NSC DP84902MS, DP84902M Datasheet
DP84902
1,7 Encoder/Decoder Circuit
General Description
The DP84902 is designed to perform the encoding and decoding for disk memory systems. It is designed to interface
directly with Integrated Read Channel Products (such as
National Semiconductor’s DP84910) and with Disk Data
Controller Products with a 2-bit NRZ interface (such as National Semiconductor’s Advanced Disk Controllers). This
Encoder/Decoder (ENDEC) circuit employs a 2/3 (1,7) Run
Length Limited (RLL) code type and supports the hard sectored format.
The DP84902 has the option of selecting either TTL or ECL
compatible code output to interface with preamplifiers commonly used in high data rate applications. This is accommplished by the setting of a bit in the control register.
The ENDEC also includes write data precompensation control circuitry which detects the need for write precompensation. This circuitry issues early and late output signals necessary for precompensation. The precompensation information is generated against a 2T pattern. The precompensation circuitry can be bypassed by the setting of a bit in the
control register.
A control reigster is included to configure the ENDEC and to
select device operation options such as output code inversion, differential code output, bypassing of the encoder, and
the use of an internal write clock.
June 1994
The DP84902 is available in 20-pin SO and 20-pin SSO
packages.
Features
Y
Operates at 2-bit Non-Return to Zero (NRZ) Data Rates
up to 50 Mbits/second
Y
Singlea5V Power Supply Operation
Y
Low Power Dissipation when TTL compatible code output is selected. 150 mW at 50 Mbits/second NRZ Rate
Y
TTL Compatible Inputs and Outputs
Y
ECL Compatible Code Outputs (patented) are control
register selectable
Y
Two-bit NRZ Interface
Y
Supports Write Data Precompensation with Early and
Late output signals
Y
Selectable use of either an Internal or External Write
Clock
Y
Power Down Mode Included
Y
DC-Erasure is available to support Analog Flaw Mapping Testing
Y
Bypass Mode available which permits Un-Encoded Test
Patterns to be issued at the CODEOUT Pin
DP84902 1,7 Encoder/Decoder Circuit
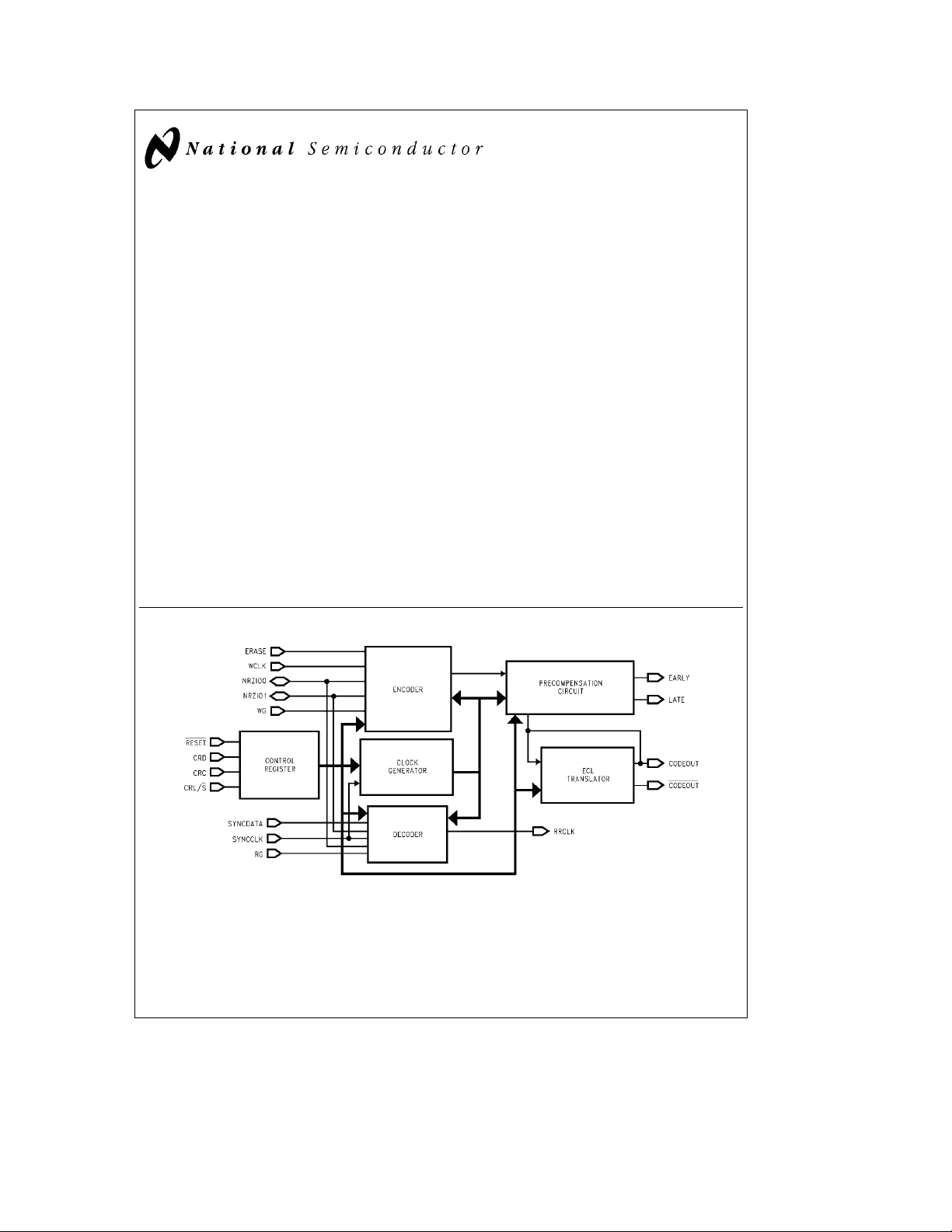
Block Diagram
FIGURE 1. DP84902 ENDEC Block Diagram
TRI-STATEÉis a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
IBM
is a registered trademark of International Business Machines Corporation.
É
C
1995 National Semiconductor Corporation RRD-B30M105/Printed in U. S. A.
TL/F/11963
TL/F/11963– 1
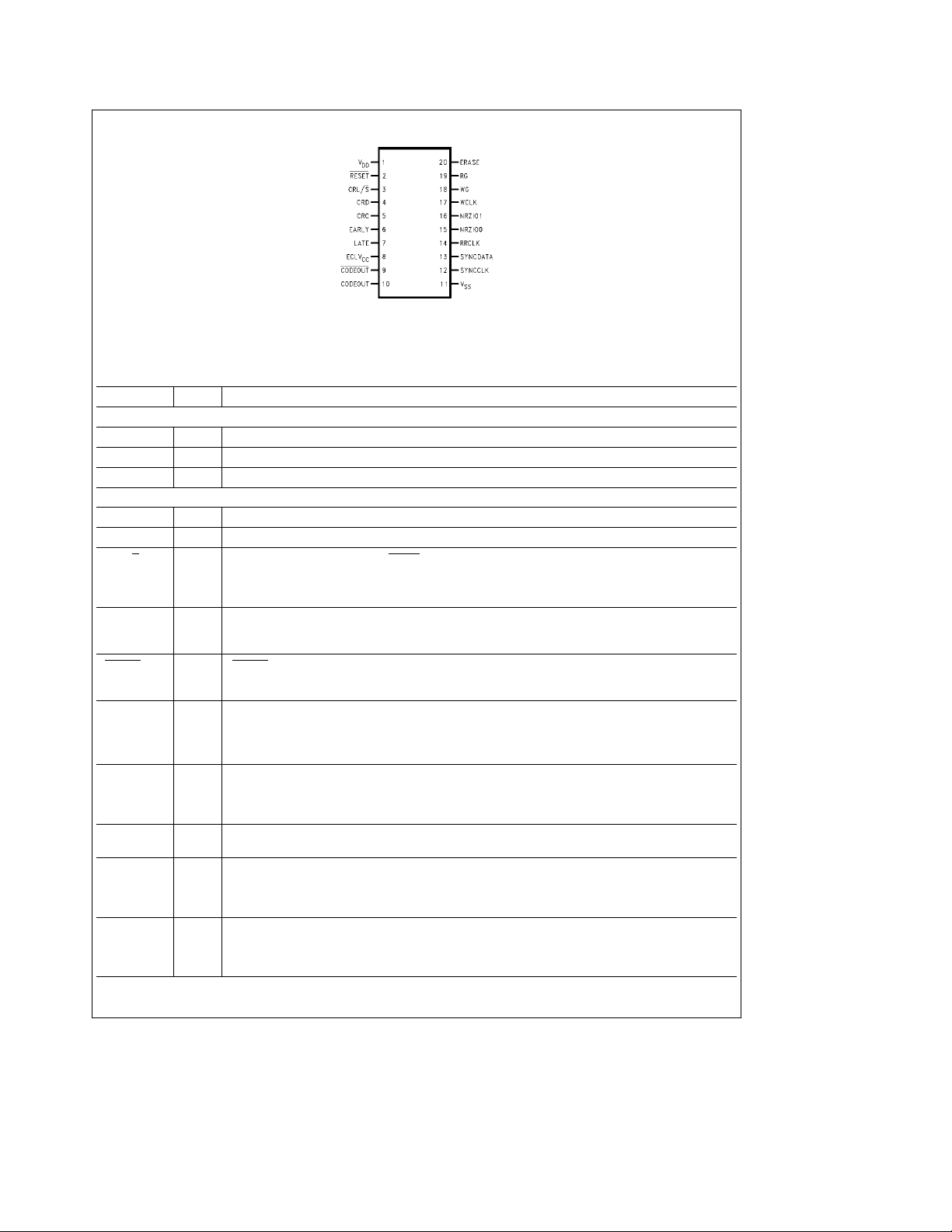
Connection Diagram
FIGURE 2. DP84902 Pinout
Order Number DP84902M or DP84902MS
See NS Package Number M20B or MSA20
TL/F/11963– 2
Pin Descriptions
Symbol Pin
Power Supply and Ground Pins
ECLV
CC
V
DD
V
SS
Input Pin Descriptions
CRC 5 CONTROL REGISTER CLOCK: Positive-edge-active control register clock input.
CRD 4 CONTROL REGISTER DATA: Control register data input
CRL/S 3 CONTROL REGISTER LATCH/SHIFT: A logical low state applied to this input allows the CONTROL
ERASE 20 ERASE: This active high input is used while in the write mode to force a logical low at the CODEOUT
RESET 2 RESET: A logical low level applied to this input forces the ENDEC to a power-on-reset state, and
RG 19 READ GATE: This input accepts a mode control signal from the controller for the decoder. It permits
SYNCCLK 12 SYNCHRONIZED CLOCK: This input accepts the code rate (1.5F) synchronized clock signal from the
SYNCDATA 13 SYNCHRONIZED DATA: This input accepts the synchronized data signal, MSB first, from the read
WCLK 17 WRITE CLOCK: This input is used only in the external write clock mode. The write clock signal (Note 1)
WG 18 WRITE GATE: This input accepts a mode control signal from the controller for the encoder. It permits
Ý
8 ECLVCCSupply Pin: 5Vg10%
1VDDSupply Pin: 5Vg10%
11 VSS: Ground reference
REGISTER CLOCK input to clock data into the control register’s shift register via the CONTROL
REGISTER DATA input. A logical high state latches the data into a bank of latches and issues the
information to the appropriate circuitry within the ENDEC.
output (or a logical high if CODEOUT is inverted). This is useful to blank out (DC erase which issues no
transitions) a track for analog flaw map tesing.
presets its control register to predetermined operating setup conditions. During normal operation, this
pin must be held at a logical high level.
the reading of data from the disk when at a logical high level. It inhibits reading and resets the decoder
state machine when at a logical low level. There are no set-up or hold timing requirements for the
enabling or disabling of this input.
read channel’s data synchronizer. This signal is used to clock the synchronized data into the decoder
on the negative edge of SYNCCLK in the read mode and is the source clock for clocking codeout data
from the encoder during the write mode.
channel’s data synchronizer for the decoder’s use.
from the controller is used to strobe the NRZ input data into the ENDEC. The write clock signal from the
controller must be the RRCLK echoed by the controller. If the external write clock mode is not selected,
this pin should be tied to V
the writing of a header and data to the disk when at a logical high level. It inhibits writing and resets the
encoder state machine when at a logical low level. There are no set-up or hold timing requirements for
the enabling or disabling of this input.
DD
or VSS.
Functional Description
2
Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Symbol Pin
Output Pin Descriptions
CODEOUT 10 (1,7) RLL CODE OUTPUT: This output issues encoded data, MSB first, to be written to the disk. The
CODEOUT 9 (1,7) RLL COMPLEMENTARY CODE OUTPUT: This output is the complement of the ECL differential
EARLY 6 EARLY PRECOMPENSATION OUTPUT: This pin is the early precompensation output. It issues a logical
LATE 7 LATE PRECOMPENSATION OUTPUT: This pin is the late precompensation output. It issues a logical
RRCLK 14 READ/REFERENCE CLOCK: This output issues read clock to the controller at all times (Note 1). This
Input/Output Pin Descriptions
NRZIO0 15 LEAST SIGNIFICANT BIT NRZ INPUT/OUTPUT: This I/O pin represents the Least Significant Bit
NRZIO1 16 MOST SIGNIFICANT BIT NRZ INPUT/OUTPUT: This I/O pin represents the Most Significant Bit (MSB)
Note 1: With the code rate at 1.5F, the effective NRZ data rate is 1F. Since this chip employs a 2-bit NRZ interface, the write (WCLK) and read/reference (RRCLK)
clocks are 0.5F.
Ý
control register controls various attributes of this output. It can be configured either as a TTL or ECL
compatible output. In the TTL mode, the sense of the output can be selectively inverted to allow the
active edge to be either the positive or negative transition and can also be put into a high impedance
state (TRI-STATE
precompensation circuitry can be bypassed. The encoder can also be bypassed thus permitting uncoded
test patterns to be issued from this pin.
CODEOUT output pin. It issues encoded data to be written to the disk. It is enabled as an ECL output by
a control register bit. If the TTL mode is selected (by a control register bit), this pin will be in a high
impedance state (TRI-STATE).
high level to indicate that early precompensation is needed. This signal is used by National
Semiconductor Integrated Read Channel Products, such as the DP8492, to precompensate the final
coded data before it goes to the read/write circuit.
high level to indicate that late precompensation is needed. This signal is used by National
Semiconductor Integrated Read Channel Products, such as the DP8492, to precompensate the final
coded data before it goes to the read/write circuit.
signal is used to clock decoded NRZ data into the controller in the read mode (READ CLOCK) and is to
be echoed back to the ENDEC by the controller in the write mode for use as a write clock (REFERENCE
CLOCK) if external write clock mode is selected in the control register.
(LSB) of NRZ data. As an input, it accepts the NRZ LSB data signal from the controller. Data is strobed
into the ENDEC on the positive-edge of the WRITE CLOCK (if external write clock mode is selected in
the control register), encoded and written to the disk in (1,7) format. This NRZ input must be low while
the preamble and address mark fields are being written. This pin is also used to transfer un-encoded test
patterns to the CODEOUT pin. As an output, it issues the decoded NRZ LSB data to the controller during
a read operation. NRZ output data will be clocked into the controller on the positive-edge of the READ/
REFERENCE CLOCK (RRCLK).
of NRZ data. As an input, it accepts the NRZ MSB data signal from the controller. Data is strobed into
the ENDEC on the positive-edge of the WRITE CLOCK (if external write clock mode is selected in the
control register), encoded, and written to the disk in (1,7) format. This NRZ input must be held low while
the preamble and address mark fields are being written. As an output, this pin issues the decoded NRZ
MSB data to the controller during a read operation. The decoded NRZ output data will be clocked into
the controller on the positive-edge of the READ/REFERENCE CLOCK (RRCLK).
) which allows the multiplexing of this pin with another device or pin. The
É
Functional Description
3
DC and AC Device Specifications
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Note: Absolute Maximum Ratings are those values beyond which the safety
of the device cannot be guaranteed. The device should not be operated at these limits. The parametric values defined in the ‘‘Electrical
Characteristics’’ tables are not guaranteed at these ratings. The ‘‘operating conditions’’ table will define the conditions for actual device
operation.
(Note)
Supply Voltage ААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААААА7V
TTL Input Maximum Voltage ААААААААААААААААААААААААА7V
Maximum Output Voltage АААААААААААААААААААААААААААА7V
ESD Susceptibility (Note 1) ААААААААААААААААААААААА2000V
Note 1: Human Body model used. (100 pF through 1.5 kX)
General Operating Conditions are guaranteed over supply voltage and operating ambient temperature
ranges unless otherwise specified.
Symbol Parameter Min
VDD, ECLV
T
A
T
S
C
LOAD
Supply Voltage 4.5 5 5.5 V N/A
CC
Operation Ambient Temperature 0 70
Storage Temperature
b
Capacitive Load on any Output ECL Output 10
TTL Output 15
I
OH
I
OL
V
IH
V
IL
f
NRZ
f
SCLK
t
PW(RESET)
t
PW(RG, WG)
Note 1: Typical values are specified at 25§C and 5V supply.
Note A: This parameter is guaranteed by outgoing testing.
Note B: The limit values have been determined by characterization data. No outgoing tests are performed.
High Logic Level Output Current
(CMOS Logic Outputs Only)
Low Logic Level Output Current EARLY, LATE 6
(CMOS Logic Outputs Only)
All Others 8 (Note A)
High Logic Level Input Voltage 2 V (Note A)
Low Logic Level Input Voltage 0.8 V (Note A)
NRZ Transfer Rate Operating Frequency 5 50 Mb/s (Note A)
SYNCCLK Operating Frequency 7.5 75 MHz (Note A)
RESET Pulse Width (negative)
(See
Figure 3
) PERIODS
5
RG or WG Wait Time after Power Down or Reset
with Respect to Positive Edge of CRL/S
(See
Figure 3
)
Pin. 10
Typ
(Note 1)
Max Units Test
65 150
b
C N/A
§
C N/A
§
pF N/A
8 mA (Note A)
mA
SYNCCLK
SYNCCLK
PERIODS
(Note A)
(Note A)
(Note B)
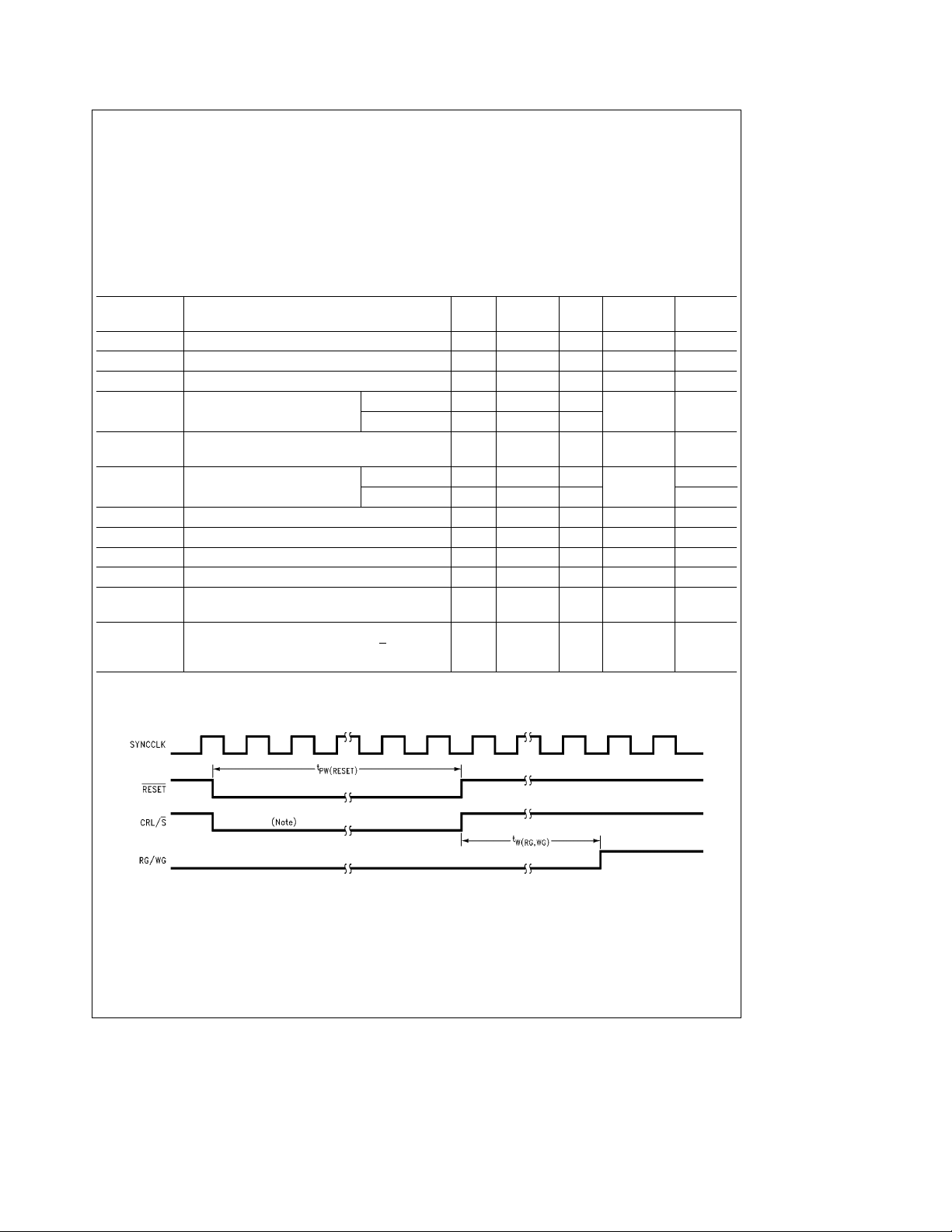
Note: Power down mode selected in control register (see Table I).
FIGURE 3. Reset Pin and Power Down Timing Diagram
TL/F/11963– 3
4
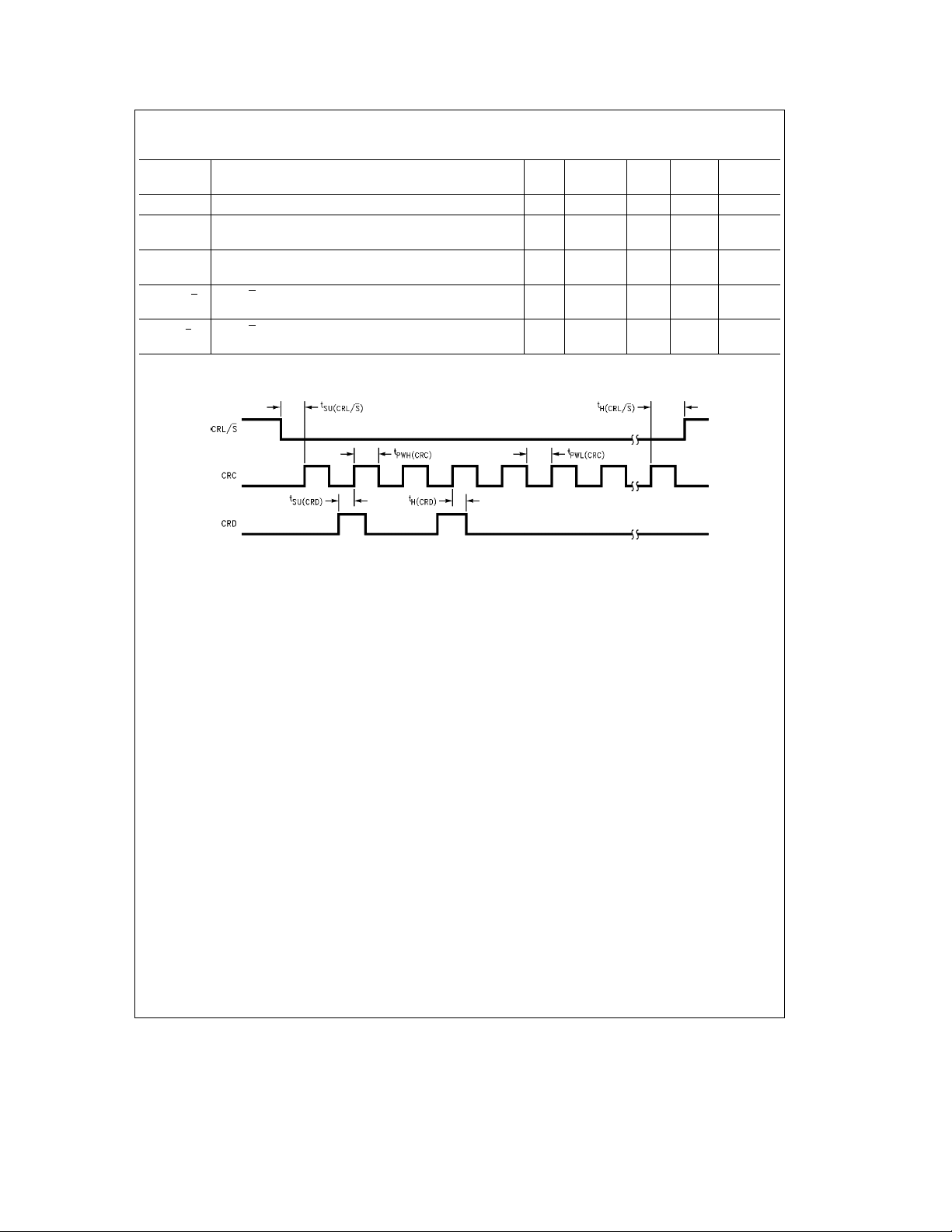
Control Register Operating Conditions are guaranteed over operating conditions (see table) unless
otherwise specified.
Symbol Parameter Min
t
PW(CRC)
t
SU(CRD)
t
H(CRD)
t
SU(CRL/S)
t
H(CRL/S)
Note 1: Typical values are specified at 25§C and 5V supply.
Note A: This parameter is guaranteed by outgoing testing.
CRC Pulse Width (positive or negative) (see
Figures 4
CRD Setup Time with respect to CRC (positive edge)
(see
Figures 4
and8)
CRD Hold Time with respect to CRC (positive edge)
(see
Figures 4
and8)
CRL/S Setup Time with respect to CRC (positive edge)
(see
Figures 4
and8)
CRL/S Hold Time with respect to CRC (positive edge)
(see
Figures 4
and8)
and9) 14 ns (Note A)
Typ
(Note 1)
Max Units Test
5 ns (Note A)
5 ns (Note A)
5 ns (Note A)
5 ns (Note A)
FIGURE 4. Control Register Timing Diagram
TL/F/11963– 4
5
 Loading...
Loading...