Page 1
TECHNICAL
MicroHAWK ID-40
NOTE
360o Barcode Reading to Omron NJ/NX Controller
Solution Overview
Six MicroHAWK ID-40 readers are connected in daisy chain conguration to an Omron NJ/NX machine controller
via EtherNet/IP. The NJ/NX controller sends a trigger to the readers, and once a reader decodes a symbol, the
read cycle is stopped for all readers. This solution includes a basic HMI user interface and an NA series panel.
This solution is useful in food and commodity applications in which a decode must be performed on a product's
barcode, but the barcode's location on the product's perimeter is not known. One example is the need to
decode a GS1 Data Matrix on a product as it travels down a conveyor. After the decoded data has been
delivered to the NJ/NX controller, the data could be written to a database as part of a pharmaceutical company's
serialization and traceability implementation.
Solution Features
• Six-reader daisy chain of MicroHAWK ID-40 readers
• Camera trigger via digital input or button on HMI
• Three counters: Trigger, Cycles Read, Overruns
• Counter resets via digital input or HMI
• Decoded data displayed on HMI
• Number ID of reader that decoded symbol displayed on HMI
• Cycle timeout congurable on HMI
• Read time displayed on HMI
• Error detection: Timeout, Overrun, Communication fault on EtherNet/IP port
Supported Symbologies
• Linear (1D) barcodes down to 10 mil:
• Ladder (Vertical) or Picket Fence (Horizontal)
• Picket fence width should not exceed 60% of the
diameter; see example of maximum-width picket
fence 1D barcode in the image below.
• Minimum 1D barcode height = 0.5 inches
• 2D barcodes down to 15 mil
• Data Matrix, Code 128, and UPC/EAN enabled
in the supplied WebLink conguration le.
Additional symbologies supported by modifying
the ID-40’s decode setting.
• 5.1 x 3.8 inch (129.5 x 96.5 millimeter) reader FOV
when ID-40s are mounted as described.
• Refer to MicroHAWK ID-40 Specication Sheet
for full list of supported symbologies.
84-9220134-02 Rev A
Maximum Picket
Fence Orientation
Page 2
Technical Note: MicroHAWK ID-40 360º Barcode Reading Solution
TECHNICAL
NOTE
Production Rates
• Solution tested at 100 FPM for high-contrast barcodes.
• Typical read rate: 1 per second.
Software
• SYSMAC Studio, Standard Edition, version 1.23.
• Internet browser to connect the MicroHAWK ID-40 to WebLink.
Hardware
This solution can be implemented on NJ or NX machine controllers. Two example hardware equipment lists are
provided. Conguration 1 uses an NJ301 and Conguration 2 uses an NX1P2.
Conguration 1 – NJ301 Controller
Quantity Part Number Description Version
6 7412-2000-2005 MicroHAWK ID-40, SXGA, HD, Autofocus, WHT, HS, X 1.3.0.3009
6 97-000012-01 Power Supply, 100-240 VAC, +24 VDC, M12 12-Pin Socket
6 61-000163-03 QX Cordset, Host, Ethernet, M12 8-Pin Plug (Screw-On)-to-RJ45, 3 m
6 98-9000054-01 Kit, Mounting, APG, MicroHAWK
1 NJ301-1100 NJ301 Machine Automation Controller 1.16
1 HMC-SD291 2 GB Memory Card
1 NJ-PA3001 NJ Power Supply Unit
1 NX-ECC202 EtherCAT Coupler Unit 1.2
1 NX-ID5142-1 16-Point - DC Input Module 1.0
1 NX-OD4256 8-Point - Transistor Output, DC 1.0
1 S8VK-G12024 NA Power Supply
1 XS5W-T421-EMD-K EtherCAT I/O Cable
1 PFP-50N DIN Track - Length: 0.5 m; Height: 7.3 mm
1 NA5-9W001B 9” NA-HMI Panel
1 E3Z-T81 E3Z Through-Beam, Infrared, Pre-Wired
3 XS6W-6LSZH8SS200CM-Y Cat 6A Ethernet Cable, 2M, Yellow
1 N/A 16-Port 100 Mbps Ethernet Switch
Page 3
Conguration 2 – NX1P2 Controller
Quantity Part Number Description Version
6 7412-2000-2005 MicroHAWK ID-40, SXGA, HD, Autofocus, WHT, HS, X 1.3.0.3009
6 97-000012-01 Power Supply, 100-240 VAC, +24 VDC, M12 12-Pin Socket
6 61-000163-03 QX Cordset, Host, Ethernet, M12 8-Pin Plug (Screw-On)-to-RJ45, 3 m
6 98-9000054-01 Kit, Mounting, APG, MicroHAWK
1 NX1P2-9024DT1
1 HMC-SD291 2 GB Memory Card
1 S8VK-C12024
1 PFP-50N DIN Track - Length: 0.5 m; Height: 7.3 mm
1 NA5-9W001B 9” NA-HMI Panel
1 E3Z-T81 E3Z Through-Beam, Infrared, Pre-Wired
3 XS6W-6LSZH8SS200CM-Y Cat 6A Ethernet cable, 2m, Yellow
1 N/A 16-Port 100 Mbps Ethernet Switch
NX1P2 CPU Unit, 1.5 MB, 32 KB, 4 Single-Axis Position Control, 14
Discrete Input Points, 10 Discrete Output Points (PNP)
Single Phase Power Supply, Universal Input (100 to 240 VAC), 120 W
Output (24 VDC @ 5 A)
1.18
Conguration Files
• SYSMAC Project le to import for Conguration 1: “6_ID40_NJ301_EIP_with_HMI_revD.smc2”
• SYSMAC Project le to import for Conguration 2: “6_ID40_NX1P2_EIP_with_HMI_revD.smc2”
• WebLink 1.3.0 Conguration le: “360_code_ID40_settings.wls”
Page 4
Technical Note: MicroHAWK ID-40 360º Barcode Reading Solution
TECHNICAL
NOTE
MicroHAWK ID-40 Setup
MicroHAWK ID-40 Hardware Mounting
1 MicroHAWK ID-40 Hardware Mounting
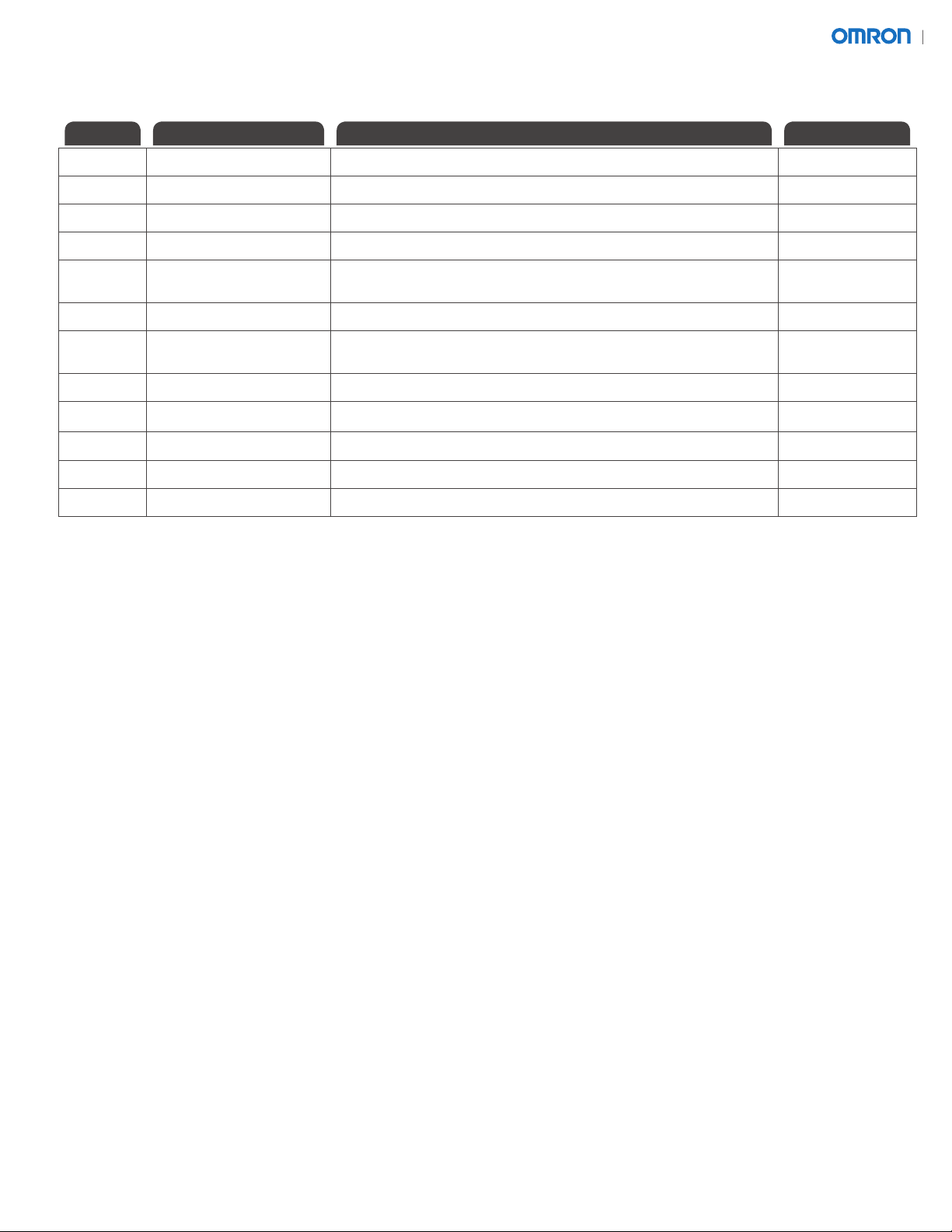
1.1 Install ID-40 readers as shown in the le “ID-40 360 read cam placement.dwg”. The basic layout is shown
below. The cameras are mounted 245 mm from the center point of the code read position. The
camera pitch (angle) should be perpendicular to the surface containing the barcode, within
+/- 5 degrees.
NOTE: The installer will need to determine the best trigger position based on the type of product to be
read on the conveyor. The current trigger position is based on a 67 mm diameter cylindrical object.
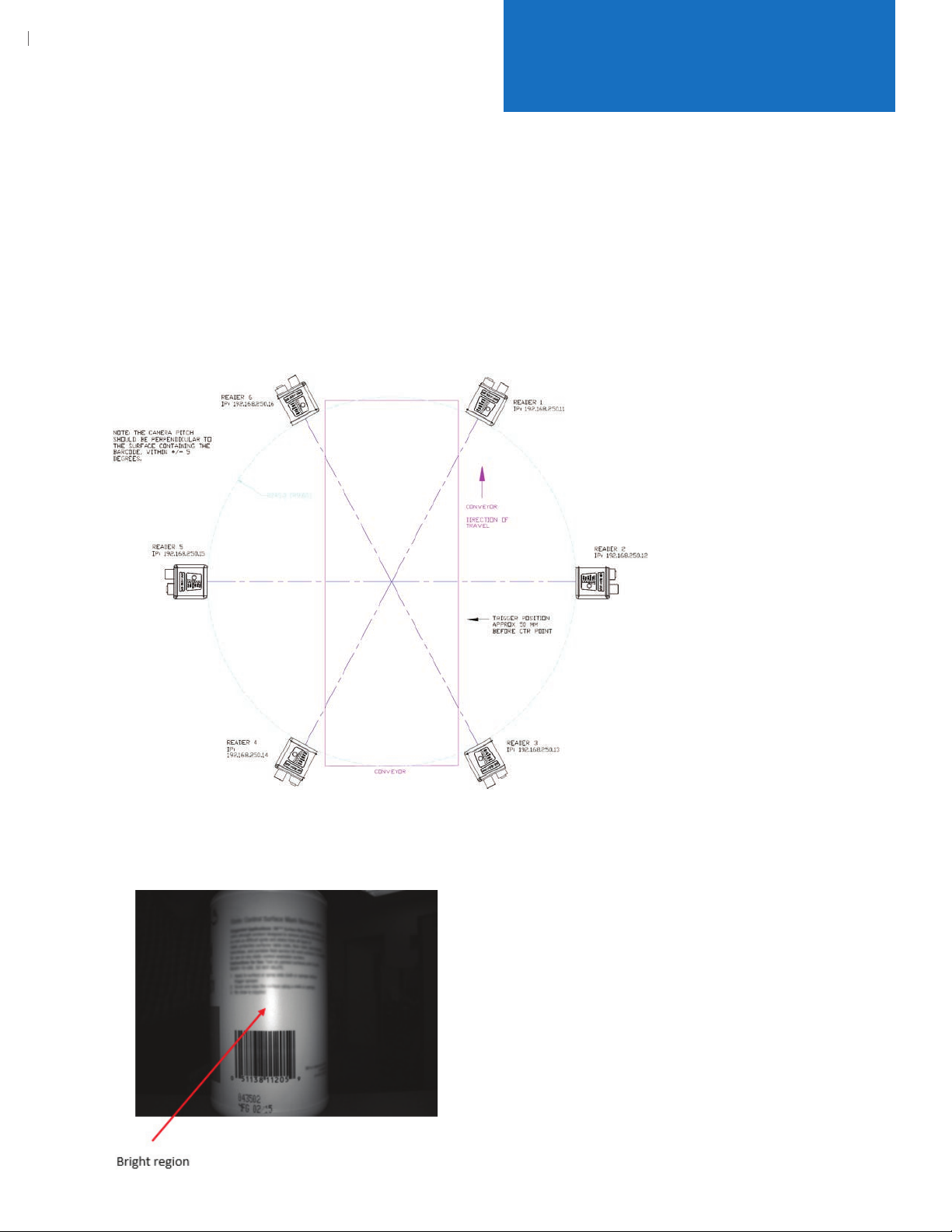
1.2 The ID-40 reader height should be adjusted so that the horizontal linear barcodes (picket fence
orientation) are typically above or below the bright reection of the reader’s illumination. The
image below shows an example in which the barcode is below the bright reection region.
Page 5
MicroHAWK ID-40 Conguration
2 MicroHAWK ID-40 Conguration
2.1 Connect the power and Ethernet cables to ONLY ID-40 reader 1.
2.2. Using an internet browser type the IP address of the camera. (The factory default IP address is
192.168.188.2. If necessary, change the PC's IP address to 192.168.188.101, subnet 255.255.0.0, to be
on the same subnet.) This will allow you to use WebLink to congure the ID-40.
2.3. Use WebLink to congure the ID-40 for your application. Select Start > Load a Setup and load the le
“360_code_ID40_settings.wls” to load most of the desired parameters to the ID-40. Some of the
important parameters are:
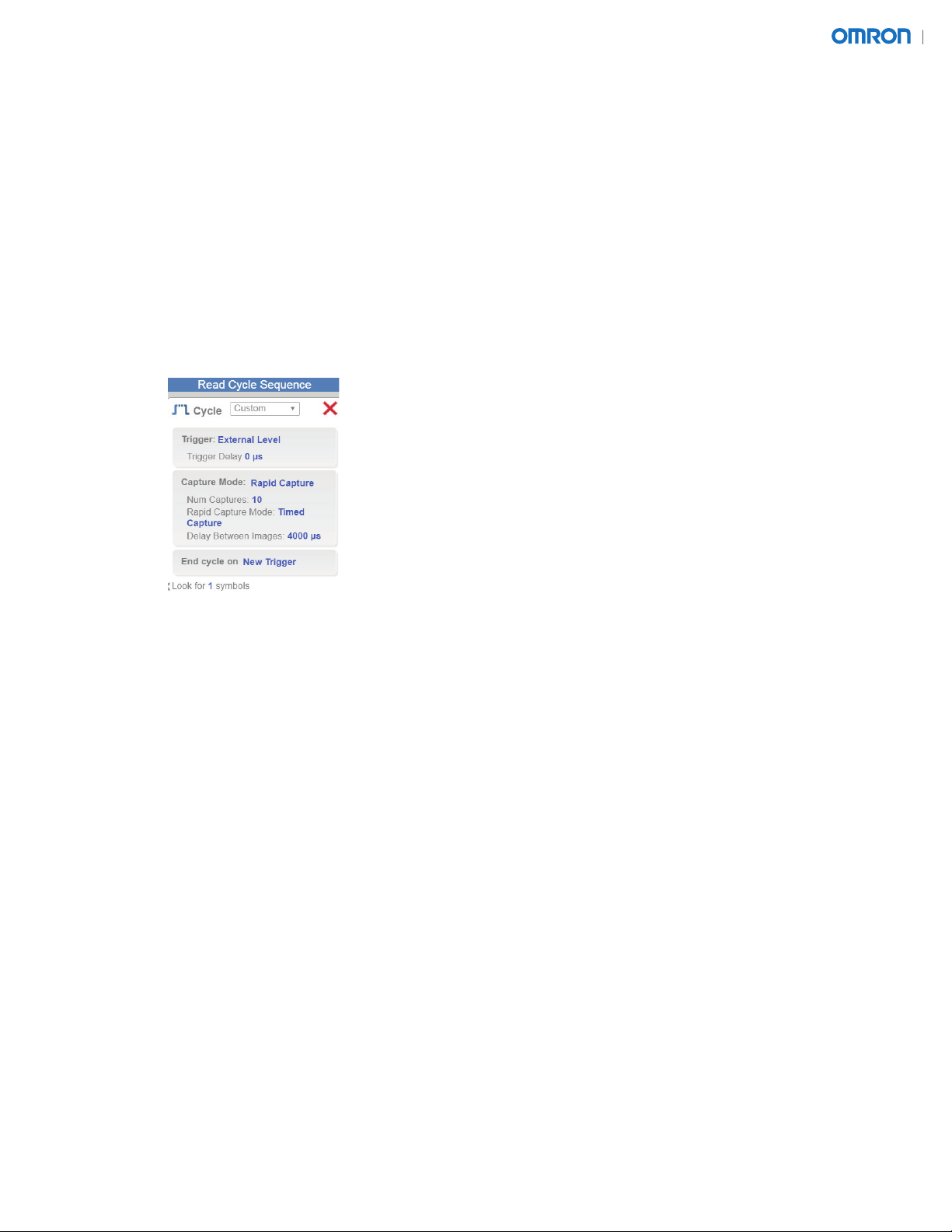
2.3.1. Read Cycle = Custom
2.3.1.1. Trigger = External Level
• External Level allows EIP trigger to control start and stop of read.
2.3.1.2. Capture Mode = Rapid Capture
2.3.1.3. Num Captures = 10
2.3.1.4. Rapid Capture Mode = Timed Capture
2.3.1.5. Delay Between Images = 4000 µs
• For parts moving at 100 FPM.
• Delay should be increased on slower moving conveyors or when Num Captures is reduced.
2.3.1.6. End cycle = New Trigger
2.3.2. Acquire
2.3.2.1. Set parameters to have focused image and freeze part movement.
2.3.2.2. Set Exposure to 1,000 µs or less to use Power Strobe (Extreme Illumination Brightness).
2.3.2.3. Learn best focus using the Spot Focus button (See the MicroHAWK ID User Manual for additional
information.)
2.3.3. Decode
2.3.3.1. Select barcode types to be read in this application. Disable unused barcode types.
Page 6
Technical Note: MicroHAWK ID-40 360º Barcode Reading Solution
2.3.4. Gear icon > Advanced > Camera Setup
2.3.4.1. Illumination Brightness = Extreme (Power Strobe)
2.3.5. Gear icon > Advanced > Read Cycle
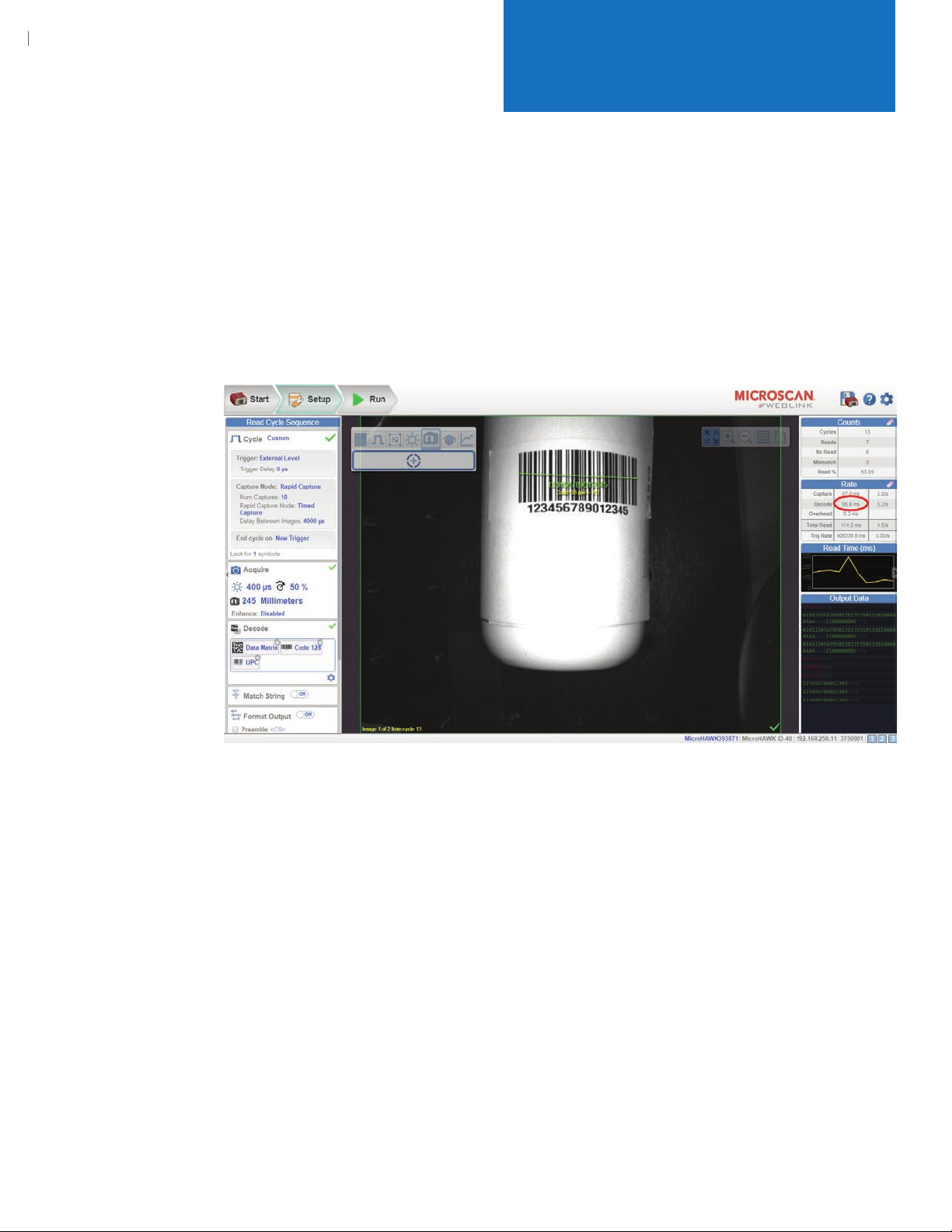
2.3.5.1. Image Processing Timeout = 150 ms
• This setting sets a limit on how long the MicroHAWK ID-40 will attempt to read the
barcode in the current image. You will need to determine the decode time for a good
read (circled in the image below) and then set this value to slightly higher. Ideally, this
time should be set as low as possible so that an unreadable image will stop
reading quickly and start processing the next image in the Rapid Capture queue.
TECHNICAL
NOTE
2.4. Click the Save button to save the changes to the reader.
2.5. Conrm that the ID-40 is reading.
2.5.1. Change Trigger to External Edge.
2.5.2. Click the Trigger button and conrm that the barcode is decodable.
2.5.3. When testing is nished, change Trigger to External Level.
2.6. Change the ID-40's IP address.
Page 7
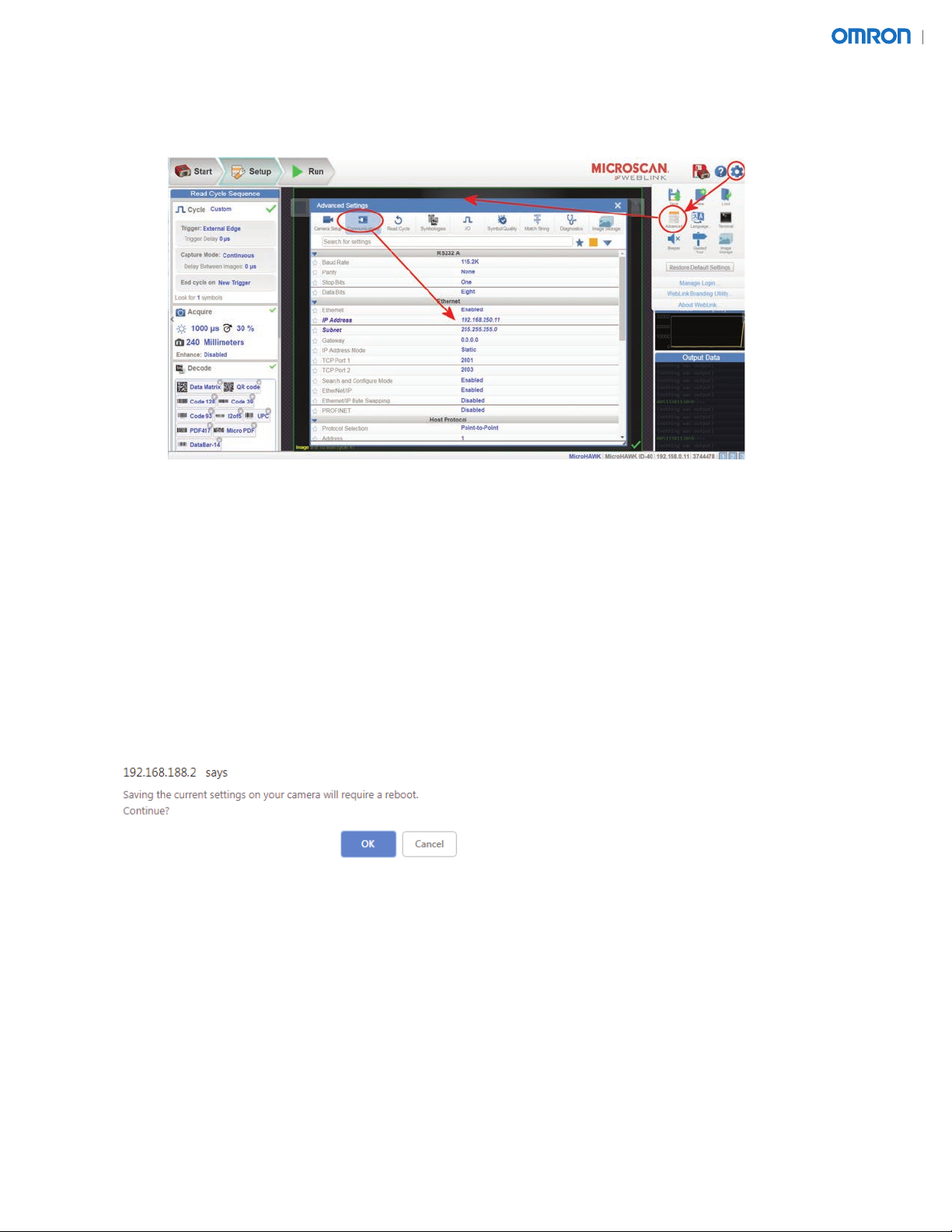
2.6.1. Click the gear icon > Advanced > Communications as shown below.
2.6.2. Set the IP addresses and subnets to the values listed below:
• Reader 1 = 192.168.250.11, subnet 255.255.255.0
• Reader 2 = 192.168.250.12, subnet 255.255.255.0
• Reader 3 = 192.168.250.13, subnet 255.255.255.0
• Reader 4 = 192.168.250.14, subnet 255.255.255.0
• Reader 5 = 192.168.250.15, subnet 255.255.255.0
• Reader 6 = 192.168.250.16, subnet 255.255.255.0
2.7. Click the Save button to save the changes to the reader. You should receive a warning stating, “Saving
the current settings on your camera will require a reboot. Continue?” Click "OK".
2.8. Repeat steps 2.1 to 2.7 for Readers 2 through 6.
2.9. Change the PC's IP address to 192.168.250.101, subnet 255.255.255.0.
2.10. Disconnect power to all the ID-40 readers and wait 10 seconds.
2.11. Connect the ID-40 reader's Ethernet cables to the Ethernet switch.
2.12. Re-connect power to the ID-40 readers. Wait 30 seconds for the readers to boot.
2.13. Using your PC's internet browser, type the IP address for reader 1 and make sure the PC connects
to WebLink.
2.14. Save the reader’s settings to a le. Click the gear icon > Advanced > Save.
2.15. Repeat steps 2.13 and 2.14 for all remaining ID-40 readers.
7
Page 8
Technical Note: MicroHAWK ID-40 360
º
Barcode Reading Solution
TECHNICAL
NOTE
MicroHAWK ID-40 EDS File Download
3. ID-40 EDS File
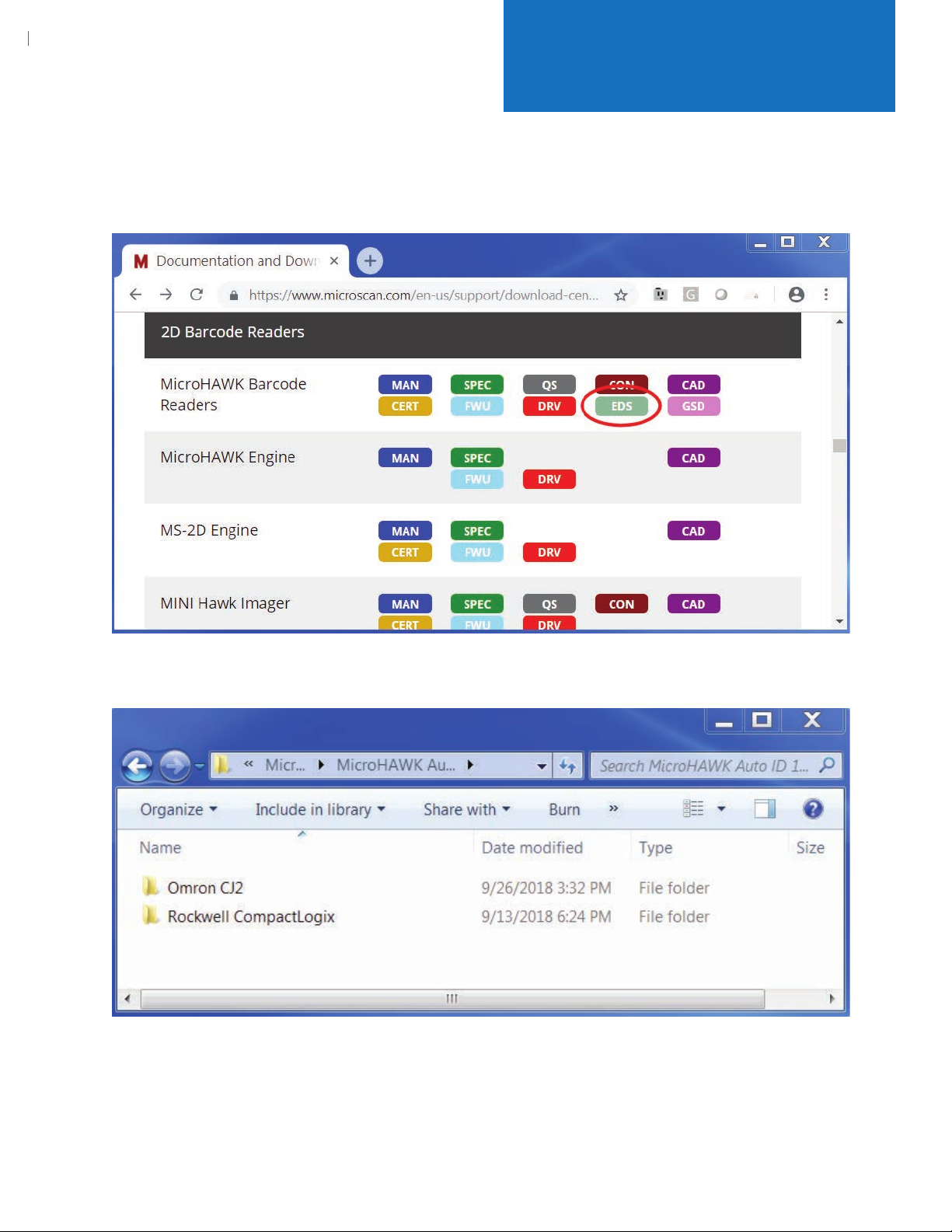
3.1. Download the MicroHAWK Barcode Reader EDS le from the Omron Microscan download center,
as shown below. (
ID%201.2%20EtherNetIP.zip.)
https://les.microscan.com/downloadcenter/MicroHAWK%20Auto%20
3.2. Extract the le “MicroHAWK Auto ID 1.2 EtherNetIP.zip” to your hard drive at “C:\MicroHAWK Auto ID 1.2
EtherNetIP”. These les will be used later.
8
Page 9

NJ/NX Controller Setup
NJ/NX Controller and NA HMI Panel Connections
4.1. For conguration 1, on the NX-ECC202, change the ADR x10 rotary switch to 7 and the x1 rotary switch to
0 as shown below.
4.2. For conguration 1, conrm that the EtherCAT cable is connected to port 2 (EtherCAT) on the NJ
controller and that the other end is connected to NX-ECC202 IN (top) port shown in the image
above. Refer to the NX-ECC202 user manual for more information.
4.3. Wire +24 VDC and 0 VDC to the NX-ECC202 unit (conguration 1) or the NX1P2 (conguration 2). Refer
to the NX-ECC202 User Manual for more information about conguration 1. Refer to the NX1P2 CPU Unit
Hardware User Manual for more information about conguration 2.
4.4. Conrm that the NJ/NX Ethernet cable is connected to port 1 on the controller and the other end is
connected to the Ethernet switch.
4.5. Conrm that the NA HMI Panel Ethernet cable is connected to port 1 on the panel and the other end of
the Ethernet cable is connected to the Ethernet switch.
4.6. Mount the sensor emitter and receiver units on opposite sides of the conveyor at the location indicated
in section 1 of this document, titled "MicroHAWK ID-40 Hardware Mounting". The emitter and receiver
units must point at each other.
4.7. For the sensor emitter and receiver, connect the brown wire to + 24 VDC, and connect the blue wire to
0 VDC.
4.8. Conrm that the sensor output (black wire) is connected to input bit 00 of the input module
(conguration 1) or the NX1P2 controller (conguration 2).
4.9. Connect the input common, labeled COM on the NX-ID5142-1 (conguration 1) or on the NX1P2
(conguration 2), to 0 VDC.
9
Page 10

Technical Note: MicroHAWK ID-40 360
º
Barcode Reading Solution
TECHNICAL
NOTE
4.10. Apply power to the power supplies powering the NJ/NX controller and NA HMI Panel.
4.11. Wait approximately 30 seconds for these components to fully power up.
4.12. At this point all components should be powered and connected to the Ethernet switch. Conrm that
network activity is seen from the NJ/NX controller, the NA HMI Panel, and the six ID-40 readers.
4.13. Conrm that the sensor signal is seen by the input module. If an object is moved slowly through the
sensor path, the input bit 00 indicator should toggle on and o. The image on the left below shows
input bit 00 = TRUE (ON) for the NX-ID5142-1 (NJ controller – conguration 1) and the image on the right
shows input bit 00 = TRUE (ON) for the NX1P2 (conguration 2).
Import Project into SYSMAC Studio
5. Import Project into SYSMAC Studio
5.1. At the SYSMAC Studio start page, select Import… as shown below.
5.2. Select the SYSMAC import le that matches the hardware conguration provided in the
Job_Files folder, shown below. For an NJ controller (conguration 1), select the le, “6_ID40_NJ301_
EIP_with_HMI_revC.smc2”. For an NX1P2 (conguration 2) select the le, “6_ID40_NX1P2_EIP_with_HMI_
revC.smc2”. Once the appropriate le is selected, click "Open".
10
Page 11
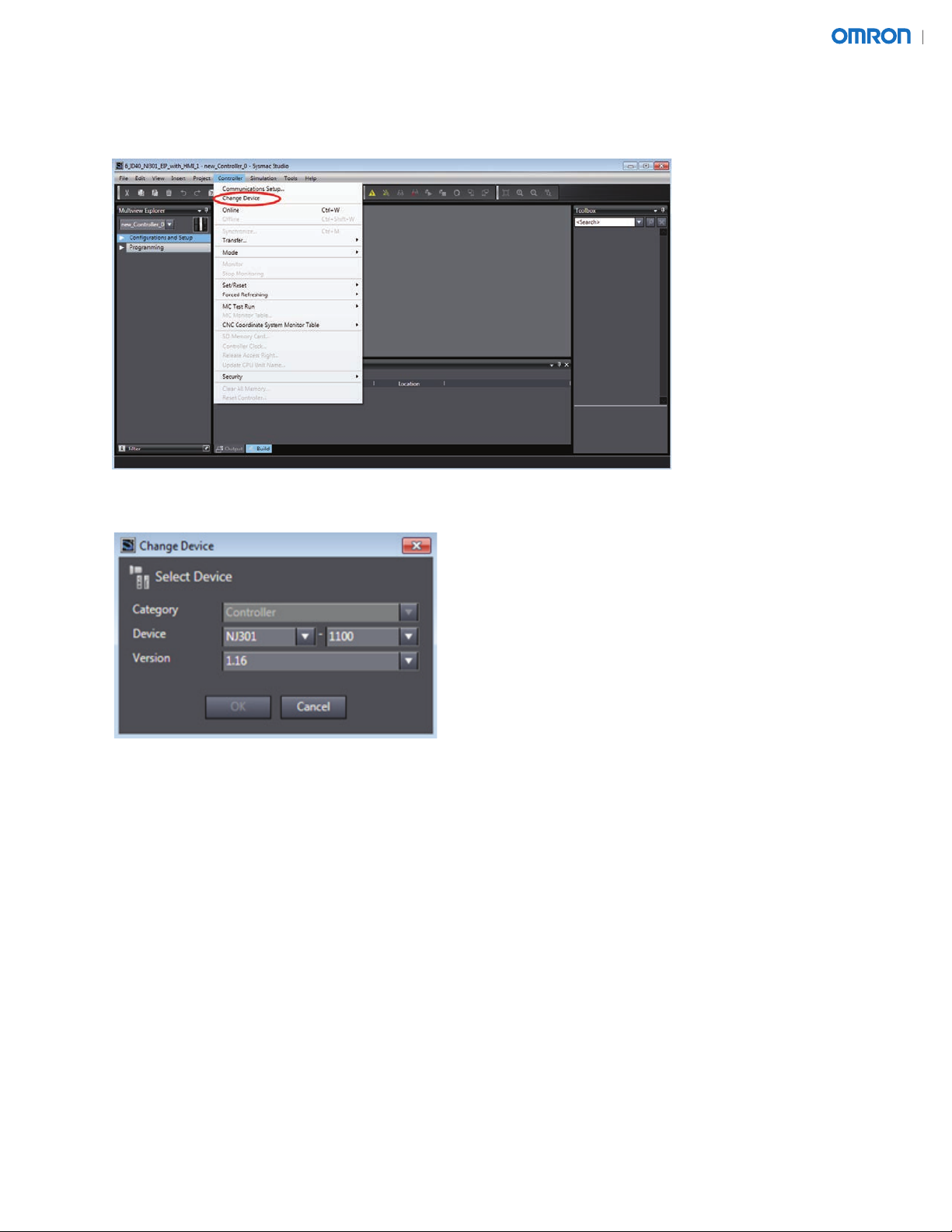
5.3. Once the project loads, select the Controller menu and click "Change Device", as shown below.
5.4. In the Change Device window shown above, modify the Device and Version selections to match the
controller that is currently used.
Establish NJ/NX Communications with PC
The default IP address for NJ/NX port 1 (EtherNet/IP) is 192.168.250.1, subnet 255.255.255.0. On some Omron
controllers, such as the NX1P2 (conguration 2), these units can only communicate via a built-in EtherNet/IP port.
On NJ and NX7 controllers (conguration 1), these units can communicate using a direct connection via USB.
This permits the user to establish an online connection with the controller, modify the built-in EtherNet/IP port
settings, and download these settings to the controller. Once the new settings are downloaded, the Omron
controller will use the new IP address. The procedure to establish a connection via USB is provided as a reference
on the following page.
11
Page 12
Technical Note: MicroHAWK ID-40 360
º
Barcode Reading Solution
TECHNICAL
NOTE
Omron NJ Controller Direct USB Connection
This type of connection can be used for modications to NJ/NX settings (such as the IP Address) or changes to
logic, but for full conguration and testing of EtherNet/IP, use the Ethernet connection described in step 7 of the
section "Omron NJ/NX Controller Ethernet Connection via a Hub".
6. NJ Direct USB Connection
6.1. Connect a USB cable from a PC to the PLC’s USB port.
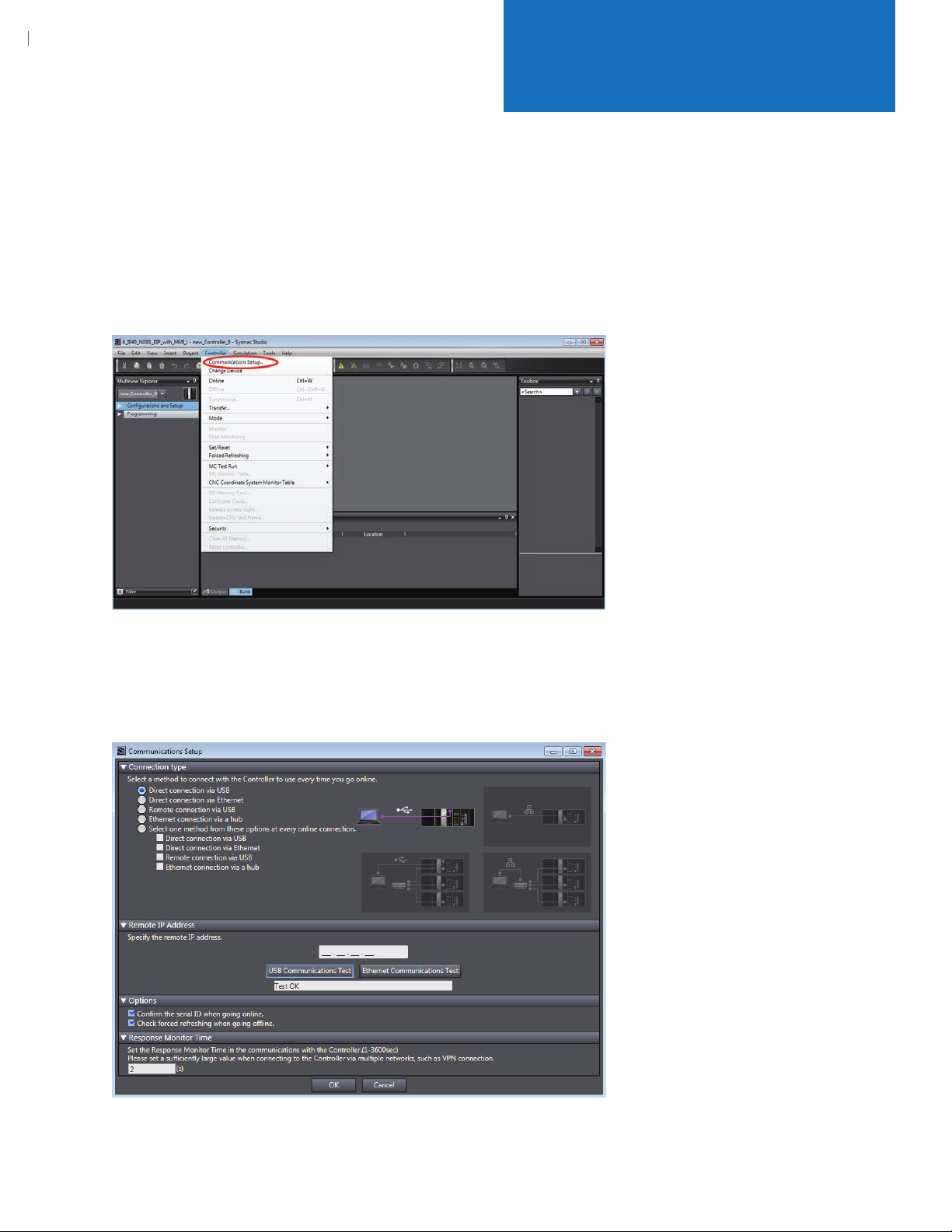
6.2. Click Controller menu > Communications Setup as shown below.
6.3. Click the "Direct Connection via USB" button as shown below.
6.4. Click "USB Communication Test".
6.5. Be sure “Test OK” shows in the white bar as shown below. This indicates that you have good
communications with the Omron controller.
6.6. Click "OK" when ready.
12
Page 13

Omron NJ/NX Controller Ethernet Connection via a Hub
7. Omron NJ/NX Controller Ethernet Connection via a Hub
7.1. Click Controller menu > Communications Setup as shown on page 14.
7.2. Click the "Ethernet Connection via a Hub" button as shown below.
7.3. Enter the IP address of the NJ/NX controller. The default address for an NJ/NX controller is 192.168.250.1.
7.4. Click "Ethernet Communication Test".
7.5. Be sure “Test OK” shows in the white bar as shown above. This indicates that you have good
communications with the Omron controller.
7.6. Click "OK" when ready.
13
Page 14

Technical Note: MicroHAWK ID-40 360
º
Barcode Reading Solution
TECHNICAL
NOTE
Modify NJ/NX Controller IP Address
8. Modify NJ/NX Controller IP Address
8.1. In the Multiview Explorer, expand “Congurations and Setup”, expand the “Controller Setup”, and
double-click “Built-in EtherNet/IP Port Settings”. The IP address will be shown for the current project,
as shown below.
8.2. Change the controller to the desired IP address. Be sure that the controller IP address is on the same
subnet as the ID-40 readers.
8.3. The controller IP address will not be changed until SYSMAC Studio goes online with the controller and
the project is synchronized (downloaded). The project download will be covered in the upcoming
section, Download Project to Controller.
ID-40 EtherNet/IP Data in NJ/NX Controller
Storing ID-40 EtherNet/IP Data in NJ/NX Controller
To establish communications between an EtherNet/IP device and the controller, a global variable needs to be
created to store the data in the ID-40 EtherNet/IP Input and Output assemblies. A custom data type formats the
data into smaller logical groups to make the data easier to use.
There are no user tasks in the following two sections, "Custom Data Types" and "Global Variables", as these items
are already included in the project. These sections are included to provide conceptual information you can apply
to other projects using EtherNet/IP to communicate with ID-40 readers.
Custom Data Types
9. Custom Data Types
9.1. To see the Custom Data Types in the Multiview Explorer, expand Programming, expand Data, and
double-click "Data Types".
14
Page 15

9.2. Two data types are created in this application. The data type for the Input Assembly 103 is called “s_ID40_
Input_type_103” and is shown below.
9.3. The data type for the Output Assembly 197 is called “s_ID40_Output_type_197” and is shown below.
Note that when creating these data types, the Oset Type must be changed to “User”.
15
Page 16

Technical Note: MicroHAWK ID-40 360
º
Barcode Reading Solution
TECHNICAL
NOTE
Global Variables
10. Global Variables
10.1. To see the Global Variables in the Multiview Explorer, expand Programming, expand Data, and
double-click "Global Variables". NOTE: Important Global Variables are identied in Appendix B.
10.2. In this application there are a total of 12 global variables used for ID-40 EtherNet/IP
communications. Six global variables, highlighted in blue in the image below, are used to store each
ID-40 input assembly. Each global variable used to store an EtherNet/IP input assembly must have
Network Publish set to Input.
10.3. Six global variables, highlighted in yellow in the image above, are used to store each ID-40 output
assembly. Each global variable used to store an EtherNet/IP output assembly must have Network Publish
set to Output.
10.4. Once the global variables to be used for EtherNet/IP communications have been created, the project
must be downloaded to the NJ/NX controller.
Download Project to Controller
Before starting this process, SYSMAC Studio should be congured to communicate using Ethernet connection
via hub. If this has not been completed, follow steps starting at 7.1, found in the section "Omron NJ/NX
Controller Ethernet Connection via a Hub".
11. Download Project to Controller
11.1. Click the "Online" button, shown below. The project's serial ID will most likely not match the
serial ID of the PLC. Click "Yes" to acknowledge the dierence and proceed.
16
Page 17

11.2. SYSMAC Studio may display a warning message if the NJ/NX does not have a name. If you see the
warning shown below, click "Yes".
11.3. Once online, a yellow line will be drawn under the toolbar. Click the "Synchronize" button, which is
identied below.
11.4. The controller synchronization page will then be displayed. Verify that the checked options match the
settings shown below. Click "Transfer to Controller", circled in red, to download the current project to
the controller.
11.5. SYSMAC Studio may display the message seen below if you are using EtherCAT devices as in the
NJ301 project le. Click "Yes" to continue the transfer.
17
Page 18

Technical Note: MicroHAWK ID-40 360
º
Barcode Reading Solution
TECHNICAL
NOTE
11.6. SYSMAC Studio may display the message seen below if it is currently in Run Mode. Click "Yes" to
continue the transfer.
11.7. The transfer may take up to 1 minute. Once synchronization is completed, you will see the
Synchronization window. Click "Close".
11.7.1. After changing the IP address of the NJ/NX controller, SYSMAC Studio may not be able to
communicate with the controller and you may need to wait for SYSMAC Studio to respond.
Go to the section "Omron NJ/NX Controller Ethernet Connection via a Hub" to re-establish
the network connection with the controller.
Congure EtherNet/IP Devices into SYSMAC Studio
Import ID-40 EDS File
12. Import ID-40 EDS le
12.1. In the Tools menu, click "EtherNet/IP Connection Settings" as shown below.
12.2. This opens the EtherNet/IP Device List. Right-click the "Node Address" of the PLC and select "Edit" as
shown below.
18
Page 19

12.3. In the Toolbox, right-click below "Target Device" and select "Display EDS Library" as shown below.
12.4. Click "Install" In the EDS Library window, shown below.
12.5. In the Install EDS File window, go to the “C:\ MicroHAWK Auto ID 1.2 EtherNetIP\Omron CJ2\eds” folder
and select the le “MicroHAWK_(35-9000034-11).eds”, as shown below. Click "Open" to load this EDS le.
12.6. You should see that a new item has been added to the EDS Library window called Microscan Systems,
Inc., as indicated by the arrow in the image below. This indicates that the MicroHAWK ID-40 EDS le has
been added to SYSMAC Studio. Click "Close".
19
Page 20

Technical Note: MicroHAWK ID-40 360
º
Barcode Reading Solution
TECHNICAL
NOTE
Add ID-40s as EtherNet/IP Devices
13. Add ID-40s as EtherNet/IP Devices
13.1. In the Toolbox, click the + button to add the ID-40s as EtherNet/IP devices, as shown below.
13.2. Enter the IP address for the rst ID-40, which in this example is 192.168.250.11. Click the "Model name"
dropdown menu and select MicroHAWK ID-40. In the Revision dropdown select 1. When completed it
should resemble the image below. Click the + button, which is found at the bottom of the Toolbox dialog.
20
Page 21

13.3. A new target device should be displayed in the Toolbox with the IP address of the reader that was just
entered.
13.4. Repeat steps 13.1 through 13.3 for the remaining ID-40 readers. Their IP addresses are listed below.
• 192.168.250.12
• 192.168.250.13
• 192.168.250.14
• 192.168.250.15
• 192.168.250.16
13.5. The Toolbox should now list all six ID-40 readers as shown below.
13.6. In the main window of SYSMAC Studio, click the "Tag Set" button, circled in the image below, and click
"Registration All" to register the ID-40 EtherNet/IP global variables.
21
Page 22

Technical Note: MicroHAWK ID-40 360
º
Barcode Reading Solution
TECHNICAL
NOTE
13.7. In the Tag Set Registration Setting window, conrm all ID-40 input and output tags are checked and click
"Register", as shown below.
13.8. Click the "Connection" button, which is circled below. Click the + button to add the rst EtherNet/IP
device (ID-40).
13.9. Click the "Target Device" dropdown eld and select the rst ID-40 reader, as shown below.
22
Page 23

13.10. Click the "Input Target Variable" (rst line), which denes the input assembly used in the EDS le, and type
103. This eld is circled in red below. Select the Originator Variable, circled in yellow, and select
ID40_Input01 in the dropdown eld. In the RPI eld, circled in green, change this value to 20.0. Note that
the RPI for the ID-40 cannot be set to an amount less than 10 ms.
13.11. Click the "Output Target Variable" (second line), which denes the output assembly used in the EDS le,
and type 197. This eld is circled in red below. Select the Originator Variable, circled in yellow, and select
ID40_Output01 in the dropdown eld.
13.12. Repeat steps 13.8 through 13.11 for the remaining ID-40 readers. When completed, your list should
appear similar to the example below.
23
Page 24

Technical Note: MicroHAWK ID-40 360
º
Barcode Reading Solution
TECHNICAL
NOTE
Transfer EtherNet/IP Conguration to NJ/NX Controller
14. Check EtherNet/IP Communications
14.1. Ensure that SYSMAC Studio is online with the controller by verifying that there is an orange line under
the toolbar. If necessary, click the "Online" button, which is identied by a red circle in the image below.
14.2. With SYSMAC Studio online, click "Transfer to Controller" as shown below.
14.3. Click "Yes" to complete the Transfer as seen below on the left. If the controller is in Run mode, you will see
the window shown below on the right. Click "Execute the Transfer to Controller operation in RUN mode".
24
Page 25

Check EtherNet/IP Communications in SYSMAC Studio
15. Check EtherNet/IP Communications in SYSMAC Studio
15.1. Click the "EtherNet/IP Device List" tab. If this tab is not present, go to the Tools menu and select
"EtherNet/IP Connection Settings". Right-click the controller IP address and select "Monitor" as shown below.
15.2. Click the "Connection Status" tab. Each connection will be listed and there should be a blue dot to the
right of each connection as shown below. In addition, the status eld should be 00:0000.
This indicates that EtherNet/IP communication has been established with that device.
NOTE: SYSMAC Studio must be Online with the controller to show EtherNet/IP connection status.
15.3. One common type of failure is displayed in the example below. In this example, the device with the IP
address 192.168.250.13 has a problem. This status code is 01:0204, but another common error code is
01:0203. Some items to check to resolve this problem:
• Verify that the ID-40 is powered.
• Verify that the ID-40 Ethernet cable is connected to the Ethernet switch.
• Verify that the ID-40 Ethernet cable is fully screwed into the camera.
• Verify that the IP address shown in SYSMAC Studio matches the ID-40.
25
Page 26

Technical Note: MicroHAWK ID-40 360
º
Barcode Reading Solution
TECHNICAL
NOTE
15.4. Once the issue has been corrected, it may take up to a minute for the Connection Status to update in
SYSMAC Studio.
15.5. Once all the connections are established as shown below, the project should be saved by going to the
File menu and selecting Save As and typing the project name.
15.6. The NJ/NX controller setup is completed.
NA-HMI Panel Setup
NA-HMI Panel Not Present
If your integration of this solution does not include a NA-HMI panel, then the remaining sections of the HA-HMI
panel setup can be skipped.
Establish NA-HMI Panel Communications
16. Establish NA-HMI Panel Communications
16.1. In the current open project, under the words “Multiview Explorer”, click the controller dropdown eld
and select HMI_NA5_0 as shown below.
16.2. Open the HMI menu and select Change Device as shown below.
26
Page 27

16.3. Change the Device and Version elds, shown below, to match the HMI panel that you are currently
using.
16.4. Open the HMI menu and select Communications Setup as shown below.
16.5. Click the Ethernet connection via a hub button as shown below.
16.6. In the Specify IP Address eld, enter the IP address for the NA-HMI panel. The default address for an
NA-HMI panel, port 1, is: 192.168.250.2.
16.7. Click "Test".
16.8. Be sure “Test OK” shows in the white bar as shown below. This will indicate you have good
communications with the Omron controller.
16.9. Click "OK" when ready.
27
Page 28

Technical Note: MicroHAWK ID-40 360
º
Barcode Reading Solution
TECHNICAL
NOTE
Modify NA-HMI Panel IP Address
17. NA-HMI Panel Download
17.1. In the Multiview Explorer, expand “Conguration and Setup” and double-click “HMI Settings”. Click
the “TCP/IP” button, circled below, to view the IP Address for Ethernet Port 1 on the NA-HMI panel.
17.2. Change the NA-HMI panel to the desired IP Address. Ensure that the IP address is on the same subnet as
the NJ/NX controller.
28
Page 29

Download the Project to the NA-HMI Panel
18. Download the Project to the NA-HMI Panel
18.1. Click the "Online" button, which is identied in the image below.
• If this is the rst time that you have used the NA-HMI panel, the rmware may need to be
updated. Please go to https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ETNHvv9KZ38 for a video showing
the rmware update process.
• You may see a warning that that the HMI device has no name. Click “Yes” to continue.
18.2. Once online with the NA-HMI panel, a yellow line will appear under the toolbar. Click the "Synchronize"
button, which is identied in the image below.
18.3. The synchronization page will be displayed as shown below. Verify that the "Store the HMI" option is
checked and click "Transfer to Device".
29
Page 30

Technical Note: MicroHAWK ID-40 360
º
Barcode Reading Solution
TECHNICAL
NOTE
18.4. The example below shows the synchronization page once it is completed. Click "Close".
HMI User Interface
At this point the user interface, shown below, is now visible on the NA-HMI panel.
30
Page 31

Finishing Solution Installation
Optimizing the Trigger Position
For the fastest read times, the trigger position should be adjusted so that the barcode is read on either the rst or
second image capture regardless of barcode orientation.
19. Optimizing the Trigger Position
19.1. On your PC, open an internet browser and type the IP address of the reader to monitor with WebLink.
In the example below, the IP address 192.168.250.11 is used to monitor reader 1.
19.2. In the WebLink display area, click the button circled in the image above so that it is highlighted blue. This
enables Show All Images Used in Read Cycle. The image in the upper left will be the rst image captured
and the last image will be the rightmost image on the bottom row. The image with the green graphics
over the barcode is the image in which the symbol was decoded.
19.3. Adjust the trigger position so that the barcode is most often read on image 1 or 2 for every reader.
This will produce the shortest decode times.
Optimize Image Capture Delay
It is important to conrm that the image capture delay is set so that the barcode has the greatest chance of
being decoded as it passes the readers. WebLink can be congured to view all images captured during the read
cycle. If the product movement between images needs adjusting, then the ID-40’s image capture delay will
need to be modied.
20. Optimize Image Capture Delay
20.1. On your PC, open an internet browser and type in the IP address of the reader to monitor with WebLink.
In the image above, the IP address 192.168.250.11 is used to monitor reader 1.
31
Page 32

Technical Note: MicroHAWK ID-40 360
º
Barcode Reading Solution
TECHNICAL
NOTE
20.2. In the WebLink display area, click the button circled in the image above so that it is highlighted blue. This
enables Show All Images Used in Read Cycle. The image in the upper left will be the rst image captured
and the last image will be the rightmost image on the bottom row. The image with the green graphics
over the barcode is the image in which the symbol was decoded.
20.3. Run a product without a barcode past the readers so that all images in the read cycle can be displayed.
Ensure that the product moves from one side of the image to the opposite side for best performance, as
shown in the example below.
20.4. If the product has completely moved beyond the image in the last image captured, reduce the Delay
Between Images to a shorter time.
20.5. If the product did not move enough, increase the Delay Between Images to a longer time.
20.6. Once the image capture delay has been set correctly, click the Save button to save changes to
the reader.
20.7. Repeat steps 20.1 through 20.6 for all ID-40 readers.
32
Page 33

Set Read Timeout
The Read Timeout is the maximum time allowed for the decode. The NJ/NX controller project has the Read
Timeout set to 2,000 milliseconds by default. This default value is dened by the value entered in the Initial Value
eld for the HMI_ReadTimeout variable. This variable can be changed at runtime by the operator using the HMI
user interface. To aid in the setting of this variable, the last read time is accessible by monitoring the ReadTime
variable via the HMI or watching this value in SYSMAC Studio.
Set Read Timeout using the HMI
21. Set Read Timeout using the HMI
21.1. Run products with barcodes past the readers at production rates.
21.2. Watch the Read Time value on the HMI and note the longest read time that was reported. In the image
below, the last decode had a read time of 860 milliseconds.
21.3. Tap the Read Timeout numeric value and an on-screen keypad will be displayed as shown below.
Enter a value higher than the longest read time and press Enter. This value will be used until modied by
the user or a power cycle occurs. On a power cycle the Read Cycle will return to the value in the
Initial Value eld in SYSMAC Studio.
33
Page 34

Technical Note: MicroHAWK ID-40 360
º
Barcode Reading Solution
TECHNICAL
NOTE
Change the Default Read Timeout
22. Change the Default Read Timeout
22.1. Open the Global Variable page in SYSMAC Studio. See step 10.1 in the section Global Variables.
22.2. Set the initial value eld of the variable ReadTime to the desired timeout in milliseconds.
22.3. Go online to the NJ/NX controller and Synchronize the project. Follow the instructions starting at 11.1 in
the section Download Project to Controller.
34
Page 35

Appendix A
Known Issues
23. Known Issues
23.1. The Min_OnTime (TOF) timer is used to extend short duration trigger signals to ensure that the ID-40
readers can have their EtherNet/IP triggers forced low (to stop the previous read if still reading), receive
the acknowledgement that the units are no longer triggered, and then trigger the readers for the
new cycle. This requires that the trigger be on for at least 3 times the RPI, which, in this project, is 20
milliseconds, for a total time of 60 milliseconds.
23.2. If the Min_OnTime timer is still executing the 60 millisecond timer and another trigger is received the
new trigger is ignored. Once the 60 millisecond timer has expired a new trigger will be processed.
23.3. All ID-40s must have their trigger set to External Level and the end cycle set to New Trigger for the NJ/NX
controller logic to function correctly.
23.4. On the rst trigger after the project is downloaded to the NJ/NX controller, the ReadTime variable will be
reported as 20,000. On subsequent triggers, the ReadTime variable will report the correct Trigger
to Result time in milliseconds.
35
Page 36

Technical Note: MicroHAWK ID-40 360
º
Barcode Reading Solution
Appendix B
Important Global Variables
Global Variable Data Type Used For Notes
ID40_Input01 S_ID40_Input_type_103 EtherNet/IP ID-40 Reader 1
ID40_Input02 S_ID40_Input_type_103 EtherNet/IP ID-40 Reader 2
ID40_Input03 S_ID40_Input_type_103 EtherNet/IP ID-40 Reader 3
ID40_Input04 S_ID40_Input_type_103 EtherNet/IP ID-40 Reader 4
ID40_Input05 S_ID40_Input_type_103 EtherNet/IP ID-40 Reader 5
ID40_Input06 S_ID40_Input_type_103 EtherNet/IP ID-40 Reader 6
ID40_Output01 S_ID40_Output_type_197 EtherNet/IP ID-40 Reader 1
ID40_Output02 S_ID40_Output_type_197 EtherNet/IP ID-40 Reader 2
ID40_Output03 S_ID40_Output_type_197 EtherNet/IP ID-40 Reader 3
ID40_Output04 S_ID40_Output_type_197 EtherNet/IP ID-40 Reader 4
TECHNICAL
NOTE
ID40_Output05 S_ID40_Output_type_197 EtherNet/IP ID-40 Reader 5
ID40_Output06 S_ID40_Output_type_197 EtherNet/IP ID-40 Reader 6
Input_Bit_00 BOOL Map to Digital Input Bit 00 Trigger Read
Input_Bit_01 BOOL Map to Digital Input Bit 01
Output_Bit_00 BOOL Map to Digital Output Bit 00 Data Valid
Output_Bit_04 BOOL Map to Digital Output Bit 04 Decode Status (TRUE on Good Read)
DecodeStatus BOOL N/A Decode Status (TRUE on Good Read)
Decode_FullResults S_ID40_Input_type_103 N/A
DecodeStr STRING[436] N/A Storage of Read String
TrigCount UDINT Counter Trigger Count
ReadCount UDINT Counter Successful Read Count
OverrunCount UDINT Counter
ReadTime LINT Time (In Milliseconds) Reports time from trigger to result
HMI_ReadTimeout LINT Time (In Milliseconds)
Reset (Clears counters, stops read cycle,
puts readers online)
Storage of all results from ID-40 that
read the barcode
Overrun Count (read cycle not completed
when next trigger was received)
Maximum time to attempt decode, Initial
value set to 2,000 milliseconds
36
Page 37

Appendix C
Useful Documentation / Files
SYSMAC Studio Operation Manual: https://industrial.omron.us/en/media/Sysmac_Studio_Ver1_18_
OperationManual_en_201704_W504-E1-20_tcm849-112701.pdf
NJ/NX CPU Unit Built-In EtherNet/IP Port: https://industrial.omron.us/en/media/NJNX-series_CPU_Unit_Built-
in_EtherNetIP_Manual_EN_201811_W506I-E3-20_tcm849-112708.pdf
NX1P2 CPU Unit Hardware User Manual: https://industrial.omron.us/en/media/NX1P2_Hardware_UsersManual_
en_201611_W578-E1-01_r2_tcm849-112522.pdf
NX1P2 Built-In I/O User Manual: https://industrial.omron.us/en/media/NX1P2_IO_Option_Boards_UsersMan_
en_201611_W579-E1-01_r22_tcm849-112521.pdf
NX-ECC202 User Manual: https://industrial.omron.us/en/media/NX-ECC_EtherCAT_Coupler_UsersManual_
en_201504_W519-E1-05_tcm849-113365.pdf
NX-Series Digital I/O: https://www.fa.omron.com.cn/data_pdf/cat/nx-id_ia_od_oc_md_ds_e_3_2_csm1057421.
pdf?id=3185
NA-HMI Firmware Update Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ETNHvv9KZ38
E3Z-T81 Sensor Information: http://www.ia.omron.com/product/item/758/
MicroHAWK ID Reader User Manual: https://les.microscan.com/downloadcenter/microhawkidmanual.pdf
MicroHAWK ID Reader EDS File: https://les.microscan.com/downloadcenter/MicroHAWK%20Auto%20ID%20
1.2%20EtherNetIP.zip
37
Page 38

Printed on recycled paper.
OMRON AUTOMATION AMERICAS HEADQUARTERS • Chicago, IL USA • 847.843.7900 • 800.556.6766 • www.omron247.com
OMRON CANADA, INC. • HEAD OFFICE
Toronto, ON, Canada • 416.286.6465 • 866.986.6766 • www.omron247.com
OMRON ELECTRONICS DE MEXICO • HEAD OFFICE
México DF • 52.
OMRON ELECTRONICS DE MEXICO • SALES OFFICE
Apodaca, N.L. • 52.81.11.56.99.20 • 01-800-226-6766 • mela@omron.com
55.59.01.43.00
• 01-800-226-6766 • mela@omron.com
Authorized Distributor:
OMRON ELETRÔNICA DO BRASIL LTDA • HEAD OFFICE
São Paulo, SP, Brasil • 55.11.2101.6300 • www.omron.com.br
OMRON ARGENTINA • SALES OFFICE
Cono Sur • 54.11.4783.5300
OTHER OMRON LATIN AMERICA SALES
54.11.4783.5300
Controllers & I/O
• Machine Automation Controllers (MAC) • Motion Controllers
• Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) • Temperature Controllers • Remote I/O
Robotics
• Industrial Robots • Mobile Robots
Operator Interfaces
• Human Machine Interface (HMI)
Motion & Drives
• Machine Automation Controllers (MAC) • Motion Controllers • Servo Systems
• Frequency Inverters
Vision, Measurement & Identification
• Vision Sensors & Systems • Measurement Sensors • Auto Identification Systems
Sensing
• Photoelectric Sensors • Fiber-Optic Sensors • Proximity Sensors
• Rotary Encoders • Ultrasonic Sensors
Safety
• Safety Light Curtains • Safety Laser Scanners • Programmable Safety Systems
• Safety Mats and Edges • Safety Door Switches • Emergency Stop Devices
• Safety Switches & Operator Controls • Safety Monitoring/Force-guided Relays
Control Components
• Power Supplies • Timers • Counters • Programmable Relays
• Digital Panel Meters • Monitoring Products
Switches & Relays
• Limit Switches • Pushbutton Switches • Electromechanical Relays
• Solid State Relays
Software
• Programming & Configuration • Runtime
MCD-128
Note: Specifications are subject to change.
© 2019 Omron. All Rights Reserved.
Printed in U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...