
MC14LC5540MOTOROLA
1
Technical Summary
This technical summary provides a brief description of the MC14LC5540
ADPCM Codec. A complete data book for the MC14LC5540 is available and
can be ordered from your local Motorola sales office. The data book number is
MC145540/D.
The MC14LC5540 ADPCM Codec is a single chip implementation of a PCM
Codec–Filter and an ADPCM encoder/decoder, and therefore provides an
efficient solution for applications requiring the digitization and compression of
voiceband signals. This device is designed to operate over a wide voltage
range, 2.7 to 5.25 V and, as such, is ideal for battery powered as well as ac
powered applications. The MC14LC5540 ADPCM Codec also includes a serial
control port and internal control and status registers that permit a microcomputer to exercise many built–in features.
The ADPCM Codec is designed to meet the 32 kbps ADPCM conformance
requirements of CCITT Recommendation G.721–1988 and ANSI T1.301. It
also meets ANSI T1.303 and CCITT Recommendation G.723–1988 for 24 kbps
ADPCM operation, and the 16 kbps ADPCM standard, CCITT Recommendation G.726. This device also meets the PCM conformance specification of the
CCITT G.714 Recommendation.
• Single 2.7 to 5.25 V Power Supply
• Typical 2.7 V Power Dissipation of 43 mW, Power–Down of 15 µW
• Differential Analog Circuit Design for Lowest Noise
• Complete Mu–Law and A–Law Companding PCM Codec–Filter
• ADPCM Transcoder for 64, 32, 24, and 16 kbps Data Rates
• Universal Programmable Dual Tone Generator
• Programmable Transmit Gain, Receive Gain, and Sidetone Gain
• Low Noise, High Gain, Three Terminal Input Operational Amplifier for
Microphone Interface
• Push–Pull, 300 Ω Power Drivers with External Gain Adjust for Receiver
Interface
• Push–Pull, 300 Ω Auxiliary Output Drivers for Ringer Interface
• Voltage Regulated Charge Pump to Power the Analog Circuitry in Low
Voltage Applications
• Receive Noise Burst Detect Algorithm
• Order Complete Document as MC145540/D
• Device Supported by MC145537EVK ADPCM Codec Evaluation Kit
This document contains information on a product under development. Motorola reserves the right to change or discontinue this product without notice.
Order this document
by MC14LC5540TS/D
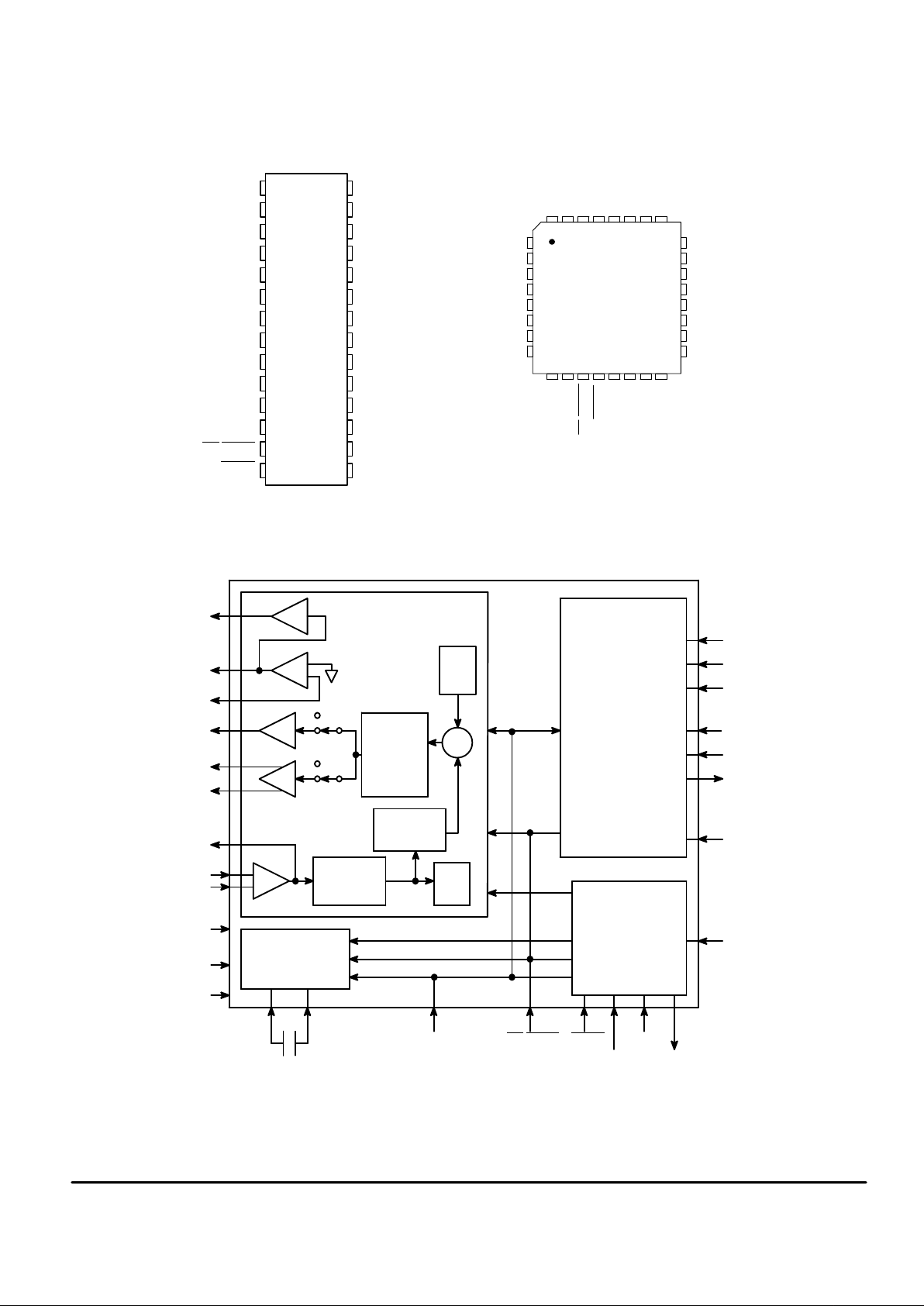
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
P SUFFIX
PLASTIC DIP
CASE 710
DW SUFFIX
SOG PACKAGE
CASE 751F
ORDERING INFORMATION
MC14LC5540P Plastic DIP
MC14LC5540DW SOG Package
MC14LC5540FU TQFP
28
1
28
1
32
1
FU SUFFIX
TQFP
CASE 873A
Motorola, Inc. 1997
REV 2
6/97 TN97060200
MC14LC5540 MOTOROLA
2
PIN ASSIGNMENT
19
18
17
16
15
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
TG
TI–
TI+
V
AG
RO
AXO–
AXO+
V
DSP
V
EXT
PI
PO–
PO+
PDI
/RESET
SCPEN
V
DD
FSR
BCLKR
DR
C1+
V
SS
SPC
DT
BCLKT
FST
SCP Rx
SCP Tx
SCPCLK
C1–
10
11
12
13
14
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
•
28–LEAD PDIP, SOG
RO
AXO–
AXO+
NC
V
DSP
NC
V
EXT
PI
PO–
PO+
PDI/RESET
SCPEN
SCP CLK
FST
V
TI+
TI–
TG
V
32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25
4
3
2
6
5
8
7
1
17
18
20
21
19
22
23
24
9 10111213141516
V
SS
C1+
NC
C1–
NC
DT
SPC
BCLKT
SCP Rx
SCP Tx FSR
DR
BCLKR
32–LEAD TQFP
DD
AG
PDI/RESET
V
DSP
AXO–
DAC
SIDETONE
GAIN
ADC
SCP Tx
TRIM GAIN
AND FILTER
–
+
PI
PO–
PO+
–1
TI+
TRIM GAIN
AND FILTER
SCP Rx
SCPCLK
SCPEN
RO
–
+
DSP
ADPCM
TRANSCODER,
RECEIVE GAIN
AND
DUAL TONE
GENERAT OR
CHARGE–PUMP
CODEC–FIL TER
SEQUENCE/
CONTROL
C1–C1+
V
SS
V
AG
V
DD
V
EXT
TI–
TG
AXO+
SPC
FSR
BCLKR
DR
DT
FST
BCLKT
Σ
BLOCK DIAGRAM

MC14LC5540MOTOROLA
3
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
POWER SUPPLY PINS
V
SS
Negative Power Supply
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 22; TQFP—Pin 21)
This is the most negative power supply and is typically
connected to 0 V.
V
EXT
External Power Supply Input
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 9; TQFP—Pin 7)
This power supply input pin must be between 2.70 and
5.25 V. Internally, it is connected to the input of the V
DSP
voltage regulator, the 5 V regulated charge pump, and all
digital I/O including the Serial Control Port and the ADPCM
Serial Data Port. This pin is also connected to the analog output drivers (PO+, PO–, AXO+, and AXO–). This pin should
be decoupled to VSS with a 0.1 µF ceramic capacitor. This
pin is internally connected to the VDD and V
DSP
pins when
the device is powered down.
V
DSP
Digital Signal Processor Power Supply Output
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 8; TQFP—Pin 5)
This pin is connected to the output of the on–chip V
DSP
voltage regulator which supplies the positive voltage to the
DSP circuitry and to the other digital blocks of the ADPCM
Codec. This pin should be decoupled to VSS with a 0.1 µF
ceramic capacitor. This pin cannot be used for powering
external loads. This pin is internally connected to the V
EXT
pin during power–down to retain memory.
V
DD
Positive Power Supply Input/Output
(PDIP, SOG, TQFP—Pin 28)
This is the positive output of the on–chip voltage regulated
charge pump and the positive power supply input to the analog sections of the device. Depending on the supply voltage
available, this pin can function in one of two different operating modes:
1. When V
EXT
is supplied from a regulated 5 V (± 5%)
power supply, VDD is an input and should be externally
connected to V
EXT
. Charge pump capacitor C1 should
not be used and the charge pump should be disabled in
BR0 (b2). In this case V
EXT
and VDD can share the same
0.1 µF ceramic decoupling capacitor to VSS.
2. When V
EXT
is supplied from 2.70 to 5.25 V, such as
battery powered applications, the charge pump should
be used. In this case, VDD is the output of the on–chip
voltage regulated charge pump and must not be connected to V
EXT
. VDD should be decoupled to VSS with a
1.0 µF ceramic capacitor. This pin cannot be used for
powering external loads in this operating mode. This pin
is internally connected to the V
EXT
pin when the charge
pump is turned off or the device is powered down.
V
AG
Analog Ground Output
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 4; TQFP—Pin 32)
This output pin provides a mid–supply analog ground regulated to 2.4 V . All analog signal processing within this device
is referenced to this pin. This pin should be decoupled to V
SS
with a 0.01 µF ceramic capacitor. If the audio signals to be
processed are referenced to VSS, then special precautions
must be utilized to avoid noise between VSS and the VAG pin.
Refer to the applications information in this document for
more information. The VAG pin becomes high impedance
when in analog power–down mode.
C1–, C1+
Charge Pump Capacitor Pins
(PDIP, SOG, TQFP—Pins 23 and 24)
These are the capacitor connections to the internal voltage
regulated charge pump that generates the VDD supply voltage. A 0.1 µF capacitor should be placed between these
pins. Note that if an external VDD is supplied, this capacitor
should not be in the circuit.
ANALOG INTERFACE PINS
TG
Transmit Gain
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 1; TQFP—Pin 29)
This is the output of the transmit gain setting operational
amplifier and the input to the transmit band–pass filter. This
op amp is capable of driving a 2 kΩ load to the VAG pin.
When TI– and TI+ are connected to VDD, the TG op amp is
powered down and the TG pin becomes a high–impedance
input to the transmit filter. All signals at this pin are referenced to the VAG pin. This pin is high impedance when the
device is in the analog power–down mode. This op amp is
powered by the VDD pin.
TI–
Transmit Analog Input (Inverting)
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 2; TQFP—Pin 30)
This is the inverting input of the transmit gain setting operational amplifier. Gain setting resistors are usually connected from this pin to TG and from this pin to the analog
signal source. The common mode range of the TI+ and TI–
pins is from 1.0 V , to VDD – 2 V . Connecting this pin and TI+
to VDD will place this amplifier’s output (TG) in a high–impedance state, thus allowing the TG pin to serve as a high–impedance input to the transmit filter.
TI+
Transmit Analog Input (Non–Inverting)
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 3; TQFP—Pin 31)
This is the non–inverting input of the transmit input gain
setting operational amplifier . This pin accommodates a differential to single–ended circuit for the input gain setting op
amp. This allows input signals that are referenced to the V
SS
pin to be level shifted to the VAG pin with minimum noise.
This pin may be connected to the VAG pin for an inverting
amplifier configuration if the input signal is already referenced to the VAG pin. The common mode range of the TI+
and TI– pins is from 1.0 V to VDD – 2 V. Connecting this pin
and TI– to VDD will place this amplifier’s output (TG) in a

MC14LC5540 MOTOROLA
4
high–impedance state, thus allowing the TG pin to serve as a
high–impedance input to the transmit filter.
RO
Receive Analog Output
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 5; TQFP—Pin 1)
This is the non–inverting output of the receive smoothing
filter from the digital–to–analog converter. This output is
capable of driving a 2 kΩ load to 1.575 V peak referenced to
the VAG pin. This pin may be dc referenced to either the V
AG
pin or a voltage of half of V
EXT
by BR2 (b7). This pin is high
impedance when the device is in the analog power–down
mode. This pin is high impedance except when it is enabled
for analog signal output.
AXO–
Auxiliary Audio Power Output (Inverting)
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 6; TQFP—Pin 3)
This is the inverting output of the auxiliary power output
drivers. The Auxiliary Power Driver is capable of differentially
driving a 300 Ω load. This power amplifier is powered from
V
EXT
and its output can swing to within 0.5 V of VSS and
V
EXT
. This pin may be dc referenced to either the VAG pin or
a voltage of half of V
EXT
by BR2 (b7). This pin is high impedance in power down. This pin is high impedance except
when it is enabled for analog signal output.
AXO+
Auxiliary Audio Power Output (Non–Inverting)
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 7; TQFP—Pin 4)
This is the non–inverting output of the auxiliary power output drivers. The Auxiliary Power Driver is capable of differentially driving a 300 Ω load. This power amplifier is powered
from V
EXT
and its output can swing to within 0.5 V of VSS and
V
EXT
. This pin may be dc referenced to either the VAG pin or
a voltage of half of V
EXT
by BR2 (b7). This pin is high impedance in power down. This pin is high impedance except
when it is enabled for analog signal output.
PI
Power Amplifier Input
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 10; TQFP—Pin 8)
This is the inverting input to the PO– amplifier. The non–
inverting input to the PO– amplifier may be dc referenced to
either the VAG pin or a voltage of half of V
EXT
by BR2 (b7).
The PI and PO– pins are used with external resistors in an
inverting op amp gain circuit to set the gain of the PO+ and
PO– push–pull power amplifier outputs. Connecting PI to
VDD will power down these amplifiers and the PO+ and PO–
outputs will be high impedance.
PO–
Power Amplifier Output (Inverting)
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 11; TQFP—Pin 9)
This is the inverting power amplifier output that is used to
provide a feedback signal to the PI pin to set the gain of the
push–pull power amplifier outputs. This power amplifier is
powered from V
EXT
and its output can swing to within 0.5 V
of VSS and V
EXT
. This should be noted when setting the gain
of this amplifier. This pin is capable of driving a 300 Ω load to
PO+ independent of supply voltage. The PO+ and PO– outputs are differential (push–pull) and capable of driving a
300 Ω load to 3.15 V peak, which is 6.3 V peak–to–peak
when a nominal 5 V power supply is used for V
EXT
. The bias
voltage and signal reference for this pin may be dc referenced to either the VAG pin or a voltage of half of V
EXT
by
BR2 (b7). Low impedance loads must be between PO+ and
PO–. This pin is high impedance when the device is in the
analog power–down mode. This pin is high impedance except when it is enabled for analog signal output.
PO+
Power Amplifier Output (Non–Inverting)
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 12; TQFP—Pin 10)
This is the non–inverting power amplifier output that is an
inverted version of the signal at PO–. This power amplifier is
powered from V
EXT
and its output can swing to within 0.5 V
of VSS and V
EXT
. This pin is capable of driving a 300 Ω load
to PO–. This pin may be dc referenced to either the VAG pin
or a voltage of half of V
EXT
by BR2 (b7). This pin is high
impedance when the device is in the analog power–down
mode. See PI and PO– for more information. This pin is high
impedance except when it is enabled for analog signal output.
ADPCM/PCM SERIAL INTERFACE PINS
FST
Frame Sync, Transmit
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 18; TQFP—Pin 16)
When used in the Long Frame Sync or Short Frame Sync
mode, this pin accepts an 8 kHz clock that synchronizes the
output of the serial ADPCM data at the DT pin.
BCLKT
Bit Clock, Transmit
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 19; TQFP—Pin 17)
When used in the Long Frame Sync or Short Frame Sync
mode, this pin accepts any bit clock frequency from 64 to
5120 kHz.
DT
Data, Transmit (PDIP, SOG—Pin 20; TQFP—Pin 18)
This pin is controlled by FST and BCLKT and is high impedance except when outputting data.
SPC
Signal Processor Clock
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 21; TQFP—Pin 19)
This input requires a 20.48 to 24.32 MHz clock signal that
is used as the DSP engine master clock. Internally the device
divides down this clock to generate the 256 kHz clock required by the PCM Codec. The SPC clock should be a multiple of 256 kHz. (This clock may be optionally specified for
higher frequencies; contact the factory for more information.)
DR
Data, Receive (PDIP, SOG, TQFP—Pin 25)
ADPCM data to be decoded are applied to this input,
which operates synchronously with FSR and BCLKR to enter
the data in a serial format.
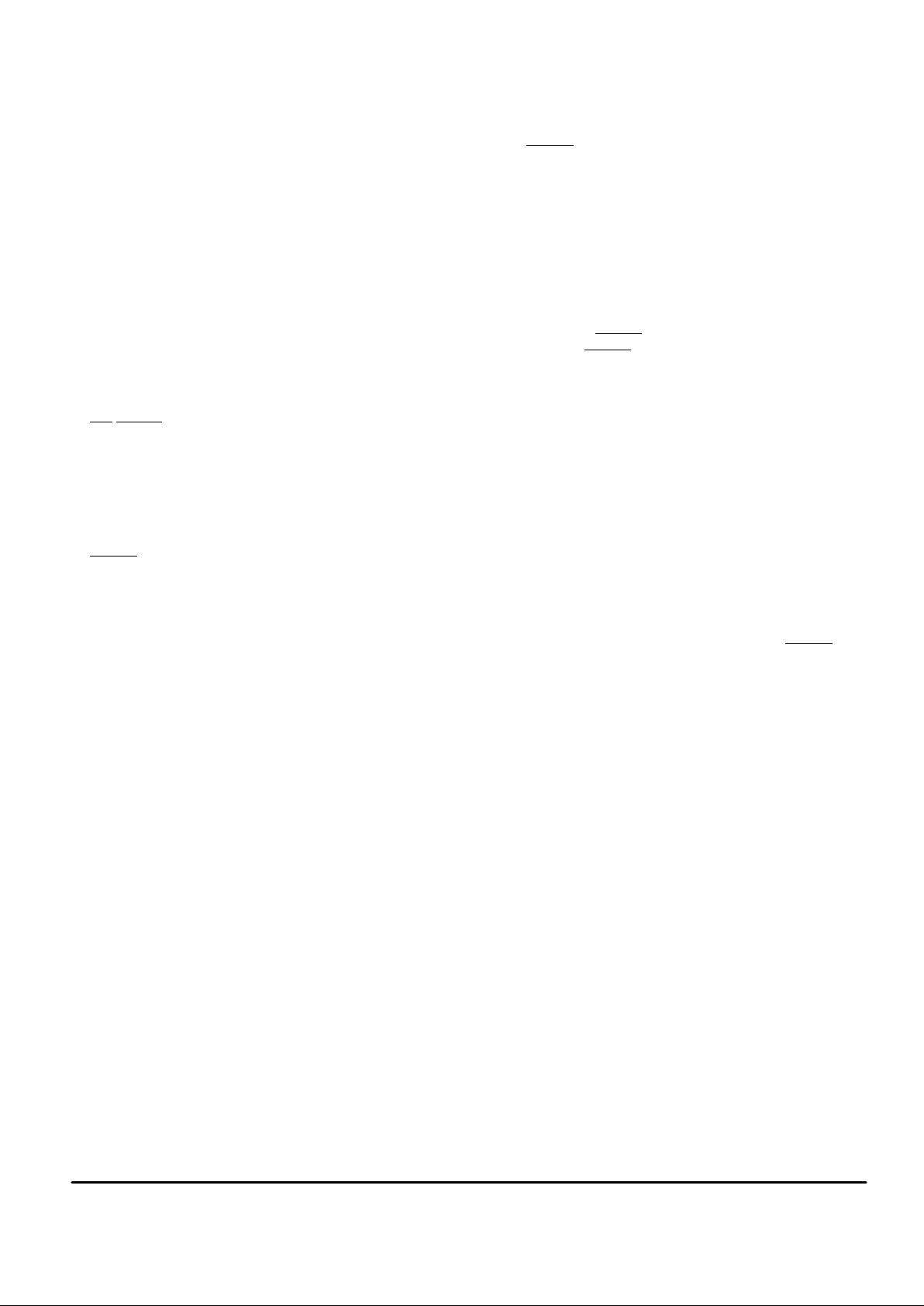
MC14LC5540MOTOROLA
5
BCLKR
Bit Clock, Receive (PDIP, SOG, TQFP—Pin 26)
When used in the Long Frame Sync or Short Frame Sync
mode, this pin accepts any bit clock frequency from 64 to
5120 kHz. This pin may be used for applying an external
256 kHz clock for sequencing the analog signal processing
functions of this device. This is selected by the SCP port at
BR0 (b7).
FSR
Frame Sync, Receive (PDIP, SOG, TQFP—Pin 27)
When used in the Long Frame Sync or Short Frame Sync
mode, this pin accepts an 8 kHz clock that synchronizes the
input of the serial ADPCM data at the DR pin. FSR can operate asynchronous to FST in the Long Frame Sync or Short
Frame Sync mode.
SERIAL CONTROL PORT INTERFACE PINS
PDI
/RESET
Power–Down Input/Reset
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 13; TQFP—Pin 11)
A logic 0 applied to this input forces the device into a low–
power dissipation mode. A rising edge on this pin causes
power to be restored and the ADPCM Reset state (specified
in the standards) to be forced.
SCPEN
Serial Control Port Enable Input
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 14; TQFP—Pin 12)
This pin, when held low, selects the Serial Control Port
(SCP) for the transfer of control and status information into
and out of the MC14LC5540 ADPCM Codec. This pin should
be held low for a total of 16 periods of the SCPCLK signal in
order for information to be transferred into or out of the
MC14LC5540 ADPCM Codec. The timing relationship between SCPEN
and SCPCLK is shown in Figures 6 through 9.
SCPCLK
Serial Control Port Clock Input
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 15; TQFP—Pin 13)
This input to the device is used for controlling the rate of
transfer of data into and out of the SCP Interface. Data are
clocked into the MC14LC5540 ADPCM Codec from SCP Rx
on rising edges of SCPCLK. Data are shifted out of the device on SCP Tx on falling edges of SCPCLK. SCPCLK can
be any frequency from 0 to 4.096 MHz. An SCP transaction
takes place when SCPEN
is brought low. Note that SCPCLK
is ignored when SCPEN is high ( i.e., it may be continuous or
it can operate in a burst mode).
SCP Tx
Serial Control Port Transmit Output
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 16; TQFP—Pin 14)
SCP Tx is used to output control and status information
from the MC14LC5540 ADPCM Codec. Data are shifted out
of SCP Tx on the falling edges of SCPCLK, most significant
bit first.
SCP Rx
Serial Control Port Receive Input
(PDIP, SOG—Pin 17; TQFP—Pin 15)
SCP Rx is used to input control and status information to
the MC14LC5540 ADPCM Codec. Data are shifted into the
device on rising edges of SCPCLK. SCP Rx is ignored when
data are being shifted out of SCP Tx or when SCPEN
is
high.
MC14LC5540 MOTOROLA
6
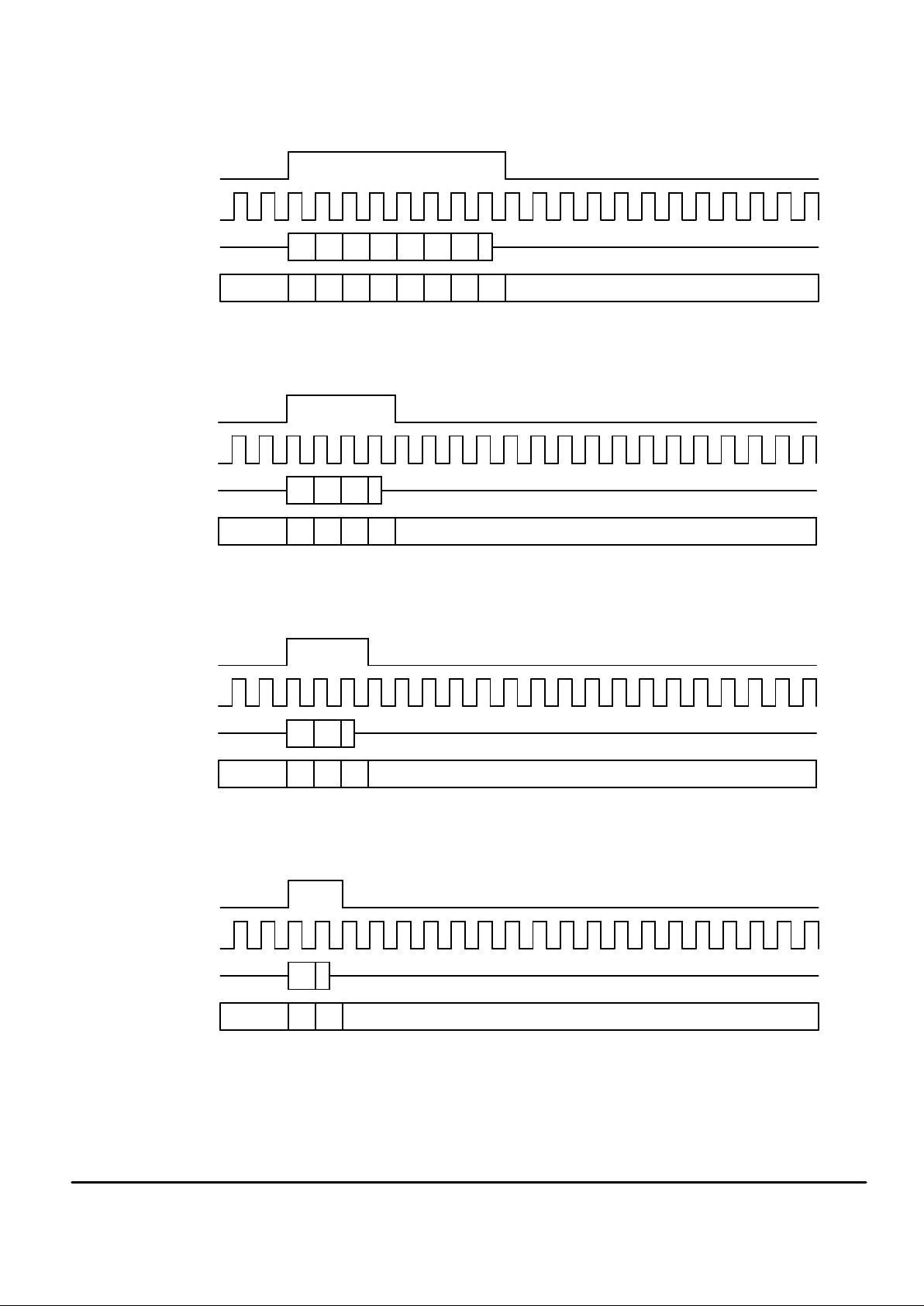
ADPCM/PCM SERIAL INTERFACE TIMING DIAGRAMS
DON’T CARE
DR
87654321
87654321
DT
BCLKT (BCLKR)
FST (FSR)
DON’T CARE
Figure 1. Long Frame Sync (64 kbps PCM Data Timing)
DR 4321
4321DT
BCLKT (BCLKR)
FST (FSR)
DON’T CARE DON’T CARE
Figure 2. Long Frame Sync (32 kbps ADPCM Data Timing)
DR 321
321DT
BCLKT (BCLKR)
FST (FSR)
DON’T CARE DON’T CARE
Figure 3. Long Frame Sync (24 kbps ADPCM Data Timing)
DR 21
21DT
BCLKT (BCLKR)
FST (FSR)
DON’T CARE DON’T CARE
Figure 4. Long Frame Sync (16 kbps ADPCM Data Timing)

MC14LC5540MOTOROLA
7
DR 4321
4321DT
BCLKT (BCLKR)
FST (FSR)
DON’T CARE DON’T CARE
Figure 5. Short Frame Sync (32 kbps ADPCM Data Timing)
A3 D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7A0A1A2R/W
SCP Tx
SCP Rx
SCPCLK
SCPEN
DON’T CARE
HIGH IMPEDANCE
DON’T CARE
Figure 6. SCP Byte Register Write Operation Using Double 8–Bit Transfer
ЗЗЗЗЗЗЗЗЗЗЗЗЗЗЗ
ÇÇÇÇ
ÇÇÇÇ
A3
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
A0A1A2R/W
SCP Tx
SCP Rx
SCPCLK
SCPEN
DON’T CARE
DON’T CARE
HIGH IMPEDANCE
Figure 7. SCP Byte Register Read Operation Using Double 8–Bit Transfer
A3 D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7A0A1A2 DON’T CARE
DON’T CARE
SCP Tx
SCP Rx
SCPCLK
SCPEN
R/W
HIGH IMPEDANCE
Figure 8. SCP Byte Register Write Operation Using Single 16–Bit Transfer

MC14LC5540 MOTOROLA
8
A3
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
A0A1A2
SCP Tx
SCP Rx
SCPCLK
SCPEN
DON’T CARER/W
HIGH IMPEDANCE
DON’T CARE
Figure 9. SCP Byte Register Read Operation Using Single 16–Bit Transfer
SERIAL CONTROL PORT (SCP) INTERFACE
The MC14LC5540 is equipped with an industry standard
Serial Control Port (SCP) Interface. The SCP is used by an
external controller, such as an M68HC05 family microcontroller, to communicate with the MC14LC5540 ADPCM
Codec.
The SCP is a full–duplex, four–wire interface used to pass
control and status information to and from the ADPCM
Codec. The SCP Interface consists of a transmit output, a
receive input, a data clock, and an enable signal. These
device pins are known as SCP Tx, SCP Rx, SCPCLK, and
SCPEN
, respectively. The SCPCLK determines the rate of
exchange of data in both the transmit and receive directions,
and the SCPEN
signal governs when this exchange is to
take place.
The operation and configuration of the ADPCM Codec is
controlled by setting the state of the control and status registers within the MC14LC5540 and then monitoring these control and status registers. The control and status registers
reside in sixteen 8–bit wide Byte Registers, BR0 – BR15. A
complete register map can be found in the Serial Control
Port Registers section.
BYTE REGISTER OPERATIONS
The sixteen byte registers are addressed by addressing a
four–bit byte register address (A3:A0) as shown in Figures 6
and 7. A second 8–bit operation transfers the data word
(D7:D0). Alternatively, these registers can be accessed with
a single 16–bit operation as shown in Figures 8 and 9.
ADPCM CODEC DEVICE DESCRIPTION
The MC14LC5540 is a single channel Mu–Law or A–Law
companding PCM Codec–Filter with an ADPCM encoder/decoder operating on a single voltage power supply from 2.7 to
5.25 V.
The MC14LC5540 ADPCM Codec is a complete solution
for digitizing and reconstructing voice in compliance with
CCITT G.714, G.721–1988, G.723–1988, G.726, and ANSI
T1.301 and T1.303 for 64, 32, 24, and 16 kbps. This device
satisfies the need for high–quality, low–power, low data rate
voice transmission, and storage applications and is offered in
three plastic packages: the 28–pin DIP and 28–pin SOIC directly replace the MC145540, and the 32–pin TQFP (Thin
Quad Flat Package) is a new addition.
Referring to Figure 10, the main functional blocks of the
MC14LC5540 are the switched capacitor technology PCM
Codec–Filter, the DSP based ADPCM encoder/decoder, and
the voltage regulated charge pump. As an introduction to the
functionality of the ADPCM Codec, a basic description of
these functional blocks follows.
PCM CODEC–FILTER BLOCK DESCRIPTION
A PCM Codec–Filter is a device used for digitizing and reconstructing the human voice. These devices were developed primarily for the telephone network to facilitate voice
switching and transmission. Once the voice is digitized, it
may be switched by digital switching methods or transmitted
long distance (T1, microwave, fiber optics, satellites, etc.)
without degradation. The name codec is an acronym from
“COder” for the analog–to–digital converter (ADC) used to
digitize voice, and “DECoder” for the digital–to–analog converter (DAC) used for reconstructing voice. A codec is a
single device that does both the ADC and DAC conversions.
To digitize voice intelligibly requires a signal to distortion of
about 30 dB for a dynamic range of about 40 dB. This may be
accomplished with a linear 13–bit ADC and DAC, but will far
exceed the required signal to distortion at amplitudes greater
than 40 dB below the peak amplitude. This excess performance is at the expense of bits of data per sample. Two
methods of data reduction are implemented by compressing
the 13–bit linear scheme to companded 8–bit schemes.
These companding schemes follow a segmented or “piecewise–linear” curve formatted as sign bit, three chord bits, and
four step bits. For a given chord, all 16 of the steps have the
same voltage weighting. As the voltage of the analog input
increases, the four step bits increment and carry to the three
chord bits, which increment. When the chord bits increment,
the step bits double their voltage weighting. This results in an
effective resolution of six bits (sign + chord + four step bits)
across a 42 dB dynamic range (seven chords above 0, by
6 dB per chord). There are two companding schemes used:
Mu–255 Law specifically in North America and A–Law
specifically in Europe. These companding schemes are
accepted world wide.

MC14LC5540MOTOROLA
9
SERIAL CONTROL PORT
SEQUENCE
AND
CONTROL
OUTPUT SHIFT
REGISTER
INPUT SHIFT
REGISTER
FSR LENGTH
CIRCUITRY
FST LENGTH
CIRCUITRY
ADPCM SERIAL
DATA PORT
ADPCM
DECODER
NOISE–BURST
DETECT CIRCUIT
ADPCM
ENCODER
COMPANDED
TO LINEAR
UNIVERSAL
DUAL TONE
GENERAT OR
LINEAR TO
COMPANDED
RECEIVE
DIGITAL GAIN
DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORANALOG INTERFACE
AND
CODEC–FILTER
POWER SUPPL Y MANAGEMENT
SUBSYSTEM
DAC
Σ
SIDETONE
GAIN
ADC
TRIM GAIN
AND FILTER
TRIM GAIN
AND FILTER
2.4 V
REFERENCE
–1
–
–
+
+
2.3 V
REGULATOR FOR
DIGITAL SIGNAL
PROCESSOR
5 V
REGULATED
CHARGE PUMP
FOR CODEC–FILTER
ANALOG
PROCESSING
PO +
PO –
PI
RO
AXO –
AXO +
TG
TI –
TI +
DR
FSR
BCLKR
BCLKT
FST
DT
SPC
PDI / RESETSCP TxSCP RxSCPCLKSCPENVC1 –C1 +
DSP
V
EXT
V
SS
V
DD
V
AG
Figure 10. ADPCM Codec Block Diagram

MC14LC5540 MOTOROLA
10
In a sampling environment, Nyquist theory says that to
properly sample a continuous signal, it must be sampled at a
frequency higher than twice the signal’s highest frequency
component. Voice contains spectral energy above 3 kHz, but
its absence is not detrimental to intelligibility. To reduce the
digital data rate, which is proportional to the sampling rate, a
sample rate of 8 kHz was adopted, consistent with a bandwidth of 3 kHz. This sampling requires a low–pass filter to
limit the high frequency energy above 3 kHz from distorting
the inband signal. The telephone line is also subject to
50/60 Hz power line coupling, which must be attenuated
from the signal by a high–pass filter before the analog–to–
digital converter.
The digital–to–analog conversion process reconstructs a
staircase version of the desired inband signal which has
spectral images of the inband signal modulated about the
sample frequency and its harmonics. These spectral images
are called aliasing components which need to be attenuated
to obtain the desired signal. The low–pass filter used to attenuate these aliasing components is typically called a reconstruction or smoothing filter.
The MC14LC5540 ADPCM Codec incorporates this codec
function as one of its main functional blocks.
ADPCM TRANSCODER BLOCK DESCRIPTION
An Adaptive Differential PCM (ADPCM) transcoder is used
to reduce the data rate required to transmit a PCM encoded
voice signal while maintaining the voice fidelity and intelligibility of the PCM signal.
The ADPCM transcoder is used on both Mu–Law and
A–Law 64 kbps data streams which represent either voice or
voice band data signals that have been digitized by a PCM
Codec–Filter. The PCM to ADPCM encoder section of this
transcoder has a type of linear predicting digital filter which is
trying to predict the next PCM sample based on the previous
history of the PCM samples. The ADPCM to PCM decoder
section implements an identical linear predicting digital filter.
The error or difference between the predicted and the true
PCM input value is the information that is sent from the encoder to the decoder as an ADPCM word. The characteristics of this ADPCM word include the number of quantized
steps (this determines the number of bits per ADPCM word)
and the actual meaning of this word is a function of the predictor’s output value, the error signal and the statistics of the
history of PCM words. The term “adaptive” applies to the
transfer function of the filter that generates the ADPCM word
which adapts to the statistics of the signals presented to it.
This means that an ADPCM word “3” does not have the
same absolute error voltage weighting for the analog signal
when the channel is quiet as it does when the channel is processing a speech signal. The ADPCM to PCM decoder section has a reciprocating filter function which interprets the
ADPCM word for proper reconstruction of the PCM sample.
The adaptive characteristics of the ADPCM algorithm
make it difficult to analyze and quantify the performance of
the ADPCM code sequence. The 32 kbps algorithm was optimized for both voice and moderate speed modems
(v 4800 baud). This optimization includes that the algorithm
supports the voice frequency band of 300 – 3400 Hz with
minimal degradation for signal–to–distortion, gain–versus–
level, idle channel noise, and other analog transmission performance. This algorithm has also been subjected to
audibility testing with many languages for Mean Opinion
Score (MOS) ratings and performed well when compared to
64 kbps PCM. The standards committees have specified
multiple 16000 word test vectors for the encoder and for the
decoder to verify compliance. To run these test vectors, the
device must be initialized to the reference state by resetting
the device.
In contrast to 64 kbps PCM, the ADPCM words appear as
random bit activity on an oscilloscope display whether the
audio channel is processing speech or a typical PCM idle
channel with nominal bit activity . The ADPCM algorithm does
not support dc signals with the exception of digital quiet,
which will result in all ones in the ADPCM channel. All digital
processing is performed on 13–bit linearizations of the 8–bit
PCM companded words, whether the words are Mu–Law or
A–Law. This allows an ADPCM channel to be intelligibly decoded into a Mu–Law PCM sequence or an A–Law PCM sequence irrespective of whether it was originally digitized as
Mu–Law or A–Law. There will be additional quantizing degradation if the companding scheme is changed because the
ADPCM algorithm is trying to reconstruct the original 13–bit
linear codes, which included companding quantization.
CHARGE PUMP
The charge pump is the functional block that allows the
analog signal processing circuitry of the MC14LC5540 to operate with a power supply voltage as low as 2.7 V. This analog signal processing circuitry includes the PCM
Codec–Filter function, the transmit trim gain, the receive trim
gain, the sidetone gain control, and the transmit input operational amplifier . This circuitry does not dissipate much current
but it does require a nominal voltage of 5 V for the VDD power
supply.
The charge pump block is a regulated voltage doubler
which takes twice the current it supplies from the voltage applied to the V
EXT
power supply pin which may range from 2.7
to 5.25 V and generates the required 5 V VDD supply. The
charge pump block receives as inputs the V
EXT
supply voltage, the same 256 kHz clock that sequences the analog signal processing circuitry, and the Charge Pump Enable signal
from the SCP block. It also makes use of the capacitor connected to the C1+ and C1– pins and the decoupling capacitor
connected to the VDD pin.
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
POWER SUPPLY CONFIGURATION
Analog Signal Processing Power Supply
All analog signal processing is powered by the VDD pin at
5 V. This voltage may be applied directly to the VDD pin or
5 V may be obtained by the on–chip 5 V regulated charge
pump which is powered from the V
EXT
pin. The V
EXT
pin is
the main positive power supply pin for this device.
For applications that are not 5 V regulated, the on–chip 5 V
regulated charge pump may be turned on and C1 will be required. VDD will require a 1.0 µF decoupling capacitor to filter
the voltage spikes of the charge pump. This allows the V
EXT
power supply to be from 2.7 to 5.25 V. This mode of operation is intended for hand held applications where three NiCad
cells or three dry cells would be the power supply.
The on–chip 5 V regulated charge pump is a single stage
charge pump that effectively series regulates the amount of
voltage it generates and internally applies this regulated
voltage to the VDD pin. This 5 V voltage is developed by

MC14LC5540MOTOROLA
11
connecting the external 0.1 µF capacitor (C1) between the
V
EXT
power supply pin and the power supply ground pin,
VSS. This puts a charge of as much as 2.7 V on C1. The
charge pump circuitry then connects the negative lead of C1
to the V
EXT
, pin which sums the voltage of C1 with the volt-
age at V
EXT
for a minimum potential voltage of 5.4 V. The
charge voltage on C1 is regulated such that the summing of
voltages is regulated to 5 V. This limits all of the voltages on
the device to safe levels for this IC fabrication technology.
This charge pumped voltage is then stored on the 1.0 µF capacitor connected at VDD and VSS, which filters and serves
as a reservoir for power. The clock period for this charge
pump is the same 256 kHz as the analog sequencing clock,
minimizing noise problems.
For applications with a regulated 5 V (± 5%) power supply,
the VDD pin and the V
EXT
pin are connected to the 5 V power
supply. These pins may share one decoupling capacitor in
this configuration as a function of external noise on the
power supply. The on–chip, 5 V regulated charge pump
should be turned off via the SCP port at register 0. The
external capacitor (C1) should not be populated for these
applications.
Digital Signal Processing Power Supply
This device has an on–chip series regulator which limits
the voltage of the Digital Signal Processing (DSP) circuitry to
about 2.3 V . This reduces the maximum power dissipation of
this circuitry. From the V
EXT
power supply pin, the DSP circuitry appears as a constant current load instead of a resistive (CV2/2) load for a constant clock frequency. This series
regulator is designed to have a low drop–out voltage, which
allows the DSP circuitry to work when the V
EXT
voltage is as
low as 2.7 V . The output of this regulator is brought out to the
V
DSP
pin for a 0.1 µF decoupling capacitor. This regulator is
not designed to power any loads external to the device.
ANALOG INTERFACE AND SIGNAL PATH
Transmit Analog
The transmit analog portion of this device includes a low–
noise, three terminal operational amplifier capable of driving
a 2 kΩ load. This op amp has inputs of TI+ and TI– and its
output is TG. This op amp is intended to be configured in an
inverting gain circuit. The analog signal may be applied directly to the TG pin if this transmit op amp is independently
powered down. Power–down may be achieved by connecting both the TI+ and TI– inputs to the VDD pin. The TG pin
becomes high impedance when the transmit op amp is powered down. The TG pin is internally connected to a time continuous three–pole anti–aliasing pre–filter. This pre–filter
incorporates a two–pole Butterworth active low–pass filter,
followed by a single passive pole. This pre–filter is followed
by a single–ended to differential converter that is clocked at
512 kHz. All subsequent analog processing utilizes fully differential circuitry. The output of the differential converter is
followed by the transmit trim gain stage. This stage is intended to compensate for gain tolerances of external components such as microphones. The amount of gain control is
0–7 dB in 1 dB steps. This stage only accommodates positive gain because the maximum signal levels of the output of
the input op amp are the same as the transmit filter and ADC,
which should nominally be next to the clip levels of this device’s circuitry. Any requirement for attenuation of the output
of the input op amp would mean that it is being overdriven.
The gain is programmed via the SCP port in BR1 (b2:b0).
The next section is a fully–differential, 5–pole switched–capacitor low–pass filter with a 3.4 kHz frequency cutoff. After
this filter is a 3–pole switched–capacitor high–pass filter having a cutoff frequency of about 200 Hz. This high–pass stage
has a transmission zero at dc that eliminates any dc coming
from the analog input or from accumulated op amp offsets in
the preceding filter stages. (This high–pass filter may be removed from the signal path under control of the SCP port
BR8 (b4).) The last stage of the high–pass filter is an autozeroed sample and hold amplifier.
One bandgap voltage reference generator and digital–to–
analog converter (DAC) are shared by the transmit and
receive sections. The autozeroed, switched–capacitor bandgap reference generates precise positive and negative reference voltages that are virtually independent of temperature
and power supply voltage. A binary–weighted capacitor
array (CDAC) forms the chords of the companding structure,
while a resistor string (RDAC) implements the linear steps
within each chord. The encode process uses the DAC, the
voltage reference, and a frame–by–frame autozeroed
comparator to implement a successive–approximation analog–to–digital conversion (ADC) algorithm. All of the analog
circuitry involved in the data conversion (the voltage reference, RDAC, CDAC, and comparator) are implemented with
a differential architecture.
The nonlinear companded Mu–Law transfer curve of the
ADC may be changed to 8–bit linear by BR8 (b5).
The input to the ADC is normally connected to the output
of the transmit filter section, but may be switched to measure
the voltage at the V
EXT
pin for battery voltage monitoring.
This is selected by the I/O Mode in BR0 (b4:b3). In this
mode, the ADC is programmed to output a linear 8–bit PCM
word for the voltage at V
EXT
which is intended to be read in
BR9 (b7:b0). The data format for the ADC output is a “Don’t
Care” for the sign bit and seven magnitude bits. The scaling
for the ADC is for 6.3 V at V
EXT
equals full scale (BIN X111
1 111). The ADPCM algorithm does not support dc signals.
Transmit Digital
The Digital Signal Processor (DSP) section of this device
is a custom designed, interrupt driven, microcoded machine
optimized for implementing the ADPCM algorithms. In the
full–duplex speech mode, the DSP services one encode interrupt and one decode interrupt per frame (125 µs). The encode algorithm (i.e., 16 kbps, 24 kbps, or 32 kbps ADPCM, or
64 kbps PCM) is determined by the length of the transmit
output enable at the FST pin. The length of the FST enable
measured in transmit data clock (BCLKT) cycles tells the device which encoding rate to use. This enable length information is used by the encoder each frame. The transmit
ADPCM word corresponding to this request will be computed
during the next frame and will be available a total of two
frames after being requested. This transmit enable length information can be delayed by the device an additional four
frames corresponding to a total of six frames. These six
frames of delay allow the device to be clocked with the same
clocks for both transmit (encode) and receive (decode), and
to be frame aligned for applications that require every sixth
frame signaling. It is important to note that the enable length
information is delayed and not the actual ADPCM (PCM)
sample word. The amount of delay for the FST enable length

MC14LC5540 MOTOROLA
12
is controlled in BR7 (b5). If the FST enable goes low before
the falling edge of BCLKT during the last bit of the ADPCM
word, the digital data output circuitry counts BCLKT cycles to
keep the data output (DT pin) low impedance for the duration
of the ADPCM data word (2, 3, 4, or 8 BCLKT cycles) minus
one half of a BCLKT cycle.
Receive Digital
The receive digital section of this device accepts serial
ADPCM (PCM) words at the DR pin under the control of the
BCLKR and FSR pins. The FSR enable duration, measured
in BCLKR cycles, tells the device which decode algorithm
(i.e., 16 kbps, 24 kbps, or 32 kbps ADPCM, or 64 kbps PCM)
the DSP machine should use for the word that is being received at the DR pin. This algorithm may be changed on a
frame by frame basis.
The DSP machine receives an interrupt when an ADPCM
word has been received and is waiting to be decoded into a
PCM word. The DSP machine performs a decode and an
encode every frame when the device is operating in its full
duplex conversation mode. The DSP machine decodes the
ADPCM word according to CCITT G.726 for 32 kbps,
24 kbps, and 16 kbps. This decoding includes the correction
for the CCITT/ANSI Sync function, except when the receive
digital gain is used. The receive digital gain is anticipated to
be user adjustable gain control in handset applications
where as much as 12 dB of gain or more than 12 dB of attenuation may be desirable. The receive digital gain is a linear
multiply performed on the 13–bit linear data before it is converted to Mu–Law or A–Law, and is programmed via the SCP
port in BR3 (b7:b0). The decoded PCM word may be read via
the SCP port in BR10 (b7:b0).
Receive Analog Signal Processing
The receive analog signal processing section includes the
DAC described above, a sample and hold amplifier, a trim
gain stage, a 5–pole, 3400 Hz switched capacitor low–pass
filter with sinX/X correction, and a 2–pole active smoothing
filter to reduce the spectral components of the switched capacitor filter. (The receive low–pass smoothing filter may be
removed from the signal path for the additional spectral components for applications using the on–chip tone generator
function described below. This low–pass filter performs the
sinX/X compensation. The receive filter is removed from the
circuit via the SCP in BR2 (b4).) The input to the smoothing
filter is the output to the receive trim gain stage. This stage is
intended to compensate for gain tolerances of external components such as handset receivers. This stage is capable of
0 to 7 dB of attenuation in 1–dB steps. This stage only accommodates attenuation because the nominal signal levels
of the DAC should be next to the clip levels of this device’s
circuitry and any positive gain would overdrive the outputs.
The gain is programmed via the SCP port in BR2 (b2:b0).The
output of the 2–pole active smoothing filter is buffered by an
amplifier which is output at the RO pin. This output is capable
of driving a 2 kΩ load to the VAG pin.
Receive Analog Output Drivers and Power Supply
The high current analog output circuitry (PO+, PO–, PI,
AXO+, AXO–) is powered by the V
EXT
power supply pin. Due
to the wide range of V
EXT
operating voltages for this device,
this circuitry and the RO pin have a programmable reference
point of either VAG (2.4 V) or V
EXT
/2. In applications where
this device is powered with 5 V , it is recommended that the dc
reference for this circuitry be programmed to VAG. This
allows maximum output signals for driving high power telephone line transformer interfaces and loud speaker/ringers.
For applications that are battery powered, VAG pin will still be
2.4 V, but the receive analog output circuitry will be powered
from as low as 2.7 V. To optimize the output power, this circuitry should be referenced to one half of the battery voltage,
V
EXT
/ 2. The RO pin is powered by the VDD pin, but its dc
reference point is programmed the same as the high current
analog output circuitry.
This device has two pairs of power amplifiers that are connected in a push–pull configuration. These push–pull power
driver pairs have similar drive capabilities, but have different
circuit configurations and different intended uses. The PO+
and PO– power drivers are intended to accommodate large
gain ranges with precise adjustment by two external resistors
for applications such as driving a telephone line or a handset
receiver. The PI pin is the inverting input to the PO– power
amplifier. The non–inverting input is internally tied to the
same reference as the RO output. This allows this amplifier
to be used in an inverting gain circuit with two external resistors. The PO+ amplifier has a gain of – 1, and is internally
connected to the PO– output. This complete power amplifier
circuit is a differential (push–pull) amplifier with adjustable
gain which is capable of driving a 300 Ω load to + 12 dBm
when V
EXT
is 5 V. The PO+ and PO– outputs are intended
to drive loads differentially and not to VSS or VAG. The PO+
and PO– power amplifiers may be powered down independently of the rest of the chip by connecting the PI pin to V
DD
or in BR2 (b5).
The other paired power driver outputs are the AXO+ and
AXO– Auxiliary outputs. These push–pull output amplifiers
are intended to drive a ringer or loud speaker with impedance as low as 300 Ω to + 12 dBm when V
EXT
is 5 V. The
AXO+ and AXO– outputs are intended to drive loads differentially and not to VSS or VAG. The AXO+ and AXO–
power amplifiers may be powered down independently of the
rest of the chip via the SCP port in BR2 (b6).
SIDETONE
The Sidetone function of this device allows a controlled
amount of the output from the transmit filter to be summed
with the output of the DAC at the input to the receive low–
pass filter. The sidetone component has gains of –8.5 dB,
–10.5 dB, –12.0 dB, –13.5 dB, –15.0 dB, –18.0 dB,
–21.5 dB, and v – 70 dB. The sidetone function is controlled
by the SCP port in BR1 (b6:b4).
UNIVERSAL TONE GENERATOR
The Universal Dual Tone Generator function supports both
the transmit and the receive sides of this device. When the
tone generator is being used, the decoder function of the
DSP circuit is disabled. The output of the tone generator is
made available to the input of the receive digital gain function
for use at the receive analog outputs. In handset applications, this could be used for generating DTMF, distinctive
ringing or call progress feedback signals. In telephone line
interface applications, this tone generator could be used for
signaling on the line. The tone generator output is also
available for the input to the encoder function of the DSP
machine for outputting at the DT pin. This function is useful in

MC14LC5540MOTOROLA
13
handset applications for non–network signaling such as information services, answering machine control, etc. At the
network interface side of a cordless telephone application,
this function could be used for dialing feedback or call progress to the handset. The tone generator function is controlled
by the SCP port in BR4, BR5, and BR7. The tone generator
does not work when the device is operated in 64 kbps mode,
except when analog loopback is enabled at BR0 (b5).
POWER–DOWN AND RESET
There are two methods of putting all of this device into a
low power consumption mode that makes the device nonfunctional and consumes virtually no power. PDI
/RESET is
the power–down input and reset pin which, when taken low,
powers down the device. Another way to power the device
down is by the SCP port at BR0. BR0 allows the analog section of this device to be powered down individually and/or the
digital section of this device to be powered down individually .
When the chip is powered down, the VAG, TG, RO, PO+,
PO–, AXO+, AXO–, DT and SCP Tx outputs are high impedance. To return the chip to the power–up state, PDI
/RESET
must be high and the SPC clock and the FST or the FSR
frame sync pulses must be present. The ADPCM algorithm is
reset to the CCITT initial state following the reset transition
from low to high logic states. The DT output will remain in a
high–impedance state for at least two FST pulses after power–up. This device is functional after being reset for full–duplex voice coding with the charge pump active.
SIGNAL PROCESSING CLOCK (SPC)
This is the clock that sequences the DSP circuit. This clock
may be asynchronous to all other functions of this device.
Clock frequencies of 20.48 MHz to 24.32 MHz are recommended. This clock is also used to drive a digitally phase–
locked prescaler that is referenced to FST (8 kHz) and
automatically determines the proper divide ratio to use for
achieving the required 256 kHz internal sequencing clock for
all analog signal processing, including analog–to–digital
conversion, digital–to–analog conversion, transmit filtering,
receive filtering and analog gain functions of this device, and
the charge pump. The SPC clock should be a multiple of 256
kHz.
The analog sequencing function of the SPC clock may be
eliminated by reprogramming the device to use the BCLKR
pin as the direct input for the required 256 kHz analog sequencing clock. The 256 kHz clock applied at BCLKR must
be an integer 32 times the FST 8 kHz clock and be approximately rising edge aligned with the FST rising edge. This
mode requires that the transmit and receive ADPCM transfers be controlled by the BCLKT pin. This is reprogrammed
via the SCP port in BR0(b7).
DIGITAL I/O
The MC14LC5540 is programmable for Mu–Law or A–
Law. The timing for the PCM data transfer is independent of
the companding scheme selected. Table 1 shows the 8–bit
data word format for positive and negative zero and full scale
for both 64 kbps companding schemes (see Figures 1
through 5 for a summary and comparison of the five PCM
data interface modes of this device).
Long Frame Sync
Long Frame Sync is the industry name for one type of
clocking format which controls the transfer of the ADPCM or
PCM data words (see Figures 1 through 4). The “Frame
Sync” or “Enable” is used for two specific synchronizing functions. The first is to synchronize the PCM data word transfer,
and the second is to control the internal analog–to–digital
and digital–to–analog conversions. The term “Sync” refers to
the function of synchronizing the PCM data word onto or off
of the multiplexed serial PCM data bus, also known as a
PCM highway. The term “Long” comes from the duration of
the frame sync measured in PCM data clock cycles. Long
Frame Sync timing occurs when the frame sync is used directly as the PCM data output driver enable. This results in
the PCM output going low impedance with the rising edge of
the transmit frame sync, and remaining low impedance for
the duration of the transmit frame sync.
The implementation of Long Frame Sync for this device
has maintained industry compatibility and been optimized for
external clocking simplicity. The PCM data output goes low
impedance with the rising edge of the FST pin but the MSB of
the data is clocked out due to the logical AND of the transmit
frame sync (FST pin) with the transmit data clock (BCLKT
pin). This allows either the rising edge of the FST enable or
the rising edge of the BCLKT data clock to be first. This implementation includes the PCM data output remaining low
impedance until the middle of the LSB (seven and a half data
clock cycles for 64 kbps PCM, three and a half data clock
cycles for 32 kbps ADPCM, etc.). This allows the frame sync
to be approximately rising edge aligned with the initiation of
the PCM data word transfer but the frame sync does not
have a precise timing requirement for the end of the PCM
data word transfer. This prevents bus contention between
similar devices on a common bus. The device recognizes
Long Frame Sync clocking when the frame sync is held high
for two consecutive falling edges of the transmit data clock.
In the full–duplex speech mode, the DSP services one encode interrupt and one decode interrupt per frame (125 µs).
The encode algorithm (i.e., 16 kbps, 24 kbps, or 32 kbps
ADPCM or 64 kbps PCM) is determined by the length of the
transmit output enable at the FST pin. The length of the FST
enable measured in transmit data clock (BCLKT) cycles tells
the device which encoding rate to use. This enable length information is used by the encoder each frame. The transmit
ADPCM word corresponding to this request will be computed
during the next frame and be available a total of two frames
after being requested. This transmit enable length information can be delayed by the device an additional four frames
corresponding to a total of six frames. This six frames of
delay allows the device to be clocked with the same clocks
for both transmit (encode) and receive (decode), and to be
frame aligned for applications that require every sixth frame
signaling. It is important to note that the enable length information is delayed and not the actual ADPCM (PCM) sample word. The amount of delay for the FST enable length is
controlled by the SCP port at BR7 (b5). The digital data output circuitry counts BCLKT cycles to keep the data output
(DT pin) low impedance for the duration of the ADPCM data
word (2, 3, 4, or 8 BCLKT cycles) minus one half of a BCLKT
cycle.

MC14LC5540 MOTOROLA
14
Table 1. PCM Full Scale and Zero Words
Mu–Law A–Law
Level
Sign Bit Chord Bits Step Bits Sign Bit Chord Bits Step Bits
+ Full Scale 1 000 0000 1 010 1010
+ Zero 1 111 1111 1 101 0101
– Zero 0 111 1111 0 101 0101
– Full Scale 0 000 0000 0 010 1010
The length of the FST enable tells the DSP what encoding
algorithm to use. The transmit logic decides on each frame
sync whether it should interpret the next frame sync pulse as
a Long or a Short Frame Sync. The device is designed to
prevent PCM bus contention by not allowing the PCM data
output to go low impedance for at least two frame sync
cycles after power is applied or when coming out of the
power–down mode.
The receive side of the device is designed to accept the
same frame sync and data clock as the transmit side and to
be able to latch its own transmit PCM data word. Thus the
PCM digital switch only needs to be able to generate one
type of frame sync for use by both transmit or receive sections of the device.
The logical AND of the receive frame sync with the receive
data clock tells the device to start latching the serial word into
the receive data input on the falling edges of the receive data
clock. The internal receive logic counts the receive data
clock falling edges while the FSR enable is high and transfers the enable length and the PCM data word into internal
registers for access by the DSP machine which also sets the
DSP’s decoder interrupt.
The receive digital section of this device accepts serial
ADPCM (PCM) words at the DR pin under the control of the
BCLKR and FSR pins. The FSR enable duration measured
in BCLKR cycles, tells the device which decode algorithm
(i.e., 16 kbps, 24 kbps, or 32 kbps ADPCM, or 64 kbps PCM)
the DSP machine should use for the word that is being received at the DR pin. This algorithm may be changed on a
frame by frame basis.
When the device is programmed to be in the PCM Codec
mode by BR0 (4:3), the device will output and input the complete 8–bit PCM words using the Long Frame Sync clocking
format as though the FST and FSR pulses were held high for
8 data clock cycles.
The DSP machine receives an interrupt when an ADPCM
word has been received and is waiting to be decoded into a
PCM word. The DSP machine performs a decode and an encode every frame when the device is operating in its full–
duplex conversation mode. The DSP machine decodes the
ADPCM word according to CCITT G.726 for 32 kbps,
24 kbps, and 16 kbps.
Short Frame Sync
Short Frame Sync is the industry name for this type of
clocking format which controls the transfer of the ADPCM
data words (see Figure 5). This device uses Short Frame
Sync timing for 32 kbps ADPCM only. The “Frame Sync” or
“Enable” is used for two specific synchronizing functions.
The first is to synchronize the ADPCM data word transfer,
and the second is to control the internal analog to digital and
digital to analog conversions. The term “Sync” refers to the
function of synchronizing the ADPCM data word onto or off of
the multiplexed serial ADPCM data bus, also known as a
PCM highway. The term “Short” comes from the duration of
the frame sync measured in PCM data clock cycles. Short
Frame Sync timing occurs when the frame sync is used as a
“pre–synchronization” pulse that is used to tell the internal
logic to clock out the ADPCM data word under complete control of the data clock. The Short Frame Sync is held high for
one falling data clock edge. The device outputs the ADPCM
data word beginning with the following rising edge of the data
clock. This results in the ADPCM output going low impedance with the rising edge of the transmit data clock, and remaining low impedance until the middle of the LSB (three
and a half PCM data clock cycles).
The device recognizes Short Frame Sync clocking when
the frame sync is held high for one and only one falling edge
of the transmit data clock. The transmit logic decides on each
frame sync whether it should interpret the next frame sync
pulse as a Long or a Short Frame Sync. It is not recommended to switch between Long Frame Sync and Short
Frame Sync clocking without going through a power–down
cycle due to bus contention problems. The device is designed to prevent PCM bus contention by not allowing the
ADPCM data output to go low impedance for at least two
frame sync cycles after power is applied or when coming out
of a powered down mode.
The receive side of the device is designed to accept the
same frame sync and data clock as the transmit side and to
be able to latch its own transmit ADPCM data word. Thus the
PCM digital switch only needs to be able to generate one
type of frame sync for use by both transmit or receive sections of the device.
The falling edge of the receive data clock (BCLKR) latching a high logic level at the receive frame sync (FSR) input
tells the device to start latching the 4–bit ADPCM serial word
into the receive data input on the following four falling edges
of the receive data clock. The internal receive logic counts
the receive data clock cycles and transfers the ADPCM data
word to a register for access by the DSP.
When the device is programmed to be in the PCM Codec
mode by BR0 (4:3), the device will output the complete 8–bit
PCM word using the Short Frame Sync clocking format. The
8–bit PCM word will be clocked out (or in) the same way that
the 4–bit ADPCM word would be, except that the fourth bit
will be valid for the full BCLKT period and the eighth bit will be
valid for only one half of the BCLKT period.

MC14LC5540MOTOROLA
15
SERIAL CONTROL PORT REGISTER MAP
The SCP register map consists of 16 byte registers. Regis-
ters BR0 – BR5 and BR7 – BR10 provide external control of
and status of the part. Register BR15 holds the value of the
mask number for the particular MC14LC5540. BR6 and
BR11 – BR14 are not defined and as such are presently reserved.
Table 2. Byte Register Map
Byte b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
BR0
Ext
256 kHz
CLK
Mu–/A–Law
Select
Analog
Loopback
I/O Mode
(1)
I/O Mode
(0)
Charge
Pump
Disable
Analog
Power
Down
Digital
Power
Down
BR1 Reserved Sidetone
Gain (2)
Sidetone
Gain (1)
Sidetone
Gain (0)
Transmit
Mute
Transmit
Gain (2)
Transmit
Gain (1)
Transmit
Gain (0)
BR2 RO
Reference
Select
AXO
Enable
PO
Disable
Receive
Filter
Disable
RO Mute Analog
Receive
Gain (2)
Analog
Receive
Gain (1)
Analog
Receive
Gain (0)
BR3 Digital Rx
Gain
Enable
Digital Rx
Gain (6)
Digital Rx
Gain (5)
Digital Rx
Gain (4)
Digital Rx
Gain (3)
Digital Rx
Gain (2)
Digital Rx
Gain (1)
Digital Rx
Gain (0)
BR4 N.B. T ime
/ Tone
Param.
(7)
N.B. Time
/ Tone
Param.
(6)
N.B. Time
/ Tone
Param.
(5)
N.B. Time
/ Tone
Param.
(4)
N.B.Time
/ Tone
Param.
(3)
N.B. Time
/ Tone
Param.
(2)
N.B. Time
/ Tone
Param.
(1)
N.B. Time
/ Tone
Param.
(0)
BR5 N.B.
Threshold
(7) /
Address
Param.
(1)
N.B.
Threshold
(6) /
Address
Param.
(0)
N.B.
Threshold
(5) /
Don’t
Care
N.B.
Threshold
(4) /
Don’t
Care
N.B.
Threshold
(3) /
Tone
Param.
(11)
N.B.
Threshold
(2) /
Tone
Param.
(10)
N.B.
Threshold
(1) /
Tone
Param.
(9)
N.B.
Threshold
(0) /
Tone
Param.
(8)
BR6 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
BR7 Tone
Param.
Status
N.B.
Detect
Enable
2/6
Delay
G.726/
Motorola
16 kbps
Tone
Enable
Reserved Tone 1
Enable
Tone 2
Enable
BR8 Software
Encoder
Reset
Software
Decoder
Reset
Linear
Codec
Mode
Highpass
Disable
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
BR9 Encoder
PCM (7)
Encoder
PCM (6)
Encoder
PCM (5)
Encoder
PCM (4)
Encoder
PCM (3)
Encoder
PCM (2)
Encoder
PCM (1)
Encoder
PCM (0)
BR10 D/A PCM
(7)
D/A PCM
(6)
D/A PCM
(5)
D/A PCM
(4)
D/A PCM
(3)
D/A PCM
(2)
D/A PCM
(1)
D/A PCM
(0)
BR11 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
BR12 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
BR13 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
BR14 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
BR15 Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Mask (3) Mask (2) Mask (1) Mask (0)
NOTE: “Setting” a bit corresponds to writing a 1 to the register and “clearing” a bit corresponds to writing a 0 to the register.

MC14LC5540 MOTOROLA
16
APPLICATION CIRCUITS
20 k
Ω
TO MICROCONTROLLER
SERIAL PERIPHERAL
INTERFACE PORT AND
RESET CIRCUIT
8 kHz
2.048 MHz
20.736 MHz
ADPCM OUT
ADPCM IN
MIC
0.1
µ
F
3 k
Ω
150
Ω
0.1 µF
RECEIVER
RINGER
20 k
Ω
20 k
Ω
+2.7 V
1 k
Ω
1 k
Ω
1.0 µF
1.0 µF
1 k
Ω
1 k
Ω
+2.7 V
C1+
C1–
SPC
SCP Rx
SCPCLK
SCP Tx
BCLKT
DT
FST
BCLKR
DR
FSR
V
DD
V
SS
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
PDI
/RESET
AXO+
AXO–
SCPEN
PI
PO–
PO+
TG
TI–
TI+
RO
V
AG
V
DSP
V
EXT
14
13
12
11
10
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
•
9
MC14LC5540
0.1 µF
150
Ω
0.1 µF
1.0
µ
F
68 µF
Figure 11. MC14LC5540 Handset Application

MC14LC5540MOTOROLA
17
NC
NC
R0 = 600
Ω
0.1 µF
RING
TIP
N = 1 N = 0.5
10 k
Ω
+5 V
NC
NC
20 k
Ω
TO MICROCONTROLLER
SERIAL PERIPHERAL
INTERFACE PORT AND
RESET CIRCUIT
8 kHz
2.048 MHz
20.48 MHz
ADPCM OUT
ADPCM IN
3 k
Ω
10 k
Ω
+5 V
C1+
C1–
SPC
SCP Rx
SCPCLK
SCP Tx
BCLKT
DT
FST
BCLKR
DR
FSR
V
DD
V
SS
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
PDI/RESET
AXO+
AXO–
SCPEN
PI
PO–
PO+
TG
TI–
TI+
RO
V
AG
V
DSP
V
EXT
14
13
12
11
10
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
•
9
MC14LC5540
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1
µ
F
150
Ω
Figure 12. MC14LC5540 Step–Up 1:0.5 Transformer Application
0.1 µF
RING
TIP
N = 1 N = 1
10 k
Ω
+5 V
NC
NC
20 k
Ω
TO MICROCONTROLLER
SERIAL PERIPHERAL
INTERFACE PORT AND
RESET CIRCUIT
8 kHz
2.048 MHz
20.736 MHz
ADPCM OUT
ADPCM IN
20 k
Ω
150
Ω
SPEAKER
10 k
Ω
+5 V
C1+
C1–
SPC
SCP Rx
SCPCLK
SCP Tx
BCLKT
DT
FST
BCLKR
DR
FSR
V
DD
V
SS
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
PDI
/RESET
AXO+
AXO–
SCPEN
PI
PO–
PO+
TG
TI–
TI+
RO
V
AG
V
DSP
V
EXT
14
13
12
11
10
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
•
9
MC14LC5540
0.1 µF
600
Ω
0.1 µF
0.1
µ
F
RO = 600
Ω
Figure 13. MC14LC5540 1:1 Transformer Application

MC14LC5540 MOTOROLA
18
Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. Motorola makes no warranty , representation or guarantee regarding
the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does Motorola assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and
specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation consequential or incidental damages. “T ypical” parameters which may be provided in Motorola
data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary in different applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating parameters, including “Typicals”
must be validated for each customer application by customer’s technical experts. Motorola does not convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of
others. Motorola products are not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the body, or other
applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any other application in which the failure of the Motorola product could create a situation where personal injury
or death may occur. Should Buyer purchase or use Motorola products for any such unintended or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Motorola
and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney fees
arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that
Motorola was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part. Motorola and are registered trademarks of Motorola, Inc. Motorola, Inc. is an Equal
Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer.
Mfax is a trademark of Motorola, Inc.
How to reach us:
USA/EUROPE/ Locations Not Listed: Motorola Literature Distribution; JAPAN: Nippon Motorola Ltd.: SPD, Strategic Planning Office, 4–32–1,
P.O. Box 5405, Denver, Colorado 80217. 303–675–2140 or 1–800–441–2447 Nishi–Gotanda, Shinagawa–ku, Tokyo 141, Japan. 81–3–5487–8488
Mfax: RMFAX0@email.sps.mot.com – TOUCHTONE 602–244–6609 ASIA/PACIFIC: Motorola Semiconductors H.K. Ltd.; 8B Tai Ping Industrial Park,
– US & Canada ONLY 1–800–774–1848 51 Ting Kok Road, T ai Po, N.T., Hong Kong. 852–26629298
INTERNET: http://motorola.com/sps
MC14LC5540TS/D
◊
 Loading...
Loading...