Page 1

R
6499
( PMff f
141;
143|
145;
151;
153
541; 543;
543-712;
545;
555
Single-needle
flatbed
sewing
machines
142;
144;
146
542;
542-748/01;
544; 546;
546-748/01
Two-needle
flatbed
sewing
machines
Instruction
Book
Page 2

/
' •
Contents
, ^
Page
1.
General
®
2.
Fundamentalsofmachine
operation
3
3.
Cleaning
and
oiling
^
4.
Winding
the
bobbin
®
5.
Changing
the
bobbin
and
threading
the
bobbin
case 7
6.
Selecting
the
correct
needle
3
Needle
systems
®
Needle
point
styles
®
Needle
and thread sizes 8
7. Changing
the
needle
8.
Threading
the
needle
^
9. Drawing up the bobbin thread
10. Regulating the thread tensions
Adjusting the upper tension
Adjusting the lower tension
11. Regulating the stitch length
12.
Regulating
the
pressureonthe
material
''S
13. Cleaning
the
sewing hook
14.
The
safety
clutch
Additional
instructions
for
Pfaff
machines'141-705/03
and
141-705/03-725/01
. 16-18
15. Regulating the stitch length
16.
Changing
the
feed
gears
'•8
17. Adjusting
the
trimmer * *
^18.
Operating
the
trimmer
^
Additional
Instructions
for
Pfaff
machines
143-705/03
21
19.
Regulating
the
stitch
length
21
Additional
Instructions
for
Pfaff
machines
145
22-24
20.
Exchanging
the
alternating
pressers
22
21.
Lubricating
the
machine
24
0-22. Setting
the
foot lift
-
Additional
Instructions
for
Pfaff
machines
151
and
153
(
Additional
Instructions
for
Pfaff
machines
142,
542-748/01,
144
and
146
25-^
r23.
Threading
the
needles
25
.
24.
Adjusting
the
puller
feedofthe
Pfaff
542-748/01
26
Additional
Instructions
for
Pfaff
machines
543-712/01
and
543-712/02
...
27
"25. Threading the needle of the Pfaff
543-712
-.-Additional
Instructions
for
Pfaff
machines
546-748/01
28—29
^26.
Setting
the
foot
lift
. . . ; ^
't27.
Adjusting
the
puller
feed
29
^Additional
instructions
for
Pfaff
machines
4141
and
4145
. -
30
^^^28.
Threadingofthe
Pfaff
4141
and
4145
8®
^
Additional
Instructions
for
Pfaff
machines
fitted
with
thread
puller/trimmer
900/».31
"
'!'29.
Pedal
operation
Guards
Trouble
shooting
^
t
..
^i2
Page 3

t.
General
•
Since
the
operationofthe
machines
listedonthe
title
pageismoreorless
the
same
the
general
instructions
compiledinthis
book
applytoallofthem.
Additional
instructions
for
the
Pfaff
141-705/03;
141-705/03-725/01;
142;
143-705
03-
144;
145;
146; 151;
153;
552-748/01;
543-712/..;
546-748/01;
4141;
4145
and
-900'..
appearatthe
backofthis
booklet.
We
reserve
the
righttomake
alterations
serving
progress.
The
illustrationsinthis
book
are also subject to change.
Itisrecommendedtorun
these
machinesatthe
following
top
speeds:
3
000
s.p.m.
Pfaff
4141
2
200
s.p.m.
Pfaff
141
and
144
2
900
s.p.m.
Pfaff
545
H3
2100
s.p.m.
2
800
s.p.m.
Pfaff
546
H2
1
300
s.p.m.
Pfaff
151
and
544
2
700
s.p.m.
Pfaff
546
H3
i
800
s.p.m.
Pfaff
153
and
542
2
600
s.p.m.
Pfaff
545
H4
i
700
s.p.m.
^ 2
500
s.p.m.
Pfaff
4145
1
600
s.p.m.
Pfaff
145
and
541
2
400
s.p.m.
Pfaff
546
H4
2
300
s.p.m.
and
543-712/..
1400
s.p.m.
When
sewing
tightly
woven
and
heavily
dressed
materials,
the
sewing
speed
should
be
reducedInorderto
prevent
overheating
of the
needle.
The
maximum
speedoftwo-needle
machines
decreasesasthe
needle
gauge
increases.
The
maximum
speeds
which
canbeattained
with
machines
fitted
with
special
attach
mentsortrimming
mechanisms
are
often
far
below
the
recommended
top
speeds
be
cause
the
natureofthe
work
and
the
thicknessofthe
material
tendtolimit
the
ma
chinescapacity.Ifthe
maximum
speedisexceeded,
trouble
may
develop
chieflyinthe
trimming mechanism.
To
avoid
troubleinthe
mechanism,
run
the
machineatabout75per
centofits
top
speed
until
the
parts
which
areinmovable
contact
have
become
thoroughly
glazed
by
their
action
upon
each
other.
This
should
normallybethe
case
after
about
two
weeks'
constant
use.
All
machines
are
regularly
equipped
withafixed
pulley
whichiscastinone
with
the
ba
ance
wheel.Ifdesired,
however,
these
machines
canbesupplied
withadisengage-
ible pulley.
If
fitted
with
the
latter
type
pulley,
the
machineisdispatched
with
the
sewing
mecha
nism
disengaged.Toengage
this
mechanism
for
sewing,
hold
the
balance
wheel
steady
with
your left hand and turn the large
lock
nut
clockwise.
2. Fundamentals of machine operation
Before
you
put
the
machineinoperation
for
the
first
time,
carefully
remove
all
dust
which
has
accumulatedintransit
and
oil
the
machine
thoroughly
(see
Chapter
3).
on
the
machine
only
with
Pfaff
sewing
machine
oil
whichIsnon-resinous
and
acid-free.
Checktomake
sure
the
finger,
take-up
lever
and
belt
guards
are
properly
fitted.
Never
runathreaded
machine
unless
you
have
fabric
under
the
presser
footorthe
vibrating
presser.
Before
you
start
sewing,
lay
both
threads
back
under
the
presser
foot
Page 4

To
prevent
thread
jamming,
hold
both
thread
ends
until
the
machine
has
madeafew
stitches. . „
Do
not
pull
the
material
during
sewing:
the
machine
wiil
feed
the
fabric
automatically.
Use needlesofthe correct
system
only
(see Chapter
6).
Never
use
rusty
needles.
Use high-quality threads
only.
Always
bring
the
take-up
levertoits
highest
point
before
you
remove
the
material.
3. Cleaning
and
oiling
Careful
cleaning
and
regular
oiling
will
Increase
the
service
lifeofyour
machine.
After
you
have
removed
the
dust
which
has
accumulatedonthe
machineintransit,
take
a
clean
rag
and
remove
the
grease
from
all
nickel-plated
and
polished
Parts.
Apply
a
few
dropsofkerosenetoall
oiling
points
marked
with
dash
linesinFigs.1.2
and
3.
raise
the
presser
foot,
unthread
the
needle,
remove
the
bobbin
case
and
let
the
J^achine
run
briefly.
Applyafew
dropsofPfaff
sewing
machine
oil
No.
280-1-120122toall
points
of
friction.
While
these
pointsoffriction
shouldbeoiled
twiceaweek,
the
sewing
hook
"lUSt
be
oiled
each
day
the
machineisin
operation.
Make
particularly
sure
that
oilisapplied
to
oilhoie R (Fig. 4).
Althougti
the
bevel
geers
ere
enclosedinceses
and
requirenospeclel
mamtenence.
itisrecommendedtoreplace
the
old
greasebyPfaff
grease
once
a
year.
Owingtothe
special
lubricating
propertiesofthis
grease,
the
flanksofthe
beve
gear teeth
shouldbegreased
only
lightly.
Page 5
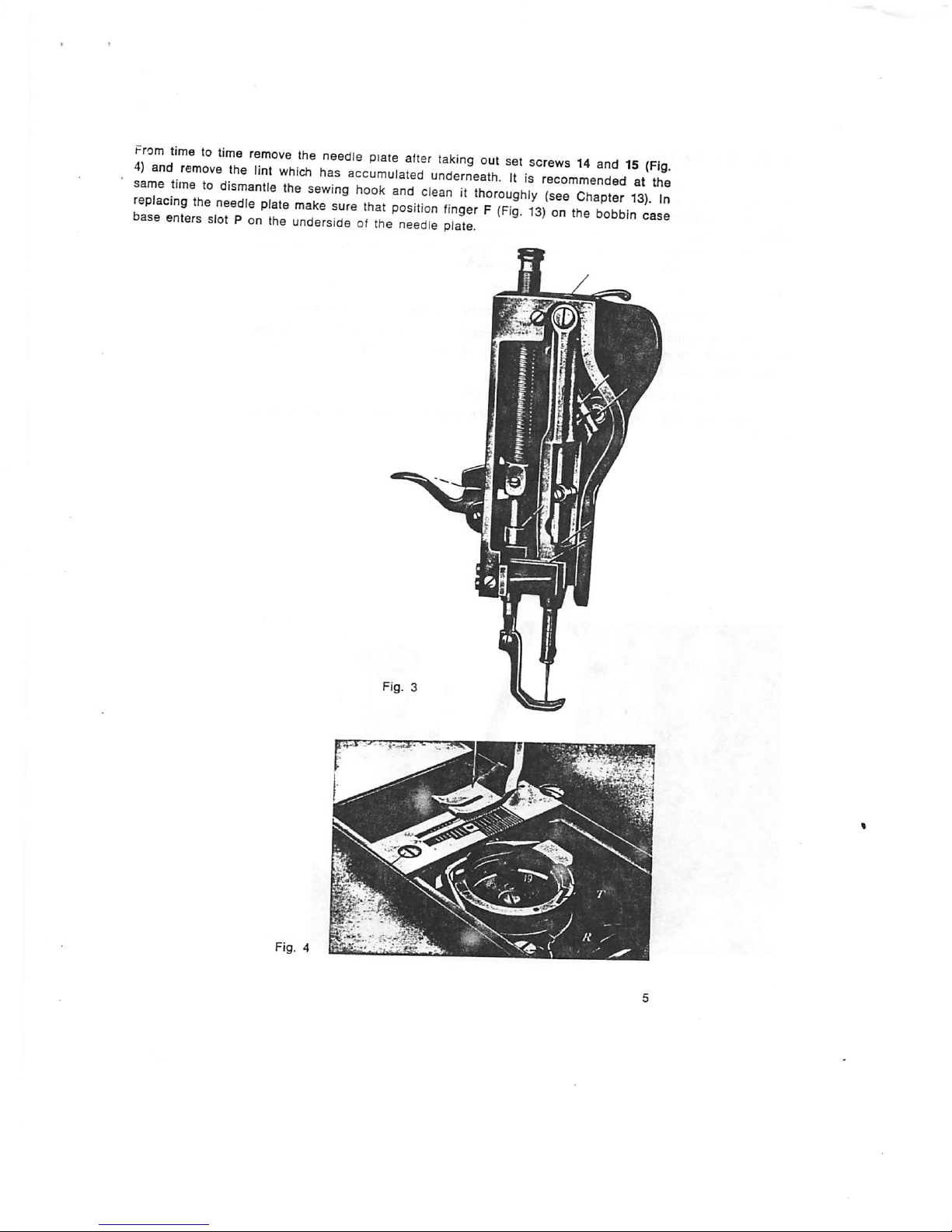
^rom
timetotime
remove
the
needle
plate
alter
taking
out
set
sorevvs14andisrpi.
repT
^-Tng'tortnd
dearnhTrougWy
(sarcTaTte?
13')
7n
jse::Lrs,rrhi\rr3ror.t~
^ -
Page 6

4. Winding
the
bobbin
Placeaspoolofttfreadonpin1(Fig.5)and
pass
the
thread
from
lefttoright
through
eyelet2,clockwise
around
and
between
tension
discs3and
from
the
inside
through
the
slotinthe
bobbin.
Windafew
turnsofthreadonthe
bobbin
and
place
the
latter
on
spindle4.Start
the
bobbin
winderbypressing
down
lever5.The
bobomiswound
automatically
while
the
machineissewing.
Whenasufficient
amountofthread
has
been
wound
on the
bobbin,alatch
stops the
bobbin
winder.
The
amountofthreadtobe
woundonthe
bobbinisregulatedbyscrew
6.
Turn
this
screw
clockwise
for
more
thread,orcounter-clockwise
lor
less
thread.
If
the
thread
should
pileupat
one
endofthe
bobbin,
adjust
the
positionofthe
bobbin
winder
tension
sideways,asmayberequired.Todo
this,
loosen
screw7,adjust
th.
tension and tighten the set screw again.
The tension on the thread is
regulatedbyturning
nut 8.
Maks
sure
the
bobbin
winder
pulley
rotatesinthe
direction
Indicatedbyan
arrow
in
Fig.
5.
R
9929
Page 7

5. Changing the bobbin and threading the bobbin case
Raise
the
needletoits
highest
position
and
open
the
bed
slide.
With
the
thumbofyou:
right
hand
open
latchB(Fig.
6),
then
push
the
thumb
nail
under
the
projecting
flange
Cofthe
bobbin
case
cap
and
lift
the
latter
outofthe
machine
with
thumb
and
fore
finger.
The
bobbinisnow
exposedinthe
bobbin
case
base
and
canbetaken
out
easily.
Placeafull
bobbininthe
bobbin
case
capsothat
the
thread
drawsontop
from
left
toward the right, as shown in
Fig.
7.
Hold
the
bobbin
steadyinthe
bobbin
case,
pull
the
thread
into
slotXand
drawitunder
tension
springY.Leavealoose
endofthread
about7mm
long
outside
the
bobbin
case.
Place
the
bobbin
case
with
the
bobbinonthe
center
studinthe
bobbin
case
base
and
close
latch B (Fig. 6) as well as the bed slide.
Note
that
the
rotary
hookofPfaff
machines
151
and
153islocatedonthe
leftofthe
needle
plate.
R
9931
Page 8

6.
Selecting
the
correct
needle
To
ensure
reliable
stitch
formation,
checktosee
that
the
correct
needleisinserted
in
the
machine.
Needle
systems
The
following
needie
systems
are
used
for
the
individual
machine
classes:
134
for
Pfaff
machines
141, 142,
143,
144. 151. 541,
542,
543
and
544.
34
for
Pfaff
machines
142; 144;
542
and
544,
when
these
machines
have
needle
holders
with
smaller
holes
(shank
size
1.65
mm).
134-35
for Pfaff
machines
142-732/09, 142-732/11, 145 H3, 146 H3, 545 H3, 546 H3,
555H3and
4141
134 FLQ for Pfaff
machines
142-720/01-6/01, 142-721/01-6/01
and
144-720/01 in
needle
gauges
from
1.6to2.2
mm
inclusive.
134
KK
for
the
Pfaff
153.
134
RER
and
134
REL
for
the
Pfaff
546
H2.
190
for
the
Pfaff
543-712/...
545
H4.
546
H4.
555
H4.
and
4145
H3.
Needle
point
styles
These
needles
are
available
with
different
type
pointstosuit
different
requirements.
The
various
needle
point
styles
are
identified
by a
letter
following
the
needle
system,
e. g.
134
R.
Fabrics
are
stitched
witharound-point
needle,
identified
by R,
while
for
leather
work
needles
are
available
with
the
following
stylesofpoints:
LR
Narrow
reverse
twist
point
LL
%
Narrow
twist
point
LACK
m
Patent
leather
point
P
m
Extra-narrow
wedge
point
PGR
m
Extra-narrow
wedge
point
with
right-twist
groove
POL
m
Extra-narrow
wedge
point
with ieft-twist
groove
S
1
Narrow
cross
point;
for
long,
straight
stitches
D
Triangular
point;
for
short,
straight
stitches
VR
#
Reverse
twist
spear
point
VL
9
Twist
spear
point
Rubberized
fabrics
and
plastic
materials
are
sewn
with
round-point
needles.
Needle
and
thread
sizes
The
correct
needle
sizeisdependent
on
the
fabric
and
thread
weights.
For
best
re
sults.
select
the
needleasthinaspossible,
but
make
sure
the
thread
can
be
pulled
through
the
needle
eye
easily.
The
needle
size
(Nm) is
indicated
on
the
shank
in
hundredths
ofamillimeter.
a
Page 9
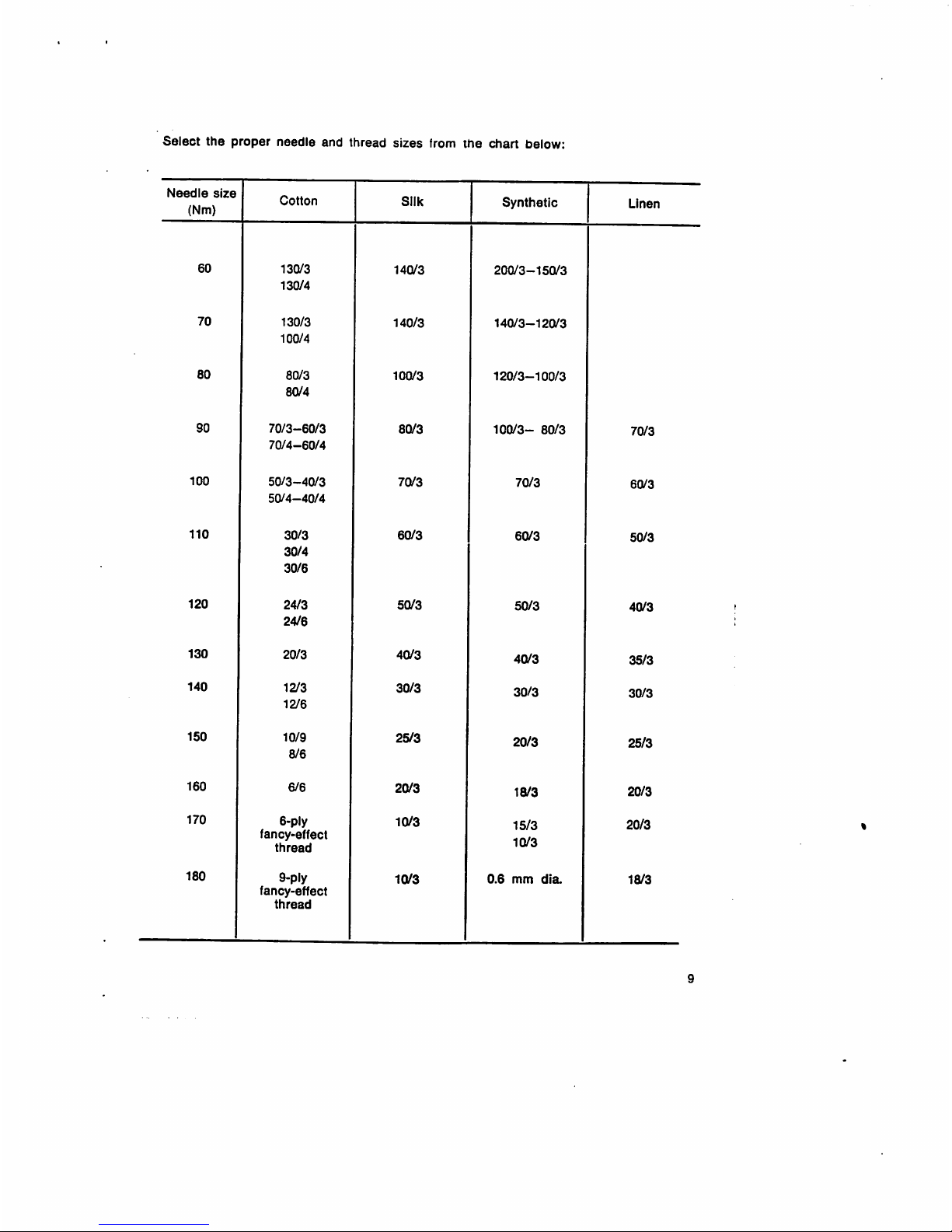
Select
the
proper
needle
and
thread
sizes
from
the
chart
below:
Needle
size
(Nm)
Cotton
Silk
Synthetic
Linen
60
130/3
130/4
140/3
200/3-150/3
70
130/3
100/4
140/3
140/3-120/3
60
80/3
80/4
100/3
120/3-100/3
SO
70/3-60/3
70/4-60/4
80/3
100/3-
80/3
70/3
100
50/3-40/3
50/4-40/4
70/3
70/3
60/3
110
30/3
30/4
30/6
60/3
60/3
50/3
120
24/3
24/6
50/3
50/3
40/3
130
20/3
40/3
40/3
35/3
140
12/3
12/6
30/3
30/3
30/3
150
10/9
8/6
25/3
20/3
25/3
160
6/6
20/3
18/3
20/3
170
6-ply
fancy>effect
thread
10/3
15/3
10/3
20/3
180
9-ply
fancy-effect
thread
10/3
0.6
mm
dia.
18/3
Page 10

The
needle
size
should
be
selectedtomatch
not
only
the
thread
weight,
but
also
the
machine
model,asfollows:
ModelA:Needle
sizes
60—
70
Model
B:
Needle
sizes
80—100
Model
C:
Needle
sizes
110—140
Model
D:
Needle
sizes
160—180
The
needle
sizeisindicated
on
the
shankinhundredths
of
millimeters.
Thus,
a No.
100
needle
hasashaft
diameter
of
100/100
= 1
mm.
7.
Changing
the
needle
Raise
the
needle
bar
to its
highest
point,
loosen
the
needle
set
screw
half a turn, anc
pull
the
damaged
needle
outofthe
needle
clamp.
Insert a new
needle
into
the
clamp,
making
sure
that
its
short
groove
faces
toward
the
sewing hook.
Push
the
needle
up as far as it will go and tighten
the
needle
set
screw
securely.
Never
use
rusty
needles.
8.
Threading
the
needle
Pass
the
thread
from
spool
1 (Fig. 8)
through
the
holesinstud2and
thread
guide
3,
around
thread
retainer4,clockwise
around
between
te'"'ion
discs5,under
thread
controller
disc
6, through
thread
check spri up and th igh
thread
guide
8, from
right to left through the hole in take-up lever j. then down and through thread guides
10, 11
and
12,
and
from left to
right
through
the
eyeofthe
needle.
The spool
holder
on top of the machine arm w'
">6
suppli'^'f on
special
request
only
because
the
thread
stand
which is
supplied
the
m
le
regularly
ensures
a
smoother
passage
of
the
threadtothe
needle.
Page 11

9,
Drawingupthe
bobbin
thread
HCd
t.e
endott.e
needle
thread
^ trne\V.~
rp;^rr:f.r:'.:e\r:.c.co..
r;:;Tr.rorHoTd".h?e:crr:;p°;'
.treads
un,,,
.he
.achma
has
.adea.a«
stitches.
10.
Regulating
the
thread
tension
Adlustlng
the
upper
tension
counter-clockwise
tor
less
Turn
tension
nutM(Fig.8)clockw.se
for
more
tens.on,
K^Khin
thread
will
draw
the needle thread
down
^or
r.Tr:iv:.ra
re
unde.s.de
o.
.he
.a.eda,.
as
shown
,n
^.
„
,ne
upper
.ensionis.00
.iph.,
.he
hobbln
.hread
winbepu.ledup(Fig.
10)
:::r::
r.,—•
-
centerofthe
material,asshownmF.g.
11.
upper
tension
too
looseorlower
tension
too
tight
Fig. 10
tension
too
tightorlower
tension
too
loose
jliCZJ
Fig.
11
Both
tensions
properly
balanced
-:rsr,vrr."-r
=».s
rcrr
.r«s
r-™
™—•
«•
pingofstitchesorthread
breaking.
Page 12

Adjusting
the
lower
tension
Take
the
bobbin
case
outofthe
machine
and
regulate
the
tensionbyturning
screw
Z
(Fig.7)with
the
hook
screwdriver,asappropriate.
Turn
this
screw
clockwise
foratight
er
tension,orcounter-clockwise
foralooser
tension.
The
tensioniscorrectifa
noticeable
resistanceofspringY(Fig.7)has to be
overcome
when
pulling
the
thread
outofthe
bobbin
case.
If
puckering
occursondelicate
materials
although
the
tension
has
been
set
correctly,
ease
both
tensions
slightly.
11. Regulating the stitch length
The
stitch
lengthisregulatedbyturning
thumb
nutS(Fig.
12)onthe
feed
regulator
lever.
R
9933
s
Fig.
12
Turn
this
nut
clockwise
for
shorter
stitches,orcounter-clockwise
for
longer
stitches.
The
numerals on the left of the scale Indicate the
stitch
lengthinmillimeters.
The letters V
andRon
the
left
sideofthe
scale
(Fig.
12)
stand
for
forward
and
backward
sewing,
respectively.
Page 13

All machines with the exception of the Pfaff 141-705/03
and
143-705/03
are
regularly fitted
with
a spring-return feed regulator. This device incorporates a spring
which
permanently
holds the feed regulator lever down in forward feeding position. When the lever is
pushed up as far as it
will
go, the machine
will
sew in reverse. And conversely, when
the
leverisreleased,
forward
sewing
willberesumed
instantly.
If
desired,
the
machine
can
be fitted with a
pedal
which
makesitpossibletoreverse
the
directionoffeed
by foot
action.
12. Regulating the pressure on
the
material
The amount of pressure to be exerted by the
presser
foot must be adapted to the ma
terial to be sewn. The pressure is set correctly if the material is advanced through the
machine evenly without being injured by the teeth of the feed dog.
The pressure on the
material
is regulated by turning screw V
(Fig.
8).
Turn
this screw
in for
more
pressure,
or out for
less
pressure.
Depending
on the
version,
Pfaff
145,
146,
545.
546
and
555
machines
are
equipped
with
one or two leaf springs on the machine arm instead of the conventional presser bar
spring
with
pressure
regulating
screw.Onthese
machines
the
presser
foot
pressure
Is
increased by
turning
knurled
nut V
(Fig.
13)
upwards,
and decreased by
turning
It
downwards.
Fig.
13
Page 14

13.
Cleaning
the
sewing
hook
The
sewing
hookIsthe
most
essential
partofthe
whole
machine
and.
for
this
reason,
shouldbecleaned
thoroughly
from
timetotime.
To do
this,
raise
the
needle
bar
to its
highest
point,
open
the
bed
slide
and
remove
the
bobbin
case
with
the
bobbin.
Take
out
the
three
screws
Ei, Ej
and
Es (Fig. 6)
and
strip
the
hook
gib.
Turn
the
balance
wheel until point S of
the
bobbin
case
baseisabouttoenter
groove
N of
the
hook
(Fig. 14). When in this position, the
bobbin
case
base
canbetipped
out
easily by
seiz
ing
center
stud
Z with
thumb
and
forefinger while
turning
the
balance
wheel
back
and
forth
lightly.
Clean
hook
and
hook
raceway
thoroughly with
kerosene.Ifthe
cotton
wool in slot 0
(Fig. 14)
should
have
become
matted,itshouldbereplaced
and
the
new
cotton
wool
be
soaked
with
oil.
Fig. 14
To clean the parts in the vicinity of the sewing hook, take out set screw 20 (Fig. 4) and
pull the hook up out of the machine. When the hook is replaced, pin 19 (Fig. 4) ensures
proper positioning and eliminates the
need
of retiming the hook.
In replacing the bobbin case base, make sure that position finger F (Fig. 14) enters slot
P on the underside of the needle plate. Replace hook gib and tighten screws Ei-
Ej. Put a drop of oil Into the hook raceway, replace the bobbin
case
with the bobbin
and
close
latch B (Fig. 6).
Never run the machine
with
the needle plate removed as this may result in damage to
the bobbin
case
or the bobbin
case
opener.
The above Instructions also apply to all two-needle sewing machines covered by this In
struction
Book.
Page 15

14.
The
safety
clutch
ModelCandDmachines
are
equipped
withasafety
clutch
which
prevents
disturbance
of
the
hook
timing and
damagetothe
bobbin
case
baseincaseofthread
jamminginthe
hook
raceway.
If an irregularly
spun
needle
thread
should
jam in
the
hook
raceway
and
block
the
sew
ing hook,
the
safety clutch
automatically
disengages
the
hook drive.
After
the
jammed
thread
has
been
removed,
tilt
back
the
sewing
head
and
rotate
the
balance
wheel,
while
holding
the
hook
drive
shaft
steady,
until
the
tipofthe
latch
is
positioned
exactly
above
the
grooveinthe
clutch
bushing.
Now
push
back
the
spring-
loaded
pinsothat
the
latch
can
snap
Into
this
groove.
To
resume
sewing,
simply
let
down
the
sewing
head
again.
R
9343
Fig. 15
Page 16

Additional
instructions
for
Pfaff
machines
141-705/03
and
141-705/03-725/01
The
Pfaff
141-705/03
and
141-705/03-725/01
have
the
same
feed
regulator.
This
new
mechanism
makesitpossibletoselect
the
proper
stitch
length
outoftwelve
different
stitch
lengths
available.
These
twelve
stitch
lengths
are
divided
into
four
stitch
length
groups
(l-IV)
having
three
predetermined
stitch
lengths
each
(Fig.
16).
The
following
taoie
lists
the
stitch
lengthsinmillimetersaswellasthe
number
of
stitches
per
inch.
For
adjustment,aswellasengagement
and
disengagementofthe
trimming
mechanism
on the
Pfaff
141-705/03-725/01.
see pages 19 and 20.
Stitch
length
group
Stitches
per
inch
33 28
25V2
23 21 19 17 15 13 12 11 10
Stitch
lengthinmm
0.8 0.9 1.0
1.1
1-2 1.3 1.5 1.7 1.9
2.1
2.3 2.6
Stitches
per
cm
12'/?1110 9 8
Th
6Vj
5Vj
5
4V2
4 3'/?
R
6575
Fig.
16
Page 17

15.
Regulating
the
stitch
length
The
stitch
lengthisregulated
as
follows:
Beginbyselecting
the
proper
stitch
length
group
from
the
table
on p. 16
and
inter
change
the
feed
gearsasindicatedinthe
feed
gear
housing
(Fig.
18).
Press
down
button
K (Fig, 17)
and
turn
the
baiance
wheei
untii
the
button
snapsinpo
sition.
Again
rotate
the
balance
wheel
backwardsorforwards
until
notch
M (Fig. 17) on
the
baiance
wheeiisopposite
the
numberofthe
stitch
length
group
chosen
(I, II. IllorIV).
Release
buttonKand
turn
feed
regulator
lever
S (Fig. 16) to
the
desired
stitch
length.
R
8994
Fig. 17
Page 18

16.
Changing
the
feed
gears
Exchanging the feed gears is greatly facilitated by the wheel puller which Is supplied
with the machine. To pull the feed
gear
off its shaft, slip the fork of the wheel puller
under
the
projecting
rim of
the
hub
and
puli (Fig. 18),
Consult the diagram on the feed
gear
housing (Fig, 18) to
see
how the feed
gears
have
to be exchanged to obtain the stitch length group and stitch length desired. Exchange
the
feed
gears
accordingly.
For better Identification, the
outside
of the feed
gears
and the
corresponding
symbols
used in the diagram are painted yellow, green, red and blue. In slipping the feed gear
onto
its shaft,
see
that
the
key on
the
shaft
enters
the
notch in
the
feed
gear
and
that
the
mating
gears
are
meshed
properly.
For instructions on how to
adjust
the
trimmer of
the
Pfaff 141-705/03-725/01.
please
refer
to
Chapters17and
18.
m
R
6585
IPI
Fig. 18
Page 19

17.
Adjusting
the
trimmer
To
take
out
the
trimming
knife
for
sharpening,
loosen
set
screwC(Fig.
19)
swinq
the
knife
halfway
between
its
operative
and
inoperative
positions
and
pull
the
knife
out
of
Its
guide.Asyou
replace
the
knife,
make
sure
its
cutting
edge
bears
lightly
against
the
edgeofthe
needle
plate
slot
which
servesasa
guide.
However,
the
knife
must
neverbeset
too
closetothis
edgeasthis
might
cause
the
knifetojamasitisthrown
outofaction.
When
the
settingiscorrect,
tighten
set
screwCsecurely.
The
cutting
strokeofthe
knife
shouldbeexactly
halvedbythe
needle
hole.Toadjust
the
positionofthe
cutting
edgeinrelationtothe
needle
hole,
loosen
nutM(Fig
19)
and
move
the
knife
carrier
forwardorbackward,asappropriate.
This
setting
also
appliestoknives
which
have
been
resharpened
repeatedly.
After
the
adjustment
tighten
lut M securely. . y ci.
The
vertical
positionofthe
knifeisadjustedbyscrewS(Fig.
19).
Turn
this
screw
clock
wisetoset
the
knife
lower,orcounter-clockwisetosetithigher.
The
knife
isset
cor
rectly,IfIts
cutting
edgeispositioned
just
above
the
bottomofthe
needle
plate
guide
Fig. 19
Page 20

It
goes
without saying
tnat
only a
sharp
and
correctly
set
knife will
produceaclean
cut.
Blunt knives are either snarpened with a triangular oilstone by hand (Fig.
2C)
or with
the aid of a knife sharpener. In sharpening the
knife,
take care that the cutting angle
is
preserved
and
that
the
cutting
edgeissharpened
thoroughly up to its
innermost
cor
nerewhich
hastotake
most
of
the
strain.
18.
Operating
the
trimmer
To
engage
the trimmer, turn lever H (Fig. 19) to the right until it
catches
on lug K on th(
knife carrier. To
disengage
it. lift lever H up slightly and swing it forward.
With the trimmer thrown out of action, the machine
can
be used for ordinary sewing
operations.
R
5436
'si«'
•
Fig.
20
Page 21

Additional
Instructions
for
PfafI
machines
143-705/03
The
general
instructions
given
for
the
Pfaff
143
apply
alsotothe
Pfaff
143-705/03
wheel-
feed
machine.Inaddition,
however,
the
following
instructions
shouldbeheeded:
9. Regulating the stitch length
On
wheel-feed
machines
the
stitch
lengthisregulated
under
the
bedplate
instead
of
on the
machine
arm.
as is
customary.
The
feed
gear
assembly
(Fig.
21)
enables
selection
of three pre-determined stitch lengths.
To
change
the
stitch
length,
pull
out
pinP(Fig.
21)
and
move
leverHto
positiona,b
or c, as
desired,
while
turning
the balance
wheel.
Let
pin
P snap
into
position.
To
convert
the
mac^iinetoanother
stitch
length
group,
consult
the
Spare
Parts
Cata
-
logue
which
contains a list of all feed gears available for this
machine.
Page 22

Additional
instructions
for
Pfaff
machines
145
Pfaff machines 145 are fitted not only with compound feed like the Pfaff 141. but also
with
alternating
pressers
which
makes them
unison-feed
machines
capable of
feeding
materials
that
are
difficulttohandle.
Apart
from
the
general
instructions
given
for
Pfaff
machines
141
and
143
which
apply
to Pfaff machines 145 also, the following special instructions should be heeded;
20.
Exchanging
the
alternating
pressers
Raise presser bar
liftera(Fig.
22) and rotate the balance wheel to bring the needle to
its
highest
point.
Loosen
screw b and
pull
out the
vibrating
presser,
rotatingitslightly
to
the
right
and
left.
R
3503
Fig. 22
Page 23

In
replacing
the
vibrating
presser
make
sure
you
pushitupasfarasIt
willgoand
orientitso
that
the
needleiscenteredinits
needle
hole.
Then
tighten
screwb(Fig.
22)
securely.
The
lifting
presser
can be
removed
only
when
the
presser
bar is
raised.Todo
this,
take out screw c
(Fig.
22)
and
pull
out the
lifting
presser.
tiltingitback
and
forth
slightly.
When
replacing the
lifting
presser. push it up as far as it
will
go so that screw c can
be pushed through the hole in its shank and tightened securely.
R
6189
'
/ ^
mmi
F H
Fig.
23
Page 24

21.
Lubricating
the
machine
Since
Pfaff
machines
145
are
fitted with
alternating
pressers,
they
haveanum
ber of additional oiling points which are marked by arrows in Figs. 22 and 23. Of these,
particularly the points of friction at the needle-bar-end of the machine, such as the
needle bar (inside needle bar frame in Fig. 22) and the sleeve take-up with its round
shank (behind needle bar in Fig. 22), require thorough and regular lubrication.
All
moving and rotating parts should be oiled regularly. To prevent soiling of the work
through dripping oil, sew a few seams on a piece of scrap material to absorb all ex
cess
oil.
Never try to remedy certain faults by applying excessive quantities of oil. Excessive
oiling
will
merely soil the work. Tnerefore, oil the machine sparingly, but regularly.
22.
Setting
the
foot
lift
To
adapt
the
foot lift to the thickness of the material to be sewn, loosen wing nut F
(Fig. 23) and adjust the position of lifting eccentric connection H in the slot of the lift
ing crank. Move the connection upward for a higher foot lift, or downward for a lower
foot
lift.
Additional
instructions
for
Pfaff
machines
151
and
153
Pfaff machines 151
and
153
are
single-needle sewing machines fitted with compound
feed
and
ordinary
drop
feed, respectively. Both have the vertical rotary hook
arranged
on
the
left of
the
needle.
The
Instructions
given in
Chapters
1-14
appytothem
also.
24
Page 25

Additional
Instructions
for
Pfaff
machines
142,144,146
and
542-748/01
23.
Threading
the
needles
To thread the left needle, pass tne thread
from
tne spool on the tnread stand through
the two upper holes in stud 1 on the machine arm (not shown In Fig.
24),
through thread
guide2.around
thread
retainer3,around
and
between
tension
discs4,down
and
iround thread controller disc 5. through thread check spring 6, up and through thread
juide
7, from right to left through the hole in take-up lever 8. down and through thread
guides
9, 10
and
11,
and
from
right
to left
through
the
eyeofthe
left
needle
12.
To
thread
the
right needle,
pass
the
thread
from
the
second
spoolonthe
thread
stand
through the two lower holes in
stud
1 (not
shown
in Fig. 24).
thence
to 2, 14, 15, 5, 6,
7. 8, 9, 10
and
16.
and
from left to right
through
the
eyeofthe
right
needle
17.
Fig. 24
Page 26

24.
Adjusting the puller feed of the
Pfaff
542-/48/01
The
Pfaff
542-748/01isequipped
withanadditional
puller
feed
whichisarranged
bacif
of
the
presser
foot
and,
actinginsynchronization
with
the
drop
feed,
ensures
even
feedingofthe
material.
The
lower
feed
rollerispositively
drivenbythe
feed
rock
shaft
via a
connecting
link.
When
the
presser
bar
lifterislowered,
the
upper
feed
rollerislowered
onto
the
lower
feed
roller
and
the
materialisfirmly
gripped
between
them.Toincrease
the
rate
of
feedofthe
puller
feed
for
sewing
materials
that
are
difficulttohandle,
loosen
the
hexa
gon
nut
and
adjust
the
positionofthe
connectioninthe
elongated
holeofleverX(Fig.
25).
Then
tighten
the
hexagon
nut
securely
again.Asa
resultofthis
adjustment
a
stronger
pullisexerted
on the
material
back
of the
presser
foot.
To
remove
the
work,
the
top
feed
rollerisraisedbypushingupthe
lifting
lever.
Operation
and
maintenanceofthis
machineisgovernedbythe
general
instructions
giveninthis
book,
except
that
the
additional
oiling
points
shownInFig.25should
be
supplied
with
oil.
'
Fig.
25
Page 27

Additional
instructions
for
Pfaff
machines
543-712/01
and
543-712/02
The
Pfaff
543-712/02rsa
single-needle
sewing
machine
equipped
withatwo-speed
btop-motor
andaroller
thread
tension,
while
the
Pfaff
543-712/01isfitted
with
a
standard
motor
andadisc-type
thread
tension.
Both
these
machines
are
equipped
with
an extra-large vertical rotary hook.
T':
»he
Pfaff
543-712Isidentical
with
thatofthe
,1
flatbed
sewmg
machinesothat
all
operating
and
servicing
instructions
given
r
the
latter
also
applytothe
former,
the
only
exception
being
Chapters8and
11.
25.
Threading the needle ofthe
Pfaff
543-712/,
Pass
the
thread
from the
spoolupand
over
the
thread
guide
at the top of the
thread
stand, down and through the
hole of the angular thread
guide on the machine arm,
and
through
the
thread
re
tainer. making
sure
that the
thread
enters
the
slot
in the
thread
retainer
stud. Now
lead it clockwise around the
roller tension of subcl.-712/02
machines or the disc-type
insionofsubcl.
-712/01 ma
chines. Then
pass
it around
the thread controller disc,
through the
thread
check
spring, up and through the
thread guide, from right to
left through the eye in the
take-up lever, down
and
through both thread guides,
and
from
lefttoright
through
the needle eye.
Fig.
26
R
9697a
Page 28

Additional
Instructions
for Pfaff machines 546-748/01
The
Pfaff
546-748/01isa
two-needle,
flatbed
sewing
machine
fitted
with
unison
feed,
two
extra-iarge
vertical
rotary
hooks
and
additional
puller
feed
which
ensures
smooth
feeding of "problem" materials.
Fitted
withasubcl.
-368/01,
-369/01or-371/01
attachment
this
machineisprimarily
intended for attaching waistbands to trousers and skirts.
Other
than
that
the
Pfaff
546-748/01isidentical
with
our
standard
two-needle,
flatbed
sewing
machinesothat
the
general
operating
and
servicing
instructions
given
for
this
machine
applytothem
also.
The
only
exceptions
are
the
instructions
for
settin.
the
foot
lift
and
adjusting
the
puller
feed
which
are
given
below.
R
9680
26.
Setting
the
foot lift
To adapt the
f«
lift the
thickness
of
the
material
to
be sewn,
loosen
wing
nut
F
(Fig. 27) and adjust the posi
tion of lifting
eccentric
con
nection
H in
the
slotofthe
lifting crank. Move
the
con
nection upward for a higher
foot lift, or downward for a
lower
foot
lift.
Then
tighten
wing nut F
securely.
If
delicate
fabrics
should
con
tinuetopucker
when
sewn
on
a
subcl.
-368/01, -369/01 or
-371/01
machine,
although
the
foot
lift
was
adjusted
correct
ly, It Is recommended to re
place the rear swing-away
folder by one having a built-
in retaining mechanism and a
regulating screw (R in Fig.
28).
To
increase
the
pressure
ex
ertedcrthe
fabricbythe
re-
Page 29

taining
tongue,
turn
screw
R
.backward;
to
decrease
the
pressure,
turnitforwards.
For
easy
removalofthe
ma*
terial,
press
against
the
knee
lever
to
raise
the
vibrating
and
lifting
pressers
and
lock
the
latterInpositionbylever
St
(Fig. 27).
Fig.
28
27.
Adjusting
the
puller
feed
The Pfaff
546-748/01
is equipped
with
an additional puller feed
which
is arranged
behind the
presser
foot and, acting in synchronization with the unison feed,
ensures
even feeding of the material. The lower feed roller is positively driven by the feed rock
shaft
via a connection and
has
a buiit-in retaining mechanism.
By lowering
presser
bar lifterSj(Fig. 27),
the
upper
feed roller is lowered
onto
the
lower feed roller and both
advance
the
material together. To increase the
rate
of feed
of the puller feed so that It
exertsastronger
pull on the material at the
backofthe
needles,
adjust
the
position of
connection
Z (Fig. 27) in relation to
the
feed lever.
Then
tighten
the
hexagon
nut securely.
Page 30

Additional
instructions
for
Pfaff
machines
4141
and
4145
Pfaff
machines
4141
and
4145
closely
resemble
Cl.
141
and
145
machinesmtheir
mecha
nical
setup,
exterior
design
and
dimensions.
Insteadofa
vertical
rotary
hook,
however,
both
machines
are
equipped
withaconstant-motion
rotary
looper
which
moves
coun
ter-clockwise.inaddition,
they
are
fitted
withathread
nipper
whichisoperatedbythe
needle
bar
crank.
Apart
from
the
needle
threading
instructions,
the
general
instructions
given
for
Pfaff
ma
chines
141
and
145
applytoPfaff
machines
4141
and
4145
also.
(Since
the
latter
ma
chines
are
chainstitch
sewing
machines,
bobbin
winding
naturallyisomitted.)
R
6312
28.
Threading
of
the
Pfaff
4141
and
4145
Pass
the
thread
from
the
spool
up to the top thread guide of
the
thread
stand,
then
down
and through both holes in the
pin on the machine arm,
through the upper hole in the
thread
guide
on the machine
arm (as shown in Fig. 29),
around
the
pin.
through
tf\
lower
holeinthe
thread
guide,
clockwise
around
and
be
tween
the
tension
discs,
from
right to left through the hole
in
the
take-up
lever, below
the
leverofthe
automatic
ten
sion,
through
the lower
thread
guide and the thread guide
on
the
needle
clamp,
and
from left to right through the
needle
eye.
Page 31

Additional
Instructions
for Pfaff machines fitted with thread pulier/trimmer •900/..
Since
these
machines
are
equipped
with
Stop
motor
and
electro-magnetic
thread
puller/trimmer,
manual
needle
positioning
and
thread
trimming
are
completely
elimi
nated.
29.
Pedal
operation
When
you
depress
the
heelofthe
pedal
at the
completionofthe
sewing
action,
the
eedle is
raised
automatically,
the
needle
thread is
pulled
to the
underside
of the
ma-
teriaJ
and
both
threads
are
trimmed.
All
you
have
to do to
remove
the
work
is raisethe
presser
foot
The
thread
ends
remaining
on the
undersideofthe
material
are
long
enough to permit them to be pasted down reliabiy.
The pedal of these machinescontrols the
following
functions:
1.
When
you
depress
the
tipofthe
pedal,
the
machine
starts
sewing.
The
harder
you
press, the faster the
machine
will
run.
(If
it is
fitted
withaninching
device,
the
pedal
will
also control slow stitch-by-stitch sewing).
2.
When
you
relieve
the
pressure
and
allow
the
pedaltoreturntoits
neutral
posi
tion, the needle is lowered for turning comers.
3.
When
you
depress
the
heelofthe
pedal,
the
needleisraisedtoits
highest
point,
the needle thread
pulled
to the underside of the material, and both threads are
trimmed.
4. When the pedal is returned to its neutral position again, the needle
remains
at its
highest
point
The
various
pedal
positions
are
shown
below:
Forward
sewing
After
sewing:
needle
down
Neutral
position
Raising
needle
and
trimming
threads
After
thread
trimming:
needle
up
Ifthe machine is fitted
with
two pedals (subcl.
pedals are simultaneously pressed forward.
-911/01),
it will
sewinreverse
when
both
31
Page 32

Guards
irra^Tn^are'Tegularly
fitted
withaguard
which
protects
the
operator's
firtgers
rjlrgrorthTfingerguard
and
the
methodoffittingitdepend
on
the
matdtine
version.
vei
Please
make
sure
that
this
guardisalways
fitted
correctly.
R
11466
....
Fig. 30
Take-up lever guard (Fig.31)
All
machines
are
normally
equipped
withatake-up
lever
safety
regulations.Itis
imperative
that
this
safety
deviceisfittedatall
times.
Page 33

Belt
guardonbalance
wheel
(Fig. 32)
This
guard
covers
the
point
where
the
belt
runs
onto
the
balance
wheel.
The
belt
guardismountedasfollows:
Guard 1 is
secured
with two
screws
2 and positioned so
that
it covers the point of belt
entrance
completely.
R
11369
A
¥rv.--:-;iSws
Page 34

Belt guard below tabletop (Fig. 33)
This guard covers the belt below the tabletop.
Loosen
wing
nut 4, and
position
guard 5 so that
motor
puliey
and
V-belt
run
freely
in
the
guard.
"
f'-vj
\
R
10865
Page 35

• #
I
{
i •«
'
Troubfe
shooting
Machlrte
skips stitches
Cause
Wrong
needle
system.
Needle
bent
Needle
inserted
incorrectly.
i
Incorrect
threading.
^hread
breaks
Cause
For
anyofthe
reasons
indicated
above.
Thread
tensions
too tight
Knotty
thread.
Needle
point
bluntordamaged.
Thread snarled up.
Faulty stitch formation
Cause
Improper
tension.
"Wrong
needle
size
and/or
thread
used.
Piecesofthread
between
tension
discs
or
under
bobbin
case
tension
spring.
Needle
breaks
Cause
Wrong
needle
system.
Needle
bent
Needle
too
thin.
Machine
binds
'Cause
• ^
Lackofoil.
Remedy
For
correct
needle
system
see
Chapter
6.
Insert
new
needleasInstructedInChapter
7
Orient
needlesothat
its
short
groove
faces'
toward
the
sewing
hook.
In Chapters S.
8, 23, 25 and 28.
Remedy
See
remedies
listed
above.
Regulate
tensionsasInstructedInChapteria
Use
high-quality
thread
only.
Replace
needle.
Check
upper
threading
from
spoolofthread
to
needle.
Remedy"^
Regulate
tensionsasinstructedInChapter
ia
See
Chapter
&
Remove
thread
and
re-adjust
tensionasIn
structed In Chapter 10.
Remedy
.
Insert
needleofcorrect
systemasInstructed
in Chapter 6.
Insert
new
needle.
Insert thicker
needta
Wrong
lubricant
^
Hook
race
obstructedbypieces
of
thread.
'
.Remedy.'
Oil
machineasInstructedInChapters
3.-13
and'21.
- •
Use
only
non-reslnous
and
add-free
sewfno
machine-oil.
Trytofree
the
jammed
threadasyou
rock
the
balance
wheel
back
and
forth.Ifthis
action
should
fall,
dismantle
the
sewing
hookasIn
structedInChapter
ia
Page 36

\} :
I-
1 *
f':'
rsaPTf
Nr.
296-12-07
064/1275
engl. P.
« • 6
M
♦
C:
*1
Printed In
West
Germany
-•??.
vlT'
 Loading...
Loading...