Kymco MO Movie125, MO Movie 150 Service Manual - chap 18 (emissioni)

18. EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM
18-0
18
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
__________________________________________________________________________________
SCHEMATIC DRAWING ............................................................ 18- 1
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM FUNCTION..... 18- 2
TROUBLESHOOTING ................................................................ 18- 2
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE ..................................................... 18- 3
SERVICE INFORMATION .......................................................... 18- 4
MOTORCYCLE ENGINE EVAPORATIVE EMISSION
CONTROL SYSTEM TEST ......................................................... 18- 5
PURGE CONTROL VALVE ........................................................ 18- 6
CHARCOAL CANISTER ............................................................. 18- 8
PCV (POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION) SYSTEM .......... 18- 9
EXHAUST EMISSION RELATED SYSTEM INSPECTION .......... 18-10
EXHAUST EMISSION TEST AND ADJUSTMENT...................... 18-10
18. EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM
18-1
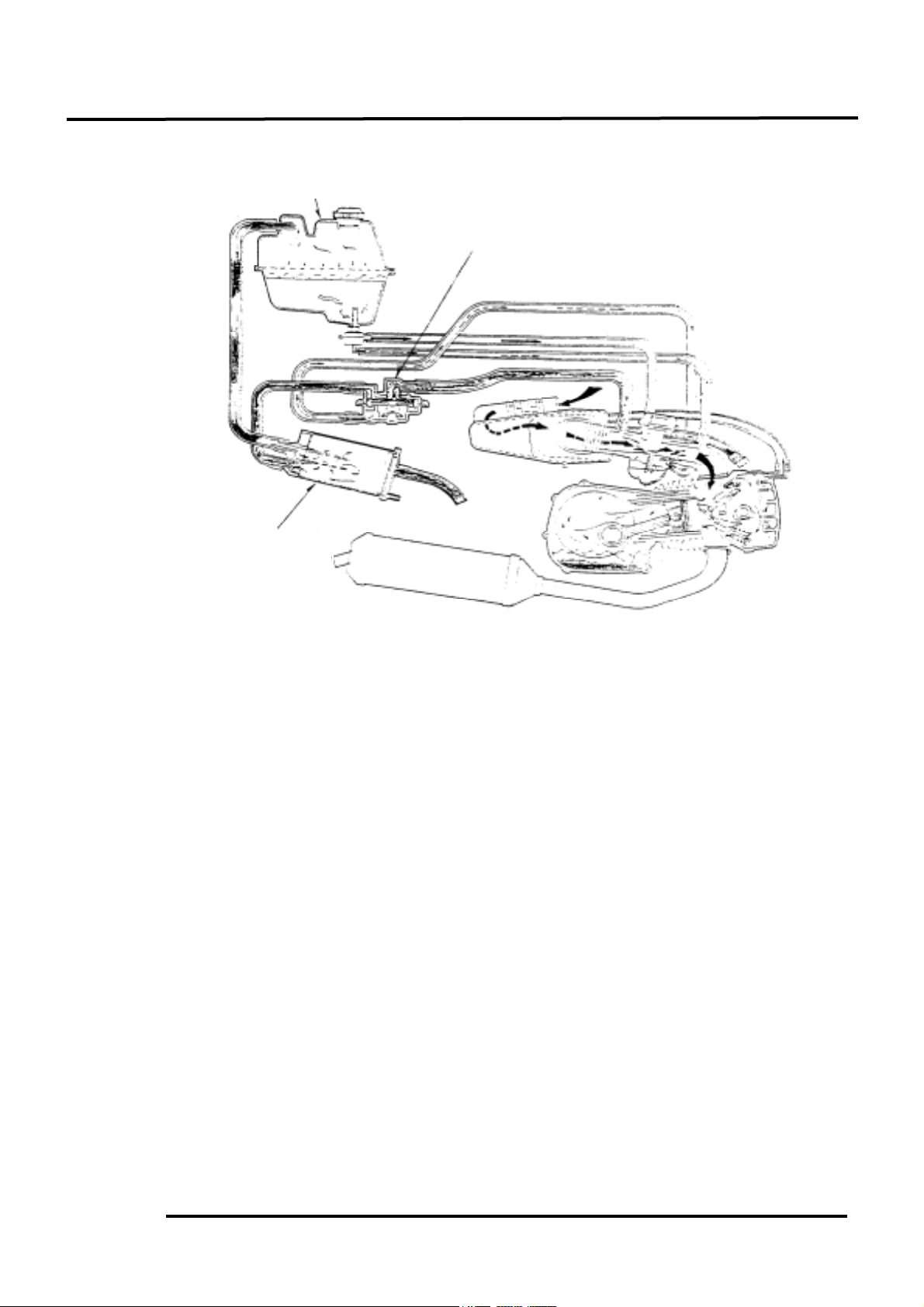
SCHEMATIC DRAWING
S EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM LOCATION
Charcoal Canister
Purge Control Valve
Fuel Tank
18. EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM
18-2
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM FUNCTION
FOREWORD:
The Evaporative Emission Control System is abbreviated to E.E.C. System. This device collects
the fuel vapor from the carburetor and fuel tank and then the fuel vapor is drawn into the engine for
re-burning to avoid air pollution caused by the fuel vapor diffused into the air.
FUNCTION
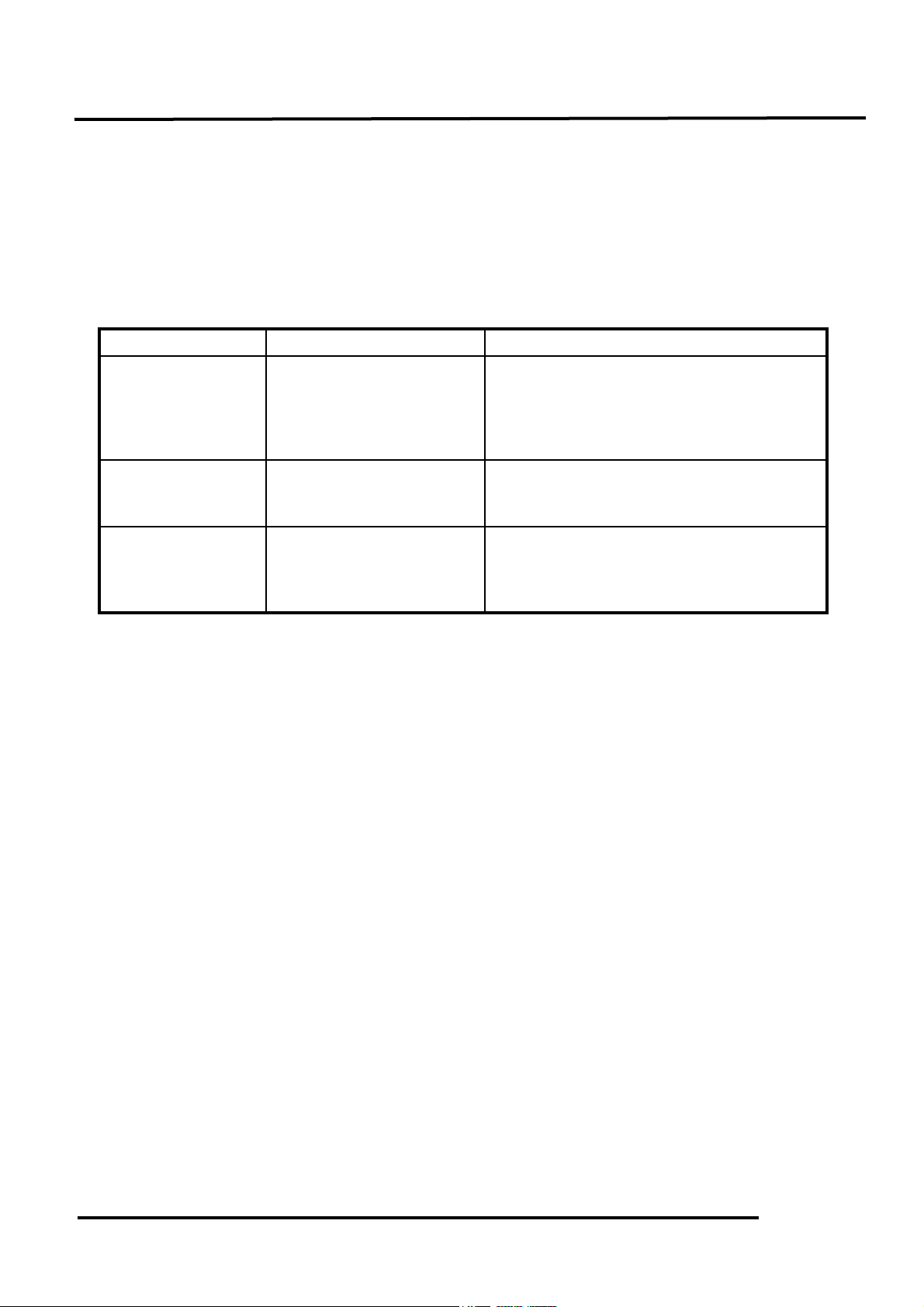
Item
Purpose
Function
Purge Control Valve
Control vaporized HC from
fuel tank not to diffuse into
the air.
The charcoal canister absorbs vaporized HC
from the fuel tank. When the engine is
running and the purge control valve is open,
the fuel vapor in the charcoal canister is
drawn into the engine for re-burning.
Charcoal Canister
Absorb and store the
vaporized HC from the fuel
tank and carburetor.
The vaporized HC is absorbed in the
charcoal canister and the specified volume of
HC in the emission should not exceed 2g.
P.C.V.
Completely recover the HC
of blow-by gas in the
crankcase for re-burning.
Through the P.C.V. system, the blow-by
gas from the crankcase is separated into fuel
vapor and fuel and then drawn into the
cylinder for re-burning.
TROUBLESHOOTING
Engine loses power or runs erratic at idle speed
1. Clogged P.C.V. system
2. Clogged air cleaner
3. Faulty purge control valve
4. Loose or broken E.E.C. system tubes or connectors
Engine idles or accelerates roughly
1. Faulty fuel cut-off valve
2. Faulty purge control valve
3. Clogged or faulty charcoal canister
18. EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM
18-3
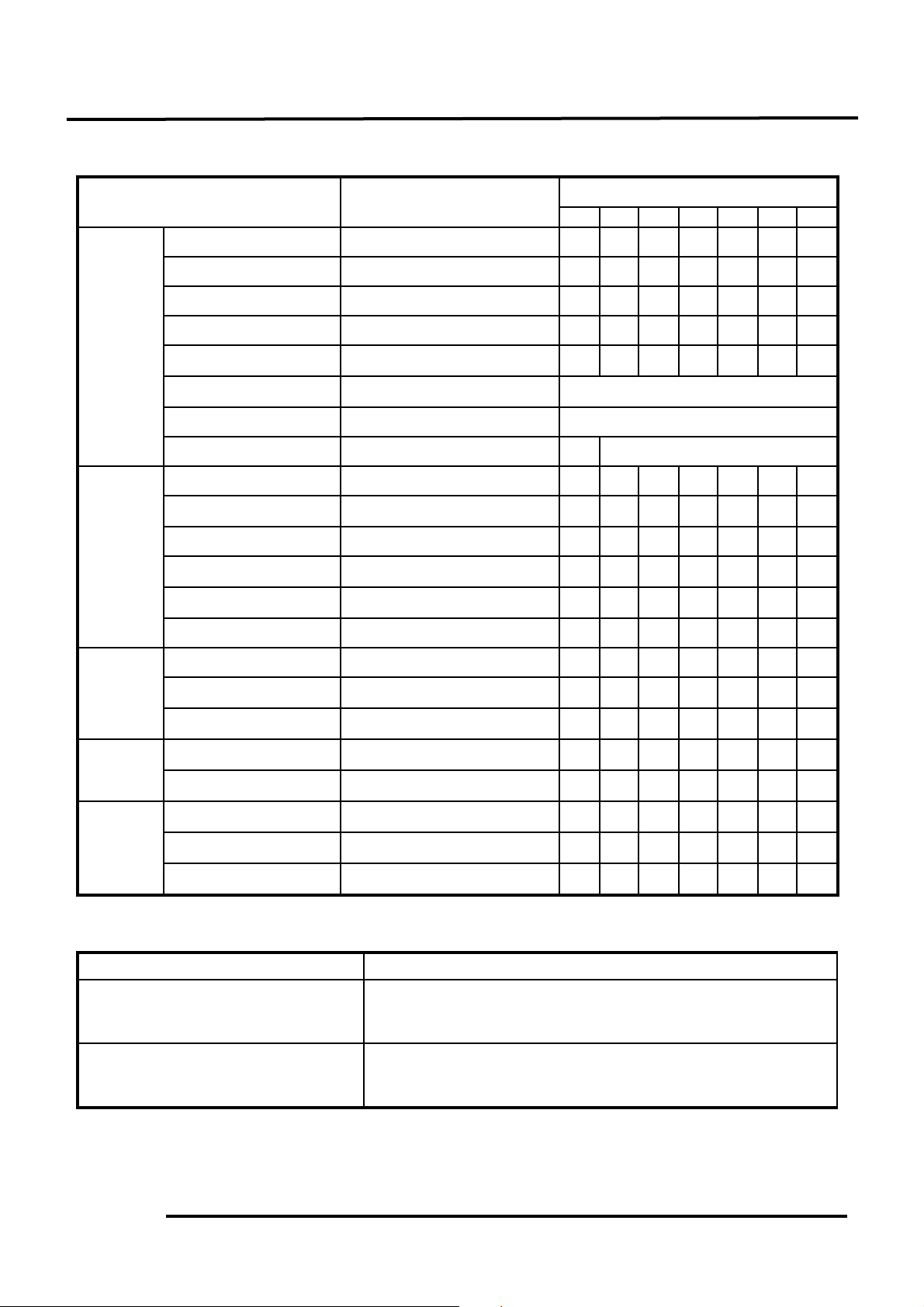
1. EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE:
Item
Inspection
Service Mileage (KM)
300
1000
3000
5000
7000
9000
1100
Drive belt
Belt thickness
○
Drive chain
Chain tension & length
○○○○○
○
Cam chain
Chain length
○○○
○
Engine
Valve clearance
IN/EX clearance
○○○○○
Parts
Manifold & cylinder
head bolts
Lock bolt
○
○
Air Cleaner
Clean or replace air cleaner
element
Clean at every 3000km and replace if
necessary
Cooling water
Check for engine cooling
Replace at every 10000km or every
Engine oil
Engine lubrication
○
Replace at every 1000km
Gear oil
Inspect or add gear oil
Fuel filter
Clean or replace fuel filter
screen
○○○
○
Fuel
Choke system
Check for proper operation
○○○
System
Fuel line connectors
Check for leaks, block or
breakage
○○○○○
○
Carburetor idle speed
Inspect, clean or adjust
○○○
Oil filter
Clean filter screen
○○○
Ignition timing
Inspect ignition timing
○○○○○
○
Ignition
Spark plug
Clean, inspect or replace
○○○○○
○
Ignition system wire
connection
Check wire connectors
○○○○○
○
Exhaust
Secondary air inlet line
Check for leaks, clogged or
loose pipe connection
○○○
Control
Intake manifold bolt
Check manifold connector
and replace if necessary
○○○○○
○
Evaporative
Engine compartment
pipe connection
Check for leaks, clogged or
loose pipe connection
○○○○○
○
Emission
Control
Charcoal canister
Check air vent hole for
damage and clean it
○○○○○
○
System
Purge control valve
Check for loose or broken
tube connectors
○○○○○
○
2. EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM IRREGULAR MAINTENANCE:
Item
Contents
*Burned crankshaft bearing
Before riding, inspect the engine for engine oil leaks to avoid
crankshaft bearing burning during riding.
*Burned cylinder or piston
Long-time or severe use may cause worn or seized cylinder or
piston. Clean or replace them with new ones.
 Loading...
Loading...