Page 1

PRESCRIBE Commands
Command Reference
Page 2

We shall have no liability or responsibility to customers or any other person or entity with respect to any liability, loss or
damage caused or alleged to be caused directly or indirectly by equipmen t sold or furnished by us, including, but not limited
to, any interruption of service, loss of business or anticipatory profits, or consequential damages resulting from the use or
operation of the equipment or software.
NO LIABILITY WILL BE ASSUMED FOR ANY DAMAGE CAUSED BY IMPROPER INSTALLATION.
Notice on Software
SOFTWARE USED WITH THIS PRINTER MUST SUPPORT THE PRINTER’S NATIVE MODE OR ONE OF ITS EMULATION MODES.
Notice
This manual, the computer programs in the page printer referred to in this manual, and any oth er copyrightable subject
matter sold or provided with or in connection with the sale of the page printer, are protected by copyright. All rights are
reserved. Copying or other reproduction of all or part of this manual, the computer programs, or any other co pyrightable
subject matter without the prior written consent of Kyocera Mita Corporation is prohib ited. Any co pies made of all or part of
this manual, the computer programs, or any other copyrightable subject must contain t he same copyright notice as the
material from which the copying is done.
The information in this manual is subject to c hange wit hout not ification. Add itiona l pages ma y be ins erted in f uture editions .
The user is asked to excuse any omissions or errors in the present edition.
No responsibility is assumed if accidents occur while the user is following the instructions in this manual. No responsibility
is assumed for defects in the printer’s firmware.
Regarding Tradenames:
PRESCRIBE is a registered trademark of Kyocera Corporation. KPDL is a trademark of Kyocera Corporation.
Diablo 630 is a product of Xerox Corp or ation. IB M Proprinter X-24E is a product of Internat ional Business Machin es Corporation. Epson LQ-850 is a product of Seiko Epson Corporation. HP LaserJet III, HP LaserJet 4, HP LaserJet 4 Plus, HP
LaserJet 5Si, HP LaserJet 5P, HP LaserJet 5M, HP LaserJet 2100, HP LaserJet 4000, and HP 7550A are products of
Hewlett-Packard Company . Hewlett-Packard, PCL, and HP-GL are registered trademarks of Hewlett-Packard Company.
Centronics is a trade name of Centronics Data Computer Corp. Other product names and company names that appear in
this manual are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
ii
Page 3

Typeface Trademark Acknowledgement
All resident fonts in the print system are licensed from Bitstream Inc. and Agfa corporation. For font license information for
each model, refer to the User’s Manual.
Helvetica, Palatino and Times are registered trademarks of Linotype-Hell AG. Centutry Schoolbook, Stymie, and CooperBlack are trademarks of Kingsley-ATF Type Corporation. ITC Avant Garde Gothic, ITC ZapfChancery, ITC ZapfDingbats,
ITC Souvenir, ITC Benguiat, and ITC Bookman are registered trademarks of International Typeface Corporation. Revue is
a trademark of Esselte Pendaflex Corporation in the U.S., Letraset Canada Ltd. in Canada, and Esselte Letraset Ltd. elsewhere.
Monotype Imaging License Agreement
1. "Software" shall mean the digitally encoded, machine readable, scalable out line data as encoded in a special format as
well as the UFST Software.
2. Yo u agree t o accep t a non -exclus iv e licen se to use the Sof tware to reproduce and dis play weights, st yles an d ve rs ions
of letters, numerals, characters and symbols ("Typefaces") solely for your own customary business or personal purposes at the address stated on the registration card you return to Monotype Imaging. Under the terms of this License
Agreement, you have the right to use the Fonts on up to three printers. If you need to have access t o the fon ts on more
than three printers, you need to acquire a multi-user license agreement which can be obtained from Monotype Imaging.
Monotype Imaging retains all rights, title and interest t o the Software and Typefaces and no rights are granted to you
other than a License to use the Software on the terms expressly set forth in this Agreement.
3. T o prot ect proprie tary righ ts of Monot ype Imaging , you agree to main tain the So ftware and other proprietary in formation
concerning the Typefaces in strict confidence and to establish reasonable procedures regulating access to and use of
the Software and Typefaces.
4. You agree not to duplicate or copy the Software or T ypefaces, except that you may make one backup copy. You agree
that any such copy shall contain the same proprietary notices as those appearing on th e original.
5. This License shall continue until the last use of the Software and Typefaces, unless sooner terminated. This License
may be terminated by Monotype Imaging if you fail to comply with the terms of this License and such failure is not remedied within thirty (30) days after notice from Mono type Imaging. When this License expires or is terminated, you shall
either return to Monotype Imaging or destroy all copies of the Sof tware and Typefaces and docume ntation as
requested.
6. You agree that you will not modify, alter, disassemble, decrypt, reverse engineer or decompile the Software.
7. Monotype Imaging warrants that for ninety (90) days after delivery, the Software will perform in accordance with Monotype Imaging-published specifications, and the diskette will be free from defects in material and workmanship. Monotype Imaging does not warrant that the Software is free from all bugs, errors and omissions.
8. THE PARTIES AGREE THAT ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WARRANTIES
OF FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND MERCHANTABILITY, ARE EXCLUDED.
9. Your exclusive remedy and the sole liability of Monotype Imaging in connection with the Software and Typefaces is
repair or replacement of defective parts, upon their return to Monotype Imaging.
10. IN NO EVENT WILL MONOTYPE IMAGING BE LIABLE FOR LOST PROFITS, LOST DATA, OR ANY OTHER INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, OR ANY DAMAGES CAUSED BY ABUSE OR MISAPPLICATION OF
THE SOFTWARE AND TYPEFACES.
11. Massachusetts U.S.A. law governs this Agreement.
12. You shall not sublicense, sell, lease, o r ot herwise transfer the Software and/or Typ efaces without the prior written consent of Monotype Imaging.
13. Use, duplication or disclosure by the Government is subject t o restrict ions as set forth in the Rights in Technical Data
and Computer Software clause at FAR 252-227-7013, subdivision (b)(3)(ii) or subparagraph (c)(1)(ii), as appropriate.
Further use, duplication or disclosure is subject to restrictions applicable t o restricted righ ts software as set forth in FAR
52.227-19 (c)(2).
14. YOU ACKNOWLEDGE THAT YOU HAVE READ THIS AGREEMENT, UNDERSTAND IT, AND AGREE TO BE
BOUND BY ITS TERMS AND CONDITIONS. NEITHER PARTY SHALL BE BOUND BY ANY STATEMENT OR REPRESENTATION NOT CONTAINED IN THIS AGREEMENT. NO CHANGE IN THIS AGREEMENT IS EFFECTIVE
UNLESS WRITTEN AND SIGNED BY PROPERLY AUTHORIZED REPRESENTATIVES OF EACH PART Y. BY OPENING THIS DISKETTE PACKAGE, YOU AGREE TO ACCEPT THE TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF THIS AGREEMENT.
iii
Page 4

This page is left blank intentionally
iv
Page 5

Table of Contents
Overview of PRESCRIBE Commands by Function 2
Access Commands——————————— —— ———————————————— 2
Print System Setting Commands ——————————————————————— 2
Margin and Page Portrait/Landscape Orientation Commands ———————————— 3
Font Commands—————————————————————————————— 4
Cursor Movement Commands ———————————————————————— 5
Vector Graphics Commands ————————————————————————— 5
Path Mode Graphics Commands ——————————————————————— 6
Raster Graphics Commands ————————————————————————— 7
Color Commands ————————————————————————————— 7
Barcode Commands ———————————————————————— ———— 8
Macro Commands ————————————————————————————— 8
Debug Commands ————————————————————————————— 9
External Media Control Commands —————————————————————— 9
e-MPS Commands ———————————————————————————— 10
PRESCRIBE Commands 11
ACLI — Add CoLor by Index ——————————————————————— 12
ALTB A — [ALlocate TaBle] Assign user-defined character table
ALTB C — [ALlocate TaBle] Convert charact
ALTB D — [ALlocate TaBle] Delete user-defined character table
ALTB E — [ALlocate TaBle] End defining combination characters
ALTB G — [ALlocate TaBle] Generate user-d
ALTB R — [ALlocate TaBle] Release user-defined character table
ALTB S — [ALlocate TaBle] Start to define the com
ALTB T — [ALlocate TaBle] define combined character by Table
ALTF — change to ALTernate Font ————————————————————— 23
AMCR — call Automatic MaCRo—————————————————————— 25
APSG — Assign Paper Source Group ———————————————————— 27
ARC — draw filled-in ARC ———————————————————————— 28
ASFN — ASsign external characters for FoNt ————————————————— 31
ASTK — Assign STacKer trays —————————————————————— 32
BARC — draw BARCode ———————————————————————— 34
BKLT — print in BooKLeT binding ———————————————————— 38
BLK — draw filled-in BLocK ——————————————————————— 40
BOX — draw BOX ——————————————————————————— 42
CALL — CALL macro —————————————————————————— 44
CCPY — Carbon CoPY—————————————————————————— 46
CDSK — Check hard DiSK ——————— ————————————————— 49
CID — Configure color-Image Data ————————————————————— 50
CIR — draw CIRcle ——————————————————————————— 52
CLIP — CLIP current path ———————————————————————— 54
CLPR — CLiP Rectangular area —————————————————————— 55
CLSP — CLoSe Path——————————————————————————— 57
CMNT — CoMmeNT —————————————————————————— 59
CMOD — Color MODe—————————————————————————— 60
COPY — set number of COPIES —————————————————————— 61
CPAL — Control PALette————————————————————————— 63
CPTH — Character PaTH ————————————————————————— 64
————————— 14
er code —————————————— 15
————————— 16
———————— 17
efined table ———————————— 18
————————— 19
bination character ——————— 20
————————— 21
Contents—i
Page 6

CSET — Change symbol SET by symbol-set ID ———————————————— 65
CSTK — select Collator STacKer ————————————— ————————— 68
CTXT — print Centered TeXT ——————————————————————— 69
DAF — Delete All Fonts ————————————————————————— 71
DAM — Delete All Macros ———————————————————————— 72
DAP — Draw to Absolute Position ————————————————————— 73
DELF — DELete Font —————————————————————————— 75
DELM — DELete Macro ————————————————————————— 76
DPAT — select Dashed PATtern —————————————————————— 78
DRP — Draw to Relative Position —————————————————————— 80
DRPA — Draw to Relative Position specified by Angle ————————————— 82
DUPX — select/deselect DUPleX mode———————————————————— 84
DXPG — select DupleX PaGe side—————————————————————— 85
DZP — Draw to Zero-relative Position ———————————————————— 87
EMCR — Enable MaCRo depending on paper source —————————————— 89
ENDB — END a two-dimensional Barcode string ———————————————— 91
ENDC — END carbon Copy ———————————————————————— 92
ENDD — END Dump —————————————————————————— 93
ENDM — END Macro —————————————————————————— 94
ENDR — END Raster data ————————————————————————— 96
EPL — select EcoPrint Level ———————————————————————— 98
EXIT — EXIT from PRESCRIBE mode ——————————————————— 99
FDIR — MP tray Feed DIRection ————————————————————— 100
FILL — FILL closed path ———————————————————————— 101
FLAT — set FLATness ————————————————————————— 104
FLST — print Font LiST ———————————————————————— 105
FOLD — FOLD printed pages —————————————————————— 107
FONT — change current FONT —————————————————————— 108
FPAT — generate Fill PATtern —————————————————————— 110
FRPO — Firmware RePrOgram —————————————————————— 112
FRPO INIT — FRPO-INITialize ————————————————————— 114
FSET — change current Font SETting by char
acteristic ———————————— 115
FTMD — bitmap FonT MoDe —————————————————————— 119
GPAT — set Gray PATtern ——————————————————————— 122
GRAY — represent GRAY———————————————————————— 124
GRRD — GRaphic data ReaD —————————————————————— 125
HUE — adjust HUE——————————————————————————— 127
INTL — InterNaTionaL characters ———————————————————— 129
JOBD — JOB Deletion ————————————————————————— 132
JOBL — print JOB List ————————————————————————— 134
JOBO — JOB Output —————————————————————————— 136
JOBP — JOB, print with Print options ——————————————————— 138
JOBS — JOB Start ——————————————————————————— 140
JOBT — JOB Terminate ————————————————————————— 144
JOG — JOG output stacks for separation —————————————————— 145
LAPI — LoaD API Program ——————————————————————— 146
LDFC — LoaD Font Character —————————————————————— 147
LDFN C — generate bitmap character for LoaDing FoNt ———————————— 149
LDFN F — create header for LoaDing FoNt ————————————————— 151
LDFN S — LoaD truetype FoNt ————————————————————— 153
LGHT — adjust LiGHTness ——————————————————————— 155
MAP — Move to Absolute Position ———————————————————— 157
MCLR — Match CoLoR ———————————————————————— 159
MCRO — define MaCRO ———————————————————————— 160
MDAT — set MeDia type ATtribute ———————————————————— 162
MID — Multi-tray ID —————————————————————————— 164
MPSS — e-MPS Storage————————————————————————— 165
Contents—ii
Page 7

MRP — Move to Relative Position ————————————————————— 166
MRPA — Move to Relative Position specified by Angle ————————————— 168
MSTK — select Mailbox STacKer ————————————————————— 170
MTYP — select Media TYPe ——————————————————————— 171
MZP — Move to Zero-relative Position ——————————————————— 173
NEWP — start NEW Path ———————————————————————— 175
OTRY — select paper Output TRaY————————————————————— 176
PAGE — start new PAGE ———————————————————————— 178
PANT — create PANTone color palette ———————————— ——————— 179
PARC — in Path, draw ARC ——————————————————————— 181
PAT — select fill PATtern ———————————————————————— 183
PCRP — in Path, Curve to Relative Position ————————————————— 185
PCZP — in Path, Curve to Zero-relative Position———————————————— 187
PDIR — set Print DIRection ———————————————————————— 189
PDRP — in Path, Draw to Relative Position —————————————————— 192
PDZP — in Path, Draw to Zero-relative Position ———————————————— 194
PELP — in Path, draw ELlipse ——————————————————————— 196
PIE — draw PIE chart —————————————————————————— 198
PMRA — in Path, Move to Relative position specified by Angle ————————— 200
PMRP — in Path, Move to Relative Position ————————————————— 202
PMZP — in Path, Move to Zero-relative Position———————————————— 204
PNCH — PuNCH ———————————————————————————— 206
PRBX — in Path, draw Round BoX ————————————————————— 208
PRRC — in Path, at Relative position, draw aRC———————————————— 210
PSRC — select Paper SouRCe ——————————————————————— 212
PXPL — PiXel PLacement ————————————————————————
213
!R! — PRESCRIBE start sequence ————————————————————— 214
RCLT — Rotated CoLlaTion———————————————————————— 216
RDMP — Received-data DuMP ——————————————————————
217
RES — RESet ————————————————————————————— 219
RESL — select RESoLution ———————————————————————— 221
RGBL — control RGB Level ——————————————————————— 222
RGST — offset ReGiSTration ——————————————————————— 224
RPCS — Return to Previous Code Set ———————————————————— 225
RPF — Return to Previous Font —————————————————————— 226
RPG — Return to Previous Graphics state —————————————————— 227
RPP — Return to Previous Position ————————————————————— 229
RPPL — Return to Previous PaLette————————————————————— 231
RPU — Return to Previous Unit —————————————————————— 232
RTTX — RoTate TeXt —————————————————————————— 233
RTXT — print Right-aligned TeXT ————————————————————— 235
RVCD — ReceiVe Compressed raster Data —————————————————— 237
RVCL — ReceiVe CoLor raster data
———————————————————— 238
RVRD — ReceiVe Raster Data —————————————————————— 239
RWER D — [Read/Write External Resource] Delete data on external media ————— 241
RWER F — [Read/Write External Resource] Form
at external media ———————— 242
RWER I — [Read/Write External Resource] automatically print partition Information — 243
RWER L — [Read/Write External Resource] print partition List—————————— 244
RWER R — [Read/Write External Resource] Read data from external media————— 245
RWER S — [Read/Write External Resource] Store TrueType font ————————— 246
RWER T — [Read/Write External Resource] set
RWER W — [Read/Write External Resource] Write data to
Terminate string ————————— 248
external media ————— 249
RWRF D — [Read/Write Resource File] Delete data on external device————— —— 251
RWRF F — [Read/Write Resource File] Format ex
ternal device—————————— 252
RWRF L — [Read/Write Resource File] print resource file List —————————— 253
RWRF P — [Read/Write Resource File] set hidden file ————————————— 254
RWRF R — [Read/Write Resource File] Read————————————————— 255
Contents—iii
Page 8

RWRF T — [Read/Write Resource File] set Terminate string —————————— 256
RWRF W — [Read/Write Resource File] Write data to external device (API program) 257
RWRF W — [Read/Write Resource File] Write data
to external device (font) ———— 258
RWRF W — [Read/Write Resource File] Write data to external device (macro) ——— 260
RWRF W — [Read/Write Resource File] Write data to external device (printable data) 261
SATU — adjust SATUration level ————————————————————— 262
SBM — Set Bottom Margin ——————————————————————— 263
SCAP — Set line CAP ————————————————————————— 265
SCCS — Save Current Code Set ————————————————————— 267
SCF — Save Current Font ———————————————————————— 269
SCG — Save Current Graphics state ———————————————————— 271
SCOL — Select COLor ————————————————————————— 273
SCP — Save Current Position —————————————————————— 274
SCPI — Set Characters Per Inch —————————————————————— 275
SCPL — Save Current PaLette —————————————————————— 277
SCRC — Set Command Recognition Character ———————————————— 278
SCS — Set Character Spacing——————————————————————— 280
SCSZ — Set Custom paper SiZe—————————————————————— 281
SCU — Save Current Unit ———————————————————————— 282
SDP — Store Dash Pattern ———————————————————————— 284
SEM — Set Emulation Mode ——————————————————————— 286
SETF — SET alternate Font ——————————————————————— 287
SFA — Set bitmap Font Attributes ————————————————————— 289
SFNT — Select current FoNT by typeface —————————————————— 293
SGPC — Set kcGl Pen Color ——————————————————————— 296
SHMI — Set HMI ——————————————————————————— 297
SIMG — Set IMaGe model ——————————————————————— 298
SIMP — create SIMPle color palette ———————————————————— 301
SIR — Set Image Refinement level ———————————————————— 303
SLJN — Set Line JoiN ————————————————————————— 304
SLM — Set Left Margin ————————————————————————— 306
SLPI — Set Lines Per Inch ———————————————————————— 308
SLPP — Set Lines Per Page ——————————————————————— 309
SLS — Set Line Spacing ———————————————————————— 311
SMLT — Set Miter LimiT ———————————————————————— 312
SMNT — Set MoNiTor simulation————————————————————— 314
SPAL — Select PALette ————————————————————————— 316
SPD — Set Pen Diameter ———————————————————————— 317
SPL — Set Page Length ————————————————————————— 319
SPO — Set Page Orientation ——————————————————————— 321
SPSZ — Set Paper SiZe ————————————————————————— 323
SPW — Set Page Width ————————————————————————— 325
SRM — Set Right Margin ———————————————————————— 327
SRO — Set Raster Options ———————————————————————— 329
SROP — Set Raster OPeration —————————————————————— 331
SSTK — select Sorter STacKer —————————————————————— 333
STAK — select paper STAcKer —————————————————————— 334
STAT — STATus ——————————————————————————— 335
STM — Set Top Margin ————————————————————————— 337
STPC — set STaPle Counter ——————————————————————— 339
STPL — STaPLe ———————————————————————————— 340
STR — SeT dot Resolution ——————————————————————— 342
STRK — STRoKe current path —————————————————————— 343
SULP — Set UnderLine Parameters ———————————————————— 345
TATR — apply Tray ATtributes—————————————————————— 347
TEXT — print TEXT —————————————————————————— 348
TPRS — Text PaRSing ————————————————————————— 350
Contents—iv
Page 9

TRSM — TRansparency Separate Mode ——————————————————— 351
UNIT — set UNIT of measurement ————————————————————— 352
UOM — Unit Of Measurement per dots ——————————————————— 354
VMAL — Virtual Mailbox ALias—————————————————————— 356
VMOB — Virtual Mailbox Output Bin———————————————————— 357
VMPW — set Virtual Mailbox PassWord——————————————————— 358
WIDE — set WIDE A4 mode ——————————————————————— 360
WRED — WRite EnD —————————————————————————— 361
XBAR — print two dimensional barco de ——————————————————— 362
XBCP 0 — select barcode type/reset all other XBCP parameters—————————— 364
XBCP 1 — specify narrowest element width ————————————————— 365
XBCP 2 — specify error correction level by percentage ————————————— 366
XBCP 3 — set error correction level ————————————————————— 367
XBCP 4 — set data code word rows ————————————————————— 368
XBCP 5 — set data code word columns ——————————————————— 369
XBCP 6 — determine aspect ratio of vertical height and horizontal width —————— 370
XBCP 7 — determine bar height —————————————————————— 372
XBCP 8 — automatically set rows and columns ———————————————— 373
XBCP 9 — enable truncation———————————————————————— 374
XBCP 10 — enable file name ——————————————————————— 375
XBCP 11 — enable block count —————————————————————— 376
XBCP 12 — enable time stamp——————————————————————— 377
XBCP 13 — enable sender ID ——————————————————————— 378
XBCP 14 — enable addressee ID —————————————————————— 379
XBCP 15 — enable file size ———————————————————————— 380
XBCP 16 — enable checksum ——————————————————————— 381
XBCP 17 — allow control of file ID ————————————————————— 382
XBCP 18 — enable Macro PDF417 symbol mode ——————————————— 384
XBCP 19 — position symbols at the specif
XBUF — define a BUFfer name —————————————————————— 390
XPAT — generate eXpanded fill PATtern —————————————————— 392
ied locations ————————————— 386
Index Index - 1
Contents—v
Page 10

Contents—vi
Page 11

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
Page 12

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
1. Overview of PRESCRIBE Commands by Function
The tables in this section list all the printing system commands supported by the various
models. Support for certain commands varies depending on the printing system model.
Access Commands
These commands provide access in and out of PRESCRIBE mode.
Command Function Page
EXIT EXIT from PRESCRIBE mode 99
!R! PRESCRIBE start sequence 214
SCRC Set Command Recognition
Print System Setting Commands
Character 278
These commands establish general printing environment parameters.
Command Function Page
COPY set number of COPIES 61
EPL select EcoPrint Level 98
FDIR MP tray Feed DIRection 100
FRPO Firmware RePrOgram 112
FRPO INIT FRPO-INITialize 114
MDAT set MeDia type ATtribute 162
MTYP select Media TYPe 171
OTRY select paper Output TRaY 176
PSRC select Paper SouRCe 212
RCLT Rotated CoLlaTion 216
RES RESet 219
RESL select RESoLution 221
RGST offset ReGiSTration 224
RPU Return to Previous Unit 232
SCSZ Set Custom paper SiZe 281
SCU Save Current Unit 282
SEM Set Emulation Mode 286
SIR Set Image Refinement level 303
SPSZ Set Paper SiZe 323
ST AK select paper STAcKer 334
ST AT STAT us 335
TRSM TRansparency Separate Mode 351
UNIT set UNIT of measurement 351
UOM Unit Of Measurement per dots 354
WIDE set WIDE A4 mode 360
2
Page 13

Overview of PRESCRIBE Commands by Function
Page Control, Text, and Comment Commands
The placement commands determine where text will be placed on the page.
Command Function Page
CMNT CoMmeNT 59
CTXT print Centered TeXT 69
PAGE start new PAGE 178
RTTX RoTate TeXt 233
RTXT print Right-aligned TeXT 235
TEXT print TEXT 347
Margin and Page Portrait/Landscape Orientation Commands
These commands are used to set the top, bottom, right, and left margins, and to specify
portrait or landscape page orientation. Normal text data is printed inside the margins, but
the TEXT and RTEXT commands can be used to print character strings or graphics
anywhere in the entire printable area of the page, regardless of the margin settings. There
are several commands for setting margins, so it is possible to select the one that best suits
the purpose at hand. Margin settings can be changed in the middle of a page.
Note that the following limitations apply to the margin setting commands.
• The right margin must be at least one space character to the right of the left margin.
• The bottom margin must be at least one line below the top margin.
• It is not possible to specify negative values as margin settings.
For example, a right margin setting beyond the printable area’s right edge would be
brought back just inside the right edge of the printable area. In like manner, it is not
possible to use a bottom margin setting that would place the bottom margin past the
bottom edge of the printable area. An easy way to set the right and bottom margins to the
very edge of the printable area is to use a large value such as 100 (centimeters).
The margins and page orientation can be reset by using the RES command.
Command Function Page
SBM Set Bottom Margin 263
SLM Set Left Margin 306
SLPP Set Lines Per Page 309
SPL Set Page Length 319
SPO Set Page Orientation 321
SPW Set Page Width 325
SRM Set Right Margin 327
STM Set Top Margin 337
Margins and page orientation are more full
Reference manual.
y explained in Section 1.3. of the Technical
3
Page 14

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
Text Spacing Commands
These commands control the line spacing, character spacing, underline spacing, and
underline thickness. The SLS and SLPI commands are used to set the line spacing. Th e
SCS and SCPI commands are used to set the character spacing. These spacing settings
may be changed even in the middle of a page.
The table below lists the minimum, maximum, and default values for the text spacing
command parameters. If values outside of the above ranges are used, the command is
ignored. If a value smaller than one dot is specified for the character spacing, it is
interpreted as 0, which results in proportional spacing.
Line spacing 1 dot
Character spacing 1 dot
Minimum value Maximum value Default value
0.01 cm
0.004 inch
0.01 cm
0.004 inch
2,047 dots
17.3 cm
6.8 inch
2,047 dots
17.3 cm
6.8 inch
6 lpi
0.423 cm
0.167 inch
10 cpi
0.254 cm
0.1 inch
Using the font mode (FTMD command), the line spacing
set automatically when the bitmap fonts are selected. Refer to the sections on the FTMD
and SFA commands for additional details.
Command Function Page
SCPI Set Characters Per Inch 275
SCS Set Character Spacing 280
SHMI Set HMI 297
SLPI Set Lines Per Inch 308
SLS Set Line Spacing 311
SULP Set UnderLine Parameters 345
Font Commands
The font commands are used to select fonts. Fonts can be selected using substitute
numbers instead of a font’s specific number. It is also possible to change the attributes of
fonts and print them in a unique style. Additionally, there are commands to download
fonts to the printing system from an external source, and to generate fonts.
Command Function Page
ALTB A [ALlocate TaBle] Assign user-defined character table 14
ALTB C [ALlocate TaBle] Convert character
ALTB D [ALlocate TaBle] Delete user-defined character table 16
ALTB E [ALlocate TaBle] End defining combination
ALTB G [ALlocate TaBle] Generate user
ALTB R [ALlocate TaBle] Release user-defined character table 19
ALTB S [ALlocate TaBle] Start to define th e combination character 20
ALTB T [ALlocate TaBle] define combined character by Table 21
ALTF change to ALTernate Font 23
ASFN ASsign external characters for FoNt 31
and character spacing can be
code 15
characters 17
-defined table 18
4
Page 15

Overview of PRESCRIBE Commands by Function
Command Function Page
CSET Change symbol SET by symbol-set ID 65
DAF Delete All Fonts 71
DELF DELete Font 75
FLST print Font LiST 105
FONT change current FONT 108
FSET change current Font SETting by characteristic 115
FTMD bitmap FonT MoDe 119
INTL InterNaTionaL characters 129
LDFC LoaD Font Character 147
LDFN C generate bitmap character f
LDFN F create header for LoaDing FoNt 151
LDFN S LoaD truetype FoNt 153
RPCS Return to Previous Code Set 225
RPF Return to Previous Font 226
SCCS Save Current Code Set 267
SCF Save Current Font 269
SETF SET alternate Font 287
SFA Set bitmap Font Attributes 289
SFNT Select current FoNT by
TPRS Text PaRSing 350
or LoaDing FoNt 149
typeface 293
Fonts are more fully explained in Chapter 4 of the Technical Reference manual.
Cursor Movement Commands
These commands move the cursor to specific positions. Cursor movements can be
established for absolute positions based on the margins, zero point positions based on the
printable area, or relative positions based on the current cursor position.
Cursor movement commands only change the position of the cursor. Also, the cursor
may not be moved outside of the printable area (see MZP command). It is possible to
store the cursor position in memory then to return to that position stored in memory.
Command Function Page
MAP Move to Absolute Position 157
MRP Move to Relative Position 166
MRPA Move to Relative Position specified by Angle 168
MZP Move to Zero-relative Position 173
RPP Return to Previous Position 229
SCP Save Current Position 274
Vector Graphics Commands
The commands below are used to create figures such as lines, circles, and rectangles, and
to add shading, simply by adding parameters.
It is possible to specify colors for all vector graphics. For details, see a color specific
command such as SCOL.
5
Page 16
PRESCRIBE Command Reference
Print settings according to command
Actual printed result
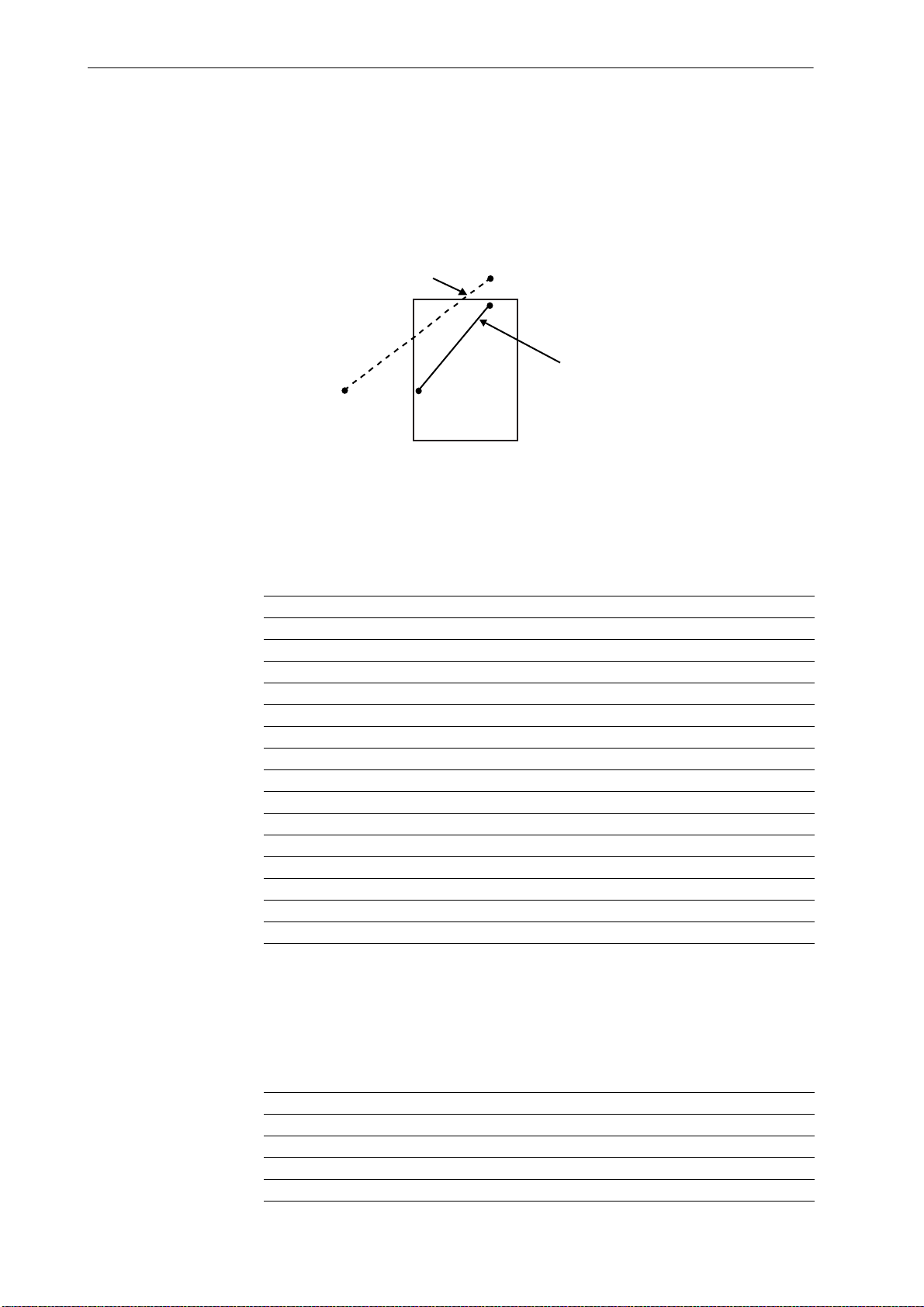
If an attempt is made to create figures outside of the printable area using these
commands, the coordinates are adjusted automatically so that the figures print inside the
printable area. As in the example below, this can produce printed results different from
what is expected.
Printing extremely complex figures can exhaust printing system memory. Downloadable
fonts can be particularly taxing on printing system memory, producing unexpected print
results. It may be possible to correct the problem by removing some of the downloaded
fonts or by simplifying the graphic. To determine current memory usage, refer to a status
page.
Command Function Page
ARC draw filled-in ARC 28
BLK draw filled-in BLocK 40
BOX draw BOX 42
CIR draw CIRcle 52
DAP Draw to Absolute Position 73
DPAT select Dashed PATtern 78
DRP Draw to Relative Position 80
DRPA Draw to Relative Position specified by Angle 82
DZP Draw to Zero-relative Position 87
FPAT generate Fill PATtern 110
GPAT set Gray PATtern 122
PAT select fill PATtern 183
PIE draw PIE chart 198
SPD Set Pe n Diam eter 317
XPAT generate eXpanded fill PATtern 392
Path Mode Graphics Commands
The following commands provide a variety of path construction operators and painting
operators for stroking or filling paths.
6
Command Function Page
CLIP CLIP current path 54
CLPR CLiP Rectangular area 55
CLSP CLoSe Path 57
CPTH Character PaTH 64
Page 17

Overview of PRESCRIBE Commands by Function
COLOR
Command Function Page
FILL FILL closed path 101
FLAT set FLATness 104
NEWP start NEW Path 175
PARC in Path, draw ARC 181
PCRP iin Path, Curve to Relative Position 185
PCZP in Path, Curve to Zero-relative Position 187
PDIR set Print DIRection 189
PDRP in Path, Draw to Relative Position 192
PDZP in Path, Draw to Zero-relative Position 194
PELP in Path, draw ELlipse 196
PMRA in Path, Move to Relative po
PMRP in Path, Move to Relative Position 202
PMZP in Path, Move to Zero-relative Position 204
PRBX in Path, draw Round BoX 208
PRRC in Path, at Relative position, draw
RPG Return to Previous Graphics state 227
SCAP Set li ne CAP 265
SCG Save Current Graphics state 271
SDP Store Dash Pattern 284
SIMG Set IMaGe model 297
SLJN Set Line JoiN 304
SMLT Set Miter LimiT 312
STRK STRoKe current path 343
sition specified by Angle 200
aRC 210
Raster Graphics Commands
Raster graphics commands can be used to draw any graphic design by specifying the
individual dots. The dot resolution is selectable from 75, 100, 150, 200, 300, 600, and
1200 dots per inch.
Command Function Page
ENDR END Raster data 96
PXPL PiXel PLacement 213
RVCD ReceiVe Compressed raster Data 237
RVRD ReceiVe Raste r Data 239
SRO Set Raster Options 329
SROP Set Raster OPeration 331
STR SeT dot Resolution 342
Color Commands
Color commands are used to create a color palette, assign colors to a palette, and specify
colors. In this manual, color commands are marked with under the command
name.
7
Page 18

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
Command Function Page
ACLI Add CoLor by Index 12
CID Configure color-Image Data 50
CMOD Color MODe 60
CPAL Control PALette 63
GRAY represent GRAY 124
GRRD GRaphic data ReaD 125
HUE adjust HUE 127
LGHT adjust LiGHTness 155
MCLR Match CoLoR 159
PANT create PANTone color palette 179
RGBL control RGB Level 222
RPPL Return to Previous PaLette 231
RVCL ReceiVe CoLor raster data 238
SATU adjust SATUration level 262
SCOL Select COLor 273
SCPL Save Current PaLette 277
SGPC Set kcGl Pen Color 296
SIMP create SIMPle color palette 301
SMNT Set MoNiTor simulation 314
SPAL Select PALette 316
Barcode Commands
Barcodes conforming to various specifications can be printed simply by specifying the
type of barcode and the barcode data. It is also possible to print barcodes with check
digits added.
Command Function Page
BARC draw BARCode 34
ENDB END a two-dimensional Barcode string 91
XBAR print two dimensional barcode 362
XBCP select barcode type/reset all other
XBUF define a BUFfer name 390
Macro Commands
A series of PRESCRIBE commands can be defined for sequential processing as a macro.
Macros are selected using the CALL command and automatically using the AMCR
command.
Command Function Page
AMCR call Automatic MaCRo 25
CALL CALL macro 44
CCPY Carbon CoPY 46
XBCP parameters, etc. 364 to 386
8
Page 19

Command Function Page
DAM Delete All Macros 72
DELM DELete Macro 76
EMCR Enable MaCRo depending on paper source 89
ENDC END carbon Copy 92
ENDM END Macro 94
MCRO define MaCRO 160
Debug Commands
These commands can be used to check the print data in hexadecimal format for print jobs
with unexpected output.
Command Function Page
ENDD END Dump 93
RDMP Received-data DuMP 217
Overview of PRESCRIBE Commands by Function
External Media Control Commands
If an external storage, such as JEIDA Ver. 4 memory card or CompactFlash card, or a
hard disk, is installed in the printing system, the following commands can be used to
write data to or read from it. These commands do not apply to the models that do not
have an external storage.
Command Function Page
RWER D [Read/Write External Resource] Delete data on external media 241
RWER F [Read/Write External Resource
RWER I [Read/Write External Resource] automatically print partition Infor-
RWER L [Read/Write External Resource] print partition List 244
RWER R [Read/Write External Resource] Read
RWER S [Read/Write External Resource] S
RWER T [Read/Write External Resource] set Terminate string 248
RWER W [Read/Write External Resource] Write data to external media 249
RWRF D [Read/Write Resource
RWRF F [Read/Write Resource File] Format external device 252
RWRF L [Read/Write Resource
RWRF P [Read/Write Resource File] set
RWRF R [Read/Write Resource File] Read 255
RWRF T [Read/Write Resource File] set
RWRF W [Read/Write Resource File] Write data to external device (API pro-
RWRF W [Read/Write Resource File] Write data to external device (font) 258
RWRF W [Read/Write Resource File] Write data to external device (macro) 260
RWRF W [Read/Write Resource File] Write data to external device (printable
WRED WRite EnD 361
mation
File] Delete data on external device 251
File] print resource file List 253
gram)
data)
] Format external media 242
243
data from external media 245
tore TrueType font 246
hidden file 254
Te rminate string 256
257
261
9
Page 20

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
Control Commands for Option Devices
A variety of options, such as feeders, sorters, document finishers, etc., are available for
print systems. The commands below provides access to the optional equipment.
Command Function Page
APSG Assign Paper Source Group 27
ASTK Assign STacKer trays 32
BKLT print in BooKLeT binding 38
CSTK select Collator STacKer 68
DUPX select/deselect DUPleX mode 84
DXPG select DupleX PaGe side 85
FOLD FOLD printed pages 107
JOG JOG output stacks for separation 145
MID Multi-tray ID 164
MSTK select Mailbox STacKer 170
PNCH PuNCH 206
SSTK select Sorter STacKer 333
STPC set STaPle Counter 339
STPL STaPLe 340
e-MPS Commands
The printing system features various job storing options – e-MPS (enhanced Multiple
Printing System) – that utilize the hard disk. For this feature to be performed, a print job
must be defined as an e-MPS job by the JOBS command. Once the job is defined and
stored in the hard disk by the JOBS command, it can be retrieved from the hard disk for
printing with various printing features such as stapling, duplex-printing, mai lboxing,
etc., added on the fly.
Command Function Page
CDSK Check hard DiSK 49
JOBD JOB Deletion 132
JOBL print JOB List 134
JOBO JOB Output 136
JOBP JOB, print with Print options 138
JOBS JOB Start 140
JOBT JOB Terminate 144
MPSS e-MPS Storage 165
VMAL Virtual Mailbox ALias 356
VMOB Virtual Mailbox Output Bin 357
VMPW set Virtual Mailbox PassWord 358
10
Page 21

2. PRESCRIBE Commands
In the command format descriptions below, the command is written in fixed-pitch
CAPITAL letters. Parameters are indicated in lowercase italics. Optional parameters,
which may be omitted, are enclosed in brackets [ ]. Three dots (...) mean that the
preceding parameters may be repeated. Except for the initial !R!, PRESCRIBE
commands may be written in lowercase letters if preferred.
Example:
!R! SFNT ’Helvetica’; EXIT;
Refer to Chapter 1 of the Technical Reference manual for the discussion on how
PRESCRIBE follows the rule regarding upper- and lowercase letters.
The functions of some PRESCRIBE commands are duplicated by the panel keys. For
example, the same status page can be printed by the STAT command or by pressing the
panel keys. The User’s Manual provides a full description of the control panel functions.
Many PRESCRIBE commands can be embedded commands within word processing
software. This support depends upon the emulation mode and the software. See
Emulation of the Technical Reference manual.
PRESCRIBE Commands
11
Page 22

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
COLOR
ACLI — Add CoLor by Index
Format
ACLI index, color1, color2, color3;
Parameters
index:
integer from 1 to 255
color1:
value for red, integer from 0 to 255, in RGB color space
value for lightness, number from 0.0 to 100.0, in L*a*b color space
color2:
color3:
Function
value for green, integer from 0 to 255, in RGB color space
value for red/green, number from 0.0 to
value for blue, integer from 0 to 255, in RGB color space
value for yellow/blue, number from 0.0 to 100.0, in L*a*b color space
The ACLI command adds a color to the currently active palette. This command is
ignored when the currently active palette is a simple color palette or the Pantone color
palette. If an index number larger than the palette size is given, this command is also
ignored. If a color is added to the existing index number, the current color for that index
number is automatically replaced with the new color.
T o add a color in a palette, the following guidelines must be used depending on the color
space used:
For RGB color space, specify the values for red, green, and blue with an integer from 0
to 255, where 0 = 0% and 255 = 100%. Any value outside this range is rounded to the
minimum or maximum value, namely 0 or 255. A fractional value beyond the decimal
point is discarded.
100.0, in L*a*b color space
For L*a*b color space, specify relative values for the lightness, red/green, and yellow/
blue with a number from 0.0 to 100.0. Any value outside this range is rounded to the
minimum or maximum value, namely 0.0 or 100.0.
12
Page 23
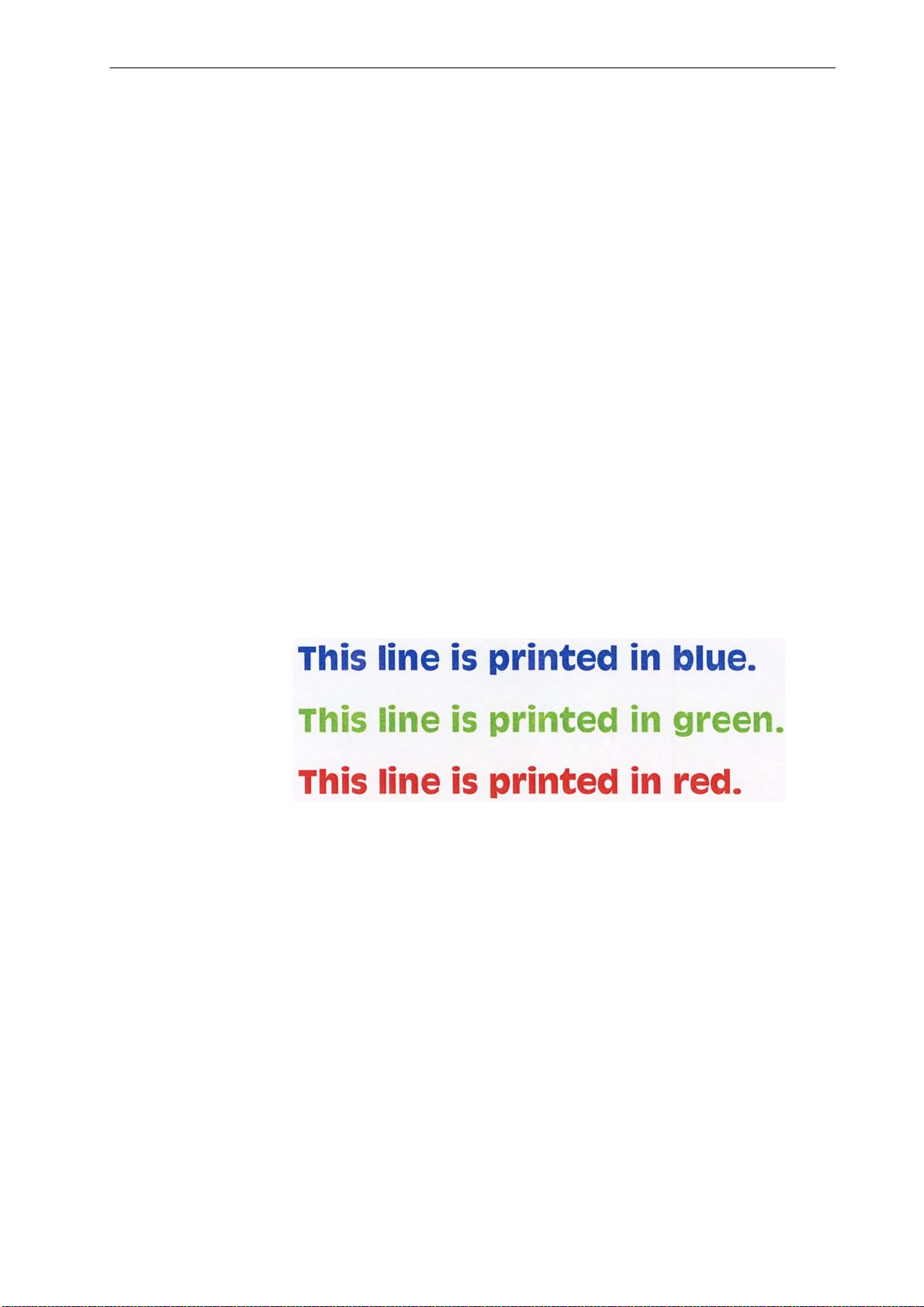
File
ACLI
!R! RES;
DAM;
UNIT C;
SFNT ’AntiqueOlive-Bd’, 20;
CPAL C; SPAL 1; CID 0, 1;
ACLI 1, 0, 0, 255;
ACLI 2, 0, 255, 0;
ACLI 3, 255, 0, 0;
MZP 1, 1; SCOL 1;
TEXT ’This line is printed in blue.’;
MZP 1, 2.4; SCOL 2;
TEXT ’This line is printed in green.’;
MZP 1, 3.8; SCOL 3;
TEXT ’This line is printed in red.’;
EXIT;
Printout
Related Commands
CPAL, SPAL
13
Page 24

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
ALTB A — [ALlocate TaBle] Assign user-defined
character table
Format
ALTB A, table-id;
Parameter
table-id:
number identifying the character table assigned to the resident font, from 1 to 65535
Function
The ALTB A command assigns the user-defined character table to the current resident
font.
File
See ALTB C on page 15.
14
Page 25

ALTB C
ALTB C — [ALlocate TaBle] Convert character code
Format
ALTB C, table-id, source-character, target-character;
Parameters
table-id:
number identifying the character table to convert the character, from 1 to 65535
source-character:
character code before conversion: 1-byte code = 0 to 255; 2-byte code = 0 to 65533, or
in hexadecimal notation ($xxxx).
target-character:
character code after conversion: 1-byte code = 0 to 255; 2-byte code = 0 to 65533, or in
hexadecimal notation ($xxxx).
Function
The ALTB C command converts the character code given as source-character to the
character code given as target-character in the user-defined character table.
If the character table having the identical number already exists, the existing character
table is replaced by the new character table.
File
In the example below, the character table number 56535 is generated by ALTB G, in
which the character ‘‘\ (backslash, character code 92)’’ is replaced with the Euro
currency symbol ‘‘a (character code 186 for Roman-9 symbol set).’’
!R!
SFNT "TimesNewRoman", 14;
CSET 4U; CMNT Roman-9;
ALTB G, 56535, 1;
ALTB C, 56535, 92, 186;
ALTB A, 56535;
TEXT "The Euro currency is symbolized as \.";
ALTB R, 56535; CMNT Release user table;
PAGE; EXIT;
Printout
15
Page 26

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
ALTB D — [ALlocate TaBle] Delete user-defined
character table
Format
ALTB D, table-id;
Parameter
table-id:
number identifying the character table, from 1 to 65535, to be deleted
Function
The ALTB D command deletes the character table defined by the user.
If the table to be deleted is currently allocate
terminate the allocation by using ALTB R before deleting. It is possible to delete all userdefined character tables at once by using ALTB D, 0;.
File
See ALTB C on page 15.
Related Commands
ALTB A, ALTB R
d to the resident font (see ALTB A),
16
Page 27

ALTB E — [ALlocate TaBle] End defining
combination characters
Format
ALTB E;
Parameter
None
Function
This command signals the end of defining combination characters in an already
generated user-defined character table which was started by the ALTB S command.
(page 20). The registered combined characters can be printed by specifying the character
code which was assigned at the time of definition.
ALTB E
Related Command
ALTB S
17
Page 28

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
ALTB G — [ALlocate TaBle] Generate user-defined
table
Format
ALTB G, table-id, table-format;
Parameters
table-id:
table ID number: 1 to 65535
table-format:
1 = 1-byte, character codes 0 to 255
2 = 2-byte, character codes 0 to 65533
Function
The ALTB G command generates a user-defined table in either 1-byte or 2-byte form at.
If the same table ID number already exists, the format table is replaced with the newly
generated table.
18
Page 29

ALTB R
ALTB R — [ALlocate TaBle] Release user-defined
character table
Format
ALTB R, table-id;
Parameter
table-id:
number identifying the character table to be released
Function
The ALTB R command terminates the assignment of the user-defined character table for
the current resident font. It is also possible to terminate the assignment of all userdefined character tables by using ALTB R, 0;.
19
Page 30

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
ALTB S — [ALlocate TaBle] Start to define the
combination character
Format
ALTB S, table-id, code[, width, height[[, x-coordinate, y-coordinate,
[paint-mode]]];
Parameters
table-id:
number identifying the character table to define the combination character, from 1 to
65535
code:
character code for which the combination character is defined. 1-byte code = 0 to 255;
2-byte code = 0 to 65533, or in hexadecimal notation ($xxxx).
width:
overall width of the combined character, represented by number from 1 to 65535 in units
where the width of the resident font character is 1000
height:
overall height of the combined character, represented by number from 1 to 65535 in units
where the height of the resident font character is 1000
x-coordinate:
X coordinate of the reference point, integer value converted in reference to 1000 units
y-coordinate:
Y coordinate of the reference point, integer value converted in reference to 1000 units
paint-mode:
paint mode: 0 = normal (filled), non-zero = line width of outline character (stroked):
1 to 100 units
Function
This command starts to define the combination of characters by specifying the region
and coordinates. The characters to combine in this region are registered using the
ALTB T command (page 21). The ALTB S sequence is terminated by the ALTB E
command. If the identical table number already exists, the existing character table is
replaced with the new character table.
20
Page 31

ALTB T — [ALlocate TaBle] define combined
(1000, 1000)
(0, 0)
Y
character by Table
Format
ALTB T, character-code, width, height, x-coordinate, y-coordinate;
Parameters
code:
character code for which the combined character is defined, or hexadecimal notation
($xxxx), JIS code
width:
character width: the value from 1 to the character width specified by ALTB S
(page 20)
ALTB T
height:
character height: the value from 1 to the character height specified by ALTB S
(page 20)
x-coordinate:
X coordinate of the reference point, integer value calculated in 1000 unit basis
y-coordinate:
Y coordinate of the reference point, integer value calculated in 1000 unit basis
Function
This command defines the region in which to store the combination of characters within
coordinates (0, 0) to (1000, 1000) by specifying a rectangular area and reference point
for the characters. There are no restrictions on the number of characters to be combined.
Example:
21
Page 32

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
File
!R! res; unit c;
SFNT ’TimesNewRoman’, 48;
ALTB G, 1000, 1;
ALTB A, 1000;
ALTB S, 1000, 64, 1800, 1000;
ALTB T, 77, 700, 700, 0, 700; CMNT M;
ALTB T, 65, 700, 700, 630, 700; CMNT A;
ALTB T, 85, 700, 700, 1050, 700; CMNT U;
ALTB T, 73, 700, 700, 1570, 700; CMNT I;
ALTB T, 36, 700, 700, 0, 0; CMNT $;
ALTB T, 57, 700, 700, 400, 0; CMNT 9;
ALTB T, 57, 700, 700, 800, 0; CMNT 9;
ALTB T, 57, 700, 700, 1200, 0; CMNT 9;
ALTB E;
MZP 2, 4; SFNT ’TimesNewRoman’,48; TEXT "HOLIDAYS!";
PAGE; EXIT;
Printout
22
Page 33

ALTF — change to ALTernate Font
Format
ALTF alternate-number;
Parameter
alternate-number: a number from 0 to 47
Function
The ALTF command changes the current font to a font designated by an alternate
number. The actual font assigned to this alternate number is set by a previous SETF
command.
The alternate number can be a bitmap font number or a number specifically assigned to
the scalable font using the SFNT command (See File on the next page).
ALTF
If no font has been assigned to the specified alternate number, the ALTF command has
no effect: the font does not change.
The ALTF command enables you to prepare a document usi ng several fonts, without
deciding in advance which specific fonts to use. For example, you could use ALTF 1 to
designate plain text and AL TF 2 to designate italics, and allow the specific size and style
of type to be determined by SETF commands at a later time.
23
Page 34

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
File
!R! RES;
SFNT "Helvetica-Nr", 12, 1000;
SFNT "TimesNewRoman-It", 11, 1001;
SETF 1, 1000;
SETF 2, 1001;
MCRO BIBLIO;
ALTF 1; TEXT %1, E; TEXT " ", E;
ENDM;
ALTF 1; TEXT "Bibliography", N, U;
TEXT, N;
CALL BIBLIO,
"Radin, Paul,",
CALL BIBLIO,
CALL BIBLIO,
PAGE;
EXIT;
ALTF 2; TEXT %2, E; TEXT " ", E;
ALTF 1; TEXT %3, N;
"Hero Cycles of the Winnebago,",
"Indiana University Publications";
"Neumann, Erich,",
"Amor and Psyche,", "Bollingen Press";
"Jung, Carl G.,", "Man and His Symbols,",
"Bollingen Press";
Printout
24
Page 35

AMCR — call Automatic MaCRo
Format
AMCR mode, [repeat-count] macro-name, parameter, ...;
Parameters
mode:
E = Enable automatic macro; Save and retain current printing parameters
T = Enable automatic macro; Do not save current printing parameters
D = Disable automatic macro
repeat-count:
number of times the macro is executed
AMCR
macro-name:
name defined by the MCRO command
parameter:
values given to the dummy parameters in the macro definition
Function
The AMCR command enables the automatic macro (overlay). It automatically executes
the macro defined by a MCRO command each time a page is printed. For example, it
would be used to print multiple copies of the same form, filled in with different text.
The AMCR command closely resembles the CALL command; therefore, the user should
refer to the section on the CALL command for further information.
When the automatic macro is enabled using mode E, the following printing system
settings are saved and retained upon completion of the macro: font information, margins,
cursor position, line spacing, character spacing, page orientation, unit of measurement,
underline parameters, and fill pattern.
When the automatic macro is enabled with mode T, the printing system settings are
modified according to the parameter settings contained in the macro.
Color specifications may be used within macros. When an auto-macro (AMCR) is
executed, the active palette and color index number are saved and restored after the
macro has executed.
The automatic macro remains enabled until the AMCR command with the mode set to D
is encountered or the printing system is switched off. Note that mode D requires no other
parameters such as repeat-count.
The following commands are invalid within a macro: ASTK, PSRC, CCPY, DUPX,
DXPG, JOBD, JOBL, JOBO, JOBP, JOBS, JOBT, JOG, LDFC, LDFN, MID, MSTK,
RDMP, SEM, SPSZ, SSTK, STAK, STAT, STPL, VMAL, VMPW
25
Page 36

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
File
!R! RES;
MCRO CROPMARK;
UNIT C;
MZP 2.46, 3.96; SCP; SCP; SCP;
MRP -.635, 0; DRP -1.9, 0; RPP;
MRP 0, -.635; DRP 0, -1.9; RPP;
MRP 14.85, 0; SCP; SCP;
MRP .635, 0; DRP 1.9, 0; RPP;
MRP 0, -.635; DRP 0, -1.9; RPP;
MRP 0, 21; SCP; SCP;
MRP .635, 0; DRP 1.9, 0; RPP;
MRP 0, .635; DRP 0, 1.9; RPP;
MRP -14.85, 0; SCP;
MRP -.635, 0; DRP -1.9, 0; RPP;
MRP 0, .635; DRP 0, 1.9;
RPP;
ENDM;
AMCR E, CROPMARK;
PAGE; UNIT C; SLM 3.6; STM 5.2; EXIT;
The text starts here.
Printout
Related Command
CCPY
26
Page 37

APSG — Assign Paper Source Group
Format
APSG group # (cassette 1), group # (cassette 2), ...group # (cassette 6);
Parameters
group #:
Number representing the group to which the cassette is grouped, from the top (1) towards
the bottom (6) cassette, as the following numbers:
0 = Ungroup the cassette
1 = Assign the cassette for group 1
2 = Assign the cassette for group 2
3 = Assign the cassette for group 3
APSG
Function
Example
The APSG command assigns the paper cassettes with group numbers, between 1 through
3, so that the grouped cassettes behave as a single paper source for bulk printing. The MP
tray cannot be assigned to a group. All 6 parameters must be given even though the
printer has less than 6 cassettes installed. For missing cassette numbers, specify 0.
The printing system will automatically switch between the paper cassettes in the group
when a cassette becomes empty. When a group contains paper of different paper sizes
and types, printing will continue for the different paper sizes and types.
If the automatic paper selection feature of the printer driver is used, APSG is disabled.
T o utilize paper source grouping, the paper source must be explicitly commanded by the
printer driver.
To set si x paper cassettes into gro up 1 (cassettes 1 and 4), group 2 (cassettes 2 and 5),
and group 3 (cassettes 3 and 6), respectively:
!R! APSG 1,2,3,1,2,3; EXIT;
In this example, when cassette 1 becomes empty, printing will continue using cassette 4
which is the other part of group 1.
The APSG sequence is valid after the printing system is switched off. To upgroup paper
cassettes, use parameter 0 as the following example:
!R! APSG 1,0,0,1,0,0; EXIT;
Paper cassettes of 2 and 5, and 3 and 6 are ungrouped, keeping paper cassettes 1 and 3
(group 1) intact.
27
Page 38

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
ARC — draw filled-in ARC
Format
ARC inner-radius, outer-radius, start-angle, end-angle;
Parameters
inner-radius:
inner radius of arc
outer-radius:
outer radius of arc
start-angle:
starting angle
end-angle:
Function
ending angle
The ARC command works in the standard graphics mode. It draws a filled-in arc-shaped
area extending from the inner radius to the outer radius, and from the starting angle to the
ending angle. The area is filled with the pattern designated by the previous PAT, FPAT, or
GPAT command. The starting and ending angles are specified in integer degrees
measured clockwise from the vertical. (Note that the PARC command measures the
angles from the positive x axis.) The cursor is located at the center of curvature of the
arc, and does not move.
If the inner radius is zero, the area has a pie-slice shape, and can be used to fill in one
sector of a pie chart.
If the inner and outer radii are nearly equal and the fill pattern is the all-black pattern
(PAT 1, for example), the result is a line arc. The line thickness is the difference between
the two radii, rather than the value designated by the SPD (set pen diameter) command.
The ARC command does not draw the boundary of the filled-in area.
28
Page 39

File
ARC
!R! RES; UNIT C;
MAP 5, 8;
PAT 52;
ARC 1, 2, -45, 45;
MAP 5, 10;
PIE 2, 0, 10, 20, 30;
ARC 0, 2, 0, 60;
PAT 20;
ARC 0, 2, 60, 180;
PAT 10;
ARC 0, 2, 180, 360;
PAT 1;
NEWP;
PMZP 4, 2;
PARC 4, 3, 1, 90, 270;
PARC 5, 4, 1, 180, 360;
PARC 6, 3, 1, 270, 90;
PARC 5, 2, 1, 0, 180;
STRK;
MRP 0.6, 1.1;
SFNT "Univers-Md";
TEXT "ARC";
PAGE; EXIT;
29
Page 40

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
Printout
Related Command
PARC
30
Page 41

ASFN — ASsign external characters for FoNt
Format
ASFN mode, font-number;
Parameters
mode:
A = assign external characters
R = release external characters
font-number:
number identifying the external character font: 1000 to 65535
ASFN
Function
The ASFN command assigns external characters which are defined by the user to the
current resident font. The external characters should be generated and downloaded in the
printing system as an external font by using the LDFC or LDFN command.
For the print systems supporting 2-byte font system, if the user-defined font is a 1-byte
code font, it is assigned to the current resident roman (ANK) font. If it is a 2-byte code
font, it is assigned to the current 2-byte font.
This command has no effect if the resident font is a bitmap font and the font to be
assigned is an outline font, or vice versa.
mode = R is used to release the current resident font from the external characters. Note
that it is necessary to release the external font assignment if you want to delete the
external font.
31
Page 42

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
ASTK — Assign STacKer trays
Format
ASTK tray1, tray2, tray3, ...;
Parameters
tray1, tray2, tray3, ...:
Number representing the tray in the optional sorter which becomes the last (bottom) tray
in each group, as counted from the top towards the bottom tray.
Function
The ASTK command assigns the sorter trays in groups so that the sorter can be shared
among the multiple users. Each parameter represents the last tray in each group of trays.
The maximum number of parameters must be equal to the number of the trays the sorter
is equipped with. By the factory default, the trays are grouped as the following table:
Group Sorter model
SO-6 SO-30 SO-60
1 1, 2 1, 2 1, 2
2 3, 4 3, 4 3, 4
3 5, 6 5, 6 5
4 7, 8 7, 8 —
59 to 159—
Equiv. ASTK command ASTK 2, 4, 6, 8; ASTK 2, 4, 6, 8; ASTK 2, 4;
The ASTK command is ignored if parameters include the value greater than the actual
number of trays. If the number of parameters is less than the maximum number of sorter
trays, the printing system automatically groups the remaining trays in one, making it the
last group. For example, the command sequence ASTK 2, 4, 6; is equivalent to ASTK 2,
4, 6, (bottom tray number);.
The tray group setting made by ASTK is stored indefinitely in the printing system’s
permanent memory while the power is off, or until it is changed by another ASTK
command. It is ignored in the normal sorter mode (FRPO S0, 0;) but the printing system
automatically sets up the previous tray group setting when the sorter is again switched to
the multiple environment mode (FRPO S0, 1; or FRPO S0, 2;).
32
Page 43

File
The following command sequence delivers print jobs to trays 4, 5, 6, and 7 (the second
group).
!R! FRPO S0, 1; CMNT Enter multiple sorter mode;
ASTK 3, 7, 9; CMNT Create three groups;
MID 2; CMNT Send the output to 2nd grp.;
SSTK; CMNT Sort;
EXIT;
Related Commands
CSTK, MID, MSTK, SSTK
ASTK
33
Page 44

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
BARC — draw BARCode
Format
BARC type, flag, ’ string’[, short, tall [, bar1, bar2, bar3, bar4, space1, space2, space3, space4]];
Parameters
type:
There are the following barcode types:
0 = UPC A
1 = UPC A with two-digit supplement
2 = UPC A with five-digit supplement
3 = UPC D-1
4 = UPC D-2
5 = UPC D-3
6 = UPC D-4
7 = UPC D-5
8 = UPC E
9 = UPC E with two-digit supplement
10 = UPC E with five-digit supplement
11 = EAN-8 (Truncated JAN)
12 = EAN-13 (Truncated JAN)
13 = DUN-14 (Distribution Unit Number, EAN)
14 = DUN-16 (Distribution Unit Number, EAN)
15 = MSI with no check digit
16 = MSI with single mod-10 check digit
17 = MSI mod-10 followed by mod-10 check digit
18 = MSI mod-11 followed by mod-10 check digit
19 = CODE 39 with no check digit
20 = CODE 39 with mod-43 check digit
21 = Interleaved two of five with no check digit
22 =Identicon two of five with no checksum
23 = Code 128 (manual mode change)
24 = Code 128 (auto mode change)
25 = Code 11 with only ‘c’
26 = Code 11 with both ‘c’ and ‘k’ checksum
27 = Code 93 with both ‘c’ and ‘k’ checksum
28 = CODABAR with no check digit (narrow gap)
29 = Matrix two of five with no checksum
31 = Industrial two of five with no checksum
32 = Ames with no checksum
33 = Delta distance ‘a’ (IBM) with no
34 = Delta distance ‘a’ (IBM) with no
35 = EAN 8 with two-digit supplement
36 = EAN 8 with five-digit supplement
37 = EAN 13 with two-digit supplement
38 = EAN 13 with five-digit supplement
39 = POSTNET
40 = FIM
41 = Interleaved two of five with check digit
42 = UPC/EAN128
checksum
checksum
34
Page 45

flag:
string:
short:
BARC
43 = CUSTOM CODE (Japan)1
44 = CODABAR with no check digit (wide gap)
Y = Print the string under the barcode
N = Do not print the string
T ext to be converted to a barcode. The text must be enclosed with single or double quote
marks.
Height of short bars in barcode types that have bars in two different heights. Height of all
bars in other cases. Default value is 1.52cm (0.6 inches, 180 dots). The unit of
measurement is determined by the UNIT command.
Minimum value 0.254cm (0.1 inch, 30 dots)
Maximum value 27.9cm (11 inches, 3300 dots)
tall:
Height of tall bars in barcode types that have bars in two different heights. Default values
are the same as that of the short height.
bar1/2/3/4:
Width of a bar.
Minimum value 0.0085cm (0.0033 inches, 1 dot)
Maximum value 1.6933cm (0.6667 inches, 200 dots)
space1/2/3/4:
The width of a space.
The minimum and maximum values are the same as that of the bar width.
Function
The BARC command converts a string to a barcode and prints it. The specification of the
type, flag and string parameters is necessary. After printing, the cursor positions at the
upper left corner of the barcode.
If a value not mentioned above is specified as the barcode type, 12 EAN-13 will be
automatically selected.
Specify the flag parameter to Y when printing the text under the printed barcode or N
when not printing the text. The text will be printed in the font currently selected for the
printing system. However, a font selection command can be written ahead of the BARC
command to print the text in an arbitrary font.
1
FS-600/FS-7000/FS-9100/FS-9500 only
Characters that can be converted
The length of the string varies depending on the type of barcode to use. Characters that
can be used for the most barcode type are described in the table below.
35
Page 46

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
Table 20 Characters that can be used
Type Max Characters to be used Default
0 11 0123456789 0
1 13 0123456789 0
2 16 0123456789 0
3 13 0123456789 0
4 18 0123456789 0
5 22 0123456789 0
6 25 0123456789 0
7 29 0123456789 0
8 6 0123456789 0
9 8 0123456789 0
10 11 0123456789 0
11 7 0123456789 0
12 12 0123456789 0
13 13 0123456789 0
14 15 0123456789 0
15 1 - 14 0123456789 0
16 1 - 14 0123456789 0
17 1 - 14 0123456789 0
18 1 - 14 0123456789 0
19 1 - 40 $%+-./0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ and spaces space
20 1 - 40 $%+-./0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ and spaces space
21 2 - 26 0123456789 0
22 1 - 25 0123456789 0
23 1 - 40 All (ASCII characters 32 - 126) space
24 2 - 40 All (ASCII characters 32 - 126) space
25 1 - 45 -0123456789 space
26 1 - 45 -0123456789 space
27 1 - 50 All (ASCII characters 32 - 126) space
28 3 - 32 $+-./0123456789:abcdetn* 29 1 - 25 0123456789 0
30 1 - 25 0123456789 0
31 1 - 25 0123456789 0
32 1 - 25 -0123456789 0
33
34 1 - 25 0123456789KLMO 0
35 9 0123456789 0
36 12 0123456789 0
37 14 0123456789 0
38 17 0123456789 0
39 139 0123456789 -
1 - 25 0123456789KLMO 0
36
Page 47

BARC
1dot bar1≤ bar2 bar3 bar4<<< 200dots≤
1dot space1≤ space2 space3 space4<<< 200dots≤
Type Max Characters to be used Default
40 1 The following FIM pattern type
41 125 0123456789 0
42 80 All (ASCII characters 32 - 126)
43 1 - 20 0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ 44 3 - 32 $+-./0123456789:abcdetn* and
A. Country Reply Mail with POSTNET
B. Business Reply, Penalty and
C. Business Reply, Penalty and Franked Mail with POSTNET
D. OCR Readable Mail without POSTNET
Franked Mail without POSTNET
spaces -
0
Length of the bars
For the UPC and EAN (JAN) barcode type, the length of the short and tall bars can be
adjusted. When adjusting the length of the tall or short bars, specify that of both tall and
short bars. If the length of only the tall or short bars is adjusted, the bars' length does not
change. It is recommended to use the dot for the unit of measurement in order to avoid
the translation error by the barcode reader. In the example below, the length of the short
bar is specified as 1.5cm and the tall bar as 1.7cm.
!R! UNIT D; BARC 8, Y, '123456', 180, 200; PAGE; EXIT;
Width and space of the bar
It is possible to adjust the widths of the bars and space between the bars. When adjusting
these widths, specify all of the eight width and space parameters. Specify the bar 1 to bar
4 in the ascending order. The values can be specified between 1 and 200 dots.
It is recommended to use the dot for the unit of width in order to avoid the translation
error by the barcode reader. The example below specifies the width of the first bar and
space as 5 dots and that of the remaining bars as 10 dots.
!R! UNIT D;
BARC 19, Y, '0123ABC', 60, 60, 5, 10, 10, 10, 10, 5, 10, 10;
PAGE;
EXIT;
37
Page 48

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
a
b
a
b
a = First page
b = Last page
BKLT — print in BooKLeT binding
Format
BKLT binding;
Parameter
binding:
number representing binding mode:
0 = None
1 = Left-to-right binding
2 = Right-to-left binding
Function
The BKLT command allows pri nti ng a job as a booklet, reordering and printing the
pages two-up on a sheet of paper. Booklet printing requires the hard disk to be installed
in the printing system.
The job to booklet-print must be defined using the JOBS command. Used together with
the FOLD command, the paper can be folded in the middle to form a booklet.
Booklet printing is possible for documents of A4, A5, B5, letter, or statement size
documents and are automatically printed on double size paper, namely A3, A4-R, B4,
ledger, or letter-R. The original page size must be specified by the SPSZ command, for
example, SPSZ 8; for A4 page size. It is also possible to reduce the original page size by
commanding the second parameter for SPSZ. For example, to print two A4 pages on a
A4 sheet, command SPSZ 8, 5;. For details on page size, refer to the SPSZ command
page in this manual. The document must have the same page size for all pages. If the
double size paper for the document is not available in the printing system, the print ing
system ignores the BKL T command and prints in the original paper size. Duplex printing
is also possible by adding the DUPX command. To correctly arrange two neighboring
pages in line, short-edge binding duplex must be used by commanding DUPX 2;.
The order of print pages can be selected by binding in either of the following manners:
38
Page 49

File
binding = 1, reading
pages from left to right
binding = 2, reading
pages from right to left
BKLT
This command is not supported by some photocopier models.
The following command sequence prints a copy of a 12-page A4 document in booklet
mode, folding the stack in the middle. The printing system will require A4-R paper to be
loaded.
!R! RES; SPSZ 8, 5;
UNIT C;
BKLT 1;
DUPX 2;
FOLD;
SFNT ’Helvetica-Bd’, 72;
JOBS 0, 1, 0, 0;
MZP 4, 5; TEXT ”Page 1”;
PAGE;
MZP 4, 5; TEXT ”Page 2”;
PAGE;
MZP 4, 5; TEXT ”Page 3”;
PAGE;
MZP 4, 5; TEXT ”Page 4”;
PAGE;
MZP 4, 5; TEXT ”Page 5”;
PAGE;
MZP 4, 5; TEXT ”Page 6”;
PAGE;
MZP 4, 5; TEXT ”Page 7”;
PAGE;
MZP 4, 5; TEXT ”Page 8”;
PAGE;
MZP 4, 5; TEXT ”Page 9”;
PAGE;
MZP 4, 5; TEXT ”Page 10”;
PAGE;
MZP 4, 5; TEXT ”Page 11”;
PAGE;
MZP 4, 5; TEXT ”Page 12”;
PAGE;
JOBT;
EXIT;
39
Page 50

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
V-option
E-option
N-option
H-option
L-option
B-option (No motion)
Left margin
BLK — draw filled-in BLocK
Format
BLK width, depth[, option];
Parameters
width:
width of the block
depth:
depth of the block
option:
B = Leave the cursor unmoved (Default)
H = Move the cursor to the horizontally adjacent corner
V = Move the cursor to the vertically adjacent corner
E = Move the cursor to the diagonally oppos
L = Move the cursor one line down
N = Move the cursor to the beginning of the next line
ite corner
40
Function
The BLK command draws a block of a specified size with one corner at the current
cursor position. The block is filled in with the pattern designated by the previous PAT,
FPAT, or GPAT command. The cursor is moved as specified by the option. If the option
is omitted, the cursor is not moved (same as option B).
Page 51

File
Printout
BLK
!R! RES; UNIT C;
MAP 5, 5;
PAT 20;
BOX 4, 1; BLK 4, 1;
MRP 0, 1.5;
BOX 4, 1; BLK 4, 1;
MRP .9, .6;
SFNT "Helvetica-Nr";
TEXT ’OVERPRINTING’;
MRP 0, 5;
PAT 29; BOX 1, -4; BLK 1, -4, H;
PAT 39; BOX 1, -3; BLK 1, -3, H;
PAT 49; BOX 1, -2; BLK 1, -2, H;
PAT 59; BOX 1, -1; BLK 1, -1, H;
PAGE;
EXIT;
41
Page 52

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
N-option
B-option (No motion)
H-option
E-option
V-option
L-option
Left margin
BOX — draw BOX
Format
BOX width, depth[, option];
Parameters
width:
width of the box
depth:
depth of the box
option:
B = Leave the cursor unmoved (Default)
H = Move the cursor to the horizontally adjacent corner
V = Move the cursor to the vertically adjacent corner
E = Move the cursor to the diagonally oppos
L = Move the cursor one line down
N = Move the cursor to the beginning of the next line
ite corner
42
Function
File
The BOX command draws a box of a specified size with one corner at the current cursor
position. The line thickness is designated by the SPD (set pen diameter) command. The
size and thickness is measured on the basis of value established in the UNIT command.
The cursor is moved as specified by the option. If the option is omitted, the cursor is not
moved (same as option B).
The BOX command draws only the outline of the box. To fill in the box, use the BLK
command.
The width and depth may use either a positive or negative value.
!R! RES; UNIT C; SPD .1;
SLM 2;
Page 53

Printout
BOX
MAP 4, 0;
SCP;
SFNT "Helvetica-Nr", 10;
BOX 4, 2, L; TEXT ’Text printed with option L’;
RPP;
BOX 4, 2, N; TEXT ’Text printed with option N’;
PAGE;
EXIT;
43
Page 54

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
CALL — CALL macro
Format
CALL[ repeat-count] macro-name, parameter-value, ...;
Parameters
repeat-count:
number of times the macro is to be executed
macro-name:
name defined by a MCRO command
parameter-values:
values given to the dummy parameters in the macro definition
Function
The CALL command executes a macro previously defined by a MCRO command. The
macro may be executed any desired number of times by specifying a repeat count. Note
that the repeat count is not followed by a comma. If the repeat count is omitted, the
macro is executed once.
Only the first four characters of the macro name are significant. They must match the
first four characters of a macro name defined by a previous MCRO command.
A parameter value consists of the characters that occur between the delimiting commas,
excluding the commas. These parameters are substituted without change for the
corresponding dummy parameter in the macro definition, except that consecutive spaces
are compressed to a single space.
When a character-string parameter is enclosed in apostrophes or quotation marks, the
enclosed string together with the enclosing apostrophes or quotation marks is substituted
for the dummy parameter. In this case, consecutive spaces are not compressed.
If a CALL command has too few parameters, it is still valid. The macro is partially
executed; any commands in the macro body without appropriate parameters will be
ignored.
The CALL command, like other commands, is limited to 255 characters in length.
44
Page 55

File
Printout
CALL
!R! RES; UNIT C; SLS .5;
CMNT Requires BX and SCREEN macros;
CMNT See ENDM command page;
MAP 9, 3; CALL BX;
MAP 7, 4; CALL 5 BX;
MAP 5, 5; CALL 9 BX;
MAP 8, 6; CALL SCREEN, 2.2, 1.7;
MAP 8.6, 7;
TEXT ’Narrow’, L;
TEXT ’screen’;
MAP 5,9; CALL SCREEN, 8.2,1.2;
MAP 8,10;
TEXT ’Wide screen’;
PAGE;
EXIT;
45
Page 56

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
CCPY — Carbon CoPY
Format
CCPY mode;
Parameter
mode:
E = enable carbon copy
D = disable carbon copy
Function
The CCPY command continuously executes different automacros using different paper
sources, enabling to apply the different form overlay using the different paper type to a
document to be carbon-copied, similarly to hand-writing carbon copy forms. The CCPY
statement should be terminated with the ENDC command.
The macro and paper source for each form should be described following the CCPY
command in a separate line using the PSRC and AMCR command, and terminated by
the TERM command. For example, the second line in the following example is applied
to the first page of the document and executes the CROPMARK macro printing the page
on the paper fed from cassette #2. The third line applies to the second page of the
document, and so on. It is possible to add as many lines as required to match the number
of pages of the document to print.
CCPY E;
PSRC 2; AMCR E, CROPMARK; TERM;
PSRC 3; AMCR E, SIGNATURE; TERM;
PSRC 4; AMCR E, COLOPHON; TERM;
ENDC;
During the carbon copy is executed, the copy count (COPY command) is forced to be 1.
To apply no overlay to a specific page, describe only the TERM command in the line
corresponding to the page. Note that the same paper source as the previous line is applied
to that line. For example:
CCPY E;
PSRC 2; AMCR E, CROPMARK; TERM;
TERM;
PSRC 4; AMCR E, COLOPHON; TERM;
ENDC;
In the example above, the second page is printed using cassette #2 with no form overlay.
46
In carbon copy, duplex printing is not possible. The paper size and the page orientation
should be consistent for all pages in the document to be carbon copied. Otherwise, the
carbon copy is cancelled.
To terminate carbon copy , send CCPY D to the printing system.
Page 57

File !R!
RES; DAM; CCPY D; UNIT C;
MCRO COVER;
UNIT C;
SFNT 'Helvetica-Bd',14;
TEXT 'Registration Form', L;
SFNT 'Helvetica', 9;
TEXT 'Please provide your personal details:';
MRP 0, .2;
BOX 6, 1;
MRP 0, .35;
TEXT ' Your Name';
ENDM;
MCRO MAIL;
UNIT C;
SFNT 'Helvetica-Bd',14;
TEXT 'Mailing Information', L;
SFNT 'Helvetica', 9;
TEXT 'Shipping Department Use Only';
MRP 0, .2;
BOX 6, 1;
MRP 0, .35;
TEXT " Client's Name";
ENDM;
CCPY
MCRO COPY;
UNIT C;
SFNT 'Helvetica-Bd',14;
TEXT "Client's Copy", L;
SFNT 'Helvetica', 9;
TEXT 'Please retain this copy for future reference.';
MRP 0, .2;
BOX 6, 1;
MRP 0, .35;
TEXT ' Registered Client';
ENDM;
CCPY E;
PSRC 1; AMCR E,COVER; TERM;
PSRC 0; AMCR E,MAIL; TERM;
PSRC 1; AMCR E,COPY; TERM;
ENDC;
EXIT;
!R! CMNT Document to be carbon-copied;
SFNT 'Helvetica', 12;
MZP 0, 1.9;
TEXT ' David Sumimoto';
PAGE;
EXIT;
47
Page 58

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
Printout
48
Page 59

CDSK — Check hard DiSK
Format
CDSK;
Parameter
None
Function
The CDSK command verifies data in the hard disk (garbage collection). It deletes
garbage jobs such as page image data that were accidentally generated in the hard disk
and normally inaccessible for deletion.
File
CDSK
!R! CDSK; EXIT;
49
Page 60

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
COLOR
CID — Configure color-Image Data
Format
CID color-space, encoding;
Parameters
color-space:
0 = Device-dependent RGB (Default)
1 = Device-dependent CMY
2 = Void
3 = CIE L*a*b
encoding:
Pixel encoding
1 = Indexed by Pixel (Default)
3 = Direct by Pixel
Function
The CID command creates a new color palette using the ID which is assigned to the
currently active palette. Note that the currently active palette is deleted by this command.
It is possible to add and change colors on this palette. However, the currently active
colors do not change even though a new palette is created with this command.
The same colors as simple colors are defined for index numbers 0 through 7 when the
RGB color space is specified. The color assignments for these indices can be changed
using the ACLI command.
Indexed by Pixel encoding assigns colors onto the palette. This is used for rendering text
and vector objects. Direct by Pixel encoding assigns colors directly to pixels. This is
used for bitmap images.
Changing a color palette does not affect color print quality on output pages.
50
Page 61

File
CID
!R! RES;
DAM;
UNIT C;
SFNT ’Helvetica-Bd’, 20;
CPAL C, 1; SPAL 1;
CID 0, 1; CMNT RGB Color Space used;
ACLI 1, 0, 0, 255;
MZP 1, 1; SCOL 1;
TEXT ’An RGB color palette is used.’
CID 3, 1; CMNT L*a*b Color Space used;
ACLI 2, 100, 75, 0;
MZP 1, 2; SCOL 2;
TEXT ’An L*a*b color palette is used.’;
Printout
PAGE;
EXIT;
51
Page 62

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
CIR — draw CIRcle
Format
CIR radius;
Parameter
radius:
radius of the circle
Function
In standard graphics mode, the CIR command draws a circle centered at the current
cursor position. The line thickness used is designated by the SPD command.
A circle can also be drawn by using the path mode graphics. Refer to the PARC
command.
File
!R! RES; UNIT C; SLS .5;
SPD .01; MAP 10, 1;
CIR .1; MRP 0, .1;
CIR .2; MRP 0, .2;
CIR .4; MRP 0, .4;
CIR .8; MRP 0, .8;
SPD .02;
CIR 1.6; MRP 0, 1.6;
CIR 3.2; MRP 0, 3.2;
SPD .2;
CIR .1; MRP .2, .4;
SFNT "Helvetica-Nr"; TEXT ’Cursor now here’;
PAGE;
EXIT;
52
Page 63

Printout
CIR
53
Page 64

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
CLIP — CLIP current path
Format
CLIP [clip-mode];
Parameter
clip-mode:
1: EO clip
2: Non-zero winding clip
Function
The CLIP command sets the current path as the clipped path. After this command is
issued, no painting is done outside the area of the path. Executing this command does not
delete the current path.
The RES command initializes paths to a state with no clip area.
54
Page 65

CLPR — CLiP Rectangular area
Format
CLPR [x1, y1, x2, y2];
Parameters
x1:
x coordinate of the top-left corner of the rectangle
y1:
y coordinate of the top-left corner of the rectangle
x2:
x coordinate of the bottom-right corner of the rectangle
CLPR
y2:
Function
y coordinate of the bottom-right corner of the rectangle
The CLPR command describes a rectangular path which intersects the inside of the texts,
current path, or raster graphics objects. The clipping rectangle does not clip those
graphics segments drawn in the standard mode graphics. Any painting operations outside
the specified rectangle is erased and those segments within it are painted on the page.
The coordinates are measured from the top and left edge limits in the units designated by
the UNIT command. If the parameters are omitted, the rectangle is equal to the size of
the current page size. If an attempt is made to position the top-left corner to the right of
the bottom-left corner [greater values for (x1, y1) than for (x2, y2)], the printing system
exchanges the coordinate values with each other.
The printing system resets the size of the rectangular clipping path to be equal to the
maximum printable area of the current page size when a PSRC, RES, SPO, or SPSZ (Set
Page SiZe) command is encountered.
55
Page 66

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
File
!R! RES; UNIT C;
NEWP;
SPD 1;
PMRA 6, 9, 3, 0;
PAT 1;
PARC 6, 9, 3, 0, 360;
CLPR 3, 6, 9, 12;
STRK;
PAGE;
EXIT;
Printout
56
Page 67

CLSP — CLoSe Path
Format
CLSP;
Parameter
None
Function
The CLSP command closes an open path by adding a line segment extending from the
end of the path to the beginning of the path.
Simply ending a path at the path’s starting point does not make it a closed path ; su ch a
path remains open until it is closed. Closure can be made either explicitly, by means of
the CLSP command, or implicitly by means of the FILL (FILL current path) command.
CLSP
File
!R! RES; UNIT C;
NEWP;
CMNT The 1 st path below is stroked without closing;
SPD .25;
PMZP 5, 10;
PMRA 5, 10, 1, 90;
PARC 5, 10, 1, 90, 270;
PARC 7, 10, 1, 270, 90;
STRK;
NEWP;
CMNT Next path is closed by CLSP before stroked;
PMZP 5, 14;
PMRA 5, 14, 1, 90;
PARC 5, 14, 1, 90, 270;
PARC 7, 14, 1, 270, 90;
CLSP;
STRK;
PAGE; EXIT;
57
Page 68

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
Printout
Related Command
NEWP
58
Page 69

CMNT — CoMmeNT
Format
CMNT string;
Parameter
string:
any character string
Function
The CMNT command adds a character string, typically a comment explaining the
purpose of the following PRESCRIBE commands. The CMNT command statement will
be ignored by the printing system.
CMNT
File
Printout
Although character strings are normally enclosed in apostrophes or quotation marks, this
is unnecessary for comment strings as long as the string does not itself contain an
apostrophe, quotation mark, or semicolon.
!R! RES;
SLM 2; STM 2;
SFNT ’TimesNewRoman’; CMNT TimesNewRoman;
EXIT;
The CMNT command in the above program reminds
you that SFNT represents the TimesNewRoman font.
59
Page 70

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
COLOR
CMOD — Color MODe
Format
CMOD mode;
Parameter
mode:
color mode:
0 = Monochrome
1 = Color (Default)
Function
The CMOD command switches between monochrome and color modes.
In monochrome mode, other color commands are still enabled, but printing is converted
nochrome or grayscale.
to mo
This command causes a page break.
60
Page 71

COPY — set number of COPIES
Format
COPY number;
Parameter
number:
number of copies
Function
The COPY command designates the number of copies for each page in a print job. This
copy count value can be changed by sending the printing system another COPY
command or by issuing a reset command. For best results, place the copy command near
the start of a job or at the top of a page. If two or more copy commands are placed on the
same page, the last one will be recognized.
COPY
File
!R! RES;
SLM 0.5;
UNIT P;
SFNT ’Helvetica-Bd’, 14.4;
SLS 17;
COPY 3;
EXIT;
Announcement
Party Tonight at 6:00
!R! PAGE; EXIT;
61
Page 72

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
Printout
62
Page 73

COLOR
CPAL — Control PALette
Format
CPAL mode[, palette-id];
Parameters
mode:
palette control mode:
A = Delete all palettes
S = Delete all stacked palettes
D = Delete the palette having the specified ID
C = Copy the active palette to the specified ID
palette-id:
number from 0 to 32767 (Default is 0)
CPAL
Function
The CPAL command controls the palette identified by palette-id in the way described by
the control mode. If palette-id is not specified, the command is applied to palette of ID 0.
No check is made whether the palette ID number given already exists for another palette.
The palette ID number is reset to 0 by RES command.
Mode A deletes all existing palettes and brings the default palette back to the default state
(ID 0). Note that non-active palettes are not deleted. Also, palette-id is not used when
mode is A.
Mode S deletes all palettes that are not active. The active palette is not affected. Also,
any ID specified by palette-id is not used.
Mode D deletes the palette having the ID specified by palette-id regardless of being
active or inactive. If the palette deleted was active, then the current palette will be a
monochrome palette having the same ID as that of the deleted palette.
Mode C copies the currently active palette to a new palette with the new ID specified by
palette-id. If the palette having the same ID already exists, that palette is overwritten.
Deleting or copying a color palette does not affect color print quality on output pages.
63
Page 74

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
CPTH — Character PaTH
Format
CPTH ’string’;
Parameter
string:
any character string except from ASCII code 31 (hex 1F) and lower
Function
The CPTH command constructs a path which adds the outlines of characters to the
current path. When stroked or filled, it prints the given string at the current cursor
position and moves the cursor to the end of the string. The current font preceding this
command must be a resident or a soft scalable font.
File
Printout
The character path can be filled in with the pattern or shade of gray designated by the
previous PAT, FPAT, or GPAT command.
!R! FSET 1p72v1s0b4148T; CMNT Univers-MdIt;
NEWP;
PMZP 2, 2;
CPTH ’Enjoy’;
STRK;
PAGE;
EXIT;
64
Page 75

CSET — Change symbol SET by symbol-set ID
Format
CSET symbol-set-id;
Parameter
symbol-set-id:
symbol set ID:
0D = ISO 60 Norway
0E = Roman Extension
0F = ISO 25 French
0G = HP German
0I = ISO 15 Italian
0K = ISO 14 JIS ASCII
0N = ECMA-94 Latin 1
0S = ISO 11 Swedish
0U = ISO 6 ASCII
1D = ISO 61 Norwegian
1E = ISO 4 U.K.
1F = ISO 69 France
1G = ISO 21 Germany
1S = ISO 15 Spanish
1U = US Legal
2K = ISO 57 Chinese
2N = ISO Latin 2
2S = ISO 17 Spain
2U = ISO 2 IRV
3R = PC Cyrillic*
3S = ISO 10 Swedish
4S = ISO 16 Portuguese
4U = Roman-9
5M = PS Math
5N = ISO Latin 5
5S = ISO 84 Portuguese
5T = ISO Windows Latin 5
6J = MS Publishing
6M = Ventura Math
6N = ISO8859/10 Latin 6
6S = ISO 85 Spanish
7J = Desktop
8G = Greek-8
8M = Math 8
8Q = PC Set 1 IBM
8T = Turkish-8
8U = Roman-8
9E = Windows Latin 2
9G = Windows 3.1 Latin/Greek
9J = PC-1004
9L = Ventura ITC Zapf Dingbats
9N = ISO Latin 9
9Q = PC Extension
CSET
65
Page 76

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
9R = Windows 3.1 Latin/Cyrillic
9T = PC-Turkish
9U = Windows 3.0
10G = PC-851 Latin/Greek
10J = PS Text
10N = ISO8859/5 Latin/Cyrillic
10R = PC-855 Cyrillic/Serbia
10U = IBM PC-8
11G = PC-869 Latin/Greek
11U = IBM PC-8 Danish/Norwegian
12G = PC-8 Latin/Greek
12J = Macintosh
12N = ISO8859/7 Latin/Greek
12R = USSR-GOST
12U = IBM PC-850
13P = ABICOMP Brazil/Portugal
13R = PC-8 Bulgarian
13U = PC-858
14G = Greek Alternate 437G
14L = PS ITC Zapf Dingbats
14P = ABICOMP International
14R = PC Ukrainian
15U = Pi Font
16U = PC-857
17U = PC 852
18N = ISO-10646
18U = PC-853 Turkish/Latin 3
19L = Windows 3.1 Baltic
19M = Symbol (Symbol-Set-SWM font only)
19U = Windows Latin 1
20U = PC-860 Portugal
21U = PC-861 Iceland
23U = PC-863 Canada-French
24Q = PC-8 Polish Mazovia
25U = PC-865 Norway
26U = PC-775 Baltic
27Q = PC-8 PC Nova
579L = Windings (More Wingbats-RegularSWM font only)
1
†
†
†
†
†
†
†
†
1
Available only with models having Agfa fonts
66
Page 77

Function
Files
CSET
‘Symbol set’ refers to a specific group of alphabetic, numeric, and symbolic characters.
The CSET command summons the symbol set to suit the various languages with the
current font. The factory default symbol set is 0U (US ASCII).
When the FSET command is used to select a font, the printing system selects a font
based on a prioritization of the font characteristics. Among the given characteristics, the
symbol set has the highest priority in the font selection process. Refer to the FSET
command page.
The available symbol sets depend on the printing system model and the fonts. If the
specified symbol set does not exist, the symbol set remains unchanged.
!R! RES;
SFNT ’Helvetica’, 24;
SLPI 3;
CMNT Current symbol set is ISO 6: ASCII;
TEXT ’@ABCDEFG’, N;
CSET 5M; CMNT Changed to PS math;
TEXT ’@ABCDEFG’;
PAGE;
EXIT;
Printout
67
Page 78

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
Note
CSTK — select Collator STacKer
Format
CSTK [tray, tray, ...]; or CSTK 0;
Parameter
tray:
number from 1 to the maximum (bottom)
Function
The CSTK command is effective only when the optional sorter is installed to the printing
system. It instructs the printing system to deliver printed pages to the sorter in the
collator mode. Each tray specified receives all copies of one page. The copies of the first
page go to the first tray, the copies of the second page to the second tray, and so on. If the
tray parameter is omitted, the trays are used in order from top to bottom.
File
The copy count must be selected with the COPY command. The maximum copy count is
the maximum capacity of the sorter trays (which varies from sorter model to model).
Upon receiving the CSTK command, the printing system automatically performs a form
feed.
The tray parameter of 0 (CSTK 0;) should be used only to deselect the collator mode and
to receive the pages in the sorter’s bulk tray (if available).
This command is irrelevant to certain combination of photocopier models and option finisher models.
!R! RES; CSTK 1, 2; COPY 2;
EXIT;
Page 1 (2 copies, tray 1) !R! PAGE; EXIT;
Page 2 (2 copies, tray 2) !R! PAGE; EXIT;
Page 3 (2 copies, tray 1) !R! PAGE; EXIT;
Page 4 (2 copies, tray 2) !R! PAGE; EXIT;
68
Page 79

CTXT — print Centered TeXT
Format
CTXT [,string][,option][,U-option];
Parameters
string:
any character string
option:
B = Leave cursor at center of string
E = Move cursor at end of string
L = Move cursor down one line
N = Move cursor to beginning of next line
CTXT
U-option:
Function
File
Underline text
The CTXT command prints the given string centered at the cursor location, then moves
the cursor as designated by the option. The string must be enclosed in either single or
double quotation marks. (If the string includes one kind of quotation marks, use the other
kind to enclose it.) If the string is omitted, nothing is printed. If the option is omitted, the
cursor is not moved. If the U-option is specified, the text is underlined. The underline
thickness and location can be set by the SULP command.
The string is not centered between the right and left margins unless the cursor is located
halfway between the margins. Before the CTXT command, the cursor should be moved
to the desired center position by a command such as MAP, MRP, or PMRP.
The length of the string is unlimited, except that the command as a whole may not be
longer than 255 characters. Carriage-return and linefeed codes in the string are ignored.
!R! RES; SLPI 3; SFNT "Helvetica-Bd", 16;
MAP 4, 1;
CTXT ’NEWS!’, L, U;
SFNT "TimesNewRoman-It", 16;
CTXT ’Unforgettable Holidays in Sydney’, L;
CTXT ’For 6 Days Only at $1000!’;
PAGE;
EXIT;
69
Page 80

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
Printout
70
Page 81

DAF — Delete All Fonts
Format
DAF;
Parameter
None
Function
The DAF command deletes all nonresident fonts and the font numbers assigned to
scalable fonts by the SFNT command from the printing system’s memory. This enables
the user to make room for new fonts, macros, and graphics.
File
DAF
Printout
!R! UNIT P; SLS 16;
SFNT ’Helvetica-Bd’, 15, 2000, 277, 2, 0;
SFNT ’Helvetica’, 15, 2001, 277, 1, .5;
FONT 10; TEXT ’1. FAREWELL TO ’, E;
FONT 2000; TEXT ’FONT 2000’, N;
FONT 2001; TEXT ’AND FONT 2001’, N;
TEXT, N;
DAF;
FONT 10; TEXT ’2. FAREWELL TO ’, E;
FONT 2000; TEXT ’FONT 2000’, N;
FONT 2001; TEXT ’AND FONT 2001’;
PAGE;
EXIT;
71
Page 82

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
DAM — Delete All Macros
Format
DAM;
Parameter
None
Function
The DAM command deletes all macro definitions made by using the PRESCRIBE
MCRO command from the printing system’s memory. This enables the user to make
room for new macros, fonts, or graphics.
File
Printout
!R! RES; UNIT C;
CMNT Print ENDM file first.;
SFNT "Helvetica-Bd";
MAP 5, 4; CALL SCREEN, 9.2, 1.7;
MAP 7, 5; TEXT ’This text is enclosed by’, L;
TEXT ’SCREEN macro.’;
DAM;
MAP 5, 6; CALL 10 BX;
MAP 5, 7; CALL SCREEN, 9.2, 1.7;
MAP 6, 8; TEXT ’SCREEN macro was deleted by DAM.’;
PAGE;
EXIT;
72
Page 83

DAP — Draw to Absolute Position
Format
DAP x-coordinate, y-coordinate;
Parameters
x-coordinate:
distance from the left margin
y-coordinate:
distance from the top margin
Function
DAP
File
The DAP command draws a line from the current cursor position to a position specified
relative to the top and left margins. The thickness of the line is designated by the SPD
(set pen diameter) command. The coordinates and line thickness are measured in the
units designated by the UNIT command.
The coordinates may be positive or negative. Negative coordinates cause the line to
extend outside the margin.
The DAP command is ignored in the path mode graphics.
!R! RES;
UNIT C;
CMNT Tree Diagram;
STM 8; SLM 8;
MAP 0, 0; DAP 2, 0.5;
MAP 0, 1; DAP 2, 0.5;
MAP 0, 1; DAP 2, 1.5;
MAP 0, 2; DAP 2, 1.5;
MAP 0, 2; DAP 2, 2.5;
MAP 0, 3; DAP 2, 2.5;
MAP 2, 0.5; DAP 4, 1;
MAP 2, 1.5; DAP 4, 1;
MAP 2, 1.5; DAP 4, 2;
MAP 2, 2.5; DAP 4, 2;
MAP 4, 1; DAP 6, 1.5;
MAP 4, 2; DAP 6, 1.5;
PAGE; EXIT;
73
Page 84

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
Printout
74
Page 85

DELF — DELete Font
Format
DELF font-number;
Parameter
font-number:
number identifying the font to be deleted
Function
The DELF command deletes any designated non-resident font from the printing system’s
memory. This enables the user to make room for new fonts, macros, and graphics.
The printing system’s memory is large but not unlimited, and judicious use of the DELF
command may prevent memory overflow. (If a memory overflow occurs, the printing
system gives an overflow warning message.) The amount of memory still available can
be viewed on a status page, available by executing the STAT command.
DELF
File
Printout
!R! UNIT P; SLS 16;
SFNT ’Helvetica-Bd’, 15, 2000, 277, 1.5, 0;
SFNT ’Helvetica’, 15, 2001, 277, 1, .5;
FONT 2000; TEXT ’1. FAREWELL TO ’, E;
FONT 2001; TEXT ’ITALICS’, N;
TEXT, N;
DELF 2001;
FONT 2000; TEXT ’2. FAREWELL TO ’, E;
FONT 2001; TEXT ’ITALICS’;
PAGE;
EXIT;
75
Page 86

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
DELM — DELete Macro
Format
DELM macro-name;
Parameter
macro-name:
name defined by a previous MCRO command
Function
The DELM command deletes a specified macro definition from the printing system’s
memory to make room for new macros, fonts, or graphics, or so that the same name can
be used for another macro.
76
Page 87

File
DELM
!R! UNIT C;
MCRO BX;
SPD .05; BOX .8, -.8; MRP 1, 0;
ENDM;
MCRO SCREEN %, width, depth;
CMNT Draws box with rounded corners;
CMNT Leaves cursor at previous position;
SPD .08;
SCP;
MRP .25, .25; ARC .23, .30, 270, 0;
MRP 0, -.25; DRP %1, 0;
MRP 0, .25; ARC .23, .30, 0, 90;
MRP .27, 0; DRP 0, %2;
MRP -.27, 0; ARC .23, .30, 90, 180;
RPP;
MRP 0, .25; DRP 0, %2;
MRP .25, 0; ARC .23, .30, 180, 270;
MRP 0, .27; DRP %1, 0;
RPP;
ENDM;
SFNT "Helvetica-Bd";
MAP 5, 4;
CALL SCREEN, 9.2, 1.7;
MAP 7, 5;
TEXT ’This text is enclosed by’, L;
Text ’SCREEN macro.’;
DELM SCREEN;
MAP 5,8;
CALL SCREEN, 9.2, 1.7;
MAP 6, 10;
TEXT ’SCREEN macro was deleted by DELM.’;
PAGE;
EXIT;
Printout
77
Page 88

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
DPAT — select Dashed PATtern
Format
DPAT number;
Parameter
number:
number from 1 to 20 (11 to 20 are for user-defined patterns.)
Function
The DPAT command specifies the pattern of alternating black and white dashes to stroke
the current path.
The resident patterns range in value between 1 and 10. Refer to resident patterns list on
page 79. Numbers 11 to 20 are reserved for use with defining particular patterns using
the SDP (Store Dash Pattern) command. If you specify a value between 11 to 20 when no
user pattern has been defined, the path will be stroked in solid black.
File
The DPAT command does not affect the line drawn by the standard graphics commands
such as DRP, BOX, ARC, etc.
!R! RES; UNIT C;
MCRO DPAT;
NEWP;
SPD .2;
SCP;
SFNT "Helvetica-Nr", 10;
TEXT ’DPAT %1’;
PMRP 1.4, -.1; DPAT %1; PDRP 9, 0;
RPP; PMRP 0, .7;
STRK;
ENDM;
MZP 5, 5;
FONT 13;
CALL DPAT,1;
CALL DPAT,2;
CALL DPAT,3;
CALL DPAT,4;
CALL DPAT,5;
CALL DPAT,6;
CALL DPAT,7;
CALL DPAT,8;
CALL DPAT,9;
CALL DPAT,10;
PAGE;
EXIT;
78
Page 89

Printout
DPAT
Related Command
SDP
79
Page 90

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
DRP — Draw to Relative Position
Format
DRP x-coordinate, y-coordinate, ...;
Parameter
x-coordinate/y-coordinate:
coordinates as measured from the current cursor position
Function
The DRP command draws a line from the current cursor position to a specified relative
position. The thickness of the line is designated by the SPD (set pen diameter) command.
The coordinates and line thickness are measured by the value designated by the UNIT
command.
File
Multiple pairs of coordinates may be specified. The printing system then draws a
connected series of line segments, proceeding from one point to the next. For example,
DRP 1, 2, 3, 4; is equivalent to DRP 1, 2; DRP 3, 4;. The coordinates may
be positive or negative.
The DRP command is ignored in the path mode graphics. To add a line segment to a
path, use the PDRP (in Path, Draw to Relative Position) command.
!R! RES;
UNIT C; SPD .3;
CMNT Cube;
MZP 5, 10;
DRP 4, 0, 2, -2, 0, -4, -4, 0, -2, 2, 0, 4;
MRP 4, 0;
DRP 0, -4, -4, 0, 4, 0, 2, -2;
PAGE;
EXIT;
80
Page 91

Printout
DRP
Related Command
PDRP
81
Page 92

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
DRPA — Draw to Relative Position specified by
Angle
Format
DRPA length, angle;
Parameters
length:
length of the line
angle:
angle in degrees, measured clockwise from the vertical
Function
File
The DRP A command draws a line of a specified length at a specified angle, starting from
the current cursor position, with the thickness designated by the SPD command.
This command is ignored if placed within a path.
!R! RES; UNIT C;
MAP 2, 11;
DRPA 2, 72;
DRPA 2, 0;
DRPA 2, 144;
DRPA 2, 72;
DRPA 2, 216;
DRPA 2, 144;
DRPA 2, 288;
DRPA 2, 216;
DRPA 2, 0;
DRPA 2, 288;
PAGE;
EXIT;
82
Page 93

Printout
DRPA
83
Page 94

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
Portrait,
long-edge
Landscape,
long-edge
Portrait,
short-edge
Landscape,
short-edge
DUPX — select/deselect DUPleX mode
Format
DUPX mode;
Parameter
mode:
a number representing one of the following binding mode:
0 = simplex mode
1 = duplex mode, long-edge binding
2 = duplex mode, short-edge binding
Function
The DUPX command is effective only when the option duplexer is installed to the
printing system. It instructs the printing system to select or deselect duplex printing and
sets the binding mode.
84
File/Printout
See DXPG on page 85.
Page 95

DXPG — select DupleX PaGe side
Format
DXPG side;
Parameter
side:
a number representing the side of the ensuing page:
0 = Select next side (the same as form feed)
1 = Select front side
2 = Select back side
Function
DXPG
The DXPG command is effective only when the option duplexer is installed to the
printing system. It ends printing on the current page in the same manner as a form feed.
However, unlike the form feed, it also selects the paper side, front or back, on which
printing of the ensuing page is printed.
The side parameter 1 prints the ensuing page begins on the front side of the next sheet,
regardless of whether the current page was printed on the front or back side of the current
sheet.
The side parameter 2 prints the ensuing page begins on the back side of the current sheet
if the current page was printed on the front side, or on the back side of the next sheet if
the current page was printed on the back side.
85
Page 96

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
This text points right side-up on the front side of the page
This text points upside-down on the reverse side of the page
File
The following example selects the duplex mode with short-edge binding, a portrait page
orientation which results in text printing on both sides of the page.
!R! CMNT Initiates a PRESCRIBE command sequence; RES;
CMNT Causes a page break and resets parameters;
DUPX 2;
CMNT Selects duplex mode, short-edge binding;
SPO P;
CMNT Selects portrait orientation;
STAK 1;
CMNT Select face-down delivery;
EXIT;
This text prints right-side up on the front side of the page
!R! DXPG 0;
CMNT Ends current page (front side of the paper);
EXIT;
This text prints upside-down on the reverse side of the page
!R! RES; EXIT;
Printout
86
Page 97

DZP — Draw to Zero-relative Position
Format
DZP x-coordinate, y-coordinate;
Parameters
x-coordinate:
distance from the left edge limit of paper
y-coordinate:
distance from the top edge limit of paper
Function
DZP
File
The DZP command draws a line from the current cursor position to a position specified
relative to the top and left edge limits of the paper.
The thickness of the line is designated by the SPD (set pen diameter) command. The
coordinates and line thickness are measured in the value designated by the UNIT
command. The coordinates should be positive or zero. Negative coordinates are treated
as zero.
The DZP command is ignored within a path construction. To add a zero-relative line
segment in a path, use the PDZP (in Path, Draw to Zero-relative Position) command.
!R! RES;UNIT C;
MZP 0, 0; DZP 0, 5;
MZP 1, 0; DZP 0, 4;
MZP 2, 0; DZP 0, 3;
MZP 3, 0; DZP 0, 2;
MZP 4, 0; DZP 0, 1;
MZP 5, 0; DZP 0, 0;
PAGE;
EXIT;
87
Page 98

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
Printout
Related Command
PDZP
88
Page 99

EMCR — Enable MaCRo depending on paper
source
Format
EMCR
EMCR mode, paper-source [ = print-side], [repeat-count] macro-name
[, parameter...];
Parameters
mode:
E = enable automatic macro
D = disable automatic macro
paper-source:
0 = multi-purpose feeder
1 = cas
2 = cas
3 = cas
4 = cas
5 = cas
6 = cas
99 = envelope or
print-side:
side of the page the macro is executed when duplex-printing
0 = front
1 = back
sette 1 (printing system’s cassette)
sette 2
sette 3
sette 4
sette 5
sette 6 (bottom)
universal feeder
repeat-count:
number of times the macro is executed
macro-name:
name defined by the MCRO command
parameter:
values given to the dummy parameters in the macro definition
89
Page 100

PRESCRIBE Command Reference
Function
The EMCR command allows separate auto macros to be assigned for each of the
separate paper sources. In duplex printing, it is also possible to assign separate auto
macros for both the front and back sides of a page.
The following commands are invalid within a macro:
AMCR, ASTK, PSRC, CCPY, DUPX, DXPG, JOBD, JOBL, JOBO, JOBP, JOBS,
JOBT, JOG, LDFC, LDFN, MID, MSTK, RDMP, SEM, SPSZ, SSTK, STAK, STAT,
STPL, VMAL, VMPW
To disable the auto macro, use EMCR D. Note that EMCD D does not require other
parameters such as paper-source.
90
 Loading...
Loading...