Page 1

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Reference Manual
January, 2015
202-11224-05
350 East Plumeria Drive
San Jose, CA 95134
USA
Page 2

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Support
Thank you for selecting NETGEAR products.
After installing your device, locate the serial number on the label of your product and use it to register your product at
https://my.netgear.com. You must register your product before you can use NETGEAR telephone support. NETGEAR
recommends registering your product through the NETGEAR website.
For product updates and web support, visit http://support.netgear.com.
Phone (US & Canada only): 1-888-NETGEAR.
Phone (Other Countries): Check the list of phone numbers at http://support.netgear.com/general/contact/default.aspx.
Compliance
For regulatory compliance information, visit http://www.netgear.com/about/regulatory.
See the regulatory compliance document before connecting the power supply.
Trademarks
© NETGEAR, Inc. NETGEAR and the NETGEAR Logo are trademarks of NETGEAR, Inc. Any non-NETGEAR trademarks are
used for reference purposes only.
Revision History
Publication Part
Number
202-11224-05 January 2015 Corrected the number of access points in the trial license (see Licenses) and
202-11224-04 January 2015 Added the following features:
Publish Date Comments
added a note about port 8443 (see page 45).
• Support for additional access points (see Supported NETGEAR Access
Points)
• Support for antennas (see Supported NETGEAR Antennas)
• RF planning, including support for heat maps (see Chapter 3, RF Planning
and Deployment)
• Controller redundancy
Manage Stacking and Redundancy)
• Support for the “Rest of the world” transmission power feature (see
Configure the General Settings)
• Capability to change the building and floor assignments for multiple access
points simultaneously (see Assign Access Points to Buildings, Floors, and
Advanced Profile Groups).
• Band steering (see Configure Radio Frequency Management for the Basic
Profile Group and Configure Radio Frequency Management for an
Advanced Profile Group)
• High-density bandwidth (see Configure Wireless Settings for the Basic
Profile Group and Configure Wireless Settings for an Advanced Profile
Group)
• Management of LED behavior for WN370 access points (see Manage the
WN370 LED Behavior for the Basic Profile Group and Manage the WN370
LED Behavior for an Advanced Profile Group)
• Capability to print a logo and message on captive portal user information
(see Add a Logo and Message on Captive Portal User Information)
• Capability to add multiple captive portal users simultaneously (see Add
Multiple Captive Portal Users Simultaneously)
, including 1:1 and N:1 redundancy (see Chapter 1
1,
2
Page 3

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
202-11224-04
(continued)
202-11224-03 January 2014 Added the following features:
202-11224-02 May 2013 Color correction and minor nontechnical edits.
202-11224-01 April 2013 First publication.
January 2015
(continued)
Added the following features:
(continued)
• Capability to locate and monitor an active WiFi client on a deployed floor
plan (see View the Clients in the Network, View Clients on Access Points
that the Wireless Controller Manages, and Monitor Local Clients in the
Network)
• Support for extended storage (see Manage External Storage)
• Support for additional access points (see Supported NETGEAR Access
Points)
• Link aggregation (see Manage the IP, VLAN, and Link Aggregation
Settings)
• Multicast rate limiting, broadcast rate limiting, and
Configure W
Wireless Settings for an Advanced Profile Group)
• Preferred band selection (see Manage the Preferred Bands)
• Stacking (see Chapter 11, Manage Stacking and Redundancy)
• Monitoring for a network with a stack of wireless controllers (see Monitor
the Network)
In addition, revised and refined many procedures.
ireless Settings for the Basic Profile Group and Configure
ARP suppression (see
3
Page 4

Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction
Chapter 2 System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
Key Features and Capabilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Package Contents. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Hardware Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Front Panel Ports, Slots, and LEDs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Back Panel Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Bottom Panel with Product Label . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
WC9500 Wireless Controller System Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Supported NETGEAR Access Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Supported NETGEAR Antennas. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
What Can You Do with the WC9500 Wireless Controller? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Licenses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
M
aintenance and Support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Basic and Advanced Setting Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Profile Group Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Basic Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Advanced Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
System Planning Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Preinstallation Planning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Before You Configure a Wireless Controller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
High-Level Configuration Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Single Controller Configuration with Basic Profile Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Single Controller Configuration with Advanced Profile Groups . . . . . . . . . . .32
Stacked Controller Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Management VLAN and Data VLAN Strategies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
High-Level Deployment Scenarios . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Scenario Example 1: Network with Single VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Scenario Example 2: Advanced Network with VLANs and SSIDs . . . . . . . . . .38
Scenario Example 3: Advanced Network with Redundancy . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Chapter 3 RF Planning and Deployment
RF Planning Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Planning Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Recommended RF Planning Procedure for a Building . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Manage a Building and Floors for an RF Plan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Add a Building and Floors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
4
Page 5

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Add a Single Floor to a Building. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Scale a Floor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Add a WiFi Coverage or WiFi Noncoverage Zone to a Floor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Remove a WiFi Coverage or WiFi Noncoverage Zone from a Floor. . . . . . . . 55
Add a WiFi Building Obstacle to a Floor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Remove a Building Obstacle from a Floor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Add a WiFi Obstruction Area. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Remove a WiFi Obstruction Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Change the Name, Map, or Dimensions of a Floor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Change the Name of a Building. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Duplicate an Entire Building with All Floors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Duplicate a Single Floor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Remove a Single Floor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Remove an Entire Building with All Its Floors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Use the WiFi Auto Planning Advisor to Generate an RF Plan for a Floor . . . . . . 64
Manually Add and Manage Access Points on a Floor Map for an RF Plan . . . . . 69
Manually Add and Manage Antennas on a Floor Map for an RF Plan. . . . . . . . . 72
Display and Recalculate the WiFi Coverage for a Heat Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Display or Change the WiFi Inventory for an RF Plan. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Download a Report for an RF Plan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
View the Heat Map for a Deployed Floor Plan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Chapter 4 Installation and Configuration Overview
Connect Your Computer to the Wireless Controller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Log In to the Wireless Controller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Roadmap for Initial Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Roadmap for Configuring Management of Your Wireless Network. . . . . . . . . . 88
Choose a Location for the Wireless Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Deploy the Wireless Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Chapter 5 Configure the System and Network Settings and
Register the Licenses
Configure the General Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Manage the Time Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Manage the IP, VLAN, and Link Aggregation Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Management VLAN Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Untagged VLAN Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Link Aggregation Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Configure the IP, VLAN, and Link Aggregation Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Manage the DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Add a DHCP Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Change the Settings for a DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Remove a DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .102
Register Your Licenses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Configure the License Server Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Register Your Licenses with the License Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Manage Certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
5
Page 6

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Configure Log, Syslog, Alarm Notification, and Email Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Configure Log Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Configure Syslog Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Configure Alarm Notification Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Configure the Email Notification Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Chapter 6 Manage Security Profiles and Profile Groups
Wireless Security Profile Concepts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Small WLAN Networks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Large WLAN Networks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Profile Naming Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Considerations Before You Configure Profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Basic and Advanced Security Configuration Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Manage Security Profiles for the Basic Profile Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Configure a Profile in the Basic Profile Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Change the Settings for a Profile in the Basic Profile Group . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Remove a Profile From the Basic Profile Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Manage Security Profiles for Advanced Profile Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Add an Advanced Profile Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Remove an Advanced Profile Group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Configure a Profile in an Advanced Profile Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Change the Settings for a Profile in an Advanced Profile Group . . . . . . . . . 131
Remove a Profile From an Advanced Profile Group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Network Authentication and Data Encryption Options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Manage Authentication Servers and Authentication Server Groups. . . . . . . . 136
Authentication Server Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Configure Basic Authentication Server Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Configure a RADIUS Authentication Server Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Remove a RADIUS Authentication Server Group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Manage MAC Authentication and MAC Authentication Groups. . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Guidelines for External MAC Authentication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Configure Basic Local MAC Authentication Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Remove a MAC Address from a Wireless Client List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Import a MAC List from a File. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Configure a Local MAC Authentication Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
Remove a Local MAC Authentication Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Select an ACL for a Profile in the Basic Profile Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Select an ACL for a Profile in an Advanced Profile Group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Chapter 7 Discover and Manage Access Points
Access Point Discovery Guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
General Discovery Guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Layer 3 Discovery Guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Discover Access Points with the Discovery Wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Discover Access Points in Factory Default State and Access
Points in a Layer 2 Subnet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Discover Access Points Installed and Working in
6
Page 7

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Standalone Mode in Different Layer 3 Networks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Manage the Managed AP List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
View the Managed AP List. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Change Access Point Information on the Managed AP List . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Remove Access Points from the Managed AP List. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Assign Access Points to Buildings, Floors, and Advanced Profile Groups . . . . 169
Chapter 8 Configure Wireless and QoS Settings
Basic and Advanced Wireless and QoS Configuration Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Configure the Radio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Configure the Radio for the Basic Profile Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Configure the Radio for an Advanced Profile Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Configure Wireless Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Configure Wireless Settings for the Basic Profile Group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Override Channel and Transmission Power in the Basic Profile Group . . . . 180
Configure Wireless Settings for an Advanced Profile Group . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
Override Channel and Transmission Power in an Advanced
Profile Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
Configure Channels. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
Specify Radio Frequency Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Radio Frequency Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
WLAN Healing Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Configure Radio Frequency Management for the Basic Profile Group . . . . 192
Configure Radio Frequency Management for an Advanced
Profile Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Manage the Preferred Bands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 198
Configure the Preferred Band for WNDAP620 Access
Points in the Basic Profile Group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 198
Configure the Preferred Band for WNDAP620 Access
Points in an Advanced Profile Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
Manage Quality of Service for an Advanced Profile Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
Quality of Service Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
Configure Quality of Service for a Profile Group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
Manage Load Balancing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
Load Balancing Concepts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
Configure Load Balancing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
Manage Rate Limiting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
Rate Limiting Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
Configure Rate Limiting for the Basic Profile Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
Configure Rate Limiting for an Advanced Profile Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 208
Manage the LED Behavior of WN370 Access Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
Manage the WN370 LED Behavior for the Basic Profile Group. . . . . . . . . . 209
Manage the WN370 LED Behavior for an Advanced Profile Group . . . . . . 210
Chapter 9 Manage Rogue Access Points,
Guest Network Access, and Users
Manage Rogue Access Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 213
7
Page 8

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Rogue Access Point Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 213
Configure Basic Rogue Detection Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 213
Classify Rogue Access Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
Import a List of Known Access Points from a File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 216
Manage Guest Network Access. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
Portal Concepts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
Configure a Portal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
Manage Users, Accounts, and Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
User and Account Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
Add a Management User . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223
Add a WiFi User . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 224
Add a Captive Portal Account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 226
Add a Logo and Message on Captive Portal User Information. . . . . . . . . . . 228
Add a Captive Portal User . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
Add Multiple Captive Portal Users Simultaneously . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 232
Change the Settings for a User or Account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235
Remove Users or Accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 236
Export a List of Users or Accounts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 236
Chapter 10 Maintain the Wireless Controller and Access Points
Manage the Configuration File or Upgrade the Firmware. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
Back Up the Configuration File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
Restore the Configuration File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
Upgrade the Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 241
Reboot the Wireless Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 244
Reset the Wireless Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
Manage External Storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 246
Manage Remote Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 247
Specify Session Time-Outs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 249
Manage the System Logs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 250
Query the System Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 250
Save the System Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 252
Clear the System Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 253
View Alerts and Events. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 253
View System Alerts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 254
View Radio Frequency Events. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 255
View Load-Balancing Events. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256
View Rate-Limit Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 257
View Redundancy Events. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 259
View Stacking Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 260
Manage Licenses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 261
View Your Licenses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 261
Retrieve Your Licenses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 263
Reboot Access Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 264
Configure Multicast Firmware Upgrade for Access Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 265
Change the Multicast Firmware Upgrade Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 266
Disable Multicast Firmware Upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 267
8
Page 9

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Chapter 11 Manage Stacking and Redundancy
Stacking Concepts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 269
Configure a Stack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 271
Remove a Wireless Controller from a Stack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273
Select Which Wireless Controller in a Stack to Configure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 274
Manage Redundancy for a Single Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 278
VRRP Redundancy Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 278
Configure a Single Controller with Redundancy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 280
Manage a Redundancy Group with N:1 Redundancy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282
VRRP N:1 Redundancy Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282
Configure a Redundancy Group with N:1 Redundancy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .285
Change a Redundant Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 287
Remove a Redundancy Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 289
Chapter 12 Monitor the Wireless Network and Its Components
Monitor the Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 291
View the Network Summary Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 291
View the Wireless Controllers in the Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 293
View the Access Points in the Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .295
View the Clients in the Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300
View the Profiles in the Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 304
Monitor the Wireless Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 306
View the Wireless Controller Summary Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 306
View Wireless Controller Usage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 308
View Access Points that the Wireless Controller Manages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 310
View Clients on Access Points that the Wireless Controller Manages . . . . 315
View Neighboring Clients that the Wireless Controller Detects . . . . . . . . . 319
View Neighboring Access Points that the Wireless Controller
Does Not Manage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .321
View Security Profiles That the Wireless Controller Manages. . . . . . . . . . . 322
View DHCP Leases That Are Provided by the Wireless Controller . . . . . . . 324
View Captive Portal Users on Access Points That the
Wireless Controller Manages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 325
Monitor the SSIDs on the Wireless Controller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 327
Monitor Local Clients in the Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 332
Chapter 13 Troubleshooting
Troubleshoot Basic Functioning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 338
Power LED Is Not Lit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 338
Status LED Never Turns Off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 338
Ethernet Port LEDs Are Not Lit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 338
Troubleshoot the Web Management Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
Check the Ethernet Cabling. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
Check the IP Address Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
Check the Internet Browser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 340
Troubleshoot a TCP/IP Network Using the Ping Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 340
9
Page 10

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Use the Reset Button to Restore Default Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 341
Resolve Problems with Date and Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 341
Resolve Problems with Access Points. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 342
Resolve Discovery Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 342
Resolve Connection Problems. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 342
Network Performance and Rogue Access Point Detection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 343
Use the Diagnostic Tools on the Wireless Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 343
Ping an Access Point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 343
Trace a Route to an Access Point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 344
Appendix A Factory Default Settings, Technical Specifications,
and Passwords Requirements
Factory Default Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 347
Technical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 348
Password Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 349
Index
10
Page 11

1. Introduction
This chapter includes the following sections:
• Key Features and Capabilities
• Package Contents
• Hardware Features
• WC9500 Wireless Controller System Components
• Supported NETGEAR Access Points
• Supported NETGEAR Antennas
• What Can You Do with the WC9500 Wireless Controller?
• Licenses
• Maintenance and Support
Note: For more information about the topics covered in this manual, visit the
support website at support.netgear.com.
1
Note: Firmware updates with new features and bug fixes are made
available from time to time on downloadcenter.netgear.com. Some
products can regularly check the site and download new firmware, or
you can check for and download new firmware manually. If the
features or behavior of your product do not match what is described in
this guide, you might need to update your firmware.
11
Page 12

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Key Features and Capabilities
The NETGEAR ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500 is a high-capacity, secured wireless
controller intended for medium- to large-sized businesses, higher education institutions,
hospitals, and hotels.
One standalone wireless controller with the appropriate licenses can support up to
300 access points. In a stacked configuration, one wireless controller with the appropriate
licenses can support up to 200 access points. A stack can support three wireless controllers.
The wireless controller supports the IEEE 802.1
future deployment. The wireless controller allows you to manage your wireless network from
a central point, implement security features centrally, support Layer 2 and Layer 3 fast
roaming, configure a guest access captive portal, and support voice over Wi-Fi (VoWi-Fi).
The wireless controller is equipped with one RJ-45 Gigabit Ethernet port and two 10 Gigabit
Ethernet (10GbE) slots with standard SFP+ form factor for optional 10GBASE or 1000BASE
GBICs. These ports are available to access the wireless controller for management and for
data and control communications between the wireless controller and the access points.
The wireless controller provides the following key features and capabilities:
• Scalable architecture with stacking
- Purchased licenses in increments of 10, 50, 100, or 200 access points allow for
support of up to a maximum number of 300 access points on a single wireless
controller in a configuration without a stack.
- A maximum of three stacked wireless controllers allows for up to 600 access points
(200 on each wireless controller in a stacked configuration) in a single network.
- Support of 802.1 1a, 802.1
for future deployment.
- Support for an extra power supply.
• Autodiscovery of access points
- Autodiscovery of access points in the same Layer 2 domain.
- Autodiscovery of access points across a Layer 3 domain.
- Automatic download of wireless controller–based firmware to discovered access
points that are added to the managed access point list.
• Centralized management
- Single point of management for the entire wireless network.
- Automatic firmware upgrade to all managed access points.
- DHCP server for IP address provisioning.
- Configurable management VLAN.
1b, 802.1 1g, and 802.1 1n modes. Ready for 802.11ac mode
1a/b/g/n protocols and is 802.11ac ready for
Introduction
12
Page 13

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
• Security
- Identity-based security authentication with an external RADIUS or LDAP (Active
Directory) server, or with an internal authentication server
.
- Support for nine access point profile groups (one basic and eight advanced) on one
wireless controller.
- Support for up to 8 profiles per access point profile group and 8 profiles per radio
(therefore, dual-band access points can support up to 16 profiles in one access point
profile group).
- Support for up to 144 profiles on one wireless controller (8 profiles per access point
group and eight groups per radio). Each profile supports settings for SSID, network
authentication, data encryption, client separation, VLAN, MAC
ACL, and wireless
QoS.
- Rogue access point detection and classification.
- Guest access and captive portal access with cost and expiration accounting.
- Scheduled wireless on/off times.
• Wi-Fi Multimedia Quality of Service and advanced wireless features
- Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) support for video, audio, and voice over Wi-Fi (VoWi-Fi).
- WMM power save option.
- Automatic WLAN healing mechanism ensures seamless coverage for wireless users.
- Layer 2 and Layer 3 seamless roaming support.
- Local Layer 2 traf
fic switching and Layer 3 traf
fic processing at access point level for
fast processing.
• Wireless and Radio Frequency (RF) management
- Automatic control of access point transmit power and channel allocation to reduce
interference.
- Automatic load balancing of clients across access points.
- Rate limiting per profile.
- Multicast and broadcast rate limiting
- ARP suppression
• Monitoring and reporting
- Monitoring of the status of the network, wireless controllers, WLANs, and clients, and
network usage statistics.
- Specific health monitoring of access points.
- Logging and emailing of system events, RF events, load-balancing events, and
rate-limiting events.
For a list of all features and capabilities of the wireless controller, see the datasheet that you
can download from
http://support.netgear.com/product/WC9500.
Introduction
13
Page 14

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Package Contents
The ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500 product package contains the following items:
• ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500 appliance
• One
• Rubber feet (four) with adhesive backing
• One rack-mount kit
• Straight-through Category 5 Ethernet cable
• ProSAFE W
AC power cable
ireless Controller WC9500 Installation Guide
If any of the parts are incorrect, missing, or damaged, contact your NETGEAR dealer
the carton, including the original packing materials, in case you need to return the product for
repair.
Hardware Features
The front panel ports, slots, and LEDs, back panel components, and bottom label of the
wireless controller are described in this section.
Front Panel Ports, Slots, and LEDs
The following figure shows the front panel of the wireless controller.
Figure 1. Front panel
The following figure shows a close-up of the left side of the front panel.
. Keep
USB port
Reset
Power
Status
Fan
Stack
Master
ID
USB
Digital access point counter
LED Mode:
Green= Link at 10G, Blink Green=10G Active,
Yellow=Link at 1G, Blink Yellow=1G Active
Reset button
LEDs (top to bottom):
Power, Status, Fan, Stack Master
Figure 2. Front panel close-up
Slots and LEDs
for optional
SFP GBIC modules
Introduction
14
LED Mode:
Left LED: Green=Link at 1G E,
Yellow=Link at 10/100M
Right LED:Green=Link,
Green Blink=Active
Ethernet port and LEDs
Page 15

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
From left to right, the wireless controller’s front panel shows the following counter, LEDs,
button, ports, and slots:
• Digital counter. Displays the number of connected access points that are in a healthy
state.
• From top to bottom:
- Power LED
- Status LED
- Fan LED
- Stack Master LED
These LEDs are described in Table 1 on page 15.
• Reset button. Using a sharp object, press and hold this button for about 10 seconds until
the Status LED blinks and the wireless controller returns to factory default settings. If you
reset the wireless controller, all configuration settings are lost and the default password is
restored.
• USB port.
• SFP slots
Allows for external storage for floor heat maps.
. T
wo SFP slots for optional 10GE SFP+ or 1G SFP gigabit interface
converters (GBICs), each slot with an LED.
• Ethernet port. One 10/100/1000 Mbps LAN Ethernet port with an RJ-45 connector, left
LED, and right LED.
The Ethernet port provides switched N-way, automatic speed
negotiating, auto MDI/MDIX technology.
• Console port. RS232 port for connecting to an optional console terminal. The port
provides a DB9 male connector
. The default baud rate is 9600 K. The configuration is 8
bits, no parity, and 1 stop bit. The console port is for debugging under guidance of
NETGEAR technical support only.
The function of each LED is described in the following table.
Table 1. LED functions
LED Status Description
Power LED Green The wireless controller is on.
Off The wireless controller is off.
If the power LED is not lit when the wireless controller is on, check the
connections and check to see if the power outlet is controlled by a wall
switch that is turned of
Status LED Yellow The wireless controller is initializing. After approximately two minutes, when
the wireless controller completes its initialization, the Status LED turns
green. If the Status LED remains yellow
LED Never T
urns Off on page 338).
Power LED Is Not Lit on page 338).
f (see
, the initialization failed (see Status
Green The wireless controller completed its initialization successfully. The Status
LED is steady green during normal operation.
Introduction
15
Page 16

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Table 1. LED functions (continued)
LED Status Description
Status LED
(continued)
Fan LED Green The fans are functioning correctly.
Stack Master
LED
SFP slot LEDs Green The slot is operating at 10G.
Left Ethernet
port LED
Right Ethernet
port LED
Off The wireless controller is not receiving power.
Blinking yellow Firmware is being upgraded.
Yellow One or more fans are not functioning correctly.
Green The wireless controller is functioning as the master controller in a stack.
Yellow The wireless controller is functioning as a slave controller in a stack.
Blinking green Data is being transmitted or received at 10G.
Yellow The slot is operating at 1G.
Blinking yellow Data is being transmitted or received at 1G.
Off The port is not connected to a powered-on Ethernet device (see Ethernet
Port LEDs Are Not Lit on page 338).
Green The port detected a link with a connected Ethernet device.
Blinking green Data is being transmitted or received.
Off The port is not connected to a powered-on Ethernet device (see Ethernet
Port LEDs Are Not Lit on page 338).
Green The port is operating at 1000 Mbps.
Yellow The port is operating at 100 Mbps or 10 Mbps.
Back Panel Features
The wireless controller comes with a single internal power supply but supports an optional
second power supply for power redundancy. The power supplies are hot-swappable.
The following figure shows the back panel of the wireless controller with a single internal
power supply, the power supply connector, and two double fans.
Power supply connector
Figure 3. Back panel
Slot for an optional
second power supply
Introduction
16
Page 17

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
From left to right, the wireless controller’s back panel components are as follows:
• Power supply. 100–240V, 5A, 47–63 Hz power supply, which includes the following
external components:
- AC power socket
not provide an on/off power switch.)
- Handle
- LED. The LED is lit green when the power supply functions correctly
power is not supplied to the power supply, or a problem occurred.
• Fans
. The handle allows for easy removal and insertion.
. Two double fans, each of which can be easily exchanged.
. Attach the power cord to this socket. (The wireless controller does
. If the LED is off,
Bottom Panel with Product Label
The product label on the bottom of the wireless controller’s enclosure displays the default IP
address, default user name, and default password, as well as regulatory compliance, input
power, and other information.
Figure 4. Product label
WC9500 Wireless Controller System Components
A WC9500 wireless controller system consists of one or more wireless controllers and a
collection of access points that are organized into groups based on location or network
access.
The wireless controller system can include a single wireless controller or a group of up to
three stacked wireless controllers that can function in a redundant configuration.
Introduction
17
Page 18

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
The WC9500 wireless controller system supports the following NETGEAR ProSAFE access
point models:
• WN370 ProSAFE Wall Mount Wireless N Access Point
• WNAP210v2 ProSAFE Wireless-N Access Point
• WNAP320 ProSAFE Wireless-N Access Point
• WND930 Outdoor Dual Band Wireless-N
• WNDAP350 ProSAFE Dual Band Wireless-N
Access Point
• WNDAP360 ProSAFE Dual Band Wireless-N Access Point
• WNDAP380R ProSAFE Dual Band Wireless-N Access Point with RFID support
• WNDAP620 ProSAFE Premium 3x3 Dual Band Wireless-N Access Point
• WNDAP660 ProSAFE Premium 3x3 Dual Band Concurrent Wireless-N Access Point
Supported NETGEAR Access Points
Y ou can connect access points to the wireless controller either directly with an Ethernet cable
through a router or switch, or remotely through a VPN network. After you use the automatic
discovery process and add access points to the managed access point list on the wireless
controller, the wireless controller converts the standard access points to dependent access
points by pushing firmware to the access points. From then on, you can centrally manage
and monitor the access points.
The following table lists the minimum firmware versions that must run on the standalone
access points before you convert them to managed access points:
Table 2. Minimum firmware versions
Access Point Model Minimum Firmware Version on
Standalone Access Point
WN370 All firmware versions are supported.
WNAP210v2 All firmware versions are supported.
WNAP320 2.1.1 or a newer version is supported.
WND930 All firmware versions are supported.
WNDAP350 2.1.7 or a newer version is supported.
WNDAP360 2.1.6 or a newer version is supported.
WNDAP380R All firmware versions are supported.
WNAP620 2.0.4 or a newer version is supported.
WNDAP660 2.0.2 or a newer version is supported.
Introduction
18
Page 19

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
A WC9500 wireless controller system supports the following access points:
• WN370 ProSAFE Wall Mounted W
- Supports concurrently 802.11b, 802.1
ireless-N Access Point
1g, and 802.11n network devices.
- Supports speeds of up to 300 Mbps for 802.11n network devices.
- Supports Power over Ethernet (PoE) with a power consumption that complies with the
802.3af standard.
- Operates in the 2.4 GHz radio band.
For product documentation and firmware, visit http://support.netgear
• WNAP210v2 ProSAFE W
- Supports 802.11b, 802.1
ireless-N
Access Point
1g, and 802.11n network devices.
.com/product/WN370.
- Supports Power over Ethernet (PoE) with a power consumption of up to 5.8W.
For product documentation and firmware, visit
http://support.netgear
.com/product/WNAP210.
Note: The WNAP210v1 cannot function in a WC9500 wireless controller
system, but the WNAP210v2 can.
• WNAP320 ProSAFE W
- Supports 802.11b, 802.1
ireless-N
Access Point
1g, and 802.11n network devices.
- Supports Power over Ethernet (PoE) with a power consumption of up to 5.8W.
- Accepts optional antennas.
For product documentation and firmware, visit
http://support.netgear
• WND930 Outdoor Dual Band W
- Supports 802.11a, 802.1
.com/product/WNAP320.
ireless-N
1b, 802.11g, and 802.11n network devices.
- Supports speeds of up to 300 Mbps for 802.11n network devices.
- Supports Power over Ethernet (PoE) with a power consumption that complies with the
802.3af or 802.3at standards.
- Operates concurrently in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz radio bands.
For product documentation and firmware, visit
http://support.netgear
• WNDAP350 ProSAFE Dual Band W
- Supports 802.11a, 802.1
.com/product/WND930.
ireless-N
1b, 802.11g, and 802.11n network devices.
Access Point
- Supports Power over Ethernet (PoE) with a power consumption of up to 10.75W.
- Operates concurrently in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz radio bands.
- Accepts optional antennas.
For product documentation and firmware, visit
http://support.netgear
.com/product/WNDAP350.
Introduction
19
Page 20

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
• WNDAP360 ProSAFE Dual Band Wireless-N Access Point
- Supports 802.11a, 802.1
1b, 802.11g, and 802.11n network devices.
- Supports Power over Ethernet (PoE) with a power consumption of up to 10.51W.
- Operates concurrently in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz radio bands.
- Accepts optional antennas.
For product documentation and firmware, visit
http://support.netgear
.com/product/WNDAP360.
• WNDAP380R ProSAFE Dual Band W
- Supports 802.11a, 802.1
1b, 802.11g, and 802.11n network devices.
ireless-N
Access Point with RFID support
- Supports Power over Ethernet (PoE) with a power consumption of up to 10.51W.
- Operates concurrently in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz radio bands.
- Accepts an RFID module for support of RFID devices and tags.
For product documentation and firmware, visit
http://support.netgear
• WNAP620 ProSAFE Premium 3x3 Dual Band W
- Supports concurrently 802.11a, 802.1
.com/product/WNDAP380R.
1b, 802.11g, and 802.11n network devices.
ireless-N
Access Point
- Supports 3x3 multiple input, multiple output (MIMO).
- Supports speeds of up to 450 Mbps for 802.1
1n network devices
- Supports Power over Ethernet (PoE) with a power consumption that complies with the
802.3af standard.
- Operates in either the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz radio band.
- Accepts optional antennas.
For product documentation and firmware, visit
http://support.netgear
• WNDAP660 ProSAFE Premium 3x3 Dual Band Concurrent W
- Supports 802.11a, 802.1
.com/product/WNDAP620.
1b, 802.11g, and 802.11n network devices.
ireless-N
Access Point
- Supports 3x3 multiple input, multiple output (MIMO).
- Supports speeds of up to 450 Mbps for 802.1
1n network devices.
- Supports Power over Ethernet (PoE) with a power consumption that complies with the
802.3at standard.
Note: If your network does not include a PoE device that can provide the
WNDAP660 access point with PoE power according to the 802.3at
standard, you can instead use two ports of a PoE device that complies
with the 802.3af standard. (The WNDAP660 access point provides two
Ethernet ports that accept PoE.)
- Operates concurrently in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz radio bands.
- Accepts optional antennas.
Introduction
20
Page 21

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
For product documentation and firmware, visit
http://support.netgear.com/product/WNDAP660.
Supported NETGEAR Antennas
A WC9500 wireless controller system supports the following antennas:
• ANT2409 ProSAFE Indoor/Outdoor 9 dBi Omni-directional Antenna
- 9 dBi omni-directional antenna for indoor or outdoor use
- WiFi signal 802.1
- Frequency range 2400–2485 MHz
- Maximum range 1
- Polarization vertical
For product documentation and firmware, visit
http://support.netgear
1g
1.5 km (7.2 miles)
.com/product/ANT2409v2.
• ANT224D10 ProSAFE 10 dBi 2x2 Indoor/Outdoor Directional
- 10 dBi directional antenna for indoor or outdoor use
- WiFi signal 802.1
- Frequency range 2400–2500 MHz
- Maximum range 8.5 km (5.28 miles)
- Polarization linear; vertical
For product documentation and firmware, visit
http://support.netgear
1n
.com/product/ANT224.
Antenna
What Can You Do with the WC9500 Wireless Controller?
You can perform the following tasks with a WC9500 wireless controller:
• Organize the Network
- Create access point profiles. Organize access points in profiles to dif
between SSIDs, client authentication, authentication settings, and wireless QoS
settings.
- Create access point profile
profile groups to differentiate between buildings, floors, businesses, business
divisions, and so on. Easily assign access points to profile groups or change
assignments.
groups. Organize access point profiles in access point
ferentiate
For more information, see
Chapter 6, Manage Security Profiles and Profile Groups.
Introduction
21
Page 22

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
• Discover Access Points in the Network and Provision IP Addresses and Firmware
- Discover access points in the network. The access points can be in factory default
state or functioning in standalone mode, but after discovery by the wireless controller
and addition to the managed access point list, the access points become dependent
(managed) access points.
- Provision IP addresses to the access points
. Use the internal DHCP server to
provision IP addresses to all or selected managed access points in the network.
- Upgrade access point firmware. Update and synchronize new firmware versions to
all managed access points in the network.
For more information, see Chapter 7, Discover and Manage Access Points.
• Centrally Manage Security in the Network
- Manage secure access to the network and secure data transmission. Manage
client authentication, encryption, wireless client security separation, and MAC
authentication in access point profiles.
- Manage authentication servers for the network. Manage all internal and external
authentication servers for the entire network or for access point profile groups.
- Manage MAC authentication. Specify trusted and untrusted MAC addresses for the
entire network.
- Manage rogue access points. Manage rogue access points and their associated
clients in the network.
- Manage guest access. Manage guest access and captive portal access to the
network.
For more information, see Chapter 9, Manage Rogue Access Points, Guest Network
Access, and Users.
• Centrally Manage the W
- Schedule the radios
point profile groups to go of
ireless Settings for the Network
. Schedule the entire network to go offline, or schedule access
fline.
- Manage wireless settings and channel allocation. Manage the wireless settings
such as wireless mode, data rate, and channel width for the entire network or for
access point profile groups, and manage channel allocation for the entire network.
- Manage QoS settings. Manage QoS queue settings for data, background, video,
and voice traffic for access point profile groups.
- Configure RF management settings
. Configure WLAN healing and wireless
coverage hole detection for the entire network or for access point profile groups.
For more information, see Chapter 8, Configure Wireless and QoS Settings.
• Manage Other Wireless Controllers in the Network
- Manage stacking
. Specify the master and slave wireless controllers in a stack and
synchronize information between the wireless controller.
For more information, see Chapter 11, Manage Stacking and Redundancy.
Introduction
22
Page 23

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
• Monitor the Network and Its Components
- Monitor the status of all wireless devices. View the status of the wireless
controllers, access points, clients, access point profiles, and the entire network, and
view network usage statistics.
- Monitor network health
down or compromised.
For more information, see Chapter 12, Monitor the Wireless Network
and Its Components.
. See which access points are healthy and which ones are
Licenses
By default, the wireless controller comes with a trial license for two access points. You must
purchase and register licenses for the access points in your network. Licenses are tied to the
serial number of the wireless controller.
You can purchase a single 200–access point license or licenses in 10–, 50–, or 100–access
point increments for support of up to 300 access points on a single wireless controller:
• 10–AP license. WC10APL
• 50–AP license. WC50APL
• 100–AP license. WC100APL
• 200–AP license. WC200APL
If you installed three wireless controllers in a stack and want to support the maximum number
of 600 access points in a stacked configuration, you must purchase three WC200APL
licenses (or a combination of other licenses that add up to a total of 600 access points).
For more information, see the datasheet that you can download from
http://support.netgear.com/product/WC9500.
For information about how to register and manage your licenses, see Register Your Licenses
on page 103 and Manage Licenses on page 261.
Maintenance and Support
NETGEAR offers technical support seven days a week, 24 hours a day. Information about
support is available on the NETGEAR ProSupport website at
http://kb.netgear.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/212.
Introduction
23
Page 24

2. System Planning and Deployment
Scenarios
This chapter includes the following sections:
• Basic and Advanced Setting Concepts
• Profile Group Concepts
• System Planning Concepts
• High-Level Configuration Examples
• Management VLAN and Data VLAN Strategies
• High-Level Deployment Scenarios
2
24
Page 25

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Basic and Advanced Setting Concepts
Y ou can deploy the wireless controller in a small wireless network with 10 or 20 access points
or in a large wireless network with up to 600 access points. Small networks require a basic
configuration, but large networks can become complex and require you to configure the
advanced features of the wireless controller.
Depending on your network configuration, use basic settings or advanced settings to
manage your access points:
• Basic settings for a typical network. The basic settings work with most common
network configurations. For example, all access points on the WLAN are for the same
organization or business and therefore adhere to the same policies and use a few service
set identifiers (SSIDs, or network names).
• Advanced settings for access point profile groups. In a large wireless network, or if
separate networks share a single WLAN, use the advanced settings to set up multiple
access point profile groups with multiple security profiles (SSIDs with associated security
settings). For example, a shopping mall might need several access point profile groups if
several businesses share a WLAN but each business maintains its own network. Larger
networks could require multiple access point profile groups to allow dif
building or department. The access points could support dif
building and department, for example, one for guests, one for management, and one for
sales.
ferent security profiles per
ferent policies per
Note: Access point profile groups are also referred to as just profile groups.
Profiles, security profiles, and SSIDs (that is, SSIDs with associated
security settings) are terms that are interchangeable.
To accommodate all types of networks, almost all configuration menus of the web
management interface are divided into basic and advanced submenus. The following figure
shows an example of the Configuration > Security > Basic submenu on the left and the
Configuration > Security > Advanced submenu on the right:
Figure 5. Basic and advanced submenus
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
25
Page 26

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Before you start the configuration of your wireless controller, decide whether you can use a
basic configuration (that is, follow the Basic submenus) or need to use an advanced
configuration (that is, follow the Advanced submenus). Once you make your choice,
configuring the wireless controller can be fairly easy if you consistently follow either the Basic
submenus or the Advanced submenus.
Profile Group Concepts
Each access point can support up to eight security profiles (16 for dual-band access points),
each with its own SSID, security settings, MAC ACL, rate-limiting settings, WMM, and so on.
The wireless controller follows the same architecture. A profile group on the wireless
controller includes all the features that you can configure for an individual access point: up to
8 profiles (16 for dual-band access points), each of which supports its own SSID, security,
MAC ACL, rate-limiting settings, WMM settings, and so on.
Basic Profile
The basic profile includes all the settings that are required to configure a fully functional
access point with up to eight security profiles (16 for dual-band access points).
After you use the automatic discovery process and add access points to the managed AP list
on the wireless controller, the access points are assigned by default to the basic profile
group.
If your network requires the wireless controller to manage multiple access points with
different configurations, use the advanced profile.
Advanced Profile
The advanced profile lets you configure up to eight access point profile groups. Each group
includes all the settings that are required to configure a fully functional access point with up to
eight security profiles (16 for dual-band access points).
For example, if your company site includes four buildings, each with a different wireless
network, you simply create four profile groups. Y
building to one profile group, all access points in another building to a second profile group,
and so on.
For each profile group, you can create an individual radio on/off schedule, RF management
settings, MAC ACL authentication, and an authentication server
group (2.4 GHz radio and 5 GHz radio), you can create individual wireless settings, WMM,
and rate-limit settings.
ou then assign all access points in one
. For each radio in a profile
The following figure shows the advanced profile group architecture. The structure that is
shown under Group-1 is implemented in all profile groups (that is, Group-2 through Group-8):
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
26
Page 27

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Group-1
Group-2
Group-3
Group-4
2.4 GHz
radio
1
2
34
5678
Security profiles
Figure 6. Advanced profile group architecture
Group-5
5 GHz
radio
1
Group-6
23
Security profiles
Group-7
4
56
Group-8
78
The following figure shows an example of three access point profile groups, in which the first
profile group (Group-1) supports five security profiles. For each profile in this profile group,
the profile name, radio mode, and authentication setting are shown. (Group-1 is the default
group in the advanced profile group configuration; you must create the other profiles groups.)
Figure 7. Example of profile groups with security profiles
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
27
Page 28

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
System Planning Concepts
This section includes the following subsections:
• Preinstallation Planning
• Before You Configure a Wireless Controller
Preinstallation Planning
Before you install any wireless controllers, determine the following:
• Number of access points required to provide seamless coverage
• Number of licenses required to cover all access points that must be managed
• Number of wireless controllers required
• 802.1
NETGEAR recommends that you perform a site survey:
1 frequency band and the channels that are optimal for WiFi usage
• To determine the current RF behavior and detect both 802.11 and non-802.11 noise, run
a spectrum analysis of the channels of the site.
• To determine the maximum throughput that is achievable on the client, run an access
point-to-client connectivity test.
• Identify potential RF obstructions and interference sources.
• Determine areas where denser coverage might be required because of heavier usage.
Before You Configure a Wireless Controller
These sections assume that you deployed at least one wireless controller in your network
and are ready to configure the wireless controller. For information about how to deploy the
wireless controller in your network, see the ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Installation Guide that you can download from http://support.netgear.com/product/WC9500.
For many configurations, you can use the default wireless settings. The IP address, VLAN,
DHCP server, client authentication, and data encryption settings are specific to your
environment. Following are short sections that describe these settings (except for IP address
settings, which are self-explanatory). For information about how to configure these settings,
see the relevant sections.
Management VLAN
The management VLAN is the dedicated VLAN for access to the wireless controller. All traf fic
that is directed to the wireless controller, including HTTP, HTTPS, SNMP, and SSH traffic, is
carried over the management VLAN.
If the management VLAN is also configured as a tagged VLAN (the most common
configuration), the packets to and from the wireless controller carry the 802.1Q VLAN header
with the assigned VLAN number. If the management VLAN is marked as untagged, the
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
28
Page 29

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
packets that are sent from the wireless controller do not carry the 802.1Q header, and all
untagged packets that are sent to the wireless controller are treated as management VLAN
traffic.
Note: Use a tagged VLAN or change the tagged VLAN ID only if the hubs
and switches on your LAN support 802.1Q. If they do not, and you did
not configure a tagged VLAN with the same VLAN ID on the hubs and
switches in your network, IP connectivity might be lost.
The management VLAN must provide IP connectivity between the wireless controller and the
access points. If the wireless controller and the access points are on different management
VLANs, external VLAN routing must allow IP connectivity between the wireless controller and
the access points.
For information about how to configure management VLANs, see Manage the IP
Link Aggregation Settings on page 95.
, VLAN, and
Client VLANs
Each authenticated wireless user is placed into a VLAN that determines the user’s DHCP
server, IP address, and Layer 2 connection. Although you could place all authenticated
wireless users into the single VLAN that is specified in the basic security profile, the wireless
controller allows you to group wireless users into separate VLANs based on the wireless
SSID to differentiate access to network resources. For example, you might place authorized
employee users into one VLAN, and itinerant users, such as contractors or guests, into a
separate VLAN. To use different VLANs, you must create different security profiles.
For information about how to configure regular VLANs, see Manage the IP, VLAN, and Link
Aggregation Settings on page 95.
DHCP Server
The wireless controller can function as a DHCP server and assign IP addresses to both
wireless and wired devices that are connected to it. You can add up to 64 DHCP server
pools, each assigned to a different VLAN.
Client Authentication and Data Encryption
A user must authenticate to the WLAN to be able to access WLAN resources. The wireless
controller supports several types of security methods, including those methods that require
an external RADIUS or LDAP authentication server.
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
29
Page 30

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
The encryption option that you can select depends upon the authentication method that you
selected. The following table lists the authentication methods available, with their
corresponding encryption options:
Table 3. Authentication and encryption options
Authentication Method Encryption Option Authentication Server
Open System 64-bit, 128-bit, or 152-bit WEP None
Shared Key 64-bit, 128-bit, or 152-bit WEP None
WPA-PSK TKIP or TKIP+AES None
WPA2-PSK AES or TKIP+AES None
WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK TKIP+AES None
WPA TKIP or TKIP+AES One of the following authentication servers:
• External RADIUS server
• Internal authentication server
• External LDAP server
WPA2 AES or TKIP+AES One of the following authentication servers:
• External RADIUS server
• Internal authentication server
• External LDAP server
WPA and WPA2 TKIP+AES One of the following authentication servers:
• External RADIUS server
• Internal authentication server
• External LDAP server
For information about how to configure client authentication, data encryption, and
authentication servers, see Chapter 6, Manage Security Profiles and Profile Groups.
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
30
Page 31

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
High-Level Configuration Examples
This section includes the following subsections:
• Single Controller Configuration with Basic Profile Group
• Single Controller Configuration with Advanced Profile Groups
• Stacked Controller Configuration
Single Controller Configuration with Basic Profile Group
A basic configuration consists of a single wireless controller that controls a collection of
access points that are organized into the basic default group.
To set up a single wireless controller system with a basic profile group:
Step Configuration Web Management Interface Path
1. Configure the system and network settings of the wireless
controller:
1. Configure the country code of operation.
2. Configure the time settings.
3. Configure the IP address of the wireless controller.
4. V
erify that VLAN 1 is set as the management VLAN and is
marked as untagged.
By default, VLAN 1 an untagged management VLAN.
5. If no network DHCP server is accessible to the access points,
configure the wireless controller’
2. Configure up to eight profiles, and for each profile, do at least the
following:
1. Configure an SSID for wireless access.
2. Configure the network authentication and data encryption.
3. Assign the VLAN.
4. If necessary for the selected network authentication option,
configure the authentication server
s DHCP server.
.
Configuration > System > General
Configuration > System > Time
Configuration > System > IP/VLAN
Configuration > System > DHCP
Server
Configuration > Profile > Basic
Configuration > Security > Basic >
Authentication Server
3. Run the Discovery Wizard and add the access points to the
managed access point list.
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
31
Access Point > Discovery Wizard
Page 32

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Single Controller Configuration with Advanced Profile Groups
A more complex configuration consists of a single wireless controller that controls a collection
of access points that are organized in access point profile groups and might use several
profiles in each access point profile group.
To set up a single wireless controller system with advanced profile groups:
Step Configuration Web Management Interface Path
1. Configure the system and network settings of the wireless
controller:
1. Configure the country code of operation.
2. Configure the time settings.
3. Configure the IP address of the wireless controller.
4. V
erify that VLAN 1 is set as the management VLAN and is
marked as untagged.
By default, VLAN 1 an untagged management VLAN.
5. If no network DHCP server is accessible to the access points,
configure the wireless controller’
2. Configure up to eight access point profile
access point profile in a group, do at least the following:
1. Configure an SSID for wireless access.
2. Configure the network authentication and data encryption.
3.
Assign the VLAN.
4. If necessary for the selected network authentication option,
configure the authentication server.
s DHCP server.
groups, and for each
Configuration > System > General
Configuration > System > Time
Configuration > System > IP/VLAN
Configuration > System > DHCP
Server
Configuration > Profile > Advanced
Configuration > Security >
Advanced > Authentication Server
3. Run the Discovery Wizard and add the access points to the
managed access point list.
4. Assign the access points to the access point profile
referred to as WLAN groups).
groups (also
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
32
Access Point > Discovery Wizard
Configuration > WLAN Network
Page 33

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Stacked Controller Configuration
A stacked controller configuration can consist of up to three wireless controllers and up to
600 access points.
Note: If the stack members are on different floors or in different buildings, you
could configure a separate access point profile group for each building or
floor.
To set up a stacked controller configuration:
Step Configuration Web Management Interface Path
1. On each individual wireless controller that you intend to make a
stack member, configure the system and network settings of the
wireless controller:
1. Configure the country code of operation.
2. Configure the time settings.
3. Configure the IP address of the wireless controller.
4. Verify that VLAN 1 is set as the management VLAN and is
marked as untagged.
By default, VLAN 1 an untagged management VLAN.
5. If no network DHCP server is accessible to the access points,
configure the wireless controller’
2. Configure the master wireless controller and deploy it in the
network.
Configure up to eight access point profile groups, and for each
access point profile in a group, do at least the following:
1. Configure an SSID for wireless access.
2. Configure the network authentication and data encryption.
3.
Assign the VLAN.
s DHCP server
.
Configuration > System > General
Configuration > System > T
Configuration > System > IP/VLAN
Configuration > System > DHCP
Server
Configuration > Profile > Advanced
ime
4. If necessary for the selected network authentication option,
configure the authentication server.
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
33
Configuration > Security >
Advanced > Authentication Server
Page 34

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Step Configuration Web Management Interface Path
3. Configure the slave wireless controllers and deploy them in the
network.
For each slave wireless controller, configure up to eight access
point profile groups, and for each access point profile in a group, do
at least the following:
1. Configure an SSID for wireless access.
2. Configure the network authentication and data encryption.
3.
Assign the VLAN.
4. If necessary for the selected network authentication option,
configure the authentication server.
4. Interconnect the wireless controllers that you intend to make
members of the stack. The connection must be a wired
connection but does not need to be a direct connection, that is, a
switch or router can be located in between the wireless
controllers that are part of a stack.
5. Configure the stacking group on the wireless controller that you
intend as the master controller
6.
Synchronize all wireless controllers that are members of the
stack.
.
Configuration > Profile > Advanced
Configuration > Security >
Advanced > Authentication Server
Stacking > Stacking
Management VLAN and Data VLAN Strategies
If your network includes 10 or more access points, NETGEAR recommends that you set up at
least two VLAN groups: a management VLAN group and a data VLAN group. If your network
is large, NETGEAR recommends that you create a number of data VLAN groups. Setting up
data VLANs for clients allows you to do the following:
• Segregate traffic by user category
• Create different policies such as access policies that are based on user category
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
34
Page 35

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
The following illustration shows a simplified view of how you can use VLANs to segregate
traffic by user category:
Management VLAN 100 Ethernet traffic
Finance VLAN 10 Ethernet traffic
Employee VLAN 20 Ethernet traffic
Deploy the wireless controller
on a trunk port if you use the
internal DHCP server
Wireless controller
WC9500
Internet
Network printer
Backend L3 switch
or router
PoE switch
Access point
WNDAP360
Finance
computer
Finance
computer
Employee
computer
Employee
computer
Figure 8. Example: Use VLANs to segregate traffic by user categories
The wireless controller uses the management VLAN to continually exchange packets with
the access points. For large networks, if all traffic uses a single VLAN, the client traffic could
potentially flood the network. If flooding occurs and the wireless controller is not able to
exchange packets with the access points, the network performance can slow down, and the
access points can lose their connectivity with the wireless controller.
If you use the internal DHCP server of the wireless controller, deploy the wireless controller
on a trunk port on your switch.
The trunk port must provide access to all VLANs.
To accommodate the traffic load of the trunk, use a high-speed port on your switch as the
trunk port. If you use an external DHCP server, you do not need to deploy the wireless
controller on a trunk port on your switch.
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
35
Page 36

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
High-Level Deployment Scenarios
This section provides three deployment scenarios to illustrate how the wireless controller can
function in various network configurations:
• Scenario Example 1: Network with Single VLAN
• Scenario Example 2: Advanced Network with VLANs and SSIDs
• Scenario Example 3: Advanced Network with Redundancy
Scenario Example 1: Network with Single VLAN
The following sample scenario consists of a simple network with a wireless controller, PoE
switch, Layer 3 switch or router, and access points:
Management VLAN Ethernet traffic
All client Ethernet traffic
Internet
Deploy the wireless controller
on a trunk port if you use the
internal DHCP server
Wireless controller
WC9500
Finance
computer
PoE switch
Marketing
computer
Network printer
Employee
computer
Backend L3 switch
or router
Access point
WNDAP360
Employee
computer
Figure 9. Example: Basic network with a single VLAN
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
36
Page 37

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
The access points and wireless controller are connected in the same subnet and use the
same IP address range that is assigned for that subnet. The configuration does not include
any routers between the access points and the wireless controller. The access points are
connected to a PoE switch, which, in turn, is connected to the wireless controller. The uplink
of the PoE switch connects to a Layer 3 switch or router that provides Internet access.
To provision the wireless controller:
Step Configuration Web Management Interface Path
1. Configure the system and network settings of the wireless
controller:
1. Configure the country code of operation.
2. Configure the time settings.
3. Configure the IP address of the wireless controller.
4. V
erify that VLAN 1 is set as the management VLAN and is
marked as untagged.
By default, VLAN 1 an untagged management VLAN.
5. If no network DHCP server is accessible to the access points,
configure the wireless controller’
2. Configure up to eight profiles, and for each profile, do at least the
following:
1. Configure an SSID for wireless access.
2. Configure the network authentication and data encryption.
3. Assign the VLAN.
4. If necessary for the selected network authentication option,
configure the authentication server
s DHCP server
.
.
Configuration > System > General
Configuration > System > Time
Configuration > System > IP/VLAN
Configuration > System > DHCP
Server
Configuration > Profile > Basic
Configuration > Security > Basic >
Authentication Server
3. Use any port of the wireless controller to connect the wireless
PoE switch.
4. Deploy the access points and connect them to the same wireless
PoE switch.
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
37
Page 38

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Step Configuration Web Management Interface Path
5. When the access points are operating, open the Discovery
Wizard to do the following:
1. Specify the state of the access points. The state can be either
factory default in a Layer 2 network or already installed and
functioning in standalone mode.
2. Run the Discovery Wizard.
3. Select the access points that you want the wireless controller to
manage and add them to the managed list.
Note: By default, all access points are added to the basic group
and all settings from the basic group (profile definition, client
authentication, authentication settings, and wireless QoS) are
applied to the access points.
Access Point > Discovery Wizard
Scenario Example 2: Advanced Network with VLANs and SSIDs
The following sample scenario consists of an advanced network with a wireless controller,
PoE switch, Layer 3 switch or router, access points, and several VLANs and SSIDs. The
wireless controller system includes the following VLANs:
• VLAN 1, the default untagged VLAN to access the wireless controller
• VLAN 10, a tagged client VLAN
• VLAN 20, another tagged client VLAN
• VLAN 100, a tagged management VLAN
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
38
Page 39

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Management VLAN 100 Ethernet traffic
Client VLAN 10 Ethernet traffic
Client VLAN 20 Ethernet traffic
SSID 1
Client VLAN 10
Wireless controller
WC9500
Backend L3 switch
or router
Internet
PoE switch
WNDAP360
WNDAP360
SSID 2
Client VLAN 20
Figure 10. Example: Advanced network with VLANs and SSIDs
The access points and wireless controller are connected in the same subnet and same VLAN
and use the same IP address range that is assigned for that subnet. The configuration does
not include any routers between the access points and the wireless controller. The access
points are connected to a PoE switch, which, in turn, is connected to the Layer 3 switch or
router that provides Internet access.
This network configuration requires the following conditions:
• VLANs 10, 20, and 100 are tagged VLANs and are configured on the wireless controller
and the PoE switch.
• The wireless controller is connected to the PoE switch through default VLAN 1. You
manage the wireless controller from a computer over VLAN 1 through the PoE switch.
• The DHCP server on the wireless controller is configured in management VLAN 100 to
enable the access points to receive an IP address through VLAN 100.
• The PoE switch port to which the wireless controller is connected is configured as a
tagged port to allow tagged traffic from VLAN 100.
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
39
Page 40

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
To provision the wireless controller:
Step Configuration Web Management Interface Path
1. Configure the basic system settings:
1. Configure the country code of operation.
2. Configure the time settings.
3. Configure the IP address of wireless controller.
4. For initial discovery and configuration of the access points,
temporarily configure management VLAN 100 as an
untagged management VLAN on the wireless controller.
5. Change default VLAN 1 to a tagged VLAN.
2. For initial discovery and configuration of the access points,
temporarily configure management VLAN 100 as an untagged
management on the PoE switch.
3. Configure either the network’s DHCP server or the wireless
controller’
If you use the wireless controller’
1. Configure the IP address range for VLAN 100.
2. Configure the other DHCP server fields, including the
4. Configure the following profiles, and configure network
authentication and data encryption for these profiles:
1. A profile with SSID 1 and VLAN 10.
s DHCP server to use VLAN 100.
s DHCP server:
gateway and DNS servers.
Configuration > System > General
Configuration > System > Time
Configuration > System > IP/VLAN
Configuration > System > DHCP
Server
Configuration > Profile > Basic
2. A profile with SSID 2 and VLAN 20.
3. If necessary for the selected network authentication options,
configure one or more authentication servers.
5. Connect the wireless controller to the PoE switch.
6. Before you connect the access points to the PoE switch, verify
that the switch ports to which you intend to connect the access
points are configured as access ports in management VLAN 100.
7. Deploy the access points and connect them to the designated
PoE switch ports.
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
Configuration > Security > Basic >
Authentication Server
40
Page 41

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Step Configuration Web Management Interface Path
8. When the access points are operating, open the Discovery
Wizard to do the following:
1. Specify the state of the access points, which is factory default
in a Layer 2 network.
2. Run the Discovery Wizard.
3. Select the access points that you want the wireless controller to
manage and add them to the managed list.
Note: By adding the access points to managed list, you enable
them to receive an IP address from the DHCP server over
management VLAN 100.
9. For each access point on the managed list, disable the untagged
VLAN and configure VLAN 100 as the management VLAN. Doing
so causes the access points to lose connectivity with the wireless
controller.
10. Restore connectivity between the access points and the wireless
controller by changing the PoE switch ports to which the access
points are connected to tagged ports.
During the discovery process, these switch ports were access
ports in management VLAN 100.
Access Point > Discovery Wizard
Scenario Example 3: Advanced Network with Redundancy
The following sample scenario consists of an advanced network with one wireless controller,
one redundant wireless controller, one core switch, two PoE switches in different buildings,
access points, and several VLANs and SSIDs. These are the components in the wireless
controller system:
• One wireless controller
• Fifty access points (managed by the wireless controller through management VLAN 1)
• One redundant wireless controller
• Four VLANs: VLAN 10, VLAN 20, VLAN 30, and VLAN 40
• Three SSIDs: SSID 1, SSID 2, and SSID 3
In this scenario, the VLANs and SSIDs are used to accommodate traffic for different user
groups in a school that is spread out over two buildings.
• Building 1:
- SSID 1 in VLAN 10 for staff traffic
- SSID 2 in VLAN 20 for middle school students
- SSID 3 in VLAN 30 for guests
• Building 2:
- SSID 1 in VLAN 10 for staff traffic
- SSID 2 in VLAN 40 for high school students
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
41
Page 42

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
- SSID 3 in VLAN 30 for guests
Internet
Backend L3 switch
or router
WC9500
Redundant WC9500
Staff VLAN 10 Ethernet traffic
Middle school VLAN 20 Ethernet traffic
High school VLAN 40 Ethernet traffic
Guest VLAN 30 Ethernet traffic
Core switch
Building 1
SSID 1 Staff VLAN 10
SSID 2 Middle school VLAN 20
SSID 3 Guest VLAN 30
PoE switch
WNDAP360
Building 2
SSID 1 Staff VLAN 10
SSID 2 High school VLAN 40
SSID 3 Guest VLAN 30
PoE switch
WNDAP360
Figure 11. Example: Advanced network with redundancy
The access points and wireless controllers are connected in the same subnet and the same
VLAN and use the same IP address range that is assigned for that subnet. The core switch is
located between the wireless controllers and the PoE switches, to which the access points
are connected. The core switch provides Internet access.
This network configuration requires the following conditions:
• VLAN 1 is configured on the wireless controllers, core switch, and PoE switches. This
VLAN is untagged.
• VLANs 10, 20, and 30 are configured on the wireless controllers, core switch, and the
PoE switch in Building 1. These VLANs are tagged.
• VLANs 1, 10, 20, 30, and 40 are configured on the wireless controllers, core switch, and
PoE switches. Except for VLAN 1, these VLANs are tagged.
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
42
Page 43

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
To provision the wireless controller:
Step Configuration Web Management Interface Path
1. Configure the basic system settings:
1. Configure the country code of operation.
2. Configure the time settings.
3. Configure the IP address of wireless controller.
4. Verify that VLAN 1 is set as the management VLAN and is
marked as untagged.
By default, VLAN 1 an untagged management VLAN.
2. Configure the following profiles, and configure network
authentication and data encryption for these profiles:
1. A profile with SSID 1 and VLAN 10.
2. A profile with SSID 2 and VLAN 20.
3. A profile with SSID 2 and VLAN 30.
4. A profile with SSID 3 and VLAN 40.
5. If necessary for the selected network authentication options,
configure one or more authentication servers.
3. Configure the following profile groups:
1. A profile group with the name Building 1, to which you add the
following profiles:
- The profile with SSID 1 and VLAN 10
- The profile with SSID 2 and VLAN 20
- The profile with SSID 2 and VLAN 30
Configuration > System > General
Configuration > System > Time
Configuration > System > IP/VLAN
Configuration > Profile > Basic
Configuration > Security > Basic >
Authentication Server
Configuration > Profile > Advanced
2. A profile group with the name Building 2, to which you add the
following profiles:
- The profile with SSID 1 and VLAN 10
- The profile with SSID 2 and VLAN 30
- The profile with SSID 3 and VLAN 40
4. Deploy the access points and connect them to PoE switches.
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
43
Page 44

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Step Configuration Web Management Interface Path
5. When the access points are operating, open the Discovery
Wizard to do the following:
1. Specify the state of the access points, which is the factory
default state in a Layer 2 network.
2. Run the Discovery Wizard.
3. Select and add the access points that you want to be managed
by the wireless controller to the managed list.
Note: By default, all access points are added to the basic group.
6. Assign the access points to the access point profile groups (also
referred to as WLAN groups) Building 1 and Building 2.
Access Point > Discovery Wizard
Configuration > WLAN Network
System Planning and Deployment Scenarios
44
Page 45

3. RF Planning and Deployment
This chapter includes the following sections:
• RF Planning Overview
• Manage a Building and Floors for an RF Plan
• Use the WiFi Auto Planning Advisor to Generate an RF Plan for a Floor
• Manually Add and Manage Access Points on a Floor Map for an RF Plan
• Manually Add and Manage Antennas on a Floor Map for an RF Plan
• Display and Recalculate the WiFi Coverage for a Heat Map
• Display or Change the WiFi Inventory for an RF Plan
• Download a Report for an RF Plan
• View the Heat Map for a Deployed Floor Plan
Note: Make sure that your computer can run Adobe Flash Player and that
Java is enabled in your browser.
3
Note: For remote access (that is, access over a WAN interface) to the
RF planning screens in the web management interface, make sure
that port 8443 is open in your computer’s firewall.
45
Page 46

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
RF Planning Overview
You can do the following with RF planning:
• Define WLAN coverage.
• Estimate the number of access points required based on signal quality and number of
clients per access point.
• Optimize the placement of access points for the best coverage.
• Monitor WLAN coverage, rogue access points, and blacklisted clients for a plan that is in
deployment.
• Identify weak signal spots and dead spots from the coverage hole and add additional
access points to mitigate the situation.
RF planning provides a view of each floor in a building, allowing you to specify how WiFi
coverage must be provided. RF planning then provides coverage maps and access point
placement locations.
For deployed RF plans, real-time calibration lets you visualize the indoor propagation of RF
signals to identify areas with a weak signal or dead spots and add additional access points in
the right location to mitigate the weak signal or dead spots.
Planning Requirements
To expedite your planning efforts, collect the information that is listed in Table 4 and Table 5
before you use RF planning.
Use a worksheet similar to the following table to collect your building information.
Table 4. Building planning table
Item Your Information
Building length
Building width
Building height
Number of floors
Distance in height between floors
Use a worksheet similar to the following table to collect your information for each floor in the
building.
Table 5. Floor planning table
Item Your Information
Floor dimensions if different from building dimensions
Length
RF Planning and Deployment
46
Page 47

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Table 5. Floor planning table (continued)
Item Your Information
Width
Height
Define WiFi coverage and noncoverage areas
WiFi coverage areas
WiFi noncoverage areas
WiFi building obstacles
Dry walls
Wood walls
Plastic walls
Glass walls
Brick walls
Concrete walls
Light doors
Metal doors
Heavy doors
Thin windows
Thick windows
Other obstacles
WiFi building obstruction areas
Cubicle office areas
Closed office areas
Elevator shafts
Warehouses with low stock
Warehouses with medium stock
Warehouses with high stock
WiFi client information
Total number of expected clients on floor
Expected number of clients per access point
WiFi radio band or bands
RF Planning and Deployment
47
Page 48

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Table 5. Floor planning table (continued)
Item Your Information
Access point protocol for each WiFi radio band
2.4 GHz (802.11b/bg/ng)
5 GHz (802.11a/na)
Access point transmission power (from full to minimum) for each WiFi radio band
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
WiFi coverage and signal strength
WiFi coverage percentage
Minimum required signal strength in dBm
Recommended RF Planning Procedure for a Building
NETGEAR recommends that you first set up your building and floors to scale and define the
floor plans. For more information, see Manage a Building and Floors for an RF Plan on
page 49.
Then, for each floor, perform the following tasks:
• Use the WiFi Auto Planning Advisor
See Use the WiFi Auto Planning Advisor to Generate an RF Plan for a Floor on page 64.
• (Optional) Manually add and fine-tune access points on each floor.
See
Manually Add and Manage Access Points on a Floor Map for an RF Plan on
page 69.
• (Optional) Manually add and fine-tune antennas.
See Manually Add and Manage Antennas on a Floor Map for an RF Plan on page 72.
• (Optional) Display the WiFi coverage.
See Display and Recalculate the WiFi Coverage for a Heat Map on page 75.
• (Optional) Display and fine-tune the WiFi inventory
Display or Change the WiFi Inventory for an RF Plan on page 77.
See
.
• (Optional) Download the report.
See Download a Report for an RF Plan on page 80.
After you install or move the physical access points and antennas according to the RF plan
for a floor
, deploy the floor plan by placing the virtual access points at the virtual locations on
the floor map to match the actual physical locations of the physical access points on the floor
RF Planning and Deployment
48
Page 49

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
as closely as possible. Doing so enables you to generate a realistic heat map for the
deployed floor plan.
For more information, see View the Heat Map for a Deployed Floor Plan on page 81.
Manage a Building and Floors for an RF Plan
This section describes how you can define a building and floors and make modifications after
you define them.
Defining a floor includes the following main tasks:
• Uploading a custom floor map and setting dimensions (see Add a Building and Floors on
page 49)
• If you do not set dimensions, scaling the floor (see Scale a Floor on page 53)
• Adding WiFi coverage zones and WiFi noncoverage zones (see Add a WiFi Coverage or
WiFi Noncoverage Zone to a Floor on page 54)
• Adding WiFi building obstacles (see Add a WiFi Building Obstacle to a Floor on page 56)
• Adding WiFi obstruction areas (see Add a WiFi Obstruction Area on page 58)
Add a Building and Floors
The wireless controller includes a default building and default floor with a default floor map.
You cannot remove the default building or default floor but you can replace the default floor
map with a custom floor map.
To add and define a building and floors:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Planning.
’s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
RF Planning and Deployment
49
Page 50

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
5. To add a building, in the building tree on the left, click the Add Building icon.
The Add Building pop-screen displays.
6. Enter a name for the building and click the Confirm button.
7. In the building tree, click the + icon of the building that you added.
The Floor-1 name displays. This default floor name was added automatically when you
added the building.
8. Click Floor-1.
The default floor map displays. This default floor map was added automatically when you
added the building.
9. T
o add a custom floor map, click the Add Floor
icon.
RF Planning and Deployment
50
Page 51

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
10. Define the floor:
a. Enter a name for the floor.
b. Upload a custom floor map by clicking the Browse button, following the directions of
your browser to navigate to a floor map, and selecting the floor map.
Y
ou can upload a plan in .png, .jpg, or .gif format.
c. T
o either specify the floor width or the floor length, do the following:
• T o specify the floor width, click the Width(X) button, select Meter or
menu, and enter the floor width.
• To specify the floor length, click the Length(Y) button, select Meter or Feet from
the menu, and enter the floor length.
Note: If you do not want to enter the length or width or the information is not
available, you can scale the floor later (see
Scale a Floor on page 53).
d. Click the Confirm button.
The floor map is uploaded and displays onscreen.
11. Click the Save
icon.
The changes are saved.
12. To add another floor and floor map, repeat Step 9 through Step 11.
Add a Single Floor to a Building
You can add a single floor to an existing building.
Feet
from the
To add a single floor to a building:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
address.
RF Planning and Deployment
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
51
Page 52

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Planning.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the name of the building to which you are adding a floor
6. Click the Add Floor
icon.
7. Define the floor:
a. Enter a name for the floor.
b. Upload a custom floor map by clicking the Browse button, following the directions of
your browser to navigate to a floor map, and selecting the floor map.
.
Y
ou can upload a plan in .png, .jpg, or .gif format.
c. T
o either specify the floor width or the floor length, do the following:
• T o specify the floor width, click the Width(X) button, select Meter or Feet from the
menu, and enter the floor width.
• To specify the floor length, click the Length(Y) button, select Meter
or Feet from
the menu, and enter the floor length.
Note: If you do not want to enter the length or width or the information is not
available, you can scale the floor later (see Scale a Floor on page 53).
RF Planning and Deployment
52
Page 53

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
d. Click the Confirm button.
The floor map is uploaded and displays onscreen.
8. Click the Save
icon.
The changes are saved.
Scale a Floor
If you did not specify the floor width or floor length while adding a new floor (see Add a
Building and Floors on page 49 or Add a Single Floor to a Building on page 51), you can do
so by scaling the floor. You must know the distance in meters or feet between two known
points on the floor.
To scale a floor:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Planning.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the + icon of the building that contains the floor
.
The floor names display.
6. Click the floor name.
The floor map displays.
7. Click the
Scale
icon.
8. Select a line between two points on the map by anchoring the line at one point and releasing
the line at the other point.
The points do not need to cover the entire length or width of the floor.
The Scale Map pop-up screen displays.
9. Select Meter or Feet from the menu and enter the distance between the two points.
10. Click the Confirm button.
RF Planning and Deployment
53
Page 54

The floor map is scaled.
ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
11. Click the Save
icon.
The changes are saved.
Add a WiFi Coverage or WiFi Noncoverage Zone to a Floor
A WiFi coverage zone on a floor is an area in which access points must provide WiFi
coverage. A WiFi noncoverage zone on a floor is an area in which access points do not need
to provide WiFi coverage, for example, a storage area.
Note: Before you add a WiFi coverage or WiFi noncoverage zone, first define
the floor dimensions (see Add a Single Floor to a Building on page 51)
or scale the floor (see Scale a Floor on page 53).
To add a WiFi coverage or WiFi noncoverage zone to a floor:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Planning.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the + icon of the building that contains the floor
.
The floor names display.
6. Click the floor name.
The floor map displays.
7. Click the Zone
icon.
8. Click either the Coverage Zone icon or the Non-AP Zone icon.
9. Anchor a rectangle at one point on the floor map and define the WiFi coverage zone or the
zone in which you do not need WiFi coverage.
10. T
o remove the zone, click the Undo link, and repeat Step 7 though Step 9.
11. Click the Save
icon.
RF Planning and Deployment
54
Page 55

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
The changes are saved.
12. To add another zone, repeat Step 7 though Step 11.
Remove a WiFi Coverage or WiFi Noncoverage Zone from a Floor
After you add and save a WiFi coverage or noncoverage zone on a floor, you can remove it
from the floor.
To remove a WiFi coverage area or WiFi noncoverage zone from a floor:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Planning.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the + icon of the building that contains the floor
The floor names display.
6. Click the floor name.
The floor map displays.
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
.
7. Click the
8. Click the zone on the map.
9. Click the Delete link.
10. Click the Save
The changes are saved.
11. To remove another zone, repeat Step 7 though Step 10.
Zone
icon.
icon.
RF Planning and Deployment
55
Page 56

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Add a WiFi Building Obstacle to a Floor
WiFi building obstacles can be any of the following predefined obstacles with their predefined
attenuation factor (WiFi signal loss) in dB or a custom defined building obstacle:
• Dry wall (4 dB)
• Wood wall (4 dB)
• Plastic wall (4 dB)
• Glass wall (8 dB)
• Brick wall (8 dB)
• Concrete wall (12 dB)
• Light door (4 dB)
• Metal door (1
• Heavy door (15 dB)
• Thin window (2 dB)
• Thick window 4 dB)
1 dB)
These obstacles contribute to the WLAN signal degradation based on their construction
materials and interferences.
Note: Before you add a building obstacle, first define the floor dimensions (see
Add a Single Floor to a Building on page 51
) or scale the floor (see Scale
a Floor on page 53).
To add a WiFi building obstacle to a floor:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser
’s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Planning.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the + icon of the building that contains the floor
The floor names display
.
6. Click the floor name.
RF Planning and Deployment
56
.
Page 57

The floor map displays.
ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
7. Click the Obstacle
icon.
8. Take one of the following actions:
• Select the icon for one of the predefined obstacles.
• Define a custom obstacle:
a. Click the Add Obstacle Type
Add New Obstacle Type pop-screen displays.
The
link.
b. Enter a name.
c. Enter the attenuation factor in dB.
d. Select a color
e. Click the Confirm
f. Click the Obstacle
.
button.
icon.
g. Select the icon for the custom obstacle that you just added.
9. Select a line between two points on the map by anchoring the line at one point and releasing
the line at the other point.
10. T
o remove the obstacle, click the Undo link, and repeat Step 7 though
11. Click the Save
icon.
Step 9.
The changes are saved.
12. To add another obstacle repeat Step 7 though Step 11.
Remove a Building Obstacle from a Floor
After you add and save a WiFi building obstacle on a floor, you can remove it from the floor.
To remove a WiFi building obstacle from a floor:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Planning.
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
The screen displays the Planning icons.
RF Planning and Deployment
57
Page 58

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
5. In the building tree on the left, click the + icon of the building that contains the floor.
The floor names display.
6. Click the floor name.
The floor map displays.
7. Click the Obstacle
icon.
8. Click the obstacle on the map.
9. Click the Delete link.
10. Click the Save
icon.
The changes are saved.
11. To remove another obstacle, repeat Step 7 though Step 10.
Add a WiFi Obstruction Area
WiFi obstructions areas can be any of the following predefined areas:
• Cubicle office area
• Closed office area
• Elevator shaft
• W
arehouse stock with low density
• Warehouse stock with medium density
• Warehouse stock with high density
These areas contribute to the WLAN signal degradation based on openness (or lack thereof)
and interferences.
Note: Before you add a WiFi obstruction area, first define the floor dimensions
(see Add a Single Floor to a Building
Scale a Floor on page 53).
To add a WiFi obstruction area to a floor:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
RF Planning and Deployment
on page 51
58
) or scale the floor (see
Page 59

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Planning.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the + icon of the building that contains the floor.
The floor names display.
6. Click the floor name.
The floor map displays.
7. Click the Area
icon.
8. Anchor a rectangle at one point on the floor map and define the WiFi obstruction area.
9. T
o remove the area, click the Undo link, and repeat Step 7 and Step 8.
10. Click the Save
icon.
The changes are saved.
11. To add another area, repeat Step 7 though Step 10.
Remove a WiFi Obstruction Area
After you add and save a WiFi obstruction area on a floor, you can remove it from the floor.
To remove a WiFi obstruction area from a floor:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Planning.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the + icon of the building that contains the floor
The floor names display.
6. Click the floor name.
The floor map displays.
RF Planning and Deployment
59
.
Page 60

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
7. Click the Area icon.
8. Click the area on the map.
9. Click the Delete link.
10. Click the Save
icon.
The changes are saved.
11. To remove another area, repeat Step 7 though Step 10.
Change the Name, Map, or Dimensions of a Floor
You can change the basic properties of a floor, including those for the default floor.
To change the name, map, or dimensions of a floor:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
4. Select Plans > Planning.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the + icon of the building that contains the floor
.
The floor names display.
6. Click the floor name.
The floor map displays.
7. Click the Edit
icon.
The floor plan information displays in a pop-up screen.
8. Change the name or dimensions of the floor, upload another floor map, or perform a
combination of these actions.
For more information about the floor settings, see Add a Single Floor to a Building
page 51.
9. Click the Confirm button.
The changes are saved.
RF Planning and Deployment
on
60
Page 61

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Change the Name of a Building
You can change only the name of a building, including the name of the default building. All
other building properties are defined through the floors and the floor plans.
To change the name of a building:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Planning.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the building name.
6. Click the Edit
A pop-up screen displays.
7. Change the name.
8. Click the Confirm button.
icon.
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
The changes are saved.
Duplicate an Entire Building with All Floors
You can duplicate an entire building with all floors and floor plans, including all floor
definitions. For information about duplicating a single floor in a building, see Duplicate a
Single Floor on page 62.
To duplicate an entire building with all floors:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
RF Planning and Deployment
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
61
Page 62

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Layout.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the building name.
6. Click the Duplicate
icon.
A pop-up screen displays.
7. Enter a name for the new building.
8. Click the Confirm button.
The new building and floor or floors are added in the building tree.
Duplicate a Single Floor
You can duplicate a single floor and floor plan, including the floor definition. For information
about duplicating an entire building with all floors, see Duplicate an Entire Building with All
Floors on page 61.
To duplicate a single floor:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Layout.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the + icon of the building that contains the floor
The floor names display.
6. Click the floor name.
RF Planning and Deployment
62
.
Page 63

The floor map displays.
ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
7. Click the Duplicate
icon.
A pop-up screen displays.
8. Specify a name for the floor and select a building:
a. Enter a name for the new floor
.
b. From the Workspace tree, select the building to which you want to add the new floor.
c. Click the
Confirm button.
The new floor is added to the building.
Remove a Single Floor
You can remove a single floor from a building. However, you cannot remove the default floor
of the default building.
To remove a single floor:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Layout.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the + icon of the building that contains the floor
The floor names display.
6. Click the floor name.
The floor map displays.
7. Click the
T
rashcan icon.
8. Confirm the removal.
The floor is removed.
.
RF Planning and Deployment
63
Page 64

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Remove an Entire Building with All Its Floors
You can remove an entire building with all its floors. However, you cannot remove the default
building.
To remove an entire building:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Layout.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the building name.
6. Click the T
7. Confirm the removal.
The building with all its floors is removed.
rashcan
icon.
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
Use the WiFi Auto Planning Advisor to Generate an RF Plan for a Floor
After you define a building and floors (see Manage a Building and Floors for an RF Plan on
page 49), you can run the WiFi auto planning advisor for a floor. This tool calculates the
number of access points and, optionally, antennas that you might need to provide WiFi
coverage for your environment and suggests the best locations on the floor for these access
points and antennas.
The WiFi auto planning advisor bases its calculations on the building and floor definitions and
lets you enter the following parameters to determine the WiFi coverage for your environment:
• NETGEAR access point (see Supported NETGEAR Access Points on page 18)
• NETGEAR antenna (see Supported NETGEAR Antennas on page 21)
• For each WiFi band of a selected access point, the following parameters:
- 802.1
- Transmit power (from minimum power to full power)
1 protocol (depending on the access point, 802.11b/g/n, 802.11a/n, or both)
RF Planning and Deployment
64
Page 65

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Note: The antenna gain and maximum number of supported clients for a
selected access point are set automatically.
• Percentage of expected WiFi coverage (from 10 percent to 100 percent)
• The minimum required signal strength (from –95 dBm to –30 dBm)
The signal strength determines the automatic channel allocation and automatic
transmission power of the access points.
• The WiFi band (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz)
• The maximum number of clients that must be supported on the floor
For you to determine the expected financial investment, the WiFi auto planning advisor also
lets you enter a price for the selected access point and a price for the selected antenna.
Whether or not you enter a price, the WiFi auto planning advisor generates an inventory list.
For more information, see Display or Change the WiFi Inventory for an RF Plan on page 77.
The WiFi auto planning advisor creates a heat map for the 2.4 GHz band, the 5 GHz band, or
for both bands. T
o optimize the WLAN network coverage and throughput for your RF plan,
you can manually fine-tune the placement of access points and antennas on the floor map.
For more information about adding and managing access points and antennas on a floor
map, see the following sections:
• Manually Add and Manage Access Points on a Floor Map for an RF Plan on page 69
• Manually Add and Manage Antennas on a Floor Map for an RF Plan on page 72
WARNING:
For each floor, you can save one floor map only. When you run the
WiFi auto planning advisor for a floor, the advisor removes all
previously placed access points and antennas from the floor map.
To run the WiFi auto planning advisor and generate an RF plan and heat map for a
floor:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
RF Planning and Deployment
65
Page 66

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
4. Select Plans > Planning.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the + icon of the building that contains the floor.
The floor names display.
6. Click the floor name.
The floor map displays.
7. Click the Advisor
icon.
8. Specify the WLAN requirements for the floor as described in the following table.
Setting Description
Select AP and External Antenna for Planning
AP Model Specify the access point that you intend to use for the floor:
1. Click the Browse button.
The access points that the wireless controller supports display in a pop-up screen.
2. Click the access point.
All calculations are performed with the selected access point.
3. Click the Confirm button.
The changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
Price($) As an option, enter the price of the access point.
RF Planning and Deployment
66
Page 67

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Setting Description
2.4G For the 2.4 GHz band, specify the transmission power in dBm for the access point.
From the Transmit Power (dBm) menu, select FULL, HALF(1/2), QUARTER(1/4)
EIGHT(1/8), or MINIMUM(1/16). The default setting is HALF(1/2).
Note: When you select an access point, the AP Protocol, Antenna Gain (dBi), and
Client Support fields are populated automatically.
5G If the selected access point supports the 5 GHz band, specify the transmission power in
dBm for the access point.
From the T
EIGHT(1/8), or MINIMUM(1/16). The default setting is HALF(1/2).
Note: When you select an access point, the AP Protocol, Antenna Gain (dBi), and
Client Support fields are populated automatically.
Antenna Model Specify the antenna that you intend to use for the floor:
1. Click the Browse button.
2. Click the antenna.
3. Click the Confirm button.
ransmit Power (dBm) menu, select FULL, HALF(1/2), QUARTER(1/4)
The antennas that the wireless controller supports for the selected access point
display in a pop-up screen.
All calculations are performed with the selected antenna.
The changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
,
,
Price($) As an option, enter the price of the antenna.
Criteria of Auto-placement
Wi-Fi Coverage
Percentage
Minimum Signal
Strength
Band From the Band menu, select 2.4G or 5G.
Maximum Clients
Supported
Move the slider to the required WiFi coverage. The minimum coverage is 10 percent;
The maximum coverage is 100 percent.
Move the slider to the minimum required signal strength. The maximum signal quality is
–30 percent; The minimum signal quality is –95 percent.
If the selected access point does not support the 5 GHz band, the menu selection is
automatically set to 2.4G.
Enter the total number of clients that must be supported simultaneously on the floor.
9. Click the Start Calculation button.
The WiFi auto planning advisor starts its calculations, displays the progress in a pop-up
screen, and generates a heat map.
RF Planning and Deployment
67
Page 68

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Signal strength at
this location
The WiFi auto planning advisor generates a heat map that suggests the required number
of access points (15 in the figure) and the locations on the floor map to achieve the
optimum WiFi coverage that is based on the WLAN requirements that you specified (see
Step 8).
10. T o see the signal strength at a location on the floor map, point to the location (-44dBm at the
location in the figure).
o switch the heat map to the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz band, on the right, click the Band
1. T
1
icon.
The Band icon displays 2.4G if the heat map for the 2.4 GHz band is shown. The Band
icon displays
5G if the heat map for the 5 GHz band is shown.
12. To move an access point to another location on the floor map, drag the access point to a
location on the floor map.
Note: Moving an access point turns off the heat map.
13. To move an antenna to another location on the floor map, drag the antenna to a location on
the floor map.
Note: Moving an antenna turns off the heat map.
14. T
o regenerate the heat map, on the right, click the HeatMap
icon.
The heat map is generated and displays. Use the color information on the right as
guidance for WiFi coverage.
15. To show the map with or without grid, on the right side, click the Grid
RF Planning and Deployment
68
icon.
Page 69

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
16. To show the access points by model or without a label, on the right side, click the Label
icon and select your preference.
By default, the access point name is shown. Because this section describes an RF plan
that is not yet deployed, the IP address and channel cannot be displayed on the map.
17. To save the floor map with its new configuration, click the Save
The settings are saved.
icon.
Manually Add and Manage Access Points on a Floor Map for an RF Plan
You can add individual access points to a floor map for an RF plan. These access points do
not need to be of the same model. After adding access points, you can change their
properties, move them to another location on the floor map, or remove them from the floor
map.
Note: Before you add any access points to a floor plan, first define the floor
dimensions (see Add a Single Floor to a Building on page 51) or scale
the floor (see Scale a Floor on page 53) and define the WiFi coverage
zone (see Add a WiFi Coverage or WiFi Noncoverage Zone to a Floor
on page 54).
To manually add and manage individual access points on a floor map for an RF plan:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Planning.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the + icon of the building that contains the floor
The floor names display.
RF Planning and Deployment
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
.
69
Page 70

6. Click the floor name.
The floor map displays.
ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
7. Click the AP
icon.
8. Specify the access point settings as described in the following table.
Setting Description
AP name Enter a name for the access point.
By default, the access points are numbered, for example, AP-16.
AP Model Specify the access point that you intend to use for the floor:
1. Click the Browse button.
The access points that the wireless controller supports display in a pop-up screen.
2. Click the access point.
All calculations are performed with the selected access point.
3. Click the Confirm button.
The changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
Price($) As an option, enter the price of the access point.
IP Address As an option, enter the IP address of the access point.
AP Type When you select an access point, this field is populated automatically.
Description As an option, enter a description for the access point.
RF Planning and Deployment
70
Page 71

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Setting Description
2.4G Specify the settings for the 2.4 GHz band:
• Enable. By default, the On radio button is selected and the 2.4 GHz band is
enabled. T
• Channel. Leave the default selection Auto to enable the access point to select a
channel automatically
• Protocol. When you select an access point, this field is populated automatically
• Transmission Power (dBm). From the menu, select FULL, HALF(1/2)
QUARTER(1/4), EIGHT(1/8), or MINIMUM(1/16). The default setting is HALF(1/2).
• Antenna Gain (dBi). When you select an access point, this field is populated
automatically
5G If the selected access point supports the 5 GHz band, specify the settings for the 5 GHz
band:
• Enable
T
o disable the 5 GHz band, select the Off
• Channel. Leave the default selection Auto to enable the access point to select a
channel automatically
• Protocol. When you select an access point, this field is populated automatically
• Transmission Power (dBm). From the menu, select FULL, HALF(1/2)
QUARTER(1/4), EIGHT(1/8), or MINIMUM(1/16). The default setting is HALF(1/2).
• Antenna Gain (dBi). When you select an access point, this field is populated
automatically.
o disable the 2.4 GHz band, select the Off radio button.
, or select a specific channel from the menu.
,
.
. By default, the On radio button is selected and the 5 GHz band is enabled.
radio button.
, or select a specific channel from the menu.
,
.
.
9. Click the Confirm button.
The changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
The new access point is placed at the top of the floor map.
10. Move the access point to the desired location on the floor map by dragging the access point
to a location on the floor map.
11. T
o change the properties for an access point, do the following:
a. Double-click the access point.
A pop-up menu displays.
b. From the pop-menu, select Edit Properties.
The Edit AP pop-up screen displays. This screen is identical to the Add AP pop-up
screen.
c. Change the properties.
For information about the properties, see the previous table.
d. Click the Confirm button.
The changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
12. T
o remove an existing access point from the floor map, do the following:
a. Click the access point to select it.
b. Click the
Delete link.
RF Planning and Deployment
71
Page 72

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
13. To add another access point to the floor map, change the properties for another access
point, move another access point on the floor map, remove another access point from the
floor map, or perform a combination of these tasks, repeat Step 7 through Step 12.
o turn the heat map on or off, on the right, click the HeatMap
14. T
If you turn on the heat map, the heat map is generated and displays. Use the color
information on the right as guidance for WiFi coverage.
Note: Adding or removing access points changes the heat map.
15. T
o switch the heat map to the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz band, on the right, click the Band
The Band icon displays 2.4G if the heat map for the 2.4 GHz band is shown. The Band
icon displays 5G if the heat map for the 5 GHz band is shown.
16. To show the map with or without grid, on the right side, click the Grid
17. To show the access points by model or without a label, on the right side, click the Label
icon and select your preference.
By default, the access point name is shown. Because this section describes an RF plan
that is not yet deployed, the IP address and channel cannot be displayed on the map.
18. To save the floor map with its new configuration, click the Save
The settings are saved.
icon.
icon.
icon.
icon.
Manually Add and Manage Antennas on a Floor Map for an RF Plan
You can add individual antennas to a floor map for an RF plan. These antennas do not need
to be of the same model. After adding antennas, you can change their properties, move them
to another location on the floor map, or remove them from the floor map.
Note: Antennas are associated with access points. Therefore, before you
add antennas to a floor plan, first add access points to the floor plan.
For more information about adding access points to a floor plan, see
Use the WiFi Auto Planning Advisor to Generate an RF Plan for a
Floor on page 64 and Manually Add and Manage Access Points on a
Floor Map for an RF Plan on page 69.
To manually add and manage individual antennas on a floor map for an RF plan:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
RF Planning and Deployment
72
Page 73

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Planning.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the + icon of the building that contains the floor
The floor names display.
6. Click the floor name.
The floor map displays.
7. Click an access point to select it.
8. Click the Antenna
Note: The Antenna
icon.
icon is masked if you do not select an access point.
.
RF Planning and Deployment
73
Page 74

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
9. Specify the antenna settings as described in the following table.
Setting Description
Name Enter a name for the antenna.
By default, the access points are numbered, for example, Antenna-1.
Model Specify the antenna that you intend to use for the floor:
1. Click the Browse button.
The antennas that the wireless controller supports display in a pop-up screen.
2. Click the antenna.
All calculations are performed with the selected antenna.
3. Click the Confirm button.
The changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
AP Type When you select an antenna, this field is populated automatically.
Angle When you add a directional antenna, by default, the antenna points to the north. You
can set the antenna direction to a desired angle.
Specify the antenna angle:
1. Click the Browse button.
A degree clock displays in a pop-up screen.
2. Click the degree at which you want to direct the antenna.
The yellow needle moves to the selected degree.
3. Click the Confirm button.
The changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
Price($) As an option, enter the price of the antenna.
Description As an option, enter a description for the access point.
2.4G Specify the settings for the 2.4 GHz band:
• Enable. By default, the On radio button is selected and the 2.4 GHz band is
enabled for the antenna.
Off
radio button.
• Antenna Gain (dBi). When you select an antenna, this field is populated
automatically
• Antenna Pattern. When you select an antenna, this field is populated
automatically
.
.
To disable the 2.4 GHz band for the antenna, select the
10. Click the Confirm button.
The changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
The new antenna is placed at the edge of the floor map and shows a connection with the
access point.
11. To move an antenna to another location on the floor map, drag the antenna to a location on
the floor map.
Note: Moving an antenna turns off the heat map.
RF Planning and Deployment
74
Page 75

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
12. To change the properties for an antenna, do the following:
a. Double-click the antenna.
A pop-up menu displays.
b. From the pop-menu, select Edit Properties.
The Edit Antenna pop-up screen displays. This screen is identical to the Add Antenna
pop-up screen.
c. Change the properties.
For information about the properties, see the previous table.
d. Click the Confirm button.
The changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
13. T
o remove an existing antenna from the floor map, do the following:
a. Click the antenna to select it.
b. Click the Delete
14. T
o add another antenna to the floor map, change the properties for another antenna, move
another antenna on the floor map, remove another antenna from the floor map, or perform a
combinations of these tasks, repeat Step 7 through Step 13
link.
.
o turn the heat map on or off, on the right, click the HeatMap
15. T
If you turn on the heat map, the heat map is generated and displays. Use the color
information on the right as guidance for WiFi coverage.
Note: Adding or removing antennas changes the heat map.
16. T
o switch the heat map to the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz band, on the right, click the Band
The Band icon displays 2.4G if the heat map for the 2.4 GHz band is shown. The Band
icon displays 5G if the heat map for the 5 GHz band is shown.
17. To show the map with or without grid, on the right side, click the Grid
18. To show the antennas by model or without a label, on the right side, click the Label
and select your preference.
By default, the antenna name is shown. The IP address and channel do not apply to an
antenna.
19. To save the floor map with its new configuration, click the Save
The settings are saved.
icon.
icon.
icon.
icon
icon.
Display and Recalculate the WiFi Coverage for a Heat Map
After you set up an RF plan and generate a heat map for a floor, you can display the WiFi
coverage and view how the WiFi coverage changes if you change the minimum signal
strength with the same number of access points and antennas.
RF Planning and Deployment
75
Page 76

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
However, the WiFi coverage tool is for display and information only. To change the actual
minimum signal strength for an RF plan, you must run the WiFi auto planning advisor again
(see Use the WiFi Auto Planning Advisor to Generate an RF Plan for a Floor on page 64).
The default minimum signal strength is –62 dBm. The WiFi coverage percentage is
calculated based on this value. You can change this value and recalculate the coverage
percentage.
To display and recalculate the WiFi coverage for an existing heat map:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Planning.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the + icon of the building that contains the floor
The floor names display.
6. Click the floor name.
The floor map displays.
.
7. On the right, click the
HeatMap
icon.
The heat map for the 2.4 GHz band is generated and displays. Use the color information
on the right as guidance for WiFi coverage.
8. To generate the heat map for the 5 GHz band, on the right, click the Band
icon.
The heat map for the 5 GHz band is generated and displays. Use the color information on
the right as guidance for WiFi coverage.
9. Click the Coverage
Note: The Coverage
icon.
icon is masked if you did not generate a heat map.
RF Planning and Deployment
76
Page 77

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
The Total Number of AP and Total Number of Antenna fields are based on the RF plan
and fixed. The Wi-Fi Coverage Percentage (%) field displays the WiFi coverage based
on the position of the Minimum Signal Strength slider at –62dBm.
10. Move the position of the Minimum Signal Strength slider to another dBm value.
11. Click the Re-Calculate button.
The W
dBm value.
12. Click the OK button.
The pop-up screen closes.
If you want to change the actual minimum signal strength for an RF plan, run the WiFi
auto planning advisor again (see Use the W
Plan for a Floor on page 64).
i-Fi Coverage Percentage (%) field displays the WiFi coverage based on the new
iFi Auto Planning Advisor to Generate an RF
Display or Change the WiFi Inventory for an RF Plan
The inventory for an RF plan of a floor displays all access points and antennas that you
added by running the WiFi auto planning advisor, the access points and antennas that you
added manually, or a combination of both.
To display or change the access point and antenna inventory for an RF plan:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
RF Planning and Deployment
77
Page 78

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
4. Select Plans > Planning.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the + icon of the building that contains the floor.
The floor names display.
6. Click the floor name.
The floor map displays.
7. Click the Inventory
icon.
By default, the AP List tab is selected and the access point inventory displays. The
inventory is based on the access points that you added by running the WiFi auto planning
advisor (see Use the WiFi Auto Planning Advisor to Generate an RF Plan for a Floor on
page 64), the access points that you added manually (see Manually Add and Manage
Access Points on a Floor Map for an RF Plan on page 69), or a combination of both.
o change the properties for an access point in the inventory, do the following:
8. T
a. Select the access point in the inventory table.
b. Click the Edit Properties button.
The Edit
AP pop-up screen displays.
c. Change the properties.
For more information about changing the properties, or for information about
removing an access point from the inventory
, see Manually Add and Manage
Points on a Floor Map for an RF Plan on page 69.
d. Click the Confirm button.
The changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
9. On the Inventory pop-up screen, click the Antenna List tab.
RF Planning and Deployment
78
Access
Page 79

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
The inventory is based on the antennas that you added by running the WiFi auto planning
advisor (see Use the WiFi Auto Planning Advisor to Generate an RF Plan for a Floor on
page 64), the antennas that you added manually (see Manually Add and Manage
Antennas on a Floor Map for an RF Plan on page 72), or a combination of both.
10. To change the properties for an antenna in the inventory, do the following:
a. Select the antenna in the inventory table.
b. Click the Edit Properties button.
The Edit
Antenna pop-up screen displays.
c. Change the properties.
For more information about changing the properties, or for information about
removing an access point from the inventory
Antennas on a Floor Map for an RF Plan
, see Manually Add and Manage
on page 72.
d. Click the Confirm button.
The changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
11. On the Inventory pop-up screen, click the OK button.
The Inventory pop-up screen closes.
12. T
o save the inventory changes, click the Save
icon.
The settings are saved.
RF Planning and Deployment
79
Page 80

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Download a Report for an RF Plan
The report for an RF plan includes the following components:
• Floor summary
• Inventory summary that could serve as a purchase list
• Detailed list of access points
• Detailed list of antennas (if you added any manually)
• Floor map with suggested locations of the access points and antennas
• Heat map for the 2.4 GHz band
• Heat map for the 5 GHz band
You can download the report as a PDF or a Microsoft Word file.
To generate and download a report for an RF plan:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Planning.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the + icon of the building that contains the floor
The floor names display.
6. Click the floor name.
The floor map displays.
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
.
7. Click the PDF
The report downloads.
8. Follow the directions of your browser to save the report.
icon or the Word icon.
RF Planning and Deployment
80
Page 81

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
View the Heat Map for a Deployed Floor Plan
For an RF plan, you can assign access points and antennas to a building and floor. However,
these access points and antennas are used only for the purpose of planning and are not
actual access points and antennas.
Access points display on the floor map of a deployed floor plan only if you assign them to the
building and floor. For information about assigning access point to a building and floor
Assign Access Points to Buildings, Floors, and Advanced Profile Groups on page 169.
A heat map lets you view in real time, by wireless frequency band, the signal strength and
wireless coverage for a floor of a building. The heat map shows the actual signal strengths
that each access point is detecting from neighbor access points.
IMPORTANT:
For the heat map to provide realistic information, you must move
each virtual access point to the virtual location on the floor map
that matches the actual physical location of the physical access
point on the floor as closely as possible.
, see
The heat map displays the following information:
• Signal strength and WiFi coverage, including weak coverage areas and coverage holes,
indicated by color
• Access points that are managed by the wireless controller
• For each access point, the following real-time information:
- Status in relation to the wireless controller (for example, Connected)
- IP address
- MAC address
- For each WiFi band, the number of connected clients
- For each WiFi band, the active channel
- For each WiFi band, the transmission (output) power
• For each antenna, the following information:
T o move the access points and antennas to the correct locations on the floor map and
generate a realistic heat map for a deployed floor plan:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
RF Planning and Deployment
81
Page 82

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Plans > Heat Map.
The screen displays the Planning icons.
5. In the building tree on the left, click the + icon of the building that contains the floor
The floor names display.
6. Click the floor name.
Access points
before placement
.
7. The first time that you view the heat map, move the access points manually on the floor
map to closely match their actual physical locations on the floor by dragging each access
point to the correct location on the floor map.
8. On the right, click the HeatMap
icon.
The heat map for the 2.4 GHz band is generated and displays. Use the color information
on the right as guidance for WiFi coverage.
9. To generate the heat map for the 5 GHz band, on the right, click the Band
icon.
The heat map for the 5 GHz band is generated and displays. Use the color information on
the right as guidance for WiFi coverage.
10. To see the information about an individual access point or antenna, point to the location.
RF Planning and Deployment
82
Page 83

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
A pop-up field displays the information.
.
11. To make adjustments to the WiFi coverage in real time, drag the access points to new
locations on the floor map.
12. To regenerate the heatmap, on the right, click the HeatMap
icon.
The heat map is generated and displays. Use the color information on the right as
guidance for WiFi coverage.
13. If you made changes to the WiFi coverage on the floor map in
Step 11, move each physical
access point to the actual physical location on the floor that matches the virtual location of
the virtual access point on the floor map as closely as possible.
In other words, reverse the process that you accomplished in Step 7 and now make sure
that the actual placement on the floor matches the virtual placement on the floor map.
RF Planning and Deployment
83
Page 84

4. Installation and Configuration
Overview
This chapter includes the following sections:
• Connect Your Computer to the Wireless Controller
• Roadmap for Initial Configuration
• Roadmap for Configuring Management of Your Wireless Network
• Choose a Location for the Wireless Controller
• Deploy the Wireless Controller
4
84
Page 85

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Connect Your Computer to the Wireless Controller
To connect to the wireless controller for initial configuration, follow the steps in this section.
You can also access the ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500 Installation Guide that you can
download from http://support.netgear.com/product/WC9500.
To connect your computer to the wireless controller:
1. Configure the computer with a static IP address of 192.168.0.210 and 255.255.255.0 as
the subnet mask.
2. Connect the wireless controller to the computer through the network or directly to the
wireless controller’
3. Connect the power cord from the wireless controller to an AC power outlet.
4. Verify that the following LEDs on the front panel are lit:
LED Description
Power The green Power LED is lit. If the Power LED is not lit, check the connections and check to see
if the power outlet is controlled by a wall switch that is turned off.
s Ethernet port.
Status The Status LED is lit yellow while the wireless controller is initializing. After approximately two
minutes, when the wireless controller completes its initialization, the Status LED turns green.
Fan The green Fan LED is lit, indicating that the fans are functioning correctly
Ethernet The right Ethernet port LED is lit green for a 1000 Mbps connection or yellow for a 100 Mbps or
10 Mbps connection. If it is not, make sure that the Ethernet cable is securely attached at both
ends.
.
Log In to the Wireless Controller
Before you log in to the wireless controller, make sure that you follow the steps in Connect
Your Computer to the Wireless Controller on page 85.
To log in to the wireless controller, you must use a web browser such as Microsoft Internet
Explorer 9 or 10, or the latest Mozilla Firefox version, or Google Chrome 24 or later with
JavaScript, cookies, and SSL enabled.
To log in to the wireless controller:
1. Open your browser and type http://192.168.0.250 in the browser ’s address field.
Installation and Configuration Overview
85
Page 86

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
The wireless controller’s login screen displays:
2. When prompted, enter admin for the user name and password for the password, both in
lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen (the path is Monitor > Controller > Summary), which shows the network status
and related information:
For information about the network status and related information, see View the Wireless
Controller Summary Screen on page 306.
Installation and Configuration Overview
86
Page 87

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Roadmap for Initial Configuration
After you connect and log in to the wireless controller, perform the initial configuration. If you
are not sure how you are going to deploy the wireless controller in your network, NETGEAR
recommends that you read Chapter 2, System Planning and Deployment Scenarios.
This section is a roadmap for basic configuration only: It provides high-level configuration
steps with references to the sections or chapters that provide detailed configuration steps.
To perform the initial configuration of the wireless controller:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Configuration > System > General.
The General Settings screen displays.
5. Enter a name for the wireless controller and select the country in which the wireless
controller is used.
6. Click the Apply button.
The changes are saved.
7. Select Configuration > System > T
’s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
ime.
The
Time Setting screen displays.
8. Select the time zone in which the wireless controller is used. Optionally, configure the NTP
settings.
For more information, see
9. Click the Apply button.
The changes are saved.
10. Select Configuration > System > IP/VLAN.
The IP Settings screen displays.
11. Enter the IP settings for your network and the VLANs that you want to assign to the wireless
controller.
Manage the Time Settings on page 94.
Installation and Configuration Overview
87
Page 88

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Note: A management VLAN is used for all SNMP and HTTP traffic to and
from the wireless controller and managed access points.
Note: Clear the Untagged VLAN check box only if the hubs and switches in
your network support the VLAN (802.1Q) standard. Likewise, change
the untagged VLAN value only if the hubs and switches in your network
support the VLAN (802.1Q) standard.
For more information, see Manage the IP, VLAN, and Link Aggregation Settings on
page 95.
12. Click the Apply button.
The changes are saved.
13. If your network does not include a DHCP server
server.
For more information, see Manage the DHCP Server on page 98.
14. Click the Apply button.
The changes are saved.
The connection to the wireless controller is terminated because you changed its IP
address.
15. Reconfigure your computer with an IP address and subnet mask that is in the same
IP subnet as the new IP address of the wireless controller.
16. Log back in to the wireless controller using its new IP address.
Continue with the following section, Roadmap for Configuring Management of Your
Wireless Network.
, configure the wireless controller’s DHCP
Roadmap for Configuring Management of Your Wireless Network
After you perform the initial configuration and change the IP address to an address that is
specific to your network (see Roadmap for Initial Configuration on page 87), you are ready to
configure the wireless controller for management of your wireless network.
This section is a roadmap only: It provides high-level configuration steps with references to
the sections or chapters that provide detailed configuration steps.
To configure the wireless controller for management of your wireless network:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
Installation and Configuration Overview
’s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
88
Page 89

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Register the licenses.
For more information, see Register Your Licenses on page 103.
5. (Optional but recommended) Replace the default certificate with a custom certificate for
certificate-based authentication of the
internal authentication server.
For more information, see Manage Certificates on page 107.
6. (Optional but recommended) Configure logs, alerts, and alarms.
For more information, see Configure Log, Syslog, Alarm Notification, and Email Settings
on page 108.
7. Configure security profiles:
a. Configure the security profiles for the basic profile group or for advanced profile
groups.
For detailed configuration steps, see:
• Manage Security Profiles for the Basic Profile Group on page 119.
• Manage Security Profiles for Advanced Profile Groups on page 124.
b. (Optional) Configure authentication servers.
For more information, see Manage Authentication Servers and Authentication Server
Groups on page 136.
c. (Optional) Configure MAC authentication.
For more information, see Manage MAC Authentication and MAC Authentication
Groups on page 142.
d. (Optional)
Assign the authentication servers and MAC
ACLs to the security profiles.
For more information, see:
• Manage Security Profiles for the Basic Profile Group on page 119.
• Manage Security Profiles for Advanced Profile Groups on page 124.
8. Configure the managed access point list:
a. Run the Discovery Wizard and add access points to the managed list.
For more information, see Discover Access Points with the Discovery Wizard on
page 154.
b. (Optional) Configure access points that are on the managed list.
For more information, see Manage the Managed AP List on page 163.
Installation and Configuration Overview
89
Page 90

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
c. (Optional) Assign access points to advanced profile groups:
For more information, see Assign Access Points to Buildings, Floors, and Advanced
Profile Groups on page 169.
9. (Optional) Configure rogue access point detection.
For more information, see Manage Rogue Access Points on page 213.
10. (Optional) Configure a guest portal or captive portal.
For more information, see Manage Guest Network Access on page 217.
11. (Optional) Configure user accounts and portal accounts.
For more information, see Manage Users, Accounts, and Passwords on page 222.
12. (Optional) Configure wireless and QoS settings.
For more information, see Chapter 8, Configure Wireless and QoS Settings.
13. (Optional but recommended) Back up the configuration.
For more information, see Back Up the Configuration File on page 239.
Choose a Location for the Wireless Controller
The wireless controller is suitable for use in an office environment where it can be
freestanding on its runner feet or mounted into a standard 19-inch equipment rack.
Alternatively , you can rack-mount the wireless controller in a wiring closet or equipment room.
A mounting kit, containing two mounting brackets and screws, is provided in the wireless
controller package.
Consider the following when deciding where to position the wireless controller:
• The unit is accessible and cables can be connected easily.
• Cabling is away from sources of electrical noise. These include lift shafts, microwave
ovens, and air-conditioning units.
• Water or moisture cannot enter the case of the unit.
• Airflow around the unit and through the vents in the side of the case is not restricted.
Provide a minimum of 25 mm or 1 inch of clearance.
• The air is as free of dust as possible.
• T
emperature operating limits are not likely to be exceeded. Install the unit in a clean,
air-conditioned environment. For information about the recommended operating
temperatures for the wireless controller, see
Technical Specifications, and Passwords Requirements.
Appendix A, Factory Default Settings,
Installation and Configuration Overview
90
Page 91

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Deploy the Wireless Controller
After you follow the steps in Roadmap for Initial Configuration on page 87 and Roadmap for
Configuring Management of Your Wireless Network on page 88, you are ready to deploy the
wireless controller in your network.
To deploy the wireless controller:
1. Disconnect the wireless controller from the computer that you used for configuration.
2. (Optional) Reconfigure the computer back to its original
3. Place the wireless controller where you intend to deploy it.
4. Connect an Ethernet cable from the wireless controller to a switch or router on your wired
network.
5. Connect the power cord to the wireless controller and plug the power cord into a power
outlet.
TCP/IP settings.
The Power
Basic Functioning on page 338.
, Status, and Ethernet LEDs light. If any of these do not light, see Troubleshoot
Installation and Configuration Overview
91
Page 92

5. Configure the System and Network
Settings and Register the Licenses
This chapter includes the following sections:
• Configure the General Settings
• Manage the Time Settings
• Manage the IP, VLAN, and Link Aggregation Settings
• Manage the DHCP Server
• Register Your Licenses
• Manage Certificates
• Configure Log, Syslog, Alarm Notification, and Email Settings
5
92
Page 93

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Configure the General Settings
Note: You must select the correct country or region of operation. It might not
be legal to operate the access points in a country or region not shown
here. If your location is not listed, check with your local government
agency or check the NETGEAR website for more information about
which channels to use.
The General Settings screen lets you configure the basic settings of your wireless controller.
To configure general settings:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Configuration > System > General.
The General Settings screen displays:
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
Configure the System and Network Settings and Register the Licenses
93
Page 94

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
5. Configure the settings as described in the following table.
Setting Description
Name Enter a unique value as the wireless controller name. NETGEAR recommends
changing the name as soon as possible after setting up.
The name must contain only alphabetical characters, numbers, and hyphens, and must
be 31 characters or less.
Country/Region From the menu, select the region of operation for the wireless controller and the access
points that the wireless controller manages.
This setting is crucial for optimal performance of the wireless controller. The wireless
controller uses the country code to determine the best wireless settings for the access
points. In the United States, the country is preset and cannot be changed on the access
points. If the country or region is not set up correctly
be able to access the access points.
Note: To enable the wireless controller to transmit at a higher power level than the level
that might be specified for your country or region, select Rest of World from the
Country/Region menu.
, the wireless controller might not
Controller
Location Code
(Optional) Enter a code to identify the physical location of the wireless controller.
If you use more than one wireless controller, a code is especially useful.
6. Click the Apply button.
The changes are saved.
Manage the Time Settings
This screen lets you configure the time-related settings of your wireless controller and
managed access points.
To configure time settings:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Configuration > System > T
Configure the System and Network Settings and Register the Licenses
ime.
94
Page 95

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
The Time Settings screen displays:
5. Configure the settings as described
6. in the following table.
Setting Description
Time Zone From the menu, select the local time zone for your country or region.
Current Time This field is a nonconfigurable field that displays the current time at your
location.
NTP Client Select the Enable radio button to use a Network
synchronize the clock of the wireless controller and managed access points.
Select the Disable
Use Custom NTP Server Select the Use Custom NTP Server check box if you want to use an alternate
NTP server. By default, the NETGEAR NTP server is used.
Hostname/IP Address Enter the host name or IP address of the NTP server, if you are using a custom
NTP server.
radio button if you do not want to use an NTP server
Time Protocol (NTP) server to
7. Click the Apply button.
The changes are saved.
Manage the IP, VLAN, and Link Aggregation Settings
You can manage the IP address, VLAN settings, and link aggregation (LAG) settings of the
wireless controller.
Management VLAN Concepts
.
Management VLANs are used for all SNMP and HTTP traffic to and from the wireless
controller and managed access points.
For large deployments, NETGEAR recommends that the wireless controller and access
points are in separate VLANs to ensure uninterrupted connectivity between the wireless
controller and the access points.
Configure the System and Network Settings and Register the Licenses
95
Page 96

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
The wireless controller and access points share heartbeat messages to keep synchronized
and share configurations and client key data to facilitate seamless roaming.
Untagged VLAN Concepts
When the Untagged VLAN check box is selected on the IP Settings screen, one VLAN can
be configured as an untagged VLAN:
• When the wireless controller sends frames associated with the untagged VLAN to the
LAN (Ethernet) interface, those frames do not carry an 802.1Q VLAN header.
• When the wireless controller receives untagged traffic from the LAN (Ethernet) interface,
those frames are assigned to the untagged VLAN.
If you clear the
(Ethernet) frames, and accepts only incoming frames that are tagged with known VLAN IDs.
Note: Clear the Untagged VLAN check box only if the hubs and switches
Changing either of these values results in a loss of IP connectivity if the hubs and switches on
your network are not configured with the corresponding VLANs.
Untagged VLAN check box, the wireless controller tags all outgoing LAN
on your LAN support the VLAN (802.1Q) standard. Likewise, change
the untagged VLAN value only if the hubs and switches on your LAN
support the VLAN (802.1Q) standard.
Link Aggregation Concepts
If you connect the two 10GE connections of the wireless controller to a switch or router, the
wireless controller supports dynamic link aggregation (802.3ad), which you can use either to
increase bandwidth or to support link redundancy.
You can enable the wireless controller to automatically create a single link aggregation group
(LAG) in which the two links share the same speed and duplex settings. The link selection for
egress traf
fic is based on the transmit hash policy.
You can also configure a standby link in which only one link in the LAG is active. The standby
link becomes active only if the active link fails. In such a situation, a failover occurs from the
failed active link to the standby link, which becomes the new active link.
Configure the IP, VLAN, and Link Aggregation Settings
You can configure the management IP address, VLAN settings, and link aggregation (LAG)
settings of the wireless controller.
To configure IP, VLAN, and LAG settings:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser
address.
Configure the System and Network Settings and Register the Licenses
’s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
96
Page 97

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Configuration > System > IP/VLAN.
The IP Settings screen displays:
5. Configure the settings as described in the following table.
Setting Description
IP Settings section
IP Address Enter the IP address of the wireless controller.
The default IP address is 192.168.0.250. To change it, enter an available IP
address from the address range used on your LAN.
IP Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask value used on your LAN.
The default value is 255.255.255.0.
Default Gateway Enter the IP address of the gateway for your LAN.
Configure the System and Network Settings and Register the Licenses
97
Page 98

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Setting Description
Primary DNS Server Enter the IP address of the primary Domain Name Server (DNS) that you want to
use.
Secondary DNS Server Enter the IP address of the secondary DNS that you want to use.
WINS Server Enter the IP address of the Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) that you want
to use.
Management VLAN Settings section
Management VLAN Enter the management VLAN.
For more information, see Management VLAN Concepts on page 95.
Untagged VLAN Select the Untagged VLAN check box if the configured VLAN is untagged.
For more information, see Untagged VLAN Concepts on page 96.
10G Port Settings section
LAG Select the LAG radio button to enable the wireless controller to automatically
create a LAG in which both links are active.
The LAG radio button and Active Standby radio button are mutually exclusive.
For more information, see Link Aggregation Concepts on page 96.
Active Standby Select the Active Standby radio button to enable the wireless controller to
automatically create a LAG in which only one link is active and the other link
functions as a standby link.
The Active Standby radio button and LAG radio button are mutually exclusive.
For more information, see Link Aggregation Concepts on page 96
.
6. Click the Apply button.
The changes are saved.
Manage the DHCP Server
Note: Make sure that a DHCP server is available; otherwise, the Discovery
Wizard does not function correctly. If your network already includes a
DHCP server, do not enable the DHCP server on the wireless
controller.
The wireless controller can function as a DHCP server. You can add multiple DHCP server
pools for different VLANs. By default, no DHCP server pool is configured on the wireless
controller but you can add one or more DHCP server pools.
Configure the System and Network Settings and Register the Licenses
98
Page 99
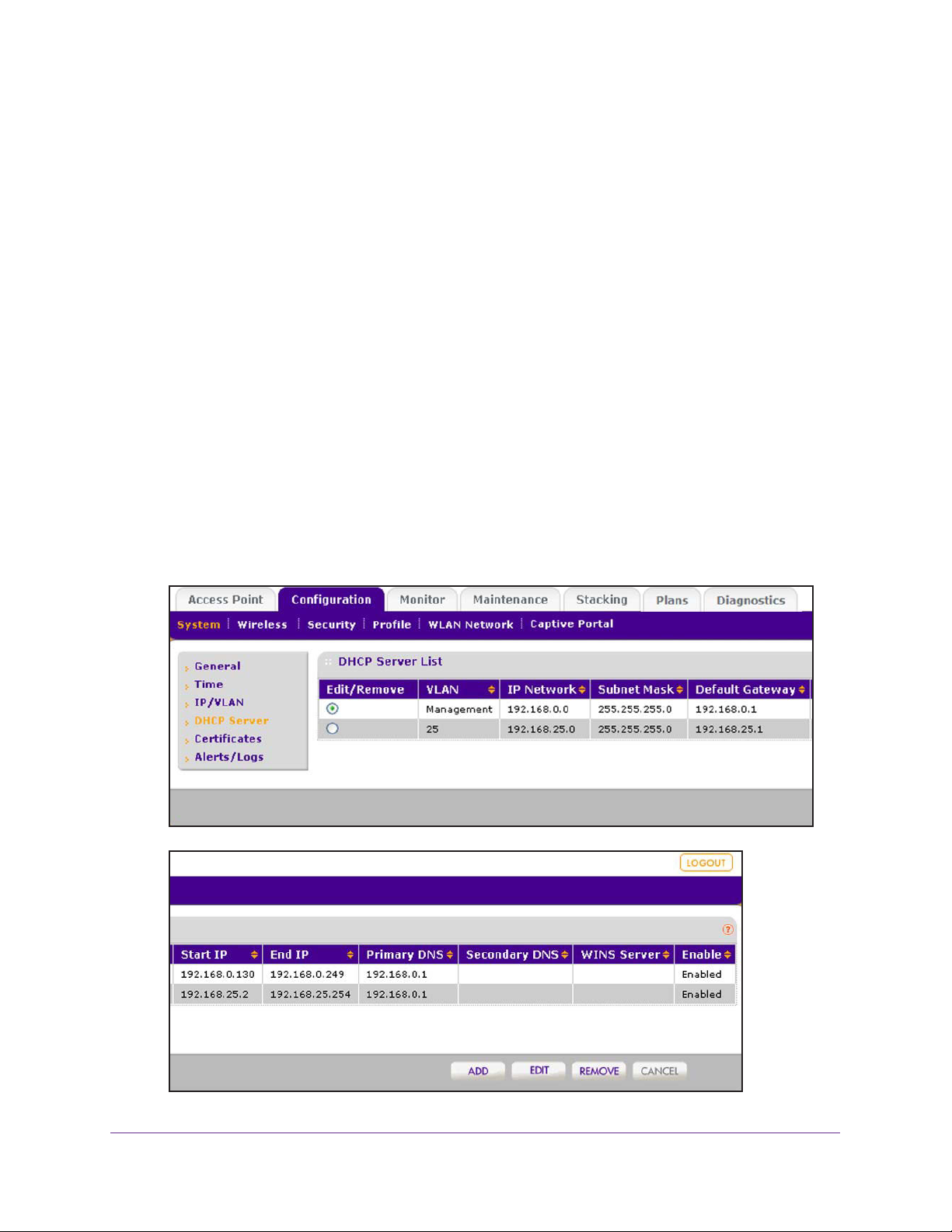
ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
Add a DHCP Server
The DHCP Server List screen lets you add a DHCP server pool.
To add a DHCP server and configure its settings:
1. Open a web browser. In the browser’
s address field, type the wireless controller’s IP
address.
By default, the IP address is 192.168.0.250.
The wireless controller’s login screen displays.
2. Enter your user name and password.
If you did not yet personalize your user name and password, enter admin for the user
name and password for the password, both in lowercase letters.
3. Click the Login button.
The wireless controller’s web management interface opens and displays the Summary
screen.
4. Select Configuration > System > DHCP Server.
The DHCP Server List screen displays. The following figure shows part of the DHCP
Server List screen. Because this screen is wide, it is shown in the following two figures:
Configure the System and Network Settings and Register the Licenses
99
Page 100

ProSAFE Wireless Controller WC9500
The DHCP Server List shows the DHCP servers that are already configured on the
wireless controller.
5. Click the Add button.
The Add DHCP Server pop-up screen displays:
6. Configure the settings as described in the following table.
Setting Description
Enabled Select the Enabled check box to enable the DHCP server.
When the check box is cleared, the DHCP server is disabled.
Use VLAN Interface Select the Use VLAN Interface
with multiple VLANs.
VLAN Enter the DHCP server VLAN ID.
The range is between 1 and 4094. The DHCP server services this VLAN.
IP Network Enter the IP address for the wireless controller in the VLAN that you specified in
the VLAN field.
Note: If you do not select the Use VLAN Interface check box, the IP address
of the wireless controller’s management VLAN is used.
Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask that is assigned to the wireless clients by the DHCP
server
.
Default Gateway Enter the IP address of the default network gateway for all traffic beyond the
local network.
Start IP Enter the start IP address of the range that the DHCP server can assign.
End IP Enter the end IP address of the range that the DHCP server can assign.
check box to allow the DHCP server to function
Configure the System and Network Settings and Register the Licenses
100
 Loading...
Loading...