Netgear GSM7248, FSM7326P, FSM7352S, GSM7352S, FSM7352PS Installation Manual

FSM73xx GSM73xx GMS72xxR – Shared access to the Internet across
Multiple routing VLANs using a Prosafe Firewall
This document describes how to:
- Create multiple routing VLANs
- Obtain Internet access on multiple VLANs using one Internet gateway
The procedure described can apply to most Layer 2 and Layer 3 Switches and VPN Firewall with new
Web Interface (defined as the one with the Menus appearing horizontally on top).
Hardware differences among different models must be taken in consideration.
NOTE:
This document is not intended to illustrate how to perform full Layer3 separation, for which Access
Control Lists (ACLs) should be used.
Table of Contents
VLAN-Definition ................................................................................................................ 2
Notes when setting-up VLANs ....................................................................................... 2
1 - Physical Setup ............................................................................................................ 3
2 - Logical Setup .............................................................................................................. 3
3 - Configuring the Switch management IP address .................................................. 4
4 - Creating a routing VLAN ........................................................................................... 6
5 - Remove ports’ VLAN membership .......................................................................... 8
6 - Enable DHCP and create a DHCP pool per VLAN ............................................. 10
8 – Configuring the switch default route ..................................................................... 14
9 – Configuring static routes on the Internet Default Gateway ............................... 16
10 – Saving the configuration ....................................................................................... 17
GSM7352S
M1 M2 M3 M4
48T46T44T42T
47T45T43T41T
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 33 35 37 39 41T 43T 45T 47T
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 38 40 42T 44T 46T 48T26 28 30 32 34 36
Default IP route : 192.168.2.254
Internet
VLAN4
192.168.4.1/24
VLAN3
192.168.3.1/24
VLAN2
192.168.2.1/24
192.168.2.x/24
DG 192.168.2.254
192.168.3.x/24
DG 192.168.3.1
192.168.4.x/24
DG 192.168.4.1
ProSafe VPN Wireless ADSL Gateway
DGFV338
LOCAL
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
100
Link/ACT
LINK/ACT
100
INTERNET
TEST
MODEL
WLANDSL
PWR
192.168.2.254/24
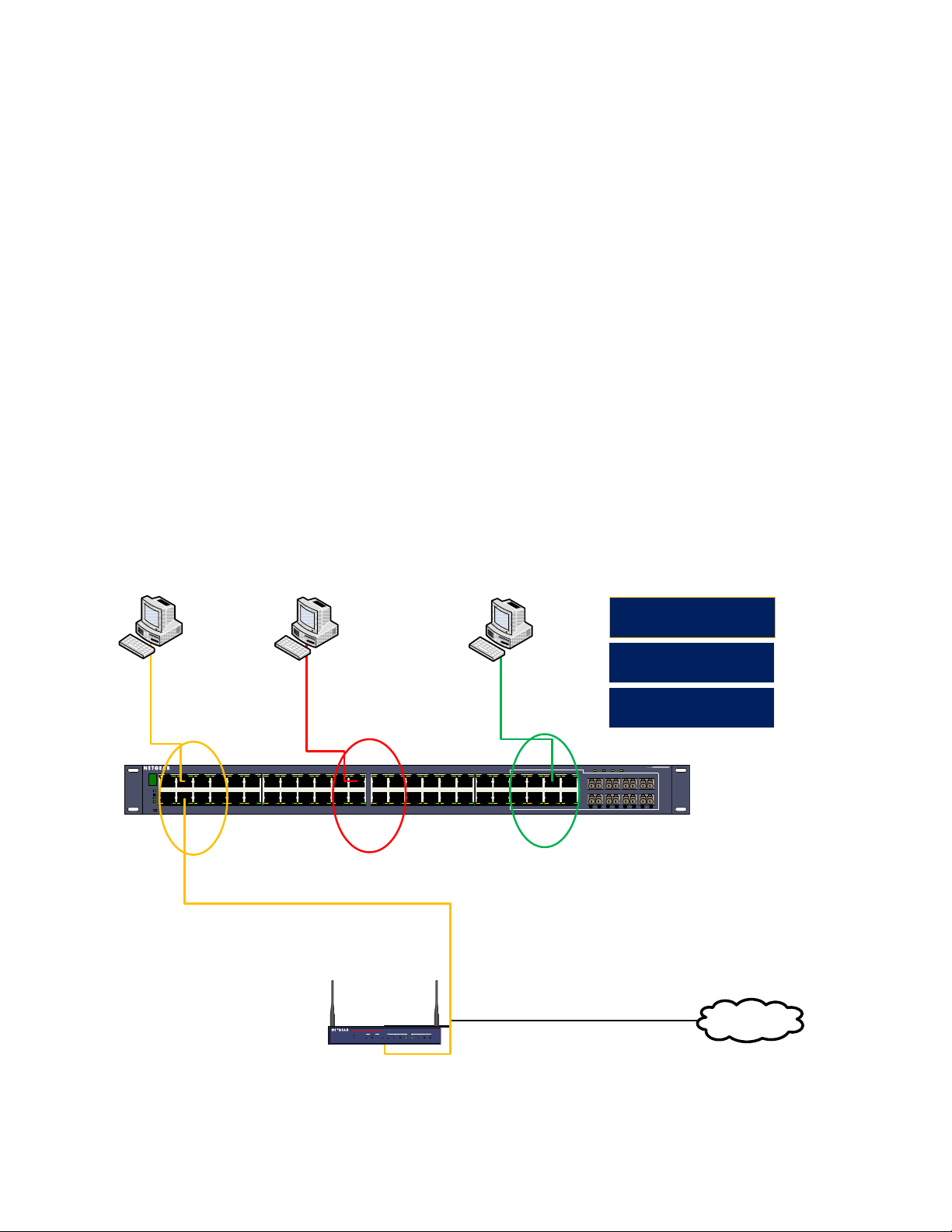
____ VLAN 4: Ports 0/41 – 0/48
PVID = 4
DHCP = 192.168.4.0/24
____ VLAN 3: Ports 0/21 – 0/28
PVID = 3
DHCP = 192.168.3.0/24
____ VLAN 2: Ports 0/1 – 0/8
PVID = 2
DHCP = 192.168.2.0/24
GSM7xxx - Shared access to the Internet across Multiple Routing VLANs using a Prosafe Firewall
DGFV338
Static routes:
192.168,3.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.1
192.168.4.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.1
VLAN-Definition
VLANs are logical subgroups within a Local Area Network (LAN), which combine user stations,
and network devices into a single unit, regardless of the physical LAN segment to which they are
attached. VLANs allow network traffic to flow more efficiently within subgroups. VLANs use
software to reduce the amount of time it takes for network changes, additions, and moves to be
implemented.
Notes when setting-up VLANs
• A VLAN does not have a minimum number of port
• VLANs work at the OSI Layer 2
• A VLAN can be created per unit, device or via logical connection/combination
• Broadcast and Multicast traffic is transmitted only in the VLAN in which traffic is generated.
• To allow traffic between VLAN a device working at protocol level (Layer 3) is required
2

1 - Physical Setup
1x GSM7352S Prosafe Layer3 - Firmware 7.2.1.6
3x Windows XP Computers (1 on each VLAN)
1 x Prosafe Firewall Router DGFV338
2 - Logical Setup
DGFV338:
LAN IP 192.168.2.254/24
DHCP enabled (192.168.2.0/24, DG 192.168.2.1, DNS 192.168.2.254)
Static routes:
GSM7352S:
VLAN1: Management VLAN
VLAN2:
VLAN3:
DHCP enabled (192.168.3.0/24, DG 192.168.3.1, DNS 192.168.2.254)
VLAN4:
IP 192.168.4.1
DHCP enabled (192.168.4.0/24, DG 192.168.4.1, DNS 192.168.2.254)
192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.1
192.168.4.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.1
IP 192.168.1.1
DG 192.168.1.254
DHCP disabled
IP 192.168.2.1
DHCP enabled on DGFV338
(192.168.2.0/24 , DG 192.168.2.1, DNS 192.168.2.254)
IP 192.168.3.1
3

3 - Configuring the Switch management IP address
The Management IP address (by default on VLAN1) can be setup using the CLI (Command Line
Interface).
The CLI should be access via HyperTerminal (or similar applications) using the Console cable
included in the box.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
User: admin
Password:
(FSM7352S) >enable
Password:
(GSM7352S) #
(GSM7352S) #network protocol none
Changing protocol mode will reset ip configuration.
Are you sure you want to continue? (y/n)y
(GSM7352S) #network parms 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.254
(GSM7352S) #show network
IP Address..................................... 192.168.1.1
Subnet Mask.................................... 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway................................ 192.168.1.254
Burned In MAC Address.......................... 00:1F:33:E6:81:A5
Locally Administered MAC Address............... 00:00:00:00:00:00
MAC Address Type............................... Burned In
Network Configuration Protocol Current......... None
Management VLAN ID............................. 1
Web Mode....................................... Enable
Java Mode...................................... Enable
(GSM7352S) #
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4
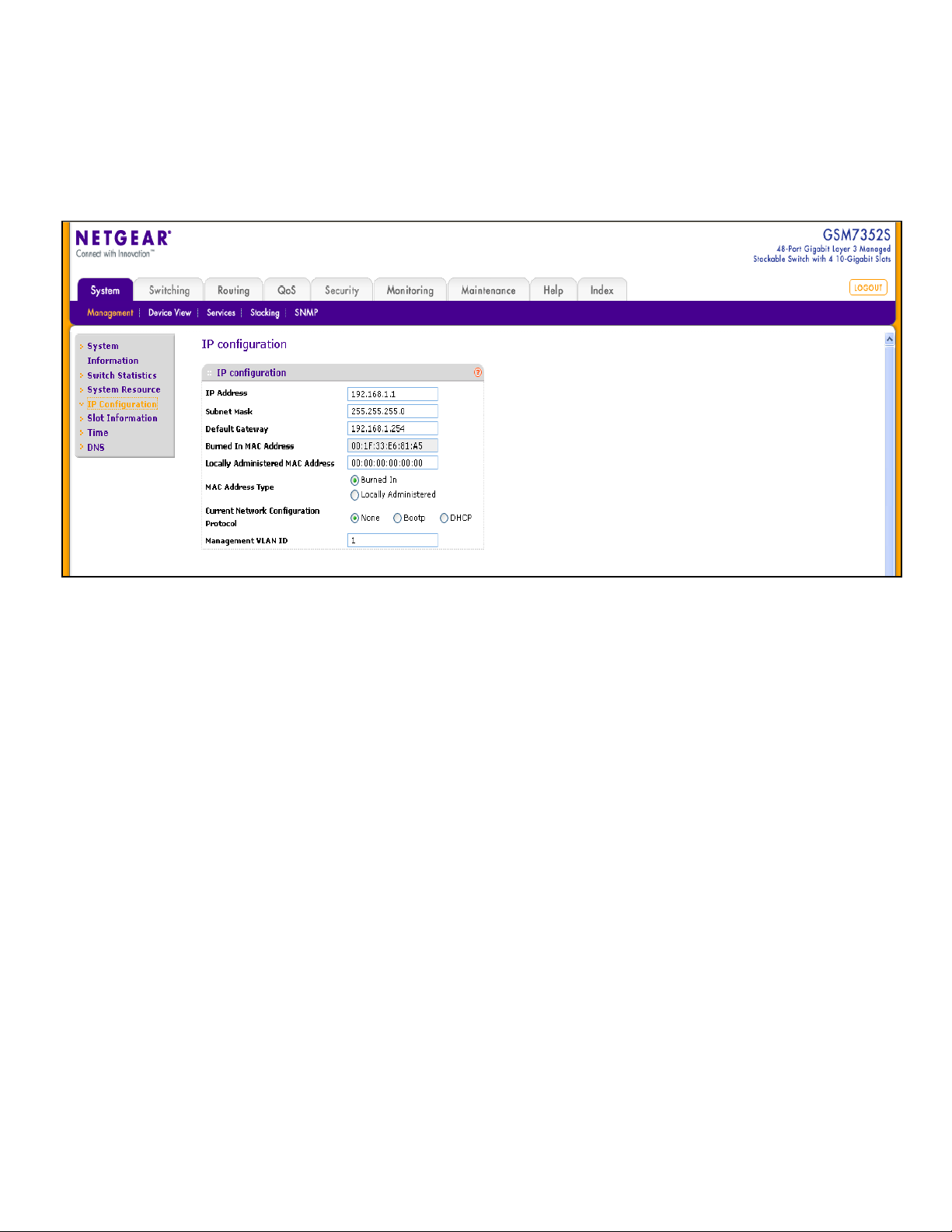
When a Management IP address is configured, the Web Interface of the switch can be accessed.
It will possible to modify the Management IP configuration via System – Management – IP
configuration including the IP address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway and Management VLAN
ID.
5
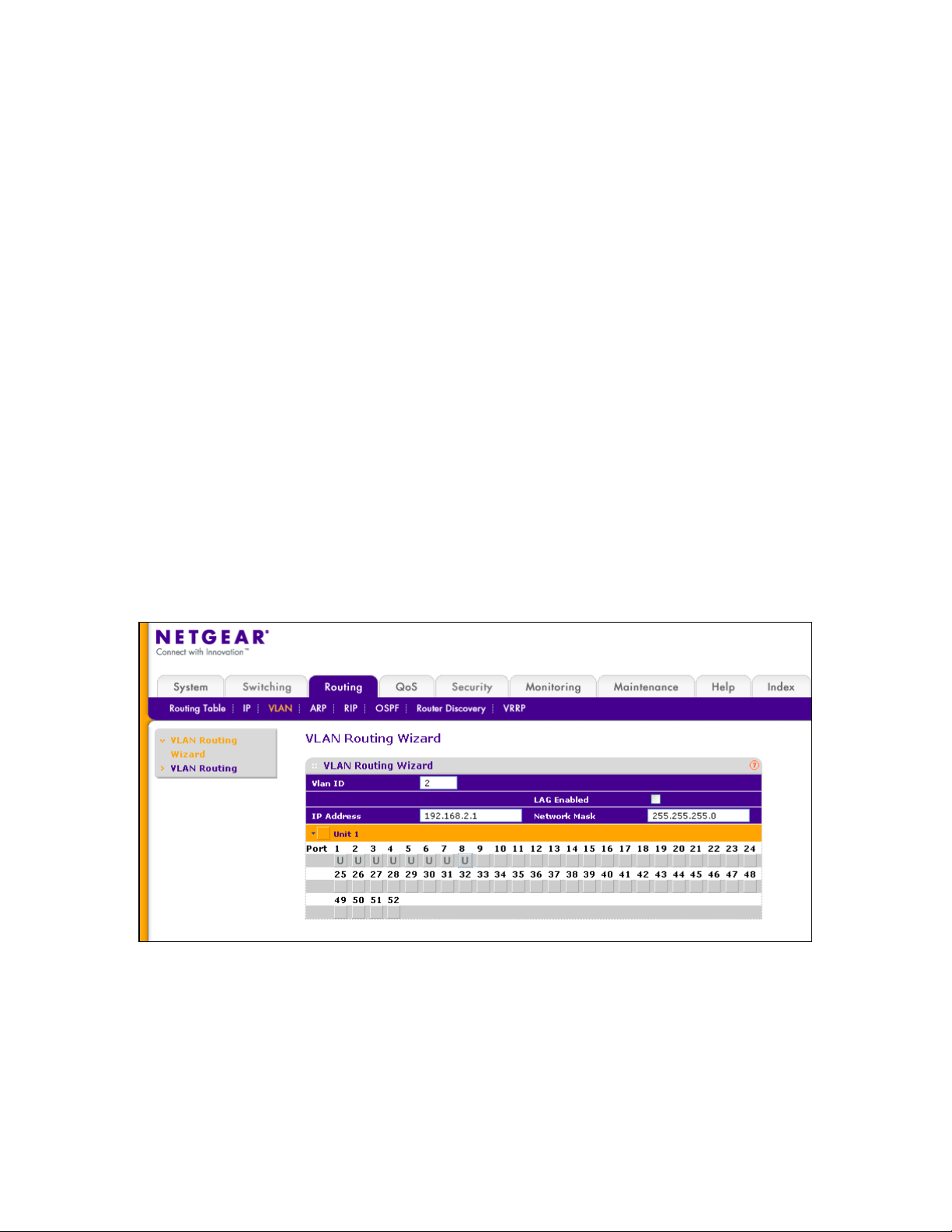
4 - Creating a routing VLAN
To create routing VLANs access the VLAN Routing Wizard via Routing VLAN.
1) Type the VLAN ID (in the example the VLAN ID is 2)
2) Specify the IP address (192.168.2.1) and the subnet mask (255.255.255.0)
3) Expand the Port list by clicking on Unit 1
4) Select the correct option for each port that will be member of the VLAN
Three options are available:
- No membership (no symbol appearing in the gray box underneath the port number)
- Untagged membership (U)
- Tagged membership (T)
In order to browse through the options just continuously click on the gray box until the correct
one is set. For this scenario we will be using the U (Untagged) option on all the ports.
5) Apply the changes
6
 Loading...
Loading...