Page 1

EPS 7000
Shared System
Users Manual
www.mgeups.com
Page 2
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS – This manual contains important instructions for all EPS 7000 Shared System that
must be followed during operation of the equipment.
WARNING: Opening enclosures expose hazardous voltages. Always refer
service to qualified personnel only.
ATTENTION: L'ouverture des cabinets expose des tensions dangereuses.
Assurez-vous toujours que le service ne soit fait que par des
personnes qualifiees.
WARNUNG! Das öffnen der Gehäuse legen gefährliche Spannungen bloss.
Service sollte immer nur von qualifizierten Personal durchgeführt
werden.
WARNING: As standards, specifications, and designs are subject to change,
please ask for confirmation of the information given in this
publication.
ATTENTION: Comme les normes, spécifications et produits peuvent changer,
veuillez demander confirmation des informations contenues dans
cette publication.
WARNUNG! Normen, Spezifizierungen und Pläne unterliegen Anderungen.
Bitte verlangen Sie eine Bestätigung über alle Informationen, die in
dieser Ausgabe gemacht wurden.
NOTE: This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance
with installation manual, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which
case the user will be required to correct the interference at his
own expense.
Important Safety information
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page ii
Page 3

EPS 7000
Shared Systems
Users Manual
For service call
1-800-523-0142
86-134005-00 X0 08/04
Copyright © 2004 MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc.
All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.
MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc.
1660 Scenic Avenue
Costa Mesa, CA 92626
(714) 557-1636
page iii
Users Manual
Page 4

EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page iv
EPS 7000
Shared Systems Users Manual
Warranty Information
Warranty
The liability of MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. hereunder is limited to replacing or repairing at MGE UPS
SYSTEMS, Inc.’s factory or on the job site at MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc.’s option, any part or parts which are
defective, including labor, for a period of 12 months from the date of purchase. The MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc.
shall have the sole right to determine if the parts are to be repaired at the job site or whether they are to be
returned to the factory for repair or replacement. All items returned to MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. for repair or
replacement must be sent freight prepaid to its factory. Purchaser must obtain MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc.’s
Return Materials Authorization prior to returning items. The above conditions must be met if warranty is to be
valid. MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. will not be liable for any damage done by unauthorized repair work, unauthorized replacement parts, from any misapplication of the item, or for damage due to accident, abuse, or Act of
God.
In no event shall the MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. be liable for loss, damage, or expense directly or indirectly
arising from the use of the units, or from any other cause, except as expressly stated in this warranty. MGE
UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. makes no warranties, express or implied, including any warranty as to merchantability or
fitness for a particular purpose or use. MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. is not liable for and Purchaser waives any
right of action it has or may have against MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. for any consequential or special damages
arising out of any breach of warranty, and for any damages Purchaser may claim for damage to any property or
injury or death to any person arising out of its purchase of the use, operation or maintenance of the product.
MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. will not be liable for any labor subcontracted or performed by Purchaser for
preparation of warranted item for return to MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc.’s factory or for preparation work for field
repair or replacement. Invoicing of MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. for labor either performed or subcontracted by
Purchaser will not be considered as a liability by the MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc.
This warranty shall be exclusive of any and all other warranties express or implied and may be modified
only by a writing signed by an officer of the MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. This warranty shall extend to the
Purchaser but to no one else. Accessories supplied by MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc., but manufactured by others,
carry any warranty the manufacturers have made to MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. and which can be passed on to
Purchaser.
MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. makes no warranty with respect to whether the products sold hereunder
infringe any patent, U.S. or foreign, and Purchaser represents that any specially ordered products do not
infringe any patent. Purchaser agrees to indemnify and hold MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. harmless from any
liability by virtue of any patent claims where Purchaser has ordered a product conforming to Purchaser’s specifications, or conforming to Purchaser’s specific design.
Purchaser has not relied and shall not rely on any oral representation regarding the Product sold
hereunder and any oral representation shall not bind MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. and shall not be part of any
warranty.
There are no warranties which extend beyond the description on the face hereof. In no event shall MGE
UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. be responsible for consequential damages or for any damages except as expressly stated
herein.
Service and Factory Repair - Call
1-800-523-0142
Direct questions about the operation, repair, or servicing of this equipment to MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc.
Technical Support Services. Include the part number and serial number of the unit in any correspondence.
Should you require factory service for your equipment, contact MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. Technical Support
Services and obtain a Return Materials Authorization (RMA) prior to shipping your unit. Never ship equipment
to MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. without first obtaining an RMA.
Proprietary Rights Statement
The information in this manual is the property of MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc., and represents a proprietary
article in which MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc., retains any and all patent rights, including exclusive rights of use
and/or manufacture and/or sale. Possession of this information does not convey any permission to reproduce,
print, or manufacture the article or articles shown herein. Such permission may be granted only by specific
written authorization, signed by an officer of MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc.
IBM, PC-AT, ES/9000, and AS/400 are trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation. MGE
and MGE UPS SYSTEMS are trademarks of MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. Other trademarks that may be used
herein are owned by their respective companies and are referred to in an editorial fashion only.
Revision History
EPS 7000 Shared Systems Users Manual
86-134005-00
Copyright © 2004 MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. All rights reserved Printed in U.S.A.
Revision: X0 R&D-001651 08/2004
Page 5
How To Use This Manual
page v
Users Manual
How To Use This Manual
This manual is designed for ease of use and easy location of information.
To quickly find the meaning of terms used within the text, look to the Glossary.
To quickly find a specific topic, look at the Table of Contents.
This manual uses Note lines and icons to convey important information.
Note lines and icons come in four variations.
WARNING: Indicates information provided to protect the User and
service personnel against safety hazards and possible
equipment damage.
CAUTION: Indicates information provided to protect the User and
service personnel against possible equipment damage.
NOTE: Indicates information provided as an operating tip or an
equipment feature.
IMPORTANT: Indicates information provided as an operating instruction
or as a tip.
Page 6

CAUTION
RECORD ALL SERIAL NUMBERS FOR THE SHARED
UPS SYSTEMS.
THESE SERIAL NUMBERS WILL BE REQUIRED IF
YOUR SYSTEM NEEDS SERVICE. KEEP THIS
MANUAL IN A PLACE WHERE YOU CAN REFERENCE
THE SERIAL NUMBERS IF SERVICE IS REQUIRED!
SSC SERIAL NUMBER: _______________________________________________
ADDITIONAL MODULE SERIAL NUMBERS:
UPS DESIGNATIONS UPS SERIAL NUMBERS
__________________________ ______________________________
__________________________ ______________________________
__________________________ ______________________________
__________________________ ______________________________
__________________________ ______________________________
__________________________ ______________________________
__________________________ ______________________________
__________________________ ______________________________
__________________________ ______________________________
__________________________ ______________________________
CAUTION: Record All Serial Numbers
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page vi
Page 7

page c i
Users Manual
Contents
section description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .page
Important Safety Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Inside Front Cover
Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .iv
Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .iv
How To Use This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .v
CAUTION: Record All Serial Numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .vi
Table of Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .c-i
Section 1 Introduction
section description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .page
1.0 Scope . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-1
1.1 Reference Manuals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-1
1.2 Section Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-1
1.3 General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-2
1.4 Specifications, Circuit Breakers and Powerflow Diagrams . . . . . . .1-3
1.4.1 Circuit Breakers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-3
1.4.2 Power Flow Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-6
1.4.2.1 Normal Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-6
1.4.2.2 On-Battery Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-7
1.5 Shared Systems Indicators and Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-9
1.5.1 Front Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-10
1.5.2 Alphanumeric Display and Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-12
1.5.2.1 Two-line Alphanumeric Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-12
1.5.2.2 Alphanumeric Display Pushbuttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-12
1.5.2.3 Numbered Lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-13
1.5.3 Hidden Panel Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-14
1.5.3.1 LED Alphanumeric Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-14
1.5.3.2 Hidden Panel Lower Pushbuttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-16
Section 2 Operation
section description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .page
2.0 Scope . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-1
2.1 Status Screen Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-1
2.2 Settings Selection Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-2
2.3 Alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-3
2.4 Voltage Measurements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-4
2.5 Current Measurements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-5
2.6 Power Frequency Measurements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-6
2.7 Battery Measurements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-7
Content
Page 8

Section 2 Operation (continued)
section description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .page
2.8 LCD Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-8
2.8.1 General Alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-8
2.8.2 Secondary Alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-9
2.9 Preparations Before Start-up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-14
2.9.1 Checks Before Start-up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-14
2.9.2 Start-up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-15
2.9.3 Checks After Start-up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-16
2.10 Shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-17
2.10.1 Emergency Shutdown Using EPO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-17
2.10.2 Normal Shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-17
2.10.3 Isolation of an Individual UPS Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-18
2.10.4 With Maintenance Bypass . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-19
2.10.5 Without Maintenance Bypass . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-19
2.11 Forced Transfers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-20
2.11.1 Uninterrupted Transfer Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-20
2.11.2 Forced Transfer from Bypass AC Input Source to Inverter . . . . . .2-20
2.11.3 Forced Transfer from Inverter to Bypass AC Input . . . . . . . . . . . .2-20
Section 3 Maintenance
section description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .page
3.0 Scope . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-1
3.1 Safety Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-1
3.2 Important Safety Instructions for Servicing Batteries . . . . . . . . . . . .3-1
3.3 Preventive Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-2
3.4 Replacement Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-2
3.5 Troubleshooting and Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-3
Glossary g-1
Contents
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page c ii
Page 9

Contents
page c iii
Users Manual
Figures
figure description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .page
1-1 EPS 7000 System., S-S Configuration, 1 GCC per Module,
located on SSC Cabinet (not shown) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-2
1-2 Circuit Breaker Locations on the EPS 7000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-3
1-3 Static Switch Cabinet (SSC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-4
1-4 Single-line Diagram, Typical UPS Shared systems Installation . . . . . . . . . .1-5
1-5 Normal Operation, Power Flow Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-6
1-6 On-Battery Operation, Power Flow Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-7
1-7 Bypass Operation, Power Flow Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-8
1-8 EPS 7000 Front Panel Indicators and Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-9
1-9 Front Panel Indicators and Control Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-10
1-10 Alphanumeric LCD Display , Settings , and
Pushbutton Indicators and Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-12
1-11 Hidden Panel Alphanumeric LEDs and
Pushbutton Indicators and Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-14
2-1 Default Status Screen Alphanumerical Display Configuration . . . . . . . . . . .2-1
2-2 Settings Selection Display Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-2
2-3 Sequential Alarm Messages for Viewing the Fault Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-3
2-4 Voltage Measurement Displays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-4
2-5 Current Measurements Displays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-5
2-6 Power and Frequency Measurements Displays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-6
2-7 Battery Measurements Displays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-7
Page 10

(This page left blank intentionally)
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page c iv
Page 11

1.0 Scope
This manual provides User instructions for operating the EPS 7000 Shared Systems (S-S). Descriptions include
section descriptions, a general overview of system internal components, circuit breaker diagrams, descriptions for
front panel displays and control indicators.
Please read this manual before installing the EPS 7000 equipment. Please retain this manual for future reference.
1.1 Reference Manuals
The EPS 7000 Installation Manual (MGE part number 86-134003-00) provides detailed operating instructions for the
EPS 7000 Single Module and Shared Systems. The EPS 7000 Single Module Users Manual, (MGE part number
86-134004-00) provides detailed operating instructions for single module systems.
86-134004-00 EPS 7000 Users Manual, Single Module
86-134003-00 EPS 7000 Installation Manual, Single Module and Shared Systems
1.2 Section Descriptions
This manual is divided into four sections:
Section 1 Introduction
This section provides User instructions for operating the EPS 7000 Shared Systems. Descriptions include section
descriptions, a general overview of system internal components, circuit breaker diagrams, descriptions for front
panel displays and control indicators.
Section 2 Operation
This section describes procedures for normal operation of EPS 7000 Shared Systems. Including interactive front
panel display, settings for language configuration, alarms message displays, voltage, current, battery measurements, with before and after start-up checks, emergency shutdown using EPO disconnects, and normal conditions
for using forced transfers.
Section 3 Maintenance
This section describes maintenance of the EPS 7000, including troubleshooting LCD alarm message, safety instructions, preventive maintenance, isolation for maintenance, and information about replacement parts.
A Glossary in the rear of this manual provides definitions of terms used within the text.
Users Manual
Introduction
Introduction
page 1 — 1
Page 12

1.3 General Description
EPS 7000 is a family of compact, high-efficiency uninterruptible power systems. Standard power ratings for singlemodule systems range from 300 to 500 kVA. EPS 7000 are optimized for compatibility with non-linear
computer-type loads. Computer-aided UPS diagnostics and modular construction assures that any required service
on the UPS can be identified and completed rapidly. Remote system monitoring, remote annunciation of UPS
performance signals, and telecommunication capabilities allow total control of the UPS by the user.
The EPS 7000, SSC, battery, and all auxiliary equipment is listed for safety by Underwriter’s Laboratories, Inc. (UL)
under UL Standard 1778 and under Canadian Standards Association (CSA) standard C22.107.
Major components of the EPS 7000 Shared Systems include:
◗ UPS Shared Systems
◗ SSC static switch cabinet
◗ SSC maintenance bypass cabinet
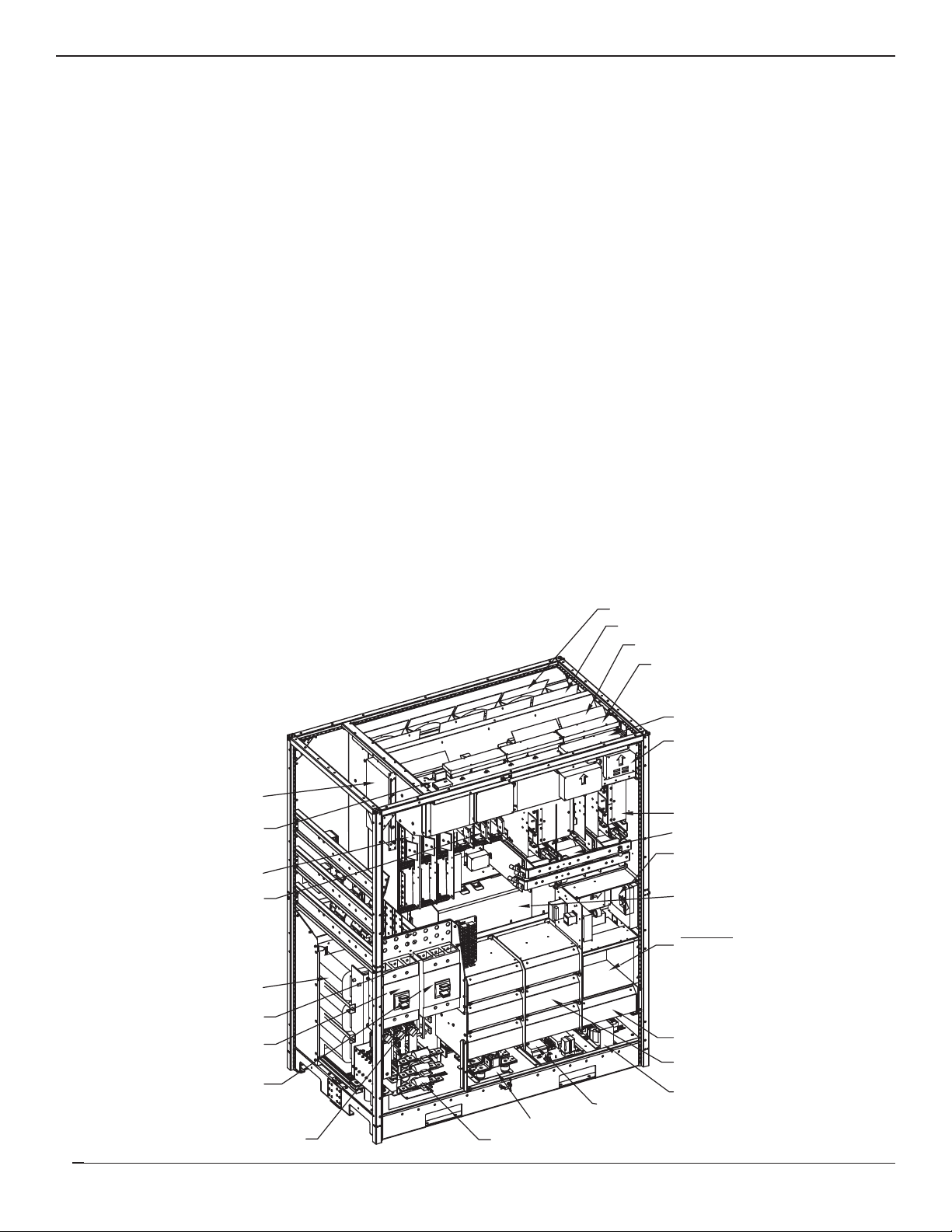
Each of these cabinets is described below. Figure 1-1 shows the Shared System.
Figure 1-1: EPS 7000 System., S-S Configuration, 1 GCC (not shown) per Module, located on SSC Cabinet.
Introduction
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 1 — 2
Page 13
Introduction
page 1 — 3
Users Manual
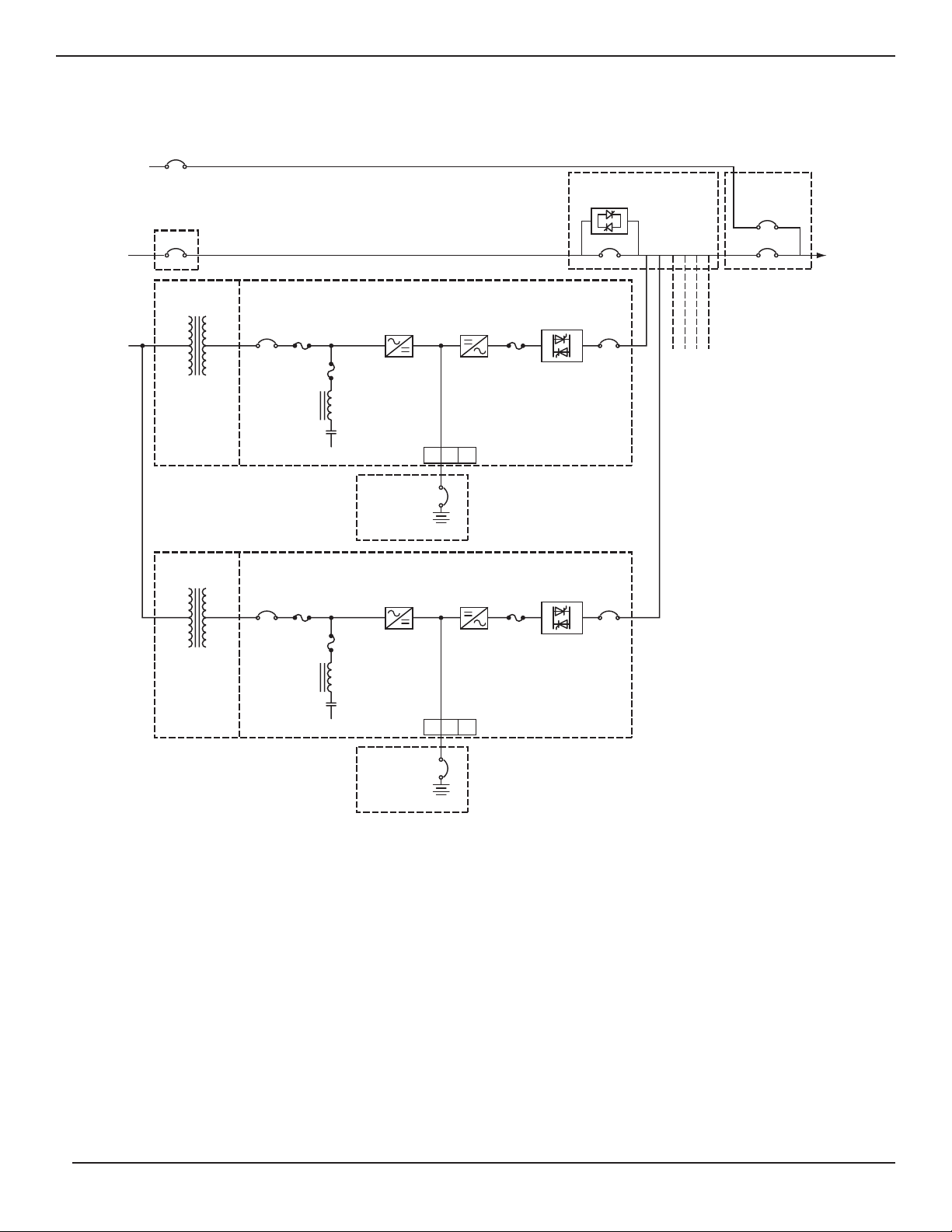
1.4 Specifications, Circuit Breakers and Powerflow Diagrams
1.4.1 Circuit Breakers
EPS 7000 circuit breakers and switches (except the battery disconnect circuit breaker QF1) are located behind the
doors of the UPS cabinet, or through the door in the optional MBC. Following is a brief description of the available
circuit breakers, contactors and switches, and their function. The single-line diagram in Figure 1-4 shows the location
of each circuit breaker, contact and switch within the electrical path, and Figures 1-2 and 1-3 show the location of each
switch, contact and circuit breaker within the enclosures. Following is a brief description of the available circuit
breakers and contacts, and their function.
Upstream of the SSC:
Q4S Customer-supplied upstream circuit breaker, used to isolate the SSC from the bypass
AC input (mains 2) source and provide back-feed protection.
In the UPS modules:
Q1 Input isolation circuit breaker, used to isolate the UPS module from the main AC input
(mains 1) source and provide input current protection.
Q5N UPS isolation circuit breaker, used to isolate the UPS module from he attached load.
In the circuit of the battery of each UPS module:
QF1 Battery disconnect circuit breaker, used to disconnect the battery from the UPS. QF1
provides isolation and protection between the UPS module and its battery system.
Figure 1-2: Component Locations on the EPS 7000.
MULTI SLOT
(OPTION)
MODEM AND PWR
SUPPLY (OPTION)
OUTPUT
STATI C
SWITCH
RECTIFIER
SERIES
FILTER
CHOKES
CONTROL
FUSES
INPUT CB/SW
OUTPUT CB/SW
Q1
Q5N
INPUT
FUSES
OUTPUT FUSES
INPUT FILTER FUSES
BLOWERS (4X)
BLOWERS (4X)
BLOWERS (3X)
RAUZ2 PCA (OPT)
RAUZ PCA
IBEZ PCA
GUI POWER SUPPLY
OBEZ PCA
BAIZ1 PCA
TREZ PCA
ALBEZ PCA
EPOZ PCA
INVERTERS (6X)
DC CAPS
APOZ PCA
ACPZ PCA
ARUZ PCA
OUTPUT XFMR
(BEHIND PANEL)
CARD CAGE
ALEZ PCA
AROZ-US PCA
CROZ-US PCA
CRIZ-US PCA
SRIZ PCA
GTCZ-7000 PCA
GT2Z-7000 PCA (OPT.)
INPUT FILTER (3X)
OUTPUT FILTER (4X)
FAN XF MRS
Page 14
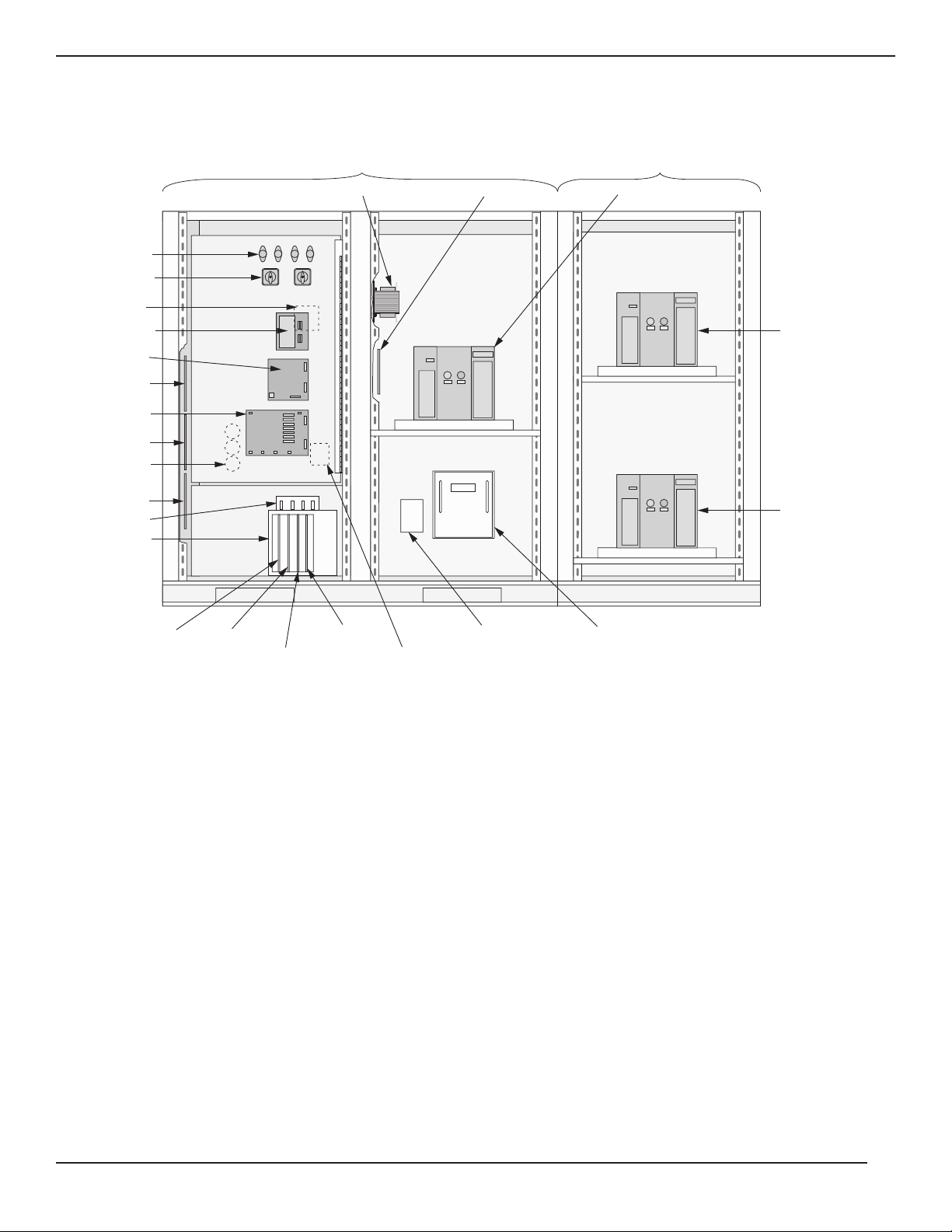
Figure 1-3: Static Switch Cabinet (SSC).
In the SSC (and optional MBC):
Q2S Wrap-around circuit breaker (automatic), used to supply the attached load via the
bypass AC input (mains 2) source.
Q3BP (Optional), system maintenance bypass circuit breaker, used to supply the attached
load via the maintenance bypass source while the SSC is being serviced.
Q5N (Optional), system isolation circuit breaker, used to isolate the shared system from the
attached load.
Introduction
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 1 — 4
FUSES
(F1, F2, F3, & F4)
ROTARY SWITCHES
(SW1, & SW2)
TRANSFORMER (T13)
FAR SIDE OF PANEL
PCA (EPOZ)
PCA (ACOZ)
PCA (RAUZ)
PCA (ACPZ)
PCA (OBEZ)
CAPACITORS
(C11, C12, & C13)
FAR SIDE OF PANEL
PCA (IBEZ)
PCA (PROZ)
CARD CAGE
STATIC SWITCH CABINET
(WITH FRONT DOORS REMOVED)
TRANSFORMER (T12)
UPS
UPS
BYPASS
BYPASS
PCA (CBOZ)
MAINTENANCE BYPASS CABINET
(WITH FRONT DOOR REMOVED)
CIRCUIT BREAKER
(Q2S)
CIRCUIT BREAKER
(Q3BP)
CIRCUIT BREAKER
(Q5N)
PCA (ALEZ)
PCA (AROZ)
PCA (SRIZ)
PCA (GTCZ)
FUSES (F11, F12, & F13)
FAR SIDE OF PANEL
STATIC SWITCH PCA
(SSSZ)
STATIC SWITCH
Page 15
Introduction
page 1 — 5
Users Manual
Figure 1-4: Single-line Diagram, Typical UPS Shared systems Installation.
MAINTENANCE
BYPASS
AC INPUT
BYPASS
AC INPUT/
MAINS 2
Q4S
(CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED)
STATIC SWITCH CABINET
STATIC SWITCH
Q2S
MAINTENANCE
BYPASS CABINET
(OPTIONAL)
Q3BP
Q5N
TO
ATTACHED
LOAD
BYPASS
AC INPUT/
MAINS 1
OPTIONAL INPUT
TRANSFORMER
(REQ'D FOR
600V MODELS)
TRANSFORMER
CABINET
OPTIONAL INPUT
TRANSFORMER
(REQ'D FOR
600V MODELS)
TRANSFORMER
CABINET
INPUT
CB
Q1
UPS
CABINET
INPUT
CB
Q1
UPS
CABINET
INPUT
FILTER (TYP.)
INPUT
FILTER (TYP.)
CHARGER
BATTERY
DISCONNECT
QF1
OR
BATTERY
CABINET(S)
CHARGER
BATTERY
DISCONNECT
QF1
OR
BATTERY
CABINET(S)
INVERTER
+ - G
INVERTER
+ - G
OUTPUT
FUSES
OUTPUT
FUSES
OUTPUT
STATIC
SWITCH
OUTPUT
STATIC
SWITCH
OUTPUT
CB
Q5N
OUTPUT
CB
Q5N
FROM ADDITIONAL
UPS MODULES
Page 16
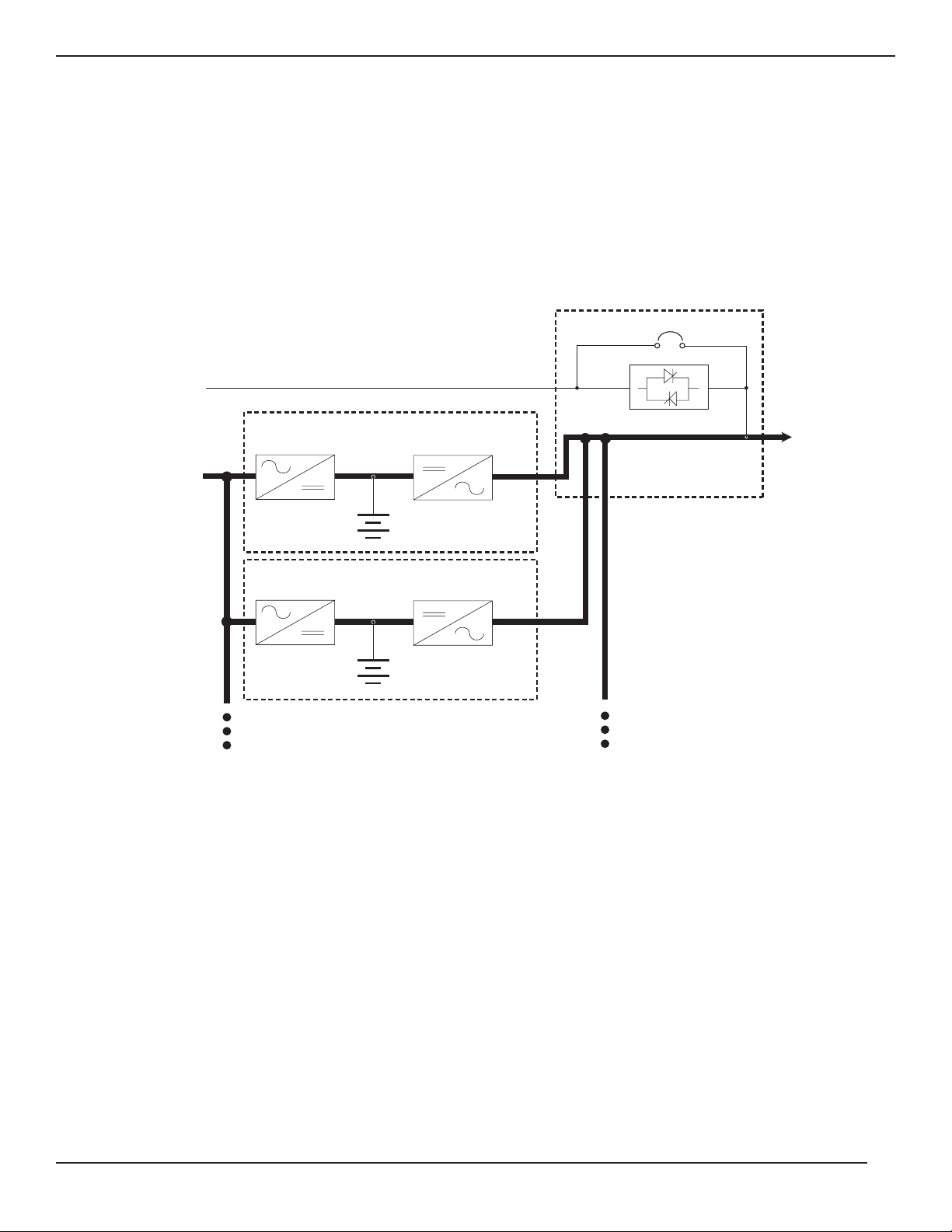
1.4.2 Power Flow Diagrams
1.4.2.1 Normal Operation
During normal operation, power flows from the main AC input source (mains 1) into the UPS rectifier/battery charger
section. The rectifier/battery charger converts the AC voltage to DC, maintains the charge of the battery, and feeds
the DC power to the inverter. The inverters regenerate AC voltage, and supply the SSC’s UPS module AC output bus.
The SSC supplies the attached load. See Figure 1-5.
Figure 1-5: Normal Operation, Power Flow Diagram.
Introduction
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 1 — 6
Bypass AC input
(mains 2)
Rectifier/battery
charger
Main AC input
(mains 1)
Inverter
Q2S
Static switch
Static switch
cabinet (SSC)
TO
ATTACHED
LOAD
Additional
modules
Battery
Rectifier/battery
charger
Battery
UPS module
Inverter
UPS module
Additional
modules
Page 17
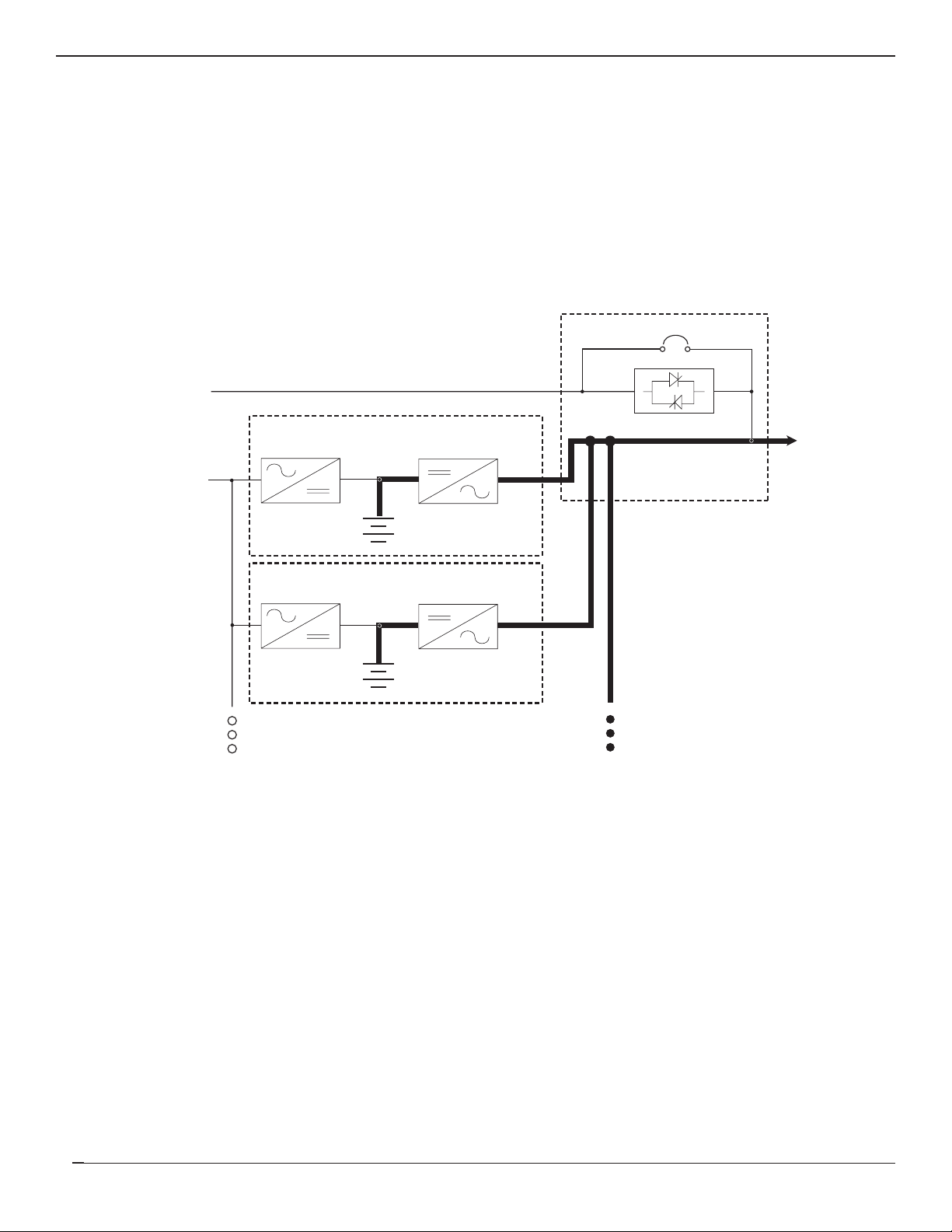
Introduction
page 1 — 7
Users Manual
1.4.2.2 On-Battery Operation
If the main AC input source (mains 1) fails or goes out of tolerance, the charger stops. Power flows from the batteries
to the UPS inverters, which in turn supplies the attached load. When the main AC input source (mains 1) returns, the
charger restarts automatically and the UPS resumes its normal operation. See Figure 1-6.
If the batteries become depleted before the main AC input source (mains 1) returns, the inverter stops and the
attached load is transferred to the bypass AC input source (mains 2) if it is available.
Figure 1-6: On-Battery Operation, Power Flow Diagram.
Bypass AC input
(mains 2)
Main AC input
(mains 1)
Rectifier/battery
charger
Inverter
Q2S
Static switch
Static switch
cabinet (SSC)
TO
ATTACHED
LOAD
Additional
modules
Battery
Rectifier/battery
charger
Battery
UPS module
Inverter
UPS module
Additional
modules
Page 18
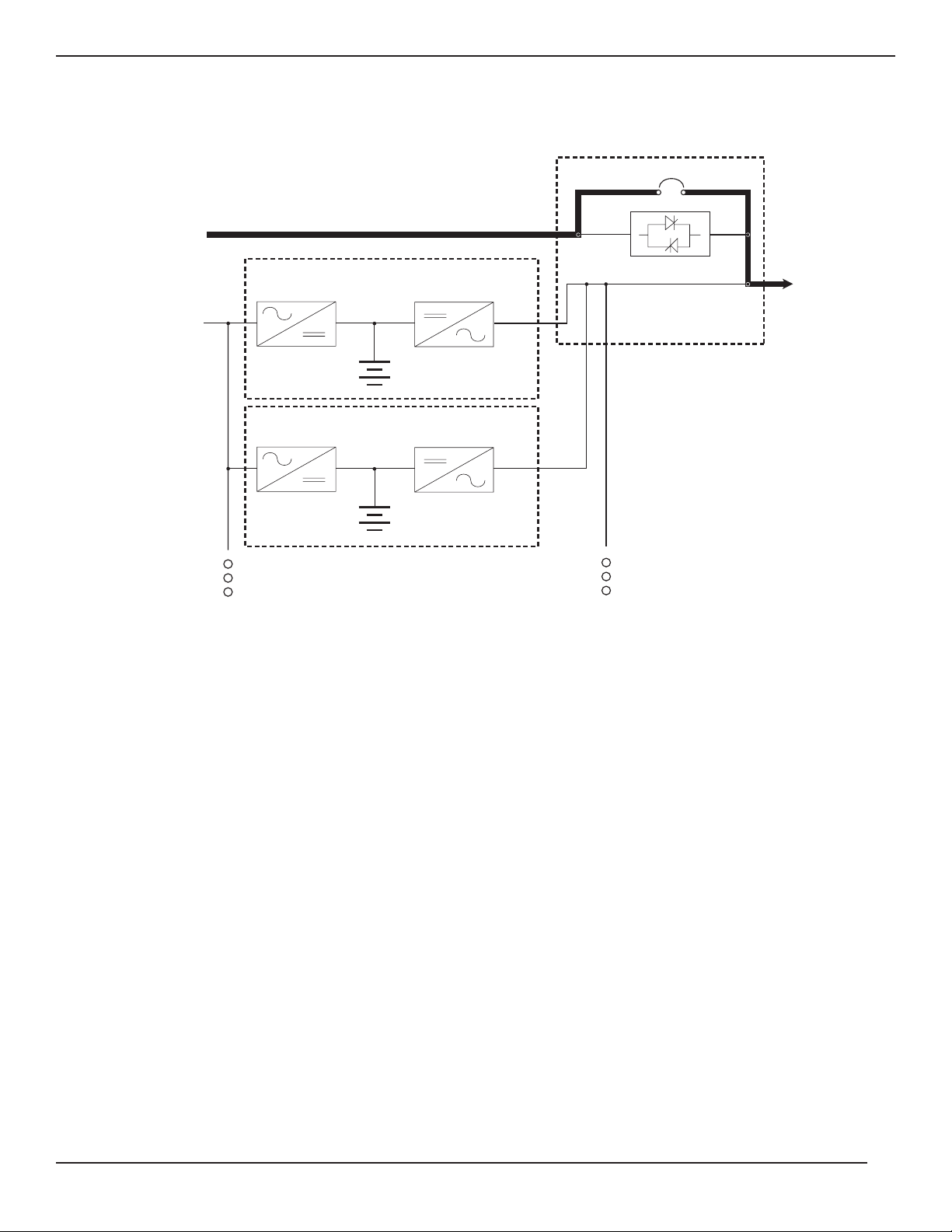
Figure 1-7: Bypass Operation, Power Flow Diagram.
Introduction
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 1 — 8
Bypass AC input
(mains 2)
Rectifier/battery
charger
Main AC input
(mains 1)
Battery
Inverter
UPS module
Q2S
Static switch
Static switch
cabinet (SSC)
TO
ATTACHED
LOAD
Additional
modules
Rectifier/battery
charger
Battery
Inverter
UPS module
Additional
modules
Page 19

Introduction
page 1 — 9
Users Manual
1.5 Shared Systems Indicators and Controls
Shared Systems indicators and controls are located in three places on the UPS cabinet: on the front panel, behind a
drop-down cover just below the front panel, and inside the cabinet doors, see Figure 1-8. In battery cabinets and
auxiliary cabinets, the controls are located behind the cabinet doors.
NOTE: The SSC does not include inverter on or inverter off pushbuttons #6 and #7, or the battery operation
LED #4.
The following display descriptions:
◗ Front Panel
◗ Alphanumeric Display
◗ Hidden Panel
Figure 1-8: EPS 7000 Front Panel Indicators and Controls.
Front Panel
Alphanumeric
Display
Hidden Panel
Cover Plate
Page 20

1.5.1 Front Panel
The UPS front panel, includes the emergency power off (EPO) pushbutton, the audible alarm, four LEDs that serve
as system status indicators, the “inverter on” pushbutton, and the “inverter off” pushbutton, (on UPS modules only).
See Figure 1-9.
Figure 1-9: Front Panel Indicators and Control Display.
CAUTION: Pressing the EPO disconnects the attached load. The
emergency power off (EPO) is to be used during emergency
situations only, where a hazard to personnel or equipment
exists, such as during a fire. DO NOT USE THE EPO TO
TURN THE UPS OFF; follow the procedures listed in
this section for turning the inverter on and off.
EPO On the left side of the front panel, an emergency power off (EPO) pushbutton is
provided, with a protective cover to guard against inadvertent operation. This
pushbutton, when activated, disconnects the main AC input (mains 1), bypass AC
input (mains 2), and battery power to the UPS, and disconnects output power to the
attached load.
Audible alarm (item 1) The audible alarm provides an audible warning to the operator by sounding
a pulsed “beep” when any of the following conditions occur:
◗ Load transferred to bypass (mains 2)
◗ Load supplied via battery
◗ Operating problem
During minor alarm conditions, the alarm sounds at a slow rate and a low sound
level. When the battery approaches the low-voltage shutdown level, the alarm
sounds louder and at an increased rate. If the inverter shuts down, the alarm
sounds loudly and continuously.
An audible alarm reset is located on the hidden panel. See Figure 1-11. Pressing it
will silence the alarm. Should a higher-level alarm condition occur after the reset
has been activated, the audible alarm will sound the new alarm condition.
Introduction
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 1 — 10
Page 21

Introduction
page 1 — 11
Users Manual
¡
Load not protected (item 2 ) This red LED turns on when any of these conditions occur:
◗ The load is no longer protected following an inverter shutdown,
or the opening of the isolation circuit breaker (Q5N).
◗ The battery circuit breaker QF1 is open, making battery power
unavailable.
⁄
Operating problem (item 3) This orange LED turns on when an operating problem exists, such as fan
failure; static switch power supply fault; battery temperature fault;
overload fault; or bypass AC input (mains 2) out of tolerance. The UPS
continues to protect the attached load.
ı
Battery (item 4) This orange LED turns on to indicate that the attached load is
being partially or completely supplied by the battery. When the main AC
input (mains 1) fails or is outside tolerance, stored battery energy is
supplied to the inverter, which in turn supplies the load.
Í
Load protected (item 5) This green LED indicates that the attached load is supplied by
the inverter and protected by the battery. During normal operation, this
LED is the only one that is on.
Inverter on (item 6) This green pushbutton is used to start the inverter. When it is pushed, the
green “load protected” LED flashes for three seconds, indicating that the start
command has been received. When the inverter has synchronized with the bypass
AC input (mains 2) source, the static switch transfers the load to the inverter output.
If the inverter cannot synchronize to the bypass AC input (mains 2) source, the load
must be forced to transfer using the hidden panel (see section 2.11, Forced
Transfers).
Inverter off (item 7) This gray pushbutton is used to stop the inverter. When it is pressed for 3
seconds, the inverter stops and the load is transferred to the bypass AC input (mains
2) source. If the uninterrupted transfer conditions are not met, this pushbutton has
no effect and the inverter can be stopped only from the hidden panel (see Section
2.11, Forced Transfers).
(UPS Modules Only)
(UPS Modules Only)
(UPS Modules Only)
Page 22

1.5.2 Alphanumeric Display and Controls
The alphanumeric display is located directly below the front panel display. See Figure 1-8. For complete instructions,
refer to section 2.0 Operation, Using the Alphanumeric Displays.
A brief description of the display and controls follow.
Figure 1-10: Alphanumeric LCD Display , Settings , and Pushbutton Indicators and Controls.
Front Panel Alphanumeric Legend: (details on following page)
ø
Settings
V Voltage A Current W.Hz Power/Frequency
ıı
Battery
⁄⁄
Alarms
ØØ
On/Off
*
Confirm/Verify
1.5.2.1 Two-line Alphanumeric Display
This 40-character, two line LCD displays general status of the UPS continuously, and displays measurements of
UPS operating parameters as selected with the control pushbuttons.
1.5.2.2 Alphanumeric Display Pushbuttons
Descriptions of the function of the alphanumeric display settings pushbuttons.
ø
Settings This pushbutton is used to select the display language and adjust the LCD screen
contrast for optimal viewing.
˘
Selection Depending on the displayed message, the “˘” key may serve to indicate selection,
negative response, and other functions.
◊
Voltage This pushbutton provides access to voltage measurements, including:
◗ Main AC input (mains 1) phase-to-phase voltage
◗ Bypass AC input (mains 2) phase-to-neutral and phase-to-phase voltage
◗ Inverter output phase-to-neutral and phase-to-phase voltage
◗ Load phase-to-neutral and phase-to-phase voltage
Introduction
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 1 — 12
LCD
display
LOAD IS PROTECTED
UPS IS ON LINE
Settings
pushbutton
W.HzAV
–
+
pushbutton
!
˘
87654321
*
Page 23

Introduction
page 1 — 13
Users Manual
Å
Current This pushbutton provides access to current measurements, including:
◗ Main AC input (mains 1) current
◗ Bypass AC input (mains 2) current
◗ Inverter output current
◗ Load current
◗ Percent current drawn by the load relative to UPS rating
◗ Crest factor per phase
„
Power/Freq. This pushbutton provides access to power and frequency measurements, including:
◗ Main AC input (mains 1) frequency
◗ Bypass AC input (mains 2) frequency
◗ Inverter frequency
◗ Power drawn by the load (in kW and kVA)
◗ Load power factor
ı
Battery This pushbutton provides access to battery measurements, including:
◗ Battery voltage
◗ Battery current
◗ Battery ambient temperature
◗ Battery time available
◗ Battery time remaining
⁄
Alarms This pushbutton is used to display current alarms, or to display stored alarms.
If the alarm key is pressed repeatedly, the display will scroll through the stored alarm
record, returning to the latest after the oldest is shown.
If a blinking character (!) appears in the display, the user may press the Alarm
pushbutton again to scroll through additional useful information.
Ø
On/off This pushbutton is reserved for future use.
°
Confirmation/Verify Depending on the displayed message, this pushbutton may serve to indicate confir-
mation, positive response, and other functions.
1.5.2.3 Numbered Lights
During normal operation, the green LED #1 will be on, indicating that the UPS core controller communicates with
the display. If there is an alarm condition, the red LED #1 will turn on.
Page 24

1.5.3 Hidden Panel Indicators
The hidden panel is located behind the hinged cover, at the lowest pane of the front panel, refer to Figure 1-8.
The hidden panel includes the alphanumeric display and controls, and following controls and indicators, see Figure 1-
11.
Figure 1-11: Hidden Panel Alphanumeric LEDs and Pushbutton Indicators and Controls.
Hidden panel alphanumeric legend: (upper display, details on following page)
A Emergency Shutdown G Battery charging L Overload
B Rectifier/Charger on H Inverter fault M Bypass outside tolerance
C Rectifier/Charger fault I Battery discharged N Maintenance position
D Input Outside Tolerance J Inverter Desynchronized
F Battery temp. outside Tolerance K Transfer Fault
(lower display)
(port) Test connector fault Clear faults (audio) Alarm reset
1 Battery charge cycle 2 Return to float voltage (key) Security
3 Inverter sync/desync 4 Forced Transfer 5 Forced Shutdown
1.5.3.1 LED Alphanumeric Indicators
Fourteen alphabetically labeled LEDs provide detailed information on UPS status as follows:
A: Emergency shutdown
This red LED indicates that the emergency power off (EPO) or remote emergency power off (REPO) has been
activated. See section 2.10.1, Emergency power off.
B: Rectifier/charger on
This green LED indicates that the rectifier/battery charger is on.
Introduction
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 1 — 14
NMLKJIHGFEDCBA
fault
12 345
Page 25

Introduction
page 1 — 15
Users Manual
C: Rectifier/charger fault
This red LED indicates an alarm condition within the rectifier/battery charger. It indicates the presence of one of the
following fault conditions:
◗ Input circuit breaker Q1 open
◗ Input power protection fuse blown
◗ Rectifier/battery charger over-temperature
◗ Battery charge overcurrent
◗ Battery overvoltage
◗ Rectifier/battery charger control board fault
◗ Power supply board fault
D: Main AC input (mains 1) outside tolerance
This orange LED indicates that the main AC input (mains 1) source is outside tolerance (voltage and/or frequency
too high or too low).
E: Reserved for future use.
F: Battery temperature outside tolerance
This orange LED indicates that the ambient temperature of the battery is too high or too low.
G: Battery charging
This orange LED indicates that the battery is being recharged. This LED functions only when the connected battery
is of the vented lead-acid type (sealed lead-acid batteries will not activate this signal).
H: Inverter fault
This red LED indicates an alarm condition in the inverter, which may be one or more of the following conditions:
◗ Inverter shutdown due to output voltage out of tolerance
◗ Inverter output protection fuse blown
◗ Inverter leg fault
◗ Inverter output transformer over-temperature
◗ Inverter leg over-temperature
◗ Internal clock fault
◗ Inverter control board fault
◗ Power supply board fault
I: Battery discharged
This orange LED indicates that the battery has reached the end of its autonomy, shutting down the inverter.
J: Inverter desynchronized
This orange LED indicates that the inverter is not synchronized with the bypass AC input (mains 2).
Page 26

K:Transfer fault
This red LED indicates a transfer fault, which may be one or more of the following conditions:
◗ Inverter output fault
◗ Static switch over-temperature
◗ Static switch power supply fault
◗ Transfer control board fault
◗ Power supply board fault
L: Overload
This orange LED indicates an alarm condition resulting from one or more of the following conditions:
◗ Inverter current above rating
◗ Output current above rating
◗ Inverter and/or static switch shutdown due to excessive load current
M: Bypass AC input (mains 2) outside tolerance
This orange LED indicates that the bypass AC input (mains 2) voltage and/or frequency are too high or too low.
N: Maintenance position
This orange LED indicates that circuit breakers QF1, Q4S, Q5N, or Q3BP are set to the maintenance position. The
UPS is not available for load protection.
1.5.3.2 Hidden Panel Lower Pushbuttons
Following are brief descriptions of the function of the hidden panel pushbuttons. See Figure 1-10.
Test connector (port) This 9-pin connector is reserved for service. It is used to connect the cabinet
to a computer, allowing system calibration, personalization, and computer-aided
diagnostics.
Clear fault log Pressing this pushbutton clears the alarms stored in memory, allowing the unit to
restart. Memorized alarms cannot be cleared until the condition causing the alarm
has been corrected.
Audible alarm reset Pressing this pushbutton stops the audible alarm. Should a new fault condition at a
higher alarm level occur, the alarm will sound again.
Battery charge cycle (pushbutton #1) Pressing this pushbutton begins a battery charging cycle. After the
cycle is complete, the rectifier/battery charger returns to float charge levels on the
battery. The battery charge cycle is not applicable to sealed lead-acid battery installations.
Introduction
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 1 — 16
Page 27

Introduction
page 1 — 17
Users Manual
Return to float voltage (pushbutton #2) This pushbutton can be used during a battery charge cycle to force
the rectifier/battery charger back to the float voltage level.
Security pushbutton (key) This pushbutton must be pressed simultaneously with any of the following
three pushbuttons. This helps guard against inadvertent transfer of the load with
interruption.
Inverter desync/sync (pushbutton #3) Pressing and holding the “security key” while pressing this
pushbutton forces the inverter output to desynchronize or synchronize to the bypass
AC input (mains 2) source.
Forced bypass to inverter (pushbutton #4) Pressing and holding the “security key” while pressing this
pushbutton forces the transfer of the load to the inverter output when the bypass is
out of tolerance. The inverter must be on; press the “inverter on” pushbutton on the
UPS front panel if necessary. The load will experience a 0.8 second interruption.
Refer to section 2.11, Forced Transfers.
Forced inverter to bypass (pushbutton #5) Pressing and holding the “security key” while pressing this
pushbutton stops the inverter and transfers the load to the bypass AC input (mains
2) even if the bypass is out of tolerance. The load will experience a 0.8 second interruption. Refer to section 2.11, Forced Transfers.
CAUTION: Using the forced transfer functions will cause the load to
experience an interruption for a minimum of 0.8 seconds. Be
certain the load can tolerate this interruption; see section
2.11 Forced Transfers.
Page 28

(This page left blank intentionally)
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 1 — 18
Page 29

Users Manual
Operation
page 2 —1
2.0 Scope
This section describes procedures for normal operation of EPS 7000 Shared Systems. Including interactive front
panel display, settings for language configuration, alarms message displays, voltage, current, battery measurements, with before and after start-up checks, emergency shutdown using EPO disconnects, and normal conditions
for using forced transfers.
2.1 Status Screen Display
The alphanumeric interactive status screen display, located in the top panel of the hidden panel, see Figure 2-1, is
the automatic default display for status setting configurations.
Figure 2-1: Default Status Screen Alphanumerical Display Configuration.
During normal operation, when there are no alarm conditions present and the load is supplied by the UPS inverter
output, the display will present the general status message:
LOAD IS PROTECTED
UPS IS ON LINE
When there are alarm conditions, the display will present a general alarm message, and the user can use the
“alarm” pushbutton (!) to determine the exact cause of the alarm condition, see section 2.3 Alarms.
The following sections present detailed operating instructions for the alphanumeric display.
Operation
General status screen.
This is the default display. It automatically reappears
if the control panel has not been used for ten minutes.
!
V
A
W.H z
+
–
Alarm display
Voltage measurements
Current measurements
Frequency and power measurements
Battery measurements
Reserved for future use (on/off controls)
*
Language and screen contrast settings
to
set
to
confirm
to
°≥
confirm
Page 30

Operation
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 2 —2
2.2 Settings Selection Screen
The settings selection screens allow the user to configure the display language and set the contrast of the LCD display.
To access the settings selection screen, press the settings pushbutton, and follow the steps. See Figure 2-2.
Figure 2-2: Settings Selection Display Screen.
IMPORTANT: Select ENGLISH U.S. as the display language to match the
displays as presented in this manual.
ø
LANGUAGE = ENGLISH U.S.
≥=SELECT *=CONFIRM.
°
DISPLAY CONTRAST
≥=SELECT *=CONFIRM.
Press the settings pushbutton to access the
language selection menu.
Select the display language: French, English
(U.K.), Spanish, Dutch, Italian, Swedish,
Portugese, English (U.S.), German, or Finnish
Press the
selection and access the contrast selection menu.
Set the display contrast by pressing the ≥
pushbutton until the desired contrast is reached.
Press the ° pushbutton to confirm the contrast
selection and return to the general status screen.
pushbutton to confirm the language
°
°
general status screen
Page 31

page 2 —3
Users Manual
2.3 Alarms
In the event of an alarm condition, the general status screen shows an alarm message. To determine the specific
condition causing the alarm, press the alarm key on the front panel and follow the sequential steps.
If there is a flashing exclamation mark (!) in the displayed message, there is additional information to be viewed, follow
the steps as indicated in Figure 2-3.
Most alarm messages are self-explanatory. See section 2.8 LCD Messages for a listing of the most common alarm
messages.
The most serious alarms are stored in the fault log, and may be viewed by following the steps shown in Figure 2-3.
To reset the alarms, press the “clear fault log” pushbutton. See section 1.5.2.2 Alphanumeric Display Pushbuttons.
Figure 2-3: Sequential Alarm Messages for Viewing the Fault Log.
Operation
ALARM
. . .
⁄
(ALARM MESSAGE NUMBER 1)
⁄
(LAST ALARM MESSAGE)
⁄
general status screen
This message on the general status screen
!
!
indicates an alarm condition. The flashing
exclamation mark ( ! ) indicates that there are
alarm messages to view. To view them, press the
"alarm" pushbutton.
The last alarm message is not followed by an
exclamation mark ( ! ). When the "alarm"
pushbutton is pressed again, the display will
return to the general status screen.
.
Page 32

EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 2 —4
Operation
2.4 Voltage Measurements
To display voltage measurements, press the “V” key on the keyboard. See Figure 2-4.
Figure 2-4: Voltage Measurement Displays.
Select voltage measurements by
pressing the
◊ pushbutton
◊
(Only in UPS modules)
(only in SSC)
(only in SSC)
(only in UPS modules)
(only in UPS modules)
INPUT VAB VBC VCA
V RMS
◊
BYPASS VAN VBN VCN
V RMS
◊
BYPASS VAB VBC VCA
V RMS
◊
INV. VAN VBN VCN
V RMS
◊
INV. VAB VBC VCA
V RMS
◊
LOAD VAN VBN VCN
V RMS
◊
LOAD VAB VBC VCA
V RMS
◊
Main input (mains 1) phase-to-phase voltages
in VAC RMS.
Bypass input (mains 2) phase-to-neutral
voltages in VAC RMS.
Bypass input (mains 2) phase-to- phase
voltages in VAC RMS.
Inverter output phase-to-neutral voltages in
VAC RMS.
Inverter output phase-to-phase voltages in
VAC RMS.
Load phase-to-neutral voltages in VAC RMS.
Load phase-to-phase voltages in VAC RMS.
Page 33

page 2 —5
Users Manual
2.5 Current Measurements
To display current measurements, press the “A” key on the keyboard. See Figure 2-5.
Figure 2-5: Current Measurements Displays.
Operation
(Only in UPS modules)
(only in SSC)
(only in UPS modules)
Select current measurements by
pressing the
Å pushbutton
Å
INPUT I1 I2 I3
A RMS
Å
BYPASS I1 I2 I3
A RMS
Å
INV. I1 I2 I3
A RMS
Å
LOAD I1 I2 I3
A RMS
Å
I LOAD / IN
=
% (IN = A)
Å
LOAD I1 I2 I3
CREST F.
Å
Main input (mains 1) currents in AAC RMS.
Bypass input (mains 2) currents in AAC RMS.
Inverter output currents in AAC RMS.
Load currents in AAC RMS.
Highest current drawn by a load phase, relative to
the current rating of the UPS module or SSC (IN).
Load crest factor for each phase.
Page 34

2.6 Power Frequency Measurements
To display power or frequency measurements, press the “W.Hz” key on the keyboard. See Figure 2-6.
Figure 2-6: Power and Frequency Measurements Displays.
Operation
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 2 —6
Select power and frequency measurements
by pressing the
„ pushbutton.
„
FREQ. INP. BYP. INV.
HZ
„
LOAD P1 P2 P3
KW
„
P LOAD / Pn
= %
(PN= KW)
„
LOAD P1 P2 P3
KVA
„
P. TOTAL P.KW P.KVA
LOAD
„
POWER FACTOR
LOAD P.F. =
„
Frequency in Hertz for the main input (mains 1),
bypass input (mains 2), and inverter output.
Real power drawn by the load in kilowatts, for
each phase.
Percentage of real power drawn by the load,
relative to the rated output of the UPS module or
SSC.
Apparent power in kVA drawn by the load for
each phase.
Total real power (in kW) and apparent power (in
kVA) drawn by the load.
Load power factor (real power divided by
apparent power)
Page 35

Operation
page 2 —7
Users Manual
2.7 Battery Measurements
To display battery voltage, current, ambient temperature, and time available or remaining, press the battery key on the
keyboard. see Figure 2-7.
Figure 2-7: Battery Measurements Displays.
Select battery measurements by
pressing the "battery" pushbutton.
ı
UBAT.
V
IBAT.
* A
ı
T BAT.
OR
AVAILABLE BAT.TIME
MN %KV LOAD =
ı
REMAINING BAT. TIME
MN %KV LOAD =
ı
°
Baattery voltage (VDC), charge (+) or discharge
C
(–) current (ADC), and battery temperature
(degrees Celsius).
If the main input (main 1) source is available, this
indicates the amount of battery time (in minutes)
available in the event of a main input outage.
If the main input (mains 1) source is out of
tolerance or is unavailable, this indicates the
amount of battery time (in minutes) remaining for
on-battery operation.
Page 36

Operation
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 2 —8
2.8 LCD Messages
This section presents the most common alarm messages that appear on the LCD (the alphanumeric section of the
“hidden” panel), and explains their meaning.
LOAD IS PROTECTED
UPS IS ON LINE
This is the normal display message. There are no alarms or problems, and the load is being supplied by the UPS
inverter.
2.8.1 General alarms
LOW LEVEL ALARM
UPS OK !
This message indicates that a problem requiring action has occurred. The load is still supplied by the
inverter. The problem is listed in the secondary alarm message (see below), as indicated by the
flashing
exclamation mark (!).
The alarm message may be viewed by pressing the “alarm” pushbutton (!)
UPS INPUT FAILURE
LOAD ON BATTERY !
This message indicates that the main AC input (mains 1) has failed or is outside of tolerance, and power to the
inverter is being supplied from the UPS battery system. The load is still supplied via the inverter.
REMAINING BAT. TIME
__ MN %KW LOAD = __
This message is automatically displayed every five seconds when the UPS is on battery. It alternates with the
previous message. The message provides an estimate of the available remaining time on battery, based on the
percentage of full rated load being supplied, the type of battery, the battery temperature, and the battery age.
UPS LOW BATTERY
SHUTDOWN IMMINENT !
This message indicates that the batteries have reached the “low battery shutdown” warning level. The user must
take steps to prepare the load for shutdown (load shedding, file saving and computer shutdown, etc.). This
message replaces the previous two messages when the batteries are nearly depleted. When this message
appears, there are only a few minutes of battery back-up time remaining.
UPS ALARM
CALL SERVICE !
This indicates that the battery disconnect circuit breaker QF1 has been open or the inverter has stopped and that
service is required. The problem is listed in the secondary alarm message (see below), as indicated by the flashing
exclamation mark (!). The secondary alarm message may be viewed by pressing the “alarm” pushbutton (!).
Page 37

Operation
page 2 —9
Users Manual
2.8.2 Secondary Alarms
The presence of these alarms is indicated by a flashing exclamation mark (!) on the general alarm message. Press
the “alarm” pushbutton to view these messages.
EMERGENCY SHUTDOWN
REPO ON !
This message indicates that the UPS has been shut down because a remote emergency power off (REPO)
pushbutton has been pressed and is still closed.
LOAD ON
BYPASS !
This message indicates that the load has been transferred to the bypass AC input (mains 2) source. The load is no
longer protected.
BYPASS PROBLEM
CHECK FREQUENCY !
This message indicates that the bypass AC input (mains 2) source is out of frequency tolerance. The inverter has
switched to free-running mode. Transfer of the load from the inverter output to the bypass AC input source requires
an interruption of power to the load.
BYPASS PROBLEM
CHECK VOLTAGE !
This message indicates that the bypass AC input (mains 2) source is out of voltage tolerance. The inverter has
switched to free-running mode. Transfer of the load from the inverter output to the bypass AC input source requires
an interruption of power to the load.
INDEPENDENT INVERTER
FREQ. COMMAND ON !
This message indicates that the inverter has been set to free-running mode. The inverter is not synchronized to the
bypass AC input (mains 2) power source. Transfer of the load from the inverter output to the bypass AC input source
requires an interruption of power to the load.
BYPASS TRANSFER
LOCKOUT COMMAND ON !
This message indicates that the UPS has been set not to transfer from the inverter to the bypass AC input (mains
2) source. In the event of an inverter shutdown, the load will be disconnected.
BATTERY CABINET
OVERTEMP. !
This message indicates that the ambient temperature of the battery is out of tolerance.
Page 38

Operation
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 2 —10
UPS INPUT PROBLEM
CHECK FREQUENCY !
This message indicates that the main AC input (mains 1) frequency is out of tolerance. The rectifier/battery charger
has shut down and the inverter is operating from its battery source.
UPS INPUT PROBLEM
CHECK VOLTAGE !
This message indicates that the main AC input (mains 1) voltage is out of tolerance. the rectifier/battery charger
has shut down and the inverter is operating from its battery source.
CHARGER SHUTDOWN
COMMAND ON !
This message indicates that the rectifier/battery charger has been instructed to shut down, for example during
progressive (stepped) transfer to a motor-generator set.
INPUT KVA LIMITED
COMMAND ON !
This message indicates that the rectifier/battery charger has been instructed to limit the power drawn from the main
AC input (mains 1) source. This condition occurs, for example, when the load is being supplied by an undersized
motor-generator set; the UPS battery source is called upon to make up the difference.
BATTERY CURRENT
LIMIT COMMAND ON !
This message indicates that the rectifier/battery charger has been instructed to limit the charge current to the
battery. Normal charge current to the battery will be supplied when the command is released. This condition occurs,
for example, when the load is being supplied by an undersized motor-generator set.
QF1 BATTERY BREAKER
OPEN !
This message indicates that the battery circuit breaker QF1 has been opened or has tripped. the load is no longer
protected, since battery power is unavailable.
LOW BATTERY
. . . !
This message indicates that the inverter has shut down, due to depletion of the battery’s stored energy.
CHARGER OFF
. . . !
This message indicates that the rectifier/battery charger has shut down.
Page 39

Operation
page 2 —11
Users Manual
CHARGER FAULT
CALL SERVICE !
This message indicates that a fault has occurred in the rectifier/battery charger, and that service is required.
Q1 UPS INPUT CB
OPEN !
This message indicates that the input isolation circuit breaker is open or has tripped. It must be closed for
rectifier/battery charger start-up.
INVERTER OVERLOAD
CHECK P.F. AND KW
This message indicates that the inverter is in an overload condition, usually due to excessive real power (kW) being
drawn by the load. The flashing “KW” indicates that the operator should check the load real power. The inverter
will keep supplying the load for a certain amount of time depending on the overload level.
INVERTER FAULT
CALL SERVICE !
This message indicates that a fault has occurred in the inverter, and that service is required.
INVERTER SHUTDOWN
OVERLOAD > I MAX!
This message indicates that an overload greater than 1.5 times the full power rating of the inverter has occurred,
and that the inverter has shut down.
INVERTER SHUTDOWN
THERMAL OVERLOAD A
This message indicates that an overload below 1.5 times the full power rating of the inverter has occurred and that
the inverter has shut down. The flashing “A” indicates that the operator should check the load current.
I LOAD > IN
CHECK LOAD A
This message indicates that the load power being drawn is greater than the UPS full load rating. The flashing “A”
indicates that the operator should check the load current. The inverter or static switch will keep supplying the load
for a certain amount of time depending on the overload level.
TRANSFER FAULT
CALL SERVICE !
This message indicates that a fault has occurred that affects the transfer of the load between the inverter and the
bypass source. Service is required.
Page 40

PH OUT OF TOLERANCE !
This message indicates that there is an out of tolerance condition between the inverter and bypass AC input (mains
2) sources. Transfer of the load between the inverter and bypass AC input will result in an interruption of load power.
Q4S BYPASS SWITCH
OPEN !
This message indicates that the circuit breaker Q4S is open. Transfer of the load from the inverter to the bypass
source is not possible.
Q5N UPS OUTPUT ISOL.
SWITCH OPEN !
This message indicates that the optional UPS isolation circuit breaker Q5N is open. The load is not supplied unless
the maintenance bypass circuit breaker Q3BP is closed.
Q3BP MAINT. BYPASS
SWITCH CLOSED !
This message indicates that the optional maintenance bypass circuit breaker Q3BP is closed. The system is set to
maintenance bypass, and the load is supplied by the bypass AC input source (mains 2).
STATIC SWITCH O.L.
EMERGENCY OFF !
This message indicates that the static switch has shut down following an overload condition, disconnecting the load.
BATTERY CHARGING !
This message indicates that the battery is being recharged.
INDEPENDENT INVERTER
FREQUENCY !
This message indicates that the inverter is operating in free-running mode, and is no longer synchronous with the
bypass AC input source (mains 2). Inverter frequency is stable within 0.1 Hz, but transfer of the load to the bypass
AC input source is not possible without an interruption of power to the load.
NUMBER OF MODULES
READY INSUFFICIENT !
This message indicates that the load cannot be transferred from the bypass input source to the UPS modules
because not enough UPS modules have been started up.
UPS
TRANSFER LOCKOUT !
This message indicates that the load cannot be transferred from the inverter to the bypass AC input (mains 2) source
without interruption because the conditions for transfer without interruption are not met or because the inverter is
operating in free-running mode or in current limit, or because the UPS has been commanded not to transfer without
interruption, or because of an internal fault. See section 2.11 Forced Transfers.
Operation
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 2 —12
Page 41

Operation
page 2 —13
Users Manual
FAN FAILURE
CALL SERVICE !
This message indicates that a fan has failed, and that service is required. Because the fans of the rectifier/battery
charger and the inverter are redundant, the load is still supplied by the inverter.
AUXILIARY CABINET FAULT
CALL SERVICE !
This message indicates that there is a fault in an auxiliary cabinet, and that service is required.
CALL SERVICE FOR
BATTERY PM !
This message indicates that the battery may have reached its end of life (based on the rated lifetime and the conditions of use).
MODULE NUMBER X
UNAVAILABLE
This message indicates that the core controller of the selected module (UPS module or SSC) is not sending data
to the alphanumeric display. The status of the module is still correctly indicated by the LEDs of the visible panel
and the hidden panel. See section 1.5 Shared Systems Indicators and Controls.
MODULE NUMBER X
FAULT
This message indicates that the core controller of the selected module (UPS module or SSC), is sending invalid
data to the alphanumeric display. The status of the module is still correctly indicated by the LEDs of the visible panel
and the hidden panel. See section 1.5 Shared Systems Indicators and Controls.
DISPLAY NUMBER X
UNAVAILABLE
This message indicates that the alphanumeric display is not operating properly. The status of the UPS module or
SSC is still correctly indicated by the LEDs of the visible panel and the hidden panel. See section 1.5 Shared
Systems Indicators and Controls.
DISPLAY NUMBER 1
UNAVAILABLE
This message indicates that the alphanumeric display is not operating properly. The status of the UPS is still
correctly indicated by the LEDs of the visible panel and the hidden panel. See section 1.5 Shared Systems
Indicators and Controls.
HARMONIC FILTER
FUSE FAILED
This message indicates that the fuse(s) protecting the input harmonic filter has opened and that service is required.
The status of the UPS is still correctly indicated by the LEDs of the visible panel. See section 1.5 Shared Systems
Indicators and Controls for front and hidden panel indicators and controls.
Page 42

2.9 Preparations Before Start-up
Preparing before start-up uses a check list to powering up the EPS 7000. Thoroughly read this manual, and
reference EPS 7000 Single Module Users Manual 86-134004-00, and Installation Manual 86-134003-00), in
conjunction with this start-up procedure, to utilize information of the controls and indicators during start-up.
2.9.1 Checks Before Start-up
Before starting the EPS 7000, thoroughly read this manual to be certain that you fully understand the operation of
the EPS 7000 Shared Systems indicators, controls, and operational sequences.
Make certain that these conditions exist (as applicable to your installation):
◗ All power and control wires have been properly connected and securely tightened.
◗ The upstream and downstream protective devices are not tripped, and have been sized properly for the
UPS and load requirements.
◗ The voltage at each main AC input circuit breaker Q1 and at the bypass input circuit breaker Q4S is the
same as indicated on the UPS nameplate, located inside the left door of the EPS 7000 UPS module.
◗ The air filters located inside each EPS 7000 module front door are properly installed and free of dust, dirt,
and debris. Make certain that no objects block the air intake around the front bottom of the enclosures, and
that the air exhaust at the top rear of the enclosures is free of obstructions.
In the individual UPS modules:
◗ Input (isolation) circuit breaker Q1 is in the OFF (open) position.
◗ Battery disconnect circuit breaker QF1 is in the OFF (open) position.
◗ Output isolation circuit breaker Q5N is in the OFF (open) position.
In the SSC:
◗ System maintenance bypass circuit breaker Q3BP is in the OFF (open) position (if present).
◗ System output isolation circuit breaker Q5N is in the OFF (open) position (if present).
◗ Input power supply switches SW1 and SW2 are in the ON (closed) position.
◗ The upstream bypass AC input (mains 2) circuit breaker (Q4S, customer-supplied) is in the OFF (open)
position.
◗ If present, the upstream maintenance bypass circuit breaker (customer-supplied) is in the OFF (open)
position.
Operation
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 2 —14
Page 43

Operation
page 2 —15
Users Manual
2.9.2 Start-up
The following start-up procedure should be performed during the initial start-up following installation of the system, and
this sequence should be followed any time that the EPS 7000 system is being restarted from an off condition (i.e., after
the UPS has been powered down by removing the upstream AC input power and opening all the circuit breakers of
the UPS).
a. Apply power to Q4S by closing the upstream circuit breaker supplying Q4S, and the upstream circuit
breaker supplying the optional maintenance bypass input (if present).
b. Apply power to the UPS modules by closing the upstream circuit breaker supplying the main AC input
(mains 1).
c. Start the SSC:
1. Close the optional system maintenance bypass circuit breaker Q3BP (if present, in the maintenance bypass
cabinet). Power is now available at the SSC output (the load is energized) via the maintenance bypass source.
2. Close the upstream circuit breaker Q4S that supplies the bypass input to the SSC. The SSC will come on-line;
after about ten (10) seconds, the wrap-around circuit breaker Q2S will automatically close.
3. Close the optional system isolation circuit breaker Q5N (if present, in the maintenance bypass cabinet).
4. Open the optional system maintenance bypass circuit breaker Q3BP (if present). The SSC is now on-line and
the load is supplied via the bypass source.
Note that if your SSC configuration does not include the maintenance bypass option, start-up requires only
closing Q4S to supply the bypass source to the SSC. All other functions are fully automatic.
d. Start the UPS modules:
1. For each module, close the input isolation circuit breaker Q1. Verify that the following conditions exist:
◗ The red “load not protected” LED is on
◗ The rectifier/battery charger automatically starts
If either condition is not present, there is a fault. Open Q1 and
contact MGE Customer Support Services.
2. For each module, close the UPS isolation circuit breaker Q5N. The fans in the UPS module will start.
3. For each module, close the battery disconnect circuit breaker QF1. The batteries are now connected to the
rectifier/battery charger, and have begun charging.
IMPORTANT: Because it is standard for the UPS module to be
programmed for automatic restart, the inverter will
automatically start after the battery disconnect circuit
breaker QF1 has been closed.
Page 44

4. If the modules are not programmed for automatic restart, for each module, press the “inverter on” pushbutton.
The green “load protected” LED will flash for about 3 seconds, indicating that the inverter is starting.
5. As soon as a sufficient number of UPS modules have been started, the SSC will automatically transfer the load
to the UPS module output. On each module, the green “load protected” LED will turn on and remain on. On
the SSC, the green “load protected” LED will turn on.
NOTE: If the transfer conditions are not satisfied (bypass AC input
sources is out of tolerance) a forced transfer is required.
Refer to section 2.11 Forced Transfers.
6. As the remaining UPS modules are turned on (per step 4 above), their respective green “load protected” LEDs
flash for three seconds, then remain on as the modules connect to the load. The load is equally shared between
modules.
2.9.3 Checks After Start-up
After initial start-up of the system, normal operation should be tested. At the minimum, the following tests should be
performed as applicable to your installation:
◗ Emergency power off (EPO) test.
◗ Remote emergency power off (REPO) test (if applicable).
◗ Inverter start and stop.
◗ Battery transfer test.
◗ Maintenance bypass procedure.
Operation
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 2 —16
Page 45

Operation
page 2 —17
Users Manual
2.10 Shutdown
Shutdown procedures in this section apply to the EPS 7000 system under normal, emergency, overload, and maintenance conditions.
2.10.1 Emergency Shutdown Using EPO
CAUTION: Pressing the EPO disconnects the attached load. The
emergency power off (EPO) is to be used during emergency
situations only, where a hazard to personnel or equipment
exists, such as during a fire. DO NOT USE THE EPO TO
TURN THE UPS OFF; follow the procedures listed in
this section for turning the inverter on and off.
During an emergency situation, such as a fire in the computer or electrical room, the UPS and all downstream
devices can be instantly shut down by pressing the “emergency power off” (EPO) pushbutton on the front panel of
the UPS cabinet, or by pressing the “remote emergency power off” (REPO) optional pushbutton located within the
room.
The EPO or REPO pushbuttons should not be used for normal shutdown of the equipment; when activated, ground
paths may be broken (depending on installation) and sensitive loads attached to the UPS may lose safety ground
connection.
Each UPS module has an EPO feature that can be activated to shut down that module only, see section 1.5 Front
Panel.
2.10.2 Normal Shutdown
To shut down the UPS, press the “inverter off” pushbutton on the module front panel for 3 seconds. To restart, press
the “inverter on” pushbutton. Note that the transfer will occur only if the inverter is synchronized to the bypass;
otherwise, a forced transfer is needed, see section 2.11 Forced Transfers.
To isolate the SSC for maintenance, or to transfer the load to maintenance bypass input source (if present),
follow the procedure that applies to your configuration.
IMPORTANT: When one UPS module in a shared system is shutdown, it
may cause the remaining modules to enter an overload or
current-limiting condition, if they are unable to fully support
the attached load. The remaining modules may shutdown
after a certain time or immediately (depending on the load
level), and the load may be transferred to the bypass AC
input source.
Page 46

2.10.3 Isolation of an Individual UPS Module
To isolate an individual UPS module for maintenance (allowing the remaining UPS modules to maintain the attached
load), follow this procedure (starting with all UPS modules operating normally, supplying the attached load):
1. Stop the inverter by pressing the “inverter off” pushbutton on the UPS module front panel for 3 seconds. The
audible alarm will sound; silence the alarm by pressing the audible alarm reset pushbutton on the hidden panel.
If the transfer conditions are not satisfied (bypass out of tolerance or other reason), a forced transfer is required;
refer to Section 2.11, Forced Transfers.
2. Open the UPS isolation circuit breaker Q5N.
3. Open the battery disconnect circuit breaker(s) QF1.
4. Open the input isolation circuit breaker Q1.
The UPS module is now isolated for maintenance. For complete protection, the upstream circuit breaker supplying
the UPS module should be opened, locked, and tagged while the UPS is being serviced.
To restart the UPS module after maintenance:
1. Close the input isolation circuit breaker Q1.
2. Close the isolation circuit breaker Q5N. The UPS module fans will start.
3. Wait for the green LED “B” on the hidden panel to turn on (indicating that the rectifier/battery charger has
started), then close the battery disconnect circuit breaker QF1. If there is more than one battery cabinet in your
configuration, close all the battery disconnect circuit breakers.
IMPORTANT: Because it is standard for the UPS module to be
programmed for automatic restart, the inverter will
automatically start after the battery disconnect circuit
breaker QF1 has been closed.
4. If the module is not programmed for automatic restart, start the inverter by pressing the “inverter on” pushbutton
on the UPS front panel. In a few moments, the inverter will start and the UPS module will resume normal
operation. If the transfer conditions are not satisfied (bypass out of tolerance or other reason), a forced transfer
will be required. See section 2.11 Forced Transfers.
Operation
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 2 —18
Page 47

Operation
page 2 —19
Users Manual
2.10.4 With Maintenance Bypass
This procedure assumes that the UPS system is operating normally, with the attached load supplied via the UPS
inverter:
1. Stop the inverter by pressing the “inverter off” pushbutton on the UPS front panel for 3 seconds. The audible
alarm will sound; silence the alarm by pressing the audible alarm reset pushbutton on the hidden panel. See
section 1.5 Shared Systems Indicators and Controls.
If the transfer conditions are not satisfied (bypass out of tolerance or another reason), a forced transfer will be
required., in this case refer to section 2.11 Forced Transfers for procedures.
2. Depress transfer initiate switch. Unlock and remove the key from key interlock. Unlock and close the maintenance bypass circuit breaker Q3BP, see Figure 1-7.
3. Open the UPS isolation circuit breaker Q5N and lock open. The SSC is now isolated from the load which is
supplied by the maintenance bypass AC input source.
4. Open the circuit breaker Q4S.
For complete protection, the upstream circuit breaker (Q4S) supplying the UPS should be opened, locked, and
tagged while the UPS is being serviced. The UPS is now isolated for maintenance.
To restart the UPS after maintenance:
1. Close the upstream bypass circuit breaker Q4S. After about 10 seconds, the wrap-around circuit breaker Q2S
will close.
2. Close the system isolation circuit breaker Q5N.
3. Open the system maintenance bypass circuit breaker Q3BP. The SSC is now on line and the load is supplied
via the bypass source.
4. Restart the UPS modules by following the procedures in section 2.9.
2.10.5 Without Maintenance Bypass
This procedure assumes that the UPS is operating normally, with the attached load supplied via the UPS inverter.
1. Isolate all the UPS modules by following the procedure in section 2.10.3 Isolation of Individual UPS Modules.
2. Open the upstream bypass circuit breaker Q4S.
CAUTION: Opening Q4S with the inverter stopped in a UPS without
maintenance bypass will disconnect the attached load.
The whole UPS system is now isolated for maintenance. For complete protection, Q4S or the upstream circuit
breaker supplying Q4S should be locked open and tagged while the UPS system is being serviced.
To restart the UPS system after maintenance:
1. Close the upstream bypass circuit breaker Q4S. After about 10 seconds, the wrap-around circuit breaker Q2S
will close and supply the attached load via the bypass source.
2. Restart the UPS modules by following the procedures in section 2.9.
Page 48

2.11 Forced Transfers
This section describes the normal transfer conditions and the procedures to be followed when issuing forced transfers.
CAUTION: Using the forced transfer functions will cause the load to
experience an interruption for a minimum of 0.8 seconds. Be
certain the load can tolerate this interruption.
2.11.1 Uninterrupted Transfer Conditions
To transfer the load between the UPS module output and the bypass AC input (mains 2) source without interruption,
the following conditions must be satisfied:
◗ UPS module output and bypass AC input phases must be in sync
◗ Bypass AC input voltage must be within 10% of nominal
◗ Bypass AC input frequency must be within a certain programmable tolerance of nominal
Provided that both the UPS module output and bypass AC input sources meet these conditions, uninterrupted
transfers can take place. If these conditions are not met, transfers cannot take place without interruption. A forced
transfer is required.
Forced transfers require a power interruption to the load of 0.8 seconds. Before issuing a forced transfer command,
be certain that the attached load can tolerate the brief outage. The following paragraphs describe the forced transfer
procedures.
2.11.2 Forced Transfer from Bypass AC Input Source to Inverter
Start the inverter by pressing the “inverter on” button on the front panel.
On the SSC hidden panel, press the “security” key and hold it while pressing the “forced bypass to inverter” key
(pushbutton #4). If enough modules are on, the load will be disconnected for 0.8 seconds, then connected to the
UPS modules.
2.11.3 Forced Transfer from Inverter to Bypass AC Input
On the UPS hidden panel, press the “security” key and hold it while pressing the “forced inverter to bypass” key
(pushbutton #5). The inverter will stop and disconnects the UPS modules. When all modules are stopped, the load
will be disconnected for 0.8 seconds; then connected to the bypass AC input source. See Figure 1-11.
IMPORTANT: When onr UPS module in a shared system is shut down, it
may cause the remaining modules to enter an overload or
current-limiting condition, if they are unable to fully support
the attached load. The remaining modules may shut down
after a certain time or immediately, (depending on the load
level), and the load may be transferred to the bypass AC
input source.
Operation
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 2 —20
Page 49

Users Manual
Maintenance
Maintenance
page 3 —1
3.0 Scope
This section describes maintenance of the EPS 7000, including safety instructions, preventive maintenance,
isolation for maintenance, information about replacement parts, and troubleshooting LCD alarm messages.
3.1 Safety Instructions
WARNING: DC input power to the inverter is normally from a battery
bank with a very high short-circuit capacity. Accidental
welding and severe burns can be caused by mistakes while
connecting or disconnecting these conductors.
ATTENTION L'entrée DC de l'onduleur est normalement alimentée par une
batterie avee un courant de court-circuit élevé. Une erreur
lors de la connexion ou deconnexion de ces conducteurs
peut causer des soudures accidentelles et des brûlures
sérieuses.
WARNUNG! Gleichstrom zum Wechselrichter kommt gewoehnlich von der
Batteriebank mit einer sehr hohen Kurzschluss
Leistungsfaehigkeit. Unbeabsichtigtes Schweissen und
schwere Verbrennungen koennen die Folgevon fehlerhafter
Verbindung und Trennung sein.
3.2 IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS FOR SERVICING BATTERIES
A. Servicing of batteries should be performed or supervised by personnel knowledgeable of batteries and the
required precautions. Keep unauthorized personnel away from batteries.
B. When replacing batteries, use the same model and manufacturer of batteries.
C. CAUTION — Do not dispose of battery or batteries in a fire. The battery may explode.
D. CAUTION — Do not open or mutilate the battery or batteries. Released electrolyte is harmful to the skin and
eyes. It may be toxic.
E. CAUTION — A battery can present a risk of electrical shock and high short-circuit current. The following precau-
tions should be observed when working with batteries:
1. Remove watches, rings, or other metal objects.
2. Use tools with insulated handles.
3. Wear rubber gloves and boots.
4. Do not lay tools or metal parts on top of batteries.
5. Disconnect charging source prior to connecting or disconnecting battery terminals.
6. Determine if the battery is inadvertently grounded. If inadvertently grounded, remove the source of ground.
Contact with any part of a grounded battery can result in electrical shock. The likelihood of such shock will
be reduced if such grounds are removed during installation and maintenance.
Page 50

3.3 Preventive Maintenance
The following preventive maintenance routines should be considered the minimum requirements; your
installation and site may require additional preventive maintenance to assure optimal performance from
your installed EPS 7000 and associated equipment. These routines should be performed twice a year
(more often if required). We strongly recommend contracting MGE Customer Support Services for
preventive and remedial maintenance.
The technician or electrician performing preventive maintenance on the UPS must thoroughly read this manual, and
reference the EPS 7000 Installation Manual for Single Module and Shared Systems (MGE part number 86-134003-
00) or the EPS 7000 Users Manual, Single Module (MGE part number 86-134004-00), to become familiar with the
indicators, controls, and operation of the EPS 7000 systems.
a. Isolate and de-energize all EPS 7000 equipment for all maintenance operations.
b. Ensure that all equipment is clean and free of loose dust, dirt, and debris. The exterior of the enclosures
may be cleaned with a mild solution of soap and water, lightly applied with a lint-free cloth.
c. Inspect the air intake and exhaust plates and clean as required. Verify that air flows freely through the
equipment. Clean the air intake and exhaust plates, and the enclosure interior, with a vacuum cleaner.
d. The EPS 7000 module is equipped with air filters that should be changed at regular intervals. Inspect the
filters regularly to determine how long the filters will last in your installation.
e. Initiate the start-up procedure, as described in the User’s guide.
f.
Test the main operating sequences as applicable to your equipment configuration and installation.
3.4 Replacement Parts
There are no user replaceable parts inside the EPS 7000.
Three levels of replacement parts are available for the EPS 7000. The three levels are designated A, B, and C. The
level that you should keep on hand for your installation will vary depending on the type of maintenance planned on
site, and the configuration of your UPS system. Having the replacement parts on hand will prevent any unacceptable delays (due to time involved obtaining spare parts) during critical periods, such as system start-up.
Any items used during start-up will be replaced by MGE at no charge. Contact MGE Customer Support Services for
specific recommendations. A description of each level is provided below:
Level Description
A This level of replacement parts consists of consumable items, specifically fuses and air filters. It
is recommended to have these items on hand during installation of the UPS systems, including
initial start-up.
B This level of replacement parts is recommended when the user can tolerate short-duration UPS
down-time to obtain replacement parts in the event of a major UPS failure. This level of replacement parts consists of consumable items, specifically fuses, air filters, an inverter leg, and the
most critical circuit board assemblies.
C This level of replacement parts is recommended when the user can tolerate only a minimum of
down-time in the event of a major UPS failure. This level of replacement parts consists of consumable items, specifically fuses, air filters, an inverter leg, and a complete set of circuit board
assemblies.
Maintenance
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 3 —2
Page 51

Maintenance
page 3 —3
Users Manual
3.5 Troubleshooting and Service
Should you encounter a problem in the operation of a UPS module and need MGE UPS Systems, Inc. to service your
product, please take into account the following recommendations.
To the extent that you feel comfortable with the unit, leave it in its current state, make a record of the display lights
and alarm messages and call either your local MGE Field Engineer or MGE’s Customer Support Services at 1-800438-7373 for assistance. Leaving the unit in its current state will enable MGE’s field engineers to troubleshoot your
product and bring it back on line more easily.
If you are not comfortable with the current status of the unit, you may want to take the following actions (listed by
order of increasing impact on ease of troubleshooting):
1. If the audible alarm is active, reset it by pressing the audible alarm reset button, (the second button from the
left on the lower hidden panel, see Figure 1-11.
2. Stop the inverter. See section 2.10 for normal and forced shutdown.
3. Open the isolation circuit breaker Q5N.
4. Open the battery circuit breaker(s) QF1.
5. Reset the alarms by pressing the fault log clear button (the left most button on the lower hidden pane.l See
Figure 1-11.
6. Open the input isolation circuit breaker Q1 or the upstream circuit breaker feeding Q1.
After taking these steps, make a record of the display lights and alarm messages, call your local MGE Field
Engineer or call
1-800-523-0142 for assistance.
Page 52

(This page left blank intentionally)
Maintenance
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page 3 —4
Page 53

Symbols Definition / Meaning
@ At.
/ And/or.
+/- Plus or Minus.
≤ Equal to or less than.
# Number.
°C Degree Celsius.
°F Degree Fahrenheit.
Ø Phase angle.
Ω Ohm; unit of resistance.
®Trade Mark.
2nd Second.
A, B, C Normal sequence of phases (clockwise) in three-phase power.
AC or ac Alternating current, also implies root-mean-square (rms).
Alphanumeric display The LCD display above the hidden panel (behind the drop-down cover) on the UPS
module and the SSC.
Ambient Temp. Temperature of surrounding air.
Ambient noise Acoustical noise of surrounding environment.
Ambient noise The noise level of the environment.
Attached load The load attached to the UPS output, such as a computer system or manufacturing
system.
Audible alarm A buzzer, located behind the front panel on the UPS module and the SSC, that sounds
when alarm conditions occur.
ANSI American National Standard Institute.
AWG American Wire Gauge.
B or BAT. or BATT. Battery.
Breaker Electrical circuit interrupter.
BTU or Btu British thermal unit. Defined as the amount of heat required to raise the tempera-
ture of one pound of water by 1°F.
BYPASS See “Static Transfer switch”.
BYPASS mode See “off-line mode”.
Users Manual
Glossary
Glossary
page g — 1
Page 54

Carrier The company or individual responsible for delivering goods from one location to another.
C Common.
CB Circuit breaker.
cm Centimeter.
dB Decibels.
DC Direct current.
Conduit A flexible or rigid tube enclosing electrical conductors.
C.S.S. Customer Support Service.
Current rating The maximum current that a conductor or equipment can carry reliably without damage.
dBA Decibel Adjusted.
dBrnC Decibel above reference noise.
DC or dc Direct current, or voltage.
Digital Meter The LCD display on the front panel of inverter system.
Earth ground A ground circuit that has contact with the earth.
Electrician Refers to an installation electrician qualified to install heavy-duty electrical components in
accordance with local codes and regulations. Not necessarily qualified to maintain or repair
electrical or electronic equipment.
FET Field effect transistor.
Freq. Frequency.
Frequency slew rate The change in frequency per unit of time. Given in term of Hz per second (Hz/sec.).
GND Ground (safety).
Hz Hertz, frequency measurement unit, 1Hz is one cycle per second.
Input branch
circuit The input circuit from the building power panel to the equipment.
Inverter An electrical circuit that generates an AC sinewave output from a DC input.
Inverter mode See “on-line” mode.
I Current.
IEC International Electrotechnical Commission.
IEEE Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers.
Input branch circuit The input circuit from the building power panel to the equipment.
Inverter An electrical circuit that generates an AC voltage source from a DC voltage source.
IGBT Insulated gate bipolar transistors
Glossary
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page g — 2
Page 55

kVA KiloVolt-Ampere; is equal to 1000 Volt-Ampere.
L Line.
LCD Liquid-Crystal Display unit.
LED Light Emitting Diode.
Load protected The attached load is being supplied by the UPS module inverter output, and the
battery is available in the event that incoming (utility) power is lost.
Load not protected The attached load is being supplied, but the battery system is unavailable.
Low battery
Shutdown The battery has reached the lowest permitted operating voltage, and the inverter has
shut down (disconnecting the load) to protect the battery from damage due to further
discharge.
Mains or Mains 1 Main AC input source.
Mains 2 Bypass AC input source.
mA Milliampere.
MAX. Maximum.
MCM Thousand circular mil; standard wire sizes for multiple stranded conductors over 4/0
AWG in diameter. M is from Roman numerical system indicating 1000.
Module Refers to individual power inverter module.
NNeutral.
NC Normally close.
NO Normally open.
NEC National Electrical Code.
NFPA National Fire Protection Association.
NO. or No. Part number.
On-battery operation The attached load is being supplied by the stored energy in the battery system.
On-line mode Inverter output power is the primary energy source to load.
Off-line mode Inverter output is off, and the load connected at the inverter output receives power
from utility line via a static transfer switch or maintenance bypass relay.
OSHA Occupational Safety and Health Agency.
PCB Printed circuit assembly.
PCB Printed circuit board.
PWM Pulse Width Modulation.
Q1 UPS input isolation circuit breaker.
Glossary
page g — 3
Users Manual
Page 56

Q3BP Optional maintenance bypass circuit breaker (in single-module UPS system); optional mainte-
nance bypass circuit breaker in MBC cabinet (in shared systems).
Q4S Control or bypass circuit breaker (in single-module UPS systems); user-supplied bypass AC
input circuit breaker supplying the SSC (in shared systems).
Q5N Optional UPS isolation circuit breaker (in single-module UPS systems); UPS module isolation
circuit breaker (in shared systems); optional SSC isolation circuit breaker (in MBC).
QF1 Battery disconnect circuit breaker.
Remote
emergency power off A switch used for shutting down electrical equipment from a location away from the equipment.
SCR Silicon controlled rectifier.
Security bypass (key) Pushbutton on the hidden panel (UPS modules and SSC) allowing forced transfers and other
commands to be issued. The security key pushbutton must be held down while the desired
function is executed.
Shipping damage Any damage done to an article while it is in transit.
SPDT Single Pole Double Throw.
SSC Static switch cabinet (in shared systems).
Static Transfer An solid state switching mechanism electronically controlled to pass AC power directly from the
utility to an output load.
Technician Refers to an electronic technician qualified to maintain and repair electronic equipment. Not
necessarily qualified to install electrical wiring.
Test connector DB-9 type connector on the LCD panel allowing MGE UPS SYSTEMS Customer Support
Service technician to access programmable and diagnostic features of the system.
UVoltage.
UF Under frequency.
UL Underwriters Laboratories, Inc.
UPS Uninterruptible power system.
UV Under voltage.
VACVolts of alternating current.
Vb Battery voltage (in volts DC).
VDC Volts of direct current.
Via By way of.
VPC Volts per cell, the measure of the electrical potential of a storage cell, such as a battery.
XFMR Transformer.
Glossary
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page g — 4
Page 57

Glossary
page g — 5
Users Manual
VVolts
VA Volt amperes
VA Volt-amps, unit for apparent power measurement, equal V x I.
VAC or Vac Voltage of AC type.
VDC or Vdc Voltage of DC type.
ve Battery voltage.
Via By way of.
Page 58

(This page left blank intentionally)
EPS 7000 Shared Systems
page g — 6
Page 59

Reorder form
1660 Scenic Avenue
Costa Mesa, CA 92626
Use this form to order additional copies of this document, or to report any errors,
omissions, or other problems you have experienced.
NAME __________________________________________________________________________________
COMPANY ________________________________________________________________________________
STREET ADDRESS _________________________________________________________________________
CITY _____________________________________ STATE __________________ ZIP ___________________
I would like to order______ (quantity @ $50.00 each) additional copies of the:
EPS 7000
Shared Systems
Users Manual
86-134005-00 X0
I would like to report the following problems with this document:
Page 60

Page 61

Page 62

1660 Scenic Avenue, Costa Mesa, California 92626 • (714) 557-1636
www.mgeups.com
 Loading...
Loading...