Panasonic TC-P50X60 Schematic
ORDER NO. MTNC130217CE
B34 Canada: B62
50 Inches Class 720p Plasma HDTV
Model No. TC-P50X60
GPH16DU Chassis
For detailed troubleshooting information and circuit explanations,
refer to the "QSM/Service Hints/Troubleshooting Information(TI)" and Seminar/Training Manual/Technical Guide(TG) documents posted on the TSN web site.
For information about this model, type TC-P2013 in the model box under "Direct Search".
© Panasonic Corporation 2013 Unauthorized copying and distribution is a violation of law.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
|
PAGE |
1 |
Safety Precautions ----------------------------------------------- |
3 |
|
1.1. General Guidelines ---------------------------------------- |
3 |
2 |
Warning -------------------------------------------------------------- |
4 |
|
2.1. Prevention of Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) |
|
|
to Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices ---------- |
4 |
|
2.2. About lead free solder (PbF) ---------------------------- |
5 |
3 |
Service Navigation------------------------------------------------ |
6 |
|
3.1. PCB Layout-------------------------------------------------- |
6 |
|
3.2. Applicable signals------------------------------------------ |
7 |
4 |
Specifications ------------------------------------------------------ |
8 |
5 |
Service Mode ------------------------------------------------------- |
9 |
|
5.1. How to enter into Service Mode ------------------------ |
9 |
|
5.2. Option - Mirror--------------------------------------------- |
11 |
6 |
Troubleshooting Guide---------------------------------------- |
12 |
7 |
Disassembly and Assembly Instructions--------------- |
13 |
|
7.1. Disassembly Flow Chart for the Unit ---------------- |
13 |
|
7.2. Disassembly Procedure for the Unit----------------- |
13 |
8 |
Measurements and Adjustments -------------------------- |
23 |
|
8.1. Adjustment------------------------------------------------- |
23 |
9 |
Block Diagram --------------------------------------------------- |
25 |
|
9.1. Main Block Diagram ------------------------------------- |
25 |
|
9.2. Block (1/4) Diagram ------------------------------------- |
26 |
|
9.3. Block (2/4) Diagram ------------------------------------- |
27 |
|
9.4. Block (3/4) Diagram ------------------------------------- |
28 |
|
9.5. Block (4/4) Diagram ------------------------------------- |
29 |
10 |
Wiring Connection Diagram --------------------------------- |
30 |
|
10.1. Caution statement.--------------------------------------- |
30 |
|
10.2. Wiring (1) --------------------------------------------------- |
30 |
|
10.3. Wiring (2) --------------------------------------------------- |
31 |
|
10.4. Wiring (3) --------------------------------------------------- |
32 |
|
10.5. Wiring (4) --------------------------------------------------- |
32 |
2
1 Safety Precautions
1.1.General Guidelines
1.When conducting repairs and servicing, do not attempt to modify the equipment, its parts or its materials.
2.When wiring units (with cables, flexible cables or lead wires) are supplied as repair parts and only one wire or some of the wires have been broken or disconnected, do not attempt to repair or re-wire the units. Replace the entire wiring unit instead.
3.When conducting repairs and servicing, do not twist the Fasten connectors but plug them straight in or unplug them straight out.
4.When servicing, observe the original lead dress. If a short circuit is found, replace all parts which have been overheated or damaged by the short circuit.
5.After servicing, see to it that all the protective devices such as insulation barriers, insulation papers shields are properly installed.
6.After servicing, make the following leakage current checks to prevent the customer from being exposed to shock hazards.
1.1.1.Leakage Current Cold Check
1.Unplug the AC cord and connect a jumper between the two prongs on the plug.
2.Measure the resistance value, with an ohmmeter, between the jumpered AC plug and each exposed metallic cabinet part on the equipment such as screwheads, connectors, control shafts, etc. When the exposed metallic part has a return path to the chassis, the reading should be between 1Mohm and 5.2Mohm. When the exposed metal does not have a return path to the chassis, the reading must be  .
.
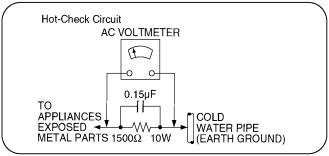
1.1.2.Leakage Current Hot Check (See
Figure 1.)
1.Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet. Do not use an isolation transformer for this check.
2.Connect a 1.5kohm, 10 watts resistor, in parallel with a 0.15 F capacitors, between each exposed metallic part on the set and a good earth ground such as a water pipe, as shown in Figure 1.
3.Use an AC voltmeter, with 1000 ohms/volt or more sensitivity, to measure the potential across the resistor.
4.Check each exposed metallic part, and measure the voltage at each point.
5.Reverse the AC plug in the AC outlet and repeat each of the above measurements.
6.The potential at any point should not exceed 0.75 volts RMS. A leakage current tester (Simpson Model 229 or equivalent) may be used to make the hot checks, leakage current must not exceed 1/2 milliamp. In case a measurement is outside of the limits specified, there is a possibility of a shock hazard, and the equipment should be repaired and rechecked before it is returned to the customer.
Figure 1
3
2 Warning
2.1.Prevention of Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) to Electrostatically
Sensitive (ES) Devices
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be damaged easily by static electricity. Such components commonly are called Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect transistors and semiconductor [chip] components. The following techniques should be used to help reduce the incidence of component damage caused by electrostatic discharge (ESD).
1.Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or semiconductor-equipped assembly, drain off any ESD on your body by touching a known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available discharging ESD wrist strap, which should be removed for potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit under test.
2.After removing an electrical assembly equipped with ES devices, place the assembly on a conductive surface such as aluminum foil, to prevent electrostatic charge buildup or exposure of the assembly.
3.Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES devices.
4.Use only an anti-static solder removal device. Some solder removal devices not classified as [anti-static (ESD protected)] can generate electrical charge sufficient to damage ES devices.
5.Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
6.Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective package until immediately before you are ready to install it. (Most replacement ES devices are packaged with leads electrically shorted together by conductive foam, aluminum foil or comparable conductive material).
7.Immediately before removing the protective material from the leads of a replacement ES device, touch the protective material to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be installed.
Caution
Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.
8.Minimize bodily motions when handling unpackaged replacement ES devices. (Otherwise ham less motion such as the brushing together of your clothes fabric or the lifting of your foot from a carpeted floor can generate static electricity (ESD) sufficient to damage an ES device).
4
2.2.About lead free solder (PbF)
Note: Lead is listed as (Pb) in the periodic table of elements.
In the information below, Pb will refer to Lead solder, and PbF will refer to Lead Free Solder. The Lead Free Solder used in our manufacturing process and discussed below is (Sn+Ag+Cu). That is Tin (Sn), Silver (Ag) and Copper (Cu) although other types are available.
This model uses Pb Free solder in it's manufacture due to environmental conservation issues. For service and repair work, we'd suggest the use of Pb free solder as well, although Pb solder may be used.
PCBs manufactured using lead free solder will have the PbF |
within a leaf Symbol PbF stamped on the back of PCB. |
Caution |
|
•Pb free solder has a higher melting point than standard solder. Typically the melting point is 50 ~ 70 °F (30~40 °C) higher. Please use a high temperature soldering iron and set it to 700 ± 20 °F (370 ± 10 °C).
•Pb free solder will tend to splash when heated too high (about 1100 °F or 600 °C).
If you must use Pb solder, please completely remove all of the Pb free solder on the pins or solder area before applying Pb solder. If this is not practical, be sure to heat the Pb free solder until it melts, before applying Pb solder.
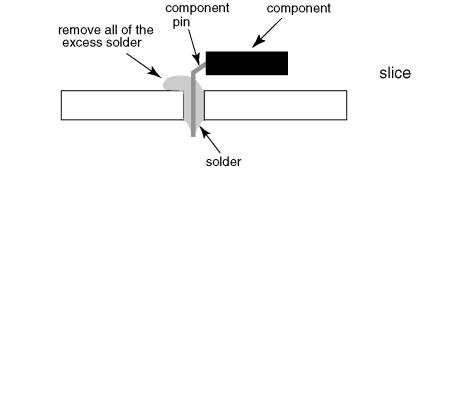
•After applying PbF solder to double layered boards, please check the component side for excess solder which may flow onto the opposite side. (see figure below)
Suggested Pb free solder
There are several kinds of Pb free solder available for purchase. This product uses Sn+Ag+Cu (tin, silver, copper) solder. However, Sn+Cu (tin, copper), Sn+Zn+Bi (tin, zinc, bismuth) solder can also be used.
5
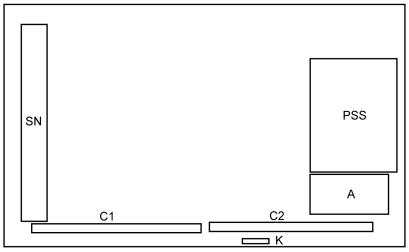
3 Service Navigation
3.1.PCB Layout
Board Name |
Function |
PSS |
Power Supply, Sustain Drive |
|
Non serviceable. |
|
PSS-Board should be exchanged for service. |
|
|
A |
Main AV input, processing |
K |
Remote receiver, Power LED, C.A.T.S sensor |
C1 |
Data Driver (Lower Right) |
C2 |
Data Driver (Lower Left) |
SN |
Scan Drive |
6
3.2.Applicable signals
Applicable input signal for Component (Y, PB, PR), HDMI
|
|
|
|
horizontal frequency (kHz) |
vertical frequency (Hz) |
525 (480) |
/ 60i |
15.73 |
59.94 |
||
525 (480) |
/60p |
31.47 |
59.94 |
||
750 (720) |
/60p |
45.00 |
59.94 |
||
1,125 |
(1,080) |
/60i |
33.75 |
59.94 |
|
1,125 |
(1,080) |
/60p |
67.43 |
59.94 |
|
1,125 |
(1,080) |
/60p |
67.50 |
60.00 |
|
1,125 |
(1,080) |
/24p* |
26.97 |
23.98 |
|
1,125 |
(1,080) |
/24p* |
27.00 |
24.00 |
|
*HDMI only
Note
•Signals other than those shown above may not be displayed properly.
•The above signals are reformatted for optimal viewing on your display.
7

4 Specifications
8

5 Service Mode
5.1.How to enter into Service Mode
5.1.1.Purpose
After exchange parts, check and adjust the contents of adjustment mode.
While pressing [VOLUME ( - )] button of the main unit, press [INFO] button of the remote control three times within 2 seconds
5.1.2.Key command
[1]button...Main items Selection in forward direction
[2]button...Main items Selection in reverse direction
[3]button...Sub items Selection in forward direction
[4]button...Sub items Selection in reverse direction
[VOL] button...Value of sub items change in forward direction ( + ), in reverse direction ( - )
5.1.3.How to exit
Switch off the power with the [POWER] button on the main unit or the [POWER] button on the remote control.
9
5.1.4.Contents of adjustment mode
•Value is shown as a hexadecimal number.
•Preset value differs depending on models.
•After entering the adjustment mode, take note of the value in each item before starting adjustment.
Main item |
Sub item |
Sample Data |
Remark |
WB-ADJ |
R-DRV |
DF |
|
|
G-DRV |
FF |
|
|
B-DRV |
7C |
|
|
ALL-DRV |
FF |
|
OPTION |
MIRROR |
00 (See Option-Mirror) |
Factory Preset |
|
Boot Loader |
ROM |
|
VSUS |
|
LOW |
See Vsus selection |
AGING |
ALL WHITE |
|
Built-in test patterns can be |
|
|
|
displayed. |
|
MIDDLE BLUE WITH MAGENTA OUTSIDE FRAME |
|
|
|
MIDDLE STEP GREEN |
|
|
|
MIDDLE STEP RED |
|
|
|
LOW STEP WHITE |
|
|
|
ALL BLUE |
|
|
|
ALL GREEN |
|
|
|
ALL RED |
|
|
|
WHITE DIAGONAL STRIPE |
|
|
|
RED DIAGONAL STRIPE |
|
|
|
GREEN DIAGONAL STRIPE |
|
|
|
BLUE DIAGONAL STRIPE |
|
|
|
A-ZONE & B-ZONE |
|
|
|
1% WINDOW |
|
|
|
COLOR BAR |
|
|
|
9 POINTS BRIGHT MEASURE |
|
|
|
2 DOT OUTSIDE FRAME |
|
|
|
DOUBLE FIXED 1% WINDOW |
|
|
|
VERTICAL LINE SCROLL |
|
|
|
ON/OFF |
|
|
|
R/G/B/W ROTATION |
|
|
|
HALF FIXED ALL WHITE |
|
|
|
ALL WHITE WITH COUNT DISPLAY |
|
|
10
 Loading...
Loading...