Page 1

OKIPAGE20 / OKIPAGE20n
LED Page Printer
Maintenance Manual
ODA/ OEL/ INT
All specifications are subject to change without notice.
Page 2

PostScript, Adobe and the PostScript logo are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated, registered
in the U.S.A.
*Times, Helvetica and Palatino are trademarks of Linotype AG and/or its subsidiaries.
ITC Avant Garde Gothic, ITC Zapf Chancery, ITC Zapf Dingbats and ITC Bookman are registered
trademarks of International Typeface Corporation.
HP and LaserJet are registered trademarks of Hewlett-Packard Company.
Diablo 630 is a registered trademark of Xerox corporation.
AppleTalk is a registered trademark of Apple Computer, Inc.
LocalTalk is a trademark of Apple Computer, Inc.
Page 3

PREFACE
This maintenance manual describes the field maintenance methods for OKIPAGE20 / OKIPAGE20n.
This manual is written for use by maintenance personnel. Note, however, that the user should refer to
the USER’S MANUAL for methods of handling and operating the equipment.
Page 4

CONTENTS
1. CONFIGURATION....................................................................................... 1 - 1
1.1 System Configuration................................................................................................. 1 - 1
1.2 Printer Configuration .................................................................................................. 1 - 2
1.3 Optional Configuration ............................................................................................... 1 - 3
1.4 Specification............................................................................................................... 1 - 5
1.5 Safety Standards ....................................................................................................... 1 - 7
1.5.1 Certification label .......................................................................................... 1 - 7
1.5.2 Warning label................................................................................................ 1 - 7
2. OPERATION DESCRIPTION ...................................................................... 2 - 1
2.1 Main Control Board (BOARD-AAA) ........................................................................... 2 - 3
2.2 Power Supply Unit ..................................................................................................... 2 - 7
2.3 Electro-photographic Process.................................................................................... 2 - 9
2.3.1 Electro-photographic process mechanism ................................................... 2 - 9
2.3.2 Electro-photographic process ....................................................................... 2 - 11
2.3.3 Process operation descriptions .................................................................... 2 - 15
2.3.4 Revision of LED Head Illumination ............................................................... 2 - 25
2.4 Paper Jam Detection ................................................................................................. 2 - 33
2.5 Cover Open................................................................................................................ 2 - 34
2.6 Toner Low Detection.................................................................................................. 2 - 35
2.7 Stacker-full Detection................................................................................................. 2 - 37
2.8 Page Size Detection .................................................................................................. 2 - 37
2.9 PostScript ROM module (BOARD-MSM or BOARD-FSL)......................................... 2 - 37
3. PARTS REPLACEMENT............................................................................. 3 - 1
3.1 Precautions for Parts Replacement ........................................................................... 3 - 1
3.2 Parts Layout...............................................................................................................3 - 3
3.3 How to Change Parts................................................................................................. 3 - 6
3.3.1 Face -up Stacker Assy ................................................................................. 3 - 7
3.3.2 Contact Assy ................................................................................................ 3 - 8
3.3.3 DC Fan Motor ............................................................................................... 3 - 9
3.3.4 OP Panel Assy ............................................................................................. 3 - 10
3.3.5 Board-AAA....................................................................................................3 - 11
3.3.6 Stacker Assy, Damper Arm, Cover Rear..................................................... 3 - 12
3.3.7 Sensor Stacker Full ...................................................................................... 3 - 13
3.3.8 Cable cover (guide film)................................................................................ 3 - 14
3.3.9 Damper......................................................................................................... 3 - 15
3.3.10 Feeder Unit-Front ......................................................................................... 3 - 16
3.3.11 Roller Assy-Regist ........................................................................................ 3 - 17
3.3.12 Motor -Main .................................................................................................. 3 - 18
3.3.13 Guide Assy-Eject .......................................................................................... 3 - 20
3.3.14 Heat Assy ..................................................................................................... 3 - 21
3.3.15 Roller feed (C) .............................................................................................. 3 - 22
3.3.16 Roller Assy-BK ............................................................................................. 3 - 23
3.3.17 Roller Assy-Feed .......................................................................................... 3 - 24
3.3.18 LED Head ..................................................................................................... 3 - 25
3.3.19 Paper cassette, ROLLER Ass-Feed, ROLLER-Assy-Hoppibg..................... 3 - 26
3.3.20 Frame Assy-Separation................................................................................ 3 - 27
3.3.21 Transfer Roller/TR Gear/TR Bearing............................................................ 3 - 28
3.3.22 EP lock shaft................................................................................................. 3 - 29
Page 5

3.3.23 LEVER Assy- Out Sensor............................................................................. 3 - 30
3.3.24 Toner sensor lever........................................................................................ 3 - 31
3.3.25 Paper sensor lever ....................................................................................... 3 - 32
3.3.26 Inlet sensor lever ..........................................................................................3 - 33
3.3.27 Power supply unit ......................................................................................... 3 - 34
3.3.28 Lever-Paper end & Lever-Paper near end ................................................... 3 - 35
3.3.29 Guide Assy-Cassette (L) .............................................................................. 3 - 37
3.3.30 Guide Assy-Cassette (R)..............................................................................3 - 38
4. ADJUSTMENT............................................................................................. 4 - 1
4.1 Maintenance Modes And Functions........................................................................... 4 - 1
4.1.1 User maintenance mode .............................................................................. 4 - 3
4.1.2 System maintenance mode .......................................................................... 4 - 7
4.1.3 Engine maintenance mode...........................................................................4 - 10
4.1.4 EEPROM initialization .................................................................................. 4 - 14
4.2 Adjustment When Replacing A Part........................................................................... 4 - 15
4.2.1 Resetting the fuser counter .......................................................................... 4 - 16
4.2.2 Destination setting ........................................................................................ 4 - 17
4.2.3 Setting of LED head drive time.....................................................................4 - 18
5. PERIODIC MAINTENANCE ........................................................................ 5 - 1
5.1 Periodic Replacing Part ............................................................................................. 5 - 1
5.2 Cleaning..................................................................................................................... 5 - 1
5.2.1 Cleaning of LED lens array........................................................................... 5 - 1
5.2.2 Cleaning the Plastic Film .............................................................................. 5 - 2
6. TROUBLESHOOTING PROCEDURES ...................................................... 6 - 1
6.1 Troubleshooting Tips ................................................................................................. 6 - 1
6.2 Points to Check before Correcting Image Problems.................................................. 6 - 1
6.3 Tips for Correcting Image Problems .......................................................................... 6 1
6.4 Preparation for Troubleshooting ................................................................................ 6 - 2
6.5 Troubleshooting Flow................................................................................................. 6 - 2
6.5.1 LCD status message/trouble list...................................................................6 - 2
6.5.2 LCD message troubleshooting .....................................................................6 - 14
6.5.3 Image troubleshooting .................................................................................. 6 - 34
7. WIRING DIAGRAM...................................................................................... 7 - 1
7.1 Interconnect Signal Diagram...................................................................................... 7 - 1
7.2 PCB Layout................................................................................................................7 - 2
7.3 Resistance Check...................................................................................................... 7 - 5
7.4 Program/Font ROM Location ..................................................................................... 7 - 7
8. PARTS LIST ................................................................................................ 8 - 1
APPENDIX A CENTRONICS PARALLEL INTERFACE ................................ A - 1
APPENDIX B RS-232C SERIAL INTERFACE ............................................... B - 1
APPENDIX C DUPLEX UNIT.......................................................................... C - 1
APPENDIX D Second/ Third Paper Feeder.................................................. D - 1
APPENDIX E Multi Feeder ............................................................................ E - 1
Page 6

1. CONFIGURATION
Page 7
1. CONFIGURATION
1.1 System Configuration
OKIPAGE20 / OKIPAGE20n consists of control and engine blocks as the standard configura-
tion (See Figure 1-1.)
In addition, the following options are also available.
PC etc.
Centronics
Parallel interface
(Bidirection)
RS-232C
Serial I/F
Printer
Operator
panel
Main control
Power
supply
unit
DC Fan
Face down
stacker
Printer
Mechanism
I/D unit
LED head
Motor-Main
Hopping motor
AC IN
120V
230V
Face up
stacker
*
*
Toner Cartridge
Front Feeder
LAN etc.
OKI HSP
interface board
(Option)
Extension D-RAM
SIMM
(Option)
4MB/ 8MB
Flash ROM SIMM
(Option)
: Paper feeding
: Singal flow
or
PostScript
SIMM
(Option)
Figure 1-1
1 - 1
Paper tray
Paper size
detection switch
High Capacity
Second Paper
Feeder
(Option)
High Capacity
Third Paper
Feeder
(Option)
*: Consumables
: produced by third vender
Multi Feeder
(Option)
Duplex Unit
(Option)
Page 8
1.2 Printer Configuration
The printer unit consists of the following hardware components:
• Electro-photographic processor
• Paper feeder
• Controller
• Operator panel
• Power supply unit
Figure 1-2 shows the printer unit configuration.
Stacker Assy
Frame-OP panel Assy
Plate-Shield
Cover-Side(I/F)
Face-up stacker Assy
Cover-Rear
Cover-Side(L) Assy
Contact Assy
Cover-Frame
Heat Assy
Cover-Side(R)
Manual Feed Assy
Base Unit
Figure 1-2
I/D Unit
1 - 2
Page 9
1.3 Optional Configuration
The options below are available for use with OKIPAGE20 / OKIPAGE20n. They are sold
separately from the printer unit.
(1) Multi Feeder
(2) Second/ Third Paper Feeder
(3) DUPLEX Unit
1 - 3
Page 10

(3) D-RAM SIMM module (72 pin SIMM, 4 MB/8 MB/16 MB/32 MB)
(4) Flash ROM module (72 pin SIMM, 4MB/8MB)
See 7.2 (1) for where
to install.
See 7.2 (1) for where
to install.
(5) PostScript ROM module (72pin SIMM)
1 - 4
See 7.2 (1) for where
to install.
Page 11

1.4 Specification
(1) Type Desk top
(2) External dimensions Height 13.0” (331 mm)
(excludes protruding Width 14.4” (366 mm)
Portion) Depth 18.2” (462 mm)
(3) Weight 19.0 kg (42 lbs) If Installed Duplex 21.3 kg (47 lbs)
(4) Development method Dry electrophotography
Exposure method LED stationary head
(5) Paper used <Type>
• Standard paper
– Xerox 4200 (20 lbs)
• Application paper (manual face-up feed)
– Label
– Envelope
– OHP paper (Transparency)
<Size>
• Standard sizes
– Letter
– Legal
– Executive
– Envelope (without Duplex printing)
–A4
– A5 (without Duplex printing)
– B5 (without Duplex printing)
– A6 (without Duplex printing)
• Applicable sizes
– Width: 3.4” to 8.5” (86 to 216 mm)
– Length: 5.5” to 14” (140 to 355.6 mm)
<Thickness>
– Automatic feed: 16 to 28 lbs (60 to 105 g/m2)
– Manual feed: Label, OHP paper (transparency)
Envelope, 16~36 lb
(6) Printing speed First print: 8 sec.
Continuous print: 20 sheets/min.
[at duplex print :10 sheets/min]
Warm-up time: 90 sec. [at room temperature 77˚F
(25˚C) and rated voltage (120 VAC)]
(7) Paper feed method Automatic feed or manual feed
(8) Paper delivery method Face down/face up
(9) Resolution 600 x 600 dots/inch (default)
600 x 1200 dots/inch
(10)Power input 120 VAC + 5.5%, –15% (ODA)
230 VAC + 10%
1 - 5
Page 12
(11) Power consumption Peak: Approx. 820W
Typical Operation: Approx. 350W
Idle: Approx. 95W
Power save mode: Approx. 25W
(12) Temperature and humidity
In operation Power off mode During Storage Unit
Temperature 50 - 90 32 - 110 14 - 110 °F
(10 - 32) (0 - 43) (–10 - 43) (°C)
Humidity
Maximum wet
bulb temperature
Minimum difference
of wet and dry
bulb temperatures
20 - 80 10 - 90 10 - 90 %RH
77 80.4 °F
(25) (26.8) (°C)
35.6 35.6 °F
(2) (2) (°C)
Notes:
1. Storage conditions specified above apply to printers in packed condition.
2. Temperature and humidity must be in the range where no condensation
occurs.
Temperature
(°C)
32
28
Operation range
10
20 80
Humidity (%)
(13) Noise During operation: 50 dBA or less (without second tray)
55 dBA or less (with second tray)
At standby: 45 dBA or less
Power save mode: 43 dBA or less
(14) Consumables Toner cartridge kit 5,000 pages(5% duty)*
Image drum cartridge 30,000 pages(at continuous Simplex printing)*
19,000 pages(3 page/job)(Simplex printing)*
* Simplex printing without Power Save.
1 - 6
Page 13
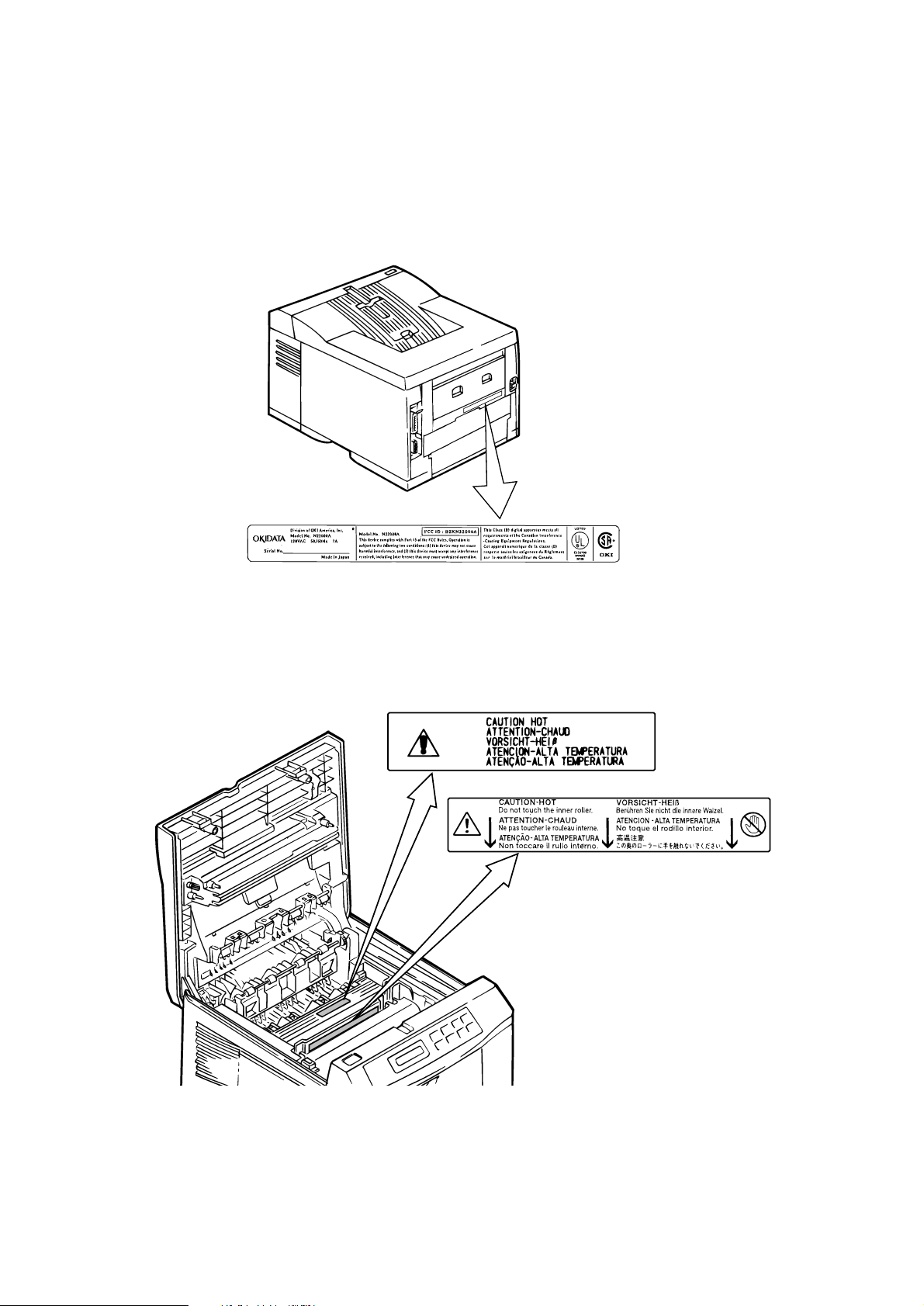
1.5 Safety Standards
1.5.1 Certification label
The safety certification label is affixed to the printer in the position below.
ex. ODA 120V
1.5.2 Warning label
The warning label is affixed to the portion which may cause an injury to human body.
Follow the instructions on warning labels during maintenance.
1 - 7
Page 14

2. OPERATION DESCRIPTION
Page 15

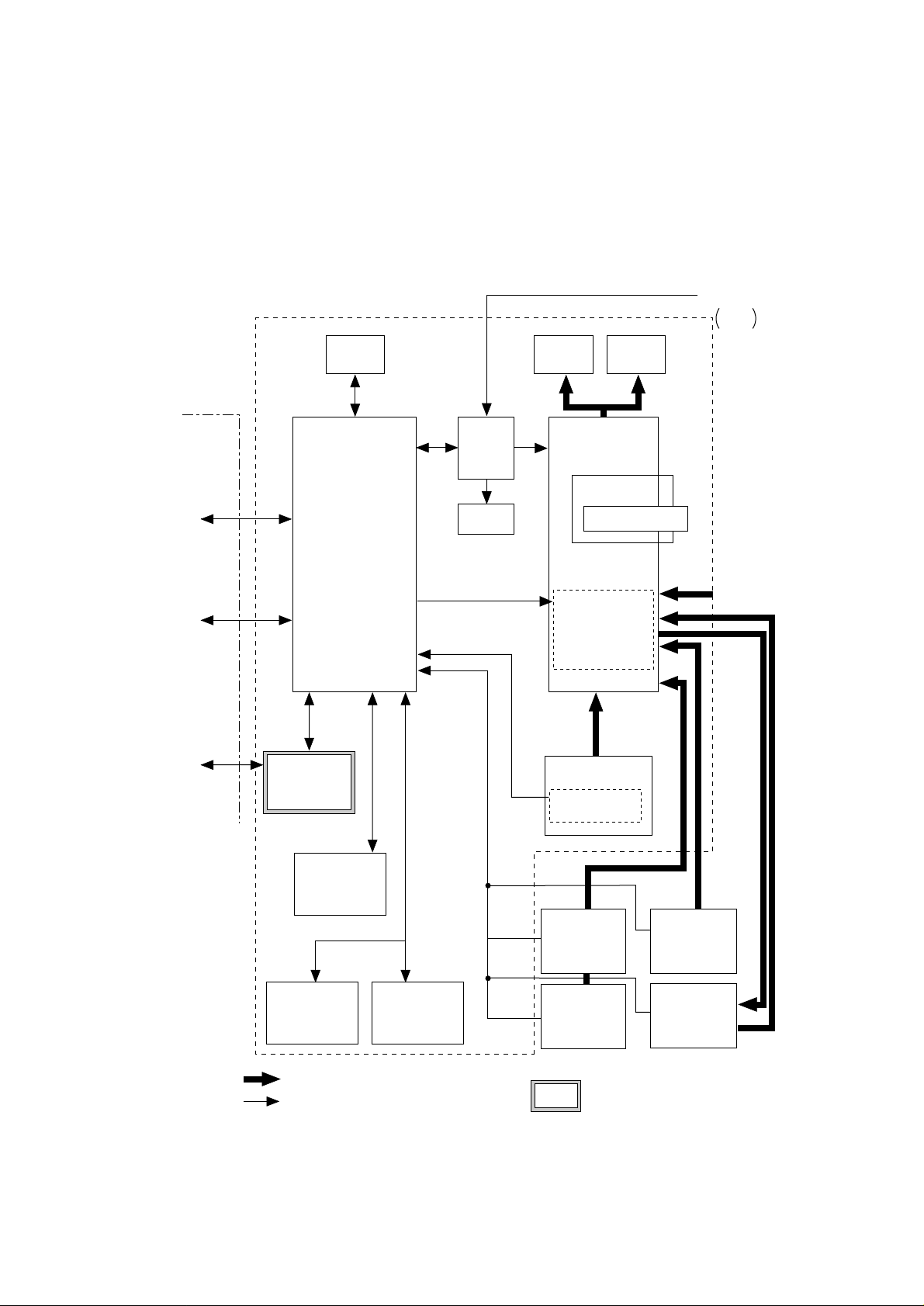
2. OPERATION DESCRIPTION
OKIPAGE20 / OKIPAGE20n consists of a main control board, a power supply unit (120V/230V),
a power supply unit (high voltage), an operator panel and an electro-photographic process
mechanism.
The control board receives data through a host I/F, decodes and edits the data, and stores the
edited data in a memory. After completing edition of one page of data, it references the font
memory and generates bit data on the same memory. At the same time, it transfers the bit image
data to an LED head in units of one dot line.
The electro-photographic process mechanism prints data on paper.
The operator panel is used for operations and status display.
Fig. 2-1 shows an OKIPAGE20 / OKIPAGE20n block diagram.
2 - 1
Page 16
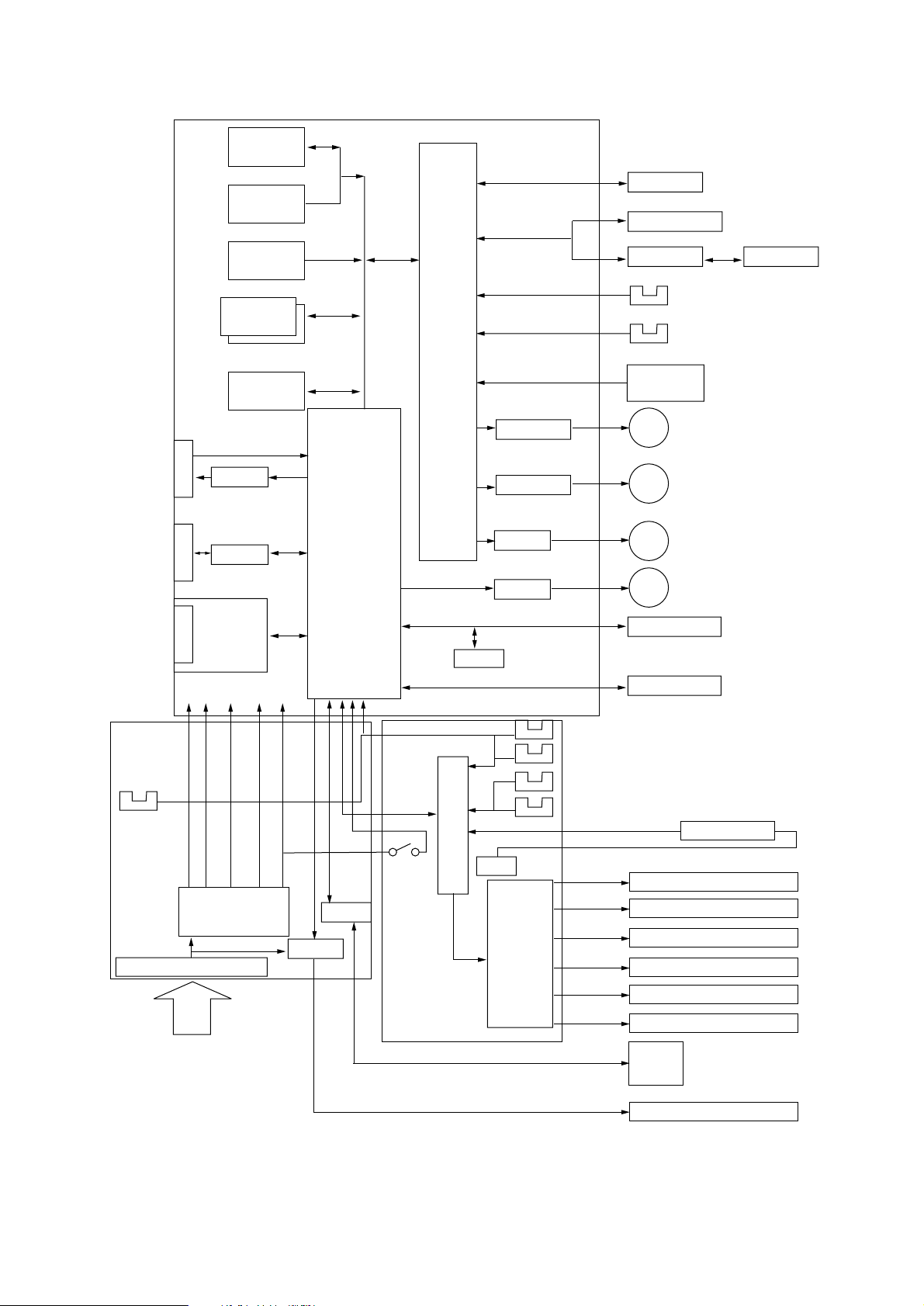
FLASH ROM
Module
or
PS ROM
Module
MAIN BOARD (BOARD-AAA)
DUPLEX unit
MULTI feeder
Centronics
I/F
RS232C
I/F
LAN etc.
(Option)
ROM
Extension
DRAM
Module
DRAM
7407
75188
OKI
HSP I/F
Board
(Option)
3V 5V +8V -8V 38V
CPU
LSI
EEPROM
TRANSISTOR
TRANSISTOR
DRIVER
DRIVER
2nd tray
Paper end sensor
Paper near end sensor
BOARD PXC
Clutch for
CL
Regist Roller
Clutch for
CL
Hopping Roller
Hopping Motor
M
Main Motor
M
Operator panel
LED HEAD
3rd tray
Tray size
sensor board
POWER
SUPPLY
UNIT
(AC120V/230V)
Outlet sensor
FILTER CIRCUIT
AC120V/230V
LOW VOLTAGE
GENERATION
CIRCUIT
Inlet sensor1
paper sensor
Inlet sensor2
Toner sensor
LSI
COVER
OPEN
SW
DRIVER
DRIVER
POWER
SUPPLY
UNIT
(high voltage)
0V
HIGH
VOLTAGE
CIRCUIT
Sub-CH
CH
TR
DB
SB
CB
Figure 2-1 OKIPAGE20 / OKIPAGE20n block diagram
THERMISTOR
SUB CHARGE ROLLER
CHARGE ROLLER
TRANFER ROLLER
DEVELOPPING ROLLER
TONER SUPPLY ROLLER
CLEANING ROLLER
FAN
HEATOR
2 - 2
Page 17

2.1 Main Control Board (BOARD-AAA)
The control board consists of an one chip CPU,a LSI, program/font ROM's, DRAM's, an
EEPROM, a host interface circuit, and a mechanism driving circuit.
(1) One-chip CPU
The one-chip CPU is a custom CPU (32-bit internal bus, 32-bit external bus, 40-MHz clock)
that incorporates an RISC CPU and its peripheral devices, and has the following functions.
Built-in device Function
Chip select controller Control of peripheral LSI, ROM, DRAM and I/O device
Bus controller
DRAM controller
DMA controller Transfer of data from Host I/F to RAM
Serial interface controller Control of RS232C serial interface
Parallel interface controller Control of Centronics parallel interface
Timer Generation of various control timing
Monitoring of paper running and paper size
Serial I/O port Control of serial interface between controller and operator panel, EEPROM
Control of a serial interface between controller and power supply board
I/O port Inputting of various sensor signals
Outputting of various control signals
Motor driver controller Control of Main Motor
Image processing circuit Executes the image data process for printing.
(2) Program/font ROM's
The program/font ROM's store the HP LJ5 emulation program and various types of font.
MASK ROM is used as the program/font ROM's.
2 - 3
Page 18
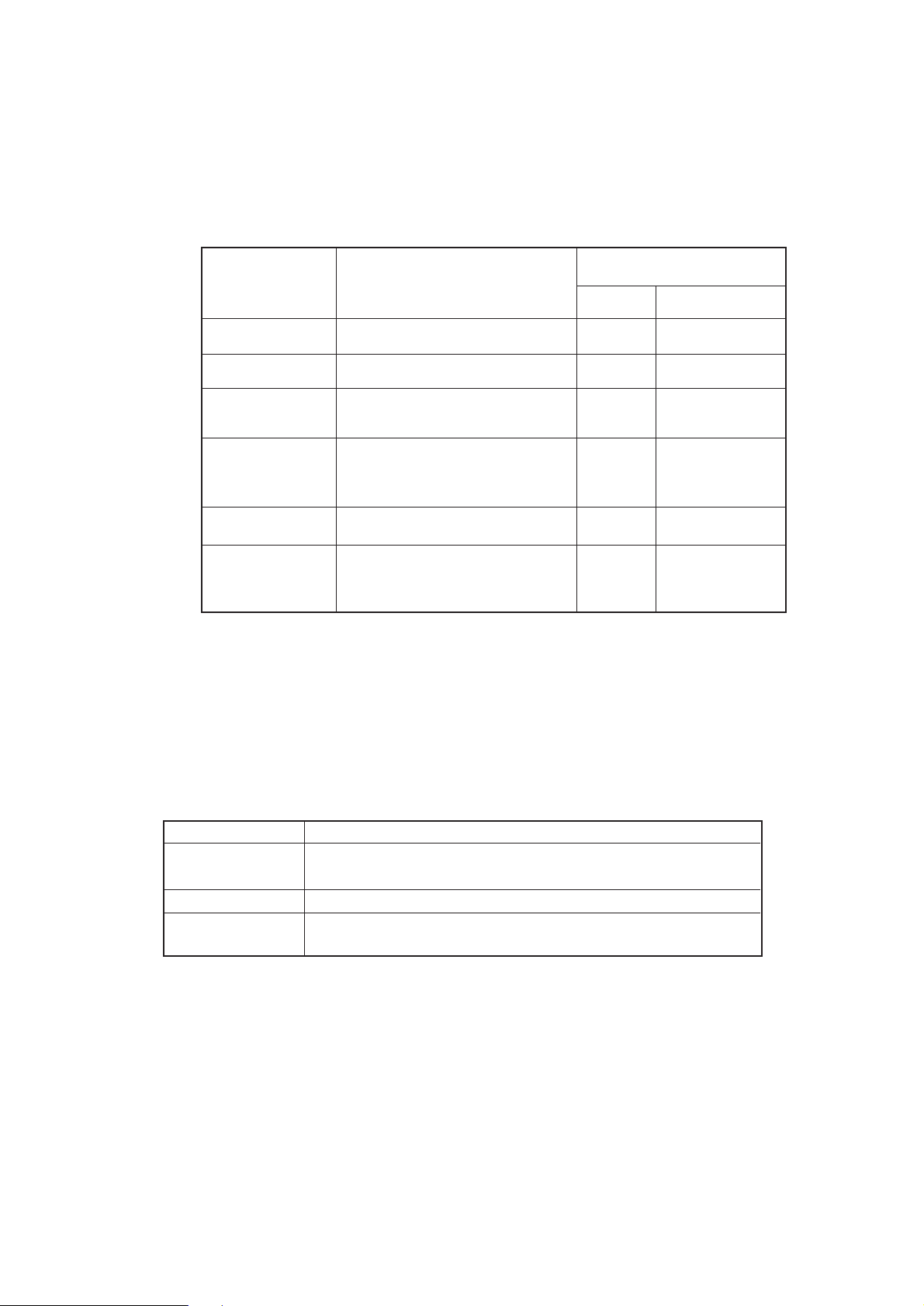
(3) DRAM's
4-Megabyte DRAM (16 Mbit DRAM x 2) is mounted as resident memory to be used for storing
the program and providing various buffers. This DRAM is expandable up to 68 Mbytes by
adding expansion memory (SIMMs). This DRAM provides the areas shown in the following
table.
Memory area Use Memory capacity setting
MENU Expansion RAM
System area Fixed Fixed
Raster buffer Enable Expandable
Receive buffer Enable Expandable
Page buffer – Expandable
DLL/macro buffer – Expandable
Font cache buffer Enable Expandable
Working area used for the program
Stores converted bit image data
Stores temporarily the data received
from the host interface
Adds print information to the analyzed
receive data and stores the resulted
data.
Stores soft fonts and macro data.
Stores bit map fonts generated by the
font rasterizer based on scalable font
information
(4) EEPROM
The EEPROM has a 1-kbit capacity and stores the following data.
• Menu data
• Various counter data (page counter, drum counter, fuser counter, etc.)
• Adjustment parameters (LED head drive time, print start position, etc.)
(5) LSI (LZ9FF22)
Built in device Function
Serial I/O port Control of serial interface between controller and 2nd tray, 3rd tray, Multi purpose feeder
Control of serial interface between controller and Duplex unit
Motor driver controller Control of Hopping motor
I/O port Inputting of various sensor signals
Outputting of various control signals
(6) Host interface
This printer has the following interfaces to the host.
• Centronics bidirectional parallel interface
• RS232C interface
• OKI HSP interface (Option)
The single effective interface or the automatic interface select mode can be selected using
the menu. If the busy state of the printer continues for a long time period, the buffer nearfull control releases the busy status at constant intervals even if the host side is busy so not
to cause the interface time-out at the host side.
2 - 4
Page 19
(a) Centronics bidirectional parallel interface
This is an interface conforming to IEEE-1284 and provides either of unidirectional and
bidirectional communications according to each of the following communication modes.
• Compatibility mode
Unidirectional communications from the host to the printer.
• Nibble mode
This mode transmits 4-bit wide data from the printer to the host. In this mode, each
1-byte data is transferred in the form of two nibbles using ERROR, BUSY, FAULT,
and SELECT signal leads. This mode can provide the bidirectional operation in
combination with the compatibility mode.
• ECP mode
This mode provides the asynchronous bidirectional interface and transmits and
receives 1-byte data using eight data signal leads under the semi-duplex control by
the host.
When the power is turned on, the compatibility mode is automatically selected. The
change to another mode from the compatibility mode is made through negotiation.
(When the BI DIRECTION is set to ENABLE in the menu, this change can be performed.)
(For the electrical/physical characteristics of this interface, see APPENDIX B)
(b) RS232C serial interface
The following protocol is supported for the serial interface conforming to EIA RS232C.
• READY/BUSY (DTR HI or DTR LO)
• X-ON/X-OFF
• RBST X-ON
(For the electrical/ physical characteristics of the interface, see APPENDIX B)
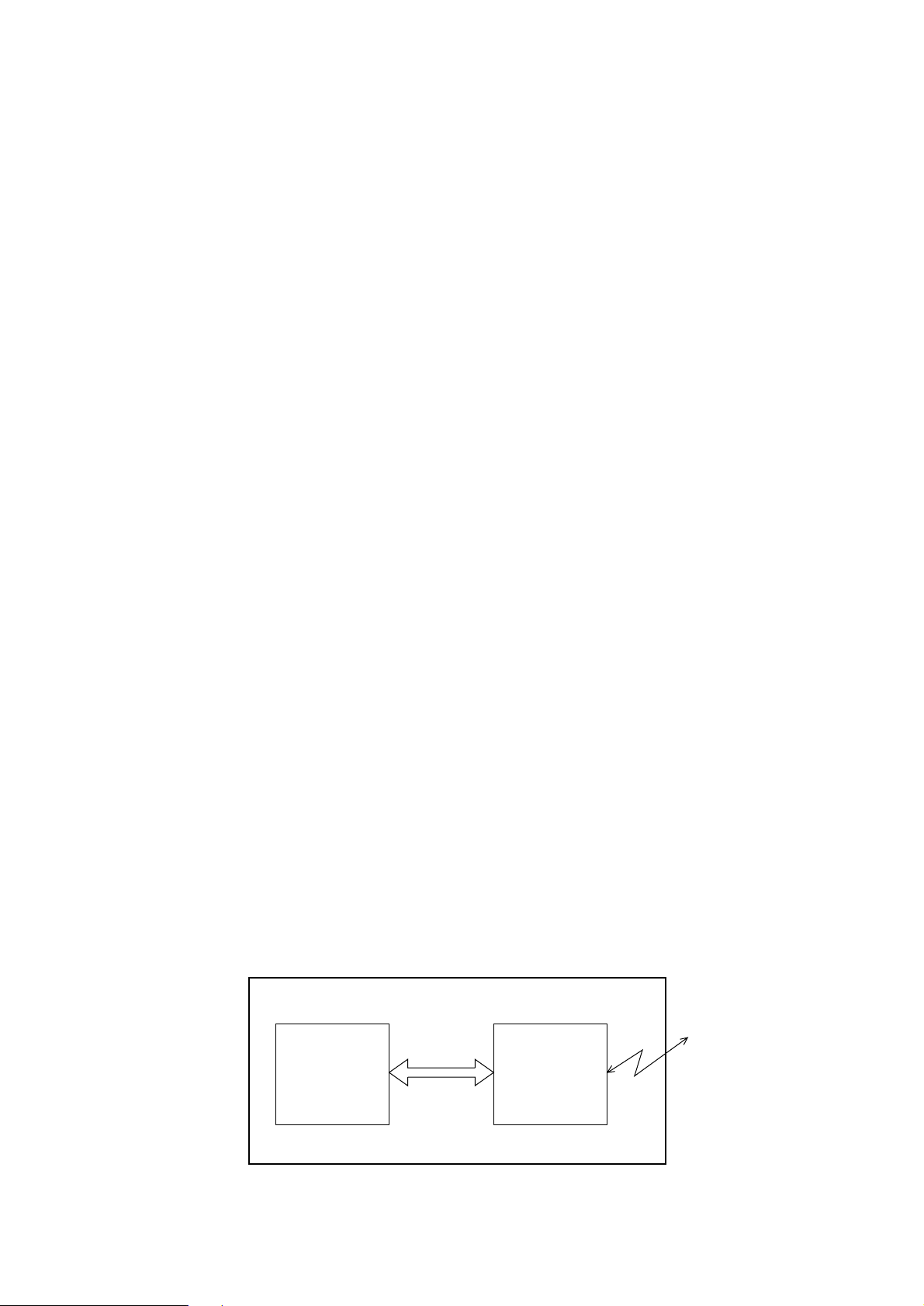
(c) OKI HSP interface (Option)
This interface (slot) is an OKI unique universal interface that provides the platform to
connect various of boards (including those supplied by third venders) such as the LAN
connection expansion board and SCSI expansion board.
Any expansion boards compatible with this interface can be mounted on the Control
board in the piggyback board from without modifying the program at the printer side. The
conceptual diagram of the OKI HSP interface is shown in Fig. 2-2.
(For the electrical/physical characteristics of the OKI HSP interface, see the OKI HSP
interface technical manual.)
Printer
Network, etc.
Control board
LAN
expansion board
OKI HSP
interface
Fig. 2-2
2 - 5
Page 20
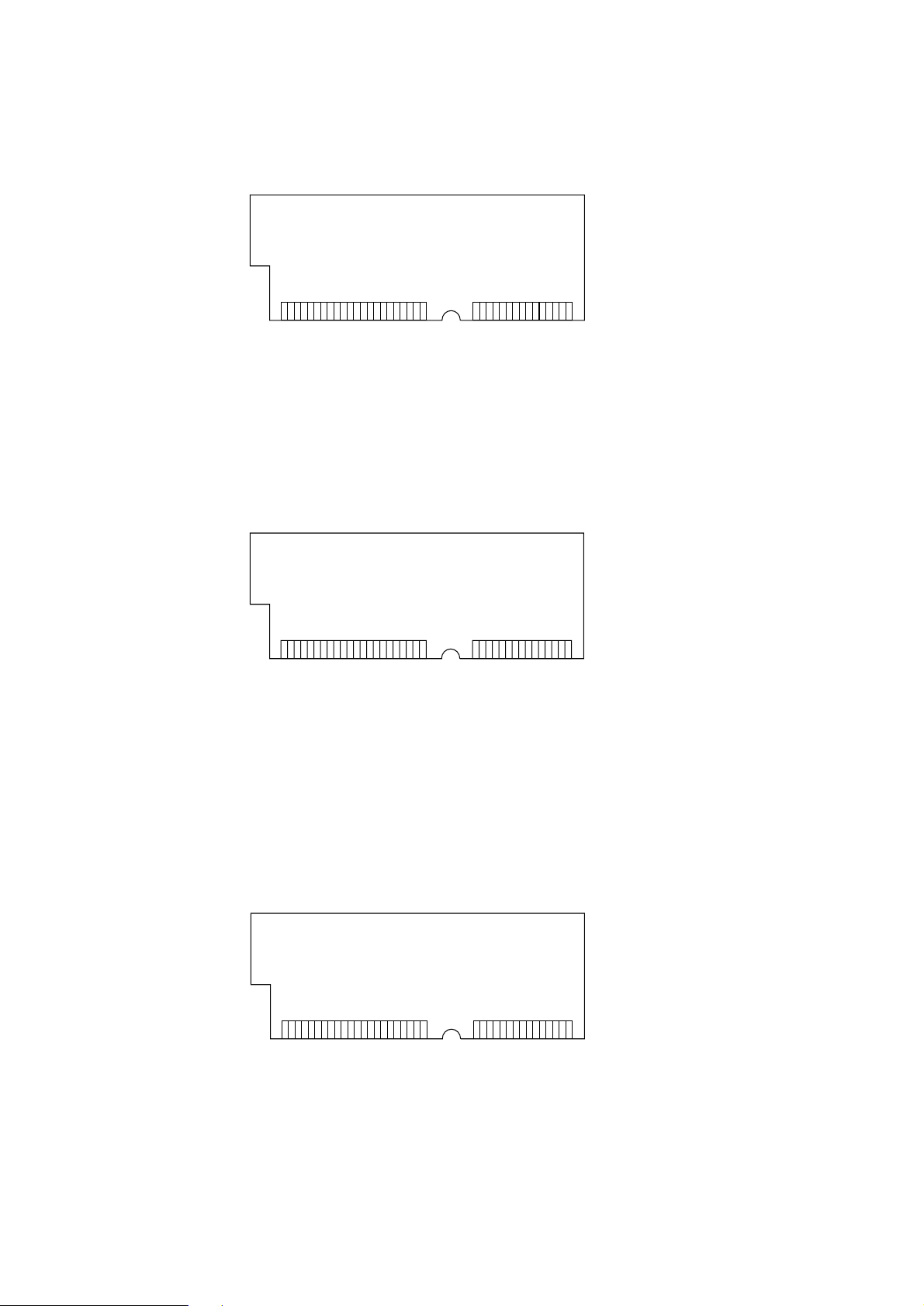
(7) RAM module
• Pin layout
1363772
• Basic specificaton
- Type: 72 pins Standerd SIMM (32 bits buss width)
- Access time: 60ns, 70ns, 80ns, 100ns
- Capacity: 4, 8, 16 or 32MB
- Parity: None
(8) Flash ROM module
• Pin layout
Board-FSL or Board-FSL-2
(4MB)
[Note : EDO SIMMtype cannot be used.]
(8MB)
1363772
• Basic specificaton
- Type: 72 pins SIIM (32 bits buss width)
- Access time: 90ns
- Capacity: 4 or 8MB
(9) PS ROM module
PS ROM module is BOARD-MSM-2 or BOARD-FSL-2
BOARD MSM-2 consists of MASK ROM
BOARD FSL-2 consists of Flash ROM (8MB).
• Pin layout
BOARD-MSM-2
or
BOARD-FSL-2
1363772
• Basic specificaton
- Type:72 pins SIIM (32 bits buss width)
- Access time: 100ns (Board-MSM-2), 90n (Board-FSL-2)
- Capacity: 4MB (Board-MSM-2), 8MB (Board-FSL-2)
• Emulation : Pstscript Level 2
2 - 6
Page 21
2.2 Power Supply Unit
The power supply unit consists of an AC filter circuit, a low voltage power supply circuit, a high
voltage power supply circuit, heater drive circuit, and photosensors.
(1) Low voltage power supply circuit
This circuit generates the following voltages.
Output voltage Use
+5 V Logic circuit supply voltage
+30 V Motor and fan drive voltage and source voltage for high-voltage supply
+8 V Reset circuit, RS232C Line voltage
–8 V RS232C Line voltage
+3.8V LED HEAD supply voltage
(2) High voltage power supply circuit
This circuit generates the following voltages necessary for electro-photographic processing
from +30 V according to the control sequence from the control board. When cover open state
is detected, +30 V supply is automatically interrupted to stop the supply of all the high-voltage
outputs.
Output Voltage Use Remarks
Sub-CH -15 µA Voltage applied to Sub charging roller
CH -1.30 KV Voltage applied to charging roller
DB -220 V/+300 V Voltage applied to developing roller
SB -450 V Voltage applied to toner supply roller
TR +4 KV/-1.3 kV Voltage applied to transfer roller Variable + Only
CB +450 V/-1350V Voltage applied to clearimng roller
(3) Photosensor
The photosensor mounted on this power supply unit supervises the paper running state
during printing.
2 - 7
Page 22
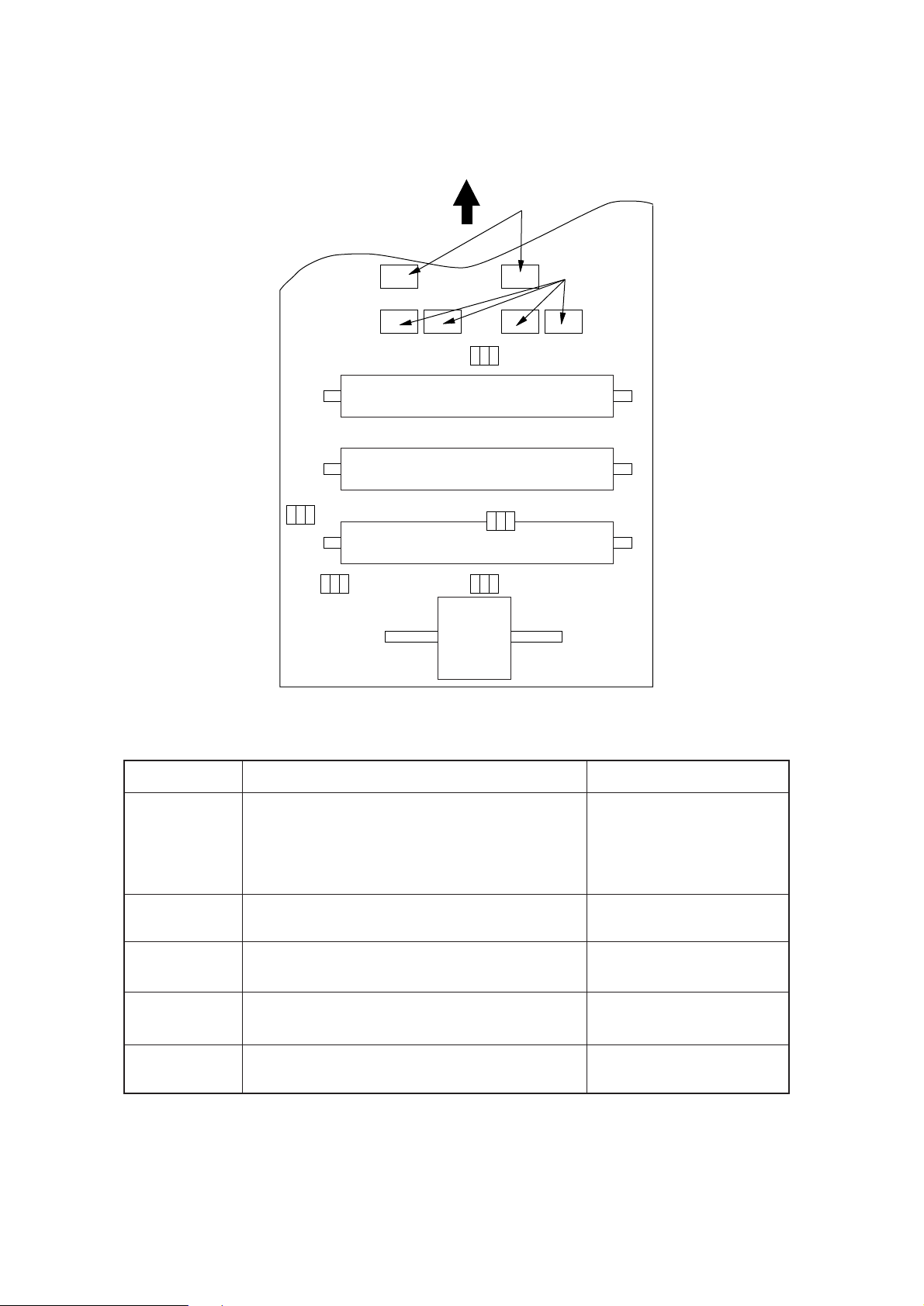
Figure 2-3 shows the sensor layout diagram.
Paper running direction
Roller-exit
Roller-feeder (c)
Outlet sensor
Roller-Heat
Roller-transfer
Sensor
Inlet sensor 1
Inlet sensor 2
Toner sensor
Inlet sensor 1
Inlet
sensor 2
Paper sensor
Roller-regist
Feed roller
Figure 2-3
Function
Detects the leading part of the paper and gives the supervision
timing for switching from hopping operation to feeding operation.
Supervises the paper running state and the paper size according to the paper reach time and running time.
Detects the form width.
ON: Paper exists.
OFF: No paper exists.
ON: A4 or larger
OFF: Smaller than A4
Sensing state
Paper sensor
Outlet sensor
Toner low sensor
Detects the leading part of the paper.
Supervises the paper running state.
Supervises the paper feed and size according to the time of
arrival to the sensor and the time of passage of paper.
Detects the lack of toner.
ON: Paper exists.
OFF: No paper exists.
ON: Paper exists.
OFF: No paper exists.
ON long: Toner low exists
OFF short: No Toner low exists
2 - 8
Page 23
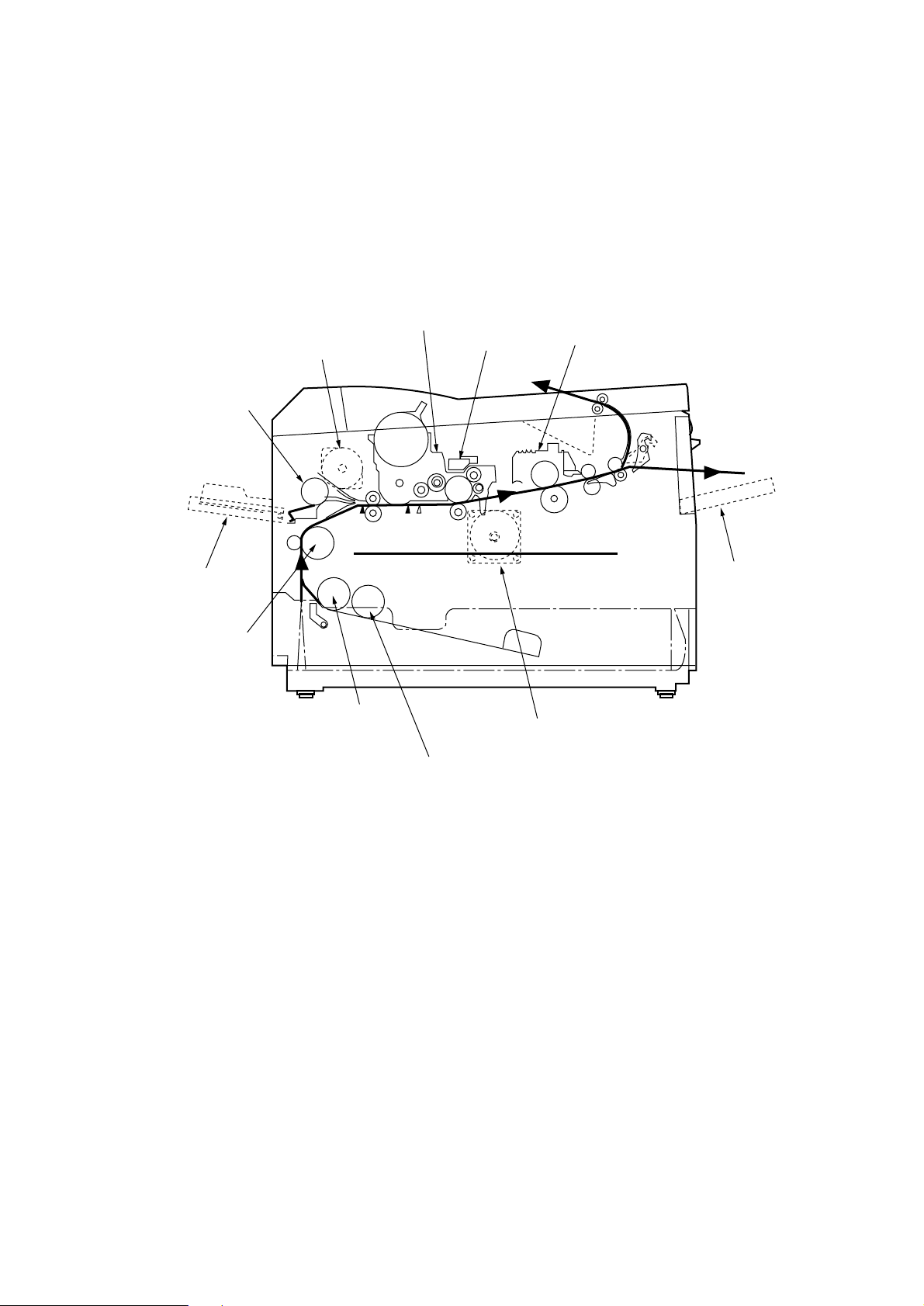
2.3 Electro-photographic Process
2.3.1 Electro-photographic process mechanism
This mechanism prints image data from the control board on the paper by electro-photographic
process.
The Figure 2-4 shows the layout of the electro-photographic process mechanism.
Front Hopping Roller
Front Feeder
Roller Assy-Feed
Image Drum Unit
Hopping Motor
1st Hopping Roller
Sub Roller
LED HEAD
Motor-Main
Heat Assy
Face Up stacker
Figure 2-4
2 - 9
Page 24

(1) Image drum unit
The image drum unit consists of a sensitive drum, a charger, and a developer. The unit forms
a toner image on the sensitive drum, using a electrostatic latent image formed by the LED
head.
(2) Hopping motor
This motor is a pulse motor of 48 steps/rotation that is two-phase excited by the signal from
the control board. It drives the hopping roller of the first tray and the front feed roller via two
one-way clutches according to the direction of rotation.
(3) Motor-Main
This motor is a pulse motor of 72 steps/rotation that is two-phase excited by the signal from
the control board and is the main motor of this mechanism.
(4) Clutch (for Regist)
Swithes the transfer of power to Roller Regist if necessary depending on the power from
Motor-Main and instructions from the control PCB.
(5) Clutch (for Feed Roller)
Swithes the transfer of power to Feed Roller if necessary depending on the power from
Motor-Main and instructions from the control PCB.
(6) LED head
Image data for each dot line from the control board is received by the shift register and latch
register. The 4992 LEDs are driven to radiate the image data to the image drum.
(7) Fuser
The fuser consists of a heater, a heat roller, a thermistor and a thermostat.
An AC voltage from the power supply board is applied to the heater under the control of the
HEATON signal from the control board. This AC voltage heats the heater. The control board
supervises the heat roller temperature via the thermistor, and regulates the heater roller at
a predetermined temperature (185 °C : Normal paper, MEDIA TYPE = MEDIUM) by
connecting or disconnecting the AC voltage supply to the heater.
If the heater roller temperature rises abnormally, the thermostat of the heater voltage supply
circuit is activated to cut the AC voltage supply forcibly.
2 - 10
Page 25

2.3.2 Electro-photographic process
The electro-photographic processing is outlined below. Figure 2-5 shows the electro-photo-
graphic printing process.
1 Charging
The surface of the image drum is uniformly charged with negative charges by applying a
negative voltage to the charge roller.
2 Exposure
Light emitted from the LED head irradiates the negatively charged surface of the image drum.
The surface potential of the irradiated part of the image drum surface is lowered, so that an
electrostatic latent image associated with the print image is formed.
3 Developing and toner recovery
When the negatively charged toner is brought into contact with the image drum, it is attracted
to the electrostatic latent image by static electricity, making the image visible.
At the same time, the residual toner on the image drum is attracted to the developing roller
by static electricity.
4 Transfer
When paper is placed over the image drum surface and a positive charge, opposite in polarity
to the toner, is applied to the reverse side of the paper from the transfer roller, the toner is
attracted by the positive charge and is transferred to the paper. As a result, the toner image
formed on the image drum is transferred to the paper.
5 Temporary cleaning
Residual toner that remains on the image drum without being transferred is made uniform
by the cleaning roller and is temporarily attracted to the cleaning roller by static electricity.
6 Fusing
The toner image transferred to the paper is fused under heat and pressure.
Figure 2-6 shows an electro-photographc process timing chart.
2 - 11
Page 26
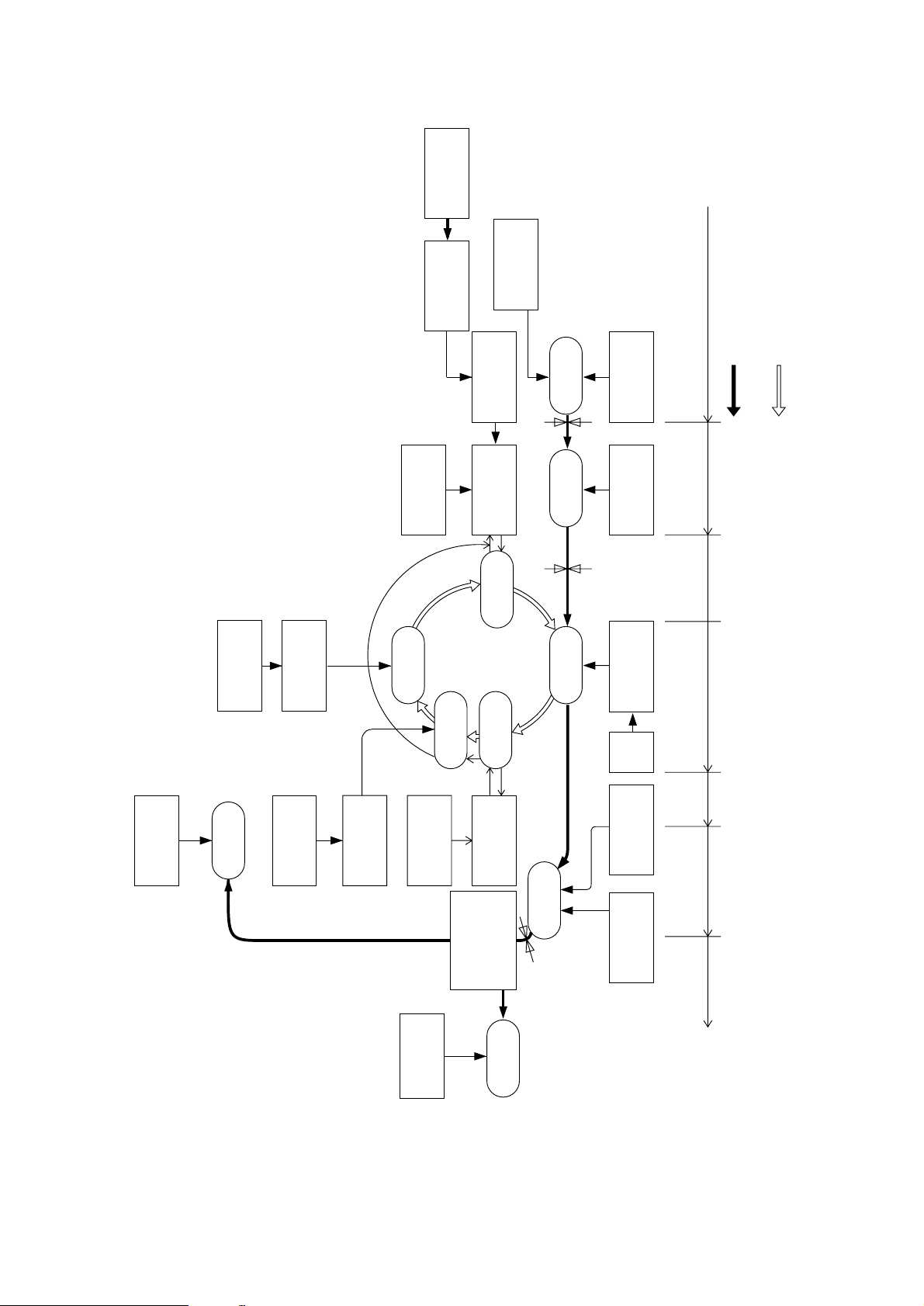
Toner
cartridge
Toner
supply roller
Front
feeder
Path of paper
feeding
Direction of
rotation of the
image drum
Image data
LED head
Power
supply
(Bias voltage)
Exposure
Doctor
Developing
Charging
blade
Inlet sensor
roller
Paper sensor
Developing
Cleaning
Paper
supply
Paper
registration
Transfer
roller
Hopping
roller
Registration
Image
production
roller
Transfer
Power
supply
developing Paper feed Paper hopping
eject
Paper
roller
eject
Paper
Power
supply
(Face down)
roller
Charger
Power
supply
eject
roller
Paper
Figure 2-5
2 - 12
Cleaning
path
Paper
roller
selector
eject
Paper
Fusing
Outlet sensor
(Face up)
Fusing pressure
Heater roller
Paper eject Fusing Cleaning Transfer
Page 27

DMON-N (DRUM MOTOR)
OFF
ON
2 - 13
Figure 2-6
HMON-N (HOPPING MOTOR)
PWM1-P (CLUCH for hopping)
PWM2-P (CLUCH for REGISTRATION)
PSIN1-N (INLETSENSOR1)
WRSENSE-N (PAPER SENSOR)
PSOUT-N (OUTLET SENSOR)
STB-N (LED HEAD)
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
PAPER TRAYPAPER PRINTER
SIMPLEX PRINTING TIMING CHART
STACKER
Page 28
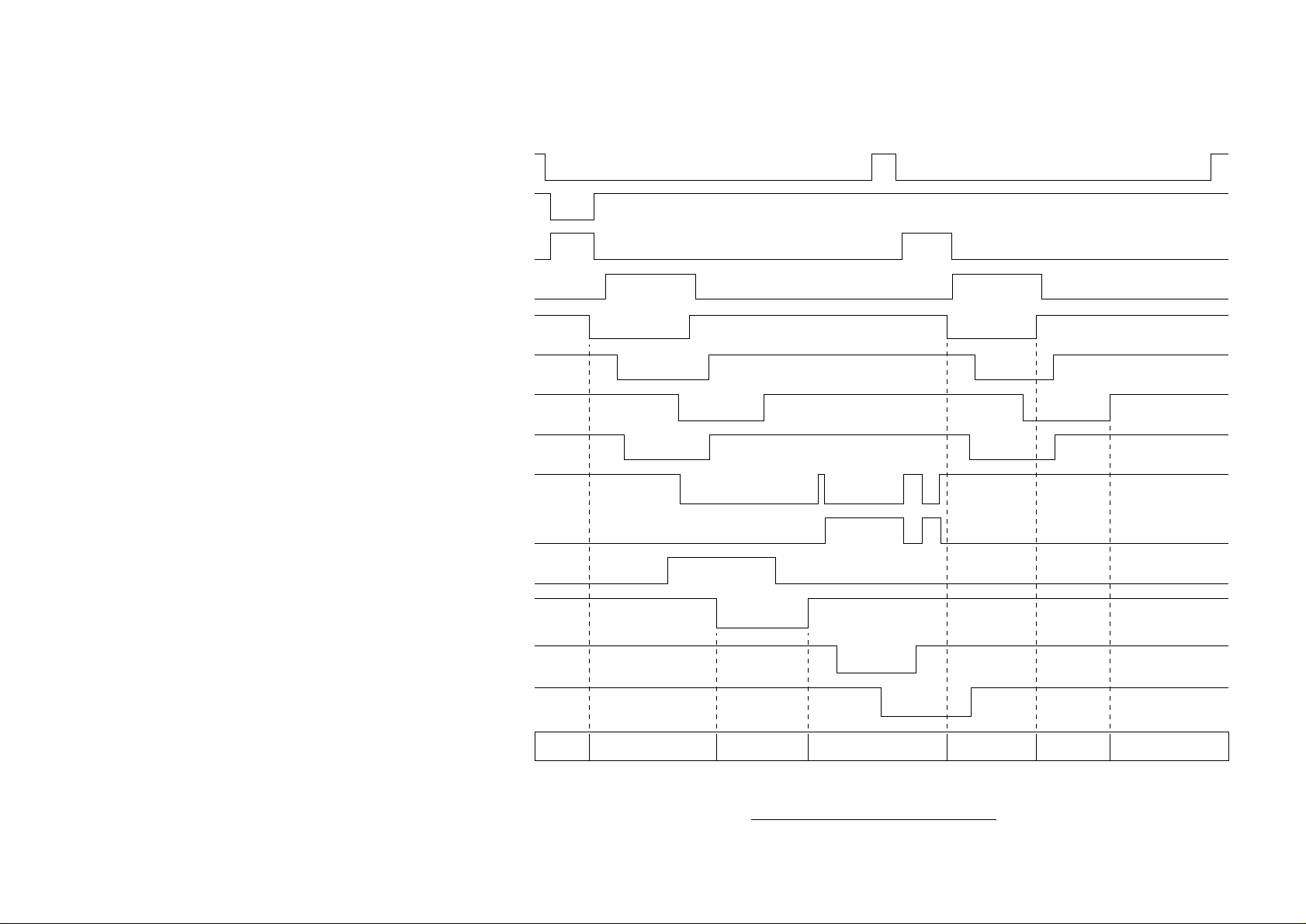
DMON-N (DRUM MOTOR)
OFF
ON
2 - 14
HMON-N (HOPPING MOTOR)
PWM1-P CLUCH for hopping)
PWM2-P (CLUCH for REGISTRATION)
PSIN1-N (INLETSENSOR1)
WRSENSE-N (PAPER SENSOR)
PSOUT-N (OUTLET SENSOR)
Figure 2-7
STB-N (LED HEAD)
DUPMON-N (MAIN MOTOR in DUPLEX
UNIT)
CLON-P (CLUCH in DUPLEX UNIT)
SLON-P (SOLENOID in DUPLEX UNIT)
DUPINSNS-N (INLET SENSOR in
DUPLEX UNIT)
DUPRSNS-N (REAR SENSOR inDUPLEX
UNIT)
DUPFSNS-N (FRONT SENSOR in
DUPLEX UNIT)
PAPER PRINTER PRINTER STACKERDUPLEX UNIT
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
PAPER
TRAY
PRINTER/
DUPLEX UNIT
DUPLEX UNIT/
PRINTER
DUPLEX PRINTING TIMING CHART
Page 29
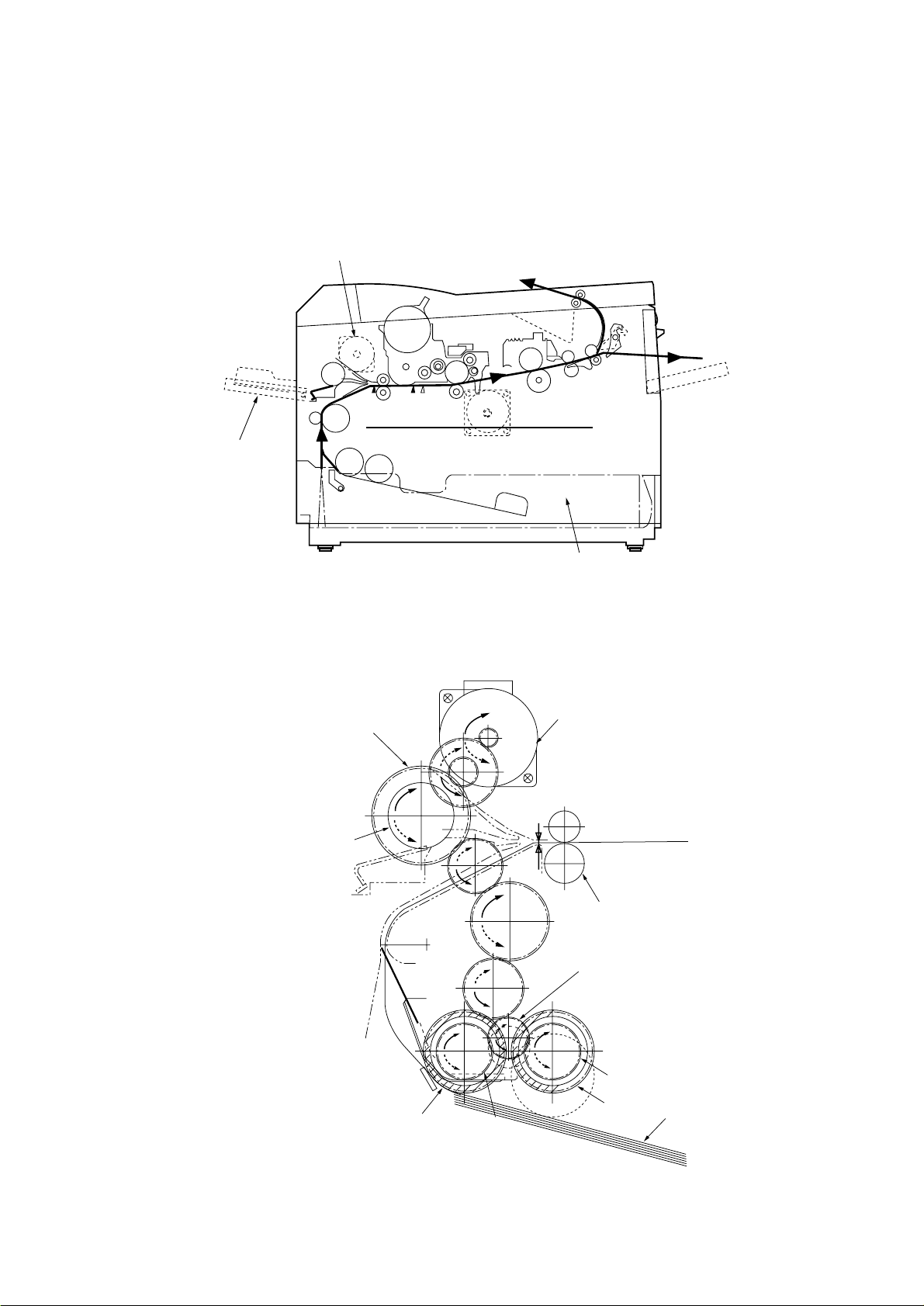
2.4.3 Process operation descriptions
(1) Hopping
Hoppings from the first tray and the front feeder are effected by a single hopping motor in the
mechanism shown below.
Hopping Motor
Front Feeder
1st Tray
Turning the Hopping motor in direction a (CW) drives the 1st Hopping Roller. Turning the
Hopping motor in direction b (CCW) drives the Front Hopping Roller. Gear C and Hopping
roller bult in one-way bearing, so that turning each of these gears in reverse direction will not
be transmitted to the corresponding roller.
(One-way Clutch build-in )
Front Hopping Roller
(One-way clutch build-in)
Gear C
(CW)
a
b
Hopping Motor
(CCW)
Inlet Sensor
Roller-Regist
Planet Gear
1st Hopping Roller
(One-way clutch build-in)
2 - 15
Gear A
Gear B
Sub Roller
Paper
Page 30
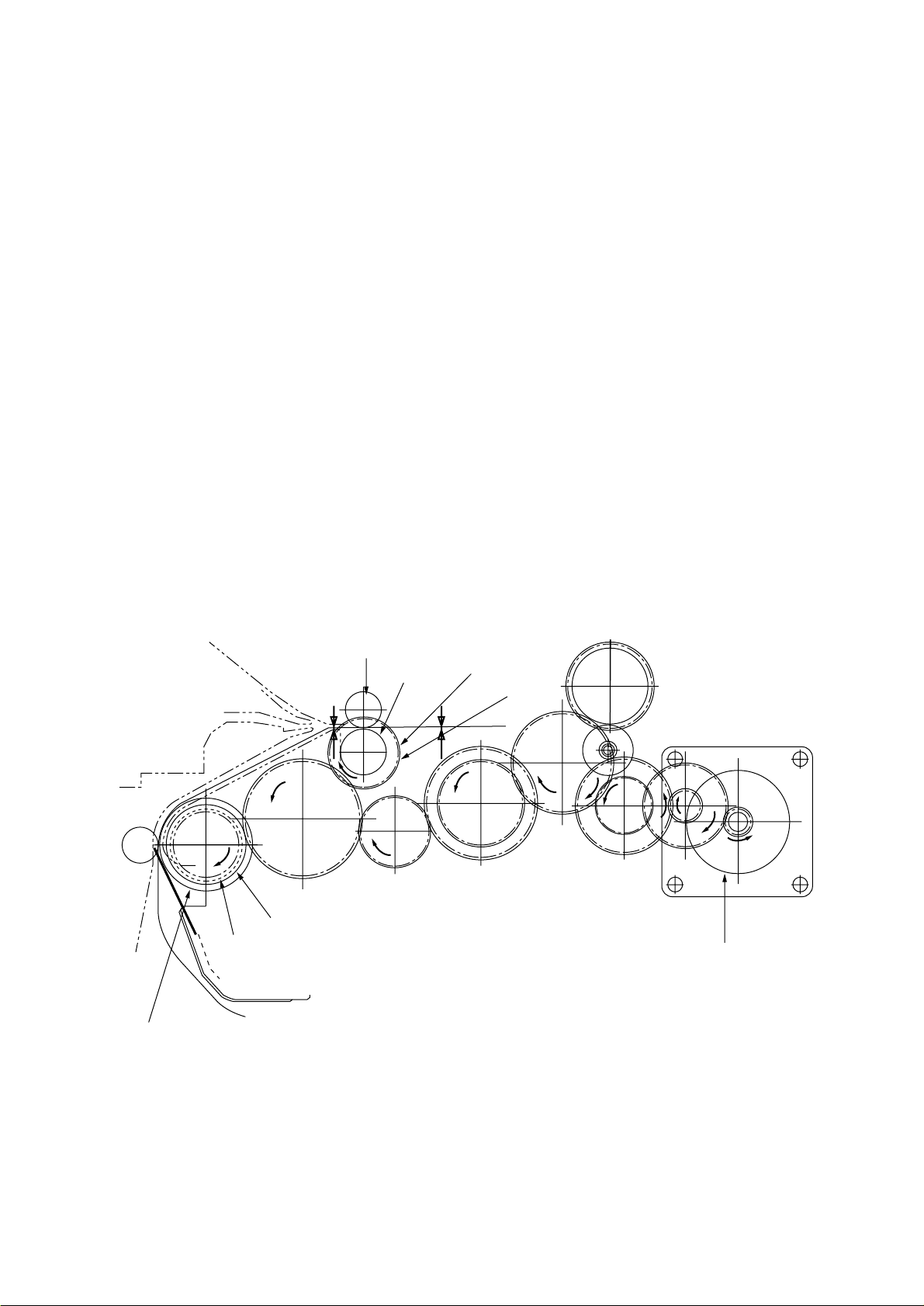
(a) Hopping from the 1st Tray
1 Hopping
Rotating the Hopping Motor in direction a (CW) drives the 1st Hopping Roller and
the Sub Roller then pick up a sheet of paper in the 1st tray. The Main Motor is always
driven in direction c (CCW) on printing. After the paper fed approx. 30mm from the
tray, the Clutch (Feed) drives the Align Roller to advance the paper until the Inlet
Sensor turns on.
2 Aligning
After turning on the Inlet Sensor, the paper fed by a predetermined length and
choked up to the wedge space formed by the Regist Roller and the Pressure Roller
so that to align the skew of paper.
3 During the paper fed from the 1st tray, the build in clutch of Gear C is idled and not
to drive the Front Hopping Roller.
4 Feeding
After aligned the paper, the Hopping Motor turned off and stop hopping. Also the
Clutch (Feed) turned off and the Align Roller idled freely. Then Clutch (Regist)
turned on and the Regist Roller start to feed the paper. After the paper fed, the 1st
Hopping Roller is freely idled by releasing build in one way clutch, also the Sub
Roller is freely idled by escaping the Planet Gear.
5 Start printing. after the paper turns off the Write Sensor.
Align Roller
Clutch (Feed)
Gear D
Pressure Roller
Inlet Sensor
Regist Roller
Gear E
Clutch (Regist)
Write Sensor
c
Main Motor
2 - 16
Page 31

(b) Hopping from the Front Feeder
1 Hopping
The Front Feeder Plate is normally locked at the lower position by the Release
Lever and turn the Micro SW on. Top of the FF Cam which attached on end of the
Front Hopping Shaft is normally located Upper position (0 to 30 degree : home
position). Rotating the Hopping Motor in direction b (CCW) drives the Front Hopping
Shaft and then attached the FF Cam and the Front Hopping Roller are driven.
During the FF Cam rotated approx. 60 degree, the Release Lever was pushed and
the Front Feeder Plate lifts up, then the Front Hopping Roller picks up a sheet of
paper. At the FF Cam rotated approx. 180 degree, the Front Feeder Plate is pushed
down and locked by the Release Lever again. At the FF Cam rotated approx. 275
degree the paper fed until the Inlet Sensor turns off.
2 Aligning
After turning on the Inlet Sensor, the paper fed by a predetermined length and
choked up to the wedge space formed by the Regist Roller and the Pressure Roller
so that to align the skew of paper.
3 During the paper fed from the Front Feeder Plate, the one way clutch of 1st Hopping
Roller is idled and not to drive the 1st Hopping Roller and the Sub Roller.
4 Feeding
After aligned the paper, the Hopping Motor turned off and stop hopping. Then Clutch
(Regist) turned on and the Regist Roller start to feed the paper. After the paper fed,
the Front Hopping Roller drives the Front Hopping Shaft and attached the FF Cam
with small idle torque of build in one way clutch and when comes into the Release
Lever, the one way clutch is slipped and the FF Cam is stopped at the upper position
(home position). The Front Hopping Roller continuously idled up to the paper away.
5 Start printing. after the paper turns off the Write Sensor.
2 - 17
Page 32

Hopping Roller
(Front Feeder)
Gear C
(one way clutch build in)
Hopping Motor
b (CCW)
Pressure Roller
Front Feeder Plate
Paper
Gear A
Hopping Roller
Inlet Sensor
d
1st Hopping Gear
(One way Gear build in)
Regist Roller
Paper
Sub Roller
0~30°
Release Lever
Front Feeder Plate
(home position)
Front Hopping Shaft
FF Cam
Micro SW
60°
180°
2 - 18
Page 33

Align Roller
Clutch (Feed)
Gear D
Pressure Roller
Inlet Sensor
Regist Roller
Gear E
Clutch (Regist)
Write Sensor
c
Main Motor
(2) Feeding
After the end of hopping, the pulse motor dedicated for driving the registration roller rotates
to drive the registration roller. The driven registration roller advances the paper until it comes
out of the registration roller.
When leading edge of the paper causes the paper sensor to turn on, the printing is started
synchronously.
Although Gear D is always rotating due to an all-time rotation of the main motor in direction
c, the regist roller would not rotate because the clutch (regist) is turned off.
After the completion of hopping, turn on the clutch (regist) to drive the regist roller. The regist
roller would drive a paper until the paper has passed.
2 - 19
Page 34

(3) Charging
Charging is effected by applying a DC minus voltage to the charge roller that is in contact with
the image drum surface.
Power
supply
Image drum
Charge roller
(4) Exposure
Power
supply
Light emitted from the LED head irradiates the image drum surface with negative charges.
The surface potential of the irradiated part of the image drum drops, thereby forming an
electrostatic latent image associated with the image signal.
LED head
Charge roller
Image drum
LED head
Paper
Image drum
2 - 20
Page 35

(5) Developing
Toner is attracted to the electrostatic latent image on the image drum surface to convert it
into a visible toner image. Developing takes place at the contact between the image drum
and the developing roller.
1 As the toner supply roller rotates while rubbing on the developing roller, a friction charge
is generated between the developing roller and the toner, allowing the toner to be
attracted to the developing roller. (The developing roller surface is charged positive and
the toner, negative.)
Doctor blade
Charge roller
Toner supply roller
Image drum
Developing roller
2 The toner attracted to the developing roller is scraped off by the doctor blade, forming
a thin coat of toner on the developing roller surface.
3 Toner is attracted to the exposed part (low-potential part) of the image drum at the
contact between the image drum and the developing roller, making the electrostatic
latent image visible.
2 - 21
Page 36

(6) Transfer
The transfer roller is composed of conductive sponge material and is designed to make the
image drum surface and the paper closely into contact.
Paper is placed over the image drum surface, and a positive charge, opposite in polarity to
the toner, is applied to the paper from its reverse side.
The application of a high positive voltage from the power supply to the transfer roller causes
the positive charge induced to the transfer roller surface to be transferred to the paper at the
contact between the transfer roller and the paper. As a results, toner charged negative that
is attracted to the image drum surface is transferred to the upper side of the paper by the
positive charge on the lower side of the paper.
Image drum
Transfer roller
Paper
Power
supply
2 - 22
Page 37

(7) Fusing
After the end of the transfer, the unfused toner image is fused on the paper under heat and
pressure as it passes between the heater roller and the back-up roller. The heater roller with
a Teflon coating incorporates a 750W heater (Halogen lamp), which heats the heat roller.
A thermistor which is in contact with the heater roller regulates the heater roller at a
predetermined temperature (about 180 ~ 200°C). A safety thermostat cuts off voltage supply
to the heater by opening the thermostat in the event of abnormal temperature rises.
The back-up roller is held under a pressure of 5 kg from the pressure spring at each side.
Heater
Paper
Separation Claw
Thermistor
Heater Roller
Roller-BK
Pressure Spring
2 - 23
Page 38

(8) Cleaning
After the end of the transfer, residual toner on the image drum is attracted to the cleaning
roller temporarily by static electricity to clean the image drum surface.
Image Drum
Cleaning Roller
Power
Supply
Transfer Roller
(9) Cleaning of rollers
The charge roller, transfer roller and cleaning roller are cleaned in the following cases:
• In warming up at power-on time
• In warming up after the cover is opened and closed
• When the number of accumulated sheets is 10 or more and the printout operation ends
Changes in bias voltage applied to each roller move adhesive toner from the roller to the
image drum and return it to the developer.
2 - 24
Page 39

2.3.4 Revision of LED Head Illumination
An LED correcting head, which is capable of correcting the illumination of the LED for each dot,
is being used in this printer. LED illumination correction function of 16 steps is carried out by using
an EEPROM which is installed in the LSI that maintains the LED illumination correction values,
and an LED correction drivers together as a pair.
The LED correcting head consists of the correction control LSI , LED drivers , and an LED array.
The block diagram of the LED correcting head is shown below.
(1) Both sides wire-bonding head
Correction Control
LSI
EEPROM
STRB4-N
STRB3-N
DATA 3
DATA 2
LED Driver LED Driver
From
CPU
LOAD
CLOCK
STRB2-N
STRB1-N
DATA 1
DATA 0
LED LED LED LED LED LED LED
LED Driver LED Driver
LED Array
In OKIPAGE 20/ OKIPAGE 20n, the correction control of LED head is excuted direction by CPU.
The procedure is as follows
(i) LED head is set to the correction control read mode and all correction data stored
in EEPROM within the correction control LSI are read by CPU, and stored
temporarily in the memory.
(ii) Next, LED head is set to the correction control direct mode and the correction data
stored temporarily in the memory is transferred directly to the LED driver.
2 - 25
Page 40

(i) Read of correction data
CLOCK
LOAD
DATA 3~0
STRB1-N
STRB2-N
STRB3-N
STRB4-N
Mode setting
RD Mode enabled
RD Mode set
RD
250ns min
High-Z
High-Z
data1 data3
correction data1
correction data2 correction data 4992
data2 data4
1000
dummy cycle
8 clocks
RD cycle
8 clocks
RD cycle
8 clocks
Head data read Correction data read
Total 19992 clocks
RD cycle
8 clocks
RD cycle
8 clocks
correction data 4991
2 - 26
Page 41

01100
CLOCK
LOAD
DATA 3~0
STRB4~1
Mode setting
Total 2496 clocks
Correction data 1
Correction data 4991
Correction data 4992
Correction data 2
Correction data 4
Correction data 3
DIRECT Mode enabled
DIRECT Mode set
DIRECT
250ns min
(ii) Transfer of correction data to head driver correction data
2 - 27
Page 42

(2) One side wire-bonding head
DATA 3
DATA 2
DATA 1
DATA 0
From
CPU
CLOCK
LOAD
STRB4-N
STRB3-N
STRB2-N
STRB1-N
Correction Control
LSI
EEPROM
LED Array
LED LED LED LED LED LED LED
LED Driver LED Driver
(i) LED head is set to the correction control read mode and all correction data stored
in EEPROM within the correction control LSI are read by CPU, and stored temporarily
in the memory.
(ii) Next, LED head is set to the correction control direct mode and the correction data
stored temporarily in the memory is transferred directly to the LED driver.
2 - 28
Page 43

(i) Read of correction data
CLOCK
LOAD
DATA 3~0
STRB1-N
STRB2-N
STRB3-N
STRB4-N
Mode setting
RD Mode enabled
RD Mode set
RD
250ns min
High-Z
High-Z
data1 data3
correction data1
correction data2 correction data 5200
data2 data4
1000
dummy cycle
8 clocks
RD cycle
8 clocks
RD cycle
8 clocks
Head data read Correction data read
Total 20824 clocks
RD cycle
8 clocks
RD cycle
8 clocks
correction data 5199
2 - 29
Page 44

01100
CLOCK
LOAD
DATA 3~0
STRB4~1
STRB1-N
STRB2-N
STRB3-N
STRB4-N
Mode setting
Total 5200 clocks
Correction data1 Correction data1300
Correction data1301
Correction data2
DIRECT Tp
Ditail figure A-D
A part of A A part of B A part of C A part of D
Tp Tp Tp
Tp > 2µs
Tp Tp Tp Tp
Tp
Correction data2600
Correction data2601
Correction data3900
Correction data3901
Correction data5200
more than 1µS
(ii) Transfer of correction data to head driver correction data
2 - 30
Page 45
The LED driver corrects the LED illumination by controlling the LED current. The LED illumination
can be set in 16 steps, with 7 steps in the direction of illumination increase in relation to the
standard value, and 8 steps in the direction of decrease. For this reason, the LED correction data
is a 4-bit data for each dot.
The relationship between the LED correction data and LED current correction steps with the LED
driver used in an LED head is shown below.
LED Correction Data
msb b3
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Corretion Data
b2
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
b1
Correction
lsb b0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
Step
+16%
+14%
+12%
+10%
+8%
+6%
+4%
+2%
0%
-2%
-4%
-6%
-8%
-10%
-12%
-14%
Correction
Mode
↑
↑
Correction by
increasing
illumination
↑
↑
↑
No correction
↓
↓
Correction by
decreasing
illumination
↓
↓
2 - 31
Page 46

The printing operation timing chart is shown below.
Normal Mode Printing Timing Chart
CLOCK
LOAD
DATA3~0
STRB1-N
STRB2-N
STRB3-N
STRB4-N
First line printing data sent Second line printing data sent
First line printing
The printing operation is carried out in normal mode. Under ordinary circumstances such as when
the power is turned on or when LOAD signal level is low, the normal mode is enabled.
The printing operation is carried out in the following sequence. First, the printing data DATA3
through DATA0 are stored, sequentially shifted, in the shift registers of the LED drivers, by the
printing data synchronous clock, CLOCK. Then the printing data stored in shift registers are
latched by the high level pulse of LOAD. The latched printing data turns the LEDs on by STRB1N through STRB4-N and actuates printing.
2 - 32
Page 47

2.4 Paper Jam Detection
The paper jam detection function supervises the paper state at power-on time and during printing.
In the event that the following state occurs, this function interrupts the printing process. If any of
the following errors is presented, recovery printing will be performed by removing the jammed
paper (namely by opening the upper cover, removing the jammed paper and closing the upper
cover).
Error Cause of error
Paper input jam • At power-on time, the paper is placed at the inlet sensor.
• After hopping operation is attempted three times, the leading part of the
Paper feed jam • At power-on time, the paper is placed at the paper sensor.
• The leading part of the paper does not reach the paper sensor within a
• The traiding part of the paper does not pass over the paper sensor within
paper does not reach the inlet sensor.
predetermined distance after the paper has reached the inlet sensor.
a predetermined distance after the leading edge of the paper has passed
over the paper sensor.
• The leading part of paper does not reach the outlet sensor within a
predetermined distance after the paper has reached the paper sensor.
Paper exit jam • At power-on time, the paper is placed on the outlet sensor.
• The paper does not pass over the outlet sensor within a predetermined
after the leading part of the paper has reached the outlet sensor.
• The paper size check with the manual feed specified considers the
reference size as free size.
Paper size error • The size of the paper is supervised by the inlet sensors 1. It is detected
that the paper does not pass over the inlet sensor 1 within predetermined
range of distance.
• The inlet sensor 2 detects that the size of the loaded paper is A4 or larger,
or smaller than A4. The detected paper size differs from the paper size
set by command or menu.
• The paper size check with the manual feed specified considers the
reference size as free size.
2 - 33
Page 48

2.5 Cover Open
When the stacker cover is opened, the cover open microswitch on the Power Supply Unit (High
voltage) is turned off to cut the supply of +30V to the high voltage power supply circuit. As a result,
all high-voltage outputs are interrupted. At the same time, the CVOPN signal is sent to the control
board to notify it of the off state of the microswitch, and the Main board performs the cover open
processing.
2 - 34
Page 49

2.6 Toner Low Detection
• Composition
The device consists of the stirring gear which rotates at a constant rate, the stirring bar and
the magnet on the stirring bar. The stirring bar rotates through the link on the protrusion in
the stirring gear.
Magnet
Stirring Bar Stirring Gear
• Operation
Toner Low is detected by monitoring the time interval of the encounter of the magnet set on
the sensor lever and the magnet on the stirring bar.
Protrusion
Stirring Gear Section
Operation during toner full state
• The stirring bar rotates due to the interlocking
with the stirring gear.
• Even when the magnet on the stirring bar
reaches the maximum height, since the other
side is being dipped in the toner, the stirring
bar is pushed by the stirring gear.
Operation during toner low state
• When the stirring bar reaches the maximum
height, since there is no resistance provided
by the toner on the other side, it falls to the
minimum height due to its own weight. Because of this, the time interval during which it
is in encounter with the magnet of the sensor
lever becomes long. By monitoring this time
interval, toner low can be detected.
Stirring Bar
Sensor Lever
Toner Sensor
Stirring Bar
Sensor Lever
2 - 35
Page 50

TONER FULL state
TNRSNS
TONER LOW state
TNRSNS
• When the toner low state is detected 2 times consecutively, Toner Low is established.
• When the toner full state is detected 2 times consecutively, Toner Low is cancelled.
• When there is no change with the toner sensor for 2 cycles (2.727 sec. x 2) or more, then the
Toner Sensor Alarm is activated.
t1 < 2.727/4
t1
2.727 SEC.
t1
2.727 SEC.
t1 > 2.727/4
• The toner sensor is not monitored while the drum motor is in halt.
2 - 36
Page 51

2.7 Stacker-full Detection
The sensor (interlocked with the lever) at the paper outlet to the stacker detects a stacker-full state
(about 250 sheets) and stops printing of the ensuing pages.
2.8 Page Size Detection
The four tab pieces are driven according to the setting position of the paper guide through the cam
interlocked with the paper guide of the paper cassette.
When the paper cassette is inserted into the printer, the state of the tab pieces is detected by the
microswitch to recognize the paper size.
State of Microswitches Paper size
SW1 SW2 SW3 SW4
0111Letter
0101Executive
0011A4
1110Legal 14
1011Legal 13
1101B5
1100A5
1001A6 (Not available)
2.9 PostScript ROM module (BOARD-MSM-2 or BOARD-FSL-2)
PostScript ROM module is mounted on SIMM socket (FSIMM1).
The PostScript ROM module consists of program/font ROM's, an EEPROM.
(1) Program/font ROM's
The program/font ROM's store the PostScript Level II program and its fonts.
BOARD-MSM-2 consists of Mask ROM.
BOARD-FSL-2 consists Flash ROM.
Mask ROM and Flash ROM is used as the program/ font ROM's.
(2) EEPROM
The EEPROM has a 4-kbit capacity and stores the PostScript's menu settings.
(3) Emulation
PostScript Level 2.
2 - 37
Page 52

3. PARTS REPLACEMENT
Page 53

3. PARTS REPLACEMENT
The section explains the procedures for replacement of parts, assemblies, and units in the field.
Only the removal procedures are explained here. Reverse the procedure for the installation.
3.1 Precautions for Parts Replacement
(1) Before starting parts replacement, remove the AC cable and interface cable.
(a) Remove the AC cable in the following procedure:
i) Turn off ("o") the power switch of the printer
ii) Disconnect the AC inlet plug of the AC cable from the AC receptacle.
iii) Disconnect the AC cable and interface cable from the printer.
(b) Reconnect the printer in the following procedure.
i) Connect the AC cable and interface cable to the printer.
ii) Connect the AC inlet plug to the AC receptacle.
iii) Turn on ("l") the power switch of the printer.
Disconnect
OFF
ON
(2) Do not try disassembly as long as the printer is operating normally.
(3) Do not remove unnecessary parts: try to keep disassembly to a minimum.
(4) Use specified service tools.
(5) When disassembling, follow the determined sequence. Otherwise, parts may be damaged.
(6) Since screws, collars and other small parts are likely to be lost, they should temporarily be
attached to the orginal positions.
(7) When handling ICs such as microprocessors, ROM and RAM, and circuit boards, do not wear
gloves that are likely to generate static electricity.
Connect
(8) Do not place printed circuit boards directly on the equipment or floor.
3 - 1
Page 54

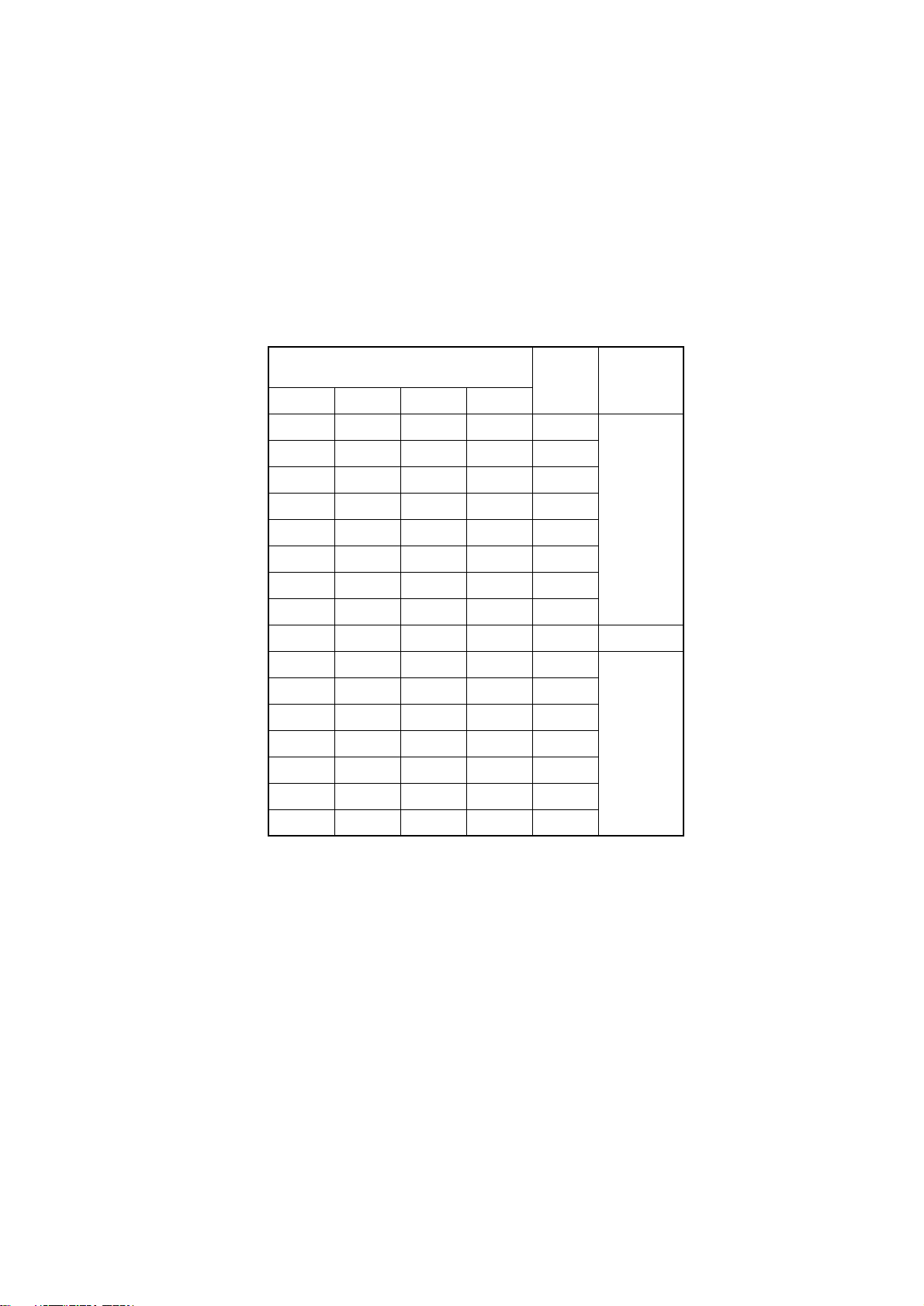
[Service Tools]
Table 3-1 shows the tools required for field replacement of printed circuit boards and units.
Table 3-1 Service Tools
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7 1
8
9
No. 1-100 Philips
screwdriver
No. 2-200 Philips
screwdriver, Magnetized
No. 3-100 screwdriver
No. 5-200 screwdriver
Digital multimeter
Pliers
Handy cleaner
LED Head cleaner
P/N 4PB4083-2248P1
Connector remover
P/N 4PP4076-5395P1
Q' ty Place of use RemarksService Tools
1
2~2.5 mm screws
1
3~5 mm screws
1
1
1
1
1
Cleans LED head
Disconnect connector
1
10
Holder-TR Eject
P/N 40596701
3 - 2
1
For removing
ROLLER-Transfer
Page 55

3.2 Parts Layout
Plate-Shield
Frame-OP panel Assy
Cover-Side(I/F)
Face-up stacker Assy
Cover-Rear
ROLLER-Transfer
Cover-Frame
Main Control Board
(Board-AAA)
Cover-Side(L) Assy
Contact Assy
Cover-Side(R)
Manual Feed Assy
Base Unit
CASE Assy-Cassette
Figure 3-1
3 - 3
Page 56

Feed Unit-FRONT
HEAT-Assy
Toner Cartridge
(Type 7)
ID Unit
(Type 7)
Motor-Main
ROLLER
Assy-Feed
GUIDE-Assy-Eject
LED HEAD
Stacker Cover
FRAME-Main
DC Fan Motor
Figure 3-2
3 - 4
Page 57

FILM-Insulation
Power Supply Unit (120V/230V)
Power Supply Unit (High Voltage)
FRAME Assy-Hopping
ROLLER Assy-Feed
GUIDE Assy-Cassette(L)
Board PXC
GUIDE
Assy-Cassette(R)
PLATE-Bottom
Figure 3-3
3 - 5
Page 58

3.3 How to Change Parts
Printer Unit
Face-up Stacker Assy
Contact Assy
OP Panel Assy
Paper Cassette,
ROLLER Ass-Feed,
ROLLER-Assy-Hopping
Transfer Roller/TR Gear/
TR Bearing
(3.3.1)
(3.3.2)
(3.3.4)
(3.3.19)
(3.3.21)
DC fan motor
HEAT Assy
Board-AAA
Feeder Unit-Front
Frame Assy-Separation
(3.3.3)
(3.3.14)
(3.3.5)
(3.3.10)
(3.3.20)
Roller Assy-BK
Stacker Assy, Damper Arm
, Cover Rear
Roller Assy-Regist
Motor-Main
Roller Assy-Feed
(3.3.16)
(3.3.6)
(3.3.11)
(3.3.12)
(3.3.17)
Sensor Stacker Full
Cable Cover
Damper
LED Head
Guide Assy-Eject
EP Lock Shaft
Lever Assy-Out Sensor
Toner Sensor Lever
Paper Sensor Lever
Inlet Sensor Lever
Power Supply Unit
Lever-Paper end &
Paper near end
(3.3.7)
(3.3.8)
(3.3.9)
(3.3.18)
(3.3.13)
(3.3.22)
(3.3.23)
(3.3.24)
(3.3.25)
(3.3.26)
(3.3.27)
(3.3.28)
Roller Feed (C)
Gudie Assy-Cassette(L)
Gudie Assy-Cassette(R)
(3.3.15)
(3.3.29)
(3.3.30)
This section explains how to change parts and assemblies appearing in the disassembly
diagram below.
3 - 6
Page 59

3.3.1 Face -up Stacker Assy
(1) Turn off the AC Power Switch and unplug the AC Power Cord from the outlet.
(2) Disconnect the Interface Cable 1.
(3) Open the face-up stacker assy 2, unhook the right and left projections, and then remove
the face-up stacker assy 2.
2
1
3 - 7
Page 60

3.3.2 Contact Assy
(1) Open the stacker assy 1 and unscrew 2 screw 2 to remove the assy -side (L)3.
(2) Unscrew 2 screws 4 and remove the plate (contact) 5 and contact Assy 6.
Note! Don’t deform the electrode plates of the contact assy 6.
2
1
3
Unlock this part before
removing
6
5
4
6
3 - 8
Page 61

3.3.3 DC Fan Motor
(1) Remove the cover assy-side (L). [See 3.3.2 (1)]
(2) Remove the DC fan motor 1 by pulling out the connector of DC fan motor 1.
1
3 - 9
Page 62

3.3.4 OP Panel Assy
(1) Disconnect the Interface cable 1.
(2) Open the stacker assy 2, unscrew 2 screws 3 and remove the cover side (I/F) 4.
(3) Remove 2 screws 5 and flexible cable 6 to remove the operator panel assy 7.
5
7
6
3
4
2
1
3 - 10
Page 63

3.3.5 Board-AAA
(1) Remove the operator panel assy and cover side (I/F). [See 3.3.4]
(2) Unscrew 2 screws 1 and remove the cover side (R) 2.
(3) Unscrew 2 screws 3 and remove plate-shield 4.
(4) Unscrew 3 screws 5 and 2 screws 6, unplug all the connectors 7 , and remove Board-AAA
8.
4
6
5
5
8
7
7
3
5
7
1
3 - 11
2
Page 64

3.3.6 Stacker Assy, Damper Arm, Cover Rear
(1) Remove the face-up stacker assy. [See 3.3.1]
(2) Remove the cover-side (L). [See 3.3.2 (1)]
(3) Remove the OP panel assy. [See 3.3.4]
(4) Remove the Board-AAA. [See 3.3.5]
(5) Loosen 2 screws, unlock the both sides latches and remove the cover rear A.
(6) Unscrew 2 screws 1 and cover frame 2.
(7) Unscrew 3 screws 3 and remove the plate assy-side (R) 4.
(8) Remove the lever back up release 5 and unlock the engagement of the projection on the
right side of gear at the right side of stacker cover.
(9) Remove a screw 6 and washer 7, and then remove the stacker assy 8.
(At this time, the damper arm 9 can also be detached simultaneously.)
A
8
7
9
5
1
2
6
3
0
3 - 12
4
Page 65

3.3.7 Sensor Stacker Full
(1) Turn the AC power switch off. Unplug the AC power cord from the outlet.
(2) Remove the Stacker assy. [See 3.3.6]
(3) Remove four screws 1. Remove stacker mount 2 by releasing the tabs at position 2A .
(4) Remove Sensor stacker full 3 by releasing speading the plastic tabs on each side of sensor
Assy 3 and lifting switch from cover.
2A
3
1
2A
1
2
3 - 13
Page 66

3.3.8 Cable cover (guide film)
(1) Turn the AC power switch off. Unplug the AC power cord from the outlet.
(2) Remove the stacker Assy. [See 3.3.6]
(3) Unscrew 2 screws 1 release tabs at portion 1A . Remove cable cover 2, guide film 3.
1A
2
3
1
Note: Use care when replacing cable cover. Do not pitch, crimp, or cut cables or
protective sheet.
3 - 14
Page 67

3.3.9 Damper
(1) Remove the damper arm. [See 3.3.6]
(2) Unscrew 2 screws 1 and remove the two damper 2.
1
2
3 - 15
Page 68

3.3.10 Feeder Unit-Front
2
(1) Open the manual feed assy 1 and release both right and left parts by pulling out the
engagements on the lower part.
(2) Stand the manual feed assy 1 on end and unhook the engagements with both right and left
manual feed hopper stays.
(3) Remove the OP panel assy. [See 3.3.4]
(4) Unscrew 5 screws 2 and remove the feeder unit-front 3.
2
2
3
1
3 - 16
Page 69

3.3.11 Roller Assy-Regist
(1) Remove the feeder unit-front. [See 3.3.10]
(2) Remove an E-ring 3, gear assy-clutch 4, and four screws 1 in this order, and lifting out the
roller assy-regist 2.
1
1
2
3
4
3 - 17
Page 70

3.3.12 Motor -Main
(1) Remove the stacker assy. [See 3.3.6]
(2) Remove the feeder unit-front. [See 3.3.10]
(At this point, the manual feed assy has not to be removed.)
(3) Remove the DC fan motor. [See 3.3.3]
(4) Remove the contact assy. [See 3.3.2]
(5) Remove the plate-FG (F) 1.
(6) Remove the TR gear 2 and roller transfer 3.(Use Holder-TR Eject F for the removal.)
(7) Unscrew 7 screws 4 and remove the main frame 5.
(8) Unlock latches at two points of the lever back up release 6 and pull out it in right direction.
(9) Unhook the EP lock spring 7 and remove the EP lock lever 8.
(10) Take off the E ring 9 and remove the plate-FG (1st ) 0 and gear assy-clutch A.
(11) Unlock 2 latches to remove the motor assy-main B and idle gear C.
(12) Unscrew 2 screws D and remove the motor -main E .
3 - 18
Page 71

2
F
3
Latch
View A
2
8
5
7
6
3
E
1
4
4
4
5
4
D
View A
4
A
0
4
C
9
B
D
3 - 19
Page 72

3.3.13 Guide Assy-Eject
(1) Remove the lever back up release. [See 3.3.12(8)]
(But the roller transfer/feeder unit front/plate-FG have not be removed)
(2) Loosen 2 screws 1, unlock the both side’s latches and remove the cover rear 2. [See 3.3.6
(5)]
(3) Unlock the latches on both sides of the guide assy-eject 3 and lifting it out.
2
1
1
3
3 - 20
Page 73

3.3.14 Heat Assy
(1) Remove the cover assy-side (L). [See 3.3.2 (1)]
(2) Unplug the connectors 1, 2.
(3) Unscrew 4 screws 3 and remove the heat assy 4 in the direction of the arrow by lifting the
right side first.
Note ! • As the heat assy 4 becomes high temperature soon after the power is turned
off, start the work after it cools off sufficiently.
• Carry out a reset of the counter after the replacement. (See Section 4.2)
3
3
2
4
1
3 - 21
Page 74

3.3.15 Roller feed (C)
(1) Remove the guide assy-eject. (See 3.3.13)
(But roller transfer/feeder unit-front/plate-FG(F) have not be removed)
(2) Remove the gear roller (C) 1 and bush 2, warp (a) part of the plate-FG (BK) 3. Take off
the carrier bearing 4 and remove the roller feed (c) 5 in the direction of the arrow.
Note ! Be careful not to deform (a) part of the plate-FG (BK) 3.
1
2
5
4
(a)
3
3 - 22
Page 75

3.3.16 Roller Assy-BK
(1) Remove the heat Assy. [See 3.3.14]
(2) Remove the lever back up release. [See 3.3.12 (8)]
(3) Unlock the engagement with the plate-FG (BK) 1 and lift out the roller heat assy 2.
2
1
3 - 23
Page 76

3.3.17 Roller Assy-Feed
(1) Remove the feeder unit -front. [See 3.3.10]
(2) Remove the roller assy-feed 1 by unlocking a latch.
1
3 - 24
Page 77

3.3.18 LED Head
(1) Remove the stacker assy 1. [See 3.3.6]
(2) Unplug the PC connector 2 and 2 LED cables 3 from the LED head 4.
(3) Open the hooks of the cover stacker 1 in the direction of the arrow and remove the LED head
4.
(4) Pull out the head spring 5 from the post.
Note: Don't remove two LED cable 3 from the PC connector 2.
1
2
5
5
3
4
3 - 25
Page 78

3.3.19 Paper cassette, ROLLER Ass-Feed, ROLLER-Assy-Hoppibg
(1) Pull out the case assy -cassette 1 from the printer.
(2) Remove the ROLLER Ass-Feed 2 and remove the ROLLER-Assy-Hopping 3.
3
2
1
3 - 26
Page 79

3.3.20 Frame Assy-Separation
(1) Turn the AC power switch off. Unplug the AC power cord from the outlet.
(2) Pull out the case Assy-Cassette 1 from the printer.[See 3.3.19(1)]
(3) Release two locks and remove frame assy-separation 2. (At this time, coil spring 3 is also
remove. Be careful not to lose this spring.)
2
3
1
Insert 1 so as to pass the both
arms of 1 behind two latches
inside the alcove of 2 unit.
3 - 27
Page 80

3.3.21 Transfer Roller/TR Gear/TR Bearing
(1) Open the stacker cover .
(2) Unlock the lock by lifting the TR gear 1 to remove the TR gear 1 and roller transfer 2.
(Use the Holder-TR Eject 5 for the removal.)
Note ! Don’t place the removed roller transfer directly on the desk and so on. When
placing it, lay a paper and the like under it.
(3) Remove right and left, 2 bearings 3 from the frame-main by sliding them inside while
pushing them. At this time, 2 transfer springs R 4 would be detached simultaneously.
5
3
1
4
2
4
1
2
2
3
1
3 - 28
Page 81

3.3.22 EP lock shaft
2
(1) Turn the AC power switch off. Unplug the AC power cord from the outlet.
(2) Remove Frame-Main [See.3.3.12(7)]
(3) Remove screw 1. Turn EP lock lever (L) Assy 2 in the direction of arrow A .
(4) Remove spring 3.
(5) Drop EP lock shaft 4 down and turn in the direction of arrows B and remove it.
1
3
4
A
B
3 - 29
Page 82

3.3.23 LEVER Assy- Out Sensor
(1) Turn the AC power switch off. Unplug the AC power cord from the outlet.
(2) Remove the frame main [See 3.3.12(7)]
(3) Press the clamp part of LEVER Assy.- Out Sensor 1. Remove the LEVER Assy.-Out Sensor
1 by pushing it upward from the lower side.
1
3 - 30
1
Page 83

3.3.24 Toner sensor lever
(1) Turn the AC power switch off. Unplug the AC power cord from the outlet.
(2) Remove the frame main [See 3.3.12(7)]
(3) Squeeze the clamp part of toner sensor lever 1 and remove the toner sensor lever 1 by
pushing it upward from the lower side.
1
1
3 - 31
Page 84

3.3.25 Paper sensor lever
(1) Turn the AC power switch off. Unplug the AC power cord from the outlet.
(2) Remove the frame main [See 3.3.12(7)]
(3) Squeeze the clamp part of the paper sensor lever 1 and remove the paper sensor lever 1
by pushing it upward from the lower side.
1
1
3 - 32
Page 85

3.3.26 Inlet sensor lever
(1) Turn the AC power switch off. Unplug the AC power cord from the outlet.
(2) Remove the frame main [See 3.3.12(7)]
(3) Squeeze the clamp part of two inlet sensor levers 1. Remove the inlet sensor levers 1
by pushing them downward.
1
1
1
3 - 33
Page 86

3.3.27 Power supply unit
(1) Turn the AC power switch off. Unplug the AC power cord from the outlet.
(2) Remove the frame main [See 3.3.12(7)]
(3) Unscrew 2 screws 1 and remove the BRACKET-AC 2.
(4) Unscrew 10 screws 3 and remove the connector 6 remove the Power supply unit [AC-
DC(120/230V)] 4 and Power supply unit (High voltage) 5.
2
3
3
4
3
6
3
5
1
3 - 34
Page 87

3.3.28 Lever-Paper end & Lever-Paper near end
(1) Turn the AC power switch off. Unplug the AC power cord from the outlet.
(2) Remove the frame main [See 3.3.12(7)]
(3) Remove screw 1 and then remove the PLATE-Base 2.
(4) Remove two Spacer-Cord(KGPS-5RF) 4 and then remove FILM-Insulation 4.
(5) Remove four screws 5 and then remove the FRAME ASS-Hopping 6.
(6) Remove the GEAR-Z58 9 and GEAR-Z42 8.
(At this time, the ADF Bearing 0 can also be detached simultaneously.)
(7) Remove the GEAR-Z38 D, ADF Bearing E, ROLLER-Guide F and SHAFT Hopping G and
Bracket-Sub roller R.
(At this time, the Kock Pin H can also be detached simultaneously.)
(8) Remove two screws 7 and then remove the SPRING-Release A and then remove the
LEVER-Sub roller B and PLATE-Hopping C.
(9) Remove the GEAR-Planet(Z28) I, Plate-Planet J, BRACKET-Spring (Sub) K and
SPRING-Sub ROLLER L.
(10) Press the clamp part of Lever-Paper end M and Lever-Paper near end N. Remove the
Lever-Paper end M and Lever-Paper near end N by pushing it upward from the FRAME
Hopping R.
(11) Remove the Connection Cord-Wire O and TR-23-11-14 R CORE P together.
(12) Remove two Photo Sensor Q.
3 - 35
Page 88

7
5
8
6
1
3
2
4
Q
N
R
5
O
F
P
C
Q
M
D
B
A
E
J
0
F
H
R
9
G
K
L
3 - 36
I
Page 89

3.3.29 Guide Assy-Cassette (L)
(1) Turn the AC power switch off. Unplug the AC power cord from the outlet.
(2) Remove Frame Main [See 3.3.12(7)]
(3) Remove PLATE-Base and FRAME Assy Hopping [See 3.3.28 (5)]
(4) Unscrew two screw 1 and then remove Guid Assy-Cassette (L) 2.
(5) Remove SPRING-Sheet 3 and then remove LINK-Sheet 4 and pull block 5.
(Pay attention the direction of hook of SPRING-Sheet 3.)
(6) Remove spring 6 and then remove cassette stopper 7.
(7) Remove screw 8 from LINK-Sheet 4 and then remove link support 9 and Roller-link 0.
(8) Remove Earth Plate L A and Plate-Earth (link) B.
6
7
A
2
B
5
8
9
3
0
4
1
3 - 37
Page 90

3.3.30 Guide Assy-Cassette (R)
(1) Turn the AC power switch off. Unplug the AC power cord from the outlet.
(2) Remove Frame Main [See 3.3.12(7)]
(3) Remove PLATE-Base and FRAME Assy Hopping [See 3.3.28 (5)]
(4) Unscrew two screw 1 and then remove Guid Assy-Cassette (R) 2.
(5) Remove SPRING-Sheet 3 and then remove LINK Sheet 4 and pull block 5.
(Pay attention the direction of hook of SPRING-Sheet 3.)
(6) Remove spring 6 and then remove cassette stopper 7.
(7) Remove screw 8 from LINK-Sheet 4 and then remove link support 9 and Roller-link 0.
(8) Unscrew two screws A and remove the Square shaped connector (176496-1) B and
Nylon Connector Cord C and TR-23-11-R CORE D.
(9) Unscrew two screws E and remove the two Plate Earth (Bottom) F.
(10) Unscrew two screws G and remove the Square shaped connector (5-176496-1) H and
Connection Cord Wire I and TR-23-11-R CORE J.
(11) Unscrew a screw K and remove the Detector spring L.
(12) Unscrew a screw M and remove the Board PXC N.
3 - 38
Page 91

1
E
E
F
G
J
M
N
I
K
H
L
7
6
3
8
9
5
F
2
D
C
4
B
0
A
3 - 39
Page 92

4. ADJUSTMENT
Page 93

4. ADJUSTMENT
This chapter explains the adjustment necessary when replacing a part. Adjustment is made by
changing a parameter value set in EEPROM on the controller PCB. A parameter is able to set
with the key operation on the operator panel. This printer has three kinds of the maintenance
mode, it is required to select one of the maintenance mode necessary when replacing a part.
4.1 Maintenance Modes And Functions
• User maintenance mode
To enter the user maintenance mode, turn on the POWER switch while pressing the MENU
key.
[Function]
There are 13 functions as follows.
• Menu reset • Y adjust
• Hex dump • Duplex Adjust
• Drum counter reset • Select paper source command parameter
• Resource Save (Second, Third, Front Tray)
• Receive Buffer Size • Page placement
• Operator panel menu disable • Setting
• X adjust • Cleaning cycle
• System maintenance mode
Note:
This mode is used only by service persons and it should not be released to the end-
users.
To enter the system maintenance mode, turn on the POWER switch while pressing the
RECOVER key.
[Function]
There are 8 functions as follows.
• Page count display
• Page count printing enable/disable
• Rolling ASCII continus prinitng
• RS232C LOOP TEST
• EEPROM reset
• HSP ERROR recovery
• HSP ERROR count display
• HSP ERROR count reset
• SIDM enable/disable
4 - 1
Page 94

• Engine maintenance mode
Note:
This mode is used only by service persons and it should not be released to the end-
users.
To enter the engine maintenance mode, turn on the POWER switch while pressing the
FORM FEED key and ENTER key.
[Function]
There are 19 functions as follows.
• Head type setting
• Head drive time setting.
• Head drive time setting at Auto head type
• Head strobe time at 600 x 1200 dpi
• Printing start position setting
• Drum counter total display
• Drum count display
• Setting of standard paper feed length
• Setting of front feeder paper feed length
• Setting of second tray paper feed length
• Selection of second tray feeder download table
• Setting of third tray paper feed length
• Selection of third tray feed download table
• Setting of Multi-purpose feeder paper feed length
• Selection of Multi-purpose feeder download table
• Setting of duplex feed length
• Fuser count indication
• Fuser count reset
• Engine reset
4 - 2
Page 95

4.1.1 User maintenance mode
• To enter the user maintenance mode, turn the power supply ON while pressing the Menu
key.
• This mode uses the menu for function selection.
• The user maintenance mode provides the following functions:
(1) Menu reset
• All settings for Menu level-1 are reset to the factory default values.
The menus for all executable emulations including options are reset to the factory
default values.
• The operation mode starts automatically upon completion of resetting.
(2) Hex dump
• The data received from the host is dumped in hexadecimal notation to the printer.
• Printing is activated automatically when the received data exceeds one page. If the
received data is less than one page, printing can be activated manually be pressing the
Form Feed key after selecting the OFF LINE mode by pressing the ON-LINE key.
(Automatic activation of printing even when the received data is less than one page by
selecting the Auto Eject function on the menu.)
• To exit from this mode is turning the power OFF.
(3) Drum counter reset
• This function resets the drum life data when the user replaces the image drum unit.
• The operation mode starts automatically upon completion of resetting.
(4) Resource Save
• Set the storage area size of resource to be stored between PCL and Postscript.
(5) Receive Buffer Size
• Set the receiving buffer.
(6) Operator panel menu disable
• This function is for enabling and disabling the operator panel menu functions (Menu 1,
Menu 2, Tray Select, Copies and Paper Size).
(7) X ADJUST
• This function is used to adjust the printing start position within the range of ±2 mm in
0.25 mm steps in the X direction.
(8) Y ADJUST
• This function is capable to adjust the printing start position within the range of ±2 mm
in 0.25 mm steps in the Y direction.
4 - 3
Page 96

(9) Duplex adjust
• The function which performs a correction in Y direction towards the sheet supplied from
the tray in double-sided printing.
(10) Select paper source command parameter (Second tray)
• The function which sets the parameter selecting the second tray by paper source
command (ESC & N # H) on PCL.
(11) Select paper source command parameter (Third tray)
• The function which sets the parameter selecting the third tray by paper source
command (ESC & N # H) on PCL.
(12) Select paper source command parameter (Front tray)
• The function which sets the parameter selecting the front tray by paper source
command (ESC & N # H) on PCL.
(13) Page placement
• The function which aligns a printing image to the right.
(14) SETTING
• This function is used to adjust to improve print quality.
-2
Rough/thick paper, Low temperature/humidity and/or blockly faded print appeared.
-1
0
Nomal media/enviroumental conditions.
+1
Rough papers, high temperature/humidity and/or snowy print of high density pattern.
+2
(15) Cleanig cycle
• Set the page interval to perform Cleaning Sequence.
When stains build up especially in using rough papers. Change the cleaning cycle.
The shorter the cycle is set, the less the stains become.
Normal : Each 20th page (default)
Middle : Each 10th page
High : Each 3th page
4 - 4
Page 97

User maintenance mode menu system
Menu key
+
Power ON
LCD display
USER MNT
Press the
Menu key.
MENU
RESET
Press the
Menu key.
HEX DUMP
Press the
Menu key.
DRUM CNT
RESET
Press the
Menu key.
RSRC SAV
Press the
Menu key.
REC BUFF
Press the
Menu key.
OP MENU
ENABLE *
Press the
Menu key.
X-ADJUST
0 mm*
Press the
Menu key.
Press the
Enter key.
Press the
Enter key.
Press the
Enter key.
Press the
or key.
Press the
or key.
Press the
or key.
Press the
or key.
MENU
RESET'NG
ON-LINE .HEX
DRUM CNT
RESET'NG
AUTO*
OFF
400KB
900KB
1.6MB
2.5MB
3.6MB
4.9MB
6.4MB
8.1MB
10.0MB
12.1MB
14.4MB
16.9MB
19.6MB
22.5MB
AUTO*
8KB
20KB
50KB
100KB
1MB
DISABLE
0 mm *
+ 0.25 mm
+ 0.75 mm
+ 1.00 mm
+ 1.25 mm
+ 1.50 mm
+ 1.75 mm
+ 2.00 mm
- 2.00 mm
- 1.75 mm
:
- 0.25 mm
After the end
of processing
End of processing is performed
by the power supply OFF.
After the end
of processing
Writing into the EEPROM is performed
when the Enter key is pressed.
Writing into the EEPROM is performed
when the Enter key is pressed.
(0.25 mm intervals)
ON-LINE***
ON-LINE***
4 - 5
Page 98

Y-ADJUST
0 mm*
DUP ADJ
2ND TRAY
3ND TRAY
FRONT
PLACE PG
SETTING
0 *
Press the
Menu key.
CLN CYCL
Press the
Menu key.
INITIALIZING
Press the
or key.
Press the
Menu key.
Press the
or key.
Press the
Menu key.
Press the
or key.
Press the
Menu key.
Press the
or key.
Press the
Menu key.
Press the
or key.
Press the
Menu key.
Press the
or key.
Press the
Menu key.
Press the
ON LINE key.
Press the
or key.
Press the
or key.
0 mm *
+ 0.25 mm
+ 0.75 mm
+ 1.00 mm
+ 1.25 mm
+ 1.50 mm
+ 1.75 mm
+ 2.00 mm
- 2.00 mm
- 1.75 mm
:
- 0.25 mm
0 mm *
+ 0.25 mm
+ 0.50 mm
+ 0.75 mm
+ 1.00 mm
:
+ 2.00 mm
- 2.00 mm
- 1.75 mm
:
- 0.25 mm
1
2
3
:
5*
:
16
1
2
3
:
9*
:
16
1
2
3
4*
:
16
CENTER*
LEFT
+2
+1
0 *
-1
- 2
NORMAL*
MIDDLE
HIGH
Writing into the EEPROM is performed
when the Enter key is pressed.
(0.25 mm intervals)
Writing into the EEPROM is performed
when the Enter key is pressed.
ON-LINE ***
4 - 6
Page 99

4.1.2 System maintenance mode
• The system maintenance mode is set when the power is turned ON while pressing the
Recover key.
• This mode adopts the menu for function selection.
• The system maintenance mode is provided with the following functions:
(1) Page count display
• The total number of pages counted at the engine is displayed on the LCD.
(2) Page count printing enable/disable
• This function selects whether to include (enable) or exclude (disable) the total number
of printed pages counted at the engine at the time of menu printing.
(3) Rolling ASCII continuous printing
• The rolling ASCII pattern is printed continuously for various engine tests.
• Press the ON-LINE key to cancel this mode.
(4) RS232C LOOP TEST
• Performs a loop test of RS 232C.
(5) EEPROM reset
• All EEPROM areas including Menu level-2 to the factory default values.
• The following items are excluded
* Head drive time setting
* Fine adjustment of printing start position
* Standard tray paper feed amount setting
• Transition to the operation mode occurs upon completion of resetting.
• Press the Menu key to update each category.
The operation returns to the first category after updating the last category.
(6) HSP ERROR recovery
• Select HSP ERROR recovery function either recover or stop.
(7) HSP ERROR count
• Display total HSP ERROR count.
4 - 7
Page 100

(8) HSP ERROR count reset
• Reset the HSP ERROR counter.
(9) SIDM enable/disable
• If it's selected disable, cannot select SIDM emulations by Menu.
4 - 8
 Loading...
Loading...