OKI ML608 User Manual

OKI Semiconductor
FEDL60851E-02
Issue Date: Dec. 16, 2002
ML60851E
USB Device Controller
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ML60851E is a general purpose Universal Serial Bus (USB) device controller. The ML60851E provides a
USB interface, control/status block, application interface, and FIFOs. The FIFO interface and two types of
transfer have been optimized for BulkOut devices such as printers and BulkIn devices such as digital still cameras
and image scanners. In addition, Mass Storage devices are also applicable to this device.
FEATURES
• USB 2.0 compliant
• Built-in USB transceiver circuit
• Full-speed (12 Mb/sec) support
• Supports printer device class, image device class, and Mass Storage device class
• Supports three types of transfer; control transfer, bulk transfer, and interrupt transfer
• Built-in FIFOs for control transfer
Two 8-byte FIFOs (one for receive FIFO and the other for transmit FIFO)
• Built-in FIFOs for bulk transfer (available for either receive FIFO or transmit FIFO)
One 64-byte FIFO
Two 64-byte FIFOs
• Built-in FIFO for interrupt transfer
One 8-byte FIFO
• Supports one control endpoint, two bulk endpoint addresses, and one interrupt endpoint address
• Two 64-byte FIFOs enable fast BulkOut transfer and BulkIn transfer
• Supports 8 bit/16 bit DMA transfer
• Supports protocol stall
is 3.0 to 3.6 V
• V
CC
• Supporting dual power supply enables 5 V application interface
• Built-in 48 MHz oscillator circuit
• Package options:
44-pin plastic QFP (QFP44-P-910-0.80-2K)(ML60851EGA)
44-pin plastic TQFP (TQFP44-P-1010-0.80-K)(ML60851ETB)
1/84
FEDL60851E-01
I
D
OKI Semiconductor
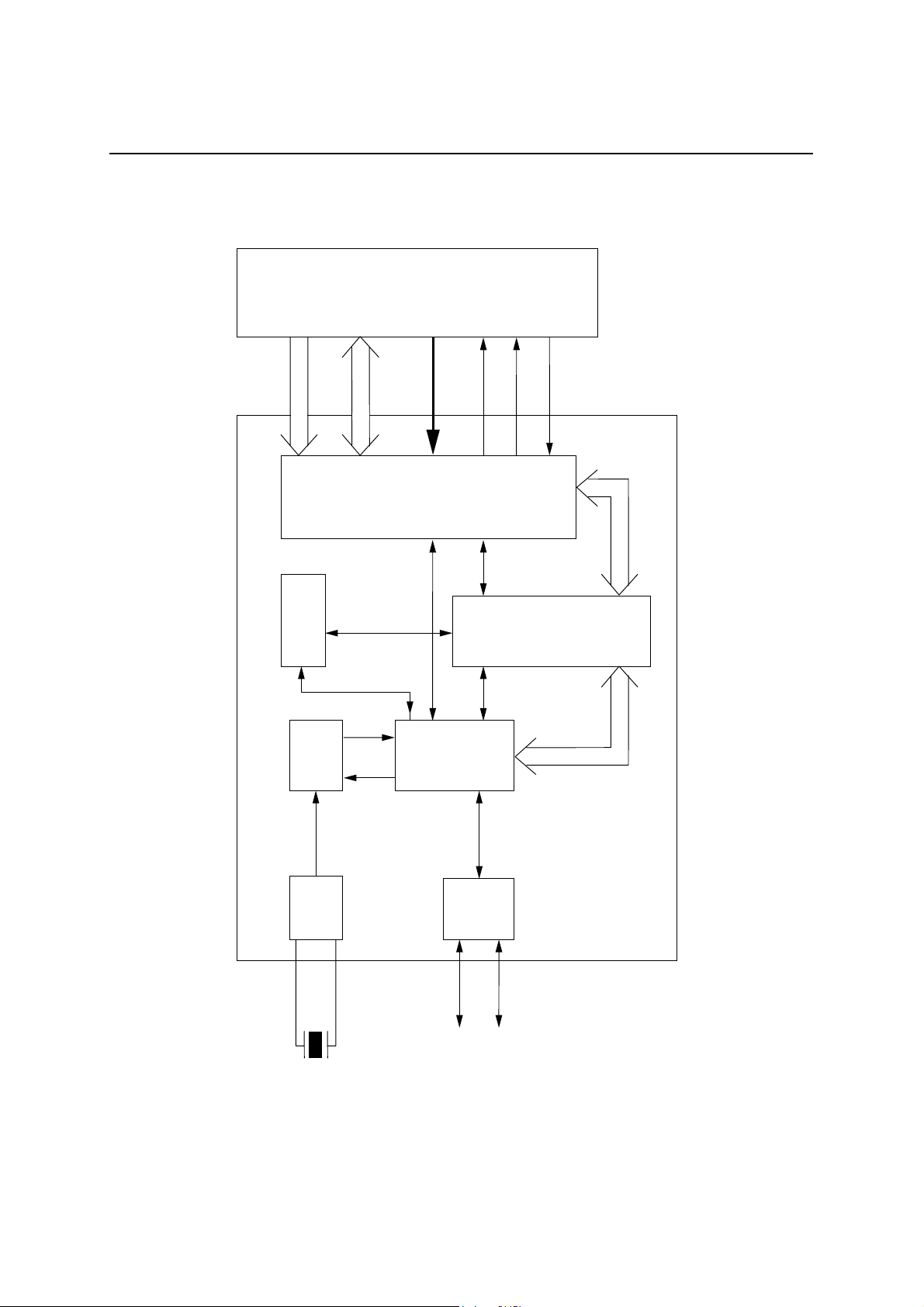
BLOCK DIAGRAM
ML60851E
A7:A0
Status/Control
DPLL
Oscillator
XIN
XOUT
48 MHz
Application
D15:D0
Application
Module
(Local MCU)
RESET
CS, WR, RD
Interface
REQ
NTR
Endpoint FIFO/
8-byte Setup Register
Protocol
Engine
USB
Transceiver
D+ D–
USB Bus
ML60851E
DACK
2/84
FEDL60851E-01
32 31 30 29
24 23 1 2 3 4 5
10 11
–
S
DWR
T
R
A0 A1 A2 A3
D
28 27 26 25
1
6 7 8 9
–
S
D
R
T
R
A4 A5 A6 A7
D
OKI Semiconductor
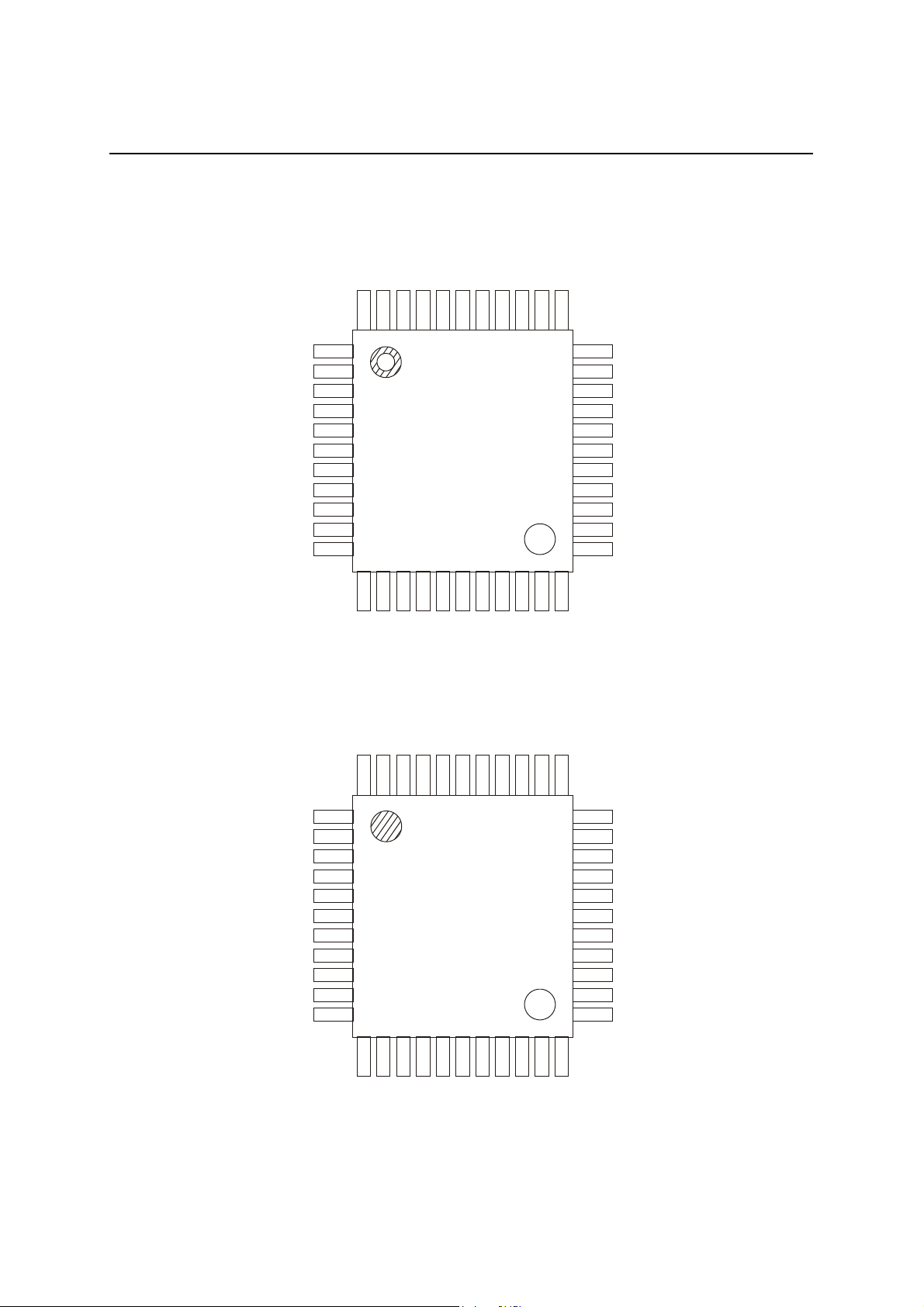
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
D+
D
V
CC3
TEST1
TEST2
XIN
XOUT
C
R
RESE
D+
D
V
CC3
TEST1
TEST2
XIN
XOUT
C
R
W
RESE
AD0 AD1 AD2
4443424140
6
7
8
9
1213141516
INT
AD0 AD1 AD2 V
4443424140
2
3
4
5
10
11
1213141516
INT
CC5
D15
D14
AD3
D13
V
GND
393837
17
D12
GND
AD4 AD5
19
18
CC5
D11
V
44-Pin Plastic QFP
CC5
SS
D15
D14
AD3
D13
V
393837
17
V
D12
SS
AD4 AD5
19
18
CC5
D11
V
44-Pin Plastic TQFP
AD6 AD7
36
35
20
21
D9
D10
AD6 AD7
36
35
20
21
D9
D10
REQ
34
22
D8
REQ
34
22
D8
33
28
27
26
25
33
32
31
30
29
24
23
ML60851E
DACK
A4
A5
A6
A7
ADSEL
ALE
DACK
A0
A1
A2
A3
ADSEL
ALE
3/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
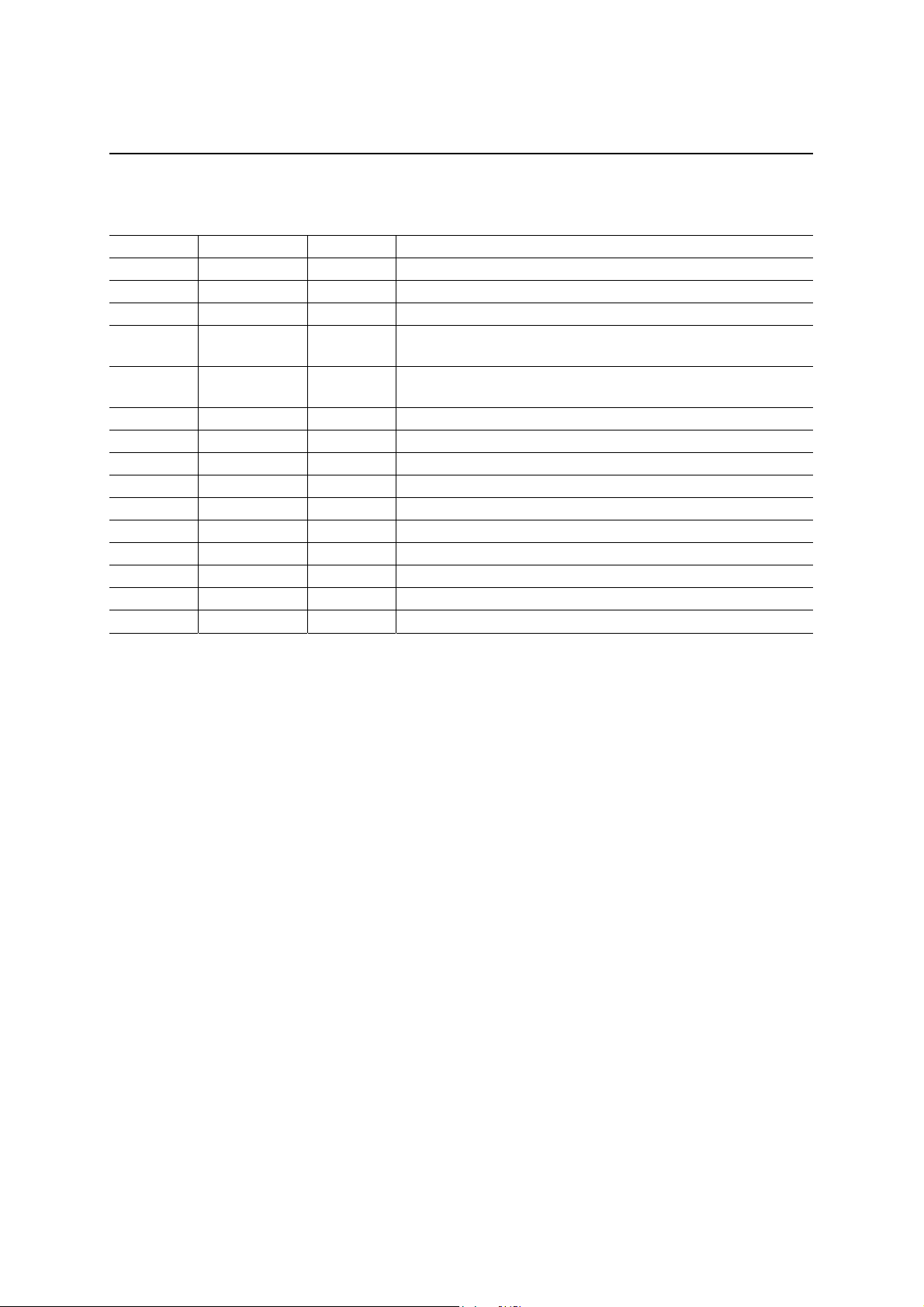
PIN DESCRIPTION
Pin Symbol Type Description
1, 2 D+, D– I/O USB data
6, 7 XIN, XOUT — Pins for external crystal oscillator
4, 5 TEST1, 2 I Test pins (normally “L”)
13 to 16,
19 to 22
35 to 38,
41 to 44
25 to 32 A7 to A0 I Address inputs
8 CS I Chip select signal input pin. LOW active
9 RD I Read signal input pin. LOW active
10 WR I Write signal input pin. LOW active
12 INTR O Interrupt request signal output pin
34 DREQ O DMA request output pin
33 DACK I DMA acknowledge signal input pin
23 ALE I Address latch enable signal input pin
24 ADSEL I Address input mode select input pin. “H”: address/data multiplex
11 RESET I System reset signal input pin. LOW active.
D15 to D8 I/O
AD7 to AD0 I/O
Data bus (MSB)
Data bus (LSB)/address inputs
ML60851E
4/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
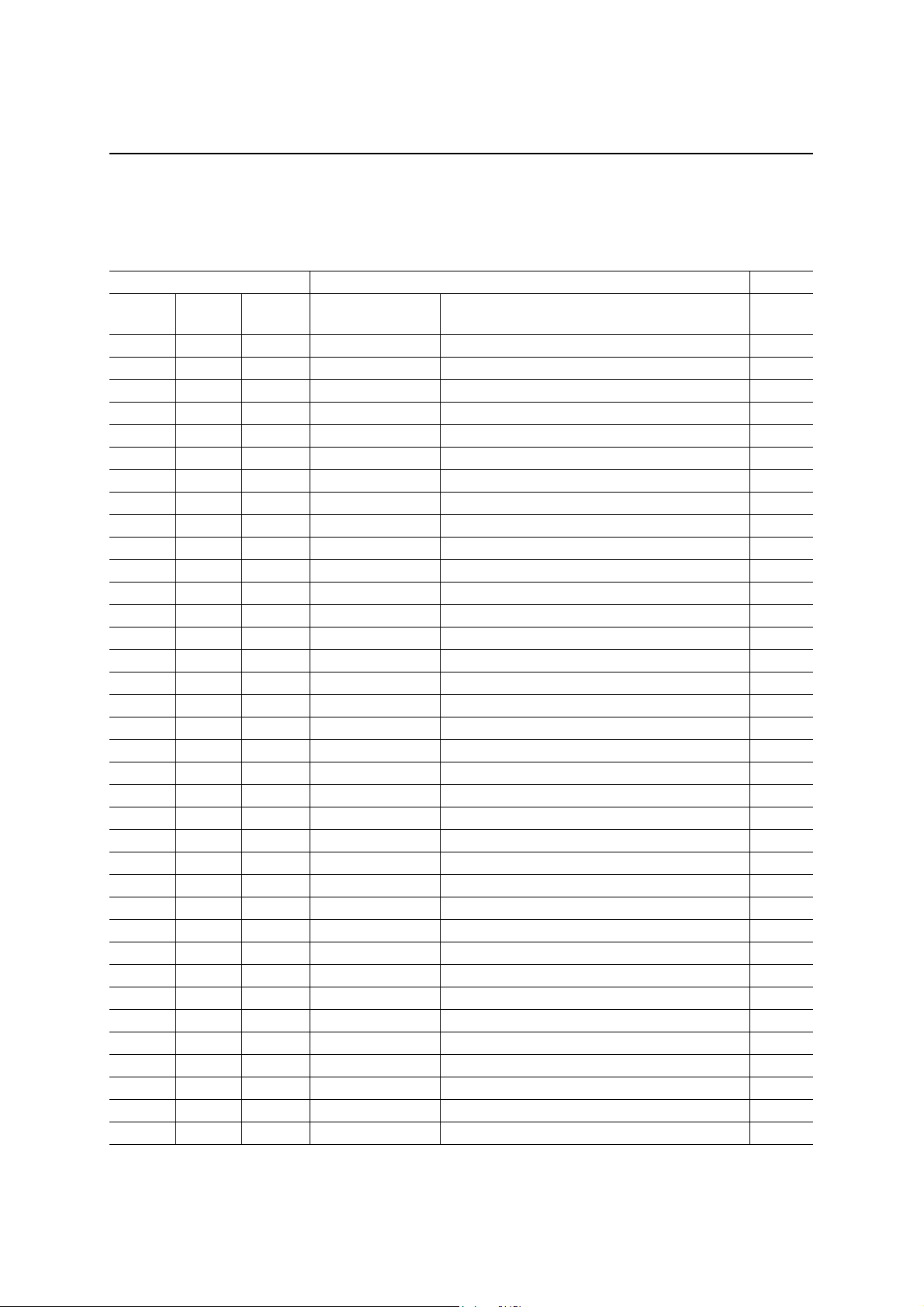
INTERNAL REGISTERS
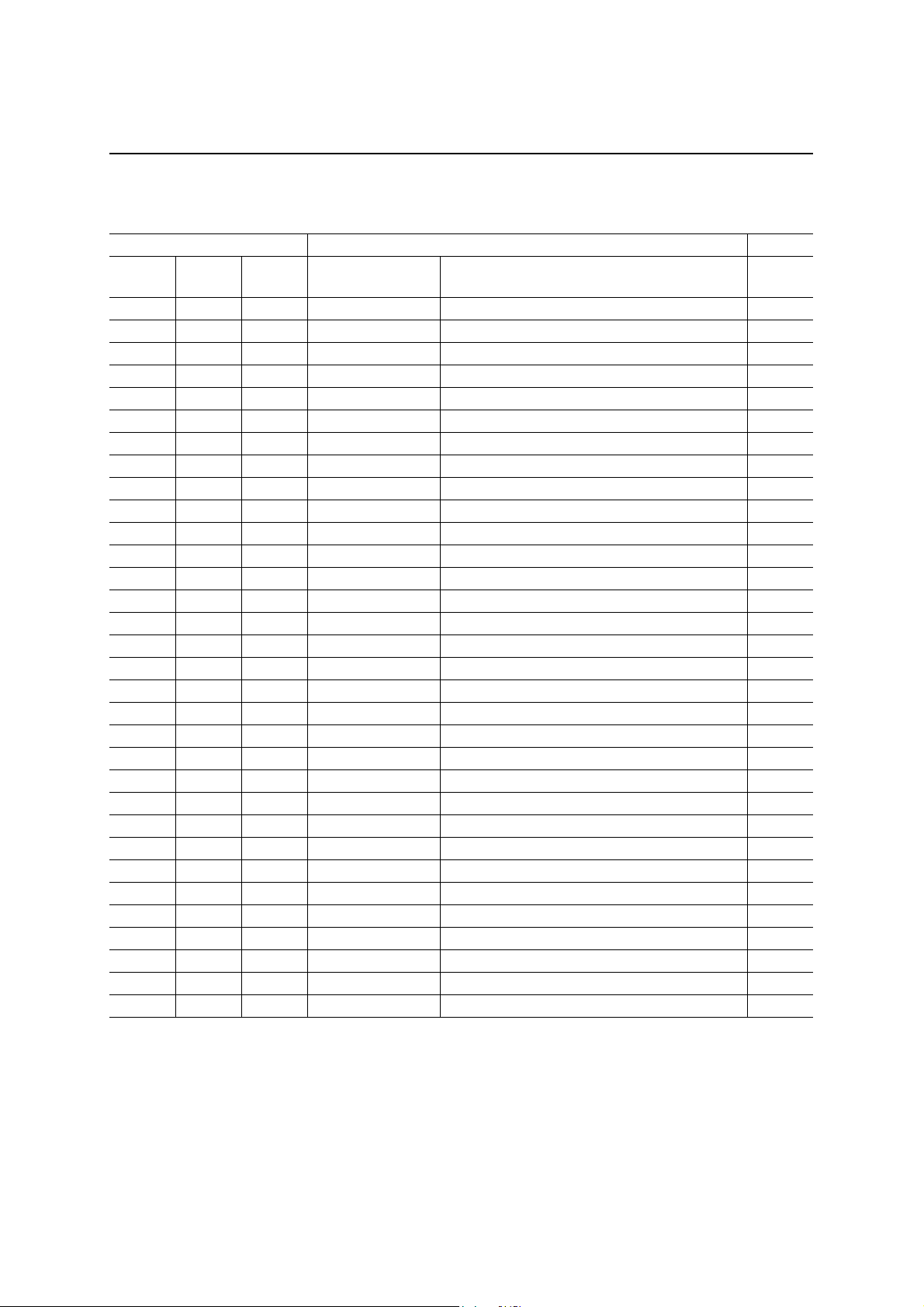
Addresses and Names of Registers
Addresses Register Page
A5:A0
00h 01b — EP0RXFIFO Endpoint 0 Receive FIFO Data 7
01h 01b — EP1RXFIFO Endpoint 1 Receive FIFO Data 7
02h 01b — EP2RXFIFO Endpoint 2 Receive FIFO Data 8
03h 01b — Reserved
00h — 11b EP0TXFIFO Endpoint 0 Transmit FIFO Data 9
01h — 11b EP1TXFIFO Endpoint 1 Transmit FIFO Data 9
02h — 11b EP2TXFIFO Endpoint 2 Transmit FIFO Data 10
03h — 11b EP3TXFIFO Endpoint 3 Transmit FIFO Data 10
00h 11b 01b DVCADR Device Address Register 11
01h 11b 01b DVCSTAT Device Status Register 11
02h 11b — PKTERR Packet Error Register 13
03h 11b — FIFOSTAT1 FIFO Status Register 1 13
04h 11b — FIFOSTAT2 FIFO Status Register 2 14
08h 11b 01b PKTRDY Endpoint Packet-Ready Register 15
09h 11b — EP0RXCNT Endpoint 0 Receive-Byte Count Register 19
0Ah 11b — EP1RXCNT Endpoint 1 Receive-Byte Count Register 19
0Bh 11b — EP2RXCNT Endpoint 2 Receive-Byte Count Register 20
0Ch 11b — Reserved
0Dh 11b — REVISION Revision Register 21
0Eh — 01b CLRFIFO Transmit FIFO Clear Register 21
0Fh — 01b SYSCON System Control Register 22
10h 11b — bmRequest Type BmRequest Type Setup Register 23
11h 11b — bRequest bRequest Setup Register 23
12h 11b — wValue LSB WValue LSB Setup Register 24
13h 11b — wValue MSB WValue MSB Setup Register 24
14h 11b — wIndex LSB WIndex LSB Setup Register 24
15h 11b — wIndex MSB WIndex MSB Setup Register 24
16h 11b — wLength LSB WLength LSB Setup Register 25
17h 11b — wLength MSB WLength MSB Setup Register 25
1Ah 11b 01b POLSEL Assertion Select Register 26
1Bh 11b 01b INTENBL Interrupt Enable Register 27
1Ch 11b — INTSTAT Interrupt Status Register 28
1Dh 11b 01b DMACON DMA Control Register 31
1Eh 11b 01b DMAINTVL DMA Interval Register 32
1Fh — — Reserved
Read
A7, A6
Write
A7, A6
Symbol Register name
5/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
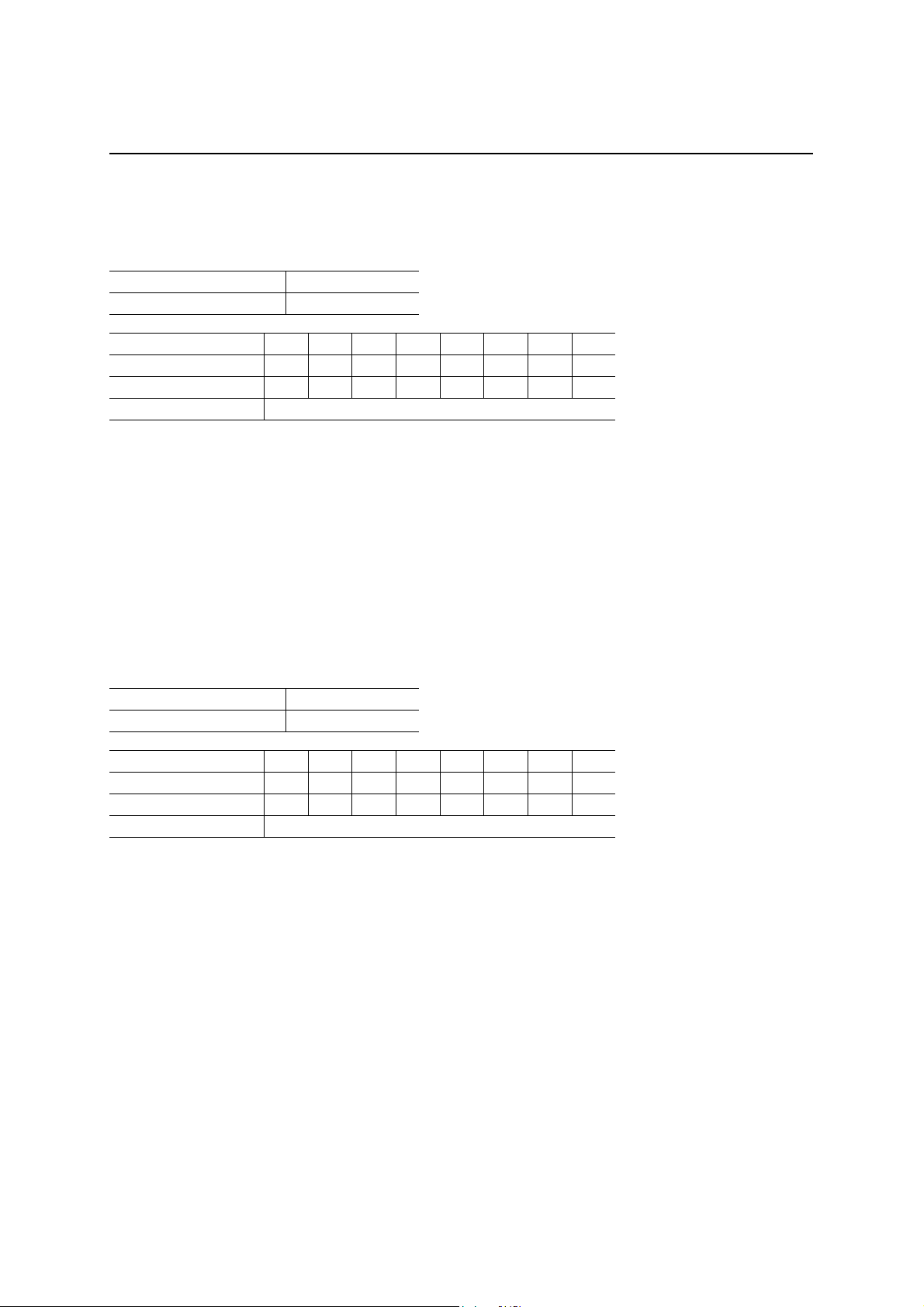
Addresses and Names of Registers (Continued)
Addresses Register Page
A5:A0
20h 11b — EP0RXCON Endpoint 0 Receive Control Register 33
21h 11b — EP0RXTGL Endpoint 0 Receive Data Toggle Register 33
22h 11b 01b EP0RXPLD Endpoint 0 Receive Payload Register 34
23h — — Reserved
24h 11b 01b EP1CON Endpoint 1 Control Register 35
25h 11b 01b EP1TGL Endpoint 1 Data Toggle Register 36
26h 11b 01b EP1PLD Endpoint 1 Payload Register 36
27h — — Reserved
28h — — Reserved
29h — — Reserved
2Ah — — Reserved
2Bh — — Reserved
2Ch — — Reserved
2Dh — — Reserved
2Eh — — Reserved
2Fh — — Reserved
30h 11b — EP0TXCON Endpoint 0 Transmit Control Register 37
31h 11b — EP0TXTGL Endpoint 0 Transmit Data Toggle Register 37
32h 11b 01b EP0TXPLD Endpoint 0 Transmit Payload Register 38
33h 11b 01b EP0STAT Endpoint 0 Status Register 39
34h 11b 01b EP2CON Endpoint 2 Control Register 41
35h 11b 01b EP2TGL Endpoint 2 Data Toggle Register 42
36h 11b 01b EP2PLD Endpoint 2 Payload Register 42
37h — — Reserved
38h 11b 01b EP3CON Endpoint 3 Control Register 43
39h 11b 01b EP3TGL Endpoint 3 Data Toggle Register 44
3Ah 11b 01b EP3PLD Endpoint 3 Payload Register 44
3Bh — — Reserved
3Ch — — Reserved
3Dh — — Reserved
3Eh — — Reserved
3Fh — — Reserved
Read
A7, A6
Write
A7, A6
Symbol Register name
6/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
FUNCTIONS OF REGISTERS
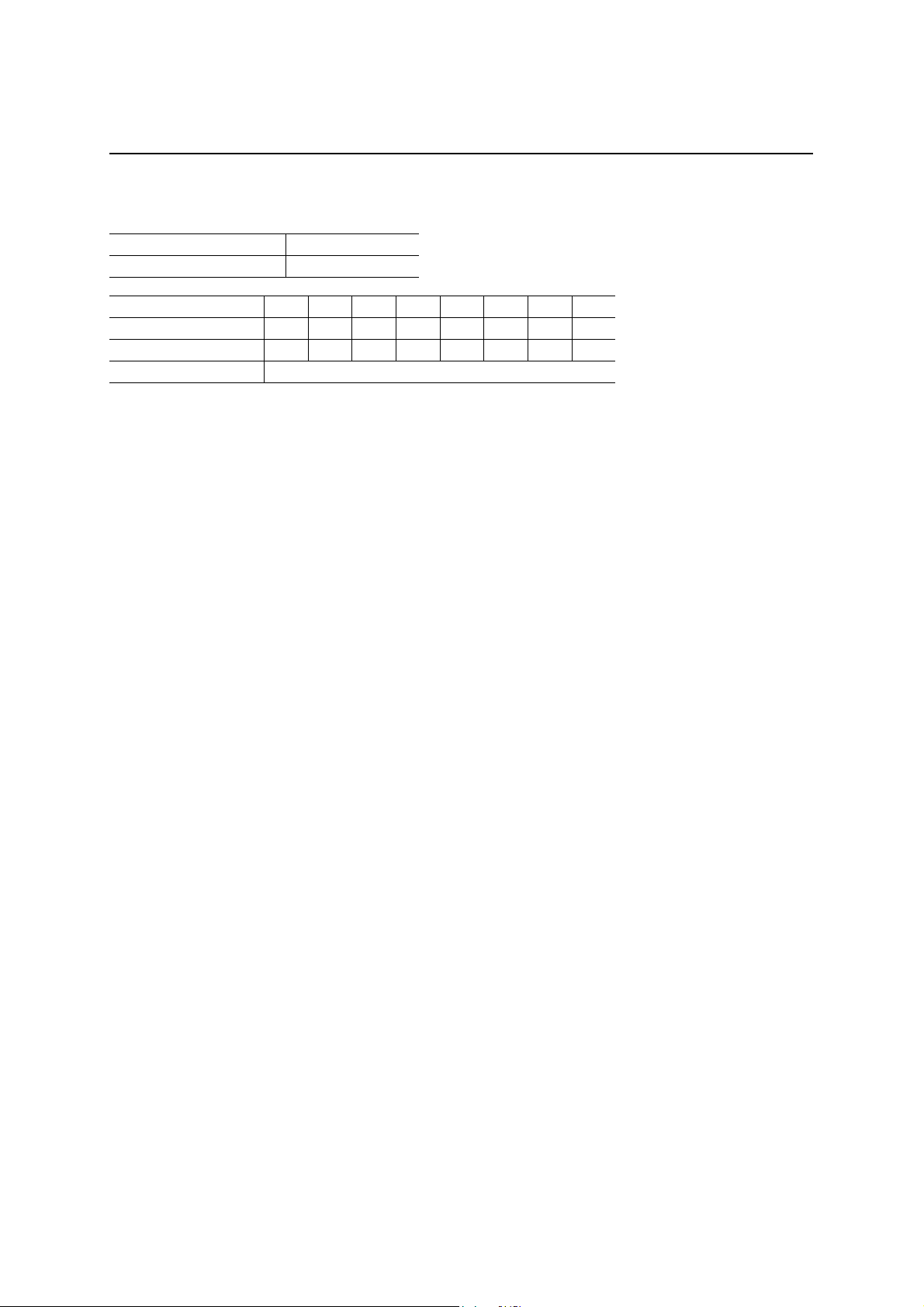
End Point 0 Receive FIFO (EP0RXFIFO)
Read address 40h
Write address —
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset × × × × × × × ×
After a bus reset × × × × × × × ×
Definition EP0 Receive data (R)
The receive data from the host computer in the data state during a c ontrol Write transfer is store d in EP0RXFIFO .
The EP0 receive data can be read out by the local MCU through reading the address 40h when the ML60851E
issues an EP0 receive packet ready interrupt request. It is possible to read successively the data in the packet by
reading continuously.
The EP0RXFIFO is cleared under the following conditions:
1. When the local MCU resets the EP0 receive packet ready bit (A “1” is written in PKTRDY(0)).
2. When a setup packet is received.
3. When the local MCU writes a “0” in the stall bit (EP0STAT(2)).
End Point 1 Receive FIFO (EP1RXFIFO)
Read address 41h
Write address —
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset × × × × × × × ×
After a bus reset × × × × × × × ×
Definition EP1 Receive data (R)
It is possible to read out the EP1 receive data by reading the address 41h. When EP1 is set for bulk reception
(BULK OUT), The local MCU should read EP1RXFIFO when the ML60851E issues an EP1 packet ready
interrupt request. It is possible to read successively the data in the packet by reading continuously. When the data
transfer direction of EP1 is set as “Transmit”, all accesses to this address will be invalid.
The EP1RXFIFO is cleared under the following conditions:
1. When an OUT token is received for EP1.
2. When the EP1 receive packet ready bit is reset. (A “1” is written in PKTRDY(1).)
3. When the local MCU writes a “0” in the stall bit (EP1CON(1)).
Even when a DMA read with a 16-bit width is made from EP1RXFIFO, the address is A7:A0 = 41h.
7/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
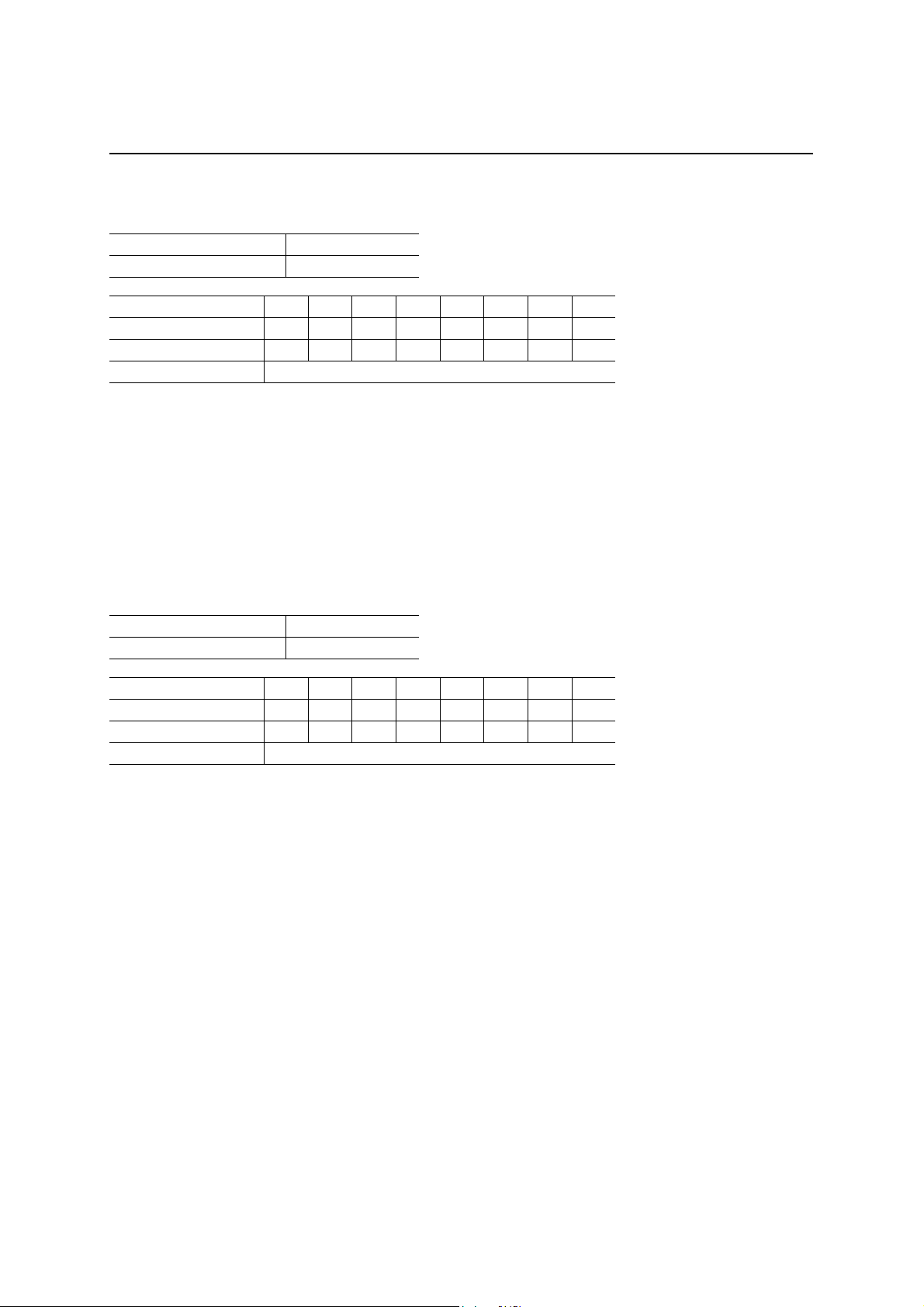
End Point 2 Receive FIFO (EP2RXFIFO)
Read address 42h
Write address —
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset × × × × × × × ×
After a bus reset × × × × × × × ×
Definition EP2 Receive data (R)
It is possible to read out the EP2 receive data by readin g the address 42h. When EP2 is set for bulk reception (Bulk
OUT), the local MCU should read EP 2RXFIFO when the M L60851E issues an EP2 packet ready interrupt request.
It is possible to read successively the data in the packet by reading continuously. When the data transfer direction
of EP2 is set as ‘Transmit’, all accesses to this address will be invalid.
The EP2RXFIFO is cleared under the following conditions:
1. When an OUT token is received for EP2.
2. When the EP2 receive packet ready bit is reset. (A “1” is written in PKTRDY(2).)
3. When the local MCU writes a “0” in the stall bit (EP2CON(1)).
8/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
End Point 0 Transmit FIFO (EP0TXFIFO)
Read address —
Write address C0h
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset × × × × × × × ×
After a bus reset × × × × × × × ×
Definition EP0 Transmit data (W)
EP0 transmit data can be written in by writing to the address C0h. The receive data from the host in the data stage
during a control read transfer is stored in EP0TXFIFO. When the ML60851E issues an EP0 transmit packet ready
interrupt request, the local MCU writes the transmit data to the address C0h. It is possible to write the packet data
successively by writing continuously.
The EP0 TXFIFO is cleared under the following conditions:
1. When an ACK is received from the host for the data transmission from EP0.
2. When a setup packet is received.
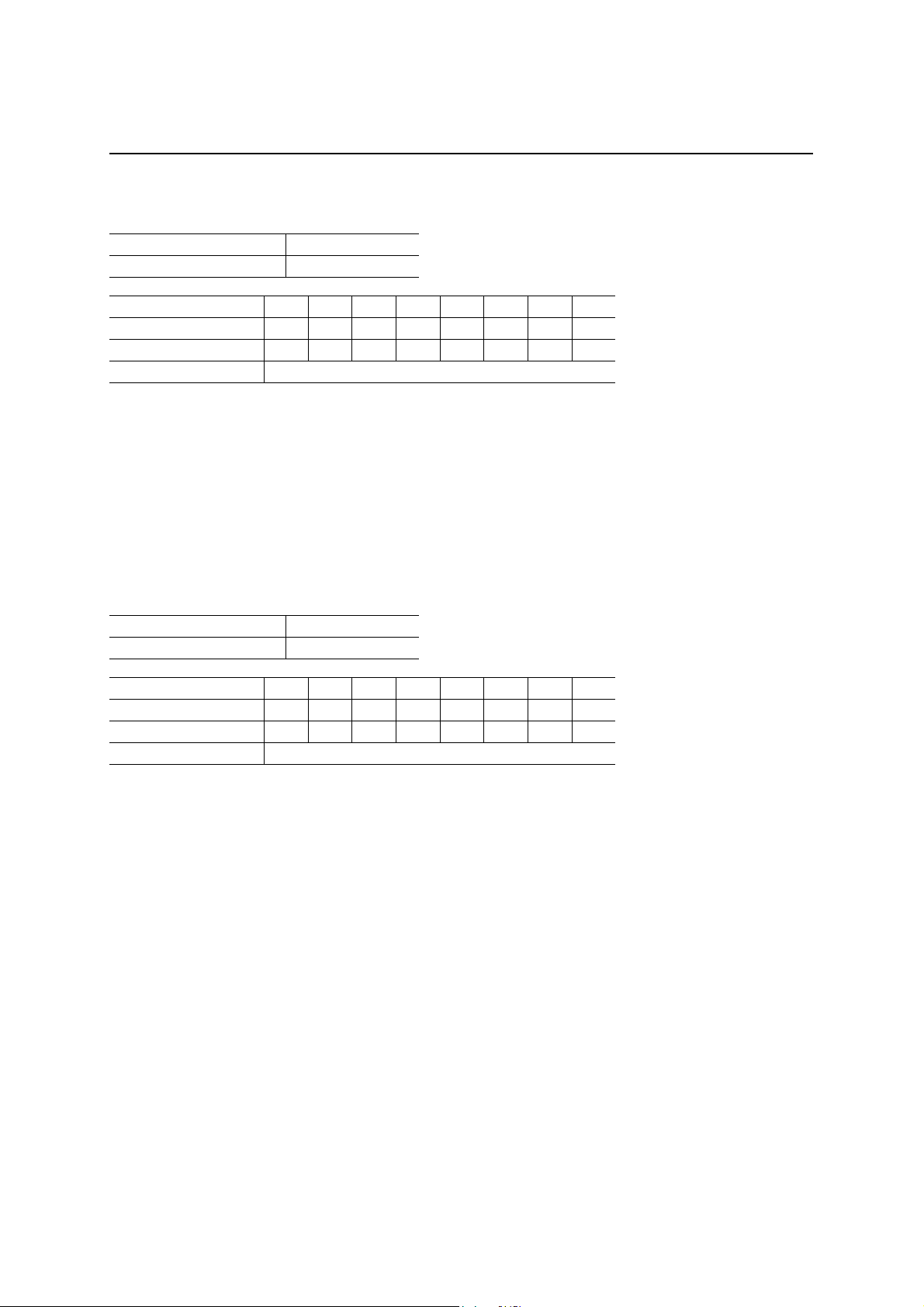
End Point 1 Transmit FIFO (EP1TXFIFO)
Read address —
Write address C1h
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset × × × × × × × ×
After a bus reset × × × × × × × ×
Definition EP1 Transmit data (W)
The EP1 transmit data can be written in by writing to the address C1h. When EP1 has been set for bulk
transmission (BULK IN), The local MCU should write the transmit data in EP1TXFIFO wh en the ML60851E
issues an EP1 packet ready interrupt request. It is possible to write the packet data successively by writing
continuously. When the data transfer direction of EP1 is set as ‘Receive’, all accesses to this address will be
invalid.
The EP1 transmit FIFO is cleared under the following conditions:
1. When an ACK is received from the host for the data transmission from EP1.
2. When the local MCU writes a “1” in the EP1FIFO clear bit (CLRFIFO(1)).
Even when a DMA write with a 16-bit width is made in EP1TXFIFO, the address is A7:A0 = 41h.
9/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
End Point 2 Transmit FIFO (EP2TXFIFO)
Read address —
Write address C2h
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset × × × × × × × ×
After a bus reset × × × × × × × ×
Definition EP2 Transmit data (W)
EP2 transmit data can be written in by writing to the address C2h. When EP2 has been set for bu lk transmission
(BULK IN), the local MCU should write the transmit data in EP2TXFIFO when the ML60851E issues an EP2
packet ready interrupt request. It is possible to write the packet data successively by writing continuously. When
the data transfer direction of EP2 is set as “Receive”, all accesses to this address will be invalid.
The EP2 TXFIFO is cleared under the following conditions:
1. When an ACK is received from the host for the data transmission from EP2.
2. When the local MCU writes a “1” in the EP2FIFO clear bit (CLRFIFO(2)).
End Point 3 Transmit FIFO (EP3TXFIFO)
Read address —
Write address C3h
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset × × × × × × × ×
After a bus reset × × × × × × × ×
Definition EP3 Transmit data (W)
EP3 transmit data can be written in by writing to the address C3h. The local MCU should write the transmit data in
EP3TXFIFO when ML60851E issues an EP3 packet ready interrupt request. It is possible to write the packet data
successively by writing continuously.
The EP3 TXFIFO is cleared under the following conditions:
1. When an ACK is received from the host for the data transmission from EP3.
2. When the local MCU writes a “1” in the EP3FIFO clear bit (CLRFIFO(3)).
10/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
Device Address Register (DVCADR)
Read address C0h
Write address 40h
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
After a bus reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Definition Device address (R/W)
The local MCU writes in this register the device address given by the SET_ADDRESS command from the host.
Thereafter, ML60851E responds only to tokens specifying this address among all the tokens from the host
computer. The default value for this register, is the default address 00h (D6:D0=00) which is specified in USB
specifiacations.
Note 1: It is possible to carry out addressing using a 7-bit address because up to 127 devices can be
connected according to the USB standard.
Note 2: Bit D7 is fixed at “0”, and even if a “1” is written in bit D7, it will be invalid.
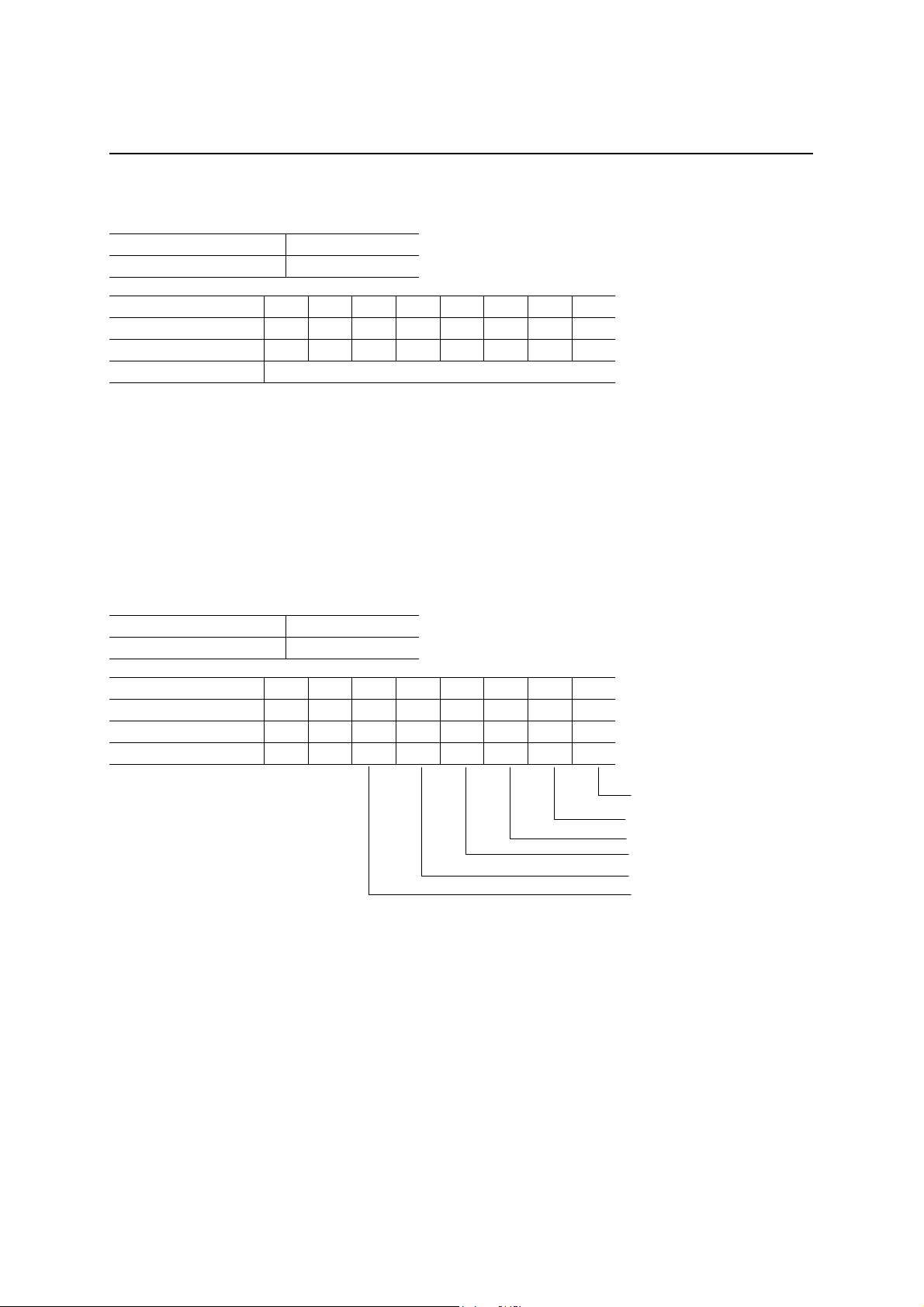
Device Status Register (DVCSTAT)
Read address C1h
Write address 41h
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
After a bus reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
Definition 0 0
Default state (R/W)
Address state (R/W)
Configuration state (R/W)
Suspend state (R)
Remote wake-up (R/W)
USB bus reset status clear (W)
This is a register for displaying the status of the device. The functions of the different bits are described below:
Bits D7 and D6 are fixed at “0” and even if a “1” is written in these bits, the write operatio n will be invalid.
Default state:
This bit is asserted in the initial state. The default state is valid from the time the power is switched ON
and the hardware resetting is complete. There is no need to write a “0” in this bit.
Address state:
Whe n a SET_ADDRESS request arrives, th e local MCU writes the device address in the device address
register. If necessary, by writing a “1” in this bit also at that time, it is possible to give an indication that
the ML60851E has entered the address state. Since the content of this bit does not affect the operation
of the ML60851E, there is no need to write in this bit if it will not be read out.
11/84

FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
Configuration state:
Thi s bit is used as an indicati on of whethe r the devi ce has entered the configuration state. The content of
this bit does not affect the operation of ML60851E and hence, it is not necessary to write to it.
If a SET_CONFIGURATION request is received from the host when the device is in the address state,
the local MCU should assert the configuration bits of EP1CON, EP2CON, or EP3CO N. At this time, it
may be useful to write a “1” to this bit to indicate that the device has entered the configuration state.
Remarks:
When all these three states are “1”, it means that this IC is normally operating. However, since Default
state bit, Address state bit and Configuration state bit do not affect the operation of the ML60851E,
there is no need to write in these bits if they will not be read out.
Suspend state:
When the idle condition continues for more than 3ms in the USB bus, the ML60851E automatically
asserts this bit thereby indicating that it is going into the suspend state. At the same time, bit D6 of the
interrupt status register INTSTAT is asserted and the INTR pin is asserted. With this, the lo cal MCU
can suppress the current consumption.
This bit is deasserted when the EOP of any type of packet is received.
Remote wake-up:
The ML60851E is in the suspend state, the remote wake-up functio n is activated when the local MCU
asserts this bit. When this bit is written while 5ms have not yet elapsed in the idle condition, the remote
wake-up signal is output aft er waiting for t he idle condition t o continue for the full 5ms per iod. Further,
when this bit is written after the idle condition has persisted for 5ms or more, the remote wake-up signal
is output immediately after this bit is written. This bit is deasserted automatically when th e suspend
state is released by receiving the resume instruction over the USB bus.
USB bus reset status clear:
When the ML60851E is in the USB bus reset interrupt state (bit D5 of the interrupt status register, that is
the USB bus reset interrupt status bit is “1” and the INTR pin is asserted), it is possible to clear the
interrupt status by writing a “1” in this bit. (This makes the USB bus reset interrupt status bit “0” and
deassertes INTR.) Although this bit can be read out, the read out value will always be “0”.
12/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
Packet Error Register (PKTERR)
Read address C2h
Write address —
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
After a bus reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Definition 0 0 0 0
Bit stuff error (R)
Data CRC error (R)
Address CRC error (R)
PID Error (R)
Each bit is asserted when the corresponding error occurs and is deasserted when SOP is received.
This register is used to report the error i nformat ion. This r egister is use ful for t he tests during developm ent, or fo r
preparing the error frequency measurement report. This register is not required by USB Specifications.
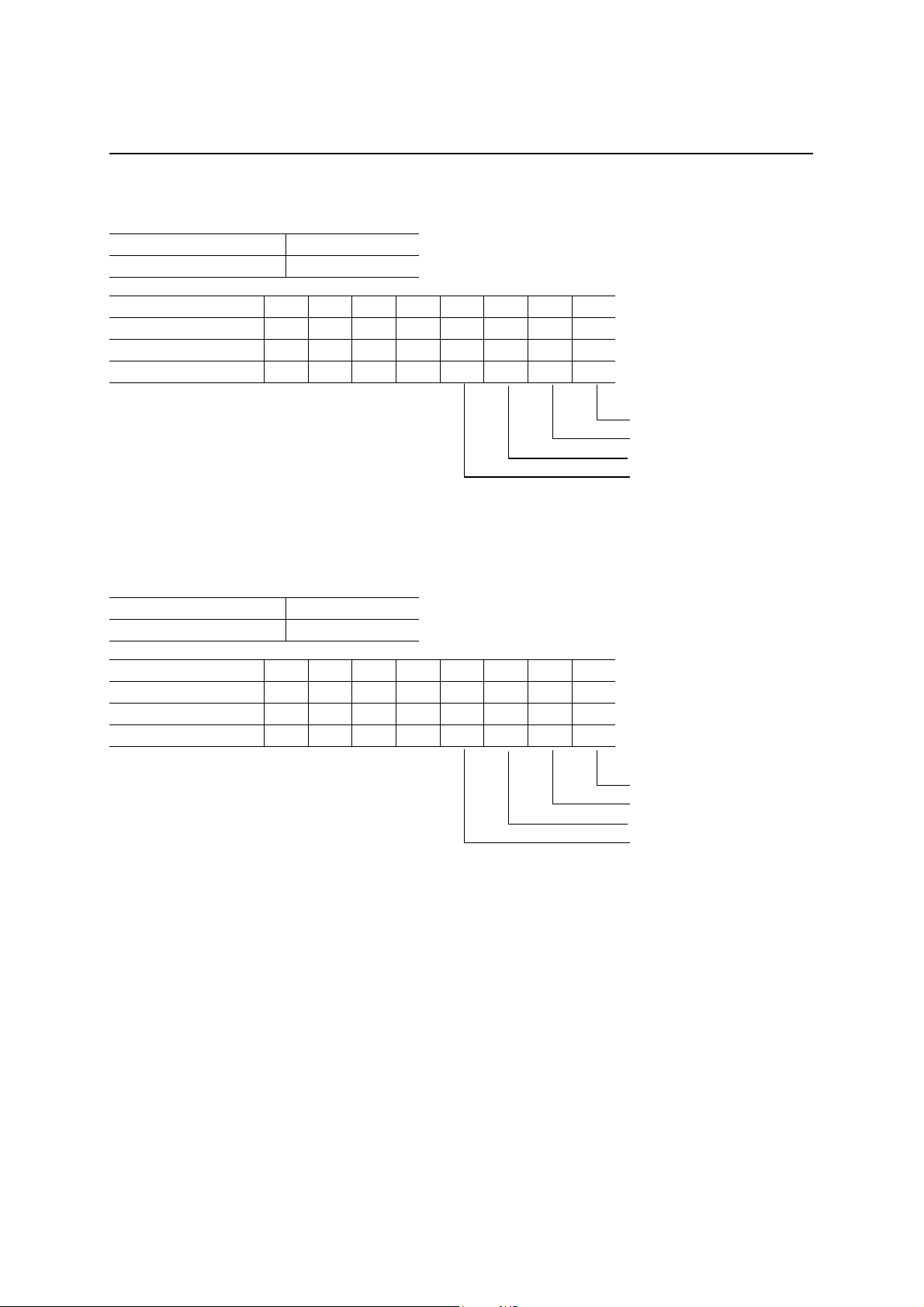
FIFO Status Register 1 (FIFOSTAT1)
Read address C3h
Write address —
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0
After a bus reset 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0
Definition 0 0 0 0
Receive FIFO0 Full (R)
Receive FIFO0 Empty (R)
FIFO1 Full (R)
FIFO1 Empty (R)
This register reports the status of EP0RXFIFO and the FIFO for EP1. Normally, there is no need to read this
register because it is sufficient to read the packet ready status before reading out or writing in a FIFO.
Receive FIFO0 Full: This bit becomes “1” when 8-bytes of data are stored in the EP0RXFIFO. This bit is
not set to “1” when a packet less than 8 bytes long (a short packet) is stored in.
Receive FIFO0 Empty: This bit will be “1” when EP0RXFIFO is empty.
FIFO1 Full: This bit becomes “1” when 64 bytes of data is stored in the FIFO for EP1. This is true
during both transmission and reception. This bit does not become “1” in the case of a
short packet. The FIFO for EP1 has a two-layer structure and can store up to 128
bytes of data. This bit indicates the status of the FIFO in which data is being written at
that time. In other words, this bit indicates the status of the FIFO into which the host
computer is writing data when EP1 is receiving data, and of the FIFO into which the
local MCU is writing data when EP1 is transmitting data.
FIFO1 Empty: This bit becomes “1” when the FIFO for EP1 is empty. This is true during both
transmission and reception. The FIFO for EP1 has a two-l ayer structure and ca n store
up to 128 bytes of data. This bit indicates the status of the FIFO which is being read
out at that time.
13/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
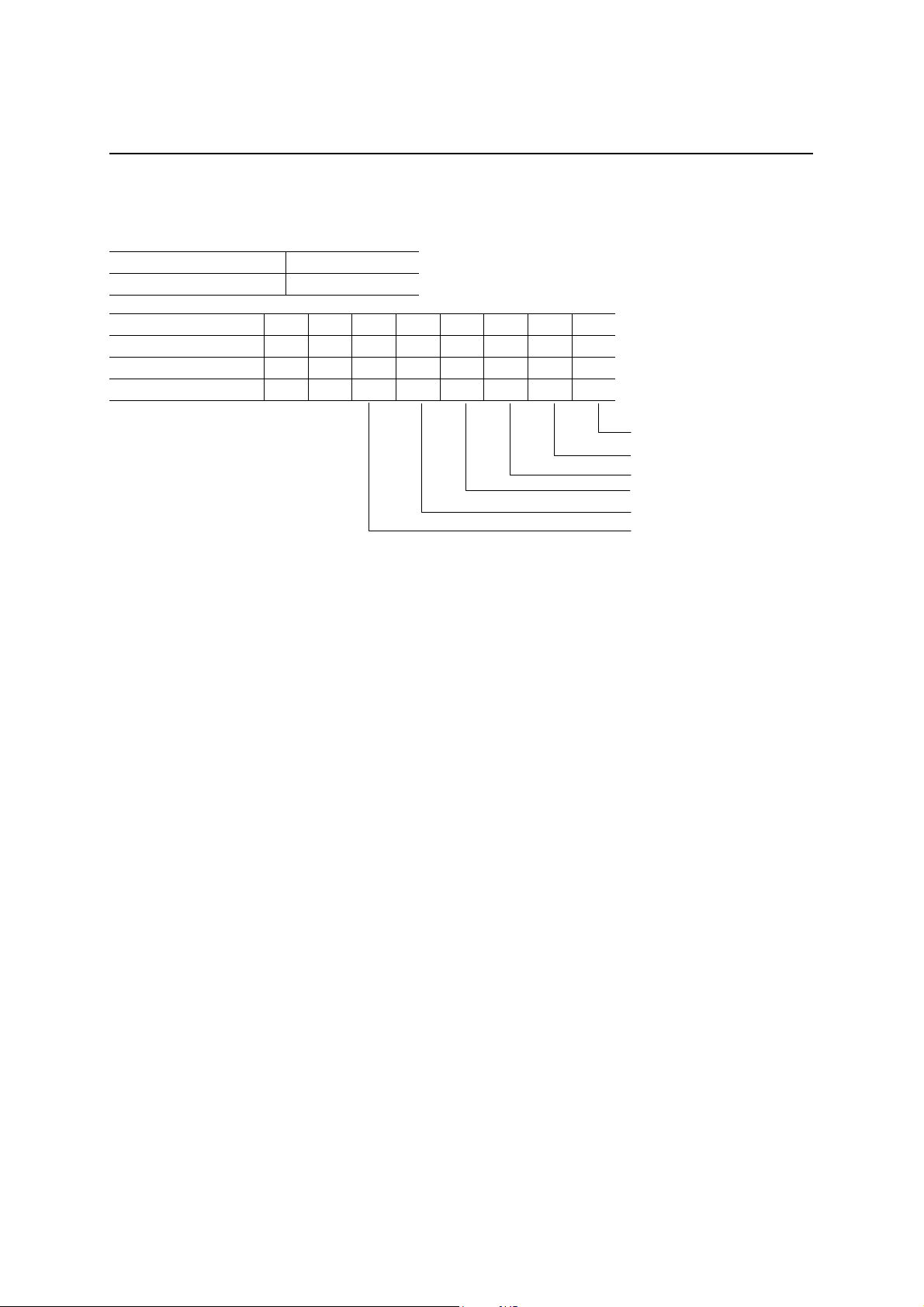
FIFO Status Register 2 (FIFOSTAT2)
Read address C4h
Write address —
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
After a bus reset 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
Definition 0 0
Transmit FIFO0 Full (R)
Transmit FIFO0 Empty (R)
FIFO2 Full (R)
FIFO2 Empty (R)
FIFO3 Full (R)
FIFO3 Empty (R)
This register reports the status of the EP0T XFIFO, the FIFO for EP2, and the FIFO for EP3. Normally, there is no
need to read this register because it is sufficient to read the packet ready status before reading out or writing in a
FIFO.
Transmit FIFO0 Full: This bit becomes “1” when 8-bytes of data is stored in the EP0TXFIFO. This bit is
not set to “1” when a packet less than 8 bytes (a short packet) is written in.
Transmit FIFO0 Empty: This bit will be “1” when the EP0 transmit FIFO0 is empty.
FIFO2 Full: This bit becomes “1” when 64 bytes of data is either stored or written in the FIFO for
EP2. This bit does not become “1” in the case of a short packet.
FIFO2 Empty: This bit becomes “1” when the FIFO of EP2 is empty.
FIFO3 Full: This bit becomes “1” when 64 bytes are written in the FIFO for EP3. This bit does not
become “1” in the case of a short packet.
FIFO3 Empty: This bit becomes “1” when the FIFO for EP3 is empty.
14/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
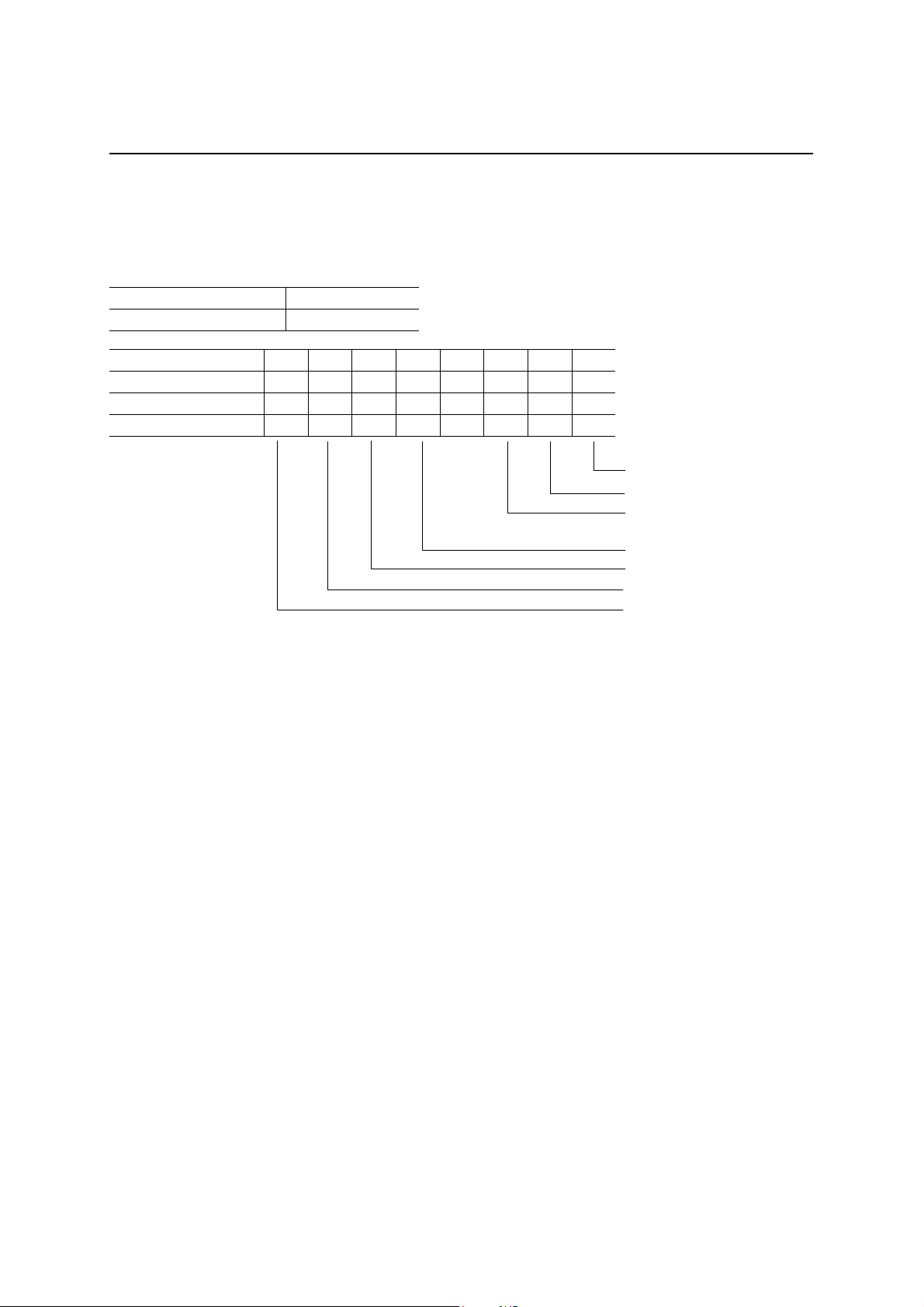
End Point Packet Ready Register (PKTRDY)
This register indicates whether or not the preparations for reading out or writing in a packet data have been
completed. In addition, this register is also used for controlling the handshake packet (ACK/NAK)
Read address C8h
Write address 48h
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
After a bus reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Definition 0
EP0 Receive packet ready (R/Reset)
EP1 Receive packet ready (R/Reset)
EP2 Receive packet ready (R/Reset)
EP0 Transmit packet ready (R/Set)
EP1 Transmit packet ready (R/Set)
EP2 Transmit packet ready (R/Set)
EP3 Transmit packet ready (R/Set)
This register in conjunction with INTENBL register is used for controlling the read/write operation of
ML60851E’s transmit and receive FIFOs. The interrupt generation and disassertion of ML60851E is closely
related to the bits in PKTRDY register and the corresponding fields in INTENBL register.
During normal operation, when ML60851E is receiving data from the host, the data packet received succussfully
without any errors will be stored in the corresponding Rx FIFO of ML60851E, at which point ML60851E will
automatically assert its Receive Packet Ready bit and generate an interrupt cause. At this time if interrupt for the
particular endpoint has been enabled in the INTENBL register, th e corresponding interrupt status bit in register
INTSTAT will be asserted and an interrupt will be generated.
In a transmit operation, when ML60851E is sending data to the host, an ACK pack et received from the host in
response to succussful transmission of a packet will cause ML60851E to automatically deassert (set to “0”) the
corresponding endpoint’s transm it packet ready bit and henc e, generat e an inte rrupt cause. To transm it subse quent
packets from this same end point, the local MCU sets the corresponding transmit packet ready bit after completion
of interrupt servicing (such as writing data in the corresponding transmit FIFO, etc.).
Bit D3 is fixed at “0”, and even if a “1” is written in this bit, that write operation will be invalid.
The operations of the different bits of PKTRDY are described in detail below.
Please note the R/Reset and R/Set notation used above. R/Reset means: the bit field can be read by the local
MCU/and it is Reset (to ‘0’) when a “1” is written to it. The R/Set means: the bit field can be read by the local
MCU/and it is Set (to ‘1’) when a 1 is written to it.
15/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
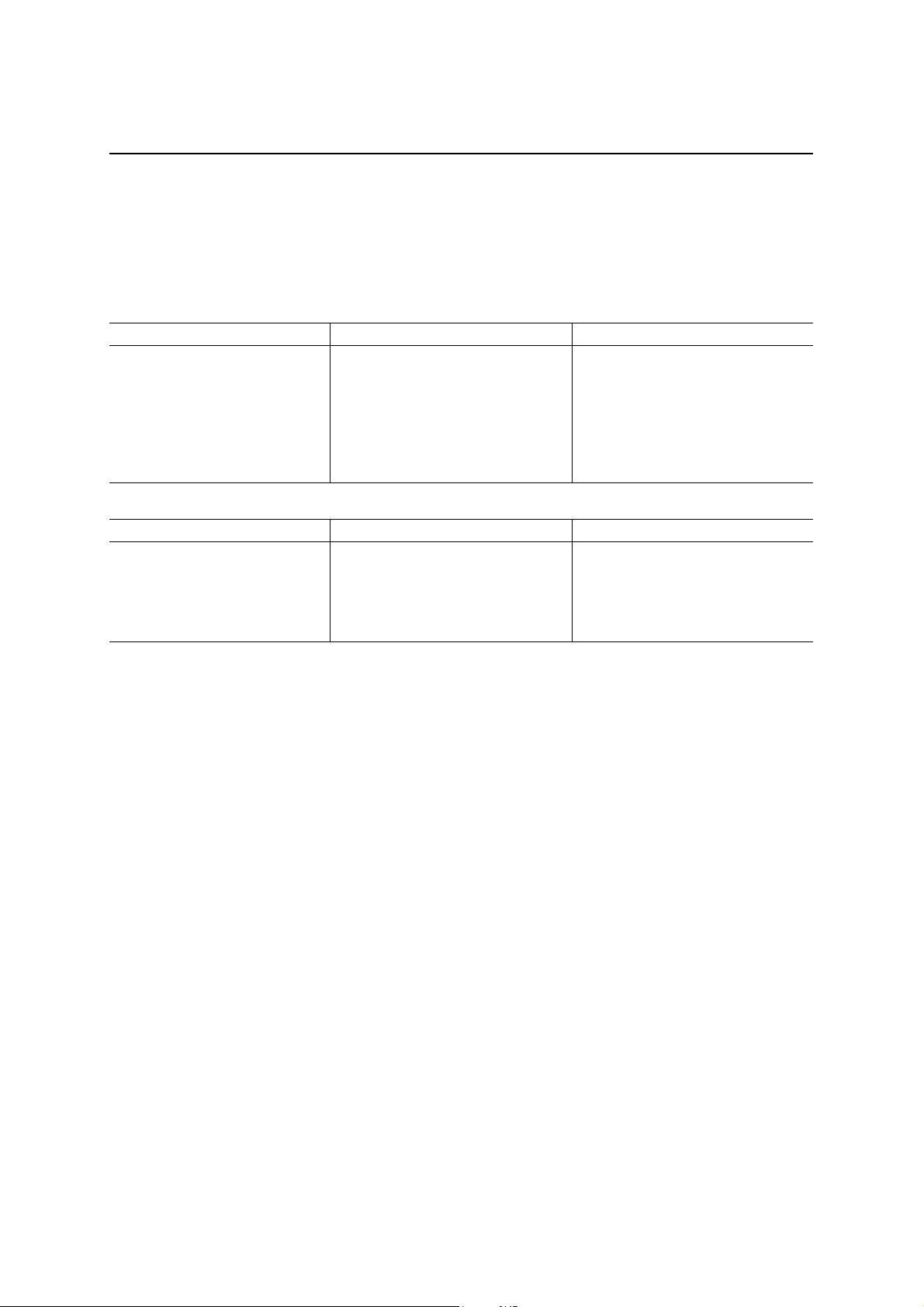
EP0 Receive packet ready bit (D0)
This bit can be read by the local MCU. Further, this bit can be set to “0” by writing “1” to the D0 bit.
The conditions of asserting and deasserting this bit are the following.
Bit name Asserting condition Action when asserted
EP0 Receive packet ready (D0) 1. When data is received in EP0
and storing of one packet of
receive data in EP0RXFIFO is
completed.
2. When a setup packet is received
during a control Read or a
control Write transfer.
EP0 is locked (that is, an NAK is
returned automatically when a data
packet is received from the host
computer).
(In the case of the asserting
condition 1, the local MCU can read
EP0RXFIFO.)
Bit name Deasserting condition Action when deasserted
EP0 Receive packet ready (D0) 1. When the local MCU resets
(writes a “1” in) this bit.
2. When the local MCU resets the
setup ready bit during a control
Write transfer.
Reception is possible in EP0.
R/Reset: Reading possible/ Reset when a “1” is written
R/Set: Reading possible/ Set when a “1” is written
ML60851E
16/84

FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
EP1 Receive Packet Ready Bit (D1)
This bit can be read by the local MCU. Further, this bit can be set to “0” by writing “1” to the D1 bit.
The conditions of asserting and deasserting this bit are the following. EP1 has a two-layer FIFO, and the packet
ready bits are present independently for layer A and layer B. The switching between these two layers is done
automatically by the ML60851E. For detailed description of double layered FIFO operation, please refer to page
77 of this manual.
Bit name Asserting condition Action when asserted
EP1 Receive packet ready (D1) When an error-free packet is
received in either layer A or layer B.
The local MCU can read the
EP1RXFIFO. EP1 is locked when
both layer A and layer B have
received a packet data.
Bit name Deasserting condition Action when deasserted
EP1 Receive packet ready (D1) When the local MCU resets (writes a
“1”) in the bits of both layer A and
layer B.
Reception is possible in EP1 when at
least one of the bits of layer A and
layer B has been reset.
See the explanation of the operation of the two-layer FIFO given in the Section on ‘Functional Description’.
EP2 Receive Packet Ready Bit (D2)
This bit can be read by the local MCU. Further, this bit can be set to “0” by writing “1” to the D2 bit.
The conditions of asserting and deasserting this bit are the following.
Bit name Asserting condition Action when asserted
EP2 Receive packet ready (D2) When an error-free packet is
received.
EP2 is locked. In other words, an
NAK is returned automatically when
a data packet is received from the
host computer.
Bit name Deasserting condition Action when deasserted
EP2 Receive packet ready (D2) When the local MCU resets (writes a
“1” in) this bit.
Data reception is possible in EP2.
EP0 Transmit Packet Ready Bit (D4)
This bit can be read by the local MCU. Further, this bit can be set to “1” by writing “1” to the D4 bit.
The conditions of asserting and deasserting this bit are the following.
Bit name Asserting condition Action when asserted
EP0 Transmit packet ready (D4) When the local MCU sets this bit. Data transmission is possible from
EP0.
Bit name Deasserting condition Action when deasserted
EP0 Transmit packet ready (D4) 1. When an ACK is received from the
host computer in response to the
data transmission from EP0.
2. When a setup packet is received.
EP0 is locked. In other words, an
NAK is returned automatically when
an IN token is received from the host
computer.
17/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
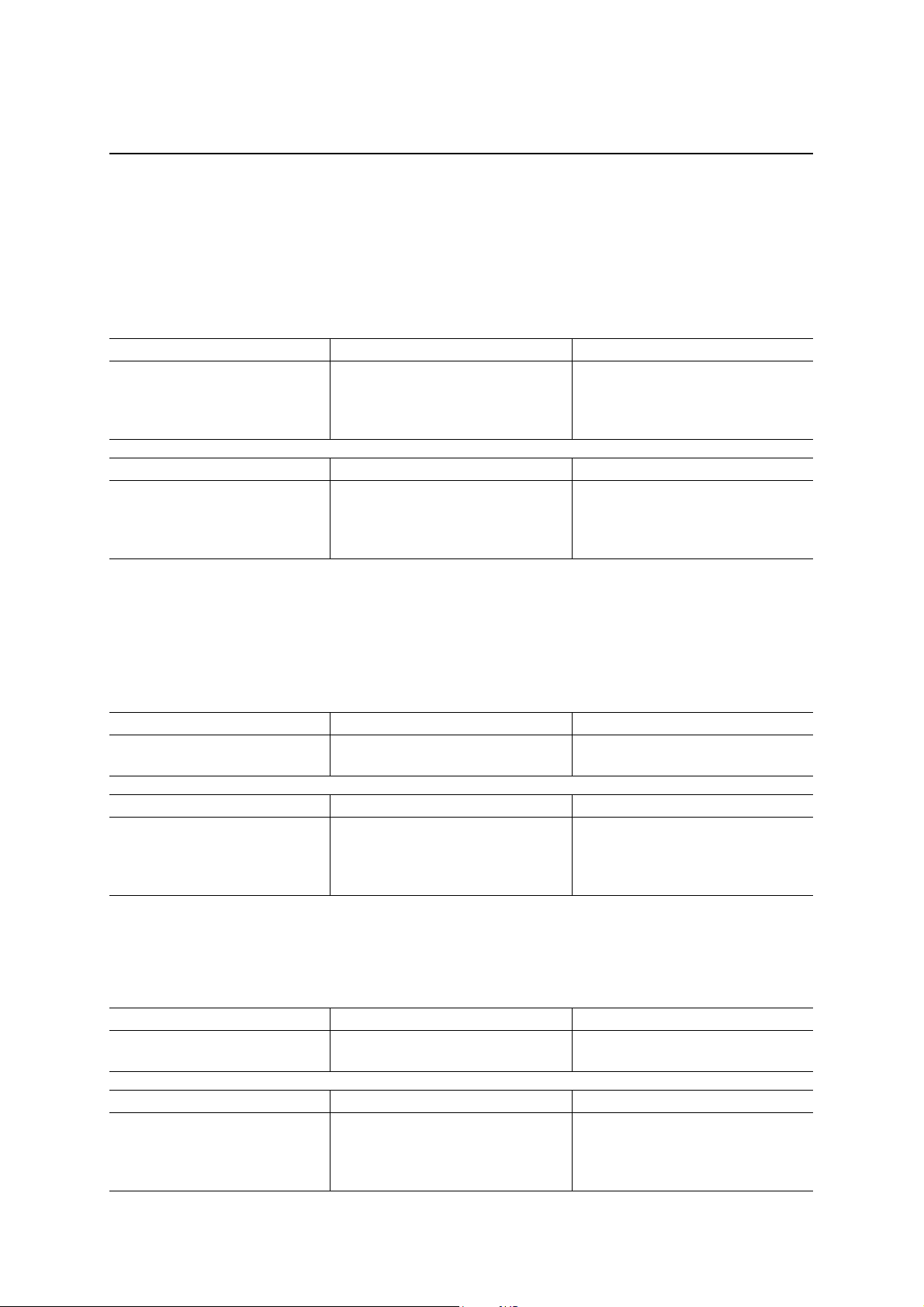
EP1 Transmit Packet Ready Bit (D5)
This bit can be read by the local MCU. Further, this bit can be set to “1” by writing “1” to the D5 bit.
The conditions of asserting and deasserting this bit are the following. EP1 has a two-layer FIFO, and the packet
ready bits are present independently for layer A and layer B. The switching between these two layers is performed
automatically by the ML60851E. For detailed description of double layered FIFO operation, please refer to page
77 of this manual.
Bit name Asserting condition Action when asserted
EP1 Transmit packet ready (D5) When the local MCU has set the bits
of both layer A and layer B.
Data transmission is possible from
EP1 when the bit for at least one of
layer A and layer B has been
asserted.
Bit name Deasserting condition Action when deasserted
EP1 Transmit packet ready (D5) When an ACK is received from the
host computer for the data
transmission from either layer A or
layer B.
EP1 is locked when both layer A and
layer B have not prepared the
transmit data.
See the explanation of the operation of the two-layer FIFO given in the Section on ‘Functional Description’.
EP2 Transmit Packet Ready Bit (D6)
This bit can be read by the local MCU. Further, this bit can be set to “1” by writing “1” to the D6 bit.
The conditions of asserting and negating this bit are the following.
Bit name Asserting condition Action when asserted
EP2 Transmit packet ready (D6) When the local MCU has set this bit. Data transmission is possible from
EP2.
Bit name Deasserting condition Action when deasserted
EP2 Transmit packet ready (D6) When an ACK is received from the
host computer in response to the
data transmission from EP2.
EP2 is locked. In other words, an
NAK is transmitted automatically
when an IN token is received from
the host.
EP3 Transmit Packet Ready Bit (D7)
This bit can be read by the local MCU. Further, this bit can be set to “1” by writing “1” to the D7 bit.
The conditions of asserting and deasserting this bit are the following.
Bit name Asserting condition Action when asserted
EP3 Transmit packet ready (D7) When the local MCU has set this bit. Data transmission is possible from
EP3.
Bit name Deasserting condition Action when deasserted
EP2 Transmit packet ready (D7) When an ACK is received from the
host computer in response to the
data transmission from EP3.
EP3 is locked. In other words, an
NAK is transmitted automatically
when an IN token is received from
the host.
18/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
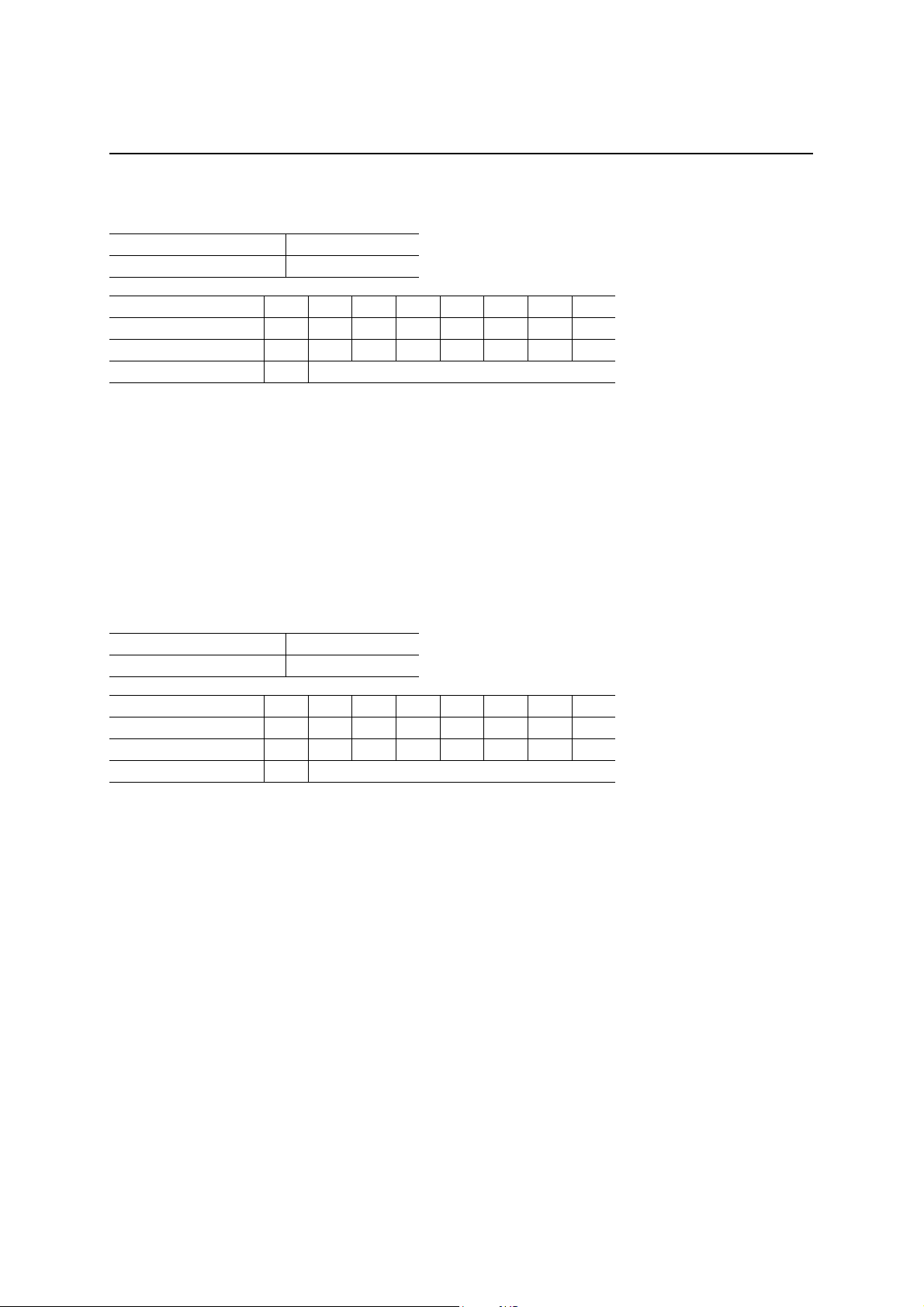
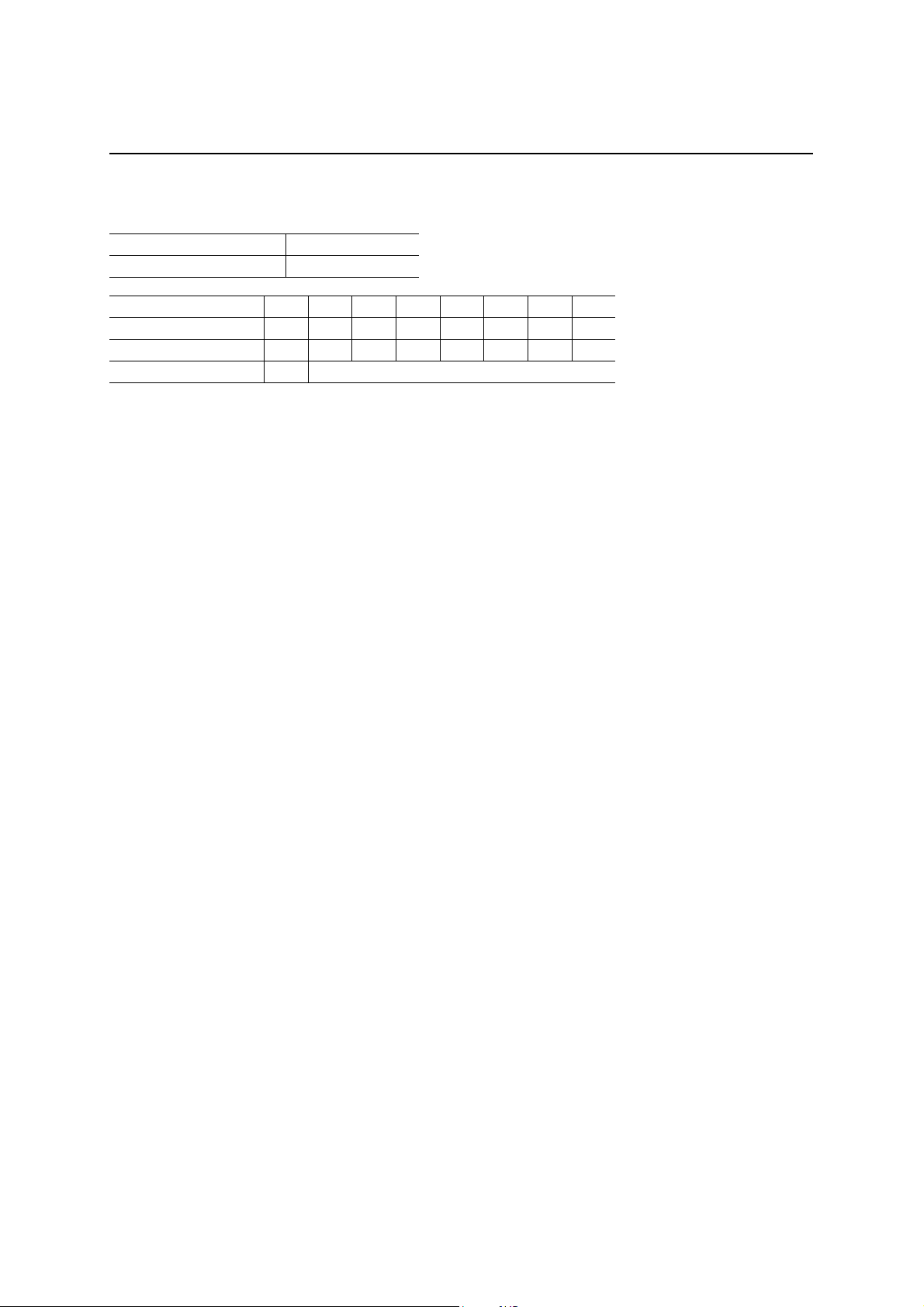
End Point 0 Receive Byte Count Register (EP0RXCNT)
Read address C9h
Write address —
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
After a bus reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Definition 0 Byte count of EP0 (R)
The ML60851E automatically counts the number of bytes in the packet be ing recei ved by EP0 and store s it in this
register. Although the counting is perf ormed u p to the m aximum packet size entered in the payloa d register in the
case of a full packet, the count will be less than this value in the case of a short packet. The local MCU refers to
this value and reads the data of one packet from the EP0RXFIFO.
The EP0 receive byte count register is cleared under the following conditions:
1. When the local MCU resets the EP0 receive packet ready bit (by writing a “1” in PKTRDY(0)).
2. When a setup packet is received.
3. When the local MCU writes a “0” in the stall bit (EP0STAT(2)).
End Point 1 Receive Byte Count Register (EP1RXCNT)
Read address CAh
Write address —
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
After a bus reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Definition 0 Byte count of EP1 (R)
The ML60851E automatically counts the number of bytes in the packet be ing recei ved by EP1 and store s it in this
register. Although the counting is perf ormed u p to the m aximum packet size entered in the payloa d register in the
case of a full packet, the count will be less than this value in the case of a short packet. The local MCU refers to
this value and reads the data of one packet from the EP1 receive FIFO.
This register is invalid when the EP1 transfer direction is set as ‘Transmit’.
The EP1 receive byte count register is cleared under the following conditions:
1. When an OUT token is received for EP1.
2. When the EP1 receive packet ready bit is reset (by writing a “1” in PKTRDY(1)).
3. When the local MCU writes a “0” in the stall bit (EP1CON(1)).
19/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
End Point 2 Receive Byte Count Register (EP2RXCNT)
Read address CBh
Write address —
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
After a bus reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Definition 0 Byte Count of EP2 (R)
The ML60851E automatically counts the number of bytes in the packet be ing recei ved by EP2 and store s it in this
register. Although the counting is perf ormed u p to the m aximum packet size entered in the payloa d register in the
case of a full packet, the count will be less than this value in the case of a short packet. The local MCU refers to
this value and reads the data of one packet from the EP2RXFIFO.
This register is invalid when the EP2 transfer direction is set as ‘Transmit’.
The EP2 receive byte count register is cleared under the following conditions:
1. When an OUT token is received for EP2.
2. When the EP2 receive packet ready bit is reset (by writing a “1” in PKTRDY(2)).
3. When the local MCU writes a “0” in the stall bit (EP2CON(1)).
20/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
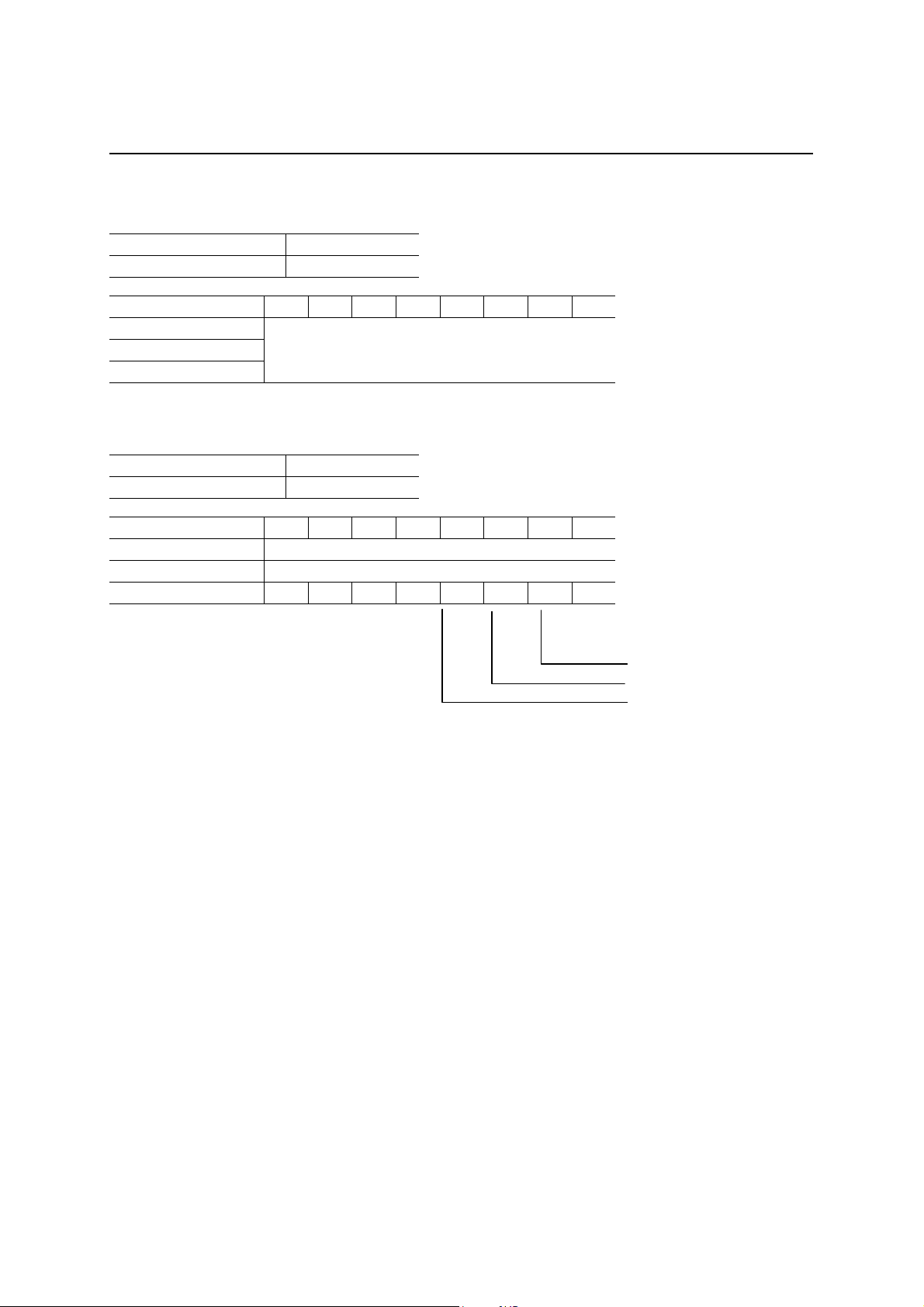
Revision Register (REVISION)
Read address CDh
Write address —
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset
After a bus reset
Definition
Revision No. of Chip
Transmit FIFO Clear Register (CLRFIFO)
Read address —
Write address 4Eh
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset Cannot be read (indeterminate)
After a bus reset Cannot be read (indeterminate)
Definition 0 0 0 0
EP1 Transmit FIFO Clear
EP2 Transmit FIFO Clear
EP3 Transmit FIFO Clear
EP1 to EP3 FIFO Clear: When each EP has been set for transmission, by writing a “1” in these bits, the
corresponding FIFOs are cleared at the Write pulse and also the corresponding EP
Packet Ready bits are reset.
21/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
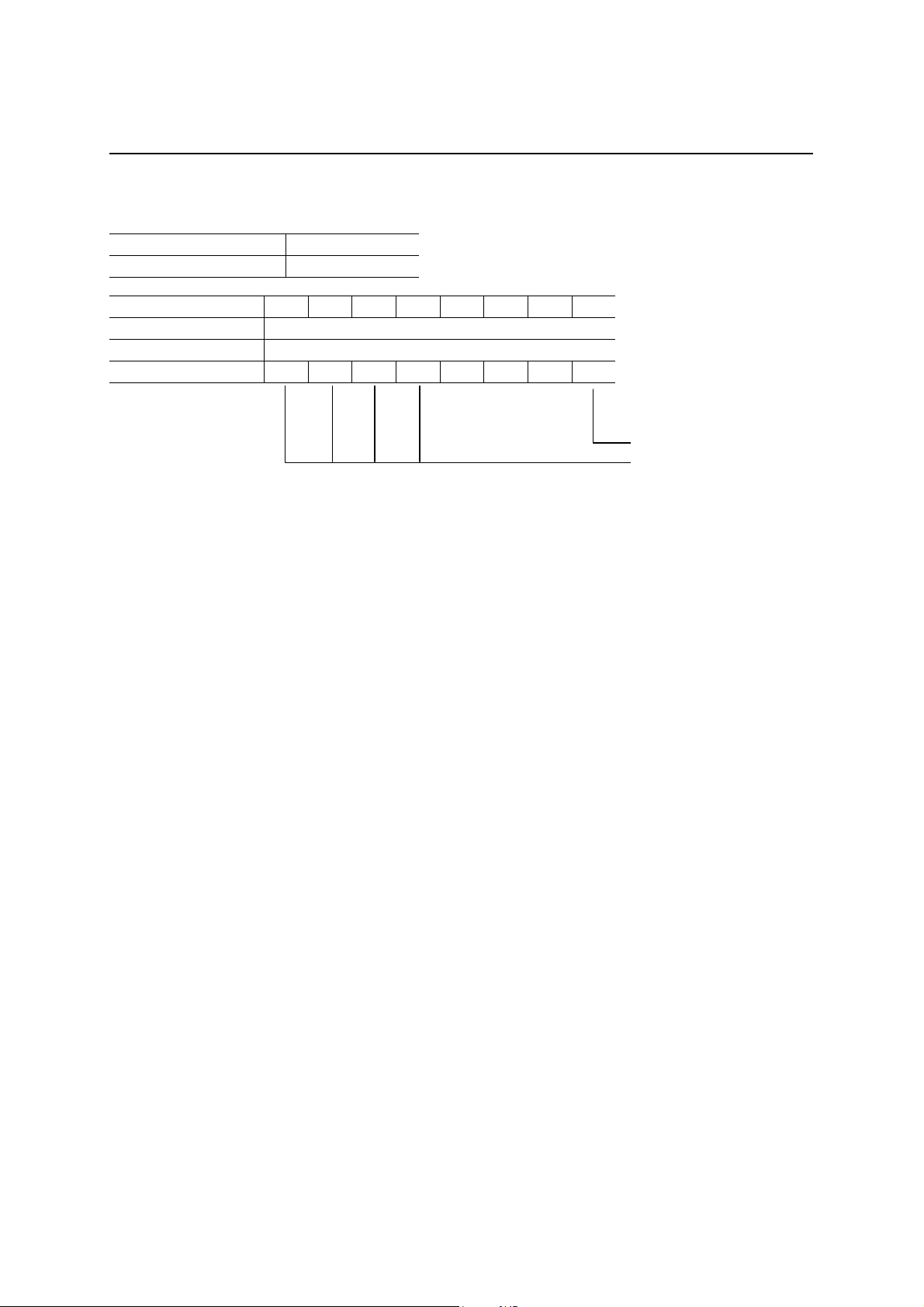
System Control Register (SYSCON)
Read address —
Write address 4Fh
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset Cannot be read (indeterminate)
After a bus reset Cannot be read (indeterminate)
Definition 0 0 0
Software Reset
Oscillation Stop Command
Software Reset: When a “1” is written in this bit, a system reset is executed at the Write pulse. This is
functionally equivalent to a hardware reset.
Oscillation Stop command: The Oscillation circuit of the ML60851 E stops and goes into the standby state w hen
1010b is written in D7 to D4 (that is, when A0h is written in this register).
Once the IC goes into the standby state, to start communication with the USB bus
thereafter, it is necessary to carry out again disconnecting, connecting, and
enumeration.
Even when th e Oscillation has stopped, although it is possible to read and write the
registers, it is impossible to read or write the FIFO.
The oscillation can be started again by asserting the RESET pin. The oscillation can
be restarted even by a software reset.
22/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
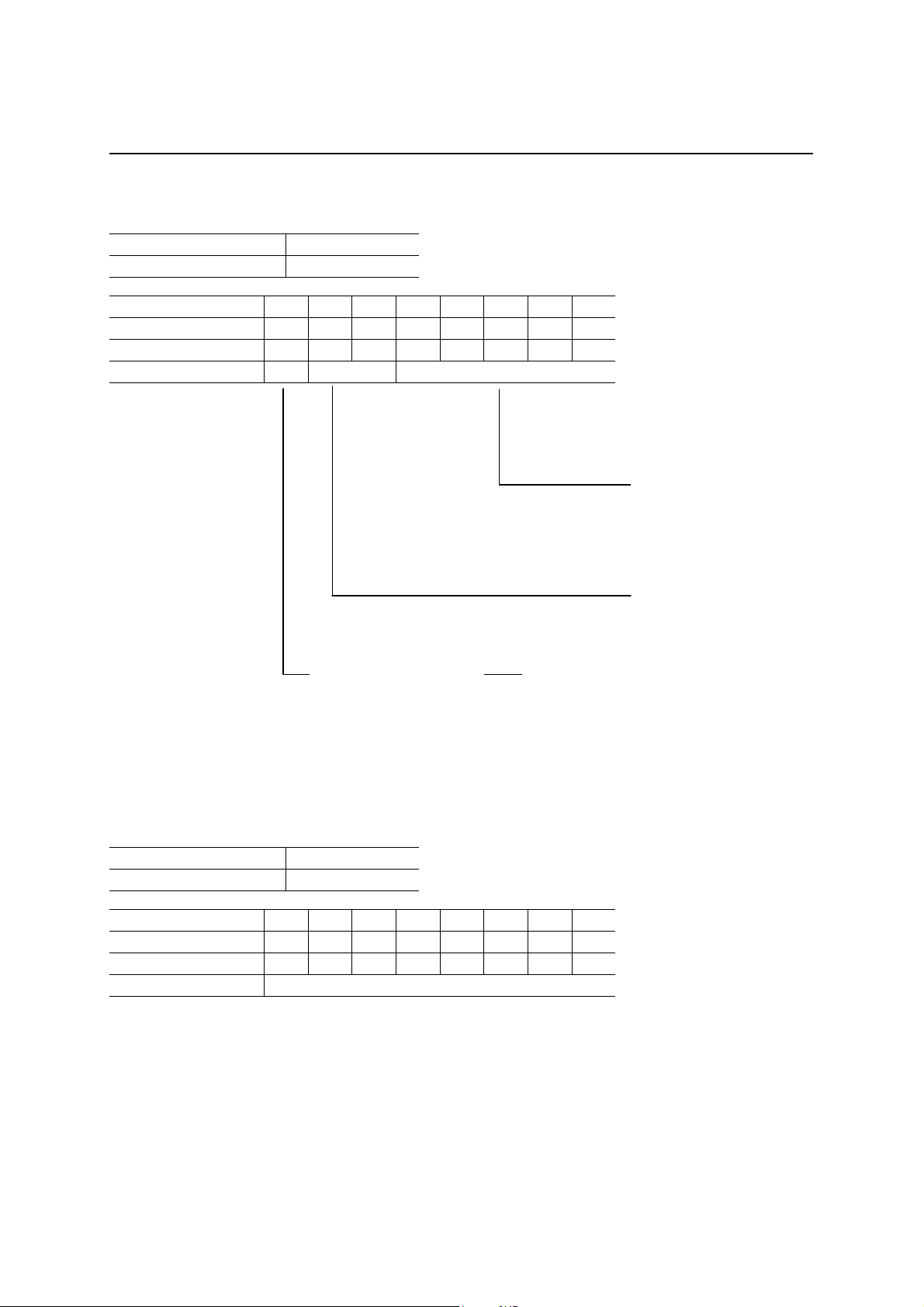
bmRequest Type Setup Register
Read address D0h
Write address —
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
After a bus reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Definition Type Receiving side
0 = Device
1 = Interface
2 = End point
3 = Others
4 to 31 = Reserved
Data Transfer Direction
0 = From the host computer to the device
1 = From the device to the host computer
0 = Standard
1 = Class
2 = Vendor
3 = Reserved
The format of the device request conform s to Sect ion 9. 3 of the USB st andards . The eight bytes of set up data se nt
by the host computer during the setu p stage of co ntrol tra nsfer are stored automatically in eight registers including
this register.
bRequest Setup Register
Read address D1h
Write address —
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
After a bus reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Definition Request Code
The request code indicating the contents of the device request is stored auto matically in this register during the
setup stage of control transfer.
23/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
wValue LSB Setup Register
Read address D2h
Write address —
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
After a bus reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Definition wValue LSB
A parameter of device request is stored in this register during the setup stage of control transfer.
wValue MSB Setup Register
Read address D3h
Write address —
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
After a bus reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Definition wValue MSB
A parameter of device request is stored in this register during the setup stage of control transfer.
wIndex LSB Setup Register
Read address D4h
Write address —
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
After a bus reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Definition wIndex LSB
A parameter of device request is stored in this register during the setup stage of control transfer.
wIndex MSB Setup Register
Read address D5h
Write address —
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
After a bus reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Definition wIndex MSB
A parameter of device request is stored in this register during the setup stage of control transfer.
ML60851E
24/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
wLength LSB Setup Register
Read address D6h
Write address —
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
After a bus reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Definition wLength LSB
A parameter of device request is stored in this register during the setup stage of control transfer.
wLength MSB Setup Register
Read address D7h
Write address —
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
After a bus reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Definition wLength MSB
A parameter of device request is stored in this register during the setup stage of control transfer.
ML60851E
25/84
FEDL60851E-01
OKI Semiconductor
ML60851E
Polarity Selection Register (POLSEL)
Read address DAh
Write address 5Ah
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
After a hardware reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
After a bus reset The previous value is retained
Definition 0 0 0 0 0
Polarity of INTR
0 = Active Low
1 = Active High
Polarity of DREQ
0 = Active Low
1 = Active High
Polarity of DACK
0 =Active High
1 =Active Low
This register is used for configuring the polarity of the interrupt and DMA signals of ML60 851E. Bits D 7 to D3 are
fixed at “0” and even if “1”s are written in them, they are ignored.
26/84
 Loading...
Loading...