Page 1

CIP
User Manual &
Installation
Guide
Page 2

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
N-TRON CIP Manual
1 Introduction ................................................................................................................................... 3
2 CIP Components .......................................................................................................................... 3
2.1 Electronic Data Sheet (EDS) ................................................................................................. 3
2.2 CIP Objects ........................................................................................................................... 3
2.2.1 TCP/IP Interface Object ................................................................................................. 6
2.2.2 Ethernet Link Object ...................................................................................................... 7
2.2.3 N-TRON Object .............................................................................................................. 9
2.3 CIP Services ........................................................................................................................ 11
2.4 Accessing Data ................................................................................................................... 11
2.4.1 Explicit Messaging ....................................................................................................... 11
2.4.2 I/O Connections ........................................................................................................... 11
3 Rockwell RSLogix 5000 – Add-On Instruction Installation ......................................................... 12
3.1 Configuration of RSLogix project ........................................................................................ 12
3.2 Input_Assembly Parameter ................................................................................................. 21
3.3 Switch_Parameters Parameter ........................................................................................... 22
3.4 Explicit Messaging Options ................................................................................................. 22
3.5 Troubleshooting................................................................................................................... 22
3.6 Sample Project .................................................................................................................... 23
4 Rockwell RSLogix 5000 – Tag reference ................................................................................... 24
4.1 Generic assembly tags ........................................................................................................ 24
4.2 7506GX2 assembly tags .................................................................................................... 33
4.3 System fault tags ................................................................................................................. 35
4.4 CIP Tags ............................................................................................................................. 36
4.5 Identity object ...................................................................................................................... 36
4.6 TCPIP object ....................................................................................................................... 36
4.7 Ethernet Link object ............................................................................................................ 37
4.8 N-TRON Switch object ........................................................................................................ 39
5 Rockwell FactoryTalk - Faceplate Installation Instructions ........................................................ 42
5.1 Configuration of FactoryTalk View Faceplate Displays....................................................... 42
5.2 Sample Project .................................................................................................................... 53
6 Rockwell FactoryTalk - Faceplate quick reference guide ........................................................... 54
6.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................... 54
6.2 Home display ....................................................................................................................... 55
6.3 Diagnostics display.............................................................................................................. 57
6.4 Settings display ................................................................................................................... 59
6.5 Alarm display ....................................................................................................................... 60
7 Support ....................................................................................................................................... 61
8 References ................................................................................................................................. 61
9 Revisions .................................................................................................................................... 61
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 2 of 61
Page 3

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
1 Introduction
EtherNet/IP™, better known as the Common Industrial Protocol (CIP™), was designed
for use in process control and industrial automation applications. CIP was designed to
provide consistent device access to eliminate the need for vendor specific software for
configuration and monitoring of individual devices.
N-TRON switches with CIP support can be used to communicate with other industrial
devices, such as Rockwell controllers.
2 CIP Components
The following CIP components are available with N-TRON CIP enabled switches.
2.1 Electronic Data Sheet (EDS)
An electronic datasheet for each N-TRON switch is provided.
In a Rockwell environment EDS files are installed using the “EDS Hardware Installation
Tool”. This allows N-TRON switches to be recognized in an RSLinx environment.
2.2 CIP Objects
“Objects” are used to organize various information about the switch. There are four types
of objects provided. Three are specified by the ODVA, and one is N-TRON specific:
Identity object
TCP/IP Interface object
Ethernet Link object
N-TRON switch object
Standard “services” are associated with objects. Services exist for reading an attribute,
setting an attribute, resetting a device, etc. See references [1] and [2] for specific details.
The following sections describe the attributes associated with each object type, such as
attribute Id number and data format. All attributes can be read, but only some can be set,
as shown by the “Set” column.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 3 of 61
Page 4
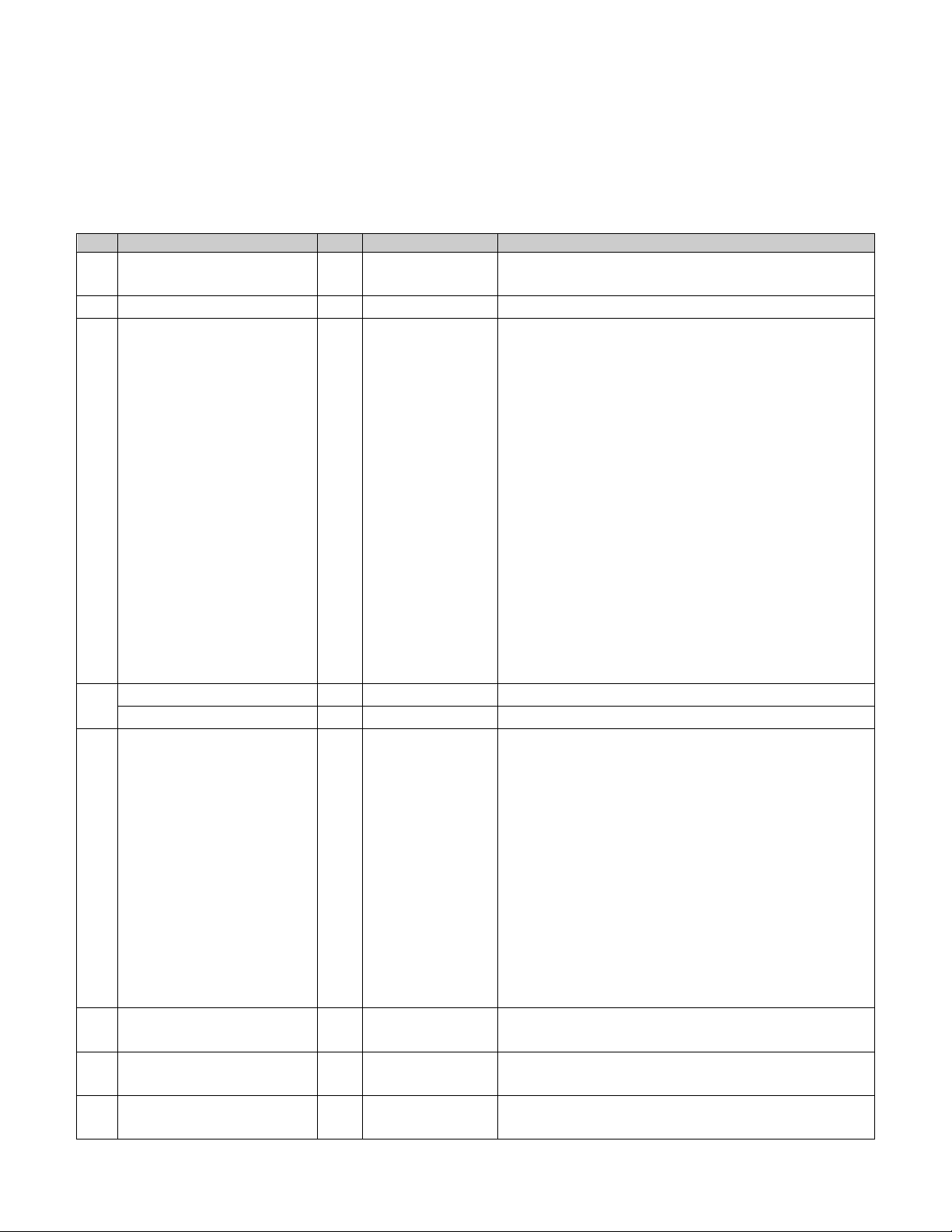
CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Id
Name
Set
Format
Description
1
Vendor ID
UINT (16)
1006. This is N-TRON’s ODVA EtherNet/IP
Vendor ID.
2
Device Type
UINT (16)
0x0C. Communications Adapter
3
Product Code
UINT (16)
Switch product code:
708TX = 701
708FX2 = 703
716TX = 705
716FX2 = 706
7018TX = 708
7018FX2 = 709
708M12 = 710
711FX3 = 711
7010TX = 713
709FX = 714
710FX2 = 715
714FX6 = 717
712FX4 = 718
7012FX2 = 719
7026TX = 720
7506GX2 = 7506
4
Major Revision
USINT (8)
Major version of CIP implementation.
Minor Revision
USINT (8)
Minor version of CIP implementation.
5
Status
WORD (16)
Summary status of device. Bits:
Bit 0 If set, device has an owner
Bit 1 reserved
Bit 2 If set, device has non-default
configuration
Bit 3 reserved
Bits 4-7 Extended device status – not used
Bit 8 Minor recoverable fault
Bit 9 Minor unrecoverable fault
Bit 10 Major recoverable fault
Bit 11 Major unrecoverable fault
Bits 12-15 reserved
(see fault table below)
6
Serial Number
UDINT (32)
Serial number of the device. This is the last 4
octets of the base switch MAC.
7
Product Name
SHORT_STRI
NG
Switch Model Number.
EX: N-TRON 7018FX2
15
Assigned_Name
Set
STRINGI
This is the user assigned switch name.
Identity Object
The identity object class (Class code = 0x01) and instance attributes are implemented as
defined by CIP Vol 1, 5-2 [1]. There is one instance (1) of this object. Service code
(0x32) will get all attributes, including optional attributes. The following table
summarizes the attributes in the Identity object.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 4 of 61
Page 5
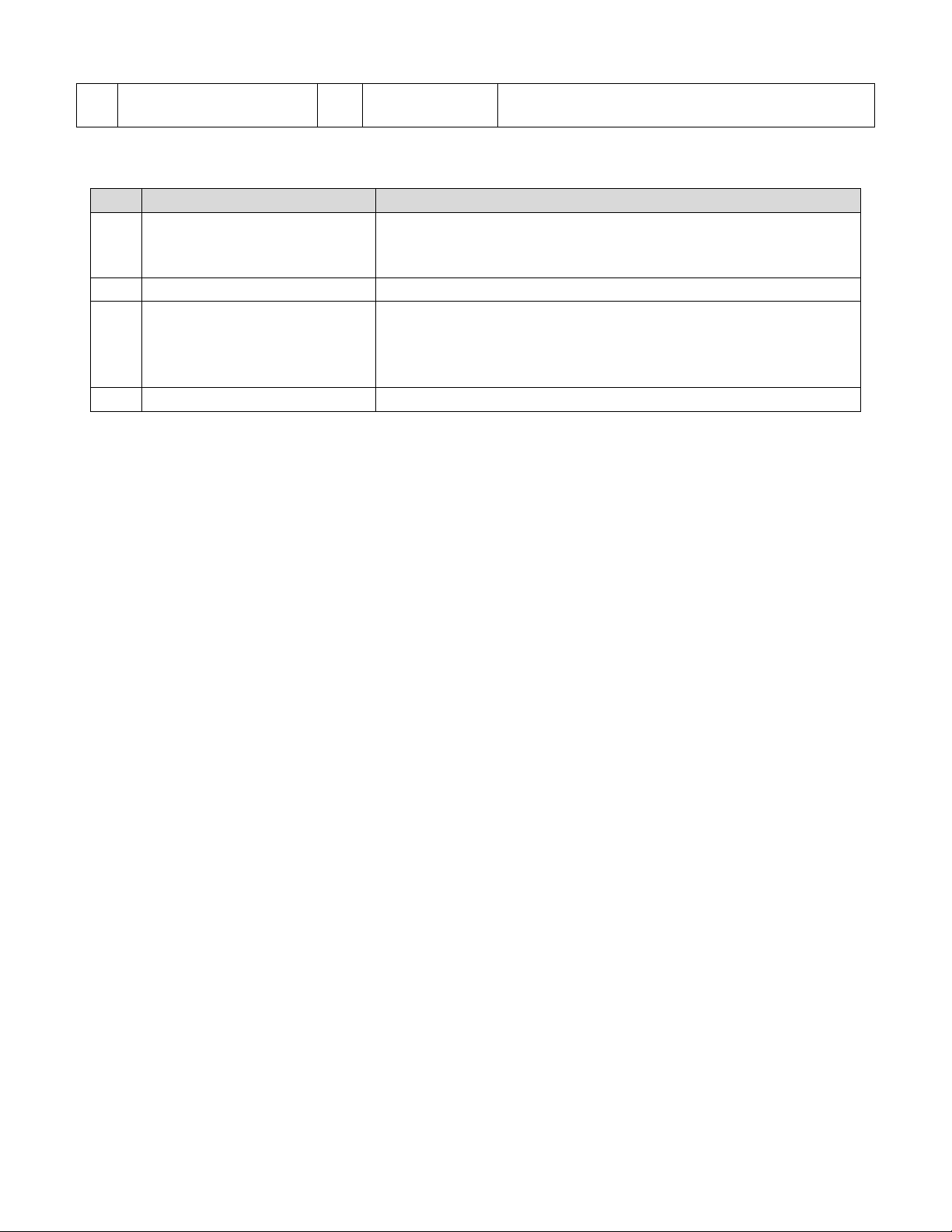
CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
17
Geographic_Location
Set
STRINGI
This is the user assigned switch location.
Bit
Called
Definition
8
Minor Recoverable Fault
Power supply 1, Power supply 2, N-Ring Full, System, Port
utilization, Temperature, N-Link partner is down, N-Link
integrity fault
9
Minor Unrecoverable Fault
Configuration device error
10
Major Recoverable Fault
N-Ring partial low, N-Ring partial high, N-Ring multiple
managers, Boot loader version, N-Link partner port unknown,
N-Link multiple masters, N-Link control fault, N-Link
configuration fault
11
Major Unrecoverable Fault
none
The table below defines fault bits within the Status attribute of the Identity object.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 5 of 61
Page 6
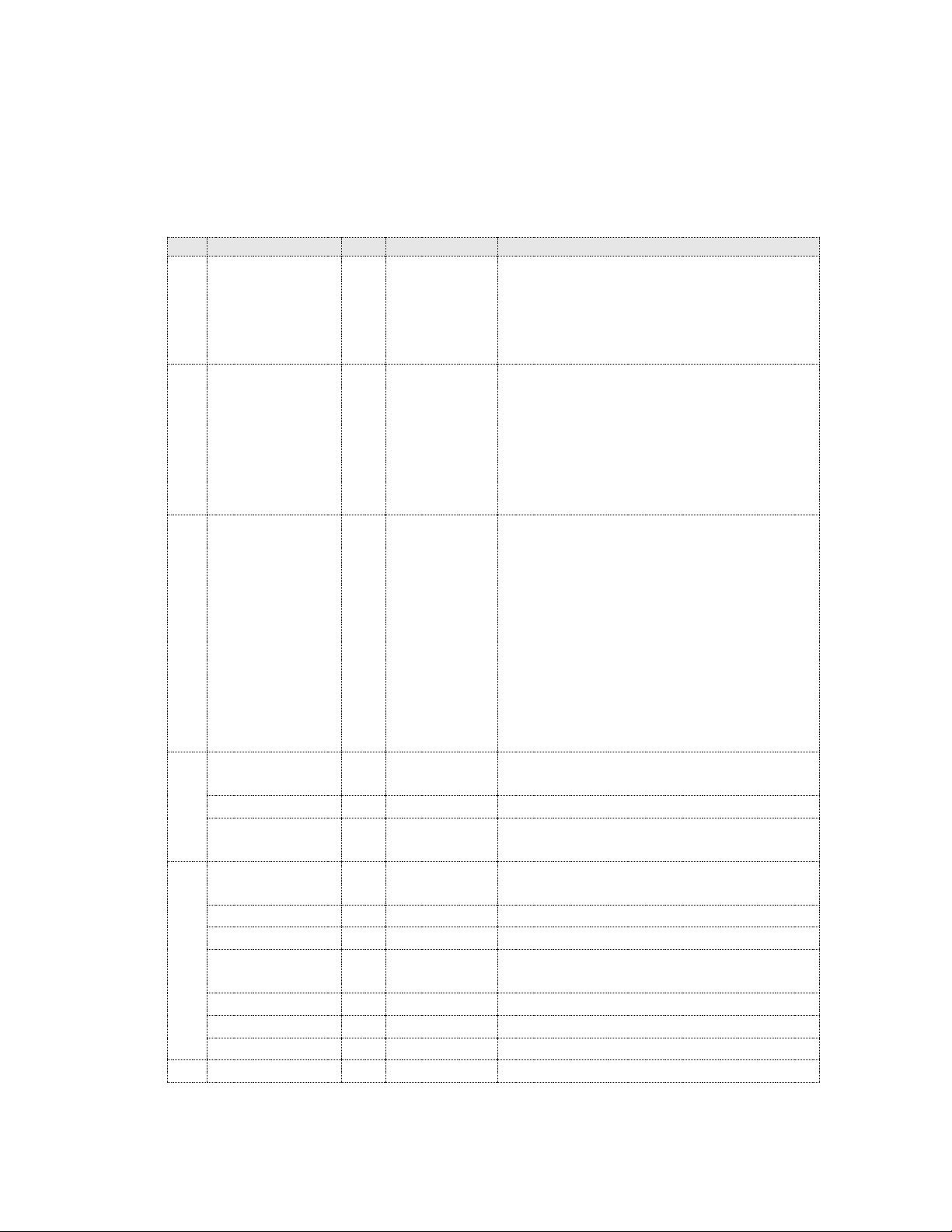
CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Id
Name
Set
Format
Description
1
Status
DWORD
(32)
Interface status
0 interface configuration attrib
not configured
1 interface configuration attrib
is valid
2
Configuration
Capability
DWORD
(32)
Interface capability flags. Bits:
0 BOOTP client capable
1 DNS client capable
2 DHCP client capable
3 DHCP-DNS update capable
4 Configuration is settable
5 Through bit 31 reserved
3
Configuration
Control
Set
DWORD
(32)
Interface control flags.
Bits 0-3:
0 use interface configuration
previously stored
1 get interface configuration
via BOOTP
2 get interface configuration
via DHCP
3 through 15 reserved
Bit 4=1 device shall resolve host names
by querying a DNS server
4
Physical Link
Object
STRUCT
of: Path Size
UINT (16)
Size of Path
Path
Padded
EPATH
Logical segments identifying the
physical link object
5
Interface
Configuration
STRUCT
of: IP Address
Set
UDINT (32)
The device’s IP address.
Network Mask
Set
UDINT (32)
The device’s network mask
Gateway
Address
Set
UDINT (32)
Default gateway address
Name Server
Set
UDINT (32)
Primary name server
Name Server 2
Set
UDINT (32)
Secondary name server
Domain Name
Set
STRING
Default domain name
6
Host Name
STRING
Host name
2.2.1 TCP/IP Interface Object
The TCP/IP Interface object class (Class code = 0xF5) and instance attributes are
implemented as defined by CIP Vol 2, 5-3 [2]. There is only one instance (1) of this
object. The following table summarizes the attributes in the TCP/IP Interface object.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 6 of 61
Page 7
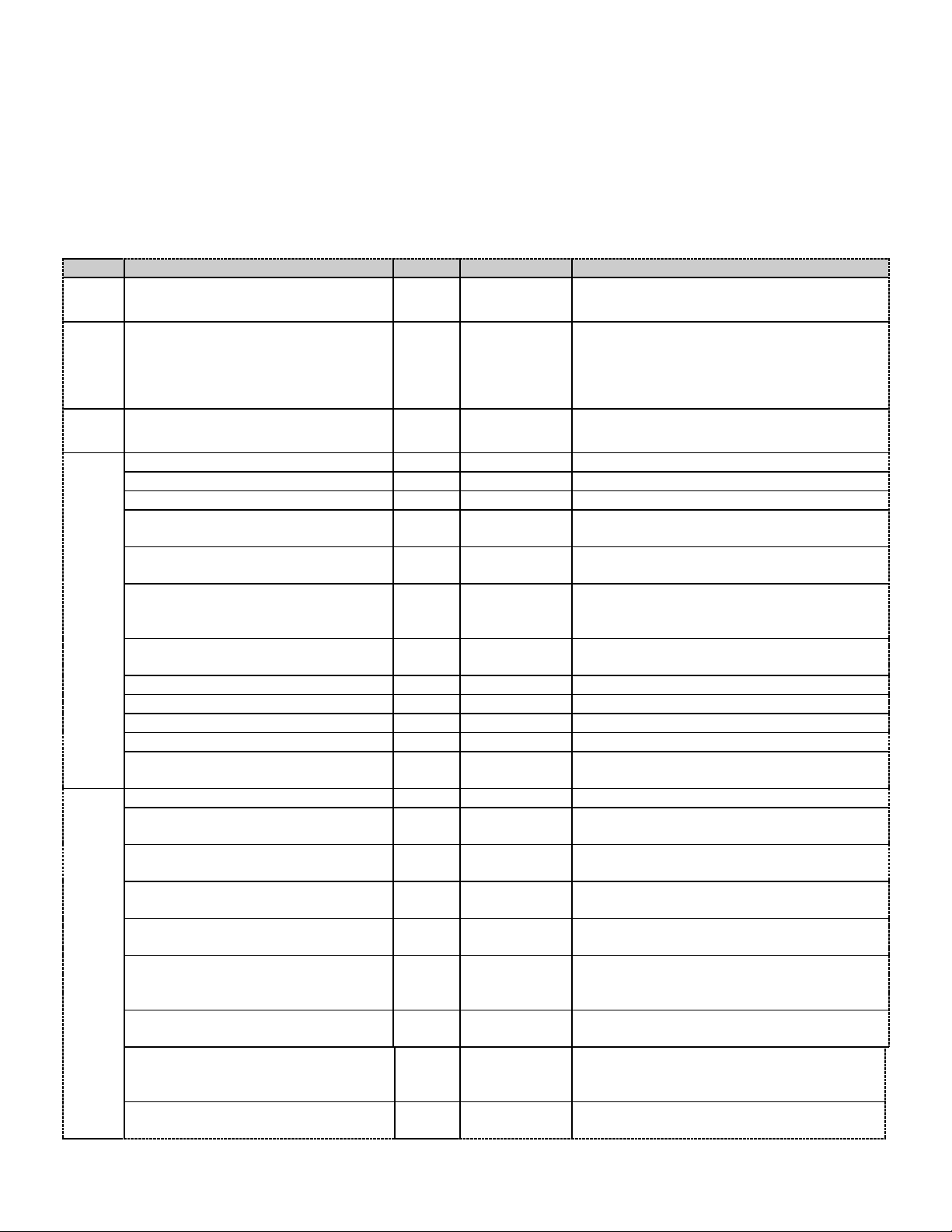
CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Id
Name
Set
Format
Description
1
Interface Speed
UDINT (32)
Interface speed currently in use. Speed
in Mbps (e.g., 0, 10, 100, 1000, etc.)
2
Interface Flags
DWORD (32)
Interface status flags Bit map of
interface flags. See section 5-4.3.2.1.
Includes Link status, duplex mode,
auto-negotiation status, etc.
3
Physical Address
ARRAY of 6
USINTs (8)
MAC address of switch port. Base
MAC plus port number.
4
Interface Counters
STRUCT of:
In Octets
UDINT (32)
Octets received on the interface.
In Ucast Packets
UDINT (32)
Unicast packets received on the interface.
In Nucast Packets
UDINT (32)
Non-unicast packets received on the
interface.
In Discards
UDINT (32)
Inbound packets received on the interface
but discarded
In Errors
UDINT (32)
= 0. Not available.
Inbound packets that contain errors (does
not include In Discards).
In Unknown Protos
UDINT (32)
= 0. Not available.
Inbound packets with unknown protocol
Out Octets
UDINT (32)
Octets sent on the interface
Out Ucast Packets
UDINT (32)
Unicast packets sent on the interface
Out Nucast Packets
UDINT (32)
Non-unicast packets sent on the interface
Out Discards
UDINT (32)
Outbound packets discarded
Out Errors
UDINT (32)
= 0. Not available.
Outbound packets that contain errors
5
Media Counters
STRUCT of:
Alignment Errors
UDINT (32)
Frames received that are not an integral
number of octets in length
FCS Errors
UDINT (32)
Frames received that do not pass the FCS
check
Single Collisions
UDINT (32)
Successfully transmitted frames which
experienced exactly one collision
Multiple Collisions
UDINT (32)
Successfully transmitted frames which
experienced more than one collision
SQE Test Errors
UDINT (32)
= 0. Not available.
Number of times SQE test error message
is generated
Deferred Transmissions
UDINT (32)
Frames for which first transmission attempt
is delayed because the medium is busy
Late Collisions
UDINT (32)
Number of times a collision is detected
later than 512 bit times into the
transmission of a packet
Excessive Collisions
UDINT (32)
Frames for which transmission fails due to
excessive collisions
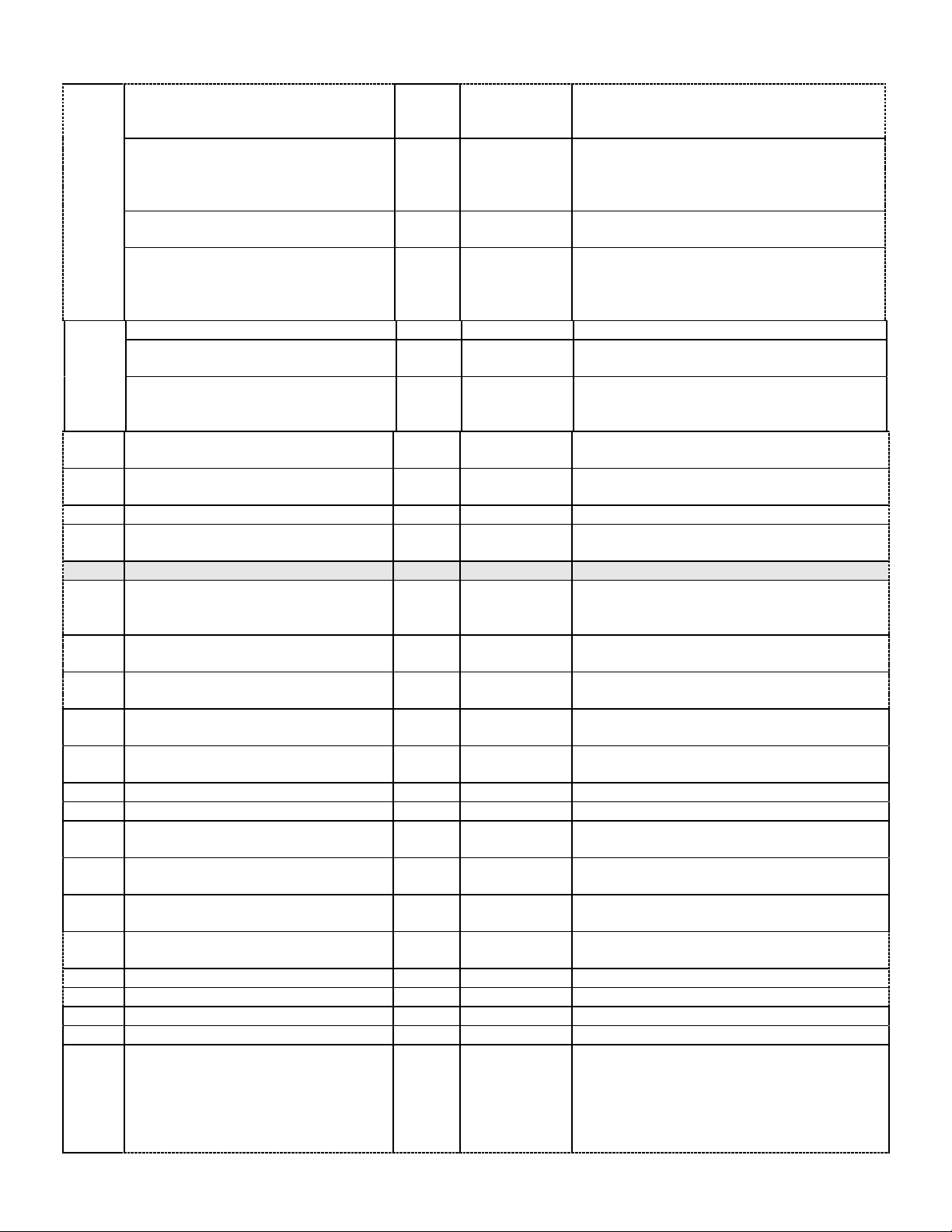
2.2.2 Ethernet Link Object
The Ethernet Link object class (Class code = 0xF6) and instance attributes are
implemented as defined by CIP Vol 2, 5-4 [2]. There is one instance of this object per
switch port where instance 1 = port 1, instance 2 = port 2, etc. As per the CIP
specification, the get all service code (0x01) will get all attributes, excluding vendor
extensions. Service code (0x32) will get all attributes, including the N-TRON vendor
extensions. The following table summarizes the attributes in the Ethernet Link object.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 7 of 61
Page 8
CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
MAC Transmit Errors
UDINT (32)
= 0. Not available.
Frames for which transmission fails due to
an internal MAC sub layer transmit error
Carrier Sense Errors
UDINT (32)
= 0. Not available.
Times that the carrier sense condition was
lost or never asserted when attempting to
transmit a frame
Frame Too Long
UDINT (32)
Frames received that exceed the
maximum permitted frame size
MAC Receive Errors
UDINT (32)
= 0. Not available.
Frames for which reception on an interface
fails due to an internal MAC sub layer
receive error
6
Interface Control
STRUCT of:
Control Bits
Set
WORD (16)
Interface Control Bits. Includes autonegotiation and duplex settings.
Forced Interface Speed
Set
UINT (16)
Speed at which the interface shall be
forced to operate. Speed in Mbps (10,
100, 1000, etc.)
7
Interface Type
USINT (8)
Type of interface: twisted pair, fiber,
internal, etc
8
Interface State
USINT (8)
Current state of the interface: operational,
disabled, etc
9
Admin State
Set
USINT (8)
Administrative state: enable, disable
10
Interface Label
SHORT_STR
ING
Human readable identification: TX1, FX1,
GB1, etc.
100
Interface Description
SHORT_STR
ING
Human readable description. For example:
Port 1 - 10/100 Mbit TX
Port 15 - 100 MBit FX
101
Interface Utilization
USINT (8)
Percentage of entire interface bandwidth
being used (0-100).
102
Utilization Alarm Upper Threshold
Set
USINT (8)
Upper percentage at which to declare a
utilization alarm (0-100).
103
Utilization Alarm Lower Threshold
Set
USINT (8)
Lower percentage at which to declare a
utilization alarm (0-100).
104
Broadcast Limit
Set
USINT (8)
Broadcast limiting percentage (0-100).
(BPCL)
105
TX Unicast Packet Rate
UDINT32
Number of TX unicast packets per second.
106
RX Unicast Packet Rate
UDINT32
Number of RX unicast packets per second.
107
TX Multicast Packet Rate
UDINT32
Number of TX multicast packets per
second
108
RX Multicast Packet Rate
UDINT32
Number of RX multicast packets per
second
109
TX Broadcast Packet Rate
UDINT32
Number of TX broadcast packets per
second.
110
RX Broadcast Packet Rate
UDINT32
Number of RX broadcast packets per
second.
111
TX Multicast Packets
UDINT32
Total number of TX multicast packets.
112
RX Multicast Packets
UDINT32
Total number of RX multicast packets.
113
TX Broadcast Packets
UDINT32
Total number of TX broadcast packets.
114
RX Broadcast Packets
UDINT32
Total number of RX broadcast packets.
115
Port Role
UDINT32
Bit mask of port roles. Bits=
0 = RSTP
1 = N-Ring
2 = N-Link Control
3 = N-Link Partner
4 = N-Link Coupler
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 8 of 61
Page 9
CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Id
Name
Set
Format
Description
1
Device Up
Time
UDINT (32)
Number of seconds since device was powered up.
2
Port Count
UDINT (32)
Total port count
3
Valid Ports
LWORD (64)
AB: DINT[2]
0 = Invalid Port, 1 = Port Exists on device
Bit 0: Port 1
Bit 1: Port 2
etc.
4
Global Admin
Status
LWORD (64)
AB: DINT[2]
0 = Port Disabled, 1 = Port Enabled
Bit 0: Port 1
Bit 1: Port 2
etc.
5
Global Link
Status
LWORD (64)
AB: DINT[2]
0 = Link Down, 1 = Link Up
Bit 0: Port 1
Bit 1: Port 2
etc.
6
System Faults
DWORD (32)
Bit 00: Power Supply 1
Bit 01: Power Supply 2
Bit 02: N-Ring Fault (complete)
Bit 03: N-Ring Partial Fault (low port)
Bit 04: N-Ring Partial Fault (high port)
Bit 05: N-Ring Multiple Managers
Bit 06: System error
Bit 07: Dongle Configuration Invalid
Bit 08: N-Link Fault
Bit 09: Boot loader version mismatch
Bit 10: Port Utilization Alarm
Bit 11: Temperature Alarm
7
IGMP Querier
Status
USINT (8)
Query Status:
0 = Disabled, 1 = Active (manual), 2 = Active
(Auto), 3 = Backup (Auto) [enabled but not active].
8
IGMP Version
USINT (8)
IGMP Version (V1, V2, V3, etc).
9
IGMP
Resource
Usage
USINT (8)
Percent of maximum capacity. Takes into account
the number of groups used per max groups and any
other possible resource limitations (0-100).
10
IGMP Active
Querier
UDINT (32)
IP of the active IGMP querier.
11
CPU Usage
USINT (8)
Percent of usage (0-100).
12
Class 1
Connections
UINT (16)
Number of CIP Ethernet/IP class 1 (multicast)
connections.
13
Class 3
Connections
UINT (16)
Number of CIP Ethernet/IP class 3 (unicast)
connections.
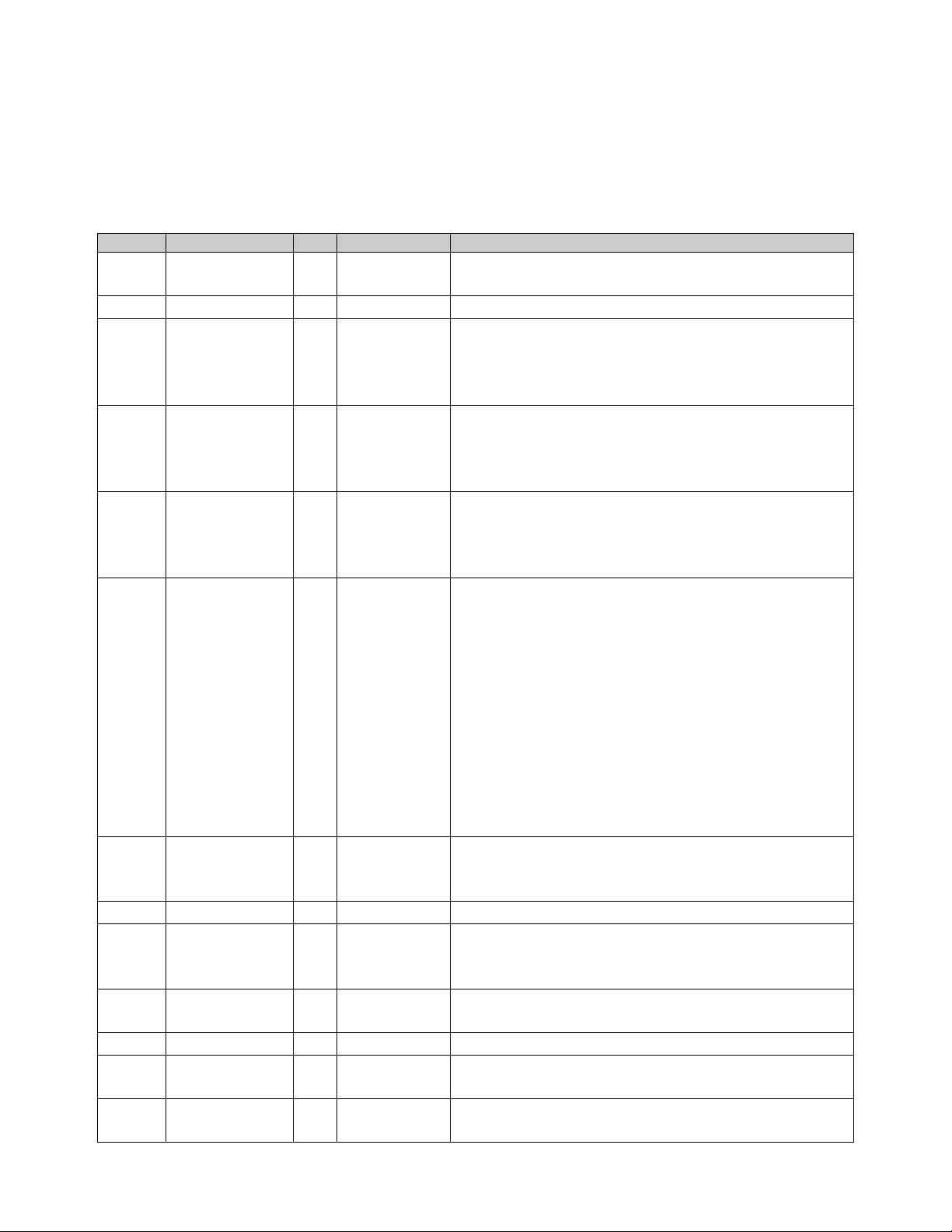
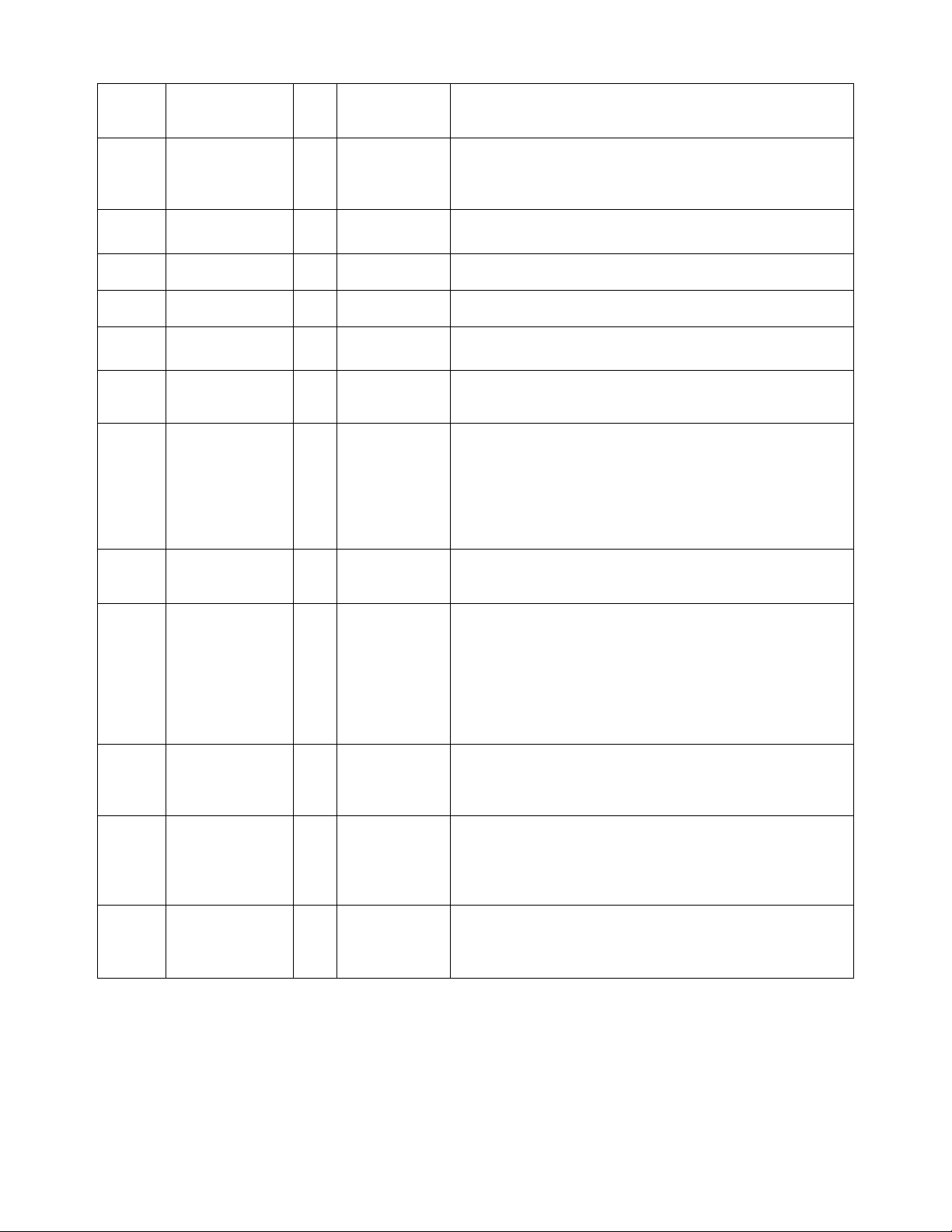
2.2.3 N-TRON Object
The N-TRON object (Class code = 0xC0) is a vendor specific object and is implemented
as defined by CIP Vol 1, 4 [1]. There is only one instance (1) of this object. The
following table summarizes the attributes of the N-TRON object.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 9 of 61
Page 10
CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
14
Temperature
Alarm Upper
Threshold
Set
INT (16)
Upper temperature (C) at which to declare an alarm
15
Temperature
Alarm Lower
Threshold
Set
INT (16)
Lower temperature (C) at which to declare an alarm
16
Contact Status
BYTE (8)
2 Bits per contact. 00=Not Present, 01=Open,
10=Closed.
17
Temperature_C
INT (16)
Temperature in degrees C. 0x7FFF = Not Supported
on device.
18
Temperature_F
INT (16)
Temperature in degrees F. 0x7FFF = Not Supported on
device.
19
Reset MIB
Counts
Set
LWORD (64)
Reset port MIB counters. (1 bit per port to reset).
20
Device MAC
Address
ARRAY of 6
USINTs (8)
MAC address of device
21
Device Role
UDINT (32)
Bit mask of device roles. Bits=
0 = N-Ring Manager
1 = N-Ring Member
2 = N-Ring AutoDetect
3 = N-Link Master
4 = N-Link Slave
5 = N-Link Coupler
22
Config Device
Status
BYTE (8)
0 = Not Supported, 1 = Not Present, 2 = Present
23
System
Configuration
Set
UDINT32
Bit mask of system config. Bits=
Bit 0: GET: Changes have been made that have not
been saved.
SET: Save system configuration to flash.
Bit 1: GET: Changes have been made that require a
reboot to take affect.
SET: Shutdown and reboot device
24
System
Firmware
Version String
SHORT_STR
ING
Human readable representation of firmware version
string.
25
System Boot
Loader
Version String
SHORT_STR
ING
Human readable representation of boot loader
version string.
26
System Fault
String
STRINGI
Human readable representation of error status.
May contain multiple errors. Length is contained
as part of the STRINGI data type.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 10 of 61
Page 11
CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Service
Code
Service Description
Identity
TCP/IP
Ethernet
Link
N-TRON
1
Get_Attributes_All
yes
yes
yes
yes
5
Reset
Yes – reset
switch or
restore factory
configuration
14
Get_Attribute_Single
yes
yes
yes
yes
16
Set_Attribute_Single
Attributes
15,17
Attributes
3,5
Attributes
6,9, 102104
Attributes
14,15,19,23
Vendor
Specific
50
Get_All_Attributes –
including vendor
defined attributes
yes yes
Object
Specific
76
Get_And_Clear
Attributes
4,5
N-TRON switch
Assembly Number
Size (bytes)
Input (to switch)*
101
4
Output (from switch)
102
104
Configuration*
103
0
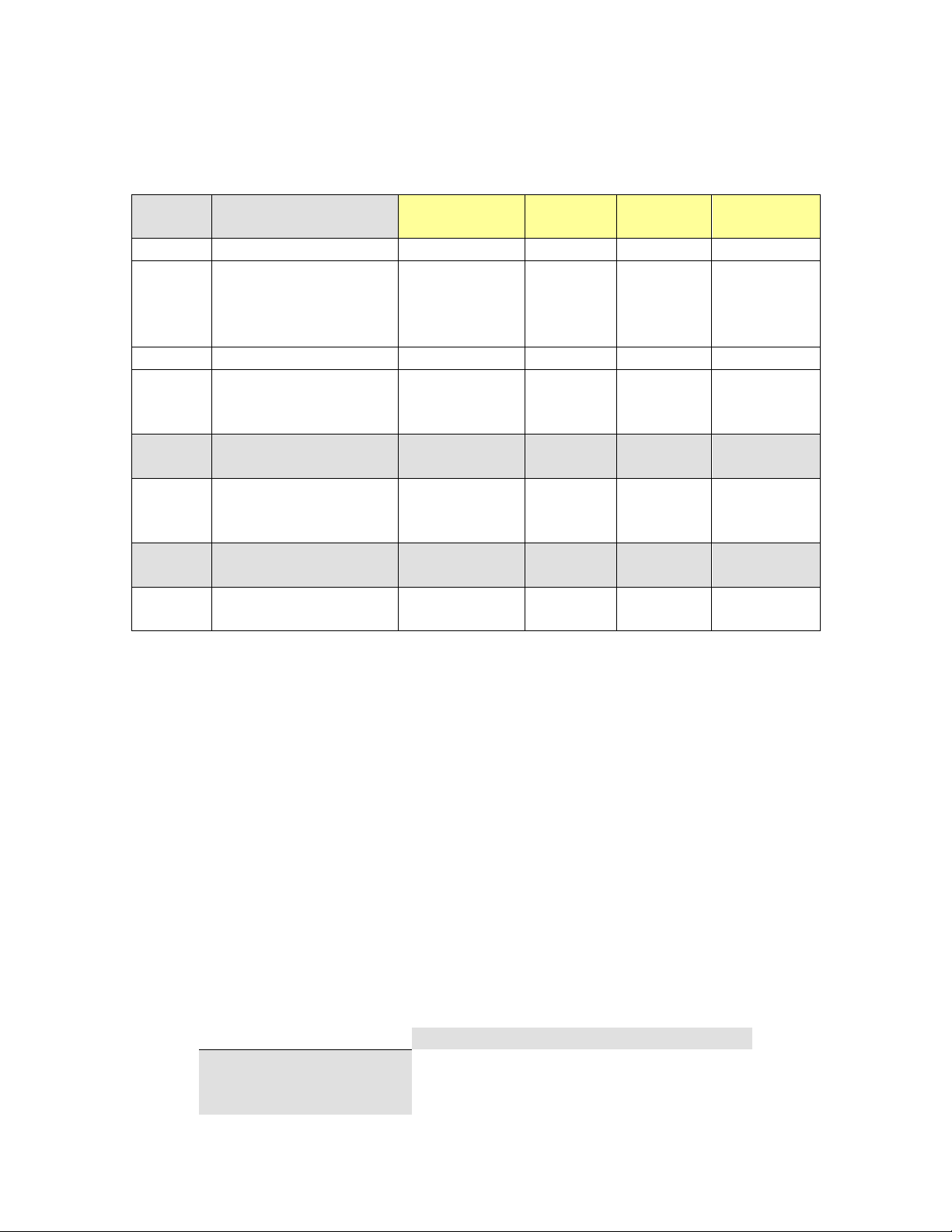
2.3 CIP Services
The table following is a summary of the supported services as defined by CIP Vol 1,
Appendix A: Explicit Messaging Services [1].
2.4 Accessing Data
2.4.1 Explicit Messaging
Explicit messaging refers to a request/response form of communications over a CIP
(TCP/IP) connection. Applications can use explicit messaging, for example, to invoke the
“Get All Attributes” service and read all attributes of the Identity object.
2.4.2 I/O Connections
I/O connections are used to send data (grouped in assemblies) between devices
periodically. The interval between sends is the “Requested Packet Interval”, or
RPI.
The N-TRON switch assemblies (Input, Output, and Configuration) are defined in
the following table.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 11 of 61
* - not currently used
Page 12

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
In an RSLogix 5000 environment, these assemblies are configured in the
“Connection Parameters” panel of the Generic Ethernet Module. (Note that input
and output assemblies are reversed.) More information is contained in the
section for Add-On Instruction installation.
3 Rockwell RSLogix 5000 – Add-On Instruction Installation
N-TRON 700-Series Switch
RSLogix Add-On Instructions (AOI)
Installation Instructions
Software installation prerequisites
1. RSLogix 5000 version 17 or later
2. N-TRON switch with firmware version 3 or later
Summary of steps
1. Import the Add-On Instruction (AOI)
2. Add your N-TRON switch to the I/O Configuration tree
3. Add an instance of the AOI in your application
4. Create and configure tags for the AOI
3.1 Configuration of RSLogix project
Extract all files from the zip file to your desktop or destination folder.
Open an RSLogix project.
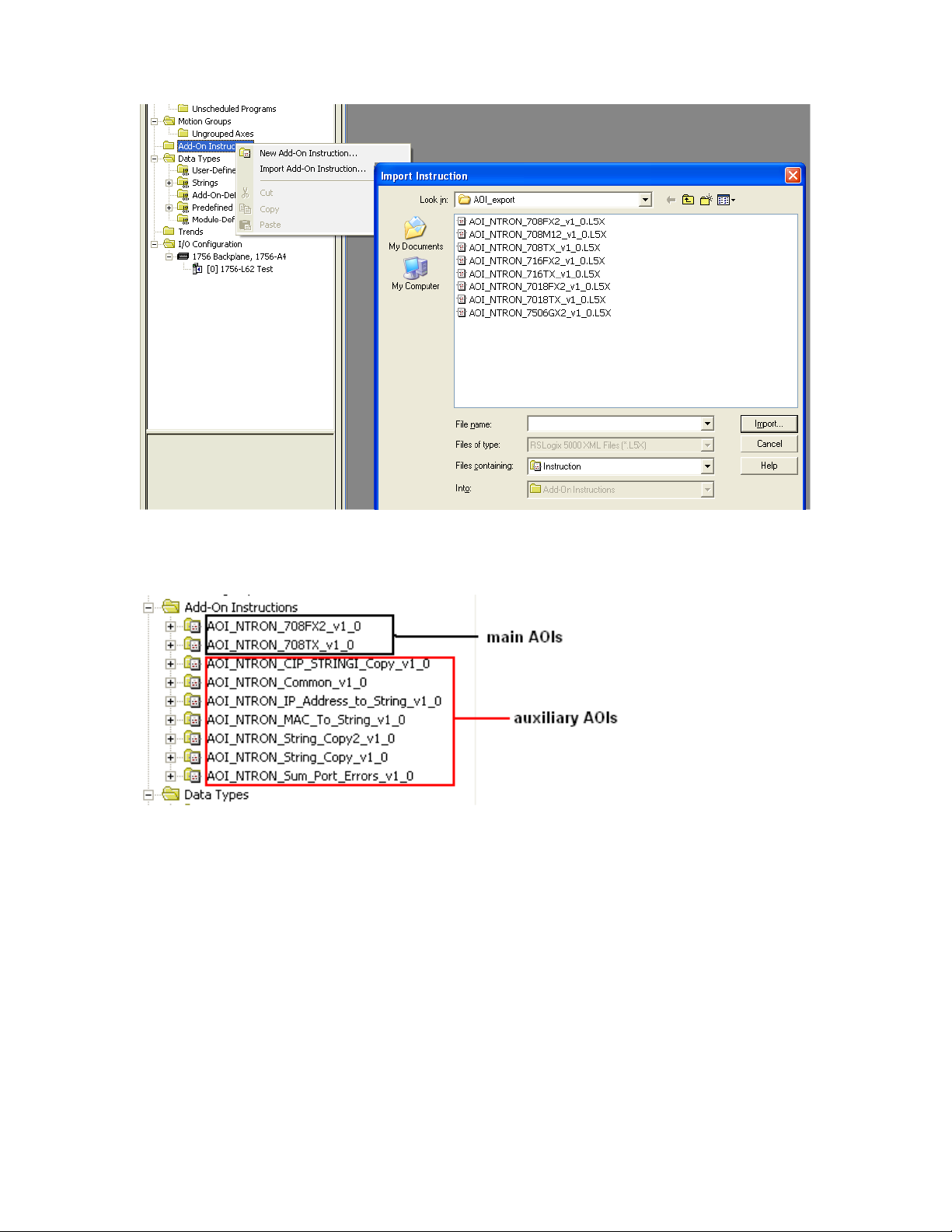
Import the N-TRON Add-On Instruction (AOI). In the controller organizer window, right
click “Add-On Instructions” folder, select “Import Add-On Instruction” and browse to
the folder containing AOI_NTRON_*.L5X files. Import an AOI for each switch type
installed.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 12 of 61
Page 13
CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
.
The Add-On Instruction tree showing AOIs for 708FX2, 708TX, and several auxiliary
AOIs.
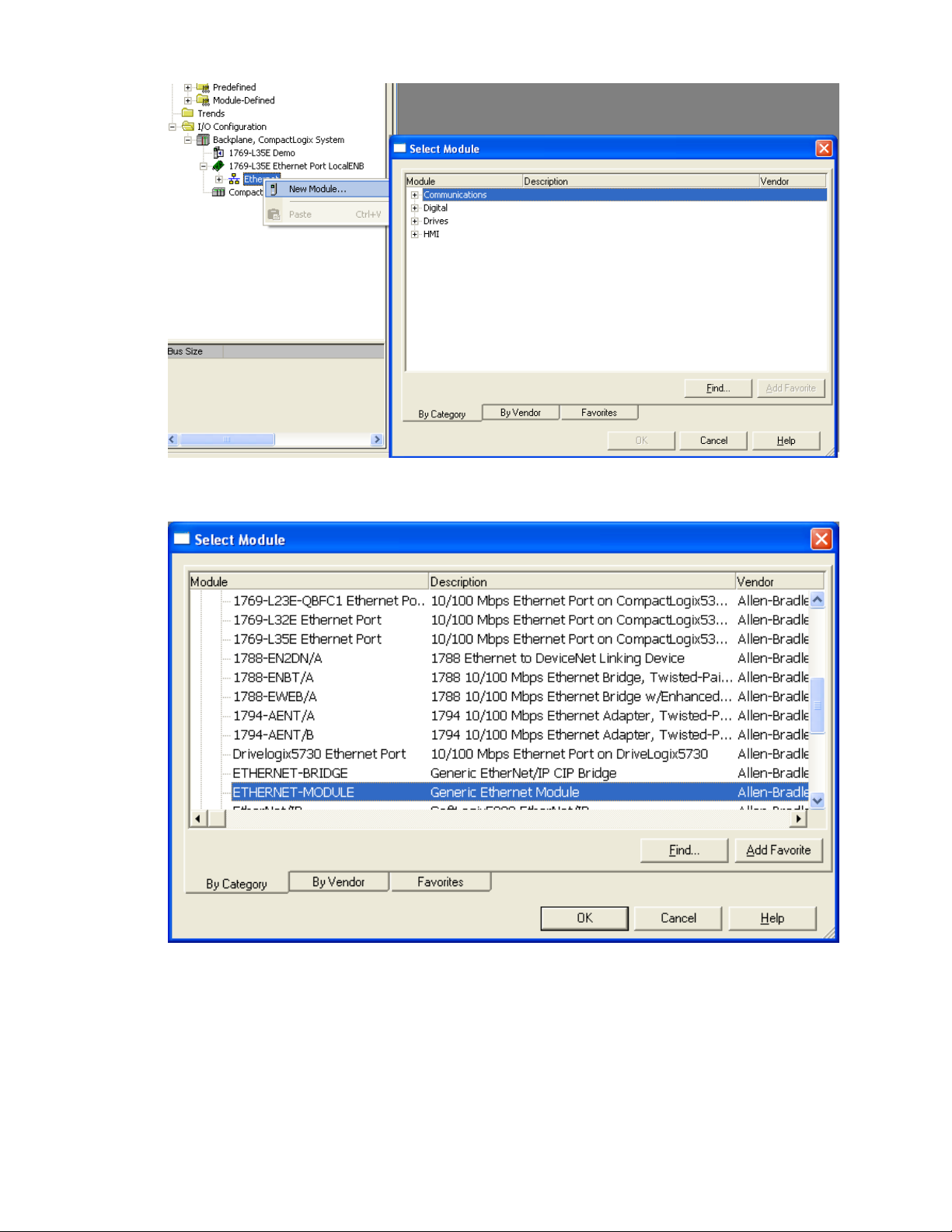
Add a Generic Ethernet Module to the I/O Configuration.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 13 of 61
Page 14
CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
The Generic Ethernet Module is located under the “Communications” group:
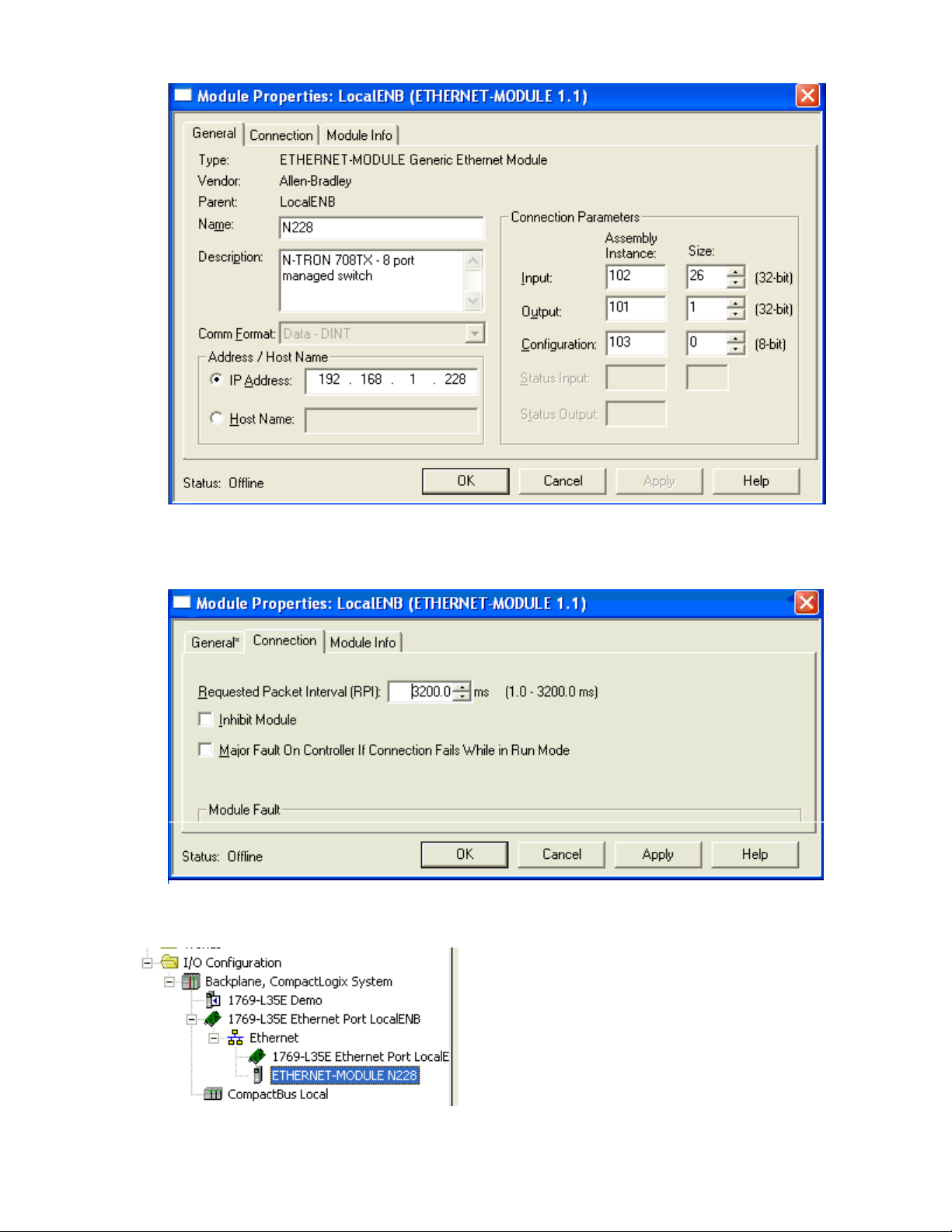
Configure the module as shown. Use the proper IP address and connection parameters for
your installation.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 14 of 61
Page 15
CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Click the Connection tab and set the desired RPI. The input assembly will be received
from the switch at the selected RPI.
Click OK The new module will appear in the I/O Configuration tree:
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 15 of 61
Page 16
CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
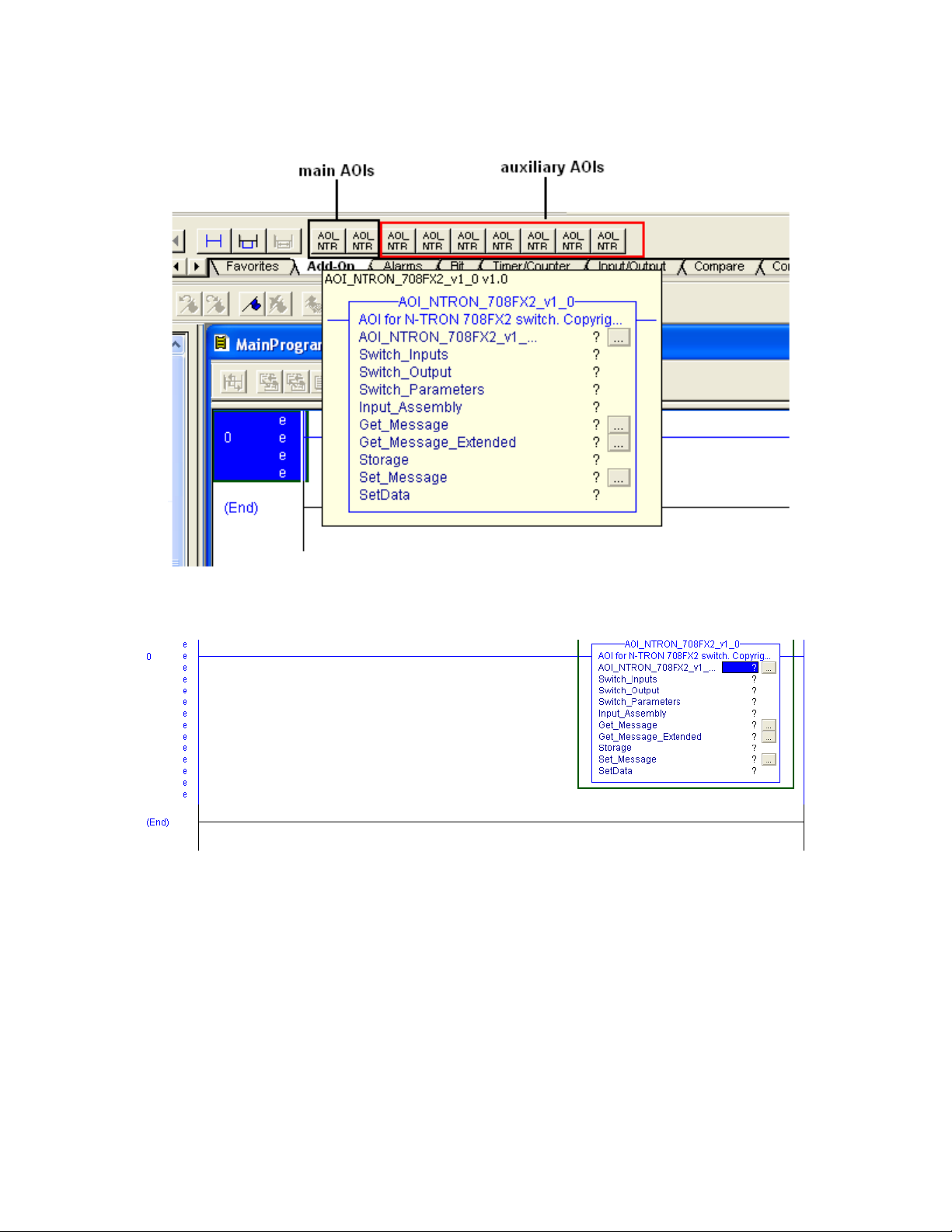
Create a new rung in the MainRoutine and add the AOI for your specific switch to the
rung.
The following will appear:
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 16 of 61
Page 17
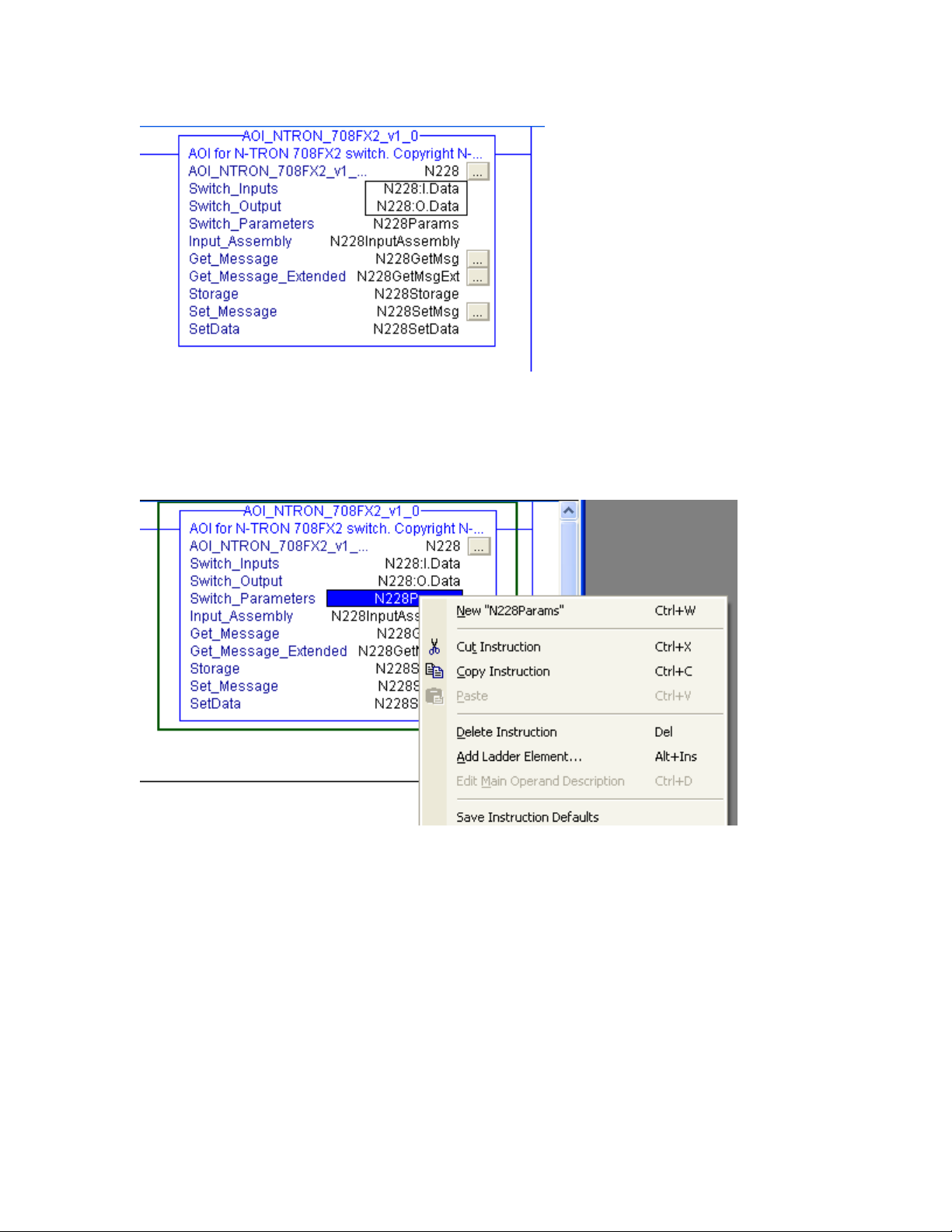
CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Add tag names for the various fields. For example:
Right click on each new tag name and create each tag. (Note that the tags for
Switch_Inputs and Switch_Outputs, shown in the rectangle above, were created when the
Generic Ethernet Module was added.)
For example:
Click the button to the right of the “Get_Message” tag and configure as shown:
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 17 of 61
Page 18
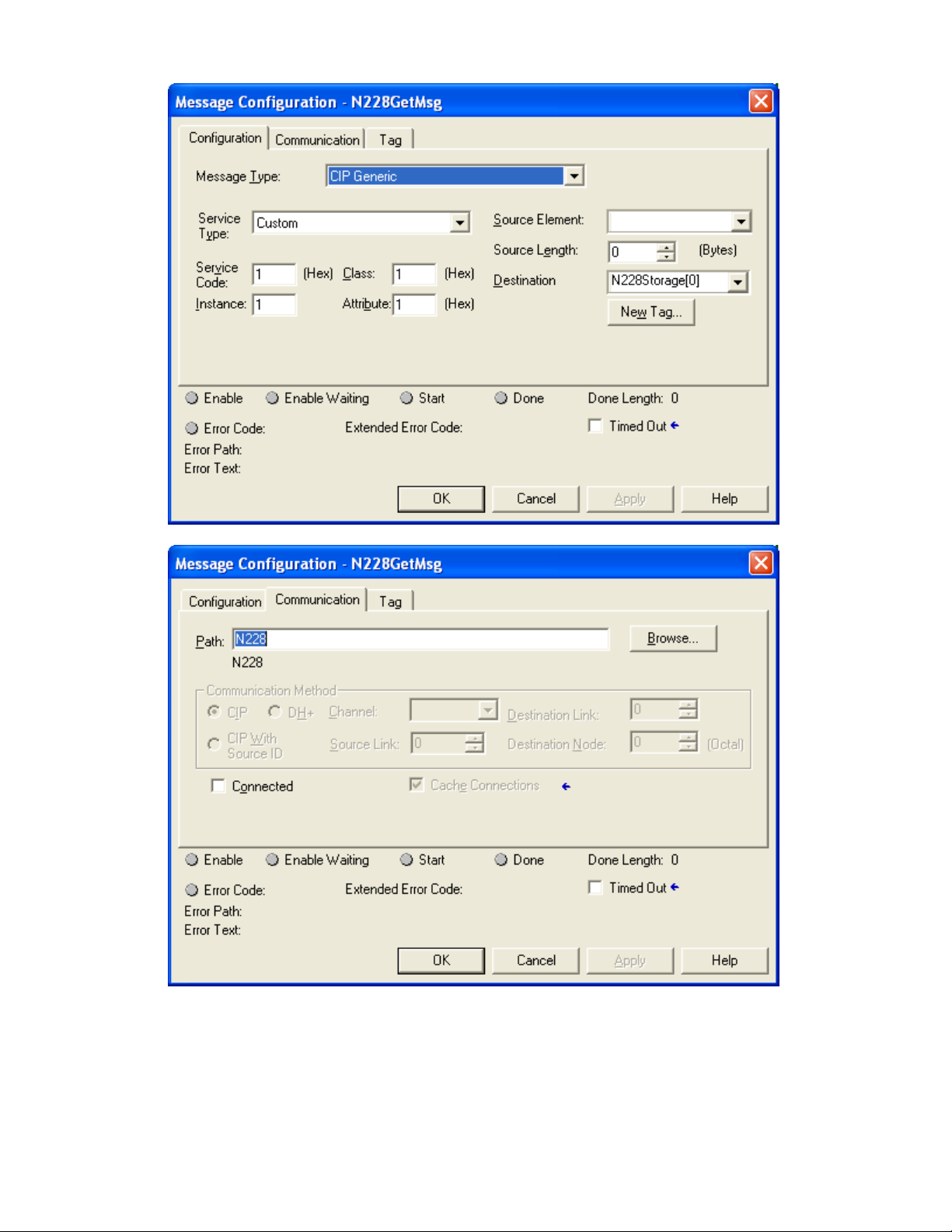
CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 18 of 61
Page 19
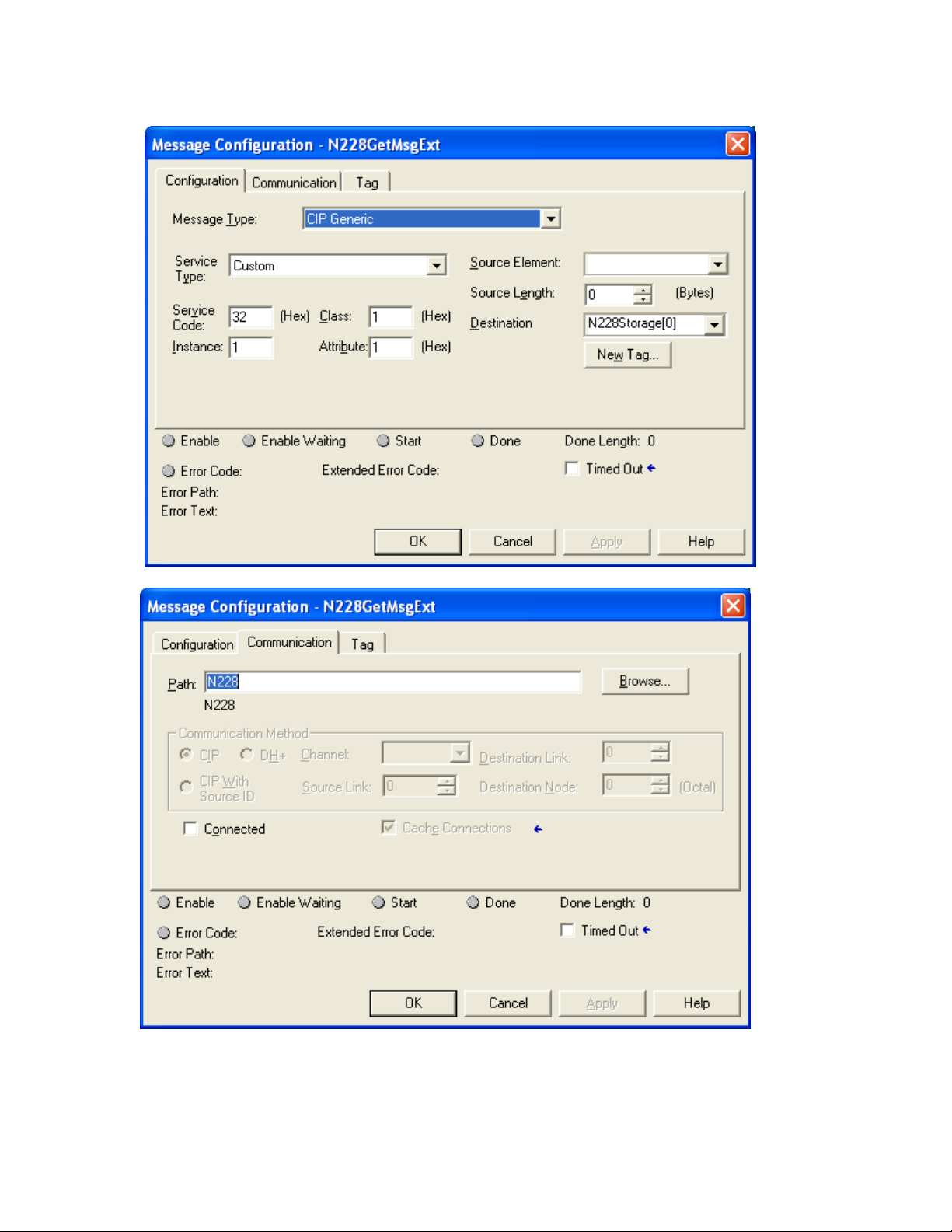
CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Click the button to the right of the “Get_Message_Extended” tag and configure as shown:
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 19 of 61
Page 20

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Click the button to the right of the “Set_Message” tag and configure as shown:
Verify your changes by clicking Logic > Verify > Controller. If there are no warnings or
errors, the RSLogix configuration is complete.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 20 of 61
Page 21

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
3.2 Input_Assembly Parameter
Some data comes from the switch at the RPI (requested packet interval) set for the
Generic Ethernet Module. The data is available in tags like these below (a mapping of the
Switch_Inputs data):
These tags represent a switch specific (708FX2) view of the assembly data.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 21 of 61
Page 22

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Name
Data Type
Description
Selected_Port
INT
Use this member to read Ethernet Link object for one port. To
read more than one port, use Read_Port_Mask. Set by the
faceplate. Port data is copied to the
UDT_NTRON_CIP_DATA_v0 data type.
Request_Data
BOOL
0 - explicit messaging is disabled; 1 - explicit messaging is
enabled
Read_Port_Mask
DINT
Set bit n to read ethernet link object for port n+1
Explicit_Messaging_Timer
_Reset
DINT
Used to control time between each MSG call to read CIP
Identity object, TCPIP object, N-TRON object, and selected
Ethernet Link objects. Minimum is 200 ms. Default is 1000
ms.
3.3 Switch_Parameters Parameter
The AOI requests additional information from the switch as needed by a faceplate display
(and when started). This includes the CIP Identity object, the CIP TCP/IP object, an
instance of the CIP Ethernet Link object, and the NTRON Switch object.
The RSLogix 5000 screenshot below shows a top level view of some of the AOI
“Switch_Parameters” structure:
N228Params.Generic_Inputs is a generic view of the assembly data from a switch.
3.4 Explicit Messaging Options
To direct the AOI to gather this information (via explicit messaging) for other purposes
(example: not using faceplates), use the following members of the N228Params.Control
tag:
Sample ladder logic rungs are available that show how to control explicit messaging.
3.5 Troubleshooting
Module Fault (Code 16#0315 Connection Request Error: Invalid segment type.
This error occurs when the assembly information specified for the Generic Ethernet
Module does not match the assembly information on the N-TRON switch.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 22 of 61
Page 23

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
3.6 Sample Project
A sample project is included in the CIP_Installation_Kit_1_5_0.zip file. It is named
NTRON_Demo.ACD.
To use the sample project, you may need to change the controller type used in your
environment, and you will need to setup the Project path.
If you have any suggestions for improving the AOI or the installation instructions, please
send them to N-TRON_Support@n-tron.com with subject “RSLogix5000 AOI”.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 23 of 61
Page 24

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Switch
Data Type
7018FX2
UDT_NTRON_Switch_7018FX2_In_v0
7018TX
UDT_NTRON_Switch_7018TX_In_v0
708FX2
UDT_NTRON_Switch_708FX2_In_v0
708M12
UDT_NTRON_Switch_708M12_In_v0
708TX
UDT_NTRON_Switch_708TX_In_v0
716FX2
UDT_NTRON_Switch_716FX2_In_v0
716TX
UDT_NTRON_Switch_716TX_In_v0
7506GX2
UDT_NTRON_Switch_7506GX2_In_v0
711FX3
UDT_NTRON_Switch_711FX3_In_v0
7010TX
UDT_NTRON_Switch_7010TX_In_v0
709FX
UDT_NTRON_Switch_709FX_In_v0
710FX2
UDT_NTRON_Switch_710FX2_In_v0
714FX6
UDT_NTRON_Switch_714FX6_In_v0
712FX4
UDT_NTRON_Switch_712FX4_In_v0
7012FX2
UDT_NTRON_Switch_7012FX2_In_v0
7026TX
UDT_NTRON_Switch_7026TX_In_v0
Name
Data Type
Description
System_Faults
UDT_NT
RON_Syst
em_Faults
_v0
Status of various system faults.
Admin_Status
DINT
Admin_Status of first 32 ports. Also available
as port specific tags.
Admin_Status_1
BOOL
1=enabled, 0=disabled
Admin_Status_2
BOOL
Admin_Status_3
BOOL
Admin_Status_4
BOOL
4 Rockwell RSLogix 5000 – Tag reference
The assembly data received from an N-TRON switch can be viewed with generic tags or
switch specific tags. Generic tags are defined by the data type
UDT_NTRON_Switch_In_v0. Switch specific tags are defined by a switch specific data
type.
Here are some of the tag descriptions:
4.1 Generic assembly tags
Data Type: UDT_NTRON_Switch_In_v0
Generic view of assembly data received from an N-TRON Switch.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 24 of 61
Page 25

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Admin_Status_5
BOOL
Admin_Status_6
BOOL
Admin_Status_7
BOOL
Admin_Status_8
BOOL
Admin_Status_9
BOOL
Admin_Status_10
BOOL
Admin_Status_11
BOOL
Admin_Status_12
BOOL
Admin_Status_13
BOOL
Admin_Status_14
BOOL
Admin_Status_15
BOOL
Admin_Status_16
BOOL
Admin_Status_17
BOOL
Admin_Status_18
BOOL
Admin_Status_19
BOOL
Admin_Status_20
BOOL
Admin_Status_21
BOOL
Admin_Status_22
BOOL
Admin_Status_23
BOOL
Admin_Status_24
BOOL
Admin_Status_25
BOOL
Admin_Status_26
BOOL
Admin_Status_27
BOOL
Admin_Status_28
BOOL
Admin_Status_29
BOOL
Admin_Status_30
BOOL
Admin_Status_31
BOOL
Admin_Status_32
BOOL
Admin_Status2
DINT
Admin_Status of second 32 ports. Also
available as port specific tags.
Admin_Status_33
BOOL
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 25 of 61
Page 26

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Admin_Status_34
BOOL
Admin_Status_35
BOOL
Admin_Status_36
BOOL
Admin_Status_37
BOOL
Admin_Status_38
BOOL
Admin_Status_39
BOOL
Admin_Status_40
BOOL
Admin_Status_41
BOOL
Admin_Status_42
BOOL
Admin_Status_43
BOOL
Admin_Status_44
BOOL
Admin_Status_45
BOOL
Admin_Status_46
BOOL
Admin_Status_47
BOOL
Admin_Status_48
BOOL
Admin_Status_49
BOOL
Admin_Status_50
BOOL
Admin_Status_51
BOOL
Admin_Status_52
BOOL
Admin_Status_53
BOOL
Admin_Status_54
BOOL
Admin_Status_55
BOOL
Admin_Status_56
BOOL
Admin_Status_57
BOOL
Admin_Status_58
BOOL
Admin_Status_59
BOOL
Admin_Status_60
BOOL
Admin_Status_61
BOOL
Admin_Status_62
BOOL
Admin_Status_63
BOOL
Admin_Status_64
BOOL
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 26 of 61
Page 27

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Link_Status
DINT
Link_Status of first 32 ports. Also available as
port specific tags.
Link_Status_1
BOOL
1=active, 0=inactive
Link_Status_2
BOOL
Link_Status_3
BOOL
Link_Status_4
BOOL
Link_Status_5
BOOL
Link_Status_6
BOOL
Link_Status_7
BOOL
Link_Status_8
BOOL
Link_Status_9
BOOL
Link_Status_10
BOOL
Link_Status_11
BOOL
Link_Status_12
BOOL
Link_Status_13
BOOL
Link_Status_14
BOOL
Link_Status_15
BOOL
Link_Status_16
BOOL
Link_Status_17
BOOL
Link_Status_18
BOOL
Link_Status_19
BOOL
Link_Status_20
BOOL
Link_Status_21
BOOL
Link_Status_22
BOOL
Link_Status_23
BOOL
Link_Status_24
BOOL
Link_Status_25
BOOL
Link_Status_26
BOOL
Link_Status_27
BOOL
Link_Status_28
BOOL
Link_Status_29
BOOL
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 27 of 61
Page 28

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Link_Status_30
BOOL
Link_Status_31
BOOL
Link_Status_32
BOOL
Link_Status2
DINT
Link_Status of second 32 ports. Also available
as port specific tags.
Link_Status_33
BOOL
Link_Status_34
BOOL
Link_Status_35
BOOL
Link_Status_36
BOOL
Link_Status_37
BOOL
Link_Status_38
BOOL
Link_Status_39
BOOL
Link_Status_40
BOOL
Link_Status_41
BOOL
Link_Status_42
BOOL
Link_Status_43
BOOL
Link_Status_44
BOOL
Link_Status_45
BOOL
Link_Status_46
BOOL
Link_Status_47
BOOL
Link_Status_48
BOOL
Link_Status_49
BOOL
Link_Status_50
BOOL
Link_Status_51
BOOL
Link_Status_52
BOOL
Link_Status_53
BOOL
Link_Status_54
BOOL
Link_Status_55
BOOL
Link_Status_56
BOOL
Link_Status_57
BOOL
Link_Status_58
BOOL
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 28 of 61
Page 29

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Link_Status_59
BOOL
Link_Status_60
BOOL
Link_Status_61
BOOL
Link_Status_62
BOOL
Link_Status_63
BOOL
Link_Status_64
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm
DINT
Bandwidth utilization alarms for first 32 ports.
Also available as port specific tags.
Utilization_Alarm_1
BOOL
1=bandwidth utilization exceeds a high or low
limit, 0=bandwidth utilization within limits
Utilization_Alarm_2
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_3
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_4
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_5
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_6
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_7
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_8
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_9
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_10
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_11
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_12
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_13
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_14
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_15
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_16
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_17
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_18
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_19
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_20
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_21
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_22
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_23
BOOL
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 29 of 61
Page 30

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Utilization_Alarm_24
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_25
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_26
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_27
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_28
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_29
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_30
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_31
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_32
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm2
DINT
Bandwidth utilization alarms for second 32
ports. Also available as port specific tags.
Utilization_Alarm_33
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_34
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_35
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_36
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_37
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_38
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_39
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_40
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_41
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_42
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_43
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_44
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_45
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_46
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_47
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_48
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_49
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_50
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_51
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_52
BOOL
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 30 of 61
Page 31

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Utilization_Alarm_53
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_54
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_55
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_56
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_57
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_58
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_59
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_60
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_61
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_62
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_63
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_64
BOOL
Class1_Connections
INT
Number of CIP Ethernet/IP class 1 (multicast)
connections
Class3_Connections
INT
Number of CIP Ethernet/IP class 3 (unicast)
connections
Temperature_C
INT
Temperature in degrees Celsius. 0x7FFF = Not
supported on device.
Temperature_F
INT
Temperature in degrees Fahrenheit. 0x7FFF =
Not supported on device.
CPU_Utilization
SINT
Percent of CPU usage, 0-100
Contact_Status
SINT
2 Bits per contact. 00=Not Present, 01=Open,
10=Closed.
Utilization_1
SINT
bandwidth utilization in percent
Utilization_2
SINT
Utilization_3
SINT
Utilization_4
SINT
Utilization_5
SINT
Utilization_6
SINT
Utilization_7
SINT
Utilization_8
SINT
Utilization_9
SINT
Utilization_10
SINT
Utilization_11
SINT
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 31 of 61
Page 32

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Utilization_12
SINT
Utilization_13
SINT
Utilization_14
SINT
Utilization_15
SINT
Utilization_16
SINT
Utilization_17
SINT
Utilization_18
SINT
Utilization_19
SINT
Utilization_20
SINT
Utilization_21
SINT
Utilization_22
SINT
Utilization_23
SINT
Utilization_24
SINT
Utilization_25
SINT
Utilization_26
SINT
Utilization_27
SINT
Utilization_28
SINT
Utilization_29
SINT
Utilization_30
SINT
Utilization_31
SINT
Utilization_32
SINT
Utilization_33
SINT
Utilization_34
SINT
Utilization_35
SINT
Utilization_36
SINT
Utilization_37
SINT
Utilization_38
SINT
Utilization_39
SINT
Utilization_40
SINT
Utilization_41
SINT
Utilization_42
SINT
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 32 of 61
Page 33

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Utilization_43
SINT
Utilization_44
SINT
Utilization_45
SINT
Utilization_46
SINT
Utilization_47
SINT
Utilization_48
SINT
Utilization_49
SINT
Utilization_50
SINT
Utilization_51
SINT
Utilization_52
SINT
Utilization_53
SINT
Utilization_54
SINT
Utilization_55
SINT
Utilization_56
SINT
Utilization_57
SINT
Utilization_58
SINT
Utilization_59
SINT
Utilization_60
SINT
Utilization_61
SINT
Utilization_62
SINT
Utilization_63
SINT
Utilization_64
SINT
Update_Counter
INT
Name
Data Type
Description
System_Faults
UDT_NTRON_
System_Faults_
v0
Status of various system faults.
4.2 7506GX2 assembly tags
Data Type: UDT_NTRON_Switch_7506GX2_In_v0
Specific view of assembly data received from an N-TRON 7506GX2 Switch.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 33 of 61
Page 34

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Admin_Status
DINT
Admin_Status of first 32 ports. Also
available as port specific tags.
Admin_Status_T1
BOOL
1=enabled, 0=disabled
Admin_Status_T2
BOOL
Admin_Status_T3
BOOL
Admin_Status_T4
BOOL
Admin_Status_GB1
BOOL
Admin_Status_GB2
BOOL
Link_Status
DINT
Link_Status of first 32 ports. Also
available as port specific tags.
Link_Status_T1
BOOL
1=active, 0=inactive
Link_Status_T2
BOOL
Link_Status_T3
BOOL
Link_Status_T4
BOOL
Link_Status_GB1
BOOL
Link_Status_GB2
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm
DINT
Bandwidth utilization alarms for first 32
ports. Also available as port specific
tags.
Utilization_Alarm_T1
BOOL
1=bandwidth utilization exceeds a high
or low limit, 0=bandwidth utilization
within limits
Utilization_Alarm_T2
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_T3
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_T4
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_G
B1
BOOL
Utilization_Alarm_G
B2
BOOL
Class1_Connections
INT
Number of CIP Ethernet/IP class 1
(multicast) connections
Class3_Connections
INT
Number of CIP Ethernet/IP class 3
(unicast) connections
Temperature_C
INT
Temperature in degrees Celsius. 0x7FFF
= Not supported on device.
Temperature_F
INT
Temperature in degrees Fahrenheit.
0x7FFF = Not supported on device.
CPU_Utilization
SINT
Percent of CPU usage, 0-100
Contact_Status
SINT
2 Bits per contact. 00=Not Present,
01=Open, 10=Closed.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 34 of 61
Page 35

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Utilization_T1
SINT
bandwidth utilization in percent
Utilization_T2
SINT
Utilization_T3
SINT
Utilization_T4
SINT
Utilization_GB1
SINT
Utilization_GB2
SINT
Name
Data
Type
Description
Faults
DINT
Power_Supply_1
BOOL
1=Indicates a low voltage on power supply V1
Power_Supply_2
BOOL
1=Indicates a low voltage on power supply V2
NRing_Full
BOOL
1=Indicates that an N-Ring connection is
completely broken.
NRing_Part_Low
BOOL
1=Indicates that an N-Ring connection is only
broken in one direction. The lower N-Ring port
is not receiving self health frames around the
N-Ring but the higher N-Ring port is.
NRing_Part_High
BOOL
1=Indicates that an N-Ring connection is only
broken in one direction. The higher N-Ring
port is not receiving self health frames around
the N-Ring but the lower N-Ring port is.
NRing_Multiple_Man
agers
BOOL
1=Indicates that more than one N-Ring
Manager exists on an N-Ring.
System
BOOL
1=Indicates a system fault.
Config_Device
BOOL
1=Indicates a problem with the configuration
device.
NLink
BOOL
1=Indicates that the N-Link Master or Slave
encountered a problem.
Boot_Loader_Version
BOOL
1=Indicates a problem with the version of the
boot loader firmware.
Port_Utilization
BOOL
1=Indicates one or more ports have exceeded a
high or low bandwidth utilization limit.
Temperature
BOOL
1=Indicates the switch temperature has
exceeded a high or low temperature limit.
4.3 System fault tags
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 35 of 61
Page 36

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Name
Data Type
Description
Vendor_ID
INT
ODVA Vendor ID. N-Tron = 1006
Device_Type
INT
0x0C. Communications Adapter
Product_Code
INT
708TX=701, 708FX2=703, 716TX=705,
716FX2=706, 7018TX=708,
7018FX2=709, 708M12=710,
711FX3=711, 7010TX=713, 709FX=714,
710FX2=715, 714FX6=717, 712FX4=718,
7506GX2=7506
Major_Revision
SINT
Major revision of the item the Identity
Object represents
Minor_Revision
SINT
Minor revision of the item the Identity
Object represents
Status
INT
Summary status of device
Serial_Number
DINT
Serial number of device
Product_Name
STRING
Human readable identification. Switch
model number. Ex: N-TRON 7018FX2
Assigned_Name
UDT_NTRO
N_String1024
User assigned switch name.
Geographic_Location
UDT_NTRO
N_String1024
This is the user assigned switch location.
Name
Data
Type
Description
Status
DINT
Interface status
Configuration_Capability
DINT
Interface capability flags
Configuration_Control
DINT
Interface control flags
4.4 CIP Tags
There are tags for each CIP object. The tags correspond to the object’s attributes.
Identity object
TCP/IP Interface object
Ethernet Link object
N-TRON switch object
4.5 Identity object
Data Type: UDT_NTRON_CIP_Identity_v0
4.6 TCPIP object
Data Type: UDT_NTRON_CIP_TCPIP_Interface_v0
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 36 of 61
Page 37

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Path_Size
INT
Size of Path
Object_Path_1
INT
Logical segments identifying the physical
link object
Object_Path_2
INT
Logical segments identifying the physical
link object
IP_Address
DINT
The device’s IP address.
Network_Mask
DINT
The device’s network mask
Gateway_Address
DINT
Default gateway address
Name_Server_1
DINT
Primary name server
Name_Server_2
DINT
Secondary name server
Domain_Name
STRING
Default domain name
Host_Name
STRING
Host name
Name
Data Type
Description
Interface_Speed
DINT
Interface speed currently in use. Speed
in Mbps (e.g., 0, 10, 100, 1000, etc.)
Interface_Flags
UDT_NTR
ON_CIP_I
nterface_Fl
ags_v0
Interface status flags
Physical_Address
SINT[6]
MAC layer address
InOctets
DINT
Octets received on the interface
InUcastPackets
DINT
Unicast packets received on the
interface
InNucastPackets
DINT
Non-unicast packets received on the
interface
InDiscards
DINT
Inbound packets received on the
interface but discarded
InErrors
DINT
Inbound packets that contain errors
(does not include In Discards)
InUnknownProtos
DINT
Inbound packets with unknown
protocol
OutOctets
DINT
Octets sent on the interface
OutUcastPackets
DINT
Unicast packets sent on the interface
OutNucastPackets
DINT
Non-unicast packets sent on the
interface
OutDiscards
DINT
Outbound packets discarded
4.7 Ethernet Link object
Data Type: UDT_NTRON_CIP_Ethernet_Link_v0
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 37 of 61
Page 38

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
OutErrors
DINT
Outbound packets that contain errors
Alignment_Errors
DINT
Frames received that are not an integral
number of octets in length
FCS_Errors
DINT
Frames received that do not pass the
FCS check
Single_Collisions
DINT
Successfully transmitted frames which
experienced exactly one collision
Multiple_Collisions
DINT
Successfully transmitted frames which
experienced more than one collision
SQE_Test_Errors
DINT
Number of times SQE test error
message is generated
Deferred_Transmissions
DINT
Frames for which first transmission
attempt is delayed because the medium
is busy
Late_Collisions
DINT
Number of times a collision is detected
later than 512 bit- times into the
transmission of a packet
Excessive_Collisions
DINT
Frames for which transmission fails due
to excessive collisions
MAC_Transmit_Errors
DINT
Frames for which transmission fails due
to an internal MAC sub layer transmit
error
Carrier_Sense_Errors
DINT
Times that the carrier sense condition
was lost or never asserted when
attempting to transmit a frame
Frame_Too_Long
DINT
Frames received that exceed the
maximum permitted frame size
MAC_Receive_Errors
DINT
Frames for which reception on an
interface fails due to an internal MAC
sub layer receive error
Control_Bits
INT
0 Auto-negotiate 0 indicates 802.3 link
auto-negotiation is disabled. 1 indicates
auto-negotiation is enabled. If autonegotiation is disabled, then the device
shall use the settings indicated by the
Forced Duplex Mode and Forced
Interface Speed bits; 1 Forced Duplex
Mode If the Auto-negotiate bit is 0, the
Forced Duplex Mode bit indicates
whether the interface shall operate in
full or half duplex mode. 0 indicates the
interface duplex should be half duplex.
1 indicates the interface duplex
Forced_Interface_Speed
INT
Speed at which the interface shall be
forced to operate. Speed in Mbps (10,
100, 1000, etc.)
Interface_Type
SINT
0-unknown, 1-internal, 2-twisted pair, 3optical
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 38 of 61
Page 39

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Interface_State
SINT
0-unknown, 1-enabled and ready, 2disabled, 3-testing
Admin_State
SINT
1=enabled, 0=disabled
Interface_Label
STRING
Label like "TX5"
Interface_Description
STRING
Something like: Port 1 - 10/100 Mbit
TX Port 15 - 100 MBit FX
Interface_Utilization
SINT
Percentage of entire interface bandwidth
being used (0-100)
Utilization_Alarm_Upper_Thres
hold
SINT
Upper percentage at which to declare a
utilization alarm (0-100).
Utilization_Alarm_Lower_Thre
shold
SINT
Lower percentage at which to declare a
utilization alarm (0-100).
Broadcast_Limit
SINT
Broadcast limiting percentage (0-100).
(BPCL)
TX_Unicast_Packet_Rate
DINT
Number of TX unicast packets per
second.
RX_Unicast_Packet_Rate
DINT
Number of RX unicast packets per
second.
TX_Multicast_Packet_Rate
DINT
Number of TX multicast packets per
second
RX_Multicast_Packet_Rate
DINT
Number of RX multicast packets per
second
TX_Broadcast_Packet_Rate
DINT
Number of TX broadcast packets per
second.
RX_Broadcast_Packet_Rate
DINT
Number of RX broadcast packets per
second
TX_Multicast_Packets
DINT
Total number of TX multicast packets.
RX_Multicast_Packets
DINT
Total number of RX multicast packets.
TX_Broadcast_Packets
DINT
Total number of TX broadcast packets.
RX_Broadcast_Packets
DINT
Total number of RX broadcast packets.
Port_Role
DINT
Bit 0 = RSTP 1 = N-Ring 2 = N-Link
Control 3 = N-Link Partner 4 = N-Link
Coupler
Name
Data Type
Description
Device_Uptime
DINT
Number of seconds since device was powered up.
Port_Count
DINT
Total port count
Valid_Ports
DINT[2]
0 = Invalid port, 1 = Port exists on device Bit 0:
Port 1 Bit 1: Port 2 etc.
4.8 N-TRON Switch object
Data Type: UDT_NTRON_CIP_Switch_v0
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 39 of 61
Page 40

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Global_Admin_Status
DINT[2]
0 = Port disabled, 1 = Port enabled Bit n: Port
n+1
Global_Link_Status
DINT[2]
0 = Link down, 1 = Link up Bit n: Port n+1
System_Faults
UDT_NTR
ON_System
_Faults_v0
Bit 00: Power Supply 1 Bit 01: Power Supply 2
Bit 02: N-Ring Fault (complete) Bit 03: N-Ring
Partial Fault (low port) Bit 04: N-Ring Partial
Fault (high port) Bit 05: N-Ring Multiple
Managers Bit 06: System error Bit 07: Dongle
Configuration Invalid Bit 08: N-Link Fault Bit
09: Boot loader version mismatch Bit 10: Port
Utilization Alarm Bit 11: Temperature Alarm
IGMP_Querier_Status
SINT
Query Status: 0 = Disabled, 1 = Active (manual),
2 = Active (Auto), 3 = Backup (Auto) [enabled
but not active].
IGMP_Version
SINT
IGMP Version (V1, V2, V3, etc).
IGMP_Resource_Usage
SINT
Percent of maximum capacity. Takes into
account the number of groups used per max
groups and any other possible resource
limitations.
IGMP_Active_Querier
DINT
IP of the active IGMP querier.
CPU_Usage
SINT
Percent usage
Class1_Connections
INT
Number of CIP Ethernet/IP class 1 (multicast)
connections.
Class3_Connections
INT
Number of CIP Ethernet/IP class 3 (unicast)
connections.
Temperature_Alarm_Upp
er_Threshold
INT
Upper temperature (C) at which to declare an
alarm
Temperature_Alarm_Lo
wer_Threshold
INT
Lower temperature (C) at which to declare an
alarm
Contact_Status
SINT
2 Bits per contact. 00=Not Present, 01=Open,
10=Closed.
Temperature_C
INT
Temperature in degrees C. Only available on
devices that support temperature.
Temperature_F
INT
Temperature in degrees F. Only available on
devices that support temperature.
Reset_MIB_Counts
DINT[2]
Reset port MIB counters. (1 bit per port to reset).
Device_MAC_Address
SINT[6]
MAC address of device
Device_Role
DINT
Bit mask of device roles. Bits= 0 = N-Ring
Manager 1 = N-Ring Member 2 = N-Ring
AutoDetect 3 = N-Link Master 4 = N-Link
Slave 5 = N-Link Coupler
Config_Device_Status
SINT
0 = Not Supported, 1 = Not Present, 2 = Present
System_Configuration
DINT
Bit mask of system config. Bits= 0 = Save
system configuration to flash 1 = Shutdown and
reboot device
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 40 of 61
Page 41

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
System_Firmware_Versi
on_String
STRING
Human readable representation of firmware
version string.
System_Boot_Loader_Ve
rsion_String
STRING
Human readable representation of boot loader
version string.
System_Fault_String
UDT_NTR
ON_String1
024
Human readable representation of error status.
May contain multiple errors. Length is contained
as part of the STRINGI data type.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 41 of 61
Page 42

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
5 Rockwell FactoryTalk - Faceplate Installation Instructions
N-TRON 700-Series Switch
FactoryTalk View ME/SE Faceplate Displays
Software installation prerequisites
3. FactoryTalk View Studio – ME/SE version 5 or later
4. N-TRON switch with firmware version 3 or later
Summary of Faceplate installation steps
1. create shortcut to PLC
2. add global objects to your project
3. add local messages
4. add images
5. import HMI tags
6. create faceplate display
7. configure display startup macro
8. configure display parameter file
9. optionally add composite switch image to display
10. optionally add specific switch image to display
In the instructions below, “ME” refers to FactoryTalk View ME (Machine Edition) and
“SE” refers to FactoryTalk View SE (Site Edition).
5.1 Configuration of FactoryTalk View Faceplate Displays
Extract all files from the zip file to your desktop or some other folder.
Start with an existing FactoryTalk View ME/SE application.
1. Configure a shortcut to the PLC that is running the NTRON AOI. Double click
Communications Setup.
In the screenshot following, the shortcut is named PLC.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 42 of 61
Page 43

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Click the “Yes” button and if ME, click the “Copy from Design to Runtime” button.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 43 of 61
Page 44

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
2. Import graphics
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 44 of 61
Page 45

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
For SE, use the FactoryTalk_View_SE folder in the above dialog.
These global objects should appear in the Explorer window:
3. Import local messages
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 45 of 61
Page 46

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Select the folder (FactoryTalk_View_ME\Display_export\Install\local) containing the
local message files (.loc). Import all NTRON*.loc files. The Explorer window should
show these files:
4. Import images.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 46 of 61
Page 47

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Select the folder (FactoryTalk_View_ME\Display_export\Install\images) containing the
image files (.bmp). Import all NTRON*.bmp files. The Explorer window should show
several new files:
5. Import tags using the Tag Import and Export Wizard. Select the NTRON-Tags.CSV to
import (FactoryTalk_View_ME\Display_export\Install\tags). The result should be these
tags:
6. To access the faceplate displays, create a display using the global object
NTRON_Display. (File > New > Display. Select all objects in the NTRON_Display
global object and paste them into the new display. Save the new display.)
Configure a macro for opening your display. Here is the ME form for this example:
Tag from screenshot: {[PLC]N228Params.Control.HMI[0].Display_Mode}
Here is the SE form:
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 47 of 61
Page 48

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Tag from screenshot: &{[PLC]N228Params.Control.HMI[0].Display_Mode} = 1;
In the macro definition (and later in the parameter file), the shortcut “PLC” was created
earlier. The other important piece is “N228Params”, which is the name of the
Switch_Parameters tag created for the NTRON_SWITCH AOI in your RSLogix project.
Example:
In the Display Settings for the NTRON_Display (open the NTRON_Display display, Edit
> Display Settings) click the Behavior panel and assign the newly created macro as the
startup macro.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 48 of 61
Page 49

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
8. Click the General tab and change Display Type and Size. Here is the ME form:
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 49 of 61
Page 50

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Here is the SE form:
On the display where you wish to show the faceplate, create a Goto Display button.
Create a parameter file that will be associated with the button.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 50 of 61
Page 51

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Substitute your shortcut for “PLC” and the name of your Switch_Parameters for
N228Params, in the parameter file.
Assign a display and parameter file to the Goto Display button. Here is the ME form:
Here is the SE form:
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 51 of 61
Page 52

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
You can also display an image of an NTRON switch using the global object
NTRON_graphic. When used, define Global Object Parameter #1 as follows:
The NTRON_graphic global object is a composite of several N-TRON switches. Due to
the number of switches, and the tags used for each switch, you may run into the limit for
maximum tags allowed on a display.
To work around this limitation, use individual global objects for each switch. These are
imported by using the BatchImport_Global_NTRON_Switches.xml import file. The
global object names contain the switch name, such as NTRON_708TX. Setup Global
Object Parameter #1 as described for the NTRON_graphic object.
For more information on the displays, including screenshots, see the Faceplate Quick
Reference.
FactoryTalk View SE Client setup:
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 52 of 61
Page 53

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
5.2 Sample Project
Refer to the ME or SE sample project archive named NTRON_demo.apa.
If you have any suggestions for improving the faceplates or the installation instructions,
please send them to N-TRON_Support@n-tron.com with subject “FactoryTalk
Faceplates”.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 53 of 61
Page 54

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
6 Rockwell FactoryTalk - Faceplate quick reference guide
6.1 Introduction
The Faceplates consists of several displays: Home, Diagnostics, Settings, and Alarm.
Click the buttons at the top of the screen to navigate between the displays. The “?” button
is used to toggle the display of help text, and the “X” button is used to exit the Faceplates.
The caption at the top includes the switch product name and the user assigned switch
name, separated by a colon.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 54 of 61
Page 55

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Field
Values
Description
IP Address
Like 192.168.1.201
Switch IP address
Subnet Mask
Like 255.255.255.0
Switch subnet mask
MAC Address
Like 00:07:AF:FE:8F:A0
MAC address of switch
Software Version
Like 3.0.2
Software version of switch
Power Input
V1
V2
V1 and V2
Unknown
AC/DC Power
V1 – Power Supply 1
V2 – Power Supply 2
Contact Status
Not Supported
Open
The status of the contact on the
switch.
6.2 Home display
This home display shows general switch information. The trend shows CPU utilization.
Some fields show simple values, such as IP Address. Others, such as Device Role, show
values that depend on the switch configuration.
The following table describes fields and values.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 55 of 61
Page 56

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Closed
N-Ring Status
Fault
Partial-Low
Partial-High
Multiple-Managers
OK
N/A (if N-Ring auto-member, or N-Ring
disabled)
Unknown (if N-Ring member)
The N-Ring status, if the switch is
configured as an N-Ring manager.
IGMP Querier
Disabled
Active-Manual
Active-Auto
Backup-Auto
Unknown
Internet Group Management
Protocol Querier status
IGMP Utilization
0-100 percent
Internet Group Management
Protocol Utilization
Config Device
Not Supported
Not Present
Present
Unknown
This field is displayed for
switches that support a
configuration device.
Role
N-Ring Manager
N-Ring Member
N-Ring AutoMember
N-Link Master
N-Ring Mem, N-Link Master
N-Ring Auto, N-Link Master
N-Link Slave
N-Ring Mem, N-Link Slave
N-Ring Auto, N-Link Slave
N-Link Coupler
N-Ring Mem, N-Link Coupler
N-Ring Auto, N-Link Coupler
Unknown
The role of the switch, which is
based on the switch configuration.
CPU Utilization
0-100 percent
CPU utilization percentage
CPU Trend
0-100 percent
Trend of CPU utilization
Port Color
Port State
Active
The port is active
Inactive
The port is inactive
Disabled
The port is administratively disabled
Error
A port utilization limit, high or low, has been exceeded
On the switch image, the color of each port changes based on the port state.
The LED at the top of the switch graphic will be green if there are no faults, red if a fault
has occurred. You can view faults on the alarms display.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 56 of 61
Page 57

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Field
Values
Description
Link Up
Yes
No
Current link state
Speed/Duplex
10/Full
100/Full
1000/Full
10/Half
100/Half
1000/Half
Unknown
This configurable field displays the current speed and
mode of the port
Admin Enabled
Yes
No
This configurable field displays the existing status of the
port whether it is Enabled/Disabled.
6.3 Diagnostics display
The diagnostics display shows information for a selected switch port. Use the buttons at
the bottom to select a switch port and use the buttons at the left to select a port variable to
trend. The highlighted variable is trended at the bottom.
The following table describes fields and values.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 57 of 61
Page 58

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Port Role
RSTP
N-Ring
N-Link Control
N-Link Partner
RSTP, NLink Partner
NRing, NLink Partner
N-Link Coupler
RSTP, NLink Coupler
The role of the port, which is based on the switch
configuration
Bandwidth Utilization
0-100 percent
Bandwidth utilization displayed as a percentage
RX Broadcast FPS
The frames per second rate of received broadcast frames.
TX Broadcast FPS
The frames per second rate of transmitted broadcast
frames.
RX Multicast FPS
The frames per second rate of received multicast frames
TX Multicast FPS
The frames per second rate of transmitted multicast frames
RX Unicast FPS
The frames per second rate of received unicast frames
TX Unicast FPS
The frames per second rate of transmitted unicast frames
Port Errors
The sum of alignment errors, FCS errors, SQE Test errors,
excessive collisions, MAC transmit errors, carrier sense
errors, frame too long, and MAC receive errors.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 58 of 61
Page 59

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Field
Value
Description
Speed/Duplex
10/Full
100/Full
1000/Full
10/Half
100/Half
1000/Half
Unknown
This configurable field displays the
current speed and mode of the port
Admin Enabled
Yes
No
This configurable field displays the
existing status of the port whether it is
Enabled/Disabled.
6.4 Settings display
The settings display allows some switch port related settings to be changed.
Use the buttons at the bottom to select a switch port and use the buttons at the left to
select a port setting to change. Use the wide up/down buttons toward the bottom to select
a value, and the Enter button to accept the change.
The following table describes fields and values.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 59 of 61
Page 60

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
Field
Values
Description
Power Supply 1
Power Supply 1 OK
Power Supply 1 Error
V1
Power Supply 2
Power Supply 2 OK
Power Supply 2 Error
V2
Boot Loader Version
Boot Loader Version OK
Boot Loader Version Error
Port Utilization
Port Utilization OK
Port Utilization Error
Shows error if utilization
limits on any port is
exceeded
N-Link
N-Link OK
N-Link Error
N-Link N/A
Shows N/A if not
configured for N-Link
N-Ring
N-Ring Error (Redundancy Lost)
N-Ring Error (Partial Low)
N-Ring Error (Partial High)
N-Ring Error (Multiple Managers)
N-Ring Error (Redundancy Lost, Mult Mgrs)
Shows N/A if not
configured for N-Ring
6.5 Alarm display
The alarm display shows the status of several alarms. Alarms with a grey background and
an “N/A” suffix do not apply for the switch type, or for the current configuration of the
switch.
Values ending with “OK” will be green, with “Error” will be red, and with “N/A” will be
gray.
The following table describes fields and values.
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 60 of 61
Page 61

CIP Manual N-TRON Corp.
N-Ring Error (Partial Low, Mult Mgrs)
N-Ring Error (Partial High, Mult Mgrs)
N-Ring OK
N-Ring N/A
Configuration Device
Configuration Device OK
Configuration Device Error
Configuration Device N/A
This field is displayed if
the switch supports a
configuration device
Temperature
Temperature OK
Temperature Error
Temperature N/A
This field is displayed if
the switch supports a
temperature sensor
Revision
Description
April-8-2010
Added switches: 711FX3, 7010TX, 709FX, 710FX2, 714FX6,
and 712FX4
September 2010
Added 7012FX2 switch
January 2011
Added 7026TX switch
The system fault string is shown at the bottom of the display
7 Support
Contact Information:
N-Tron Corp.
820 South University Blvd. Suite 4E
Mobile, AL 36609
TEL: (251) 342-2164
FAX: (251) 342-6353
WEBSITE: www.n-tron.com
E-MAIL: N-TRON_Support@n-tron.com
8 References
[1] The CIP Networks Library, Volume 1: Common Industrial Protocol (CIP™),
Edition 3.5, Publication Number: PUB00001, Open DeviceNet Vendor
Association, Inc., 4220 Varsity Drive, Suite A, Ann Arbor, MI 48108-5006 USA
[2] The CIP Networks Library, Volume 2: EtherNet/IP Adaptation of CIP, Edition
1.6, Publication Number: PUB00002, Open DeviceNet Vendor Association, Inc.,
4220 Varsity Drive, Suite A, Ann Arbor, MI 48108-5006 USA
9 Revisions
Revision February 18, 2011 Page 61 of 61
 Loading...
Loading...