Page 1
Cat. No.W426-E1-09
Cat. No. Z264-E2-04-X Smart Sensor ZFX-C USER´S MANUAL
SYSMAC
CJ1W-NC271/NC471/
NCF71/NCF71-MA
CS1W-NC271/NC471/NCF71
Position Control Units
OPERATION MANUAL
Page 2

CJ1W-NC271/NC471/NCF71/NCF71-MA
CS1W-NC271/NC471/NCF71
Position Control Units
Operation Manual
Revised October 2008
Page 3

iv
Page 4

v
Notice:
OMRON products are manufactured for use according to proper procedures by a qualified operator
and only for the purposes described in this manual.
The following conventions are used to indicate and classify precautions in this manual. Always heed
the information provided with them. Failure to heed precautions can result in injury to people or damage to property.
!DANGER Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or
serious injury. Additionally, there may be severe property damage.
!WARNING Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or
serious injury. Additionally, there may be severe property damage.
!Caution Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or
moderate injury, or property damage.
OMRON Product References
All OMRON products are capitalized in this manual. The word “Unit” is also capitalized when it refers to
an OMRON product, regardless of whether or not it appears in the proper name of the product.
The abbreviation “Ch,” which appears in some displays and on some OMRON products, often means
“word” and is abbreviated “Wd” in documentation in this sense.
The abbreviation “PLC” means Programmable Controller. “PC” is used, however, in some Programming Device displays to mean Programmable Controller.
Visual Aids
The following headings appear in the left column of the manual to help you locate different types of
information.
Note Indicates information of particular interest for efficient and convenient opera-
tion of the product.
1,2,3... 1. Indicates lists of one sort or another, such as procedures, checklists, etc.
OMRON, 2004
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form, o
r
by any means, mechanical, electronic, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission o
f
OMRON.
No patent liability is assumed with respect to the use of the information contained herein. Moreover, because OMRON is constantly striving to improve its high-quality products, the information contained in this manual is subject to change without
notice. Every precaution has been taken in the preparation of this manual. Nevertheless, OMRON assumes no responsibility
for errors or omissions. Neither is any liability assumed for damages resulting from the use of the information contained in
this publication.
Page 5

vi
Page 6

vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PRECAUTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxiii
1 Intended Audience. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxiv
2 General Precautions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxiv
3 Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxiv
4 Operating Environment Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxv
5 Application Precautions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxvi
6 Conformance to EC Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxviii
SECTION 1
Features and System Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1-1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1-2 System Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1-3 Basic Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1-4 List of Functions and Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1-5 List of Functions by Purpose. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
1-6 Comparison with Existing Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
SECTION 2
Basic Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2-1 Basic Flow of Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
2-2 Starting Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
SECTION 3
Installation and Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
3-1 Nomenclature and Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
3-2 Installing the Position Control Unit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
3-3 External I/O Circuits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
3-4 Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
SECTION 4
Data Areas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
4-1 Overall Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
4-2 Data Areas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
4-3 Common Parameter Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
4-4 Axis Parameter Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
4-5 Servo Parameter Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
4-6 Common Operating Memory Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
4-7 Axis Operating Output Memory Areas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
4-8 Axis Operating Input Memory Areas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Page 7

viii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 5
Transferring and Saving Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
5-1 Transferring Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
5-2 Transferring PCU Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
5-3 Transferring Servo Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
SECTION 6
MECHATROLINK . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
6-1 MECHATROLINK Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
6-2 MECHATROLINK Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223
6-3 MECHATROLINK Communications Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 232
6-4 Standard Settings for Servo Drives Using MECHATROLINK. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 247
SECTION 7
Position Control Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 255
7-1 PCU Control System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256
7-2 Control Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 257
7-3 Coordinate System and Present Position. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 260
7-4 Acceleration and Deceleration Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 261
7-5 Limit Input Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 270
SECTION 8
Defining the Origin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273
8-1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 274
8-2 Origin Search Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 275
8-3 Present Position Preset. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 296
8-4 Origin Return. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 298
8-5 Phase Z Margin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 303
8-6 Absolute Encoder Origin. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .305
SECTION 9
Positioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 317
9-1 Direct Operation Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .318
9-2 Direct Operation Procedure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .319
9-3 PCU Data Settings for Direct Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 319
9-4 Using Direct Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 323
9-5 Interrupt Feeding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 331
9-6 Torque Limit Function. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 334
9-7 Linear Interpolation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
Page 8

ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 10
Other Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 349
10-1 Servo Lock/Unlock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 350
10-2 Jogging. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 351
10-3 Override . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 355
10-4 Torque Limits. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
10-5 Speed Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 364
10-6 Torque Control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 375
10-7 Backlash Compensation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 381
10-8 Software Limits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 383
10-9 Stop Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 388
10-10 DEVIATION COUNTER RESET. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 393
SECTION 11
Sample Programs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 397
11-1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 398
11-2 Basic Program Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .399
11-3 Application Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 424
SECTION 12
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 455
12-1 Overview of PCU Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 456
12-2 Troubleshooting Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .460
12-3 LED Error Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 461
12-4 Error Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 464
12-5 Troubleshooting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 477
12-6 Error Reset. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 482
12-7 CPU Unit Error Display. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 484
SECTION 13
Maintenance and Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 485
13-1 Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 486
13-2 Inspection Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 486
13-3 Handling Precautions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 487
13-4 Procedure for Replacing a PCU. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 487
Page 9

x
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Appendices
A Performance Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 491
B List of Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 495
C Operation Area I/O Allocations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 559
D List of Error Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 571
E Changing to CS1W/CJ1W-NC271/471/F71 from CS1W/CJ1W-NC113/133/213/233/413/433 579
F Additional Functions for the CJ1W-NCF71-MA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 601
Index. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 605
Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 615
Page 10

xi
About this Manual:
This manual describes the installation and operation of the CJ1W-NC271/NC471/NCF71/NCF71-MA
and CS1W-NC271/NC471/NCF71 Position Control Units and includes the sections described below.
Please read this manual carefully and be sure you understand the information provided before
attempting to install or operate the Position Control Unit. Be sure to read the precautions provided in
the following section.
Precautions provide general precautions for using the Position Control Unit, Programmable Controller,
and related devices.
Section 1 introduces the features of the Position Control Unit, explains the system configuration in
which it is used, and also provides information on basic operations, functions and specifications.
Section 2 provides an overview of the procedures required to use the Position Control Unit.
Section 3 provides information on nomenclature and functions, and describes the procedures required
for wiring and installation. Information on the MECHATROLINK-II Application Module is also provided.
Section 4 provides an overview of the parameter and data settings used in Position Control Unit operation and provides information on memory allocations.
Section 5 explains how to transfer and save parameters and data using the data transfer bits.
Section 6 provides an overview of MECHATROLINK communications, and includes information on
settings and procedures required to use MECHATROLINK with the Position Control Unit.
Section 7 provides an overview of the control system used by the Position Control Unit, including information on the control units, coordinate system, acceleration/deceleration operations, and limit input
operations.
Section 8 provides information on the various operations used to determine the origin, including origin
searches, origin returns, presetting the present position, calculating phase Z margins, and using the
absolute encoder.
Section 9 provides an overview of direct operation and describes the parameter settings, data settings, and procedures required to perform direct operation. Information on interrupt feeding and torque
limits is also provided here.
Section 10 describes the servo lock/unlock, jogging, override, torque limits, speed control, torque control, backlash compensation, software limits, and stop functions.
Section 11 provides basic program examples and application examples for using the Position Control
Unit.
Section 12 provides information on troubleshooting errors that may occur, including details on the
meaning of indicator displays and error codes, and the procedures required to reset errors in the Unit
or axes.
Section 13 describes methods for inspecting and maintaining the Position Control Unit and the procedure required to replace a Position Control Unit.
The Appendices provide information on the performance characteristics, lists of parameters, I/O allocations in the operation areas, lists of error codes, alarm/warning displays, and information required
when changing to the CJ1W-NC271/NC471/NCF71/NCF71-MA or CS1W-NC271/NC471/NCF71 from
a CJ1W/CS1W-NC113/133/213/233/413/433 Position Control Unit.
!WARNING Failure to read and understand the information provided in this manual may result in per-
sonal injury or death, damage to the product, or product failure. Please read each section
in its entirety and be sure you understand the information provided in the section and
related sections before attempting any of the procedures or operations given.
Page 11
xii
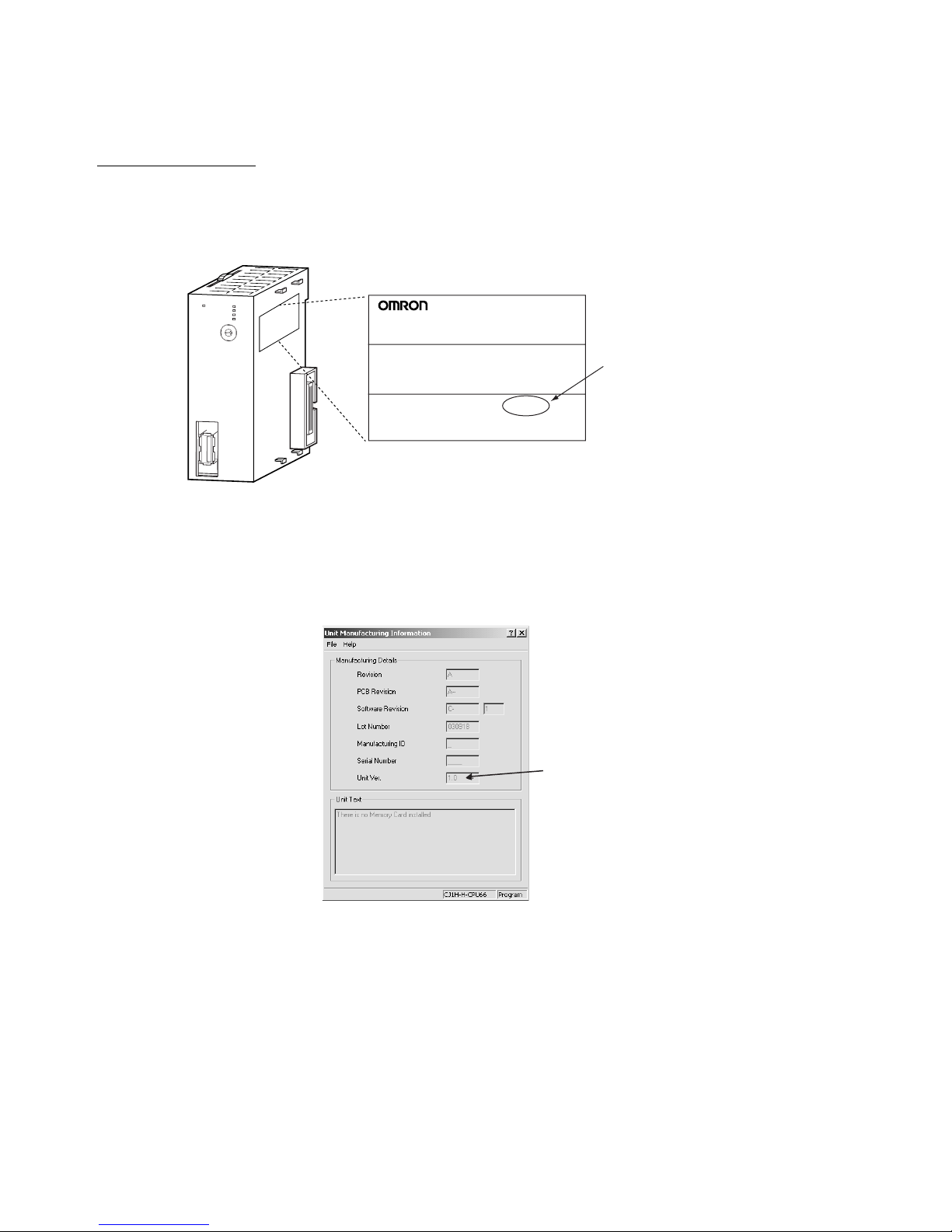
Unit Versions of Position Control Units
Unit Versions A “unit version” has been introduced to manage Position Control Units accord-
ing to differences in functionality accompanying Unit upgrades.
Notation of Unit Versions
on Products
The unit version is given to the right of the lot number on the nameplate of the
products for which unit versions are being managed, as shown below.
The unit version of Position Control Units starts with unit version 1.0.
Confirming Unit Versions
with Support Software
CX-Programmer version 4.0 can be used to confirm the unit version using the
Unit Manufacturing Information.
In the IO Table Window, right-click the Position Control Unit and select Unit
Manufacturing information.
The following Unit Manufacturing information Dialog Box will be displayed.
The unit version is displayed as 1.0 in the Unit Version Number field of the
above example. Use the above display to confirm the unit version of the Unit
connected online.
Using Unit Version Label A unit version label is provided with the Position Control Unit. This label can
be attached to the front of the Position Control Unit to differentiate between
Position Control Units with different unit versions.
CJ1W-NCF71
NC UNIT
Lot No. 040401 0000 Ver.1.0
OMRON Corporation MADE IN JAPAN
CJ1W-NCF71
R
U
N
E
R
C
E
R
H
E
R
M
M
LK
N
C
F71
U
N
IT
No.
M
LK
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
Unit version
Example for unit version 1.0
Product nameplate
Unit version
Page 12
xiii
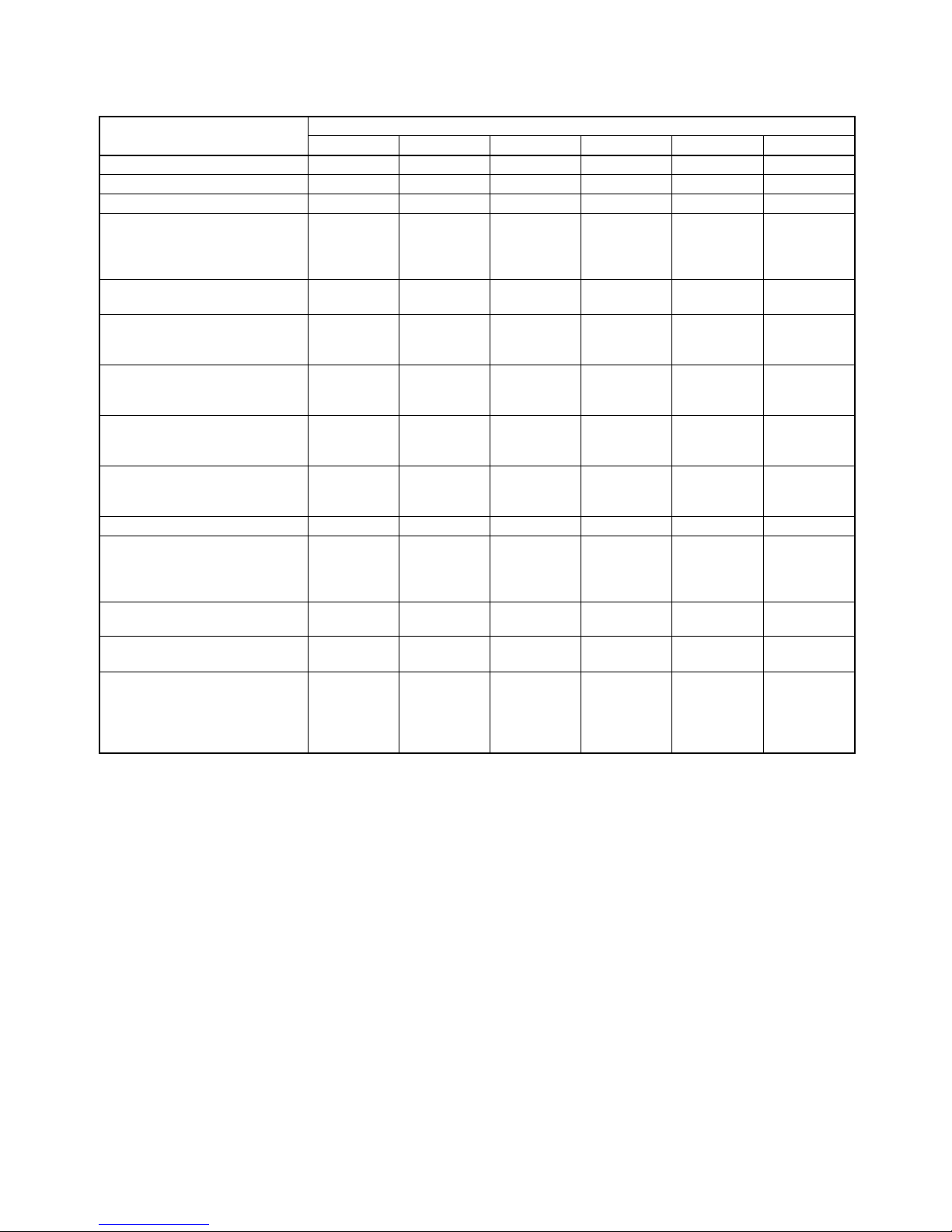
Functions Supported According to Position Control Unit Versions
Model CJ1W-NC@71/CS1W-NC@71
Unit Ver. 1 .0 Unit Ver. 1.1 Unit Ver. 1.2 Unit Ver. 1.3 Unit Ver. 2. 0 Unit Ver. 2.1
Linear interpolation --- Supported. Supported. Supported. Supported. Supported.
Absolute encoder setup function --- --- Supported. Supported. Supported. Supported.
Deviation counter reset --- --- --- Supported. Supported. Supported.
Establishing connections even
when there are unconnected
axes or axes with alarms that
cannot be cleared
--- --- --- Supported. Supported. Supported.
Transferring servo parameters
even when there is an axis error
--- --- --- Supported. Supported. Supported.
Creating servo locks during software limit detection when an
absolute encoder is used
--- --- --- Supported. Supported. Supported.
Driver main circuit OFF error
detection only when the servo is
locked
--- --- --- Supported. Supported. Supported.
Using Holding Area address
H512 and onwards for function
block address allocations
--- --- --- Supported. Supported. Supported.
Addition of supported models:
SMARTSTEP Junior Servo
Drives (R7D-ZN@-ML2)
--- --- --- --- Supported. Supported.
Addition of rejoin function --- --- --- --- Supported. Supported.
Eliminating connection restric-
tion when Servo Drive alarms
occur (enabling connection
when alarm A.C90 occurs)
--- --- --- --- Supported. Supported.
Addition of origin search operation modes
--- --- --- --- Supported. Supported.
Addition of origin search preset
function
--- --- --- --- Supported. Supported.
Faster setting for transfer cycle
and communications cycle
when setting the absolute
encoder PG zero point position
offset with an origin search
--- --- --- --- --- Supported.
Page 13
xiv
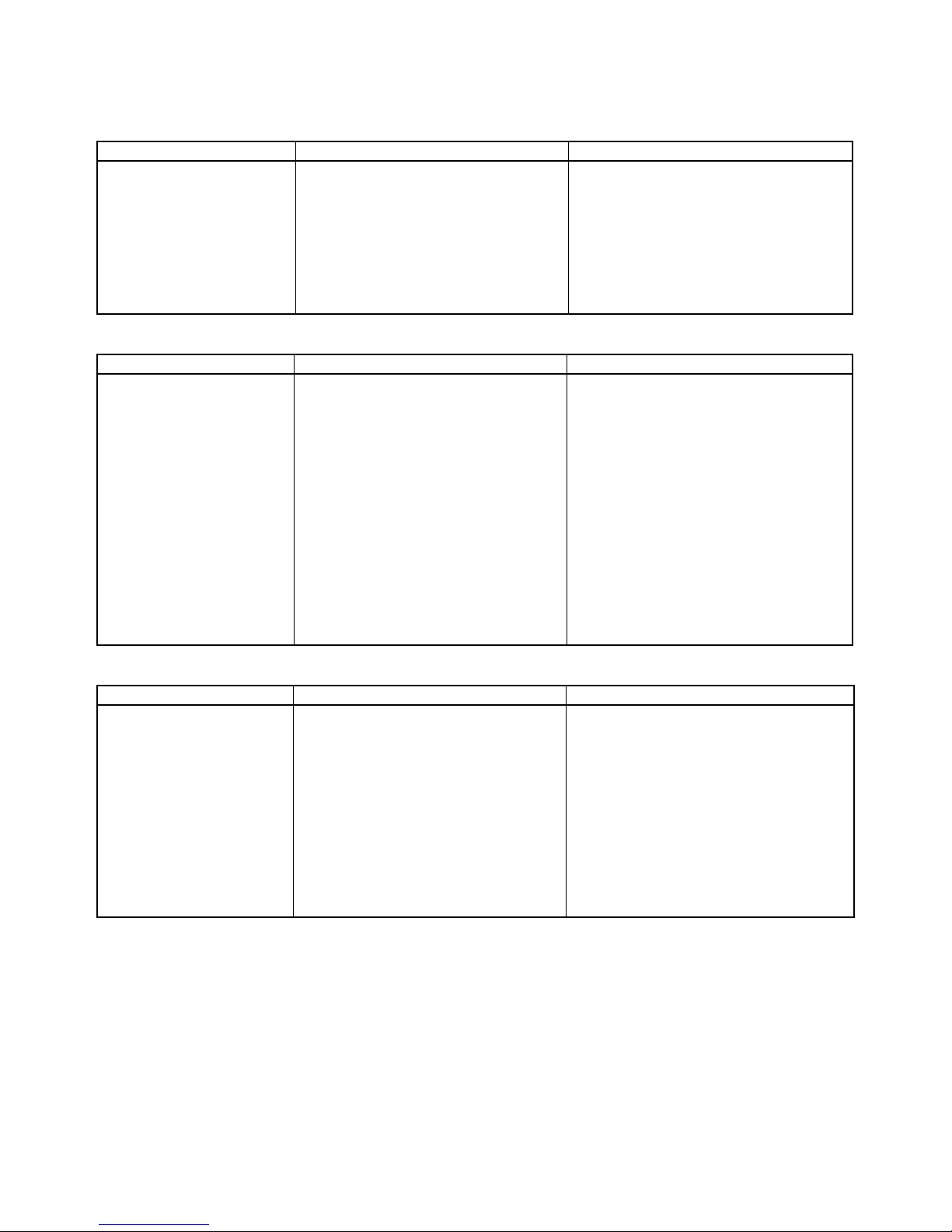
Upgrades Made According to Unit Versions of the Position Control Unit
Unit Version 1.0 to Unit Version 1.1
Unit Version 1.1 to Unit Version 1.2
Unit Version 1.2 to Unit Version 1.3
Functional upgrade Unit version 1.0 Unit version 1.1
Addition of linear interpolation
function
Linear interpolation cannot be used.
Linear interpolation can be performed for
positioning operations combining one or
more axes.
Linear interpolation can performed for up to
four axes each of axes 1 to 4 and axes 5 to 8
for Servo Drive axes connected to the Position Control Unit. (Refer to 9-7 Linear Inter-
polation.)
Functional upgrade Unit version 1.1 Unit version 1.2
Addition of setup function for
absolute encoders
An absolute encoder must be set up the
first time it is used, when the rotation data
is initialized to 0, or when the absolute
encoder is left for a long period of time
without the battery connected.
With Position Control Units with unit version 1.1 or earlier, the following operation
is used to set up the absolute encoder.
• Special software (personal computer
monitoring software) must be connected
to the Servo Drive to perform the setup
operation.
With Position Control Units with unit version
1.2 or later, the following operation can be
used to set up the absolute encoder.
• Special software (personal computer monitoring software) can be connected to the
Servo Drive to perform the setup operation.
• When the Position Control Unit is used with
a CPU Unit with unit version 3.0 or later, the
absolute encoder can be set up from the
program by using a function block from the
OMRON FB Library.
• The absolute encoder can be set up from
the CX-Motion-NCF. (Refer to 8-6-4
Absolute Encoder Setup.)
Functional upgrade Unit version 1.2 Unit version 1.3
Addition of deviation counter
reset function
The deviation counter in the Servo Drive
cannot be reset from the Position Control
Unit during position control operations.
The deviation counter in the Servo Drive can
be reset from the Position Control Unit during
position control operations.
To deviation reset function in the Position
Control Unit works by sending a movement
command in the opposite direction and of the
same size as the current position deviation
so that the current command position equals
the current feedback position.
(Refer to 10-10 DEVIATION COUNTER
RESET.)
Page 14
xv
Establishing connections
when there are unconnected
axes or axes with alarms that
cannot be cleared
If any of the axes registered in the scan list
are not connected, have the control power
supply interrupted, or have an alarm that
can be reset only by cycling the power
supply, an MLK initialization error (Unit
error code 0020 (hex) will occur after the
connections are established and operations using MECHATROLINK communications will not be possible any axes,
including those without errors.
To start MECHATROLINK communications
normally, all errors must be cleared for all
axes registered in the scan list before connections can be established.
Axis operations using MECHATROLINK communications are possible for any axes registered in the scan list and for which
MECHATROLINK communications have
been started (see note) regardless of
whether there are Servo Drive alarms.
If there are any axes with alarms, they will be
indicated by the Error Flags and error code in
the Axis Operating Input Memory Areas.
If there are alarms in the Servo Drive that can
be cleared only by recycling the power, they
will be detected as Unit errors (MLK initialization errors) for Units with unit version 1.1 or
earlier, but they will be detected in the individual axis areas.
Note If R88D-WN@-ML2 W-series Servo
Drives (Models with Built-in MECHATROLINK-II Communications) are connected, an encoder communications
error (A.C9@) will occur in the Servo
Drive and it will not be possible to start
MECHATROLINK communications for
Units with unit version 1.3 or earlier.
(Refer to 6-3-2 MECHATROLINK Communi-
cations Status.)
Transferring parameters when
there are axis errors
Servo parameters cannot be transferred
(i.e., written, read, or saved) for axes with
errors. The errors must first be reset to
clear the axis error status before Servo
parameters can be transferred.
Servo parameters can be transferred (i.e.,
written, read, or saved) for axes with errors. If
the axis error already exists, it will not be
overwritten even if an error occurs during
parameter transfer.
If Servo parameters are written when there is
an axis error, be sure to confirm that the
parameters were transferred correctly.
(Refer to 5-3 Transferring Servo Parameters.)
Locking the servo when a
software limit is being
detected for a Motor with an
absolute encoder
If an attempt is made to lock the Servo
when an absolute encoder is used, the
software limits are enabled, and the
present position is within the software limit
area, a software limit error will occur and
the Servo lock operation will be canceled.
To lock the Servo in the above situation,
the software limit must first be disabled.
The Servo can be locked at any position,
regardless of the type of encoder and the
software limit settings.
(Refer to 10-8-4 Software Limit Operation.)
Functional upgrade Unit version 1.2 Unit version 1.3
Page 15
xvi
Unit Version 1.3 to Unit Version 2.0
Detecting driver main circuit
OFF errors only when the
Servo is locked
Servo Drive main circuit OFF errors are
detected regardless of whether the Servo
is locked for the axis. Once a Servo Drive
main circuit OFF error is detected, it will
continue to be detected even if the error is
reset until the main circuit power supply is
restored.
Servo Drive main circuit OFF errors are
detected only when the Servo is locked for
the axis.
The Position Control Unit will automatically
unlock the Servo when a Servo Drive main
circuit OFF error is detected, allowing the
error to be cleared even while the main circuit
power supply is interrupted.
If an attempt is made to lock the Servo while
the main circuit power supply is interrupted, a
Servo Drive main circuit OFF error will be
detected again.
(Refer to 12-4-2 List of Error Codes.)
Allocating holding addresses
H512 and higher as function
block addresses
The function blocks in the OMRON FB
Library for the Position Control Unit cannot
be used if H512 (default setting) or higher
are allocated for non-holding areas of function block addresses.
If H512 or higher are allocated, a function
block error will occur when the function
block is executed.
The CX-Programmer must be used to
change the setting to other unused words
(e.g., in the DM or EM Area).
The function blocks in the OMRON FB
Library for the Position Control Unit can be
used if H512 (default setting) or higher are
allocated for non-holding areas of function
block addresses.
Functional upgrade Unit version 1.3 Unit version 2.0
Addition of applicable models
Applicable Models
•R88D-WT@W-series Servo Drives (with
JUSP-NS115 MECHATROLINK-II Application Module mounted)
•R88D-WN@-ML2 W-series Servo Drives
(Models with Built-in MECHATROLINK-II
Communications)
Applicable Models
•R88D-WT@W-series Servo Drives (with
JUSP-NS115 MECHATROLINK-II Application Module mounted)
•R88D-WN@-ML2 W-series Servo Drives
(Models with Built-in MECHATROLINK-II
Communications)
•R7D-ZN@-ML2 SMARTSTEP Junior Servo
Drive (Models with Built-in MECHATROLINK-II Communications)
Functional upgrade Unit version 1.2 Unit version 1.3
Page 16
xvii
Addition of rejoin function MECHATROLINK communications are
started and stopped at the same time for
all axes registered in the scan list.
The following functions are supported in
addition to starting and stopping MECHATROLINK communications for all axes at the
same time.
• Rejoin Function
An axis for which communications have
been stopped, e.g., due to a communications error, can be restarted without stopping communications for the other axes.
(Refer to 6-3-4 Rejoining the Connection.)
• Setting the Axes to Be Connected
Axes registered in the scan list can be set
temporarily so that they are not registered.
The axes can be set so that they are temporarily not used without resetting the scan
list. Operations can be performed without
errors occurring for these axes.
(Refer to 6-3-5 Specifying the Axes to Con-
nect.)
The Axis Communications Status Flags have
also been changed for the above functions.
Refer to the note following this table for
details.
Eliminating connection restriction when Servo Drive alarms
occur (enabling connection
when alarm A.C90 occurs)
If an encoder communications error
(A.C90) occurs for a R88D-WN@-ML2 Wseries Servo Drive (Model with Built-in
MECHATROLINK-II Communications),
MECHATROLINK communications cannot
be started with that Servo Drive.
MECHATROLINK communications can be
started under the conditions given at the left,
and operations, such as transferring Servo
Parameters, can be performed.
Addition of origin search operation modes
Three origin search operation pattern are
possible by combining the following settings:
• Origin search operations: 3 settings
(Reversal modes 1 and 2, and Singledirection mode)
• Origin detection method: 1 setting
(With origin proximity input signal reversal)
Eleven origin search operation pattern are
possible by combining the following settings:
• Origin search operations: 4 settings
(Reversal modes 1, 2, and 3, and Singledirection mode)
• Origin detection methods: 3 settings (With
origin proximity input signal reversal, Without origin proximity input signal reversal,
Not use origin proximity input signal)
(Refer to 8-2-4 Origin Search Operation.)
Functional upgrade Unit version 1.3 Unit version 2.0
:
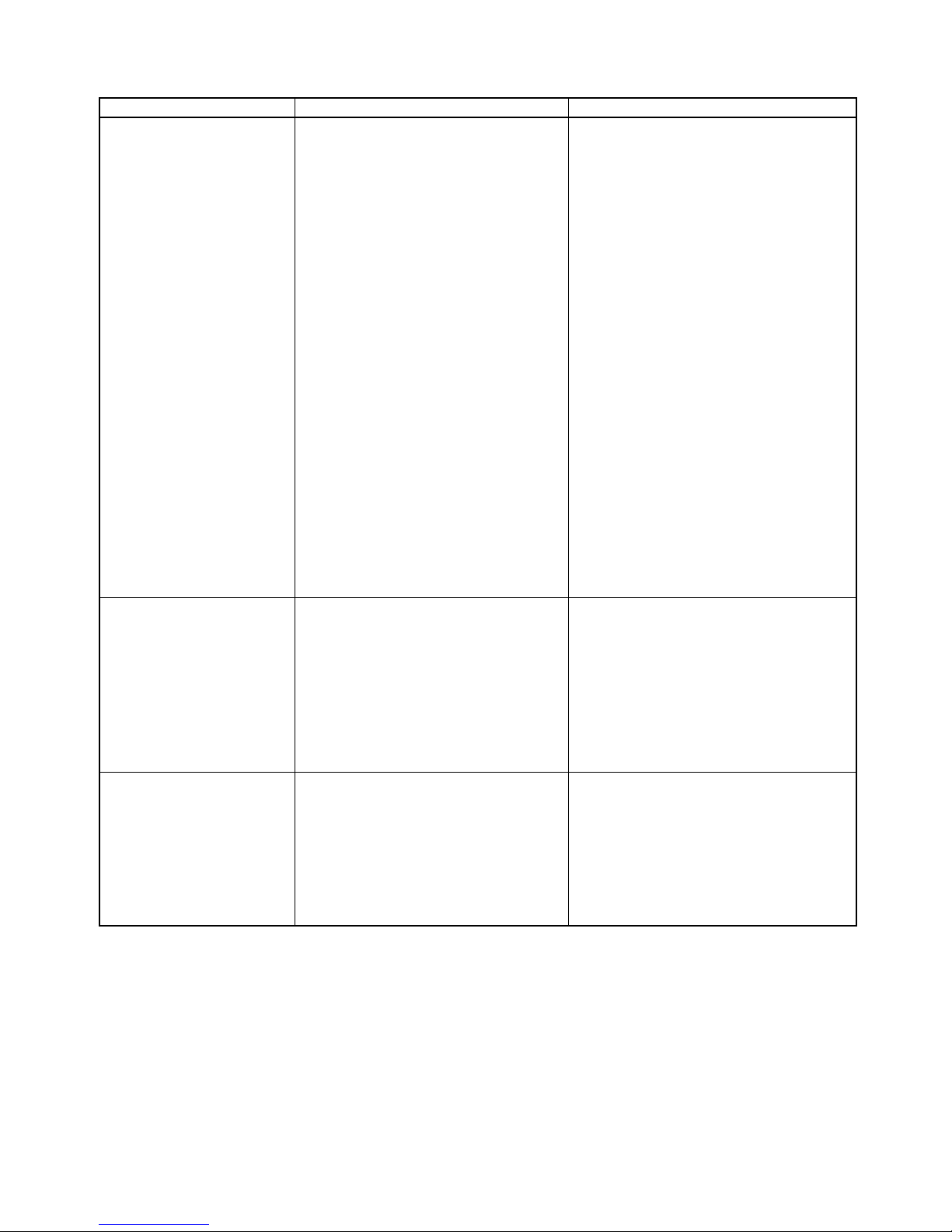
Combinations supported by unit version 1.3 or earlie
r
:
Combinations supported by unit version 2.0 or later
Origin search operation
Origin
detection
method
Reversal
mode 1
Reversal
mode 2
Single-
direction
mode
Reversal
mode 3
(See note.)
(See note.)
(See note.)
Note: Origin search operation patterns supported by
absolute encoders.
With origin
proximity
input signal
reversal
Without
origin
proximity
input signal
reversal
Not use
origin
proximity
input signal
Page 17
xviii
Note Changes in Axis Communications Status Flags
The conditions for setting and resetting the Axis Communications Status
Flags in word n+22 of the Common Operating Memory Area have been
changed accompanying the addition of the rejoin function. New conditions are
underlined in the following table.
With unit version 1.3 or earlier, once MECHATROLINK communications have been started by establishing connections, the Axis Communications Status Flags will not change unless communications
are disconnected (including Unit errors that required disconnection).
With unit version 2.0 or later, the Axis Communications Status Flags will turn OFF after connections
have been established whenever axis operation becomes impossible due to a communications error
(synchronous communications alarm or communications alarm).
Unit Version 2.0 to Unit Version 2.1
Addition of origin search preset function
The preset function cannot be used during
origin searches.
The preset function can be used during origin searches.
For any of the origin search operations the
present position can be automatically set to
any specified value at the end of the origin
search. When using reversal mode 1 and an
absolute encoder, an offset can also be set
for the absolute origin.
(Refer to 8-2-6 Origin Search Preset and 8-6-
2 Absolute Encoder Operating Procedure.)
Functional upgrade Unit version 1.3 or earlier Unit version 2.0 or later
Setting conditions • The flags will turn ON when connections
are made for the axes registered in the
scan list and MECHATROLINK communications start.
• The flags will turn ON when connections
are made for the axes registered in the
scan list and MECHATROLINK communications start.
• The flag will turn ON when the rejoin function is used to start MECHATROLINK communications for an axis registered in the
scan list.
Resetting conditions • The flags will remain OFF when MECHA-
TROLINK communications cannot be
started when connections are made for
the axes registered in the scan list.
• The flags will turn OFF if MECHATROLINK communications stop because
the axis is disconnected.
• The flags will turn OFF if a Unit error
occurs that requires disconnection.
• The flags will remain OFF when MECHATROLINK communications cannot be
started when connections are made for the
axes registered in the scan list.
• The flags will turn OFF if MECHATROLINK
communications stop because the axis is
disconnected.
• The flags will turn OFF if a Unit error occurs
that requires disconnection.
• The flags will turn OFF whenever a communications error occurs after MECHATROLINK communications have been
started for the axis.
Functional upgrade Unit version 2.0 Unit version 2.1
Faster setting of transfer cycle
and communications cycle when
setting the absolute encoder PG
zero point position offset with an
origin search
A longer communications cycle must be
set using the settings given in a separate
table when the absolute encoder PG zero
point position offset is set with an origin
search.
The same communications cycle can be
set regardless of whether the absolute
encoder PG zero point position offset is
set with an origin search.
Functional upgrade Unit version 1.3 Unit version 2.0
Page 18

xix
Read and Understand this Manual
Please read and understand this manual before using the product. Please consult your OMRON
representative if you have any questions or comments.
Warranty and Limitations of Liability
WARRANTY
OMRON's exclusive warranty is that the products are free from defects in materials and workmanship for a
period of one year (or other period if specified) from date of sale by OMRON.
OMRON MAKES NO WARRANTY OR REPRESENTATION, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING NONINFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, OR FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE OF THE
PRODUCTS. ANY BUYER OR USER ACKNOWLEDGES THAT THE BUYER OR USER ALONE HAS
DETERMINED THAT THE PRODUCTS WILL SUITABLY MEET THE REQUIREMENTS OF THEIR
INTENDED USE. OMRON DISCLAIMS ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED.
LIMITATIONS OF LIABILITY
OMRON SHALL NOT BE RESPONSIBLE FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES,
LOSS OF PROFITS OR COMMERCIAL LOSS IN ANY WAY CONNECTED WITH THE PRODUCTS,
WHETHER SUCH CLAIM IS BASED ON CONTRACT, WARRANTY, NEGLIGENCE, OR STRICT
LIABILITY.
In no event shall the responsibility of OMRON for any act exceed the individual price of the product on which
liability is asserted.
IN NO EVENT SHALL OMRON BE RESPONSIBLE FOR WARRANTY, REPAIR, OR OTHER CLAIMS
REGARDING THE PRODUCTS UNLESS OMRON'S ANALYSIS CONFIRMS THAT THE PRODUCTS
WERE PROPERLY HANDLED, STORED, INSTALLED, AND MAINTAINED AND NOT SUBJECT TO
CONTAMINATION, ABUSE, MISUSE, OR INAPPROPRIATE MODIFICATION OR REPAIR.
Page 19

xx
Application Considerations
SUITABILITY FOR USE
OMRON shall not be responsible for conformity with any standards, codes, or regulations that apply to the
combination of products in the customer's application or use of the products.
At the customer's request, OMRON will provide applicable third party certification documents identifying
ratings and limitations of use that apply to the products. This information by itself is not sufficient for a
complete determination of the suitability of the products in combination with the end product, machine,
system, or other application or use.
The following are some examples of applications for which particular attention must be given. This is not
intended to be an exhaustive list of all possible uses of the products, nor is it intended to imply that the uses
listed may be suitable for the products:
• Outdoor use, uses involving potential chemical contamination or electrical interference, or conditions or
uses not described in this manual.
• Nuclear energy control systems, combustion systems, railroad systems, aviation systems, medical
equipment, amusement machines, vehicles, safety equipment, and installations subject to separate
industry or government regulations.
• Systems, machines, and equipment that could present a risk to life or property.
Please know and observe all prohibitions of use applicable to the products.
NEVER USE THE PRODUCTS FOR AN APPLICATION INVOLVING SERIOUS RISK TO LIFE OR
PROPERTY WITHOUT ENSURING THAT THE SYSTEM AS A WHOLE HAS BEEN DESIGNED TO
ADDRESS THE RISKS, AND THAT THE OMRON PRODUCTS ARE PROPERLY RATED AND INSTALLED
FOR THE INTENDED USE WITHIN THE OVERALL EQUIPMENT OR SYSTEM.
PROGRAMMABLE PRODUCTS
OMRON shall not be responsible for the user's programming of a programmable product, or any
consequence thereof.
Page 20

xxi
Disclaimers
CHANGE IN SPECIFICATIONS
Product specifications and accessories may be changed at any time based on improvements and other
reasons.
It is our practice to change model numbers when published ratings or features are changed, or when
significant construction changes are made. However, some specifications of the products may be changed
without any notice. When in doubt, special model numbers may be assigned to fix or establish key
specifications for your application on your request. Please consult with your OMRON representative at any
time to confirm actual specifications of purchased products.
DIMENSIONS AND WEIGHTS
Dimensions and weights are nominal and are not to be used for manufacturing purposes, even when
tolerances are shown.
PERFORMANCE DATA
Performance data given in this manual is provided as a guide for the user in determining suitability and does
not constitute a warranty. It may represent the result of OMRON's test conditions, and the users must
correlate it to actual application requirements. Actual performance is subject to the OMRON Warranty and
Limitations of Liability.
ERRORS AND OMISSIONS
The information in this manual has been carefully checked and is believed to be accurate; however, no
responsibility is assumed for clerical, typographical, or proofreading errors, or omissions.
Page 21

xxii
Page 22

xxiii
PRECAUTIONS
This section provides general precautions for using the Position Control Unit and related devices.
The information contained in this section is important for the safe and reliable application of Position Control Units. You
must read this section and understand the information contained before attempting to set up or operate a Position Control
Unit.
1 Intended Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxiv
2 General Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxiv
3 Safety Precautions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxiv
4 Operating Environment Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxv
5 Application Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxvi
6 Conformance to EC Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxviii
6-1 Applicable Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxviii
6-2 Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxviii
6-3 Conformance to EC Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxviii
6-4 Installation within Control Panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxviii
Page 23

xxiv
Intended Audience 1
1 Intended Audience
This manual is intended for the following personnel, who must also have
knowledge of electrical systems (an electrical engineer or the equivalent).
• Personnel in charge of installing FA systems.
• Personnel in charge of designing FA systems.
• Personnel in charge of managing FA systems and facilities.
2 General Precautions
The user must operate the product according to the performance specifications described in the operation manuals.
Before using the product under conditions which are not described in the
manual or applying the product to nuclear control systems, railroad systems,
aviation systems, vehicles, combustion systems, medical equipment, amusement machines, safety equipment, and other systems, machines, and equipment that may have a serious influence on lives and property if used
improperly, consult your OMRON representative.
Make sure that the ratings and performance characteristics of the product are
sufficient for the systems, machines, and equipment, and be sure to provide
the systems, machines, and equipment with double safety mechanisms.
This manual provides information for programming and operating the Unit. Be
sure to read this manual before attempting to use the Unit and keep this manual close at hand for reference during operation.
!WARNING It is extremely important that a Position Control Units and related devices be
used for the specified purpose and under the specified conditions, especially
in applications that can directly or indirectly affect human life. You must consult with your OMRON representative before applying Position Control Units
and related devices to the above-mentioned applications.
3 Safety Precautions
!WARNING Do not attempt to take any Unit apart while the power is being supplied. Doing
so may result in electric shock.
!WARNING Do not attempt to disassemble, repair, or modify any Units. Any attempt to do
so may result in malfunction, fire, or electric shock.
!WARNING Never touch any of the terminals while power is being supplied. Doing so may
result in serious electric shock.
!WARNING Provide safety measures in external circuits (i.e., not in the Programmable
Controller or Position Control Unit) to ensure safety in the system if an abnormality occurs due to malfunction of the PLC, malfunction of the PCU (Position
Control Unit), or external factors affecting the operation of the PLC or PCU.
Not providing sufficient safety measures may result in serious accidents.
Page 24

xxv
Operating Environment Precautions 4
• Emergency stop circuits, interlock circuits, limit circuits, and similar safety
measures must be provided in external control circuits.
• The PLC will turn OFF all outputs when its self-diagnosis function detects
any error or when a severe failure alarm (FALS) instruction is executed.
As a countermeasure for such errors, external safety measures must be
provided to ensure safety in the system.
• The PLC or PCU outputs may remain ON or OFF due to deposits on or
burning of the output relays, or destruction of the output transistors. As a
countermeasure for such problems, external safety measures must be
provided to ensure safety in the system.
• When the 24-V DC output (service power supply to the PLC) is overloaded or short-circuited, the voltage may drop and result in the outputs
being turned OFF. As a countermeasure for such problems, external
safety measures must be provided to ensure safety in the system.
• External safety measures must also be taken to ensure safety in the event
of unexpected operation when connecting or disconnecting the PCU’s
connectors.
!Caution Execute online editing only after confirming that no adverse effects will be
caused by extending the cycle time. Otherwise, the input signals may not be
readable.
!Caution Confirm safety at the destination node before transferring a program to
another node or changing contents of the I/O memory area. Doing either of
these without confirming safety may result in injury.
4 Operating Environment Precautions
!Caution Do not operate the control system in the following locations:
• Locations subject to direct sunlight.
• Locations subject to temperatures or humidity outside the range specified
in the specifications.
• Locations subject to condensation as the result of severe changes in temperature.
• Locations subject to corrosive or flammable gases.
• Locations subject to dust (especially iron dust) or salts.
• Locations subject to exposure to water, oil, or chemicals.
• Locations subject to shock or vibration.
!Caution Take appropriate and sufficient countermeasures when installing systems in
the following locations:
• Locations subject to static electricity or other forms of noise.
• Locations subject to strong electromagnetic fields.
• Locations subject to possible exposure to radioactivity.
• Locations close to power supplies.
Page 25

xxvi
Application Precautions 5
!Caution The operating environment of the PLC System can have a large effect on the
longevity and reliability of the system. Improper operating environments can
lead to malfunction, failure, and other unforeseeable problems with the PLC
System. Make sure that the operating environment is within the specified conditions at installation and remains within the specified conditions during the
life of the system.
5 Application Precautions
Observe the following precautions when using the PLC System.
!WARNING Always heed these precautions. Failure to abide by the following precautions
could lead to serious or possibly fatal injury.
• Always connect to a ground of 100
Ω or less when installing the Units. Not
connecting to a ground of 100
Ω or less may result in electric shock.
• Always turn OFF the power supply to the PLC before attempting any of
the following. Not turning OFF the power supply may result in malfunction
or electric shock.
• Mounting or dismounting Power Supply Units, I/O Units, CPU Units, Inner Boards, or any other Units.
• Assembling the Units.
• Setting DIP switches or rotary switches.
• Connecting cables or wiring the system.
• Connecting or disconnecting the connectors.
!Caution Failure to abide by the following precautions could lead to faulty operation of
the PLC, the PCU, or the system, or could damage the PLC or PCU. Always
heed these precautions.
• Fail-safe measures must be taken by the customer to ensure safety in the
event of incorrect, missing, or abnormal signals caused by broken signal
lines, momentary power interruptions, or other causes. Not doing so may
cause malfunction resulting in serious injury.
• Interlock circuits, limit circuits, and similar safety measures in external circuits (i.e., not in the Programmable Controller) must be provided by the
customer.
• Install external breakers and take other safety measures against short-circuiting in external wiring. Insufficient safety measures against short-circuiting may result in burning.
• For CS-series PLCs, always tighten the mounting screw at the bottom of
the PCU to a torque of 0.4 N
⋅m.
• For CJ-series PLCs, lock the sliders securely until they click into place
when connecting the Power Supply Unit, CPU Unit, I/O Units, Special I/O
Units, or CPU Bus Units. Functions may not work correctly if the sliders
are not locked properly.
• Always attach the End Cover provided with the CPU Unit to the Unit on
the right end of the PLC. The CJ-series PLC will not operate properly if
the End Cover is not attached.
Page 26

xxvii
Application Precautions 5
• Take appropriate measures to ensure that the specified power with the
rated voltage and frequency is supplied in places where the power supply
is unstable. An incorrect power supply may result in malfunction.
• Remove the label after the completion of wiring to ensure proper heat dissipation. Leaving the label attached may result in malfunction.
• Disconnect the LG (line ground) terminal and GR (ground) terminal before
performing withstand voltage and insulation resistance tests.
• Confirm that set parameters and data operate properly.
• Perform wiring according to specified procedures.
• Double-check all wiring and switch settings before turning ON the power
supply. Incorrect wiring may result in burning.
• Check the user program for proper execution before actually running it on
the Unit. Not checking the program may result in unexpected operation.
• Confirm that no adverse effect will occur in the system before attempting
any of the following. Not doing so may result in an unexpected operation.
• Changing the operating mode of the PLC (including setting the Startup
Mode).
• Force-setting/force-resetting any bit in memory.
• Changing the present value of any word or any set value in memory.
• After replacing Units, resume operation only after transferring to the new
CPU Unit, Special I/O Units, CPU Bus Units, and externally connected
devices the contents of the DM Area, Holding Area, and other data
required for resuming operation. Not doing so may result in an unexpected operation.
• Do not pull on the cables or bend the cables beyond their natural limit.
Doing either of these may break the cables.
• Do not place objects on top of the cables or other wiring lines. Doing so
may break the cables.
• Before touching a Unit, be sure to first touch a grounded metallic object in
order to discharge any static build-up. Not doing so may result in malfunction or damage.
• Never turn OFF the power to the Unit while transferring data.
Page 27

xxviii
Conformance to EC Directives 6
6 Conformance to EC Directives
6-1 Applicable Directives
•EMC Directives
6-2 Concepts
EMC Directives
OMRON devices that comply with EC Directives also conform to the related
EMC standards so that they can be more easily built into other devices or the
overall machine. The actual products have been checked for conformity to
EMC standards (see the following note). Whether the products conform to the
standards in the system used by the customer, however, must be checked by
the customer.
EMC-related performance of the OMRON devices that comply with EC Directives will vary depending on the configuration, wiring, and other conditions of
the equipment or control panel on which the OMRON devices are installed.
The customer must, therefore, perform the final check to confirm that devices
and the overall machine conform to EMC standards.
Note Applicable EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) standards are as follows:
EMS (Electromagnetic Susceptibility): EN61000-6-2
EMI (Electromagnetic Interference): EN61000-6-4
(Radiated emission: 10-m regulations)
6-3 Conformance to EC Directives
The PCUs comply with EC Directives. To ensure that the machine or device in
which a PCU is used complies with EC Directives, the PCU must be installed
as follows:
1,2,3... 1. The PCU is defined as a in-panel device and must be installed within a
control panel.
2. Reinforced insulation or double insulation must be used for the DC power
supplies used for I/O.
3. PCUs complying with EC directives also meet the common emission standard (EN61000-6-4). The measures required to ensure that the standard
is met will vary with the overall configuration of the control panel, the other
devices connected to the control panel, wiring, and other conditions. The
customer must therefore confirm that EC directives are met for the overall
machine or device, particularly for the radiated emission requirement
(10 m).
6-4 Installation within Control Panels
Unnecessary clearance in cable inlet or outlet ports, operation panel mounting holes, or in the control panel door may cause electromagnetic wave leakage or interference. In this case, the product may fail to meet EC Directives. In
order to prevent such interference, fill clearances in the control panel with conductive packing. (In places where conductive packing comes in contact with
the control panel, ensure electrical conductivity by removing the paint coating
or masking these parts when painting.)
Page 28

1
SECTION 1
Features and System Configuration
This section introduces the features of the Position Control Unit, explains the system configuration in which it is used, and
also provides information on basic operations, functions and specifications.
1-1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1-2 System Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1-3 Basic Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1-3-1 Position Control (Direct Operation) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1-3-2 Speed Control and Torque Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1-3-3 Other Operations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1-4 List of Functions and Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1-4-1 General Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1-4-2 List of Functions and Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1-5 List of Functions by Purpose . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1-6 Comparison with Existing Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Page 29
2
Fe at ur e s Section 1-1
1-1 Features
The Position Control Unit is a CS/CJ-series CPU Bus Unit. The Position Control Unit (PCU) receives commands from the CPU Unit's internal Auxiliary
Area and outputs positioning commands to MECHATROLINK-II Servo Drives.
MECHATROLINK is a registered trademark of MECHATROLINK Members
Association.
Compatible with the
MECHATROLINK-II Highspeed Field Network
A MECHATROLINK-II high-speed (10 Mbps) communications interface is
used to control Servo Drives for up to 16 axes with a single CS/CJ-series Unit.
Shielded twisted-pair cables in daisy-chain formation make wiring simple and
enable multi-axis systems that require less wiring and are smaller in size.
High-speed, Highprecision Control Using
Data Communications
Optimal motor performance can be achieved by transmitting data using communications between the Programmable Controller (PLC) and Servo Drives,
without having to set an upper limit for the designated speed. High-speed and
high-precision position control using high-resolution motors are possible.
Position Control (Direct
Operation)
Positioning can be performed simply by directly setting the target position and
target speed from the CPU Unit. Positioning to either absolute or relative positions is also possible. Interrupt feeding is also supported. With interrupt feeding, positioning is continued for a specified amount after an interrupt input
signal is received, and then the axis is stopped.
Speed Control and Torque
Control
The Servo Drive's speed and torque can be controlled by directly specifying
the target speed and torque from the CPU Unit.
Compatible with
Servomotors with
Absolute Encoders
The PCU is compatible with Servomotors that have absolute encoders. Using
such Servomotors eliminates the need to repeatedly perform origin searches.
Transfer Data between
Host PLC and Servo Drive
The Servo Drive's parameters and monitors can be set from the CPU Unit. All
the data for the multi-axis system can be centrally controlled from the host
PLC. This removes the difficulty in starting up devices or setting data when
replacing a Unit.
CJ1W-NC271/471/F71 CS1W-NC271/471/F71
R
U
N
E
R
C
E
R
H
E
R
M
M
L
K
N
C
F71
U
N
IT
No.
M
LK
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
Position Control Unit
RUN
ERC
ERH
ERM
MLK
NCF71
CS
UNIT
No.
9
8
5
4
3
2
1
0
M
L
K
Page 30
3
System Configuration Section 1-2
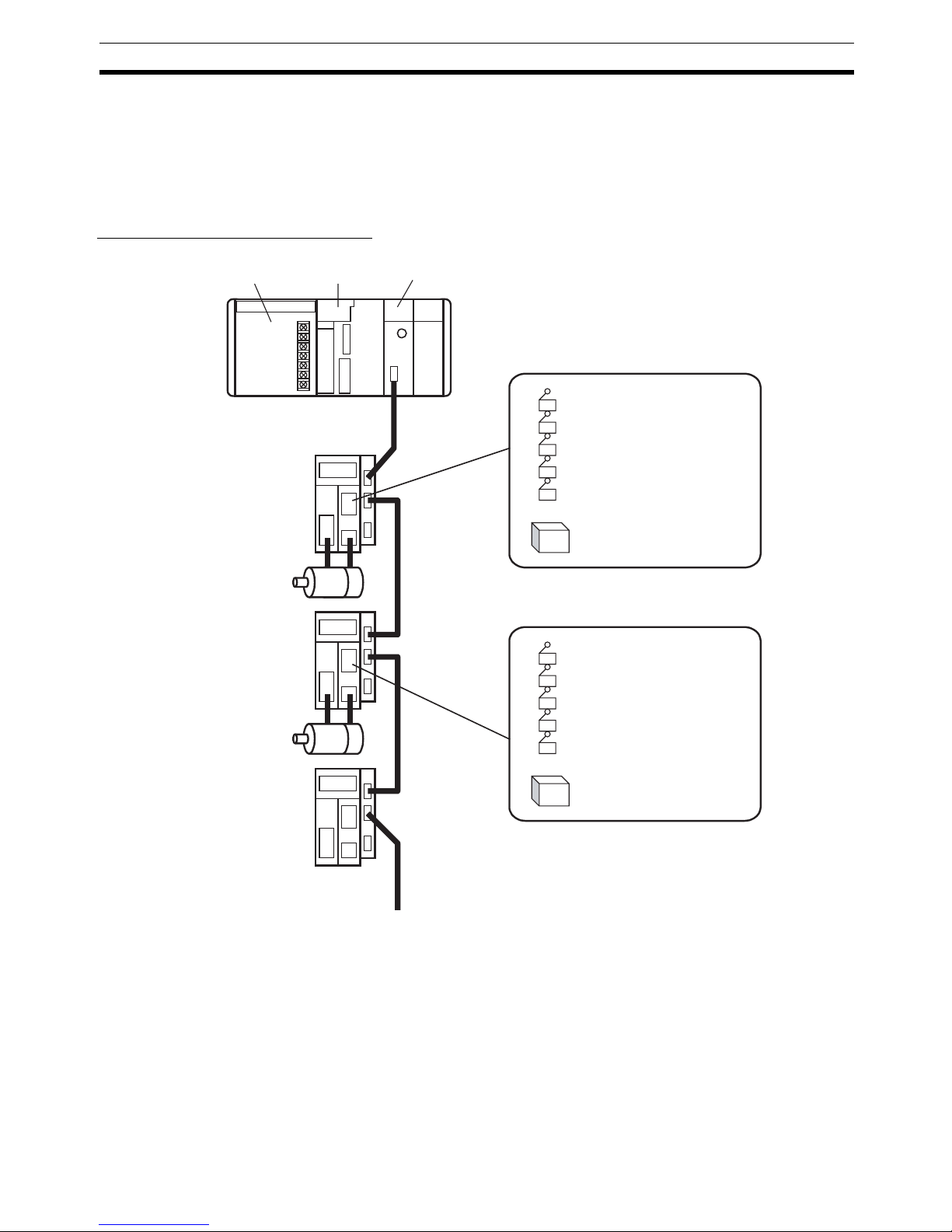
1-2 System Configuration
The PCU receives commands from the CPU Unit's ladder program and control signal status (forward/reverse rotation limit, origin, origin proximity, and
interrupt input signals) from devices connected externally to the Servo Drive,
and uses them to control Servo Drive positioning.
System Configuration Example
Power Supply Unit
CJ-series
CPU Unit
CJ1W-NCF71
Position Control Unit
Servo Drive
Servomotor
Servo Drive
Servomotor
Servo Drive
MECHATROLINK-II
(16 axes max.)
External inputs
External inputs
Forward rotation limit input signal
Reverse rotation limit input signal
Origin input signal
Origin proximity input signal
Interrupt input signal
Etc.
24-V DC power supply
for interface
Forward rotation limit input signal
Reverse rotation limit input signal
Origin input signal
Origin proximity input signal
Interrupt input signal
24-V DC power supply
for interface
Etc.
Page 31

4
Basic Operations Section 1-3
1-3 Basic Operations
The PCU's operations are as follows:
1-3-1 Position Control (Direct Operation)
Positioning can be executed either to an absolute position (i.e., to an absolute
position from the origin) or to an incremental position (i.e., to a position relative to the present position). Interrupt feeding is also possible, whereby an
axis is moved a specified amount when an interrupt input signal is received
and then stopped.
Absolute Movements and
Relative Movements
With absolute and relative movements, position and speed data are set
directly from the ladder program in the CPU Unit. Positioning is executed
according to operating commands sent to the PCU from the CPU Unit. It is
also possible to change the speed or to send commands to move axes to different positions while positioning is being performed.
Origin searches
CJ1W-NC@71/CS1W-NC@71
Position Control Unit functions
Position control
(direct operation)
Speed control
Torque control
Other operations
Absolute movement
Relative movement
Interrupt feeding
Jogging
Overrides
Present position preset
Stop functions
Backlash compensation
Time
Speed
Start
Start
Position changed, start
New target position
X
Y
Speed changed
Target position before
position changed
Page 32

5
Basic Operations Section 1-3
Interrupt Feeding When an interrupt input signal is received, positioning is continued for the
specified amount of movement and then stopped.
Linear Interpolation Linear interpolation can be performed for a combination of axes (Unit Ver. 1.1
or later).
1-3-2 Speed Control and Torque Control
Speed command data and torque command data are set from the CPU Unit.
Speed control and torque control of the Servomotor are executed by sending
operating commands to the PCU from the CPU Unit.
1-3-3 Other Operations
Origin Searches The origin search operations find the origin for a designated axis.
Jogging Jogging moves a specified axis at a designated speed and then stops it.
Overrides When an override is enabled during positioning, the target speed is changed
to the override speed.
Present Position Preset
(Changing the Present
Position)
The PRESENT POSITION PRESET command changes the present position
to a specified position.
Stop Functions The DECELERATION STOP command decelerates positioning to a stop.
The EMERGENCY STOP command cancels operating commands immediately and stops the axis after moving it for the number of pulses remaining in
the Servo Drive's deviation counter.
Time
Speed
Interrupt input
Specified amount of movement (a
negative direction can also be set)
Time
Speed
A
× 1.5
1
0
A
Override set value: 150%
Override Enable Bit
Page 33

6
List of Functions and Specifications Section 1-4
1-4 List of Functions and Specifications
1-4-1 General Specifications
Specifications not listed above conform to general CS/CJ Series specifications.
1-4-2 List of Functions and Specifications
Item Specification
Model CJ1W-NC271/471/F71 CS1W-NC271/471/F71
Internal current
consumption
360 mA max. at 5 V DC
Dimensions 31 × 90 × 65 mm (W × H × D) 130 × 35 × 101 mm (W × H × D)
Weight 95 g max. 188 g max.
Ambient operat-
ing temperature
0 to 55°C
Approved standards
CE, cULus, and C-tick
Item Specification
Unit classification CPU Bus Unit
Applicable PLCs CS/CJ Series
Possible unit number settings 0 to F
I/O allocations Common Operating Memory Area Words allocated in CPU Bus Unit Area: 25 words (15 output words,
10 input words)
Axis Operating Memory Area Allocated in one of the following areas (user-specified):
CIO, Work, Auxiliary, Holding, DM, or EM Area.
Number of words allocated: 50 words (25 output words, 25 input
words) × Highest axis No. used
Compatible devices • OMRON G-series Servo Drives
(Built-in MECHATROLINK-II communications)
• OMRON W-series Servo Drives
(equipped with MECHATROLINK-II Application Module or built-in
MECHATROLINK-II communications)
• OMRON SMARTSTEP Junior Servo Drives
(Built-in MECHATROLINK-II communications)
Note SMARTSTEP Junior Servo Drive are supported by Position
Control Units with unit version 2.0 or later.
Control method Control commands executed using MECHATROLINK-II synchro-
nous communications.
Maximum number of controlled axes CS1W/CJ1W-NC271: 2 axes, CS1W/CJ1W-NC471: 4 axes,
CS1W/CJ1W-NCF71: 16 axes
Control units Position command unit Command unit: Depends on the Electronic Gear Setting in the
Servo Parameters.
Default setting: Pulses
Speed command unit for position
control
Command units/s
Acceleration/deceleration speeds
for position control
10,000 command units/s
2
Speed command unit for speed
control
0.001% of the motor's momentary maximum rotation speed
Torque command unit for torque
control
0.001% of the motor's momentary maximum torque
Page 34

7
List of Functions and Specifications Section 1-4
Control command range
Position command range −2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 (command units)
Speed command range for position
control
0 to 2,147,483,647 (command units/s)
Acceleration/deceleration speeds
for position control
1 to 65,535 (10,000 command units/s
2
)
Speed command range for speed
control
−199.999% to 199.999%
The upper limit of the speed command range depends on the
specifications of the Servo Drive.
Torque command range for torque
control
−199.999% to 199.999%
The upper limit of the torque command range depends on the
specifications of the Servo Drive.
Control functions
Servo lock/unlock Creates (Servo lock) or releases (Servo unlock) the position loop
on the PCU.
Position control Positions to an absolute position or relative position according to
the target position and target speed specified from the ladder program.
Origin determination • Origin search: Establishes the origin using the specified search
method.
• Present position preset: Changes the present position to a specified position to establish the origin.
• Origin return: Returns the axis from any position to the established origin.
• Absolute encoder origin: Establishes the origin using a Servomotor that has an absolute encoder, without having to use an origin
search.
Jogging Outputs pulses at a fixed speed in the forward rotation or reverse
rotation direction.
Interrupt feeding Performs positioning by moving the axis a fixed amount when an
external interrupt input is received while the axis is moving.
Speed control Performs speed control by sending a command to the Servo Drive
speed loop.
Torque control Performs torque control by sending a command to the Servo Drive
current loop.
Stop functions • Deceleration stop: Decelerates the moving axis to a stop.
• Emergency stop: Positions the moving axis for the number of
pulses remaining in the deviation counter and then stops the axis.
Auxiliary functions
Acceleration/deceleration curves Sets one of the following: a trapezoidal (linear) curve, an exponen-
tial curve, or an S-curve (moving average).
Torque limit Restricts the output torque during axis operation.
Override Multiplies the axis command speed by a specified ratio.
Override: 0.01% to 327.67%
Servo parameter transfer Reads and writes the Servo Drive parameters from the ladder pro-
gram in the CPU Unit.
Monitoring function Monitors the control status of the Servo Drive, such as the com-
mand coordinate positions, feedback position, current speed, and
torque.
Software limits Limits software operation within the positioning range during posi-
tion control.
Backlash compensation Compensates for the amount of play in the mechanical system
according to a set value.
Deviation counter reset The position deviation in the Servo Drive’s deviation counter can
be reset to 0 (unit version 1.3 or later).
External I/O Position Control Unit One MECHATROLINK-II interface port
Servo Drive I/O Forward/reverse rotation limit inputs, origin proximity inputs, exter-
nal interrupt inputs 1 to 3 (can be used as external origin inputs)
Item Specification
Page 35

8
List of Functions by Purpose Section 1-5
1-5 List of Functions by Purpose
Self-diagnostic functions Watchdog, flash memory check, memory corruption check
Error detection functions Overtravel, Servo Drive alarm detection, CPU error, MECHA-
TROLINK communications error, Unit setting error
Purpose Category Name Basic function Details
Establishing the
mechanical origin of
the machine
Origin determination
Origin search The motor is operated to estab-
lished the origin.
8-2 Origin Search
Operation
Present position preset The position where the motor is
stopped is set to a specified position to establish the origin.
8-3 Present Position
Preset
Origin return The axis is returned to the estab-
lished origin.
8-4 Origin Return
Absolute encoder origin The origin is established using a
Servomotor with an absolute
encoder, so origin searches are
not required at machine startup.
8-6 Absolute
Encoder Origin
Point-to-point (PTP)
positioning
Position control
Direct operation (absolute movement or relative
movement)
The position and speed are specified to perform positioning using
an absolute or relative movement.
9-4 Using Direct
Operation
Changing the target
position and speed
as required during
positioning
Direct operation:
Changing target position
or changing target speed
The target position or target
speed is changed during positioning with direct operation.
9-4-3 Changing Target Position
9-4-4 Changing Target Speed
Performing positioning for a specified
distance from an
external input point
during positioning
Interrupt feeding When an interrupt input signal
turns ON during positioning with
direct operation, operation
switches to positioning for a fixed
amount.
9-5 Interrupt Feeding
Performing manual
feeding for adjustment or other purpose
Jogging The axis is moved at a fixed
speed in the forward rotation or
reverse rotation direction.
10-2 Jogging
Reducing shock
while device is operating
Auxiliary
functions
Acceleration/deceleration curves
Acceleration/deceleration is performed according to the basic
trapezoidal curve (linear acceleration/deceleration), an exponential
curve, or an S-curve, which
greatly helps to reduce mechanical vibration.
7-4 Acceleration and
Deceleration Operations
Temporarily multiplying the machine's
operating speed by a
constant ratio to perform startup adjustments
Overrides The axis command speed is mul-
tiplied by a constant ratio.
10-3 Override
Restricting output
torque during control operations such
as pushing control
Torque limit A constant limit is applied to the
output torque of the Servomotor
during positioning.
10-4 Torque Limits
Stopping the device
during operation
Stop function
Deceleration stop or
emergency stop
The moving axis is decelerated to
a stop or the axis is moved for the
number of pulses remaining in the
deviation counter and then
stopped.
10-9 Stop Functions
Changing the Servo
Drive settings from
the PLC
Data transfer
function
Reading/writing Servo
parameters
Servo Drive parameters are read
or written from the CPU Unit.
5-3 Transferring
Servo Parameters
Item Specification
Page 36

9
Comparison with Existing Models Section 1-6
1-6 Comparison with Existing Models
Performing speed
feeding in rotary control such as sheet
feeding.
Speed control
Speed control The speed command value is
directly specified to control the
Servomotor rotation.
10-5 Speed Control
Changing the output
torque sequentially
during control operations such as tightening.
Torque control
Torque control The torque command value is
directly specified to control the
Servomotor's output torque.
10-6 Torque Control
Functions and
performance
CJ1W-NC@71
CS1W-NC@71
CJ1W-NC@13/@33
CS1W-NC@13/@33
Unit type CPU Bus Unit Special I/O Unit
Unit number alloca-
tion
Unit numbers can be set from 0 to F
(CPU Bus Units).
Unit numbers can be set from 0 to 95.
• One-axis and two-axis PCUs: One unit number
used.
• Four-axis PCUs: Two unit numbers used.
Control method Commands are executed using MECHA-
TROLINK-II synchronous communications.
Open-loop control is performed using a pulse
train output.
Format of data
exchanged between
PLC and PCU
Binary (hexadecimal)
Example: Present position is output to the PLC
in 32-bit signed binary format.
Same as CJ1W-NC@71/CS1W-NC@71.
Position command
range
−2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
(Unit depends on Servo Parameters)
−1,073,741,823 to 1,073,741,823 pulses
Present position
range
−2,147,483,648~2,147,483,647
(Unit depends on Servo parameters)
−2,147,483,647 to 2,147,483,647 pulses
Zone range No zone functions −1,073,741,823 to 1,073,741,823 pulses
Speed command
range
Position control:
0 to 2,147,483,647 (command units/s)
(Upper limit speed depends on Servo Drive
and Servomotor.)
Speed control:
−199.999% to 199.999%
(percentage of Servomotor’s momentary maximum rotation speed)
The upper limit of the speed command range
depends on the specifications of the Servo
Drive.
1 to 500,000 (unit: 1 pps)
Torque command
range
−199.999% to 199.999%
(percentage of Servomotor's momentary maximum torque)
The upper limit of the torque command range
depends on the specifications of the Servo
Drive.
None
Overrides 0.01% to 327.67% in increments of 0.01% 1% to 999% in increments of 1%
Memory operation
function
None Absolute/relative movement, linear interpolation,
interrupt feeding, speed control, forced interrupt,
and teaching
Purpose Category Name Basic function Details
Page 37

10
Comparison with Existing Models Section 1-6
Note The response time depends on the cycle time of the PLC and the MECHA-
TROLINK communications settings. The time shown in the table is the maximum value obtained when calculated according to specified measurement
conditions. For details, refer to Appendix A Performance Characteristics.
Origin search Origin search method:
• The origin input signal is detected after the origin proximity input signal turns OFF.
• The origin input signal is detected after the origin proximity input signal turns ON. (Unit version 2.0 or later)
• The origin input signal is detected without
using the origin proximity input signal. (Unit
version 2.0 or later)
Origin search methods:
• The origin input signal is detected after the origin proximity input signal turns ON.
• The origin input signal is detected after the origin proximity input signal turns OFF.
• The origin input signal is detected without
using the origin proximity input signal.
Origin compensation: After detecting the origin
input signal, positioning is performed for the origin return final travel distance (specified in Servo
Parameters).
Origin compensation: The axis is moved for the
amount specified by the origin compensation
data (specified from the Unit) at the proximity
speed.
Acceleration/deceleration curves
Trapezoidal curve, exponential curve, or S-curve
S-curve acceleration/deceleration uses a moving average.
Trapezoidal curve or S-curve
S-curve acceleration/deceleration uses a tertiary function.
Setting acceleration/
deceleration speeds
Accelerations and decelerations are specified in
units of 10,000 command units/s
2
. Servo param-
eters are set individually for each axis.
The times in milliseconds required to reach the
maximum speed from the initial speed and to
reach the initial speed from the maximum speed
are specified
Direct operation: Acceleration/deceleration
speeds are specified as operation data from the
PLC.
Memory operation: Up to 9 acceleration/deceleration speeds per axis are recorded in the Unit.
Deviation counter
reset
Supported (unit version 1.3 or later). Supported.
Emergency stop A hardware input contact is not provided on the
Position Control Unit.
Stopping is possible after moving the number of
pulses remaining in the deviation counter by
using an allocated operation bit.
The PCU's hardware input contact is used.
Data transfer method Writes/reads using the Data Transfer Bit. • Data can be read or written using the Data
Transfer Bit.
• Data can be read or written using the IOWR/
IORD instruction.
Saving data Parameters can be saved to the flash memory in
the PCU.
Servo Parameters are saved in the Servo Drive.
Axis Parameters and Zone Data are saved in the
flash memory in the PCU.
CPU Unit cycle time
extension for END
refresh
1 ms max. per 16 axes (using the CS1/CJ1-H
CPU Unit)
0.5 ms max. per PCU
Response time 4 ms max. (time from when the start commands
for the ladder program are sent until the Servo
Drive receives the control command when four
axes are connected) (See note.)
4 ms max. (time from when the start commands
for the ladder program are sent until the Position
Control Unit performs pulse output when all axes
of a four-axis Unit are being operated simultaneously)
Functions and
performance
CJ1W-NC@71
CS1W-NC@71
CJ1W-NC@13/@33
CS1W-NC@13/@33
Page 38

11
SECTION 2
Basic Procedures
This section provides an overview of the procedures required to use the Position Control Unit.
2-1 Basic Flow of Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2-2 Starting Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2-2-1 Overview of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2-2-2 System Configuration and Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2-2-3 Setting the PCU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2-2-4 Starting MECHATROLINK Communications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
2-2-5 Setting Servo Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
2-2-6 Operating the Servomotor from the PCU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Page 39

12
Basic Flow of Operations Section 2-1
2-1 Basic Flow of Operations
The basic flow of Position Control Unit (PCU) operation is described in this
section. The steps from installation through setting the MECHATROLINK
devices are required only when installing the devices for the first time. When
PCU and MECHATROLINK device settings have been completed, start operation from starting MECHATROLINK communications in the flow of operation.
Note (1) Perform wiring according to instructions given in the Servomotor and Ser-
vo Drive's operation manuals.
(2) Refer to the CJ Series PLC Operation Manual.
Install the PCU.
START
(See note 1.)
Set the unit number of the PCU.
Connect the Servo Drives to the PCU.
(See note 1.)
Create the I/O tables for the PLC.
Turn ON the power to the PLC.
(See note 2.)
Flow of operation Details
Installation
Set the station addresses of the Servo Drives.
Wiring
Connect the Servomotors to the Servo Drives.
Connect the Servo Drives to the external input
devices.
PLC Settings
PCU Settings
Transfer the common parameters from the CPU
Unit to the PCU using the WRITE DATA Bit in
the Common Operating Memory Area.
Transfer the axis parameters from the CPU Unit
to the PCU using the WRITE DATA Bit in the
Common Operating Memory Area.
Transfer only the axis parameters
for the axes to be used.
Save the transferred common parameters and
axis parameters to the PCU's flash memory
using the SAVE DATA Bit in the PCU's
Common Operating Memory Area.
Restart the PCU or cycle the power to the PLC.
The PCU can now communicate
with MECHATROLINK devices.
(Continued on next page.)
3-2 Installing the Position
Control Unit
3-1 Nomenclature and
Functions
3-3 External I/O Circuits
3-4 Wiring
4-3 Common Parameter Area
4-6 Common Operating
Memory Area
5-2-1 Writing PCU
Parameters
4-4 Axis Parameter Area
5-2-1 Writing PCU
Parameters
5-2-3 Saving PCU
Parameters
Page 40

13
Basic Flow of Operations Section 2-1
YES
NO
YES
NO
Flow of operation Details
Starting MECHATROLINK communications (setup)
(Continued from previous page.)
Turn ON the power to the Servo Drives.
Turn ON the CONNECT Bit in the PCU's
Common Operating Memory Area.
Check that communications are established with
the connected devices by referring to the axis
communications status in the PCU's Common
Operating Memory Area.
Are communications established
with all devices?
The MECHATROLINK devices can
now be operated from the PCU.
Setting the MECHATROLINK devices
Transfer the Servo parameters from the CPU
Unit to the PCU using the WRITE SERVO PARAMETER Bit and SAVE SERVO PARAMETER
Bit in the PCU's Axis Operating Memory Areas.
Transfer (save) only the Servo
Parameters for the axes to be used.
Use either of the following methods to enable
the parameter settings for offline parameters.
1) Perform the device setup.
2) Turn OFF the CONNECT Bit (releases the
connection) in the PCU's Common Operating
Memory Area, and after Servo
communications have stopped, cycle the
Servo Drive power.
The Servo Parameters that have
been set are now enabled.
Starting MECHATROLINK communications
Turn ON the power to the Servo Drives and
external input devices.
Turn ON the CONNECT Bit in the PCU's
Common Operating Memory Area.
Check that communications are established with
the connected devices by referring to the axis
communications status in the PCU's Common
Operating Memory Area.
Communications are established
with all devices?
The MECHATROLINK devices can
now be operated from the PCU.
(Continued on next page.)
4-6 Common Operating
Memory Area
6-3-1 Establishing
Connections
6-3-2 MECHATROLINK
Communications Status
6-3-3 MECHATROLINK
Communications Errors
12-5 Troubleshooting
4-5 Servo Parameter Area
4-7 Axis Operating Output
Memory Areas
4-8 Axis Operating Input
Memory Areas
5-3-1 Writing Servo
Parameters
5-3-3 Saving Servo
Parameters
6-3-1 Establishing
Connections
6-4 Standard Settings for
Servo Drives Using
MECHATROLINK
5-3-4 Device Setup
4-6 Common Operating
Memory Area
6-3-1 Establishing
Connections
6-3-2 MECHATROLINK
Communications Status
6-3-3 MECHATROLINK
Communications Errors
12-5 Troubleshooting
Page 41

14
Basic Flow of Operations Section 2-1
Flow of operation Details
Servo lock
(Continued from previous page.)
Turn ON the SERVO LOCK Bit in the PCU's
Axis Operating Memory Area.
Check that the SVON Flag indicating the Servo
Drive status in the PCU's Axis Operating
Memory Area is ON.
The Servomotor axis operations can
now be controlled from the PCU.
Jogging
Set the jog speed in the speed command value
of the PCU's Axis Operating Memory Area.
Set the acceleration and deceleration
times in the Servo parameters.
Set the feed direction in the Direction
Designation Bit of the PCU's Axis Operating
Memory Area.
Turn ON the JOG Bit in the PCU's Axis
Operating Memory Area.
Stop the jogging operation by turning OFF the
JOG Bit in the PCU's Axis Operating Memory
Area.
Check whether jogging has stopped by
monitoring whether the Busy Flag is OFF in the
PCU's Axis Operating Memory Area.
Origin determination
Set the Origin Search Speed in the speed
command value of the PCU's Axis Operating
Memory Area.
Set the Origin Search Approach
Speeds 1 and 2 in the Servo
Parameters.
Turn ON the ORIGIN SEARCH Bit in the PCU's
Axis Operating Memory Area.
Check whether the ORIGIN SEARCH operation
has completed by monitoring the PCU
Positioning Completed Flag and No Origin Flag
in the PCU's Axis Operating Memory Area.
(Continued on next page.)
4-7 Axis Operating Output
Memory Areas
4-8 Axis Operating Input
Memory Areas
10-1 Servo Lock/Unlock
4-7 Axis Operating Output
Memory Areas
4-8 Axis Operating Input
Memory Areas
7-4 Acceleration and
Deceleration Operations
10-2 Jogging
4-7 Axis Operating Output
Memory Areas
4-8 Axis Operating Input
Memory Areas
7-4 Acceleration and
Deceleration Operations
SECTION 8 Defining the
Origin
Page 42

15
Basic Flow of Operations Section 2-1
Turn OFF the power to the CPU Unit.
END
Flow of operation Details
Positioning
(Continued from previous page.)
Set the target position in the position command
value of the PCU's Axis Operating Memory Area.
Set the target speed in the speed command value of the PCU's Axis Operating Memory Area.
Set the acceleration and deceleration
times for positioning in the Servo
Parameters.
Turn ON the Movement Bit (ABSOLUTE
MOVEMENT or RELATIVE MOVEMENT) in the
PCU's Axis Operating Memory Area.
Check whether the positioning operation has
completed by monitoring the PCU Positioning
Completed Flag in the PCU's Axis Operating
Memory Area.
Stopping operation
Start axis operation using jogging, an origin
search, or direct operation.
Turn ON the Deceleration Stop Bit or
Emergency Stop Bit in the PCU's Axis Operating
Memory Area.
Set the deceleration time for a
deceleration stop in the Servo
Parameters.
Check whether the positioning operation has
stopped by monitoring whether the Stop
Execution Flag is ON in the PCU's Axis
Operating Memory Area.
Servo Unlock
Turn ON the SERVO UNLOCK Bit in the PCU's
Axis Operating Memory Area.
Check that the SVON Flag indicating the Servo
Drive status in the PCU's Axis Operating
Memory Area is OFF.
Finishing operation
Stop Servo communications by turning OFF the
CONNECT Bit (releases connection) in the
PCU's Common Operating Memory Area.
Turn OFF the power to the Servo Drives and
external input devices.
4-7 Axis Operating Output
Memory Areas
4-8 Axis Operating Input
Memory Areas
7-4 Acceleration and
Deceleration Operations
9-1 Direct Operation
Overview
4-7 Axis Operating Output
Memory Areas
4-8 Axis Operating Input
Memory Areas
7-4 Acceleration and
Deceleration Operations
10-9 Stop Functions
4-7 Axis Operating Output
Memory Areas
4-8 Axis Operating Input
Memory Areas
10-1 Servo Lock/Unlock
4-6 Common Operating
Memory Area
6-3-1 Establishing
Connections
6-3-2 MECHATROLINK
Communications Status
Page 43

16
Starting Operation Section 2-2
2-2 Starting Operation
Examples of operating the Servomotor using RELATIVE MOVEMENT commands for direct operation are provided in this section for first-time users of a
PCU.
2-2-1 Overview of Operation
The following example is for operating the Servomotor using direct operation
under the following operation conditions. An OMRON W-series Servomotor
and a Servo Drive with a Yaskawa JUSP-NS115 MECHATROLINK-II Application Module installed is used.
Only the minimum parameters required to operate the Servomotor are set in
this example. Default settings are used for the PCU and Servo Drive parameters that are not set.
A Programming Console is used in this operation example without using a
ladder program and with the PLC in PROGRAM mode to manually perform
the settings and execute the start commands that are required to operate the
Servomotor. The Programming Console is used to set the required data for
direct operation and then turn ON the RELATIVE MOVEMENT Bit to operate
the motor.
2-2-2 System Configuration and Wiring
The following system configuration is used. In this example, only the motor is
operated, without using a mechanical system. The unit number of the PCU is
0, and the station address of the MECHATROLINK-II Application Module is 1.
0.1 s0.1 s
100 kpulses/s
Speed
Target speed: 100,000 (pulses/s)
Target position: 500,000 pulses
Time
Page 44

17
Starting Operation Section 2-2
The devices used in this configuration diagram example are as follows:
Each of the above devices is in its factory-shipped condition.
Setting the PCU Unit Number
Set the unit number using the rotary switch on the front of the PCU.
Unit number: 0
Setting the Station Address of the MECHATROLINK-II Application Module
Set the station address of the MECHATROLINK-II Application Module using
the rotary switch (SW1) on the Module. Use the default settings for the DIP
switch (SW2).
SW1: 1
SW2: Default settings (pin 1: ON; pin 2: ON; pin 3: OFF; pin 4: OFF)
Device Model
CPU Unit CJ1H-CPU67H
Power Supply Unit CJ1W-PA202
Position Control Unit CJ1W-NCF71
Programming Console C200H-PRO27
Programming Console Connecting Cable CS1W-CN224 (2 m)
Servo Drive R88D-WT01HL
Servomotor R88M-W10030L
Servomotor Encoder Cable R88A-CRWA003C (3 m)
Servomotor Power Cable R88A-CAWA003S (3 m)
MECHATROLINK-II Application Module JUSP-NS115 (Yaskawa)
MECHATROLINK-II Connection Cable JEPMC-W6003-01 (Yaskawa) (1 m)
MECHATROLINK-II Terminator JEPMC-W6022 (Yaskawa)
CPU Unit
Position Control Unit
Power Supply Unit
Programming Console
MECHATROLINK-II
Application Module
Servo Drive
Servomotor
MECHATROLINK-II Terminator
MECHATROLINK-II Connection Cable
Page 45

18
Starting Operation Section 2-2
Wiring Wire the Units as shown in the following diagram.
The Servo Drive's CN1 input signals depend on the input signal allocations,
which are set in this operation example. Of these allocated input signals, the
forward drive prohibit input (forward rotation limit input) and reverse drive prohibit input (reverse rotation limit input) are used as N.C. contacts. Therefore,
connect them so that they are normally ON. The origin proximity signal and
external latch inputs 1 to 3 are not used in this operation example and therefore do not need to be wired.
The above diagram shows the wiring for the PCU, Servo Drive, MECHATROLINK-II Application Module, and external control input signals at the
Servo Drive. Refer to each of the CPU Unit and Servo Drive operation manuals for details on wiring the CPU Unit and Servo Drive power supply and connecting the Servo Drive and Servomotor.
2-2-3 Setting the PCU
Creating I/O Tables Turn ON the power to the PLC and create the I/O tables. Refer to the CJ
Series PLC Operation Manual for details on creating I/O tables.
Setting Common
Parameters
Set the Common Parameters of the PCU. The minimum required Common
Parameters that must be set are as follows:
• Axis Operating Output Memory Area designation
• Axis Operating Input Memory Area designation
• Scan list setting (information registered for axes connected to MECHATROLINK communications)
Common Parameters are transferred to the PCU using the WRITE DATA Bit in
the Common Operating Memory Area. D01000 to D01011 are used for data
to be transferred.
CN6A
CN6B
CN1
+24VIN
(Not used.)
DEC
POT
NOT
EXT1
EXT2
EXT3
47
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
24 V D
C
MLK
CJ1W-NCF71
JEPMC-W6003-01
JEPMC-W6022
Terminator
JUSP-NS115 R88D-WT01HL
Origin proximity signal
Forward rotation limit
input
Reverse rotation limit
input
Page 46

19
Starting Operation Section 2-2
Common Parameters Set
in the PCU
The following settings are made in D01000 to D01011 as the Common
Parameters to be set in the PCU. Refer to the following table for setting
details.
The above settings enable the Servo Drive connected to MECHATROLINK to
be controlled from the ladder program through the I/O words that are allocated
as shown in the following diagram.
Writing Common
Parameters to the PCU
The Common Parameter settings in D01000 to D01011 are written to the
PCU. Make the settings for transferring data to the PCU's Common Operating
Memory Area as shown below.
Data is written to the PCU by turning ON the WRITE DATA Bit in the Common
Operating Memory Area. For the PCU with unit number 0, the WRITE DATA
Bit is allocated in CIO 150001. Turn ON this bit using the Programming Console.
DM word Set value Common Parameter Details
D01000 00B0 hex Axis Operating Output
Memory Areas
Set the beginning word of
the Axis Operating Output
Memory Areas to CIO 100.
Axis 1 output words:
CIO 100 to CIO 124
D01001 0064 hex Beginning word of Axis
Operating Output Memory
Areas
D01002 00B0 hex Axis Operating Input Mem-
ory Areas
Set the beginning word of
the Axis Operating Input
Memory Area to CIO 500.
Axis 1 input words: CIO 500
to CIO 524
D01003 01F4 hex Beginning word of Axis
Operating Input Memory
Areas
D01004 0040 hex Scan list setting (axes 1 and 2)Allocate axis 1 of the PCU
to the Servo Drive.
D01005 to
D01011
Set all
words to
0000 hex.
Scan list setting
(axes 3 to 16)
Position Control Unit
Axis 1: Servo
Axis 2: None
Axis 3: None
CPU Unit
Ladder program
Axis 1 output data
CIO 100 to
CIO 124
Axis 1 input data
CIO 500 to
CIO 524
Start
command,
etc.
Present position, etc.
Registered
connections
MECHATROLINK
Servo Drive
Word Set value Data transfer
setting name
Details
CIO 1506 000C hex Number of write
words
Number of write words: 0C hex =
12 decimal
CIO 1507 0082 hex Write source area Beginning word of write data:
D01000
CIO 1508 03E8 hex Write source word
CIO 1509 1838 hex Write destination
address
Write destination address in PCU:
1838 hex = Beginning word of
Common Parameter Area
CIO 1500
01
This bit transfers data according to the data transfer
settings when it is turned ON.
WRITE DATA Bit
Page 47

20
Starting Operation Section 2-2
While data is being written to the PCU, the Data Transferring Flag in the Common Operating Memory Area turns ON. When data has finished being written,
the Data Transferring Flag turns OFF. For the PCU with unit number 0, the
Data Transferring Flag is allocated in CIO 151514.
The following diagram shows the operation for writing data to the PCU.
Setting Axis
Parameters
In this operation example, the PCU's default settings are used for each axis
parameter, so they do not need to be transferred to the PCU.
Saving PCU Settings The Common Parameters are saved in the PCU's flash memory.
Data is saved to the PCU's flash memory by turning ON the SAVE DATA Bit in
the Common Operating Memory Area. For the PCU with unit number 0, the
SAVE DATA Bit is allocated in CIO 150003. Turn ON this bit using the Programming Console.
While data is being saved to flash memory, the Data Transferring Flag in the
Common Operating Memory Area turns ON. When data has finished being
saved, the Data Transferring Flag turns OFF. For the PCU with unit number 0,
the Data Transferring Flag is allocated in CIO 151514.
CIO 1515
14
Data Transferring Flag
This flag is ON while data is being written.
When writing is completed, the flag turns OFF.
CIO 1506
CIO 1507
CIO 1508
CIO 1509
CIO 1500
01
D01000
D01001
D01002
D01003
D01004
D01005
D01011
000C hex
0082 hex
03E8 hex
1838 hex
00B0 hex
0064 hex
00B0 hex
01F4 hex
0040 hex
0000
0000
1838 hex
1839 hex
183A hex
183B hex
183C hex
183D hex
1843 hex
00B0 hex
0064 hex
00B0 hex
01F4 hex
0040 hex
0000
0000
CPU Unit Position Control Unit
CIO 1515
14
Common Operating Memory Area
Number of write words (12)
Write source area
(D01000)
Write destination address
(1838 hex)
WRITE DATA Bit
Data Transferring Flag (ON while data is being written)
DM Area
::
Beginning word of Axis
Operating Output Memory
Area (100 words)
Beginning word of Axis
Operating Input Memory
Area (500 words)
Scan list setting
Axis 1: Registered to Servo Drive
Axes 2 to 16: Not used.
Internal address
::
CIO 1500
03
SAVE DATA Bit
This bit saves parameters in the PCU's
flash memory when it is turned ON.
Page 48

21
Starting Operation Section 2-2
Restarting the PCU After the PCU settings have been saved, restart the PCU to enable the set-
tings. Either cycle the power to the CPU Unit, or restart the PCU. For the PCU
with unit number 0, the Restart Bit is allocated in A50100.
Note Do not turn OFF the power to the PLC or restart the PCU while data is being
saved to the PCU’s flash memory. Doing so may corrupt the PCU’s memory.
Always make sure that the Data Transferring Flag is OFF before turning OFF
the power to the CPU Unit or restarting the PCU.
2-2-4 Starting MECHATROLINK Communications
Communications are started with the Servo Drive connected to MECHATROLINK based on the Common Parameter settings in the PCU.
MECHATROLINK communications are started by turning ON the CONNECT
Bit in the Common Operating Memory Area. For the PCU with unit number 0,
the CONNECT Bit is allocated in CIO 150100. Turn ON this bit using the Programming Console.
When connections are established, the PCU starts communications with the
MECHATROLINK devices (Servo Drives) registered in the scan list set in the
Common Parameters. When communications with the registered device are
normal, the corresponding bits for the axes in the Axis Communications Status of the Common Operating Memory Area are turned ON. For the PCU with
unit number 0, the Axis Communications Status is allocated in the bits of CIO
1522.
When communications with the registered devices are not normal, the corresponding bits for the axes in the Axis Communications Status bits of the Common Operating Memory Area are not turned ON and an MLK initialization
error (Unit error code 0020 hex) occurs in the PCU. Any axis errors that occur
can be checked using the Axis Error Flags and error codes in the Axis Operating Memory Areas.
The Connection Status Flag in the Common Operating Memory Area will turn
ON at the start of communications when the CONNECT Bit turns ON, regardless of whether communications with all registered devices are normal.
In this operation example, if MECHATROLINK communications are started
normally, the status of each flag is as follows:
Connection status (CIO 151615): 1 (Connection established)
Axis communications status (CIO 1522): 0001 (bit 00 = Communications
established with axis 1)
CIO 1515
14
This flag is ON while data is being saved.
When data saving is completed, the flag turns OFF.
Data Transferring Flag
CIO 1501
00
CONNECT Bit
This bit starts MECHATOROLINK
communications when it is turned ON.
CIO 1522
00
Bits 00 to 15 show the communications status
for axes 1 to 16, respectively. When an axis
registered in the scan list is communicating
normally, the corresponding bit turns ON.
Axis Communicating Bit for Axis 1
Page 49

22
Starting Operation Section 2-2
Unit Error Flag (CIO 151512): 0 (No error)
Unit error code (CIO 1521): 0000 (No error)
Axis Error Flag for axis 1 (CIO 50012): 0 (No error) (See note.)
Axis error code for axis 1 (CIO 504): 0000 (No error) (See note.)
Note The Axis Operating Memory Area for axis 1 depends on the Axis Operating
Input Memory Area settings in the Common Parameters.
2-2-5 Setting Servo Parameters
The Servo Parameters are set in the connected Servo Drive. The following
table shows an example of settings for the Servo Drive's external input signal
allocations (input signal selection).
These settings are standard for input signals when an R88D-WT@ Servo
Drive and JUSP-NS115 MECHATROLINK-II Application Module are used
together.
Transferring Servo
Parameters
Servo Parameters are transferred to the Servo Drive via the PCU using the
SAVE SERVO PARAMETER Bits in the PCU's Axis Operating Output Memory
Areas. The Servo Parameters are transferred one at a time. The following
three parameters must be set as shown below to allocate the above input signals.
Input
terminal
(CN1)
Input
signal
name
Setting Servo Drive default
setting
40 --- Not used RUN (RUN command input)
41 DEC Origin return deceleration
limit switch
(origin proximity input signal)
MING (gain reduction input)
42 POT Forward drive prohibit input
(forward rotation limit input
signal)
Not allocated.
43 NOT Reverse drive prohibit input
(reverse rotation limit input
signal)
Not allocated.
44 EXT1 External latch signal 1
(external interrupt input signal 1)
RESET (alarm reset input)
45 EXT2 External latch signal 2
(external interrupt input signal 2)
PCL (forward rotation current limit input)
46 EXT3 External latch signal 3
(external interrupt input signal 3)
NCL (reverse rotation current limit input)
Parameter No. Parameter name Set value
Pn50A Input signal selection 1 2881
Pn50B Input signal selection 2 8883
Pn511 Input signal selection 5 6541
Page 50

23
Starting Operation Section 2-2
Preparing Servo
Parameters to Be Set in
the Servo Drive
The settings for the parameter number, parameter size, and write data are set
in the Axis Operating Output Memory Area as Servo Parameters to be set in
the Servo Drive. In this operation example, the Common Parameters are set
so that the beginning word of the Axis Operating Output Memory Area for axis
1 is allocated in CIO 100. Therefore, the setting words for the Servo Parameters for axis 1 are allocated as follows:
Writing Servo Parameters
to the Servo Drive
The Servo Parameter settings in CIO 117 to CIO 120 are written to the Servo
Drive. In this example, to transfer three Servo Parameters, execute the operation to write to the Servo Drive three times.
Writing the Pn50A Set Value
To write the Pn50A settings, first make the settings for transferring Servo
Parameters to the PCU's Axis Operating Output Memory Areas as shown
below.
In this example, to keep the Servo Parameters even if the Servo Drive power
is turned OFF, the Servo Parameters are saved in the non-volatile memory
(flash memory) in the Servo Drive. Servo Parameters are written from the
PCU to the non-volatile memory (flash memory) of the Servo Drive by turning
ON the SAVE SERVO PARAMETER Bit in the Axis Operating Output Memory
Area.
In this operation example, the Common Parameters are set so that the beginning word of the Axis Operating Output Memory Area for axis 1 is allocated in
CIO 100. Therefore, the SAVE SERVO PARAMETER Bit for axis 1 is allocated
in CIO 10114. Turn ON this bit using the Programming Console.
While Servo Parameters are being saved to the Servo Drive, the Servo
Parameter Transferring Flag in the Axis Operating Input Memory Area turns
ON. When the Servo Parameters have finished being saved, the Servo
Parameter Transferring Flag turns OFF.
In this operation example, the Common Parameters are set so that the beginning word of the Axis Operating Input Memory Area for axis 1 is allocated in
CIO 500. Therefore, the Servo Parameter Transferring Flag for axis 1 is allocated in CIO 50014.
Word Details
CIO 117 Servo Parameter No.
CIO 118 Parameter size (Unit: bytes)
CIO 119 Write data (rightmost word)
CIO 120 Write data (leftmost word)
Word Set value Parameter transfer
setting
Details
CIO 117 050A hex Servo Parameter No. Write Servo Parameter No.:
Pn50A
CIO 118 0002 Parameter size Write parameter size: 2 (bytes)
CIO 119 2881 hex Write data (rightmost
word)
Write Servo Parameter set value:
2881
CIO 120 --- Write data (leftmost
word)
Parameter size is 2 bytes (1 word,
so this is not used.) The set value
is ignored.
CIO 101
14
SAVE SERVO PARAMETER Bit
This bit saves the Servo parameters according to the
parameter transfer settings when it is turned ON.
Page 51

24
Starting Operation Section 2-2
The set values for Pn50B and Pn511 are written in the same way, i.e., by
changing the details of the Servo Parameters to be transferred and turning
ON the WRITE DATA Bit.
Writing the Pn50B Set Value
Writing the Pn511 Setting
The following diagram shows the operation used to transfer parameters to the
Servo Drive.
Word Set value Parameter transfer
setting
Details
CIO 117 050B hex Servo Parameter No. Write Servo Parameter No.:
Pn50B
CIO 118 0002 hex Parameter size Write parameter size: 2 (bytes)
CIO 119 8883 hex Write data (rightmost
word)
Write Servo Parameter setting:
8883
CIO 120 --- Write data (leftmost
word)
Parameter size is two bytes (one
word, so this is not used.) The set-
ting is ignored.
Word Set value Parameter transfer
setting
Details
CIO 117 0511 hex Servo Parameter No. Write Servo Parameter No.: Pn511
CIO 118 0002 hex Parameter size Write parameter size: 2 (bytes)
CIO 119 6541 hex Write data (rightmost
word)
Write Servo Parameter setting:
6541
CIO 120 --- Write data (leftmost
word)
Parameter size is two bytes (i.e.,
one word, so this is not used.) The
setting is ignored.
CIO 500
14
Servo Parameter Transferring Flag
This flag is ON while Servo parameters are being
saved, and turns OFF when saving is completed.
CIO 117
CIO 118
CIO 119
CIO 120
050A hex
0002 hex
2881 hex
CPU Unit
CIO 101
14
Pn50A
2881
Servo Drive (Axis 1)
CIO 500
14
---
Servo parameter No. (Pn50A)
Parameter length (2 bytes)
Set value (2881)
Axis Operating Input Memory Area
(Axis 1)
Axis Operating Output Memory Area
(Axis 1)
Servo Parameters Transferring Flag (ON while transferring)
PCU
MECHATROLINK
Non-volatile memory
Servo Parameters
saved.
Page 52

25
Starting Operation Section 2-2
Ending MECHATROLINK Communications
The Servo Parameters written to the Servo Drive consist of online and offline
parameters. Online parameters are enabled as soon as they are written,
whereas offline parameters are not.
The input signal selection parameters set here are offline parameters that are
enabled by cycling the power to the Servo Drive or executing the device setup
operation. In this example, the Servo Drive power is cycled. First, stop
MECHATROLINK communications before turning OFF the power supply to
the Servo Drive.
MECHATROLINK communications are stopped by turning OFF the CONNECT Bit in the Common Operating Memory Area. For the PCU with unit
number 0, the CONNECT Bit is allocated in CIO 150100. Use the Programming Console to turn OFF this bit, which was turned ON at the start of
MECHATROLINK communications.
When MECHATROLINK communications stop, the Connection Status Flag in
the Common Operating Memory Area turns OFF. For the PCU with unit number 0, the Connection Status Flag is allocated in CIO 151615.
Turning the Servo Drive Power OFF and ON Again
After writing Servo Parameters, and when MECHATROLINK communications
have stopped, enable the Servo Parameters by cycling the power to the Servo
Drive. This procedure completes settings for the PCU and Servo Drive.
Unless changes in installation, wiring, or parameter settings are required, the
above operation does not need to be performed a second time.
2-2-6 Operating the Servomotor from the PCU
Starting MECHATROLINK Communications
Perform the operations described in 2-2-4 Starting MECHATROLINK Communications and then start communications with the Servo Drive connected to
MECHATROLINK.
Servo Lock The servo lock of the Servomotor connected to MECHATROLINK can be set
by turning ON the SERVO LOCK Bit in the Axis Operating Output Memory
Area.
In this operation example, the Common Parameters are set so that the beginning word of the Axis Operating Output Memory Area for axis 1 is allocated in
CIO 100. Therefore, the SERVO LOCK Bit for axis 1 is allocated in CIO
10100. Turn ON this bit using the Programming Console.
CIO 1501
00
CONNECT Bit
MECHATROLINK communications stop
when this bit is turned OFF.
CIO 1516
15
Connection Status Flag
This flag turns ON when MECHATROLINK
communications start and turns OFF when
MECHATROLINK communications stop.
Page 53

26
Starting Operation Section 2-2
When the servo lock operation is performed, the Servomotor is placed in
servo lock status. The SVON (Servo ON) Flag indicating servo status in the
Axis Operating Input Memory Area turns ON when an R88D-WT@ Servo
Drive and JUSP-NS115 MECHATROLINK-II Application Module are used
together.
In this operation example, the Common Parameters are set so that the beginning word of the Axis Operating Input Memory Area for axis 1 is allocated in
CIO 500. Therefore, the SVON Flag for axis 1 is allocated in CIO 50103.
When the servo lock is no longer required, turn OFF the corresponding
SERVO LOCK Bit in the Axis Operating Output Memory Area.
Positioning Using the Direct Operation RELATIVE MOVEMENT Command
Positioning can be performed for axis 1 using the RELATIVE MOVEMENT
command for direct operation. The RELATIVE MOVEMENT command for
direct operation sends information on the target position and target speed to
the Axis Operating Output Memory Area when the RELATIVE MOVEMENT
Bit turns ON.
In this operation example, the Common Parameters are set so that the beginning word of the Axis Operating Output Memory Area for axis 1 is allocated in
CIO 100. Therefore, the target position and target speed are set as follows:
The RELATIVE MOVEMENT Bit for axis 1 is allocated in CIO 10004. Therefore, turn this bit ON using the Programming Console.
CIO 101
00
SERVO LOCK Bit
This bit places the Servomotor in Servo lock status
when it is turned ON.
CIO 501
03
SVON Flag
When the Servomotor is in Servo lock status, this
flag is ON. When the Servomotor is in Servo
unlock status, this flag turns OFF.
Word Set value Parameter transfer
setting
Details
CIO 102 A120 hex Position command
value (rightmost
word)
Target position: 0007 A120 hex =
500,000 pulses
CIO 103 0007 hex Position command
value (leftmost word)
CIO 104 86A0 hex Speed command
value (rightmost
word)
Target speed: 0001 86A0 hex =
100,000 pulses/s
CIO 105 0001 hex Speed command
value (leftmost word)
CIO 100
04
RELATIVE MOVEMENT Bit
This bit executes the RELATIVE MOVEMENT
command for direct operation when it is turned ON.
Page 54

27
Starting Operation Section 2-2
The Servomotor starts rotating up to the target speed of 100,000 pulses/s and
stops at 500,000 pulses. The acceleration/deceleration speed depends on the
Servo Parameters set for the Servo Drive. When a W-series Servo Drive and
the JUSP-NS115 are used together, the acceleration and deceleration speeds
are set in the Servo Parameters as follows:
In this operation example, the default settings are used for the acceleration/
deceleration constants. With the default settings, the acceleration/deceleration movement uses a linear acceleration/deceleration waveform, and the
slope of the acceleration and deceleration is 1,000,000 pulses/s
2
.The target
speed is 100,000 pulses/s, so after starting, the motor accelerates up to the
target speed in 0.1 s, and decelerates to a stop from the target speed in 0.1 s.
The present position of each axis can be monitored in the Axis Operating
Input Memory Areas.
In this operation example, the Common Parameters are set so that the beginning word of the Axis Operating Input Memory Area for axis 1 is allocated in
CIO 500. Therefore, the present position (feedback present position) for axis 1
is allocated in CIO 506 and CIO 507.
Parameter
No.
Parameter name Default Unit Setting in this
example
Pn80A First-step linear
acceleration constant
100 10,000 command
units/s
2
Not used.
Pn80B Second-step linear
acceleration constant
100 10,000 command
units/s
2
1,000,000
pulses/s
2
Pn80C Acceleration con-
stant switching
speed
0 100 command
units/s
Default settings
used.
Pn80D First-step linear
deceleration constant
100 10,000 command
units/s
2
Not used.
Pn80E Second-step linear
deceleration constant
100 10,000 command
units/s
2
1,000,000
pulses/s
2
Pn80F Deceleration con-
stant switching
speed
0 100 command
units/s
Default settings
used.
Speed
Pn80B
(Second-step Linear Acceleration Constant)
Pn80C
(Acceleration Constant Switching Speed)
Pn80E
(Second-step Linear Deceleration Constant)
Pn80F
(Deceleration Constant Switching Speed)
In this operation example, the acceleration/deceleration constant switching
speed is 0. Therefore, from startup, the motor accelerates according to the
Second-step Linear Acceleration Constant and decelerates using the
Second-step Linear Deceleration Constant until stopping. The First-step
Acceleration/Deceleration Constants are not used.
Time
CIO 506
CIO 507
Feedback present position
(rightmost word)
Feedback present position (leftmost word)
Page 55

28
Starting Operation Section 2-2
The following diagram shows the operation for the RELATIVE MOVEMENT
command.
Servo Unlock The Servomotor connected to MECHATROLINK can be set to servo unlock
status by turning ON the SERVO UNLOCK Bit in the Axis Operating Output
Memory Area.
In this operation example, the Common Parameters are set so that the beginning word of the Axis Operating Output Memory Area for axis 1 is allocated in
CIO 100. Therefore, the SERVO UNLOCK Bit for axis 1 is allocated in CIO
10101. Turn ON this bit using the Programming Console.
When the servo unlock operation is performed, the Servomotor is placed in
servo unlock status. The SVON (Servo ON) Flag indicating servo status in the
Axis Operating Memory Areas turns OFF when using an R88D-WT@ Servo
Drive with a JUSP-NS115 MECHATROLINK-II Application Module.
In this operation example, the Common Parameters are set so that the beginning word of the Axis Operating Input Memory Area for axis 1 is allocated in
CIO 500. Therefore, the SVON Flag for axis 1 is allocated in CIO 50103.
When the servo unlock status is no longer required, turn OFF the corresponding SERVO UNLOCK Bit in the Axis Operating Output Memory Area.
Stopping MECHATROLINK Communications
Always stop MECHATROLINK communications before turning OFF the power
supply to the Servo Drive. MECHATROLINK communications are stopped by
turning OFF the CONNECT Bit in the Common Operating Memory Area.
For the PCU with unit number 0, the CONNECT Bit is allocated in CIO
150100. Use the Programming Console to turn OFF this bit, which was turned
ON at the start of MECHATROLINK communications.
CIO 102
CIO 103
CIO 104
CIO 105
A120 hex
0007 hex
86A0 hex
0001 hex
CPU Unit
CIO 100
04
CIO 506
CIO 507
Axis Operating Output Memory Area
(Axis 1)
Target position: 0007 A120 hex
= 500,000 pulses
Target speed: 0001 86A0 hex
= 100,000 pulses/s
Axis Operating Input Memory Area
(Axis 1)
Feedback present position
(rightmost word)
Feedback present position (leftmost word)
RELATIVE
MOVEMENT Bit
PCU
MECHATROLINK
Servo Drive/
Servomotor (Axis 1)
100,000 pulses/s
500,000 pulses
CIO 101
01
SERVO UNLOCK Bit
This bit places the Servomotor in servo unlock
status when it is turned ON.
CIO 501
03
SVON Flag
This flag turns ON when the Servomotor is in servo
lock status, and turns OFF when the Servomotor is
in servo unlock status.
Page 56

29
Starting Operation Section 2-2
When MECHATROLINK communications stop, the Connection Status Flag in
the Common Operating Memory Area turns OFF. For the PCU with unit number 0, the Connection Status Flag is allocated in CIO 151615.
This completes the operations example for operating the Servomotor using
the RELATIVE MOVEMENT command for direct operation. In this operation
example, the commands are sent manually from the Programming Console,
but the basic operation flow is the same when sequences are programmed
into the ladder program. Other functions are also used in the same way by
changing the parameter settings and manipulating bits.
CIO 1501
00
CONNECT Bit
This bit stops MECHATROLINK communications
when it is turned OFF.
CIO 1516
15
Connection Status Flag
This flag turns ON when MECHATROLINK
communications start and turns OFF when
MECHATROLINK communications stop.
Page 57

30
Starting Operation Section 2-2
Page 58

31
SECTION 3
Installation and Wiring
This section provides information on nomenclature and functions, and describes the procedures required for wiring and
installation. Information on the MECHATROLINK-II Application Module is also provided.
3-1 Nomenclature and Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
3-1-1 Nomenclature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
3-1-2 MECHATROLINK-II Application Module for W-series Servo Drives 33
3-2 Installing the Position Control Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
3-2-1 System Configuration Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
3-2-2 Unit Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
3-2-3 Installation Precautions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
3-2-4 Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
3-3 External I/O Circuits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
3-3-1 PCU I/O Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3-3-2 G-series Servo Drive I/O Signals (R88D-GN@-ML2
with Built-in MECHATROLINK-II Communications) . . . . . . . . . . 40
3-3-3 W-series Servo Drive I/O Signals (R88D-WT@ with JUSP-NS115) 44
3-3-4 W-series Servo Drive I/O Signals (R88D-WN@-ML2
with MECHATROLINK-II Built-in Communications) . . . . . . . . . . 47
3-3-5 SMARTSTEP Junior Servo Drive I/O Signals (R7D-ZN@-ML2
with Built-in MECHATROLINK-II Communications) . . . . . . . . . . 50
3-4 Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
3-4-1 MECHATROLINK-II Communications Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
3-4-2 Wiring the Servo Drive I/O Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Page 59

32
Nomenclature and Functions Section 3-1
3-1 Nomenclature and Functions
3-1-1 Nomenclature
LED Indicators
For details on errors, refer to SECTION 12 Troubleshooting.
LED Name Color Status Details
RUN Run Green Lit The PCU is operating normally.
Not lit Other condition
ERC Unit Error Red Lit A fatal error has occurred in the
PCU and operation cannot continue.
Flashing A non-fatal error has occurred in
the PCU and operation can continue.
Not lit Other condition
ERH CPU Unit Error Red Lit An error has occurred in the PLC.
Not lit Other condition
ERM MECHA-
TROLINK
Device Error
Red Lit An error has occurred in MECHA-
TROLINK communications.
Flashing An error has occurred in a con-
nected MECHATROLINK device.
Not lit Other condition
MLK MECHA-
TROLINK Communications
Status
Yellow Lit MECHATROLINK communica-
tions in progress
Not lit MECHATROLINK communica-
tions stopped
CJ1W-NC@71 CS1W-NC@71
RUN
ERC
ERH
ERM
MLK
NCF71
UNIT
No.
MLK
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
Unit Number Setting Switch
Sets the PCU's unit number.
LED Indicators
Indicate the PCU's operating status.
MECHATROLINK-II
Communications Connector
Connects to the MECHATROLINK-II
Connection Cable.
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
NCF71
RUN
ERC
UNIT
No.
ERH
ERM
MLK
MLK
Page 60

33
Nomenclature and Functions Section 3-1
Unit Number Setting
Switch (UNIT No.)
Set the unit number using the rotary switch on the front of the PCU. The
PCU's unit number is a CPU Bus Unit unit number.
Setting range: 0 to F (Unit numbers 0 to 15)
Note The factory default setting is 0.
The unit number setting determines which words are allocated to the PCU in
the CPU Bus Unit Area within the CPU Unit's CIO Area.
The PCU uses this allocated area as the “Common Operating Memory Area.”
For details, refer to 4-6 Common Operating Memory Area.
Note Always turn OFF the power supply before changing the Unit Number Setting
Switch's setting.
MECHATROLINK-II
Communications
Connector
This connector connects the PCU with MECHATROLINK devices through the
special MECHATROLINK-II Connection Cable.
For details on MECHATROLINK-II Connection Cable models and configuration, refer to 3-4-1 MECHATROLINK-II Communications Wiring.
3-1-2 MECHATROLINK-II Application Module for W-series Servo Drives
The following MECHATROLINK-II Application Module must be mounted to a
an R88D-WT@ W-series Servo Drive without built-in MECHATROLINK-II
communications to enable connection to the PCU through MECHATROLINKII.
When a MECHATROLINK-II Application Module must be mounted to a Wseries Servo Drive, use the following device versions.
The versions of both the W-series Servo Drive and MECHATROLINK-II Application Module can be found on the nameplate on the side of each device. If an
earlier version of the device is used, it will not function properly. Always use
products with versions listed in the table above (or later versions).
Nomenclature This section provides a basic description of the JUSP-NS115 MECHA-
TROLINK-II Application Module's LED Indicators and Setting Switches.
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
UNIT
No.
UNIT
No.
F
E
D
C
B
A
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
CJ1W-NC@71 CS1W-NC@71
Unit number Allocated words Unit number Allocated words
0 1500 to 1524 8 1700 to 1724
1 1525 to 1549 9 1725 to 1749
2 1550 to 1574 10 1750 to 1774
3 1575 to 1599 11 1775 to 1799
4 1600 to 1624 12 1800 to 1824
5 1625 to 1649 13 1825 to 1849
6 1650 to 1674 14 1850 to 1874
7 1675 to 1699 15 1875 to 1899
Name Model number Manufacturer
MECHATROLINK-II Application
Module
JUSP-NS115 Yaskawa Electric Corporation
Device Compatible versions
W-series Servo Drive Ver. 39 or later
MECHATROLINK-II Application Module VER. @@@03 or later
Page 61

34
Nomenclature and Functions Section 3-1
For details, refer to the JUSP-NS115 MECHATROLINK-II Application Module
User’s Manual.
Note Refer to the user’s manual for the Servo Drive for the nomenclature and func-
tions of Servo Drives with Built-in MECHATROLINK-II Communications.
• G-series Servo Drives with Built-in MECHATROLINK-II Communications
(R88D-GN@-ML2)
• W-series Servo Drives with Built-in MECHATROLINK-II Communications
(R88D-WN@-ML2)
• SMARTSTEP Junior Servo Drives with Built-in MECHATROLINK-II Com-
munications (R7D-ZN@-ML2)
LED Indicators The LED Indicators show the operating status of the JUSP-NS115.
Note The Alarm Status LED will also be lit when MECHATROLINK communications
are not established with the PCU.
Station Address Setting
Switch (SW1)
Set the Servo Drive's station address in conjunction with the MECHATROLINK-II communications setting on pin 3 of the Communications Setting
DIP Switch (SW2).
Setting Range: 0 to F (See the following table.)
Note The factory default setting is 1.
Communications Setting
DIP Switch (SW2)
Sets the MECHATROLINK-II communications settings.
A
R
LED Name Color Status Details
A Alarm Status Red Lit An alarm occurred in the Servo
Drive. (See note.)
Not lit Other condition
R MECHA-
TROLINK-II
Communications Status
Green Lit MECHATROLINK communica-
tions in progress
Not lit MECHATROLINK communica-
tions stopped
0
8
C
4
3
2
1F
E
D
5
6
7
9
A
B
Pin 3 of
SW2
SW1 Station
address
Note
OFF 0 --- Cannot be used. Do not set.
1 to F 1 to 15 ---
ON 0 16 ---
1 to F --- Cannot be used when connecting to the
PCU. Do not set.
1 2 3 4
O
N
Page 62

35
Installing the Position Control Unit Section 3-2
Note (1) In some devices, the number of transmission bytes is expressed as “30
bytes,” but the meaning is the same as this 32-byte setting.
(2) The MECHATROLINK-II Application Module can be ordered from
OMRON with the following model number.
3-2 Installing the Position Control Unit
3-2-1 System Configuration Precautions
• The I/O words allocated to the PCU as a CPU Bus Unit are not determined by the Unit's mounting order, but by the unit number set on the Unit
Number Setting Switch on the front of the Unit.
• The PCU can be mounted in either the CPU Rack or an Expansion Rack
(only up to 10 Units per Rack for a CJ-series PLC) and up to 16 Units can
be controlled by one CPU Unit.
• The CS1W-NC@71 can be mounted to a CS1W-BC@@3 CPU Backplane
or a CS1W-BI@@3 Expansion Backplane.
3-2-2 Unit Installation
Use the following procedure to install the PCU.
CJ1W-NC@71
1,2,3... 1. Align the connectors correctly and mount the PCU.
Pin Function Setting Contents Default
setting
Note
1 Baud rate OFF 4 Mbps ON Turn ON this pin (10
Mbps) when connecting to the PCU.
ON 10 Mbps
2 Transmission
bytes
OFF 17 bytes ON Turn ON this pin (32
bytes) when connecting to the PCU.
ON 32 bytes
(See note.)
3 Station address OFF 1 to 15 OFF See the explanation of
SW1.
ON 16 to 30
4 Reserved by the
system.
OFF --- OFF Leave this pin OFF.
Name Yaskawa Electric Co.
model number
OMRON model
number
MECHATROLINK-II Application
Module
JUSP-NS115 FNY-NS115
Page 63

36
Installing the Position Control Unit Section 3-2
2. Secure the PCU by sliding the yellow latches on the top and bottom until
they click and lock.
Note If the latches are not completely locked, the PCU may not function properly.
To remove the PCU, slide the latches in the “release” direction and remove the
PCU.
CS1W-NC@71
1,2,3... 1. Catch the hook on the top back of the PCU on the Backplane to mount the
unit.
PA205R
P
O
W
E
R
IN
P
U
T
A
C
1
0
0
-2
40
V
L2/N
L1
D
C
2
4
V
A
C
2
4
0
V
O
U
T
P
U
T
R
U
N
PERIPHE
RAL
E
R
R
/A
L
M
R
U
N
IN
H
C
O
M
M
P
R
P
H
L
C
O
N
T
R
O
LL
E
R
CJ1G-CPU44
SYSMAC
P
R
O
G
R
A
M
M
A
B
L
E
P
O
R
T
O
P
E
N
B
U
S
Y
M
C
P
W
R
Connector
R
U
N
E
R
C
E
R
H
E
R
M
M
L
K
N
C
F
7
1
UNIT
No
.
M
L
K
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
PA205R
P
O
W
E
R
IN
P
U
T
A
C
1
0
0
-2
40
V
L2/N
L1
D
C
2
4
V
A
C
2
4
0
V
O
U
T
P
U
T
R
U
N
PERIPHE
RAL
E
R
R
/A
L
M
R
U
N
IN
H
C
O
M
M
P
R
P
H
L
C
O
N
T
R
O
LLE
R
CJ1G-CPU44
SYSMAC
P
R
O
G
R
A
M
M
A
B
L
E
P
O
R
T
O
P
E
N
B
U
S
Y
M
C
P
W
R
RUN
ERC
ERH
ERM
MLK
NCF71
U
N
IT
N
o
.
M
LK
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
Latch
Lock
Release
Backplane
Mounting hook
Page 64

37
Installing the Position Control Unit Section 3-2
2. Insert the connector on the back of the CPU properly into the connector on
the Backplane.
3. Tighten the screw on the bottom of the PCU using a Phillip’s screwdriver.
When mounting the PCU inside equipment, provide the minimum space indicated in the diagram to enable mounting/dismounting the PCU and to ensure proper ventilation.
Note Always tighten the mounting screw on the bottom of the PCU to a torque of
0.4 N
⋅m.
To remove the PCU, loosen the screw at the bottom of the PCU using a Phillip’s screwdriver and then lift up on the bottom of the PCU.
3-2-3 Installation Precautions
• Always turn OFF the CPU Unit's power supply before connecting or disconnecting cables or the Unit itself.
• To minimize the effects of noise, place I/O wiring in a separate duct from
high-voltage lines and power lines.
• Wire strands may be scattered around during wiring, so leave the protective label on top of the PCU to prevent any wire strands from getting inside
the PCU. Once the wiring has been completed, be sure to remove the
label to allow ventilation.
Duct
20 mm min.
20 mm min.
PCU
Backplane
Phillip’s screwdriver
Page 65

38
Installing the Position Control Unit Section 3-2
3-2-4 Dimensions
CJ1W-NC@71
RUN
ERC
ERH
ERM
MLK
N
C
F71
U
N
IT
No.
MLK
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
Remove the label after
wiring is completed.
RUN
ERC
ERH
ERM
MLK
NCF71
CS
UNIT
No.
9
8
5
4
3
2
1
0
MLK
RUN
ERC
ERH
ERM
MLK
NCF71
UNIT
No.
MLK
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
65
90
31
2.7
2.7
Page 66

39
External I/O Circuits Section 3-3
CS1W-NC@71
Dimensions Mounted to Backplane
3-3 External I/O Circuits
This section describes the external I/O when a Position Control Unit is used
with any of the following Servo Drives.
• G-series Servo Drives (R88D-GN@-ML2 with built-in MECHATROLINK-II
communications)
• W-series Servo Drives (equipped with R88D-WT@ and JUSP-NS115)
• W-series Servo Drives (R88D-WN@-ML2 with built-in MECHATROLINK-II
communications)
• SMARTSTEP Junior Servo Drives (R7D-ZN@-ML2 with built-in MECHATROLINK-II communications)
35
130
101 6.2
NCF71
RUN
ERC
UNIT
No.
ERH
ERM
MLK
MLK
123
Approx. 193
Backplane
Connecting Cable
Page 67

40
External I/O Circuits Section 3-3
3-3-1 PCU I/O Signals
MECHATROLINK Connector (MLK)
3-3-2 G-series Servo Drive I/O Signals (R88D-GN@-ML2 with Built-in
MECHATROLINK-II Communications)
This section describes the standard I/O signals used with a Position Control
Unit when using a G-series Servo Drive with Built-in MECHATROLINK-II
Communications.
Use the OMNUC G Series AC Servomotors/Servo Drives with Built-in
MECHATROLINK-II Communications User's Manual (Cat. No. I566) together
with this manual for information on I/O signals.
Terminal Arrangement of the Control I/O Connector (CN1)
When using G-series Servo Drives with built-in MECHATROLINK-II communications, the default control I/O signal allocations are the standard Servo Drive
settings for using MECHATROLINK.
The following diagram shows the terminal arrangement of the Servo Drive's
Control I/O Connector (CN1) when MECHATROLINK is being used with the
Servo Drive's default settings.
This diagram shows only the I/O signals used when connecting to the PCU.
For details on the Servo Drive's standard settings, refer to 6-4 Standard Set-
tings for Servo Drives Using MECHATROLINK.
Connector
specifications
Explanation
Name MLK MECHATROLINK-II connector
Connector used USB connector DUSB-ARA41-T11 (made by DDK) or
equivalent
Applicable connector USB connector DUSB-APA41-B1-C50 (made by DDK),
including shell
Pin arrangement
I/O
1(NC)
2
SRD−
I/O
3 SRD+ I /O
4 (NC)
1
4
Pin Name Description
---
---
---
Send/receive data −
---
---
Send/receive data +
Shell Shield Shield ground
Page 68

41
External I/O Circuits Section 3-3
Note (1) Do not connect anything to unused pins (*).
(2) Inputs for pins 19 and 20 are determined by parameter settings. The dia-
gram shows the default configuration.
CN1 Connector (36 Pin)
1 19 POT
2 20 NOT
3 21 DEC
4 22 IN0
5 23 IN2
624
725
826
927
10 28
11 29
12 30
13 31
14 32
15 33
16 34 BAT
17 35 OUTM1COM
18 36 OUTM1
STOP Emergency
Stop Input
EXT2 External Latch
Signal 2
IN1
External
General-purpose
Input 1
NCL
Reverse Torque
Limit Input
--- *
--- *
--- *
--- *
ALMCOM Alarm Output
+24VIN
EXT3
EXT1
PCL
--- *
--- *
--- *
/ALM
--- *
--- *
--- *
OUTM2
COM
OUTM3
COM
Origin Proximity
Input
External General-purpose Input 2
--- *
--- *
OUTM2
OUTM3
BATCOM
--- *
12 to 24-VDC
Power Supply
Input
External Latch
Signal 3
External Latch
Signal 1
Forward
Torque Limit
Input
Alarm Output
Reverse Drive
Prohibit Input
External
Generalpurpose Input 0
Generalpurpose
Output 2
Generalpurpose
Output 3
Backup
Battery Input
Generalpurpose
Output 1
Forward Drive
Prohibit Input
General-purpose Output 2
General-purpose Output 3
Backup Battery
Input
General-purpose Output 1
Name Model Manufacturer
Servo Drive Connector 52986-3679 Molex Japan
Cable Connector 10136-3000PE Sumitomo 3M
Cable Case (Shell Kit) 10336-52A0-008 Sumitomo 3M
Page 69

42
External I/O Circuits Section 3-3
Control I/O Signals The following table shows the names and functions of the Servo Drive's con-
trol I/O signals.
CN1 Control Input Signals
Pin No. Symbol Name Function/Interface
1 +24VIN 12 to 24-VDC
Power Supply
Input
Power supply input terminal (12 to 24 VDC) for sequence inputs.
2 STOP Emergency
Stop Input
Input for emergency stop.
When this signal is enabled and pin 1 is not connected to pin 2, an
Emergency Stop Input error (alarm code 87) occurs. Set this signal
to be enabled or disabled in the Emergency Stop Input Setting
(Pn041). (Factory default: Enable)
3 EXT3 External Latch
Signal 3
This external signal input latches the current value feedback pulse
counter.
The position data is obtained the moment the input is turned ON.
Minimal signal width must be 1 ms or more.
4 EXT2 External Latch
Signal 2
5 EXT1 External Latch
Signal 1
6 IN1 External Gen-
eral-purpose
Input 1
This input is used as external general-purpose input 1.
7 PCL Forward Torque
Limit Input
When the Torque Limit Selection (Pn003) is set to 3 or 5, this signal
input selects the torque limit.
8 NCL Reverse Torque
Limit Input
19 to 20 POT Forward Drive
Prohibit Input
Forward, reverse drive rotation overtravel Input.
Pn004 chooses between enable and disable.
Pn044 sets the function assignment for pins 19 and 20.
Pn066 selects the operation.
NOT Reverse Drive
Prohibit Input
21 DEC Origin Proximity
Input
Connect the origin proximity input signal in the origin search operation.
Pn042 changes the logic of the sensor.
22 IN0 External Gen-
eral-purpose
Input 0
This input is used as external general-purpose input 0.
23 IN2 External Gen-
eral-purpose
Input 2
This input is used as external general-purpose input 2.
11 --- Not used Do not connect anything.
12 --- Not used Do not connect anything.
13 --- Not used Do not connect anything.
14 --- Not used Do not connect anything.
9 --- Not used Do not connect anything.
10 --- Not used Do not connect anything.
27 --- Not used Do not connect anything.
28 --- Not used Do not connect anything.
34 BAT Backup battery
input
Connect a battery to these terminals as a backup when the absolute encoder is stopped. A cable with a battery is not required if a
battery is connected to these terminals. (Backup voltage: 3.6 V)
33 BATCOM
17 --- Not used Do not connect anything.
24 --- Not used Do not connect anything.
25 --- Not used Do not connect anything.
26 --- Not used Do not connect anything.
18 --- Not used Do not connect anything.
Page 70

43
External I/O Circuits Section 3-3
CN1 Control Input Signal Connection Diagram
Note (1) If the limit input signal inputs (Servo Drive's forward drive prohibited sig-
nal and reverse drive prohibited signal) are not allocated, the Servo Drive
will not stop the Servomotor when the signal is input, and the Position
Control Unit will also not detect limit inputs as errors. When using a Position Control Unit, always allocate the Servo Drive's forward drive prohibited signal and reverse drive prohibited signal to enable use of the limit
input signals. (Refer to 6-4 Standard Settings for Servo Drives Using
MECHATROLINK.)
(2) The signal width of the limit input signals (forward drive prohibited signal
and reverse drive prohibited signal) and origin proximity input signal (origin return deceleration limit switch) must be longer than the MECHATROLINK communications cycle. If the input signal width is shorter than
the communications cycle, the Position Control Unit will be unable to detect the input signal.
(3) When selecting a sensor for the origin proximity input signal (origin return
deceleration LS), use a sensor such as a Photoelectric Sensor, which
does not have chattering, because the origin signal is detected after the
input goes from ON to OFF during the origin search. If a switch with contacts is used, the origin position may shift due to the switch contact's chattering.
CN1 Control Output
Signals
1+24VIN
4.7 kΩ
External power supply:
12 VDC ±5% to
24 VDC ±5%
Power supply capacity:
50 mA min. (per Unit)
To other input circuit
ground commons
To other input circuits
Photocoupler inpu
t
Signal Levels
ON level: 10 V min.
OFF level: 3 V max.
Pin No. Symbol Name Function/Interface
15 /ALM Alarm Output The output is OFF when an
alarm is generated in the Servo
Drive.
16 ALMCOM
29 OUTM2 General-purpose Out-
put 2 (READY)
This is a general-purpose output. The function for this output
is selected by changing the
parameter.
Refer to Output Signal Assignment Details on the next page.
30 OUTM2COM
31 OUTM3 General-purpose Out-
put 3 (CLIM)
32 OUTM3COM
36 OUTM1 General-purpose Out-
put 1 (BKIR)
35 OUTM1COM
Page 71

44
External I/O Circuits Section 3-3
■ Output Signal Assignment Details
Control Output Circuits
3-3-3 W-series Servo Drive I/O Signals (R88D-WT@ with JUSP-NS115)
This section explains the I/O signals used between the PCU and a W-series
Servo Drive equipped with a JUSP-NS115 MECHATROLINK-II Application
Module.
Use the OMNUC W Series User's Manual together with this manual for information on I/O signals.
Terminal Arrangement of the Control I/O Connector (CN1)
The following diagram shows the terminal arrangement of the W-series Servo
Drive's Control I/O Connector (CN1) when MECHATROLINK is being used
with the Servo Drive's standard settings.
This diagram shows only the I/O signals used when connecting to the PCU.
For details on the Servo Drive's standard settings, refer to 6-4 Standard Set-
tings for Servo Drives Using MECHATROLINK.
Pn112 (General-purpose Output 1
Function Selection)
Pn113 (General-purpose Output 2
Function Selection)
Pn114 (General-purpose Output 3
Function Selection)
OUTM1 (General-purpose Output 1)
OUTM2 (General-purpose Output 2)
OUTM3 (General-purpose Output 3)
0 Not assigned No output. Always OFF.
1 INP1 Positioning Completed 1 output
assignment.
2 VCMP Speed Conformity Signal out-
put assignment.
3 TGON Servomotor Rotation Speed
Detection output assignment.
4 READY Servo Ready output assign-
ment.
5 CLIM Current Limit Detection output
assignment.
6 VLIM Speed Limit Detection output
assignment.
7 BKIR Brake Interlock output assign-
ment.
8 WARN Warning Signal output assign-
ment.
9 INP2 Positioning Completed 2 output
assignment.
Servo Drive
To other output
circuits
External power supply
24 VDC ±1 V
Maximum operating voltage: 30 VDC
Maximum output current: 50 mA
Di: Diode for preventing surge voltage
(Use high-speed diodes.)
X
Di
X
Di
+
+
−
−
Page 72

45
External I/O Circuits Section 3-3
Note (1) Do not connect wiring to unused pins.
(2) Connect the control I/O signal cable's shield wire to the connector shell.
The connector on the Servo Drive side is connected to the FG (frame
ground).
CN1 Connector (50 Pin)
1 26 INP1COM
2 27 BKIR
3 28 BKIRCOM
4 29 READY
5 30 READYCOM
631
732
833
934
10 35
11 36
12 37
13 38
14 39
15 40
16 41 DEC
17 42 POT
18 43 NOT
19 44 EXT1
20 45 EXT2
21 46 EXT3
22 47 +24VIN
23 48
24 49
25 INP1 50
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
BATGND
Backup battery
− input
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
BAT
--- ---
Positioning
completed
output 1
Brake interlock output
Servo ready
output
ALM
Alarm output
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
Origin return
deceleration LS
input
Reverse drive
prohibit input
External
latch 2 input
+24 VDC control power supply input
--- ---
Positioning
completed output 1 common
Brake interlock
output common
Servo ready
output common
ALMCOM Alarm output
common
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
---
Unused input
Forward drive
prohibit input
External latch 1
input
External latch 3
input
--- ---
--- ---
Backup battery
+ input
Name Model Manufacturer
Receptacle on Servo Drive Side 10250-52A2JL Sumitomo 3M
Soldered Plug on Cable Side 10150-3000VE Sumitomo 3M
Case on Cable Side 10350-52A0-008 Sumitomo 3M
Page 73

46
External I/O Circuits Section 3-3
Control I/O Signals The following tables show the names and functions of the Servo Drive's con-
trol I/O signals.
CN1 Control Input Signals
Control Input Circuit
Note (1) If the limit input signal inputs (Servo Drive's forward drive prohibited sig-
nal and reverse drive prohibited signal) are not allocated, the Servo Drive
will not stop the Servomotor when the signal is input, and the Position
Control Unit will also not detect limit inputs as errors. When using a Position Control Unit, always allocate the Servo Drive's forward drive prohibited signal and reverse drive prohibited signal to enable use of the limit
input signals. (Refer to 6-4 Standard Settings for Servo Drives Using
MECHATROLINK.)
(2) The signal width of the limit input signals (forward drive prohibited signal
and reverse drive prohibited signal) and origin proximity input signal (origin return deceleration limit switch) must be longer than the MECHATROLINK communications cycle. If the input signal width is shorter than
the communications cycle, the Position Control Unit will be unable to detect the input signal.
Pin
no.
Signal Name Function/Interface Control
mode
40 --- Not used. This control input signal is not used with the standard set-
tings.
---
41 DEC Origin return deceleration LSUsed as the origin proximity input signal during the origin
search operation.
With the standard settings, the signal is enabled when ON.
Position
42 POT Forward drive prohibit
input (Positive overtravel)
Used as the forward limit input.
With the standard settings, the input is normally closed and
operates as follows:
OFF: Drive prohibited ON: Drive allowed
All modes
43 NOT Reverse drive prohibit
input (Negative overtravel)
Used as the reverse limit input.
With the standard settings, the input is normally closed and
operates as follows
OFF: Drive prohibited ON: Drive allowed
All modes
44 EXT1 External latch 1 input Input signal used for external interrupts.
Used as an external interrupt input signal during interrupt
feeding or an external origin input signal during an origin
search.
With the standard settings, the signal is enabled when ON.
Position
45 EXT2 External latch 2 input
46 EXT3 External latch 3 input
47 +24VIN +24 VDC control power
supply
This is the input terminal for the +24 VDC control input
power supply.
All modes
Servo Drive
Photocoupler input (24 VDC, 7 mA)
3.3 k
3.3 k
47
40
To other input circuits
+24VIN
Minimum ON time: 2 ms
To other input circuits GND common
• Signal levels ON: Min. voltage (+24VIN − 11 V)
OFF: Max. voltage (+24VIN − 1 V)
External power supply
24 ± 1 VDC
Power supply capacity
50 mA min. (per Unit)
Page 74

47
External I/O Circuits Section 3-3
(3) When selecting a sensor for the origin proximity input signal (origin return
deceleration LS), use a sensor such as a Photoelectric Sensor, which
does not have chattering, because the origin signal is detected after the
input goes from ON to OFF during the origin search. If a switch with contacts is used, the origin position may shift due to the switch contact's chattering.
CN1 Control Output Signals
Control Output Circuit
Note The circuit is equipped with an auto-resetting circuit breaker to protect the out-
put. Even if an overcurrent trips the breaker, the breaker will reset automatically after a certain time elapses with no current. (Ver. 37 and later Servo
Drives are equipped with the auto-resetting circuit breakers.)
3-3-4 W-series Servo Drive I/O Signals (R88D-WN@-ML2 with
MECHATROLINK-II Built-in Communications)
This section explains the I/O signals used between the PCU and a W-series
Servo Drive equipped with built-in MECHATROLINK-II communications.
Use the OMNUC W Series User's Manual (Cat. No. I544) together with this
manual for information on I/O signals.
Terminal Arrangement of the Control I/O Connector (CN1)
When using W-series Servo Drives equipped with built-in MECHATROLINK-II
communications, the default control I/O signal allocations are the standard
Servo Drive settings for using MECHATROLINK.
The following diagram shows the terminal arrangement of the W-series Servo
Drive's Control I/O Connector (CN1) when MECHATROLINK is being used
with the Servo Drive's default settings.
This diagram shows only the I/O signals used when connecting to the PCU.
Pin no. Signal Name Function/Interface Control
mode
25 INP1 Positioning completed
output 1
The position deviation is less than positioning completion range 1 (Pn500). (This signal is always OFF in control modes other than position control mode.)
Position
26 INP1COM
27 BKIR Brake interlock output This is the holding brake timing signal that is output
according to the settings in parameters Pn506, Pn507,
and Pn508.
All modes
28 BKIRCOM
29 READY Servo ready output Turned ON if there are no errors after the control and
main circuit power supplies are turned ON.
All modes
30 READYCOM
31 ALM
Alarm output This output turns OFF when there is a Servo Drive
alarm.
All modes
32 ALMCOM
Shell FG Frame ground Use this terminal to connect the cable's shield and FG
wire.
All modes
Servo Drive
To other output circuit
X
Di
+
−
See note.
Di: Diode providing surge-voltage protection (Use a high-speed diode.)
External power
supply
24 ± 1 VDC
Voltage: 30 VDC max.
Output current: 50 mA max.
Page 75

48
External I/O Circuits Section 3-3
For details on the Servo Drive's standard settings, refer to 6-4 Standard Settings for Servo Drives Using MECHATROLINK.
Note (1) Do not connect wiring to unused pins.
(2) Connect the control I/O signal cable's shield wire to the connector shell.
The connector on the Servo Drive side is connected to the FG (frame
ground).
CN1 Connector (26 Pins)
Control I/O Signals The following tables show the names and functions of the Servo Drive's con-
trol I/O signals.
Control Input Signals
1 14 BAT
2 15 BATGND
316
417
518
6 +24VIN 19
7 POT 20
8 NOT 21
9 DEC 22
10 EXT1 23 SO2+
11 EXT2 24 SO2−
12 EXT3 25 SO3+
13 26 SO3−
BKIR
(SO1+)
--- ---
---
BKIRCOM
(SO1−)
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
--- ---
Brake interlock
output
Forward drive
prohibited
Origin return
deceleration
limit switch
External latch
2 input
Unused input
Brake interlock
output common
Reverse drive
prohibited
External latch
1 input
External latch
3 input
Backup battery
+ input
Unused output
Unused output
Backup battery
− input
Unused output
Unused output
24-VDC
control power
supply
ALM
Alarm output
ALMCOM
Alarm output
common
Name Model Manufacturer
Receptacle on Servo Drive Side 10226-52A2JL Sumitomo 3M
Soldered Plug on Cable Side 10126-3000VE Sumitomo 3M
Case on Cable Side 10326-52A0-008 Sumitomo 3M
Pin No. Symbol Name Function/Interface Control mode
6 +24VIN +24 VDC control
power supply
This is the input terminal for the +24 VDC control
input power supply.
All modes
7 POT Forward drive pro-
hibited
Used as the forward limit input.
With the standard settings, the input is normally
closed and operates as follows:
OFF: Drive prohibited ON: Drive allowed
All modes
8 NOT Reverse drive pro-
hibited
Used as the reverse limit input.
With the standard settings, the input is normally
closed and operates as follows
OFF: Drive prohibited ON: Drive allowed
All modes
9 DEC Origin return decel-
eration limit switch
Used as the origin proximity input signal during the
origin search operation.
With the standard settings, the signal is enabled
when ON.
Position
Page 76

49
External I/O Circuits Section 3-3
Control Input Circuit
Note (1) If the limit input signal inputs (Servo Drive's forward drive prohibited sig-
nal and reverse drive prohibited signal) are not allocated, the Servo Drive
will not stop the Servomotor when the signal is input, and the Position
Control Unit will also not detect limit inputs as errors. When using a Position Control Unit, always allocate the Servo Drive's forward drive prohibited signal and reverse drive prohibited signal to enable use of the limit
input signals. (Refer to 6-4 Standard Settings for Servo Drives Using
MECHATROLINK.)
(2) The signal width of the limit input signals (forward drive prohibited signal
and reverse drive prohibited signal) and origin proximity input signal (origin return deceleration limit switch) must be longer than the MECHATROLINK communications cycle. If the input signal width is shorter than
the communications cycle, the Position Control Unit will be unable to detect the input signal.
(3) When selecting a sensor for the origin proximity input signal (origin return
deceleration LS), use a sensor such as a Photoelectric Sensor, which
does not have chattering, because the origin signal is detected after the
input goes from ON to OFF during the origin search. If a switch with contacts is used, the origin position may shift due to the switch contact's chattering.
Control Output Signals
10 EXT1 External latch 1 input Input signal used for external interrupts.
Used as an external interrupt input signal during
interrupt feeding or an external origin input signal
during an origin search.
With the standard settings, the signal is enabled
when ON.
Position
11 EXT2 External latch 2 input
12 EXT3 External latch 3 input
13 --- Not used. This control input signal is not used with the standard
settings.
---
Pin No. Symbol Name Function/Interface Control mode
Servo Drive
Photocoupler input (24 VDC, 7 mA)
3.3 k
3.3 k
6
9
To other input circuits
+24VIN
Minimum ON time: 2 ms
To other input circuits GND common
• Signal levels ON: Min. voltage (+24VIN − 11 V)
OFF: Max. voltage (+24VIN − 1 V)
External power supply
24 ± 1 VDC
Power supply capacity
50 mA min. (per Unit)
Pin No. Symbol Name Function/Interface Control mode
1 BKIR
(SO1+)
Brake interlock output
This is the holding brake timing signal that is output
according to the settings in parameters Pn506,
Pn507, and Pn508.
All modes
2 BKIRCOM
(SO1−)
3ALM
Alarm output This output turns OFF when there is a Servo Drive
alarm.
All modes
4ALMCOM
Page 77

50
External I/O Circuits Section 3-3
Control Output Circuit
Note The circuit is equipped with an auto-resetting circuit breaker to protect the out-
put. Even if an overcurrent trips the breaker, the breaker will reset automatically after a certain time elapses with no current.
3-3-5 SMARTSTEP Junior Servo Drive I/O Signals (R7D-ZN@-ML2 with
Built-in MECHATROLINK-II Communications)
This section describes the standard I/O signals used with a Position Control
Unit when using a SMARTSTEP Junior Servo Drive with Built-in MECHATROLINK-II Communications.
Refer also to the SMARTSTEP Junior Servo Drive with MECHATROLINK-II
Communications User’s Manual (Cat. No. I554).
Terminal Arrangement of Control I/O Connector (CN1)
The default control I/O signal allocations for a SMARTSTEP Junior Servo
Drive with MECHATROLINK-II Communications are set to the standard Servo
Drive settings for using MECHATROLINK. The default pin arrangement of the
control I/O connector (CN1) on the Servo Drive are shown below.
Only the I/O signals that are connected to the Position Control Unit are shown.
Refer to 6-4 Standard Settings for Servo Drives Using MECHATROLINK for
the standard Servo Drive settings for using MECHATROLINK.
Note (1) Do not connect unused pins.
23 SO2+ General-purpose
output
These control input signals are not used with the
standard settings.
All modes
24 SO2−
25 SO3+
26 SO3−
Shell FG Frame ground Use this terminal to connect the cable's shield and
FG wire.
All modes
Pin No. Symbol Name Function/Interface Control mode
Servo Drive
To other output circuit
X
Di
+
−
See note.
Di: Diode providing surge-voltage protection (Use a high-speed diode.)
External power
supply
24 ± 1 VDC
Voltage: 30 VDC max.
Output current: 50 mA max.
1 EXT1 External
latch signal
1 input
8 --- ---
2 DEC Origin prox-
imity input
9 --- ---
3NOT Reverse
drive inhibit
input
10 --- ---
4POT Forward
drive inhibit
input
11 --- ---
5+24VIN+24 VDC
control
power supply input
12 ALM
Alarm output
6 STOP Emergency
stop input
13 BKIR Brake inter-
lock output
70GND Output
ground
common
14 --- ---
Page 78

51
External I/O Circuits Section 3-3
(2) Connect the shield in the control I/O signal cable to the connector hood.
At the Servo Drive connector, connect it to the FG (Frame ground).
CN1 Connector (14 Pins)
Control I/O Signals The names and functions of Servo Drive control I/O signals are given in the
following table.
CN1 Control Input Signals
Control Input Circuits
Name Model Manufacturer
Receptacle on Servo Drive Side 10226-52A2JL Sumitomo 3M
Soldered Plug on Cable Side 10126-3000VE Sumitomo 3M
Case on Cable Side 10326-52A0-008 Sumitomo 3M
Pin
No.
Signal Name Function/interface Control
mode
1 EXT1 External latch signal 1 input An external interrupt input signal.
Use as an external interrupt signal for
interrupt feeding or as external origin
input signal for origin searches. The
signal is valid when ON.
Position
2 DEC Origin proximity input The origin proximity input signal for ori-
gin searches.
The signal is valid when ON.
All modes
3 NOT Reverse drive inhibit input The limit input in the reverse direction.
This input operates as follows (i.e., like
a NC contact):
OFF: Drive prohibited, ON: Drive
enabled
All modes
4 POT Forward drive inhibit input The limit input in the forward direction.
This input operates as follows (i.e., like
a NC contact):
OFF: Drive prohibited, ON: Drive
enabled
All modes
5 +24VIN +24-V power supply input for
control DC
The +24 VDC input terminal for the control input power supply.
All modes
6 STOP Emergency stop input An external input signal used to stop
power supply to the motor.
This input is used when an error occurs
to unlock the Servo from a host controller.
This input operates as follows (i.e., like
a NC contact):
OFF: Power to motor stopped (Servo
cannot be locked).
ON: Power can be supplied to motor
(Servo can be locked).
All modes
EXT
1
5
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
External power supply
24±1 VDC
Power supply capacity
50 mA max. (per Unit)
Photocoupler input:
7 mA at 24 VDC
Minimum ON time: 40 ms
To ground common for
other input circuit
Other input circuit
Signal Levels: ON: (+24 VIN − 11) V min.
OFF: (+24 VIN − 1) V max.
Servo Drive
EXT
1
5
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
External power supply
24±1 VDC
Power supply capacity
50 mA max. (per Unit)
Photocoupler input:
7 mA at 24 VDC
Minimum ON time: 40 ms
To ground common for
other input circuit
Other input circuit
Signal Levels: ON: (+24 VIN − 11) V min.
OFF: (+24 VIN − 1) V max.
Servo Drive
Page 79

52
External I/O Circuits Section 3-3
Note (1) If the limit input signal inputs (Servo Drive's forward drive prohibited sig-
nal and reverse drive prohibited signal) are not allocated, the Servo Drive
will not stop the Servomotor when the signal is input, and the Position
Control Unit will also not detect limit inputs as errors. When using a Position Control Unit, always allocate the Servo Drive's forward drive prohibited signal and reverse drive prohibited signal to enable use of the limit
input signals. (Refer to 6-4 Standard Settings for Servo Drives Using
MECHATROLINK.)
(2) The signal width of the limit input signals (forward drive prohibited signal
and reverse drive prohibited signal) and origin proximity input signal (origin return deceleration limit switch) must be longer than the MECHATROLINK communications cycle. If the input signal width is shorter than
the communications cycle, the Position Control Unit will be unable to detect the input signal.
(3) When selecting a sensor for the origin proximity input signal (origin return
deceleration LS), use a sensor such as a Photoelectric Sensor, which
does not have chattering, because the origin signal is detected after the
input goes from ON to OFF during the origin search. If a switch with contacts is used, the origin position may shift due to the switch contact's chattering.
(4) The SMARTSTEP Junior Servo Drive's emergency stop input stops the
Servomotor using software processing. If required for system safety, add
a safety circuit in an external circuit.
CN1 Control Output Signals
Control Input Circuits
Note The circuit is equipped with an auto-resetting circuit breaker to pro-
tect the output. Even if an overcurrent trips the breaker, the breaker
will reset automatically after a certain time elapses with no current.
Pin No. Signal Name Function/interface Control mode
7 0GND Output ground common The ground common for control output sig-
nals.
All modes
12 ALM Alarm output Turns OFF when an alarm occurs in the
Servo Drive.
All modes
13 BKIR Brake interlock output Output as a timing signal for a holding brake
when the Servo is locked or unlocked.
All modes
Shell FG Frame ground The connection point for the cable shield
and FG line.
All modes
Di
Di
12
13
7 0GND
ALM
BKIR
Servo Drive
External power
supply: 24±1 VDC
Maximum applicable voltage: 30 VDC
Maximum output current: 50 mA
Di: Diode to suppress surge voltage
(Use a high-speed diode.)
Page 80

53
Wiring Section 3-4
3-4 Wiring
This section provides examples of the connections between the PCU and
Servo Drive as well as the Servo Drive's control I/O connections.
3-4-1 MECHATROLINK-II Communications Wiring
Use the special MECHATROLINK-II Connection Cable to connect the PCU
and Servo Drive (MECHATROLINK-II Application Module).
Connection Cable Use the following cables (made by Yaskawa Electric) to connect MECHA-
TROLINK-II devices.
Termina tors Make sure to connect the following Terminator at the end of the MECHA-
TROLINK-II communications line.
Repeaters The wiring distance for the MECHATROLINK-II can be extended to a maxi-
mum of 100 m by using Repeaters.
Note MECHATROLINK-II Connection Cables and Terminators can be ordered from
OMRON with the following model numbers.
Name Model number Cable length Manufacturer
MECHATROLINK-II
Connection Cable
(USB connectors
and ferrite cores on
both ends)
JEPMC-W6003-A5 0.5 m Yaskawa Electric
Corporation
JEPMC-W6003-01 1.0 m
JEPMC-W6003-03 3.0 m
JEPMC-W6003-05 5.0 m
JEPMC-W6003-10 10 m
JEPMC-W6003-20 20 m
JEPMC-W6003-30 30 m
Name Model number Manufacturer
MECHATROLINK-II Terminator JEPMC-W6022 Yaskawa Electric Corporation
Name Model number Manufacturer
MECHATROLINK-II Repeater JEPMC-REP2000 Yaskawa Electric Corporation
Name Yaskawa Electric Co.
model number
OMRON model
number
MECHATROLINK-II Connection
Cable (USB connectors and ferrite
cores on both ends)
JEPMC-W6003-A5 FNY-W6003-A5
JEPMC-W6003-01 FNY-W6003-01
JEPMC-W6003-03 FNY-W6003-03
JEPMC-W6003-05 FNY-W6003-05
JEPMC-W6003-10 FNY-W6003-10
JEPMC-W6003-20 FNY-W6003-20
JEPMC-W6003-30 FNY-W6003-30
MECHATROLINK-II Terminator JEPMC-W6022 FNY-W6022
MECHATROLINK-II Repeater JEPMC-REP2000 FNY-REP2000
Page 81

54
Wiring Section 3-4
MECHATROLINK-II Communications Connections
The following example shows a PCU connected with several Servo Drives
with the MECHATROLINK-II Connection Cables.
Note When not using Repeaters, the maximum total length of the Connection
Cable (L1 + L2 + ... + Ln) is 50 m when using fewer than 16 axes or 30 m
when using 16 axes.
MECHATROLINK-II
Connection Cable Length
The maximum total length of the Connection Cables depends on the number
of MECHATROLINK devices (Servo Drives) being connected, as shown in the
following table.
Note The number of devices in the table for when Repeaters are used does not
include the Repeaters. For example, if using one MECHATROLINK device
between the PCU and the Repeater and 15 MECHATROLINK devices
between the Repeater and the Terminator, there will be 16 MECHATROLINK
devices and the maximum total cable length is 100 m.
Note Always turn OFF the power supply to the PCU and Servo Drives before con-
necting or disconnecting MECHATROLINK-II Connection Cables or the Terminator.
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
NS115 NS115 NS115
Position Control Unit
L1 L2 Ln
Terminator
Repeaters Number of MECHATROLINK
devices
Minimum cable
length between
devices
Maximum total
cable length
Without
Repeaters
15 or fewer 0.5 m min. 50 m max.
16 0.5 m min. 30 m max.
With
Repeaters
Between PCU
and Repeater
14 or fewer 0.5 m min. 50 m max.
15 0.5 m min. 30 m max.
Between
Repeater and
Terminator
15 or fewer 0.5 m min. 50 m max.
16 0.5 m min. 30 m max.
Page 82

55
Wiring Section 3-4
3-4-2 Wiring the Servo Drive I/O Signals
The following example shows a Servo Drive's control I/O signal connections
when a Position Control Unit is connected to a G-series Servo Drive, a Wseries Servo Drive, or a SMARTSTEP Junior Servo Drive.
For details on connecting the Servo Drive to the power supply or Servomotor,
refer to the Servo Drive operation manual.
Control I/O Connector (CN1) Connection Example
R88D-GN@-ML2 (Equipped with Built-in MECHATROLINK-II Communications)
Note (1) If a backup battery is connected, a cable with a battery is not required.
/ALM
ALMCOM
15
16
8NCL
7PCL
6
IN1
5EXT1
4
EXT2
3
EXT3
2STOP
1+24VIN
19POT
20NOT
21DEC
FG
BAT
BATCOM
34
33
22IN0
23IN2
4.7k
1k
4.7k
1k
4.7k
1k
4.7k
1k
4.7k
1k
4.7k
1k
4.7k
1k
4.7k
1k
4.7k
1k
4.7k
1k
4.7k
1k
4.7 k
1k
OUTM1
OUTM1COM
36
35
OUTM2
OUTM2COM
29
30
OUTM3
OUTM3COM
31
32
12 to 24 VDC
Alarm Output
General-purpose Output 1
General-purpose Output 2
General-purpose Output 3
Shell
Backup Battery (See note 1.)
Emergency
Stop
External
Latch 3
External
Latch 2
External
Latch 1
Generalpurpose
Input 1
Forward
Torque
Limit Input
Reverse
TorqueLimit Input
Forward
Drive Prohibit Input
Reverse
Drive Prohibit Input
Origin
Proximity
Input
Generalpurpose
Input0
Generalpurpose
Input 2
Page 83

56
Wiring Section 3-4
(2) Inputs for pins 19 and 20 are determined by parameter settings. The dia-
gram shows the default configuration.
R88D-WT@ with JUSP-NS115
The following example shows the connections when the standard I/O signal
settings are being used.
R88D-WN@-ML2 (Equipped with Built-in MECHATROLINK-II Communications)
INP1
Positioning completed
output 1
INP1COM
Max. voltage:
30 VDC
Max. output current:
50 mA
BKIR
Brake interlock output
BKIRCOM
READY
Servo ready output
READYCOM
25
26
27
28
29
30
46
45EXT2
EXT3
44EXT1
43NOT
42
41DEC
POT
Not used.
3.3 kΩ
40
47
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
24 VDC +24VIN
Shell
FG
Frame ground
Origin return
deceleration LS
Forward drive
prohibited signal
Reverse drive
prohibited signal
External latch 1
input
External latch 2
input
External latch 3
input
31
32
ALM
Alarm output
ALMCOM
Not used.
24 VDC +24VIN
Shell
FG
Frame ground
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
Origin return
deceleration LS
Forward drive
prohibited signal
Reverse drive
prohibited signal
External latch 1
input
External latch 2
input
External latch 3
input
SO2+
Not used.
SO2
−
SO1+
Brake interlock output
SO1
−
SO3+
Not used.
SO3
−
ALM
Alarm output
ALMCOM
Max. voltage:
30 VDC
Max. output current:
50 mA
POT
DEC
EXT1
EXT2
EXT3
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
1
2
23
24
25
26
3
4
Page 84

57
Wiring Section 3-4
R7D-ZN@-ML2 (Equipped with Built-in MECHATROLINK-II Communications)
Note When a Servo Drive is controlled through MECHATROLINK-II communica-
tions, software processes are used to stop the Servomotor when the corresponding PCU control signal is received, the Servo Drive's drive prohibited
input signal is received, or an error occurs. Use an external fail-safe circuit
(outside of the Servo Drive), such as a circuit that disconnects the Servo
Drive's main power supply, to stop the system in an emergency.
Components Provided to Wire Control I/O Signals
The following components are provided to wire the Control I/O Connector
(CN1) on a G-series, W-series, or SMARTSTEP Junior Servo Drive.
Control I/O Connector
(R88A-CNU01C)
This connector connects to the Control I/O Connector (CN1) on a G-series
Servo Drive (R88D- GN@-ML2).
Use this connector when making your own control cable.
Dimensions
Control I/O Connector
(R88A-CNU11C)
This connector connects to the W-series Servo Drive’s Control I/O Connector
(CN1).
Use this connector when making your own control cable.
1
12
5
3
2
3.3 kΩ
4
+24VIN
24 VDC
FG
6
POT
NOT
DEC
EXT1
STOP
Forward rotation
drive prohibit
Reverse rotation
drive prohibit
Emergency stop
input
Origin
proximity input
External latch
signal 1
BKIR
Brake interlock
Maximum
operating voltage:
30 V DC
Maximum output
current: 50 mA
Frame ground
Shell
13
7
/ALM
Alarm output
0GND
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
3.3 kΩ
52.4
39
t = 18
Connector Plug model
10136-3000PE (Sumitomo 3M)
Connector Case model
10336-52A0-008 (Sumitomo 3M)
Page 85

58
Wiring Section 3-4
Dimensions
Control I/O Connector
(R88A-CNW01C)
This connector connects to the R88D-WN@-ML2 W-series Servo Drive's Control I/O Connector (CN1).
Use this connector when making your own control cable.
Dimensions
Control I/O Connector
(R7A-CNA01R)
This connector connects to the R7D-ZN@-ML2 SMARTSTEP Junior Servo
Drive's Control I/O Connector (CN1).
Use this connector when making your own control cable.
General-purpose Control
Cable (R88A-CPW@S)
This cable has a connector already attached, which connects to the R88DWT@ W-series Servo Drive's Control I/O Connector (CN1). There is no connector attached to the other end of the cable. Attach an appropriate connector
to connect the desired I/O device in order to use the cable.
Standard Cables
39
52.4
t = 18
Connector Plug model
10150-3000VE (Sumitomo 3M)
Connector Case model
10350-52A0-008 (Sumitomo 3M)
37.2
39
t = 14
Connector plug: 10126-3000VE (Sumitomo 3M)
Connector case: 10326-52A0-008 (Sumitomo 3M)
29.5
39
t = 12.7
Driver end
R7D-ZP@
Model Length (L) Sheath diameter Approx. weight
R88A-CPW001S 1 m 12.8-mm dia. 0.3 kg
R88A-CPW002S 2 m 0.6 kg
Page 86

59
Wiring Section 3-4
Connection Configuration and Dimensions
Wiring
Connector Plug model: 10150-3000VE (Sumitomo 3M)
Connector Case model: 10350-52A0-008 (Sumitomo 3M)
Cable: 24 AWG, 25 wire, UL20276
Note (1) Wires with the same wire color and number of marks make up a twisted
pair.
For example, the Orange/Red (
−) and Orange/Black (−) wires make up a
twisted pair.
(2) The I/O signals listed in the table above are applicable only when con-
necting to the PCU. Do not wire any unused signals.
Connector Terminal Block
Cables (XW2Z-@J-B33)
This is the Connector Terminal Block Cable for G-series Servo Drives (R88DWN@-ML2 with built-in MECHATROLINK-II communications).
Controller
Servo Drive
R88D-WT@
t = 18
39L
No. Wire/Marking colors Signal No. Wire/Marking colors Signal
1 Yellow/Black (− − −) --- 27 White/Red (− −) BKIR
2Pink/Black (− − − −) --- 28 White/Black (− −) BKIRCOM
3 Yellow/Red (− − − − −) --- 29 Yellow/Red (− −) READY
4 Pink/Red (− − − −) --- 30 Yellow/Black (− −) READYCOM
5 Orange/Red (−) --- 31 Pink/Red (− −) ---
6 Orange/Black (−) --- 32 Pink/Black (− −) ---
7Gray/Red (−) --- 33 Orange/Red (− − −) ---
8Gray/Black (−) --- 34 Orange/Black (− − −) ---
9 White/Red (−) --- 35 Gray/Black (− − −) --10 White/Black (−) --- 36 Gray/Red (− − −) ---
11 Yellow/Red (−) --- 37 White/Red (− − −) ---
12 Yellow/Black (−) --- 38 White/Black (− − −) ---
13 Yellow/Black (− − − − −) --- 39 Yellow/Red (− − −) ---
14 Pink/Black (−) --- 40 Pink/Red (− − −) (Not used.)
15 Pink/Red (−) --- 41 Pink/Black (− − −)DEC
16 Orange/Red (− − − − −) --- 42 Orange/Red (− − − −)POT
17 Orange/Black (− − − − −) --- 43 Orange/Black (− − − −)NOT
18 Pink/Red (− − − − −) --- 44 Gray/Black (− − − −) EXT1
19 Gray/Red (− −) --- 45 White/Red (− − − −) EXT2
20 Gray/Black (− −) --- 46 White/Black (− − − −) EXT3
21 Gray/Red (− − − − −) --- 47 Gray/Red (− − − −)+24VIN
22 Gray/Black (− − − − −) --- 48 Yellow/Red (− − − −) ---
23 White/Red (− − − − −) --- 49 Yellow/Black (− − − −) ---
24 White/Black (− − − − −) --- 50 Pink/Black (− − − − −) ---
25 Orange/Red (− −) INP1 Shell --- FG
26 Orange/Black (− −)INP1COM
Page 87

60
Wiring Section 3-4
Standard Cables
Connection Configuration and Dimensions
Wiring
Connector Terminal Block
Cables (XW2Z-@J-B15)
This cable connects to the R88D-WT@ W-series Servo Drive’s connector terminal block.
Standard Cables
Connection Configuration and Dimensions
Model Length (L) Outer diameter of
cable
Approx. weight
XW2Z-100J-B33 1 m 8.0 dia. 0.1 kg
XW2Z-200J-B33 2 m 0.2 kg
43.5
39L
XW2B-20G4
XW2B-20G5
XW2D-20G6
6
30
t=18
Connector terminal
block end
Servo Drive end
R88D-GN@
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
No.
1 +24VIN
2
STOP
21
19
POT
20
33 BATCOM
34 BAT
35 OUTM1COM
36 OUTM1
16 ALMCOM
15 /ALM
DEC
NOT
1111
EXT1
EXT2
5
4
3 EXT3
12
12
FG
+24VIN
STOP
POT
BATCOM
BAT
OUTM1COM
OUTM1
ALMCOM
/ALM
DEC
NOT
EXT1
EXT2
EXT3
FG
0V
+24VIN
0V
+24VIN
0V
Servo Drive
Signal
Terminal block
Connector
Signal
Shell
Not specified.
Blue/Red (1)
Blue/Black (1)
Pink/Red (1)
Pink/Black (1)
Green/Red (1)
Green/Black (1)
Orange/Red (1)
Orange/Black (1)
Gray/Red (1)
Gray/Black (1)
Blue/Red (2)
Blue/Black (2)
Pink/Red (2)
Green/Red (2)
Green/Black (2)
Orange/Red (2)
Orange/Black (2)
Gray/Red (2)
Gray/Black (2)
Wire/mark
color
• Wires with the same wire color and the same
number of marks form a twisted pair.
A pink/red (1) wire and pink/black (1) wire form a
twisted pair.
Servo Drive Connector
Connector plug: 10136-3000PE (Sumitomo 3M)
Connector case: 10336-52A0-008 (Sumitomo 3M)
Terminal Block Connector
Connector socket: XG4M-2030 (OMRON)
Strain relief: XG4T-2004 (OMRON)
Cable
AWG28
×10P UL2464
Model Length (L) Approx. weight
XW2Z-100J-B15 1 m 0.1 kg
XW2Z-200J-B15 2 m 0.2 kg
30
t=18
Connector terminal
block end
Servo Drive end
XW2B-20G4
XW2B-20G5
XW2D-20G6
R88D-WT@
52.4
39L6
Page 88

61
Wiring Section 3-4
Wiring
Connector on Servo Drive End
Connector Plug: 10150-300VE (Sumitomo 3M)
Connector Case: 10350-52A0-008 (Sumitomo 3M)
Connector on Connector Terminal Block End
Connector Socket: XG4M-2030 (OMRON)
Strain Relief: XG4T-2004 (OMRON)
Cable: AWG28
× 3P + AWG28 × 7C UL2464
Note Signal names for the connector on the Servo Drive end are for standard I/O
allocations.
Connector Terminal Block
Cables (XW2Z-@J-B16)
This is the Connector Terminal Block Cable for W-series Servo Drives (R88DWN@-ML2 with built-in MECHATROLINK-II communications).
Standard Cables
Connection Configuration and Dimensions
Connector terminal block end
Name
+24 V
0 V
+24 V
0 V
+24 V
0 V
DEC
POT
NOT
EXT1
EXT2
EXT3
BATGND
BAT
BKIRCOM
BKIR
ALMCOM
ALM
FG
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Servo Drive end
Name
+24 VIN
DEC
POT
NOT
EXT1
EXT2
EXT3
BATGND
BAT
BKIRCOM
BKIR
ALMCOM
ALM
FG
No.
47
41
42
43
44
45
46
22
21
28
27
32
31
Shell
Model Length (L) Approx. weight
XW2Z-100J-B16 1 m 0.1 kg
XW2Z-200J-B16 2 m 0.2 kg
XW2B-20G4
XW2B-20G5
XW2D-20G6
R88D-WN@-ML2
37.2
30
39L6
t=14
Connector terminal
block end
Servo Drive end
Page 89

62
Wiring Section 3-4
Wiring
Connector on Servo Drive End
Connector Plug: 10126-300VE (Sumitomo 3M)
Connector Case: 10326-52A0-008 (Sumitomo 3M)
Connector on Connector Terminal Block End
Connector Socket: XG4M-2030 (OMRON)
Strain Relief: XG4T-2004 (OMRON)
Cable: AWG28
× 3P + AWG28 × 7C UL2464
Note Signal names for the connector on the Servo Drive end are for standard I/O
allocations.
Connector Terminal Block
Cable (XW2Z-@J-B19)
This is the Connector Terminal Block Cable for the SMARTSTEP Junior Servo
Drive Control I/O Connector (CN1).
Standard Cables
Connection Configuration and Dimensions
Connector terminal block end
Name
+24 V
0 V
+24 V
0 V
+24 V
0 V
DEC
POT
NOT
EXT1
EXT2
EXT3
BATGND
BAT
BKIRCOM
BKIR
ALMCOM
ALM
FG
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Servo Drive end
Name
+24 VIN
DEC
POT
NOT
EXT1
EXT2
EXT3
BATGND
BAT
BKIRCOM
BKIR
ALMCOM
ALM
FG
No.
6
9
7
8
10
11
12
15
14
2
1
4
3
Shell
Model Length (L) Outer diameter of cable Approx. weight
XW2Z-100J-B19 1 m 8 dia. 0.1 kg
XW2Z-200J-B19 2 m 0.2 kg
39
29.5
t=12.7
6 L
XW2B-20G4
XW2B-20G5
XW2D-20G6
R7D-Z@
Connector terminal
block end
Servo Drive en
d
Page 90

63
Wiring Section 3-4
Wiring
Connector at Connector Terminal Block
Connector Socket: XG4M-2030
Strain Relief: XG4T-5004
Cable: AWG28-10P UL20276
Connector at Servo Drive
Connector Plug: 10114-3000PE (Sumitomo 3M)
Connector Case: 10314-52A0-008 (Sumitomo 3M)
Connector-Terminal
Conversion Units
The Connector-Terminal Block Conversion Unit can be used along with a
Connector Terminal Block Cable (XW2Z-@J-B15/B16/B19/B33) to convert the
control I/O connector (CN1) of a G-series Servo Drive, W-series Servo Drive,
or SMARTSTEP Junior Servo Drive to a terminal block.
XW2B-20G4
The XW2B-20G4 is an M3 Screw Terminal Block.
11
22
33
44
55
66
77
88
99
10 10
11 11
12 12
13 13
14 14
15 15
16 16
17 17
18 18
19 19
20 20
+24VIN
+24VIN
+24VIN
EXT1
DEC
NOT
POT
STOP
0GND
BKIR
/ALM
5
1
2
3
4
8
9
10
11
6
7
13
14
12
No.No.No.
+24VIN
EXT1
DEC
NOT
POT
STOP
0GND
BKIR
/ALM
FG
Terminal Block
Connector
Servo Drive end
Signal
Wire code/Mark color
Signal
Blue/Red (−)
Shield
Shell Shield
Pink/Red (−)
Pink/Black (−)
Green/Red (−)
Green/Black (−)
Orange/Red (−)
Orange/Black (−)
Grey/Red (−)
Grey/Black (−)
Blue/Red (− −)
Blue/Black (− −)
Pink/Red (− −)
Pink/Black (− −)
Green/Red (− −)
Page 91

64
Wiring Section 3-4
Dimensions
Note (1) Use 0.30 to 1.25 mm2 wire (AWG22 to AWG16).
(2) The wire inlet is 1.8 mm (height) × 2.5 mm (width).
(3) Strip the insulation from the end of the wire for 6 mm as shown below.
XW2B-20G5
The XW2B-20G5 is an M3.5 Screw Terminal Block.
Dimensions
• Terminal block pitch: 8.5 mm
3.5
19
19
20
20
67.5
15.5
45
3.5
29.5
5.08
20.5
38.1
(45.3)
Terminal Block
Flat cable connector (MIL plug)
Two,
3.5-dia.
6 mm
112.5
Two, 3.5-dia.
3.5
8.5
7.3
7
3.5
29.5
45
15.5
43.5
20.5
(45.3)
7
Flat cable connector (MIL connector)
Terminal block
Page 92

65
Wiring Section 3-4
Note (1) When using crimp terminals, use crimp terminals with the following di-
mensions.
(2) When connecting wires and crimp terminals to a terminal block, tighten
them with a tightening torque of 0.59 N·m.
XW2D-20G6
The XW2D-20G6 is an M3 Screw Terminal Block.
Dimensions
Note (1) When using crimp terminals, use crimp terminals with the following di-
mensions.
Applicable Crimp Terminals Applicable Wires
Round Crimp
Te r mi n al s
1.25-3 AWG22-16
(0.3 to 1.25 mm2)
2-3.5 AWG16-14
(1.25 to 2.0 mm2)
Fork Terminals 1.25Y-3 AWG22-16
(0.3 to 1.25 mm2)
2-3.5 AWG16-14
(1.25 to 2.0 mm
2
)
6.8 mm max.
3.7 mm
6.8 mm max.
3.2-mm dia.
Round Crimp Terminals
Fork Terminals
A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 A10
B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B 6 B7 B
8 B9
B10
79
57
Two, 4.5-dia.
(39.1)
17.6
39
6
40
(4.5)
Page 93

66
Wiring Section 3-4
(2) When connecting wires and crimp terminals to a terminal block, tighten
them with a tightening torque of 0.7 N·m.
The following diagrams show typical connections between a host device and
Servo Drives using a MECHATROLINK-II communications cable.
■ G-series Servo Drives
Terminal Block Wiring Example (Same for XW2B-20G4, XW2B-20G5, and
XW2D-20G6)
Note (1) Absolute encoder backup battery 3.6 to 4.5 V
(2) The XB contacts are used to turn ON/OFF the electromagnetic brake.
(3) Assign BKIR (brake interlock) to CN1-36 pin to use.
(4) The absolute encoder backup battery is not required when using a Ser-
vomotor with an incremental encoder.
(5) Connect the absolute encoder backup battery to only one of either the
connector terminal block or absolute encoder backup battery cable.
(6) Use cable clips with double-sided adhesive tape to secure the absolute
encoder backup battery in place.
Applicable Crimp Terminals Applicable Wires
Round Crimp
Te r mi n al s
1.25-3 AWG22-16
(0.3 to 1.25 mm2)
Fork Terminals 1.25Y-3 AWG22-16
(0.3 to 1.25 mm2)
5.8 mm max.
3.2-mm dia.
3.2 mm
5.8 mm max.
Round Crimp Terminals
Fork Terminals
STOP POT EXT1 EXT3 BAT
OUTM1
/ALM
DEC EXT2
BAT
COM
NOT
OUTM1
COM
FG
ALM
COM
X1 XB
+24 V
24 VDC
24 VDC
+24 V +24 V
0 V
0 V
0 V
(See note 3.)
(See note 2.)
(See
note
1.)
Page 94

67
Wiring Section 3-4
■ W-series Servo Drives
Terminal Block Wiring Example (Same for All Models; with Standard
Settings for I/O Allocations)
Note (1) Absolute Encoder Backup Battery: 2.8 to 4.5 V
When using a motor with an absolute encoder, connect a backup battery
to one of the following: The Servo Drive for the R88D-WT@, the battery
cable for the R88D-WN@-ML2, or the Connector Terminal Block.
(2) Do not connect anything to unused terminals.
Terminal Block Wiring Example (XW2B-20G4, XW2B-20G5, and XW2D20G6)
Note (1) Use a maximum of 300 mA total for the 24-VDC inputs.
(2) Do not use inputs other than sensor inputs.
FG
X X
Not used
24 VDC
+24 V +24 V +24 V
0 V
0 V 0 V
DEC
24 VDC
NOT
POT
EXT1 EXT3
BAT
BKIR ALM
EXT2
BAT
GND
BKIR
COM
ALM
COM
+24 V
1
24 VDC 24 VDC
220
X
FG
+24 V +24 V EXT1
NOT
0 V0 V
0 V
POTDEC
STOP
BKIR ALM
0GND
XB
19
Page 95

68
Wiring Section 3-4
Terminal Block Signal Names
Wiring Precautions The electronic control devices may malfunction due to noise from nearby
power supply lines, external loads, or other sources.
Malfunctions caused by noise can be troublesome because it can be difficult
to recreate the situation and to identify the noise source.
Use the following methods to eliminate malfunctions due to noise and improve
the system's reliability.
• When selecting wiring components, use wires or cables that meet or
exceed the specifications listed in the Servo Drive User's Manual.
• Wire the control lines (communications lines, external I/O signal lines,
etc.) separately from the power lines (AC power supply lines and motor
power lines). Do not wire these lines together in the same duct or bundle
them together.
• Use shielded cables for the control lines.
• Use the specified special cables to connect the PCU and Servo Drives.
• Always connect surge suppressors to nearby inductive loads (relays or
solenoids).
Terminal Block
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
+24VIN
+24VIN
+24VIN
EXT1
DEC
NOT
POT
STOP
0GND
BKIR
/ALM
Shield
No.
Signal
DC
RY
DC relay
+
−
Surge suppresso
r
AC
RY
AC relay
Surge suppressor
(Example: Okaya Electric CR-50500 or equivalent)
Solenoid
SOL
Surgesuppressing
diode
Page 96

69
Wiring Section 3-4
Note Connect surge-suppressing diodes or surge suppressors close to relays. Use
surge-suppressing diodes with a dielectric strength of at least 5 times the circuit voltage.
• Noise may be transferred through the power line if there is nearby equipment that generates high-frequency noise or the power supply is shared
with equipment such as an electric welder or electric discharge equipment. In this case, insert a noise filter in the power supply input line.
• Connect to a ground of 100
Ω or less and use the thickest possible wire,
greater than 1.25 mm
2
.
• Twisted-pair cable is recommended for power lines.
Page 97

70
Wiring Section 3-4
Page 98

71
SECTION 4
Data Areas
This section provides an overview of the parameter and data settings used in Position Control Unit operation and provides
information on memory allocations.
4-1 Overall Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
4-2 Data Areas. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
4-3 Common Parameter Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
4-3-1 Common Parameters Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
4-3-2 Common Parameter Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
4-4 Axis Parameter Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
4-4-1 Axis Parameters Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
4-4-2 Axis Parameter Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
4-5 Servo Parameter Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
4-5-1 G-series Servo Drive (R88D-GN@-ML2 with Built-in
MECHATROLINK-II Communications) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
4-5-2 W-series Servo Drives (R88D-WT@ with JUSP-NS115) . . . . . . . . 117
4-5-3 W-series Servo Drive (R88D-WN@-ML2 with Built-in
MECHATROLINK-II Communications) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
4-5-4 SMARTSTEP Junior Servo Drive (R7D-ZN@-ML2 with Built-in
MECHATROLINK-II Communications) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
4-6 Common Operating Memory Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
4-6-1 Common Operating Memory Area Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
4-6-2 Common Operating Memory Area Words . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
4-7 Axis Operating Output Memory Areas. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
4-7-1 Axis Operating Output Memory Area Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
4-7-2 Axis Operating Output Memory Area Allocations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
4-7-3 Axis Operating Output Memory Area Priority. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
4-8 Axis Operating Input Memory Areas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
4-8-1 Axis Operating Input Memory Area Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
4-8-2 Axis Operating Input Memory Area Allocations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
4-8-3 Axis Control Status Flags. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
4-8-4 Servo Status Flags. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
4-8-5 External I/O Status Bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
4-8-6 Expanded Monitoring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Page 99

72
Overall Structure Section 4-1
4-1 Overall Structure
The PCU is used by exchanging data with the CPU Unit as shown in the following diagram.
PCU's Internal Memory
CPU Bus Unit Area
User-specified words
(Input)
(Output)
PCUCPU Unit
Status/Data
Result
Settings
Commands
Servo Drive
Status
Axis parameters
Flash memory
Save data
Common Operating
Memory Area
I/O refresh
Axis Operating
Memory Areas
(Input)
(Output)
Servo parameter
transfer data
Data
transfer
User-specified words
(for data transfer)
Common parameter
area
Axis parameter
area
Common
parameters
Operating
commands
Status
Operating
commands
Communications
cycle
Status
Servo
Parameters
(RAM)
Servo parameters
(non-volatile
memory)
Command
execution
Page 100

73
Overall Structure Section 4-1
The data handled by the PCU can be classified into the following six types.
Using these data/parameter settings, the PCU executes operation (1) using
the operation settings specified in the common parameters, axis parameters,
and Servo parameters (2) based on operating commands received from the
Axis Operating Memory Areas.
The common parameters, axis parameters, and certain Servo parameters are
the basic settings for the PCU and the axes to be controlled. Therefore, these
settings must be set when using the PCU. Make the settings for other data/
parameters according to the kind of operation required.
Data name Contents Setting area Enable timing
Common
Parameter Area
This area contains the parameters
for basic setting of PCU operation,
such as allocation of the Axis
Operating Memory Areas and
MECHATROLINK communications.
The common parameters must be
set to use the PCU.
PCU's internal memory
(The parameter settings
can be saved in the
PCU's flash memory.)
The settings saved in the PCU are
enabled when read to the PCU internal
memory at power ON or restart.
Axis Parameter
Areas
These areas contain the parameters for axis control settings, such
as the origin input signal selection
and origin search method.
PCU's internal memory
(The parameter settings
can be saved in the
PCU's flash memory.)
The settings saved in the PCU are read
to the PCU internal memory at power
ON or restart.
When the settings are written, they are
refreshed immediately and are enabled
after they have been written.
Servo Parameter Area
These parameters are for setting
Servo Drive operation.
Servo Drive's internal
memory
(The parameter settings
can be saved in the
Servo Drive's internal
non-volatile memory.)
Online Servo Parameters are enabled
as soon as they are written, and offline
Servo parameters are enabled after the
Servo Drive power is turned OFF and
ON again, or after executing DEVICE
SETUP.
Common Operating Memory
Area
This area is for settings for common PCU operations, such as
communications control and transferring common parameters. The
status of these operations is also
input to this area.
CPU Unit's CPU Bus Unit
Area
Data is updated with every I/O refresh
of the CPU Unit.
The set data is enabled and used with
the startup of each operation.
Axis Operating
Output Memory
Areas
These areas are for settings and
operations of axis operation, such
as positioning/speed commands
and operating commands for direct
operation, origin search, and jogging.
CPU Unit's memory area
set in the common
parameters.
Data is updated with every I/O refresh
of the CPU Unit.
The set data is enabled and used with
the startup of each operation.
Axis Operating
Input Memory
Areas
These areas are used to input status information for axis operations, such as present position and
axis operation status.
CPU Unit's memory area
set in the common
parameters.
Data is updated with every I/O refresh
of the CPU Unit.
 Loading...
Loading...