Page 1
ST7001 RS232C Control
Specification: Rev.1.01
Marantz
RS232C Control Specification
for
ST7001
Category
Document Version
: Stereo Tuner
: 1.01
Date
Number of Page
: 2006/08/10
: 14
Marantz America, Inc. 2006
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the written consent of copyright.
All specifications might be subject to change without notice.
Page 2

RS232C Control Specification RS232C Control Specification Page: 2 / 14
Document Version [1.01]
Table of Contents
Global Description ................................................................................................................................................ 3
1.
1-1. Overview........................................................................................................................................................... 3
1-2. Block Diagram.................................................................................................................................................. 3
1-3. Interface connection specification of the product........................................................................................... 3
1-4. Assumptions and Dependencies.................................................................................................................... 3
2. Detailed Description..............................................................................................................................................4
2-1. Connection format ........................................................................................................................................... 4
2-1-1. Physical connection................................................................................................................................. 4
2-1-1-1. Data transmission sequence from Host to Slave ..........................................................................4
2-1-1-2. Data transmission sequence from Slave to Host ..........................................................................4
2-2. Transmission data format................................................................................................................................ 5
2-2-1. Transmission data format from Host to Slave........................................................................................ 5
2-2-1-1. Form1: Command ........................................................................................................................... 5
2-2-1-2. Form2: Status request ..................................................................................................................... 5
2-2-2. Transmission data format from Slave to Host........................................................................................5
2-2-2-1. Form1: ACK/NAK ............................................................................................................................ 5
2-2-2-2. Form2: Status answer and Auto status feedback.......................................................................... 5
2-3. The transaction sequences and the regulations............................................................................................ 6
2-3-1. The transaction sequences..................................................................................................................... 6
2-3-2. The transaction regulations..................................................................................................................... 6
2-3-3. Specification of Auto status feedback ..................................................................................................... 6
2-3-4. Example of the transactions.................................................................................................................... 6
2-3-5. Examples of the handshaking flowchart ................................................................................................7
2-3-5-1. Example of successful handshaking.............................................................................................. 7
2-3-5-2. Examples of handshaking error...................................................................................................... 7
3. Recommendations of Command, Status and Layer definition..................................................................... 8
4. Definitions of Command, Status and Layer......................................................................................................9
4-1. Commands....................................................................................................................................................... 9
4-1-1. Normal Command list.............................................................................................................................. 9
4-2. Status request and Status answer list...........................................................................................................12
4-2-1. Normal Status request and Status (answer and feedback) list........................................................... 12
4-2-2. Special Status request and Status answer list .....................................................................................13
4-2-3. Layer of the statuses .............................................................................................................................14
5. Revision history...................................................................................................................................................14
Company Restricted
Page 3
RS232C Control Specification RS232C Control Specification Page: 3 / 14
R
Document Version [1.01]
1. Global Description
1-1. Overview
A Host controller can control or watch out the product as a Slave very easily via the communication cable.
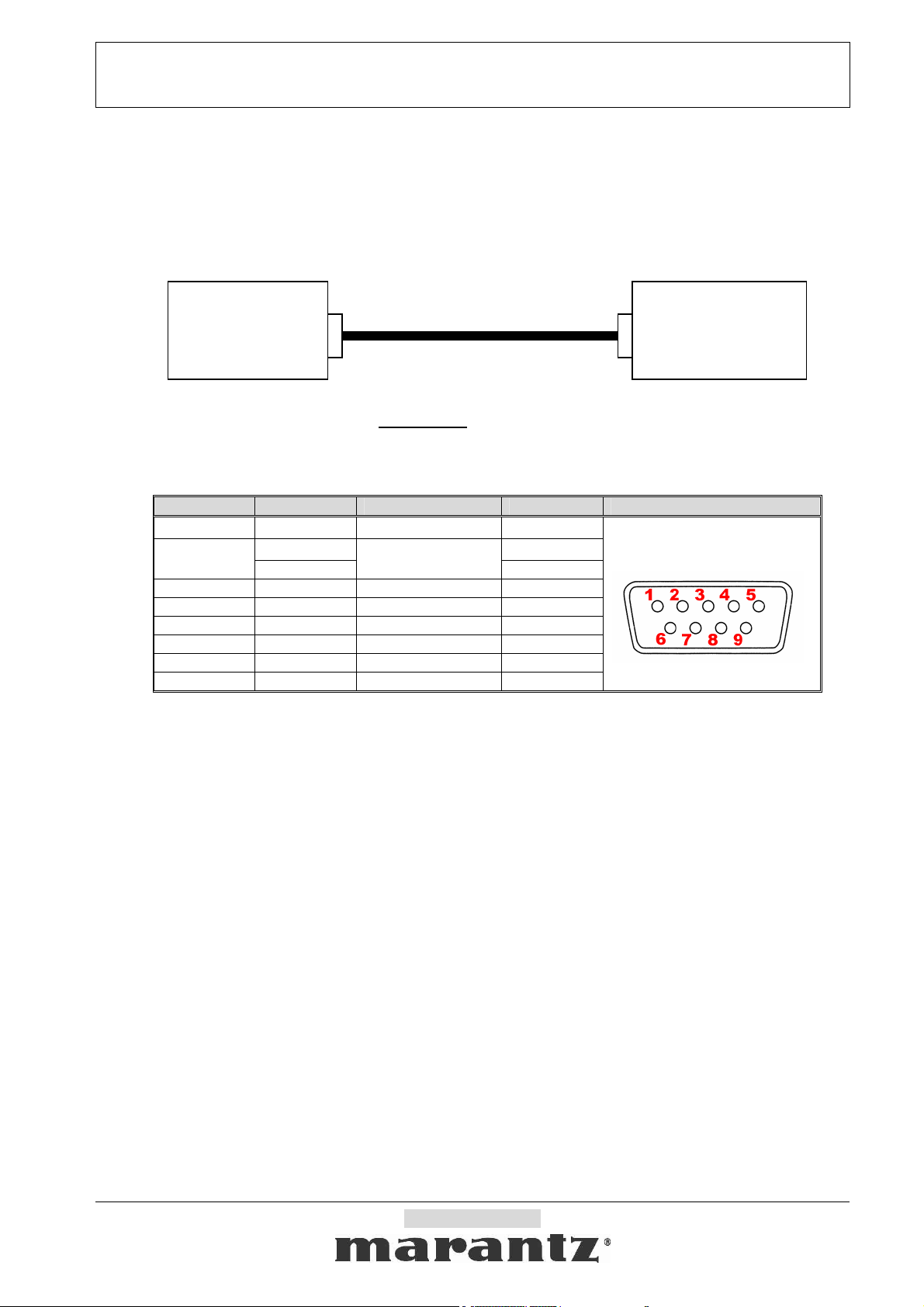
1-2. Block Diagram
* The product has D-SUB 9pin male connector.
* RS232C cable has to be the Straight type
1-3. Interface connection specification of the product
uP Interface Signal name Connection device D-Sub Pin Connecter
1-4. Assumptions and Dependencies
HOST
(Controller)
- N.C. - 1
TxD (output) 2 UART
RxD (input)
- N.C. - 4
- GND GND 5
- N.C. - 6
- N.C. - 7
- N.C. - 8
- N.C. - 9
RS232C cable (straight)
.
RS232C
Level shift driver
3
SLAVE
(The product)
Connector
D-SUB (9pin, male)
<The product connector>
S232C D-SUB (9pin,male)
Company Restricted
Page 4
RS232C Control Specification RS232C Control Specification Page: 4 / 14
Document Version [1.01]
2. Detailed Description
The interface specification between the product and a Host controller is described below.
2-1. Connection format
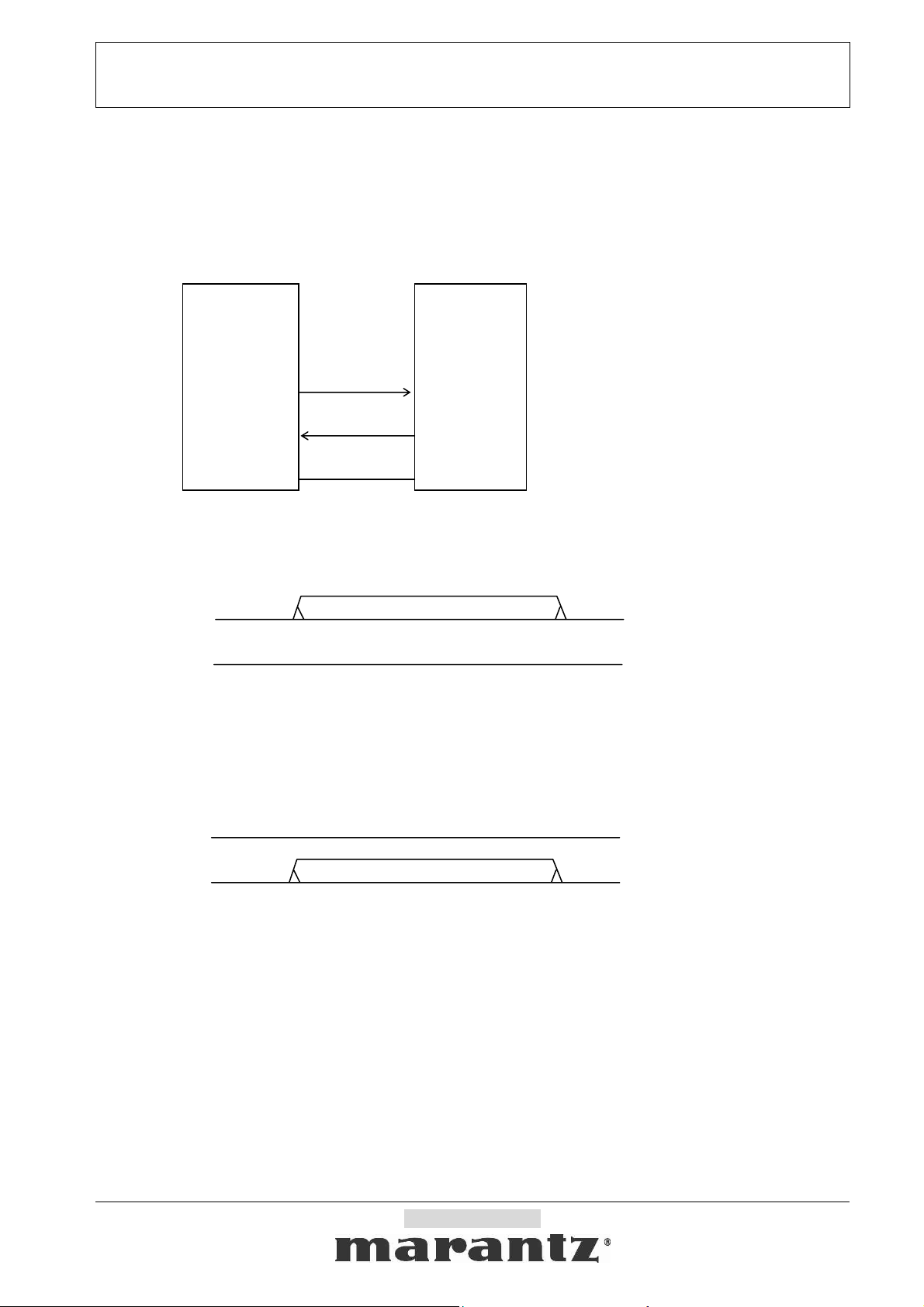
2-1-1. Physical connection
Host (Controller) Slave (the product)
(Serial setting <RS232C basic>)
Baud Rate : 9600bps
TxD
Data Bits : 8bit
Parity : None
RxD
Stop bit : 1bit
Handshaking : None
2-1-1-1. Data transmission sequence from Host to Slave
Host (Controller) Slave (The product)
2-1-1-2. Data transmission sequence from Slave to Host
GND
TxD → RxD
RxD ← TxD
1. Host starts a data transmission from TxD.
2. Host performs the data transmission of the number of required bytes, and ends a transmission.
Host (Controller) Slave (The product)
TxD → RxD
RxD ← TxD
1. Slave starts a data transmission from TxD.
2. Slave performs the data transmission of the number of required bytes, and ends a transmission.
RxD
TxD
GND
Company Restricted
Page 5
RS232C Control Specification RS232C Control Specification Page: 5 / 14
Document Version [1.01]
2-2. Transmission data format
2-2-1. Transmission data format from Host to Slave
There are two kinds of transmission data form from Host shown below.
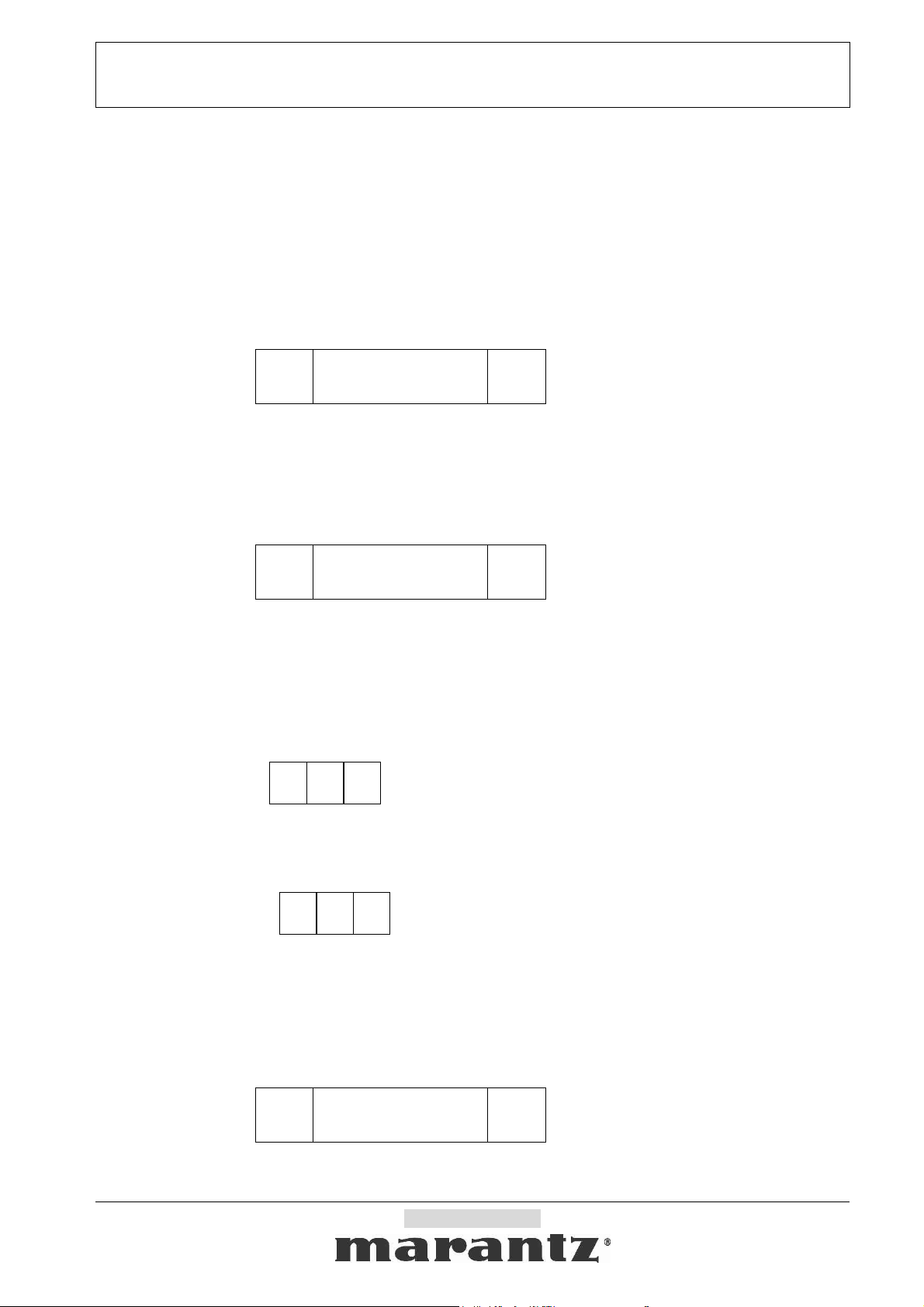
2-2-1-1. Form1: Command
Command is a data that requests some status change.
Start character : ’@’
COMMAND : see “Command list”
End character (CR) : 0Dh
Start
‘@’
2-2-1-2. Form2: Status request
Status request is a data that requests an answer of some status.
Start character : ’@’
Request status : see “Status request list”
Request character : ‘?’
End character (CR) : 0Dh
Start
‘@’
2-2-2. Transmission data format from Slave to Host
There are two kinds of transmission data form from Slave shown below.
2-2-2-1. Form1: ACK/NAK
ACK is a reply data from Slave when Slave got an acceptable command data from Host.
(ACK is sent to Host when Slave has no related status by the Command.)
Start character : ’@’, ACK : 06h, End character (CR) : 0Dh
‘
@
NAK is a reply data from Slave when Slave got an incorrect Command data, Status request data or
some other data from Host.
Start character : ’@’, NAK : 15h, End character (CR) : 0Dh
2-2-2-2. Form2: Status answer and Auto status feedback
Status answers are reply data when Slave got an acceptable Request status or Command data from
Host. Auto status feedbacks are sent to Host data when a Slave’s status is changed.
Start character : ’@’
Answer character : see “Status list”
End character (CR) : 0Dh
Start
‘@’
Command
“xxx:”+”...”
Request status
“xxx:?”+”...”
ACK
r
06h
’
NAK
r
15h
‘
@
’
Status
“xxx:”+”...”
End
0Dh
End
0Dh
CR
0Dh
CR
0Dh
End
0Dh
Company Restricted
Page 6

RS232C Control Specification RS232C Control Specification Page: 6 / 14
Document Version [1.01]
2-3. The transaction sequences and the regulations
2-3-1. The transaction sequences
The transactions have three kinds of sequence.
*A transaction is a Command from Host then Slave will be an answer by Status answer, ACK or NAK.
*A transaction is a Status request from Host then Slave will be an answer by Status answer or NAK.
*A transaction is Auto status feedback from Slave when a Slave’s status changed. (If the auto status
feedback is enabled.)
2-3-2. The transaction regulations
The transactions have some kinds of regulation.
* An answer (ACK, NAK or Status answer) transmittion by Slave has to finish within 500ms when got a
Command or a Status request from Host.
* Host must not transmit an another Command or Status request until "it receives a answer by a
previous Command or Status request" or "it passes a term of waitinng time from a finishing of previous
transmission of a Command or a Status request ".
* Slave has to finish a transaction under 500ms when it sends Auto status feedback data.
2-3-3. Specification of Auto status feedback
There are some specific regulations about Auto status feedback.
* The product status has segmented into four layers of 1, 2, 3 and 4.
* The status of layer 1 are assigned most kindly status to Host. (The statuses of layer 2 are assigned
kindly status, the statuses of layer 3 are not so need status to Host and the statuses of layer 4 are
probably no wished statuses.)
* Each layer status can control transmit enable or disable by Host command. (The product default
would be all disables.)
* Slave sends auto status feedback by itself when the status is changed and if the status feedback is
enabled.
* The product defined and segmentationed layers are takeing in status list.
2-3-4. Example of the transactions
<Host> <Slave>
TxD RxD
RxD TxD
Command
max. 0.5sec
Status answer,
ACK or NAK
a transaction a transaction
Example of the transactions
Company Restricted
Status
request
max. 0.5sec
Status answer
Page 7

RS232C Control Specification RS232C Control Specification Page: 7 / 14
p
p
A
A
Document Version [1.01]
2-3-5. Examples of the handshaking flowchart
2-3-5-1. Example of successful handshaking
SLAVEHOST
Com mand
Status
request
Com mand
acce
Request
acce
Changed
som e status!
tab le
Related
Status answer
or
Status
answer
uto status
feedback
CK
tab le
The product can reply ACK instead of related status, if the product can not send the related status
immediatly.
2-3-5-2. Examples of handshaking error
SLAVEHOST
Com m and
Com m and
in c o rre ct
NAK
Status
request
Request
in c o rre ct
NAK
Company Restricted
Page 8

RS232C Control Specification RS232C Control Specification Page: 8 / 14
Document Version [1.01]
3. Recommendations of Command, Status and Layer definition
- All Commands, Statuses and Layers will be defined other specific document.
- [MANDATORY] The product MUST have Commands and the Statuses same as a remote controller
buttons (IR controller) of the product.
- All Commands are required working by discreate as ON/OFF commands. (It means that do not support
TOGGLE command only. )
- All Commands and Statuses are defined same chharacter size except ACK/NAK on the product.
( Recommended character length : 3~6 characters )
-
It permits attaching 0x0A character to a reply characters from the product. In this case, must suppose that the object
is followed altogether.
- Recommend to supports numbers or values direct setting command, if it has variable numbers or
values.
Company Restricted
Page 9

RS232C Control Specification RS232C Control Specification Page: 9 / 14
Document Version [1.01]
4. Definitions of Command, Status and Layer
This section is told how to define “Command”, “Status” and “Layer” of this product.
4-1. Commands
This chapter will show the commands of this product.
4-1-1. Normal Command list
Command Reply from Slave
POWER
BAND
SLEEP
DIMMER
TOGGLE “PWR:0”
OFF “PWR:1”
ON “PWR:2”
TOGGLE
(work on same as RC)
BAND 1 (FM) “BND:1”
BAND 2 (AM) “BND:2”
BAND 3 (DAB) “BND:3”
BAND 4 (XM) “BND:4”
VALUE “SLP:0xxx”
OFF “SLP:1”
ON
(work on same as RC)
TOGGLE
(work on same as RC)
DIMMER OFF “DIM:1”
DIMMER 1 “DIM:2”
DIMMER 2 “DIM:3”
“BND:0”
“SLP:2”
“DIM:0”
“PWR:1” (OFF),
“PWR:2” (ON)
“BND:1”(FM),
“BND:2”(AM),
“BND:3”(DAB),
“BND:4”(XM)
“SLP:xxx”
xxx = 001 ~120 min
xxx = 000(OFF)
“DIM:1”, (DIMMER OFF)
“DIM:2”, (DIMMER 1)
“DIM:3”, (DIMMER 2)
DISPLAY
TOGGLE
(work on same as RC)
“DIP:0”
“DIP:1” (Frequency),
“DIP:2” (Reserved),
“DIP:3” (RDS Station Name),
“DIP:4” (RDS PS),
“DIP:5” (RDS PTY),
“DIP:6” (RDS CT),
“DIP:7” (DAB DLS),
“DIP:8” (DAB Ensemble Name),
“DIP:9” (DAB PTY),
“DIP:A” (DAB Ch. and Freq.),
“DIP:B” (DAB Time and Date),
“DIP:C” (DAB Bit Error),
“DIP:D” (XM Default),
“DIP:E” (XM Category),
“DIP:F” (XM Sig. Sattus),
Company Restricted
Page 10

RS232C Control Specification RS232C Control Specification Page: 10 / 14
Document Version [1.01]
Command Reply from Slave
VALUE “TFQ:0xxxxx“ (xxxxx = freq.)
Frequency
UP
(work on same as
RC)
DOWN
(work on same as
RC)
Auto-UP “TFQ:3“
“TFQ:1“
“TFQ:2“
“TFQ:xxxxx”
(xxxxx = Frequency)
if ( xxxxx < 00512 ) band = XM;
else if (xxxxx < 02000)
band=AM;
else band=FM;
(ex.“08750” = FM87.50MHz)
Auto-DOWN “TFQ:4“
VALUE “TPR:0www”
Preset
UP
(work on same as
RC)
DOWN
(work on same as
RC)
“TPR:1”
“TPR:2”
“TPR:www”
(www = current preset nr.)
(www = 000 is no preset mode)
(www = 001 ~ 200)
001 = A1, 009 = A9, 010= A10
011=B1,...100 =J10
101=K1,...200=T10(for XM)
Tuner mode
TOGGLE
(work on same as
RC)
OFF(MONO) “TMD:1”
“TMD:0”
“TMD:0”( - ),
“TMD:1” (MONO),
“TMD:2” (AUTO)
ON(AUTO) “TMD:2”
Command Reply from Slave
Numeric Key [1]
Numeric Key [2]
Numeric Key [3]
Numeric Key [4]
Numeric Key [5]
Numeric Key [6]
Numeric Key [7]
Numeric Key [8]
Numeric Key [9]
Numeric Key [10]
(work on same as
RC)
(work on same as
RC)
(work on same as
RC)
(work on same as
RC)
(work on same as
RC)
(work on same as
RC)
(work on same as
RC)
(work on same as
RC)
(work on same as
RC)
(work on same as
RC)
“NUM:1”
“NUM:2”
“NUM:3”
“NUM:4”
“NUM:5”
“NUM:6”
“NUM:7”
“NUM:8”
“NUM:9”
“MUN:A”
ACK
ACK
ACK
ACK
ACK
ACK
ACK
ACK
ACK
ACK
Company Restricted
Page 11

RS232C Control Specification RS232C Control Specification Page: 11 / 14
Document Version [1.01]
Command Reply from Slave
GROUP DOWN “MGP:1”
“MGP:0”, (None)
“MGP:A”,
“MGP:B”,
“MGP:C”,
“MGP:D”,
“MGP:E”,
“MGP:F”,
“MGP:G”,
“MGP:H”,
“MGP:I”,
“MGP:J”,
“MGP:K”,
“MGP:L”,
“MGP:M”,
“MGP:N”,
“MGP:O”,
“MGP:P”,
“MGP:Q”,
“MGP:R”,
“MGP:S”,
“MGP:T”
“TIM:abc”
(prg1=a, 2=b, 3=c)
see status answer
“TNO:1” (TUNER1),
“TNO:2”,(TUNER2)
“TNO:3”(TUNER3)
“CAT:yxx”
y = 1(un search), 2(in search)
xx = Category no,
01~32(00=None)
Memory Group
TIMER
Tuner No. Display
XM Category Search
Specific Commands
GROUP UP “MGP:2”
GROUP A “MGP:A”
GROUP B “MGP:B”
GROUP C “MGP:C”
GROUP D “MGP:D”
GROUP E “MGP:E”
GROUP F “MGP:F”
GROUP G “MGP:G”
GROUP H “MGP:E”
GROUP I “MGP:I”
GROUP J “MGP:J”
GROUP K “MGP:K” (for XM Grp A)
GROUP L “MGP:L” (for XM Grp B)
GROUP M “MGP:M” (for XM Grp C)
GROUP N “MGP:N” (for XM Grp D)
GROUP O “MGP:O” (for XM Grp E)
GROUP P “MGP:P” (for XM Grp F)
GROUP Q “MGP:Q” (for XM Grp G)
GROUP R “MGP:R” (for XM Grp H)
GROUP S “MGP:S” (for XM Grp I)
GROUP T “MGP:T” (for XM Grp J)
Command Reply from Slave
TOGGLE “TIM:0x” (x=prg.1,2 or 3)
OFF “TIM:1x” (x=prg.1,2 or 3)
ON “TIM:2x” (x=prg.1,2 or 3)
Tuner Display 1
Tuner Display 2 “TNO:2”
Tuner Display 3
Command Reply from Slave
VAL U E “ C AT:0xx”
CH. UP “CAT:1”
CH. DOWN “CAT:2”
CAT. NEXT “CAT:3”
CAT. PREV. “CAT:4”
“TNO:1”
“TNO:3”
Command from Host Reply from Slave
Auto status feedback
(The product default is disabled
all auto status feedback.)
“AST:x” (x = ‘0’ ~ ’F’)
bit 3 : Layer 4 ( 1 = Enable, 0 = Disable)
bit 2 : Layer 3 ( 1 = Enable, 0 = Disable)
bit 1 : Layer 2 ( 1 = Enable, 0 = Disable)
bit 0 : Layer 1 ( 1 = Enable, 0 = Disable)
same as
command define
(Default ivalue = 0)
Company Restricted
Page 12

RS232C Control Specification RS232C Control Specification Page: 12 / 14
Document Version [1.01]
4-2. Status request and Status answer list
4-2-1. Normal Status request and Status (answer and feedback) list
Status request Status answer and feedback
POWER “PWR:?”
BAND “BND:?”
SLEEP “SLP:?”
DIMMER “DIM:?”
DISPLAY “DIP:?”
Status request Status answer and feedback
Tuner Frequency “TFQ:?” “TFQ:xxxxx”
Tuner Preset “TPR:?” “TPR:www”
Tuner mode “TMD:?”
TUNED Status “TUD:?”
Status request Status answer and feedback
TIMER “TIM:?”
Tuner Number Display “TNO:?”
OFF “PWR:1”
ON “PWR:2”
BAND 1 (FM) “BND:1”
BAND 2 (AM) “BND:2”
BAND 3 (DAB) “BND:3”
BAND 4 (XM) “BND:4”
“SLP:xxx” (xxx = 000 = OFF)
(xxx = 001~ 120min)
DIMMER OFF “DIM:1”
DIMMER LEVEL 1 “DIM:2”
DIMMER LEVEL 2 “DIM:3”
MODE 1 (Frequency)
MODE 2 (Reserved)
MODE 3 (Reserved)
MODE 4 (RDS PS)
MODE 5 (RDS PTY)
MODE 6 (RDS CT)
MODE 7 (DAB DLS)
MODE 8 (DAB Ensemble Name)
MODE 9 (DAB PTY)
MODE 10 (DAB Ch. and Freq.)
MODE 11 (DAB Time and Date)
MODE 12 (DAB Bit Error)
MODE 13 (XM Default)
MODE 14 (XM Category)
MODE 15 (XM Signal Status)
OFF ( MONO) “TMD:1”
AUTO “TMD:2”
Not TUNED “TUD:1”
TUNED “TUD:2”
TIMER OFF=1, TIMER ON=2
(prg.1=a, prg.2=b, prg. 3=c)
(Do not indicate on FL display)
same as command
reply
(see Command list)
“DIP:1”,
“DIP:2”,
“DIP:3”,
“DIP:4”,
“DIP:5”,
“DIP:6”,
“DIP:7”,
“DIP:8”,
“DIP:9”,
“DIP:A”,
“DIP:B”,
“DIP:C”,
“DIP:D”,
“DIP:E”,
“DIP:F”
same as command reply
(see Command list)
same as command reply
(see Command list)
“TIM:abc”
(abc : OFF=1, ON=2)
“TNO:1” (Tuner 1)
“TNO:2” (Tuner 2)
“TNO:3” (Tuner 3)
Company Restricted
Page 13

RS232C Control Specification RS232C Control Specification Page: 13 / 14
Document Version [1.01]
Status request Status answer and feedback
Group none “MGP:0”
Group A “MGP:A”
Group B “MGP:B”
Group C “MGP:C”
Group D “MGP:D”
Group E “MGP:E”
Group F “MGP:F”
Group G “MGP:G”
Group H “MGP:H”
Group I “MGP:I”
Memory Group “MGP:?”
Group J “MGP:J”
Group K (for XM Grp A) “MGP:K”
Group L (for XM Grp B) “MGP:L”
Group M (for XM Grp C) “MGP:M”
Group N (for XM Grp D) “MGP:N”
Group O (for XM Grp E) “MGP:O”
Group P (for XM Grp F) “MGP:P”
Group Q (for XM Grp G) “MGP:Q”
Group R (for XM Grp H) “MGP:R”
Group S (for XM Grp I) “MGP:S”
Group T (for XM Grp J) “MGP:T”
Status request Status answer and feedback
“CAT:1xx”
Un Category Search
XM Category Search “CAT:?”
In Category Search
xx = Category no,
01~32(00=None)
“CAT:2xx”
xx = Category no,
01~32(00=None)
Status request Status answer and feedback
XM Channel Name “CHN:?” Channel name 8 char.
XM Artist Name “ARN:?” Artist name 16 char.
XM Song Title(Name ) “SON:?” Song name 16 char.
“CHN:xxxxxxxx”
xxxxxxxx = name 8bytes
“ARN:xxxx...”
xxxx... = name 16bytes
“SON:xxxx...”
xxxx... = name 16bytes
(No XM Selected) “SST:0”
NO “SST:1”
XM Signal Status “SST:?”
WEAK “SST:2”
MARGINAL “SST3”
STRONG “SST4”
4-2-2. Special Status request and Status answer list
Status request Status answer and feedback
Auto status feedback “AST:?” see command list
Read Host I/F
Software Version
“RSV:?”
“RSV:xx” (xx = ‘0’~’9’, ‘A’~’Z’ or ‘a’~’z’)
Set Default Value = 01
Company Restricted
Page 14

RS232C Control Specification RS232C Control Specification Page: 14 / 14
Document Version [1.01]
4-2-3. Layer of the statuses
Status Layer
POWER “PWR:” 1
BAND “BND:” 1
SLEEP “SLP:” 2
DIMMER “DIM:” 2
DISPLAY “DIP:” 1
Frequency “TFQ:” 3
PRESET “TPR:” 2
TUNER MODE “TMD:” 2
TUNED Status “TUD:” 2
TIMER “TIM:” 2
Memory Group “MGP:” 2
Tuner No. Display “TNO:” 1
Status Layer
Numeric Keys “NUM:” 0 (wite only)
Status Layer
XM Catecory Search “CAT:” 1
Status Layer
XM Channel Name “CHN:” 2 (read only)
XM Artist Name “ARN:” 4 (read only)
XM Song Title “SON:” 4 (read only)
XM Signal Status “SST:” 4 (read only)
Status Layer
Auto status feedback “AST:” 1
Read Host I/F Software version “RSV:” 1
5. Revision history
Rev. Date Owner Change description
1.0 08/04/06 Marantz America, Inc. Issued Revision1.0
1.01 08/10/06 Marantz America, Inc. Detail protocols are added
Company Restricted
 Loading...
Loading...