Panasonic TX-32C300, TX-32CW304, TX-40C300, TX-40CW304 Schematic

Service Manual
© Panasonic Corporation 2015.
Unauthorized copying and
distribution is a violation of law.
ORDER No. MQM1505001V2
There are special components used in this equipment which are important for safety. These parts are marked in the
Schematic Diagrams, Circuit Board Diagrams, Explorer Views and Replacement Parts List. It is essential that these
critical parts should be replaced with manufacturer´s specified parts to prevent shock, fire or other hazards. Do not
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE
This service information is designed for experienced repair technicians only and is not designed for use by the general public. It does not
Warning
LCD Television
TX-24CR300 / TX-24CR300
TX-24CW304 / TX-32C300
TX-32CW304 / TX-40C300
TX-40CW304 / TX-40CR300
TX-48CW304 / TX-48C300
TX-48CR300
MB97 Chassis
contain warnings or cautions to advise non-technical individuals of potencial dangers in attempting to service a product. Products
powered by electricity should be serviced or repaired only by experienced professional technicians. Any attempt to service or repair the
product or products deal within this service information by anyone else could result in serious injury or death.
modify the original design without permission of manufacturer.
0

CONTENTS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS ........................................... 2
GENERAL GUIDE LINES ...................................... 2
TOUCH – CURRENT CHECK ............................... 2
PREVENTION OF ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE
(ESD) TO ELECTROSTATICALLY SENSITIVE (ES)
DEVICES .................................................................... 3
ABOUT LEAD FREE SOLDER (PBF) ......................... 4
SERVICE NAVIGATION ............................................. 5
SERVICE HINTS......................................................... 7
SERVICE MODE FUNCTION ..................................... 9
SOFTWARE UPDATE ............................................ 10
HOTEL MODE .......................................................... 11
PARTS LOCATION ................................................... 14
LOCATION OF LEAD WIRING ................................ 15
BLOCK DIAGRAM .................................................... 19
EXPLODED VIEW .................................................... 20
1
Safety Precautions
Fig. 2
TO
APPLIANCES
EXPOSED
METAL PARTS
Resistance values in ohms ()
V
R0=500
RS=1500
CS=0.22F
10k
0.022F
COLD
WATER PIPE
(EARTH GROUND)
V: Voltmeter or oscilloscope
(r.m.s. or peak reading)
Measuring network for TOUCH CURRENTS
Input resistance: 1M
Input capacitance:200pF
Frequency range: 15Hz to 1MHz and d.c.respectively
NOTE – Appropriate measures should be taken to obtain the correct value in case of non-sinusoidal waveforms
U2 (V)
U1 (V)
General Guide Lines
1. When servicing, observe the original lead dress. If a short circuit is found, replace all parts which have been overheated
or damaged by the short circuit.
2. After servicing, see to it that all the protective devices such as insulation barriers, insulation papers shields are properly
installed.
3. After servicing, make the following touch current checks to prevent the customer from being exposed to shock hazards.
Touch-Current Check
1. Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet. Do not use an isolation transformer for this check.
2. Connect a measuring network for touch currents between each exposed metallic part on the set and a good earth
ground such as a water pipe, as shown in Fig. 2.
3. Use Leakage Current Tester (Simpson 228 or equivalent) to measure the potential across the measuring network.
4. Check each exposed metallic part, and measure the voltage at each point.
5. Reserve the AC plug in the AC outlet and repeat each of the above measure.
6. The potential at any point (TOUCH CURRENT) expressed as voltage U1 and U2, does not exceed the following values:
For a. c.: U1 = 35 V (peak) and U2 = 0.35 V (peak);
For d. c.: U1 = 1.0 V,
Note:
The limit value of U2 = 0.35 V (peak) for a. c. and U1 = 1.0 V for d. c. correspond to the values 0.7 mA (peak) a. c. and
2.0 mA d. c.
The limit value U1 = 35 V (peak) for a. c. correspond to the value 70 mA (peak) a. c. for frequencies greater than 100
kHz.
7. In case a measurement is out of the limits specified, there is a possibility of a shock hazard, and the equipment should
be repaired and rechecked before it is returned to the customer.
2
Prevention of Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) to Electrostatically
There are special components used in this equipment which are important for safety.
These parts are marked by in schematic diagrams, exploded views and replacement parts list. It is essential that
these critical parts should be replaced with manufacturer’s specified parts to prevent shock, fire, or other hazards. Do
not modify the original design without permission of manufacturer.
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE
Sensitive (ES) Devices
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be damaged easily by static electricity. Such components commonly are
called Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect
transistors and semiconductor "chip" components. The following techniques should be used to help reduce the incidence of
component damage caused by electrostatic discharge (ESD).
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or semiconductor-equipped assembly, drain off any ESD on
your body by touching a known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available discharging ESD
wrist strap, which should be removed for potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equipped with ES devices, place the assembly on a conductive surface such as
aluminum foil, to prevent electrostatic charge build up or exposure of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES devices.
4. Use only an anti-static solder removal device. Some solder removal devices not classified as "anti-static (ESD
protected)" can generate electrical charge sufficient to damage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective package until immediately before you are ready to install it.
(Most replacement ES devices are packaged with leads electrically shorted together by conductive foam, aluminum foil
or comparable conductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the leads of a replacement ES device, touch the protective
material to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be installed.
Caution
Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.
8. Minimize bodily motions when handling unpackaged replacement ES devices. (Otherwise harmless motion such as the
brushing together of your clothes fabric or the lifting of your foot from a carpeted floor can generate static electricity
(ESD) sufficient to damage an ES device).
3
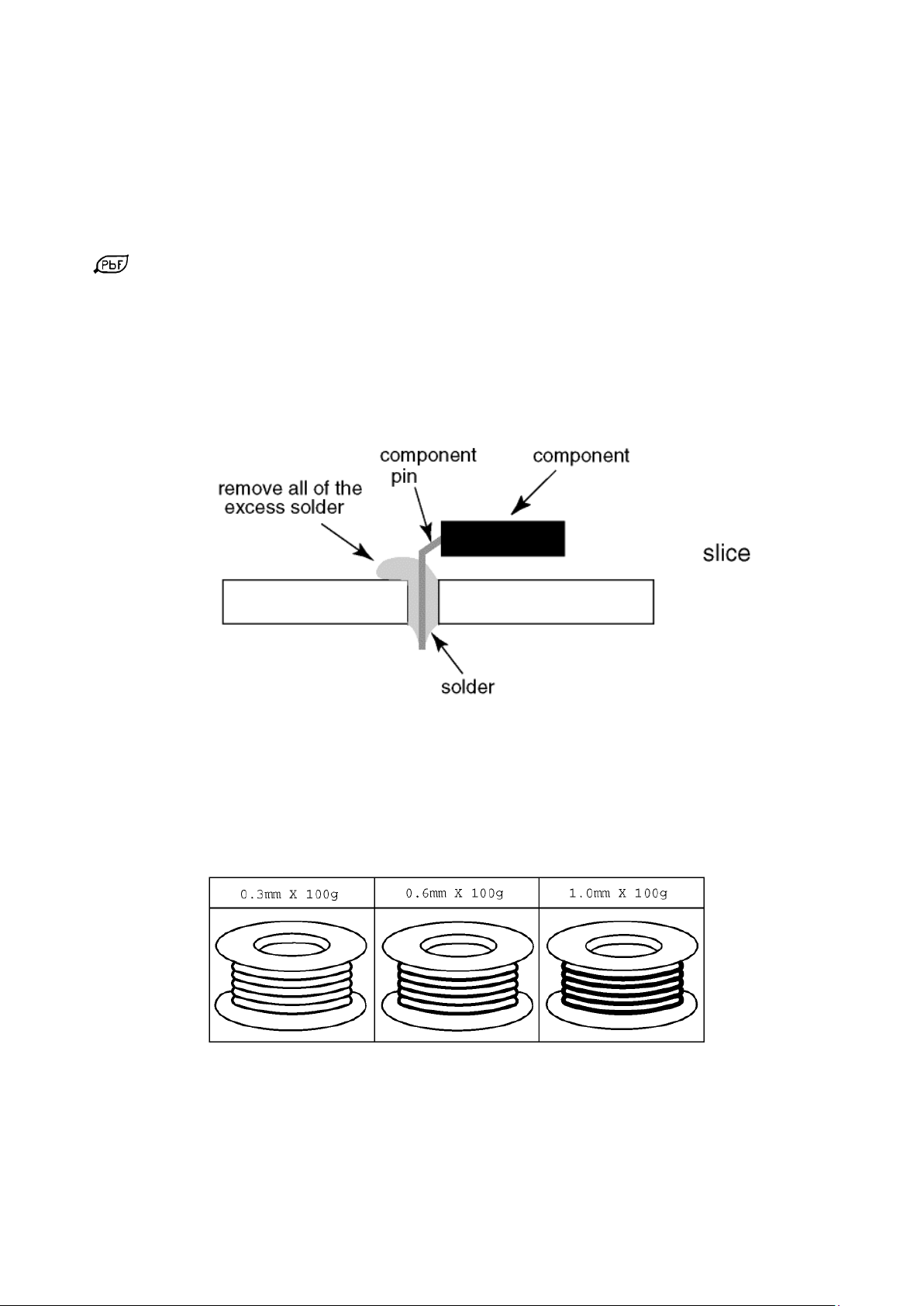
About lead free solder (PbF)
Fig.3
Fig.4
Note: Lead is listed as (Pb) in the periodic table of elements.
In the information below, Pb will refer to Lead solder, and PbF will refer to Lead Free Solder.
The Lead Free Solder used in our manufacturing process and discussed below is (Sn+Ag+Cu).
That is Tin (Sn), Silver (Ag) and Copper (Cu) although other types are available.
This model uses Pb Free solder in it’s manufacture due to environmental conservation issues. For service and repair work,
we’d suggest the use of Pb free solder as well, although Pb solder may be used.
PCBs manufactured using lead free solder will have the PbF within a leaf Symbol
stamped on the back of PCB.
Caution
Pb free solder has a higher melting point than standard solder. Typically the melting point is 50 ~ 70 °F (30~40°C)
higher. Please use a high temperature soldering iron and set it to 700 ± 20 °F (370 ± 10 °C).
Pb free solder will tend to splash when heated too high (about 1100 °F or 600 °C).
If you must use Pb solder, please completely remove all of the Pb free solder on the pins or solder area before
applying Pb solder. If this is not practical, be sure to heat the Pb free solder until it melts, before applying Pb solder.
After applying PbF solder to double layered boards, please check the component side for excess solder which may
flow onto the opposite side. (see Fig.3)
Suggested Pb free solder
There are several kinds of Pb free solder available for purchase. This product uses Sn+Ag+Cu (tin, silver, copper) solder.
However, Sn+Cu (tin, copper), Sn+Zn+Bi (tin, zinc, bismuth) solder can also be used. (see Fig.4)
4
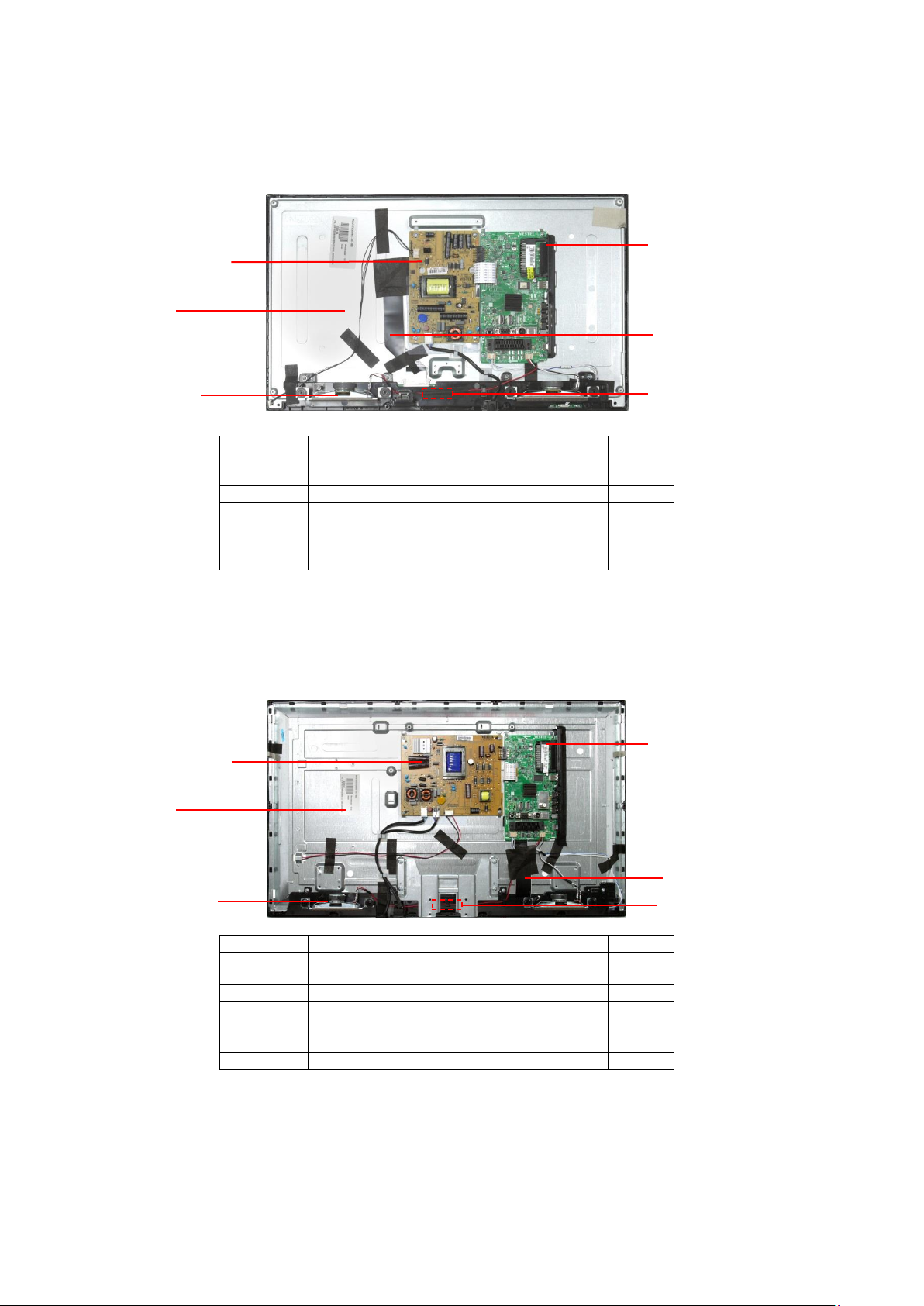
Service Navigation
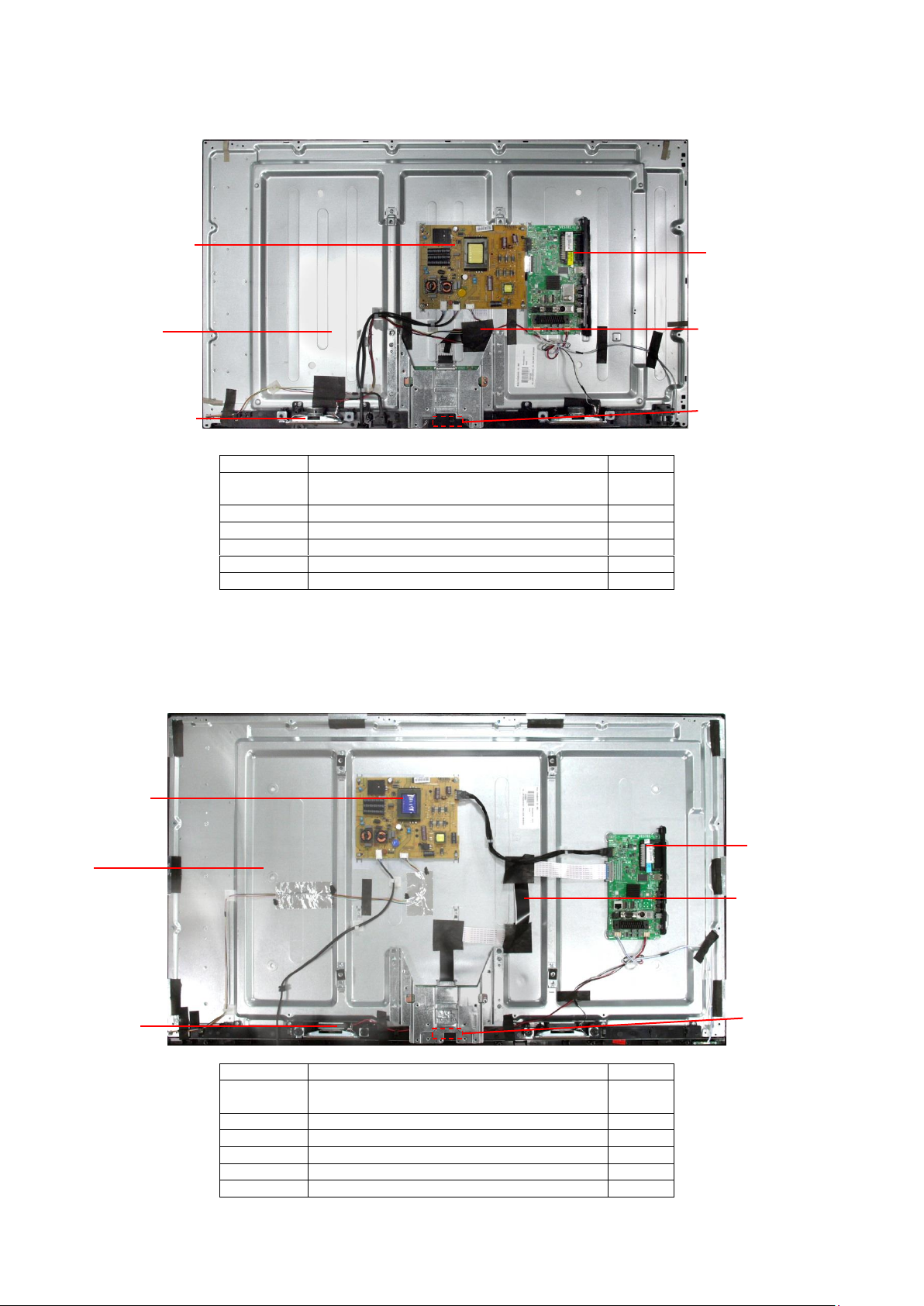
Name
Function
Position
Main-Board
AV Terminal, HDMI, USB, TUNER DVB-A/T/C,
CI-Slot, Headphones, Speaker out,
1
P-Board
Main Input, Power Supply, Back Light
2
LED-Board
Remote Receiver
3
Panel
LCD-Panel / Backlight
4
Speaker
5
LVDS Cable
6
(1) Main-BOARD
(3) LED-BOARD
(2) P-BOARD
(4) Panel
(5) Speaker
(6) LVDS Cable
24 inch Models
Name
Function
Position
Main-Board
AV Terminal, HDMI, USB, TUNER DVB-A/T/C,
CI-Slot, Headphones, Speaker out,
1
P-Board
Main Input, Power Supply, Back Light
2
LED-Board
Remote Receiver
3
Panel
LCD-Panel / Backlight
4
Speaker
5
LVDS Cable
6
(3) LED-BOARD
(2) P-BOARD
(4) Panel
(5) Speaker
(6) LVDS Cable
32 inch Models
(1) Main BOARD
Chassis Board Layout
5
Name
Function
Position
Main-Board
AV Terminal, HDMI, USB, TUNER DVB-A/T/C,
CI-Slot, Headphones, Speaker out,
1
P-Board
Main Input, Power Supply, Back Light
2
LED-Board
Remote Receiver
3
Panel
LCD-Panel / Backlight
4
Speaker
5
LVDS Cable
6
(1) Main-BOARD
(3) LED-BOARD
(2) P-BOARD
(4) Panel
(5) Speaker
(6) LVDS Cable
Name
Function
Position
Main-Board
AV Terminal, HDMI, USB, TUNER DVB-A/T/C,
CI-Slot, Headphones, Speaker out,
1
P-Board
Main Input, Power Supply, Back Light
2
LED-Board
Remote Receiver
3
Panel
LCD-Panel / Backlight
4
Speaker
5
LVDS Cable
6
48 inch Models
40 inch Models
(1) Main-BOARD
(3) LED-BOARD
(2) P-BOARD
(4) Panel
(5) Speaker
(6) LVDS Cable
6
 Loading...
Loading...