Page 1

The Curie
UV-VIS Emission Spectrofluorometer
Installation and Operation Manual
Document Number 640-11100-000-02-0406
Offices:
E-mail: Info@OceanOptics.com (General sales inquiries)
Ocean Optics, Inc.
830 Douglas Ave., Dunedin, FL, USA 34698
Phone 727.733.2447
Fax 727.733.3962
8 a.m.– 8 p.m. (Mon-Thu), 8 a.m.– 6 p.m. (Fri) EST
Ocean Optics B.V. (Europe)
Geograaf 24, 6921 EW DUIVEN, The Netherlands
Phone 31-(0)26-3190500
F ax 31-(0)26-3190505
Info@OceanOpticsBV.com (European sales inquiries)
Orders@OceanOptics.com (Questions about orders)
TechSupport@OceanOptics.com (Technical support)
000-00000-000-02-06
Page 2

Copyright © 2001-2006 Ocean Optics, Inc.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, by any means, electronic,
mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without written permission from Ocean Optics, Inc.
This manual is sold as part of an order and subject to the condition that it shall not, by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, re-sold, hired out or
otherwise circulated without the prior consent of Ocean Optics, Inc. in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published.
Trademarks
All products and services herein are the trademarks, service marks, registered trademarks or registered service marks of their respective owners.
Limit of Liability
Every effort has been made to make this manual as complete and as accurate as possible, but no warranty or fitness is implied. The information
provided is on an “as is” basis. Ocean Optics, Inc. shall have neither liability nor responsibility to any person or entity with respect to any loss or
damages arising from the information contained in this manual.
Page 3

Table of Contents
About This Manual .......................................................................................................... iii
Document Purpose and Intended Audience.............................................................................. iii
Document Summary.................................................................................................................. iii
Product-Related Documentation ............................................................................................... iii
Upgrades......................................................................................................................... iv
Chapter 1: Introduction ......................................................................1
Overview ......................................................................................................................... 1
Features of the Curie System.......................................................................................... 1
Curie System Contents ................................................................................................... 2
Other Items Included with Shipment ......................................................................................... 3
Operating Requirements ................................................................................................. 4
Recommended Additions ..........................................................................................................4
Installing OOIBase32 Software ....................................................................................... 4
Installing Custom Curie Software to Activate Relative Irradiance Mode................................... 6
Connecting the Curie to a PC.......................................................................................... 7
Connecting the Power Cord ............................................................................................ 7
Chapter 2: Configuration....................................................................9
Introduction...................................................................................................................... 9
Configuring the Curie in OOIBase32............................................................................... 9
Initial Start-up ............................................................................................................................ 9
Operator and Serial Number Dialog Box................................................................................... 9
Default Spectrometer Configuration File ................................................................................... 10
Configure Hardware Screen...................................................................................................... 10
Spectrometer Configuration Dialog Box ....................................................................................11
Enabling the Pushbutton ........................................................................................................... 12
Autoincrementing Filenames..................................................................................................... 13
Disabling the Pushbutton........................................................................................................... 14
Turning on the Light Source ............................................................................................ 15
Configuring Data Acquisition Parameters ................................................................................. 16
640-11100-000-02-0406 i
Page 4

Table of Contents
Chapter 3: Using the Curie System...................................................19
Introduction...................................................................................................................... 19
Performing Experiments with the Curie System .............................................................. 19
Preparing for Experiments......................................................................................................... 19
Performing a Fluorescence Experiment .................................................................................... 20
Application Tips ......................................................................................................................... 28
Chapter 4: Troubleshooting...............................................................33
Introduction...................................................................................................................... 33
Problem 1: Curie System Connected to PC Prior to OOIBase32 Installation.................. 33
Removing the Unknown Device from Windows Device Manager............................................. 33
Removing Improperly Installed Files ......................................................................................... 35
Problem 2: Older Version of OOIBase32 Installed.......................................................... 36
Appendix A: Specifications................................................................37
Curie System................................................................................................................... 37
Compatibility for Desktop or Notebook PCs .................................................................... 40
Appendix B: Calibrating the Wavelength of the Curie Spectrometer
..............................................................................................................41
About Wavelength Calibration......................................................................................... 41
Calibrating the Wavelength of the Spectrometer............................................................. 42
Preparing for Calibration............................................................................................................ 42
Calibrating the Spectrometer..................................................................................................... 42
Saving the New Calibration Coefficients ................................................................................... 44
Appendix C: Relative Irradiance Mode..............................................47
Calibrating the Spectrometer for Relative Irradiance....................................................... 48
Preparing for Calibration............................................................................................................ 48
Calibrating the Spectrometer..................................................................................................... 49
Appendix D: Filter Sets.......................................................................51
Index .....................................................................................................53
ii 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 5
About This Manual
Document Purpose and Intended Audience
This document provides you with an installation section to get your system up and running. In addition to
Curie installation and operation instructions, this manual also includes information for locating the
OOIBase32 installation instructions (see Product-Related Documentation
Document Summary
Chapter Description
Chapter 1: Introduction Provides a list of system components, and
operating requirements. Also contains
instructions for connecting the Curie system to
a PC.
).
Chapter 2: Configuration Contains instructions for configuring the Curie
system with the OOIBase32 application
software.
Chapter 3: Using the Curie System Contains instructions for performing
experiments using the Curie system.
Chapter 4: Troubleshooting Provides a list of possible problems that you
may encounter when using your Curie system
and suggested solutions.
Appendix A: Specifications Provides product specifications for the Curie
system.
Appendix B: Calibrating the Wavelength of the
Curie Spectrometer
Appendix C: Relative Irradiance Mode
Appendix D: Filter Sets
Provides instructions for calibrating the
wavelength of the Curie system.
Contains information about Relative Irradiance
Mode.
Contains specifications for the filters supplied
with the Curie.
Product-Related Documentation
• OOIBase32 Spectrometer Operating Software, Operating Instructions
Correcting Device Driver Issues
•
External Triggering Options
•
640-11100-000-02-0406 iii
Page 6

About This Manual
You can access documentation for Ocean Optics products by visiting our website at
http://www.oceanoptics.com. Select Technical → Operating Instructions, then choose the appropriate
document from the available drop-down lists. Or, use the Search by Model Number field at the bottom
of the web page.
You can also access operating instructions for Ocean Optics products on the Software and Technical
Resources CD included with the system.
Engineering-level documentation is located on our website at Technical → Engineering Docs.
Upgrades
Occasionally, you may find that you need Ocean Optics to make a change or an upgrade to your system.
To facilitate these changes, you must first contact Customer Support and obtain a Return Merchandise
Authorization (RMA) number. Please contact Ocean Optics for specific instructions when returning a
product.
iv 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 7

Chapter 1
Introduction
Overview
The Ocean Optics Curie UV-VIS Emission Spectrofluorometer is a self-contained fluorescence system
(the Curie system) that represents a new level of innovation and simplicity in spectroscopy. This
standalone system contains all the components required to make fluorescence measurements in a single
package with a remarkably compact footprint.
The Curie is a high-sensitivity cuvette spectrofluorometer for measuring fluorophores in liquids. The
Curie is a versatile lab system distinguished by internal filtering technology that helps to discriminate
between powerful excitation source wavelengths and the weak spectral emissions from samples, so that
additional correction for excitation and emission is unnecessary and data is more reliable.
Features of the Curie System
Your Curie system offers the following features:
• A high-sensitivity 2048-element CCD-array detector.
• Full spectral analysis (i.e., 2048 wavelengths over the 200–850 nm spectral range). The Curie
system is preloaded with a microcode that allows you to select a delay between activation of the
excitation source and the start of the emission fluorometer’s integration time (available in future
versions of the Curie). This gated-mode operation is ideal for measuring fluorophores that have
long fluorescence lifetimes, such as lanthanides.
640-11100-000-02-0406 1
Page 8
1: Introduction
• Novel filtering technology. The Curie system is the only emission fluorometer with built-in linear
variable filters (LVFs). These LVFs are ideal for spectrally shaping the excitation energy from
the onboard pulsed-xenon excitation source, and eliminate the need for scanning
monochromators. Each filter’s transmission or blocking band can be moved throughout
230–500 nm or 300–750 nm wavelengths.
• A pushbutton to enable the software trigger for automatic spectral saving.
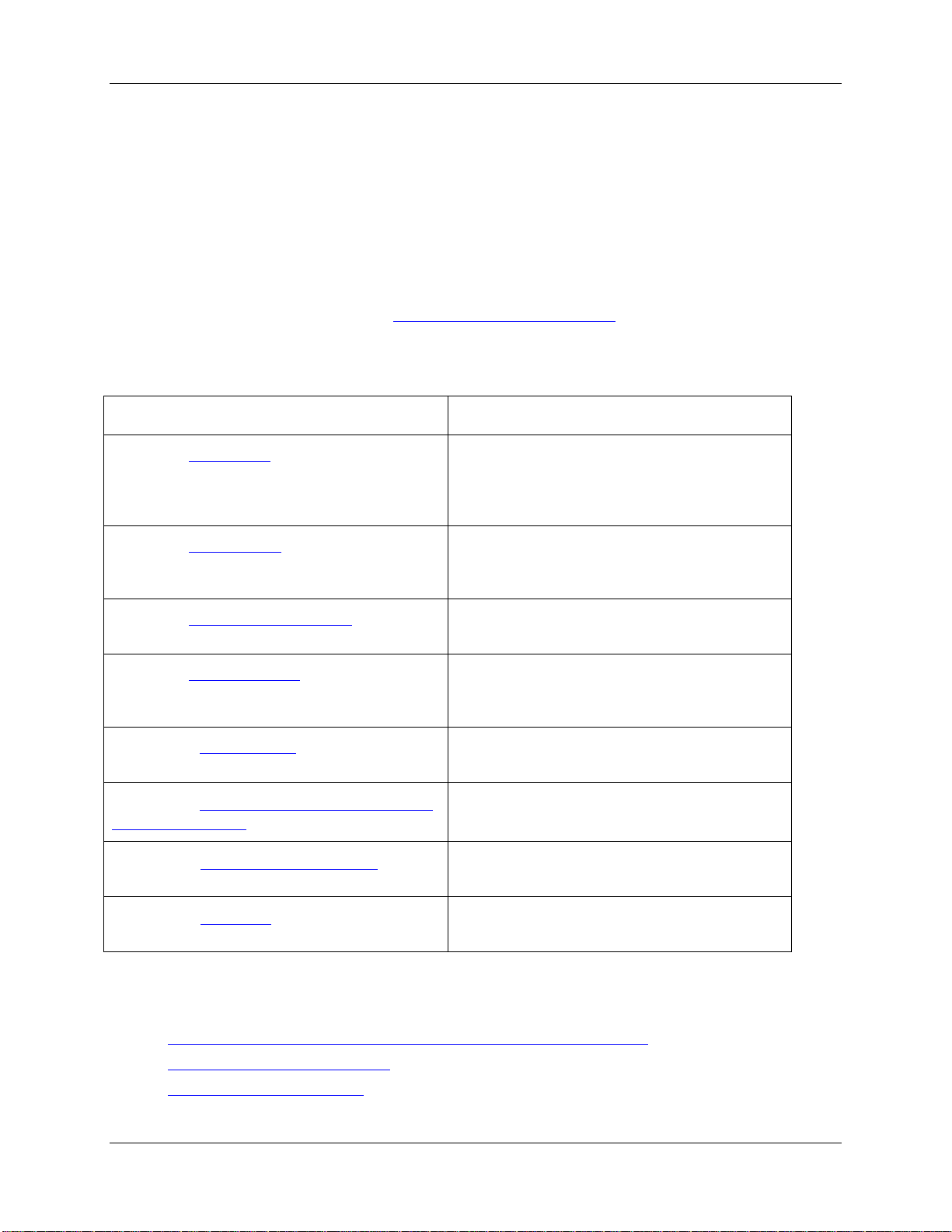
Curie System Contents
The Curie system contains a USB2000 spectrometer that features a microcode optimized for gated
fluorescence measurements and a pulsed xenon light source. It also comes equipped with a set of Linear
Variable Filters (LVFs) mounted internally on sliding rails. The LVFs allow you to specify the excitation
wavelength range for the measurement and eliminate the need for scanning monochromators found in
other systems.
The Curie also features two user-selectable mirrors; one for use with the UV LVF filters optimized for
UV light (a cold mirror) and one standard mirror for use with the VIS LVF filters. A knob on the top of
the unit allows you to select the mirror to use for a specific measurement. A pushbutton allows you to
easily save a spectrum.
A storage compartment is provided on the side of the Curie for storing filters and cuvettes for your
experiments. A switch allows you to operate the light source and the fan.
Curie System Front View
2 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 9

1: Introduction
Curie System Left Panel
Other Items Included with Shipment
Your Curie Fluorescence System from Ocean Optics should also contain the following items:
Packing List: The packing list is located inside a plastic bag attached to the outside of the
shipment box (the invoice is mailed separately). The items listed on the packing slip include all of
the Curie components that have been shipped to you, as well as important information such as the
shipping and billing addresses, and any components that may be on back order.
OOIBase32 software (on the Software and Technical Resources CD)
Curie software (on the Custom Software CD)
USB cable (USB-CBL-1)
12 VDC power supply (WT-12V)
One pack of disposable cuvettes (CVD-UV1S-SAM)
One CVD-DIFFUSE
One filter set containing commonly used filters. See Appendix D, Filter Sets for more
information.
One quartz cuvette (CV-FL-Q-10)
Wavelength Calibration Data Sheet: This data sheet contains information unique to the individual
spectrometer contained in your Curie system. The operating software reads this calibration data
from your spectrometer when it interfaces to a PC through the USB port. Should you need to
reenter it at any time, select Spectrometer | Configure | Wavelength Calibration tab in the
OOIBase32 software. See the OOIBase32 documentation for more information (refer to Product-
Related Documentation for instructions on accessing OOIBase32 documentation).
Note
Please keep the Wavelength Calibration Data sheet for future reference.
640-11100-000-02-0406 3
Page 10

1: Introduction
Software and Technical Resources CD: Each Curie system order comes with Ocean Optics’
Software and Technical Resources CD. This CD contains all Ocean Optics software and manuals
for software operation, spectrometers, and spectroscopic accessories.
Documentation is provided in Portable Document Format (PDF). You need the Adobe Acrobat
Reader (version 6.0 or higher) to view these files. The Adobe Acrobat Reader is included on the
CD and will install automatically (if needed) when you attempt to view a document.
With the exception of OOIBase32 Spectrometer operating software, all Ocean Optics software is
password-protected. Passwords for purchased software are located on the back of the Software
and Technical Resources CD package.
Operating Requirements
You must have the following components to use the Curie Fluorescence System:
Ocean Optics Curie Self-contained Fluorescence System and included accessories (including the
12 VDC power supply)
Windows-based PC with USB connectivity
USB device cable (included)
OOIBase32 operating software (included)
Recommended Additions
The following products, available from Ocean Optics, are recommended additions to your system:
Tungsten light source enabling relative irradiance measurements (LS-1-LL)
PS-HG1-ADP cuvette adapter for LS-1-LL for performing in-house relative irradiance
measurements
Fiber Optic Cable ( QP50-2-VIS/NIR) for performing in-house relative irradiance measurements
and wavelength calibration
HG-1 Mercury Argon Calibration Source for Curie wavelength calibration
Annual Service Package (ASP)
Installing OOIBase32 Software
Caution
Do NOT connect the Curie System to your PC until after you have installed the
OOIBase32 software. Follow the instructions below or in the OOIBase32 manual
(see Product-Related Documentation
) to properly connect and configure your system.
► Procedure
To install OOIBase32 software,
1. Close all other applications running on the PC.
4 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 11

1: Introduction
2. Start the OOIBase32 installation process.
Installing from CD:
a. Insert the Software and Technical Resources CD containing the OOIBase32 software.
The CD interface automatically launches.
b. Click on Install Ocean Optics Software.
c. Click on OOIBase32 Operating Software. The installation process begins.
Installing from the Web:
a. Go to
http://www.oceanoptics.com/technical/softwaredownloads.asp.
b. Right-click on OOIBase32™ Spectrometer Opera ting Software and select Save
Target As… to download the executable to your machine.
c. Double-click on the downloaded file. The installation process begins.
3. Click the Next button at the Welcome screen. The Read Me File screen appears.
4. Read the Read Me file and click the Next button. The Choose Destination Location screen
appears.
5. Click the Browse button to customize your installation location, or click the Next button to
proceed. The Backup Replaced Files screen appears.
6. Click the Yes button to back up replaced files (OOIBase32 prompts you for a backup location), or
click the No button to proceed. The Select Program Manager Group screen appears.
7. Select a program manager group, and then click the Next button. The Start Installation screen
appears.
8. Click the Next button to begin installation. The OOIBase32 Platinum password screen appears.
9. Enter your OOIBase32 Platinum password here, if necessary. Otherwise, click the OK button to
start the install of the free version of OOIBase32.
10. Click the Finish button when the installation completes.
11. Click the OK button to restart your computer.
You have now installed the OOIBase32 software.
640-11100-000-02-0406 5
Page 12
1: Introduction
Installing Custom Curie Software to Activate Relative
Irradiance Mode
Caution
Do NOT connect the Curie System to your PC until after you have installed the
OOIBase32 software. Follow the instructions below or in the OOIBase32 manual
(see Product-Related Documentation
Prior to shipping, your Curie system was calibrated at the factory to allow for operation in Relative
Irradiance mode. Relative Irradiance mode compensates for the grating efficiency and detector sensitivity
of a specific spectrophotometer (see the OOIBase32 manual for more information). It is recommended
that you run your experiments in this mode to achieve true peak shapes and ratios. Follow the protocol
below to install the calibration performed on your Curie instrument. Once you have followed this
protocol, your Curie will be operating in Relative Irradiance mode when you open the OOIBase32
software.
) to properly connect and configure your system.
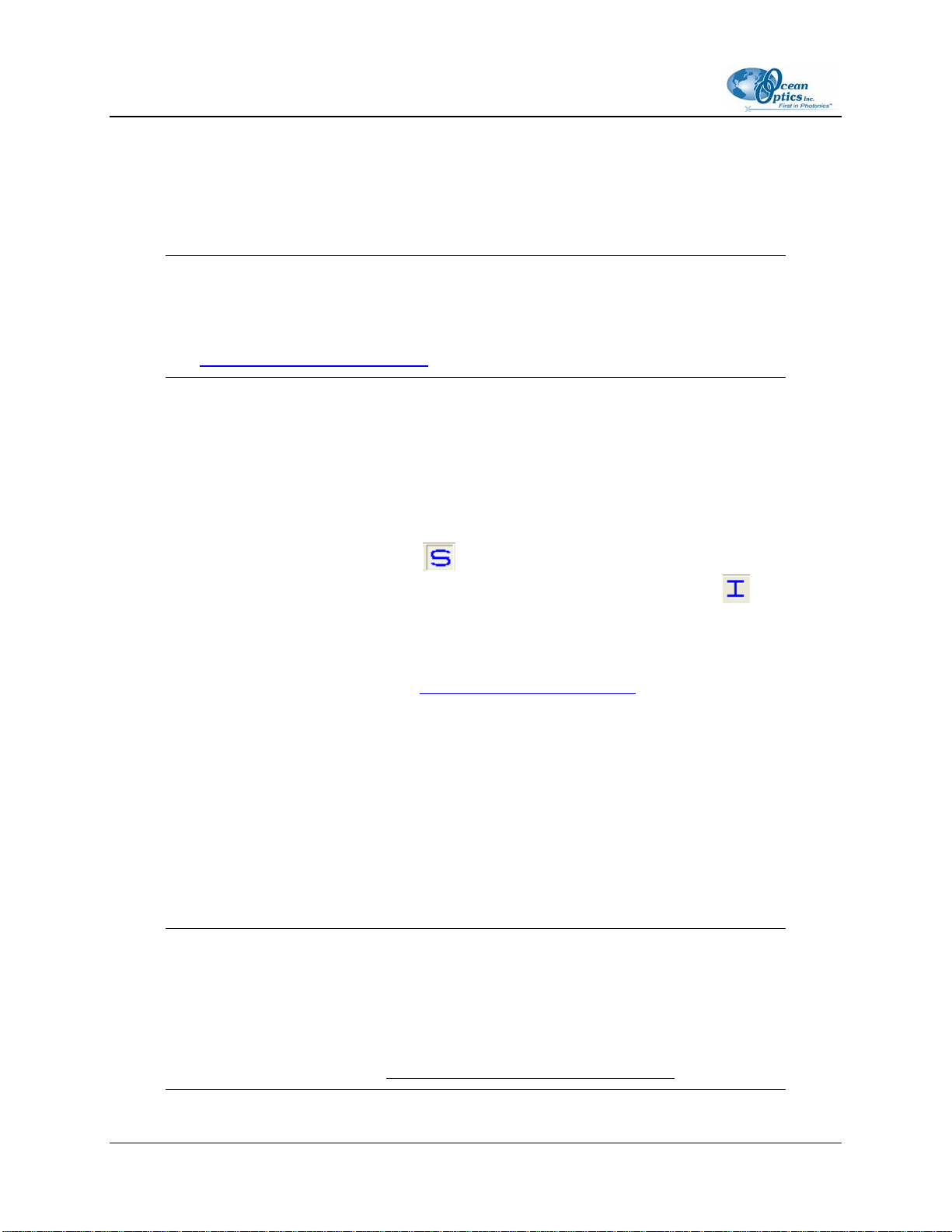
To escape Relative Irradiance mode, click S (
signal mode. You can then switch back to Relative Irradiance mode by clicking on the I (
OOIBASE toolbar.
►
Procedure
1. Install the OOIBase32 software (see Installing OOIBase32 Software for installation instructions).
2. After OOIBase32 has installed completely and your computer has restarted, insert the Custom
Software CD.
3. Copy all of the files on the Custom Software CD into your C:\Program Files\Ocean
Optics\OOIBase32 directory. Click OK when prompted to overwrite the files currently in that
directory.
4. Double click on the ConfigurationTree.reg file. Click OK when prompted to allow the file to
write to the registry.
The OOIBase32 software is now ready to run. You can access OOIBase32 via your Start toolbar
or from the C:\Program Files\Ocean Optics\OOIBase32 directory.
) on the OOIBase toolbar. Your system returns to raw
) on the
Note
When the software from the Custom Software CD is run, two File Open Mismatch
screens appear (one for the Reference file and one for the Electrical Dark file) informing
you that the acquisition parameters in your Curie file do not match the current
parameters. Select Yes to use the parameters from the Curie file. You can change these
parameters later, if desired (see Configuring Data Acquisition Parameters
).
6 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 13
1: Introduction
Connecting the Curie to a PC
The Curie connects to a PC via a standard USB device cable. USB 1.1 is currently supported.
Caution
Before connecting the Curie to your PC, be sure to install the OOIBase32
Spectrometer Operating Software that comes on the Software and Technical
Resources CD. This software contains the necessary USB drivers for the Curie
system. You should also install the Curie Custom Software to allow for
measurements in Relative Irradiance mode.
► Procedure
To connect the Curie system to your PC,
1. Install the OOIBase32 Spectrometer Operating Software from the Software and Technical
Resources CD (see Installing OOIBase32 Software
should also install the Curie Custom Software from the Custom Software CD (see Installing
Custom Curie Software to Activate Relative Irradiance Mode
2. Once the software is installed, insert the rectangular end of the USB device cable into any USB
port on your PC and the square end into the USB connector on the side of the Curie. The system
automatically discovers and installs the appropriate USB drivers for the Curie.
). To activate Relative Irradiance mode, you
).
Note
The Curie only supports USB connectivity. You cannot use the RS-232 serial port
standard to connect the Curie to your PC.
Connecting the Power Cord
A 12 VDC power supply ( WT-12V) is supplied with your Curie system and is needed to power its pulsed
xenon light source. Plug one end of the power cord into the round power receptacle on the side of the
Curie and the other end into an appropriate power source. Once you have plugged in the power supply,
turn the light source on by placing the power switch on the end of the Curie in the up (on) position.
640-11100-000-02-0406 7
Page 14

1: Introduction
8 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 15

Chapter 2
Configuration
Introduction
This chapter provides instructions for configuring the OOIBase32 Configure Spectrometer options so that
the application recognizes your connected Curie system.
Configuring the Curie in OOIBase32
Once the Curie system is installed (see Installing OOIBase32 Software), you must configure
OOIBase32’s Configure Spectrometer options so that the application recognizes the connected Curie
system and its components.
Note
See the OOIBase32 Spectrometer Operating Software, Operating Instructions for
detailed instructions on configuring your spectrometer in OOIBase32. See Product-
Related Documentation for information on locating this document.
Initial Start-up
The following sections provide information for initially configuring the Curie system in OOIBase32.
With your Curie attached to the computer via the USB port and plugged into the wall power outlet, start
the OOIBase32 software application.
Operator and Serial Number Dialog Box
The Operator and Serial Number dialog box prompts you to enter a user name and software serial
number into OOIBase32. Some of the data files use this information in the data file headers. Since
OOIBase32 is free software, it requires no serial number for installation. You can leave the field as is.
640-11100-000-02-0406 9
Page 16
2: Configuration
Default Spectrometer Configuration File
The Default Spectrometer Configuration File screen prompts you to select a default .SPEC file to use
with the Curie system. The .SPEC file extension is preceded by the unique serial number of the
spectrometer in your Curie system (for example, USBA001.SPEC).
Navigate to the OOIBase32 installation directory and select the default .SPEC file, then proceed. Do not
specify a .SPEC file located on removable media (such as a floppy disk). The Configure Hardware
screen appears.
Configure Hardware Screen
The Configure Hardware screen prompts you to enter spectrometer-specific information into
OOIBase32. Typically, you only need to enter this information once upon first running the OOIBase32
application. However, you can access this screen at any time by selecting Configure | Hardware from
the OOIBase32 menu bar.
Procedure
►
To configure the Curie system, do the following:
1. In the Spectrometer Type field, select S2000/PC2000/PC104/USB2000/H2000 from the drop-
down list.
2. In the A/D Converter Type field, select USB2000 from the drop-down list.
10 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 17
2: Configuration
3. In the USB Serial Number field, select the serial number of the USB2000 spectrometer in your
Curie system from the drop-down list.
4. Click OK.
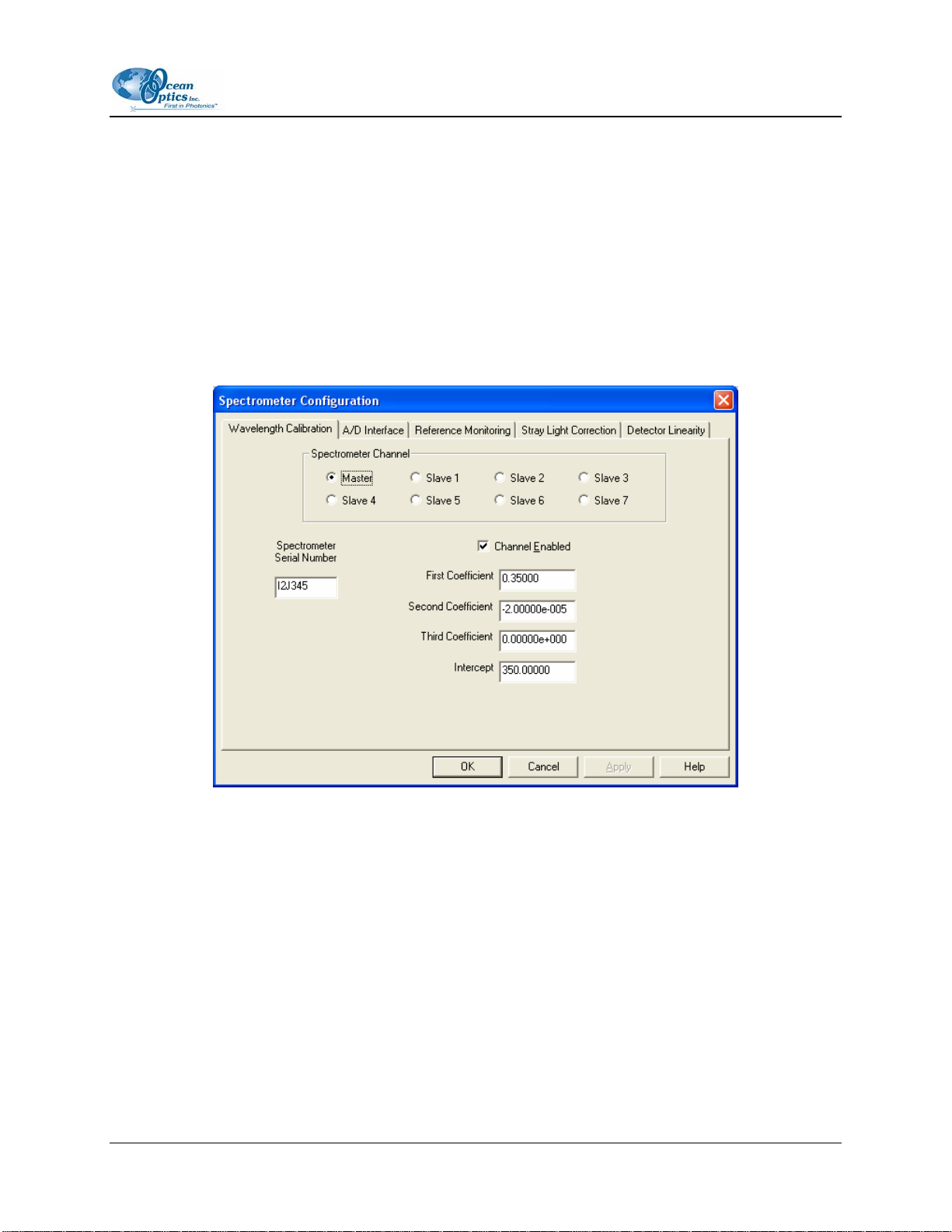
Spectrometer Configuration Dialog Box
► Procedure
To set the system parameters, do the following:
1. Select Spectrometer | Configure from the menu. The Spectrometer Configuration screen
appears.
2. On the Wavelength Calibration tab, ensure that the calibration coefficients (read from a memory
chip in the Curie spectrometer) match the coefficients listed on the Wavelength Calibration data
sheet that came with your spectrometer.
3. Ensure that both the Master and Channel Enabled are selected.
4. Select the A/D Interface tab.
640-11100-000-02-0406 11
Page 18

2: Configuration
5. On the A/D Interface tab, enter the same values that you entered in the Configure Hardware
screen (see Configure Hardware Screen
stored in the .SPEC file.
). When you exit the OOIBase32 application, this data is
6. Click OK to save the data and close the Spectrometer Configuration screen.
Upon exiting OOIBase32, the software stores this configuration information in a spectrometer
configuration file named [your serial number].SPEC. Upon restart, OOIBase32 loads this as the
default .SPEC file. You can change the name of this file by selecting Spectrometer | Save
Configuration As from the menu and changing the name of the saved .SPEC file.
Enabling the Pushbutton
The Curie features a pushbutton software trigger. To use the pushbutton feature to save spectral data, you
must enable Software Trigger mode in the OOIBase32 software. Note that when the pushbutton feature is
enabled, the spectrum on the screen will only update after the pushbutoon is pushed. The display is frozen
until the pushbutton is used.
See Autoincrementing Filenames
file with the base name and numerical index that you specify.
Procedure
►
To enable the pushbutton feature in the OOIBase32 software, do the following:
1. Select Spectrum | Configure Data Acquisition from the menu or click the
Configure Data Acquisition screen appears.
2. Select the External Trigger tab.
to save all spectra in the spectral window automatically and name the
button. The
12 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 19

2: Configuration
3. In the External Trigger Mode field, select Software Trigger to enable the pushbutton.
4. To save files when the pushbutton is pushed, enable the Automatically save file on trigger
option.
5. Click OK.
Autoincrementing Filenames
When the pushbutton feature is enabled, the Autoincrement Filenames option allows you to choose a
name and save spectra automatically when you push the button on the Curie system or when you click the
Save command in OOIBase32. Select File | Autoincrement Filenames | Enabled to enable this feature.
When you enable this feature, choosing any save command automatically saves all spectra in the spectral
window and names the file with a base name and numerical index you specify.
The following table illustrates a sample file name structure:
Test
00012
Master
Irradiance
In this example, the specified values result in an autoincremented filename of
Test.00012.Master.Irradiance.
The base name that you specified.
A sequential numerical index beginning from a user-specified number.
The spectrometer channel name, which OOIBase32 automatically adds to the
filename.
The file extension, which OOIBase32 automatically adds to the filename. In this
instance, it indicates that OOIBase32 saved the data while in relative irradiance
mode.
640-11100-000-02-0406 13
Page 20

2: Configuration
Note
If you do not enable the Autoincrement Filenames function, a save file dialog box will
open every time you push the button (if enabled) or choose a save command.
► Procedure
To configure the Autoincrement Filenames function, do the following:
1. Select File | Autoincrement Filenames | Enabled from the OOIBase32 menu to enable the
feature.
2. Select File | Autoincrement Filenames | Show Name to enable the Show Name option. When
you enable both this option and the Autoincrement Filenames option, the filename of the next
saved file displays in the title bar of OOIBase32.
3. Select File | Autoincrement Filenames | Configure to configure the following parameters:
a. Base name for autoincremented files.
b. Starting index for autoincremented files. For example, if you enter “1” here, the number
in the saved filename will appear as 00001. The next saved file will have 00002 in the
filename, etc.
Disabling the Pushbutton
► Procedure
To disable the pushbutton feature,
1. Select Spectrum | Configure Data Acquisition from the menu or click the
Configure Data Acquisition screen appears.
2. Select the External Trigger tab.
14 640-11100-000-02-0406
button. The
Page 21

2: Configuration
3. In the External Trigger Mode field, select None to disable the pushbutton, and click OK.
4. Push the pushbutton on the Curie. The pushbutton is now inactive.
Note
If you are unable to access the menu after clicking on it, push the pushbutton on the Curie
and try accessing the menu again.
Turning on the Light Source
There are two ways that you can turn on the lamp using OOIBase 32 software:
• Method 1: Check the Strobe Enable box on the Strobe tab in the Configure Data Acquisition
screen.
Procedure
►
1. Select Spectrum | Configure Data Acquisition from the menu or click the Data Acquisition
button (
2. Select the Strobe tab.
3. Check the Strobe Enable box.
). The Configure Data Acquisition screen appears.
640-11100-000-02-0406 15
Page 22

2: Configuration
• Method 2: Check the Strobe/Lamp Enable box on the Acquisition Parameters toolbar.
Once you enable the strobe via any of the options listed above, the lamp activates and a trace displays on
the graph when the CVD-DIFFUSE is placed in the cuvette holder. See Using the CVD-DIFFUSE
more detailed information on using the CVD-DIFFUSE with your Curie system. Adding a sample in the
cuvette holder should change the graph accordingly. If these results occur, your hardware and software
have been installed correctly.
for
Configuring Data Acquisition Parameters
► Procedure
1. Using OOIBase32, select Spectrum | Configure Data Acquisition from the menu or click the
button. The Configure Data Acquisition screen appears with the Basic tab selected.
2. On the Basic tab, configure the integration time, averaging, and boxcar smoothing values. See the
OOIBase32 Spectrometer Operating Software, Operating Instructions for more information. See
Performing a Fluorescence Experiment
data acquisition parameters for your measurement.
for more detailed information on choosing the optimal
16 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 23

2: Configuration
3. On the External Trigger tab, configure your external triggering mode to activate your
pushbutton and data save option, if necessary. Then, click OK.
Note
See Enabling the Pushbutton to set the External Trigger when using the Curie pushbutton
feature.
4. Flip the light switch on the side of the Curie to the ON position.
640-11100-000-02-0406 17
Page 24

2: Configuration
5. On the OOIBase32 main screen, check the Strobe/Lamp Enable option. The pulsed xenon lamp
activates, and a fluctuating trace appears on the graph when the CVD-DIFFUSE is placed in the
cuvette holder. See Using the CVD-DIFFUSE
for more detailed information on using the CVDDIFFUSE with your Curie system. If you put a sample into the cuvette holder, the graph trace
should change accordingly. When this occurs, you will know that the software and hardware are
correctly installed.
18 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 25

Chapter 3
Using the Curie System
Introduction
This chapter provides you with instructions for performing experiments using the Curie system with the
OOIBase32 application.
Performing Experiments with the Curie System
The Curie system allows you to detect picomolar-range concentrations of fluorophores in solution with
emission from 200–850 nm.
Preparing for Experiments
The following procedures walk you through the steps necessary to carry out a fluorescence measurement
with your Curie system and OOIBase32 software.
Before performing an experiment, ensure the following:
• Both the Curie system and the OOIBase32 application with Curie custom software have been
correctly installed.
• The Wavelength Calibration Curie system configurations in OOIBase32 are correct. The
calibration coefficients (read from a memory chip in the USB2000 spectrometer) must match
the coefficients listed on the Wavelength Calibration data sheet that came with your
spectrometer (see Spectrometer Configuration Dialog Box
• Both the Master and Channel Enabled options are enabled (see Spectrometer Configuration
Dialog Box
Intercept should correspond to those of your Curie system.
• The minimum integration time is set to 20 milliseconds or greater. If you set the integration
time below 20 milliseconds, the lamp is driven too fast and the spectrum is more unstable.
• The A/D Interface settings are correct (see Spectrometer Configuration Dialog Box
and 5
• Your Curie is plugged in and turned on (the switch on the end of the Curie is in the up or on
position).
Once you have installed and configured your hardware and software, and have set up your system, you
are ready to take a fluorescence measurement.
, Step 3). The First Coefficient, Second Coefficient, Third Coefficient, and
).
, Step 2).
, Steps 4
640-11100-000-02-0406 19
Page 26

3: Using the Curie System
Performing a Fluorescence Experiment
You can take a fluorescence reading in either Relative Irradiance mode (I) or Scope mode (S).
Relative Irradiance mode – Relative Irradiance mode is the preferred mode for fluorescence experiments.
Relative irradiance spectra are a measure of the intensity of a light source relative to a reference emission
source. There are two methods of performing a fluorescence experiment in Relative Irradiance mode: use
the custom Curie software provided with your Curie system to start OOIBASE32 in Relative Irradiance
mode using the calibration files generated during factory calibration, or perform your own radiometric
calibration using a blackbody of known color temperature. See Appendix C, Relative Irradiance Mode
for more information.
• Scope mode – Scope mode is the preferred mode for choosing the excitation wavelengths with
the linear variable filters and configuring your acquisition parameters. The signal graphed in
Scope mode is the raw voltage coming out of the A/D converter. This spectral view mode
provides complete control of signal processing functions before taking absorbance, transmission,
reflection, and relative irradiance measurements. This mode reflects the intensity of the light
source, the reflectivity of the grating and mirrors in the spectrometer, the response of the detector,
and the spectral characteristics of the sample. Use Scope mode when configuring your setup,
adjusting the integration time, and choosing your excitation wavelengths with linear variable
filters.
An example of Curie spectra for quinine sulfate measured in Scope mode (S) and Relative Irradiance
mode (I) is shown below.
,
20 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 27

3: Using the Curie System
As shown in the figure, the shape of the fluorescence spectrum is impacted by the measurement mode
chosen. The preferred mode for fluorescence measurements is Relative Irradiance mode because the
impact of variables such as the intensity of the light source, the reflectivity of the grating and mirrors in
the spectrometer, the response of the detector, and the spectral characteristics of the sample do not affect
the shape of the spectrum. When the Curie custom software is installed and used, the software is
automatically placed in Relative Irradiance mode using the factory calibration performed for your Curie
(see Installing Custom Curie Software to Activate Relative Irradiance Mode
the Curie software from the Custom Software CD).
The first step in measuring fluorescence from your sample is to choose the excitation wavelength for your
measurement. See Selecting the Excitation Wavelength
excitation wavelength range.
for the options available for selecting the
for instructions on installing
Selecting the Excitation Wavelength
The pulsed xenon light source included in your Curie system is a broadband light source capable of
providing excitation energy throughout the UV/VIS (200 to 850 nm) region. To avoid masking your
fluorescence signal with the broadband energy from the light source, the wavelength range for excitation
can be chosen using the novel, LVF technology or discrete bandpass filters.
The Curie offers you three filtering options to select the excitation wavelength:
• Linear variable bandpass filters – See Selecting the Excitation Wavelength Range with LVF
Filters
.
• Discrete bandpass filters – See Selecting the Excitation Wavelength Range with Discrete
Bandpass Filters
• No filters – For fluorescence measurements made without filters, there is a possibility that the
broadband light source will be scattered into the detector and overlap the fluorescence emission.
You can check this by using a cuvette containing solvent only (no fluorophore) to see if your
excitation energy is scattered into the detector. The presence of peaks in the spectrum for your
solvent alone would suggest that your solvent has a background fluorescence or that excitation
energy is being scattered into your detector.
.
Selecting the Excitation Wavelength Range with Discrete Bandpass Filters
The Curie system provides two slots to hold the filters, one for an excitation filter and one for an emission
filter. Note that the linear variable filters must be in the No LVF position (thumbscrews positioned closest
to the end cap) to access the excitation filter slot.
If you have a 1-inch diameter bandpass filter that you would prefer to use for your measurements, you can
place it in the empty filter holder provided or replace the existing filter in one of the other filter holders.
To replace an existing filter, loosen the setscrew at the bottom of the filter holder to remove the filter,
then insert your own filter and tighten the screw. Your filter must be 1 inch in diameter to fit in the
supplied filter holder.
640-11100-000-02-0406 21
Page 28

3: Using the Curie System
Selecting the Excitation Wavelength Range with LVF Filters
To set the excitation wavelength range with the LVF filters, place the software in Scope mode. If you are
running Curie custom software, click
system returns to raw signal mode. You can then switch back to Relative Irradiance mode for your
measurement after the excitation wavelength range is chosen by clicking on the
The sections below describe the steps necessary to select your excitation wavelength range with the
intergrated LVF filters. You must use the CVD-DIFFUSE located in the storage compartment door of
your Curie to deflect the filtered light energy into the detector (see Using the CVD-DIFFUSE
the wavelength range necessary for your emission, you must also determine which set of LVF filters to
use (only one set of LVF filters is used at a time – see LVF filter description below) and which mirror you
need to use (see Selecting the Mirror for Use with the LVFs
22 640-11100-000-02-0406
on the toolbar to escape Relative Irradiance mode. Your
on the toolbar.
). Based on
).
Page 29

3: Using the Curie System
• The UV LVF filter can be used to select excitation energy in the 230 to 500 nm range. The
bandwidth is fixed and varies from 30 to 40 nm. For UV excitation light, adjust the UV LVF filter
to select your wavelength range. The UV LVF filter is used with the UV (Cold) mirror (Mirror
Adjustment knob turned so that the UV label is closest to the cuvette holder – see Selecting the
Mirror for Use with the LVFs
).
• The VIS LVF filter can be used to select excitation energy in the 300 to 750 nm range. The
bandwidth is fixed and varies from 30 to 40 nm. For VIS excitation light, adjust the VIS filter to
select your wavelength range. The VIS LVF filter is used with the standard mirror (Mirror
Adjustment knob turned so that the VIS label is closest to the cuvette holder – see Selecting the
Mirror for Use with the LVFs
).
Using the CVD-DIFFUSE
A white, cuvette shaped CVD-DIFFUSE is provided with your Curie system (stored in the side storage
door of the Curie) to help you select the excitation wavelength for your measurement. With the detector
located at 90 degrees relative to the light source, the CVD-DIFFUSE provides a way to deflect the light
energy into the detector. The CVD-DIFFUSE is a 1-cm piece of PTFE material used to deflect the light
from the light source into the spectrometer. Insert the CVD into the Curie’s cuvette holder as shown in the
figure below.
Selecting the Mirror for Use with the LVFs
There are two mirrors available in the Curie system:
• Standard mirror – (Mirror Adjustment Knob turned with VIS label closest to the cuvette holder).
Reflects visible and UV light from the light source into the cuvette holder. Use this mirror setting
with the VIS LVF filter. In the figure below, the spectrum of the xenon lamp reflected off of the
standard mirror is shown.
640-11100-000-02-0406 23
Page 30

3: Using the Curie System
Xenon Lamp Reflected Off of Standard Mirror
• Cold mirror – (Mirror Adjustment Knob turned with UV label closest to the cuvette holder).
Reflects only the UV light from your light source into the cuvette holder. The Cold mirror option
is included in your Curie system because the UV LVF filter does not block light above 500 nm.
If your emission occurs above 500 nm, use the cold mirror with the UV LVF filter to select your
excitation wavelength range. The cold mirror setting is used with the UV LVF filter to keep
excitation energy above 500 nm from overlapping with your emission.
Mirror Mechanism (located inside Curie)
24 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 31

3: Using the Curie System
In the figure below, the spectrum of the xenon lamp reflected off of the cold mirror is shown.
Note that less visible light is reflected from the cold mirror.
Xenon Lamp Reflected Off of Cold Mirror
To select the mirror for your measurement, lift and turn the mirror adjustment knob on the Curie
clockwise to select the desired mirror. When the UV LVF is used, choose the cold mirror by turning the
mirror knob until the UV label on the mirror knob is closest to the cuvette holder.
640-11100-000-02-0406 25
Page 32

3: Using the Curie System
Adjusting the LVFs to Select the Excitation Wavelength Range
With the software in Scope mode, the CVD-DIFFUSE in the cuvette holder and the correct mirror chosen,
loosen the thumbscrews and slide the handles (one for UV and one for VIS) on the Curie to select the
excitation wavelength range. You can only adjust and use one LVF time; the other LVF must be in the No
LVF position.
In the figures below, the spectra for light passing through the UV LVF filter set at 350 nm and the VIS
LVF filter set at 500 nm are shown.
26 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 33

3: Using the Curie System
Curie UV LVF 350 nm
640-11100-000-02-0406 27
Page 34

3: Using the Curie System
Curie VIS LVF 500 nm
Once you have chosen your excitation wavelength range, make a note of the location on the LVF scale
and lock the filter in place with the thumbscrew. Before making your fluorescence measurement, switch
back to Relative Irradiance mode by clicking on the
on the OOIBASE toolbar.
Measuring Fluorescence with your Curie System
After you have chosen your excitation wavelength range, you are ready to make your measurements in
Relative Irradiance mode. Remove the CVD-DIFFUSE from the cuvette holder, place the software in
Relative Irradiance mode by clicking on the
cuvette holder. Depending on the spectrum that you see, the data acquisition parameters and filtering can
be adjusted to provide optimal data.
on the OOIBASE toolbar and place your sample in the
Application Tips
If the signal you collect . . . You can . . . By . . .
Saturates the spectrometer
(peaks are off the scale)
Decrease the light level
on scale in Scope mode
• Decreasing the integration time, or
• Incorporating LVFs into your experiment
28 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 35

3: Using the Curie System
If the signal you collect . . . You can . . . By . . .
Has too little light Increase the light level on
scale in Scope mode
Examples of Saturated Signal
• Increasing the integration time, or
• Removing LVFs from the light path
Saturated Fluorescein Signal in Scope Mode
640-11100-000-02-0406
29
Page 36

3: Using the Curie System
Saturated Fluorescein Signal in Relative Irradiance Mode
30 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 37

3: Using the Curie System
Examples of Unsaturated Signal
Unsaturated Fluorescein Signal in Scope Mode
640-11100-000-02-0406 31
Page 38

3: Using the Curie System
Unsaturated Fluorescein Signal in Relative Irradiance Mode
32 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 39

Chapter 4
Troubleshooting
Introduction
This chapter contains the steps you need to take to solve possible problems that you may encounter with
your Curie system installation.
Problem 1: Curie System Connected to PC Prior
to OOIBase32 Installation
If your Curie system was connected to the computer prior to installing your OOIBase32 software
application, you may encounter installation issues that you must correct before your Ocean Optics device
will operate properly. Perform the following steps:
1. Remove the unknown device from the Windows Device Manager.
2. Remove improperly installed files.
Note
If these steps do not correct your device driver problem, you will need to obtain the
Correcting Device Driver Issues document from the Ocean Optics website at
http://www.oceanoptics.com/technical/engineering/correctingdevicedriverissues.pdf.
Removing the Unknown Device from Windows Device Manager
► Procedure
Perform the following procedure to remove the unknown device:
1. Open the Windows Device Manager as follows:
• For Windows 98/ME:
a. From the desktop, right-click My Computer. A pop-up menu appears.
b. Select Properties.
c. Select the Device Manager tab.
640-11100-000-02-0406 33
Page 40

4: Troubleshooting
• For Windows 2000/XP:
a. From the desktop, right-click My Computer and select Properties. The System
Properties screen appears.
b. Select the Hardware tab.
c. Click the Device Manager button.
34 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 41

4: Troubleshooting
2. Locate Other Devices and expand the selection by clicking on the " + " sign to the immediate
left.
Note
Improperly installed USB devices can also appear under the Universal Serial Bus
Controller option. Be sure to check this location if you cannot locate the unknown
device.
3. Locate the unknown device (marked with a large question mark). Right-click on the Unknown
Device listing and select either the Uninstall or Remove option.
4. Click OK to continue. A warning appears confirming the removal of the unknown device.
5. Click OK again to confirm the device removal.
6. Disconnect the Curie system from your computer.
Removing Improperly Installed Files
► Procedure
To remove improperly installed files, do the following:
1. Open Windows Explorer.
2. Navigate to the WINDOWS | inf directory.
Note
If the INF directory is not visible, you must disable Hide protected operating system
files and Hide extension for unknown file types in Windows Folder Options.
For Windows 98, access Windows Folder Options from Windows Explorer, under View |
Options.
For Windows 2000/XP, access Windows Folder Options from Windows Explorer, under
Tools | Folder Options and select the View tab.
3. Delete the ooi_usb.inf and ooi_usb.PNF files in the INF directory.
4. Navigate to the Windows | system32 | drivers directory.
5. Delete the ezusb.sys file.
6. Reinstall your Ocean Optics application and reboot the computer when prompted.
7. Plug in your Curie system.
The computer should now be able to install the correct drivers for your Curie system.
640-11100-000-02-0406 35
Page 42

4: Troubleshooting
Problem 2: Older Version of OOIBase32 Installed
If the computer you want to use to interface to your Curie system already has an older version of the
OOIBase32 application installed, you must install the latest OOIBase32 version instead.
Note
You do not need to uninstall the older version of the OOIBase32 software before you
install the latest version.
Obtain the latest version of OOIBase32 from the Software and Technical Resources CD included with
your Curie system, or from the Ocean Optics website at
http://www.oceanoptics.com/technical/softwaredownloads.asp.
36 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 43

Curie System
Table 1: Curie System Specifications
Specification Value
System
Dimensions 33 cm x 24.9 cm x 12.8 cm
Appendix A
Specifications
Weight 6.75 kg
Temperature Limits 0–60 °C
Humidity Limits 0–90%, noncondensing
Power Consumption 90 mA @ 5 VDC and 0.2 A @ 12 VDC for a total of 2.9 W
Wavelength Range 250 to 800 nm
LVF Range (Excitation Range) 220 to 700 nm
Optical Resolution ~10 nm
Light Source Pulsed xenon
Warm-up Time < 5 minutes
A/D Resolution 12 bit
Board Architecture USB 1.1
Wavelength Accuracy 1 pixel (~0.35 nm)
Photometric Accuracy <0.1%
Stray Lights ~0.05% at 600 nm, <0.10% at 435 nm
640-11100-000-02-0406 37
Page 44

A: Specifications
Table 1: Curie System Specifications (Cont’d)
Specification Value
Optical Bench and Detector
Detector 2048-element linear silicon CCD array
Number of Elements 2048 pixels
Pixel Size 14 µm x 200 µm
Well Depth ~62,500 electrons
Usable Range 200–1100 nm
Dynamic Range:
System
Single Aquisition
Sensitivity (estimate):
At 400 nm
At 600 nm
At 800 nm
8
2 x 10
2000:1
90 photons/count
41 photons/count
203 photons/count
2.9 x 10
17
joule/count
2.9 x 1017 watts/count (for a 1-second integration time)
Dark Noise 2.5–4.0 (RMS)
Grating Grating #2
Slit 200 µm slit
Focal Length:
Input
Output
42 mm
68 mm
Order Sorting None
Resolution ~ 10 nm (FWHM)
Bulb Life (hours) >1 x 108 flashes
38 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 45

A: Specifications
Table 1: Curie System Specifications (Cont’d)
Specification Value
Optical Bench and Detector (Cont’d)
Stray Light:
At 600 nm < 0.05%
At 435 nm < 0.10%
At 250 nm < 0.10%
Signal-to-Noise 250:1 (at full signal)
Pulsed Xenon Light Source
Voltage 11–28 VDC
DC Current 0.2 amps RMS
Peak Current 1.0 amps
Trigger 1 TTL
Vref (Vo/Vref = 127.5) 3.14–4.7 VDC
1
Opto-isolated, +5V TTL compatible, 20–50 mA peak input, 10–100 µsec pulse width, leading edge trigger, internal
resistor 150 Ω
Table 2: Electrical Output
Specification Value
Voltage 400–600 VDC adjustable
Power (Joules/sec) 2 watts maximum (power = Joules x flash rate)
Standard Discharge Capacitor 0.047, 0.10, or 0.22 µfd
Flash Rate (Hz) F
= 2/E, where E = 1/2CV2
MAX
640-11100-000-02-0406 39
Page 46

A: Specifications
Table 3: Discharge Capacitor Options
Capacitor (µfd) Max Input/Flash (mJ) Max Flash Rate
@600 VDC (Hz)
0.22 40 50 115
0.10 18 111 250
0.47 8.5 235 530
Max Flash Rate
@400 VDC (Hz)
Table 4: Light Output
Specification Value
Spectral Range 160–4,000 nm
Stability (CV) 1 < 3%
Lifetime >1 x 109 Flashes
1
CV or Coefficient of variation is defined as CV% = (Standard deviation of 20 flashes) / (Mean of 20 flashes)
Compatibility for Desktop or Notebook PCs
To use the Curie Self-contained Fluorescence System with your PC, your PC must meet the following
requirements:
• IBM-compatible PC with Pentium or higher microprocessor
• 32 MB RAM
• Ocean Optics’ OOIBase32 32-bit Spectrometer operating software
• Windows 98/ME/2000/XP operating system
40 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 47

Appendix B
Calibrating the Wavelength of
the Curie Spectrometer
Your Curie system’s spectrometer is calibrated before it leaves Ocean Optics and the values are on the
CD that you received with your product. However, the wavelength for all spectrometers will drift slightly
as a function of time and environmental conditions, requiring you to recalibrate.
About Wavelength Calibration
You are going to be solving the following equation, which shows that the relationship between pixel
number and wavelength is a third-order polynomial:
3
Where: λ = Wavelength of pixel p
C
C
C
You will be calculating the value for
I = Wavelength of pixel 0
= First coefficient (nm/pixel)
1
= Second coefficient (nm/pixel2)
2
= Second coefficient (nm/pixel3)
3
λ
= I + C1 p + C2 p2 + C3 p
p
I and the three Cs.
640-11100-000-02-0406 41
Page 48

B: Calibrating the Wavelength of the Curie Spectrometer
Calibrating the Wavelength of the Spectrometer
Preparing for Calibration
To recalibrate the wavelength of your Curie spectrometer, you need the following:
A light source capable of producing spectral lines.
Note
Ocean Optics’ HG-1 Mercury Argon Calibration Light Source is ideal for recalibration. If
you do not have an HG-1, you will need a light source that produces several (at least 4-6)
spectral lines in the wavelength region of your spectrometer.
The Curie system
An optical fiber (maximum 50µm works best)
PS-HG1-ADP Cuvette Adapter
A spreadsheet program (Excel or Quattro Pro, for example) or a calculator that performs third-
order linear regressions
Note
If you are using Microsoft Excel, choose Tools | Add-Ins and select AnalysisToolPak
and AnalysisTookPak-VBA.
Calibrating the Spectrometer
► Procedure
Perform the steps below to calibrate the wavelength of the Curie spectrometer:
1. Connect the HG-1 to the cuvette adapter via an optical fiber, and then insert the adapter into the
cuvette holder of the Curie system so that light from the lamp enters the spectrometer.
2. Place OOIBase32 into Scope mode and take a spectrum of your light source. Adjust the
integration time (or the A/D conversion frequency) until there are several peaks on the screen that
are not off-scale.
3. Move the cursor to one of the peaks and position the cursor so that it is at the point of maximum
intensity.
4. Record the pixel number that is displayed in the status bar or legend (located beneath the graph).
Repeat this step for all of the peaks in your spectrum.
42 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 49

B: Calibrating the Wavelength of the Curie Spectrometer
5. Use the spreadsheet program or calculator to create a table like the one shown in the following
figure. In the first column, place the exact or true wavelength of the spectral lines that you used.
In the second column of this worksheet, place the observed pixel number.
In the third column, calculate the pixel number squared.
In the fourth column, calculate the pixel number cubed.
Independent
Variable
Dependent
Variables
Values Computed
from the Regression
Output
True Wavelength
(nm)
253.65
296.73
302.15
313.16
334.15
365.02
404.66
407.78
435.84
546.07
576.96
579.07
696.54
706.72
727.29
738.40
751.47
Pixel # Pixel #
175
296
312
342
402
490
604
613
694
1022
1116
1122
1491
1523
1590
1627
1669
116964
161604
240100
364816
375769
481636
1044484
1245456
1258884
2223081
2319529
2528100
2647129
2785561
30625
87616
97344
2
Pixel # 3
5359375
25934336
30371328
40001688
64964808
117649000
220348864
230346397
334255384
1067462648
1389928896
1412467848
3314613771
3532642667
4019679000
4306878883
4649101309
Predicted
Wavelength
253.56
296.72
302.40
313.02
334.19
365.05
404.67
407.78
435.65
546.13
577.05
579.01
696.70
706.62
727.24
738.53
751.27
Difference
0.09
0.01
-0.25
0.13
-0.05
-0.04
-0.01
0.00
0.19
-0.06
-0.09
0.06
-0.15
0.10
0.06
-0.13
0.19
6. Use the spreadsheet or a calculator to calculate the wavelength calibration coefficients. In the
spreadsheet program, find the functions to perform linear regressions.
• If using Quattro Pro, look under Tools | Advanced Math
• If using Excel, look under Analysis ToolPak
640-11100-000-02-0406
43
Page 50

B: Calibrating the Wavelength of the Curie Spectrometer
7. Select the true wavelength as the dependent variable (Y). Select the pixel number, pixel number
squared, and the pixel number cubed as the independent variables (X). After executing the
regression, you will obtain an output similar to the one shown below.
Regression Statistics
Multiple R 0.999999831
R Square 0.999999663
Adjusted R Square 0.999999607
Standard Error 0.125540214
Observations 22
R Squared
Intercept
Coefficients Standard Error
Intercept 190.473993 0.369047536 First coefficient
X Variable 1 0.36263983 0.001684745
X Variable 2-1.174416E-05 8.35279E-07
X Variable 3-2.523787E-09 2.656608E-10 S
Third coefficient
econd coefficient
The figure above notes the numbers of importance.
8. Record the Intercept, as well as the First, Second, and Third Coefficients. Also, the value for R
Squared should be very close to 1. If it is not, you have most likely assigned one of your
wavelengths incorrectly.
Keep these values at hand.
Saving the New Calibration Coefficients
Wavelength calibration coefficients unique to each Curie system are programmed into an EEPROM
memory chip on the spectrometer in your Curie system.
You can save over old calibration coefficients with new ones. OOIBase32 reads these coefficients from
the EEPROM on the spectrometer.
Procedure
►
To save wavelength calibration coefficients, do the following:
1. Ensure that the Curie system is connected to the PC and that no other applications are running.
2. Point your browser to
scroll down to Microcode. Select USB EEPROM Programmer.
3. Save the setup file to your computer.
4. Run the Setup.exe file to install the software. The Welcome screen appears.
http://www.oceanoptics.com/technical/softwaredownloads.asp and
5. Click the Next button. The Destination Location screen appears.
6. Accept the default installation location, or click the Browse button to specify a directory. Then,
click the Next button. The Program Manager Group screen appears.
44
640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 51

B: Calibrating the Wavelength of the Curie Spectrometer
7. Click the Next button. The Start Installation screen appears.
8. Click the Next button to begin the installation. Once the installation finishes, the Installation
Complete screen appears.
9. Click Finish and reboot the computer when prompted.
10. Navigate to the USB EEPROM Programmer and run the software.
11. Click on the Curie device displayed in the left pane of the USB Programmer screen.
12. Double-click on each of the calibration coefficients displayed in the right pane of the USB
Programmer screen and enter the new values acquired in Steps 5 and 6 of the Calibrating the
Spectrometer
section in this Appendix.
13. Repeat Step 12
for all of the new values.
14. Click Save All Values to save the information, and then exit the USB Programmer software.
The new wavelength calibration coefficients are now loaded onto the EEPROM memory chip on the
spectrometer.
640-11100-000-02-0406 45
Page 52

B: Calibrating the Wavelength of the Curie Spectrometer
46 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 53

Appendix C
Relative Irradiance Mode
Irradiance is the amount of energy at each wavelength emitted from a radiant sample. In relative terms, it
is a comparison of the fraction of energy the sample emits and the energy the sampling system collects
from a lamp with a blackbody energy distribution (normalized to 1 at the energy maximum). OOIBase32
calculates relative irradiance with the following equation:
S
- D
λ
Rλ - D
λ
)
λ
Where:
Iλ = B
λ
(
= Relative energy of the reference (calculated from the color temperature) at wavelength λ
B
λ
= Sample intensity at wavelength λ
S
λ
= Dark intensity at wavelength λ
D
λ
= Reference intensity at wavelength λ
R
λ
The figure below shows a typical relative irradiance setup: Use a light source with a known color
temperature such as the LS-1-LL to take a reference spectrum. The light source is coupled to the cuvette
adapter (such as the PS-HG1-ADP) with a fiber. The cuvette adapter is used to reflect light energy into
the spectrometer. The spectrometer then transmits the information to the PC, which compares the
measured spectra against the reference spectrum, thus removing wavelength-dependent instrument
response from the measurement.
640-11100-000-02-0406 47
Page 54

C: Relative Irradiance Mode
Common applications include characterizing the light output of LEDs, incandescent lamps, and other
radiant energy sources such as sunlight. Relative irradiance measurements also include fluorescence
measurements, which measure the energy given off by materials excited by light at shorter wavelengths.
Before you can access Relative Irradiance Mode, you must take a reference spectrum in Scope Mode of a
blackbody of known color temperature. Additionally, you must obtain a dark spectrum by removing the
fiber from the reference lamp and preventing light from entering it.
An example of Curie spectra for quinine sulfate measured in Scope mode (S) versus Relative Irradiance
mode (I) is shown below.
Calibrating the Spectrometer for Relative Irradiance
Preparing for Calibration
To recalibrate your Curie for relative irradiance, you need the following:
A light source of known color temperature. Ocean Optics’ LS-1-LL is ideal for recalibration.
The Curie system
An optical fiber (maximum 50µm works best)
A cuvette wavelength calibration adapter such as the PS-HG1-ADP
A spreadsheet program (Excel or Quattro Pro, for example) or a calculator that performs third-
order linear regressions
48 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 55

C: Relative Irradiance Mode
Note
If you are using Microsoft Excel, choose Tools | Add-Ins and select AnalysisToolPak
and AnalysisToolPak-VBA.
Calibrating the Spectrometer
► Procedure
Perform the steps below to calibrate for relative irradiance:
1. Disable the light source in the Curie system by using the power switch on the light source or by
disabling the spectrometer strobe function on the Strobe tab in the Configure Data Acquisition
screen in the OOIBase32 software.
2. Connect the light source to the cuvette adapter via an optical fiber, and then insert the adapter into
the cuvette holder of the Curie system so that light from the lamp enters the spectrometer.
3. Place OOIBase32 into Scope mode by clicking the Scope Mode icon (
selecting Spectrum | Scope Mode from the menu bar, or by typing CTRL + SHIFT + S.
4. Take a reference spectrum of your light source. Adjust the integration time (or the A/D
conversion frequency) until the spectrum is on the scale (below 4000 counts).
5. In the Reference Color Temperature dialog box, enter the color temperature of the light source
(in Kelvin) and click OK. For the LS-1-LL, enter 2800.
6. Click the Store Reference spectrum icon on the toolbar or select Spectrum | Store Reference
from the menu bar to store the reference. This command merely stores a reference spectrum in
memory. You must select File | Save | Reference from the menu bar to permanently save the
spectrum to disk.
7. Turn off the LS-1-LL light source. Then, take a dark spectrum by clicking the Store Dark
Spectrum icon on the toolbar or by selecting Spectrum | Store Dark from the menu bar. This
command merely stores a dark spectrum in memory. You must select File | Save | Dark from the
menu to permanently save the spectrum to disk.
8. Place OOIBase32 into Relative Irradiance mode by clicking the Relative Irradiance Mode icon
) on the toolbar, or by selecting Spectrum | Relative Irradiance Mode from the menu bar.
(
) on the toolbar, or by
640-11100-000-02-0406 49
Page 56

C: Relative Irradiance Mode
50 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 57

Appendix D
Filter Sets
The following table lists the specifications for the filters included with the Curie.
Wavelength Information
Type Center Lambda FWHM Lambda (50%) Lambda 100%) Name
Bandpass 330 140 --- --- U330
Bandpass 407 104 --- --- BG-12
Bandpass 526 53 --- --- VG-9
Longpass --- --- 420 495 GG-420
Longpass --- --- 530 590 OG-530
Longpass --- --- 550 610 OG-550
Longpass --- --- 610 660 RG-610
640-11100-000-02-0406 51
Page 58

D: Filter Sets
52 640-11100-000-02-0406
Page 59

Index
A
application tips, 28
C
calibration
preparing for, 42, 48
procedure, 42, 49
saving new coefficients, 44
spectrometer, 42, 48
wavelength, 41
compatibility
PC, 40
configuration
with OOIBase32, 9
configuration file
default spectrometer, 10
configure
data acquisition, 14, 16
hardware, 10
spectrometer, 11
Configure Hardware screen, 10
connecting to a PC, 7
connecting to a power source, 7
CVD-DIFFUSE, 3, 23
E
enable pushbutton, 12
excitation wavelength, 21
bandpass filter, 21
LVF fliter, 22
experiments
performing, 19
preparing for, 19
F
features, 1
File Menu Functions
Autoincrement Filenames, 13
filter sets, 51
fluorescence measurement, 28
I
Install
From CD, 5
From Web, 5
items included with shipment, 3
M
D
Data Acquisition Parameters, 14, 16
default spectrometer configuration file, 10
disable pushbutton, 14
document
audience, iii
purpose, iii
summary, iii
640-11100-000-02-0406 53
mirror
selection, 23
standard, 25
Page 60

Index
O
OOIBase32
Install, 4
operating requirements, 4
operator, 9
P
PC
compatibility, 40
power connection, 7
power supply, 3
pushbutton, 12, 14
R
Relative Irradiance mode, 47
removing
improperly installed files, 35
unknown device, 33
S
saturated signal examples, 29
serial number, 9
specifications, 37, 38, 39
detector, 38
light source discharge capacitor options, 40
light source electrical output, 39
light source input, 39
light source light output, 40
optical bench, 38
system, 37
start-up, 9
system contents, 2
T
troubleshooting, 33
U
unsaturated signal examples, 31
upgrades, iv
W
Wavelength Calibration, 41
54 0-000-02-0406
640-1110
 Loading...
Loading...