Nokia 5160, NSW-1 Service Manual

PAMS Technical Documentation
NSC/W–1/3 Series Transceivers
Disassembly &
Troubleshooting
Instructions
Original 11/99

NSC/W–1/3
PAMS
Disassembly & Troubleshooting Instructions
CONTENTS
Disassembly 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Introduction 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Abbreviations in RF–fault finding charts 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Interface signals between RF and BB/DSP 6. . . . . . . . . . . .
Trouble Shooting 10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Phone is totally dead 10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
The phone doesn’t register to the network 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Flash programming doesn’t work 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power doesn’t stay on, or phone is jammed 14. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Display Information: Contact Service 16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Audio failure 17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Charging failure 19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiver Fault AMPS 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Instructions 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Path of the received signal 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiver Fault AMPS 21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiver Fault TDMA800 23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiver Fault TDMA1900 (only for dualbander) 25. . . . . . .
Transmitter Fault – General 27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Path of the transmitted signal 27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmitter Fault AMPS 28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmitter Fault TDMA800 30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmitter Fault TDMA1900 31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Control Loop 33. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Synthesizers 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
19.44 MHz reference oscillator 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
58.32 MHz 3–multiplier 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
19.44 MHz oscillator and 3–multiplier troubleshooting 35. .
VHF VCO 36. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
VHF VCO troubleshooting 37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
AMPS & TDMA UHF SYNTHESIZER 38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1GHz UHFsynthesizer troubleshooting 38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TDMA1900 UHF Synthesizer 2 GHz (DUALBANDER) 39. .
2 GHz UHF synthesizer troubleshooting 39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
About RF ASICs and MMIC PA 40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General information 40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PLUSSA ASIC 40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiver front ends 42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MMIC Power Amplifiers 42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PENTA regulator 43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TDMA1900 UPCONVERTER 44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TDMA1900 PLL 44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Technical Documentation
Page No
Page 2
Original 11/99
PAMS
NSC/W–1/3
Technical Documentation
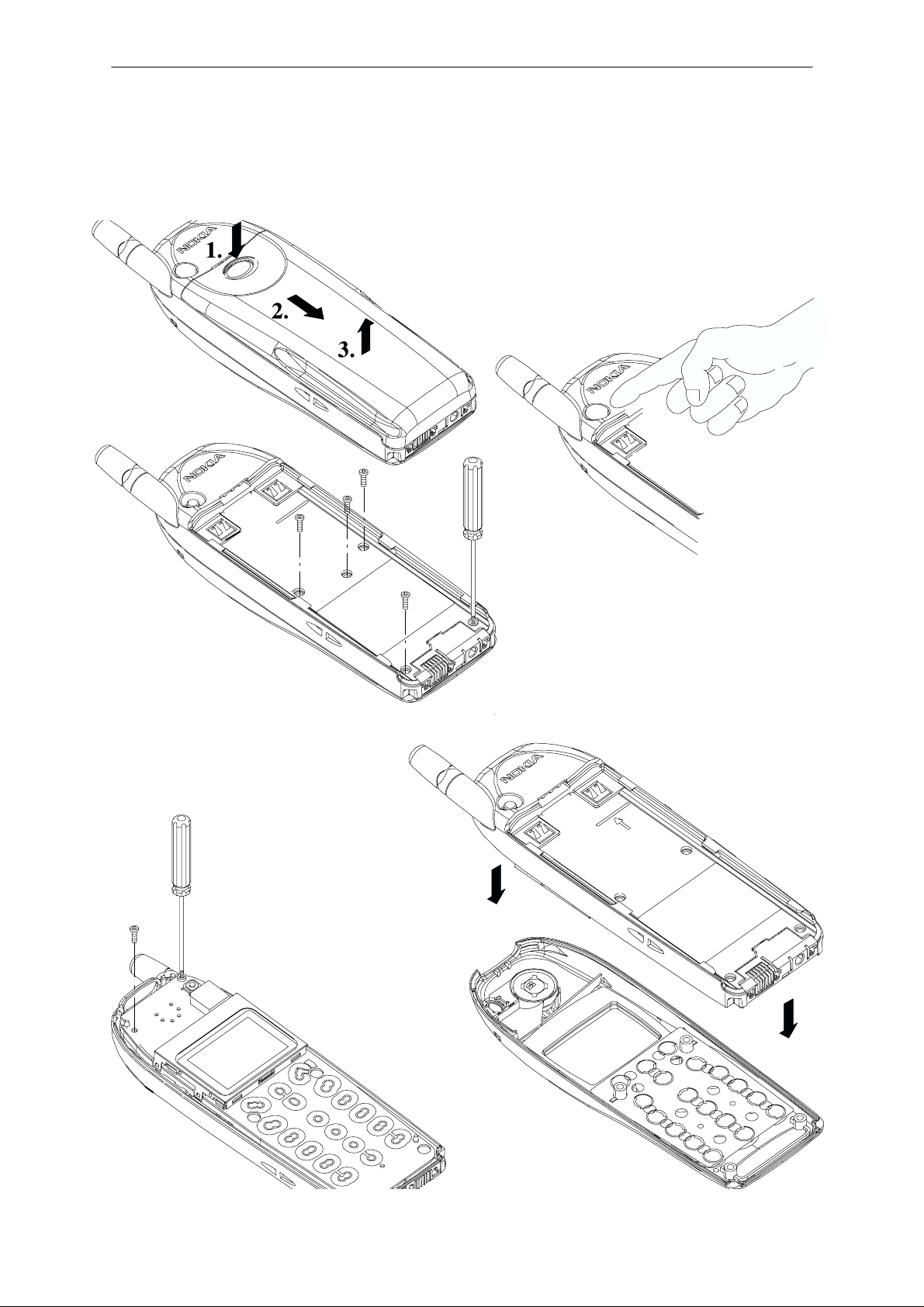
Disassembly
NOTE: Do not attempt antenna removal white the covers are on. The antenna can be removed only when the phone covers are off
Disassembly & Troubleshooting Instructions
Remove battery
Remove dust cap by finger nail
Remove back cover
screws (4pcs phase1,
5 pcs phase 2).
NOTE!
When assembling the
B cover screws, use
17 Ncm torque.
Turn around.
Remove UI module
screws (2 pcs)
Carefully remove A–cov-
er, keymat, powerkeymat
and speaker will follow.
Note snap fixings !
Original 11/99
Page 3
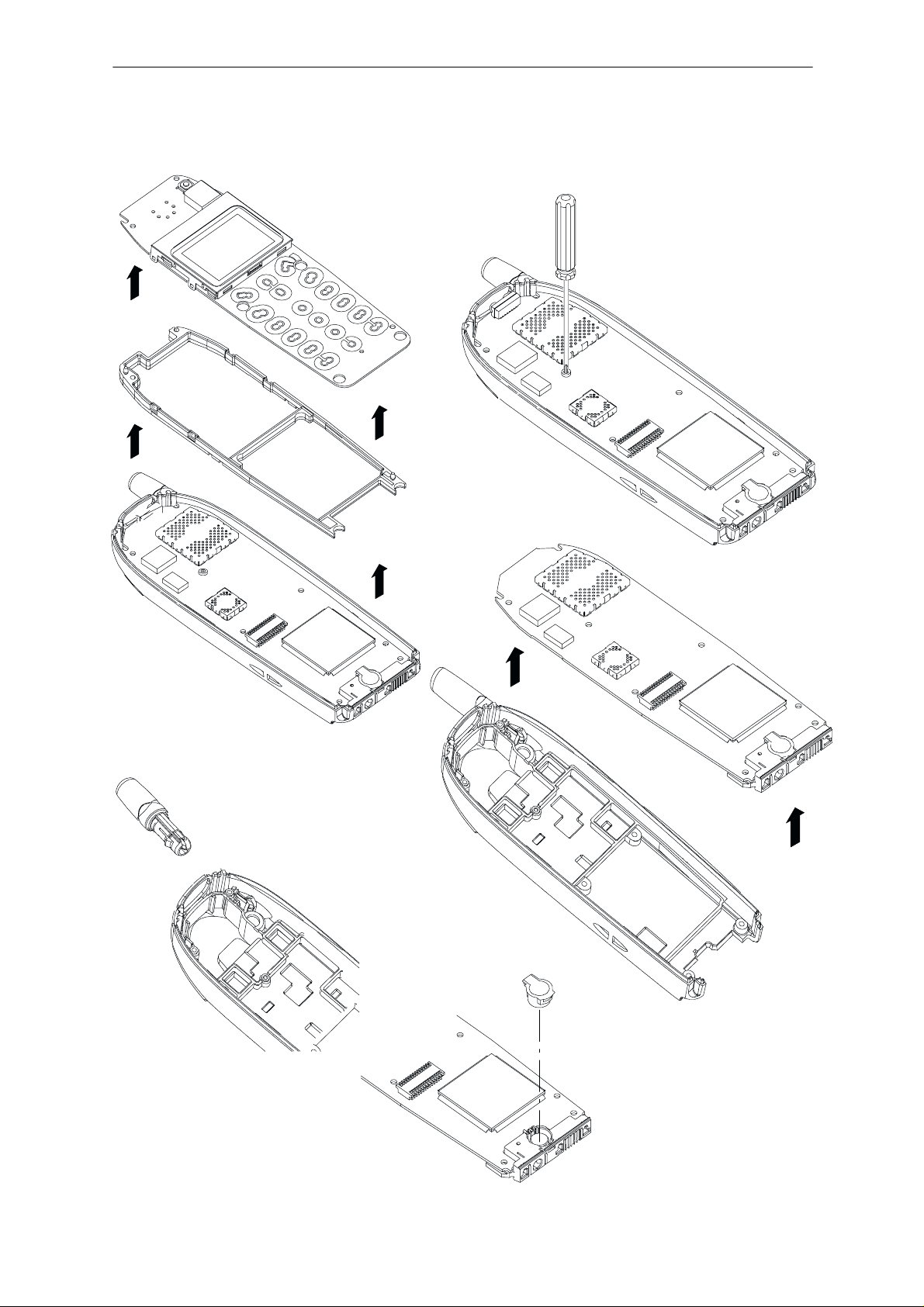
NSC/W–1/3
PAMS
Disassembly & Troubleshooting Instructions
Remove UI–module
and frame
Technical Documentation
Remove engine module
screw (1 pc). Phase 1
version does not have
the screw, phase 2 has.
To remove antenna :
push in snap at antenna
base with screwdriver tip
while pushing antenna
out of B cover.
Remove engine
module
Page 4
Remove
microphone
Original 11/99

PAMS
NSC/W–1/3
Technical Documentation
Introduction
RF–measurements must be done using a spectrum analyzer and an high–
frequency probe. (Local and reference frequencies and RF power levels in
the intermediate stages of the chain) Oscilloscope is used to measure DC–
voltages and low frequency signals. Multimeter is also a useful measurement equipment in fault finding.
The external RF connector must be used when reasonable to improve the
reliability of the measurement results.
The RF–section is mainly built around the PLUSSA IC (N750). The RF block
has separate external filters, UHF synthesizer , Power Amplifier , TX Driver,
frontend and upconverter circuit for both frequency bands. In the
TDMA1900 mode the external regulator is used to provide supply voltage for
RF parts.
Before changing single ASICs or components, please check the following :
1. The soldering and connections of pins of the ASICS are OK
2. Supply voltages and control signals are OK
3.Signals of the synthesizers are coming to ASICS. This to prevent the unnecessary changing of the ASICS.
Disassembly & Troubleshooting Instructions
NOTE! Grounding of the P A–IC is directly underneath so it is hard to check.
The P A–module is static discharge sensitive! So ESD protection must be
used when dealing with P A–IC (ground straps and ESD soldering tools). The
P A is also a moisture sensitive components and it is important to follow additional information about handling the component.
There are still lots of discrete components (resistors, inductors and capacitors) troubleshooting of which comprises just checking that the component
is soldered or it is not missing from PCB.
Abbreviations in RF–fault finding charts
TP Test Point
BB Baseband
f: Frequency of signal (measured with spectrum analyzer)
LO Local Oscillator
P: Power of signal in desibels (dB)
(measured with spectrum analyzer)
PA Power Amplifier
PCB Printed Circuit Board
PLL Phase Locked Loop
RF Radio Frequency
RX Receiver
T: Time between pulses
TX Transmitter
UHF Ultra High Frequency
V: Voltage of signal (measured with oscilloscope)
VCO Voltage controlled oscillator
VHF Very High Frequency
AF: Audio Frequency
Original 11/99
Page 5
NSC/W–1/3
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
PAMS
Disassembly & Troubleshooting Instructions
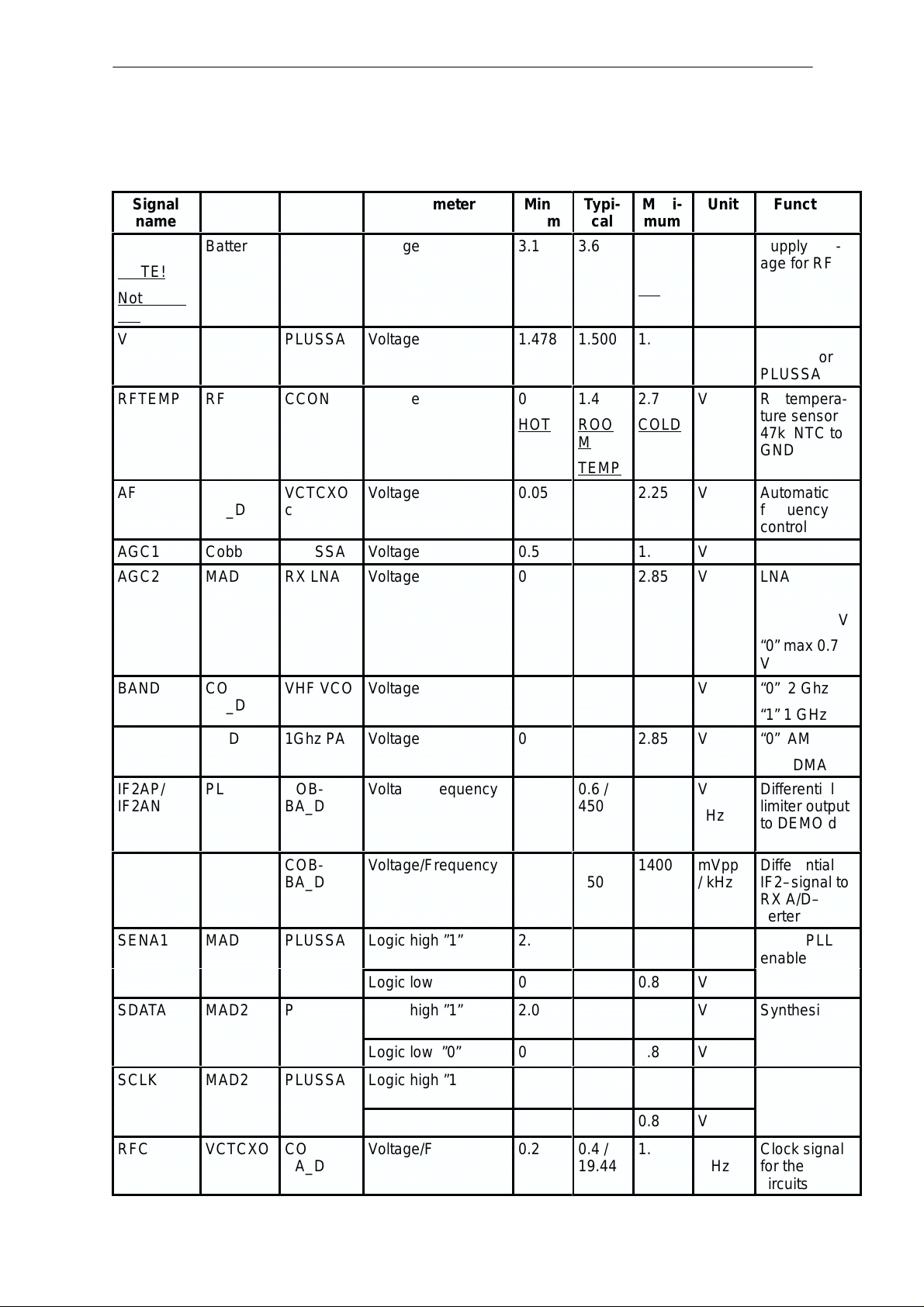
Interface signals between RF and BB/DSP
Signal
name
VBAT
ÁÁÁ
NOTE!
ÁÁÁ
Not char-
ÁÁÁ
ger
VREF
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
RFTEMP
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
AFC
ÁÁÁ
AGC1
AGC2
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
BAND
ÁÁÁ
MODE
ÁÁÁ
IF2AP/
ÁÁÁ
IF2AN
ÁÁÁ
IF2DP /
ÁÁÁ
IF2DN
ÁÁÁ
SENA1
ÁÁÁ
From
Battery
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
CCONT
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
RF
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
COBBA_D
ÁÁ
Cobba_D
MAD
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
COBBA_D
ÁÁ
MAD
ÁÁ
PLUSSA
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
PLUSSA
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
MAD
ÁÁ
To
RF
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
PLUSSA
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
CCONT
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
VCTCXO
c
ÁÁÁ
PLUSSA
RX LNA
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
VHF VCO
ÁÁÁ
1Ghz P A
ÁÁÁ
COB-
ÁÁÁ
BA_D
ÁÁÁ
COB-
ÁÁÁ
BA_D
ÁÁÁ
PLUSSA
ÁÁÁ
Parameter
Voltage
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
Voltage
БББББ
БББББ
Voltage
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
Voltage
БББББ
Voltage
Voltage
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
Voltage
БББББ
Voltage
БББББ
Voltage/Frequency
БББББ
БББББ
Voltage/Frequency
БББББ
БББББ
Logic high ”1”
БББББ
Logic low ”0”
Minimum
3.1
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
1.478
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0
ÁÁ
HOT
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0.05
ÁÁ
0.5
0
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0
ÁÁ
0
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.0
ÁÁ
0
Technical Documentation
Typi-
cal
3.6
1.500
1.4
ROO
M
TEMP
1.1
0.6 /
450
170 /
450
Maxi-
mum
5.3
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
5.0
ÁÁ
1.523
Á
Á
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.7
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁ
COLD
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.25
Á
ÁÁ
1.4
2.85
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.85
ÁÁÁÁ
2.85
ÁÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
1400
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0.8
Unit
V
Á
Á
Á
V
Á
Á
V
Á
Á
Á
V
Á
V
V
Á
Á
Á
Á
V
Á
V
Á
Vpp /
Á
kHz
Á
mVpp
Á
/ kHz
Á
V
Á
V
Function
Supply volt-
ÁÁÁÁ
age for RF
ÁÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁÁ
Reference
ÁÁÁÁ
voltage for
PLUSSA
ÁÁÁÁ
RF temperature sensor
ÁÁÁÁ
47k NTC to
ÁÁÁÁ
GND
ÁÁÁÁ
Automatic
frequency
ÁÁÁÁ
control
LNA Gain
ÁÁÁÁ
switch
ÁÁÁÁ
“1” min 2.0 V
ÁÁÁÁ
“0” max 0.7
ÁÁÁÁ
V
“0” 2 Ghz
ÁÁÁÁ
“1” 1 GHz
“0” AMPS
ÁÁÁÁ
“1” TDMA
Differential
ÁÁÁÁ
limiter output
to DEMO de-
ÁÁÁÁ
tector
Differential
ÁÁÁÁ
IF2–signal to
RX A/D–con-
ÁÁÁÁ
verter
1 Ghz PLL
ÁÁÁÁ
enable
SDATA
ÁÁÁ
SCLK
ÁÁÁ
RFC
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Page 6
MAD2
ÁÁ
MAD2
ÁÁ
VCTCXO
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
PLUSSA
ÁÁÁ
PLUSSA
ÁÁÁ
COB-
ÁÁÁ
BA_D
ÁÁÁ
Logic high ”1”
БББББ
Logic low ”0”
Logic high ”1”
БББББ
Logic low ”0”
Voltage/Frequency
БББББ
БББББ
2.0
ÁÁ
0
2.0
ÁÁ
0
0.2
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁÁÁ
0.8
ÁÁÁÁ
0.8
0.4 /
19.44
1.0
Á
Á
V
V
V
V
Vpp /
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
MHz
Original 11/99
Á
Á
Á
Á
Synthesizer
ÁÁÁÁ
data
Synthesizer
ÁÁÁÁ
clock
Clock signal
ÁÁÁÁ
for the logic
circuits
ÁÁÁÁ
PAMS
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
NSC/W–1/3
Technical Documentation
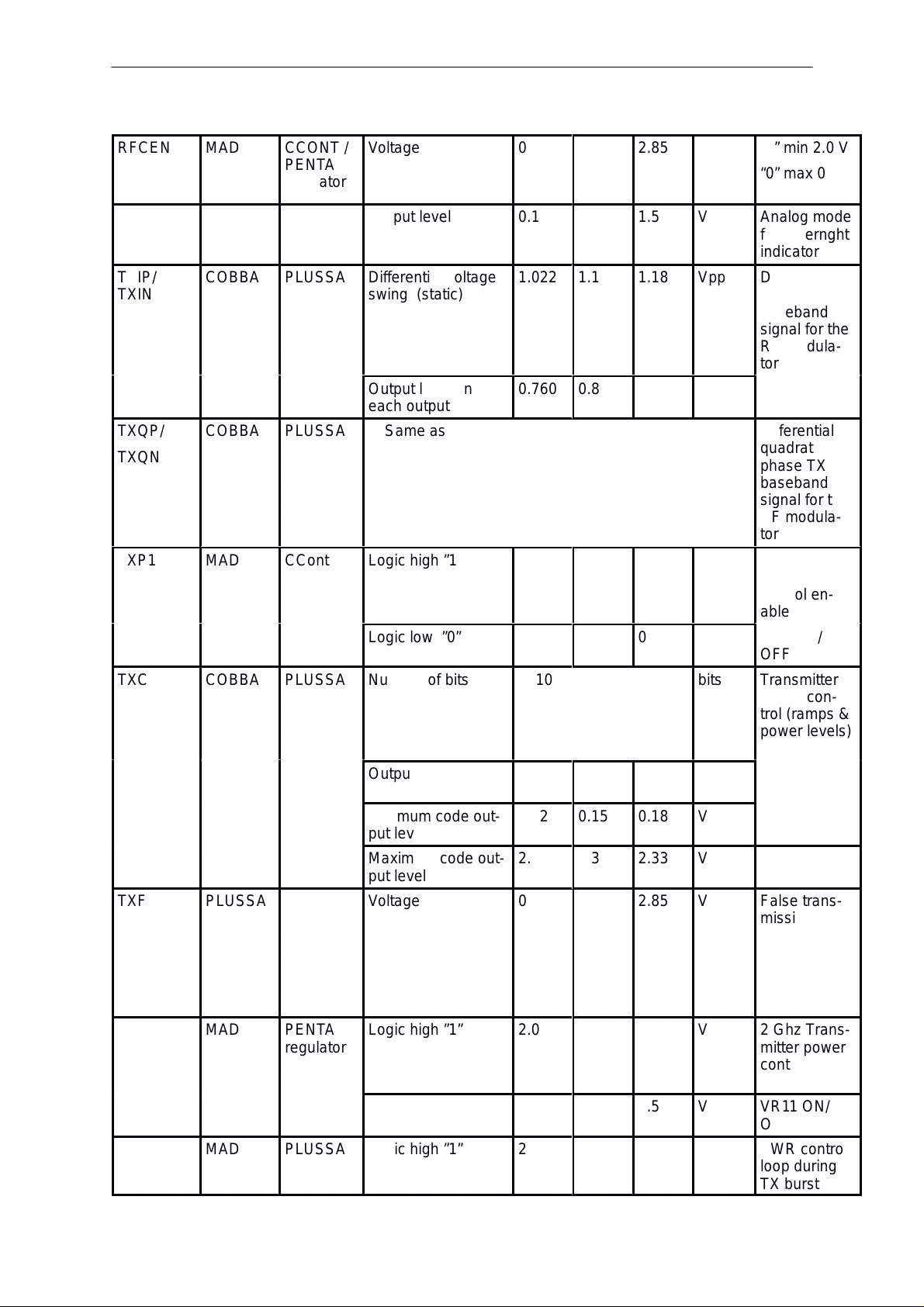
RFCEN
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
RSSI
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
TXIP/
TXIN
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁБББББ
TXQP/
ÁÁÁ
TXQN
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
TXP1
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
MAD
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
PLUSSA
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
COBBA
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
COBBA
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
MAD
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
CCONT /
ÁÁÁ
PENTA
regulator
ÁÁÁ
CCONT
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
PLUSSA
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
PLUSSA
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
CCont
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Voltage
БББББ
БББББ
Output level
БББББ
БББББ
Differential voltage
swing (static)
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
Output level on
each output
Same as TXIP/
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
Logic high ”1”
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
Disassembly & Troubleshooting Instructions
TXIN
Logic low ”0”
TXC
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
COBBA
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
PLUSSA
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Number of bits
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
0
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0.1
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
1.022
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0.760
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.0
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
10
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
1.1
0.8
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
2.85
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
1.5
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
1.18
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0.84
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0.5
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
V
V
Vpp
V
V
V
bits
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
“1” min 2.0 V
ÁÁÁÁ
“0” max 0.4
ÁÁÁÁ
V
Analog mode
ÁÁÁÁ
field sternght
indicator
ÁÁÁÁ
Differential
in–phase TX
ÁÁÁÁ
baseband
ÁÁÁÁ
signal for the
RF modula-
ÁÁÁÁ
tor
ÁÁÁÁ
Differential
ÁÁÁÁ
quadrature
phase TX
ÁÁÁÁ
baseband
ÁÁÁÁ
signal for the
RF modula-
ÁÁÁÁ
tor
1 Ghz Trans-
ÁÁÁÁ
mitter power
ÁÁÁÁ
control enable
ÁÁÁÁ
VR7 ON/
OFF
Transmitter
ÁÁÁÁ
power con-
ÁÁÁÁ
trol (ramps &
power levels)
ÁÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁБББББ
Output voltage
swing
Minimum code out-
ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁБББББ
put level
Maximum code out-
ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁБББББ
TXF
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
TXP2
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁБББББ
TXA
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Original 11/99
PLUSSA
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
MAD
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
MAD
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
MAD
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
PENTA
ÁÁÁ
regulator
ÁÁÁ
PLUSSA
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
put level
Voltage
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
Logic high ”1”
БББББ
БББББ
Logic low ”0”
Logic high ”1”
БББББ
БББББ
2.09
ÁÁ
0.12
ÁÁ
2.27
ÁÁ
0
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.0
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.5
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.15
0.15
2.3
Á
Á
Á
2.21
0.18
2.33
2.85
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
0.5
ÁÁÁÁ
Á
Á
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
V
Á
ÁÁÁÁ
V
Á
ÁÁÁÁ
V
Á
V
Á
Á
Á
Á
V
Á
Á
ÁÁÁÁ
False transmission indi-
ÁÁÁÁ
cator, func-
ÁÁÁÁ
tion controlled via
ÁÁÁÁ
PLUSSA
ÁÁÁÁ
register
2 Ghz Trans-
ÁÁÁÁ
mitter power
control en-
ÁÁÁÁ
able
V
V
Á
Á
Á
VR11 ON/
ÁÁÁÁ
OFF
PWR control
ÁÁÁÁ
loop during
TX burst
ÁÁÁÁ
Page 7
NSC/W–1/3
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
PAMS
Disassembly & Troubleshooting Instructions
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
TXLX1
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
TXLX2
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
SENA2
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
MAD
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
MAD
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
MAD
ÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
RF
ÁÁÁ
TDMA
ÁÁÁ
800
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
RF TDMA
1900
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
2 Ghz
ÁÁÁ
UHF PLL
Logic low ”0”
БББББ
БББББ
Logic high ”1”
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
Logic low ”0”
БББББ
БББББ
Logic high ”1”
БББББ
БББББ
Logic low ”0”
БББББ
БББББ
Logic high ”1”
БББББ
Logic low ”0”
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.1
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.1
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.0
ÁÁ
0
Technical Documentation
0.2
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0.6
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0.6
Á
Á
ÁÁÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0.8
V
Á
Á
PWR control
ÁÁÁÁ
loop during
ramp up/
ÁÁÁÁ
down
V
V
V
V
V
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Low power
ÁÁÁÁ
level mode
ÁÁÁÁ
for power detector
ÁÁÁÁ
High power
level mode
ÁÁÁÁ
for power
ÁÁÁÁ
detector
Low power
level mode
ÁÁÁÁ
for power de-
ÁÁÁÁ
tector
High power
ÁÁÁÁ
detector
mode power
ÁÁÁÁ
detector
2 Ghz PLL
ÁÁÁÁ
enable
V
RXPWR1
ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁБББББ
RXPWR2
ÁÁÁ
MAD
MAD
ÁÁ
CCONT
PENTA
ÁÁÁ
Logic high ”1”
Logic low ”0”
Logic high ”1”
БББББ
Logic low ”0”
RXPWR3
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
MAD
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
PENTA
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Logic high ”1”
БББББ
БББББ
Logic low ”0”
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
SPWR1
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
COB-
ÁÁ
BA_D
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
CCONT
ÁÁÁ
БББББ
БББББ
Logic high ”1”
БББББ
Logic low ”0”
SPWR2
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
COB-
ÁÁ
BA_D
ÁÁ
CCONT
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Logic high ”1”
БББББ
БББББ
Logic low ”0”
SPWR3
ÁÁÁ
COBBA_D
ÁÁ
PENTA
ÁÁÁ
Logic high ”1”
БББББ
Logic low ”0”
2.0
0
ÁÁ
2.0
ÁÁ
0
2.0
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.0
ÁÁ
0
2.0
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0
2.0
ÁÁ
0
0.8
ÁÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁÁ
0.8
Á
Á
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0.8
Á
Á
ÁÁÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0.5
Á
Á
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0.5
ÁÁÁÁ
0.5
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
VR4 ON
VR4 OFF
ÁÁÁÁ
VR8 ON,
1Ghz fron-
ÁÁÁÁ
tend
VR8 OFF
VR9 ON
ÁÁÁÁ
2Ghz fron-
ÁÁÁÁ
tend
VR9 OFF
ÁÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁÁ
VR2 ON ,
ÁÁÁÁ
1Ghz UHF
VR2 OFF
VR3 ON,
ÁÁÁÁ
VHF ON/
OFF
ÁÁÁÁ
VR3 OFF
VR10 ON ,
2Ghz UHF
ÁÁÁÁ
VR10 OFF
TXPWR1
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁБББББ
Page 8
MAD
ÁÁ
CCont
ÁÁÁ
Logic high ”1”
БББББ
Logic low ”0”
2.0
ÁÁ
0
ÁÁ
ÁÁÁÁ
0.5
ÁÁÁÁ
V
Á
VR5 ON , TX
pwr control
ÁÁÁÁ
enable
V
Á
VR5 OFF
ÁÁÁÁ
Original 11/99
PAMS
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁÁ
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
NSC/W–1/3
Technical Documentation
TXWR2
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
TXWR3
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
VR1
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
VR2
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
VR3
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
VR4
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
VR5
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
VR6
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
VR7
ÁÁÁ
V5V
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
MAD
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
MAD
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
CCont
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
CCont
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
CCont
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
CCont
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
CCont
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
CCont
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
CCont
ÁÁ
CCont
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
PENTA
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
TDMA800
ÁÁÁ
TX–mixer
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
RF
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
RF
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
RF
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
RF
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
RF
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
RF
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
RF
ÁÁÁ
PLUSSA
ÁÁÁ
ÁÁÁ
Disassembly & Troubleshooting Instructions
Logic high ”1”
БББББ
БББББ
Logic low ”0”
Logic high ”1”
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
Logic low ”0”
Voltage
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
Voltage
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
Voltage
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
Voltage
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
Voltage
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
Voltage
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
БББББ
Voltage
БББББ
Voltage
БББББ
БББББ
2.0
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0
2.0
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0
2.7
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.7
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.7
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.7
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
3.1
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.7
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.7
ÁÁ
4.8
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.8
2.8
2.8
2.8
3.6
2.8
2.8
5.0
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0.5
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
0.5
2.85
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.85
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.85
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.85
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
5.3
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.85
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
2.85
ÁÁ
5.2
ÁÁ
ÁÁ
V
Á
Á
VR12 ON ,
ÁÁÁÁ
TDMA1900
TX–mixer
ÁÁÁÁ
enable
V
V
V
Á
Á
Á
VR12 OFF
AMPS &
ÁÁÁÁ
TDMA800
ÁÁÁÁ
TX–mixer
enable
ÁÁÁÁ
TX–mixer
disable
V
V
V
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Supply for
ÁÁÁÁ
VCTCXO,
ÁÁÁÁ
Plussa VHF
prescaler
ÁÁÁÁ
and bias, 2
ÁÁÁÁ
Ghz PLL and
ÁÁÁÁ
3x
Supply volt-
age for
ÁÁÁÁ
1GHZ UHF
ÁÁÁÁ
VCO and
prescaler
ÁÁÁÁ
Supply voltage for VHF
ÁÁÁÁ
VCO, LO
ÁÁÁÁ
buffer, 1 Ghz
TX–mixer
ÁÁÁÁ
and TXF
V
V
V
V
V
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Á
Supply volt-
ÁÁÁÁ
age for
ÁÁÁÁ
PLUSSA IF–
parts and IF–
ÁÁÁÁ
amplifier
Supply volt-
ÁÁÁÁ
age for
modulator,
ÁÁÁÁ
TX pwr con-
ÁÁÁÁ
trol
Supply volt-
ÁÁÁÁ
age for
PLUSSA dig-
ÁÁÁÁ
ital parts and
ÁÁÁÁ
Cobba_D
ÁÁÁÁ
analog supply
ÁÁÁÁ
TX PA bias
and driver
ÁÁÁÁ
supply
Plussa and 2
ÁÁÁÁ
Ghz PLL
chargepump
ÁÁÁÁ
Original 11/99
Page 9

NSC/W–1/3
PAMS
Disassembly & Troubleshooting Instructions
Trouble Shooting
The following hints should facility finding the cause of the problem when the
circuitry seems to be faulty . This trouble shooting instruction is divided in following section.
1. Phone is totally dead
2. Flash programming doesn‘t work
3. Power doesn‘t stay on or the phone is jammed
4. Display information: Contact Service
5. Phone doesn‘t register to the network or phone doesn‘t make a call.
6. Audio fault.
7. Charging fault
The first thing to do is carry out a through visual check of the module. Ensure
in particular that:
a) there are not any mechanical damages
b) soldered joints are OK
Technical Documentation
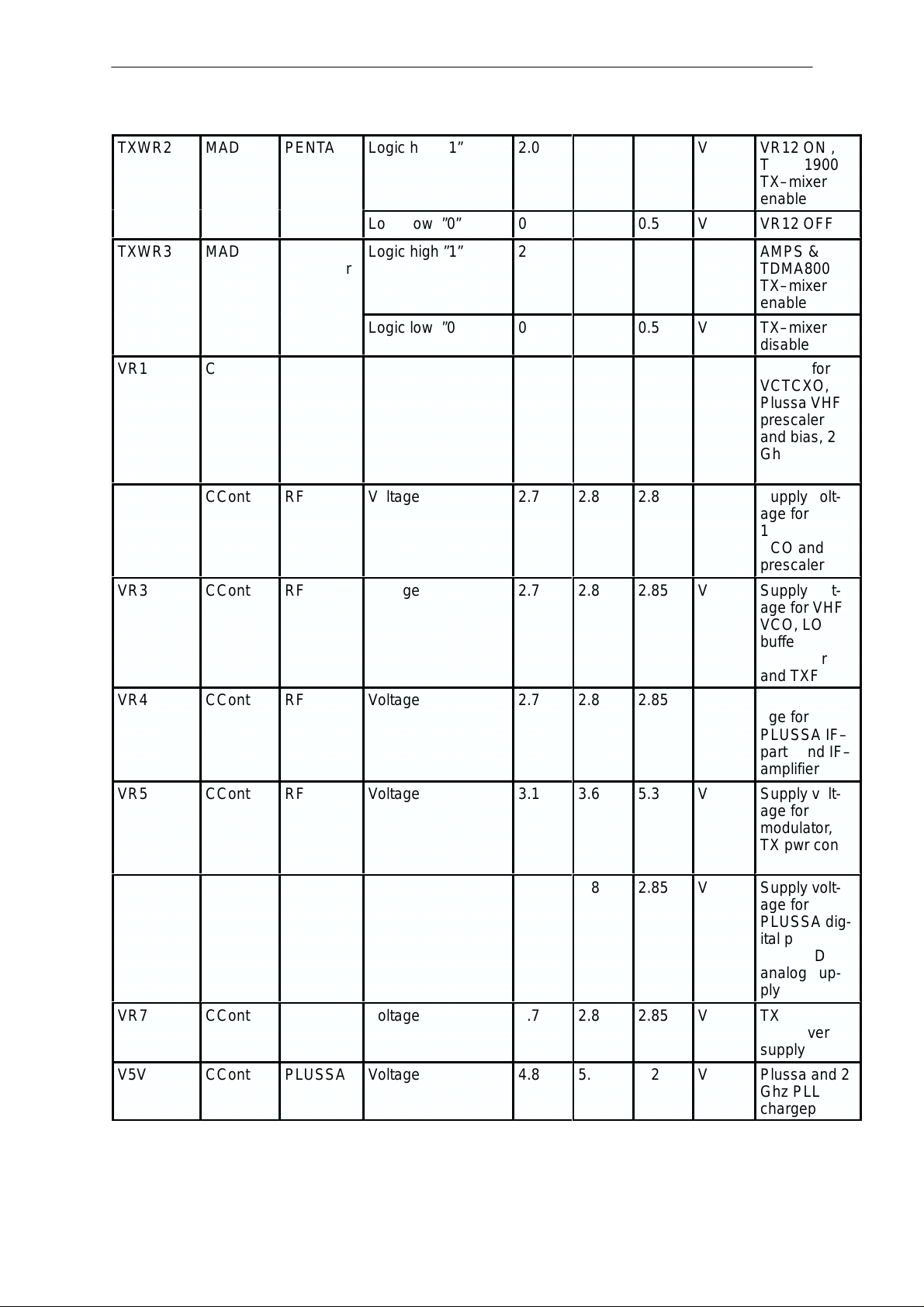
Phone is totally dead
This means that phone doesn’t take current at all when the power switch is
pressed or when the watchdog disable pin (X101 pin 11) is grounded.
Used battery voltage must be higher than 3.0 V. Otherwise the hardware of
CCONT (N150) prevents totally from switching.
Page 10
Original 11/99
PAMS
NSC/W–1/3
Technical Documentation
Disassembly & Troubleshooting Instructions
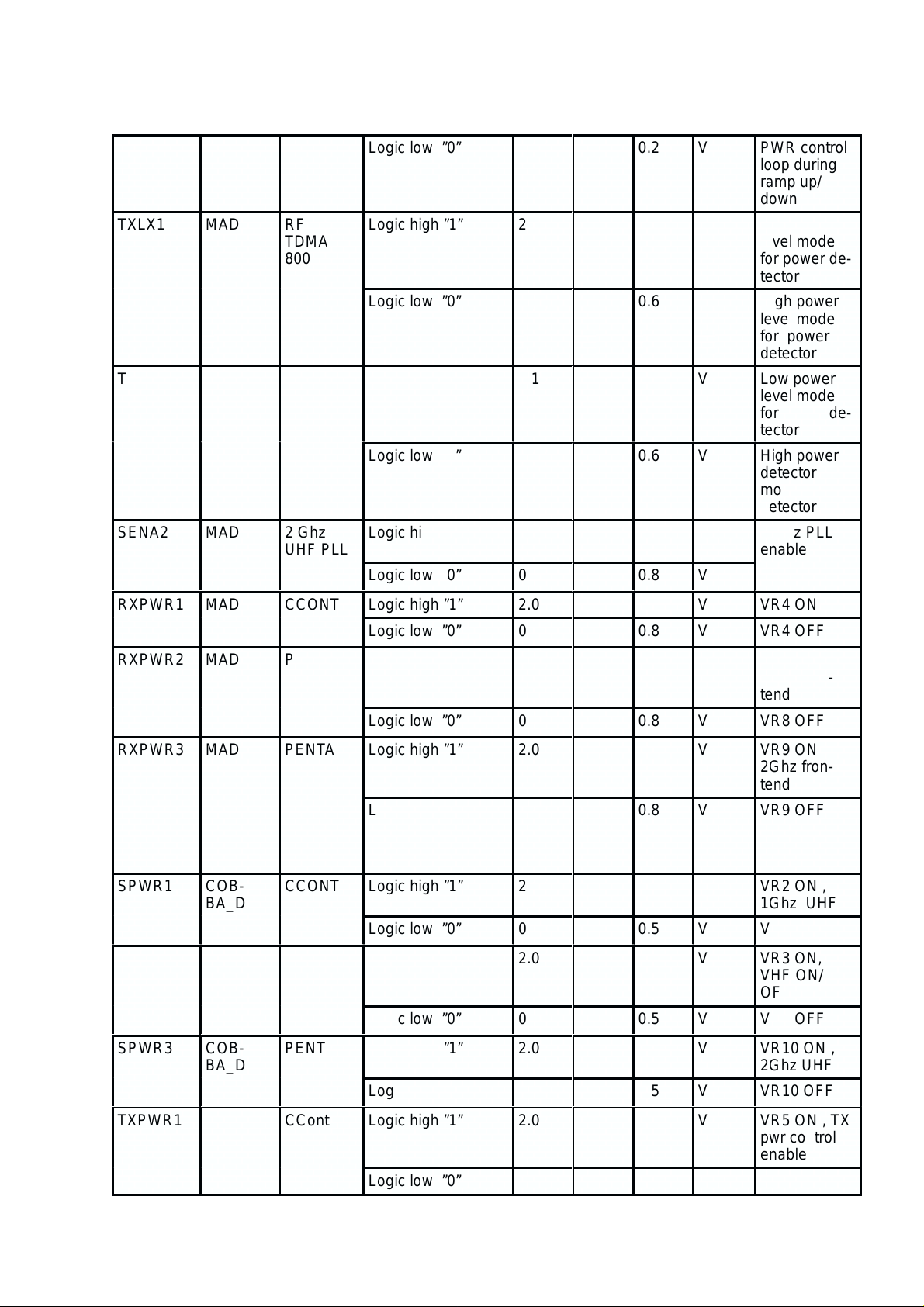
The phone doesn’t register to the network or phone doesn’t make a call
Phone doesn’t register to the network
phone doesn’t make a call
Analog supply voltage VCOBBA is >2.7 V
at pin 7,12 ... of Cobba (N250)
Analog reference voltage Vref is 1.5 V
at pin 9 of Cobba (N250)
RX AMPS: VR1, VR2, VR4/VR8, VR6, V5V
RX DAMPS: VR1, VR2, VR4/8, VR6, V5V
RX TDMA: VR1, VR6, V5V, VR9, VR10, VR12
TX AMPS: VR3, VR5, VR7, TXPWR3
TX DAMPS: VR3, VR5, VR7, VR7_bias, TXPWR3
TX TDMA: VR11
Note; Each VR is to be checked only once!
or
YES
YES
YES
Check
NO
N250
NO Check
R256
NO
MAD D202
CCONT N150
PENTA N702
YES
Synthesizer lines: SEna2 (N880 pin 13 ),
SClk (N880 pin 11)
SData (N880 pin 12)
pulses 0 –> 1 during off burst
YES
NO
MAD
D202
AGC1 (N250 pin 14) 0 ––>2.3 V max during receiving burst
AFC (N250 pin 13) 0 – 1.2 V typ. during receiving burst
YES
Analog data signal IF2AN (N250 pin 8) –> 0.6 Vpp, 0–>2.2 V DC
Analog data signal IF2AP (N250 pin 7) –> 0.6 Vpp, 0–>2.2 V DC
Digital data signal IF2DN (N250 pin 10) –>170 mVpp typ,
0–> 2.7 V DC
Digital data signal IF2DP (N250 pin9) –>170 mVpp typ, 0–>2.7 V DC
Frequency is 450 MHz
YES
DAX signal (N250 pin 62) pulses 1 –> 0 during receiving slot
YES
TX control lines: TxC (N750 pin 11) 0 –> 2.3 Vmax during transmit burst
TXA (N750 pin 2) goes 0–>1 (2.8 V) during modulation
TXLX1 (D202 pin 96) and TXLX2 (D202 pin 98) 0–> 1 (2.8 V)
TXLX are low during PL7 to PL2 and high during PL10 to PL 8
YES
NO
NO
COBBA
N250
NO
Check
N250 if DC is failed
Check
RF part if benefit signal is failed
Check
N250
Check
NO
N250 if TxC is failed
Check
D202 if TXA is failed
Analog data signals: TxIN (N250 pin 21) 0–> 0.8 V DC during transmit slot
Used IQ signals are biased to 0.8V DC and AC amplitude is 400 mVpp
Original 11/99
TxIP (N250 pin 20) 0 –>0.8 V DC during transmit slot
TxQN (N250 pin 19) 0 –>0.8 V DC during transmit slot
TxQP (N250 pin 18) 0 –>0.8 V DC during transmit slot
max, frequency is 12 kHz max
NO
Check
N250
YES Check
RF part
Page 11
NSC/W–1/3
PAMS
Disassembly & Troubleshooting Instructions
Phone is totally dead
YES
Tp5
VBAT is 3.6 V
YES
Voltage at pin 29 of CCONT (N150)
is 3.6 V
YES
N 150 pin 55 (VBB) 2.8 V(=TP14)
N150 pin 25 (VXO) 2.8 V/TP10)
when PWR switch is pressed
or watchdog disable pin is grounded
YES
See section: Power Doesn’t Stay On
NO Failure in VBAT line
Check X105, X104, Z100
NO
Faulty circuit N150
CCONT (N150) pin 29 0V when
NO
PWR switch is pressed or
watchdog disable pin is (X101)
grounded
Faulty circuit N150
YES
Technical Documentation
Check R164, X102
NO
Check UI module
Check watchdog disable line to
X101
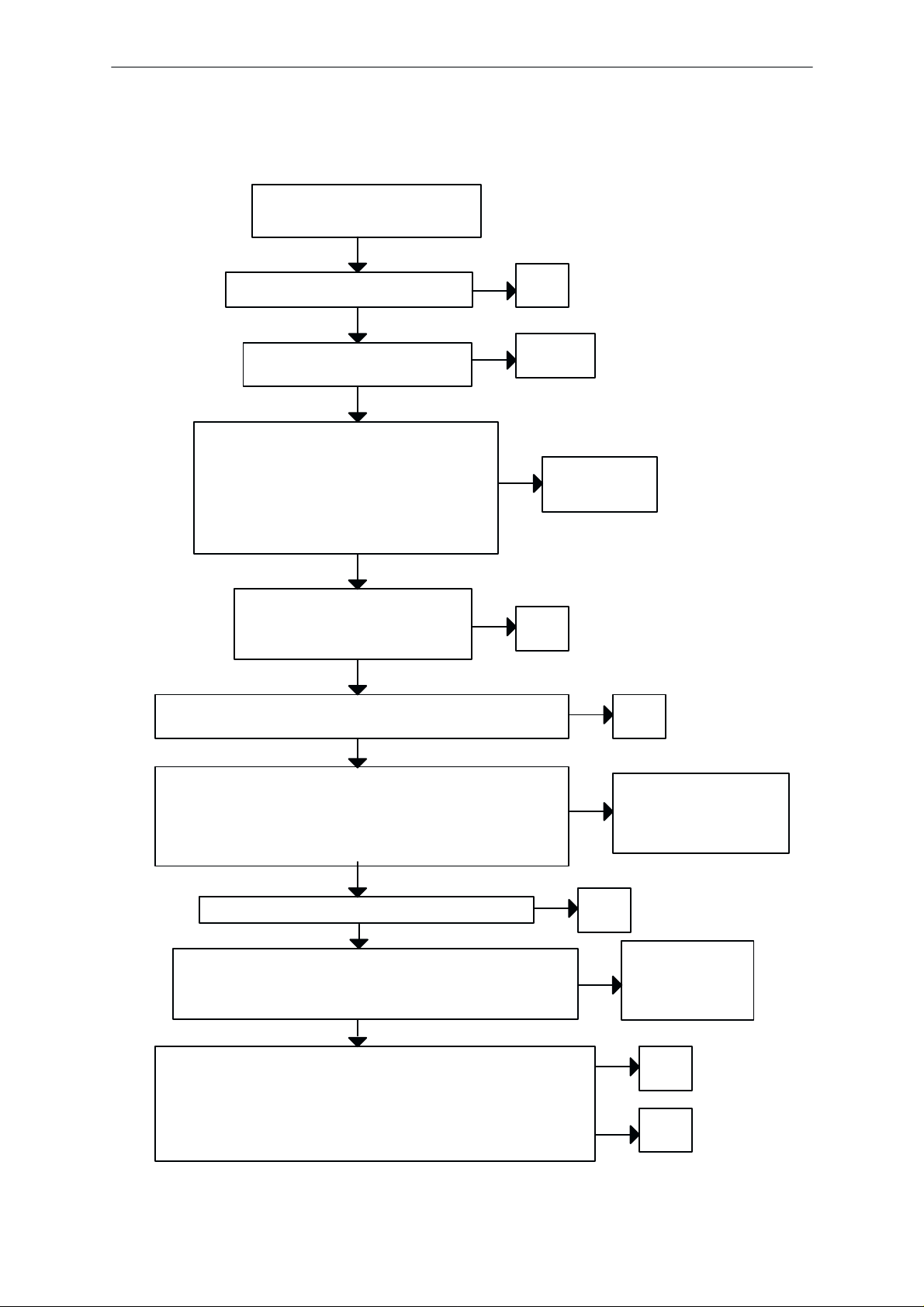
Flash programming doesn’t work
The flash programming can be done via panel connector X101 or via system
connector X100.
The main differences between these are:
a) FLASH programming voltage is produced different way.
b) Signal routings are different.
In flash programming error cases the flash prommer can give some information about a fault.
The fault information messages could be:
– MCU doesn’t boot
– Serial clock line failure
– Serial data line failure
– External RAM fault
– Algorithm file or alias ID doesn’t find
– MCU flash Vpp error
In cases that the flash programming doesn’t succeed there is a possibility to
check short circuits between the memories and the MCU (MAD1).
This test is useful to do, when the fault information is: MCU doesn’t boot, Serial clock line failure or Serial data line failure.
Page 12
Original 11/99
PAMS
NSC/W–1/3
Technical Documentation
Disassembly & Troubleshooting Instructions
Flash progrmming doesn’t work
YES
If the fault information from the prommer is:
External RAM fault
YES
Check pins of SRAM (D200)
Check control lines of SRAM:
RAMSelX ...
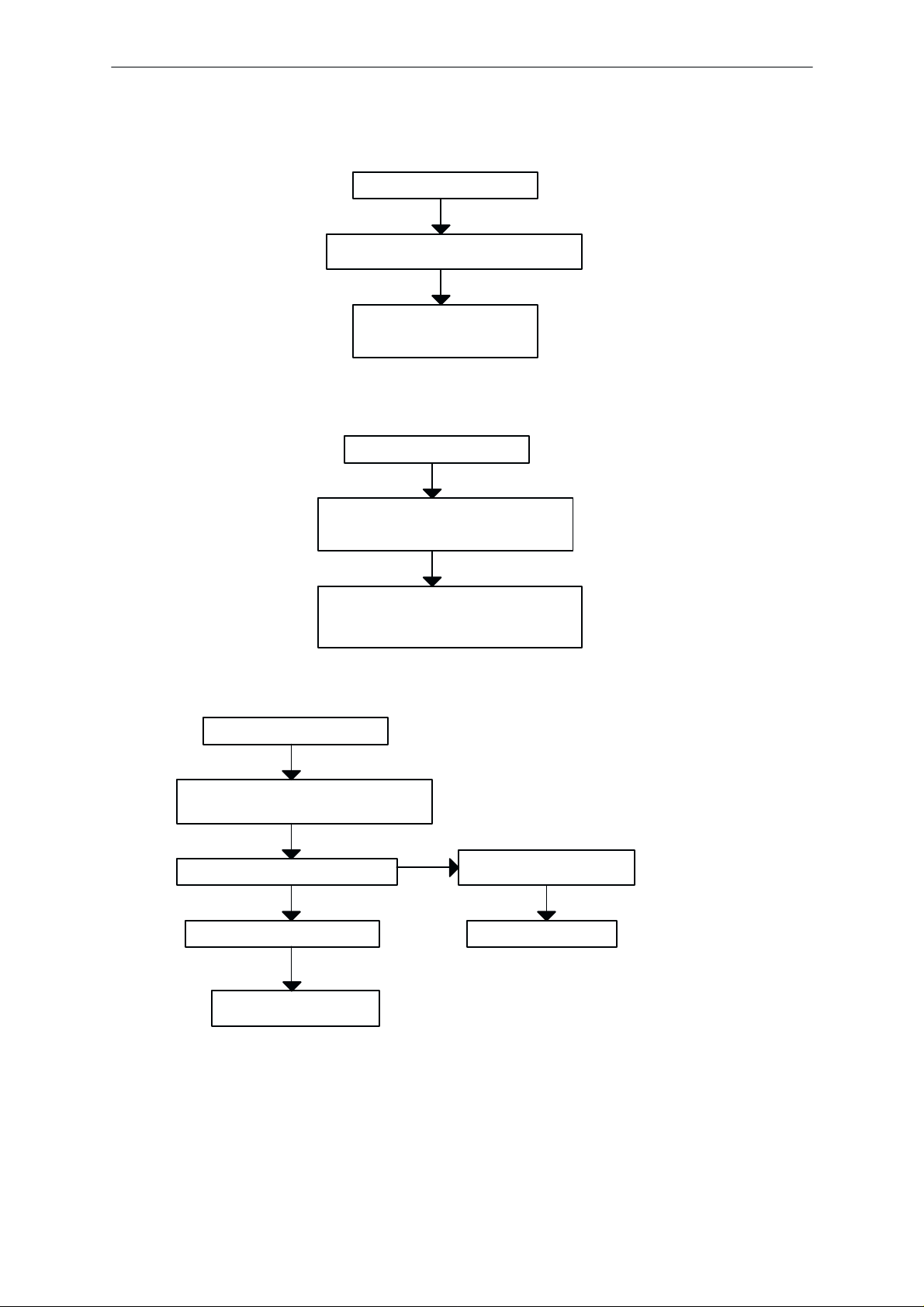
Flash progrmming doesn’t work
YES
If the fault information from the prommer is:
Algorithm file or alias ID doesn’t find, ID is
unknown etc.
YES
Check pins of FLASH (D201)
Check control lines and upper data lines (15:8)
of FLASH: ROM1SelX...
Flash progrmming doesn’t work
YES
If the fault information from the prommer is:
MCU flash Vpp error
YES
Vpp > 2.8 V in D201 pin 13)
YES
Check pins of FLASH D201
OK
Faulty component D201
NO
Vpp > 2.8 V in pin 13 of D201
YES
Check UI connector X102
Original 11/99
Page 13

NSC/W–1/3
PAMS
Disassembly & Troubleshooting Instructions
Technical Documentation
Power doesn’t stay on, or phone is jammed
If this kind of fault has come after flash programming, there are most probably open pins in ICs.
The soldered joints of ICs: D202 (MAD1), D201 (FLASH), N150 (CCONT),
D200 (SRAM) are useful to check first.
Normally the power will be switched of by CCONT (N150) after 30 seconds,
if the watchdog of the CCONT can not be served by software.
The watchdog updating can be seen by oscilloscope at pin 50 (DataselX) of
CCONT.
In a normal case there is a short pulse from ”1” –> 0 every 8 seconds.
The power off function of CCONT can be prevented by connecting a short
circuit wire from CCONT pin 29 to ground.
Page 14
Original 11/99
 Loading...
Loading...