Page 1

USER MANUAL
iTrans
FIXED POINT SINGLE OR DUAL
GAS MONITOR WITH DUAL
ANALOG OUTPUTS
Part Number: 77023554-1
Version: 16.0
Release Date: April 20, 2016
The Fixed Gas Detection Experts
FIXED POINT SINGLE OR DUAL GAS MONITOR WITH DUAL
ANALOG OUTPUTS
Page 2

Copyright © 2016 by Oldham S.A.S
All rights reserved. No reproduction of all or part of this document, in any form, is
permitted without the written consent of Oldham S.A.S.
is a trademark of Oldham.
ModBus® is a registered trademark of Schneider Automation Inc.
ModBus® protocol™ is a trademark of Schneider Automation Inc.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective
owners.
All of the information that is provided in this document is accurate to the best of
our knowledge.
As a result of continuous research and development, the specifications of this
product may be changed without prior notice.
Oldham S.A.S
Rue Orfila
Z.I. Est – CS 20417
F–62027 ARRAS Cedex
Tel.: +33 (0)3 21 60 80 80
Fax: +33 (0) 3 21 60 80 00
ii iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 3
Warnings and Cautionary Statements
CAUTION: Failure to perform certain procedures or note certain conditions may
impair the performance of the monitor. For maximum safety and performance,
please read and follow the procedures and conditions outlined below.
Oxygen deficient atmospheres may cause combustible gas readings that use
catalytic LEL sensors to be lower than actual concentrations.
Oxygen enriched atmospheres may cause combustible gas readings that use
catalytic LEL sensors to be higher than actual concentrations.
Calibrate the catalytic combustible gas sensor after each incident where the
combustible gas content causes the instrument to enter in the OVER-RANGE
alarm condition.
Silicone compound vapors may affect the catalytic combustible gas sensor and
cause readings of combustible gas to be lower than actual gas concentrations. If
the sensor has been used in an area where silicone vapors were present, always
calibrate the instrument before continued use to ensure accurate measurements.
Sensor openings must be kept clean. Obstruction of the sensor openings may
cause readings to be lower than actual gas concentrations.
Sudden changes in atmospheric pressure may cause temporary fluctuations in
the oxygen readings.
Alarms relays are non-latching.
When connecting 4-20 mA outputs to inductive loads, Oldham recommends
using an isolation barrier in line with the 4-20 mA signal.
Interior grounding terminal is to be used for grounding, the exterior terminal is
only to be used for bonding
iTrans Stand-Alone versions with on-board visible alarm are to be
installed in ordinary locations only; however, remote sensors can be
installed in hazardous locations (Gas dependent. Read Agency
Approvals paragraph).
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual iii
Page 4
CALIBRATION ALERT: Gas detection instruments are potential life-saving
devices. Recognizing this fact, calibration for the toxic and catalytic LEL sensors
should be at least at quarterly intervals, while the infrared sensor should be
calibrated on an annual basis with function test every 6 months.
Further, Oldham recommends prudent testing and/or includes calibration after a
gas alarm. All calibration service to sensors should be recorded and accessible.
CAUTION: For safety reasons, this equipment must be operated and serviced by
qualified personnel only.
iv iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 5

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Table of Contents
Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
1.1. Overview of the Gas Monitor ............................................................................1-1
1.2. Specifications .........................................................................................................................1-1
1.3. Agency Approvals - CSA .......................................................................................................1-3
1.4. Special Instructions for Safe Use (EU) ..................................................................................1-5
CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE OVERVIEW
2.1. Main Electronics Unit (Housing) ...........................................................................................2-1
2.2. Sensor .....................................................................................................................................2-2
2.3. Display ....................................................................................................................................2-3
2.4. Inputs – Intrusive and Non-Intrusive ......................................................................................2-3
2.5. Electronics Modules ...............................................................................................................2-4
CHAPTER 3: INSTALLATION
3.1. Introduction ............................................................................................................................3-1
3.2. Installation Considerations .....................................................................................................3-1
3.3. Wall Mounting........................................................................................................................3-1
3.4. Column Mounting ..................................................................................................................3-1
CHAPTER 4: SYSTEM WIRING
4.1. Introduction ............................................................................................................................4-1
4.2. Wiring Preparation .................................................................................................................4-1
4.3. Alarm Relay Wiring (J1, J5, and J6) ......................................................................................4-2
4.4. Power and Output Wiring (J1) ...............................................................................................4-3
4.5. Sensor Wiring (J3) ..................................................................................................................4-4
4.6. Digital ModBus RTU Interface Wiring (J1) ..........................................................................4-9
4.6.1. ModBus Interface Wiring Overview..........................................................................4-9
4.6.2. Setting the ModBus Address on the ......................................................4-9
4.6.3. Setting the ModBus Address for Stand-Alone Sensors ...........................................4-10
4.7. Wiring Conclusion................................................................................................................4-12
CHAPTER 5: OPERATION
5.1. Initial Start-up .........................................................................................................................5-1
5.2. Warm-up Period .....................................................................................................................5-1
5.3. Normal Operating Mode.........................................................................................................5-2
5.4. Programming Mode Overview ...............................................................................................5-3
5.5. Programming Mode – Non-intrusive Operation .....................................................................5-4
5.5.1. Introduction ................................................................................................................5-4
5.5.2. Sensor Type ...............................................................................................................5-5
5.5.3. Zeroing .......................................................................................................................5-5
5.5.4. Calibration ..................................................................................................................5-6
5.5.5. Changing Span Gas Concentration ............................................................................5-7
5.5.6. Sensor Span Reserve ..................................................................................................5-8
5.6. Programming Mode – Push Button Operation .......................................................................5-8
5.6.1. Introduction ................................................................................................................5-8
5.6.2. Entering Programming Mode and Selecting a Channel .............................................5-9
5.6.3. Set Low Alarm .........................................................................................................5-10
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual v
Page 6

Table of Contents iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
5.6.4. Set High Alarm ........................................................................................................5-10
5.6.5. 4-20 mA Analog Output Range ...............................................................................5-10
5.6.6. Set System Time – Minute .......................................................................................5-11
5.6.7. Set System Time – Hour ..........................................................................................5-11
5.6.8. Set System Time – Date ...........................................................................................5-12
5.6.9. Set System Time – Month ........................................................................................5-12
5.6.10. Set System Time – Year ..........................................................................................5-13
5.6.11. Zeroing ....................................................................................................................5-13
5.6.12. Calibration ...............................................................................................................5-14
5.6.13. Changing Span Gas Concentration ..........................................................................5-15
5.6.14. Sensor Span Reserve ................................................................................................5-16
5.6. Special Notes on Using Broadband Infrared (BBIR) Sensors ..............................................5-17
CHAPTER 6: MODBUS INTERFACE
6.1. Introduction ............................................................................................................................6-1
6.2. Sample Gas Reading via ModBus Network ...........................................................................6-1
6.3. ModBus Register List ............................................................................................6-2
6.4. ModBus Resources .................................................................................................................6-6
6.5. Termination ............................................................................................................................6-6
CHAPTER 7: MAINTENANCE
7.1. Introduction ............................................................................................................................7-1
7.2. Sensor Replacement ...............................................................................................................7-2
7.3. Zero and Calibration ...............................................................................................................7-2
CHAPTER 8: TROUBLESHOOTING
8.1. Introduction ............................................................................................................................8-1
8.2. Diagnosing Common Problems ..............................................................................................8-1
8.3. Fault Codes .............................................................................................................................8-2
8.4. Function Codes .......................................................................................................................8-3
CHAPTER 9: WARRANTY
9.1. Warranty .................................................................................................................................9-1
9.2. Limitation of Liability ............................................................................................................9-1
APPENDIX A: ACRONYMS AND ABBREVIATIONS
APPENDIX B: DECIMAL, BINARY, AND HEXADECIMAL EQUIVALENTS
APPENDIX C: ORDERING MATRIX
APPENDIX D: FACTORY DEFAULT SETTINGS
APPENDIX E: EU DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY CERTIFICATE
APPENDIX F: INDEX
vi iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 7
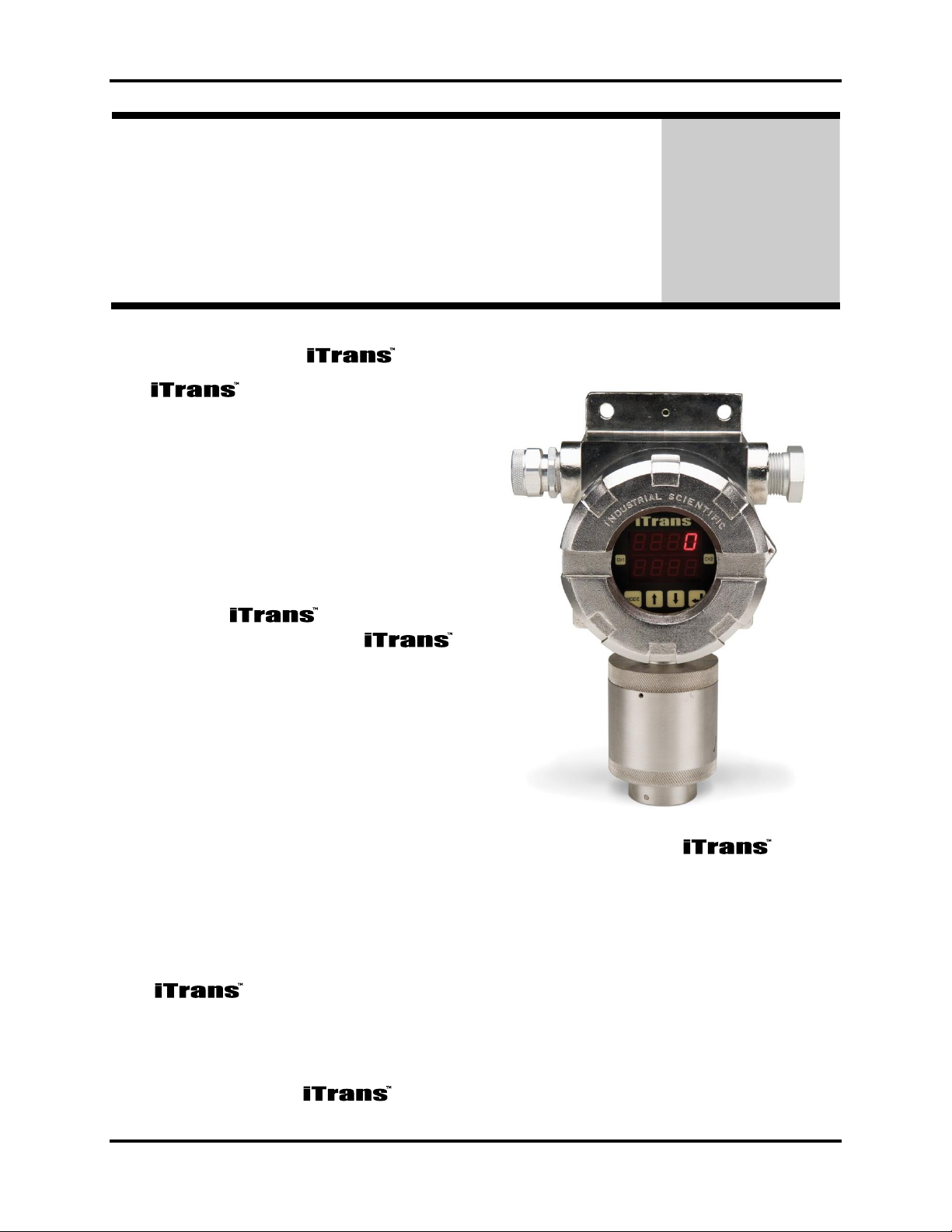
iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Introduction
INTRODUCTION
Chapter
1
The fixed gas monitor is an
independent monitor capable of
displaying one or two gas
concentrations as well as sensor or
instrument comes standard with
independent 4-20 mA outputs for each
channel, making it ideal for interfacing
to control units. A digital ModBus
RTU interface is also available,
allowing the to interface to
digital control systems. The
is available with an optional relay
board, allowing the unit to directly
control external devices such as fans,
pumps, alarm horns, or warning lights.
Two of the relays can be programmed
for alarm activation, while the third
relay is a fault protection relay.
Figure 1-1. Typical Gas
Monitor with Single Gas Sensor
(Stainless Steel Option)
1.1. Overview of the Gas Monitor
Calibration, changing span gas concentration, and checking the instrument’s
configuration are easily accomplished using the non-intrusive magnetic wand.
The is powered with a 24 VDC (12-28 VDC) power supply and
provides a 4-20 mA control signal for each sensor.
1.2. Specifications
Specifications for the gas monitor are listed in Table 1-1.
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 1-1
Page 8
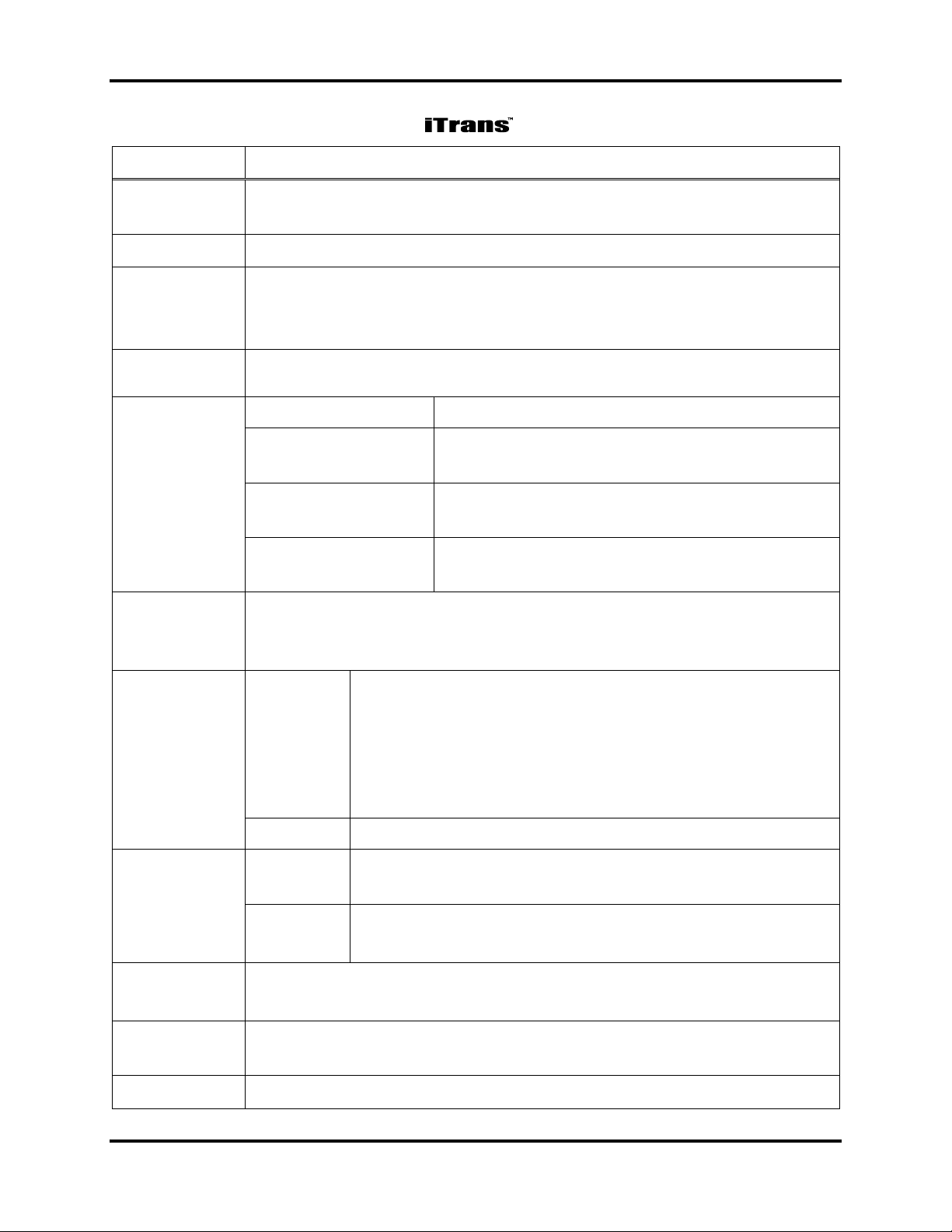
Introduction iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
Item
Description
Enclosure
Cast aluminum, poly-bonded coating or 316 stainless steel. Both are
explosion-proof, NEMA 4X, IP66 rated.
Dimensions
5.0 6.0 5.0 inches (127 153 129 mm)
Sensors
Combustible Gases: Catalytic bead and/or Non-Dispersive Infrared
(NDIR)
Oxygen/Toxic Gases: Electrochemical diffusion
Input Voltage
12-28 VDC operating range (24 VDC typical), 350 mA (nominal)
Maximum current draw of 600 mA with 2 LEL sensors installed
Input Current
(Max)
Toxic Gas/Oxygen
150 mA @ 24 VDC (single gas)
Combustible Gases
(Catalytic)
175 mA @ 24 VDC, 0.6 A peak (single gas)
Combustible Gases
(Infrared)
150 mA @ 24 VDC, 0.6 A peak (single gas)
Combined
Catalytic/Infrared
280 mA @ 24 VDC (two gas)
Display
Dual-channel split-screen LED display (4-digit, 7-segment
arrangement per channel) provides simultaneous display of one or two
gases.
Signal
Outputs
Digital
ModBus RTU: RS485 digital communication with
ModBus RTU software protocol system at 9600 baud.
Three- or four-wire system accommodates over 200
devices in bus configuration. Address selection through
on-board 8-position DIP switch. NOTE: ModBus is not
to be used for CSA C22.2 No. 152 compliance.
Analog
4-20 mA (linear analog)
Alarm Relays
Quantity
3 alarm relays: Two user-programmable relays, SPST,
N.O.; plus one fault relay, SPST, N.C.
Contact
Capacity
5A @ 30 VDC
5A @ 30 VAC
Temperature
Range
-40º C ~ +75º C (-40º F ~ +167º F)
-20º C ~ +50º C (-4º F ~ +122º F) for BBIR only
Humidity
Range
10% - 90% RH (non-condensing), typical
Pressure
Atmospheric pressure 10%
Table 1-1. Specifications for the Monitor
1-2 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 9
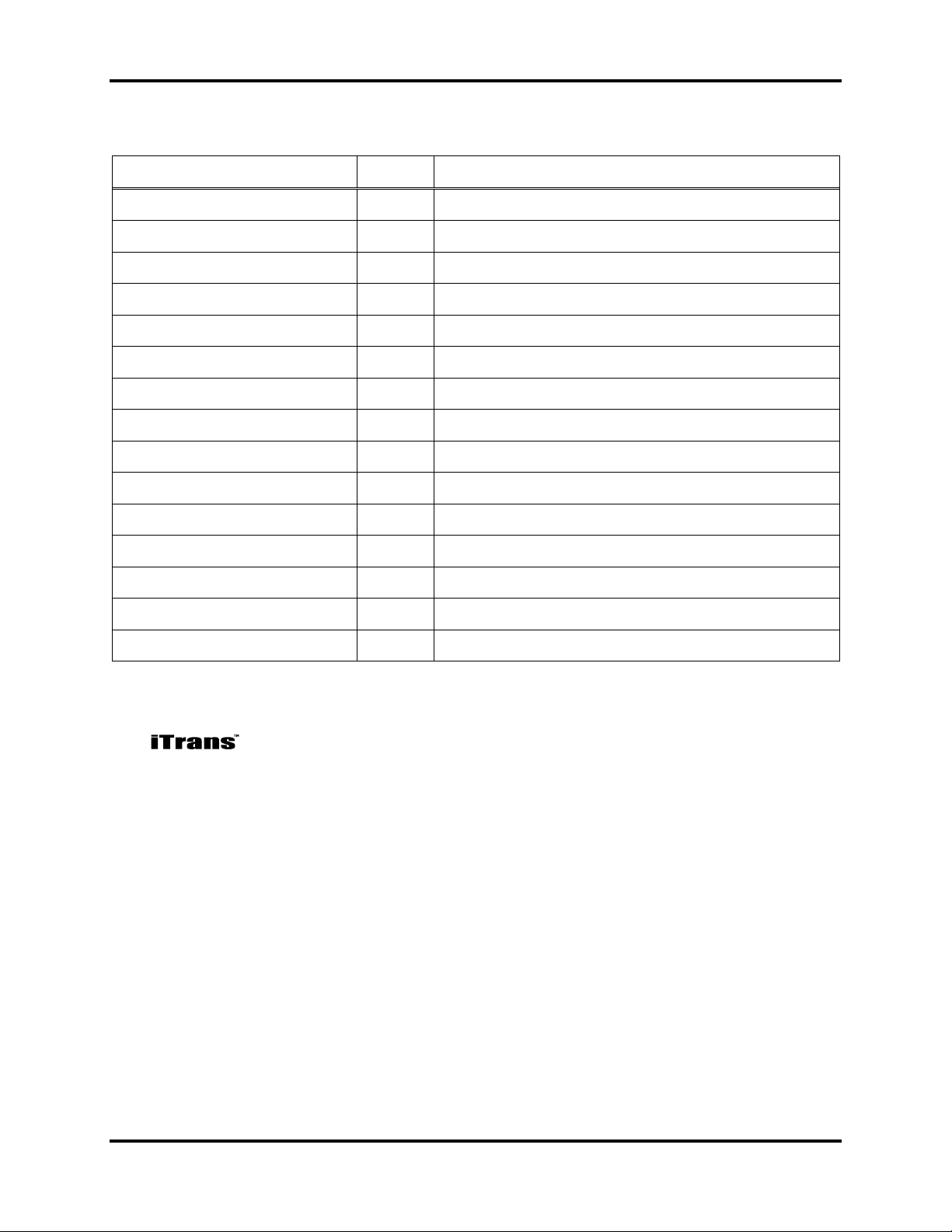
iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Introduction
Sensor
Gas
Range/Resolution
Combustible Gases
LEL
0 -100% LEL in 1% increments
Hydrogen
H2
0 - 999 ppm in 1 ppm increments
Oxygen
O2
0 - 30.0% by vol. in 0.1% increments
Ammonia
NH3
0 - 500 ppm in 1 ppm increments
Carbon Monoxide
CO
0 - 999 ppm in 1 ppm increments
Carbon Monoxide/H2 Null
CO
0 - 999 ppm in 1 ppm increments
Hydrogen Sulfide
H2S
0 - 500 ppm in 1 ppm increments
Sulfur Dioxide
SO2
0.2 - 99.9 ppm in 0.1 ppm increments
Hydrogen Cyanide
HCN
0.2 – 30.0 ppm in 0.1 ppm increments
Hydrogen Chloride
HCl
0.2 - 30.0 ppm in 0.1 ppm increments
Phosphine
PH3
0 - 1.00 ppm in 0.01 ppm increments
Nitrogen Dioxide
NO2
0.2 - 99.9 ppm in 0.1 ppm increments
Nitric Oxide
NO
0 - 999 ppm in 1 ppm increments
Chlorine
Cl2
0.2 - 99.9 ppm in 0.1 ppm increments
Chlorine Dioxide
ClO2
0.02 - 1.00 ppm in 0.01 ppm increments
Table 1-2. Sensor Ranges
1.3. Agency Approvals
The is certified by CSA, a NRTL laboratory, to the following US and
Canadian Standards.
UL Std No. 916-Energy Management Equipment
UL Std No. 1203-Explosion-Proof and Dust-Ignition-Proof
o Electrical Equipment for Use in Hazardous (Classified) Locations
UL Std No. 1604-Division 2 Hazardous Location Electrical Equipment
ISA S12.13 Part I-2000-Performance Requirements, Combustible Gas
Detectors (catalytic sensors only)
CSA Std C22.2 No.30-M1986-Explosion-Proof Enclosures for Use in
Class I Hazardous Locations
CSA Std C22.2 No.142-M1987-Process Control Equipment
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 1-3
Page 10

Introduction iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
CSA Std C22.2 No. 152-M1984-Combustible Gas Detection Instruments
(catalytic sensors only)
CSA Std C22.2 No. 213-M1987-Non-incendive Electrical Equipment for
Use in Class I, Division 2 Hazardous Locations
Marking: Transmitter Class I, Div 1, Groups B, C, D – AEx d IIB + H2 T5
Sensor
Ambient for Model 7701-5857 Fixed IR sensor (BBIR) is -20C to +55C. Ambient for all other devices is
-40C to +75C.
(gas dependent)
(1)
Class I, Div 1, Groups B, C, D – AEx d IIB + H2 T5
(2)
Class I, Div 2, Groups A, B, C, D – AEx d IIB + H2 T5
The is certified under the IECEx scheme to:
IEC 60079-0:2007 - Electrical apparatus for potentially explosive
atmospheres–General requirements.
IEC 60079-1:2003 - Electrical apparatus for potentially explosive
atmospheres–Flameproof enclosures ‘d’.
IEC 60079-15:2005 - Electrical apparatus for explosive gas atmospheres.
Type of protection "n".
Marking: Transmitter Ex d IIB+H2 T5; IP66; Ta (-40°C to +75°C)
Sensor
(gas dependent)
(1)
Ex d IIB+H2 T5 ; IP66 ; Ta (-40°C to +75°C)
(2)
Ex nA II T5; Ta (-40°C to +75°C)
The complies with relevant provisions, per listed standards, of European
ATEX Directive 94/9/EC and EMC Directive 89/336/EEC, amended by Directives
92/31/EEC and 93/68/EEC, and is constructed with reference to published
standards of Directive 72/23/EEC, to eliminate electrical risks and fulfill 1.2.7 of
Annex II of Directive 94/9/EC.
EN 60079-0:2004 - Electrical apparatus for potentially explosive
atmospheres – General requirements.
EN 60079-1:2004 - Electrical apparatus for potentially explosive
atmospheres – Flameproof enclosures ‘d’.
EN 60079-15:2003 - Electrical apparatus for explosive gas atmospheres.
Type of protection “n”.
1-4 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 11

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Introduction
EN 50270: Electromagnetic compatibility - Electrical apparatus for the
detection and measurement of combustible gases, toxic gases or oxygen (for
Type 2 [Industrial] Apparatus).
The EC type examination certificate is KEMA 04 ATEX 2216X, with
Marking code: Transmitter Ex d IIB+H2 T5; Ta (-40°C to +75°C)
Sensor
(gas dependent)
(1)
Ex d IIB+H2 T5 ; Ta (-40°C to +75°C)
(2)
Ex nA II T5; Ta (-40°C to +75°C)
(1)
LEL, H2, O2, CO, H2S, SO2, HCN, PH3, NO2, NO, CO2
(2)
Cl2, HCl, NH3, ClO2
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 1-5
Page 12

Introduction iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
1.4. Special Instructions for Safe Use (EU)
Cable connection: The cable entry device shall be of a certified flameproof
type, suitable for the conditions of use and correctly installed.
Conduit Connection: An Ex d certified sealing device, such as, a conduit
seal with setting compound, suitable for the conditions of use, and correctly
installed, shall be provided immediately to the entrance of the housing.
Unused openings: Unused openings shall be closed with suitable Ex d
certified closing elements.
Dual Onboard: The “Y” adapter parts used to assemble dual onboard
configurations do not have Atex approval. Consult factory for dual onboard
Atex options.
1-6 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 13

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Introduction
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 1-7
Page 14

Page 15
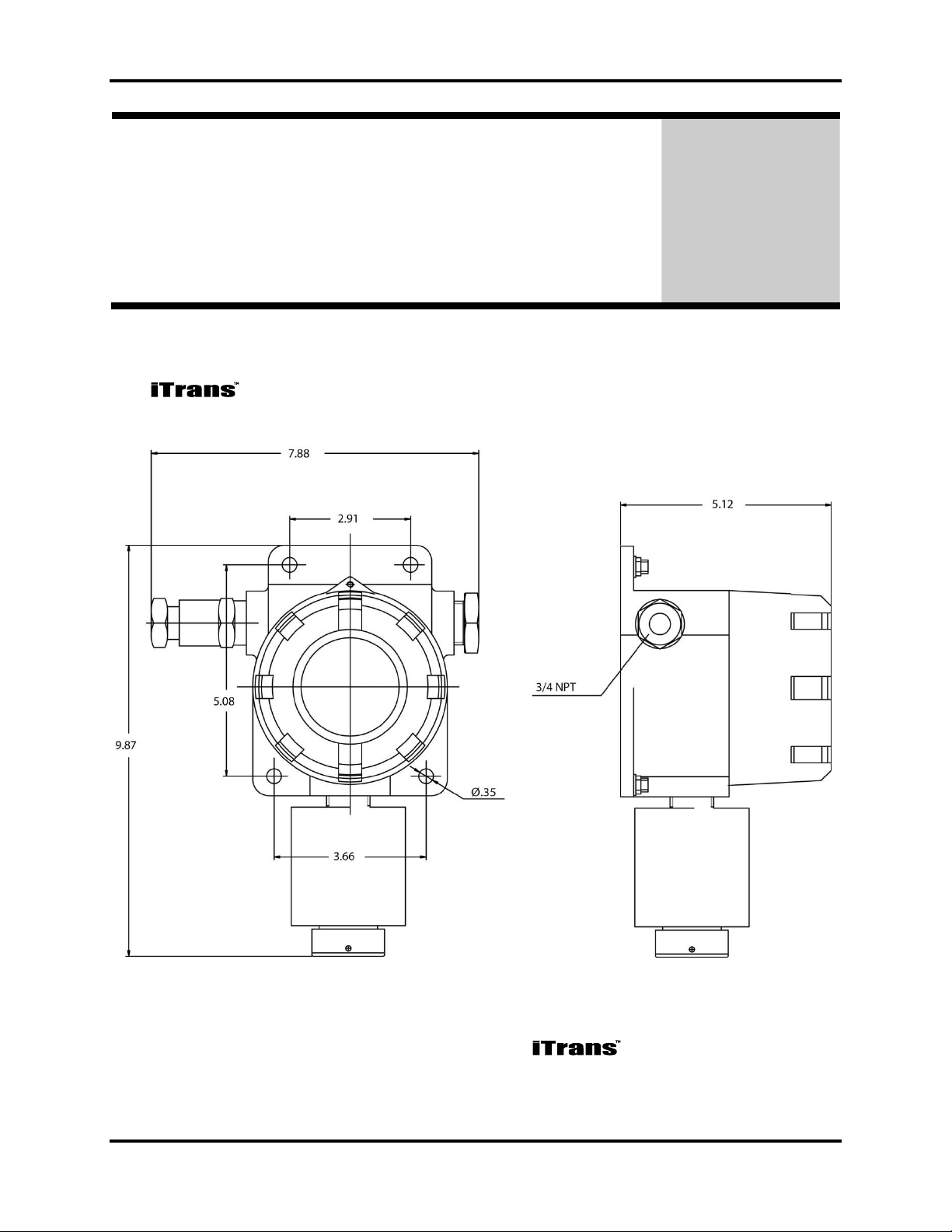
iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Hardware Overview
HARDWARE OVERVIEW
Chapter
2
2.1. Main Electronics Unit (Housing)
The body is a cast aluminum housing that contains the electronics of the
gas monitor. Details of a single-gas housing are shown in Figure 2-1.
Figure 2-1. Details of a Single-Gas Gas Monitor
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 2-1
NOTE: Dimensions are in inches.
Page 16
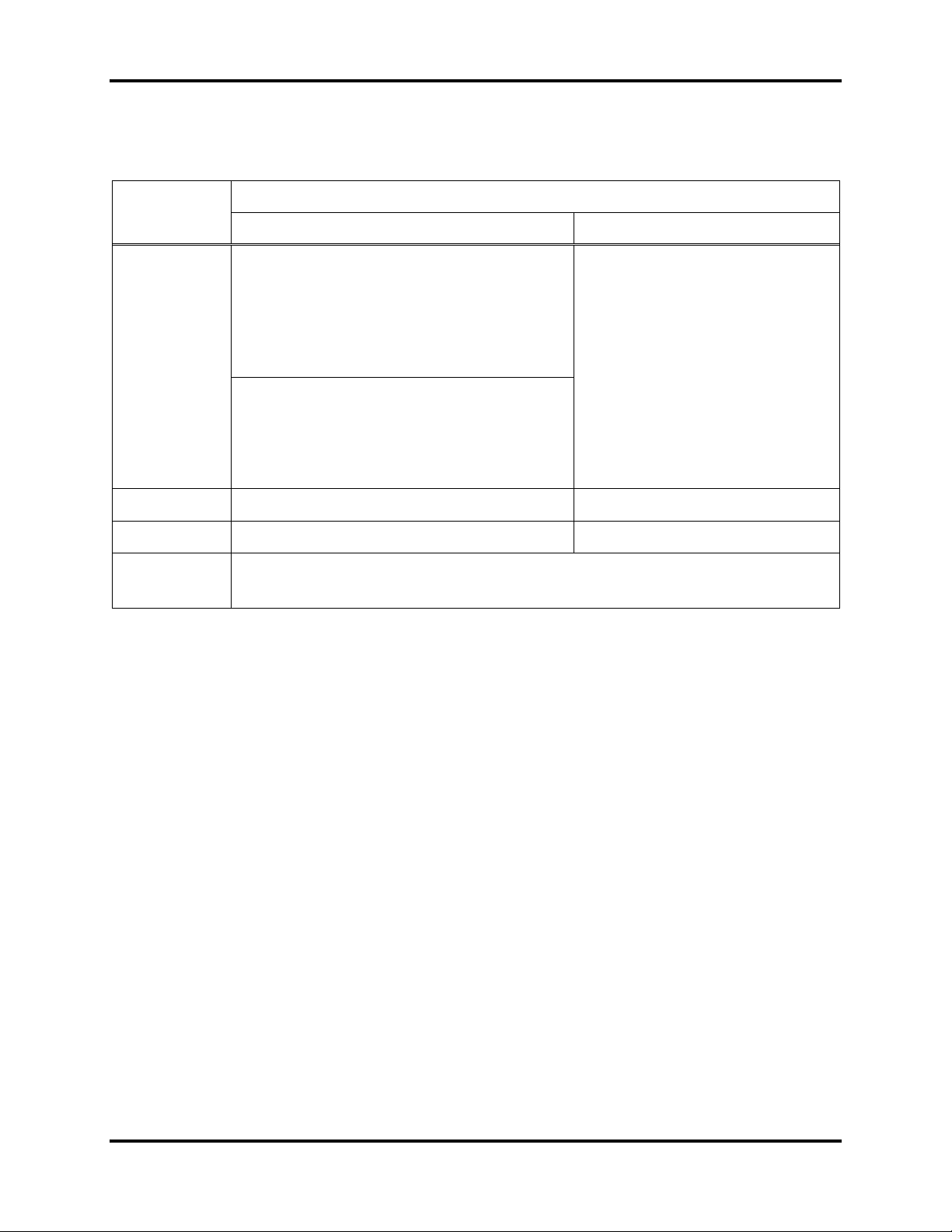
Hardware Overview iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
Item
Descriptions
Catalytic and Toxics
Infrared (BBIR)
Sensor
Housing
Material
Aluminum, Anodized
Explosion-proof: Class I, Divisions 1
and 2, Groups B, C, D and Ex d IIB
+H2 T5 (ATEX and IECEx), Ex d
IICT6 Gb (China)
Stainless Steel
Explosion-proof: Class I,
Divisions 1 and 2 Groups B,
C, D, and Ex d IIB +H2 T4
(Europe), Ex d IIC T4 or IIC
T6 (China)
Aluminum, Anodized w/Gore-Tex
Membrane: Class I, Division 2, Groups
A, B, C, D and Ex nA IIC T5 (IECEx)
and Ex nA II T5 (ATEX).
Dimensions
3.0 3.0 inches (76 76 mm)
3.5 3.0 inches (89 76 mm)
Accuracy
< 3% Toxic and Oxygen
< 5% Combustibles
Protection
Class
IP 66 or NEMA4X
2.2. Sensor
Table 2-3. Sensor Specifications
2-2 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 17
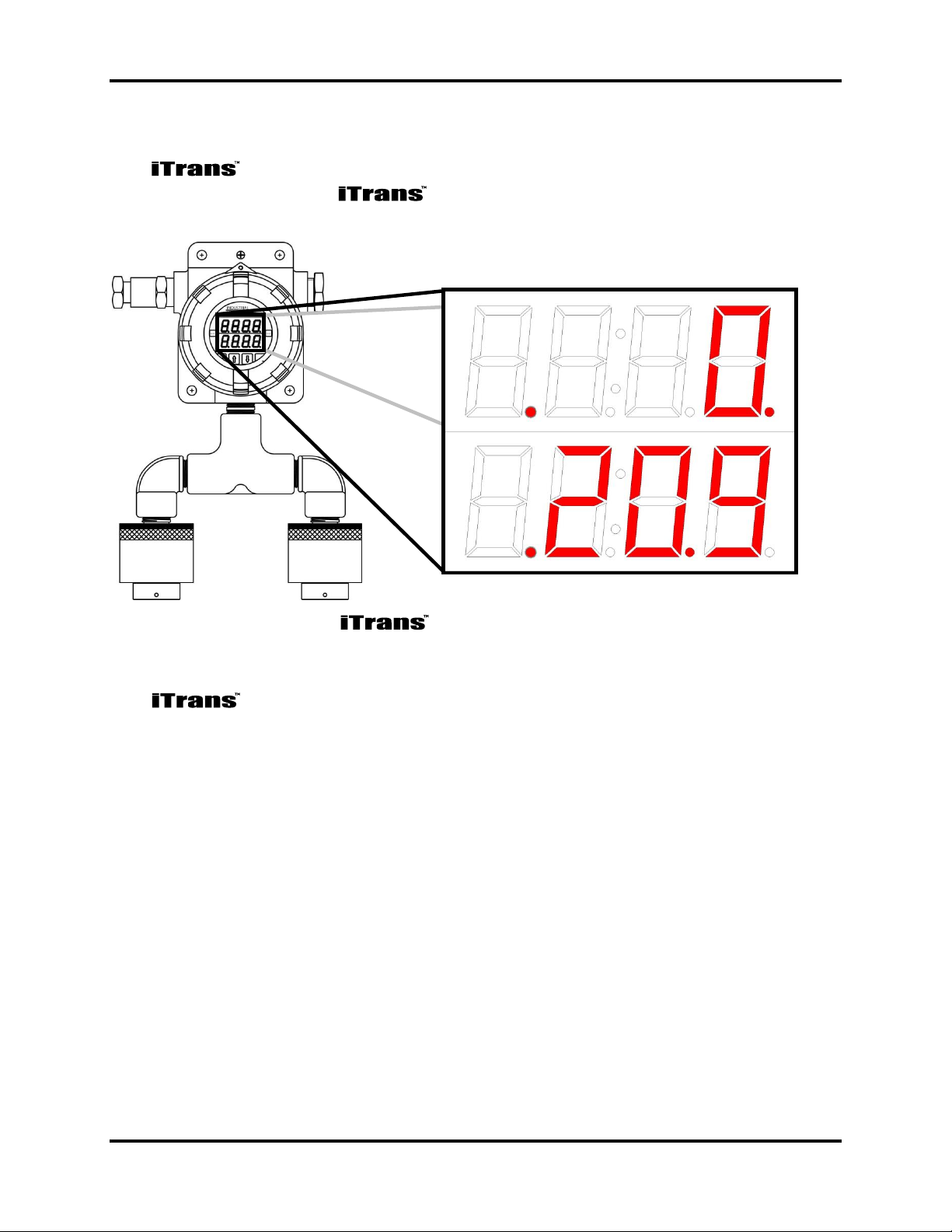
iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Hardware Overview
2.3. Display
The gas monitor has a 4-digit, 7-segment LED display for each of 2
channels. A dual-gas sensor and sample display are shown in
Figure 2-2.
Figure 2-2. The Display (Dual-Gas Monitor Shown)
2.4. Inputs – Intrusive and Non-Intrusive
The gas monitor can be configured using intrusive and non-intrusive
means. Both methods of configuration are accomplished through physical inputs
that are visible behind the glass panel of the gas monitor.
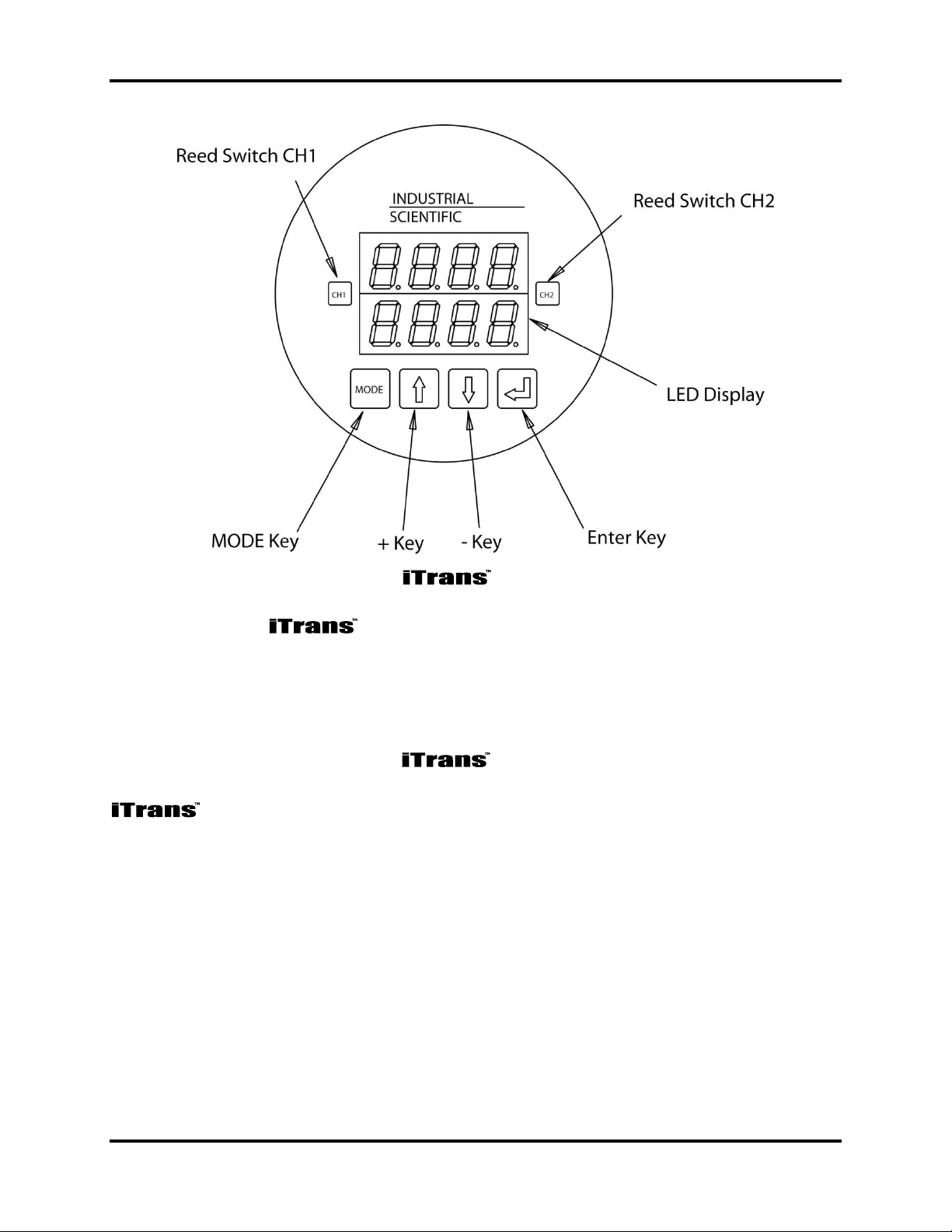
A set of four keys are used when intrusive programming is appropriate (i.e., when
the enclosure can be removed and when the keys can be manually pressed). These
keys are the mode, increment (+), decrement (-), and enter keys. Refer to
Figure 2-3.
For applications that require non-intrusive manipulation, two magneticallyactivated reed switches are used to accomplish programming without removing the
cover. A magnetic wand is positioned over the appropriate reed switch (above the
glass face plate) without the wand physically touching the reed switches. The
locations of the reed switches are shown in Figure 2-3.
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 2-3
Page 18
Hardware Overview iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
Figure 2-3. Locations of Input Keys and Reed Switches
Programming the gas monitor in both intrusive and non-intrusive modes
is explained in detail in Chapter 5: Operation.
2.5. Electronics Modules
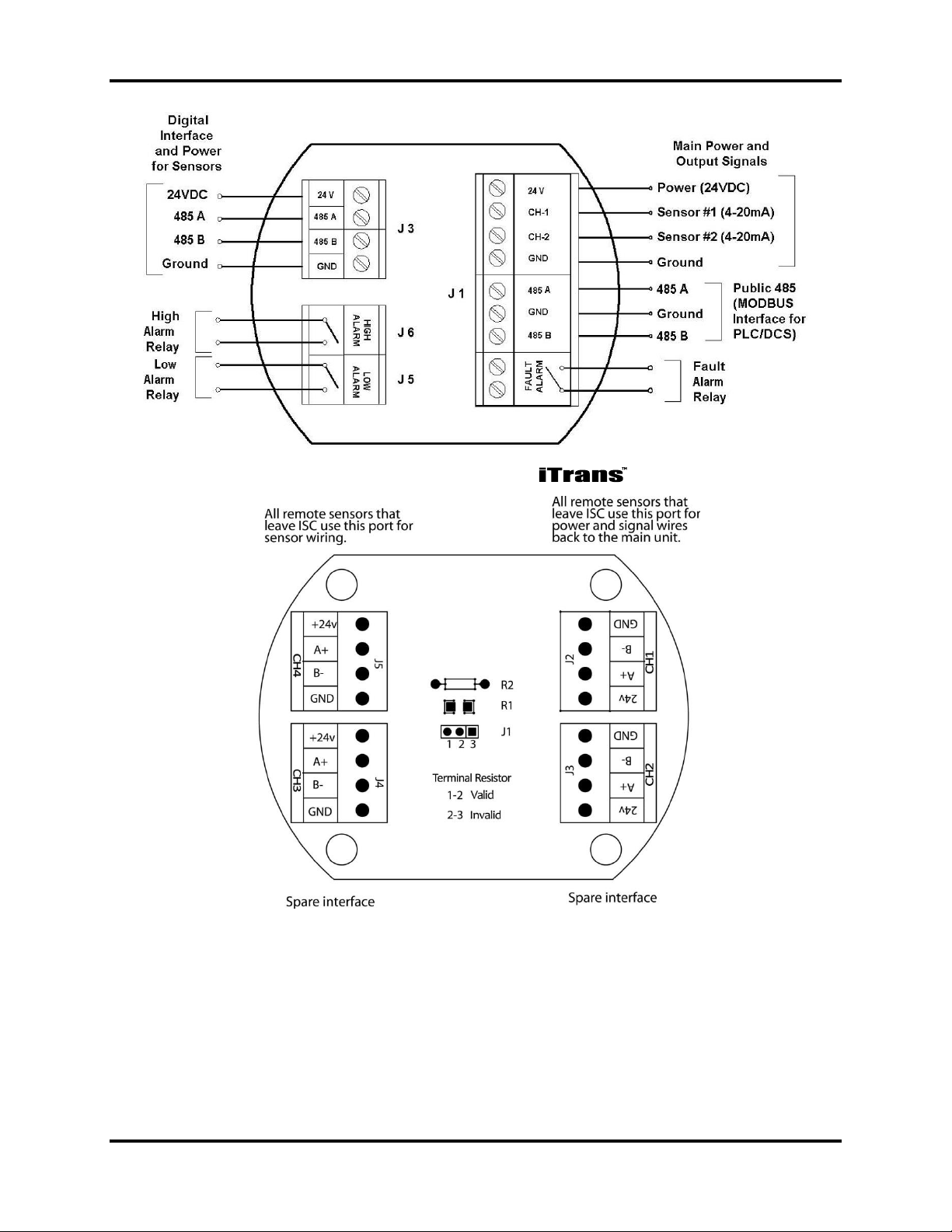
The electronics module of the gas monitor contains connectors and
jumpers for wiring and configuring the device. The electronics module for a main
unit is shown in Figure 2-4. The electronics module for a remote unit is
shown in Figure 2-5. Wiring details are explained in Chapter 4: System Wiring.
2-4 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 19
iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Hardware Overview
Figure 2-4. Electronics Module for (Main Unit)
Figure 2-5. Electronics Board for Remote Sensor
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 2-5
Page 20

Hardware Overview iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
2-6 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 21

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Installation
INSTALLATION
Chapter
3
3.1. Introduction
The can be mounted in one of two ways. The unit can be wall-mounted
using the wall mounting holes in the enclosure, or it can be mounted onto a column
using U-bolts. Each of these options is discussed in this chapter. Be sure to
review the installation considerations before mounting the gas monitor.
3.2. Installation Considerations
Regardless of the installation type (wall mounting or column mounting), the
should be installed at or near the location of a possible leak or the source
of emissions. Installation height depends on the density of the gas being monitored.
Moreover, speed and direction of air flow, and relative position to potential leaking
points should also be considered.
IMPORTANT: The gas monitor must not be installed on vibrating or
heat generating sources.
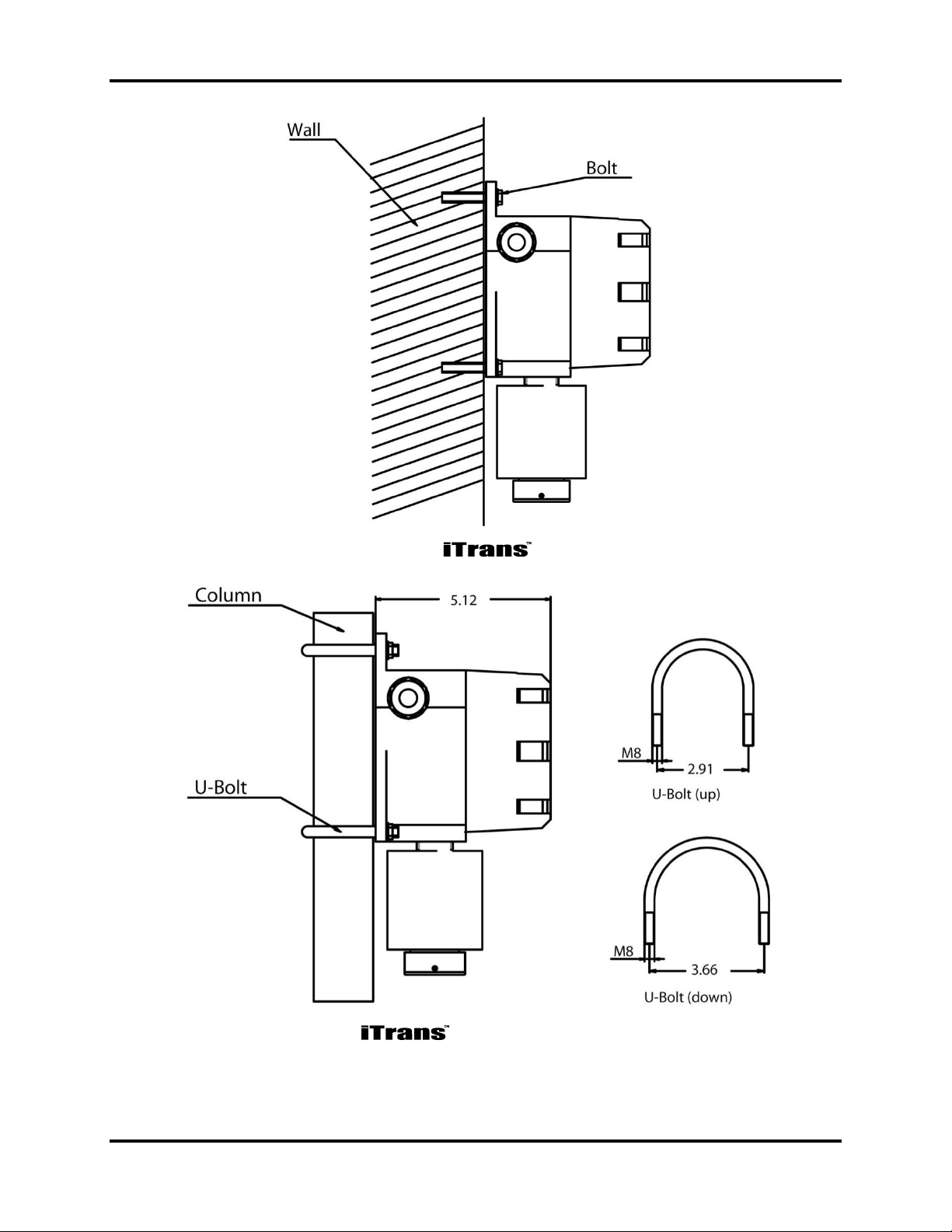
3.3. Wall Mounting
If your application is best addressed using a wall-mounted gas monitor, then use
the four 8 mm mounting holes in the enclosure to secure the to an appropriate
location on the wall. Refer to Figure 3-1.
3.4. Column Mounting
If your application is best addressed using a column-mounted gas monitor, then use
the four 8 mm mounting holes and two U-bolts to secure the to an appropriately
located segment of a target pipe or conduit. Refer to Figure 3-2.
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 3-1
Page 22
Installation iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
Figure 3-1. Mounting the Gas Monitor on a Wall
Figure 3-2. Mounting the Gas Monitor on a Column Using U-Bolts
3-2 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 23
iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor System Wiring
SYSTEM WIRING
Chapter
4
4.1. Introduction
This chapter outlines the steps required for wiring the gas monitor. These steps
include the following:
Wiring Preparation Sensor Wiring
Alarm Relay Wiring Power and Output Wiring
ModBus Interface Wiring.
Each of these steps is outlined in the sections that follow.
IMPORTANT: Perform all wiring in accordance with local electrical codes and
local authorities having jurisdiction.
IMPORTANT: DC signal and AC power should not be run in the same conduit.
NOTE: All field wiring colors are arbitrary (unless provided by Oldham).
4.2. Wiring Preparation
1. Collect the appropriate types and lengths of wire.
For control wire, use #18 AWG insulated, shielded cable.
For signal and power wire, use three-conductor (or four-conductor for dual
channel) #18 AWG insulated and shielded cable.
For digital ModBus signal and power, use a minimum of five-conductor
#18 AWG insulated and shielded cable.
2. Power down the unit.
3. Unthread the windowed top from the housing.
4. Gently pull out the electronics module and place it safely to the side of the unit.
5. Thread control, signal, and power wires into the transmitter housing.
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 4-1
Page 24
System Wiring iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
6. Shielding from either the controller or remote sensors should be bonded to the
enclosure screw located inside the .
IMPORTANT: Use of this product in areas where it may be subject to large
amounts of electromagnetic interference may affect the reliable operation of this
device and should be avoided.
WARNING: Supply wire with a minimum rating of 90oC must be used for
interconnection to the .
NOTE: For classified locations, a “poured” wire seal must be installed within
18 inches of the main unit for both power entry and remote sensors.
NOTE: Remove power from the before making any wiring connections.
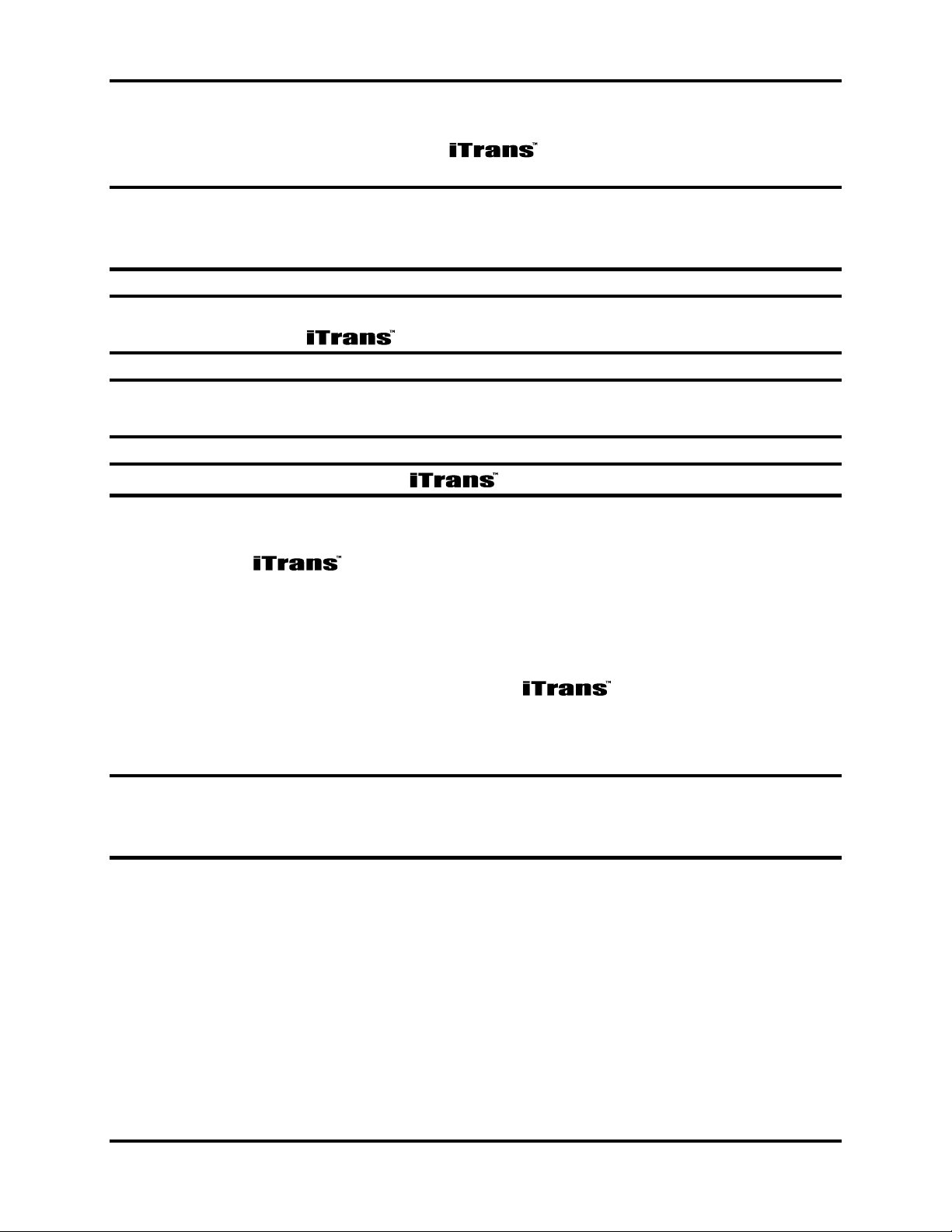
4.3. Alarm Relay Wiring (J1, J5, and J6)
To connect the control wires to the three relay terminals on the relay
board, wire the unit to the connectors shown in Figure 2-4. The low alarm relay
is activated when the low alarm threshold is met. This is a non-latching, Normally
Open (NO) contact. The high alarm relay is activated when the high alarm
threshold is met. This is a non-latching, Normally Open (NO) contact. The fault
alarm relay is activated upon power-up of the . When the fault condition
is met, the circuit opens. This is an Electronically closed (NO) contact. See Figure
4-1 for relay wiring.
NOTE: It is recommended that on-board relays should not be used to drive loads
directly. On-board relays should be used to drive a secondary, higher-power relay
which is connected to the control device (e.g., strobe, siren, exhaust fan, etc.).
4-2 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 25
iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor System Wiring
Figure 4-1. Alarm Relay Connectors J6, J5 and J1
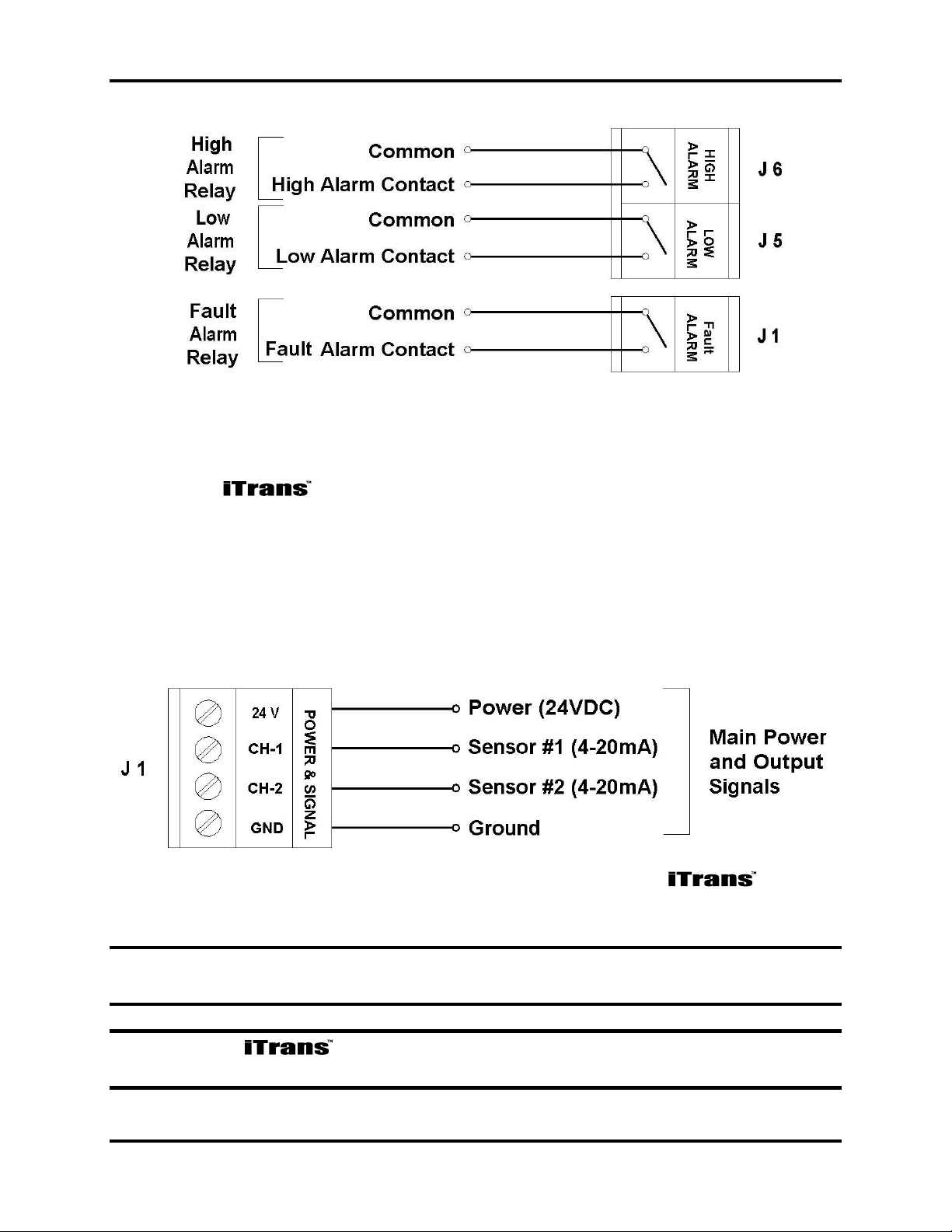
4.4. Power and Output Wiring (J1)
Connect the power and signal wires to the appropriate wiring terminals
as follows.
24 V: Connect 24 VDC (12-28 VDC) supply power
CH 1: Channel 1, 4-20 mA output signal
CH 2: Channel 2, 4-20 mA output signal
GND: DC return
Figure 4-2. Power and Signal Connector J1 on the
NOTE: Use supplied green conductor for enclosure ground. Public 485 GND is
to be used for ModBus digital ground.
NOTE: The is a 3- or 4-wire 4-20 mA device. For dual sensor
configuration you must have a second 4-20 mA signal wire pulled to the unit.
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 4-3
Page 26
System Wiring iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
NOTE: When not using 4-20 mA outputs, use the supplied resistors to connect
CH-1 and CH-2 to GND. If these resistors are not connected and the 4-20 mA
outputs are not used, a “P” will appear on the display, indicating an open loop
condition.
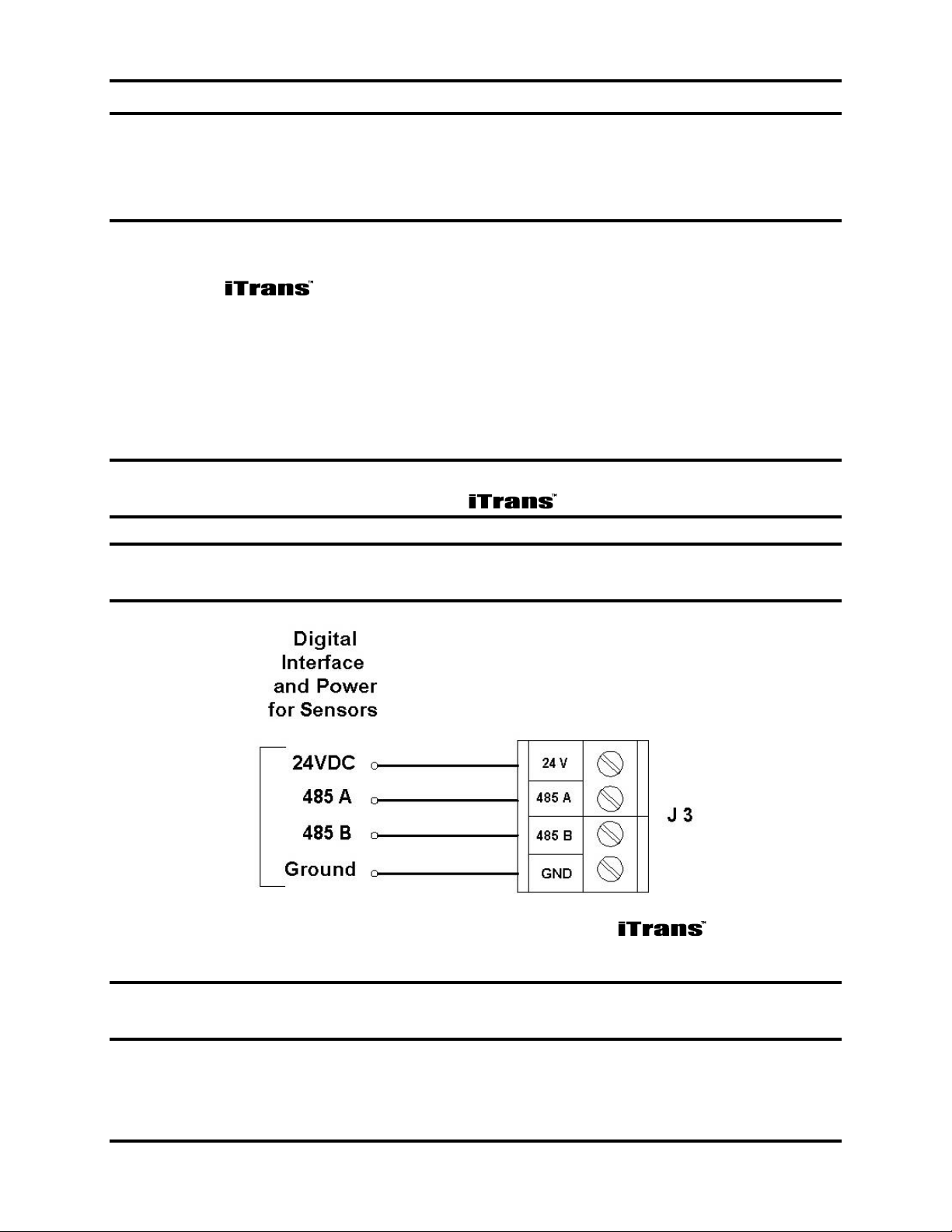
4.5. Sensor Wiring (J3)
Connect the sensor wires (for on-board, remote or stand-alone) to the
appropriate wiring terminals as follows.
24 V: Red wire from sensor head (Red wire on BBIR)
485A: Yellow wire from sensor head (White wire on BBIR)
485B: Black wire from sensor head (Green wire on BBIR)
GND: Green wire from sensor head (Black wire on BBIR)
NOTE: Shielding from either the controller or remote sensors should be bonded
to the enclosure screw located inside the .
NOTE: The 24 V terminal supplies 24 VDC to the sensor for power. This
terminal should not be connected to the output of a 24 VDC power supply.
Figure 4-3. Sensor Connector J3 on the
NOTE: For dual-sensor configurations, place both of the same colored wires in
the appropriate terminal block and firmly tighten.
4-4 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 27
iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor System Wiring
NOTE: Use #18 AWG shielded cable for remote sensors. Maximum distance is
200 meters (BBIR maximum distance is 300 feet with #18 AWG wire).
NOTE: When wiring remote sensors to the , “485 B” on J3 should be
connected to “B-” in the remote sensor enclosure, and “485 A” on J3 should be
connected to “A+” in the remote sensor enclosure.
NOTE: For remote or standalone sensors, there are four terminal blocks located in
the remote sensor housing. These terminal blocks are all tied together and follow
the same wiring scheme mentioned above.
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 4-5
Page 28

System Wiring iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
Figure 4-4. Wiring Diagram for a Single On-board Sensor
4-6 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 29

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor System Wiring
Figure 4-5. Wiring Diagram for a Remote Sensor (Stand Alone)
NOTE: When the remote sensor is at distances of 200 meters or further, and the
sensor is not communicating, the jumper may need to be moved to terminals 1-2.
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 4-7
Page 30

System Wiring iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
NOTE: If using remote sensors and the does not recognize the sensor
upon power up (displays a sensor fault), check the placement of this jumper. If the
jumper is on terminals 1-2, move the jumper to terminals 2-3.
For digital ModBus signal and power use a minimum of 4 conductors #18 AWG
insulated and shielded cable.
Shielding from either the controller or remote sensors should be bonded to the
enclosure screw located inside the .
Figure 4-6. Wiring Diagram for Dual On-board Sensors
4-8 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 31

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor System Wiring
Figure 4-7. Wiring Remote Sensors Back to
Figure 4-8. Wiring Dual Remote Sensors
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 4-9
Page 32

System Wiring iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
4.6. Digital ModBus RTU Interface Wiring (J1)
4.6.1. ModBus Interface Wiring Overview
To interface the to a digital controller, PLC, or HMI, connect the power
and ground to the appropriate terminals mentioned above. The digital signals are
wired into the RS485A and RS485B terminals on the board. See Figure 4-9.
Figure 4-9. Wiring Diagram for the ModBus Interface
4.6.2. Setting the ModBus Address on the
Located on the back of the electronics module is an 8-position DIP switch.
This switch bank is used to set the ModBus Slave Address for the
unit. The address can be set from 1 to 255. Use the DIP switches to set the
binary representation of the desired address. 1 is bit zero, and 8 is bit 7. ON
represents a 1, and OFF represents zero. Refer to Appendix B for hex-todecimal equivalents.
Figure 4-10. Switch Bank for Setting ModBus Slave Address
4-10 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 33

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor System Wiring
Figure 4-11. Setting the ModBus Address (Example Address of 240 Decimal)
4.6.3. Setting the ModBus Address for Stand-Alone Sensors
NOTE: This section is only necessary if you are connecting a sensor directly to a
ModBus controller, PLC, or digital system.
For stand-alone sensor heads used in a ModBus network, the address is set in the
same manner. Once the aluminum sensor head is removed with the sensor board,
the sensor electronics module is exposed. On the back of the sensor electronics
module is a small 8-position DIP switch. The address can be set from 1 to 255 in a
similar manner as setting the ModBus address on the except pin 8 on the
sensor’s 8-position DIP switch is the least significant bit, and pin 1 is the most
significant bit.
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 4-11
Page 34

System Wiring iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
Figure 4-12. Location of Address DIP Switch on Sensor Electronics Module
Figure 4-13. Setting the ModBus Address for a Stand-Alone Sensor
4-12 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 35

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor System Wiring
NOTE: If adding a second sensor to an existing module, set the ModBus address
to which represents 11110000 binary (and 240 decimal). See
Chapter 6 for more information on the ModBus interface. (Note that DIP switches
are pre-set at the factory for all dual-sensor units).
4.7. Wiring Conclusion
Once wiring is complete, place the electronics module back in the
housing by pressing the standoff banana jacks into the mating plugs. Be careful
not to pinch any of the wiring. After the module is in place, secure the windowed
top back on the housing and power up the unit.
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 4-13
Page 36

Page 37

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Operation
OPERATION
Chapter
5
During this warm-up period, the
4-20 mA outputs are limited to 3 mA
(16 mA for oxygen). After the three
minute warm-up, the unit will enter
the Normal Operating Mode. If during
the warm-up period, the unit fails a
self test, the display will show a fault
code, and the fault relay will be
activated. Fault codes are located in
Chapter 8.
Figure 5-1. Sample Fault Code Display
5.1. Initial Start-up
Once power is applied (12-28 VDC), the is operational. The LED
display powers up, and the system enters a start-up period. During this start-up
period, the identifies the sensors that are connected and then enters a
three minute warm-up period.
NOTE: Upon initial power up, broadband infrared (BBIR) sensors do not store or
transmit the default values for Low Alarm, High Alarm, and 4-20 mA range to the
unit. These values are set to zero, and must be set following the
procedures outlined later in this manual.
5.2. Warm-up Period
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 5-1
Page 38

Operation iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
In Normal Operating Mode, the
gas monitor will display the
instantaneous readings for each sensor
wired into the unit. The top of the
display shows the gas
reading for Sensor 1. Sensor 1 should
have the internal dip switches set to 00
hex or 0F hex. The bottom row of the
display shows the gas
reading for Sensor 2. Sensor 2 should
have the internal dip switches set to F0
hex.
Figure 5-2. Sample Dual-Sensor
Display
As gas concentrations increase, the
respective channel’s readings will
respond accordingly. If low or high
alarm levels are exceeded, an alarm
indication will appear in the first digit
of the display. An “L” indicates a low
alarm while an “H” indicates a high
alarm. If a 4-20 mA fault occurs,
either a “P” indicating an open loop, or
an “U” indicating 4-20 over-range will
be present.
Figure 5-3. Sample Low and High
Alarm Displays
5.3. Normal Operating Mode
From the Normal Operating Mode, the can enter into the program mode
in one of two ways. To enter the Program Mode without opening the enclosure,
pass over the embedded reed switch located under CH1 with the magnetic wand
(see Figure 5-4). This will enter you into the non-intrusive program mode.
In this mode you can check sensor type, zero the unit, calibrate the unit, change the
span gas value, and view sensor span. With the enclosure top removed, Program
Mode can be entered using the “MODE” key. The available functions are listed in
Chapter 8: Troubleshooting.
5-2 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 39

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Operation
Figure 5-4. Locations of Reed Switches and Push Buttons
5.4. Programming Mode Overview
NOTE: Zeroing and calibrating the instrument can be accomplished one of two
ways via programming mode. Zeroing and calibrating (as well as other
programming options) can be entered either from the keypad or non-intrusively
using the magnetic wand. Refer to the sections and subsections within this chapter
for detailed information.
When in the Programming Mode, either via the magnetic wand or keypad
operation, the top line of the main display area shows a status bit and three data
bits. The bottom line of the display shows the timers (see Figure 5-5). The
decimals on the far right of each line of the display are channel indicators. The top
decimal indicates channel 1 is being programmed, and the bottom decimal
indicates channel 2.
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 5-3
Page 40

Operation iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
Figure 5-5. Components of the Display
5.5. Programming Mode – Non-intrusive Operation
5.5.1. Introduction
Non-intrusive calibration and programming is accomplished using a magnetic
wand that comes with the unit. Placing the magnetic wand over the
embedded reed switches located under the CH1 and CH2 designations (see
Figure 5-4) of the faceplate will allow you to scroll through menus and enter the
desired function. The functions available through non-intrusive operation are as
follows.
Sensor Type
Zero
Calibration
Span Gas Value
Span Reserve (in this order).
NOTE: Please see the Chapter 8 for a complete list of functions and function
codes.
5-4 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 41

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Operation
To enter non-intrusive operation
during the Normal Operating Mode,
place the magnetic wand over the CH1
designation. The will
display the sensor type for channel 1
for 5 seconds then enter in the Zero
Menu.
Figure 5-6. Sample Display Entering
Non-Intrusive Mode
Zeroing is the first option in the setup
menu. A “0 ” is displayed in the status
bit of the display to designate this
function. A 10 second timer is
displayed on the bottom line of the
LED display. To initiate zeroing, place
the magnetic wand over CH2 during
the 10-second countdown. If you do
not initiate zeroing during the 10second countdown, the will
return to the Normal Operating Mode.
To abrot zeroing at any time, place the
magnatic wand over CH1.
Figure 5-7. Sample Zeroing Display
5.5.2. Sensor Type
NOTE: If you want to operate channel 2, place the magnetic wand on CH2 first to
enter the setup menu.
Once non-intrusive mode is entered, placing the magnetic wand over CH1, will
allow scrolling through all of the functions that are available. Once the desired
function is reached, a 10-second timer will appear on the bottom row of the LED
display. During this 10-second time out, if the magnetic wand is placed over CH2,
that function is entered. Once a function is entered, a new timer will appear.
5.5.3. Zeroing
If you initiate zeroing, the status bit will start to flash. Once zeroing is complete,
the unit will return to the Normal Operating Mode.
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 5-5
Page 42

Operation iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
Calibration is the next available
option. Calibration is designated with
a “C” in the status bit. A 10 second
timer is displayed on the bottom line
of the LED display. To initiate
calibration, place the magnetic wand
over CH2 during the 10-second
countdown. If you do not initiate
calibration during the 10-second
countdown, the will return
to the Normal Operating Mode. If you
initiate calibration, the status bit will
start to flash and the will
enter the zeroing process.
Figure 5-8. Sample Calibration Display
The will automatically zero
before calibration. Zeroing is
designated with a flashing “0” in the
status bit. Once zeroing is complete,
the will automatically enter
the calibration routine. Calibration is
designated with a flashing “C” in the
status bit.
After zeroing finishes, the is
ready to calibrate. When the flashing
“C” appears on the display, apply
calibration gas. As the
responds to the gas, the current
reading will be displayed on the top
line of the LED display. To abort
calibration at any time, place the
magnetic wand over CH1.
Figure 5-9. Sample Zeroing Display
5.5.4. Calibration
NOTE: Before the will calibrate, the unit will enter the zeroing process.
Please make sure that you apply Zero Air to the instrument while it is zeroing.
5-6 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 43

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Operation
NOTE: Check and verify span setting
before starting a calibration.
NOTE: See Appendix D for a
complete list of factory default span
gases.
NOTE: Flow rate for calibration is
0.5 liter per minute (LPM) except for
NH3, ClO2, Cl2, NO2, SO2, and HCl
which require 1.0 LPM.
Figure 5-10. Apply CalGas Display
The option after calibration is Span
Gas Concentration. The span option is
designated with a flashing “S” in the
status bit with the current span value
next to it. To change the span value,
place the magnetic wand over CH2
during the 10-second countdown. If
you do not place the magnet over CH1
during the 10-second countdown, the
will return to the Normal
Operating Mode. If you initiate the
change span option, the status bit will
start to flash and the span
value can now be changed.
The current span value is displayed on
the top line of the LED display. To
increment the span value, pass the
magnetic wand over CH1. When the
desired value is reached, pass the
magnetic wand over CH2 to accept
and save changes. Passing over CH1
or letting the timer count down to zero
without saving the new value, will
take you back into the Programming
Mode.
Figure 5-11. Sample Span Gas
Concentration Display
Figure 5-12. Flashing Status Bit
5.5.5. Changing Span Gas Concentration
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 5-7
Page 44

Operation iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
The last option available is viewing
the sensor span reserve. The span
reserve option is designated with an
“r” in the status bit. The current span
reserve is displayed on the top line of
the LED display.
Figure 5-13. Sample Span Reserve
Display
In a safe environment where the
windowed top of the transmitter can be
removed, there are more programming
options available. These programming
options include all of the functions
available in the non-intrusive mode as
well as a few others. These items are
password protected. To enter the
programming options, press the
“Mode” key. The access code is
“Mode”, “Up”, “Down”, “Up”,
“Enter”.
Figure 5-14. Sample Code Entry
Display
NOTE: Span Gas Concentration for combustibles can be set from 0% to
100%LEL. For the sake of resolution, the Span Gas Concentration should be set
above 20% LEL.
5.5.6. Sensor Span Reserve
5.6. Programming Mode – Push Button Operation
5.6.1. Introduction
Once the correct password has been entered, the user will have to select a channel
for programming. But in case of wrong password or time out (10 second) the
display will revert back to Normal Operating Mode.
5-8 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 45

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Operation
On entering the correct password, the
channel selection screen will be
displayed on the LED display. Press
the “Mode” button to switch between
the available channels then press the
“” button to confirm the channel
selection.
Once a channel is selected, the gas
type for that sensor is displayed on the
top row of the LED display for 5-7
second. After that the LED display
will show the list of available
functions. Use the arrow keys to scroll
through the list of functions available.
Figure 5-15. Sample Channel Selection
Display
The low alarm setpoint is designated
with an “L” displayed in the status bit
and current low alarm value displayed
next to it. To change the low alarm
setpoint, press the “” button during
the 10-second countdown. If you do
not press “” during the 10-second
countdown, the will return
to the Normal Operating Mode. If you
initiate the low alarm option, the status
bit will start to flash and the
low alarm setpoint can be changed by
Figure 5-16. Sample Low Alarm
Setpoint Display
NOTE: If display shows “ iNet” confirm setting is “0” to ensure proper function
of onboard relay.
NOTE: Please see Chapter 8 for a complete list of functions and function codes.
5.6.2. Entering Programming Mode and Selecting a Channel
NOTE: If you have a dual-sensor unit, use the “Mode” button to switch between
the channel.
5.6.3. Set Low Alarm
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 5-9
Page 46

Operation iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
When the desired value is reached,
press the “” key to accept and save
the new value. If the value is not
saved before the time-out, the
will go back to the
Programming Mode.
5.6.5. 4-20 mA Analog Output
Range
The range of 4-20 mA analog output is
set to full range as factory default. For
full range values, see Appendix D. If
the user desires to change the output
scaling of the 4-20 mA analog signal,
they can do so.
Figure 5-17. Sample High Alarm
Setpoint Display
using the “” and “” keys. When the desired value is reached, press the “” key
to accept and save the new value. If the value is not saved before the time-out, the
will go back to the Programming Mode.
5.6.4. Set High Alarm
The high alarm setpoint is designated with an “H” displayed in the status bit and
the current high alarm value displayed next to it. To change the high alarm
setpoint, press the “” button during the 10-second countdown. If you do not
press “” during the 10-second countdown, the will return to the
Normal Operating Mode. If you initiate the high alarm option, the status bit will
start to flash and the high alarm setpoint can be changed by using the “”
and “” keys.
NOTE: Only the upper end range can be changed. The low end is always set for
4 mA.
5-10 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 47

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Operation
The 4-20 mA setpoint is designated
with a “4” displayed in status bit and
the current high end range next to it.
To change the range, press the “”
button during the 10-second
countdown. If you do not press “”
during the 10-second countdown, the
will return to the Normal
Operating Mode. If you initiate the
4-20 mA range option, the status bit
will start to flash and the
range setpoint can be changed by
using the “” and “” keys.
When the desired value is reached,
press the “” key. If the value is not
saved before the time-out, the
will go back to the
Programming Mode.
Figure 5-18. Changing the Analog
Output Upper Value
The system’s clock minute setting is
designated with a “1” in the status
bit and current value next to it. To
change the minutes, press the “”
button during the 10-second
countdown. If you do not press “”
during the 10-second countdown, the
will return to the Normal
Operating Mode. If you initiate the
minutes option, the status bit will
start to flash and the
minute can be changed by using the
“” and “” keys.
Figure 5-19. Setting System Time
(Minutes)
5.6.6. Set System Time – Minute
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 5-11
Page 48

Operation iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
The system’s clock hour setting is
designated with an “h” in the status
bit and current value next to it. To
change the hour, press the “” button
during the 10-second countdown. If
you do not press “” during the 10second countdown, the will
return to the Normal Operating Mode.
If you initiate the hours option, the
status bit will start to flash and the
hour can be changed by
using the “” and “” keys.
Figure 5-20. Setting System Time (Hour)
The system’s day of the month setting
is designated with a “d” in the status
bit and current value next to it. To
change the day, press the “” button
during the 10-second countdown. If
you do not press “” during the 10second countdown, the will
return to the Normal Operating Mode.
If you initiate the days option, the
status bit will start to flash and the
day can be changed by
using the “” and “” keys.
Figure 5-21. Setting System Date
When the desired value is reached, press the “” key. If the value is not saved
before the time-out, the will go back to the Programming Mode.
5.6.7. Set System Time – Hour
When the desired value is reached, press the “” key. If the value is not saved
before the time-out, the will go back to the Programming Mode.
5.6.8. Set System Time – Day
When the desired value is reached, press the “” key. If the value is not saved
before the time-out, the will go back to the Programming Mode.
5-12 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 49

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Operation
The system’s month setting is
designated with an “E” in the status bit
and current value next to it. To
change the month, press the “”
button during the 10-second
countdown. If you do not press “”
during the 10-second countdown, the
will return to the Normal
Operating Mode. If you initiate the
month option, the status bit will start
to flash and the month value
can be changed by using the “” and
“” keys.
Figure 5-22. Setting System Month
The system’s year setting is designated
with an “8” in the status bit and
current value next to it. To change the
year, press the “” button during the
10-second countdown. If you do not
press “” during the 10-second
countdown, the will return
to the Normal Operating Mode”. If
you initiate the year option, the status
bit will start to flash and the
year value can be changed by using
the “” and “” keys.
Figure 5-23. Setting System Year
5.6.9. Set System Time – Month
When the desired value is reached, press the “” key. If the value is not saved
before the time-out, the will go back to the Programming Mode.
5.6.10. Set System Time – Year
When the desired value is reached, press the “” key. If the value is not saved
before the time-out, the will go back to the Programming Mode.
5.6.11. Zeroing
Zeroing is an option available both through the keypad and non-intrusively. A “0 ”
is displayed in the status bit of the display to designate this function. A 10 second
timer is displayed on the bottom line of the LED display.
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 5-13
Page 50

Operation iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
To initiate zeroing, press the “” key
during the 10-second countdown. If
you do not initiate zeroing during the
10-second countdown, the
will return to the Normal Operating
Mode. If you initiate zeroing, the
status bit will start to flash. Once
zeroing is complete, the unit will
return to the Normal Operating Mode.
To abort zeroing at any time, press the
“Mode” key.
Figure 5-24. Sample Zeroing Display
The calibration option is also available
through the keypad. Calibration is
designated with a “C” in the status bit.
A 10 second timer is displayed on the
bottom line of the LED display. To
initiate calibration, press the “”key
during the 10-second countdown. If
you do not initiate calibration during
the 10-second countdown, the
will return to the Normal
Operating Mode. If you initiate
calibration, the status bit will start to
flash and the will enter the
zeroing process.
Figure 5-25. Sample Calibration
Display
5.6.12. Calibration
NOTE: Before the will calibrate, the unit will enter the zeroing process.
Please make sure that you do not apply gas to the instrument while it is zeroing.
The will automatically zero before calibration. Zeroing is designated
with a flashing “0” in the status bit. Once zeroing is complete, the will
automatically enter the calibration routine. Calibration is designated with a
flashing “C” in the status bit.
After zeroing finishes, the is ready to calibrate. When the flashing “C”
appears on the display, apply calibration gas. As the responds to the gas,
5-14 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 51

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Operation
The span option is designated with a
flashing “S” in the status bit with the
current span value next to it. To
change the span value, press the “”
key during the 10-second countdown.
If you do not press the “” during the
10-second countdown, the
will return to the Normal Operating
Mode. If you initiate the change span
option, the status bit will start to flash
and the span value can now
be changed.
Figure 5-26. Sample Span Gas
Concentration Display
The current span value is displayed on
the top line of the LED display. Use
the “” and “” keys to change the
span value. When the desired value is
reached, press the “” key to save
changes. Pressing the “Mode” key or
letting the timer count down to zero
without saving the new value, will
take you back into the Programming
Mode.
Figure 5-27. Flashing Status Bit
the current reading will be displayed on the top line of the LED display. To abort
calibration at any time, press the “Mode” key.
NOTE: Check and verify span setting before starting a calibration.
NOTE: Please refer to Appendix D for a complete list of factory default span
gases.
NOTE: Flow rate for calibration is 0.5 liter per minute (LPM) except for NH3,
ClO2, Cl2, NO2, SO2, and HCl which require 1.0 LPM.
5.6.13. Changing Span Gas Concentration
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 5-15
Page 52

Operation iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
The span reserve option is designated
with an “r” in the status bit. The
current span reserve is displayed on
the top line of the LED display.
NOTE: There are a few other options
that appear that do not have any
function associated with them. These
are reserved for future functionality.
Figure 5-28. Sample Span Reserve
Display
NOTE: If the “” key is not pressed, the new span value will not be saved.
NOTE: Span Gas Concentration for combustibles can be set from 0% to
100%LEL. For the sake of resolution, we suggest that Span Gas Concentration
should be set above 20% LEL.
5.6.14. Sensor Span Reserve
5.7. Special Notes on Using Broadband Infrared (BBIR) Sensors
The broadband infrared (BBIR) sensor currently used with the gas
monitor does not fully support or follow all of the functionality or procedures listed
within this manual. Differences between the functionality of the BBIR sensor and
the operation explained in this manual are as follows:
There is no real time clock in the BBIR sensor. When looking at the clock
settings, they will be displayed as time and date of initial test. If you set
these values, they will not increment.
Low alarm, high alarm, and 4-20 mA range are factory pre-set to 10, 20, and
100 respectively.
When calibrating the BBIR sensor, the display will not show the actual
concentration of gas applied, it will display zero. Once the calibration is
complete, the display will switch from zero to the actual concentration of gas
applied.
The Span Gas Concentration is fixed at 50% LEL and cannot be changed.
The typical zero time for the BBIR sensor is 3 minutes.
The typical calibration time for the BBIR sensor is 3 minutes.
5-16 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 53

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Operation
After a calibration, the span reserve for the BBIR sensor is not available to
the end user.
The BBIR sensor’s digital address is set at the factory for Channel 1
operation (0x0F) or Channel 2 operation (0xF0). This digital address
cannot be changed in the field.
If you have any questions concerning the functionality of the BBIR sensor and the
, please contact Oldham at 1-713-559-9280 or
americas@oldhamgas.com.
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 5-17
Page 54

Operation iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
5-18 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 55

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor ModBus Interface
MODBUS INTERFACE
Chapter
6
Characteristic
Description
Hardware
2-wire mode (not 4-wire)
Baud Rate
9600
Electrical Standard
TIA/EIA-485
Transmission Mode
RTU mode (not ASCII)
Message Coding System
8-bit
Start Bits
1
Data Bits
8 (LSB sent first)
Parity Bits
0
Stop Bits
1
6.1. Introduction
When programming the ModBus ID address on the electronics module
or on the smart sensor board, use the binary reference chart on the following page.
A “1” represents “ON” on the switch bank, and position 1 of the switch bank
represents the right most binary digit (LSB).
ModBus characteristics for the are listed below.
Table 6-1. ModBus Characteristics for the Gas Monitor
Important: When commissioning master and slave units on a ModBus network, it
is critical to ensure that every device on the ModBus network must have a unique
address. Otherwise, abnormal behavior of the entire serial bus can occur.
6.2. Sample Gas Reading via ModBus Network
To get a gas reading for Channel 1, you must read register 40102. This register
holds the gas reading in ppm.
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 6-1
Page 56

ModBus Interface iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
Addr
Inst
R/W
Host
R/W
Range
Description
40101
R/W
R/W
MSB = $01 to $FF
LSB = $01 to $F7
Sensor Type
Holds the sensor instrument type code and
ModBus address. The most significant byte
(MSB) holds a value indicating the type of
instrument (see below). The least significant
byte (LSB) holds a value which is the ModBus
address of the sensor.
MSB = Instrument type code $01 to $FF
$03 = BBIR (broad band infrared)
$04 = TOX (toxic)
$05 = OXY (oxygen)
$06 = AAW (toxic)
$07 = CAT (catalytic)
LSB = MODBUS sensor address $01 to $F7
(1 to 247)
40102
W R $0000 to $FFFF
Gas Reading
Holds the gas reading in ppm or percent
depending upon the sensor in the instrument.
The range is from $0000 to $FFFF and
represents a signed decimal value range
from -32768 to +32767.
Examples:
+5 ppm = register value of 0000510 = $0005
-5 ppm = register value of 6553110 = $FFFB
Example: Gas reading of 5 ppm = register value of $0005.
Example: Gas reading of 20.9% = register value of $0209.
For Channel 2 you can access the gas reading by looking at register 40202.
For a full list of ModBus commands and registers that are accessible on the
, refer to the next section or, for the most up-to-date list, contact the
Technical Support group of Oldham at 1-713-559-9280.
6.3. ModBus Register List
ModBus register addresses are provided in Table 6-2.
Table 6-2. ModBus Registers
6-2 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 57

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor ModBus Interface
Addr
Inst
R/W
Host
R/W
Range
Description
40103
R*
R*
MSB = $01 to $FF
LSB = $01 to $FF
Gas Type
Holds the decimal place holder and the gas type
code. The most significant byte (MSB) holds
the number of decimal places to be used in
calculations for this gas. This decimal locator
applies to all subsequent values of gas readings
within other registers. This can be read by the
instrument. The least significant byte (LSB)
holds a code which identifies the gas type.
This can be read by the host.
MSB = Decimal place holder $01 to $FF
LSB = Gas type code $01 to $FF
$01 CO Carbon Monoxide
$02 H2S Hydrogen Sulfide
$03 SO2 Sulfur Dioxide
$04 NO2 Nitrogen Dioxide
$05 Cl2 Chlorine
$06 ClO2 Chlorine Dioxide
$07 HCN Hydrogen Cyanide
$08 PH3 Phosphine
$09 H2 Hydrogen
$0C NO Nitric Oxide
$0D NH3 Ammonia
$0E HCl Hydrogen Chloride
$14 O2 Oxygen
$15 CH4 Methane
$16 LEL Lower Explosive Limit
(Combustible Gases)
Examples:
$0107 = 1 decimal place for gas type HCN
$0002 = 0 decimal places for gas type H2S
$0206 = 2 decimal places for ClO2
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 6-3
Page 58

ModBus Interface iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
Addr
Inst
R/W
Host
R/W
Range
Description
40105
W
R/W
$0000 to $FFFF
Instrument Mode
Holds code for current mode of instrument.
Possible working modes of instrument are listed
below.
$0001 Normal
$0002 Calibration
$0003 Warm-up
$0006 Zeroing
$0008 Fault
$0009 Reset
Examples:
Sensor in zero fault = $0008
Sensor zeroing = $0006
40106
W R $0000 to $FFFF
Status Bits
Holds 16 bits of status for various parameters in
the instrument. A bit value of “1” indicates that
the associated fault condition is present.
Bit 15 = current loop open
Bit 14 = current loop shorted
Bit 13 = power fault
Bit 12 = 5 volt fault
Bit 11 = missing sensor
Bit 10 = (not defined)
:
Bit 6 = (not defined)
Bit 5 = zero fault
Bit 4 = calibration fault
Bit 3 = over-range
Bit 2 = failed sensor
Bit 1 = high alarm
Bit 0 = low alarm
Examples:
Missing sensor = Bit 11 is set = $0800
Power fault and
failed sensor = Bits 13 and 2 set = $2004
40115
W
R
Last Alarm Date (mmdd)
Holds the month and day when the instrument
had the last alarm.
6-4 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 59

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor ModBus Interface
Addr
Inst
R/W
Host
R/W
Range
Description
High byte = $01 to $0C
Low byte = $01 to $1F
Examples:
Dec 25 is represented as $0C19
June 31 is represented as $061F
40116
W
R
Last Alarm Date (00yy)
Holds the last two digits of the year when the
instrument was last in alarm. The first two
digits are assumed to be “20”.
High byte = $00, Low byte = $02 to $63
Examples:
2002 is represented by $02
2099 is represented by $63
40117
R
R/W
MSB=$01 to $0C,
LSB=$01 to $1F
RTC Month and Day
Holds the month and day to which the real time
clock (RTC) calendar should be set. The most
significant byte (MSB) represents the month
from $01 to $0C (1-12). The least significant
byte (LSB) represents the day of the month
from $01 to $1F (1-31).
Examples:
December 25 = $0C19
June 31 = $061F
40118
R
R/W
$0002 to $0063
RTC Year (00yy)
Holds the year to which the real time clock
(RTC) should be set. The most significant byte
(MSB) is always $00. The least significant byte
(LSB) represents the two-digit year (within the
21st century), from $02 (which represents 2002)
to $063 (which represents 2099).
Examples:
2002 = 02 (+ base year of 2000) = $0002
2010 = 10 (+ base year of 2000) = $000A
2099 = 99 (+ base year of 2000) = $0063
40119
R
R/W
MSB=$00 to $18,
LSB=$00 to $3C
RTC Hours and Minutes
Holds the hours and minutes to which the RTC
should be set. The most significant byte (MSB)
represents the hour from $00 to $18 (00-24).
The least significant byte (LSB) represents the
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 6-5
Page 60

ModBus Interface iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
Addr
Inst
R/W
Host
R/W
Range
Description
minutes from $00 to $3C (00 to 60). Note that
the seconds default to zero ($00) each time the
hours and minutes are set.
Examples:
13:05 = $0D05
24:00 = $1800
40124
R
R/W
$0000 to $FFFF
Low Alarm Display Setting
Holds the value of the gas reading at which the
low alarm display will activate.
40125
R
R/W
$0000 to $FFFF
High Alarm Display Setting
Holds the value of the gas reading at which the
high alarm display will activate.
40126
R
R/W
$0000 to $03E8
Cal Gas Value
Holds the value of the calibration gas to be used
on the instrument. The range is from $0000 to
$03E8 (0 to 100010).
40127
R/W R $0000 to $FFFF
Loop High Scaling
Holds a value which indicates the gas reading
represented by a 20 mA loop output signal. The
range is from $0000 to $FFFF.
440102
R R $0000 to $FFFF
WX Scaled Reading
Use with WX series controller.
NOTE: To get the ModBus reading, register 40103 must be read as well as
register 40102. Register 40103 specifies where the decimal should be placed.
6.4. ModBus Resources
ModBus is a public protocol that can be freely adopted by any developer or
manufacturer desiring to implement it. While a detailed discussion of ModBus
protocol is beyond the scope of this manual, there are a number of up-to-date
resources available on the internet for those wishing to investigate ModBus further.
The most complete resource is www.modbus.org.
6-6 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 61

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor ModBus Interface
6.5. Termination
When putting devices on the ModBus network, a terminating resistor may be
required for the last device on the network (please see www.modbus.org for more
details). The has a blue jumper on the “public” jumper that can be used
to jumper in a 120-Ohm terminating resistor. By default, this jumper is not in
place. Oldham does not recommend changing the placement of any of the other
jumpers on this board.
Figure 6-1. Location of Jumpers
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual 6-7
Page 62

ModBus Interface iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
6-8 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 63

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Maintenance
MAINTENANCE
Chapter
7
7.1. Introduction
Sensors have a variable life dependent on the sensor and the environment in which
they operate. Oxygen sensor life is about 2 years and toxic gas sensor life is
normally 2 years or greater. The catalytic combustible gas sensors normally
operate in excess of 3 years, while the infrared sensor carries a 5-year warranty
with an anticipated life of 7 or more years.
Sensors have baseline drift and their characteristics change with time. Thus, the
must be calibrated on a regular basis. Gas detection instruments are
potential life-saving devices. In recognition of this fact, calibration for the toxic
and catalytic LEL sensors should be at least at quarterly intervals, while the
Infrared sensor should be calibrated on an annual basis with functional tests every
6 months.
Further, Oldham recommends prudent testing and/or calibration after a gas alarm.
All calibration/service to the sensors should be recorded and accessible.
NOTE: Other than regular calibrations, the require no other routine
maintenance.
NOTE: Take special care with handling and storing sensors. They are delicate
and can be damaged by storage in environments outside the specified temperature,
pressure, and humidity limits.
NOTE: Sensors are susceptible to damage from high pressure or low pressure,
especially if the change is sudden. Also, sensors should not be operated at
pressures that are 10% above or below atmospheric pressure.
(P/N: 77023554) iTrans User Manual 7-1
Page 64

Maintenance iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
NOTE: If sensors and the surrounding environment must be washed down at any
time, cover the opening of the sensor housing to protect it from water or excess
moisture. Remove cover when wash down is complete. An optional splashguard
is available for continuous protection.
7.2. Sensor Replacement
Sensor replacement must be done by qualified personnel. To replace the sensor,
shut down power to the unit. Un-thread the sensor-housing cap from the sensor
housing. There is a set screw that secures the cap to the housing. Once the cap is
removed, remove the old sensor and sensor board. When installing the new
sensor/sensor board make sure you line up the notch in the board with the
alignment pin. After the new sensor is in place, screw the sensor cap back on to
the housing and secure the set screw.
Once the new sensor is in place and has time to settle out, it should be zeroed and
calibrated for accuracy.
7.3. Zero and Calibration
Zeroing and calibrating the instrument can be accomplished one of two ways.
These routines can be entered either from the keypad or non-intrusively using the
magnetic wand. See Chapter 5: Operation for step-by-step procedures for zeroing
and calibrating the using the magnetic wand. Chapter 5 also contains
information on keypad zeroing and calibration.
7-2 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 65

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Troubleshooting
TROUBLESHOOTING
Chapter
8
Symptom
Problem
Solution
LED display does not
light up.
Input voltage is too low
Electronics module has
failed
Check for presence of input
voltage.
Output outside
4-20 mA range
Unit in calibration mode
Electronics module has
failed
Exit calibration mode.
Replace electronics module.
Output does not
change when gas
concentration
changes
Electronics module has
failed
Replace electronics module.
Cannot calibrate
SPAN
Sensor has failed
Electronics module has
failed
Replace sensor and
calibrate.
Replace electronics module
and calibrate.
8.1. Introduction
This chapter provides troubleshooting information for the gas monitor.
8.2. Diagnosing Common Problems
Table 8-1. Common Problems
(P/N: 77023554) iTrans User Manual 8-1
Page 66

Troubleshooting iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
Symptom
Problem
Solution
Reading drifts by 10
counts over a short
time period (in a
stable temperature
environment)
Sensor has failed
Electronics module has
failed
Replace sensor and
calibrate.
Replace electronics module
and calibrate.
In calibration, LED
displays wrong value.
Sensor has failed
Electronics module has
failed
Replace sensor and
calibrate.
Replace electronics module
and calibrate.
Reed Switch does not
work
Electronics module has
failed
Reed Switch is damaged
Replace electronics module
and calibrate.
Replace the reed switch.
“P” appears on the
display
Open loop on a 4-20 mA
channel
Place a 100-Ohm load
resistor from the mA output
pin to ground.
“U” appears on the
display
4-20 mA signal is in over
range
Ensure the sensor is
working properly and the
4-20 mA is scaled correctly.
Fault
Code
LED
Display
Status
Bit
4-20 mA
Output
Description
0FFF
0.
Flashing
1 mA
Zeroing error – Recover after
calibrating
CFFF
C.
Flashing
1 mA
Calibration error – Recover after
calibrating or replacing the sensor
1FFF
1.
Flashing
1 mA
SMART sensor error
2FFF
2.
Flashing
1 mA
Sensor error
8.3. Fault Codes
Table 8-2. Fault Codes
8-2 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 67

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Troubleshooting
Function
Code
LED Display
Description
Status
Bit
Data Area
L
L.
Low Alarm
Set the relay low alarm value
H
H.
High Alarm
Set the relay high alarm value
4
4.
Range of 4-20 mA
Set the range of 4-20 mA output
1
1.
Minute
Set system time – minute
H
h.
Hour
Set system time – hour
D
d.
Date
Set system time – date
E
E.
Month
Set system time – month
8
8.
Year
Set system time – year
0
0.
Zeroing
C
C.
Calibration
S
S.
Span Gas Concentration
Set span gas concentration
R
r.
Sensor Span Reserve
Check the span reserve
2
2.
Date
The latest alarm time-date
3
3.
Month
The latest alarm time-month
6
6.
Date
The latest calibration time-date
7
7.
Month
The latest calibration timemonth
9
9.
Year
The latest calibration time-year
8.4. Function Codes
Table 8-3. Function Codes
(P/N: 77023554) iTrans User Manual 8-3
Page 68

Troubleshooting iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
8-4 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 69

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Warranty
WARRANTY
Chapter
9
9.1. Warranty
Oldham fixed system products are warranted to be free from defects in material
and workmanship for a period of eighteen (18) months from the date of shipment,
or one (1) year from the date of first use, whichever occurs first, except where
otherwise stated in writing in Oldham literature accompanying the product.
The above warranty does not include sensors, pumps, or filters, all of which are
warranted to be free from defects in material and workmanship for one year from
the date of shipment, except where otherwise stated in writing in Oldham literature
accompanying the product. In addition, Oldham warrants the Infrared sensor used
to monitor LEL Methane Propane to be free from defects in material and
workmanship for a period of sixty-six (66) months from the date of shipment, or
five (5) years from the date of first use, whichever occurs first, except where
otherwise stated in writing in Oldham literature accompanying the product.
9.2. Limitation of Liability
Oldham makes no other warranties, either expressed or implied, including, but not
limited to the warranties of merchantability or fitness for particular purpose.
Should the product fail to conform to the above warranty, buyer’s only remedy and
Oldham’s only obligation shall be, at Oldham’s sole option, replacement or repair
of such non-conforming goods or refund of the original purchase price of the nonconforming goods. In no event will Oldham be liable for any other special,
incidental or consequential damages, including loss of profit or loss of use, arising
out of the sale, manufacture or use of any products sold hereunder whether such
claim is pleaded in contract or in tort, including strict liability in tort.
It shall be an express condition to Oldham’s warranty that all products be carefully
inspected for damage by buyer upon receipt, be properly calibrated for buyer’s
particular use, and be used, repaired, and maintained in strict accordance with the
instructions set forth in Oldham’s product literature. Repair or maintenance by
non-qualified personnel will invalidate the warranty, as will the use of non-
(P/N: 77023554) iTrans User Manual 9-1
Page 70

Warranty iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
approved consumables or spare parts. As with any other sophisticated product, it is
essential and a condition of Oldham’s warranty that all personnel using the
products be fully acquainted with their use, capabilities and limitations as set forth
in the applicable product literature. Buyer acknowledges that it alone has
determined the intended purpose and suitability of the goods purchased. It is
expressly agreed by the parties that any technical or other advice given by Oldham
with respect to the use of the goods or services is given without charge and at
buyer’s risk; therefore, Oldham assumes no obligation or liability for the advice
given or results obtained.
SPECIFICATIONS SUBJECT TO CHANGE
9-2 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 71

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Appendix A
ACRONYMS AND
ABBREVIATIONS
Appendix
A
Abbr
Definition
A
Ampere
ABS
acrylonitrile butadiene styrene
ASCII
American Standard Code for Information Interchange
BBIR
broadband infrared
bit
binary digit
bps
bits per second
C
centigrade
CALI
calibration
CAT
catalytic
Ch
channel
CH4
methane
chem
chemical
Cl2
chlorine
ClO2
chlorine dioxide
CO
carbon monoxide
CSA
Canadian Standards Association
DC
direct current
DCS
distributed control system
DIP
dual in-line package
DISP
display
F
Fahrenheit
FAQ
frequently asked questions
FAUL
fault
FIFO
first-in-first-out
GND
ground
This appendix contains acronyms and abbreviations that are used within this
document.
Table A-1. Acronyms and Abbreviations
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual A-1
Page 72

Appendix A iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
Abbr
Definition
H2
hydrogen
H2S
hydrogen sulfide
HCl
hydrogen chloride
HCN
hydrogen cyanide
LED
light emitting diode
LEL
lower explosive limit (combustible gases)
LSB
least significant bit
mA
milliampere
mm
millimeter
MSB
most significant bit
NC
normally closed
NDIR
non-dispersive infrared
NEMA
National Electrical Manufacturers Association
NH3
ammonia
NO
normally open, Nitric Oxide
NO2
nitrogen dioxide
NOR
normal mode
NRTL
nationally recognized testing laboratory
O2
oxygen
OXY
oxygen
PH3
phosphine
PLC
programmable logic controller
ppm
parts per million
REST
restart
RH
relative humidity
RTC
real time clock
RTU
remote terminal unit
SO2
sulfur dioxide
SPST
single-pole, single-throw
TOX
toxic
V
Volts
A-2 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 73

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Appendix B
DECIMAL, BINARY, AND
HEXADECIMAL
EQUIVALENTS
Appendix
B
0x00 = 000
0x20 = 032
0x40 = 064
0x60 = 096
0x80 = 128
0xA0 = 160
0xC0 = 192
0xE0 = 224
0x01 = 001
0x21 = 033
0x41 = 065
0x61 = 097
0x81 = 129
0xA1 = 161
0xC1 = 193
0xE1 = 225
0x02 = 002
0x22 = 034
0x42 = 066
0x62 = 098
0x82 = 130
0xA2 = 162
0xC2 = 194
0xE2 = 226
0x03 = 003
0x23 = 035
0x43 = 067
0x63 = 099
0x83 = 131
0xA3 = 163
0xC3 = 195
0xE3 = 227
0x04 = 004
0x24 = 036
0x44 = 068
0x64 = 100
0x84 = 132
0xA4 = 164
0xC4 = 196
0xE4 = 228
0x05 = 005
0x25 = 037
0x45 = 069
0x65 = 101
0x85 = 133
0xA5 = 165
0xC5 = 197
0xE5 = 229
0x06 = 006
0x26 = 038
0x46 = 070
0x66 = 102
0x86 = 134
0xA6 = 166
0xC6 = 198
0xE6 = 230
0x07 = 007
0x27 = 039
0x47 = 071
0x67 = 103
0x87 = 135
0xA7 = 167
0xC7 = 199
0xE7 = 231
0x08 = 008
0x28 = 040
0x48 = 072
0x68 = 104
0x88 = 136
0xA8 = 168
0xC8 = 200
0xE8 = 232
0x09 = 009
0x29 = 041
0x49 = 073
0x69 = 105
0x89 = 137
0xA9 = 169
0xC9 = 201
0xE9 = 233
0x0A = 010
0x2A = 042
0x4A = 074
0x6A = 106
0x8A = 138
0xAA = 170
0xCA = 202
0xEA = 234
0x0B = 011
0x2B = 043
0x4B = 075
0x6B = 107
0x8B = 139
0xAB = 171
0xCB = 203
0xEB = 235
0x0C = 012
0x2C = 044
0x4C = 076
0x6C = 108
0x8C = 140
0xAC = 172
0xCC = 204
0xEC = 236
0x0D = 013
0x2D = 045
0x4D = 077
0x6D = 109
0x8D = 141
0xAD = 173
0xCD = 205
0xED = 237
0x0E = 014
0x2E = 046
0x4E = 078
0x6E = 110
0x8E = 142
0xAE = 174
0xCE = 206
0xEE = 238
0x0F = 015
0x2F = 047
0x4F = 079
0x6F = 111
0x8F = 143
0xAF = 175
0xCF = 207
0xEF = 239
0x10 = 016
0x30 = 048
0x50 = 080
0x70 = 112
0x90 = 144
0xB0 = 176
0xD0 = 208
0xF0 = 240
0x11 = 017
0x31 = 049
0x51 = 081
0x71 = 113
0x91 = 145
0xB1 = 177
0xD1 = 209
0xF1 = 241
0x12 = 018
0x32 = 050
0x52 = 082
0x72 = 114
0x92 = 146
0xB2 = 178
0xD2 = 210
0xF2 = 242
0x13 = 019
0x33 = 051
0x53 = 083
0x73 = 115
0x93 = 147
0xB3 = 179
0xD3 = 211
0xF3 = 243
0x14 = 020
0x34 = 052
0x54 = 084
0x74 = 116
0x94 = 148
0xB4 = 180
0xD4 = 212
0xF4 = 244
0x15 = 021
0x35 = 053
0x55 = 085
0x75 = 117
0x95 = 149
0xB5 = 181
0xD5 = 213
0xF5 = 245
0x16 = 022
0x36 = 054
0x56 = 086
0x76 = 118
0x96 = 150
0xB6 = 182
0xD6 = 214
0xF6 = 246
0x17 = 023
0x37 = 055
0x57 = 087
0x77 = 119
0x97 = 151
0xB7 = 183
0xD7 = 215
0xF7 = 247
0x18 = 024
0x38 = 056
0x58 = 088
0x78 = 120
0x98 = 152
0xB8 = 184
0xD8 = 216
0xF8 = 248
0x19 = 025
0x39 = 057
0x59 = 089
0x79 = 121
0x99 = 153
0xB9 = 185
0xD9 = 217
0xF9 = 249
0x1A = 026
0x3A = 058
0x5A = 090
0x7A = 122
0x9A = 154
0xBA = 186
0xDA = 218
0xFA = 250
0x1B = 027
0x3B = 059
0x5B = 091
0x7B = 123
0x9B = 155
0xBB = 187
0xDB = 219
0xFB = 251
0x1C = 028
0x3C = 060
0x5C = 092
0x7C = 124
0x9C = 156
0xBC = 188
0xDC = 220
0xFC = 252
0x1D = 029
0x3D = 061
0x5D = 093
0x7D = 125
0x9D = 157
0xBD = 189
0xDD = 221
0xFD = 253
0x1E = 030
0x3E = 062
0x5E = 094
0x7E = 126
0x9E = 158
0xBE = 190
0xDE = 222
0xFE = 254
0x1F = 031
0x3F = 063
0x5F = 095
0x7F = 127
0x9F = 159
0xBF = 191
0xDF = 223
0xFF = 255
This appendix lists the hexadecimal and binary equivalents of decimal numbers.
ModBus device addresses are entered in hexadecimal format. This table provides a
cross reference if only decimal addresses are known. Hexadecimal numbers are
shown in 0x00 format on the left. Decimal equivalents are shown on the right.
Refer to Table B-1. Decimal and binary equivalents are shown in Table B-2.
Table B-1. Hexadecimal and Decimal Equivalents
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual B-1
Page 74

Appendix B iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
Dec
Binary
Dec
Binary
Dec
Binary
Dec
Binary
0
00000000
64
01000000
128
10000000
192
11000000
1
00000001
65
01000001
129
10000001
193
11000001
2
00000010
66
01000010
130
10000010
194
11000010
3
00000011
67
01000011
131
10000011
195
11000011
4
00000100
68
01000100
132
10000100
196
11000100
5
00000101
69
01000101
133
10000101
197
11000101
6
00000110
70
01000110
134
10000110
198
11000110
7
00000111
71
01000111
135
10000111
199
11000111
8
00001000
72
01001000
136
10001000
200
11001000
9
00001001
73
01001001
137
10001001
201
11001001
10
00001010
74
01001010
138
10001010
202
11001010
11
00001011
75
01001011
139
10001011
203
11001011
12
00001100
76
01001100
140
10001100
204
11001100
13
00001101
77
01001101
141
10001101
205
11001101
14
00001110
78
01001110
142
10001110
206
11001110
15
00001111
79
01001111
143
10001111
207
11001111
16
00010000
80
01010000
144
10010000
208
11010000
17
00010001
81
01010001
145
10010001
209
11010001
18
00010010
82
01010010
146
10010010
210
11010010
19
00010011
83
01010011
147
10010011
211
11010011
20
00010100
84
01010100
148
10010100
212
11010100
21
00010101
85
01010101
149
10010101
213
11010101
22
00010110
86
01010110
150
10010110
214
11010110
23
00010111
87
01010111
151
10010111
215
11010111
24
00011000
88
01011000
152
10011000
216
11011000
25
00011001
89
01011001
153
10011001
217
11011001
26
00011010
90
01011010
154
10011010
218
11011010
27
00011011
91
01011011
155
10011011
219
11011011
28
00011100
92
01011100
156
10011100
220
11011100
29
00011101
93
01011101
157
10011101
221
11011101
30
00011110
94
01011110
158
10011110
222
11011110
31
00011111
95
01011111
159
10011111
223
11011111
32
00100000
96
01100000
160
10100000
224
11100000
33
00100001
97
01100001
161
10100001
225
11100001
34
00100010
98
01100010
162
10100010
226
11100010
35
00100011
99
01100011
163
10100011
227
11100011
36
00100100
100
01100100
164
10100100
228
11100100
37
00100101
101
01100101
165
10100101
229
11100101
38
00100110
102
01100110
166
10100110
230
11100110
39
00100111
103
01100111
167
10100111
231
11100111
40
00101000
104
01101000
168
10101000
232
11101000
41
00101001
105
01101001
169
10101001
233
11101001
42
00101010
106
01101010
170
10101010
234
11101010
43
00101011
107
01101011
171
10101011
235
11101011
44
00101100
108
01101100
172
10101100
236
11101100
45
00101101
109
01101101
173
10101101
237
11101101
46
00101110
110
01101110
174
10101110
238
11101110
47
00101111
111
01101111
175
10101111
239
11101111
48
00110000
112
01110000
176
10110000
240
11110000
49
00110001
113
01110001
177
10110001
241
11110001
50
00110010
114
01110010
178
10110010
242
11110010
51
00110011
115
01110011
179
10110011
243
11110011
52
00110100
116
01110100
180
10110100
244
11110100
53
00110101
117
01110101
181
10110101
245
11110101
54
00110110
118
01110110
182
10110110
246
11110110
55
00110111
119
01110111
183
10110111
247
11110111
56
00111000
120
01111000
184
10111000
248
11111000
57
00111001
121
01111001
185
10111001
249
11111001
58
00111010
122
01111010
186
10111010
250
11111010
59
00111011
123
01111011
187
10111011
251
11111011
60
00111100
124
01111100
188
10111100
252
11111100
61
00111101
125
01111101
189
10111101
253
11111101
62
00111110
126
01111110
190
10111110
254
11111110
63
00111111
127
01111111
191
10111111
255
11111111
Table B-2. Decimal and Binary Equivalents
B-2 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 75

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Appendix C
ORDERING MATRIX
Appendix
C
Base part number 7814635-ABCDEFG
Single or dual on-board or remote toxic, combustible and oxygen sensors with dual 4-20 mA outputs (one
per sensor) or ModBus RTU outputs. Remote sensor capable of operation up to 200 meters from main
transmitter. Operating temperature range –20C to +50C.
Example: 7814635-1C21241 =On-board LEL (4-20 mA scale 0-100) and remote mount H2S (4-20 mA scale 0-500)
with relays
A = Sensor 1 Configuration
E = Sensor 2 Configuration
B = Gas sensor 1
F = Gas sensor 2
C = 4-20 mA output scale for sensor 1
G = 4-20 mA output scale for sensor 2
D = Optional on-board relays
A - Sensor 1
E – Sensor 2
0 = No sensor
1 = Explosion Proof / On-board
1 = Explosion Proof / On-board
2 = Explosion Proof / Remote
2 = Explosion Proof / Remote
3 = Non-hazardous Remote/Duct
Mount
3 = Non-hazardous Remote/Duct
Mount
4 = Explosion Proof / On-board with
Splash Guard
4 = Explosion Proof / On-board with
Splash Guard
5 = Explosion Proof / Remote with
Splash Guard
5 = Explosion Proof / Remote with
Splash Guard
6 = Stainless Steel / On-board
7 = Stainless Steel / Remote
7 = Stainless Steel / Remote
B - Gas sensor 1
F - Gas sensor 2
1 = Carbon Monoxide (CO)
1 = Carbon Monoxide (CO)
2 = Nitric Oxide (NO)
2 = Nitric Oxide (NO)
3 = Ammonia (NH3)
3 = Ammonia (NH3)
4 = Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)
4 = Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)
5 = Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
5 = Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
6 = Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2)
6 = Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2)
7 = Chlorine (Cl2)
7 = Chlorine (Cl2)
8 = Chlorine Dioxide (ClO2)
8 = Chlorine Dioxide (ClO2)
9 = Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN)
9 = Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN)
A = Oxygen (O2)
A = Oxygen (O2)
B = LEL Infrared (obsolete)
B = LEL Infrared (obsolete)
C = LEL Catalytic Plug-In (factory
C = LEL Catalytic Plug-In (factory
This appendix provides an ordering matrix for the gas monitor.
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual C-1
Page 76

Appendix C iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
Pentane calibration)
Pentane calibration)
D = Carbon Monoxide – Hydrogen Null (CO –
H2)
D = Carbon Monoxide – Hydrogen Null (CO –H2)
F = Hydrogen Chloride (HCl)
F = Hydrogen Chloride (HCl)
G = LEL Infrared Propane (obsolete)
G = LEL Infrared Propane (obsolete)
K = Phosphine (PH3)
K = Phosphine (PH3)
L = Hydrogen (H2)
L = Hydrogen (H2)
C = 4-20 mA output scale for sensor 1
G = 4-20 mA output scale for sensor 2
0 = 0 - 999
0 = 0 - 999
1 = 0 - 500
1 = 0 - 500
2 = 0 - 100
2 = 0 - 100
3 = 0 - 50
3 = 0 - 50
4 = 0 - 30
4 = 0 - 30
5 = 0 - 10
5 = 0 - 10
6 = 0 - 2
6 = 0 - 2
7 = 0 - 1
7 = 0 - 1
8 = 0 - 20
8 = 0 - 20
9 = 0 - 200
9 = 0 - 200
D – Optional On-board Relays
0 = No Relay Module
1 = With Optional On-board Relays
C-2 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 77

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Appendix D
FACTORY DEFAULT
SETTINGS
Appendix
D
Sensor Name
Range
Resolution
Cal Gas
Default
Low
Alarm
Default
High
Alarm
CO
0-999 ppm
1 ppm
100 ppm
35 ppm
70 ppm
H2S
0-500 ppm
1 ppm
25 ppm
10 ppm
20 ppm
SO2
0-99.9 ppm
0.1 ppm
5 ppm
2.0 ppm
4.0 ppm
NO2
0-99.9 ppm
0.1 ppm
5 ppm
1.0 ppm
2.0 ppm
Cl2
0-99.9 ppm
0.1 ppm
10 ppm
0.5 ppm
1.0 ppm
ClO2
0-1.00 ppm
0.01 ppm
0.90 ppm
0.30 ppm
0.50 ppm
HCN
0-30.0 ppm
0.1 ppm
10 ppm
5.0 ppm
10.0 ppm
PH3
0-1.00 ppm
0.01 ppm
1.0 ppm
0.30 ppm
0.60 ppm
CO/H2 NULL
0-999 ppm
1 ppm
100 ppm
35 ppm
70 ppm
NO
0-999 ppm
1 ppm
25 ppm
25 ppm
50 ppm
NH3
0-500 ppm
1 ppm
25 ppm
25 ppm
50 ppm
HCl
0-30.0 ppm
0.1 ppm
10 ppm
5.0 ppm
10.0 ppm
H2
0-999 ppm
1 ppm
100 ppm
50 ppm
100 ppm
O2
0-30% Vol.
0.1% Vol.
20.9%
19.5%
23.5%
Infrared, LEL
0-100% LEL
1% LEL
50% LEL
10%LEL
20%LEL
Combustible, LEL
0-100% LEL
1% LEL
25% LEL
10%LEL
20%LEL
This appendix lists factory default settings based on the individual
sensor(s) used. Refer to Table D-1.
Table D-1. Factory Default Settings
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual D-1
Page 78

Appendix D iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
D-2 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 79

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Appendix E
EU DECLARATION OF
CONFORMITY CERTIFICATE
Appendix
E
(P/N: 77023554-1) iTrans User Manual E-1
Page 80

Appendix E iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
E-2 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 81

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Index
INDEX
Appendix
F
Index
Locator page numbers appear in regular type faces for standard index references
(e.g., 3-7). Boldface index references (e.g., 3-3) correspond to information found
in photos or illustrations. Italic index references (e.g., 3-3) correspond to
information found in tables.
#18 AWG........................................4-1, 4-4, 4-7, 5-17
120-Ohm terminating resistor ................................ 6-7
4-20 mA output(s) .. iii, 1-1, 1-2, 4-3, 5-1,, 5-11, 5-16,
8-1, 8-2, 8-3, C-1, C-2
changing upper range ...................................... 5-10
fault ................................................................... 5-2
fixed lower range ............................................ 5-10
not using............................................................ 4-4
abbreviations .......................................................... A-1
access code ............................................................ 5-8
accuracy ............................................................. ii, 2-2
acronyms................................................................ A-1
address
selection ............................................................ 1-2
setting ................................................................ 4-9
unique ............................................................... 6-1
agency approvals ................................................... 1-3
air flow................................................................... 3-1
alarm(s)
activation........................................................... 1-1
condition ............................................................. iii
date .................................................................... 5-4
horns ................................................................. 1-1
indication .......................................................... 5-2
month ................................................................ 5-4
over-range alarm ................................................. iii
relays ................................................................. 1-2
Numbers
A
capacity ........................................................ 1-2
wiring (J1, J5, J6) ......................................... 4-2
aluminum ............................................... 1-2, 2-1, 4-10
ammonia ........................................................ 1-3, C-1
analog signal ........................................................ 5-10
anticipated life ....................................................... 7-1
apply calibration gas .............................................. 5-6
arrow keys ........................ 5-9, 5-10, 5-11, 5-12, 5-13
atmospheric pressure ................................. iii, 1-2, 7-1
B
banana jacks ......................................................... 4-12
baud rate ................................................................ 6-1
BBIR ............................ 4-4, 5-1, 5-16, 5-17, 6-2, A-1
address ............................................................ 5-17
calibrating ....................................................... 5-16
calibration time ...................................... 5-16, 5-17
span reserve .................................................... 5-17
zero time ................................................ 5-16, 5-17
binary ............................................................. 4-9, A-1
blue jumper ............................................................ 6-7
broadband infrared ....................... 5-1, 5-16, 5-17, A-1
C
cable entry device .................................................. 2-5
calibration 1-1, 5-4, 5-6, 5-7, 5-14, 5-17, 6-4, 6-6, 7-1,
7-2, 8-1, 8-2, A-3, B-1
aborting ............................................................. 5-6
Page 82

Index iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
after alarms ......................................................... iii
BBIR sensor .................................................... 5-16
flow rate ................................................... 5-6, 5-15
frequency ............................................................ iii
span setting .............................................. 5-6, 5-15
time ................................................................. 5-17
BBIR .......................................................... 5-16
zeroing before ................................................. 5-14
carbon monoxide ............................. 1-3, 6-4, A-1,B-1
catalytic combustible gas sensors .............. iii,2-2, B-1
CH4 ....................................................................... A-1
change span ......................................................... 5-15
initiating ............................................................ 5-7
channel indicators ........................................... 5-3, 5-4
chlorine ........................................... 1-3, 6-4, A-1, B-1
chlorine dioxide ...................................... 1-3, 6-4, B-1
Cl2 ......................................................................... A-1
class I hazardous locations..................................... 1-3
classified locations ................................................. 4-2
ClO2 ...................................................................... A-1
clock settings .............................................. 5-16, 5-17
closing elements .................................................... 2-5
CO ........................................................................ A-1
column mounting ............................................ 3-1, 3-2
combustible gases ......................................... 2-3, A-2
commissioning ....................................................... 6-1
common problems ................................................. 8-1
conduit seal ............................................................ 2-5
configuration ................................................... 1-1, 2-3
dual sensor ................................................. 4-3, 4-4
Conformity Certificate, EC Declaration ................ E-1
connectors .............................................................. 2-4
control signal ......................................................... 1-1
control wire ............................................................ 4-1
countdown .. 5-5, 5-6, 5-7, 5-9, 5,10, 5-11, 5-12, 5-13,
5-14, 5-15
CSA approvals ....................................................... 1-3
C22.2 No. 152 compliance................................ 1-2
Std C22.2 No. 152-M1984 ................................ 1-3
Std C22.2 No. 213-M1987 ................................ 1-4
Std C22.2 No. 142-M1987 ................................ 1-3
Std C22.2 No. 30-M1986 .................................. 1-3
current draw ........................................................... 1-2
D
data bits ..................................................... 5-3,5-4, 6-1
decimals ................................................................. 5-3
Declaration of Conformity Certificate ................... E-1
decrement key ........................................................ 2-3
digital control systems ........................................... 1-1
digital controller .................................................... 4-9
digital ground ......................................................... 4-3
dimensions ............................................................. 2-2
DIP switch ....................................1-2, 4-9, 4-10, 4-12
location ............................................................. 4-9
setting addresses ............................................. 4-10
Directive 72/23/EEC .............................................. 1-4
Directive 92/31/EEC .............................................. 1-4
Directive 93/68/EEC .............................................. 1-4
Directive 94/9/EC .................................................. 1-4
display 1-2, 2-3, 5-1, 5-2, 5-3, 5-5, 5-6, 5-13, 5-14, 5-
16, 6-6, 8-2, A-1
specifications .................................................... 1-2
Distributed Control System (DCS) ....................... A-1
driving loads from relays ....................................... 4-2
dual-sensor ............................................. 4-4, 4-12, 5-9
dust-ignition-proof ................................................. 1-3
E
EC Declaration of Conformity Certificate ............. E-1
electrical risks ........................................................ 1-4
electrochemical diffusion....................................... 1-2
electromagnetic compatibility ............................... 1-4
electromagnetic interference .................................. 4-2
electronics module 2-4, 2-5, 4-1, 4-9, 4-10, 4-12, 8-1,
8-2
EMC Directive 89/336/EEC .................................. 1-4
emissions ............................................................... 3-1
EN 50014 ............................................................... 1-4
EN 50018 ............................................................... 1-4
EN 50270 ............................................................... 1-4
enclosure ..........................................1-2, 2-3, 3-1, 5-2
ground ............................................................... 4-3
screw .......................................................... 4-4, 4-7
shielding ..................................................... 4-2, 4-7
Energy Management Equipment ........................... 1-3
enter key ................................................................ 2-3
European ATEX Directive 94/9/EC ...................... 1-4
excess moisture ...................................................... 7-2
exhaust fan ............................................................. 4-2
explosion-proof ............................................... 1-2, 1-3
F
factory default .............................. 5-6, 5-10, 5 -15, B-1
fans ........................................................................ 1-1
fault code ........................................................ 5-1, 8-2
fault protection relay .............................................. 1-1
fault relay ........................................................ 1-2, 5-1
flashing ..................... 5-6, 5-7, 5-12, 5-13, 5-14, 5-15
flow rate ........................................................ 5-6, 5-15
four keys ................................................................ 2-3
function codes ........................................................ 8-3
function test, frequency ........................................... iii
functions, available .................................. 5-4, 5-8, 5-9
future functionality .............................................. 5-16
G
gas concentrations...................................... iii, 1-1, 5-2
lower than normal readings ................................. iii
gas reading ............................................... 6-1, 6-2, 6-6
gas sensor, combustible ........................................... iii
F-2 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 83

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Index
GND ..................................................................... A-1
green conductor ..................................................... 4-3
ground .............................................. 4-3, 4-9, 8-2, A-1
H
H2 ................................................................ ......... A-2
H2S ........................................................................ A-1
heat generating sources .......................................... 3-1
hexadecimal format ............................................... A-1
high alarm ....................... 5-1, 5-2, 5-16, 6-6, 8-3, D-1
relay .............................................4-2, 5-4, 6-6, 8-3
setpoint ............................................................ 5-10
threshold ........................................................... 4-2
high pressure .......................................................... 7-1
higher-power relay ................................................. 4-2
HMI ....................................................................... 4-9
housing ................................... 1-5, 2-1, 4-5, 4-12, 7-2
humidity ................................................................. 7-1
range ................................................................. 1-2
hydrogen ......................................... 1-3, 6-4, A-2, B-1
hydrogen chloride .................................................. 1-3
hydrogen cyanide ................................................... 1-3
hydrogen sulfide ................................................... A-2
I
increment key ........................................................ 2-3
infrared ............................. 1-2, 1-4, 2-2, 7-1, 9-1, D-1
calibration frequency .......................................... iii
input current, maximum ........................................ 1-2
input keys............................................................... 2-4
input voltage ................................................... 1-2, 8-1
installation ............................................................. 3-1
intrusive programming .......................................... 2-4
four keys ........................................................... 2-3
ISA S12.13 Part I-2000 ......................................... 1-3
J
jumpers ........................................................... 2-4, 6-7
K
KEMA 04 ATEX 2216X ................................ ....... 1-4
keypad ................................................. 5-13, 5-14, 7-2
keys ................................................................. 2-3, 2-4
L
LED display ............... 1-2, 2-3, 5-1, 5-5, 5-6, 5-7, 5-8,
5-9, 5-13, 5-14, 5-15, 5-16, 8-1
LEL sensors ...................................... iii, 1-2, 1-4, 5-8,
5-16, 6-3, 7-1, 9-1, C-1
life span ....................................................... iii, iv, 7-1
limitation of liability .............................................. 9-1
local authorities ..................................................... 4-1
low alarm ............................................. 5-1, 5-16, 6 -6,
8-3
relay ............................................4-2, 6-4, 6-6, 8-3
setpoint .............................................................. 5-9
threshold ........................................................... 4-2
low pressure ........................................................... 7-1
Lower Explosive Limit (LEL) ............................. A-2
M
magnetic wand ........... 1-1, 2-3, 5-2, 5-3, 5-4, 5-5, 5-6,
5-7, 7-2
main electronics unit .............................................. 2-1
maintenance ........................................................... 7-1
routine ............................................................... 7-1
master .................................................................... 6-1
message coding system .......................................... 6-1
methane................................................................. A-1
ModBus ......................................................... 6-1, A-1
address switch bank location ............................ 4-9
baud rate..................................................... 1-2, 6-1
characteristics ................................................... 6-1
commands ......................................................... 6-2
configuration ..................................................... 1-2
data bits ............................................................. 6-1
digital ground .................................................... 4-3
electrical standard ............................................. 6-1
message coding system ..................................... 6-1
number of devices ............................................. 1-2
parity bits .......................................................... 6-1
power wire ........................................................ 4-1
registers ............................................................. 6-2
resources ........................................................... 6-6
RTU ............................................ 1-1, 1-2, 4-9, B-1
signal wire ......................................................... 4-1
slave address ..................................................... 4-9
software protocol .............................................. 1-2
start bits ............................................................. 6-1
stop bits ............................................................. 6-1
terminating resistor ........................................... 6-7
transmission mode ............................................ 6-1
mode key ................................... 2-3,5-2, 5-5, 5-8, 6-1
mounting
holes .................................................................. 3-1
pipe or conduit .................................................. 3-1
N
NDIR ............................................................. 1-2, A-2
network .................................................................. 6-1
nitric oxide ............................................. 1-3, A-1, B-2
nitrogen dioxide .............................. 1-3, 6-4, A-1, B-2
NO2 ....................................................................... A-2
non-intrusive ............... 1-1, 2-3, 2-4, 5-2, 5-4, 5-5, 5-8
available functions ............................................ 5-4
non-latching ...................................................... iii, 4-2
normal mode ......................................................... A-2
Normal Operating Mode ... 5-1, 5-2, 5-5, 5-6, 5-7, 5-9,
5-10, 5-11, 5-12, 5-13, 5-14, 5-15
Normally Closed (NC) contact .............................. 4-2
Page 84

Index iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor
Normally Open (NO) contact ................................ 4-2
NRTL laboratory ................................................... 1-3
O
O2 ................................................................ ......... A-2
open loop condition ............................................... 5-2
operating range ...................................................... 1-2
ordering matrix ...................................................... B-1
output wiring, J1 .................................................... 4-3
outputs ................................................................... 1-2
over-range
alarm ................................................................... iii
condition ........................................................... 5-2
oxygen ....................................... iii, 1-2, 1-3, 2-2, 6-3,
7-1, A-2, B-2
P
parity bits ............................................................... 6-1
password ................................................................ 5-8
phosphine ....................................................... 1-3, B-2
PLC ........................................................................ 4-9
poured wire seal ..................................................... 4-2
power ......................... 1-1, 4-1, 4-2, 4-3, 4-4, 4-7, 4-9,
4-12, 5-1, 5-16, 6-4, 7-2
AC and DC in same conduit ............................. 4-1
supply ......................................................... 1-1, 4-4
wire recommendations ...................................... 4-1
wiring, J1 .......................................................... 4-3
pressure .................................................................. 7-1
range ................................................................. 1-2
program mode ........................................................ 5-2
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) ................ A-2
programming
access code ........................................................ 5-8
mode .........................................5-3, 5-4, 5-7, 5-10,
5-11, 5-12, 5-13, 5-15
protection class ...................................................... 2-2
protocol .................................................................. 6-6
public 485 GND .................................................... 4-3
pumps ............................................................. 1-1, 9-1
push button operation ............................................ 5-8
Q
qualified personnel .......................................... iv, 9-2
R
real time clock ............................. 5-16, 5-17, 6-5, A-2
reed switch ................................ 2-3, 2-4, 5-2, 5-4, 8-2
location ...................................................... 2-3, 2-4
register 40102 ........................................................ 6-1
register 40202 ........................................................ 6-2
relay board ...................................................... 1-1, 4-2
relays ................................................. iii, 1-1, 1-2, B-1
contact capacity................................................. 1-2
driving loads ..................................................... 4-2
non-latching ...................................................... 4-2
user-programmable ........................................... 1-2
remote sensor .................................................. 4-5, 4-6
Remote Terminal Unit (RTU) ....................... 6-1, A-2
remote unit ............................................................. 2-4
replacing sensors.................................................... 7-2
resistors .................................................................. 4-4
resolution ............................................................. 5-16
span gas concentration ...................................... 5-8
restart .................................................................... A-2
routine maintenance ............................................... 7-1
RS485 .................................................................... 1-2
S
safety ........................................................................iv
sealing device ........................................................ 1-5
secondary higher-power relay ................................ 4-2
self test ................................................................... 5-1
sensor(s) ............................ 1-4, 4-2, 4-4, 4-5, 4-7, 5-1,
5-17, 7-1, 7-2, 9-1
ATEX-certified ................................................. 1-4
board ................................................. 4-10, 6-1, 7-2
calibration service to ........................................... iii
catalytic ............................................................. 7-1
error .................................................................. 8-2
handling ............................................................ 7-1
head ................................................................... 4-4
maximum distance ................................... 4-4, 5-17
openings .............................................................. iii
ranges ................................................................ 1-3
remote ............................................... 4-2, 4-4, 5-17
replacement ....................................................... 7-2
span ............................................................ 5-2, 5-8
specifications .................................................... 2-2
storing ............................................................... 7-1
type ..................................................... 2-2, 5-4, 5-5
wiring, J3 .......................................................... 4-4
serial bus
abnormal behavior ............................................ 6-1
setpoint ................................................ 5-9, 5-10, 5-11
setting compound ................................................... 1-5
setup menu ............................................................. 5-5
shielded cable .................................4-1, 4-4, 4-7, 5-17
shielding .................................................. 4-2, 4-4, 4-7
screw ................................................................. 4-2
signal outputs ......................................................... 1-2
signal wire ............................................................. 4-3
recommendations .............................................. 4-1
silicone compound vapors ....................................... iii
silicone vapors ......................................................... iii
siren ....................................................................... 4-2
slave address .......................................................... 4-9
slave units .............................................................. 6-1
SMART sensor ...................................................... 8-2
error .................................................................. 5-2
SO2 ........................................................................ A-2
F-4 iTrans User Manual (P/N: 77023554-1)
Page 85

iTrans Fixed Point Single/Dual Gas Monitor Index
span gas .................................. 1-1, 5-2, 5-6, 5-15, 8-3
concentration ............. 1-1, 5-7, 5-8, 5-15, 5-16, 8-3
option ....................................................... 5-7, 5-15
value .................................................................. 5-4
span reserve .......................... 5-8, 5-16, 5-17, 7-3, 8-4
BBIR ............................................................... 5-17
span setting ................................................... 5-6, 5-15
span value ..................................................... 5-7, 5-15
aborting ........................................................... 5-16
changing ............................................................ 5-7
specifications .................................................. 1-1, 1-2
sensors............................................................... 2-2
splashguard ............................................................ 7-2
SPST relays ................................................... 1-2, A-2
stainless steel ......................................................... 1-2
standards
Canadian ........................................................... 1-3
US ..................................................................... 1-3
start bits ................................................................. 6-1
start-up ................................................................... 5-1
status bit .. 5-3, 5-4, 5-5, 5-6, 5-7, 5-8, 5-9, 5-10, 5-11,
5-12, 5-13, 5-14, 5-15, 5-16
flashing ...................................................... 5-6, 5-7
stop bits .................................................................. 6-1
strobe ..................................................................... 4-2
sulfur dioxide .......................................... 1-3, 6-4, A-2
switch bank
location ............................................................. 4-9
setting addresses ............................................. 4-10
T
technical support .................................................... 6-2
temperature ............................................................ 7-1
range ................................................................. 1-2
terminal blocks ............................................... 4-4, 4-5
terminating resistor ................................ ......... 4-6, 6-7
TIA/EIA-485 ......................................................... 6-1
time, setting ......................................................... 5-11
timers .................... 5-3, 5-5, 5-6, 5-7, 5-13, 5-14, 5-15
toxic ....................................................................... 1-2
transmission mode ................................................. 6-1
transmitter ............................................... 4-1, 5 -8, B -1
troubleshooting ...................................................... 8-1
U
U-bolts ............................................................ 3-1, 3-2
UL Std No. 1203 ................................ .................... 1-3
UL Std No. 1604 .................................................... 1-3
UL Std No. 916 ...................................................... 1-3
user-programmable relays ..................................... 1-2
V
vibrating sources .................................................... 3-1
W
wall mounting ................................................. 3-1, 3-2
warm-up period ..................................................... 5-1
warning lights ........................................................ 1-1
warranty ................................................................. 9-1
water ...................................................................... 7-2
windowed top ........................................ 4-1, 4-12, 5-8
wiring ...................................... 2-4, 4-1, 4-2, 4-5, 4-12
chassis ground ................................................... 4-1
colors ................................................................ 4-1
input sensors ..................................................... 4-1
supply power ..................................................... 4-1
terminals .................................................... 4-3, 4-4
wiring diagrams
dual on-board sensors ....................................... 4-7
dual remote sensors ........................................... 4-8
ModBus interface .............................................. 4-9
remote sensor .................................................... 4-6
remote sensors back to iTrans ........................... 4-8
single on-board sensor ...................................... 4-5
www.modbus.org............................................ 6-6, 6-7
Z
zero time ....................................................... 5-4, 5-17
BBIR ............................................................... 5-16
zero air ................................................................... 5-6
zeroing ............ 5-2, 5-3, 5-5, 5-6, 5-13, 5-14, 7-2, 8-3
error .................................................................. 8-2
two methods ...................................................... 5-3
Page 86

Page 87

Page 88

The Fixed Gas Detection Experts
EUROPEAN PLANT AND OFFICES
Z.I. Est – rue Orfila CS 20417 – 62027 Arras Cedex FRANCE
Tel: +33 (0)3 21 60 80 80 – Fax: +33 (0)3 21 60 80 00
Website: http://www.oldhamgas.com
AMERICAS
Tel: +1-713-559-9280
Fax: +1-281-292-2860
americas@oldhamgas.com
ASIA PACIFIC
Tel: +86-21-3127-6373
Fax: +86-21-3127-6365
sales@oldhamgas.com
EUROPE
Tel: +33-321-608-080
Fax: +33-321-608-000
info@oldhamgas.com
 Loading...
Loading...