Philips PCF8574P, PCF8574TS Datasheet

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
PCF8574
Remote 8-bit I/O expander for
2
I
C-bus
Product specification
Supersedes data of September 1994
File under Integrated Circuits, IC12
1997 Apr 02

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Remote 8-bit I/O expander for I2C-bus
CONTENTS
1 FEATURES
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
4 BLOCK DIAGRAM
5 PINNING
6 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE I2C-BUS
6.1 Bit transfer
6.2 Start and stop conditions
6.3 System configuration
6.4 Acknowledge
7 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
7.1 Addressing
7.2 Interrupt
7.3 Quasi-bidirectional I/Os
8 LIMITING VALUES
9 HANDLING
10 DC CHARACTERISTICS
11 I2C-BUS TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
12 PACKAGE OUTLINES
13 SOLDERING
13.1 Introduction
13.2 DIP
13.2.1 Soldering by dipping or by wave
13.2.2 Repairing soldered joints
13.3 SO and SSOP
13.3.1 Reflow soldering
13.3.2 Wave soldering
13.3.3 Repairing soldered joints
14 DEFINITIONS
15 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
16 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
PCF8574
1997 Apr 02 2

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Remote 8-bit I/O expander for I2C-bus
1 FEATURES
• Operating supply voltage 2.5 to 6 V
• Low standby current consumption of 10 µA maximum
• I2C to parallel port expander
• Open-drain interrupt output
• 8-bit remote I/O port for the I2C-bus
• Compatible with most microcontrollers
• Latched outputs with high current drive capability for
directly driving LEDs
• Address by 3 hardware address pins for use of up to
8 devices (up to 16 with PCF8574A)
• DIP16, or space-saving SO16 or SSOP20 packages.
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE NUMBER
PCF8574P;
PCF8574AP
PCF8574T;
PCF8574AT
PCF8574TS SSOP20 plastic shrink small outline package; 20 leads; body width 4.4 mm SOT266-1
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
DIP16 plastic dual in-line package; 16 leads (300 mil) SOT38-1
SO16 plastic small outline package; 16 leads; body width 7.5 mm SOT162-1
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The PCF8574 is a silicon CMOS circuit. It provides general
purpose remote I/O expansion for most microcontroller
families via the two-line bidirectional bus (I2C).
The device consists of an 8-bit quasi-bidirectional port and
an I2C-bus interface. The PCF8574 has a low current
consumption and includes latched outputs with high
current drive capability for directly driving LEDs. It also
possesses an interrupt line (INT) which can be connected
to the interrupt logic of the microcontroller. By sending an
interrupt signal on this line, the remote I/O can inform the
microcontroller if there is incoming data on its ports without
having to communicate via the I2C-bus. This means that
the PCF8574 can remain a simple slave device.
The PCF8574 and PCF8574A versions differ only in their
slave address as shown in Fig.9.
PACKAGE
PCF8574
1997 Apr 02 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Remote 8-bit I/O expander for I2C-bus
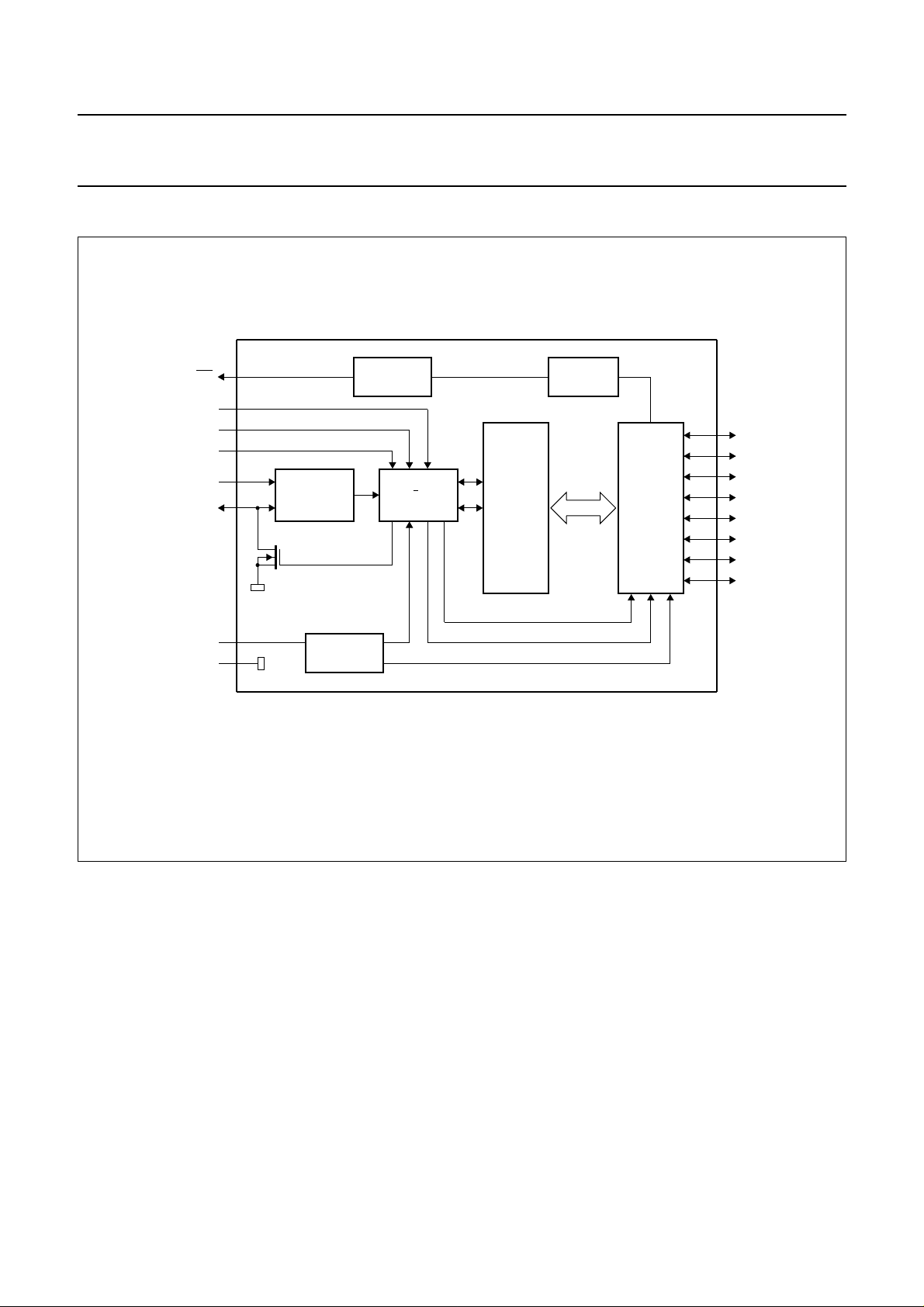
4 BLOCK DIAGRAM
handbook, full pagewidth
INT
A0
A1
A2
SCL
SDA
13
1
2
3
14
15
INPUT
FILTER
INTERRUPT
LOGIC
2
I C BUS
CONTROL
PCF8574
SHIFT
REGISTER
LP FILTER
8 BIT
I/O
PORT
PCF8574
4
5
6
7
9
10
11
12
P0
P1
P2
P3
P4
P5
P6
P7
WRITE pulse
DD
SS
16
8
POWER-ON
RESET
V
V
READ pulse
MBD980
Fig.1 Block diagram (SOT38-1 and SOT162-1).
1997 Apr 02 4

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Remote 8-bit I/O expander for I2C-bus
5 PINNING
SYMBOL
DIP16; SO16 SSOP20
A0 1 6 address input 0
A1 2 7 address input 1
A2 3 9 address input 2
P0 4 10 quasi-bidirectional I/O 0
P1 5 11 quasi-bidirectional I/O 1
P2 6 12 quasi-bidirectional I/O 2
P3 7 14 quasi-bidirectional I/O 3
V
SS
P4 9 16 quasi-bidirectional I/O 4
P5 10 17 quasi-bidirectional I/O 5
P6 11 19 quasi-bidirectional I/O 6
P7 12 20 quasi-bidirectional I/O 7
INT 13 1 interrupt output (active LOW)
SCL 14 2 serial clock line
SDA 15 4 serial data line
V
DD
16 5 supply voltage
n.c. − 3 not connected
n.c. − 8 not connected
n.c. − 13 not connected
n.c. − 18 not connected
PIN
8 15 supply ground
PCF8574
DESCRIPTION
handbook, halfpage
1
A0
2
A1
A2
3
4
P0
P1
P2
P3
V
SS
5
6
7
8
PCF8574
PCF8574A
MBD979
V
16
DD
15
SDA
14
SCL
13
INT
12
P7
P6
11
10
P5
9
P4
Fig.2 Pin configuration (DIP16; SO16).
1997 Apr 02 5
handbook, halfpage
Fig.3 Pin configuration (SSOP20).
INT
SCL
n.c.
SDA
V
DD
A0
A1
n.c.
A2
P0
1
2
3
4
5
PCF8574TS
6
7
8
9
10
MBD978
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
P7
P6
n.c.
P5
P4
V
P3
n.c.
P2
P1
SS

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Remote 8-bit I/O expander for I2C-bus
6 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE I2C-BUS
The I2C-bus is for 2-way, 2-line communication between
different ICs or modules. The two lines are a serial data
line (SDA) and a serial clock line (SCL). Both lines must be
connected to a positive supply via a pull-up resistor when
connected to the output stages of a device. Data transfer
may be initiated only when the bus is not busy.
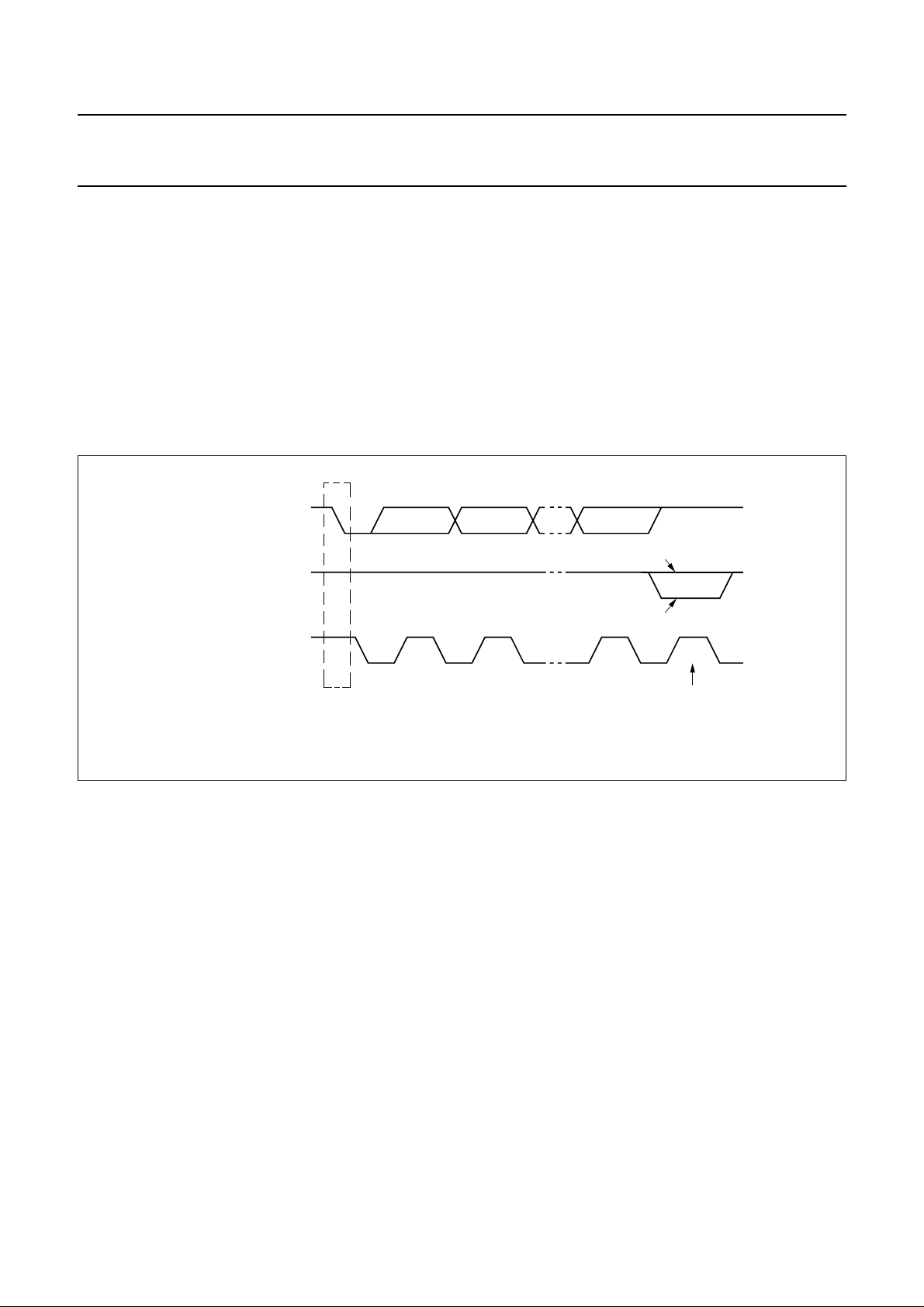
6.1 Bit transfer
One data bit is transferred during each clock pulse. The
data on the SDA line must remain stable during the HIGH
period of the clock pulse as changes in the data line at this
time will be interpreted as control signals (see Fig.4).
SDA
SCL
PCF8574
6.2 Start and stop conditions
Both data and clock lines remain HIGH when the bus is not
busy. A HIGH-to-LOW transition of the data line, while the
clock is HIGH is defined as the start condition (S).
A LOW-to-HIGH transition of the data line while the clock
is HIGH is defined as the stop condition (P) (see Fig.5).
6.3 System configuration
A device generating a message is a ‘transmitter’, a device
receiving is the ‘receiver’. The device that controls the
message is the ‘master’ and the devices which are
controlled by the master are the ‘slaves’ (see Fig.6).
SDA
SCL
SDA
SCL
START condition
MASTER
TRANSMITTER /
RECEIVER
data line
stable;
data valid
change
of data
allowed
Fig.4 Bit transfer.
S
Fig.5 Definition of start and stop conditions.
SLAVE
RECEIVER
SLAVE
TRANSMITTER /
RECEIVER
MBC621
P
STOP condition
MASTER
TRANSMITTER
SDA
SCL
MBC622
MASTER
TRANSMITTER /
RECEIVER
MBA605
Fig.6 System configuration.
1997 Apr 02 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Remote 8-bit I/O expander for I2C-bus
6.4 Acknowledge
The number of data bytes transferred between the start
and the stop conditions from transmitter to receiver is not
limited. Each byte of eight bits is followed by one
acknowledge bit. The acknowledge bit is a HIGH level put
on the bus by the transmitter whereas the master
generates an extra acknowledge related clock pulse.
A slave receiver which is addressed must generate an
acknowledge after the reception of each byte. Also a
master must generate an acknowledge after the reception
of each byte that has been clocked out of the slave
DATA OUTPUT
BY TRANSMITTER
DATA OUTPUT
BY RECEIVER
PCF8574
transmitter. The device that acknowledges has to pull
down the SDA line during the acknowledge clock pulse, so
that the SDA line is stable LOW during the HIGH period of
the acknowledge related clock pulse, set-up and hold
times must be taken into account.
A master receiver must signal an end of data to the
transmitter by not generating an acknowledge on the last
byte that has been clocked out of the slave. In this event
the transmitter must leave the data line HIGH to enable the
master to generate a stop condition.
not acknowledge
acknowledge
SCL FROM
MASTER
S
START
CONDITION
Fig.7 Acknowledgment on the I2C-bus.
MBC602
9821
clock pulse for
acknowledgement
1997 Apr 02 7

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Remote 8-bit I/O expander for I2C-bus
7 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
handbook, full pagewidth
write pulse
data from
shift register
power-on
reset
read pulse
data to
shift register
DQ
FF
C
I
S
DQ
FF
C
I
S
100
µA
MBD977
V
DD
P0 to P7
V
SS
to interrupt
logic
PCF8574
Fig.8 Simplified schematic diagram of each I/O.
7.1 Addressing
For addressing see Figs 9, 10 and 11.
handbook, full pagewidth
S 0 1 0 0 A2 A1 A0 0 A 1 0
slave address
a. b.
(a) PCF8574.
(b) PCF8574A.
Fig.9 PCF8574 and PCF8574A slave addresses.
Each of the PCF8574’s eight I/Os can be independently
used as an input or output. Input data is transferred from
the port to the microcontroller by the READ mode
(see Fig.11). Output data is transmitted to the port by the
WRITE mode (see Fig.10).
slave address
S 0 1 1 A2 A1 A0
A
MBD973
1997 Apr 02 8
 Loading...
Loading...