NSC 5962-9571101QXA, 5962-9571101QEA, 5962-9571001QEA, 5962-9570901QXA, 5962-9570901QEA Datasheet

LM2990
Negative Low Dropout Regulator
General Description
The LM2990 is a three-terminal, low dropout, 1 ampere
negative voltage regulator available with fixed output voltages of −5, −5.2, −12, and −15V.
The LM2990 uses new circuit design techniques to provide
low dropout and low quiescent current. The dropout voltage
at 1A load current is typically 0.6V and a guaranteed
worst-case maximum of 1V over the entire operating temperature range. The quiescent current is typically 1 mA with
1A load current and an input-output voltage differential
greater than 3V. A unique circuit design of the internal bias
supply limits the quiescent current to only 9 mA (typical)
when the regulator is in the dropoutmode(V
OUT−VIN
≤ 3V).
Output voltage accuracy is guaranteed to
±
5%over load,
and temperature extremes.
The LM2990 is short-circuit proof, and thermal shutdown in-
cludes hysteresis to enhance the reliability of the device
when overloaded for an extended period of time. The
LM2990 is availableina3-leadTO-220 package and is rated
for operation over the automotive temperature range of
−40˚C to +125˚C.
Features
n 5%output accuracy over entire operating range
n Output current in excess of 1A
n Dropout voltage typically 0.6V at 1A load
n Low quiescent current
n Internal short circuit current limit
n Internal thermal shutdown with hysteresis
n Functional complement to the LM2940 series
Applications
n Post switcher regulator
n Local, on-card, regulation
n Battery operated equipment
Typical Application
Ordering Information and Connection Diagrams
Temperature
Range
Output Voltage Package
-5.0 -5.2 -12 -15
−40˚C to
+125˚C
LM2990T-5.0 LM2990T-5.2 LM2990T-12 LM2990T-15 TO-220
LM2990S-5.0 LM2990S-12 LM2990S-15 TO-263
−55˚C to
+125˚C
LM2990J-5.0-QML
5962-9571101QEA
LM2990J-12-QML
5962-9571001QEA
LM2990J-15-QML
5962-9570901QEA
J16A
LM2990WG5.0-QML
5962-9571101QXA
WG16A
DS010801-1
*Required if the regulator is located further than 6 inches from the power supply filter capacitors. A 1 µF solid tantalum or a 10 µF aluminum electrolytic
capacitor is recommended.
*
*
Required for stability. Must be at least a 10 µF aluminum electrolytic ora1µFsolid tantalum to maintain stability. May be increased without bound to
maintain regulation during transients. Locate the capacitor as close as possible to the regulator. The equivalent series resistance (ESR) is critical, and
should be less than 10Ω over the same operating temperature range as the regulator.
June 1999
LM2990 Negative Low Dropout Regulator
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation DS010801 www.national.com
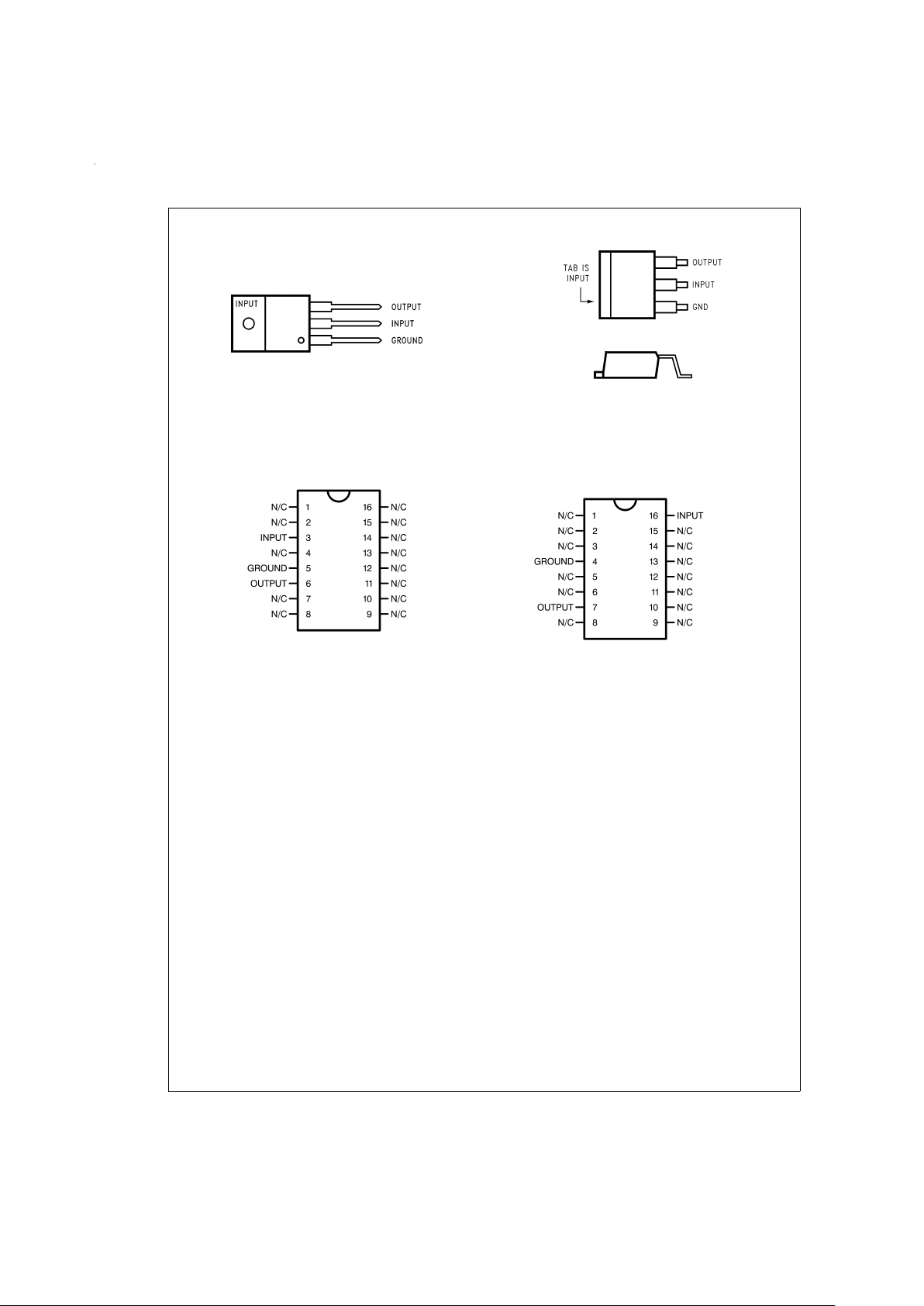
Ordering Information and
Connection Diagrams
(Continued)
3-Lead TO-220
DS010801-2
Front View
Order Number LM2990T-5.0, LM2990T-5.2, LM2990T-12
or LM2990T-15
See NS Package Number T03B
TO-263 Surface-Mount Package
DS010801-11
Top View
DS010801-12
Side View
Order Number LM2990S-5.0, LM2990S-12 or
LM2990S-15
See NS Package Number TS3B
16-Lead Ceramic Dual-in-Line Package
DS010801-33
Top View
Order Number
LM2990J-5.0-QML (5962-9571101QEA),
LM2990J-12-QML (5962-9571001QEA), or
LM2990J-15-QML (5962-9570901QEA),
See NS Package Number J16A
16-Lead Ceramic Surface Mount Package
DS010801-34
Top View
Order Number
LM2990WG5.0-QML (5962-9571101QXEA)
See NS Package Number WG16A
www.national.com 2

Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Input Voltage −26V to +0.3V
ESD Susceptibility (Note 2) 2 kV
Power Dissipation (Note 3) Internally Limited
Junction Temperature (T
Jmax
) 125˚C
Storage Temperature −65˚C to +150˚C
Lead Temperature
(Soldering, 10 sec.) 260˚C
Operating Ratings(Note 1)
Junction Temperature Range (T
J
) −40˚C to +125˚C
Maximum Input Voltage (Operational) −26V
Electrical Characteristics
V
IN
=
−5V+V
O(NOM)
(Note 6) , I
O
=
1A, C
O
=
47 µF, unless otherwise specified. Boldface limits apply over the entire operat-
ing temperature range, −40˚C ≤ T
J
≤ 125˚C, all other limits apply for T
J
=
25˚C.
LM2990-5.0 LM2990-5.2 Units
(Limit)
Parameter Conditions Typ Limit Typ Limit
(Note 4) (Note 5) (Note 4) (Note 5)
Output Voltage (V
O
)5mA≤I
O
≤1A
−5
−4.90
−5.2
−5.10 V (max)
−5.10 −5.30 mV (min)
V
5mA≤I
O
≤1A −4.75 −4.94 V (max)
−5.25 −5.46 V (min)
Line Regulation I
O
=
5 mA, 4 40 4 40 mV (max)
V
O(NOM)
−1V>V
IN
>
−26V
Load Regulation 50 mA ≤ I
O
≤ 1A 1 40 1 40 mV (max)
Dropout Voltage I
O
=
0.1A, ∆V
O
≤ 100 mV 0.1 0.3 0.1 0.3 V (max)
I
O
=
1A, ∆V
O
≤ 100 mV 0.6 1 0.6 1 V (max)
Quiescent Current (I
q
)IO≤1A 1515mA(max)
I
O
=
1A, V
IN
=
V
O(NOM)
9 50 9 50 mA (max)
Short Circuit Current R
L
=
1Ω (Note 7) 1.8 1.5 1.8 1.5 A (min)
Maximum Output Current (Note 7) 1.8 1.5 1.8 1.5 A (min)
Ripple Rejection V
ripple
=
1V
rms
, 58 50 58 50 dB (min)
ƒ
ripple
=
1 kHz, I
O
=
5mA
Output Noise Voltage 10 Hz–100 kHz, I
O
=
5 mA 250 750 250 750 µV (max)
Long Term Stability 1000 Hours 2000 2000 ppm
Electrical Characteristics
V
IN
=
−5V+V
O(NOM)
(Note 6) , I
O
=
1A, C
O
=
47 µF, unless otherwise specified. Boldface limits apply over the entire operat-
ing temperature range, −40˚C ≤ T
J
≤ 125˚C, all other limits apply for T
J
=
25˚C.
LM2990-12 LM2990-15 Units
(Limit)
Parameter Conditions Typ Limit Typ Limit
(Note 4) (Note 5) (Note 4) (Note 5)
Output Voltage (V
O
)5mA≤I
O
≤1A
−12
−11.76
−15
−14.70 V (max)
−12.24 −15.30 V (min)
V
5mA≤I
O
≤1A −11.40 −14.25 V (max)
−12.60 −15.75 V (min)
Line Regulation I
O
=
5 mA, 6 60 6 60 mV (max)
V
O(NOM)
−1V>V
IN
>
−26V
Load Regulation 50 mA ≤ I
O
≤ 1A 3 50 3 50 mV (max)
Dropout Voltage I
O
=
0.1A, ∆V
O
≤ 100 mV 0.1 0.3 0.1 0.3 V (max)
I
O
=
1A, ∆V
O
≤ 100 mV 0.6 1 0.6 1 V (max)
Quiescent Current (I
q
)IO≤1A 1515mA(max)
I
O
=
1A, V
IN
=
V
O(NOM)
9 50 9 50 mA (max)
www.national.com3

Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
V
IN
=
−5V+V
O(NOM)
(Note 6) , I
O
=
1A, C
O
=
47 µF, unless otherwise specified. Boldface limits apply over the entire operat-
ing temperature range, −40˚C ≤ T
J
≤ 125˚C, all other limits apply for T
J
=
25˚C.
LM2990-12 LM2990-15 Units
(Limit)
Parameter Conditions Typ Limit Typ Limit
(Note 4) (Note 5) (Note 4) (Note 5)
Short Circuit Current R
L
=
1Ω (Note 7) 1.2 0.9 1.0 0.75 A (min)
Maximum Output Current (Note 7) 1.8 1.4 1.8 1.4 A (min)
Ripple Rejection V
ripple
=
1V
rms
, 52 42 52 42 dB (min)
ƒ
ripple
=
1 kHz, I
O
=
5mA
Output Noise Voltage 10 Hz–100 kHz, I
O
=
5 mA 500 1500 600 1800 µV (max)
Long Term Stability 1000 Hours 2000 2000 ppm
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is intended to be functional, but do not guarantee specific performance limits. For guaranteed specifications and test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics.
Note 2: Human body model, 100 pF discharged through a 1.5 kΩ resistor.
Note 3: The maximum power dissipation is a function of T
Jmax
, θJA, and TA. The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient temperature is P
D
=
(T
Jmax
−TA)/θJA. If this dissipation is exceeded, the die temperature will rise above 125˚C, and the LM2990 will eventually go into thermal shutdown at a TJof approximately
160˚C. For the LM2990, the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance, is 53˚C/W, 73˚C/W for the TO-263, and the junction-to-case thermal resistance is 3˚C. If the
TO-263 package is used, the thermal resistance can be reduced by increasing the P.C. board copper area thermally connected to the package. Using 0.5 square
inches of copper area, θ
JA
is 50˚C/W; with 1 square inch of copper area, θJAis 37˚C/W; and with 1.6 or more square inches of copper area, θJAis 32˚C/W.
Note 4: Typicals are at T
J
=
25˚C and represent the most likely parametric norm.
Note 5: Limits are guaranteed and 100%production tested.
Note 6: V
O(NOM)
is the nominal (typical) regulator output voltage, −5V, −5.2V, −12V or −15V.
Note 7: The short circuit current is less than the maximum output current with the −12V and −15V versions due to internal foldback current limiting. The −5V and
−5.2V versions, tested with a lower input voltage, does not reach the foldback current limit and therefore conducts a higher short circuit current level. If the LM2990
output is pulled above ground, the maximum allowed current sunk back into the LM2990 is 1.5A.
Definition of Terms
Dropout Voltage: The input-output voltage differential at
which the circuit ceases to regulate against further reduction
in input voltage. Measured when the output voltage has
dropped 100 mV from the nominal value obtained at (V
O
+
5V) input, dropout voltage is dependent upon load current
and junction temperature.
Input Voltage:The DC voltage applied to the input terminals
with respect to ground.
Input-Output Differential: The voltage difference between
the unregulated input voltage and the regulated output voltage for which the regulator will operate.
Line Regulation: The change in output voltage for a change
in the input voltage. The measurement is made under conditions of low dissipation or by using pulse techniques such
that the average chip temperature is not significantly affected.
Load Regulation: The change in output voltage for a
change in load current at constant chip temperature.
Long Term Stability: Output voltage stability under accellerated life-test conditions after 1000 hours with maximum
rated voltage and junction temperature.
Output Noise Voltage: The rms AC voltage at the output,
with constant load and no input ripple, measured over a
specified frequency range.
Quiescent Current: That part of the positive input current
that does not contribute to the positive load current. The
regulator ground lead current.
Ripple Rejection: The ratio of the peak-to-peak input ripple
voltage to the peak-to-peak output ripple voltage.
Temperature Stability of V
O
: The percentage change in
output voltage for a thermal variation from room temperature
to either temperature extreme.
www.national.com 4
 Loading...
Loading...