Page 1

20
504030
Laser Locator
Operating Instructions
Laser Locator / Laser Locator Plus
English
Version 1.0
Page 2
Laser Locator
Congratulations on purchasing
your Laser Locator.
Laser Locator =
4 instruments in 1:
• Binoculars
Superb optics in a robust,
watertight, rubber-armoured
casing.
• Digital Compass
Displays magnetic azimuth or
grid azimuth in degrees, gon or
mils.
• Laser Rangefinder
Measures from 5 m to over
4 km (depending on model,
visibility and nature of target
objects).
• Inclinometer
Displays vertical angles
between -45° and +45°.
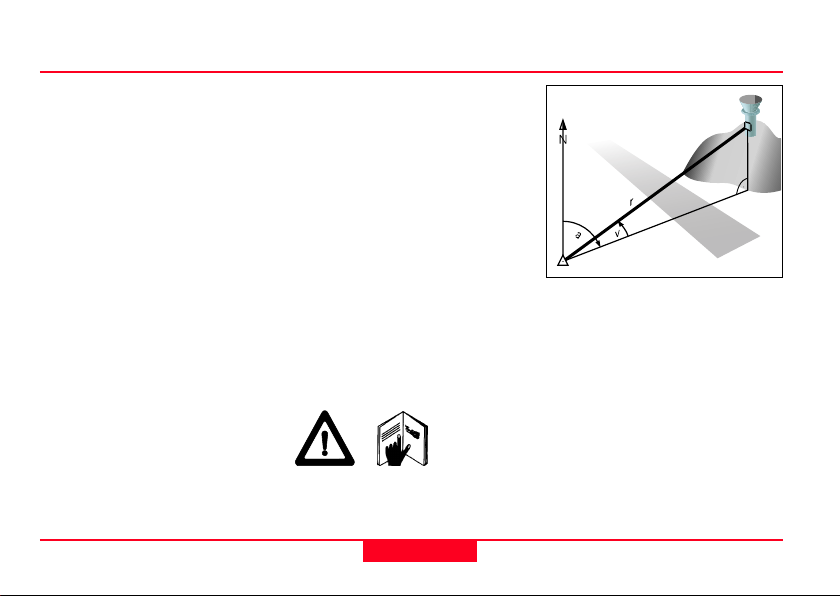
Laser Locator
The object is marked by a red
square that appears at the
centre of the field of vision when
you press one of the two
measurement keys.
r Range (slope distance)
a Azimuth (bearing, horizontal
direction, angle between
north and object)
v Vertical angle (inclination,
elevation)
For safe use of the Laser Locator, please note the detailed safety
directions included in the Operating Instructions.
© 2001 Leica Geosystems AG, ® All rights reserved.
2
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 3

Contents
Getting started ___________________________________________________________6
Changing the battery __________________________________________________ 6
Adjusting the neck strap _______________________________________________7
Removing the neck strap _______________________________________________7
Storing the Laser Locator ______________________________________________7
Eyepiece viewing distance ______________________________________________ 8
Eye-base adjustment __________________________________________________8
Dioptric adjustment ___________________________________________________ 8
Using the Laser Locator ________________________________________________ 9
Distance measurements ___________________________________________________ 10
Factors affecting measurement range ____________________________________ 10
Distance measurement (slope distance) __________________________________ 11
Multiple object measurement ___________________________________________12
Combined measurement with data transfer (distance, azimuth, inclination) _______ 13
Horizontal dist. and height difference between your position and a remote object __14
Distance between two objects __________________________________________ 15
Horizontal and vertical distance between two objects ________________________ 16
Laser Locator-1.0 en
3
Contents
Page 4

Contents
Azimuth and inclination measurement _______________________________________ 17
Factors influencing azimuth accuracy ____________________________________ 17
Azimuth measurement ________________________________________________18
Combined azimuth and inclination angle measurement ______________________ 19
Azimuth and distance between two objects ________________________________20
Relative horizontal and vertical angle ____________________________________ 21
Data transfer ____________________________________________________________22
Connecting / disconnecting the interface cable _____________________________ 22
Cable configuration __________________________________________________23
Interface parameters _________________________________________________ 23
Data transfer format __________________________________________________ 24
Configuration ____________________________________________________________25
Measuring 3 distances ________________________________________________25
Settings ________________________________________________________________26
Setting the measurement units _________________________________________ 26
Declination compensation _____________________________________________ 27
Declination display ___________________________________________________27
Contents
4
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 5

Contents
Declination setting / correction __________________________________________ 28
Compass calibration _________________________________________________ 29
General instructions __________________________________________________ 29
Operator guidance ___________________________________________________30
Calibration procedure ________________________________________________31
Troubleshooting _________________________________________________________ 33
Safety notices ___________________________________________________________38
Care / cleaning___________________________________________________________40
Technical data ___________________________________________________________41
Equipment ______________________________________________________________ 43
Customer service ________________________________________________________44
Laser Locator-1.0 en
5
Contents
Page 6
Getting started
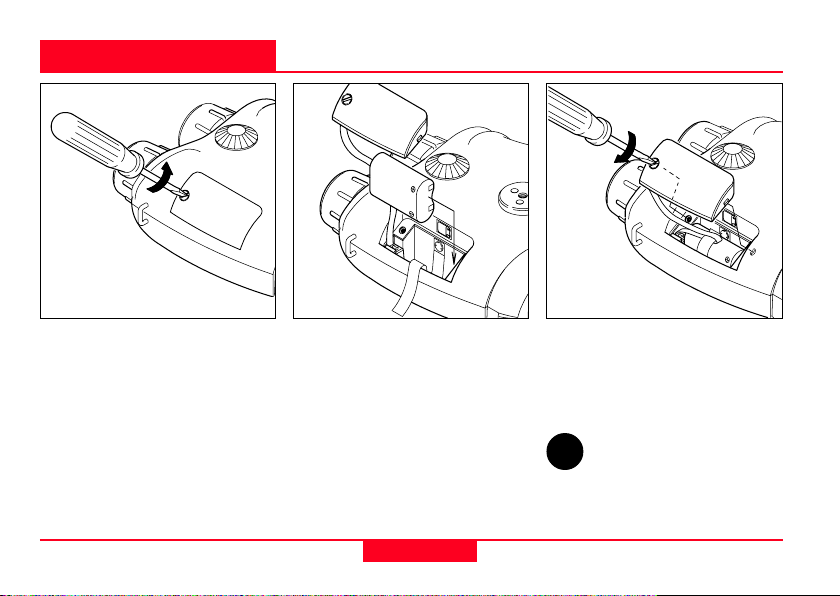
Changing the battery
Open the battery compartment
using a suitable tool, or a coin.
Insert a 6V lithium battery,
SANYO type 2CR5 or equivalent.
Ensure that the drawing ribbon
lies above the securing tape of
the battery cover. Keep the
battery cover seals and the
instrument case clean.
Getting started
Refit the battery cover and retighten the screw.
The Laser Locator monitors the
battery’s condition. If the display
shows ”LobAtt”, this indicates
that the battery is used up. You
can still get readings, but the
battery needs to be replaced
soon.
6
The ”LobAtt” display may also
appear under cold conditions,
since low temperature reduces
the battery performance.
Remove the Laser Locator
i
battery before a prolonged
period of non-use.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 7
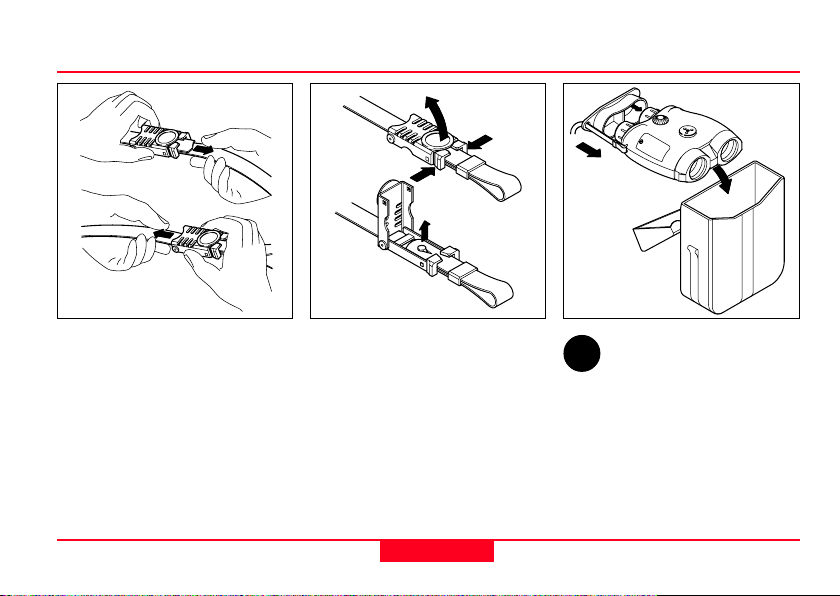
Storing the Laser LocatorRemoving the neck strapAdjusting the neck strap
Adjust the length of the neck
strap by pulling the strap slowly
but firmly around the back of the
catch.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Open both catches:
Squeeze the two clips together
and lift the cover. Remove the
strap ends and pull them
through the lugs on the Laser
Locator.
7
To protect from dirt:
i
Always fit the eyepiece
cover and keep your Laser
Locator in its pouch when not in
use.
Getting started
Page 8
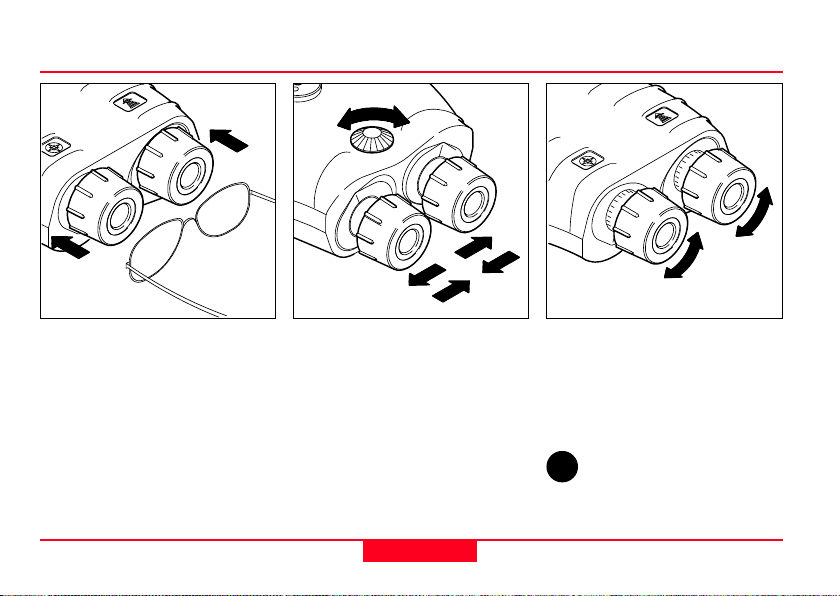
Eyepiece viewing distance Dioptric adjustmentEye-base adjustment
When using the Laser Locator
with glasses, push the eyecups
fully inwards.
When using the Laser Locator
without glasses, pull the
eyecups out to the stop.
Getting started
+
Turn the adjusting knob until the
left and right fields of view fuse
to form a circular image.
-
+
-
8
+
+
-
-
Sight on an object farther than
100 m away and rotate the
eyepieces to obtain a sharp
image. Standard setting:
0 dioptres.
If the Laser Locator is
i
being used by a number of
different people, remember your
personal dioptric setting.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 9
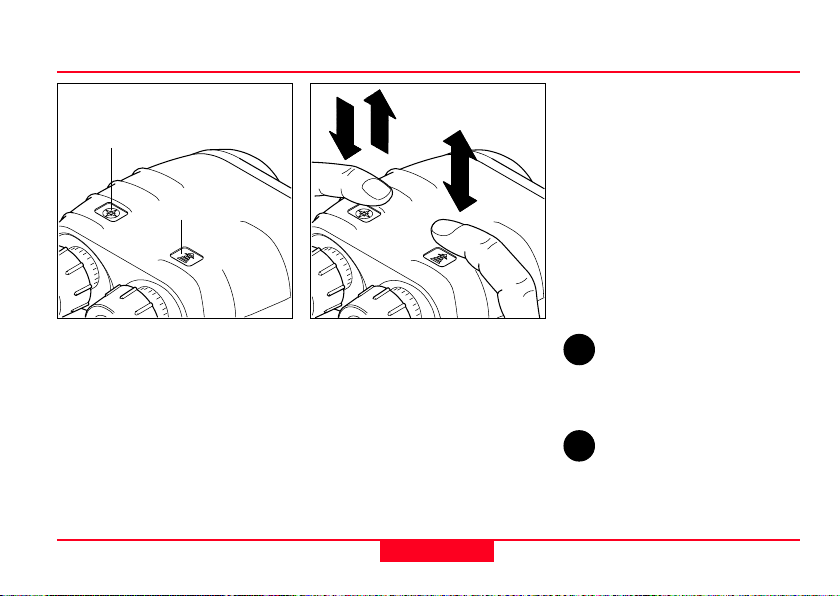
Using the Laser Locator
Azimuth key
Distance key
3x
Double arrow plus a number:
Press and release the key in
rapid succession (e.g. triple click)
Sight the object to be measured
using the pointing circle.
Hold the Laser Locator steady
during measurement.
The Laser Locator displays the
measurement result, then
switches itself off automatically
after a few seconds.
The Laser Locator is operated
entirely by means of the keys on
the top of the casing.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Key operation is indicated by the
following symbols:
Downward arrow: press and
hold down the key.
Upward arrow: release the key
Double arrow: press and release
the key (click)
9
You can prolong the display
i
period by holding down the
measuring key while the result is
displayed.
The last blinking digit
i
indicates decimeters.
Getting started
Page 10
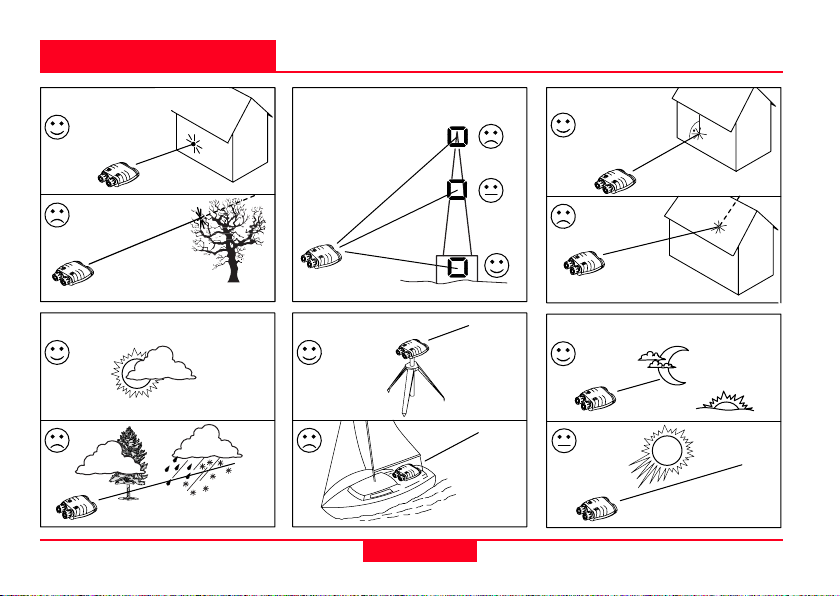
Distance measurements
Reflective properties Size of the target Oblique surfaces
Factors affecting measurement range
Atmospheric conditions
Distance measurements
Vibration Lighting conditions
10
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 11

Distance measurement (slope distance)
Press and hold the distance key;
the pointing circle appears in the
field of view.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Sight the pointing circle on the
object.
11
Hold the Laser Locator steady
as you release the distance key.
Read off the distance.
If "----" appears in the display, the
object lies outside the measuring
range, or measuring conditions
are poor (see page 10).
Setting measurement units:
i
see page 26
Distance measurements
Page 12
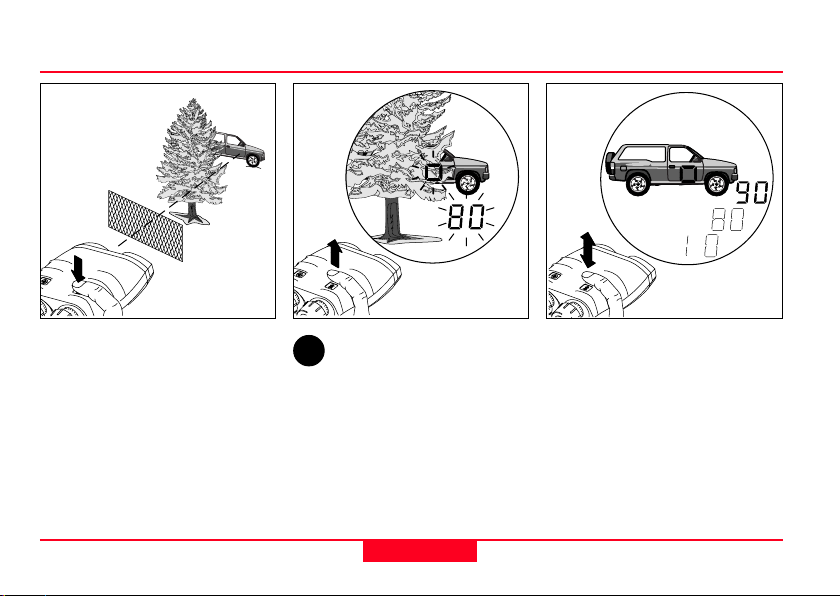
Multiple object measurement
Up to 3 separate distances can
be obtained with a single
measurement, for example
when:
- the laser beam passes through
objects in front of the main
target (bushes, shrubs, etc.)
- there are reflective objects
behind the main target
(mountains, etc.)
Distance measurements
To use this feature, ”3diS on”
i
(3 distances) must be
activated via the configuration
menu; see page 25.
Sight on the most visible portion
of the object. Operate the Laser
Locator as described under
”distance measurement”.
12
The distance display blinks for a
few seconds after a multiple
distance measurement. Click the
distance key repeatedly to
obtain all the measured
distances in succession.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 13
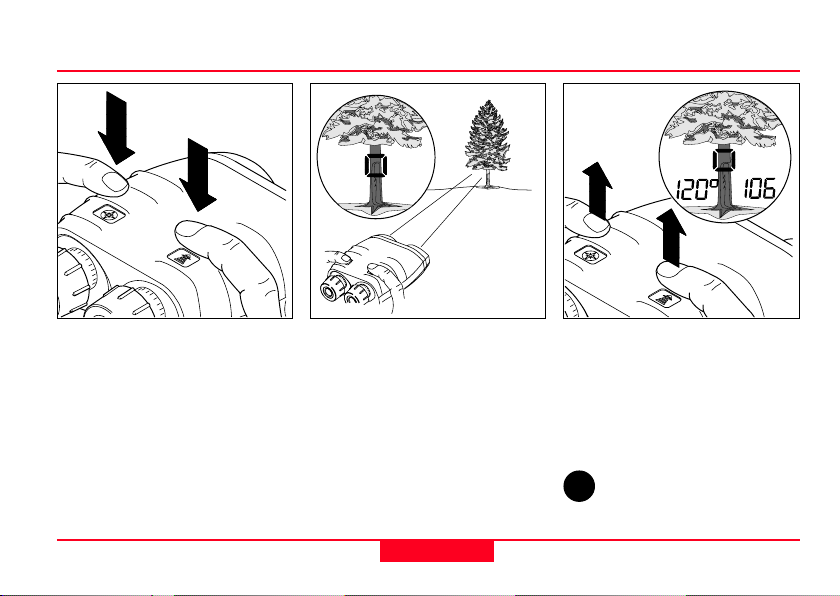
Combined measurement with data transfer (distance, azimuth, inclination)
Measurement data is transmitted
via the (optional) interface cable
immediately after the
measurement is taken (see
page 22).
It is not possible to store
measurement data in the Laser
Locator itself.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Hold down both keys simultaneously; the pointing circle appears,
together with the current azimuth.
Sight the object with the pointing
circle.
Release both keys while holding
the Laser Locator steady.
13
The azimuth appears at the left
and the distance at the right of
the field of view.
The inclination angle is not
displayed, but it is sent via the
data interface.
Setting measurement units:
i
see page 26.
Distance measurements
Page 14
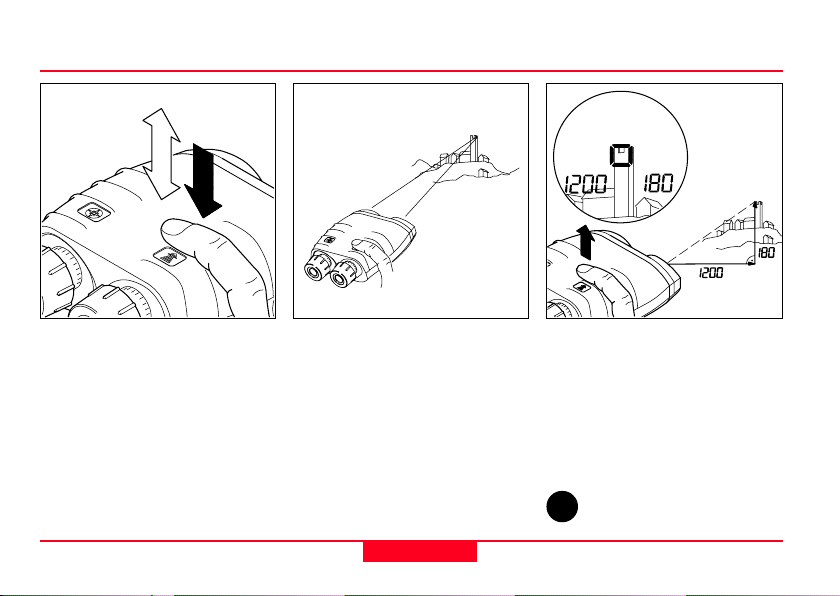
Horizontal dist. and height difference between your position and a remote object
Click the distance key once,
then press and hold it down.
The pointing circle appears.
Distance measurements
Sight the object with the pointing
circle.
14
Release the distance key while
holding the Laser Locator
steady.
The horizontal distance appears
at the left and the height difference at the right of the field of
view.
Setting measurement units:
i
see page 26.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 15

Distance between two objects
Press and hold the distance key.
The pointing circle appears.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Sight the first object with the
pointing circle.
Click the azimuth key while
holding the Laser Locator
steady.
The first object measurement is
confirmed (1-P = first point).
15
Sight the second object with the
pointing circle.
Release the distance key while
holding the Laser Locator
steady.
The distance between the two
objects is displayed.
Setting measurement units:
i
see page 26.
Distance measurements
Page 16

Horizontal and vertical distance between two objects
Click the distance key once,
then immediately press and hold
it down.
The pointing circle appears.
Distance measurements
Sight the first object with the
pointing circle.
Click the azimuth key while
holding the Laser Locator
steady.
The first object measurement is
confirmed (1-P = first point).
16
Sight the second object with the
pointing circle.
Release the distance key while
holding the Laser Locator steady.
The horizontal distance appears
at the left and the vertical
distance at the right of the field
of view.
Setting measurement units:
i
see page 26.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 17

Azimuth and inclination measurement
The Laser Locator has a digital
compass that works similarly to
a magnetic compass. Metal
objects and magnetic fields can
cause errors in directional
readings. Nonmagnetic metals
and alloys do not affect the
compass readings.
Countermeasures:
i
Calibrate the compass (see
pages 30–32) after every battery
change.
Observe the minimum safe
distances shown opposite when
making azimuth measurements
or calibrating the compass:
55 m
Factors influencing azimuth accuracy
10 m
Laser Locator-1.0 en
2 m
17
0.5 m
Azimuth and inclination measurement
Page 18

Azimuth measurement
Press and hold the azimuth key.
The pointing circle appears,
together with the current azimuth.
The display updates twice per
second.
Sight the object with the pointing
circle, then release the azimuth
key while holding the Laser
Locator steady.
The most recently measured
azimuth is displayed.
Azimuth and inclination measurement
18
Setting measurement units:
i
see page 26.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 19

Combined azimuth and inclination angle measurement
Click the azimuth key once, then
immediately press and hold it
down.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
The following items appear in
the field of view:
- the pointing circle
- the current azimuth at the left
- the current angle of inclination
at the right.
Sight the object with the pointing
circle, then release the azimuth
key while holding the Laser
Locator steady.
19
Azimuth and inclination measurement
The azimuth and angle of
inclination to the object are
displayed.
Setting measurement
i
units: see page 26.
Page 20

Azimuth and distance between two objects
Press and hold the azimuth key.
The pointing circle appears,
together with the current
azimuth.
Sight the first object with the
pointing circle.
Click the distance key (> 0.5 s)
while holding the Laser Locator
steady.
The first object measurement is
confirmed (1-P = first point).
Azimuth and inclination measurement
20
Sight the second object with the
pointing circle.
Release the azimuth key while
holding the Laser Locator steady.
The azimuth appears at the left
and the distance at the right of
the field of view.
Setting measurement units:
i
see page 26.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 21

Relative horizontal and vertical angle
Click the azimuth key once, then
immediately press and hold it
down.
The following items appear in
the field of view:
- the pointing circle
- the current azimuth at the left
- the current angle of inclination
at the right
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Sight the first object with the
pointing circle.
Click the distance key while
holding the Laser Locator
steady.
Both angles are set to zero.
Sight the second object and
release the azimuth key. The
relative angles appear in the
field of view.
21
Azimuth and inclination measurement
Page 22

Data transfer
On the underside of the Laser
Locators is a socket for sending
data to:
- personal computers or laptops
- modems
- fire control systems
Our customer service will
i
be pleased to inform you
about special accessories for
transmitting and analysing data.
Caution
Incorrect handling can damage
the socket and optional
interface cable.
Connecting / disconnecting the interface cable
Lemo
plug
To plug:
Align the respective red markings
on the Lemo plug and socket.
Slide the plug carefully into the
socket until the locking
mechanism engages.
To unplug:
Grasp the plug grip
- between two fingers,
- draw it carefully back to the
stop to disengage the locking
mechanism,
- pull back a little harder until the
plug slips out of the socket.
Data transfer
22
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 23

Cable configuration Interface parameters
AZI 1
DIST 2
GND 3
SDS_IN 4
SDS_OUT 5
Lemo plug
FHB.0B.305.CLCD 42Z
The optional interface cable is
intended for connection to a PC
serial interface with a 9-pin
D plug.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
ws
rt
sw
gn
bl
3 m
D plug, 9-pin female
23
Interface ......................... RS 232
Data
9
transmission ........ unidirectional
8
Baud rate .................... 1200 bps
7
Parity ..................................none
6
Data bits ................................... 8
5
Stop bits ................................... 1
4
Handshake ......................... none
3
2
1
Data transfer
Page 24

Data transfer format
Every measurement (distance,
azimuth, inclination) is transmitted
as 10 ASCII characters:
Z XXXXXX XY <CR>
value
Checksum
Start character
Measurement
End character
A complete set of measurements therefore consists of 30
ASCII characters.
Before and after this continuous
string, a steady logic 1 is
transmitted while the Laser
Locator is powered on.
Data transfer
Start character for measurement
value:
d ................................... distance
a .................................... azimuth
e ................... angle of inclination
(elevation)
Start character for error report:
C ......................... compass error
R ..........................distance error
M ............................... instrument
(main board) error
Measurement value: 6 integer
digits or six-digit hexadecimal
error code.
The data transmitted comprises:
- distance in decimetres, with
0.5 m resolution
- azimuth and inclination in
milliradians (full circle =
6'283.2 mrad) and 0.2 mrad
resolution.
24
Measurement
examples:
47'1240/0
31'416/0
0/5'236
N
0/0
°
0
3
+
0/57'596
-30°
15'708/0
Checksum: 2 hexadecimal
digits. These correspond to the
8 LSBs (least significant bits) of
the ASCII measurement value
and the start character.
End character: 1 position for line
feed (CR).
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 25

Configuration
Measuring 3 distances
5x
Click the distance key five times
in rapid succession. The
configuration settings appear in
the field of view.
In the following configuration
menue the multiple object
measurement "3dIS"
(3 Distances) can be switched
on or off.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
The function "3dIS on"
i
allows up to 3 distances to
be displayed from a single
measurement (see page 12).
Click the azimuth key until the
desired function status for
"3dIS" appears (function on or
OFF).
25
5x
Click the distance key five times
in rapid succession to save your
settings.
If the distance key is not correctly
clicked five times, the previous
settings remain unchanged and
"Old Conf" is displayed.
Configuration
Page 26

Settings
Setting the measurement units
5x
Various angle and distance
measurement units may be set
via the configuration menu.
Click the azimuth key five times
in rapid succession.
"Unit SEtt" appears briefly,
followed by the measurement
units currently in use by the
Laser Locator.
Settings
Click the distance key until the
desired units appear in the field
of view:
- at the left: angular unit in mils,
gon or degrees
- at the right: distance unit in
metres (SI-Unit), yards, or feet.
26
5x
Click the azimuth key five times
in rapid succession to save your
preferred units.
If the azimuth key is not correctly
clicked five times, the previous
settings remain unchanged and
"Old Unit" is displayed.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 27

Declination compensation Declination display
Declination represents the
deviation between magnetic
north and grid north.
Declination is displayed in the
currently selected angular units
(see page 26).
Declination
- varies from location to location
- varies from time to time
- is specified on most land and
sea maps
To refer the azimuth angle to
grid north: enter the local
declination value into the Laser
Locator.
To refer the azimuth angle to
magnetic north: enter a zero
declination value into the Laser
Locator.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
3x
Click the azimuth key three
times in rapid succession.
The current declination value is
displayed for 10 seconds.
The Laser Locator displays
"Old dECL" before switching
itself off (the declination value is
unchanged).
27
The stored declination
i
value
- is reset to 0 when the
measurement units are
changed (see page 26);
- is retained when the battery is
exhausted or replaced;
- is factory-set to 0.
Settings
Page 28

Declination setting / correction
3x
Click the azimuth key three
times in rapid succession.
The stored declination value is
displayed.
Settings
Distance key
- short click: the declination
value increments by one unit;
- long click (hold down the key
for longer than half a second):
the declination value
decrements by one unit.
28
3x
Click the azimuth key three
times in rapid succession to
store the new declination value.
If the azimuth key is not correctly
clicked three times, the previous
settings remain unchanged and
"Old dECL" is displayed.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 29

Compass calibration General instructions
How?
When?
Where?
There is a choice of two
calibration procedures:
• 4 point calibration (4 Pt Co)
achieves adequate precision
for most applications.
• 12 point calibration (12 Pt Co)
is performed at the factory
under optimal conditions.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
After every battery change.
After the Laser Locator has
been exposed to strong
magnetic fields.
When metallic parts have been
attached to the Laser Locator.
Check the stored
i
declination after every
compass calibration, and correct
if necessary.
29
In an open area (e.g. a field) at
an adequate distance from
buildings and metallic objects
(see page 17). Ensure that there
are no buried pipes, cables, etc.
in the vicinity.
Never calibrate the compass
i
inside a building, or in the
vicinity of disruptive magnetic
fields!
Settings
Page 30

Operator guidance
turn UP
+20°
(rtrn hori)
-20°
turn dn
rot 90°
(undo tilt)
-20°
(tilt left)
The Laser Locator needs to be
swivelled in various directions
during calibration. Instructions
for the required direction of
movement appear successively
in the display:
turn UP .................... tilt upwards
rtrn hori ....... return to horizontal
turn dn ................. tilt downwards
rot 90° ................... rotate by 90°
Settings
tilt left ....... tilt the left side of the
Laser Locator downwards
undo tilt ....... return to horizontal
Instructions in brackets
i
apply to 12 point calibration
only.
Always turn in the same
direction for all ”rot 90°”
instructions.
30
Important:
Perform each movement slowly
and steadily, until the next
instruction appears.
When you see the "StOP"
instruction, immediately hold
the Laser Locator still and on
no account move it while "StOP"
is displayed.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 31

Calibration procedure
4x
Point the Laser Locator roughly
northwards.
Click the azimuth key four times
in rapid succession.
"FIEL Co" appears briefly,
followed by "4 Pt Co" for the
regular 4 point calibration.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Only click the distance key
i
if you want to perform the
special 12 point calibration.
"12 Pt Co" is displayed.
The selected calibration
procedure begins in a few
moments.
Move the Laser Locator according
to the displayed instructions.
31
After the last instruction,
analysis begins and the pointing
circle blinks for 4 sec. (4 Pt Co)
or 30–60 sec. (12 Pt Co).
You then see
- "Good Co": indicates
successful calibration.
- "bAd Co" followed by "rES Co":
indicates that the calibration
data are unusable.
Settings
Page 32

Calibration procedure (continued)
After 12 point calibration,
i
the Laser Locator can be
put down as soon as the
pointing circle starts blinking.
You can check the results later
by clicking the azimuth key.
Magnetic interference can still
lead to inaccurate measurements,
even if calibration was successful.
For this reason, you should
verify compass accuracy after a
successful calibration: perform
several azimuth measurements
on known landmarks and
compare the results.
After calibration, the Laser
Locator acts on the
measurement results as follows:
Possible causes of calibration
failure:
• The Laser Locator was moved
while a "StOP" instruction was
displayed.
• Movements performed too fast,
or jerkily.
• Strong magnetic disturbances
in the vicinity.
Display Action
"Good Co"
"bAd Co"
"bAd Co" + "rES Co"
Store the newly determined
constants.
Store the newly determined
constants.
Reset constants to factory
values.
If you get a "bAd Co", reattempt
calibration until "Good Co"
appears. Consider moving to an
alternative position.
Settings
32
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 33

Troubleshooting
Problem Possible cause Solution
You cannot see a circular
image with both eyes.
Measurements cannot be
taken.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Eye-base or eyecup incorrectly
adjusted.
Eyes are not positioned on the
Laser Locator’s optical axis.
The battery has run out.
Battery contacts corroded.
Low temperature reduces
battery performance.
Extreme heat shortens battery
life.
33
Adjust the eye-base or eyecup
following the instructions on
page 8.
Reposition your head, or the
instrument.
Replace the battery. Preferably
use SANYO type.
Clean the battery contacts.
Carry the Laser Locator close
to your body.
Do not store the battery at
temperatures in excess of
+70°C.
Troubleshooting
Page 34

Troubleshooting (continued)
Problem Possible cause Solution
"- - - -" appears in the display
when distance is measured.
Troubleshooting
The distance is outside the
specified measuring range.
Inadequate reflectance:
• object too small or inaccurately
targeted;
• The Laser Locator was shaken
during measurement;
• Bad weather conditions (haze,
fog, turbulence).
34
See the specified measuring
range on page 41.
See the list of factors affecting
measuring range on page 10.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 35

Troubleshooting (continued)
Problem Possible cause Solution
Distance display blinks.
The Laser Locator measures
objects in front or behind the
intended object (e.g. bushes ->
object -> mountain).
These symbols are displayed
during azimuth measurement:
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Multiple object measurement is
activated: ”3dIS on”.
The Laser Locator only displays
the distance to the most
reflective object in the line of
vision.
The permissible angle of
inclination of ±45° has been
exceeded:
tilted too far upwards
tilted too far downwards
tilted too far to the right
tilted too far to the left
35
Click the distance key to display
distances in succession (see
page 12).
Activate multiple object
measurement: ”3dIS on” (see
page 25).
Do not over-tilt or bank the
Laser Locator.
Troubleshooting
Page 36

Troubleshooting (continued)
Problem Possible cause Solution
Inaccurate azimuth
measurement values.
The expected display does not
appear after clicking a key
several times.
Troubleshooting
Incorrect declination value has
been stored.
Disruptive magnetic fields at the
measuring position.
Calibration in an area with
magnetic interference.
Altered magnetic conditions
within the instrument after a
battery change.
Key was pressed too slowly, or
with insufficient force.
36
Store the correct declination
value (see page 28).
See the factors affecting
measurement accuracy on
page 17.
Recalibrate the compass (see
pages 29-32).
Recalibrate the compass.
Press and release the key in
rapid succession. Always
press the key down until there
is an audible click.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 37

Troubleshooting (continued)
Problem Possible cause Solution
”Lo bAtt” is displayed. The battery is used up.
Reduced battery performance at
low temperature.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
37
You can still get some readings,
but the battery needs to be
replaced soon.
You can still get some readings,
but the Laser Locator or the
battery needs to be warmed
up (e.g. on your body).
Troubleshooting
Page 38

Safety notices
Intended purpose
The Laser Locator
- is designed as a navigation aid;
- is to be used in addition to
other instruments or techniques;
- must never be used as a sole
navigation instrument.
Limitations of use
The Laser Locator must not be
used in the vicinity of sensitive
electrical equipment.
All other usage limitations are
mentioned in the technical
specifications.
Inappropriate use
• Laser Locator deployment
without prior knowledge of the
operating instructions and
safety notices.
• Changes and modifications to
the Laser Locator by the
customer.
• Use of third-party accessories
not expressly approved by
Leica Geosystems AG.
Inappropriate use brings the risk
of
- injuries;
- instrument errors;
- damage to property;
- malfunction;
Blinding hazard
• Do not look into powerful light
sources with the Laser
Locator.
• Do not open the Laser Locator.
The built-in laser can cause
eye injuries.
Explosion hazard
The battery must not be
- short-circuited;
- recharged;
- mechanically modified;
- placed in fire or heated above
+85°C with the Laser Locator.
Safety notices
38
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 39

Safety notices (continued)
Physical injury hazard
• Do not place the Laser Locator
on a vehicle parcel-shelf or
dashboard – risk of injury
when braking.
• Check the carrying strap at
regular intervals, and replace it
if damaged.
Environmental hazard
The Laser Locator contains
certain components that should
be treated as hazardous waste,
and must therefore be disposed
of via a specialist dealer.
Deposit used batteries at a
proper collection point.
Avoiding storage and
transport damage
• When not in use, always keep
the Laser Locator in its pouch
with the eyepiece protection
caps fitted.
• Remove the battery prior to
prolonged storage. Battery
leakage can damage the Laser
Locator!
• Observe the permissible
storage temperatures.
• Do not expose the Laser
Locator to strong mechanical
shocks or abrupt temperature
transitions during transport
(moisture condensation).
• Use the pouch and transit case
or equivalent packaging for
shipment.
Avoiding measurement errors
• Note the factors affecting
measurement accuracy (see
pages 10, 17, 32).
• Always perform test
measurements after the Laser
Locator has been exposed to
rough handling (vibration, falls,
etc.), and before carrying out
important measurement tasks.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
39
Safety notices
Page 40

Care / cleaning
The Laser Locator’s
performance and serviceability
are conditional on regular care
and immediate attention to
problems:
• Do not touch glass lenses with
fingers.
• Do not soil the operating keys
with oil or grease.
• Avoid abrupt temperature
transitions, since these can
cause condensation moisture
to develop inside the Laser
Locator.
The Laser Locator does not
need special care or cleansers.
Therefore
- do not use any kind of
impregnated cloth intended for
cleaning spectacle lenses,
- do not use any solvent except
water, e.g. no alcohol or
cleansers.
Lens cleaning
Particles of dirt should be blown
off or removed using a soft brush.
Finger prints may be cleaned
first by wiping with a damp cloth,
followed by soft, clean optical
tissue or chamois leather.
Cleaning the casing
Wipe the casing with a damp
cloth.
Pay special attention to dirt and
grease around the keys.
Blow out the Laser Locator
interface cable socket, and
clean it carefully.
Allow the Laser Locator to dry
fully before packing.
Cleaning the interface cable
Protect the cable from damp
and dirt as much as possible!
Wipe the cable with a damp
cloth. Blow out soiled cable
plugs with clean air, and leave
them to dry.
Care / cleaning
40
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 41

Technical data
Optics
Magnification ......................... 7x
Clear objective diameter .. 42 mm
Exit pupil diameter ............ 6 mm
Eye relief ...................... 18,5 mm
Field of view
@ 1000 metres ................ 120 m
Axial resolution ......... better than
6 arcseconds
Interpupillary distance
adjustment .......... 58,5-71,5 mm
Focus ................................. fixed
Dioptric correction ........ > ± 4 dpt
Pointing circle illuminates to
indicate laser direction and
approximate laser spot size on
target.
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Rangefinder Laser Locator Laser Locator Plus
Laser type: IR diode ........ 860 nm 1550 nm
Eye safety ........................ Class 1 Class 1
Safety standards .............. EN 60825 (91) EN 60825-1 (94)
Measurement range ........ 5 m - 2500 m 5 m - 6000 m
Spec. measurement range 25 m - 1500 m 25 m - 4000 m
Visibility ............................ 10 km 20 km
Target size ....................... 4 x 4 m 8 x 8 m
Albedo .............................. 0.4 at 860 nm 0.4 at 1550 nm
Detection probability ........ >90% >90%
Accuracy (1σ) from:
50 m - 2000 m ................. ± 1 m ± 2 m
2001 m - 4000 m ............. ± 3 m ± 3 m
False alarm rate ............... < 2% < 2%
Beam divergence ............. ≤ 1.5 mrad ≤ 2x2 mrad
Display resolution 0.5 m < 999.5 m 0.5 m < 999.5 m
41
IEC 825 (90) IEC 825-1 (93)
ANSI Z 136.1 (93) ANSI Z 136.1 (93)
FDA 21 CFR, FDA 21 CFR,
Ch 1§ 1040 (1988) Ch 1§ 1040 (1988)
others 1 m, others 1 m,
0.1 m in height 0.1 m in height
Technical data
Page 42

Technical data (continued)
Magnetic compass
(azimuth and inclination)
Miscellaneous
Azimuth measurement
range .................................. 360°
Accuracy (1σ):
Azimuth ......................... ± 10 mil
Inclination ....................... ± 3 mil
Display
resolution ........ 10 mil /1°/ 1 gon
Maximum inclination /
bank angle ........................ ± 45°
Compass calibration ........... user
initiated, menu driven
Declination ..........± 99° / 990 mil
(adjustable)
Technical data
Power supply .................................... 6V lithium battery (type 2CR5)
Battery capacity ................................... approx. 2400 measurements
Protective covering .......................................environmentally sealed,
Immersion proofing .............................. 10 min. in 1 m depth of water
Operational temperature range .................................. -35° bis +63°C
Storage temperature range (without battery) ............. -40° bis +85°C
Shock resistance .......................................... 30 g / 11 ms / xyz axes
Vibration resistance ............................... 10 to 500 Hz for 10 minutes
Dimensions ..........................................................205 x 178 x 82 mm
Tripod bush thread .................................................................... A 1/4"
Weight .................................... 1710 g (including eyepiece protection
Interface .............................................. RS-232, unidirectional output
42
impact-resistant rubber armour casing
and battery type 2CR5)
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 43

Equipment
Shipping inventory
SVP240
SEB50
Laser Locator-1.0 en
STR1
SEV48
Order no. Description
––– Laser Locator / Laser Locator Plus
535 314 SEB50 lithium battery, 6 volt, SANYO type 2CR5
636 895 SVP240 grey pouch with accessories
636 965 STR1 neck strap
Optional equipment:
706 271 SEV48 interface cable, shielded, 3 m long
722 804 GEV154 interface cable to GPS
43
Equipment
Page 44

Customer service
Our customer and information
service will be glad to offer
assistance if your instrument
requires maintenance, if it
sustains damage, or if you
require any other information:
Leica Geosystems AG
Defense & Special Projects
Heinrich-Wild-Strasse
CH-9435 Heerbrugg
(Switzerland)
Telephone: +41 71 727 31 31
Fax: +41 71 727 46 79
Internet:
www.leica-geosystems.com
SQS certification attests that
Leica Geosystems AG
Heerbrugg operates a quality
management system that
complies with international
standards for quality and quality
management systems (ISO 9001)
and environmental management
systems (ISO 14001).
Total Quality Management – our
commitment to total customer
satisfaction. Ask your local Leica
representative for more
information about our TQM
programme.
CopyrightQuality system
Without the prior written
permission of Leica Geosystems
AG (Heerbrugg, Switzerland),
this document may neither be
copied in part or whole by
mechanical, photographic,
electronic or any other means
(this includes converting it to
any machine-readable form), nor
be stored in an information
storage system, nor be used for
any purpose other than that
intended, nor be made available
or passed on to any third party
who has not been expressly
authorised by Leica
Geosystems AG.
Customer service
44
Laser Locator-1.0 en
Page 45

Eye safety
IEC 825-1 (1990 / 1993)
EN 60825 (1991 / 1994)
ANSI Z 136.1 (1993)
FDA 21 CFR Ch 1§ 1040 (1988)
CLASS 1
LASER PRODUCT
Laser Locator-1.0 en
45
Customer service
Page 46

725351-1.0 en SW 1.4
Printed in Switzerland
Copyright by Leica Geosystems AG
Heerbrugg, Switzerland 2001
Translation of original text (724805-1.0 de SW 1.4)
Leica Geosystems AG
Defense & Special Projects
CH-9435 Heerbrugg (Switzerland)
Telephone +41 71 727 31 31
Fax +41 71 727 46 79
www.leica-geosystems.com/optronics
 Loading...
Loading...