundancy methods on a device are mutually exclusive at any one time. When changing to another Ring Redundancy method,
deactivate the function for the time being.
Note: The following usage of the term “ring manager” instead of “redundancy
manager” makes the function easier to understand.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
12
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 13
Ring Redundancy
2.1 Example of HIPER-Ring
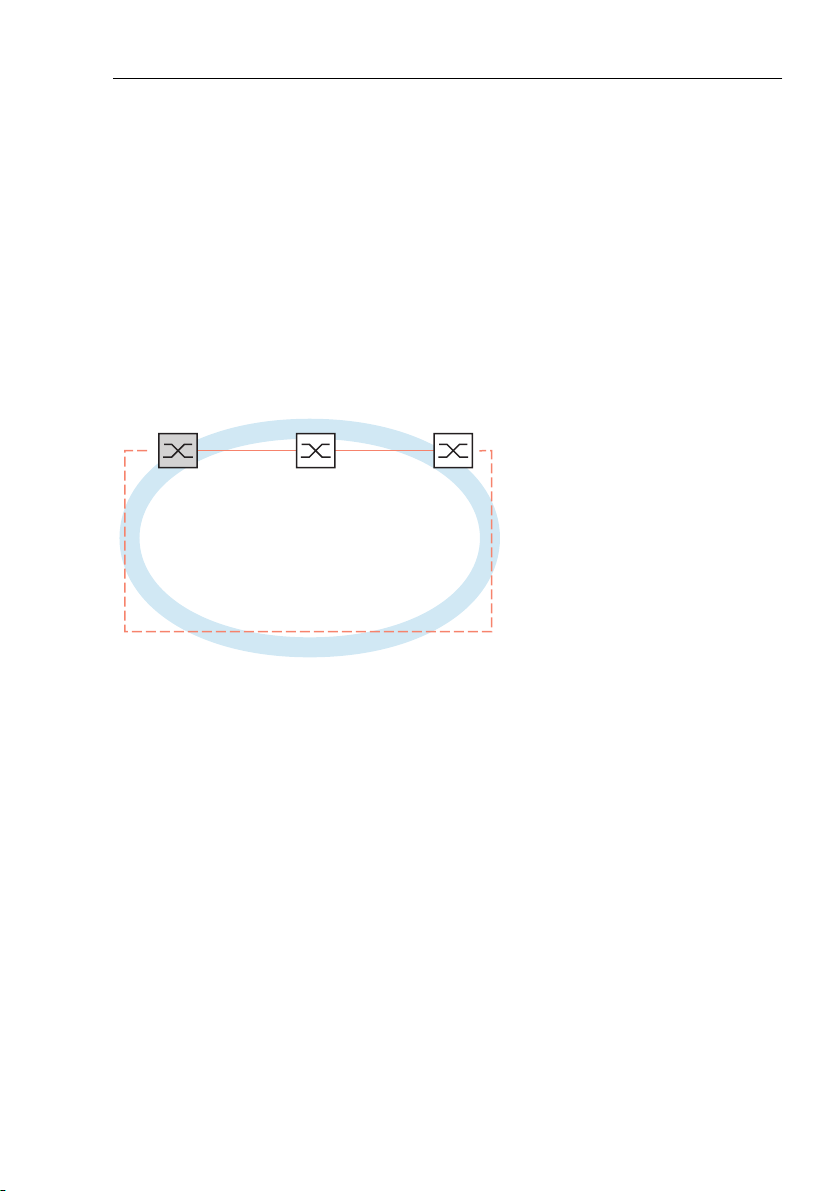
2.1 Example of HIPER-Ring
A network contains a backbone in a line structure with 3 devices. To increase
the redundancy reliability of the backbone, you have decided to convert the
line structure to a HIPER-Ring. You use ports 1 and 2 in module 1 of the
devices to connect the lines.
12 3
1.1 1.2 1.1 1.2 1.1 1.2
RM
Figure 3: Example of HIPER-Ring
RM = Ring Manager
—— main line
- - - redundant line
The following example configuration describes the configuration of the ring
manager device (1). The two other devices (2 to 3) are configured in the
same way, but without activating the ring manager function. Select the
“Standard” value for the ring recovery, or leave the field empty.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
13
Page 14

Ring Redundancy
2.1 Example of HIPER-Ring
Note: As an alternative to using software to configure the HIPER-Ring, with
devices PSSnet SHL you can also use a DIP switch to enter a number of settings. You can also use a DIP switch to enter a setting for whether the configuration via DIP switch or the configuration via software has priority. The
state on delivery is “Software Configuration”.
Note: Configure all the devices of the HIPER-Ring individually. Before you
connect the redundant line, you must complete the configuration of all the
devices of the HIPER-Ring. You thus avoid loops during the configuration
phase.
14
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 15

Ring Redundancy
2.1 Example of HIPER-Ring
2.1.1 Setting up and configuring the HIPER-Ring
Set up the network to meet your requirements.
You configure all 6 ports so that the transmission speed and the duplex
settings of the lines correspond to the following table:
Bit rate 100 Mbit/s 1000 Mbit/s
Autonegotiation
(automatic configuration)
Port on on
Duplex Full –
Table 2: Port settings for ring ports
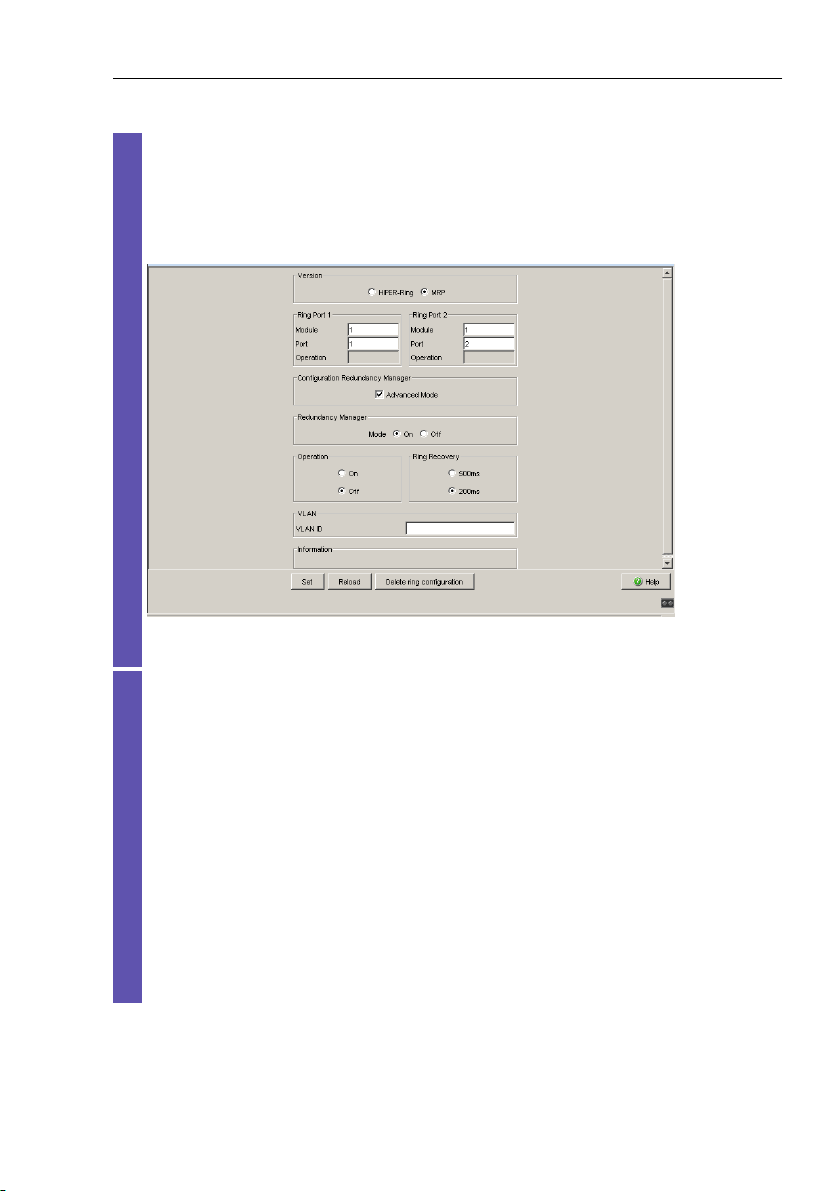
Select the Redundancy:Ring Redundancy dialog.
Under “Version”, select HIPER-Ring.
Define the desired ring ports 1 and 2 by making the corresponding
entries in the module and port fields. If it is not possible to enter a
module, then there is only one module in the device that is taken
over as a default.
off on
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
15
Page 16
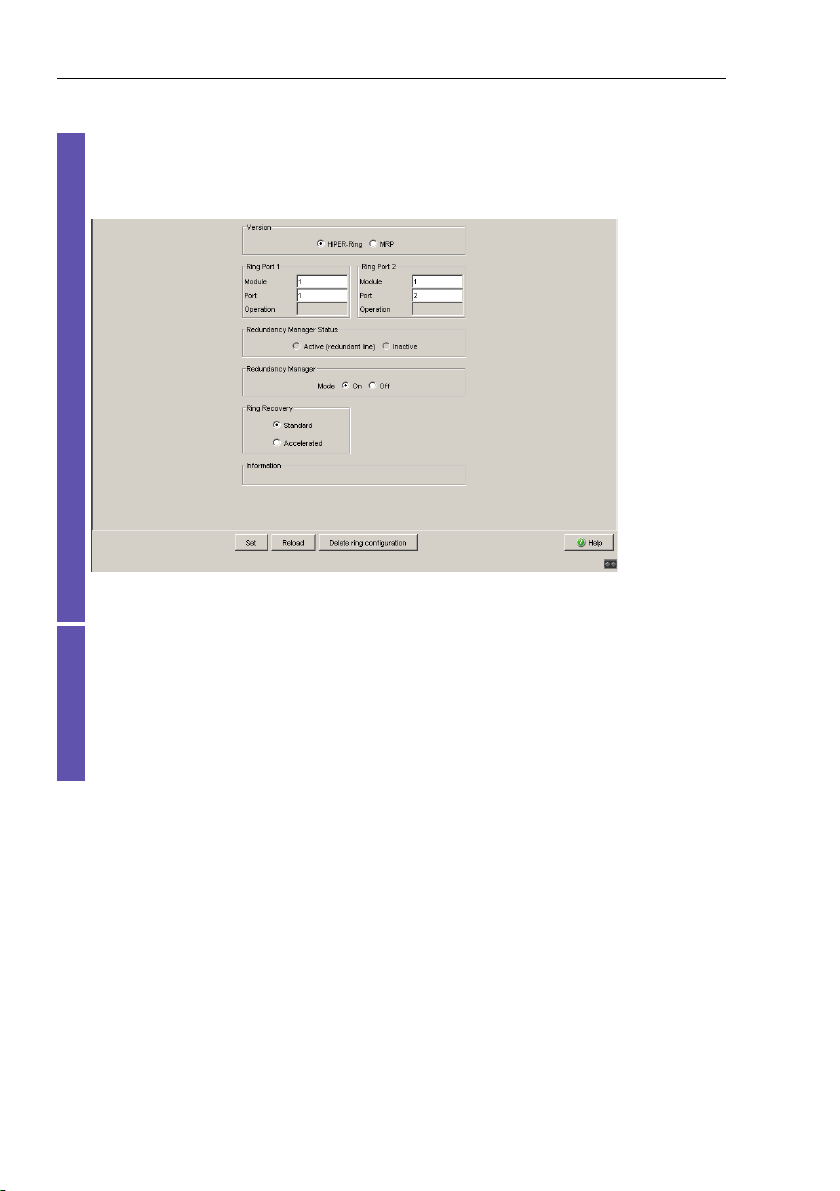
Ring Redundancy
Display in “Operation” field:
– active: This port is switched on and has a link.
– inactive: This port is switched off or it has no link.
Figure 4: Ring Redundancy dialog
2.1 Example of HIPER-Ring
Activate the ring manager for this device. Do not activate the ring
manager for any other device in the HIPER-Ring.
In the “Ring Recovery” frame, select the value “Standard” (default).
Note: Settings in the “Ring Recovery” frame are only effective for
devices that you have configured as ring managers.
Click on “Set” to temporarily save the entry in the configuration.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
16
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 17
Ring Redundancy
enable Switch to the Privileged EXEC mode.
configure Switch to the Configuration mode.
hiper-ring mode ring-manager Select the HIPER-Ring ring redundancy and de-
fine the device as ring manager.
Switch's HIPER Ring mode set to ring-manager
hiper-ring port primary 1/1 Define port 1 in module 1 as ring port 1.
HIPER Ring primary port set to 1/1
hiper-ring port secondary 1/2 Define port 2 in module 1 as ring port 2.
HIPER Ring secondary port set to 1/2
exit Switch to the privileged EXEC mode.
show hiper-ring Display the HIPER-Ring parameters.
HIPER Ring Mode of the Switch.................. ring-manager
configuration determined by.................. management
HIPER Ring Primary Port of the Switch.......... 1/1, state active
HIPER Ring Secondary Port of the Switch........ 1/2, state active
HIPER Ring Redundancy Manager State............ active
HIPER Ring Redundancy State (red. guaranteed).. no (rm is active)
HIPER Ring Setup Info (Config. failure)........ no error
HIPER Ring Recovery Delay...................... 500ms
2.1 Example of HIPER-Ring
Now proceed in the same way for the other two devices.
Note: If you have configured VLANS, note the VLAN configuration of the ring
ports.
In the configuration of the HIPER-Ring, you select for the ring ports
– VLAN ID 1 and
– VLAN membership Untagged in the static VLAN table
Note: Deactivate the Spanning Tree protocol on the ports connected to the
HIPER-Ring because Spanning Tree and Ring Redundancy affect each other. If you enable the HIPER-Ring function by means of the DIP switch,
RSTP will be disabled automatically.
Now you connect the line to the ring. To do this, you connect the two
devices to the ends of the line using their ring ports.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
17
Page 18

Ring Redundancy
2.1 Example of HIPER-Ring
The displays in the “Redundancy Manger Status” frame mean:
– “Active (redundant line)”: The ring is open, which means that a data
line or a network component within the ring is down.
– “Inactive”: The ring is closed, which means that the data lines and
network components are working.
The displays in the “Information” frame mean
– “Redundancy existing”: One of the lines affected by the function can
fail, whereby the redundant line will then take over the function of the
failed line.
– “Configuration failure”: The function is incorrectly configured or there
is an error in the ring port connection.
Note: When you use the DIP switch to switch from a normal port to a ring
port, the device makes the required settings for the pre-defined ring ports in
the configuration table. The port which has been switched back from a ring
port to a normal port keeps the ring port settings (transmission speed and
mode). Independently of the DIP switch setting, you can still change all the
ports via the software.
18
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 19
Ring Redundancy
2.2 Example of MRP-Ring
2.2 Example of MRP-Ring
A network contains a backbone in a line structure with 3 devices. To increase
the redundancy reliability of the backbone, you have decided to convert the
line structure to a ring redundancy. In contrast to the previous example,
devices from different manufacturers are being used which do not all support
the HIPER-Ring protocol. All the devices have MRP as the ring redundancy
protocol, so you decide to use MRP. You use ports 1 and 2 in module 1 of
the devices to connect the lines.
12 3
1.1 1.2 1.1 1.2 1.1 1.2
RM
Figure 5: Example of MRP-Ring
RM = Ring Manager
—— main line
- - - redundant line
The following example configuration describes the configuration of the ring
manager device (1). You configure the two other devices (2 to 3) in the same
way, but without activating the ring manager function. This example does not
use a VLAN. You have entered 200 ms as the ring recovery time, and all the
devices support the advanced mode of the ring manager.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
19
Page 20

Ring Redundancy
2.2 Example of MRP-Ring
Note: Configure all the devices of the MRP-Ring individually. Before you
connect the redundant line, you must complete the configuration of all the devices of the MRP-Ring. You thus avoid loops during the configuration phase.
Set up the network to meet your requirements.
You configure all 6 ports so that the transmission speed and the duplex
settings of the lines correspond to the following table:
Bit rate 100 Mbit/s 1000 Mbit/s
Autonegotiation
(automatic configuration)
Port on on
Duplex Full –
Table 3: Port settings for ring ports
off on
Select the Redundancy:Ring Redundancy dialog.
Under “Version”, select MRP.
Define the desired ring ports 1 and 2 by making the corresponding
entries in the module and port fields. If it is not possible to enter a
module, then there is only one module in the device that is taken
over as a default.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
20
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 21
Ring Redundancy
Display in “Operation” field:
forwarding: this port is switched on and has a link.
blocked: this port is blocked and has a link.
disabled: this port is switched off
not connected: this port has no link.
2.2 Example of MRP-Ring
Figure 6: Ring Redundancy dialog
In the “Ring Recovery” frame, select 200ms.
Note: If selecting 200ms for the ring recovery does not provide the ring
stability necessary to meet the requirements of your network, you select
500ms.
Note: Settings in the “Ring Recovery” frame are only effective for
devices that you have configured as ring managers.
Under “Configuration Redundancy Manager”, activate the advanced
mode.
Activate the ring manager for this device. Do not activate the ring
manager for any other device in the MRP-Ring.
Leave the VLAN ID as 0 in the VLAN field.
Switch the operation of the MRP-Ring on.
Click on “Set” to temporarily save the entry in the configuration.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
21
Page 22

Ring Redundancy
2.2 Example of MRP-Ring
The displays in the “Information” frame mean
– “Redundancy existing”: One of the lines affected by the function can
fail, whereby the redundant line will then take over the function of the
failed line.
– “Configuration failure”: The function is incorrectly configured or there
is an error in the ring port connection.
The “VLAN” frame enables you to assign the MRP-Ring to a VLAN:
If VLANs are configured, you make the following selections in the
“VLAN” frame:
- VLAN ID 0, if the MRP-Ring configuration is not to be assigned to
a VLAN, as in this example.
Note the VLAN configuration of the ring ports. Select VLAN ID 1 and
VLAN membership Untagged in the static VLAN table for the ring
ports.
- a VLAN ID >0, if the MRP-Ring configuration is to be assigned to
this VLAN.
Enter this VLAN ID in the MRP-Ring configuration for all devices in
this MRP-Ring.
Note the VLAN configuration of the ring ports. For all ring ports in this
MRP-Ring, select this VLAN ID and the VLAN membership Tagged
in the static VLAN table.
Note: For all devices in an MRP-Ring, activate the MRP compatibility in the
Rapid Spanning Tree:Global dialog if you want to use RSTP in the
MRP-Ring. If this is not possible, perhaps because individual devices do not
support the MRP compatibility, you deactivate the Spanning Tree protocol at
the ports connected to the MRP-Ring. Spanning Tree and Ring Redundancy
affect each other.
Note: If you want to configure an MRP-Ring using the Command Line Interface, you must define an additional parameter. When configured using CLI,
an MRP-Ring is addressed via its MRP domain ID. The MRP domain ID is a
sequence of 16 number blocks (8-bit values). Use the default domain of 255
255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 for the MRP
domain ID.
This default domain is also used internally for a configuration via the Webbased interface.
Configure all the devices within an MRP-Ring with the same MRP domain ID.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
22
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 23
Ring Redundancy
enable Switch to the Privileged EXEC mode.
configure Switch to the Configuration mode.
mrp new-domain default domain Create a new MRP-Ring with the default domain
MRP domain created:
Domain ID:
255.255.255.255.255.255.255.255.255.255.255.255.255.255.255.255
(Default MRP domain)
mrp current-domain
port primary 1/1
Primary Port set to 1/1
mrp current-domain
port secondary 1/2
Secondary Port set to 1/2
mrp current-domain mode
manager
Mode of Switch set to Manager
mrp current-domain recovery-
delay 200ms
Recovery delay set to 200ms
mrp current-domain advanced-
mode enable
Advanced Mode (react on link change) set to Enabled
mrp current-domain operation enable Activate the MRP-Ring.
Operation set to Enabled
exit Go back one level.
show mrp Show the current parameters of the MRP-Ring
Domain ID:
255.255.255.255.255.255.255.255.255.255.255.255.255.255.255.255
(Default MRP domain)
Configuration Settings:
Advanced Mode (react on link change).... Enabled
Manager Priority........................ 32768
Mode of Switch (administrative setting). Manager
Mode of Switch (real operating state)... Manager
Domain Name............................. <empty>
Recovery delay.......................... 200ms
Port Number, Primary.................... 1/1, State: Not Connected
Port Number, Secondary.................. 1/2, State: Not Connected
VLAN ID................................. 0 (No VLAN)
Operation............................... Enabled
ID
255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,
255,255,255,255,255.
Define port 1 in module 1 as ring port 1 (primary).
Define port 2 in module 1 as ring port 2 (secondary).
Define this device as the ring manager.
Define 200ms as the value for the “Ring Recovery”.
Activate the “MRP Advanced Mode”.
(abbreviated display).
2.2 Example of MRP-Ring
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
23
Page 24

Ring Redundancy
2.2 Example of MRP-Ring
Now you connect the line to the ring. To do this, you connect the two
devices to the ends of the line using their ring ports.
24
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 25

Ring/Network coupling
3 Ring/Network coupling
This device allows the redundant coupling of redundant rings and network
segments. Two rings/network segments are connected via two separate
paths.
The ring/network coupling supports the following devices:
X PSSnet SHL
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
25
Page 26

Ring/Network coupling
3.1 Variants of the ring/network coupling
3.1 Variants of the ring/network
coupling
The redundant coupling is effected by the one-Switch coupling of two ports
of one device in the first ring/network to one port each of two devices in a
second ring/network segment (see fig. 8).
Immediately after the main line fails, the device opens the redundant line.
When the main line is OK again, the main line is opened again and the
redundant line is blocked again.
An error is detected and eliminated within 500 ms (typically 150 ms).
The redundant coupling is effected by the two-Switch coupling of one port
each on two devices in the first ring/network to one port each of two devices
in the second ring/network segment (see fig. 14).
The device in the redundant line and the device in the main line use control
packets to inform each other about their operating states, via the Ethernet or
the control line.
Immediately after the main line fails, the redundant device opens the redundant line. As soon as the main line is OK again, the device in the main line
informs the redundant device. The main line is opened again, and the redundant line is blocked again.
An error is detected and eliminated within 500 ms (typically 150 ms).
The type of coupling primarily depends on the topological conditions and the
desired level of safety (see table 4).
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
26
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 27

Ring/Network coupling
3.1 Variants of the ring/network coupling
One-Switch coupling Two-Switch coupling Two-Switch coupling
Application The two devices are in
impractical topological
positions.
Therefore, putting a
line between them
would involve a lot of
work for two-Switch
coupling.
Disadvantage If the Switch config-
ured for the redundant
coupling fails, no connection remains
between the networks.
Advantage Less work involved in
connecting the two
devices to the network
(compared with twoSwitch coupling).
The two devices are in
practical topological
positions.
Putting down a control
line would involve a lot
of work.
Much work involved in
connecting the two
devices to the network
(compared with oneSwitch coupling).
If one of the devices
configured for the redundant coupling fails,
there is still a connection between the networks.
with control line
The two devices are in
practical topological
positions.
Putting down a control
line would not involve
much work.
Much work involved in
connecting the two
devices to the network
(compared with oneSwitch and two-Switch
coupling).
If one of the devices
configured for the redundant coupling fails,
there is still a connection between the networks.
Table 4: Selection criteria for the variants of the redundant coupling
Note: The choice of configuration primarily depends on the topological
conditions and the desired level of security (see table 4).
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
27
Page 28

Ring/Network coupling
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network coupling
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network
coupling
3.2.1 STAND-BY switch
The devices have a STAND-BY switch, with which you can define the role of
the device within a Ring/Network coupling.
Depending on the device, this switch is a DIP switch or a software switch
(Redundancy:Ring/Network Coupling dialog). By setting this switch,
you define whether the device has the main coupling or the redundant coupling within a Ring/Network coupling.
Device type STAND-BY switch type
PSSnet SHL Can be switched between DIP switch and software switch
Table 5: Overview of the STAND-BY switch types
Depending on the device and model, set the STAND-BY switch in accordance with the following table (see table 6):
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
28
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 29

Ring/Network coupling
Device with Choice of main coupling or redundant coupling
DIP switch On “STAND-BY” DIP switch
DIP switch/software switch
option
Software switch In the Redundancy:Ring/Network Coupling dialog
According to the option selected
- on “STAND-BY” DIP switch or in the
- Redundancy:Ring/Network Coupling dialog, by making selection in “Select configuration”.
Note: These devices have a DIP switch, with which you can choose
between the software configuration and the DIP switch configuration. If you have set the software configuration, changing the other
DIP switches has no effect.
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network cou-
Table 6: Setting the STAND-BY switch
Select the Redundancy:Ring/Network Coupling dialog.
You first select the configuration you want: One-Switch coupling
(“1”), two-Switch coupling (“2”) or two-Switch coupling with control
line (“3”), (see fig. 7).
pling
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
29
Page 30

Ring/Network coupling
Figure 7: Selecting the configuration
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network cou-
Depending on the STAND-BY DIP switch position, the dialog displays
those configurations that are not possible in gray. If you want to select
one of these grayed-out configurations, you put the STAND-BY DIP
switch on the Switch into the other position.
pling
One-Switch coupling
Assign the device the DIP switch setting “STAND-BY”, or use the software configuration to assign the redundancy function to it.
Two-Switch coupling
Assign the device in the redundant line the DIP switch setting “STANDBY”, or use the software configuration to assign the redundancy function to it.
Note: For redundancy security reasons, the combination of Rapid Spanning
Tree and Ring/Network Coupling is not possible.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
30
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 31

Ring/Network coupling
3.2.2 One-Switch coupling
1
RM
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network coupling
5
3
IO
4
STAND-BY
RM
Figure 8: Example of one-Switch coupling
1: Backbone
2: Ring
3: Partner coupling port
4: Coupling port
5: Main Line
6: Redundant Line
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
6
2
31
Page 32

Ring/Network coupling
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network coupling
The coupling between two networks is effected by the main line (thick blue
line), which is connected to the partner coupling port. If the main line fails, the
redundant line (thick blue dotted line), which is connected to the coupling
port, takes over coupling the two networks. The coupling is effected by one
Switch.
Select the Redundancy:Ring/Network Coupling dialog.
Select one-Switch coupling (see fig. 9).
2 1
IO
STAND-BY
Figure 9: One-Switch-coupling
1: Coupling port
2: Partner coupling port
The following settings apply to the Switch displayed in blue in the
selected graphic.
Select the partner coupling port (see fig. 10), (see table 7).
With “Partner coupling port” you specify at which port you are
connecting the control line.
The following tables show the selection options and default settings for the
ports used in the Ring/Network coupling.
Device Partner coupling port Coupling port
PSSnet SHL All ports (default setting: port 1.3) All ports (default setting: port 1.4)
Table 7: Port assignment for one-Switch coupling
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
32
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 33

Ring/Network coupling
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network cou-
Note: Configure the partner coupling port and the HIPER-Ring ports on
different ports.
Select the coupling port (see fig. 10), (see table 7).
With “Coupling port” you specify at which port you are connecting
the redundant line.
Note: Configure the coupling port and the redundancy ring ports on
different ports.
Activate the function in the “Operation” frame (see fig. 16).
You now connect the redundant line.
The displays in the “Select port” frame mean (see fig. 10):
– “Port mode”: The port is either active or in stand-by mode.
– “Port state”: The port is either connected or not connected.
The displays in the “Information” frame mean (see fig. 10):
– “Redundancy existing”: One of the lines affected can fail, as a
redundant line will then take over the function of the failed line.
– “Configuration failure”: The function is incomplete or incorrectly
configured.
pling
Figure 10: Selecting the port and enabling/disabling operation
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
33
Page 34

Ring/Network coupling
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network cou-
Note: The following settings are required for the coupling ports (you
select the Basic Settings:Port Configuration dialog):
– Port: on
– Automatic configuration (autonegotiation):
on for twisted-pair connections
– Manual configuration: 100 Mbit/s FDX
for glass fiber connections
Note: If VLANS are configured, note the VLAN configuration of the
coupling and partner coupling ports.
In the Network/Ring Coupling configuration, select for the coupling and
partner coupling ports
– VLAN ID 1 and “Ingress Filtering” disabled in the port table and
– VLAN membership U in the static VLAN table.
Redundancy mode
In the “Redundancy Mode” frame, select (see fig. 11)
– “Redundant Ring/Network Coupling” or
– “Extended Redundancy”.
pling
Figure 11: Selecting the redundancy mode
With the “Redundant Ring/Network Coupling” setting, either the main
line or the redundant line is active. Both lines are never active simultaneously.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
34
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 35

Ring/Network coupling
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network cou-
With the “Extended Redundancy” setting, the main line and the redundant line are simultaneously active if the connection line between the
devices in the connected network fails (see fig. 12).
During the reconfiguration period, there may be package duplications.
Therefore, only select this setting if your application detects package
duplications.
Figure 12: Extended redundancy
Coupling mode
The coupling mode indicates the type of the connected network.
In the “Coupling Mode” frame, select (see fig. 13)
– “Ring Coupling” or
– “Network Coupling”
pling
Figure 13: Selecting the coupling mode
Select “Ring coupling” if you are connecting a redundancy ring.
Select “Network Coupling” if you are connecting a line structure.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
35
Page 36

Ring/Network coupling
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network cou-
Delete coupling configuration
The “Delete coupling configuration” button in the dialog allows you
to reset all the coupling settings of the device to the state on delivery.
pling
36
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 37

Ring/Network coupling
3.2.3 Two-Switch coupling
RM
1
34
RM
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network coupling
IO
STAND-BY
Figure 14: Example of two-Switch coupling
1: Backbone
2: Ring
3: Main line
4: Redundant line
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
2
IO
STAND-BY
37
Page 38

Ring/Network coupling
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network coupling
The coupling between two networks is effected by the main line (thick blue
line). If the main line fails, the redundant line (thick blue dotted line) takes
over coupling the two networks.
The coupling is effected by two Switches.
The switches send their control packages via the Ethernet.
The Switch to which you connect the main line, and the Switch to which you
connect the redundant line, are partners as regards the coupling.
Connect the two partners via their ring ports.
Select the Redundancy:Ring/Network Coupling dialog.
Select two-Switch main coupling (see fig. 15).
1
2
IO
STAND-BY
Figure 15: Two-Switch coupling
1: Coupling port
2: Partner coupling port
The following settings apply to the Switch displayed in blue in the
selected graphic.
Select the coupling port (see fig. 10), (see table 7).
With “Coupling port” you specify at which port you are connecting
the redundant line.
If the STANDBY DIP switch is OFF, connect the main line to the coupling
port.
Device Coupling port
PSSnet SHL Adjustable for all ports (default setting: port 1.4)
Table 8: Port assignment for the redundant coupling (two-Switch coupling)
38
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 39

Ring/Network coupling
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network coupling
Note: Configure the coupling port and the redundancy ring ports on different
ports.
Activate the function in the “Operation” frame (see fig. 16).
You now connect the redundant line.
The displays in the “Select port” frame mean (see fig. 16):
– “Port mode”: The port is either active or in stand-by mode.
– “Port state”: The port is either connected or not connected.
– “IP Address”: The IP address of the partner, if the partner is already
operating in the network.
The displays in the “Information” frame mean (see fig. 23):
– “Redundancy existing”: One of the lines affected can fail, as a
redundant line will then take over the function of the failed line.
– “Configuration failure”: The function is incomplete or incorrectly
configured.
Figure 16: Selecting the port and enabling/disabling operation
To avoid continuous loops, the Switch sets the port state of the coupling
port to “off” if you:
– switch off operation or
– change the configuration
while the connections are in operation at these ports.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
39
Page 40

Ring/Network coupling
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network coupling
Note: The following settings are required for the coupling ports (you
select the Basic Settings:Port Configuration dialog):
– Port: on
– Automatic configuration (autonegotiation):
on for twisted-pair connections
– Manual configuration: 100 Mbit/s FDX
for glass fiber connections
Note: If VLANS are configured, note the VLAN configuration of the
coupling and partner coupling ports.
In the Network/Ring Coupling configuration, select for the coupling and
partner coupling ports
– VLAN ID 1 and “Ingress Filtering” disabled in the port table and
– VLAN membership U in the static VLAN table.
Note: If you are operating the Ring Manager and two-Switch coupling functions at the same time, there is the risk of creating a loop.
Select two-Switch redundant coupling (see fig. 18).
2
1
IO
STAND-BY
Figure 17: Two-Switch coupling
1: Coupling port
2: Partner coupling port
The following settings apply to the Switch displayed in blue in the
selected graphic.
Select the coupling port (see fig. 16), (see table 7).
With “Coupling port” you specify at which port you are connecting
the network segments.
If the STANDBY DIP switch is ON, connect the main line to the
coupling port.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
40
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 41

Ring/Network coupling
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network coupling
Note: Configure the coupling port and the redundancy ring ports on different
ports.
Activate the function in the “Operation” frame (see fig. 16).
The displays in the “Select port” frame mean (see fig. 16):
– “Port mode”: The port is either active or in stand-by mode.
– “Port state”: The port is either connected or not connected.
– “IP Address”: The IP address of the partner, if the partner is already
operating in the network.
The displays in the “Information” frame mean (see fig. 16):
– “Redundancy existing”: One of the lines affected can fail, as a
redundant line will then take over the function of the failed line.
– “Configuration failure”: The function is incomplete or incorrectly
configured.
To avoid continuous loops, the Switch sets the port state of the coupling
port to “off” if you:
– switch off operation or
– change the configuration
while the connections are in operation at these ports.
Note: The following settings are required for the coupling ports (you
select the Basic Settings:Port Configuration dialog):
– Port: on
– Automatic configuration (autonegotiation):
on for twisted-pair connections
– Manual configuration: 100 Mbit/s FDX
for glass fiber connections
Note: If VLANS are configured, note the VLAN configuration of the
coupling and partner coupling ports.
In the Network/Ring Coupling configuration, select for the coupling and
partner coupling ports
– VLAN ID 1 and “Ingress Filtering” disabled in the port table and
– VLAN membership U in the static VLAN table.
Note: If you are operating the Ring Manager and two-Switch coupling
functions at the same time, there is the risk of creating a loop.
Redundancy mode
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
41
Page 42

Ring/Network coupling
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network cou-
In the “Redundancy Mode” frame, select (see fig. 18)
– “Redundant Ring/Network Coupling” or
– “Extended Redundancy”.
pling
Figure 18: Selecting the redundancy mode
With the “Redundant Ring/Network Coupling” setting, either the main
line or the redundant line is active. Both lines are never active simultaneously.
With the “Extended Redundancy” setting, the main line and the redundant line are simultaneously active if the connection line between the
devices in the connected network fails (see fig. 12).
During the reconfiguration period, there may be package duplications.
Therefore, only select this setting if your application detects package
duplications.
Figure 19: Extended redundancy
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
42
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 43

Ring/Network coupling
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network cou-
Coupling mode
The coupling mode indicates the type of the connected network.
In the “Coupling Mode” frame, select (see fig. 20)
– “Ring Coupling” or
– “Network Coupling”
pling
Figure 20: Selecting the coupling mode
Select “Ring coupling” if you are connecting a redundancy ring.
Select “Network Coupling” if you are connecting a line structure.
Delete coupling configuration
The “Delete coupling configuration” button in the dialog allows you
to reset all the coupling settings of the device to the state on delivery.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
43
Page 44

Ring/Network coupling
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network cou-
3.2.4 Two-Switch coupling with control line
RM
1
34
RM
5
pling
IO
STAND-BY
IO
STAND-BY
2
Figure 21: Example of Two-Switch coupling with control line
1: Backbone
2: Ring
3: Main line
4: Redundant line
5: Control line
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
44
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 45

Ring/Network coupling
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network coupling
The coupling between two networks is effected by the main line (thick blue
line). If the main line fails, the redundant line (thick blue dotted line) takes
over coupling the two networks.
The coupling is effected by two Switches.
The Switches send their control packets via a control line.
The device to which you connect the main line, and the device to which you
connect the redundant line, are partners as regards the coupling.
Connect the two partners via their ring ports.
Select the Redundancy:Ring/Network Coupling dialog.
Select two-Switch main coupling
with control line (see fig. 22).
3
12
IO
STAND-BY
Figure 22: Two-Switch coupling with control line
1: Coupling port
2: Partner coupling port
3: Control line
The following settings apply to the Switch displayed in blue in the
selected graphic.
Select the coupling port (see fig. 23), (see table 9).
With “Coupling port” you specify at which port you are connecting
the redundant line.
If the STANDBY DIP switch is OFF, connect the main line to the coupling
port.
Select the control port (see fig. 23), (see table 9).
With “Control port” you specify at which port you are connecting the
control line.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
45
Page 46

Ring/Network coupling
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network coupling
Device Coupling port Control port
PSSnet SHL Adjustable for all ports
(default setting: port 1.4)
Table 9: Port assignment for the redundant coupling (two-Switch coupling with con-
trol line)
Adjustable for all ports
(default setting: port 1.3)
Note: Configure the coupling port and the redundancy ring ports on different
ports.
Activate the function in the “Operation” frame (see fig. 16).
You now connect the redundant line and the control line.
The displays in the “Select port” frame mean (see fig. 23):
– “Port mode”: The port is either active or in stand-by mode.
– “Port state”: The port is either connected or not connected.
– “IP Address”: The IP address of the partner, if the partner is already
operating in the network.
The displays in the “Information” frame mean (see fig. 23):
– “Redundancy existing”: One of the lines affected can fail, as a
redundant line will then take over the function of the failed line.
– “Configuration failure”: The function is incomplete or incorrectly
configured.
46
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 47
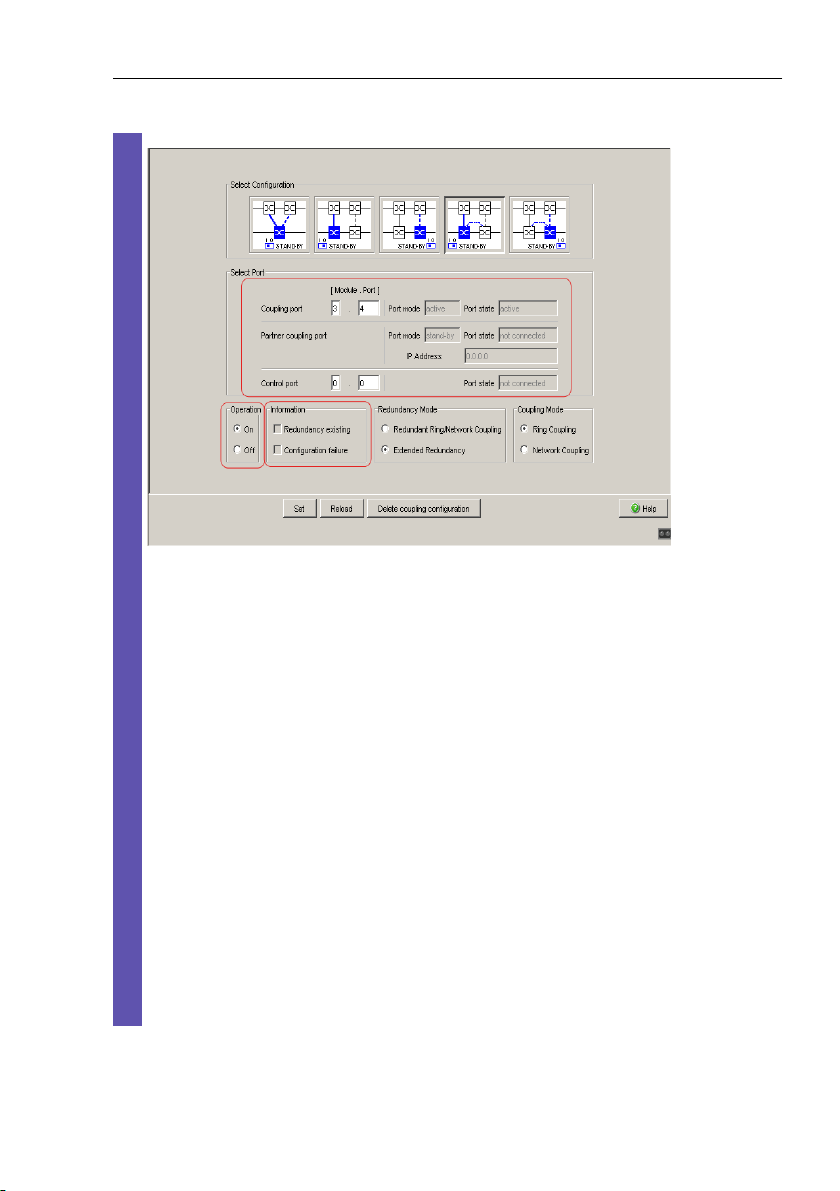
Ring/Network coupling
Figure 23: Selecting the port and enabling/disabling operation
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network cou-
To avoid continuous loops, the Switch sets the port state of the coupling
port to “off” if you:
– switch off operation or
– change the configuration
while the connections are in operation at these ports.
Note: The following settings are required for the coupling ports (you
select the Basic Settings:Port Configuration dialog):
– Port: on
– Automatic configuration (autonegotiation):
on for twisted-pair connections
– Manual configuration: 100 Mbit/s FDX
for glass fiber connections
Note: If VLANS are configured, note the VLAN configuration of the
coupling and partner coupling ports.
In the Network/Ring Coupling configuration, select for the coupling and
partner coupling ports
– VLAN ID 1 and “Ingress Filtering” disabled in the port table and
– VLAN membership U in the static VLAN table.
pling
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
47
Page 48

Ring/Network coupling
Select two-Switch redundant coupling
with control line (see fig. 24).
3
12
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network coupling
STAND-BY
IO
Figure 24: Two-Switch coupling with control line
1: Coupling port
2: Partner coupling port
3: Control line
The following settings apply to the Switch displayed in blue in the
selected graphic.
Select the coupling port (see fig. 23), (see table 9).
With “Coupling port” you specify at which port you are connecting
the network segments.
If the STANDBY DIP switch is ON, connect the main line to the
coupling port.
Select the control port (see fig. 23), (see table 9).
With “Control port” you specify at which port you are connecting the
control line.
Note: Configure the coupling port and the redundancy ring ports on different
ports.
Activate the function in the “Operation” frame (see fig. 16).
You now connect the redundant line and the control line.
The displays in the “Select port” frame mean (see fig. 23):
– “Port mode”: The port is either active or in stand-by mode.
– “Port state”: The port is either connected or not connected.
– “IP Address”: The IP address of the partner, if the partner is already
operating in the network.
48
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 49

Ring/Network coupling
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network cou-
The displays in the “Information” frame mean (see fig. 23):
– “Redundancy existing”: One of the lines affected can fail, as a
redundant line will then take over the function of the failed line.
– “Configuration failure”: The function is incomplete or incorrectly
configured.
To avoid continuous loops, the Switch sets the port state of the coupling
port to “off” if you:
– switch off operation or
– change the configuration
while the connections are in operation at these ports.
Note: The following settings are required for the coupling ports (you
select the Basic Settings:Port Configuration dialog):
– Port: on
– Automatic configuration (autonegotiation):
on for twisted-pair connections
– Manual configuration: 100 Mbit/s FDX
for glass fiber connections
Note: If VLANS are configured, note the VLAN configuration of the
coupling and partner coupling ports.
In the Network/Ring Coupling configuration, select for the coupling and
partner coupling ports
– VLAN ID 1 and “Ingress Filtering” disabled in the port table and
– VLAN membership U in the static VLAN table.
pling
Redundancy mode
In the “Redundancy Mode” frame, select (see fig. 25)
– “Redundant Ring/Network Coupling” or
– “Extended Redundancy”.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
49
Page 50

Ring/Network coupling
Figure 25: Selecting the redundancy mode
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network cou-
With the “Redundant Ring/Network Coupling” setting, either the main
line or the redundant line is active. Both lines are never active simultaneously.
With the “Extended Redundancy” setting, the main line and the redundant line are simultaneously active if the connection line between the
devices in the connected network fails (see fig. 12).
During the reconfiguration period, there may be package duplications.
Therefore, only select this setting if your application detects package
duplications.
pling
Figure 26: Extended redundancy
Coupling mode
The coupling mode indicates the type of the connected network.
In the “Coupling Mode” frame, select (see fig. 27)
– “Ring Coupling” or
– “Network Coupling”
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
50
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 51

Ring/Network coupling
Figure 27: Selecting the coupling mode
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network cou-
Select “Ring coupling” if you are connecting a redundancy ring.
Select “Network Coupling” if you are connecting a line structure.
Delete coupling configuration
The “Delete coupling configuration” button in the dialog allows you
to reset all the coupling settings of the device to the state on delivery.
pling
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
51
Page 52

Ring/Network coupling
3.2 Preparing a Ring/Network coupling
52
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 53

Rapid Spanning Tree
4 Rapid Spanning Tree
Note: The Spanning Tree and Rapid Spanning Tree protocols based on
IEEE 802.1D-2004 and IEEE 802.1w respectively are protocols for MAC
bridges. For this reason, the following description of these protocols usually
employs the term bridge instead of switch.
Local networks are getting bigger and bigger. This applies to both the
geographical expansion and the number of network participants. Therefore,
it usually makes sense to use multiple bridges, for example:
X to reduce the network load in sub-areas,
X to set up redundant connections and
X to overcome distance limitations.
However, using multiple bridges with multiple redundant connections
between the subnetworks can lead to loops and thus the total failure of the
network. To prevent this, the (Rapid) Spanning Tree Algorithm was developed. The Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) enables redundancy by
interrupting loops.
RSTP is a further development of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and is
compatible with it. If a connection or a bridge fails, the STP requires a maximum of 30 seconds to reconfigure. This was no longer acceptable in timesensitive applications. The STP was therefore developed to the RSTP, leading to average reconfiguration times of less than a second. If you use RSTP
in a ring topology with 10 - 20 devices, you can achieve reconfiguration
times in the range of milliseconds.
Note: RSTP resolves a given topology to a tree structure (Spanning Tree).
The number of devices in a branch (from the root to the branch tip) is limited
by the parameter Max Age. The default value for Max Age is 20, it can be
increased to 40.
You should note the following here: If the root device fails and another device
takes over the root function, the largest possible number of devices decreases accordingly.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
53
Page 54

Rapid Spanning Tree
When network segments are connected to a MRP ring and you enable MRP
compatibility, a peculiarity results. If the root bridge is located inside the MRP
ring, the devices inside the MRP ring are combined into one virtual device for
the purpose of calculating the branch length.
Note: The RSTP Standard dictates that all the devices within a network work
with the (Rapid) Spanning Tree Algorithm. However, if STP and RSTP are
used at the same time, the advantages of faster reconfiguration with RSTP
are lost. RSTP devices also work in a limited MSTP environment within the
scope of their functionality.
Note: Due to a change in the IEEE 802.1D-2004 standard on which RSTP is
based, the Standards Commission has reduced the maximum value for the
“Hello Time” from 10 to 2. When earlier firmware versions are upgraded to
version 5.x or higher, the firmware automatically changes a locally entered
“Hello Time” value greater than 2 to 2.
If the device is not the RSTP root, “Hello Time” values greater than 2 can remain valid, depending on the firmware version of the root device.
54
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 55

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.1 The Spanning Tree Protocol
4.1 The Spanning Tree Protocol
Because RSTP is a further development of the STP, all the following
descriptions of the STP also apply to the RSTP.
4.1.1 The tasks of the STP
The Spanning Tree Algorithm reduces network topologies that are set up
using bridges, and that have ring structures with redundant connections, to a
tree structure. In doing this, STP divides up the ring structures on the basis
of specified rules by deactivating redundant paths. If a path is interrupted by
mistake, the STP reactivates the path just deactivated. This enables redundant connections for increased data safety.
In forming the tree structure, the STP determines what is known as a root
bridge. This forms the basis of the STP tree structure.
Features of the STP algorithm:
X automatic reconfiguration of the tree structure in the case of a bridge error
or the interruption of a data path
X the tree structure is stabilized up to the maximum network size (up to
39 hops, depending on the setting for “Max. Age”)
X stabilization is effected within a brief, specified period
X topology can be specified and reproduced by the administrator
X transparency for the terminal devices
X low network load relative to the available transmission capacity due to the
tree structure created
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
55
Page 56

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.1 The Spanning Tree Protocol
4.1.2 Bridge parameters
Each bridge is uniquely described using parameters:
X Bridge Identifier
X Root Path Costs for the bridge ports
X Port Identifier
4.1.3 Bridge Identifier
The Bridge Identifier consists of 8 bytes. The two highest-value bytes are the
priority. The default setting for the priority number is 32,768, but the
Management Administrator can change this when configuring the network.
The six lowest-value bytes of the bridge identifier are the MAC address of the
bridge. The MAC address guarantees that every bridge has a different bridge
identifier.
The bridge with the smallest number for the bridge identifier has the highest
priority.
Figure 28: Bridge Identifier
56
LSBMSB
MAC AddressPriority
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 57

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.1 The Spanning Tree Protocol
4.1.4 Root Path Costs
Every path that connects two bridges is assigned costs for the transmission
(path costs). The Switch specifies this value based on the transmission
speed (see table 10). It assigns the higher path costs to paths with lower
transmission speeds.
Alternatively, the Administrator can specify the path costs. Like the Switch,
the Administrator assigns the higher path costs to paths with lower transmission speeds. However, since the Administrator can choose this value freely,
he has a tool with which he can give a certain path an advantage among
redundant paths.
The root path costs are the sum of all the individual path costs for all paths
along which a data packet travels between the connected port of a bridge and
the root bridge.
PC = 200
000
Bridge 2 Bridge 3
Bridge 1
PC = 200
PC = 2 000 000
PC
000
Figure 29: Path costs
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Path costs
Ethernet (100 Mbit/s)
Ethernet (10 Mbit/s)
57
Page 58

Rapid Spanning Tree
Data rate Recommended value Recommended range Possible range
<=100 KBit/s 200.000.000* 20.000.000-200.000.000 1-200.000.000
1 MBit/s 20.000.000* 2.000.000-200.000.000 1-200.000.000
10 MBit/s 2.000.000* 200.000-20.000.000 1-200.000.000
100 MBit/s 200.000* 20.000-2.000.000 1-200.000.000
1 GBit/s 20.000 2.000-200.000 1-200.000.000
10 GBit/s 2.000 200-20.000 1-200.000.000
100 GBit/s 200 20-2.000 1-200.000.000
1 TBit/s 20 2-200 1-200.000.000
10 TBit/s 2 1-20 1-200.000.000
4.1 The Spanning Tree Protocol
Table 10: Recommended path costs for RSTP based on the data rate
* Bridges that conform with IEEE 802.1D, 1998 edition, and only support
16-bit values for the path costs should use the value 65 535 for path costs
when they are used in conjunction with bridges that support 32-bit values
for the path costs.
4.1.5 Port Identifier
The Port Identifier consists of 2 bytes. One part, the lowest-value byte, signifies the fixed relationship with the physical port number. This part ensures
that no port of a bridge has the same identifier as another port of this bridge.
The second part is the port priority, which is specified by the Administrator
(default value: 128). It also applies here that the port with the smallest
number for the port identifier has the highest priority.
MSB LSB
Priority Port number
Figure 30: Port Identifier
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
58
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 59

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.2 Rules for creating the tree structure
4.2 Rules for creating the tree
structure
4.2.1 Bridge information
To calculate the tree structure, the bridges require more detailed information
about the other bridges located in the network.
To obtain this information, each bridge sends a BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data
Unit) to the other bridges.
The contents of a BPDU include
X bridge identifier,
X root path costs and
X port identifier
(see IEEE 802.1D).
4.2.2 Setting up the tree structure
X The bridge with the smallest number for the bridge identifier is the root
bridge. It is the root of the tree structure.
X The structure of the tree depends on the root path costs. STP selects the
structure so that the path costs between each individual bridge and the
root bridge are kept to a minimum.
X In the case of a number of paths with the same root path costs, the priority
of the bridge identifier for the bridge connected to one of these paths
decides which bridge should block.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
59
Page 60

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.2 Rules for creating the tree structure
X If two paths with the same root path costs lead out from a bridge, the port
identifier is used as the last criterion (see fig. 30). This decides which port
is selected.
Determine root path
Equal
path costs?
yes
Equal
priority in
bridge identification?
yes
Equal
port priority?
yes
no
no
no
Path with lowest
path costs = root path
Path with highest
priority in bridge
identification = root path
Path with highest
port priority
= root path
Path with lowest
port number
= root path
Figure 31: Flow diagram for specifying the root path
Root path determined
60
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 61

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.3 Example of specifying the root
paths
4.3 Example of specifying the
root paths
The network plan (see fig. 32) can be used to create the flow diagram (see
fig. 31) for defining the root path. The Administrator defined a different priority
in the bridge identifier for each bridge. The bridge with the smallest number
for the bridge identifier is the root bridge, in this case bridge 1. In the
example, all the sub-paths have the same path costs. The path between
bridge 2 and bridge 3 is interrupted, because a connection from bridge 3 to
the root bridge via bridge 2 would double the path costs.
The path from bridge 6 to the root bridge is interesting:
X The path via bridge 5 and bridge 3 creates the same root path costs as
the path via bridge 4 and bridge 2.
X The path via bridge 4 is selected because value 28 672 for the priority in
the bridge identifier is smaller than value 32 768.
X However, there are two paths between bridge 6 and bridge 4. The port
identifier is decisive here.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
61
Page 62

Rapid Spanning Tree
P-BID = 16 384
Bridge 1
4.3 Example of specifying the root
paths
P-BID = 20 480
Bridge 2
P-BID = 40 960
P-BID = 24 576
Bridge 3
Bridge 7
P-BID = 28 672
Bridge 4
Port 1
Port 3
P-BID = 36 864
P-BID = 32 768
Bridge 5
Port 2
P-BID Priority of the bridge identifikation (BID)
= BID without MAC Address
Root path
Interrupted path
Bridge 6
Figure 32: Example of specifying the root path
62
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 63

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.4 Example of manipulating the root
paths
4.4 Example of manipulating the
root paths
The network plan (see fig. 32) can be used to create the flow diagram (see
fig. 31) for defining the root path. The Administrator
– left the default value of 32 768 for each bridge apart from bridge 1, and
– gave bridge 1 the value 16 384, thus making it the root bridge.
In the example, all the sub-paths have the same path costs. The path
between bridge 2 and bridge 3 is interrupted, because a connection from
bridge 3 to the root bridge via bridge 2 would double the path costs.
The path from bridge 6 to the root bridge is interesting:
X The path via bridge 5 and bridge 3 creates the same root path costs as
the path via bridge 4 and bridge 2.
X STP selects the path using the bridge that has the lowest MAC address
in the bridge identification (bridge 4 in the illustration).
X However, there are two paths between bridge 6 and bridge 4. The port
identifier is decisive here.
Note: Because the Administrator does not change the default values for the
priorities of the bridges in the bridge identifier, apart from the value for the
root bridge, the MAC address in the bridge identifier alone determines which
bridge becomes the new root bridge if the root bridge goes down.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
63
Page 64

Rapid Spanning Tree
P-BID = 16 384
Bridge 1
4.4 Example of manipulating the root
paths
P-BID = 32 768
Bridge 2
P-BID = 32 768
P-BID = 32 768
Bridge 3
Bridge 7
P-BID = 32 768
Bridge 4
Port 1
Port 3
P-BID = 32 768
P-BID = 32 768
Bridge 5
Port 2
P-BID Priority of the bridge identifikation (BID)
= BID without MAC Address
Root path
Interrupted path
Bridge 6
Figure 33: Example of manipulating the root path
64
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 65

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.5 Example of manipulating the tree
structure
4.5 Example of manipulating the
tree structure
The Management Administrator soon discovers that this configuration with
bridge 1 as the root bridge (see on page 61 „Example of specifying the root
paths“) is unfavorable. On the paths from bridge 1 to bridge 2 and bridge 1 to
bridge 3, the control packets which the root bridge sends to all other bridges
are adding up.
If the Management Administrator makes bridge 2 the root bridge, the burden
of the control packets on the subnetworks is distributed much more evenly.
The result is the configuration shown here (see fig. 34). The distances
between the individual bridges and the root bridge are now shorter.
P-BID = 16 384
Bridge 2
P-BID = 40 960
Bridge 7
P-BID Priority of the bridge identifikation (BID)
= BID without MAC Address
Root path
Interrupted path
P-BID = 20 480
Bridge 4
Port 1
Port 2
P-BID = 36 864
Port 3
Bridge 6
P-BID = 24 576
Bridge 3
P-BID = 28 672
Bridge 5
Figure 34: Example of manipulating the tree structure
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
P-BID = 32 768
Bridge 1
65
Page 66

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.6 The Rapid Spanning Tree
Protocol
4.6 The Rapid Spanning Tree
Protocol
The RSTP takes over the calculation of the tree structure by the STP unchanged. RSTP merely changes parameters, and adds new parameters and
mechanism that speed up the reconfiguration in the case of a failure.
The ports play a significant role in this context.
4.6.1 Port roles
RSTP assigns each bridge port one of the following roles (see fig. 35):
X Root port
This is the port at which a bridge receives data packets with the lowest
path costs from the root bridge.
If there are multiple ports with the same low path costs, the bridge
identifier determines which port is the root port.
If there are multiple ports with the same low path costs and the same
bridge identifier, the port identifier determines which port is the root port
(see fig. 31).
The root bridge does not have a root port.
X Designated port
The bridge in a network segment that has the lowest root path costs is the
designated bridge. If multiple bridges have the same root path costs, then
the bridge with the smallest value for the bridge identifier becomes the
designated bridge. The port on this bridge that connects it to a network
segment that leads from the root bridge, is the designated port.
X Edge port
Every network segment in which there are no additional RSTP bridges is
connected with exactly one designated port. This designated port is then
also an edge port. The distinction of an edge port is the fact that it does
not receive any RST BPDUs (Rapid Spanning Tree Bridge Protocol Data
Unit).
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
66
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 67

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.6 The Rapid Spanning Tree
Protocol
X Alternate port
This is a blocked port that takes over the task of the bridge port if the
connection to the root bridge fails. The alternate port guarantees the
connection of the bridge to the root bridge.
X Backup port
This is a blocked port that serves as a backup in case the connection to
the designated port of this network segment (without RSTP bridge) fails.
X Disabled port
This is the port that does not play any role with the Spanning Tree
Operation, and is therefore switched off or does not have any connection.
P-BID = 16 384
Bridge 1
P-BID = 20 480
Bridge 2
P-BID = 40 960
Bridge 7
P-BID = 28 672
Bridge 4
P-BID = 24 576
Bridge 3
P-BID = 32 768
Port 1
Bridge 5
Figure 35: Port role assignment
Port 2
P-BID
Priority of the bridge identifikation (BID)
= BID without MAC Address
Root path
Interrupted path
Root port
Designated port
Alternate port
Backup port
Edge port
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
67
Page 68

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.6 The Rapid Spanning Tree
Protocol
4.6.2 Port states
Depending on the tree structure and the state of the selected connection
paths, the RSTP assigns the ports their states.
STP port state Administrative
bridge port
state
DISABLED Disabled FALSE Discarding* Excluded (disabled)
DISABLED Enabled FALSE Discarding* Excluded (disabled)
BLOCKING Enabled TRUE Discarding** Excluded (alternate, backup)
LISTENING Enabled TRUE Discarding** Included (root, designated)
LEARNING Enabled TRUE Learning Included (root, designated)
FORWARDING Enabled TRUE Forwarding Included (root, designated)
MAC
operational
RSTP
Port state
Active topology
(port role)
Table 11: Relationship between port state values in STP and RSTP.
* the dot1d MIB shows “Disabled”
** the dot1d MIB shows “Blocked”
Meaning of the RSTP port states:
X Disabled = port does not belong to the active topology
X Discarding = no address learning in FDB and no data traffic apart from
sending and receiving
X Learning = address learning active (FDB) and no data traffic apart from
BPDUs
X Forwarding = address learning active (FDB) and sending and receiving
active from all frames (not only BPDUs)
68
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 69

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.6 The Rapid Spanning Tree
Protocol
4.6.3 Spanning Tree Priority Vector
To assign roles to the ports, the RSTP bridges exchange configuration
information with each other. This information is known as the Spanning Tree
Priority Vector. It is part of the RST BPDUs and contains the following
information:
X Bridge identifier of the root bridges
X Root path costs for the sending bridges
X Bridge identifier for the sending bridges
X Port identifiers of the ports through which the message was sent
X Port identifiers of the ports through which the message was received
Based on this information, the bridges participating in RSTP are able to
calculate port roles themselves and define the port states of their own ports.
4.6.4 Fast reconfiguration
Why can RSTP react faster than STP to an interruption of the root path?
X Introduction of edge ports
During a reconfiguration, RSTP switches an edge port into the transmission mode after three seconds and then waits for the “Hello Time” (see
table 12) to elapse, to be sure that no bridge sending BPDUs is
connected.
When the user is sure that a terminal device is connected at this port and
will remain connected, he can switch off RSTP at this port. Thus no
waiting times occur at this port in the case of a reconfiguration.
X Introduction of alternate ports
As the port roles are already distributed in normal operation, a bridge can
immediately switch from the root port to the alternate port after the
connection to the root bridge is lost.
X Communication with neighboring bridges (point-to-point connections)
Decentralized, direct communication between neighboring bridges
enables immediate reaction to status changes in the spanning tree
architecture.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
69
Page 70

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.6 The Rapid Spanning Tree
Protocol
X Filter table
With STP, the age of the entries in the filter table determines the updating.
RSTP immediately deletes the entries in those ports affected by a
reconfiguration.
X Reaction to events
Without having to adhere to any time specifications, RSTP immediately
reacts to events such as connection interruptions, connection
reinstatements, etc.
Note: The price to be paid for this fast reconfiguration is the risk that data
packets may be duplicated or mixed up during the reconfiguration phase. If
this is unacceptable for your application, switch to the slower Spanning Tree
Protocol or select one of the other, faster redundancy procedures described
in this manual.
4.6.5 Configuring the Rapid Spanning Tree
Set up the network to meet your requirements.
Note: Before you connect the redundant lines, you must complete the
configuration of the RSTP.
You thus avoid loops during the configuration phase.
Select the Redundancy:Rapid Spanning Tree:Global dialog.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
70
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 71

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.6 The Rapid Spanning Tree
Switch on RSTP on every device
Figure 36: Operation on/off
You now connect the redundant lines.
Define the desired Switch as the root Switch by assigning it the
lowest priority in the bridge information among all the Switches in the
network, in the “Protocol Configuration/Information” frame. Note that
only multiples of 4096 can be entered for this value (see table 12).
In the “Root Information” frame, the dialog shows this device as the
root.
A root switch has no root port and no root costs.
As required, you change the default priority value of 32768 in other
Switches in the network in the same way to the value you want
(multiple of 4096).
For each of these Switches, check the display
in the “Root Information” frame:
– Root-Id: Displays the bridge identifier of the root Switch
– Root Port: Displays the port that leads to the root Switch
– Root Cost: Displays the root costs to the root Switch
in the “Protocol Configuration/Information” frame:
– Priority: Displays the priority in the bridge identifier for this Switch
– MAC Address: Displays the MAC address of this Switch
– Topology Changes: Displays the number of changes since
the start of RSTP
– Time since last change: Displays the time that has elapsed since
the last network reconfiguration
Protocol
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
71
Page 72

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.6 The Rapid Spanning Tree
If required, change the values for “Hello Time”, “Forward Delay” and
“Max. Age” in the root Switch. The root Switch then transfers this
data to the other Switches. The dialog displays the data received
from the root Switch in the left column. In the right column you enter
the values which shall apply when this Switch becomes a root
Switch. For the configuration, take note of table 12.
Protocol
Figure 37: Assigning Hello Time, Forward Delay und Max. Age
The times entered in the RSTP dialog are in units of 1 s.
Example: Hello Time = 2 corresponds to 2 seconds.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
72
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 73

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.6 The Rapid Spanning Tree
Protocol
Parameter Meaning Value range Default setting
Priority The priority and the MAC address go
together to make up the bridge
identification.
Hello Time The left column shows the value cur-
rently being used by the root bridge.
The device periodically receives configuration frames (Hello frames) from
the root bridge. The Hello Time
shows the time between two successive configuration frames sent by the
root bridge. If you configure the current device as the root bridge, the
other devices in the entire network
will assume the value in the right column.
Forward Delay The left column shows the value cur-
rently being used by the root bridge.
The predecessor protocol STP used
the parameter to control (delay) the
transition time between the states
„disabled“, „blocking“, „learning“,
?„forwarding“. Since the introduction
of RSTP, this parameter has only
secondary relevance because state
transitions are negotiated between
RSTP bridges without a given time
delay. If you configure the current device as the root bridge, the other devices in the entire network will
assume the value in the right column.
Max Age The left column shows the value cur-
rently being used by the root Switch.
Contrary to the past (STP) meaning,
Max Age now (for RSTP) denotes the
maximum permissible branch length
(number of devices to the root
bridge). If you configure the current
device as the root bridge, the other
devices in the entire network will assume the value in the right column.
0 < n*4,096 < 61,440 32.768
1 - 2 2
4 - 30 (see a:) 30
6 - 40 (see a:) 6
Table 12: Global RSTP settings
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
73
Page 74

Rapid Spanning Tree
Diameter = 7
4.6 The Rapid Spanning Tree
Protocol
1
123 45
23 4 5
12 3 4
Age = 5
67
Age = 4
= Root
Figure 38: Definition of diameter and age
The diameter is the number of connections between the two devices furthest
away from the root bridge.
The parameters
– Forward Delay and
– Max Age
have a relationship to each other:
Forward Delay >= (Max Age/2) + 1
If you enter values that contradict this relationship, the device then
replaces these values with a default value or with the last valid values.
As required, change and verify the settings and displays that relate
to each individual port (menu bar: Rapid Spanning Tree - Port).
74
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 75

Rapid Spanning Tree
Figure 39: Configuring the RSTP port
4.6 The Rapid Spanning Tree
Note: Deactivate the Spanning Tree Protocol for the ports connected to
a redundant ring, because the Spanning Tree and the
Ring Redundancy work with different reaction times.
Protocol
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
75
Page 76

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.6 The Rapid Spanning Tree
Protocol
Parameter Meaning Value range Default setting
STP State Enable
Port State Displays the port state disabled,
Priority Here you enter the first byte of the
Port Path Cost Enter the path costs to indicate pref-
Admin Edge
Port
Oper Edge Port Is „true“ if no RSTP frames were
Auto Edge Port The setting for Auto Edge Port only
Here you can turn RSTP on or off
for this port. If you turn RSTP off for
this port while RSTP is globally enabled for the device, the device will
discard RSTP frames received on
this port.
port identification.
erence for redundant paths. If the
value is “0”, the Switch automatically calculates the path costs depending on the transmission rate.
If the parameter is set to „true“, the
port will transition to the forwarding
state. If the port nevertheless receives a RSTP frame, it will transition to the blocking state and the
bridge will then determine the new
port role.
.If the parameter’s value is „false“,
the port remains in the blocked state
until the bridge has determined the
port role. Only after that will the port
transition to its final state.
received, i. e., a terminal device that
sends no RSTP frames is connected to this port. Is „false“ if RSTP
frames were received, i. e., no
terminal device but a bridge is
connected.
takes effect if the parameter Oper
Edge Port has been set to „false“.
if Auto Edge Port is set to „true“, the
port will transition to the forwarding
state within 1.5 * Hello Time
(3 seconds). If is is set to „false“, it
will take 30 seconds until the edge
port forwards data frames.
on,
off
forwarding,
discarding,
blocking,
learning
16 < n*16 < 240 128
0 - 200.000.000 0
true, false false
true, false -
true, false false
on
-
Table 13: Port-related RSTP settings and displays
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
76
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 77

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.6 The Rapid Spanning Tree
Protocol
Parameter Meaning Value range Default setting
Oper PointToPoint
Designated
Root
Designated
Costs
Designated Port Display of the port identifier of the
Table 13: Port-related RSTP settings and displays
If this port has a full-duplex link to
another RSTP device, the value for
Oper PointToPoint will become
„true“, else it will become „false“
(e. g., if a hub is connected). A
Point-to-point connection is a direct
connection between two RSTP devices. The direct, local communications between the two switches
results in a short reconfiguration
time.
Displays the bridge identification of
the designated root Switch for this
port.
Display of the costs of the path from
this port to the root Switch.
port that creates the connection to
the root Switch for this port (on the
designated Switch).
true, false auto
Bridge identification
(hexadecimal)
Costs -
Port identification
(hexadecimal) and
port number
(is calculated):
FDX = true
HDX = false
-
-
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
77
Page 78

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.7 Combination of RSTP and MRP
4.7 Combination of RSTP
and MRP
In the MRP compatibility mode, the device allows you to combine RSTP with
MRP.
With the combination of RSTP and MRP, the fast switching times of MRP are
maintained.
The RSTP diameter (see fig. 38) depends on the “Max Age”. It applies to the
devices outside the MRP-Ring.
Note: The combination of RSTP and MRP requires the root bridge and the
backup root bridge to be within the MRP-Ring.
1
RM
2
Figure 40: Combination of RSTP and MRP
1: MRP-Ring
2: RSTP-Ring
RM: Ring Manager
78
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 79

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.7 Combination of RSTP and MRP
To combine RSTP with MRP, you perform the following steps in sequence:
X Configure MRP on all devices in the MRP-Ring.
X Activate RSTP at the RSTP ports and also at the MRP-Ring ports.
X Configure the RSTP root bridge and the RSTP backup root bridge in the
MRP-Ring:
– Set the priority.
– If you exceed the RSTP diameter specified by the preset value of
Max Age = 20, you modify “Max Age” and “Forward Delay”.
X Activate RSTP globally.
X Activate the MRP compatibility mode.
X After configuring all the participating devices, connect the redundant
RSTP connection.
4.7.1 Application example for the combination of
RSTP and MRP
The figure (see fig. 41) shows an example for the combination of RSTP and
MRP.
Parameter S1 S2 S3 S4
MRP settings
Ring redundancy: MRP version MRP MRP
Ring port 1 1.1 1.2
Ring port 2 1.1 1.2
Redundancy Manager mode On Off – –
MRP operation On On Off Off
RSTP settings
For each RSTP port: STP State Enable On On On On
Protocol Configuration: Priority
(S2<S1<S3 and S2<S1<S4)
RSTP:Global: Operation On On On On
RSTP:Global: MRP compatibility On On – –
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
4096 0 32768 32768
79
Page 80

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.7 Combination of RSTP and MRP
Prerequisities for further configuration:
X You have configured the MRP settings for the devices in accordance with
the above table.
1
RM
1.1 1.11.2
S1
1.3
1.3
1.2
S2
2
1.2
1.1
S4
1.1
S3
Figure 41: Application example for the combination of RSTP and MRP
1: MRP-Ring
2: RSTP-Ring
3: Redundant RSTP connection
RM: Ring Manager
3
1.2
80
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 81

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.7 Combination of RSTP and MRP
Activate RSTP at the ports here using S1 as an example.
enable Switch to the Privileged EXEC mode.
configure Switch to the Configuration mode.
interface 1/1 Switch to the Interface Configuration mode of
spanning-tree port mode Activate RSTP at port.
exit Switch to the Configuration mode.
interface 1/2 Switch to the interface configuration mode for
spanning-tree port mode Activate RSTP at port.
exit Switch to the Configuration mode.
interface 1/3 Switch to the interface configuration mode for
spanning-tree port mode Activate RSTP at port.
exit Switch to the Configuration mode.
interface 1/1.
port 1.2.
port 1.3.
Configure globally here using S1 as an example:
– the RSTP priority
– global operation
– the MRP compatibility mode
spanning-tree mst priority 0
4096
spanning-tree Activate RSTP operation globally.
spanning-tree stp-mrp-mode Activate MRP compatibility.
Set the RSTP priority to the value 4096.
Configure all the participating devices in accordance with the table.
Connect the redundant RSTP connection.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
81
Page 82

Rapid Spanning Tree
4.7 Combination of RSTP and MRP
82
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
Page 83

Index
A Index
A
Advanced Mode 19
Age 74
Alternate port 67
B
Backup port 67
Bridge Identifier 56
C
Configuration error 18, 22
Configuring the HIPER-Ring 14
D
Designated bridge 66
Designated port 66
Diameter 74
Disabled port 67
E
Edge port 66
F
FAQ 85
Forward Delay 73
H
Hello Time 73
HIPER-Ring 9
HiVision 5
I
Industry protocols 5
R
Rapid Spanning Tree 9, 53
Redundancy 5
Redundancy existing 18, 22
Redundancy functions 9
Redundancy Manager 12
Redundant 11
Redundant coupling 9
Ring 11
Ring Manager 12
Ring structure 12
Ring/Network Coupling 9
Root port 66
RST BPDU 66, 69
RSTP 9
S
Symbol 7
T
Technical questions 85
Training courses 85
Two-Switch coupling 30
Two-Switch coupling with control line 30
V
VLAN 17
L
Loops 39, 41, 47, 49
M
Max Age 73
N
Network load 55
Network Management Software 5
O
One-Switch coupling 30
P
Port state 68
PROFINET 5
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
83
Page 84

Index
84
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Release 5.0 04/09
Page 85

Further support
B Further support
Technical questions and training courses
In the event of technical queries, please contact your local Pilz distributor
or Pilz office.
You can find the addresses of our distributors on the Internet:
www.pilz.com.
Our support line is also at your disposal:
X Tel. +49 711 3409 444
X Fax +49 711 3409 144
The current training courses to technology and products can be found
under www.pilz.com.
PSSnet SHL - Redundancy Configuration
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix- Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern
85
Page 86

1001653 – EN- 01, 2010-03 Printed in Germany
© Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, 2010
 Loading...
Loading...