OKI ML53812-2 Datasheet

D
ATA SHEET
O K I N E T W O R K P R O D U C T S
ML53812-2
H.100/H.110 CT Bus System Interface and
Time-Slot Interchange
January 2000

Revision History
September 1999 320101-005 Previous Release
January 2000 320101-006 Timing tables altered on page 50:
“Local Clock and Frame Synchronization Timing”,
“Local Clock to CT Bus Clock Skew”, and
“Local Serial Stream Timing”
Timing diagram (Figure 11) atered on page 51:
“Local Clock and Frame Synchronization Timing”
Oki Semiconductor

Contents
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Pin Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
ML53812-2 176-Pin LQFP Pin Assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Signal descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Local Bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
CT Bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Test Access Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Pin Continuity Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Analog PLL Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Microprocessor Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Analog PLL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Slave PLL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Master PLL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Reference Master . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Local Clock and Frame Sync . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Local Streams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
CT Bus Streams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
CT_D disable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Diagnostic Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
GPIO Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Message Channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Microprocessor Address Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Command/Status Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Internal Address Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Configuration Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Device ID Registers (Read Only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Stream Switch Routing Registers, AR = 1007h:1000h (Ch. 7:0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Stream Switch Connection Mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Transmit Switch Routing Registers, AR = 20ffh:2000h (Ch. 255:0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Receive Switch Routing Registers, AR = 30ffh:3000h (Ch. 255:0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Indirect Transmit Switch Parallel Access Registers, AR = 40ffh:4000h (Ch. 255:0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Indirect Receive Switch Parallel Access Registers, AR = 50ffh:5000h (Ch. 255:0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Electrical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Absolute Maximum Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Recommended Operating Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
DC Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
AC Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
H.100/H.110 Bus Timing Specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Clock Skew Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
ML53812-2 Package specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
LQFP176 Package Outlines and Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
LQFP176 Mounting Pad Reference Measurements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Oki Semiconductor

■ ■
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Oki Semiconductor

ML53812-2
H.100/H.110CT Bus System Interface and Time Slot Interchange
1.0 DESCRIPTION
The ML53812-2 is a complete CT Bus system interface and time slot interchange device that provides a
cost-effective connection between a computer board’s telephony interfaces or signal processing resources
and the CT Bus. The ML53812-2 is an evolution of existing time-slot interchange ICs which offers seam-
less interoperability with SCbus devices.
A key element in computer telephony (CT) equipment is the auxiliary telecom bus. Most manufacturers
of high-capacity CT equipment have used one or more types of telecom buses to transport and switch
low-latency communications traffic between boards within the computer, bypassing the computer’s
main I/O and memory buses. To simplify the integration of devices that incorporate a telecom bus, the
Enterprise Computer Telephony Forum (ECTF) developed a standard bus (H.100/H.110 CT Bus™) that
provides compatibility modes with the most prevalent telecom buses today (SCbus™ and MVIP-90™),
as well as the capacity and feature set needed to support the next generation of high capacity CT servers.
The new CT Bus is embraced by Dialogic under the Signal Computing System Architecture™ (SCSA™)
umbrella of open standards for building interoperable CT systems.
The ML53812-2 runs in both 4 MHz and 8 MHz SCbus modes and supports the switching features
needed to integrate CT Bus devices with 4 MHz SCbus, 8 MHz SCbus, and 2 MHz MVIP-90 devices.
Because the H.100/H.110 CT Bus uses an identical switching model and clock speeds to that used for the
SCbus, developers have unparalleled flexibility in integrating these two types of devices, or in transition-
ing from one type to the other.
The ML53812-2 takes full advantage of the mandatory and optional features defined in the ECTF H.100
and H.110 interoperability specifications. It is a non-blocking 512 x 4096 time slot switch, interfacing up
to 512 ports on its parent device to any of the 4096 time slots on the new CT Bus. The high number of local
time slots available makes it easier to design high-density CT hardware, supporting as many as eight net-
work interfaces or 256 voice processing ports per chip.
This powerful chip is offered in an ultra slim profile (176-pin LQFP package, with a 24 mm x 24 mm x 1.4
mm body size) that makes it possible to mount the chip on either side of the board. The chip is fully soft-
ware programmable, and can be controlled by a variety of microprocessors, including Intel and Motorola
in both multiplexed and nonmultiplexed modes.
1Oki Semiconductor

■
ML53812-2 ■ ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
2.0 FEATURES
• High functionality, low cost implementation of
the ECTF H.100/H.110 interoperability
specifications.
• Simple to connect PCI and cPCI™ board-level
circuitry to the universally accepted CT Bus™.
• Ultra slim profiling (176-pin LQFP package).
• Up to 512 programmable connections (256
transmit and 256 receive) to any of the 4096
time slots on the H.100/H.110 CT Bus.
• 8-channel stream-to-stream switching for data
stream connections at variable rates.
• Implementation of all compatibility signals for
complete interoperability with existing 4 MHz
SCbus™, 8 MHz SCbus, 2 MHz MVIP-90™
devices, and H-MVIP™.
• Provides reliable clock synchronization for
network-grade connection to digital network
interfaces.
2.1 Applications
• Supports all H.100/H.110 CT Bus clock fallback
features.
• Choice of constant or minimum switching
delay on a per time slot basis.
• 3.3 V I/O with 5 V tolerant input.
• Supports multiplexed and nonmultiplexed
address/data bus modes for both Intel and
Motorola microprocessors.
• Supports CT Bus optional message channel
interface, for both H.100 (PCI) and H.110 (cPCI)
applications.
• Supports a variety of framing formats via a
configurable local bus.
• Efficient microprocessor interface access to
Local and CT Bus data streams through direct
parallel access to/from transmit and receive
switch.
• Low and high-density computer telephony hardware (PCI and cPCI platforms)
• Enhanced service platforms
• Private branch exchanges (PBXs)
• Wireless base stations
• Internet telephony systems
• Digital trunking equipment
2 Oki Semiconductor

––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– ■ ML53812-2
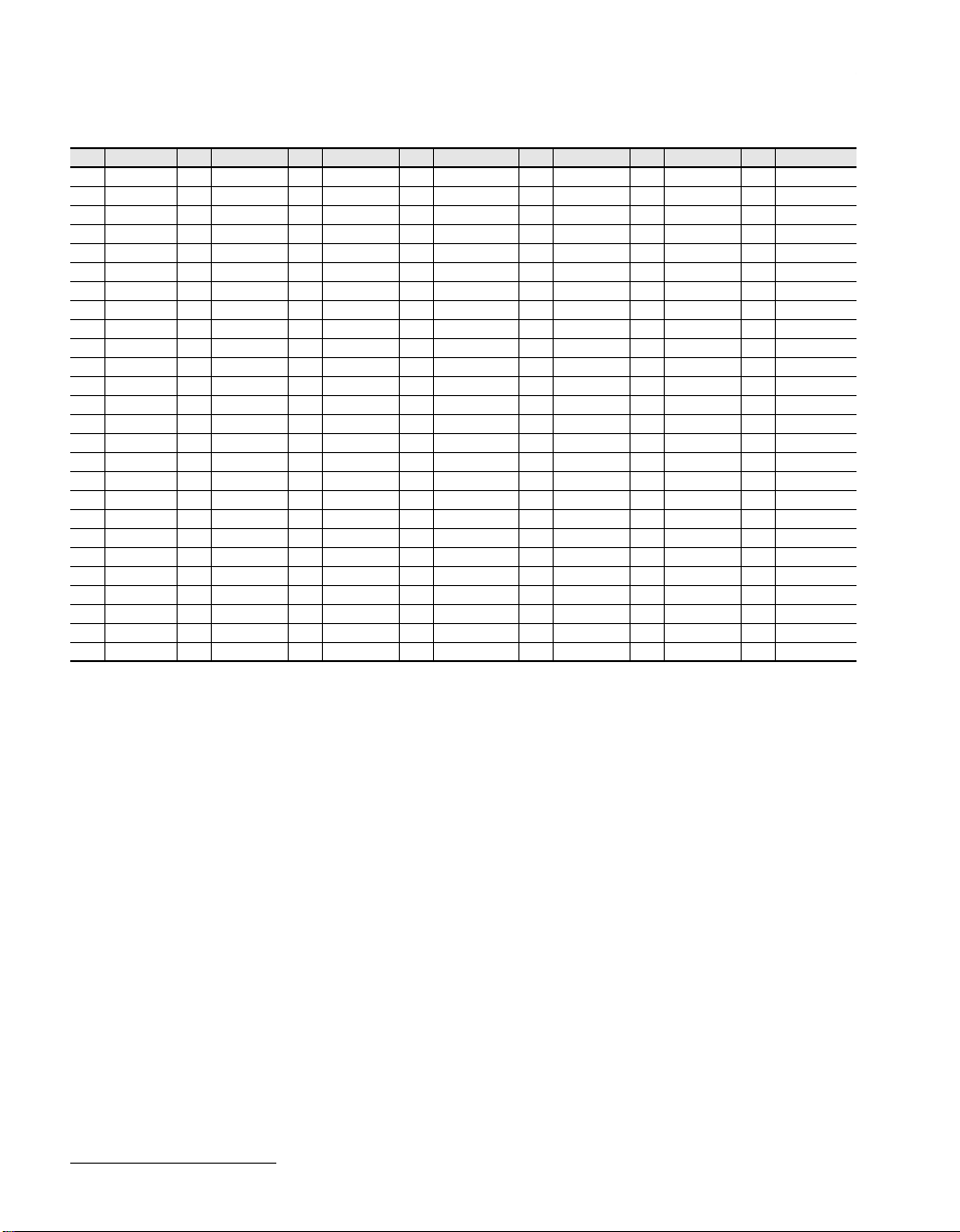
3.0 PIN CONFIGURATION
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
■
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
123456789
1011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041424344
Figure 1. ML53812-2 176-Pin LQFP Pin Configuration
3Oki Semiconductor
■
ML53812-2 ■ ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
3.1 ML53812-2 176-Pin LQFP Pin Assignment
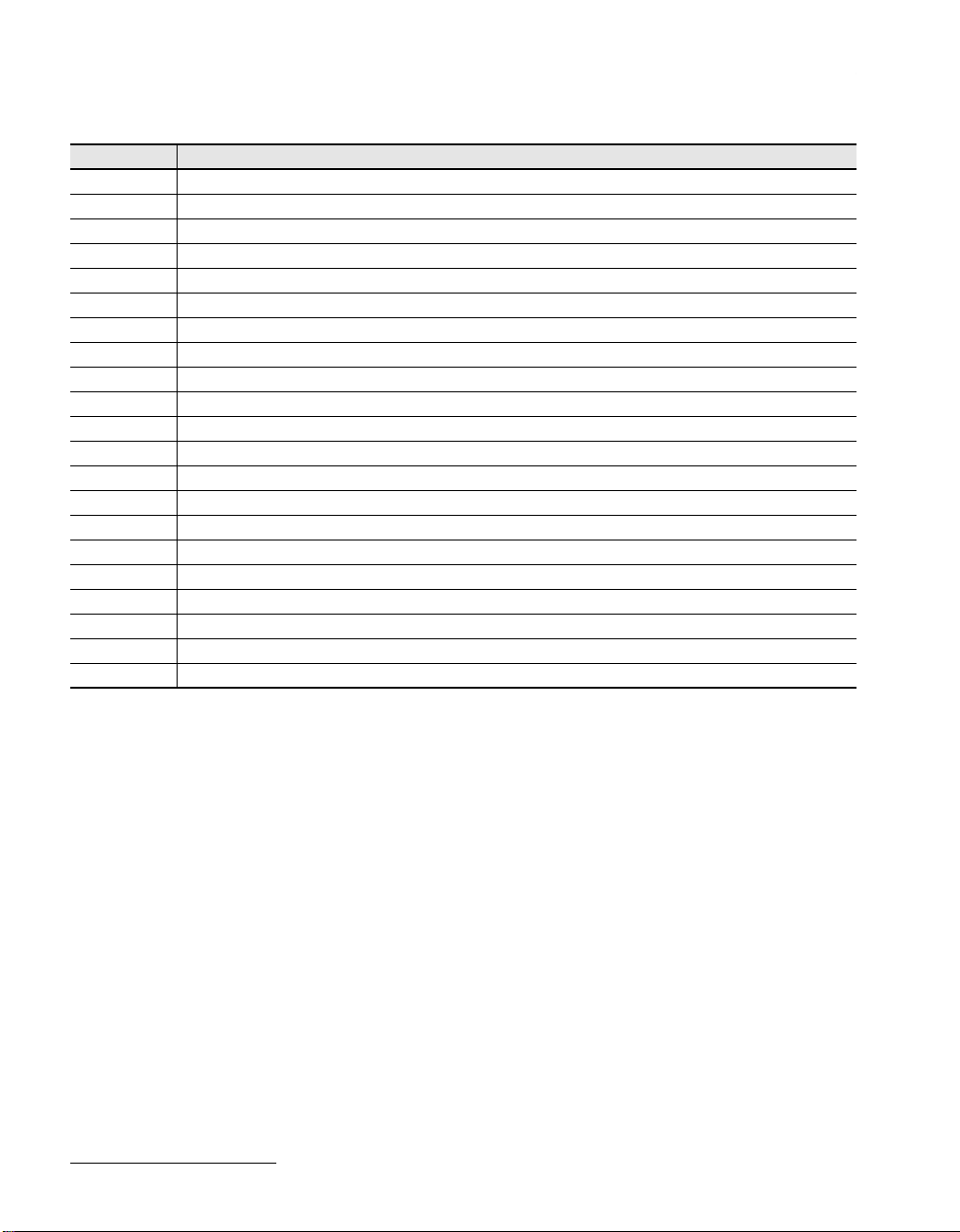
Pin Pin Name Pin Pin Name Pin Pin Name Pin Pin Name Pin Pin Name Pin Pin Name Pin Pin Name
1 VDDC 27 D_6 53 VSSO 79 VDDO 105 CT_D_9 131 CT_D_25 157 L_SI_6
2 ALE 28 A_6 54 APPL_CLKREF 80 CT_FRAME_B_N 106 CT_D_10 132 VSSC 158 L_SI_7
3 VDDO 29 D_7 55 APLL_TEST 81 VSSO 107 VDDO 133 VDDC 159 VSSO
4 CS_N 30 A_7 56 TMS 82 CT_NETREF_2 108 CT_D_11 134 CT_D_26 160 L_SO_0
5 RD_N 31 A_8 57 TCK 83 CT_NETREF_1 109 VSSO 135 VDDO 161 L_SO_1
6 WR_N 32 A_9 58 TRST_N 84 VDDO 110 CT_D_12 136 CT_D_27 162 L_SO_2
7 VSSO 33 NC 59 TDI 85 CT_C8_A 111 CT_D_13 137 VSSO 163 L_SO_3
8 RESET 34 VDDO 60 TDO 86 VSSO 112 VDDO 138 CT_D_28 164 VDDO
9 I_N 35 L_NETREF_0 61 VDDO 87 CT_FRAME_A_N 113 CT_D_14 139 CT_D_29 165 L_SO_4
10 INT 36 L_NETREF_1 62 MC_TXD 88 VSSC 114 VSSO 140 VDDO 166 L_SO_5
11 VDDO 37 L_NETREF_2 63 MC_RXD 89 VDDC 115 CT_D_15 141 CT_D_30 167 L_SO_6
12 D_0 38 L_NETREF_3 64 MC_CLK 90 CT_D_0 116 CT_D_16 142 CT_D_31 168 L_SO_7
13 A_0 39 VSSO 65 VSSO 91 VDDO 117 VDDO 143 VSSO 169 VSSO
14 D_1 40 L_NETREF_4 66 C16_NEG_N 92 CT_D_1 118 CT_D_17 144 GPIO_0 170 L_CLK_0
15 A_1 41 L_NETREF_5 67 C16_POS_N 93 CT_D_2 119 CT_D_18 145 GPIO_1 171 L_FS_0
16 VSSO 42 L_NETREF_6 68 VDDO 94 VSSO 120 VSSO 146 VDDO 172 L_CLK_1
17 D_2 43 L_NETREF_7 69 C4_N 95 CT_D_3 121 CT_D_19 147 GPIO_2 173 L_FS_1
18 A_2 44 VSSC 70 C2 96 CT_D_4 122 VDDO 148 GPIO_3 174 CT_D_DISABLE
19 D_3 45 VDDC 71 VSSO 97 VDDO 123 CT_D_20 149 VSSO 175 TEST
20 A_3 46 VDDO 72 SCLKX2_N 98 CT_D_5 124 VSSO 150 L_SI_0 176 VSSC
21 VDDO 47 APLL_VDDO 73 SCLK 99 VSSO 125 CT_D_21 151 L_SI_1
22 D_4 48 APLL_VDDC 74 VDDO 100 CT_D_6 126 CT_D_22 152 L_SI_2
23 A_4 49 APPL_PC 75 FR_COMP_N 101 VDDO 127 VDDO 153 L_SI_3
24 D_5 50 APPL_VCO 76 CT_MC 102 CT_D_7 128 CT_D_23 154 VDDO
25 A_5 51 APPL_VSSC 77 VSSO 103 CT_D_8 129 CT_D_24 155 L_SI_4
26 VSSO 52 APLL_VSSO 78 CT_C8_B 104 VSSO 130 VSSO 156 L_SI_5
[1]
1. In this document, signals ending with “_N” are “active low” (eg. CS_N). Note that in the H.100/H110 specification, active low is indicated with a
preceding forward slash (eg. /CS).
4 Oki Semiconductor

––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– ■ ML53812-2
4.0 SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS
Signal Description
Name
D_[7:0] Microprocessor Data Bus. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 8 mA, 5V tolerant)
A_ [9:0] Microprocessor Address Bus. (Input, TTL Schmitt, 5V tolerant)
ALE (AS) Intel Bus Mode - Address Latch Enable. Motorola Bus Mode - Address Strobe. The Microprocessor Address Bus A[9:0] is latched
CS_N Chip Select. This active low signal selects the ML53812-2 for a microprocessor read or write operation. (Input, TTL Schmitt, 5V
RD_N (STRB_N) Intel Bus Mode - Microprocessor Bus Read. Motorola Bus Mode - Microprocessor Bus Strobe. (Input, TTL Schmitt, 5V tolerant)
WR_N (R/W_N) Intel Bus Mode - Microprocessor Bus Write. Motorola Bus Mode - Microprocessor Bus Read/Write signal.
RESET Reset. This active high input signal initializes the microprocessor interface, configuration, and routing registers. (Input, TTL
I_N (M) Microprocessor Bus Mode. When this input is low, Intel Bus Mode is selected. When this input is high, Motorola Bus Mode is
CT_D_DISABLE CT_D Global disable. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 8 mA, 50 k Pull Up, 5V tolerant)
L_NETREF_[7:0] Local Network Reference [7:0] Input. (Input, TTL Schmitt, 50 k Pull Up, 5V tolerant)
L_SI_[7:0] Local bus Serial Input Data Input. (Input, TTL Schmitt, 50 k Pull Up, 5V tolerant)
MC_TXD Message Channel Transmit Data Input. (Input, TTL Schmitt, 50 k Pull Up, 5V tolerant)
APLL_CLKREF Analog PLL Clock Reference Input. (Input, TTL Schmitt, 50 k Pull Up, 5V tolerant)
APLL_VDDO +3.3 Volt Analog PLL I/O Power Supply
APLL_VDDC +3.3 Volt Analog PLL Core Power Supply
APLL_PC Analog PLL Phase Comparator Analog Output
APLL_VCO Analog PLL VCO Analog Input
APLL_VSSC Analog PLL Core Ground
APLL_VSSO Analog PLL I/O Ground
APLL_TEST Analog PLL Test Enable Input. (Input, TTL Schmitt, 50 k Pull Up, 5V tolerant)
TEST Test Select. This input enables the pin continuity test. (Input, TTL Schmitt, 50 k Pull Up, 5V tolerant)
TMS Test Access Port Mode Select. (Input, TTL Schmitt, 50 k Pull Up, 5V tolerant)
TCK Test Access Port Clock. (Input, TTL Schmitt, 50 k Pull Up, 5V tolerant)
TRST_N Test Access Port Reset. (active low). (Input, TTL Schmitt, 50 k Pull Up, 5V tolerant)
TDI Test Access Port Data Input. (Input, TTL Schmitt, 50 k Pull Up, 5V tolerant)
INT Interrupt Output. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 50 k Pull Up, 8 mA, 5V tolerant)
CT_D_[31:0] CT Bus Serial Data Streams. (I/O, PCI, 5V tolerant)
CT_FRAME_A_N CT Bus "A" Frame Sync. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 24 mA, 5V tolerant)
CT_C8_A CT Bus "A" 8 MHz Clock. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 24 mA, 5V tolerant)
CT_NETREF_1 CT Bus Network Reference 1. (I/O, PCI, 5V tolerant)
CT_NETREF_2 CT Bus Network Reference 2. (I/O, PCI, 5V tolerant)
CT_FRAME_B_N CT Bus "B" Frame Sync. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 24 mA, 5V tolerant)
CT_C8_B CT Bus "B" 8 MHz Clock. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 24 mA, 5V tolerant)
CT_MC CT Bus Message Channel. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 24 mA, 5V tolerant)
[1]
Description
internally on the falling edge of this signal. (Input, TTL Schmitt, 5V tolerant)
tolerant)
(Input, TTL Schmitt, 5V tolerant)
Schmitt, 5V tolerant)
selected. (Input, TTL Schmitt, 5V tolerant)
■
5Oki Semiconductor
■
ML53812-2 ■ ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Signal Description
Name
FR_COMP_N Compatibility frame sync used by SCbus, MVIP-90, and H-MVIP. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 24 mA, 5V tolerant)
SCLK SCbus Clock. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 24 mA, 5V tolerant)
SCLKX2_N SCbus X2 Clock. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 24 mA, 5V tolerant)
C2 MVIP-90 2.048 MHz Clock. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 6 mA, 5V tolerant)
C4_N MVIP-90 4.096 MHz Clock. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 6 mA, 5V tolerant)
C16_POS_N H-MVIP 16.384 MHz Positive active low Clock. High to low transition on frame boundary. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 24 mA, 5V tolerant)
C16_NEG_N H-MVIP 16.384 MHz Negative active low Clock. Low to high transition on frame boundary. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 24 mA, 5V tolerant)
L_CLK_1 Local bus Clock 1. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 24 mA, 50 k Pull Up, 5 V tolerant)
L_FS_1 Local bus Frame Sync 1. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 24 mA, 50 k Pull Up, 5V tolerant)
L_CLK_0 Local bus Clock 0. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 24 mA, 50 k Pull Up, 5 V tolerant)
L_FS_0 Local bus Frame Sync 0. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 50 k Pull Up, 24 mA, 5V tolerant)
L_SO_[7:0] Local bus Serial Output Data Streams. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 50 k Pull Up, 8 mA, 5V tolerant)
MC_CLK Message Channel Clock Output. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 50 k Pull Up, 6 mA, 5V tolerant)
MC_RXD Message Channel Receive Data Output. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 50 k Pull Up, 6 mA, 5V tolerant)
GPIO_[3:0] General Purpose I/O ports. (I/O, TTL Schmitt, 24 mA, 50 k Pull Up, 5V tolerant)
TDO Test Access Port Data Output. (Output, 6 mA, 5V tolerant)
NC No Connect
VDDO +3.3 Volt I/O Power Supply
VSSO I/O Ground
VDDC +3.3 Volt Core Power Supply
VSSC Core Ground
1. Signals ending in “_N” are active low.
[1]
Description
6 Oki Semiconductor

––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– ■ ML53812-2
5.0 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The ML53812-2 has the following interfaces:
■
• Microprocessor Interface
• Local Serial Data In
• Local Serial Data Out
• Local Timing
Microprocessor
Interface
Local Serial
Data In
Local Serial
Data Out
Local Timing
APLL
Reference Clock
Configuration &
Routing Register
Internal Control
• Analog PLL Reference Clock
• CT Bus Timing
• CT Bus Serial Data
8 Channel
Stream Switch
256 x 4096
Transmit Switch
Local
Connect
4352 x 256
Receive Switch
Internal Timing
Slave Digital
PLL
Master
Digital PLL
Analog
PLL
131.072 MHz
Figure 2. Block Diagram
CT Bus Serial Data
CT Bus Timing
5.1 Local Bus
The local bus consists of up to eight serial input ports and eight serial output ports, totalling 512 possible
local bus connections to the CT Bus. The input and output ports can be configured independently as two
groups of four 2 Mb/s streams, two 4 Mb/s streams, or one 8 Mb/s stream. The chip includes two independent, configurable local clock and frame synchronization signals. The local clocks have configurable
polarity and frequency that can be set to 2 MHz, 4 MHz, 8 MHz, or 16 MHz regardless of local stream
data rate. The local frame syncs also have a configurable polarity and can be set to use one of three framing formats (early, straddle, or late).
To transfer data to and from the local bus, the ML53812-2 allows the user to select a minimum delay or
constant delay buffer mode on a per channel basis. In the minimum delay mode, the input-output buffer
transfer occurs on the next 2 Mb/s time slot boundary, reducing any potential channel delay for classic
voice processing applications. In the constant delay mode, the buffer transfer occurs at the frame boundary for bundling and proper switching of wide-band data, for data sent on the ISDN H channel.
7Oki Semiconductor

■
ML53812-2 ■ ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
5.2 CT Bus
The ML53812-2 provides access to all 4096 CT Bus time slots. The upper 16 data lines run at 8 Mb/s,
while the lower 16 data lines can be configured, in groups of four, to run at 8 Mb/s, 4 Mb/s, or 2 Mb/s
for compatibility with SCbus and MVIP-90 devices.
The chip uses an internal analog phase locked loop (PLL) as a rate multiplier to produce a 131.072 MHz
internal clock locked to a variety of reference frequencies. This high frequency internal clock provides
fine grained correction steps (7.6 nS) for the master and slave digital PLLs. The main CT Bus network reference signal can be configured to run at 8 kHz, 1.544 MHz, or 2048 MHz. The timing for the CT Bus can
be configured to be derived from the local clock and frame sync signals to allow multiple chips to be connected to the CT Bus without overloading the reference clock line.
The ML53812-2 incorporates internal master digital PLL circuitry that is designed to meet the jitter attenuation, holdover and Maximum Time Interval Error (MTIE) requirements of 62411 Stratum 3,4 and 4E.
This enables the ML53812-2 to be well suited for developers of digital telephone network interfaces,
where reliable clock synchronization is critical. Because the circuitry is internal, board designers do not
have to add expensive or custom circuitry to support these types of environments.
The ML53812-2 also includes an 8-channel stream-to-stream switch to connect one CT Bus data stream to
another at the same or different data rates. This type of connection makes it possible for CT Bus compatible devices (such as SCbus and MVIP-90) to efficiently exchange data even though they operate at different rates. This stream switch enables switching between any of the 32 CT Bus data streams operating at
2, 4, or 8 Mb/s. Depending upon the data stream rates, the stream switch provides a minimum of 256 and
a maximum of 1024 unidirectional time slot connections. Stream switches in other ML53812-2 devices,
within a system, may be used simultaneously to increase switching capability.
5.3 Test Access Port
The current version of the ML53812-2 does not support IEEE 1149.1 Boundary Scan. The Test Access Port
on the ML53812-2 passes TDI through to TDO when TMS and TRST_N are both high which simplifiers
the transition to eventual Boundary Scan support. Drive TMS and TRST_N both low for normal operation.
5.4 Pin Continuity Test
For normal operation, the TEST pin is driven low. When the TEST pin is high, all pins except VDD, VSS,
NC, APLL_PC, APLL_VCO, TMS, TCK, TRST_N, TDI, TDO, TEST are sequentially "NAND’ed" with
ALE and output on TDO. This test allows each input pin to be toggled and a corresponding output to be
observed on the TDO pin to verify the proper connection of the ML53812-2 to a printed circuit board.
5.5 Analog PLL Test
For normal operation, the APLL_TEST pin is driven low.
5.6 Microprocessor Interface
Both Intel and Motorola microprocessor bus interfaces are supported. Drive I_N (M) low for Intel mode
and high for Motorola mode. Multiplexed addresses are latched on the falling edge of ALE (AS). If multiplexed address is not used, drive ALE (AS) high. Multiplexed address and data must be connected to
both A_ and D_ pins.
8 Oki Semiconductor

––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– ■ ML53812-2
5.7 Analog PLL
The analog PLL is used to create an internal 131.072 MHz clock locked to one of several reference frequencies. The analog PLL reference signal is input on the APLL_CLKREF pin and should be a stable
clock typically
±
25 ppm. An external loop filter is required (see
Figure 3
).
■
0.01 µF
R2
100Ω
CI
R1
19 kΩ
APLL_PC
APLL_VCO
APLL_VSS
Figure 3. Analog PLL Loop Filter
5.8 Slave PLL
The slave PLL is used to generate all of the internal timing for the ML53812-2. Even when the ML538122 is enabled as master, the slave PLL is still in operation. The slave PLL is a fast tracking digital PLL operating at 131.072 MHz.
The slave PLL can be configured to lock to one of the following sources:
• CT_C8_A and CT_FRAME_A
• CT_C8_B and CT_FRAME_B
• SCLK and FR_COMP
• C2 and FR_COMP
• L_CLK_0 and L_FS_0
• L_CLK_1 and L_FS_1
5.9 Master PLL
The master PLL is used to generate timing for the CT Bus. The master PLL is a digital PLL operating at
131.072 MHz. When operating as primary master the PLL can lock to one of eight local network references, or one of two CT Bus network references. These reference signals may be 8 kHz, 1.536 MHz, 1.544
MHz or 2.048 MHz. When operating as secondary master the PLL locks to the primary CT Bus master.
The master PLL can be configured to automatically switch from secondary to primary in the event of a
CT Bus timing error.
The master PLL can be configured to drive either the CT Bus "A" or "B" signals as well as all of the compatibility clocks defined in the H.100/H.110 Specifications.
When operating as the primary master, the PLL provides jitter attenuation with a cut-off frequency of
1.25 Hz and a roll-off of 20dB per decade. When operating as the secondary master, the PLL is fast tracking.
When operating as the primary master, the PLL has a lock range of ±488 ppm (minus the tolerance of
APLL_CLKREF source). The maximum lock time is 3s. Holdover stability is 0.06 ppm, resulting in a
frame slip rate of 42/day, assuming no drift in APLL_CLKREF source, exceeding the 62411 Stratum 3
requirement of 255/day. During normal operation new holdover values are updated at 128ms intervals.
9Oki Semiconductor

■
ML53812-2 ■ ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
To make an MTIE compliant reference switch, enable "Condition Master PLL reference", select the "Master PLL Reference", and configure the "Master PLL Mode " to normal.The master PLL will be locked to
the selected reference.
The following sequence will produce an MTIE-compliant reference switch:
1. Change the "Master PLL Mode" from Normal to Holdover. The master PLL can also be configured to
make this change automatically in the event of a master PLL error.
2. Change the "Master PLL Reference Select" to the new reference, or change the reference source of
CT_NETREF.
3. Change the "Master PLL Mode" back to Normal.
MTIE Specifications
ML53812-2
MTIE during rearrangement 100 ns 1 µs
Phase change slope 81 ns / 1.326 ms 81 ns / 1.326 ms
62411 Stratum 3 and 4E
5.10 Reference Master
CT_NETREF_1 and CT_NETREF_2 can be independently configured to output a reference signal to the
CT Bus selected from one of eight local network reference inputs. The local network references can be
passed through or divided by 192, 193, or 256.
5.11 Local Clock and Frame Sync
Two sets of local clock and frame sync are provided. A variety of clock frequencies, polarities, and framing formats may be selected to allow "glue less" local port interfacing. Each set of local clock and frame
sync may be configured separately. The frequency selection is independent of the local stream rate.
5.12 Local Streams
The local streams consist of up to eight serial input ports and eight serial output ports, defined as two
groups of 128 time-slots. Each group can be independently configured to operate as four 2 Mb/s streams,
two 4 Mb/s streams, or one 8 Mb/s stream.
Local Stream Time Slot to Channel Mapping
Local stream 8Mb/s stream rate time slot 127:0 4Mb/s stream rate time slot 63:0 2Mb/s stream rate time slot 31:0
L_SI_0,L_SO_0 channel 127:0 channel 63:0 channel 31:0
L_SI_1,L_SO_1 - channel 127:64 channel 63:32
L_SI_2,L_SO_2 - - channel 95:64
L_SI_3,L_SO_3 - - channel 127:96
L_SI_4,L_SO_4 channel 255:128 channel 191:128 channel 159:128
L_SI_5,L_SO_5 - channel 255:192 channel 191:160
L_SI_6,L_SO_6 - - channel 223:192
L_SI_7,L_SO_7 - - channel 255:224
10 Oki Semiconductor

––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– ■ ML53812-2
5.13 CT Bus Streams
Connection to all 32 CT Bus streams is supported without restriction. The upper 16 streams run at 8Mb/s
while the lower 16 may be configured, in groups of four, to operate at 8Mb/s, 4Mb/s, or 2Mb/s.
5.14 CT_D disable
The user may disable all CT_D output streams in the event of a bus timing error. When enabled, an error
on the slave PLL reference source causes the CT_D streams to be tri-stated until an entire frame time
without errors has passed. The CT_D_DISABLE signal is provided to link multiple ML53812-2 devices.
5.15 Diagnostic Mode
Diagnostic mode tri-states all CT Bus signals while internally looping-back CT Bus outputs to inputs.
This mode allows a printed circuit board containing the ML53812-2 to be thoroughly tested without
causing CT Bus errors.
5.16 Interrupts
The ML53812-2 supports the following interrupt sources:
• CT Bus A Error
• CT Bus B Error
CT Bus A (CT Bus B) error is detected when CT_C8_A (CT_C8_B) rising edge does not occur within
35 ns of the expected time, relative to the previous period (see
Figure 4
) or when CT_FRAME_A_N
(CT_FRAME_B_N) low does not occur when expected. (See ECTF H.100/H.110 Specifications for
details on CT_C8_(A/B) and CT_FRAME_(A/B)_N signal timing.)
• SCbus Error
SCbus error is detected when SCLK does not transition at close to the expected frequency (C_[25:24]
determines the expected frequency) or FR_COMP_N low does not occur when expected. (See ECTF
H.100/H.110 Specifications for details on SCLK, SCLKx2, and FR_COMP_N signal timing.)
• MVIP Error
MVIP error is detected when C2 does not transition at close to 2 MHz, or FR_COMP_N low does not
occur when expected. (See ECTF H.100/H.110 Specifications for details on C2 and FR_COMP_N signal timing).
• Master PLL Out of Lock Error
Master PLL error is detected when the master PLL is not locked to the selected Reference defined by
C_[43:40].
• Frame Boundary
Frame Boundary interrupt is not an error condition, and occurs when the internal state machine
crosses a frame boundary.
• GPIO
GPIO interrupt occurs when one or more of the GPIO inputs match the programmed latch polarity,
defined by C_[167:136].
■
11Oki Semiconductor

■
ML53812-2 ■ ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
The interrupts are both globally and individually maskable, and are signaled to the processor via the INT
pin (pin 10). The INT pin can be configured to operate as either push-pull or open drain, and its polarity
(active high or active low) is also selectable.
All of these interrupt latches have an individual enable/clear register and an individual interrupt mask
register associated with them.
Rising edge of CT_C8 occurring
after this limit will trigger an
interrupt (if enabled).
CT_C8_(A/B)
Expected Delay (Approx. 125 ns) Late Allowance (35 ns)
Figure 4. CT_C8_A and CT_C8_B Error Detection
5.17 GPIO Ports
Four general purpose input/output ports are provided. The ports may be individually configured to a
variety of modes and can also be used as interrupt sources. Possible uses of the GPIO ports would be controlling H.100/H.110 termination switches or implementing the SCbus CLKFAIL signal.
5.18 Message Channel
The ML53812-2 provides a complete interface between the CT_MC CT Bus signal and a local HDLC controller. This includes generation of MC_CLK as well as buffering of MC_TXD and MC_RXD.
12 Oki Semiconductor

––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– ■ ML53812-2
6.0 REGISTERS
6.1 Microprocessor Address Map
With Direct Parallel Access Disabled (C_[96] = 0) (Default)
A_[2:0]
7h Reserved
6h Data Register 2 (DR_2)
5h Data Register 1 (DR_1)
4h Data Register 0 (DR_0)
3h Reserved
2h Address Register 1 (AR_1)
1h Address Register 0 (AR_0)
0h Command/Status Register
With Direct Parallel Access Enabled (C_[96] = 1)
A_[9:0]
3FFh:300h Direct Receive Switch Parallel Access Ch. 255:0
2FFh:200h Direct Transmit Switch Parallel Access Ch. 255:0
1FFh:008h Reserved
007h Reserved
006h Data Register 2 (DR_2)
005h Data Register 1 (DR_1)
004h Data Register 0 (DR_0)
003h Reserved
002h Address Register 1 (AR_1)
001h Address Register 0 (AR_0)
000h Command/Status Register
Register
Register
■
13Oki Semiconductor

■
ML53812-2 ■ ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
6.2 Command/Status Register
D_[7:0]
0 Busy (Read Only)
1 Read Command (Write Only)
2 Write Command (Write Only)
3 Terminate Command (Write Only)
4 Reserved
5 Reserved
6 Reserved
7 Reset (Read/Write)
Definition
Busy (D_0) (Read Only)
This bit is set ("1") when a Command that requires synchronization with the ML53812-2's internal state machine has been initiated, and cleared ("0")
when the command has been completed.
For Commands that do not require synchronization this bit is always clear ("0").
The following commands require synchronization:
• Routing Memory Write command
• In-Direct Parallel Access Read or Write command
Read (D_1) (Write Only)
Setting this bit ("1") initiates a synchronized read of the register pointed to by the Address Register. When the Busy bit is clear ("0"), the contents of
the register to be read are available by reading the Data Register. It is NOT necessary to clear ("0") this bit after it has been set ("1").
Note: For "Reads" that do not require synchronization (all "Reads" except In-Direct Parallel Access Read) it is
not necessary to set this bit. The Data Registers can be read immediately after writing the Address Register.
Write (D_2) (Write Only)
Setting this bit ("1") initiates a write of the register pointed to by the Address Register. It is NOT necessary to clear ("0") this bit after it has been set ("1").
Terminate (D_3) (Write Only)
Setting this bit ("1") terminates a command that requires synchronization with the ML53812-2's internal state machine. The command in process is
completed asynchronously and the Busy bit is cleared. It is NOT necessary to clear ("0") this bit after it has been set ("1").
Reset (D_7) (Read/Write)
Setting this bit ("1") resets the ML53812-2 and initializes the Configuration and Routing Registers. This command is analogous to the function of the
RESET pin. Clearing this bit ("0") returns the ML53812-2 to normal operation, ready to be configured.
14 Oki Semiconductor

––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– ■ ML53812-2
■
6.3 Internal Address Map
AR
0014h:0000h Configuration
00ffh:00fch Device ID
1007h:1000h Stream Switch Routing Ch. 7:0
20ffh:2000h Transmit Switch Routing Ch. 255:0
30ffh:3000h Receive Switch Routing Ch. 255:0
40ffh:4000h Indirect Transmit Switch Parallel Access Ch. 255:0
50ffh:5000h Indirect Receive Switch Parallel Access Ch. 255:0
1. AR is the concatenation of AR_1 and AR_0.
2. All other locations reserved (Read-back = 00, Write has no effect).
[1] [2]
Register
15Oki Semiconductor

■
ML53812-2 ■ ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
6.4 Configuration Registers
Note: All "Reserved" configuration registers should be written "0".
Configuration Register Byte 0, AR = 0000h
DR_0
0 0 Diagnostic Mode
1 1 Test Mode
2 2 APLL Power-down Mode
3 3 APLL Bypass Mode
[7:4] [7:4] APLL CLKREF Frequency [3:0]
C Definition
Diagnostic Mode (C_ [0]) (Read/Write)
Set to 0 for normal operation
0
→
Diagnostic Mode Disabled
1
→
Diagnostic Mode Enabled (Default)
Test Mode (C_ [1]) (Read/Write)
Enables testing with the slave DPLL bypassed. Set to 0 for normal operation.
0
→
Test Mode Disabled (Default)
1
→
Test Mode Enabled
APLL Power-down Mode (C_ [2]) (Read/Write)
Powers down analog PLL, resets APLL charge pump. Set to 0 for normal operation.
0
→
APLL Power-down Mode Disabled
1
→
APLL Power-down Mode Enabled (Default)
APLL Bypass Mode (C_ [3]) (Read/Write)
APLL Bypass used during simulation and testing. Set to 0 for normal operation.
0 → APLL Bypass Mode Disabled
1 → APLL Bypass Mode Enabled (Default)
APLL CLKREF Frequency [3:0] (C_ [7:4]) (Read/Write)
Put APLL in Power-down (C_[2] = 1) when changing APLL CLKREF Frequency.
0h → 65.536 MHz (32 X 2.048 MHz) (Default)
1h → 49.152 MHz (24 X 2.048 MHz)
2h → 32.768 MHz (16 X 2.048 MHz)
3h → 16.384 MHz (8 X 2.048 MHz)
4h → 8.192 MHz (4 X 2.048 MHz)
5h → 4.096 MHz (2 X 2.048 MHz)
6h → 2.048 MHz
7h - fh → Reserved
16 Oki Semiconductor
 Loading...
Loading...