
DATA SHEET ¡
ML54051
NAND Flash Memory Controller
PRELIMINARY
SECOND EDITION
ISSUE DATE : JAN. 1999

E2Y0002-29-11
NOTICE
1. The information contained herein can change without notice owing to product and/or
technical improvements. Before using the product, please make sure that the information
being referred to is up-to-date.
2. The outline of action and examples for application circuits described herein have been
chosen as an explanation for the standard action and performance of the product. When
planning to use the product, please ensure that the external conditions are reflected in the
actual circuit, assembly, and program designs.
3. When designing your product, please use our product below the specified maximum
ratings and within the specified operating ranges including, but not limited to, operating
voltage, power dissipation, and operating temperature.
4. Oki assumes no responsibility or liability whatsoever for any failure or unusual or
unexpected operation resulting from misuse, neglect, improper installation, repair, alteration
or accident, improper handling, or unusual physical or electrical stress including, but not
limited to, exposure to parameters beyond the specified maximum ratings or operation
outside the specified operating range.
5. Neither indemnity against nor license of a third party’s industrial and intellectual property
right, etc. is granted by us in connection with the use of the product and/or the information
and drawings contained herein. No responsibility is assumed by us for any infringement
of a third party’s right which may result from the use thereof.
6. The products listed in this document are intended for use in general electronics equipment
for commercial applications (e.g., office automation, communication equipment,
measurement equipment, consumer electronics, etc.). These products are not authorized
for use in any system or application that requires special or enhanced quality and reliability
characteristics nor in any system or application where the failure of such system or
application may result in the loss or damage of property, or death or injury to humans.
Such applications include, but are not limited to, traffic and automotive equipment, safety
devices, aerospace equipment, nuclear power control, medical equipment, and life-support
systems.
7. Certain products in this document may need government approval before they can be
exported to particular countries. The purchaser assumes the responsibility of determining
the legality of export of these products and will take appropriate and necessary steps at their
own expense for these.
8. No part of the contents cotained herein may be reprinted or reproduced without our prior
permission.
9. MS-DOS is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Copyright 1999 Oki Electric Industry Co., Ltd.
Printed in Japan

Table of Contents
1. FEATURES...........................................................................................................2
2. BLOCK DIAGRAM ............................................................................................... 2
3. PIN SPECIFICATIONS ........................................................................................ 3
3.1 Host Interface (PCMCIA) .................................................................................... 3
3.2 NAND Flash Memory Interface .......................................................................... 4
3.3 External SRAM Interface .................................................................................... 5
3.4 Extended Bus Interface ...................................................................................... 5
3.5 Other Interfaces .................................................................................................. 5
3.6 Power Supply....................................................................................................... 6
3.7 Pin Totals ............................................................................................................. 6
3.8 Pin Configuration ................................................................................................ 7
4. FUNCTIONS ........................................................................................................ 8
5. SECTOR FORMATTER AND SEQUENCER....................................................... 9
5.1 Data Formats ....................................................................................................... 9
5.1.1 Data Format Within Sector ........................................................................ 9
5.1.2 Data Format Within Port .......................................................................... 10
5.1.3 Substitute Management Information Format ........................................... 11
5.2 Write Sector Commands .................................................................................. 12
5.2.1 Dual Port Control ..................................................................................... 12
5.2.2 Block Control ........................................................................................... 12
5.3 Substitute Processing (Defect Management)................................................. 13
5.3.1 Substitute Management Information Format Processing ........................ 13
5.3.1.1 Sector Management .............................................................................. 13
5.3.1.2 Substitute Management Information Management............................... 14
5.4 Generation of Substitute Management Information ...................................... 14
5.5 Substitute Processing....................................................................................... 15
5.6 Substitute Destination Detection Processing ................................................ 16
6. ATA REGISTERS ...............................................................................................17
6.1 Memory Mapped Configuration ....................................................................... 17
6.2 I/O Mapped 16 Contiguous Registers Configuration .................................... 18
6.3 Primary I/O Mapped Configuration ................................................................. 18
6.4 Secondary I/O Mapped Configuration ............................................................ 19
6.5 True IDE Mapped Configuration ...................................................................... 19
6.6 ATA Registers .................................................................................................... 20
6.6.1 Data Register (Write/Read) ...................................................................... 20
6.6.2 Error Register (Read Only) ....................................................................... 20
6.6.3 Feature Register (Write Only) ................................................................... 20
6.6.4 Sector Count Register (Write/Read) ........................................................ 20
6.6.5 Sector Number Register (Write/Read) ..................................................... 21
6.6.6 Cylinder Low Register (Write/Read) ......................................................... 21
6.6.7 Cylinder High Register (Write/Read) ........................................................ 21
6.6.8 Drive Head Register (Write/Read) ............................................................ 21
6.6.9 Status Register & Alternate Status Register (Read Only) ........................ 22
6.6.10 Device Control Register (Write Only) ....................................................... 22
6.6.11 Command Register (Write Only) .............................................................. 22

7. PCMCIA INTERFACE ........................................................................................ 23
7.1 ATA Commands (Standard).............................................................................. 23
7.2 Commands for CompactFlash ......................................................................... 24
7.3 Vendor-Unique Commands.............................................................................. 24
7.4 Card Information Structure .............................................................................. 24
7.5 Identify Information........................................................................................... 24
7.6 Number of Installed Memory Chips and CHS Structure................................ 25
7.7 Modes................................................................................................................. 27
7.7.1 Memory Mapped ..................................................................................... 27
7.7.2 I/O Mapped 16 Contiguous Registers ..................................................... 27
7.7.3 Primary I/O Mapped ................................................................................ 27
7.7.4 Secondary I/O Mapped ........................................................................... 27
7.7.5 True IDE ................................................................................................... 27
8. CHIP MODES .................................................................................................... 28
8.1 Types .................................................................................................................. 28
8.2 Settings .............................................................................................................. 28
8.3 Pin Assignment.................................................................................................. 28
9. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS .................................................................. 29
9.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................................. 29
9.2 Recommended Operating Conditions............................................................. 29
9.3 DC Characteristics ............................................................................................ 29
10. BUS SPECIFICATIONS .....................................................................................30
10.1 I/O Mode ........................................................................................................... 30
10.2 Bus Timing Specifications ............................................................................... 30
10.3 Power ON/OFF, Reset, Busy Timing .............................................................. 30
11. PACKAGE DIMENSIONS ..................................................................................31
12. APPLICATION EXAMPLES ...............................................................................32

E2F0018-29-13
Preliminary
¡ Semiconductor ML54051
¡ Semiconductor
This version: Jan. 1999
Previous version: Oct. 1998
ML54051
NAND Flash Memory Controller
The ML54051 is a controller that integrates into a single chip a host interface that conforms to
PCMCIA, an interface to a buffer used for data transfer, the necessary functions to control NAND
memory, and a microcontroller.
Internal 256 byte RAM is provided for storage of the card information structure (CIS). Also,
128KB of SRAM may be connected as a buffer for data transfer.
A maximum of 16 chips of 64 Mbit or larger NAND flash memory can be controlled when the chip
is used as stand-alone. If a decoder circuit is externally added, a maximum of 64 chips can be
controlled.
CompactFlashTM is a trademark of SanDisk Corporation.
1/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
1. FEATURES
• Single chip controller with internal microcontroller (min. 4 cycles/instruction execution)
• Operating voltage: 3.3 V, Interface voltage: 3.3 V/5 V
• Internal 256B RAM for card information structure (CIS) storage
• Conforms to PC card standard - PC card ATA specification
• Auto-sleep mode support
• True IDE Mode support
• ECC system by BCH code (3-bit random error correction is possible for user data and ECC data)
• Substitute control function (defect management function)
• Debug mode support
• External buffer (128KB SRAM) control is possible
• High-speed operation via dual port bus control
• Low power consumption due to single chip controller
• Control of multiple NAND flash memories (64MB to 512MB) is possible
Chip stand-alone : 16 pcs max.
Chip and external decoder circuit : 64 pcs max.
• 144-pin LQFP package (LQFP144-P-2020-0.50-K)
2. BLOCK DIAGRAM
PCMCIA
I/F
Host I/F
PCMCIA
ATA
CIS
External
CPU Bus
ECC
MPU
RAMROM
RAM Arbiter
External
SRAM
Media I/F
NAND
Flash
Bus
2/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
p
3. PIN SPECIFICATIONS
Refer to Section 12, “Application Examples” for specific connection examples.
3.1 Host Interface (PCMCIA)
Signal Name
ha [10:0]
hd [15:0]
hcen [2:1]
hiordn
hiowrn
hoen
hwen
hregn
hirqn
hstschgn
hinpackn
hiois16n O 1 16-bit address enable signal (when the card is configured as an I/O card,
hwaitn O 1 Wait signal
hspkr B 1 Audio digital waveform signal
hrst I 1 Reset signal
hcseln I/(O) 1 Cable select signal (used only in True IDE Mode, GND: Master, X: Slave)
Type
I
B
I
I
I
I
I
I
O
O
O
Pin Count
11
16
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Total 42
Description
Address bus (A10 is MSB, A0 is LSB)
Data bus (D15 is MSB, D0 is LSB)
Card enable signal (hcen1 controls even addresses and hcen2 controls odd
addresses. The combination of ha0, hcen1 and hcen2 allows even/odd
addresses to be accessed by hd[7:0].)
I/O read signal (control signal to read data from ATA registers)
I/O write signal (control signal to write data to ATA registers)
Output enable signal
Write enable signal
Register select & I/O Enable signal
Interrupt request signal (when the card is configured as an I/O card)
Card status change signal (signal to change the status of the configuration
status register)
Input port acknowledge signal (acknowledge signal during I/O read)
this signal indicates that 16-bit addresses are enabled)
ins
* In an external CPU connection mode, hcseln functions as a control signal (xint) for the
extended bus.
I: Input, O: Output, B: Bidirectional
3/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
3.2 NAND Flash Memory Interface
Signal Name
maio [7:0]
macle
maale
maren
mawen
marbn
mbio [7:0]
mbcle
mbale
mbren
mbwen
mbrbn I 1 Port B ready/busy signal (signal to check internal status of device)
mctl I 1 Chip enable signal mode select (mcen[7:0] control)
mcen [7:0] O 8 Chip enable signals
mwpn O 1 Write protect signal (signal to forcibly prohibit write and erase operations)
Type
B
O
O
O
O
I
B
O
O
O
O
Pin Count
8
1
1
1
1
1
8
1
1
1
1
Total 36 pins
Description
Port A I/O bus
Port A command latch enable signal (signal to control latching of an
operation command into a device)
Port A address latch enable signal (signal to control latching of an address
or input data into a device)
Port A read enable signal
Port A write enable signal (signal to latch data into a device)
Port A ready/busy signal (signal to check internal status of device)
Port B I/O bus
Port B command latch enable signal (signal to control latching of an
operation command into a device)
Port B address latch enable signal (signal to control latching of an address
or input data into a device)
Port B read enable signal
Port B write enable signal (signal to latch data into a device)
mct1 = 0 : Chip enable signal
mct1 = 1 : Chip select and chip enable signals
* mcen[7:0] performs 2 types of operations depending upon the mctl signal.
If mctl = 0, mcen[7:0] functions as the chip enable signals.
If mctl = 1, mcen[5:1] functions as the chip select signals and mcen[0] functions as the chip
enable signal.
In the latter case, mcen[5:1] and mcen[0] must be connected to an external decoder and
mcen[7:6] are not used.
* In an external CPU connection mode, mctl and mcen[7:6] function as control signals (xpsen,
xrst, xclk, respectively) for the extended bus.
4/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
p
p
3.3 External SRAM Interface
Signal Name
ra [16:0]
rd [7:0] B 8 Data bus for external SRAM
rren O 1 Read enable signal for external SRAM
rwen O 1 Write enable signal for external SRAM
rcen O 1 Chip enable signal for external SRAM
TypeOPin Count
17
Total 28
ins
Address bus for external SRAM
Description
3.4 Extended Bus Interface
The extended bus interface is a signal line for the ML54051’s internal microcontroller. The
extended bus interface is used for purposes such as debugging.
Signal Name
xah [15:8]
xad [7:0] B 8 Address/data bus for extended bus
xrd B 1 Read signal for extended bus
xwr B 1 Write signal for extended bus
xale B 1 Address latch enable signal for extended bus
xpsen I (1) Program store enable signal for extended bus
xint O (1) Interrupt signal for extended bus
xrst O (1) Reset signal for extended bus
xclk O (1) Clock signal for extended bus
TypeBPin Count
8
Total 19 pins
Address bus for extended bus
Description
* In an external ROM connection mode, xah, xad, xrd, xwr, and xale are used to connect to
external ROM.
3.5 Other Interfaces
Signal Name
txd/pcfg [0]
rxd/pcfg [1] I 1
porn I 1 Power-on-reset signal (connect to power monitor circuit)
xin I 1 Clock I/O (connect a crystal oscillator between xin and xout)
xout O 1
TypeBPin Count
1
Total 5
ins
Serial data I/O and chip mode setting
Description
* The chip mode is determined depending upon the status of pcfg[1:0] when the porn signal
rises.
pcfg[1:0] = 11 : Normal mode
pcfg[1:0] = 01 : External CPU connection mode
pcfg[1:0] = 10 : External ROM connection mode
pcfg[1:0] = 00 : Test mode (normally not used)
5/33
¡ Semiconductor ML54051
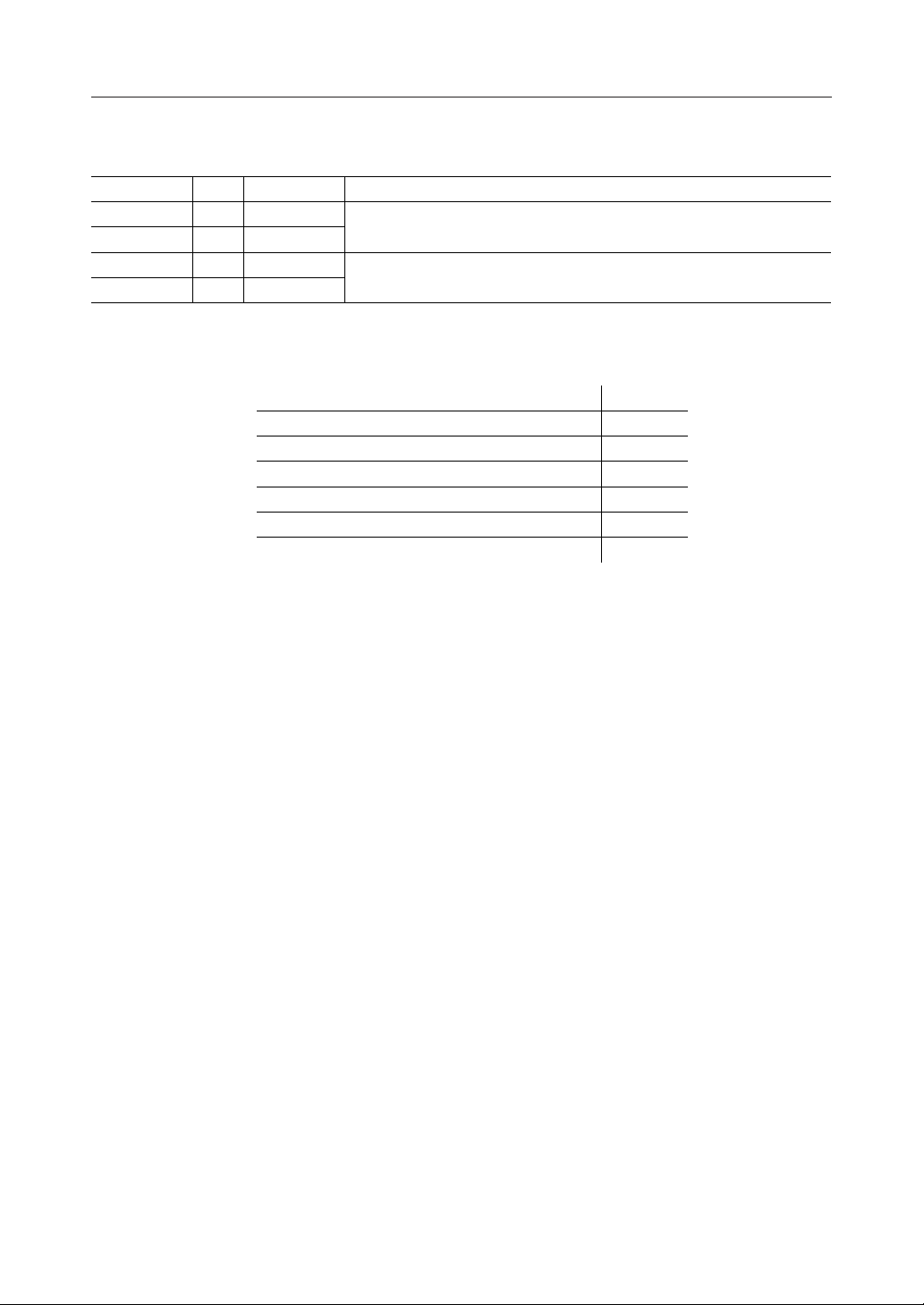
3.6 Power Supply
Signal Name
VDD-CORE
VSS-CORE DC 2
VDD DC 4 Power supply for I/O pad
VSS DC 6
TypeDCPin Count
2
Total 14 pins
Power supply for core
3.7 Pin Totals
Host Interface 42
NAND Flash Memory Interface 36
External SRAM Interface 28
Extended Bus Interface 19
Other Interfaces 5
Power Supply 14
Total 144
Description
6/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
3.8 Pin Configuration
porn
mwpn
mctl
rxd
txd
ra12
ra13
ra11
ra14
ra10
ra15
ra9
ra16
ra8
rwen
rd4
rd3
rd5
VDD-CORE
VDD
VSS
rd2
rd6
rd1
rd7
rd0
rren
rcen
ra7
ra0
ra6
ra1
ra5
ra2
ra4
ra3
144
143
142
141
140
139
138
137
136
135
134
133
132
131
130
129
128
127
126
125
124
123
122
121
120
119
118
117
116
115
114
113
112
111
110
macle
maale
maren
mawen
marbn
VSS
xout
xin
maio0
maio7
maio1
maio6
maio2
maio5
VDD
maio3
maio4
mcen0
VSS-CORE
mcen1
mcen2
mcen3
mcen4
mcen5
mcen6
mcen7
VSS
mbcle
mbale
mbren
mbwen
mbrbn
mbio0
mbio7
mbio1
mbio6
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
3839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566676869707172
37
ML54051
109
108
107
106
105
104
103
102
101
100
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
hd3
hd11
hd4
hd12
hd5
hd13
hd6
VSS
hd14
hd7
hd15
hce1n
hce2n
ha10
hoen
hiordn
ha9
hiowrn
VSS-CORE
ha8
hwen
ha7
hirqn
ha6
hcseln
VDD
ha5
ha4
hrst
ha3
hwaitn
ha2
hinpackn
ha1
hregn
ha0
mbio2
mbio5
mbio3
mbio4
VDD
xrdn
xale
VSS
xad7
xad6
xad5
xad4
xad3
xad2
xad1
xad0
xa15
144-Pin Plastic LQFP
xa14
xa13
VDD-CORE
xa12
xa11
xa10
xa9
xa8
xwrn
hd10
hd9
VSS
hiois16n
hd2
hd8
hd1
hstschgn
hd0
hspkr
7/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
4. FUNCTIONS
(1) Sector Formatter and Sequencer
The sector formatter and sequencer control the logical format of the NAND flash memory
and efficiently perform defect management (substitute processing).
(2) PCMCIA Interface
The PCMCIA interface conforms to PCMCIA-ATA specification. Since True IDE Mode is
also supported, the general usefulness of this interface is increased.
(3) Chip Modes
An external ROM connection mode for the ML54051’s internal microcontroller and an
external CPU connection mode are supported. With these modes, evaluation can be
performed efficiently.
(4) Auto-Sleep Mode
If there is no access from the host over a specific period of time, operation automatically
transfers to the sleep mode.
(5) Dual Port Bus Control Mode
When erasing data or writing the same data, two port buses (Port A, Port B) can be utilized
simultaneously for high-speed operation.
8/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
5. SECTOR FORMATTER AND SEQUENCER
5.1 Data Formats
5.1.1 Data Format Within Sector
User data, ECC data and Header data are stored at the top of the sector first.
ECC data contains the ECC information for user data and ECC data. Since the same flag data is
stored in all pages (sectors) within the same block, the validity of flag data of the specified page
can be verified by comparing it to the flag data of another page. For this reason, ECC information
is not provided for the header data.
512 bytes
User Data
8 bits
Flag
5 bits
Column No.
17 bits
Address
12 bits
Substitute Destination Address
10 bytes
ECC Data
Flag … page (sector) status
FFh: Good (normal data storage)
F0h: Bad (uncorrectable error, before substitution)
0Fh: Change (substitution completed)
Other than above: Null (abnormal)
Address … block address (supports up to 4096 blocks: 512 Mbits)
Column No. : supports up to column number 31 (00h to 1Fh)
Substitute destination address: block address within spare area
Supports up to 4096 blocks (512 Mbits)
Value to be stored in substitute destination address, substitute source address
• Normal data = block address
• Substitute destination sector = substitute source address
• Substitute source sector = substitute destination address
6 bytes
Header Data
23 bits
Count
Count… number of writes (supports up to 8,388,607 writes)
A substitute process is performed to a block that reaches the number of writes
previously set.
9/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
5.1.2 Data Format Within Port
Each chip is partitioned into a user area to store user data, a spare area to transfer data in defective
sectors, and a substitute management information area to keep sector transfer information. The
port views this configuration as a single chip.
Substitute processing is performed in block units, not in sector units. If the process is performed
in sector units, a single block will have data from various addresses at random, which delays the
substitute processing.
A substitute management information is made per port; while a copy of substitute management
information is reserved as a back-up.
Port A
Chip 1
Chip 3
Chip n – 1
Port B
User Area
Spare Area
Substitute Management
Information Area
Chip 2
User Area
Spare Area
Substitute Management
Information Area
User Area • • •
Spare Area
Chip 4
User Area • • •
Spare Area
User Area
Spare Area
Chip n
User Area
Spare Area
10/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
5.1.3 Substitute Management Information Format
The location of management information itself specifies a substitute destination. And an original
sector locations is identified by a column number and a block address to be stored in a
management information. Please note that a substitute management information cannot be
transfered to other chips.
3 bytes
3 bytes
3 bytes
666666[h]
666666[h]
Page 1 • • • • • • • • •
Page m-1 Identify Information [512 bytes]
Page m CIS Information [256 bytes] Unused [248 bytes]
D-List
(orig.)
•
•
•
D-List
(duplicate)
Management
Info. n-2
Port A Chip 1
Management
Info. 1
Port A Chip 1
Management Info.
•
•
•
512 bytes
Management
Info. n
Port A Chip 3
Management
Info. 1
Port A Chip 3
2 bytes
3 bytes
D-List
Unused
Identify Info.
D-List
Unused
Identify Info.
•
•
•
Unused D-List
Identify Info.
3 bytes
10 bytes
Unique Info.
Unique Info.
•
•
Unique Info. E CC Header
ECC
ECC
•
•
•
6 bytes
Header
Header
•
•
•
•
•
•
HeaderECC
• Management Information (3 bytes)
Stores substitute origin information
7 bits 5 bits 12 bits
Blank Column No.
Address of an original block to be substituted
Column No. : 0 to 31
The following values have unique meanings.
55 55 55 [h] Reconstructed D-List Block Registered Position
66 66 66 [h] Spare Block for D-List Use
0F 0F 0F [h] Error Occurred D-List Block/Unusable Spare Block
FF FF FF [h] Usable/Unused Spare Block
• D-List Identify Information (3 bytes)
Indicates that the sector is valid (fixed values: 4Fh, 4Bh, 49h)
• Unique Information (3 bytes)
During the low level format, stores total number of chips, chip number, and individual
memory type information
1 byte
Total No. of Chips
1 byte
Chip No.
Individual Memory Type Info.
1 byte
Total No. of chips: The number of chips connected to the ML54051 (1 to 64)
Chip No. : The chip number that contains the substitute management information (0 or 1)
Individual memory type info. : Number of blocks per chip (4 bits) and number of pages per
block (4 bits)
Memory Capacity Number of Blocks Per Chip Number of Pages Per Block
64 Mbit
128 Mbit
1[h] (1024 Block)
256 Mbit 2[h] (2048 Block) 1[h] (32 Page)
512 Mbit 4[h] (4096 Block)
0[h] (16 Page)
11/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
5.2 Write Sector Commands
Two methods are reserved for a faster access.
5.2.1 Dual Port Control
By controlling Port A and Port B independently, 2 chips can be accessed simultaneously when
erasing data or writing the same data, which doubles the access time.
Port A
Chip 1
Port B
Chip 2
Chip 3 Chip 5
Chip 4 Chip 6
• • •
• • •
5.2.2 Block Control
When the host requests a write that includes Block 1 of Port B, if it is unnecessary to save the stored
data, a block read will not be performed for the shaded section of the diagram below, which saves
read time.
This is enabled by making use of NAND flash memory characteristics to erase data in a unit of
a block.
Port A Block 1
Port B Block 1
Port A Block 2
12/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
5.3 Substitute Processing (Defect Management)
Substitute processing (defect management) is made through the following four processes in
block units.
1. Substitute management information format processing
: Information management of defective sector addresses,
substitute destination addresses, etc.
2. Substitute management information generation processing
: Generates substitute management information for entire
card during low level format
3. Substitute processing : Replaces a defective sector with a normal sector
4. Substitute destination detection : Detects substitute destination of defective sector that was
substituted
5.3.1 Substitute Management Information Format Processing
See section 5.1, “Data Formats”, for the data formats of defective sector information and transfer
destination information to be stored.
5.3.1.1 Sector Management
A header section is read before reading or writing data. A flag of a header section indicates if a
sector is normal.
(1) User area
Flag
FFh
0Fh The substitute destination obtained by substitute
F0h The substitute destination obtained by substitute
Other values The substitute destination is detected from the
The specified sector is accessed.
The substitute destination obtained by substitute
destination detection processing is accessed.
An uncorrectable error (UNC) is returned and
processing is aborted.
The substitute destination is detected from the
substitute management information and the
substitute destination is accessed.
If the substitute destination cannot be detected,
a substitute processing error (DWF) is returned
and processing is aborted.
Read
Write
The specified sector is accessed.
destination detection processing is accessed.
processing is accessed.
substitute management information and the
substitute destination is accessed.
If the substitute destination cannot be detected,
the substitute destination obtained by substitute
processing is accessed.
Note: Because the user area is controlled in block units, the flag values of all sectors are the
same within a block.
13/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
(2) Spare area
Flag
FFh
0Fh —
F0h The block is labeled as a BAD block. Substitute
Other values The substitute destination is detected from the
The specified sector is accessed.
An uncorrectable error (UNC) is returned and
processing is aborted.
An uncorrectable error (UNC) is returned and
processing is aborted.
Read
—
Write
The specified sector is accessed.
processing is performed again to change the
substitute destination.
substitute management information and the
substitute destination is accessed.
If the substitute destination cannot be detected,
the substitute destination obtained by substitute
processing is accessed.
Note: The same flag control is performed in spare areas and user areas.
(3) D-List area
Flag
FFh
Other values Substitute management information (duplicate)
The specified sector is accessed.
Substitute management information (duplicate)
is used as the new substitute management
information (original). Substitute management
information (duplicate) is written to another
block and used as new substitute management
information (duplicate).
When the Flag of the substitute management
information (duplicate) is not equal to FFh,
substitute management information is
reconstructed.
Read
Write
The specified sector is accessed.
is used as the new substitute management
information (original). Substitute management
information (duplicate) is written to another
block and used as new substitute management
information (duplicate).
When the Flag of the substitute management
information (duplicate) is not equal to FFh,
substitute management information is
reconstructed.
5.3.1.2 Substitute Management Information Management
In accordance with section 5.1.3, “Substitute Management Information Format”, substitute
management information is arranged beginning at the rear of the spare area.
If two pieces of substitute management information cannot be read correctly, the substitute
source is read from the address of the header section in each sector of a substituted block within
the spare area, a substitute management information is reconstructed.
5.4 Generation of Substitute Management Information
Substitute management information is generated in all chips. An issue of Low Level Format
command as one of the vendor-unique commands initiates a scanning on memories, and
defective block locations in spare area and in user area are identified and substitute correspondance
is registered as a default setting of a substitute management information.
14/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
5.5 Substitute Processing
When a defective sector is found in a user area, the user area block containing the defective sector
will be substituted with another normal block of the spare area.
Substitute processing
Unused block detection
within same port
Unused block?
Yes
Register in substitute management
information (original)
Register in substitute management
information (duplicate)
Generate and write defective
block data
Write to substitute destination
of user data
End
No
Set error indicating no substitute
destination
Defective block data: Index to show a block contains a defective sector(s).
This index is stored in the header section of a block.
15/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
5.6 Substitute Destination Detection Processing
If the sector accessed in the user area is defective and has already been substituted, the substitute
destination is detected.
Substitute destination search
Flag?
0Fh
This chip?
No
Yes
Acquire from header section
Acquisition OK?
No
Yes
Acquire from substitute
management information
Yes
Value other than 0Fh (excluding FFh)
of same port
Acquisition OK?
No
Acquire from header
section of substituted
block of spare area
F0h
UNC error, abort
processing
Yes
Acquisition OK?
No
End Error end
16/33
¡ Semiconductor ML54051
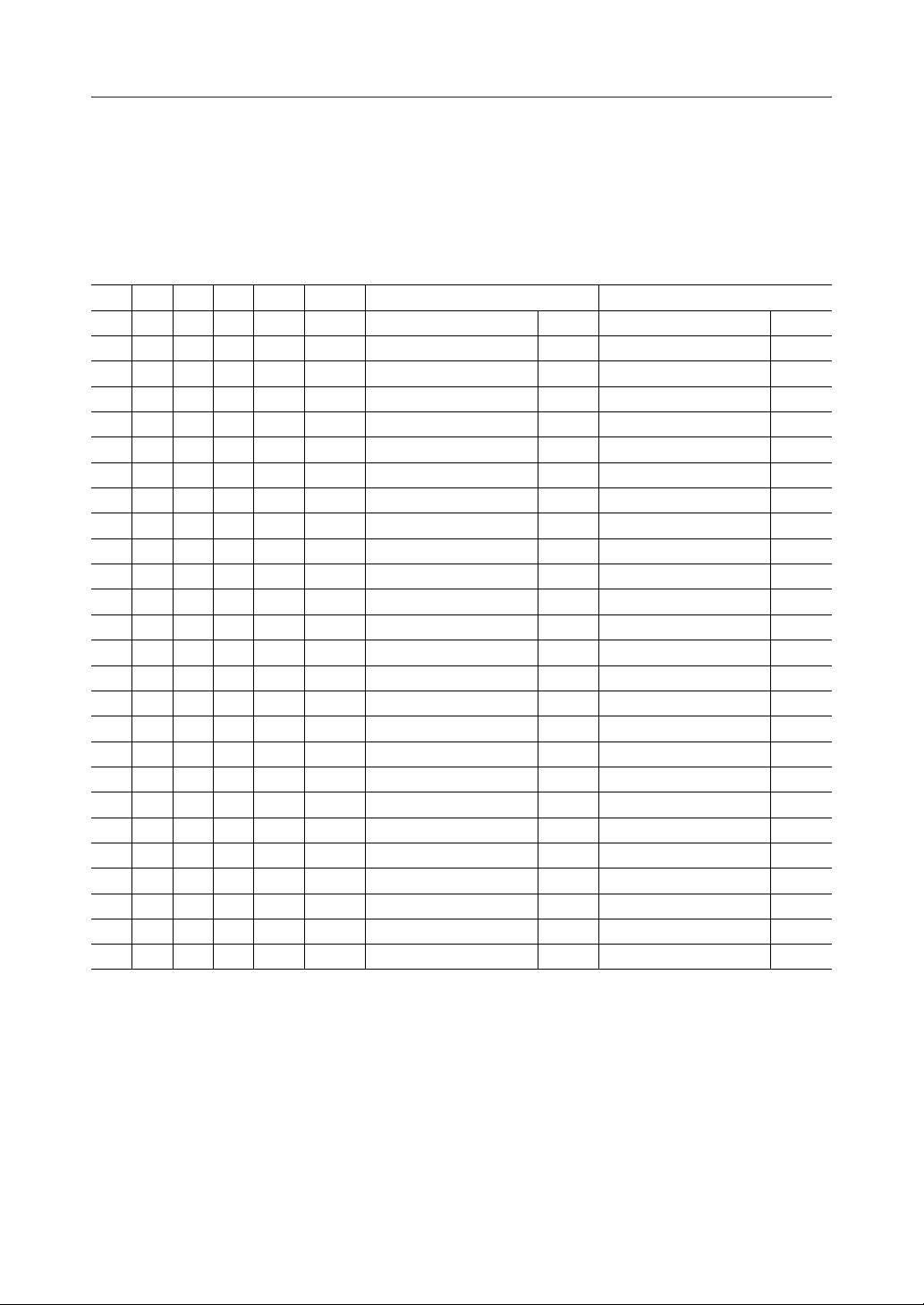
6. ATA REGISTERS
When a mode such as memory mode or I/O mode is configured, the host must use different
addresses for access.
6.1 Memory Mapped Configuration
-CE1 -CE2
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
-REG
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
A10
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
A9-A4
A3-A0 Read (-OE = L) Write (-WE = L)
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Don't care
(000x)
0h
1h
(000x)
2h
3h
(001x)
4h
5h
(010x)
6h
7h
(011x)
(100x)
8h
9h
(100x)
Dh
(110x)
Eh
Fh
(111x)
*
(xxx0)
(xxx1)
*
16-bit Data
8-bit Data
Error
Error
Sector Count
Sector Number
Sector Number
Cylinder Low
Cylinder High
Cylinder High
Drive/Head
Status
Status
Duplicate Data
Duplicate Even
Duplicate Odd
Duplicate Odd
Duplicate Error
Duplicate Error
Alternate Status
Drive Address
Drive Address
16-bit Data
Even Data
Odd Data
Odd Data
D15 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D15 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D15 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
16-bit Data
8-bit Data
Features
Features
Sector Count
Sector Number
Sector Number
Cylinder Low
Cylinder High
Cylinder High
Drive/Head
Command
Command
Duplicate Data
Duplicate Even
Duplicate Odd
Duplicate Odd
Duplicate Features
Duplicate Features
Device Control
Not Used
Not Used
16-bit Data
Even Data
Odd Data
Odd Data
D15 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D15 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D15 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
17/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
6.2 I/O Mapped 16 Contiguous Registers Configuration
-CE1 -CE2
0
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
-REG
A9-A4
A3-A0 Read (-IORD = L) Write (-IOWR = L)
*
*
*
(000x)
*
*
*
(001x)
*
*
*
(010x)
*
*
*
(011x)
*
*
*
*
(100x)
*
*
(110x)
*
*
*
(111x)
*
* Don't care
0h
0h
1h
2h
3h
4h
5h
6h
7h
8h
8h
9h
Dh
Eh
Fh
16-bit Data
8-bit Data
Error
Error
Sector Count
Sector Number
Sector Number
Cylinder Low
Cylinder High
Cylinder High
Drive/Head
Status
Status
Duplicate Data
Duplicate Even
Duplicate Odd
Duplicate Odd
Duplicate Error
Duplicate Error
Alternate Status
Drive Address
Drive Address
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
6.3 Primary I/O Mapped Configuration
D15 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D15 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
16-bit Data
8-bit Data
Features
Features
Sector Count
Sector Number
Sector Number
Cylinder Low
Cylinder High
Cylinder High
Drive/Head
Command
Command
Duplicate Data
Duplicate Even
Duplicate Odd
Duplicate Odd
Duplicate Features
Duplicate Features
Device Control
Not Used
Not Used
D15 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D15 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
-CE1 -CE2
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
1
-REG
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
A9-A0
1F0h
1F0h
1F1h
1F0h/1F1h
1F2h
1F3h
1F2h/1F3h
1F4h
1F5h
1F4h/1F5h
1F6h
1F7h
1F6h/1F7h
3F6h
3F7h
3F6h/3F7h
Read (-IORD = L) Write (-IOWR = L)
16-bit Data
8-bit Data
Error
Error
Sector Count
Sector Number
Sector Number
Cylinder Low
Cylinder High
Cylinder High
Drive/Head
Status
Status
Alternate Status
Drive Address
Drive Address
D15 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
16-bit Data
8-bit Data
Features
Features
Sector Count
Sector Number
Sector Number
Cylinder Low
Cylinder High
Cylinder High
Drive/Head
Command
Command
Device Control
Not Used
Not Used
D15 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
18/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
6.4 Secondary I/O Mapped Configuration
-CE1 -CE2
0
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
1
-REG
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
A9-A0
170h
170h
171h
170h/171h
172h
173h
172h/173h
174h
175h
174h/175h
176h
177h
176h/177h
376h
377h
376h/377h
16-bit Data
8-bit Data
Error
Error
Sector Count
Sector Number
Sector Number
Cylinder Low
Cylinder High
Cylinder High
Drive/Head
Status
Status
Alternate Status
Drive Address
Drive Address
6.5 True IDE Mapped Configuration
Read (-IORD = L) Write (-IOWR = L)
D15 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
16-bit Data
8-bit Data
Features
Features
Sector Count
Sector Number
Sector Number
Cylinder Low
Cylinder High
Cylinder High
Drive/Head
Command
Command
Device Control
Not Used
Not Used
D15 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D15 : D8
D7 : D0
• Command Block Register
-CE1 -CE2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
-REG
A9-A3
A2-A0 Read (-IORD = L) Write (-IOWR = L)
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
*
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Don't care
0h
1h
2h
3h
4h
5h
6h
7h
(xxx)
• Control Block Register
-CE1 -CE2
1
1
1
1
1
-REG
A9-A3
A2-A0 Read (-IORD = L) Write (-IOWR = L)
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
*
*
*
*
*
* Don't care
(xxx)
(0xx)
(10x)
6h
7h
16-bit Data
Error
Sector Count
Sector Number
Cylinder Low
Cylinder High
Drive/Head
Status
Not Used
High Impedance
High Impedance
High Impedance
Alternate Status
Drive Address
D15 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D17 : D0
D7 : D0
16-bit Data
Features
Sector Count
Sector Number
Cylinder Low
Cylinder High
Drive/Head
Command
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Device Control
Not Used
D15 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
D7 : D0
19/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
6.6 ATA Registers
ATA registers realize functions of the PC Card ATA Specifications.
6.6.1 Data Register (Write/Read)
This 16-bit or 8-bit register is used in the transfer of data blocks between the internal data buffer
and the host. Data can be transferred via consecutive 16-bit or 8-bit accesses to the data register.
6.6.2 Error Register (Read Only)
Additional information regarding the cause of a processing error in the previously executed
command is indicated. If the error bit of the status register has been set, the host must examine
this register.
D7
BBK
D6
UNC
D5
D4
0
IDNF
D3
0
D2
ABRT
D1
0
D0
AMNF
BBK : This bit is set when a Bad Block is detected.
UNC : This bit is set when an Uncorrectable Error is encountered.
IDNF : The requested sector ID is in error or cannot be found.
ABRT : This bit is set if the command has been aborted or when an invalid command has been
issued.
AMNF : This bit is set in case of a general error.
6.6.3 Feature Register (Write Only)
This register is used to write information related to commands.
D7 D6 D5 D4
Feature Bytes
D3 D2 D1 D0
6.6.4 Sector Count Register (Write/Read)
This register is used to specify the number of sectors or address of logical blocks to be processed
by a command. By reading this register after a command has been completed, the host can check
the number of sectors not processed by the command.
D7 D6 D5 D4
D3 D2 D1 D0
Sector Count
20/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
6.6.5 Sector Number Register (Write/Read)
This register is used to specify the sector number or logical block address where processing by
the command will begin. By reading this register after a command has been completed, the host
can check the sector number or logical block address processed by the command.
D7 D6 D5 D4
Sector Number/LBA7-LBA0
D3 D2 D1 D0
6.6.6 Cylinder Low Register (Write/Read)
This register is used to specify the lower cylinder number or the logical block address where
processing by the command will begin. By reading this register after a command has been
completed, the host can check the last lower cylinder number or logical block address that was
processed by the command.
D7 D6 D5 D4
Cylinder Low/LBA15-LBA8
D3 D2 D1 D0
6.6.7 Cylinder High Register (Write/Read)
This register is used to specify the upper cylinder number or the logical block address where
processing by the command will begin. By reading this register after a command has been
completed, the host can check the last upper cylinder number or logical block address that was
processed by the command.
D7 D6 D5 D4
Cylinder High/LBA23-LBA16
D3 D2 D1 D0
6.6.8 Drive Head Register (Write/Read)
This register is used to specify the head number or the logical block address where processing
by the command will begin. By reading this register after a command has been completed, the
host can check the last upper head number or logical block address that was processed by the
command.
D7
1
D6
LBA
D5
1
D4
DRV#
D3
HS3/LBA27D2HS2/LBA26D1HS1/LBA25D0HSO/LBA24
LBA: 1: LBA (logical block address) mode
0: CHS address mode
DRV#: card number 0: drive 0 is selected
1: drive 1 is selected
If the value of the Drive# bit of the socket copy register matches the value of this bit, this
controller will execute the command.
21/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
6.6.9 Status Register & Alternate Status Register (Read Only)
This register indicates the internal status of the controller. When the host reads this register, the
controller clears pending interrupt requests. However, even if the alternate status register is
read, interrupts requests will not be cleared.
D7
BUSY
D6
RDY
D5
DWF
D4
DSC
D3
DRQ
D2
CORR
D1
IDX
D0
ERR
BUSY: This bit is set in the following cases:
•from the time when the host writes a command to the command register
until processing of the command is completed
•when hardware and software resets have been executed from the host
RDY: This bit indicates Drive Ready.
DWF: This bit is set when an error related to substitute processing occurs during
access to the internal flash memory. If this bit is set, commands that follow
may not execute properly.
DSC: This bit is always set to 1.
DRQ: During execution of a command that involves data transfer, this bit is set once
the transfer preparations are made.
CORR: This bit indicates that a correctable error has occurred during access to flash
memory.
IDX: This bit is always set to 0.
ERR: This bit is set when an error occurs during command execution. Detailed
information is set in the error register.
6.6.10 Device Control Register (Write Only)
This register is used to control interrupt requests from the card and to specify software reset.
D7 D6 D5
X
D4 D3
SRST: While this bit is 1, the controller is in the reset state.
-IEN: 1: Interrupt signal mask, 0: Interrupt signal non-mask
6.6.11 Command Register (Write Only)
This register is used to set the command code.
D7 D6 D5 D4
Command Code
D2
1
D3 D2 D1 D0
SRST
D1
-IEN
D0
0
22/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
7. PCMCIA INTERFACE
7.1 ATA Commands (Standard)
Supported ATA commands are listed below.
CodeCommand FR SC SN CY DH C/R/W
Check Power Mode
Execute Drive Diagnostic
Format Track
Identify Drive
Idle
Idle Immediate
Initialize Drive Parameters
Read Buffer
Read Long Sector
Read Multiple
Read Sector (s)
Read Verify Sector (s)
Recalibrate
Seek
Set Features
Set Multiple Mode
Set Sleep Mode
Standby
Standby Immediate
Write Buffer
Write Long Sector
Write Multiple
Write Sector (s)
98h, E5h
90h
50h
ECh
97h, E3h
95h, E1h
91h
E4h
22h, 23h
C4h
20h, 21h
40h, 41h
1xh
7xh
EFh
C6h
99h, E6h
96h, E2h
94h, E0h
E8h
32h, 33h
C5h
30h, 31h
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
———
——
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
C
C
W
R
C
C
C
R
R
R
R
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
W
W
W
W
FR: Features register SC: Sector count register SN: Sector number register
CY: Cylinder register DH: Drive/head register
C/R/W: C - Control, R - Read, W - Write
: modified, valid — : invalid
23/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
7.2 Commands for CompactFlash
Supported CompactFlash commands are listed below.
CodeCommand FR SC SN CY DH C/R/W
Request Sense
Erase Sector (s)
Translate Sector
Wear Level
Write Multiple w/o Erase
Write Sector (s) w/o Erase
03h
C0h
87h
F5h
CDh
38h
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
C
C
R
C
W
W
7.3 Vendor-Unique Commands
Vendor-unique commands can be executed by writing “FFh” data to the command register when
a value from the below chart has been written to the feature register.
Command Code FR C/R/W
Low Level Format
Change Information
Change Physical Cylinder
Read All
Un Lock
FFh Undefined
FFh Undefined
FFh Undefined
FFh Undefined
FFh Undefined
Initialization of substitute information, all sectors
Change CIS/Identify information
Set maximum value of physical cylinder
Read 528 bytes of the specified page
Vendor-unique commands that follow are valid
Description
C
W
C
R
C
Change Physical Cylinder: Sets the maximum value of the user area that is accessible from the
host. For details, refer to section 7.6, “Number of Installed Memory Chips and CHS Structure.”
7.4 Card Information Structure
The desired card information structure (CIS) can be stored by the change information command.
7.5 Identify Information
The desired identify information can be stored by the change information command.
24/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
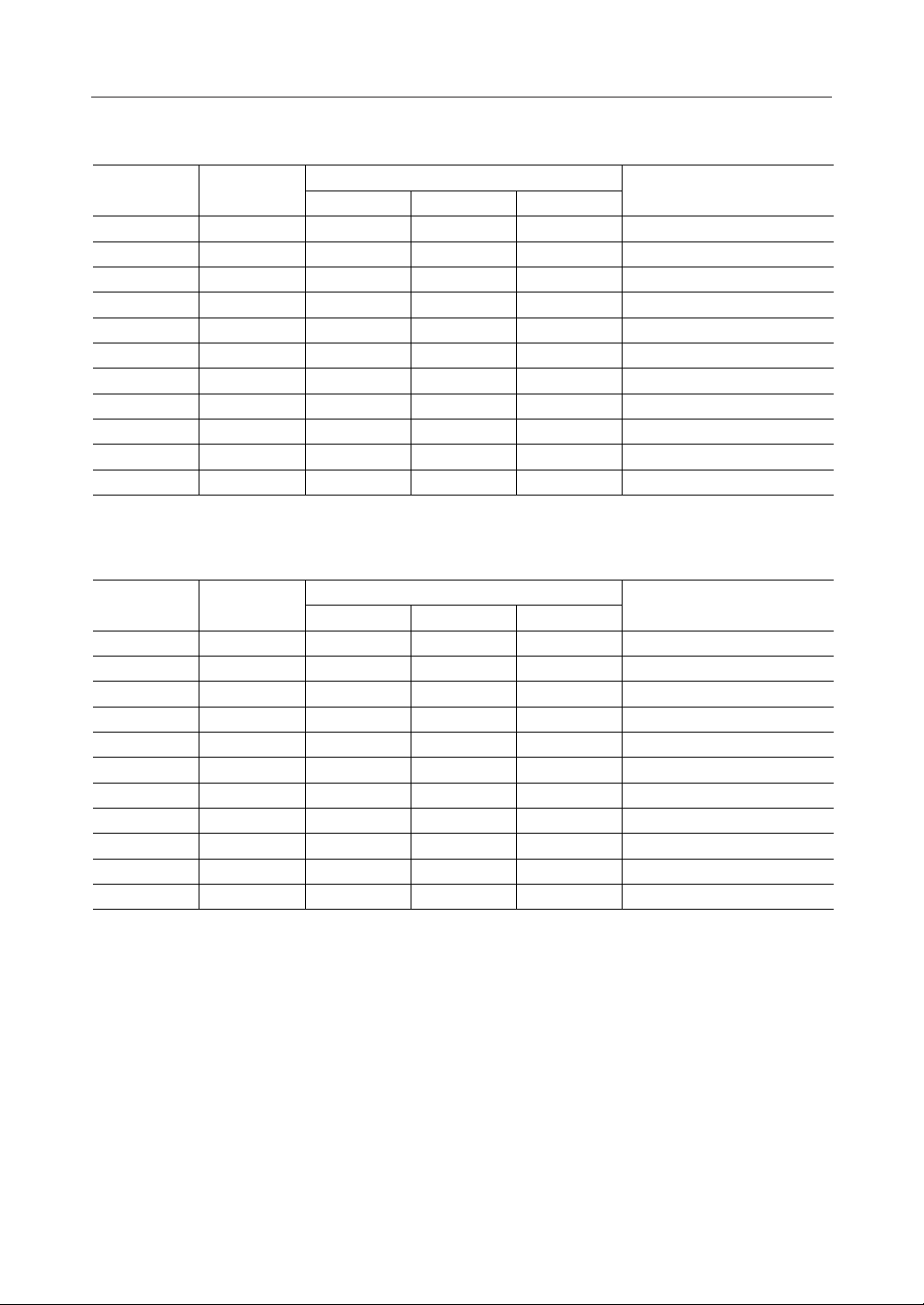
7.6 Number of Installed Memory Chips and CHS Structure
NAND flash memory is erased in block units. Since block erasing is also performed during a 1page (sector) write, efficiency is increased during write operations by serially addressing sectors
within the same block.
The CHS structure and number of installed memory chips when using 64, 128, 256 and 512 Mbit
memory are listed below (where C is the default value). The C value of the CHS address can be
set by the change physical cylinder command (a vendor-unique command).
• 64 Mbit Memory
Capacity No. of Chips
8
16
32
48
64
80
96
112
128
144
160
• 128 Mbit Memory
Capacity No. of Chips
16
32
64
96
128
160
192
224
256
288
320
10
12
14
16
18
20
10
12
14
16
18
20
CHS
CS
1
2
4
6
8
1
2
4
6
8
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
CS
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
H
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
CHS
H
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
16
32
32
32
32
32
32
32
32
32
32
32
64
64
64
64
64
64
64
64
64
64
LBA Max. (Hex)
16000
(3E80)
32000
(7D00)
64000
(FA00)
96000
(17700)
128000
(1F400)
160000
(27100)
192000
(2EE00)
224000
(36B00)
256000
(3E800)
288000
(46500)
320000
(4E200)
LBA Max. (Hex)
32000
(7D00)
64000
(FA00)
128000
(1F400)
192000
(2EE00)
256000
(3E800)
320000
(4E200)
384000
(5DC00)
448000
(6D600)
512000
(7D000)
576000
(8CA00)
640000
(9C400)
25/33
¡ Semiconductor ML54051
• 256 Mbit Memory
Capacity No. of Chips
32
64
128
192
256
320
384
448
512
576
640
• 512 Mbit Memory
Capacity No. of Chips
64
128
256
384
512
640
768
896
1024
1152
1280
10
12
14
16
18
20
10
12
14
16
18
20
CHS
CS
1
2
4
6
8
1
2
4
6
8
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
—
—
CS
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
—
—
—
—
—
—
H
2
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
—
—
CHS
H
4
4
8
12
16
—
—
—
—
—
—
32
64
64
64
64
64
64
64
64
—
—
32
64
64
64
64
—
—
—
—
—
—
LBA Max. (Hex)
64000
(FA00)
128000
(1F400)
256000
(3E800)
384000
(5DC00)
512000
(7D000)
640000
(9C400)
768000
(BB800)
896000
(DAC00)
1024000
1152000
1280000
LBA Max. (Hex)
1024000
1280000
1536000
1792000
2048000
2304000
2560000
128000
256000
512000
768000
(FA000)
(119400)
(138800)
(1F400)
(3E800)
(7D000)
(BB800)
(FA000)
(138800)
(177000)
(1B5800)
(1F4000)
(232800)
(271000)
26/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
7.7 Modes
7.7.1 Memory Mapped
In the memory mapped mode, ATA registers appear in the 0 to 2K window of common memory
space.
7.7.2 I/O Mapped 16 Contiguous Registers
In the I/O mapped 16 contiguous registers mode, contiguous ATA registers appear in I/O space.
7.7.3 Primary I/O Mapped
In the primary I/O mapped mode, ATA registers appear in 1F0h to 1F7h and 3F6h to 3F7h of the
standard I/O address space.
7.7.4 Secondary I/O Mapped
In the secondary I/O mapped mode, ATA registers appear in 170h to 177h and 376h to 377h of
the standard I/O address space.
7.7.5 True IDE
This mode is compatible with True IDE Mode.
27/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
8. CHIP MODES
8.1 Types
There are four types of chip modes. Note that default pin assignments change depending upon
the chip mode.
• Normal Mode
This mode is normally used.
• External ROM Connection Mode
This mode is used for connection to external ROM.
• External CPU Connection Mode
This mode is used for debugging. When this mode is activated, the internal microcontroller
does not operate.
• Test Mode
This mode is used for testing. The test mode is not normally used.
8.2 Settings
Chip modes are determined by the status of pcfg[1:0] when the power-on-reset signal (porn
signal) rises.
pcfg [1 : 0] = 11 Normal Mode
pcfg [1 : 0] = 01 External CPU Connection Mode
pcfg [1 : 0] = 10 External ROM Connection Mode
pcfg [1 : 0] = 00 Test Mode
8.3 Pin Assignment
Interface Normal
Extended Bus (Low-Level) xah [15 : 8] xah [15 : 8]xah [15 : 8] O I/O I/O
Extended Bus (Low-Level) xad [7 : 0] xad [7 : 0]xad [7 : 0] O I/O I/O
Extended Bus (Low-Level) xrd xrdxrd O O I
Extended Bus (Low-Level) xwr xwrxwr O O I
Extended Bus (Low-Level) xale xalexale O O I
Host hcseln hcseln xinthcseln I I O
NAND Flash mctl mctl xpsennxpsenn I I I
NAND Flash mcen [7] mcen [7] xrstxrst O O O
NAND Flash mcen [6] mcen [6] xclkxclk O O O
Signal Name
External ROM Connection External CPU Connection
28/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
9. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
9.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter
Power Supply Voltage
Input Voltage
Output Voltage
Input Current
Normal Buffer
5 V Tolerant Buffer
Normal Buffer
5 V Tolerant Buffer
Normal Buffer
5 V Tolerant Buffer
Symbol
V
DD
V
I
V
O
I
I
Condition
Tj = 25°C
The standard is
VSS = 0 V
Rating
–0.3 to +4.6
–0.3 to V
–0.3 to +6.0
–0.3 to V
–0.3 to +6.0
–10 to +10
–6 to +6
DD
DD
+ 0.3
+ 0.3
Storage Temperature Tstg –65 to +150 °C
9.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
Parameter
Power Supply Voltage
Operating Temperature Tj –40 to +85 °C
Symbol
V
DD
Range
3.0 to 3.6
9.3 DC Characteristics
= 3.0 to 3.6 V, VSS = 0 V, Tj = –40 to +85°C)
(V
DD
Parameter Symbol
High Level Input Voltage
Low Level Input Voltage V
Schmitt Trigger Threshold Voltage
High Level Output Voltage V
Low Level Output Voltage V
High Level Input Current I
Low Level Input Current I
Output Leakage Current
Standby Power Supply Current I
V
V
V
DV
I
I
DDS
OH
OL
IH
IL
OZH
OZL
Condition
IH
IL
t+
t–
t
5 V tolerant input
——–0.3 +0.8
— 1.5— 2.0
— 1.00.7 —
Vt+ – V
t–
TTL normal input
2.0 V
IOH = –100 mA—VDD – 0.2 —
IOL = 2, 4, 8 mA —2.4 —
IOH = –100 mA—— 0.2
IOL = 2, 4, 8 mA —— 0.4
VIH = V
DD
VIL = V
SS
–1 —
(50 kW pull-up) –66–170 –15
VOL = V
DD
VOL = V
SS
(50 kW pull-up) –66–170 –15
Output open —–10 +10
Rating
Typ.Min. Max.
—
DD
+ 0.3
—2.0 5.5
0.50.4 —
0.01—1
+0.01
0.01—1
–0.01–1 —
Unit
V
mA
Unit
V
Unit
V
mA
Note 1 : Listed values are for a normal buffer and a 5 V tolerant buffer unless otherwise
specified.
Note 2 : Typical values are indicated for a typical condition at V
= 3.3 V and Tj = 25°C.
DD
29/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
10. BUS SPECIFICATIONS
10.1 I/O Mode
The I/O mode conforms to PCMCIA-ATA and IDE specifications.
10.2 Bus Timing Specifications
Bus timing conforms to PCMCIA-ATA, IDE and NAND flash memory specifications.
10.3 Power ON/OFF, Reset, Busy Timing
Parameter Symbol
-CE Signal Level
V
(CE)
I
Condition
0 V £ V
2.0 V £ V
VIH £ V
CC
CC
< 2.0 V
< V
CC
IH
Reset Setup Time tsu (RESET) — TBD
Ready Release Delay Time td (BSY) — TBD
-CE Recovery Time trec (VCC) — TBD
VCC Rise Time tpr 10%Æ(VCC + 5%) 90% *1 TBD
VCC Fall Time tpf (VCC – 5%) 90%Æ10% *1 TBD
tw (RESET) — TBD
Reset Width
th (Hi-Z RESET)
ts (Hi-Z RESET)
— TBD
— TBD
Specified Value
Min. Max.
0V
V
– 0.1 VI Max.
CC
V
VI Max.
IH
Max.
I
Unit
V
ms
ms
ms
ms
ms
ms
ms
ms
*1: tpr and tpf are defined as the time of the “straight-line change from 10% to 90% of VCC”,
and vice-versa. Even if the rise and fall waveforms are non-linear, the maximum slope of
the waveform must meet these specifications.
tpr
V
CC
-CE1, -CE2
tsu(RESET)
V
IH
2 V
tsu(CE)
tw(RESET)td(BSY)th(Hi-Z RESET)
RESET
+RDY/-BSY
V
CC
-CE1, -CE2
RESET
Hi-Z
ts(Hi-Z RESET)
trec(VCC)
2 V
Hi-Z
tpf
V
IH
30/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
11. PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
(Unit : mm)
LQFP144-P-2020-0.50-K
Mirror finish
Package material
Lead frame material
Pin treatment
Solder plate thickness
Package weight (g)
Epoxy resin
42 alloy
Solder plating
5 mm or more
1.37 TYP.
Notes for Mounting the Surface Mount Type Package
The SOP, QFP, TSOP, SOJ, QFJ (PLCC), SHP and BGA are surface mount type packages, which
are very susceptible to heat in reflow mounting and humidity absorbed in storage.
Therefore, before you perform reflow mounting, contact Oki’s responsible sales person for the
product name, package name, pin number, package code and desired mounting conditions
(reflow method, temperature and times).
31/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
12. APPLICATION EXAMPLES
Stand-Alone Chip
Connecter
5 to 3
VCC
-CE1
-CE2
-OE
-WE
RDY/-BSY/-IREQ
WP/-IOIS16
-IORD
-IOWR
RST
-WAIT
-INPACK
-REG
SPKR
-STSCHG
A25
-CD1
-CD2
GND
20 MHz
Vlt
Dct
Address
Cnv
ML54051 SRAM
ha0-10
hd0-15D0-15 Data
hcen1
hcen2
hoen
hwen
hirqn
hiois16n
hiordn
hiowrn
hrst
hwaitn
hinpackn
hregn
hspkr
hstschgn
hcseln
porn
xin
xout
mctl
txd
rxd
ra0-16A0-10
rd0-7
rren
rwen
rcen
maio0-7
maren
mawen
marbn
macle
maale
mbio0-7
mbren
mbwen
mbrbn
mbcle
mbale
mwpn
mcen0
mcen1
mcen2
mcen3
mcen4
mcen5
mcen6
mcen7
Address
Address/Data
Address/Data
A0-16
D0-7Data
-OE
-WE
-CE
I/O1-8
-RE
-WE
R/-B
CLE
ALE
-WP
-CE
I/O1-8
-RE
-WE
R/-B
CLE
ALE
-WP
-CE
I/O1-8
-RE
-WE
1
2
R/-B
3 • • • • •
CLE
ALE
-WP
-CE
I/O1-8
-RE
-WE
R/-B
4 • • • • •
CLE
ALE
-WP
-CE
-RE
-WE
R/-B
CLE
ALE
-WP
-CE
-RE
-WE
R/-B
CLE
ALE
-WP
-CE
I/O1-8
15
I/O1-8
16
32/33

¡ Semiconductor ML54051
Chip and External Decoder Circuit
Connecter
5 to 3
VCC
-CE1
-CE2
-OE
-WE
RDY/-BSY/-IREQ
WP/-IOIS16
-IORD
-IOWR
RST
-WAIT
-INPACK
-REG
SPKR
-STSCHG
A25
-CD1
-CD2
GND
20 MHz
Vlt
Dct
Address
Cnv
ML54051 SRAM
ha0-10
hd0-15D0-15 Data
hcen1
hcen2
hoen
hwen
hirqn
hiois16n
hiordn
hiowrn
hrst
hwaitn
hinpackn
hregn
hspkr
hstschgn
hcseln
porn
xin
xout
mctl
txd
rxd
ra0-16A0-10
rd0-7
rren
rwen
rcen
maio0-7
maren
mawen
marbn
macle
maale
mbio0-7
mbren
mbwen
mbrbn
mbcle
mbale
mwpn
mcen0
mcen1
mcen2
mcen3
mcen4
mcen5
mcen6
mcen7
Address
Address/Data
Address/Data
Decorder
en
in0
in1
in2
in3
in4
out30
out31
A0-16
D0-7Data
-OE
-WE
-CE
out0
out1
out2
-RE
-WE
R/-B
CLE
ALE
-WP
-CE
-RE
-WE
R/-B
CLE
ALE
-WP
-CE
I/O1-8
I/O1-8
I/O1-8
-RE
-WE
1
2
R/-B
3 • • • • •
CLE
ALE
-WP
-CE
I/O1-8
-RE
-WE
R/-B
4 • • • • •
CLE
ALE
-WP
-CE
-RE
-WE
R/-B
CLE
ALE
-WP
-CE
-RE
-WE
R/-B
CLE
ALE
-WP
-CE
I/O1-8
63
I/O1-8
64
33/33
 Loading...
Loading...