Page 1
Technical Reference
April 2004
Lexmark and Lexmark with diamond design are trademarks of Lexmark International, Inc.,
registered in the United States and/or other countries.
© 2004 Lexmark International, Inc.
740 West New Circle Road
Lexington, Kentucky 40550
www.lexmark.com
Page 2

s
s
s
©
Edition: April 2004
The following paragraph does not apply to any country where such provisions are inconsistent with local law: LEXMARK
INTERNATIONAL, INC., PROVIDES THIS PUBLICATION “AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED T O, THE IMPLIED W ARRANTIES OF MERCHANT ABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A P AR TICULAR
PURPOSE. Some states do not allow disclaimer of express or implied warranties in certain transactions; therefore, this statement may not
apply to you.
This publication could include technical inaccuracies or typographical errors. Changes are periodically made to the information herein; these
changes will be incorporated in later editions. Improvements or changes in the products or the programs described may be made at any time.
Comments about this publication may be addressed to Lexmark International, Inc., Department F95/032-2, 740 West New Circle Road,
Lexington, Kentucky 40550, U.S.A. In the United Kingdom and Eire, send to Lexmark International Ltd., Marketing and Services
Department, Westhorpe House, Westhorpe, Marlow Bucks SL7 3RQ. Lexmark may use or distribute any of the information you supply in
any way it believes appropriate without incurring any obligation to you. You can purchase additional copies of publications related to this
product by calling 1-800-553-9727. In the United Kingdom and Eire, call +44 (0)8704 440 044. In other countries, contact your point of
purchase.
References in this publication to products, programs, or services do not imply that the manufacturer intends to make these available in all
countries in which it operates. Any reference to a product, program, or service is not intended to state or imply that only that product,
program, or service may be used. Any functionally equivalent product, program, or service that does not infringe any existing intellectual
property right may be used instead. Evaluation and verification of operation in conjunction with other products, programs, or services, except
those expressly designated by the manufacturer, are the user’s responsibility.
Lexmark, Lexmark with diamond design, MarkNet, MarkVision, and Optra are trademarks of Lexmark International, Inc., registered in the
United States and/or other countries. ColorGrade, PerfectFinish, and PictureGrade are trademarks of Lexmark International, Inc.
The following terms are trademarks or registered trademarks of other companies:
Albertus The Monotype Corporation plc
Antique Olive Monsieur Marcel OLIVE
Apple-Chancery Apple Computer, Inc.
Arial The Monotype Corporation plc
Candid Agfa Corporation
CG Omega Product of Agfa Corporation
CG Times Based on Times New Roman under license
Chicago Apple Computer, Inc.
Clarendon Linotype-Hell AG and/or its subsidiaries
Eurostile Nebiolo
Geneva Apple Computer, Inc.
GillSans The Monotype Corporation plc
Helvetica Linotype-Hell AG and/or its subsidiaries
Hoefler Jonathan Hoefler Type Foundry
ITC Avant Garde Gothic International Typeface Corporation
AppleT alk, EtherTalk, LocalTalk, and Macintosh are trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc., registered in the United States and other countries.
PCL® is a registered trademark of the Hewlett-Packard Company. PCL 3, PCL 5, and PCL 6 are Hewlett-Packard Company’s designations
of a set of printer commands (language) and functions included in its printer products. These printers are intended to be compatible wit h
the PCL 3, PCL 5, and PCL 6 languages. This means these printers recognize PCL 3, PCL 5, and PCL 6 commands used in various
application programs, and that the printer emulates the functions corresponding to the commands.
PostScript
commands (language) and functions included in its software products. These printers are intended to be compatible with the PostScript
language. This means these printers recognize PostScript commands used in various application programs, and that the printer emulates
the functions corresponding to the commands.
Other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Safety Information
®
is a registered trademark of Adobe Systems Incorporated. PostScript is Adobe Systems’ designation of a set of printer
• If your product is not marked with this symbol , it must be connected to an electrical outlet that is properly grounded.
CAUTION: Do not use the fax feature during a lightning storm. Do not set up this product or make any electrical or cabling connections,
such as the power cord or telephone, during a lightning storm.
• The power cord must be connected to an electrical outlet that is near the product and easily accessible.
• Refer to the Setup Guid e for additional safety information, and for setting up the equipment.
• Refer service or repairs, other than those described in the operating instructions, to a professional service person.
from The Monotype Corporation plc, is a
product of Agfa Corporation
ITC Bookman International Typeface Corporation
ITC Lubalin Graph International Typeface Corporation
ITC Mona Lisa International Typeface Corporation
ITC Zapf Chancery International Typeface Corporation
Joanna MT The Monotype Corporation plc
Marigold Arthur Baker
Monaco Apple Computer, Inc.
New York Apple Computer, Inc.
Oxford Arthur Baker
Palatino Linotype-Hell AG and/or its subsidiarie
Stempel Garamond Linotype-Hell AG and/or its subsidiarie
Taffy Agfa Corporation
Times New Roman The Monotype Corporation plc
TrueType Apple Computer, Inc.
Univers Linotype-Hell AG and/or its subsidiarie
Wingdings Microsoft Corporation
1998, 2004 Lexmark International, Inc.
All rights reserved.
UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT RIGHTS
This software and any accompanying documentation provided under this agreement are commercial computer software and documentation
developed exclusively at private expense.
Page 3

Contents
Introduction ......................................................................1-1
Overview............................................................................................................. 1-1
Navigational Tips......................................................................... .... ..... ..............1-4
Printing the File........................ ..... ................................. .... .................................1-4
Bibliography........................................................................................................1-5
PCL Emulation..................................................................2-1
TOC-1
Contents
Selecting PCL Emulation....................................................................................2-1
Using SmartSwitch........................................................................................2-1
Using the Operator Panel or MarkVision Professional ..................................2-1
Using Your Software Program......................................................................2-2
Page Formatting.................................................................................................2-3
Printable Areas..............................................................................................2-3
Lexmark C510(n) ..........................................................................................2-4
Lexmark X422...............................................................................................2-5
Print Area Menu Item..........................................................................................2-6
Font and Symbol Set Support for the Lexmark X422.........................................2-8
Forward and Backward Compatibility Modes for the Lexmark X422 ............2-9
Selecting Symbol Sets for the Lexmark X422.............................................2-14
Font and Symbol Set Support for the Lexmark C510(n)..................................2-18
Forward and Backward Comp atibility Modes for the Lexmark C510(n)......2-19
Selecting Symbol Sets for the Lexmark C510(n)........................................2-24
Command Structure.........................................................................................2-28
Control Codes.............................................................................................2-28
Commands..................................................................................................2-28
PCL Emulation Commands..............................................................................2-31
PCL Emulation Commands by Function..................................................... 2-31
GL/2 Commands..............................................................................................2-53
Raster Image Graphics.....................................................................................2-57
Raster Compression Mode.........................................................................2-57
Macros..............................................................................................................2-64
Page 4

TOC-2
Contents
Printer Job Language ......................................................3-1
PJL Command Notation.....................................................................................3-1
Kernel Commands........................................... .... ..... ..... ................................ .....3-2
Job Separation Commands................................................................................3-4
Environment Commands and Variables.............................................................3-7
Status Readback Commands...........................................................................3-54
Status Message Format...................................................................................3-61
Information Messages.................................................................................3-61
Auto-Continuable Conditions......................................................................3-63
Attendance Conditions................................................................................3-67
Operator Intervention - Paper Handling......................................................3-72
Operator Intervention - Paper Jams............................................................3-75
Service Errors .............................................................................................3-80
Device Attendance Commands........................................................................3-80
Unique PJL Commands....................................................................................3-82
File Commands for Flash or Disk................................................................3-86
File and Device Protection Commands............................................................3-93
Protecting a File or Device..........................................................................3-93
Unlocking a Protected File or Device..........................................................3-95
Re-Locking a Protected File or Device........................................................3-96
Unlocking a Protected File or Device for the Current Job...........................3-97
Recovering Lost Passwords........................................................................3-98
PostScript Emulation.......................................................4-1
Selecting PostScript Emulation..........................................................................4-1
Using SmartSwitch........................................................................................4-1
Using the Operator Panel or MarkVision Professional ..................................4-1
Using Your Software Program......................................................................4-2
Page Formatting.................................................................................................4-3
Printable Areas..............................................................................................4-3
Logical Page Size.........................................................................................4-4
PostScript Emulation Fonts for the Lexmark X422.............................................4-6
PostScript Emulation Fonts for the Lexmark C510(n)........................................4-8
Supplemental Operators...................................................................................4-11
Command Format.......................................................................................4-11
Paper Size Support.....................................................................................4-12
Paper Tray Support.....................................................................................4-15
Page 5

TOC-3
Envelope Size Support................................................................................4-20
Envelope Tray Support...............................................................................4-22
Supplemental Operator Summary...............................................................4-24
Page Device Parameters..................................................................................4-59
Interpreter Parameters.....................................................................................4-73
User Parameters.........................................................................................4-73
System Parameters.....................................................................................4-76
Device Parameters......................................................................................4-82
Status and Error Messages............................................................. ...............4-103
Tagged Binary Not Active .........................................................................4-103
Tagged Binary Active................................................................................4-103
Status Messages.......................................................................................4-104
Unsolicited Messages.................................... ..... ................................. .... .4-105
Contents
Switching Languages ......................................................5-1
SmartSwitch .......................................................................................................5-1
Setting SmartSwitch for Different Interfaces.................................................5-2
Printer Job Language.........................................................................................5-2
Sniffing................................................................................................................5-3
Flash Memory and Disk...................................................6-1
Resource Data Collection (Download Target)....................................................6-2
Storing Resources on Flash Memory or Disk................................................6-3
Viewing the Contents of Flash Memory and Disk...............................................6-3
Password Protection................ ..... ..... .... ................................. ..... .... ...................6-7
Rewriting the Flash Content...............................................................................6-8
Accessing Files with PostScript Emulation.........................................................6-9
File Naming Conventions..............................................................................6-9
Device Search Order...................................................................................6-12
Performance..................................................................................................... 6-13
Job Buffering....................................................................................................6-13
Creating a Partition.....................................................................................6-14
Enabling Job Buffering.................................................................... ..... .......6-14
Disabling Job Buffering...............................................................................6-15
Recovering from a Power Loss...................................................................6-15
Page 6

TOC-4
Contents
Printer Specifications ......................................................7-1
Airflow Requirement............................................ ................................. .... .....7-1
Noise Emission Levels..................................................................................7-1
Electrical Specifications................................................................................7-2
Power Requirements.....................................................................................7-2
Physical Specifications..................................................................................7-3
Clearance Requirements .............................................................................7-3
Environmental Conditions................................... ..... .... ..... ..... .......................7-4
Altitude Specifications...................................................................................7-4
Atmospheric Pressure...................................................................................7-4
Power On to Ready State Time Period ........................................................7-5
Time to Print the First Page .........................................................................7-5
Printer Interfaces..............................................................8-1
Setting Up the Communications Port.................................................................8-2
Setting Up the Communications Port Using Windows 95/98/Me..................8-2
Setting Up the Communications Port Using Windows NT 4.0 ......................8-3
Setting Up the Communications Port Using Windows 2000.........................8-4
Setting Up the Communications Port Using Windows XP ............................8-5
Deciding Which Interface to Use........................................................................8-6
Parallel Interface.................................................................................................8-7
Standard Parallel Connector.........................................................................8-8
Optional Parallel Connector..........................................................................8-8
Parallel Connector Pin Assignments.............................................................8-8
Using the INIT* Signal to Initialize...............................................................8-11
Computer-to-Printer Communications.........................................................8-11
Printer-to-Computer Communication (Advanced Status)............................8-17
Parallel Mode 1...........................................................................................8-18
Parallel Mode 2...........................................................................................8-19
Signal Descriptions........................................ ................................. ..... .... ...8-19
Serial Interface.................................................................................................8-22
Using the RS-232C Serial Interface............................................................ 8-23
Using the RS-422 Serial Interface...............................................................8-33
Network Support...............................................................................................8-39
Input Buffer.......................................................................................................8-40
Page 7

TOC-5
PCL Support ....................................................................A-1
PJL Support.....................................................................B-1
PostScript Support .........................................................C-1
Contents
Index................................................................................. X-1
Page 8

1-1
CHAPTER 1: Introduction
Overview
The followi ng edition of the Technical Reference contains information about printer
commands and printer languages supported by the following Lexmark printers:
• Lexmark™ C510(n)
Introduction
• Lexmark X422
To determine which commands and languages your printer supports, see the
appendixes in the back of this document or refer to your printer user documentation.
If your printer is not included in this edition of the Technical Reference, it may be
avail able in another versi on. Visit the Lexmark Web site at www.lexmark.com/
publications for more information.
Page 9

1-2
Introduction
Printed documentation is also av ailab le fo r some Lexmark printers . Obtain the correct
part number from the following table, call 1-800-553-9727, and select option #1 to
order a Technical Reference for your printer.
Table 1-1: Technical Reference Documentation Available in Hard Cop y
If you need a Technical Refe rence for the... Order Lexmark part number...
Optra™ K 11A4079
Optra N 11A9979
Optra SC 11C0905
Optra E310 12A2194
The Technical Reference is divided into the following:
Chapter 2: “PCL Emulation”
Shows how to select PCL emulation and discusses PCL emulation commands, GL/2
commands, and resident font and symbol set support.
Chapter 3: “Printer Job Language”
Contains detailed inf ormation about certain commands that cause t he printer to enter
PCL emulation, P ostScript emulation, and P ersonal Printer Data Stream (PPDS), and
many other types of commands.
Chapter 4: “Post Scri pt Emulation”
Provides information about PostScript emulation and explains PostScript emulation
supplemental operators.
Chapter 5: “Switching Languages”
Describes ways to switch printer languages and explains when you may want to
choose one method over another.
Chapter 6: “Flash Memory and Disk”
Provides inf ormation about using the flash memory and hard disk. It describes how to
manage printer memory, store resources (such as fonts and macros), and manage
files.
Page 10

1-3
Chapter 7: “Printer Specifications”
Lists printer specifications, including information about hardware and environmental
conditions.
Chapter 8: “Printer Interfaces”
Provides information on printer interfaces, including information about parallel and
serial interface, network support, and communication protocols.
See the tables in the three appendixes to determine if your printer supports a
particular PCL emulation, PJL, or P ostScript emulation command. The appendixes
are:
Introduction
Appendix A: “PCL Support”
Appendix B: “PJL Support”
Appendix C: “PostScript Support”
Page 11
Navigational Tips
If you are not familiar with PDF files, the following tips ma y help you find the
information you need.
• To move forward and backward through this document:
– Select an option under View in the menu bar at the top of the page.
– Use the arrows in the toolbar at the top of the page, or the up arrow and
down arrow keys on the keyboard.
– Press the Page Up and Pag e Down keys on the keyboard.
– Use the scroll bar to the right of the page.
– Click the page number bo x on the st atus bar at the bo ttom of th e page and
type the page you want.
1-4
Introduction
• To increase or decrease the magnification of the pages:
– Select the magnifying glass icon on the toolbar at the top of the page and
– Click the magnification box on the status bar and select an opti on from t he
• To jump directly to a particular section or key word in this document:
– Click one of the bookmarks in the overview window to the left of the page.
– Click a topic in the document’s table of contents.
– Select Tools from the menu bar and then choose Find or Search.
– Click the binoculars icon on the toolbar and then type a word in the t ext bo x.
– Click a cross-reference to a figure, page number, or heading in the docu-
Printing the File
then draw a bo x around the area you want to view.
drop-down menu.
ment itself.
Although this book was designed primarily for online viewing, you can print a hard
copy by clicking File on the toolbar, and then choosing Print. Make sure you’ve
selected the correct printer , range of pages, and number of copie s before you click OK.
You should be aware that if you print this document on a color printer, the color you
see on the paper may not match the color you see on your computer monitor.
Page 12

Bibliography
For detailed information about PCL emulation printer commands, PostScr ipt
emulation printer commands and operators, and interfaces, refer to the following
documentation:
1-5
Introduction
• Hewlett-Packard DeskJet Printer Family Technical Reference, C2121-90101
• Hewlett-Packard LaserJet 4 Typography and Graphics, Random House
Electronic Publishing
• Hewlett-Packard PCL 5 Color Technical Reference Manual, 5961-0635
• Hewlett-Packard PCL 5 Printer Language Technical Reference Manual,
5961-0509
• Hewlett-P ackar d Po stScript SIMM Technical Reference, I/O De vice Operators
and Paramet ers, C2080-90921
• Hewlett-Packard Printer Job Language Technical Reference Manual,
5961H0512
• IBM Personal System/2 Hardware Interface Technical Reference, S68X-2330
• Interface between Data Terminal Equipment and Data Communications
Equipment Employing Serial Binary Data Interchange, Electronic Industries
Association, publications EIA RS-232C and EIA\TIA-232-E
• Network Printing Alliance Protocol, A Printer/Host Control Specification
Developed by the NPA, Level 1, Revisio n N
• PostScript Language Reference Manual (Third Edition), Adobe Systems
Incorporated, Addison-Wesley Publishing
Page 13
2-1
CHAPTER 2: PCL Emulation
When you select PCL emulation as the printer language, the printer supports the
Hewlett-Packard Company’s LaserJet Printer Command Language. This chapter
shows how to select PCL emulation and discusses PCL emulation commands, along
with resident PCL emulation font and symbol set support.
T o det ermine which commands your printer supports, see Appendix A: “PCL Support”
on page A-1.
PCL
Selecting PCL Emulation
Using SmartSwitch
When SmartSwitch is enabled f or both printer languages on an interf ace (f or example ,
Paral lel, USB, Serial Option 1, or Network Option 1), the printer automa tically switches
to the printer language being sent by your software program. The printer is shipped
with SmartSwitch enabled for both printer languages in all interfaces. The printer
examines all print jobs and switches dynamically betwe en PostScript emulation and
PCL emulation.
Using the Operator Panel or MarkVision Professional
If SmartSwitch is set to Off for both printer languages, you can select PCL emulation
from your printer operator panel or from MarkVision™ Professional. Refer to your
printer user documentation fo r information on changing menu settings.
Page 14

Using Your Software Program
To select PCL emulation, use the Printer Job Language (PJL) Enter Language
Command. See “ENTER LANGUAGE Command” on page 3-3 for more information.
See “Printer Job Language” on page 3-1 for the syntax and use of PJL.
Warning: When you change printer languages, you may lose some or all previously
downloaded resources, unless
are stored in flash memory or on disk.
2-2
Resource Save is set to On or the resources
PCL
Page 15
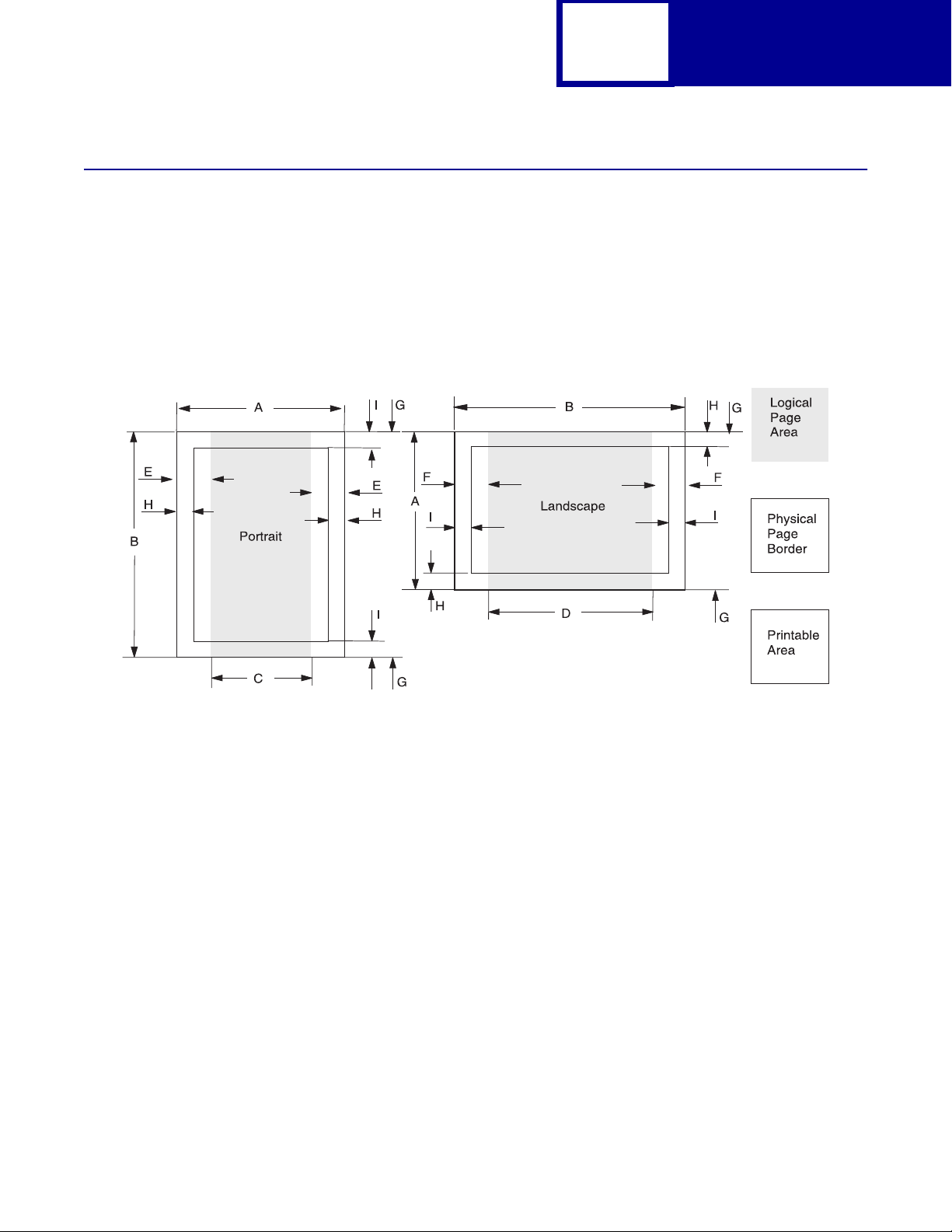
Page Formatting
The printable areas and logi cal pages f or PCL emulation (both portrait and landscape
orientation) are illustrated below. See the Legend that follows for definitions of areas
A through I.
Printable Areas
2-3
PCL
Legend:
A Portrait physical page width and landscape physical page length
B Portrait physical page length and landscape physical page width
C Portrait logical page width
D Landscape logical page width
E Distance between the side edge of the physical page and the logical page in portrait
F Distance between the side edge of the physical page and the logical page in landscape
G Distance between the top and bottom edge of the physical page and logical page
H Distance between the left and right edge of the physical page and the printable area in
portrait, or distance between the top and bottom edge of the physical page and printable
area in landscape
I Distance between the top and bottom edge of the physical page and the printable area in
portrait, or distance between the left and right edge of the physical page and the
printable area in landscape
Note: The tables beginning on page 2-4 list the page sizes and dimensions of each
area labeled on the preceding diagram for all paper and envelope sizes your
printer supports. If information about your printer is not included in the
following tables, see page 1-1 for information on how to get a Technical
Reference f or your printer.
Page 16
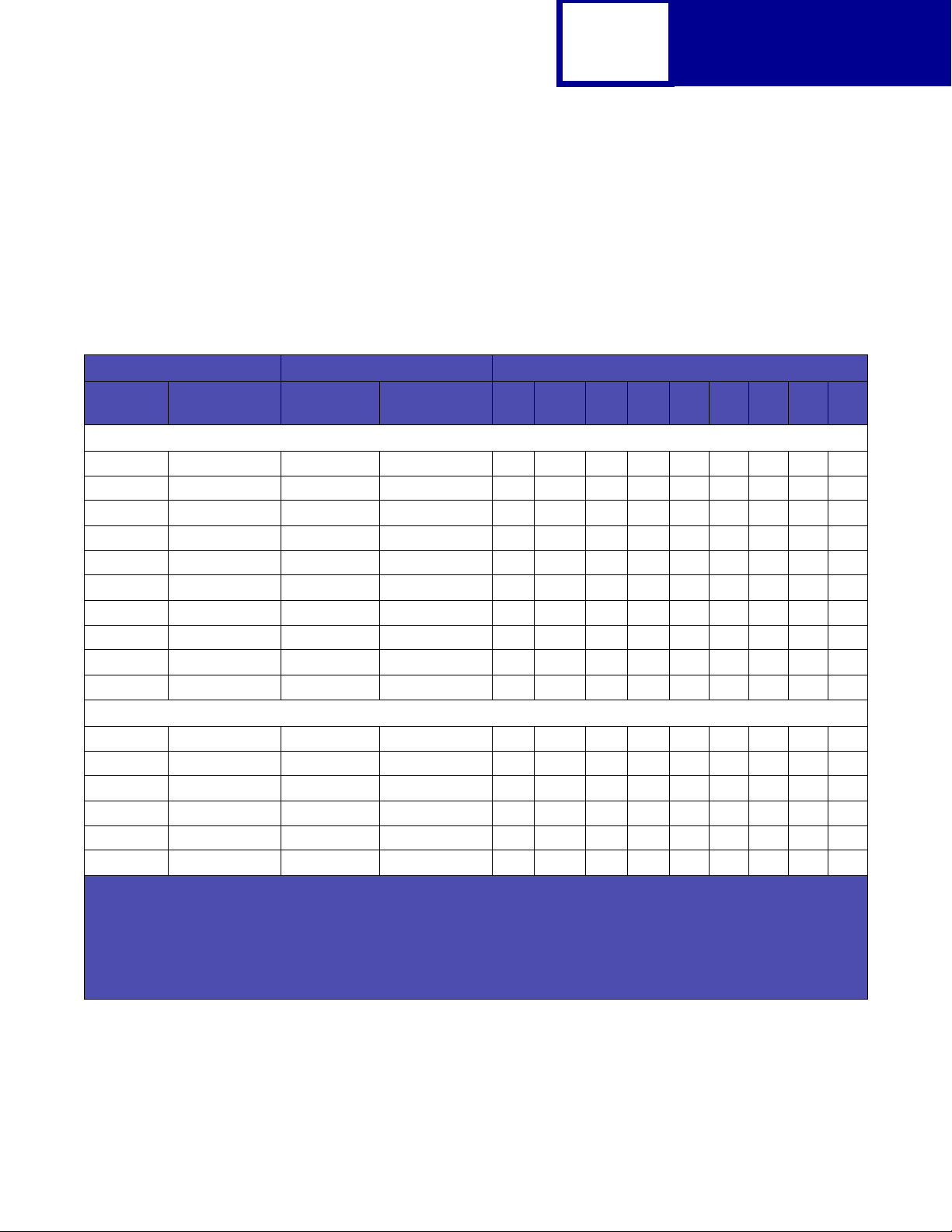
Lexmark C510(n)
The following table lists page sizes and print area dimensions for all paper and
envel ope sizes the Lexmark C510(n) p rinter supports. For more inf ormation about the
printable areas and logical pages for PCL emulation, see “Printable Areas” on
page 2-3.
Table 2-1: Lexmark C510(n) Paper and Envelope Dimensions
2-4
PCL
Selection Paper/Envelope Dimensions Dimensions by Area (pels)
Page Size
2
Parm
Name mm inches A B C D E F G H I
1
Paper
13, 613 A5 148 x 210 5.83 x 8.27 3496 4960 3196 4720 142 118 0 100 100
12, 45, 612 JIS B5 Paper 182 x 257 7.2 x 10.1 4300 6070 4000 5830 150 120 0 100 100
26, 626 A4 (198 mm)
26, 626 A4 (203 mm)
1, 601 Executive 184 x 267 7.25 x 10.5 4350 6300 4050 6060 150 120 0 100 100
2, 602 Letter 216 x 279 8.5 x 11 5100 6600 4800 6360 150 120 0 100 100
3, 603 Legal
4 or 10 Folio
15 Statement 139.7 x 215.9 5.5 x 8.5 3300 5100 3000 4860 150 120 0 100 100
101 Universal
3
210 x 297 8.3 x 11.7 4960 7014 4676 6778 142 118 0 80 80
3
210 x 297 8.3 x 11.7 4960 7014 4800 6778 80 118 0 80 80
5
5
5
216 x 356 8.5 x 14 5100 8400 4800 8160 150 120 0 100 100
216 x 330 8.5 x 13 5100 7800 4800 7560 150 120 0 100 100
216 x 356 8.5 x 14 5100 8500 4800 8260 150 120 0 100 100
Envelope
90 DL 220 x 110 8.66 x 4.33 2598 5196 2314 4960 142 118 0 100 100
91 C5 229 x 162 9.02 x 6.38 3826 5408 3542 5172 142 118 0 100 100
4
99
, 100 B5 Envelope 250 x 176 9.84 x 6.93 4156 5904 3872 5668 142 118 0 100 100
5
600 Other Envelope
89 9 (Com 9) 225 x 98 8.875 x 3.875 2326 5324 2024 5084 150 120 0 100 100
81 10 (Com 10) 241 x 105 9.5 x 4.125 2474 5700 2174 5460 150 120 0 100 100
1
Pel dimensions are for 600 dpi.
2
Page Size Parameters are explained in Table 2-16 on page 2-33.
3
The width of the logical page for A4 paper can be changed from the printer operator panel or your software application.
4
Paper ID 99 will be supported for backward compatibility with other Lexmark printers. Paper ID 99 has the same logical
216 x 356 8.5 x 14 5100 8400 4800 8160 150 120 0 100 412
paper size as ID 100 (compatible with HP LaserJet 5Si/5SiMx) but is 8 pels wider than the Lexmark 4039.
5
The Lexmark C510(n) supports this size media only with an optional legal tray.
Note: The explanat ion of the printab le area assumes the
Normal. For more information about Print Area, see page 2-6.
to
Print Area menu item is set
Page 17
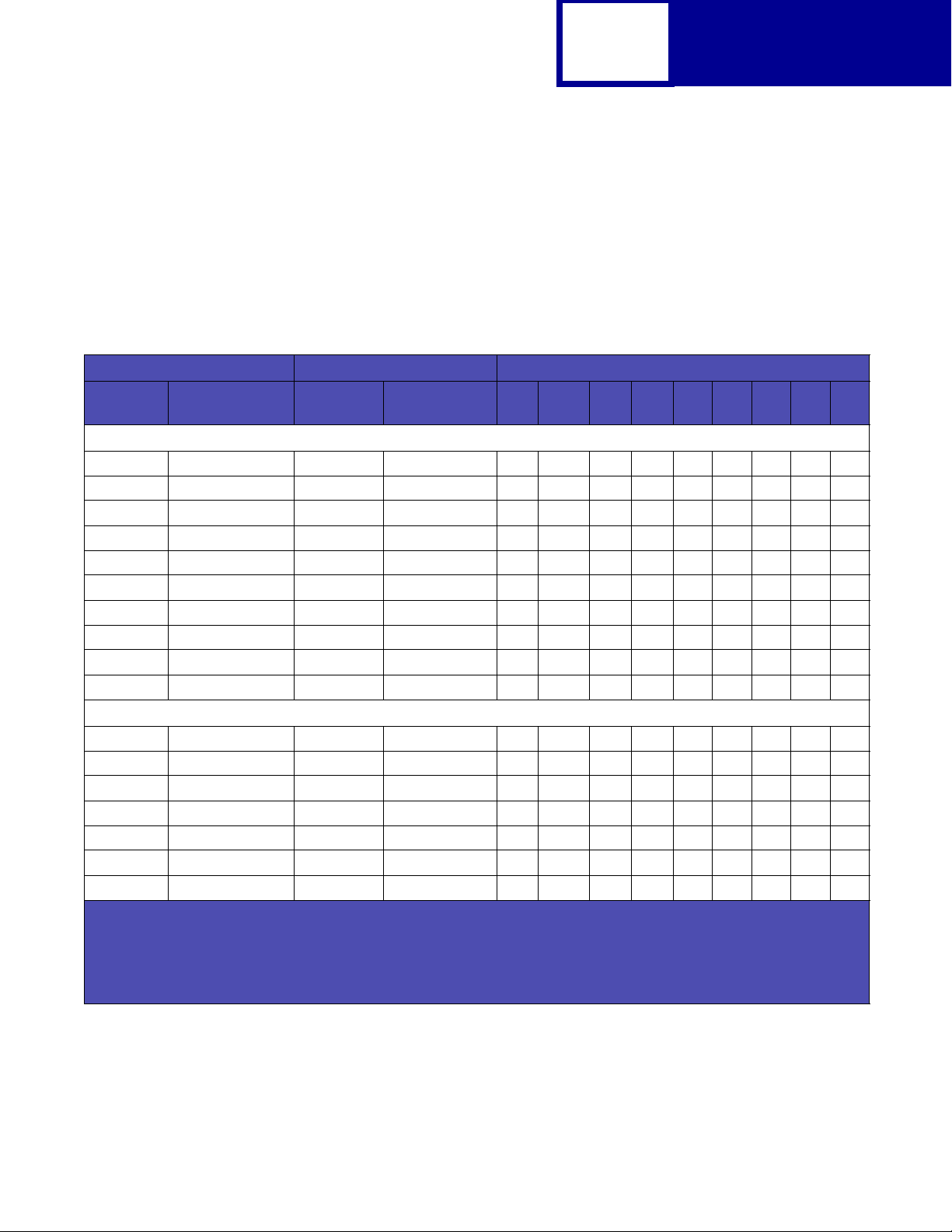
Lexmark X422
The following table lists page sizes and print area dimensions for all paper and
envel ope sizes the Lexmark X422 printer supports. For more information about the
printable areas and logical pages for PCL emulation, see “Printable Areas” on
page 2-3.
Table 2-2: Lexmark X422 Paper and Envelope Dimensions
2-5
PCL
Selection Paper/Envelope Dimensions Dimensions by Area (pels)
Page Size
2
Parm
13, 613 A5 148 x 210 5.83 x 8.27 3496 4960 3196 4720 142 118 0 100 100
12, 45, 612 JIS B5 Paper 182 x 257 7.2 x 10.1 4300 6070 4000 5830 150 120 0 100 100
26, 626 A4 (198 mm)
26, 626 A4 (203 mm)
1, 601 Executive 184 x 267 7.25 x 10.5 4350 6300 4050 6060 150 120 0 100 100
2, 602 Letter 216 x 279 8.5 x 11 5100 6600 4800 6360 150 120 0 100 100
3, 603 Legal 216 x 356 8.5 x 14 5100 8400 4800 8160 150 120 0 100 100
4 or 10 Folio 216 x 330 8.5 x 13 5100 7800 4800 7560 150 120 0 100 100
15 Statement 139.7 x 215.9 5.5 x 8.5 3300 5100 3000 4860 150 120 0 100 100
101 Universal 216 x 356 8.5 x 14 5100 8500 4800 8260 150 120 0 100 100
90 DL 220 x 110 8.66 x 4.33 2598 5196 2314 4960 142 118 0 100 100
91 C5 229 x 162 9.02 x 6.38 3826 5408 3542 5172 142 118 0 100 100
4
99
, 100 B5 Envelope 250 x 176 9.84 x 6.93 4156 5904 3872 5668 142 118 0 100 100
600 Other Envelope 229 x 356 9.02 x 14 5100 8400 4800 8160 150 120 0 100 100
80 7-3/4 Monarch 191 x 98 7.5 x 3.875 2326 4500 2024 4260 150 120 0 100 100
89 9 (Com 9) 225 x 98 8.875 x 3.875 2326 5324 2024 5084 150 120 0 100 100
81 10 (Com 10) 241 x 105 9.5 x 4.125 2474 5700 2174 5460 150 120 0 100 100
1
Pel dimensions are for 600 dpi.
2
Page Size Parameters are explained in Table 2-16 on page 2-33.
3
The width of the logical page for A4 paper can be changed from the printer operator panel or your software application.
4
Paper ID 99 will be supported for backward compatibility with other Lexmark printers. Paper ID 99 has the same logical
paper size as ID 100 (compatible with HP LaserJet 5Si/5SiMx) but is 8 pels wider than the Lexmark 4039.
Name mm inches A B C D E F G H I
Paper
3
3
210 x 297 8.3 x 11.7 4960 7014 4676 6778 142 118 0 80 80
210 x 297 8.3 x 11.7 4960 7014 4800 6778 80 118 0 80 80
Envelope
1
Note: The explanat ion of the printab le area assumes the
Normal. For more information about Print Area, see page 2-6.
to
Print Area menu item is set
Page 18
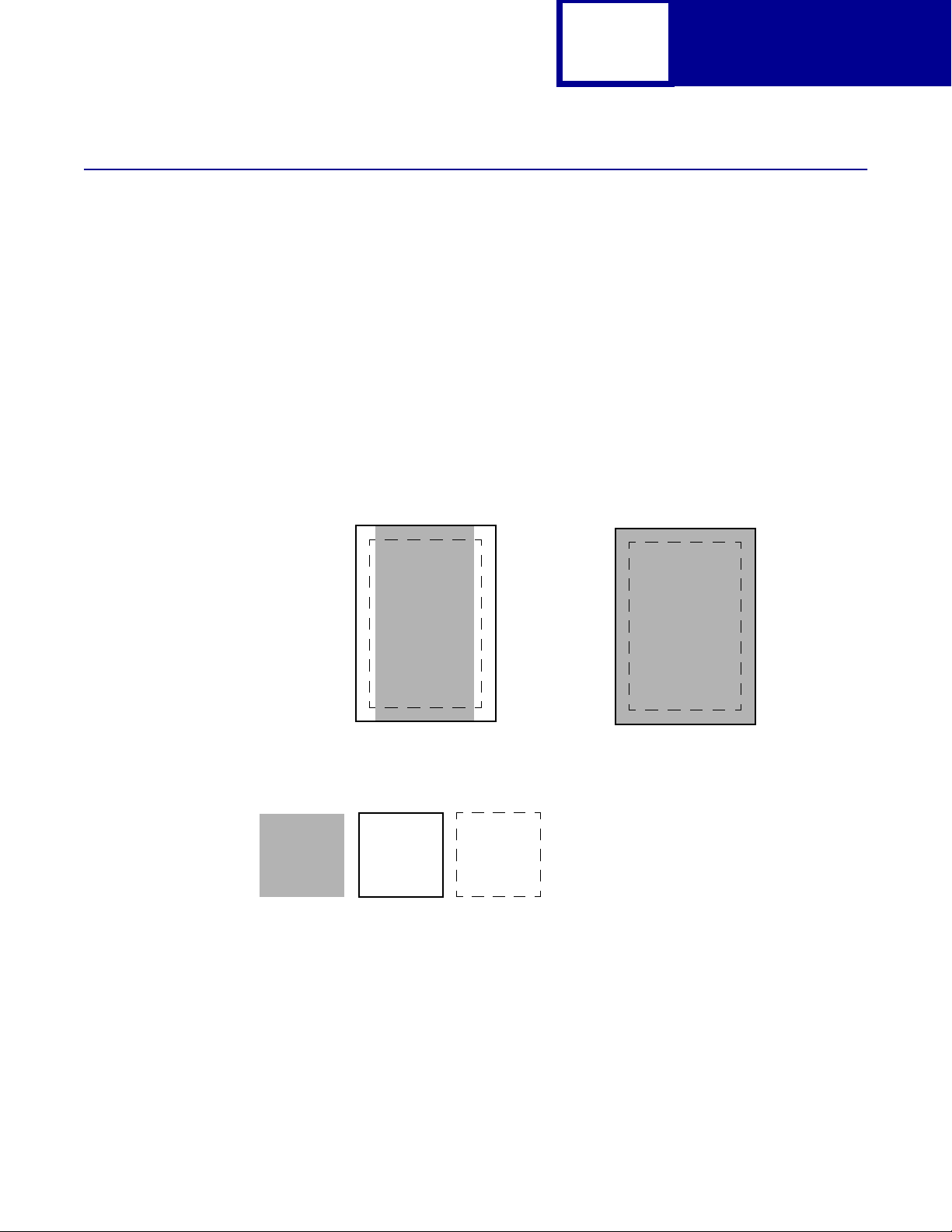
Print Area Menu Item
The printable area is the area on a sheet of paper within which a pel can be printed.
Logical page is a conceptual entity that defi nes the area in which margins (top , bottom,
left, right) may be set and the area in which the PCL cursor may be positioned.
The physical page border is the actual physical boundaries of a page.
The
Print Area menu item is available from the printer operator panel or through
MarkVision Professional. For some printers , Print Area supports three values: Normal,
Whole Page, and Fit to Page. Refer to your printer user documentation for more
information.
2-6
PCL
Normal setting
Legend:
PCL
Logical
Page
Area
The Normal setting, which is t he factory def ault, means the printable area incl udes the
entire page except the narrow border around the edge of the page. This is the
nonprintable area. The printer measures margin settings relative to the logical page.
Physical
Page
Border
PCL
Printable
Area
Only Portrait Orientation shown for all settings
Whole Page setting
For a more detailed explanation of the Normal setting, see “Printable Areas” on
page 2-3.
Page 19
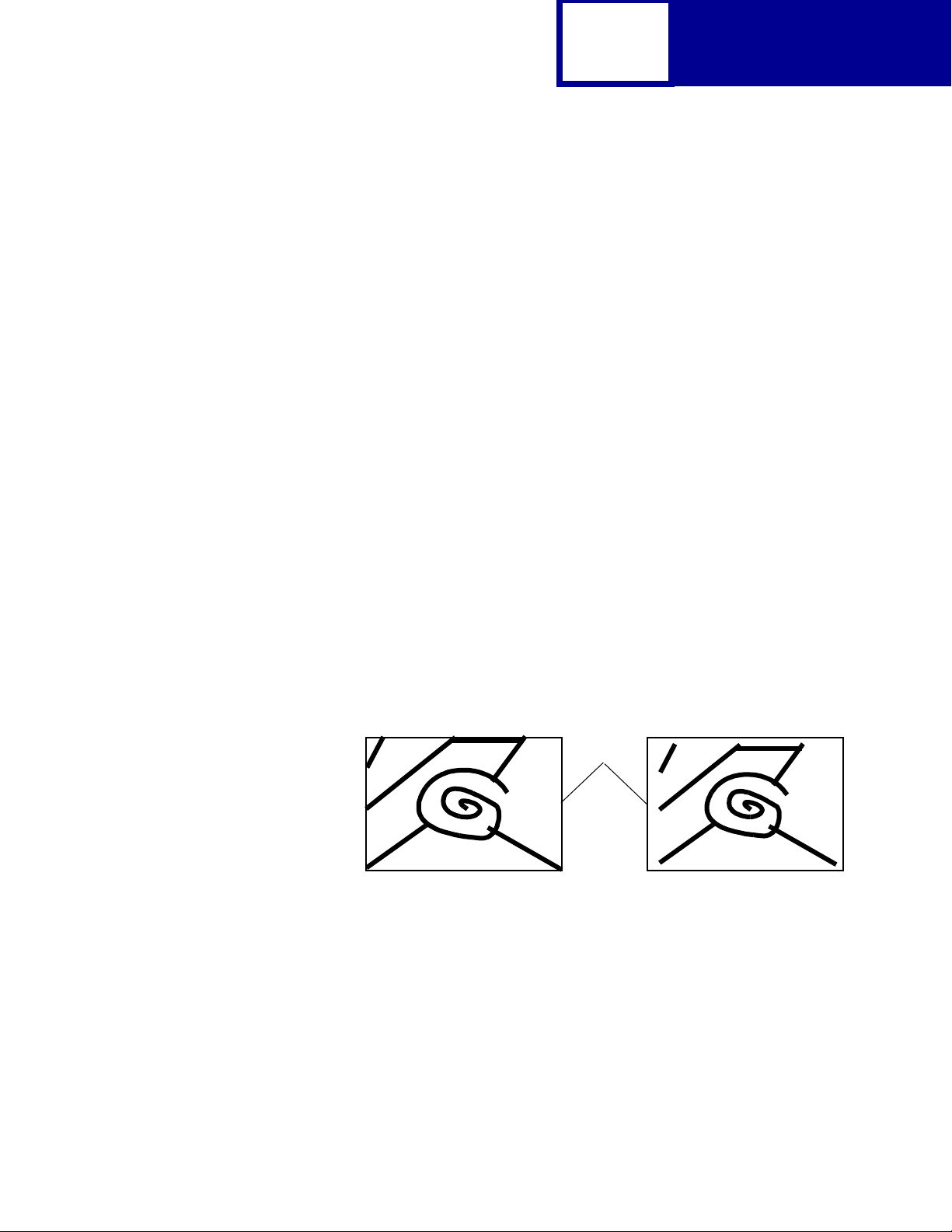
2-7
PCL
The Whole Page setting only affects pages printed when using PCL emulation. If
Whole Page is selected, the PCL language sets the logical page area equal to the
physical page dimens ions. Since the logical page dimensions and the physical page
dimensions are the same, in theory, the cursor may be positioned anywhere on the
page. Howe v er, the PCL language clips the image to the printab le area. So , the Whole
Page sett ing is useful f or printing scanne d images that e xtend from edge to edg e of a
page.
Some printers offer the Fit to Page setting. When Fit to Page is selected, PCL
emulation or P o stScript emul ation formats a page using a printable area equal to the
physical page, which is from one edge of the page to the ot her edge of the page. If you
use this setting, no clipping occurs. In Fit to Page, the PCL emulation logical page
dimensions are equal to the physical page dimensions, as in the Whole Page sett ing .
The printer holds this f ormatted image in memory , but when t he page prints, the image
is compressed a small amount in both horizontal and vertical directions, and then
centered on the physical page f or lett er-siz e paper onl y. This process creates a small
margin around the image. This artificial margin pre ven ts printing from one edge to the
other, since doing so could contaminate the printer and cause printing problems.
The following illustrations show an image held in memory for printing from one edge
to the other and how the image would actually print based on the Fit to Page setting.
Notice that a small border appears at t he edges of the printed page , and t he image is
slightly compressed.
Physical
Page
Edge
Formatted Image with Fit to Page Printed Image with Fit to Page
Page 20

2-8
PCL
Font and Symbol Set Support for the Lexmark X422
Your printer has 91 resident fonts in PCL emulation, including 89 scalable fonts and
two bitmapped fonts.
Several parameters are used to select a font from the data stream. These include
symbol set, spacing, point or pitch, styl e, weight, and typeface number. For scalable
fonts, you can vary the size of a font by specifying pitch or point size. For bitmapped
fonts , you must choose the pi tch or point size li sted on the font sample pa ges. You can
print the font sample pages from the MFP control panel, using a PJL command (see
“LPRINTPCLFONTS” on page 3-83.) or through MarkVision Professional. Refer to
your printer user documentation for more information.
A symbol set defines which characters are available for a font and the code point for
each of these character s . Your printer supports 88 symbol sets . The tab les begi nning
on page 2-14 show the symbol sets available for each font in PCL emulation. Not all
fonts support all symbol sets.
You can select a font as the PCL emulation default from the MFP control panel or
through MarkVision Professional . Refer to your printer user documentation for more
information.
The fonts are divided int o three major groups. The first 47 f onts (R0 through R46)
shown on the font sample pages are the standard PCL emulation fonts. The next 39
fonts (R47 through R85) are called Type 1 fonts and were originally defined for
Post Script emulation, but now also work in the PCL em ulation. The last fiv e fon ts (R86
through R90) include three different Code 3 of 9 bar code fonts, OCR-A and OCR-B
fonts.
The fonts are f urther divided into f ont groups A, B , and C indicat ing which symbol set s
are supported by each fo nt. For a list of the 47 s tand ard PCL em ulati on fonts, as w ell
as the OCR and Code 3 of 9 bar code fonts, see Table 2-3 on page 2-9. For a list of
the 39 Type 1 fonts, see Table 2-4 on page 2-12. Both tables list the forward and
backward compatibility font selection commands and the font group (A, B, or C) for
each font. F or more inf ormation on for ward and backw ard compatibili ty, see page 2-9.
For more information on selecting symbol sets, see page 2-14.
For compatibility purposes, you can disable Type 1 fonts with the Printer Job
Language (PJL) LTYPE1FONTS command. The factory default for these fonts is
Enabled. See LTYPE1FONTS on page 3-47 for more information.
Page 21
2-9
PCL
You can also select fonts using PJL commands . The selection parameter is the
number portion from the font identifi er sho wn on t he font sample pages, such as 0 or
76 from font identifi ers R0 or R76. Use the PJL v a lues sho wn in the tables beginning
on page 2-14 to select a symbol set. If a symbol set does not have a PJL value, use
the symbol set ID to select the symbol set. A f ont selection can be eit her temporary or
set as the default.
Use the followi ng PJL comman ds to sel ect fonts: FONTSOURCE, FONTNUMBER,
PITCH, PTSIZE, SYMSET, SET, DEFAULT. See Table 3-5: “Common Variables for
PCL Emulation” on page 3-48 for more information about these commands.
Forward and Backward Compatibility Modes for the Lexmark X422
Your PCL emulation has forward and backward compatibility modes. The forward
compatibility mode is used to emulate the fonts in the Hewlett-Packard Company’s
LaserJet 4050. The backward compatibility mode is used for compatibility w i t h the
Hewlett-Packard Company’s LaserJet 5 and the Lexmark family of printers.
Standard PCL Emulation Fonts, OCR and Code 3 of 9 bar code fonts
Table 2-3 on page 2-9 lists the font selection commands for forward and backward
compatibility mode for each of the 47 standard PCL emulation fonts, the OCR and
Code 3 of 9 bar code fonts. Since t he font selection commands f o r the forward and
backward compati bility modes are i dentical, the y are list ed together in the tab le . Most
fonts are assig ned a font group indicating which symbol sets that font supports.
To determine which symbol sets are supported by a particular font, find the font
group (A, B, or C) for the font in Table 2-3, and then see T able 2-5 on page 2-14 for the
symbol sets that belong to that group.
Table 2-3: Forward and Backward Compatibility Font Selection Commands
Forward and Backward
Standard PCL Emulation
Font Name
Courier 0 0 4099 A
Courier Italic 1 0 4099 A
Courier Bold 0 3 4099 A
Courier Bold Italic 1 3 4099 A
1
For the symbol sets supported by this font, see Table 2-6: “Non-Text PCL Emulation
Symbol Sets” on page 2-16.
Compatibility Mode
Style Bold Typeface
Font
Group
Page 22
2-10
PCL
Table 2-3: Forward and Backward Compatibility Font Selection
Forward and Backward
Standard PCL Emulation
Font Name
CG Times 0 0 4101 A
CG Times Italic 1 0 4101 A
CG Times Bold 0 3 4101 A
CG Times Bold Italic 1 3 4101 A
Univers Medium 0 0 4148 A
Univers Medium Italic 1 0 4148 A
Univers Bold 0 3 4148 A
Univers Bold Italic 1 3 4148 A
Letter Gothic 0 0 4102 B
Compatibility Mode
Style Bold Typeface
Font
Group
Letter Gothic Italic 1 0 4102 B
Letter Gothic Bold 0 3 4102 B
Univers Condensed Medium 4 0 4148 B
Univers Condensed Medium Italic 5 0 4148 B
Univers Condensed Bold 4 3 4148 B
Univers Condensed Bold Italic 5 3 4148 B
Garamond Antiqua 0 0 4197 B
Garamond Kursiv 1 0 4197 B
Garamond Halbfett 0 3 4197 B
Garamond Kursiv Halbfett 1 3 4197 B
CG Omega 0 0 4113 B
CG Omega Italic 1 0 4113 B
CG Omega Bold 0 3 4113 B
CG Omega Bold Italic 1 3 4113 B
Antique Olive 0 0 4168 B
Antique Olive Italic 1 0 4168 B
Antique Olive Bold 0 3 4168 B
Albertus Medium 0 1 4362 B
Albertus Extra Bold 0 4 4362 B
Clarendon Condensed Bold 4 3 4140 B
Marigold 0 0 4297 B
Coronet 1 0 4116 B
1
For the symbol sets supported by this font, see Table 2-6: “Non-Text PCL Emulation
Symbol Sets” on page 2-16.
Page 23
2-11
PCL
Table 2-3: Forward and Backward Compatibility Font Selection
Forward and Backward
Standard PCL Emulation
Font Name
Times New Roman 0 0 16901 B
Times New Roman Italic 1 0 16901 B
Times New Roman Bold 0 3 16901 B
Times New Roman BoldItalic 1 3 16901 B
Arial 0 0 16602 B
Arial Italic 1 0 16602 B
Arial Bold 0 3 16602 B
Arial Bold Italic 1 3 16602 B
1
Symbol
Wingdings
Line Printer 16
POSTNET Bar Code
OCR-A
OCR-B
C39 Narrow
C39 Regular
C39 Wide
1
For the symbol sets supported by this font, see Table 2-6: “Non-Text PCL Emulation
Symbol Sets” on page 2-16.
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Compatibility Mode
Style Bold Typeface
0 0 16686
0 0 31402
000 A
000
0 0 23584
0 0 23590 D
0 0 32774
0 0 32772
0 0 32777
Font
Group
Page 24
Type 1 Fonts
2-12
PCL
Thirty of the Type 1 fonts have different font selection parameters in the forward and
backward compatib ility modes and 9 of the fonts work only in the forward compat ibility
mode. With the appropriate printer driver installed and selected, your software
application selects these fonts.
The followi ng table shows the f ont selection commands for forward and backward
compatibility modes and indicates the font group for each font. All Type 1 fonts are
supported by both the Hewlett-Packard Company’s LaserJet 4050 and the
Lexmark family of printers unless otherwise noted.
To determine which symbol sets are supported by a particular font, find the font
group (A, B, or C) for the font in Table 2-4, and then see T able 2-5 on page 2-14 for the
symbol sets that belong to that group.
Table 2-4: Forward and Backward Compatibility Font Selection Commands
Forward Compatibility
Mode
Type 1 Font name
ITC Avant Garde Book 0 0 24607 0 0 61471 B
ITC Avant Garde Book Oblique 1 0 24607 1 0 61471 B
ITC Avant Garde Demi
ITC Avant Garde Demi Oblique
ITC Bookman Light 0 -3 24623 0 -3 61487 B
ITC Bookman Light Italic 1 -3 24623 1 -3 61487 B
ITC Bookman Demi 0 2 24623 0 2 61487 B
ITC Bookman Demi Italic 1 2 24623 1 2 61487 B
Century Schoolbook Roman 0 0 24703 0 0 61463 B
Century Schoolbook Italic 1 0 24703 1 0 61463 B
Century Schoolbook Bold 0 3 24703 0 3 61463 B
Century Schoolbook Bold Italic 1 3 24703 1 3 61463 B
Helvetica 0 0 24580 0 0 61444 B
Helvetica Italic 1 0 24580 1 0 61444 B
Helvetica Bold 0 3 24580 0 3 61444 B
1
1
Style Bold Typeface Style Bold Typeface
0 2 24607 0 3 61471 B
1 2 24607 1 3 61471 B
Backward Compatibility
Mode
Font
Group
Helvetica Bold Italic 1 3 24580 1 3 61444 B
Helvetica Narrow 4 0 24580 4 0 61444 B
1
Notice the values for forward compatibility and backward compatibility modes differ slightly for Bold.
2
This font is not implemented in the Hewlett-Packard Company’s LaserJet 4050.
3
For the symbol sets supported by this font, see Table 2-6: “Non-Text PCL Emulation Symbol Sets” on page 2-16.
Page 25
2-13
Table 2-4: Forward and Backward Compatibility Font Selection Commands (Continued)
PCL
Forward Compatibility
Mode
Type 1 Font name
Helvetica Narrow Italic 5 0 24580 5 0 61444 B
Helvetica Narrow Bold 4 3 24580 4 3 61444 B
Helvetica Narrow Bold Italic 5 3 24580 5 3 61444 B
Helvetica Light
Helvetica Light Oblique
Helvetica Black
Helvetica Black Oblique
Palatino Roman 0 0 24591 0 0 61455 B
Palatino Italic 1 0 24591 1 0 61455 B
Palatino Bold 0 3 24591 0 3 61455 B
Palatino Bold Italic 1 3 24591 1 3 61455 B
ITC Zapf Chancery Medium Italic 1 0 45099 1 0 61483 B
ITC Zapf Dingbats
CourierPS 0024579 B
CourierPS Oblique 1 0 24579 B
2
2
2
2
3
Style Bold Typeface Style Bold Typeface
0 -3 24580 0 -3 61444 C
1 -3 24580 1 -3 61444 C
0 5 24580 0 5 61444 C
1 5 24580 1 5 61444 C
0 0 45101 0 0 61485
Backward Compatibility
Mode
Font
Group
CourierPS Bold 0 3 24579 B
CourierPS Bold Oblique 1 3 24579 B
Times Roman 0025093 B
Times Italic 1 0 25093 B
Times Bold 0325093 B
Times Bold Italic 1 3 25093 B
SymbolPS
1
Notice the values for forward compatibility and backward compatibility modes differ slightly for Bold.
2
This font is not implemented in the Hewlett-Packard Company’s LaserJet 4050.
3
For the symbol sets supported by this font, see Table 2-6: “Non-Text PCL Emulation Symbol Sets” on page 2-16.
3
0045358
Page 26
2-14
PCL
Your Lexmark printer defaults to the forward compatibility mode to enable a
Hewlett-Packard Company’s driver to select the forward compatib ility fonts . The
Lexmark PCL driver uses the bac kw ard compat ibil ity mode and tempor arily switches
the printer to this mode. The PCL (PJL) commands to s witch t he def ault compati bility
modes are:
ESC
Forward
%-12345X@PJL DEFAULT LPARM:PCL LFONTCOMPATIBILITY=PCL6
@PJL RESET
ESC
%-12345X
Backward
ESC
%-12345X@PJL DEFAULT LPARM:PCL LFONTCOMPATIBILITY=PCL5
@PJL RESET
ESC
%-12345X
Selecting Symbol Sets for the Lexmark X422
To determine which symbol sets a font or typeface from Table 2-3 or Table 2-4
supports, see the complete listing of PCL emulation fonts and symbol sets in the
follo w ing tables.
Table 2-5: Symbol Set Support for PCL Emulation Text Fonts
✓ Indicates the sym bol set i s supported
by the fonts in the font group.
Symbol Set A B C D
Roman Extension 0E
Roman-8 8U ROMAN8
PC-8 Code Page 437 10U PC8
PC-8 Danish/Norwegian (437N) 11U PC8DN
Symbol
Set ID
PJL Value
Font Group
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓ ✓
PC-850 Multilingual 12U PC850
PC-852 Latin 2 17U PC852
PC-8 Turkish (437T) 9T PC8TK
PC-775 Baltic (PC-8 Latin 6) 26U
PC-1004 OS/2 9J
Legal 1U LEGAL
DeskTop 7J DESKTOP
MC Text 12J
PS Text 10J PSTEXT
✓✓✓✓
✓✓ ✓
✓✓
✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓ ✓
✓✓
✓✓✓
✓✓✓
Page 27
2-15
Table 2-5: Symbol Set Support for PCL Emulation Text Fonts (Continued)
✓ Indicates the sym bol set i s supported
by the fonts in the font group.
Symbol Set A B C D
Symbol
Set ID
PJL Value
Font Group
PCL
PS Math 5M PSMATH
Math-8 8M MATH8
Pi Font 15U PIFONT
Microsoft Publishing 6J MSPUBL
Windows 3.0 Latin 1 9U WIN30
Windows Latin 1 19U WINL1
Windows Latin 2 9E WINL2
Windows Latin 5 5T WINL5
Windows Latin 6 (Baltic) 19L
ISO 8859-1 Latin 1 (ECMA-94) 0N ISOL1
ISO 8859-2 Latin 2 2N ISOL2
ISO 8859-9 Latin 5 5N ISOL5
ISO 8859-10 Latin 6 6N
ISO 8859-15 Latin 9 9N
PC-858 Multilingual Euro 13U
✓✓
✓✓
✓✓
✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓ ✓
✓✓
✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓ ✓
✓✓
✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
Roman-9 4U
V en tura International 13J VNINTL
V entura US 14J VNUS
V entura Math 6M VNMATH
PC-861 Iceland 21U
PC-863 Canadian French 23U
PC-865 Nordic 25U
PC-860 Portugal 20U
ABICOMP International 14P
ABICOMP Brazil/Portugal 13P
PC-8 PC Nova 27Q
PC-857 Lat in 5 (Turkish) 16U
Turkish-8 8T
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓
✓✓ ✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓ ✓
✓✓
✓✓
Page 28
2-16
Table 2-5: Symbol Set Support for PCL Emulation Text Fonts (Continued)
✓ Indicates the sym bol set i s supported
by the fonts in the font group.
Symbol Set A B C D
Symbol
Set ID
PJL Value
Font Group
PCL
PC-853 Lat in 3 (Turkish) 18U
PC-8 Polish Mazovia 24Q
Windows Cyrillic 9R
ISO 8859-5 Latin/Cyrillic 10N
PC-866 Cyrillic 3R
PC-855 Cyrillic 10R
Russian-GOST 12R
PC-8 Bulgarian 13R
Ukrainian 14R
Windows Greek 9G
ISO 8859-7 Latin/Greek 12N
PC-869 Greece 11G
PC-851 Greece 10G
PC-8 Latin/Greek 12G
Greek-8 8G
✓
✓✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
PC-8 Greek Alternate (437G) 14G
Table 2-6: Non-Text PCL Emulation Symbol Sets
Symbol
Symbol Set
PC-911 Katakana 3K Line Printer 16
Symbol 19M Symbol, SymbolPS
Wingdings 579L Wingding
POSTNET Bar Code 15Y POSTNET Bar Code
Ventura ITC Zapf Dingbats 9L ITC Zapf Dingbats
PS ITC Zapf Dingbats 10L ITC Zapf Dingbats
PCL ITC Zapf Dingbats 14L ITC Zapf Dingbats
C39 Bar Code (Uppercase) 9Y Code 3 of 9
C39 Bar Code (plu s Lowercase) 109Y Code 3 of 9
Set ID
✓
Fonts
Page 29
Table 2-6: Non-Text PCL Emulation Symbol Sets
Symbol
Symbol Set
Set ID
Fonts
2-17
PCL
C39 Bar Code (plus Human
Readable)
OCR-A 0O OCR-A
OCR-B 1O OCR-B
209Y Code 3 of 9
All fonts that support the Roman-8 (8U) symbol set also support the following
19 symbol sets.
Table 2-7: ISO PCL Emulation Symbol Sets
Symbol
Set ID
1E ISO 4: United Kingdom
0U ISO 6: ASCII
0S ISO 11: Swedish for Names
0I ISO 15: Italian
2S ISO 17: Spanish
1G ISO 21: German
0D ISO 60: Norwegian Version 1
1F ISO 69: French
Symbol Set
2U ISO 2: IRV (International Ref Version)
0F ISO 25: French
0G ISO: HP German
0K ISO 14: JIS ASCII
2K ISO 57: Chinese
3S ISO 10: Swedish
1S ISO: HP Spanish
6S ISO 85: Spanish
4S ISO 16: Portuguese
5S ISO 84: Portuguese
1D ISO 61: Norwegian Version 2
Page 30

2-18
Font and Symbol Set Support for the Lexmark C510(n)
Your printer has 91 resident fonts in PCL emulation, including 89 scalable fonts and
two bitmapped fonts.
Several parameters are used to select a font from the data stream. These include
symbol set, spacing, point or pitch, styl e, weight, and typeface number. For scalable
fonts, you can vary the size of a font by specifying pitch or point size. For bitmapped
fonts , you must choose the pi tch or point size li sted on the font sample pa ges. You can
print the font sample pages from the printer operator panel, using a PJL command
(see “LPRINTPCLFONTS” on page 3-83.) or through MarkVision Professional. Ref er
to your printer user documentation for more information.
PCL
A symbol set defines which characters are available for a font and the code point for
each of these character s . Your printer supports 88 symbol sets . The tab les begi nning
on page 2-14 show the symbol sets available for each font in PCL emulation. Not all
fonts support all symbol sets.
You can select a font as the PCL emulation default from the printer operator panel or
through MarkVision Professional . Refer to your printer user documentation for more
information.
The fonts are divided int o three major groups. The first 47 f onts (R0 through R46)
shown on the font sample pages are the standard PCL emulation fonts. The next 39
fonts (R47 through R85) are called Type 1 fonts and were originally defined for
Post Script emulation, but now also work in the PCL em ulation. The last fiv e fon ts (R86
through R90) include three different Code 3 of 9 bar code fonts, OCR-A and OCR-B
fonts.
The fonts are f urther divided into f ont groups A, B , and C indicat ing which symbol set s
are supported by each fo nt. For a list of the 47 s tand ard PCL em ulati on fonts, as w ell
as the OCR and Code 3 of 9 bar code fonts, see Table 2-3 on page 2-9. For a list of
the 39 Type 1 fonts, see Table 2-4 on page 2-12. Both tables list the forward and
backward compatibility font selection commands and the font group (A, B, or C) for
each font. F or more inf ormation on for ward and backw ard compatibili ty, see page 2-9.
For more information on selecting symbol sets, see page 2-14.
For compatibility purposes, you can disable Type 1 fonts with the Printer Job
Language (PJL) LTYPE1FONTS command. The factory default for these fonts is
Enabled. See LTYPE1FONTS on page 3-47 for more information.
Page 31

2-19
PCL
You can also select fonts using PJL commands . The selection parameter is the
number portion from the font identifi er sho wn on t he font sample pages, such as 0 or
76 from font identifi ers R0 or R76. Use the PJL v a lues sho wn in the tables beginning
on page 2-14 to select a symbol set. If a symbol set does not have a PJL value, use
the symbol set ID to select the symbol set. A f ont selection can be eit her temporary or
set as the default.
Use the followi ng PJL comman ds to sel ect fonts: FONTSOURCE, FONTNUMBER,
PITCH, PTSIZE, SYMSET, SET, DEFAULT. See Table 3-5: “Common Variables for
PCL Emulation” on page 3-48 for more information about these commands.
Forward and Backward Compatibility Modes for the Lexmark C510(n)
Your PCL emulation has forward and backward compatibility modes. The forward
compatibility mode is used to emulate the fonts in the Hewlett-Packard Company’s
LaserJet 4050. The backward compatibility mode is used for compatibility w i t h the
Hewlett-Packard Company’s LaserJet 5 and the Lexmark family of printers.
Standard PCL Emulation Fonts, OCR and Code 3 of 9 bar code fonts
Table 2-3 on page 2-9 lists the font selection commands for forward and backward
compatibility mode for each of the 47 standard PCL emulation fonts, the OCR and
Code 3 of 9 bar code fonts. Since t he font selection commands f o r the forward and
backward compati bility modes are i dentical, the y are list ed together in the tab le . Most
fonts are assig ned a font group indicating which symbol sets that font supports.
To determine which symbol sets are supported by a particular font, find the font
group (A, B, or C) for the font in Table 2-3, and then see T able 2-5 on page 2-14 for the
symbol sets that belong to that group.
Table 2-8: Forward and Backward Compatibility Font Selection Commands
Forward and Backward
Standard PCL Emulation
Font Name
Compatibility Mode
Style Bold Typeface
Font
Group
Courier 0 0 4099 A
Courier Italic 1 0 4099 A
Courier Bold 0 3 4099 A
1
For the symbol sets supported by this font, see Table 2-6: “Non-Text PCL Emulation
Symbol Sets” on page 2-16.
Page 32

2-20
PCL
Table 2-8: Forward and Backward Compatibility Font Selection
Forward and Backward
Standard PCL Emulation
Font Name
Courier Bold Italic 1 3 4099 A
CG Times 0 0 4101 A
CG Times Italic 1 0 4101 A
CG Times Bold 0 3 4101 A
CG Times Bold Italic 1 3 4101 A
Univers Medium 0 0 4148 A
Univers Medium Italic 1 0 4148 A
Univers Bold 0 3 4148 A
Univers Bold Italic 1 3 4148 A
Compatibility Mode
Style Bold Typeface
Font
Group
Letter Gothic 0 0 4102 B
Letter Gothic Italic 1 0 4102 B
Letter Gothic Bold 0 3 4102 B
Univers Condensed Medium 4 0 4148 B
Univers Condensed Medium Italic 5 0 4148 B
Univers Condensed Bold 4 3 4148 B
Univers Condensed Bold Italic 5 3 4148 B
Garamond Antiqua 0 0 4197 B
Garamond Kursiv 1 0 4197 B
Garamond Halbfett 0 3 4197 B
Garamond Kursiv Halbfett 1 3 4197 B
CG Omega 0 0 4113 B
CG Omega Italic 1 0 4113 B
CG Omega Bold 0 3 4113 B
CG Omega Bold Italic 1 3 4113 B
Antique Olive 0 0 4168 B
Antique Olive Italic 1 0 4168 B
Antique Olive Bold 0 3 4168 B
Albertus Medium 0 1 4362 B
Albertus Extra Bold 0 4 4362 B
Clarendon Condensed Bold 4 3 4140 B
Marigold 0 0 4297 B
1
For the symbol sets supported by this font, see Table 2-6: “Non-Text PCL Emulation
Symbol Sets” on page 2-16.
Page 33

2-21
PCL
Table 2-8: Forward and Backward Compatibility Font Selection
Forward and Backward
Standard PCL Emulation
Font Name
Coronet 1 0 4116 B
Times New Roman 0 0 16901 B
Times New Roman Italic 1 0 16901 B
Times New Roman Bold 0 3 16901 B
Times New Roman BoldItalic 1 3 16901 B
Arial 0 0 16602 B
Arial Italic 1 0 16602 B
Arial Bold 0 3 16602 B
Arial Bold Italic 1 3 16602 B
1
Symbol
Wingdings
Line Printer 16
POSTNET Bar Code
OCR-A
OCR-B
C39 Narrow
C39 Regular
C39 Wide
1
For the symbol sets supported by this font, see Table 2-6: “Non-Text PCL Emulation
Symbol Sets” on page 2-16.
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Compatibility Mode
Style Bold Typeface
0 0 16686
0 0 31402
000 A
000
0 0 23584
0 0 23590 D
0 0 32774
0 0 32772
0 0 32777
Font
Group
Page 34

Type 1 Fonts
2-22
PCL
Thirty of the Type 1 fonts have different font selection parameters in the forward and
backward compatib ility modes and 9 of the fonts work only in the forward compat ibility
mode. With the appropriate printer driver installed and selected, your software
application selects these fonts.
The followi ng table shows the f ont selection commands for forward and backward
compatibility modes and indicates the font group for each font. All Type 1 fonts are
supported by both the Hewlett-Packard Company’s LaserJet 4050 and the
Lexmark family of printers unless otherwise noted.
To determine which symbol sets are supported by a particular font, find the font
group (A, B, or C) for the font in Table 2-4, and then see T able 2-5 on page 2-14 for the
symbol sets that belong to that group.
Table 2-9: Forward and Backward Compatibility Font Selection Commands
Forward Compatibility
Mode
Type 1 Font name
ITC Avant Garde Book 0 0 24607 0 0 61471 B
ITC Avant Garde Book Oblique 1 0 24607 1 0 61471 B
ITC Avant Garde Demi
ITC Avant Garde Demi Oblique
ITC Bookman Light 0 -3 24623 0 -3 61487 B
ITC Bookman Light Italic 1 -3 24623 1 -3 61487 B
ITC Bookman Demi 0 2 24623 0 2 61487 B
ITC Bookman Demi Italic 1 2 24623 1 2 61487 B
Century Schoolbook Roman 0 0 24703 0 0 61463 B
Century Schoolbook Italic 1 0 24703 1 0 61463 B
Century Schoolbook Bold 0 3 24703 0 3 61463 B
Century Schoolbook Bold Italic 1 3 24703 1 3 61463 B
Helvetica 0 0 24580 0 0 61444 B
Helvetica Italic 1 0 24580 1 0 61444 B
Helvetica Bold 0 3 24580 0 3 61444 B
1
1
Style Bold Typeface Style Bold Typeface
0 2 24607 0 3 61471 B
1 2 24607 1 3 61471 B
Backward Compatibility
Mode
Font
Group
Helvetica Bold Italic 1 3 24580 1 3 61444 B
Helvetica Narrow 4 0 24580 4 0 61444 B
1
Notice the values for forward compatibility and backward compatibility modes differ slightly for Bold.
2
This font is not implemented in the Hewlett-Packard Company’s LaserJet 4050.
3
For the symbol sets supported by this font, see Table 2-6: “Non-Text PCL Emulation Symbol Sets” on page 2-16.
Page 35

2-23
Table 2-9: Forward and Backward Compatibility Font Selection Commands (Continued)
PCL
Forward Compatibility
Mode
Type 1 Font name
Helvetica Narrow Italic 5 0 24580 5 0 61444 B
Helvetica Narrow Bold 4 3 24580 4 3 61444 B
Helvetica Narrow Bold Italic 5 3 24580 5 3 61444 B
Helvetica Light
Helvetica Light Oblique
Helvetica Black
Helvetica Black Oblique
Palatino Roman 0 0 24591 0 0 61455 B
Palatino Italic 1 0 24591 1 0 61455 B
Palatino Bold 0 3 24591 0 3 61455 B
Palatino Bold Italic 1 3 24591 1 3 61455 B
ITC Zapf Chancery Medium Italic 1 0 45099 1 0 61483 B
ITC Zapf Dingbats
CourierPS 0024579 B
CourierPS Oblique 1 0 24579 B
2
2
2
2
3
Style Bold Typeface Style Bold Typeface
0 -3 24580 0 -3 61444 C
1 -3 24580 1 -3 61444 C
0 5 24580 0 5 61444 C
1 5 24580 1 5 61444 C
0 0 45101 0 0 61485
Backward Compatibility
Mode
Font
Group
CourierPS Bold 0 3 24579 B
CourierPS Bold Oblique 1 3 24579 B
Times Roman 0025093 B
Times Italic 1 0 25093 B
Times Bold 0325093 B
Times Bold Italic 1 3 25093 B
SymbolPS
1
Notice the values for forward compatibility and backward compatibility modes differ slightly for Bold.
2
This font is not implemented in the Hewlett-Packard Company’s LaserJet 4050.
3
For the symbol sets supported by this font, see Table 2-6: “Non-Text PCL Emulation Symbol Sets” on page 2-16.
3
0045358
Page 36

2-24
PCL
Your Lexmark printer defaults to the forward compatibility mode to enable a
Hewlett-Packard Company’s driver to select the forward compatib ility fonts . The
Lexmark PCL driver uses the bac kw ard compat ibil ity mode and tempor arily switches
the printer to this mode. The PCL (PJL) commands to s witch t he def ault compati bility
modes are:
ESC
Forward
%-12345X@PJL DEFAULT LPARM:PCL LFONTCOMPATIBILITY=PCL6
@PJL RESET
ESC
%-12345X
Backward
ESC
%-12345X@PJL DEFAULT LPARM:PCL LFONTCOMPATIBILITY=PCL5
@PJL RESET
ESC
%-12345X
Selecting Symbol Sets for the Lexmark C510(n)
To determine which symbol sets a font or typeface from Table 2-3 or Table 2-4
supports, see the complete listing of PCL emulation fonts and symbol sets in the
follo w ing tables.
Table 2-10: Symbol Set Support for PCL Emulation Text Fonts
✓ Indicates the sym bol set i s supported
by the fonts in the font group.
Symbol Set A B C D
Roman Extension 0E
Roman-8 8U ROMAN8
PC-8 Code Page 437 10U PC8
PC-8 Danish/Norwegian (437N) 11U PC8DN
Symbol
Set ID
PJL Value
Font Group
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓ ✓
PC-850 Multilingual 12U PC850
PC-852 Latin 2 17U PC852
PC-8 Turkish (437T) 9T PC8TK
PC-775 Baltic (PC-8 Latin 6) 26U
PC-1004 OS/2 9J
Legal 1U LEGAL
DeskTop 7J DESKTOP
MC Text 12J
PS Text 10J PSTEXT
✓✓✓✓
✓✓ ✓
✓✓
✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓ ✓
✓✓
✓✓✓
✓✓✓
Page 37

2-25
Table 2-10: Symbol Set Support for PCL Emulation Text Fonts (Continued)
✓ Indicates the sym bol set i s supported
by the fonts in the font group.
Symbol Set A B C D
Symbol
Set ID
PJL Value
Font Group
PCL
PS Math 5M PSMATH
Math-8 8M MATH8
Pi Font 15U PIFONT
Microsoft Publishing 6J MSPUBL
Windows 3.0 Latin 1 9U WIN30
Windows Latin 1 19U WINL1
Windows Latin 2 9E WINL2
Windows Latin 5 5T WINL5
Windows Latin 6 (Baltic) 19L
ISO 8859-1 Latin 1 (ECMA-94) 0N ISOL1
ISO 8859-2 Latin 2 2N ISOL2
ISO 8859-9 Latin 5 5N ISOL5
ISO 8859-10 Latin 6 6N
ISO 8859-15 Latin 9 9N
PC-858 Multilingual Euro 13U
✓✓
✓✓
✓✓
✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓ ✓
✓✓
✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓ ✓
✓✓
✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
Roman-9 4U
V en tura International 13J VNINTL
V entura US 14J VNUS
V entura Math 6M VNMATH
PC-861 Iceland 21U
PC-863 Canadian French 23U
PC-865 Nordic 25U
PC-860 Portugal 20U
ABICOMP International 14P
ABICOMP Brazil/Portugal 13P
PC-8 PC Nova 27Q
PC-857 Lat in 5 (Turkish) 16U
Turkish-8 8T
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓
✓✓ ✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓✓✓
✓✓ ✓
✓✓
✓✓
Page 38

2-26
Table 2-10: Symbol Set Support for PCL Emulation Text Fonts (Continued)
✓ Indicates the sym bol set i s supported
by the fonts in the font group.
Symbol Set A B C D
Symbol
Set ID
PJL Value
Font Group
PCL
PC-853 Lat in 3 (Turkish) 18U
PC-8 Polish Mazovia 24Q
Windows Cyrillic 9R
ISO 8859-5 Latin/Cyrillic 10N
PC-866 Cyrillic 3R
PC-855 Cyrillic 10R
Russian-GOST 12R
PC-8 Bulgarian 13R
Ukrainian 14R
Windows Greek 9G
ISO 8859-7 Latin/Greek 12N
PC-869 Greece 11G
PC-851 Greece 10G
PC-8 Latin/Greek 12G
Greek-8 8G
✓
✓✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
✓
PC-8 Greek Alternate (437G) 14G
Table 2-11: Non-Text PCL Emulation Symbol Sets
Symbol
Symbol Set
PC-911 Katakana 3K Line Printer 16
Symbol 19M Symbol, SymbolPS
Wingdings 579L Wingding
POSTNET Bar Code 15Y POSTNET Bar Code
Ventura ITC Zapf Dingbats 9L ITC Zapf Dingbats
PS ITC Zapf Dingbats 10L ITC Zapf Dingbats
PCL ITC Zapf Dingbats 14L ITC Zapf Dingbats
C39 Bar Code (Uppercase) 9Y Code 3 of 9
C39 Bar Code (plu s Lowercase) 109Y Code 3 of 9
Set ID
✓
Fonts
Page 39

Table 2-11: Non-Text PCL Emulation Symbol Sets
Symbol
Symbol Set
Set ID
Fonts
2-27
PCL
C39 Bar Code (plus Human
Readable)
OCR-A 0O OCR-A
OCR-B 1O OCR-B
209Y Code 3 of 9
All fonts that support the Roman-8 (8U) symbol set also support the following
19 symbol sets.
Table 2-12: ISO PCL Emulation Symbol Sets
Symbol
Set ID
1E ISO 4: United Kingdom
0U ISO 6: ASCII
0S ISO 11: Swedish for Names
0I ISO 15: Italian
2S ISO 17: Spanish
1G ISO 21: German
0D ISO 60: Norwegian Version 1
1F ISO 69: French
Symbol Set
2U ISO 2: IRV (International Ref Version)
0F ISO 25: French
0G ISO: HP German
0K ISO 14: JIS ASCII
2K ISO 57: Chinese
3S ISO 10: Swedish
1S ISO: HP Spanish
6S ISO 85: Spanish
4S ISO 16: Portuguese
5S ISO 84: Portuguese
1D ISO 61: Norwegian Version 2
Page 40

2-28
PCL
Command Structure
This section introduces the different types of PCL emulation commands and their
structure, or syntax. It also demonstrates how you can link commands to abbreviate
them.
Control Codes
Control Codes are single-character instructions.
Table 2-13: Control Codes
Code Dec Hex Function Result
BS 8 08 Backspace Moves the cursor toward the left margin one horizontal space equal to
the last printed character
HT 9 09 Horizontal Tab Moves the cursor to the next defined tab stop
LF 10 0A Line Feed Advances the cursor to the s am e horiz o ntal pos iti on on the following line
as determined by either the Vertical Motion Index (VMI) or Set Line
Spacing command
FF 12 0C Form Feed Advances the cursor to the same horizontal position at the top margin of
the next page
CR 13 0D Carriage Return Moves the cursor to the left margin
SP 32 20 Space Moves the cursor to the right one column
SI 15 0F Primary Font Selects the primary font
SO 14 0E Secondary Font Selects the secondary font
Commands
PCL commands are multibyte s trings (also known as “escape sequences ”) that begi n
ESC
with the Escape control code (
code notifies the printer that the cha racters that f ol lo w are to be int erpreted as part of
a command and are not control codes or data to be printed.
, ←, decimal 27, or h ex adecimal 1B). The
ESC
control
Page 41

Command Structure
Most PCL emulation commands have the following structure:
ESC
& a # C
Spaces have been added to thi s example for readability. The command parameter
variables are indicated by a number sign (#).
Table 2-14: Description of Command Structure
Element Description
ESC
& Parameterized character from American National Standard Code for Information
a Group character from ASCII table (range 96 to 126 decimal) that specifies a group
# Decimal character string v al ue wi thin spe cified n umeric ra nge s; may be preceded b y
2-29
Decimal 27 or hex 1B
Interchange (ASCII) table (range 33 to 47 decimal)
type of control
a + or – sign and contain a decimal point
PCL
C Termination character from ASCII table (range 64 to 94 decimal)
Command Parameters
A command parameter sets the value f or a c ommand. Thi s value stays const ant until
either a differ ent value resets the command or a command resets the printer to th e
default v alues . F or e x ample , after the printer re ceiv es a command that select s a right
margin beginning at column 63, the right margin of each printed page begins at
column 63. That margin sta ys constant until a right margin command with a differ ent
value resets it or until the printer is reset.
Paramet ers for each command are listed in the command tables beginning on
page 2-31. Use the Symbol Set Tables to determine the decimal or hexadecimal v alue
for each par ameter. To determine a decimal or hex value, first locate the value of the
parameter you requi re in the Symbol Set Table. The decimal v alue is th e value sh own
in the bottom of the cell or bo x wit h that par ameter. To find a hex v alue , go str aight up
the grid from the desired paramet er and read the value in the top heading . This i s the
first character of the hex value. Next, go straight across the grid to the left of the
parameter and read the v alue in the left column heading. This is the seco nd character
of the hex v alue. F or e xample,
of the three values
documentation to determine which to use.) The example on the following page sets
the pitch of the primary font to 16.66 characters per inch.
ESC
(←) is coded 1B in Hex and 27 in decimal. (Any one
←, 1B, or 27 might be used in your application. Read your
Page 42

Example:
ESC
(s16.66H
• Decimal: 27 40 115 49 54 46 54 54 72
• Hex: 1B 28 73 31 36 2E 36 36 48
Use the plus symbol (+) or the minus symbol (–) to select a position relative to the
current cursor position. For examp le:
ESC
&a6C Move to horizontal cursor position, column si x
ESC
&a+6C Move six columns to the right of the current position
ESC
&a-6C Move six columns to the left of the current position
Linking Commands
2-30
PCL
You can combine PCL emulation commands by linking them if the first 3 bytes of the
commands are identical. The combined, short form sends the first 3 bytes only once
in the string. To combine commands:
• Use the first 3 byt es (char acters) of the command onl y once at t he start of the
command string.
• Make the last letter of each command in the string lowercase.
• Capitalize the last letter of the string.
For example, notice that the first 3 bytes of these two commands are the same:
ESC
(s10H Select 10 characters per inch
ESC
(s4099T Select Courier typeface
To combine these two commands, use this form:
ESC
(s10h4099T
which is 3 bytes shorter than the long form:
ESC
(s10H
ESC
(s4099T
You can combine more than two commands; for e x ample, you can add Select Strok e
ESC
Weight Bold (
ESC
(s10h3b4099T
(s3B) to the previous two commands:
or in the long form:
ESC
(s10H
ESC
(s3B
ESC
(s4099T
Page 43

PCL Emulation Commands
See the follo wing tables for a listing of the commands grouped by function.
To determine which commands your printer supports, see “Table A-1: PCL Emulation
Commands” on page A-1.
PCL Emulation Commands by Function
Table 2-15: Job Control
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
E Printer Reset
• Prints any partial pages.
• Resets printer environment to defaults.
• Deletes all temporary downloaded resources.
ESC
&d#A
0 = Collation off
1 ... 999 (number of Copies)
ESC
&l#X
# = number of Copies (1 to 32767)
Default = 1
ESC
&l#S
0 Single-Sided (Default)
1 Duplex Long-Edge Binding
2 Duplex Short-Edge Binding
100 Manual Duplex First Sides
101 Manual Duplex Second Sides
ESC
&l#U
# = number of Decipoints
Range = -32767 to 32767
(1 Decipoint = 1/720 inch)
Default = 0
ESC
&l#Z
# = number of Decipoints
Range = -32767 to 32767
(1 Decipoint = 1/720 inch)
Default = 0
Number of Collated Copies
Turns collation of pages off or sets the number of collated copies.
Number of Copies
Affects the page currently in process and subsequent pages.
Simplex/D uplex Print
Long-edge or short-edge bind ing ref ers to the sid e of the ph ysical page
where binding occurs.
Long-Edge Offset Registration
Also known as Left Offset.
Adjusts placement of logical page alo ng t he wi dth of the physical pag e .
Short-Edge Offset Registration
Also known as Top Offset.
Adjusts placement of logical page along the length of the physical
page.
2-31
PCL
Page 44

2-32
Table 2-15: Job Control (Continued)
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
&u#D
Range = (96, 100, 120, 144, 150, 160, 180,
200, 225, 240, 288, 300, 3 60, 4 00, 450, 480 ,
600, 720, 800, 900, 120 0, 14 40, 180 0, 24 00,
3600, 7200)
Default = 300 units per inch
ESC
%–12345X Universal Exit Language (UEL) / Start of PJL
Unit of Measure
Sets the size for the PCL Unit (units per inch).
The Unit of Measure defines the unit used in the following commands:
• Horizontal Cursor Position by PCL Unit (
• Ve rtical Cursor Position by PCL Unit (
• Horizontal Rectangle Size by PCL Unit (
• Vertical Rectangle Size by PCL Unit (
The Unit of Measure also affects the rounding of character
escapements and the Horizontal Motion Index.
Note: This comman d doe s n ot af fect the interpretation of binary raster
data for bitmapped fonts, raster graphics, or user defined fill patterns.
This command terminates the current printer langua ge and allo w s
switching into PJL. For more information, see “UNIVERSAL EXIT
LANGUAGE Command” on page 3-2.
ESC
ESC
ESC
*p#X)
*p#Y)
ESC
*c#A)
*c#B)
PCL
Page 45

Table 2-16: Page Contr ol
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
&l#A
Paper
1 Executive
2 Letter
3 Legal
4, 10 F oli o
6, 11 Ledger (11 x 17)
13, 25 A5 Paper
15 Statement
26 A4 Paper
27 A3 Paper
12, 45 B5 Paper
46 B4 Paper
101 Custom Paper/Universal
Envelopes
80 Monarch 7 3/4
81 Commercial 10
89 Commercial 9
90 DL
91 C5
99, 100 B5 Envelope
600 Other Envelope
ESC
&l#H
0 Active Source or Eject Page
1 Tray 1 (Default)
2 Manual Paper Feed
3 Manual Envelope Feed
4Tray2
5Tray3
6 Optional Envelope Feeder
7Auto Select
8 Multipurpose Feeder
20 Tray 4
21 Tray 5
62 Optional Paper Source
ESC
&f#G
# = number of Decipoints
(1 Decipoint = 1/720 inch)
ESC
&f#F
# = number of Decipoints
(1 Decipoint = 1/720 inch)
Set Page Size
Selects the physical size of the paper, which also determines the
logical page dimensions. See the tables beginning on page 2-4 for the
paper and envelope dimensions your printer supports.
If the requested pa ge siz e is no t in the requested source o r if no so urce
is requested, sources are checked for the requested size in the
following order: multipurpose f eeder, tray 1, tray 2, tray 3, tray 4, tray 5,
and envelope feeder.
Notes:
• When the printer receives the page size command, any partially
formatted pages are printed, and the cursor position and margins
are reset.
• Duplex printing is not supported on any envelope.
• The size loaded in the active source is checked to see if it matches
the requested size. If the multipurpose feeder is configured as
Cassette or Manual, the same applies; however, if the multipurpose
feeder is configured as First and media is loaded in the
multipurpose feeder, then, regardless of media size, it is the source
used until it is empty.
Paper Source
Selects the paper feed source.
Note: If the paper source is changed for the back of a duplexed page,
a blank back page prints, the paper source changes, and the
information f or the b ack side of t he page i s printed on the fron t side of a
page sent from the new paper source.
Set Universal Width
Sets the width of the Universal size in decipoints.
Set Universal Height
Sets the height of the Universal size in decipoints.
2-33
PCL
Page 46

Table 2-16: Page Control (Continued)
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
&f#O
0Short-edge
1 Long-edge
ESC
&f#W [custom name]
# = number of bytes in the custom name
ESC
&l#O
0 Portrait (Default)
1 Landscape
2 Reverse Portrait
3 Reverse Landscape
ESC
&a#P
# = Degrees (0, 90, 180, 270)
Default = 0
ESC
&c#T
0 Horizontal Printing
-1 Vertical Rotated Printing
ESC
&a#L
# = Column
Default = 0
ESC
&a#M
# = Column
Default = Logical Page Width
ESC
9 Clear Horizontal Margins
ESC
&l#E
# = number of Lines
Default = 3 (1/2 inch)
ESC
&l1T J ob Separation
Set Universal Feed Direction
Sets the feed direction of Universal size. Feed direction means which
side of the print media, either the short edge or the long edge, feeds
first through the printer first.
Set Universal Custom Name
Sets the user-specified custom name for the Universal paper size
being used.
Select Orientation
Specifies the position of the logical page with respect to the physical
page.
Note: Resets margins, number of printable lines per page, and cursor
position.
Print Direction
Rotates coordinate system counter-clockwise in 90° increments with
respect to current orientation.
Note: Margins are not rotated or cleared.
Character Text Path Direction
Vertically rotates text for use in vertical writing, such as printing
Japanese text.
Set Left Margin
Sets left margin to left edge of the designated column.
Note: The colu mn widt h i s defined b y the sp ace char a cter of the ac tiv e
font and the Horizontal Motion Index (HMI).
Set Right Margin
Sets right margin to right edge of the designated column.
Note: The colu mn widt h i s defined b y the sp ace char a cter of the ac tiv e
font and the HMI.
Clears left and right margins.
Set Top Margin
Sets the number of lines betw een the top of the physical page and firs t
line of print. Line height is determined by the current Vertical Motion
Index (VMI) and/or line spacing value.
Note: Setting a top margin of 0 results in the first line of text falling
outside of the printable area.
This command is parsed and ignored.
2-34
PCL
Page 47

Table 2-16: Page Control (Continued)
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
&l#F
# = number of Lines
Default = 60 or 64 (Country specific)
ESC
&l#G
0 Auto Select (uses the active bin)
1 Standard Bin
2Bin 1 or Rear Bin
3Bin 1 or Rear Bin
4Bin 2
5Bin 3
6Bin 4
7Bin 5
8Bin 6
9Bin 7
10 Bin 8
11 Bin 9
12 Bin 10
ESC
&l#L
0 Off
1 On (Default)
ESC
&k#H
# = number of 1/120 inch increments
(Valid to 4 decimal places)
ESC
&l#C
# = number of 1/48 inch increments
(Valid to 4 decimal places)
Default = 8
Set Text Length
Sets the bottom margin length in lines, measured from the first line of
the page.
Text Length equals Logical Page Length –1 inch (–1/2 inch for top and
–1/2 inch for bottom).
Set Output Bin
Sets the exit path to direct paper to one of the output bins.
Skip Perforation
Perforation area includes the area from the bottom margin of the
current page to the top margin of the next page. When skipping
perforations, a line feed past the bottom margin ejects a page and
places the cursor at the top margin of the next page.
Set Horizontal Motion Index (HMI)
Sets the width of all characters for fixed-space fonts. Sets only the
width of the space for proportional spaced fonts.
Set Vertical Motion Index (VMI)
Sets Vertical Motion Index in 1/48 inch increments. The VMI
determines the vertical distance between lines.
Notes:
• For some printers, you can change the default VMI from the printer
operator panel or through MarkVision Professional by using the
Lines Per Page menu item. Ref er to your printer user doc umentation
for more information.
• Use of this command alters any previous Set Line Spacing
command settings.
2-35
PCL
Page 48

Table 2-16: Page Control (Continued)
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
&l#D
1 1 line/inch
22 lines/inch
33 lines/inch
44 lines/inch
6 6 lines/inch (Default)
88 lines/inch
12 12 lines/inch
16 16 lines/inch
24 24 lines/inch
48 48 lines/inch
E
SC
&a#G
0Next Side
1 Front Side
2Back Side
ESC
&l#P
# = number from 0 to 14
0 = default page length is used
(1 to 14 new page length is set)
ESC
&k#W
5 Turn Text Scale Mode OFF
6 Turn Text Scale Mode ON
Set Line Spacing (Alternative Method)
Specifies VMI in lines per inch.
Notes:
• For some printers, you can change the default VMI from the printer
operator panel or through MarkVision Professional by using the
Lines Per Page menu item. Ref er to your printer user doc umentation
for more information.
• Unsupported values are ignored.
• Use of this command alters any earlier VMI setting.
Duplex Page Side Selection
Specifies which physical page side to print next when duplex printing.
Note: When the duplex option is not in sta ll ed, th is command causes a
conditional page eject.
Set Page Length
Sets the logical page length in number of lines.
Notes:
• This command is sent at the beginning of a page in a print job and
prior to any printable data.
• When the command is sent, the current page is closed and printed.
• Unsupported values are ignored.
Te xt Scal e Mode
Allows 66 lines of text at six lines per inch to print on an effective page
length of 10 1/2 inches.
Notes:
• Unsupported values are ignored.
• The command is ignored when the printer is in landscape mode.
2-36
PCL
Page 49

Table 2-17: Alphanumeric ID
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
&n#W [operation] [string]
# = number of data bytes that make up the
operation and string
Operation
operation = 100 or 1 byte = 0x64 or
For example:
100 Media Select
String
string = See Alphanumeric String list at
right
'd' ascii
Alphanumeric ID
Selects the media type using a character string. The string ID is case
sensitive and may be up to 511 bytes long.
The string ID specifies the media type requested.
Media Type Alphanumeric String
Plain Paper Plain
Bond Bond
Transparency Transparency
Card Stock Card Stock
Labels Labels
Letterhead Letterhead
Pre-printed Preprinted
Colored Paper Color
Envelope Envelope
Custom Type 1 Custom Type 1 or User Type 1
Custom Type 2 Custom Type 2 or User Type 2
Custom Type 3 Custom Type 3 or User Type 3
Custom Type 4 Custom Type 4 or User Type 4
Custom Type 5 Custom Type 5 or User Type 5
Custom Type 6 Custom Type 6 or User Type 6
2-37
PCL
For example, the following shows the command and parameters used
to select bond paper:
To select letterhead paper:
ESC
&n5WdBond
ESC
&n11WdLetterhead
Table 2-18: Cursor Positioning
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
&a#C
# = number of Columns
ESC
&a#H
# = number of Decipoints
(1 Decipoint = 1/720 inch)
ESC
*p#X
# = number of PCL Units
1
Param eter prece ded b y + or – sign denot es a re lative cursor mov e f rom the curren t curs or posi tion. P ar amete r without a
sign denotes an absolute cursor move from the top left margin.
1
1
1
Horizontal Cursor Position (in Columns)
Moves the cursor to a new position along the horizontal axis.
Note: The column wid t h is de termined by the space c har acter width of
the active font or the Horizontal Motion Index (HMI), if set.
Horizontal Cursor Position (in Decipoints)
Moves the cursor to a new position along the horizontal axis.
Horizontal Cursor Position (in PCL Units)
Moves the cursor to a new position along the horizontal axis.
Note: PCL units are set by the Unit-of-Measure Command.
Page 50

2-38
PCL
Table 2-18: Cursor Positioning (Continued)
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
&a#R
# = number of Row s
ESC
&a#V
# = number of Decipoints
(1 Decipoint = 1/720 inch)
ESC
*p#Y
# = number of PCL Units
ESC
= Half Line-Feed
ESC
&k#G
0 CR=CR, LF=LF, FF=FF (Default)
1 CR=CR+LF, LF=LF, FF=FF
2 CR=CR, LF=CR+LF, FF=CR+FF
3 CR=CR+LF, LF=CR+LF, FF=CR+FF
ESC
&f#S
0 Push
1 Pop
1
Param eter prece ded b y + or – sign denot es a re lative cursor mov e f rom the curren t curs or posi tion. P ar amete r without a
sign denotes an absolute cursor move from the top left margin.
1
1
1
Vertical Cursor Position (in Rows)
Moves the cursor to a new position along the vertical axis.
Note: Row height is determined by either the Vertical Motion Index
(VMI) or the Set Line Spacing Command.
Vertical Cursor Position (in Decipoints)
Moves the cursor to a new position along the vertical axis.
Vertical Cursor Position (in PCL Units)
Moves the cursor to a new position along the vertical axis.
Note: PCL units are set by the Unit-of-Measure Command.
Moves the cursor down 1/2 line (1/2 of the current VMI).
Set Line Termination
Controls how the printer responds to the Carriage Return (CR), Line
Feed (LF), and Form Feed (FF) control codes.
Push / Pop Cursor Position
Sets up a cursor position stack for storing and recalling various cursor
positions. The stack can store up to 20 cursor positions.
Page 51

Note: For the commands listed in Table 2-19, font selection is based on all
parameters set fol lowing the best fit selection rules .
Table 2-19: Font Selection
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
(# (primary)
ESC
)# (secondary)
# = symbol set ID
Default = 10U (PC-8) or 12U
(PC-850), [Country specific]
ESC
(s#P (primary)
ESC
)s#P (secondary)
0 Fixed (Default)
1 Proportional
ESC
(s#H (primary)
ESC
)s#H (secondary)
# = characters per inch
Default = 10
ESC
(s#V (primary)
ESC
)s#V (secondary)
# = height in points (.25 to 999.75)
Default = 12
ESC
(s#S (primary)
ESC
)s#S (secondary)
0 Upright (Default)
1 Italic
4 Condensed
5 Condensed Italic
8 Compressed
24 Expanded
32 Outline
64 Inline
128 Shadowed
160 Outline Shadowed
Select Symbol Set
See “Font and Symbol Set Support for the Lexmark X422” on page2-8,
or “Font and Symbol Set Support for the Lexm ark C510(n)” on page 2-18
for more information.
Note: The line-draw characters are contained in the symbol set ID 10U,
PC-8. The non-U.S. characters are contained in symbol set ID 12U,
PC-850.
Select Spacing
Selects a font with proportional or fixed spacing.
Select Pitch
Selects the number of characters per inch (cpi) for a fixed-space
bitmapped or monospaced scalable font. Valid to 2 decimal places.
Note: Pitch is not needed for proportional spaced fonts.
Height (Select Point Size)
Sets the font height in points. Valid to 2 decimal places.
Note: Point size is not needed for monospaced fonts. For fonts larger
than 12 points, it may be necessary to change the line spacing.
Select Style
Identifies the ph ysical trai ts of a char acter and the compo sition of the f ont
symbols.
Note: You can only use this command to select fonts currently available
in the printer. It cannot alter the appearance of the available fonts.
2-39
PCL
Page 52

Table 2-19: Font Selection (Continued)
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
(s#B (primary)
ESC
)s#B (secondary)
-7 Ultra Thin
-6 Extra Thin
-5 Thin
-4 Extra Light
-3 Light
-2 Demi Light
-1 Semi Light
0 Medium (Default)
1 Semi Bold
2 Demi Bold
3 Bold
4 Extra Bold
5 Black
6 Extra Black
7 Ultra Black
ESC
(s#T (primary)
ESC
)s#T (secondary)
# Typeface identifier (0 - 65535)
Note: For a list of typeface nu mbers, see
Table2-3 on page 2-9 and Table 2-8 on
page 2-19.
ESC
(#X (primary)
ESC
)#X (secondary)
# = Font ID (0 - 32767)
ESC
(3@ (primary)
ESC
)3@ (secondary)
ESC
&p#X[data]
# = number of data of bytes to print as text
ESC
&d#D
0,1 Fixed
2 Fixed - double
3Floating
4 Floating - double
ESC
&d@ Underline - Disable
Select Stroke Weight
Selects a font with a particular thickness.
Note: This command will not alter the stroke weight of an available font.
Select Typeface
Selects the best fit font design.
To obtain the typeface v alues for download ed fonts, print the f ont list fro m
the printer operator panel or through MarkVision Professional. Refer to
your printer user documentation for more information.
On the printout, the typeface number is the last number on the font
selection command example line. The examp le lin e is b elow the name of
the font. In the following example, the typeface number is underlined:
RO Courier
<<ESC>>(<<symset>><<ESC>>(s0p<<pitch>>h0s0b4099T
Select Font by Font ID
Selects the font by the identification number.
Select Default Font
Sets all font selection characteristics to the Default Font.
Transparent Print Data
Prints the next number of bytes as text.
Select Underline Type (Enable)
Notes:
• Fixed underline is drawn 5 pels below cursor position.
• Floating underline position is determined by all the positions of the
characters with descenders in the fonts that are to be underlined.
• Underline thickness is 1/100 inch.
2-40
PCL
Page 53

Table 2-19: Font Selection (Continued)
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
&t#P
0, 1 1 byte characters
21 1 or 2 byte characters
31 1 or 2 byte characters
38 1 or 2 byte characters
1008 1, 2, or 3 byte characters (UTF-8)
ESC
&k#S
0 10.00 cpi
2 16.66 cpi
4 12.00 cpi
Table 2-20: User-Defined Symbol Set
Te xt Parsing Method
Communicates to the PCL parser whether character codes are
interpreted as 1-byte or 2-byte character codes.
Select Primary and Secondary Pitch
Selects the pitch for the primary and secondary font.
2-41
PCL
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
*c#R
# = Symbol Set ID (0 - 32767)
Default = 0
ESC
(f#W[data]
# = number of data bytes
ESC
*c#S
0 Delete all (temporary and permanent)
1 Delete all temporary
2 Delete current (ID)
4 Make current temporary
5 Make current permanent
Symbol Set ID Code
Sets the symbol set identification for the symbol set downloaded.
Define Symbol Set
Contains the data for the user-defined symbol sets.
Symbol Set Control
Manages user-defined symbol sets.
Page 54

Table 2-21: Font Creation
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
*c#D
# = Font ID # (0 - 32767)
Default = 0
ESC
)s#W[data]
# = number of data bytes
ESC
*c#F
0 Delete all (temporary and permanent)
1 Delete all temporary
2 Delete previous font ID
3 Delete previous specifi ed ch ar ac ter
4 Make previous font ID temporary
5 Make previous font ID permanent
6 Copy current font
ESC
*c#E
# = Code Point (0 - 65536)
Default = 0
ESC
(s#W[data]
# = number of data bytes
Set Font ID
Sets the identification number for the font being downloaded.
Load Font Header
Downloads soft font header information.
Note: Set Font ID before using this command.
Caution: Font Control
Manages soft fonts.
Set Character Code
Sets the decimal code point associated with the next character
downloaded or deleted.
Load Character
Downloads character descriptor and data to the current character
code.
2-42
PCL
Table 2-22: Macros
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
&f#Y
# = Macro ID (0 - 32767)
Default = 0
ESC
&f#X
0 Start definition
1 End definition
2 Execute macro (previous macro ID)
3 Call macro (previous macro ID)
4 Enable overlay (previous macro ID)
5 Disable overlay
6 Delete all macros
7 Delete all temporary macros
8 Delete current macro ID
9 Make last ID temporary
10 Make last ID permanent
Set Macro ID
Sets the ID for the macro you have created on flash or disk.
Macro Control
Manages use of macros.
Notes:
• GL/2 comm and s are sup ported inside mac ros.
• Only ca ll a nd execute mac ro c om ma nds are all owed within a macr o.
• A macro ma y call or e xecut e another macro . This is cal led nesting. A
maximum of two nesting levels are allowed, for a total of three
levels.
See “Macros” on page 2-64 for additional information.
Page 55

Table 2-23: Print Model
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
*c#G
Gray Scale Fills
0 White (default)
1-2 2% gray
3-10 10% gray
11-20 15% gray
21-35 30% gray
36-55 45% gray
56-80 70% gray
81-99 90% gray
100 100% gray (Black)
Cross-Hatch Fills
1 Horizontal line
2 Vertical line
3 Diagonal line
4 Diagonal line
5 Square grid
6 Diagonal grid
User-Defined Patterns
# = User-Defined Pattern ID
ESC
*v#N
0 Transparent (Default)
1 Opaque
ESC
*v#O
0 Transparent (Default)
1 Opaque
ESC
*l#O
# = logical operation, value (0 to 255)
Default = 252
ESC
*l#R
0 Grid Intersection (Default)
1 Grid Centered
ESC
*v#T
0 Solid Black (Default)
1Solid White
2 Gray Shading Pattern
3 Cross-Hatch Pattern
4 User Defined Pattern
9 True gray Level Fill
Area Fill ID
Selects pattern used to fill a rectangular area.
Note: This command is also used to set the user-defined pattern ID.
Source Transparenc y Mode
Affects copying of white pixels from the source onto the destination
image.
Pattern Transparency Mode
Affects copying of white pixels from the pattern onto the destination
image.
Logical Operation
Defines boolean operations to be performed on data already printed
and data about to be printed.
Pixel Placement
Determines how pixels are placed for a rectangular area fill and GL/2
objects.
Pixel Placement does not affect text or raster images.
Select Current Pattern
Selects pattern used when printing text and raster images.
2-43
PCL
Page 56

Table 2-24: User -Defined Pattern
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
*c#W[data]
# = number of data bytes
ESC
*p#R
0 Rotate with print (Default)
1Fixed
ESC
*c#Q
0 Delete all patterns (temporary and
permanent)
1 Delete all temporary patterns
2 Delete pattern (last ID specified)
4 Make pat tern of la st ID # temporary
5 Make pattern of last ID # permanent
User-Defined Pattern
Downloads binary pattern data.
Set Pattern Reference Point
Sets pattern reference point to the current cursor position for userdefined patterns.
Note: Default pattern reference point is the upper left corner of logical
page.
Caution: Pattern Control
Manages use of user-defined patterns.
Note: Use Area Fill ID command (
2-44
ESC
*c#G) to set ID.
PCL
Table 2-25: Rectangular Area Fill Graphics
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
*c#H
# = Number of Decipoints (0 - 32767)
(1 Decipoint = 1/720 inch)
Default = 0, valid to 4 decimal places
ESC
*c#A
# = Number of PCL Units (0 - 32767)
Default = 0
ESC
*c#V
# = Number of Decipoints (0 - 32767)
(1 Decipoint = 1/720 inch)
Default = 0, valid to 4 decimal places
ESC
*c#B
# = Number of PCL Units (0 - 32767)
Default = 0
Horizontal Rectangle Size (in Decipoints)
Specifies the rectangle width in decipoints.
Horizontal Rectangle Size (in PCL Units)
Specifies the rectangle width in PCL units.
Note: Size of PCL Units is set by Unit-of-Measure command.
Vertical Rectangle Size (in Decipoints)
Specifies the rectangle height in decipoints.
Vertical Rectangle Size (in PCL Units)
Specifies the rectangle height in PCL units.
Note: Size of PCL Units is set by Unit-of-Measure command.
Page 57

Table 2-25: Rectangular Area Fill Graphics (Continued)
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
*c#G
Gray Scale Fills
0 White (default)
1-2 2% Gray
3-10 10% Gray
11-20 15% Gray
21-35 30% Gray
36-55 45% Gray
56-80 70% Gray
81-99 90% Gray
100 100% Gray (Black)
Cross-Hatch Fills
1 Horizontal Line
2 Vertical Line
3 Diagonal Line
4 Diagonal Line
5 Square Grid
6 Diagonal Grid
User-Defined Patterns
# = User-Defined Pattern ID
ESC
*c#P
0 Black Fill (Default)
1White Fill
2Gray Fill
3 Pre-Defined Cross-Hatch
Pattern Fill
4 User-Defined Pattern
5 Current Pattern Fill
9 True gray Level Fill
Area Fill ID
Selects pattern used to fill rectangle area.
Note: This command is also used to set the user-defined pattern ID.
Fill Rectangular Area
Fills a rectangular area defined by Horizontal and Vertical Rectangle
Sizes with selected pattern.
2-45
PCL
Page 58

Table 2-26: Raster Graphics
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
*t#R
75 75 dpi
100 100 dpi
150 150 dpi
200 200 dpi
300 300 dpi
600 600 dpi
1200 1200 dpi
ESC
*r#F
0 Rotate with print
3 Fixed (Default)
ESC
*r#S
# = Number of Input Pixels
ESC
*r#T
# = Number of Raster Lines
ESC
*r#A
0 Left Graphics Margin at 0 (Default)
1 Current Cursor Position
2 At logical left page limit with scaling
On
3 At current cursor position with
scaling On
ESC
*b#V[data]
# = Number of Data Bytes
ESC
*b#Y
# = Number of Raster Lines
Raster Resolution
Note: 200 dpi is only supported when the printer is operating in
600 dpi or 1200 dpi mode.
Raster Graphics Presentation
Sets the Raster Image Orientation in relation to the logical page.
Raster Width (Source)
Sets width of clip window for raster graphics.
Raster Height (Source)
Sets height of clip window for raster graphics.
Start Raster Graphics
Sets the left margin for raster graphics.
Transfer Raster Data by Plane
This command is used when the r ast er data is encod ed b y plan e as
specified by the Simple Color command or the Configure Image
Data command. The command sends each plane in the row except
the last.
Y Offset
Moves cursor position down by the specified number of raster lines.
2-46
PCL
Page 59

Table 2-26: Raster Graphics (Continued)
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
*b#M
0 Uncoded (Default)
1 Run-Length Encoded
2 Tagged Image File Format (TIFF)
byte
3 Delta Row
5 Adaptive Compression
9 Replacement Delta Row
999 Zlib
1002 Group 4
1003 Group 3 one dimensional
1004 Group 3 two dimensional K=2
1005 Group 3 two dimensional K=4
1006 TIFF word (16 bit)
1007 TIFF double-word (32 bit)
1008 Adaptive compression (includes TIFF
word and TIFF double-word)
ESC
*b#W[data]
# = Number of Data Bytes
ESC
*rB End Raster Graphics (Version B)
ESC
*rC End Raster Graphics (Version C)
ESC
*t#H Raster Width (Destination)
Set Raster Compression Mode
Identifies the co mpres sion mode the ho st uses to tr ansfer RIG data.
For instance, this command can be run-length encoding or TIFF
encoding.
Note: For further information, see “Raster Compression Mode” on
page 2-57 and “Group 3 and Group 4 Raster Compression” on
page 2-62.
Transfer Raster Data by Row/Block
Transfers RIG data.
Note: After each command, the cursor position is moved to the
beginning of the next raster row.
Signals end of raster graphics transfer. If a Raster Height is
specified, the cursor is moved to the first raster row past the Raster
Height.
Same as Version B, but:
• Resets compression mode to uncoded.
• Sets left graphics margin to 0.
Sets the width of the destination raster.
2-47
PCL
Page 60

Table 2-26: Raster Graphics (Continued)
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
*t#V Raster Height (Destination)
Sets the height of the destination raster.
ESC
*g#W[data]
# - 8 (K-only) or 26 (KCMY)
Data
Byte 0 - 0x02 (constant)
Byte 1 - number of colors
0x01 - K only
0x04 - CMYK
Byte 2,3 - X res for K plane
0x012C (300) or 0x0258 (600)
Byte 4,5 - Y res for K plane
0x012C (300) or 0x0258 (600)
Byte 6,7 - K plane intensity levels
0x02 (1 bit/plane) or 0x04 (2 bits/plane)
Byte 8,9 - X res for C plane
0x012C (300) or 0x0258 (600)
Byte 10,11 - Y res for C plane
0x012C (300) or 0x0258 (600)
Byte 12,1 3 - C plane intensity levels
0x02 (1 bit/plane) or 0x04 (2 bits/plane)
Byte 14,15 - X res for M plane
0x012C (300) or 0x0258 (600)
Byte 16,17 - Y res for M plane
0x012C (300) or 0x0258 (600)
Byte 18,19 - M plane intensity levels
0x02 (1 bit/plane) or 0x04 (2 bits/plane)
Byte 20,21 - X res for Y plane
0x012C (300) or 0x0258 (600)
Byte 22,23 - Y res for Y plane
0x012C (300) or 0x0258 (600)
Byte 24,2 5 - Y plane intensity levels
0x02 (1 bit/plane) or 0x04 (2 bits/plane)
Set Raster Configuration
Sets the configuration of the destination raster.
2-48
PCL
Page 61

Table 2-27: Color Extensions
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
&b#M
0 Print in mixed render algorithm
mode
1 Print using gray scale equivalent
ESC
&p#C
0 Delete all palettes except those
in stack (active palette is
deleted)
1 Delete all palettes in stack
(active palette not affected)
2 Delete palette specified by
Palette Control ID
6 Copy active palette to ID
specified by Palette Control ID
ESC
&p#I
0 to 32767 Palette ID number
ESC
&p#S
0 to 32767 Palette ID number
ESC
*l#W[data]
0 Resets or initializes the color
lookup tables for each primary
color to the unity curve
770, Data Data for color lookup table
ESC
*m#W[data]
7 to 32767, Data Data size and data of
byte-aligned binary data
that specifies a matrix or
matrices for the primary
colors
ESC
*o#W[data]
1 to 32767, Data Specifies lightness,
saturation, and image
scaling
ESC
*p#P
0 Push (Save) Palette
1 Pop (Restore) Palette
ESC
*r#U
-4 4 planes, device KCMY palette
-3 3 planes, device CMY palette
1 Single plane, K (black) palette
3 3 planes, device RGB palette
Monochrome Print Mode
Changes each color value to its gray scale equivalent.
Palette Control
Provides palette management.
Palette Control ID
Indicates the ID number used by the Palette Control command.
Select Palette
Selects a new active palette by indicating the ID number.
Color Lookup Tables
Enables the color lookup tables and specifies the table to use.
Download Dither Matrix
Downloads a device dependent user-defined dither matrix.
Driver Configuration Command
Indicates the lightness, saturation, and scaling algorithm to be
applied to a job.
Push/Pop P ale tte
Saves (push) the current palette and then restores (pop) it from the
palette stack.
Simple Color
Creates a fixed-size palette. The color specification of the palette
cannot be modified.
2-49
PCL
Page 62

Table 2-27: Color Extensions (Continued)
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
*t#I
0 Gamma Correction Off
0.0 to 4.0 Gamma Number
ESC
*t#J Render Algorithm
ESC
*v#A
-32767.0 to 32767.0
ESC
*v#B
-32767.0 to 32767.0
ESC
*v#C
-32767.0 to 32767.0
ESC
*v#I
# = Palette Index
0 to 2n – 1 = Palette Index
ESC
*v#S
# = Palette Index
0 to 2n – 1 = Palette Index
ESC
*v#W[data] Configure Image Data
ESC
*i#W[data] Viewing Illuminant
Gamma Correction
Improves the perceptual correctness of color data sent from the
monitor to any other non-linear device by adjusting the brightness
and darkness.
Selects the algorithm used for dithering images and fills.
Color Component One
Indicates the first primary color specified by the Assign Color Index
command.
Color Component Two
Indicates t he second primary color specified by the Assign Color
Index command.
Color Component Three
Indicates the third primary color spec ified by the Ass ign C olor Index
command.
Assign Color Index
Designates the three current color components to the specified
palette index number. n represents the number of bits per index.
Foreground Color
Sets the foreground color to the specified index in the current
palette. n represents the current palette size.
Creates programmable palettes.
8, Data
Designates the relative white point used in determining a viewing
illuminant condition.
2-50
PCL
Page 63

Table 2-28: Status Readback
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
*s#T
0 Invalid location (Default)
1 Use currently selected location
2 All locations
3 Internal (resident)
4 Downloaded entity
5 Cartridge
7 User-installable flash
200 Disk
ESC
*s#U
0All
1 If download, temporary; otherwise,
highest priority
2 If download, permanent; otherwise,
next higher priority
ESC
*s#I
0Font
1Macro
2 User-defined pattern
3 Symbol set (for unbound scalable
fonts)
4 Font extended
ESC
*s1M Free Space
ESC
&r#F
0 Flush all complete pages
1 Flush all pages
ESC
*s#X
-32767 to 32767
Default = 0
Set Status Readback Location Type
Sets the status location type to the specified value.
The 5 value for Cartridge may be specified, but since your printer
does not support font cards or cartridges, the command is ignored.
The 7 value for User-installable flash is only valid when flash
memory is installed.
The 200 value is only valid when a hard disk is installed.
Set Status Readback Location Unit
Sets the status location unit to the specified value.
The location unit is used along with the location type to identify a
location for the Inquire Status Readback Entity command.
Note: The unit value is interpreted differently, depending on the
location type specified.
Inquire Status Readback Entity
Returns the requested information set by Set Status Readback
Location Type and Set Status Readback Location Unit.
Returns the total available memory and the largest available block
of memory.
Flush All Pages
Holds print jobs in the print buffer until the current job finishes
printing.
Echo
Returns # back to host computer.
2-51
PCL
Page 64

Table 2-29: Picture Frame
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
*c#X
# of Decipoints: 0 to 32767
(1 Decipoint = 1/720 inch)
ESC
*c#Y
# of Decipoints: 0 to 32767
(1 Decipoint = 1/720 inch)
ESC
*c0T
0 Set Anchor Point to Cursor Po sition
ESC
*c#K
Size in inches: 0 to 32767
ESC
*c#L
Size in inches: 0 to 32767
ESC
%#B
0 Use Previous GL/2 Pen Position
1 Use Current PCL Cursor Position
ESC
%#A
0 Use Previous PCL Cursor Position
1 Use Current GL/2 Pen Position
Picture Frame Horizontal Size (in Decipoints)
Specifies the horizontal dimension of the picture frame used when
printing a GL/2 plot.
Picture Frame Vertical Size (in Decipoints)
Specifies the vertical dimension of the picture frame used when
printing a GL/2 plot.
Set Picture Frame Anchor Point
Sets the position of the picture frame anchor point to the cursor
position. The picture frame anchor point defines the location of the
upper left corner of the picture frame.
GL/2 Horizontal Plot Size
Specifies the horizontal scaling factor used when importing an
image into the picture frame.
GL/2 Vertical Plot Size
Specifies the vertical scaling factor used when importing an image
into the picture frame.
Enter GL/2 Language
Exits PCL emulation and uses GL/2 commands to print.
Enter PCL Emulation
Exits GL/2 mode and uses PCL emulation commands to print.
2-52
PCL
Table 2-30: Miscellaneous Commands
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
&s#C
0 Enable
1 Disable (Default)
ESC
Y Display Functions On
End-Of-Line Text Wrap
Enabling End-Of-Line Text Wrap moves portions of lines that extend
into the unprintable area to the next line. Disabling drops the portion
extending into the unprintable area.
Prints all control codes and escape sequences rather than executing
them.
Notes:
• To prevent characters from falling outside the right margin (and not
printing), enable End-Of-Line Text Wrap (
• To see the control characters and other blank codepoints in symbol
set Roman8 (8U), set the symbol set to PC-8 (10U).
ESC
&s0C).
Page 65

Table 2-30: Miscellaneous Commands (Continued)
Command / Parameters Function / Result
ESC
Z Display Functions Off
Turns off Display Functions; resumes normal command processing.
ESC
z Print Test Page
Causes a test page to print.
ESC
*o#M(b)
-1 Ink Saver
0Normal
1Best
ESC
&l#M(b)
0 Plain P ape r
1Bond
2 Coated P ape r
3 Glossy Paper
4 Transparency
101 Photo Paper
102 Card Stock
103 Labels
104 Envelope
105 Letterhead
106 Preprinted
107 Colored Paper
108 Iron On
Print Quality
Selects the print quality setting for the page.
Paper Type
Selects the paper type setting for the page.
2-53
PCL
GL/2 Commands
Note: GL/2 is not a stand-alone plotter emul ation. It can only be entered from within
PCL emulation and cannot be used with software without a unique printer
driver written explicitly for GL/2.
The followi ng tables list the GL/2 commands by group. To determine which GL/2
commands your printer supports, see “Table A-2: GL/2 Commands” on page A-6.
Table 2-31: Configuration Group
Command / Parameter Command Name
CO "text" Comment
DF; Default Values
IN (n); Initialize
IP (X
, YP1(, XP2, YP2)); Input P1 and P2
P1
Page 66

2-54
PCL
Table 2-31: Configuration Group (Continued)
Command / Parameter Command Name
IR (XP1, YP1(, XP2, YP2)); Input Relative P1 and P2
IW (X
, Y1, X2, Y2); Input Window
1
MC (mode(, opcode)); Logical Operation
PP (mode); Pixel Placement
RO (angle); Rotate Coordinate System
SC (X
min, Xmax
, Y
min
, Y
(, type(, left, bottom))); Scale
max
Table 2-32: Vector Group
Command / Parameter Command Name
AA X
AR X
AT X
BR X
BZ X
CI radius(, chord_angle); Circle
PA (X, Y(,...)); Plot Absolute
PD (X, Y(,...)); Pen Down
PE (flag(value) | coordinates (...)); Polyline Encoded
PR (X, Y(,...)); Plot Relative
PU (X, Y(,...)); Pen Up
RT X
WU (type); Pen Width Units
, Y
center
, Y
center
inter, Yinter
, X2, Y2, X3, Y3(,...); Bezier Relative
1, Y1
, Y1, X2, Y2, X3, Y3(,...); Bezier Absolute
1
incr inter
, sweep_angl e(, ch ord_ ang le); Arc Absolute
center
, sweep_angl e(, cho rd_angle); Arc Relative
center
, X
, Y
(, chord_angle); Absolute Arc Three P oin t
end
, X
incr end
, Y
(, chord_angle); Arc Relativ e Three Point
incr end
, Y
end
incr inter
Table 2-33: Polygon Group
Command / Parameter Command Name
EA X, Y; Edge Rectangle Absolute
EP; Edge Polygon
ER X, Y; Edge Rectangle Relative
EW radius, start_angle, sweep_angle(, chord_angle); Edge Wedge
FP (0); Fill Polygon, Odd/Even
FP 1; Fill Polygon, Non-Zero Winding
PM (mode); Polygon Mode
Page 67

2-55
PCL
Table 2-33: Polygon Group (Continued)
Command / Parameter Command Name
RA X, Y; Fill Rectangle Absolute
RR X, Y; Fill Rectangle Relative
WG radius, start_angle, sweep_angle(, chord_angle); Fill Wedge
Table 2-34: Character Group
Command / Parameter Command Name
AD (kind, value(,...)); Define Alternate Font
CF (mode(, pen)); Character Fill
CP (spaces, lines); Character Plot
DI (run, rise); Absolute Direction
DR (run, rise); Relative Direction
DT (label_terminator(, mode)); Define Label Terminator
DV (path(, line)); Define Variable Text Path
ES (width(, height)); Extra Space
FI font_ID; Primary Font
FN font_ID; Secondary Font
LB char...char label_terminator; Label
LM (mode,[row number]) Label Mode
LO (position); Label Origin
LO 21; Uses PCL Label Origin
SA; Select Alternate Font
SB (mode); Scalable or Bitmapped Fonts
SD (kind, value(,...)); Define Standard Font
SI (width, height); Absolute Character Size
SL (tangent); Character Slant
SR (width, height); Relative Character Size
SS; Select Standard Font
TD (mode); Transparent Data
Page 68

2-56
PCL
Table 2-35: Line and Fill Attributes Group
Command / Parameter Command Name
AC (X, Y); Anchor Corner
CR (red
, blue
black ref
FT (fill_type(, option1(, option2)); Fill Type
FT22, (PCL User-Defined Pattern ID); Fill Type
FT 9, level; Fill Type
LA (kind, value(,...));. Line Attributes
LT (pattern_number(, pattern_length(, mode))); Line Type
NP (number) ; Number of Pens
black ref
white ref
, red
white ref
);
, green
black ref
, green
white ref
, blue
Color Range
PC (pen (, red, green, blue)); Pen Color
PW (width(, pen)); Pen Width
RF (index(, width, height(, pen, ...))); Define Raster Fill
SM (character); Symbol Mode
SP (pen); Select Pen
SV (screen_type(, option1(, option2))); Screened Vectors
SV (9, level,) Screened Vectors
TM (width, height(, number...)); Threshold Matrix
TR (mode); Transparency Mode
UL (index(, gap,...gap)); User Defined Line
WU (type); Pen Width Units
Page 69

Raster Image Graphics
These commands utilize the raster area. Before sending data, set the presentation
mode, the resolution, the compression mode, the raster height and width, and start
raster graphi cs. These parameters are in ef fect until y ou overwrite them with a diff erent
command or there is a printer reset.
To ensure that the printed image appears in the expected area, set width and height
parameters.
Raster Compression Mode
2-57
PCL
The Raster Compression Mode command determines how raster data is coded. It
affects the amount of code required to create an image, and the efficiency of image
printing.
Syntax:
ESC
*b#M
Parameters:
0 Uncoded (default)
1 Run-Length Encoded
2 Tagged Image File Format (TIFF) Byte
3Delta Row
5 Adaptive Compression
9 Replacement Delta Row
999 Zlib
1002 Group 4
1003 Group 3 one dimensional
1004 Group 3 two dimensional K=2
1005 Group 3 two dimensional K=4
1006 TIFF word (16 bit)
1007 TIFF double-word (32 bit)
1008 Adaptive Compress ion (includes TIFF word and TIFF double-word)
Page 70

Uncoded Data
2-58
PCL
Descriptions and examples o f the different parameters appear on the f ollowing pages.
Each example dr aw s the same squar e outli ne 64 bits (8 b yt es) wi de b y 64 sca n lines
long.
Uncoded Data is not compressed. Only those bytes needed to form the image are
sent. Each bit represents a sing le dot. In the first byt e, bit 7 corresponds to th e first dot
in the raster row, bit 5 to the third dot, and so forth.
Example:
ESC
*p300x300Y |Move the cursor to 1" x 1" (1 in. from top margin
and 1 in. from left edge of logical page)
ESC
*t100R |Set resolution to 100 dots per inch
ESC
*r0F |Rotate image to match current orientation
ESC
*b0M |Set compression mode to Uncoded
ESC
*r1A |Start raste r graphics at current position
ESC
*b8W 'FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF'x |Raster data uncompressed
ESC
*b8W '80 00 00 00 00 00 00 01'x
ESC
*b8W '80 00 00 00 00 00 00 01'x
...
ESC
*b8W '80 00 00 00 00 00 00 01'x
ESC
*b8W 'FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF'x
ESC
*rB |End graphics
|Repeat to provide 64 total scan lines
Page 71

Run-Length Encoded Data
Run-Length Encoded Data is interpreted in pairs of bytes. The first byte:
• Acts as a counter , or control byte.
• Indicates how many times to repeat the data in the second byte.
• Can be from 0 (no repetition) to 255.
• The second byte is the data byte.
Example:
ESC
*p300x600Y |Move cursor to 1" x 2"
ESC
*b1M |Set compression to Run-Length
ESC
*r1A |Start raste r graphics at current position
ESC
*b2W '07FF'x |Run-Length: 8x'FF'x
ESC
*b6W '0080 0500 0001'x |1x'80'x, 6x'00'x, 1x'01'x
ESC
*b6W '0080 0500 0001'x |1x'80'x, 6x'00'x, 1x'01'x
... |...
ESC
*b6W '0080 0500 0001'x |1x'80'x, 6x'00'x, 1x'01'x
ESC
*b2W '07FF'x |8x'FF'x
ESC
*rB |End graphics
2-59
PCL
Tagged Image File Format
TIFF “Packbits” contain a control byte (a signed number) that indi cates whether the
raster data bytes are to be repeated (up to 127 times) or printed as encoded data.
• For control values of 0 through 127, the next (Control+1) byte(s) is uncoded.
• For control values of -1 through -127 ('FF'x - '81'x), the next byte is repeated
(Abs(Control)+1) times.
Example:
ESC
*p300x900Y |Move cursor to 1" x 3"
ESC
*b2M |Set compression to TIFF
ESC
*r1A |Start Raster Graphics at current position
ESC
*b2W 'F9FF'x | TIFF: 8x'FF'x
ESC
*b6W '0080 FB00 0001'x |1:'80'x, 6x'00'x, 1: '01'x or
ESC
*b9W '078000000000000001'x |8: '8000000000000001'x
... |...
ESC
*b6W '0080 FB00 0001'x |1:'80'x, 6x'00'x, 1: '01'x
ESC
*b2W 'F9FF'x |8x'FF'x
ESC
*rB |End graphics
Page 72

Delta Row
2-60
PCL
Delta Row is a compressi on mode that i dentifies and transmits only those bytes
different from the ones in a preceding row. The control byte consists of two parts:
• High 3 bits: Number of bytes to replace +1 (1 to 8).
• Low 5 bits: Offset from last un modified b yte (0- 30); i f the offset i s 31, the next
byte(s) is added to the offset until the next byte is not 255.
Example:
ESC
*p300x1200Y |Move cursor to 1" x 4"
ESC
*b3M |Set compression to Delta Row
ESC
*r1A |Start raste r graphics at current position
|Num Offset
ESC
*b9W 'E0FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF'x |'111 00000'b=8 at 0: 'FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF'x
ESC
*b9W 'E08000000000000001'x |8 at 0: '8000000000000001'x
ESC
*b0W |No bytes change
...
ESC
*b0W |No bytes change
ESC
*b9W 'E0FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF'x |8 at 0: '8FFFFFFFFFFFFFF'x
ESC
*rB |End graphics
Page 73

Adaptive Compression
Adaptive compression all ows the combined us e of compression methods 0 t hrough 3
(Uncoded, Run-Length Encoded, TIFF, and Delta Row). It also allows the printing of
empty rows (all zeros) or duplicate rows.
• The Transfer Raster Data command size includes al l rows (scan lines).
• Scan Mode and SizeH,L are three-byte primary control strings: CountH and
CountL.
Table 2-36: Adaptive Compression Contr o l Strings
Scan Mode CountH,CountL Data
0 Data sizeH,L Uncoded raster scan data
1 Data sizeH,L Size of Run-length encoded data (high,low)
2 Data sizeH,L Size of Tagged Image File Format (TIFF) data
(high,low)
2-61
PCL
3 Data SizeH,L Size of Delta Row data (high,low)
4 NumberH,L of empty
rows
5 NumberH,L of duplicate
rows
254 Data SizeH,L TIFF word
255 Data SizeH,L TIFF double-word
None
None
Example:
ESC
*p300x1500Y |Move cursor to 1" x 5"
ESC
*b5M |Set the compression to Adaptive Compression
ESC
*b29W |Raster Data: 29 bytes follow
'03 0009'x 'E0FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF'x | Delta Row: 8 at 0: 'FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFh'x
'01 0006'x '0080 FB00 0001'x | Run Length: 1:'80'x, 6x'00'x, 1:'01'x
'05 0035'x | Duplicate rows: 61 times
'02 0002'x 'F9FF 'x | TIFF: 8x'FF'x
ESC
*rB |End graphics
Page 74

Zlib
2-62
Zlib is a generic compression method. It refers to a standard f or compr ession as w el l
as the library that implements the standard.
The zlib compression method uses the deflate al gorithm. This same algorithm is used
by more widely known co mp ression utilities such as PKZIP and GZIP.
Compressed data is a series of variably-sized blocks. An encoder determines ho w to
break the data into bloc ks and finds the best compression method to use for each
block.
An encoder works based on the fol lowing principles. The encode r creates a dictionary
containing different characters in a set of data. Short strings of bits represent more
commonly occurring characters, and long strings of bits represent less frequently
used characters . A pro babi lity tr ee de termines which char acte rs are fr equent ly used.
Repeated patterns in a string of characters are identified and stored, so the string
doesn’t have to be stored multiple times.
PCL
A three-bit zlib header is added to the beginning of a block to describe the type of
compression used and indicates whether the block is a final block. Ot her information
in the header includes checksums, compression algorithm used, and the level of
compression. In compress ion all check sums are set to z ero and in decompressi on the
checksums are ignored.
The memory required for zlib compre ssi on and decompres si on is i ndependent of t he
size of the data to be compressed or decompressed.
The number 999 does not conflict with other compression types, so it is used to
represent zlib compression. See page 2-57 for more inf o rmation.
Group 3 and Group 4 Raster Compression
Since Group 4 images do not use line endings, the width of the image must be
specified using the Raster Width command (
The compressed image data is sent to the printer using the Transfer Raster Data
ESC
command (
Transfer Raster Data command is 32K bytes. Images larger than 32K bytes must be
broken up and sent using multiple commands. It does not matter where the image is
broken, or how many Transfer Raster Data commands are used. Once the image is
started (with a Transfer Raster Data command), no ot her commands are al low ed until
the entire image has been sent.
*b#W). The maximum number of bytes that can be sent using the
ESC
*r#S).
Page 75

2-63
PCL
The follo wing example prints a Group 4 image file that is 256 bi ts wide and 9,645 byte s
long:
ESC
*b1002M |Set Raster Compression to Group 4
ESC
*r256S |Define width of image in input bits
ESC
*r1A |Start Raster Graphics at current position
ESC
*b9645W |9,645 bytes of a Group 4 image
...[Group 4 image data]...
ESC
*rB |End Raster Graphics
All lines of data must be the same length. If the y are not, zeroes (0) must be added to
attain the same length.
Note: If the uncompressed image extends beyond the logical page dimensions or
beyond the raster width specified in the Raster Width command (
image is clipped at print time.
ESC
*r#S), the
Additional Compression Modes
When the compression mode is 1008 (Lexmark Adaptive), TIFF word and doubleword can be printed using compression scan modes 254 and 255 respectiv ely. This
compression method sends a raster image as a bl ock of raster data.
Page 76

Macros
2-64
PCL
When creating a macro, first assign it an ID number. If this number is identical to an
existing macro ID in RAM, the old macro is deleted when you specify the Macro
Control Start Definition. Next, start the macro definition, send the contents of the
macro, and stop the macro definition.
Note: Although a macro may be called or executed from within another macro
(nesting), a macro cannot be defined within another macro definition. Each
macro must be defined separately.
Example:
This example creates a macro to print the Wigit Corp . logo , then calls the logo macro
in the body of a letter.
ESC
&f1Y |Set the macro ID to 1
ESC
&f0X |Star t the macro definition
ESC
&a+72H |Relative move right 1/10 inch (+ 72/720th)
ESC
(8U |Select Roman-8 symbol set
ESC
(s1p18v0s3b4101T |Select CG Times 18 point bold
W |Print W
ESC
&a-21.6H |Relative move left 0.03 inch
ESC
(s12v1S |Select (CG Times) 12 point (bold) it alic
igit | P rint igit
ESC
&a+72H |Relative move right 1/10 inch
ESC
(s18v0S |Select 18 point and turn off italic
C |Print C
ESC
(s12v1S |Select 12 point italic
orp. |Print orp.
ESC
&a+72H |Relative move right 1/10 inch
ESC
&f1X |End of macro definition
ESC
&f10X |Make Macro ID 1 permanent
...
...
From:
ESC
&f1y3X |Set the macro ID to 1 and call the macro
|Print the header From:
... |Print the letter
Thank you for ... |Print the closing
ESC
&f1y3X |Set the macro ID to 1 and call the macro
...
Page 77

3-1
PJL
CHAPTER 3: Printer Job Language
Your printer supports complete Printer Job Language (PJL) commands, including
certain commands that cause the printer to enter PCL emulation, PostScript
emulation, and Personal Printer Data Stream (PPDS).
To determine which commands your printer supports, see Appendix B: “PJL Support”
on page B-1.
PJL Command Notation
The syntax for each supported PJL command is listed in this chapter. The following
character codes are used throughout the chapter to illustrate the syntax of each PJL
command.
Table 3-1: PJL Command Notation
Character
Code
<ESC> Escape Character 0x1B 27
<LF> Line Feed Character 0x0A 10
<CR> Carriage Return Character 0x0D 13
<FF> Form Feed Character 0x0C 12
<HT> Horizontal Tab 0x09 9
<UEL> Universal Exit Language 0x1B 25 2D 31
Description Hex Code Decimal Code
32 33 34 35 58
Page 78

Notes:
• Parameters enclosed in square br ackets ([ ]) are optiona l and not required
for command execution.
• The PJL interpreter requires uppercase for the
mands except the Universal Exit Language (UEL) command. The rest of t he
PJL command is not case sensitive . The UEL command is case sensitive.
• All PJL commands except UEL must be terminated with a line feed character (<LF>).
Kernel Commands
3-2
PJL
@PJL prefix for all PJL com-
UNIVERSAL EXIT LANGUAGE Command
The Universal Exit Language (UEL) command terminates the current printer language
and allows dynamic switching into PJL.
Syntax:
<ESC>%-12345X
Notes:
• If the printer receives this command while in PCL emulation, it performs a
ESC
Printer Language Reset (
• If the printer receives this command while in PostScript emulation, it per f orms
an End-of-Job (EOJ) command before exiting PostScript emulation (Ctrl-D).
The PJL commands must immediately follow the UEL command (that is, the
UEL syntax must be immediately fol lowed by the
E) before exiting PCL emulation.
@PJL of the next PJL command).
X in the
Page 79

3-3
PJL
ENTER LANGUAGE Command
This command causes the printer to enter the specified language , such as
PCL emulation, PostScript emulation, or PPDS.
Syntax:
@PJL ENTER LANGUAGE = language[<CR>]<LF>
Notes:
• language is PCL, PCL3, PCLXL, PostScript, or PPDS.
• You can use uppercase, lower case, or mix ed case . (@PJL must be uppercase ;
all others can be mixed or lowercase.)
Example:
@PJL ENTER LANGUAGE = PostScript[<CR>]<LF>
enters PostScript emulation.
COMMENT Command
This command lets you add descriptive comments to your PJL job.
Syntax:
@PJL COMMENT words[<CR>]<LF>
Notes:
• When the printer receives this command, it is ignored.
• The words parameter can be any combination of printable characters,
spaces, and horizontal tabs.
• The COMMENT command is terminated by the line feed character (<LF>).
Page 80

Job Separation Commands
Your printer supports the PJL JOB and EOJ commands. When the printer receives a
JOB command, the print timeout is multipli ed by 10; when the printer receives a PJL
EOJ command, the print timeout is reset to the user default. The
appears on the printer operator panel displa y or through MarkVision Prof essional until
an EOJ command is received or until the print timeout expires.
Your printer also supports the PASSWORD parameter for the PJL JOB command.
JOB Command
3-4
PJL
Waiting message
The host computer can use the JOB command to separate print data into various
parts or jobs. Specifically, the JOB command signifies to the printer the start of a print
job. Use the EOJ command to signify the end of a job. In addition, use the JOB/EOJ
pair to accomplish the following:
• Provide a job name (the name displa ys on the printer operator panel or
through MarkVision Professional).
• Indicate which pages of the job should be printed.
• Monitor the job status as it prints.
Syntax:
@PJL JOB [NAME = "job name"] [START = first page]
[END = last page] [PASSWORD = number][<CR>]<LF>
Notes:
• The JOB command should only be used in conjunction with the EOJ
command.
• After receiving a JOB command, the printer does not process a UEL
command as a PJL job boundary until it receives the corresponding EOJ.
Instead, UELs occurring within a JOB/EOJ pair are processed as printer
ESC
language resets (for example, PCL
E).
Page 81

3-5
PJL
Parameters:
NAME = "job name"
Use the NAME parameter to assign a character string name to a particular job.
The name may be any combination of printable char ac ters , spaces or horiz ontal
tabs up to a maximum of 80 characters, spaces, or tabs. The
enclosed in double quotes, as indicated by the command syntax.
START = first page
Use the START parameter in conjunction with the END parameter to skip the
printing of a particular portion of the job. The emulator discards pages of a job
until the page specified by this parameter is reached. The
from 1 to 2,147,483,647. Omission of the START parameter causes the printer to
start printing with page 1 of the job.
job name must be
first page range is
END = last page
Use the END parameter in conjunction with the START parameter t o skip the
printing of a particular portion of the job. The emulator discar ds all pages of a job
after the
to page 1 of the print job and its range is from 1 to 2,147,483,647. Omissi on of
the END parameter causes the printer to print all pages to the end of the job.
PASSWORD = number
A system administrator can control which jobs, and therefore which users, are
allowed to modify the printer default or NVRAM variables by declaring a PJL
password. With a PJL password declared, the PASSWORD parameter with the
correct PASSWORD number must be specified in order to modify the default
printer environment.
A PJL JOB command with the correct PASSWORD must be issued before any
PJL command can modify an NVRAM setting. The PJL EOJ command
terminates the job and disables any further modification of NVRAM. If a PJL
password is declar ed and the wrong PASSWORD number is specified on the
PJL JOB command, the printer will dela y one half of a sec ond bef ore pro cessing
the next command.
last page has been printed. The specification of last page is relative
Page 82

3-6
PJL
For detailed information on PJL password protection, see “File and Device
Protection Commands” on page 3-93.
Note: Setting a default PJL password disables the use of PJL DEFAULT and
INITIALIZE commands. (See “DEFAULT Command” on page 3-8 and
“INITIALIZE Command” on page 3-11.)
EOJ Command
The EOJ command signifies the end of a print job.
Syntax:
@PJL EOJ [NAME = "job name"][<CR>]<LF>
Note:
Only use the EOJ command in conjunction with the JOB command.
Parameter:
NAME = "job name"
Use the NAME parameter to assign a character string name to a particular job.
The name may be any combination of printable char acters, spaces, or horizont al
tabs up to a maximum of 80 characters, spaces, or tabs. The NAME string may
be different fr om the NAME st ring specifie d in the JOB command. The
must be enclosed in double quotes.
job name
Page 83

3-7
Environmen t Commands and Variables
This section describes the printer en vironment variab les and the PJL commands used
to modify or query the variables.
Note: The word common applies to those va riables common to both your printer
and the Hewlett-Packard Company’s LaserJet printers.
Table 3-2: Environment Variable Categories
Beginning
Categories
Common Variables for Both Printer Languages 3-12
Printer Unique Variables for Both Printer Languages 3-19
Common Variables for PCL emulation 3-48
on Page ...
PJL
Printer Unique Variables for PCL emulation 3-49
Common Variables for PostScript emulation 3-51
Printer Unique Variables for PostScript emulation 3-52
Printer Unique LRESOURCE Variables 3-53
The follow ing commands modify t he envir onment v ariab les, and are described in this
section:
• DEFAULT
• SET
• INITIALIZE
• RESET
The following commands query the environment variables, and are described in
“Status Readback Commands” on page 3-54.
• INQUIRE
• DINQUIRE
• INFO
• ECHO
Page 84

3-8
PJL
DEFAULT Command
This command modifies the default setti ng f or the specif ied en viro nment variab le and
stores the setting in the printer NVRAM. The new setting is act ivated with the
occurrence of the next PJL reset condition.
Syntax:
@PJL DEFAULT [command modifier:value] variable=value[<CR>]<LF>
[command modifier:value]
The [command modifier:value] parameter specifies the type of PJL variables
to be modified. The variables supported are listed in the tables beginning on
page 3-12.
• A [command modifier:value] parameter is not required f or v ariab les list ed in
the tables “Common Variables for Both Printer Languages” on page 3-12,
and “Printer Unique Variables for Both Printe r Languages” on page 3-19.
• LPARM:PCL is used with variables specific to PCL emulation. (See the tables
“Common V ariables for PCL Emulation” on page 3-48, and “Printer Unique
Variables for PCL Emulation” on page 3-49.)
• LPARM:POSTSCRIPT is used f or v ariabl es specific to PostScript emulation. (See
the tables “Common Variables for PostScript Emulation” on page 3-51, and
“Printer Unique Variables fo r PostScript Emulation” on page 3-52.)
• LRESOURCE:"device:filename.filetype" is required for LRESOURCE
variables. (See the table “Printer Unique LRESOURCE Variables” on
page 3-53.)
Values for "
device flash, flash1, disk, or disk1 (case insensitive)
filename A unique identifier for a file , such as the macro ID for a PCL
device:filename.filetype" are:
macro, the symbol set ID for a PCL symbol set, the f ont ID
for a PCL f ont, and so on. The
filename is case sensitive.
filetype An identifier that categorizes the file, such as p5macro for
PCL macros or
“Table 3-22: V ariables fo r Flash and Disk File and P ass word
Commands” on page 3-87 for a complete list of the
supported file types. The
p5symset for PCL symbol sets. See
filetype is case sensitive.
Page 85

3-9
PJL
variable=value
The supported variables and values are listed in the tables beginning on page 3-12.
Note: Variables may be modified by the DEFAULT command, except those marked
Read Only. Some variables may only be modified using the PJL SET
command. These variables cannot be modified using the DEFAULT
command. They are marked Set Only.
SET Command
This command modifies the current set ting for the specif ied environment v ariable. The
new setting is active immediately, and remains active until the next occurrence of a
PJL reset condition.
Use the SET command to modify any currently defined en vironment variable that
cannot be set using the desired printer language. For example, use the PJL SET
command to set Print Quality Enhancement Technology (PQET) or P age Prot ect,
which cannot be set within a printer language such as PCL emulation.
Syntax:
@PJL SET [command modifier:value] variable=value[<CR>]<LF>
where
[command modifier:value]
The [command modifier:value] parameter specifies the type of PJL variables
to be modified. The variables supported are listed in the tables beginning on
page 3-12.
• A [command modifier:value] is not required f or variab les list ed in the tables
“Common Variables for Both Printer Languages” on page 3-12, and “Printer
Unique Variables for Both Printer Languages” on page 3-19.
• LPARM:PCL is used with variables specific to PCL emulation. (See the tables
“Common V ariables for PCL Emulation” on page 3-48, and “Printer Unique
Variables for PCL Emulation” on page 3-49.)
• LPARM:POSTSCRIPT is used for variables specific for PostScript emulation.
(See the tables “Common Variables for PostScript Emulation” on page 3-51,
and “Printer Unique Variables for PostScript Emulation” on page 3-52.)
Page 86

3-10
PJL
• LRESOURCE:"device:filename.filetype" is required for LRESOURCE
variables. (See “Table 3-9: Printer Unique LRESOURCE Variab les” on
page 3-53.)
Values for "
device flash, flash1, disk, or disk1 (case insensitive)
filename A unique identifier for a file , such as the macro ID for a PCL
filetype An identifier that categorizes the file, such as p5macro for
variable=value
The supported variables and values are listed in the tables beginning on
page 3-12.
Note: Variables may be modified by the DEFAULT command, except those marked
Read Only. Some variables may only be modified using the PJL SET
command. These variables cannot be modified using the DEFAULT
command. They are marked Set Only.
device:filename.filetype" are:
macro, the symbol set ID for a PCL symbol set, the f ont ID
for a PCL f ont, and so on. The
PCL macros or
table beginning on page 3-87 for a complete list of the
supported file types. The
p5symset for PCL symbol sets. See the
filename is case sensitive.
filetype is case sensitive.
Page 87

3-11
PJL
INITIALIZE Command
This command restores both the current and def ault environment variables to their
factory defau lt values and updates the printer NVRAM. This command affects all of
the variables listed in “Table 3-3: Common Variables for Both Printer Languages” on
page 3-12 through “Table 3-8: Printer Unique Variables for PostScript Emulation” on
page 3-52, except the following:
• All read only variables
• PASSWORD
• LANG
• LRESOURCESAVE
• LDOWNLOADTARGET
• LPPDS
• LHONORINIT
• LUSDEFAULTS
• PARALLEL
• RESOURCESAVE
Note: This command does not aff ect LRESOURCE variables listed in
“Table 3-9: Printer Unique LRESOURCE Variables” on page 3-53.
Syntax:
@PJL INITIALIZE[<CR>]<LF>
RESET Command
This command resets the current environment variables to the settings stored in the
printer NVRAM. Therefore, any variables modifi ed by the PJL SET command are
returned to their default value after execution of the PJL RESET command.
Syntax:
@PJL RESET[<CR>]<LF>
Page 88

3-12
PJL
Common Variables for Both Printer Languages
Note: The word common applies to those va riables common to both your printer
and the Hewlett-Packard Company’s LaserJet printers.
The followi ng common variables are supported for both PCL emulation and P ostScript
emulation, unless otherwise noted. Therefore, the [
parameter should not be specified.
To determine which variables your printer supports, see “Table B-1: Common
Variables for Both Printer Languages” on page B-1.
Table 3-3: Common Variables for Both Printer Languages
Variable Function Selections Factory Default
command modifier:value]
AUTOCONT
(DEFAULT only)
BINDING Duplex Bind LONGEDGE, SHORTEDGE LONGEDGE
BITSPERPIXEL Image
CLEARABLEWARNINGS
(READ only)
Auto Continue 0, 5 to 255, OFF, ON
A value of 0 or OFF indicates Auto Continue is
disabled. A v alu e of ON indi cates A uto Contin ue is se t
to 30.
INQUIRE or DINQUI RE on the Auto Continue variable
return s a numeric value.
Note: If a value greater than 255 is s pecif ied b y a SE T
or DEFAULT command, the value is changed to 255.
1, 2, 4, Auto
Enhancement
Technology and
Image
Enhancement
Technology Type
Auto Continue
from operator
panel non-fatal
warning messages
A value of 1 indicates the Image Enhancement
Technology setting is set to Off. A value of 2 or 4
indicates the Image Enhanc em ent Technology setti ng
is set to On.
INQUIRE or DINQUIRE returns the value of Image
Enhancement Technology as follows:
• If Image Enhan cemen t Technology is s et to Off , 1 is
returned.
• If Image Enh ancement Technology is set to O n, 2 or
4 is returned depending on the Image
Enhancement Technology Type setting. If Image
Enhancement Technology Type is set to On, the
numerical value of BITSPERPIXEL is returned. If
Image Enhancement Technology Type is set to
Auto , a v alu e of 2 or 4 is returned depe nding o n the
amount of total memory installed.
JOB, ON
If Auto Continue is set to On, JOB is returned.
If Auto Continue is set to Off, ON is returned.
0
1
ON
COPIES Number of copies
of each page
1 to 999
Note: If a value greater than 999 is s pecif ied b y a SE T
or DEFAULT command, the value is changed to 999.
1
Page 89

3-13
PJL
Table 3-3: Common Variables for Both Printer Languages (Continued)
Variable Function Selections Factory Default
CPLOCK
(DEFAULT only)
Disables menus ON, OFF
ON disables the printer operator panel menus.
OFF enables menu s.
OFF
DENSITY Print Dar kness 1 to 5
• 1 = Lightest
• 2 = Lighter
• 3 = Normal
• 4 = Darker
• 5 = Darkest
To determine the default value of your printer, see
“Table B-1: Common Variables for Both Printer
Languages” on pageB-1.
DUPLEX Duplex ON, OFF OFF
ECONOMODE Toner Saver ON, OFF OFF
FORMATTERNUMBER
(READ only)
FORMLINES Lines per page 1 to 255
Unique printer
identifier
The value of the NVRAM serial number field is
returned.
The NVRAM serial number field is set to the printer
serial number. In order to guarantee that a unique
identifier ex ists in this field, th e printer writes a ra ndom
alphanumeric string into this fi eld whene v er the critical
byte area in NVRAM is re-initialized.
Note: If a value greater than 255 is s pecif ied b y a SE T
or DEFAULT command, the value is changed to 255.
2, 3, 4
(Model specific)
Set by printer
manufacturer
60, 64
(Country specific)
HOLD
(SET only)
HOLDKEY
(SET only)
Print and Hold ON, OFF, STORE, PROOF
The HOLD variable interacts with the HOLDKEY and
HOLDTYPE variables. For more information, see
HOLDTYPE on page 3-14.
Print and Hold PIN “PIN”
PIN is a text string c onsis ting of e xac tly f ou r n umer als .
Only the numerals 1 through 6 are valid.
Note: A null (“ “) string is an acceptable value and
indicates no PIN is specified.
The HOLDKEY variable interacts with the HOLD and
HOLDTYPE variables. For more information, see
HOLDTYPE as follows.
OFF
NULL
(no PIN)
Page 90

3-14
PJL
Table 3-3: Common Variables for Both Printer Languages (Continued)
Variable Function Selections Factory Default
HOLDTYPE
(SET only)
Print and Hold
Type
PUBLIC, PRIVATE
The HOLD, HOLDKEY, and HOLDTYPE variables
interact with each other as follows:
• When HOLD is set to On, HOLDKEY is set to a
valid PIN, and HOLDTYPE is set to Private,
Confidential Print capabili ty is a vailable.
• When HOLD is set to On, HOLDKEY is set to “ ”,
and HOLDTYPE is set to Public, Repeat Print
capability is available.
• When HOLD is set to Stor e , HOLDKEY is s et to “ ”,
and HOLDTYPE is set to Public, Reserve Print
capability is available.
• When HOLD is set to Pr oof, HOLDKEY is set to “ ”,
and HOLDTYPE is set to Public, Verify Print
capability is available.
• Print and Hold capabilities are not available with
any other possible combination of HOLD,
HOLDKEY, and HOLDTYPE settings.
PUBLIC
IMAGEADAPT
(DEFAULT only)
INTRAY2 Tray lock - Tray 2 UNLOCKED, LOCKED UNLOCKED
INTRAY3 Tray lock - Tray 3 UNLOCKED, LOCKED UNLOCKED
INTRAY4 Tray lock - Tray 4 UNLOCKED, LOCKED UNLOCKED
INTRAY5 Tray lock - Tray 5 UNLOCKED, LOCKED UNLOCKED
INTRAY1SIZE
(SET only)
INTRAY2SIZE
(SET only)
INTRAY3SIZE
(SET only)
INTRAY4SIZE
(SET only)
INTRAY5SIZE
(SET only)
Resolution
reduction
Tray 1 installed
size, default
formatting size
Tray 2 installed
size, default
formatting size
Tray 3 installed
size, default
formatting size
Tray 4 installed
size, default
formatting size
Tray 5 installed
size, default
formatting size
ON, OFF ON
A3, A3+, A4, A5, B4, B4PAPER, B5PAPER, JISB4,
JISB5, CUSTOM, EXECUTIVE, FOLIO, LEDGER,
LEGAL, LETTER, 11X17, COM10, COM9,
MONARCH, DL, C5, B5, OTHERENVELOPE,
STATEMENT
A3, A3+, A4, A5, B4, B4PAPER, B5PAPER, JISB4,
JISB5, CUSTOM, EXECUTIVE, FOLIO, LEDGER,
LEGAL, LETTER, 11X17, STATEMENT
A3, A3+, A4, A5, B4, B4PAPER, B5PAPER, JISB4,
JISB5, CUSTOM, EXECUTIVE, FOLIO, LEDGER,
LEGAL, LETTER, 11X17, STATEMENT
A3, A3+, A4, A5, B4, B4PAPER, B5PAPER, JISB4,
JISB5, CUSTOM, EXECUTIVE, FOLIO, LEDGER,
LEGAL, LETTER, 11X17, STATEMENT
A3, A3+, A4, A5, B4, B4PAPER, B5PAPER, JISB4,
JISB5, CUSTOM, EXECUTIVE, FOLIO, LEDGER,
LEGAL, LETTER, 11X17, STATEMENT
LETTER, A4
(Country specific)
LETTER, A4
(Country specific)
LETTER, A4
(Country specific)
LETTER, A4
(Country specific)
LETTER, A4
(Country specific)
JOBNAME
(SET only)
Print and Hold
Jobname
“jobname”
jobname is a text string truncated to 24 characters.
Note: A null (“ ”) string is an acceptable value and
indicates no Print and Hold Jobname is specified.
NULL
(No jobname)
Page 91

3-15
PJL
Table 3-3: Common Variables for Both Printer Languages (Continued)
Variable Function Selections Factory Default
JOBOFFSET Offset Pages ON, OFF, BETWEENJOBS, BETWEENCOPIES
INQUIRE or DINQUIRE returns the value of Offset
Pages as follows:
• If Offset Pages is set to Off, OFF is returned.
• If Offset Pages is set to Between Jobs or Between
Copies, ON is returned.
Offset refers to stacking entire print jobs or copies of
the same print job in two separate g ro ups i n an output
bin.
LANG
(DEFAULT only)
Default display
language
DANISH, GERMAN, ENGLISH, SPANISH, FRENCH,
ITALIAN, DUTCH, NORWEGIAN, SWEDISH,
PORTUGUESE, FINNISH, JAPANESE, RUSSIAN,
POLISH, HUNGARIAN, TURKISH, CZECH
OFF
Country specific
LOWTONER
(DEFAULT only)
MANUALFEED
(READ only)
MEDIATYPE Default paper
MPTRAY
(DEFAULT only)
Toner Alarm ON, OFF, CONTINUE, STOP
Manual feed
selection
source, def aul t
formatting size
Multipurpose
feeder
configuration
A value of ON or CONTINUE indicates the Toner
Alarm setting is set Off. The value of OFF or STOP
indicates the Toner Alarm setting is Single.
INQUIRE or DINQUIRE re turns the value of the Toner
Alarm as follows:
• If Toner Alarm is set to Off, CONTINUE is returned.
• If Toner Alarm is set to Single, STOP is returned.
• If Toner Alarm is set to Continuous, STOP is
returned.
OFF
Printer always returns OFF.
PLAIN, COATED, GLOSSY, PHOTO,
GREETINGCARD, IRONON, BOND,
TRANSPARENCY, CARDSTOCK, LABELS,
LETTERHEAD, PREPRINTED, COLORED,
ENVELOPE, CUSTOMTYPE1, CUSTOMTYPE2,
CUSTOMTYPE3, CUST OMTYPE4, CUST OMTYPE5,
CUSTOMTYPE6, “name”
name is a variable that allows for custom naming of
custom print material types. The text string is
truncated to 24 characters.
CASSETTE, MANUAL, FIRST
Sets the configuration of the Multipurpose Feeder.
ON, CONTINUE
(Model specific)
OFF
PLAIN
CASSETTE
ORIENTATION Print orientation PORTRAIT, LANDSCAPE
This variable does not affect P os tScript em ul ati on.
PORTRAIT
Page 92

3-16
PJL
Table 3-3: Common Variables for Both Printer Languages (Continued)
Variable Function Selections Factory Default
OUTBIN Output Bin UPPER, LOWER, OPTIONALOUTBIN1,
OPTIONALOUTBIN2, OPTIONALOUTBIN3,
OPTIONALOUTBIN4, OPTIONALOUTBIN5,
OPTIONALOUTBIN6, OPTIONALOUTBIN7,
OPTIONALOUTBIN8, OPTIONALOUTBIN9,
OPTIONALOUTBIN10, “name”
name is a variable that allows for custom naming of
optional output bins. The text string is truncated to 24
characters.
A DINQUIRE or INQUIRE on the Output Bin setting
returns:
DINQUIRE or
Output Bin setting INQUIRE va lue
UPPER
Standard Bin UPPER
Bin 1 OPTIONALOUTBIN1
Bin 2 OPTIONALOUTBIN2
Bin 3 OPTIONALOUTBIN3
Bin 4 OPTIONALOUTBIN4
Bin 5 OPTIONALOUTBIN5
Bin 6 OPTIONALOUTBIN6
Bin 7 OPTIONALOUTBIN7
Bin 8 OPTIONALOUTBIN8
Bin 9 OPTIONALOUTBIN9
Bin 10 OPTIONALOUTBIN10
“name”“name”
PAGEPROTECT Page Protect AUTO, ON
A value of ON indi cates the Page Protect se tting i s set
On. The value of AUTO indicates the Page Protect
setting is set Off.
INQUIRE or DINQUIRE returns the value of the Page
Protect as follows:
• If Pa ge Prote ct is se t Off, AUTO is returned.
• If Page Protect is set On, ON is returned.
PAPER Default paper
source, def aul t
formatting size
Paper: A3, A3+, A4, A5, B4, B4PAPER, B5PAPER,
JISB4, JISB5, CUSTOM, EXECUTIVE, FOLIO,
LEDGER, LEGAL, LETTER, STATEMENT, 11X17
Envelopes: COM10, COM9, MONARCH, DL, C5, B5,
OTHERENVELOPE
AUTO
LETTER, A4
(Country specific)
Page 93

3-17
PJL
Table 3-3: Common Variables for Both Printer Languages (Continued)
Variable Function Selections Factory Default
PARALLEL
(DEFAULT only)
(Port Specific)
Parallel Protocol SLOW, FAST
A value of SLOW indicates the Parallel Protocol
setting is Standard. The value of FAST indicates the
Parallel Protocol setting is FASTBYTES.
INQUIRE or DINQUIRE returns the value of the
Parallel Protocol as follows:
• If Parallel Protocol is set as Standard, SLOW is
returned.
• If Parallel Protocol is set as Fastbytes, FAST is
returned.
FAST
PASSWORD
(DEFAULT only)
PERSONALITY
(Port specific)
POWERSAVE
(DEFAULT only)
Default password
for PJL NVRAM
security
SmartSwitch
settings
Power Save
feature
0 to 65535
Locks the printer operator panel to keep the user
defaults from changing. Refer to your printer user
documentation for more information.
The Default PJL password is 0.
If the PJL password is not equal to 0, a DINQUIRE or
INQUIRE on the PASSWORD variable returns
ENABLED. If the PJL password is equal to 0, a
DINQUIRE or INQUIRE on the PASSWORD variable
returns DISABLED. See the PASSWORD parameter
of the JOB command on page 3-5 for more
information.
PCL, POSTSCRIPT, A UTO
PERSONALITY controls the SmartSwitch settings for
the interface link on which the PJL command is
received.
If AUTO is sent, both
Smartswitch
If PCL is sent,
SmartSwitch
If POSTSCRIPT is sent,
OFF and
When queried, AUTO is returned if both SmartSwitch
settings are ON. If one SmartSwitch setting is OFF,
the printer language wh ose SmartSwitch sett ing is ON
is returned. If both SmartSwitch settings are OFF, the
default printer language is returned.
ON, OFF
ON enables the power-saving feature.
OFF disables the power-saving feature.
Note: Some printer models released in the year 2000
or later designated as Energy Star printers cannot
have Power Saver disabled.
menu settings are set to ON.
is set to ON.
PS SmartSwitch is set to ON.
PS SmartSwitch and PCL
PS SmartSwitch is set to OFF and PCL
PCL SmartSwitch is set to
0
AUTO
ON
Page 94

3-18
PJL
Table 3-3: Common Variables for Both Printer Languages (Continued)
Variable Function Selections Factory Default
POWERSAVETIME
(DEFAULT only)
QTY
(SET only)
REPRINT Jam Recovery ON, OFF, AUTO AUTO
Power Save time,
in minutes
Collation Collated Copies
(QTY)
0 to 120 (Model specific)
0 to 240 (Model specific)
(0 indicates the Power Sa ve r Time f e atur e is disab le d.)
The time the printer remains idle before it enters
Power Save mode when POWERSAVE is On.
Note: If a value greater than 120 or 240 is specified by
a SET or DEF A U LT command, the value is cha nged to
120 or 240 based on the printer model.
0 to 999
Used to request the number of collated copies of a
print job.
If Collation - Collated Co pies (QTY) is n ot equal to 0, a
DINQUIRE or INQUIRE returns the numerical setting
for QTY. If Collation - Collated Copies (QTY) is set to
Off, a DINQUIRE or INQUIRE returns 0.
Note: If a value greater than 999 is s pecif ied b y a SE T
or DEFAULT command, the value is changed to 999.
20
0
RESOLUTION Print Resolution 300, 600, 1200 600
RESOURCESAVE
(DEFAULT only)
RET Print Quality
TIMEOUT Print timeout,
Resource Save ON, OFF, AUTO
ON indicates Resource Save is set On.
OFF and AUTO indicate Resource Save is set to Off.
See “Table B-1: Common Variables for Both Printer
Languages” on pageB-1 for the default value of your
printer.
OFF, DARK, MEDIUM, LIGHT, ON
Enhancement
Technology
(PQET)
in seconds
If this value is set through PJL, the same value is
returned on a PJL inquiry.
DARK, MEDIUM, LIGHT, and ON values indicate that
PQET is On. OFF indicates PQET is Off.
0 to 255
The time the printer remains idle before the job is
forced to print.
Note: If a value greater than 255 is s pecif ied b y a SE T
or DEFAULT command, the value is changed to 255.
OFF, AUTO
(Model specific)
ON
90
Page 95

3-19
PJL
Table 3-3: Common Variables for Both Printer Languages (Continued)
Variable Function Selections Factory Default
USERNAME
(SET only)
WIDEA4 A4 width NO, YES
Print and Hold
Username
“username”
username is a text string truncated to 24 characters.
Note: A null (“ “) string is an acceptable value and
indicates no Print and Hold Username is specified.
NO indicates the A4 width is 198 mm.
YES indicates the A4 width is 203 mm.
NULL
(No username)
NO
Printer Unique Variables for Both Printer Languages
The following variables are unique to some Lexmark printers and are supported for
both PCL emulation and PostScript emulation. Theref ore, the [
modifier:value
] parameter should not be specified.
command
To determine which variables your printer supports, see “Table B-2: Printer Unique
PJL Variables fo r Both Printer Languages” on page B-3.
Table 3-4: Printer Unique Variables for Both Printer Languages
Variable Function Selections Factory Default
LACTIVEBINRESET
(DEFAULT only)
LADVANCEDSTATUS
(DEFAULT only)
(Port specific)
LALARMCONTROL
(DEFAULT only)
LAUTOCRLF Auto CR after LFON, OFF OFF
LAUTOLFCR Auto LF after CRON, OFF OFF
LBLANKPAGES Blank Pages DONOTPRINT, PRINT
Active Bin
Reset
Advanced
Status
Alarm Control OFF, SINGLE, CONTINUOUS SINGLE
MANUAL, AUTOMATIC MANUAL
ON, OFF
ON enables parall el bid irec ti ona l supp ort.
OFF disables parallel bidirectional support.
Note: Some printers have a fixed value of
DONOTPRINT.
ON
DONOTPRINT
LBONDLENGTH
(DEFAULT only)
LBONDLOADING
(DEFAULT only)
Bond Length NORMAL, SHORT NO RMAL
Bond Paper
Loading
OFF, DUPLEX OFF
Page 96

3-20
PJL
Table 3-4: Printer Unique Variables for Both Printer Languages (Continued)
Variable Function Selections Factory Default
LBONDOUTBIN
(DEFAULT only)
Assign
Type/Bin - Bond
UPPER, LOWER, DISABLED, OPTIONALOUTBIN1,
OPTIONALOUTBIN2, OPTIONALOUTBIN3,
OPTIONALOUTBIN4, OPTIONALOUTBIN5,
OPTIONALOUTBIN6, OPTIONALOUTBIN7,
OPTIONALOUTBIN8, OPTIONALOUTBIN9,
OPTIONALOUTBIN10, “name”
name is a variable that allows for custom naming of
optional output bins. The text string is truncated to 24
characters.
Specifies a selected output bin for jobs printed on
bond paper.
A DINQUIRE or INQUIRE on the Assign Type/Bin Bond setting returns:
Assign Typ e/Bin - DINQUIRE or
Bond setting INQUIRE value
UPPER,
DISABLED
(Model specific)
Standard Bin UPPER
Bin 1 OPTIONALOUTBIN1
Bin 2 OPTIONALOUTBIN2
Bin 3 OPTIONALOUTBIN3
Bin 4 OPTIONALOUTBIN4
Bin 5 OPTIONALOUTBIN5
Bin 6 OPTIONALOUTBIN6
Bin 7 OPTIONALOUTBIN7
Bin 8 OPTIONALOUTBIN8
Bin 9 OPTIONALOUTBIN9
Bin 10 OPTIONALOUTBIN10
“name”“name”
LBONDTEXTURE
(DEFAULT only)
LBONDWEIGHT
(DEFAULT only)
LBWLOCK Black & White
LCANCEL Cancel Control ON, OFF ON
LCARDSTOCKLENGTH
(DEFAULT only)
LCARDSTOCKLOADING
(DEFAULT only)
Bond Texture SMOOTH, NORMAL, ROUGH ROUGH
Bond Weight LIGHT, NORM AL, HE AVY NORMAL
ON, OFF OFF
Lock
Card Stock
Length
Card Stock
Paper Loading
NORMAL, SHORT NORMAL
OFF, DUPLEX OFF
Page 97

3-21
PJL
Table 3-4: Printer Unique Variables for Both Printer Languages (Continued)
Variable Function Selections Factory Default
LCARDSTOCKOUTBIN
(DEFAULT only)
Assign
Type/Bin Card Stock
UPPER, LOWER, DISABLED, OPTIONALOUTBIN1,
OPTIONALOUTBIN2, OPTIONALOUTBIN3,
OPTIONALOUTBIN4, OPTIONALOUTBIN5,
OPTIONALOUTBIN6, OPTIONALOUTBIN7,
OPTIONALOUTBIN8, OPTIONALOUTBIN9,
OPTIONALOUTBIN10, “name”
name is a variable that allows for custom naming of
optional output bins. The text string is truncated to 24
characters.
Specifies a selected o utput bin f or jobs printed o n card
stock.
A DINQUIRE or INQUIRE on the Assign Type/Bin Card Stock setting returns:
Assign Typ e/Bin - DINQUIRE or
Card Stock setting INQUIRE value
UPPER,
DISABLED
(Model specific)
Standard Bin UPPER
Bin 1 OPTIONALOUTBIN1
Bin 2 OPTIONALOUTBIN2
Bin 3 OPTIONALOUTBIN3
Bin 4 OPTIONALOUTBIN4
Bin 5 OPTIONALOUTBIN5
Bin 6 OPTIONALOUTBIN6
Bin 7 OPTIONALOUTBIN7
Bin 8 OPTIONALOUTBIN8
Bin 9 OPTIONALOUTBIN9
Bin 10 OPTIONALOUTBIN10
“name”“name”
LCARDSTOCKTEXTURE
(DEFAULT only)
LCARDSTOCKWEIGHT
(DEFAULT only)
LCOLLATION Collation Mode ON, OFF
LCOLORCORRECTION Indicates which
LCOLOREDLENGTH
(DEFAULT only)
Card Stock
Texture
Card Stock
Weight
color target the
printer
emulates
Colored Paper
Length
SMOOTH, NORMAL, ROUGH NORMAL
LIGHT, NORMAL, HEAVY NORMAL
If Collation is ON, the pages of the print job are
collated. For example, if the job contains three pages
and two copies are requested, collated output prints
pages 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3. If collation is set to OFF,
uncollated output prints pages 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3.
NONE, DISPLAY, SWOP, OFF, AUTO, VIVID,
DUOTONE, MANUAL
See “Table B-2: Printer Unique PJL V ariabl es for Both
Printer Languages” on pageB-3 for the default value
of your printer .
NORMAL, SHORT NORMAL
OFF
AUTO, VIVID
(Model specific)
Page 98

3-22
PJL
Table 3-4: Printer Unique Variables for Both Printer Languages (Continued)
Variable Function Selections Factory Default
LCOLOREDLOADING
(DEFAULT only)
LCOLOREDOUTBIN
(DEFAULT only)
Colored Paper
Loading
Assign
Type/Bin Colored Paper
OFF, DUPLEX OFF
UPPER, LOWER, DISABLED, OPTIONALOUTBIN1,
OPTIONALOUTBIN2, OPTIONALOUTBIN3,
OPTIONALOUTBIN4, OPTIONALOUTBIN5,
OPTIONALOUTBIN6, OPTIONALOUTBIN7,
OPTIONALOUTBIN8, OPTIONALOUTBIN9,
OPTIONALOUTBIN10, “name”
name is a variable that allows for custom naming of
optional output bins. The text string is truncated to 24
characters.
Specifies a selected output bin for jobs printed on
colored paper.
A DINQUIRE or INQUIRE on the Assign Type/Bin Colored Paper setting returns:
Assign Typ e/Bin - DINQUIRE or
Colored Paper INQUIRE value
setting
UPPER,
DISABLED
(Model specific)
Standard Bin UPPER
Bin 1 OPTIONALOUTBIN1
Bin 2 OPTIONALOUTBIN2
Bin 3 OPTIONALOUTBIN3
Bin 4 OPTIONALOUTBIN4
Bin 5 OPTIONALOUTBIN5
Bin 6 OPTIONALOUTBIN6
Bin 7 OPTIONALOUTBIN7
Bin 8 OPTIONALOUTBIN8
Bin 9 OPTIONALOUTBIN9
Bin 10 OPTIONALOUTBIN10
“name”“name”
LCOLOREDTEXTURE
(DEFAULT only)
LCOLOREDWEIGHT
(DEFAULT only)
LCOLORMODEL Color Model CMYK, RGB, BLACK RGB, CMYK
LCUSTOMPAPERUNITS Universal Units
LCUSTOMPAPERWIDTH Universal Width 76 to 915 in increments of 1 mm
Colored Paper
Texture
Colored Paper
Weight
of Measure
SMOOTH, NORMAL, ROUGH NORMAL
LIGHT, NORMAL, HEAVY NORMAL
(Model specific)
INCHES, MILLIMETERS INCHES,
MILLIMETERS
(Country specific)
216, 305 mm
3 to 36.01 in increments of 0.01 in.
Note: Values are determined to be inches or
millimeters based on the LCUSTOMPAPERUNITS
setting.
8.5, 12 in.
(Model and
country specific)
Page 99

3-23
PJL
Table 3-4: Printer Unique Variables for Both Printer Languages (Continued)
Variable Function Selections Factory Default
LCUSTOMPAPERHEIGHT Universal
Height
LCUSTOMPAPERFEED Universal Feed
Direction
76 to 915 in increments of 1 mm
3 to 36.01 in increments of 0.01 in.
Note: Values are determined to be inches or
millimeters based on the LCUSTOMPAPERUNITS
setting.
SHORTEDGE, LONGEDGE SHORTEDGE
356, 360, 457 mm
14, 14.17, 18 in.
(Model and
country specific)
LCUSTOMTYPE1LENGTH
(DEFAULT only)
LCUSTOMTYPE1LOADING
(DEFAULT only)
LCUSTOMTYPE1MEDIA
(DEFAULT only)
LCUSTOMTYPE1NAME
(DEFAULT only)
Custom Type 1
Length
Custom Type 1
Paper Loading
Custom Type 1
Media
Custom Type 1
Name
NORMAL, SHORT NORMAL
OFF, DUPLEX OFF
PAPER, COATED, GLOSSY, TRANSPARENCY,
LABELS, CARDSTOCK, ENVELOPE,
COTT ONPAPER
"name"
name is a variable that allows for custom naming of
print material types. The text string is truncated to 24
characters.
When queried, the quotes are not returned around the
string name. The default name is returned unless you
have specified a custom name.
PAPER
CUSTOMTYPE1
Page 100

3-24
PJL
Table 3-4: Printer Unique Variables for Both Printer Languages (Continued)
Variable Function Selections Factory Default
LCUSTOMTYPE1OUTBIN
(DEFAULT only)
Assign
Type/Bin Custom Type 1
UPPER, LOWER, DISABLED, OPTIONALOUTBIN1,
OPTIONALOUTBIN2, OPTIONALOUTBIN3,
OPTIONALOUTBIN4, OPTIONALOUTBIN5,
OPTIONALOUTBIN6, OPTIONALOUTBIN7,
OPTIONALOUTBIN8, OPTIONALOUTBIN9,
OPTIONALOUTBIN10, “name”
name is a variable that allows for custom naming of
optional output bins. The text string is truncated to 24
characters.
Specifies a selected output bin for jobs printed on
custom ty pe 1 paper.
A DINQUIRE or INQUIRE on the Assign Type/Bin Custom Type 1 setting returns:
Assign Typ e/Bin - DINQUIRE or
Custom Type 1 INQUIRE value
setting
UPPER,
DISABLED
(Model specific)
LCUSTOMTYPE1TEXTURE
(DEFAULT only)
LCUSTOMTYPE1WEIGHT
(DEFAULT only)
LCUSTOMTYPE2LENGTH
(DEFAULT only)
LCUSTOMTYPE2LOADING
(DEFAULT only)
LCUSTOMTYPE2MEDIA
(DEFAULT only)
Custom Type 1
Texture
Custom Type 1
Weight
Custom Type 2
Length
Custom Type 2
Paper Loading
Custom Type 2
Media
Standard Bin UPPER
Bin 1 OPTIONALOUTBIN1
Bin 2 OPTIONALOUTBIN2
Bin 3 OPTIONALOUTBIN3
Bin 4 OPTIONALOUTBIN4
Bin 5 OPTIONALOUTBIN5
Bin 6 OPTIONALOUTBIN6
Bin 7 OPTIONALOUTBIN7
Bin 8 OPTIONALOUTBIN8
Bin 9 OPTIONALOUTBIN9
Bin 10 OPTIONALOUTBIN10
“name”“name”
SMOOTH, NORMAL, ROUGH NORMAL
LIGHT, NORMAL, HEAVY NORMAL
NORMAL, SHORT NORMAL
OFF, DUPLEX OFF
PAPER, COATED, GLOSSY, TRANSPARENCY,
LABELS, CARDSTOCK, ENVELOPE,
COTT ONPAPER
PAPER
 Loading...
Loading...