Page 1

Warning
When installing, servicing, or replacing parts for this product, do not perform any action that is not prescribed in the
owner's manual.
Do not apply excessive force to the electronic components or connectors on the circuit board, and do not disassemble it.
Electrical shock, fire, or malfunction may result.
Before installing this product, disconnect the power supply cable of the device in which it is being installed, and disconnect any cables that connect peripheral devices. Failure to do so may cause electrical shock or malfunctions.
Caution
Do not allow this product to become wet, and do not place objects on top of it. Doing so will cause malfunctions.
Before touching this product, touch a metal part of the device into which it will be installed, so that any static electricity
in your body will be discharged. Failure to do so will risk damaging the electronic components by static electricity.
When handling this product, be careful not to touch the leads (wires protruding from the electronic components) on the
rear side of the circuit board. Injury may result.
When installing this product, do not touch any unrelated parts or circuit boards. Electric shock or malfunction may result.
When installing this product, be careful not to cut yourself on any sharp edges or parts of this product or of the device into
which this product is being installed.
When installing this product, be careful not to drop screws etc. into the device into which this product is being installed.
The manufacturer makes no warrantee regarding possible malfunctions or damage that may result from improper use or
modification. The manufacturer also will take no responsibility for any damages that may result from loss or disappearance of data.
Installing this product
For the procedure of installing this product, refer to the owner's manual of the device into which the product is being
installed. If you have any questions, please contact your local Korg distributor.
Cautions when installing an option board
In order to install the board correctly, please pay attention to the following points.
Be careful of static electricity, which may damage components inside the product or on the board. Before beginning the
installation, touch an unpainted metal part of the chassis or the grounding terminal of a grounded device to discharge any
static electricity that may be present in your body.
Perform the installation according to the steps given in the directions, making sure that the board is installed correctly and
in the correct orientation.
Verify that the option board has been installed correctly. If installation is incorrect, faulty connections or a shorted power
supply can cause malfunctions.
All the screws that are removed will be used, so be careful not to lose any.
Using screws of the incorrect shape or length can cause malfunctions or damage to the product. Use only the screws that
were included with the option board or the screws that were fastened in the instrument.
When installing or removing the board, be careful not to drop parts or the option board into the instrument.
Make sure that the attaching screws are tightened firmly, and are not loose.
Handle the board with care. Subjecting it to physical shock (by dropping or pressing it) may cause damage or malfunctions.
Be careful not to touch any exposed metal portions of the circuit board, or any parts that are not essential to the installation
process.
2
Page 2

Installing this product..................................................... 2
Cautions when installing an option board.................... 2
1. Introduction ................................................................. 4
Features of the EXB-MOSS .......................................................... 4
2.The structure of bank F programs.............................. 5
Program structure .......................................................................... 5
Features of the oscillator ............................................................... 6
3. Bank F operations ....................................................... 7
Loading the preset programs......................................................... 7
Selecting a program/combination .................................................. 7
Editing a program .......................................................................... 7
Editing a combination .................................................................... 8
Sequencer and Song Play modes ................................................. 9
Control change transmission/reception for the EXB-MOSS ........ 10
4. Parameters ................................................................. 11
Program mode ........................................................................... 11
Program P0: Play ...............................................................................11
Program P1: Edit-Basic ...................................................................... 12
Program P2: Edit-Pitch.......................................................................36
Program P3: Edit-Filter.......................................................................38
Program P4: Edit-Amp .......................................................................40
Program P5: Edit-Common LFO ........................................................43
Program P6: Edit-Common EG .......................................................... 45
Program P7: Edit-Arpeggiator ............................................................46
Program P8: Edit-Insert Effect ...........................................................46
Program P9: Edit-Master Effect......................................................... 46
Combination mode .................................................................... 47
Combination P4: MOSS Setup ............................................... 47
Appendices .................................................................... 48
Cautions when using bank F ....................................................... 48
Affix the Sondius-XG label........................................................... 48
Modulation Source List ................................................................ 48
Voice Name List........................................................................... 49
3
Page 3

1. Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the Korg EXB-MOSS DSP
synthesizer board. In order to enjoy long and troublefree use, please read this manual carefully and use the
EXB-MOSS correctly.
Before you use this product, you must read the
“Safety Precautions” listed in the beginning of
the Parameter Guide.
This manual explains the Bank F parameters
that are added when the EXB-MOSS is
installed. For details on the parameters other
than Bank F, refer to the TRITON’s Parameter
Guide and Basic Guide etc.
Features of the EXB-MOSS
The EXB-MOSS is an option board containing a
MOSS (Multi-Oscillator Synthesis System) tone
generator with six-voice polyphony.
The MOSS tone generator is a physical modeling tone
generator that uses Sondius-XG* technology.
When the EXB-MOSS is installed into the TRITON,
you will be able to use the 128 MOSS tone generator
programs in program bank F.
Bank F is dedicated to MOSS tone generator
programs. Bank F programs can be selected for a
timbre/track in Combination, Song, and Song Play
modes. You can also create combinations or songs
that combine bank F programs with other programs
from banks A–E or G.
Broadly speaking, a MOSS tone generator program
consists of voice, EG, LFO, effect, and control
sections.
The voice section contains an oscillator and a filter.
— The oscillator provides two oscillators (1 and 2),
which can use thirteen different oscillator algorithms,
including Standard, Ring Modulation, VPM, Resonance, Organ Model, and Electric Piano Model. The
oscillator also provides a sub oscillator and a noise
generator.
— The filter provides five types of filters (two filter
systems), including a Human Voice Filter that lets you
simultaneously set two center frequencies, and a Dual
Band Pass Filter that lets you simulate the body
resonances of a violin or guitar.
Five EG units and four LFO units can be used to
modulate this voice section in order to create timevarying movement of pitch, tone, and volume.
* This product was developed under license of
physical modeling tone generator patents (http://
www.sondius-xg.com) owned by Stanford University
USA and Yamaha Corporation.
4
Page 4

2.The structure of bank F programs
Program structure
The programs of bank F have the following structure.
Oscillator
This section produces the waveform that is the basis
of the sound.
Settings are made by the “Program P1: Edit-Basic”
and “Program P2: Edit-Pitch” parameters.
— OSC 1, 2
Thirteen oscillator types (methods of sound generation) are provided. Of these, you can select two
oscillator types for use together, and make basic
settings for the pitch and waveform. However for
some oscillator types, only one type can be used.
Settings are made by the parameters of “1–1: Prog
Basic,” “1–2: OSC Basic,” “1–3: OSC1,” and “1–4:
OSC2.”
— Sub oscillator
One of four basic waveforms can be selected. Its pitch
can be set in the same way as OSC1 and 2.
These settings are made by the parameters of “1–2:
OSC Basic” and “2–3: SubOSC P.Mod.”
— Noise generator
This produces white noise, which can be passed
through a multi-mode filter (low pass filter, high pass
filter, band pass filter).
Settings are made by the “1–5: Noise Generator”
parameters.
Filter
This section processes the waveform by attenuating or
boosting specific frequency ranges. Two multi-mode
filters are provided. As filter types, you can select
from low pass, high pass, band pass, band reject, or
dual band pass filters. These filters can be used to
modify the brightness of the sound. You can also
select the connection routing between the two filters
and the mixer and amp.
Settings are made by the “Program P3: Edit-Filter”
parameters.
Amp
This section modifies the volume of the sound that is
output from the filter. There are two independent
amps. The signal that is input to each will depend on
the filter connections. The amp section also provides a
special envelope generator for controlling the amp
(Amp EG).
These settings are made by the “Program P4: EditAmp” parameters.
Effect
This section applies effects to the signal that is output
from the amp. It has the same parameter structure as
the programs of other banks.
Settings are made by the “Program P7: EditArpeggiator” and “Program P8: Edit-Insert Effect”
parameters.
Mixer
This section mixes the signals from oscillators 1 and
2, the sub oscillator, the noise generator, and the
feedback from the amp, and outputs the result to
multi-mode filters 1 and 2 (filter section).
Settings are made by the “1–6: Mixer” parameters.
OSC
Oscillator 1
Oscillator 2
Sub Oscillator
Noise Generator
Mixer
Filter
Filter 1
Mixer
LPF/HPF/BPF/BRF/2BPF
Filter 2
LPF/HPF/BPF/BRF/2BPF
EG1 EG2 EG3 EG4 Amp.EG
LFO1 LFO2 LFO3 LFO4
LFO
This section provides four LFO units. Each LFO can
be used as a modulation source for various parameters, to apply cyclic change to the sound.
Settings are made by the “Program P5: Edit-Common
LFO” parameters.
AMP
Amp1
Amp2
Feedback
FX
Pan
Insert
Effect
Joy Stick, Ribbon Controller
& other controllers
Master
Effect
Master
EQ
L/Mono
R
INDIVIDUAL
1, 2, 3, 4
5
Page 5

EG
This section provides four general-purpose EG units.
Each EG can be used as a modulation source for
various parameters, to apply time-variant change to
the sound.
Settings are made by the “Program P6: Edit-Common
EG” parameters.
Arpeggiator
The arpeggiator can be used in the same way as for
the programs of other banks. Settings are made by the
“Program P7: Edit-Arpeggiator” parameters.
Program Basic
Here you can make settings for functions such as
Scale, Key Assign, and Controllers (joystick, ribbon
controller etc.). Settings are made by the “1–1: Prog
Basic” and “1–7: Controller Setup” parameters.
Resonance
This oscillator uses filter resonance, and is an
especially effective way to produce mallet sounds and
pad sounds. (☞p.20 of this manual)
Ring Modulation
Cross Modulation
Sync Modulation
These are special oscillators for generating the sounds
which could be produced on an analog synthesizer by
modulating one oscillator with another. These allow
you to produce sounds with complex overtone
structures such as bells, metallic sounds, and gongs.
(☞p.21–23 of this manual)
Organ Model
This simulates a drawbar organ with three drawbars
(when one oscillator is used) or six drawbars (when
two oscillators are used) (☞page 23 of this manual).
Since each drawbar can use one of four types of
waveform, a wide range of tones can be produced.
Features of the oscillator
In a bank F program, you can choose from 13
oscillator types for OSC1 and 9 oscillator types for
OSC2.
In Program P1 “1–1: Program Basic” or “1–2: OSC
Basic” you can select the oscillator type for OSC1 and
OSC2, and use them together.
If a Single Size oscillator (Standard–E. Piano Model)
is selected for OSC1, you can select a Standard–E.
Piano Model for OSC2 as well. If a Double Size
oscillator (Brass Model–Bowed String Model) is
selected for OSC1, OSC2 will be unavailable.
Standard
This simulates the oscillator of an analog synthesizer.
You can use PWM (pulse width modulation) etc. to
produce the same results as on an analog synthesizer.
(☞p.14 of this manual)
Comb Filter
This oscillator creates pitched components from noise
or an impulse. In addition to producing noisy sounds,
it can also produce a wide variety of sound ranging
from synth basses to string-like sound. (☞p.17 of this
manual)
E. Piano Model (electric piano model)
This is a physical model that simulates a warm vintage
electric piano. (☞p.24 of this manual)
Brass Model
This is a physical model that simulates a brass
instrument such as a trumpet or trombone. (☞p.25 of
this manual)
Reed Model
This is a physical model that simulates a woodwind
instrument such as a sax or flute. (☞p.27 of this
manual)
Plucked String Model
This is a physical model that simulates plucked string
instrument such as guitar or bass. (☞p.29 of this
manual)
Bowed String Model
This is a physical model that simulates a bowed string.
(☞p.31 of this manual)
VPM (Variable Phase Modulation)
This oscillator uses phase modulation to generate
harmonics. A rich harmonic structure can be created
by using phase modulation between two oscillators
and the wave shaping table. (☞p.18 of this manual)
6
Page 6

3. Bank F operations
Loading the preset programs
Please load the “EXBMOSS-00FD” data from the
floppy disk included with the EXB-MOSS. For details
on the procedure, refer to “Disk mode” of the TRITON Basic Guide. The floppy disk contains the
following data.
MOSS.PCG
Program Bank A*, B*, F
Combination Bank A*, B
Drum Kits 00–15(A/B)*
Arpeggio Pattern 000–199(A/B)*
Global setting*
MOSS.SNG
Cue List
Demo Song "Feet Hurt MOSS" by Scott Frankfurt
©1999 Bleach Bros. Music
(breachbros@earthlink.net) - all rights reserved.
Program bank F contains programs that use the EXBMOSS.
Combination bank B contain combinations that use
bank F programs together with the TRITON’s
preloaded programs of banks A and B.
* Same as the preloaded data of the TRITON.
When you load MOSS.PCG
Programs, combinations, drum kits, arpeggio patterns,
and global settings will be written into the TRITON’s
internal memory.
Selecting a program/
combination
In “Program P0: Play,” you can select a bank F
program 000–127 in the same way as for banks A–E.
You can also select programs from the “Category/
Program Select” menu or the “Bank/Program Select”
menu.
Combinations can be selected in “Combination P0:
Play,” and also from the “Category/Combination
Select” menu or the “Bank/Combination Select”
menu.
For a list of the programs/combinations in the
included floppy disk, refer to “Voice Name List” on
p.49 of this manual.
Editing a program
If a bank F MOSS tone generator program is selected
in “Program P0: Play,” you can use P1–P9 to edit the
program parameters. For details on the program
parameters, refer to the “Parameters” section that
begins on p.11 of this manual.
The performance editor parameter “Pitch
Stretch” of “Program P0: Play” cannot be used
for bank F programs.
When you load MOSS.PCG, all the current
contents of internal memory will be erased and
overwritten.
When you load MOSS.SNG
Demo songs that use the bank F programs etc. of
MOSS.PCG will be loaded. These songs can be
played in Sequencer mode.
When you select and load MOSS.SNG, all the
current contents of sequencer memory will be
erased and overwritten.
7
Page 7

Editing a combination
You can select a bank F program for a timbre in a
combination, and use it in the combination together
with programs of banks A–E and G. Different MOSS
tone generator programs from bank F can be selected
for two or more timbres, and used multi-timbrally. In
this case, the total polyphony of the MOSS tone
generator programs will be six voices.
Insertion/master effect settings and the routing
to the individual audio outputs cannot be made
independently for multiple timbres.
If you change programs while a bank F
program is sounding, the bank F program will
stop sounding.
When playing multi-timbrally and a bank F
program is being sounded, selecting a bank F
program for the timbre number prior to that
timbre number will cause noise to be heard in
the currently-sounding bank F program.
Editing a combination
Here’s how to select programs and set the parameters
that determine how each program will sound.
(1) Select Combination P0: Play.
For details on how to enter each page, refer to p.52
“Combination mode” in the TRITON Basic Guide.
(2) Select the combination number that
you wish to edit.
(3) Select the Combination P4: MOSS
Setup tab.
Before you select a bank F program, make settings
here to specify how the MOSS tone generator will
sound.
8
(4) Set the Voice Allocation Reserve
parameter to specify the polyphony for
each timbre.
For each timbre, specify the number of voices that
will be allocated when a MOSS tone generator
program is selected. A total of six voices can be
allocated.
For example, you might allocate two voices to timbre
1 for a bass-type MOSS program, and up to four
voices to timbre 2 for an electric piano MOSS
program.
These settings have no effect on the programs
of banks A–E and G.
When the timbre bank/program is changed to
switch a timbre from a bank F program to a
bank A–E or G program, the bank A–E or G
program will sound as usual.
When the timbre bank/program is changed to
switch a timbre from a bank A–E or G
program to a bank F program, it will sound
according to the setting you make here.
Timbres for which a value of 0 is set will not
sound if a bank F program is selected.
(5) Set the MOSS BUS Select Reference.
The bank F programs will be routed to the insertion/
master effects or individual audio output according to
the settings of the timbre you select here.
The timbre 1–8 you select here does not have
to be using a bank F program.
Bank F programs can be used for two or more timbres
according to the “Voice Allocation Reserve” setting.
However, settings for insertion/master effects and
routing to individual audio outputs can not be made
independently for two or more timbres.
Timbre settings for insertion/master effects and
routing to individual audio outputs are made in the
Program P8: Routing tab. Use the following procedure
to make settings.
Example)
1. Set “MOSS BUS Select Reference” to Timbre 1.
2. In the Program P8: Routing tab, set the timbre 1
“IFX/Indiv.Out BUS Select” to L/R.
All bank F programs that you selected will be sent to
L/R (without using the insertion effects).
3. Set the timbre 1 parameters “Send 1” and “Send 2”
to 064 and 127 respectively.
The signal will be sent to MFX1 and MFX2 at the
specified levels.
4. If you wish to use an insertion effect, set “IFX/
Indiv.Out BUS Select” to IFX1–IFX5. If you wish to
output to the [AUDIO OUT INDIVIDUAL] 1–4 jacks,
select 1–4, 1/2, or 3/4.
Page 8

The actual levels of send 1 and 2 for a timbre
using a bank A–E or G program is determined
by multiplying the timbre setting by the send
level of the program, but for timbres that use a
bank F program, the send level setting of the
timbre will be the actual level.
This setting has no effect for bank A–E or G
programs.
(6) Select Combination P1: Edit-Program/
Mixer.
Sequencer and Song Play
modes
Bank F programs can be selected for playback of a
song or Standard MIDI File, or for performance from
the keyboard. In the same way as in a combination,
bank F programs can be selected for two or more
tracks and used multi-timbrally. In this case, the total
polyphony of the bank F programs will be six
voices.
Insertion/master effect settings and individual
audio output routing cannot be specified
independently for each track.
Details of the settings, the operation of each parameter, and cautions are the same as for combinations.
Refer to “Editing a combination” on p.8 of this
manual.
☞ Sequencer P4: MOSS T01–08, MOSS T09–16 tabs
☞ Song Play P1: MOSS T01–08, MOSS T09–16 tabs
(7) In “Bank/Program,” select a bank F
program.
Programs can also be selected from the “Category/Program
Select” menu or the “Bank/Program Select” menu.
(8) Use “Pan” to adjust the panpot of the
timbre.
When a bank F program is selected, the Random
setting will not be available. If Random is selected,
the sound will be placed in the center, as with C064.
(9) Use “Volume” to adjust the volume of
the timbre.
(10) Make settings for other parameters.
In the same way as for programs of other banks, set the
parameters of each timbre, and make arpeggiator settings and
insertion/master effect settings.
However when a bank F program is selected for a timbre, the
following parameters will function as explained below.
— “OSC Select” will have no effect. (Combination P2:
OSC tab)
The “Detune” range will be ±100. Even if the absolute
—
value of the parameter setting is greater than 100, the actual
detune value will be ±100 cents. (Program P2: OSC tab)
— The Key Zone / Vel Zone “Top Slope” and
“Bottom Slope” settings will have no effect. (Program
P4: Key Z, Vel Z tabs)
9
Page 9

Control change transmission/
reception for the EXB-MOSS
In the same way as bank A–E or G programs, bank F
programs can receive MIDI control changes CC#70–
79, and can be operated by the front panel realtime
control knobs 1–4 in A-mode. In B-mode, CC#70–79
can be assigned as knob functions, and used to control
the program sound. These settings can be saved by
writing them in Program mode.
☞ Refer to p.223 of the TRITON Parameter Guide.
CC#70: Sustain Level
“Sustain Level” (Program P4: AmpEG tab, Program P6)
This controls the EG that is selected by Filter
EG (Program P3: Filter 1/2 tab) and Amp
Level EG (Program P4: Amp 1/2 Level tab).
CC#71: Filter Resonance Level
“Filter A Resonance” (Program P3: Filter 1/2 tab)
“Filter B Resonance” (Program P3: Filter 1/2 tab)
CC#72: Release Time
“Release Time” (Program P4: AmpEG tab, Program P6)
This controls the EG that is selected by Filter
EG (Program P3: Filter 1/2 tab) and Amp
Level EG (Program P4: Amp 1/2 Level tab).
CC#73: Attack Time
“Attack Time” (Program P4: AmpEG tab, Program P6)
“Time Modulation At” (Program P4: AmpEG tab,
Program P6)
CC#76: Pitch LFO Speed
“LFO1–4 Frequency” (Program P5: LFO1–4 tabs)
If LFO 1–4 is selected for Pitch Modulation
AMS1, AMS2 (Program P2: OSC1/2 Pitch
Mod. tab) or Common Pitch Modulation AMS
(Program P2: Common Pitch Mod. tab), this
control change message will control that LFO.
CC#77: Pitch LFO Intensity
“Pitch Modulation AMS1 Intensity” (Program P2:
OSC1/2 Pitch Mod. tab)
“Pitch Modulation AMS2 Intensity” (Program P2:
OSC1/2 Pitch Mod. tab)
“Common Pitch Modulation AMS Intensity” (Program P2: Common Pitch Mod. tab)
If LFO 1–4 is selected for the corresponding
AMS, this control change message will control
that LFO.
CC#78: Pitch LFO Delay
“LFO1, 2, 3, 4 Fade” (Program P5)
If LFO 1–4 is selected for Pitch Modulation
AMS1, AMS2 (Program P2: OSC1/2 Pitch
Mod. tab) or Common Pitch Modulation AMS
(Program P2: Common Pitch Mod. tab), this
control change message will control that LFO.
CC#79: Filter EG Intensity
“Filter A EG Intensity” (Program P3: Filter 1/2 tab)
“Filter B EG Intensity” (Program P3: Filter 1/2 tab)
This controls the EG that is selected by Filter
EG (Program P3: Filter 1/2 tab) and Amp
Level EG (Program P4: Amp 1/2 Level tab).
CC#74: Low Pass Filter Cutoff Frequency
“Filter A Frequency” (Program P3: Filter 1/2 tab)
“Filter B Frequency” (Program P3: Filter 1/2 tab)
CC#75: Decay Time
“Decay Time” (Program P4: AmpEG tab, Program
P6: EG1–4 tabs)
“Slope Time” (Program P4: AmpEG tab, Program P6:
EG1–4 tabs)
This controls the EG that is selected by Filter
EG (Program P3: Filter 1/2 tab) and Amp
Level EG (Program P4: Amp 1/2 Level tab).
10
Page 10

4. Parameters
This document explains the parameters that appear the
screen pages that are added when the EXB-MOSS is
installed. For details on the other screen pages, refer to
the Parameter Guide and Basic Guide etc. of the
TRITON.
In Program mode, you can use the Write Program
page menu command to write an edited program into
the specified program number.
When you press the front panel [REC/WRITE]
key, the “Update Program” dialog box will
appear. Here too, you can write to the currently selected program.
Be sure to write important programs that you
edit. If you turn off the power or select another
program before you write, your edits cannot be
recovered. Refer to “Saving data” on p.37 of
the TRITON Basic Guide.
Program mode
Program P0: Play
0–1: Perf.Edit (Performance Edit)
Here you can select a program and perform simple
editing.
For details on the parameters, refer to p.1 “1. Program
mode” of the TRITON Parameter Guide.
Parameters that can be controlled from the Performance
Editor
Octave Octave of OSC1, OSC2, and Sub OSC
Pitch Cannot be used for bank F.
OSC Balance OSC 1 and 2 levels of OSC Mixer 1
and 2
Amp Level Output level
Attack Time Amp EG, EG1,2,3,4
Attack Time, Time Modulation At
(controls the EG selected by Filter 1, 2,
Filter EG, Amp 1, 2, and Amp Level
EG)
Decay Time Amp EG, EG 1, 2, 3, 4
Decay Time, Slope Filter (controls the
EG selected by Filter 1, 2, FilterEG,
Amp1, 2, and Amp Level EG)
IFX Balance Wet/dry balance of each effect IFX1–5
MFX Balance Master effect return 1, 2
Depending on the oscillator types or effect
types used by the programs, a certain interval
of time may be required after a program is
selected until it actually changes.
0–2: Arpeggio
Here you can perform simple editing of the
arpeggiator.
For details on the parameters, refer to p.3 “0–2:
Arpeggio” of the TRITON’s Parameter Guide.
11
Page 11

Program P1: Edit-Basic
Here, you can select programs and perform simple
editing.
1–1: Program Basic
1–1a
1–1b
OSC 2 (Oscillator 2 Type)
[Standard…E. Piano Model]
Selects the oscillator type for oscillator 2. Refer to OSC 1.
1–1b: Unison
Here, you can make settings for unison mode.
Unison [OFF, 2voices, 3voices, 6voices]
Specifies the number of notes which will be sounded
in unison. With a setting of OFF, unison will not be
used.
The maximum polyphony will be three notes with a
1–1c
setting of 2voices, two notes for a setting of 3voices,
and one note for a setting of 6voices.
1–1d
1–1a: Multi OSC Setup
Here, you can make settings for the oscillator.
The parameters that are set in “1–3: OSC 1” and “1–4:
OSC 2” will differ depending on the oscillator type
that is selected here. (Link: 1–2a, 1–2b)
OSC 1 (Oscillator 1 Type)
[Standard…Bowed String Model]
Selects the oscillator type for oscillator 1.
For details on the oscillator types, refer to “Features of
the oscillator” on p. 4 of this manual.
Single Size
Standard
Comb Filter
VPM (Variable Phase Moulation)
Resonance
Ring Modulation
Cross Modulation
Sync Modulation
Organ Model
E. Piano Model
Double Size
Brass Model
Reed Model
Plucked String Model
Bowed String Model
When Double Size (Brass Model, Reed
Model, Plucked String Model, or Bowed
String Model) are selected, OSC 2 cannot be
used.
12
Mode [Fixed, Dynamic]
Specifies how the number of voices specified by the
“Unison” setting will be allocated.
With a setting of Fixed, the number of voices
specified by the “Unison” setting will always sound.
With a setting of Dynamic, the number of voices will
be determined by the current note-playing situation.
Detune [0…99]
Detunes the notes that are sounded simultaneously by
the Unison function.
1–1c: Voice Assign Mode
Here, you can specify how notes will sound when
keys are pressed.
Poly, Mono (Single, Multi)
Selects whether the sound will be played monophonically or polyphonically.
Poly: Polyphonic playing
Mono (Single): Single-triggered monophonic playing
Mono (Multi): Multi-triggered monophonic playing.
When Poly is selected, the Retrigger Control
and Threshold parameters will be unavailable.
Retrigger (Retrigger Contol) [Off…MIDI:CC#83]
“Retrigger” refers to the action of resetting the EG and
LFO at the time of note-on (the EG will return to its
start level, and the LFO will return to the beginning of
the cycle of its waveform). Here you can select the
controller which will specify whether or not the sound
will be retriggered when a note-on occurs.
Threshold (Retrigger Control Threshold) [1…127]
Specifies the value at which EG and LFO will be
retriggered by a note-on.
The state of the controller selected by Retrigger
Control (i.e., whether the controller value is above or
below the specified Threshold value) will determine
whether or not the sound will be retriggered when a
note-on occurs.
Page 12

The operation of this function will differ depending on
the “Voice Assign Mode” setting.
With a setting of Mono (Single), retriggering will
occur if the controller is above the threshold value. If
Retrigger Control is OFF, retriggering will not occur.
With a setting of Mono (Multi), retriggering will
occur if the controller is below the threshold value. If
Retrigger Control is OFF, retriggering will always
occur.
If a note-on occurs when all notes are off,
retriggering will always occur.
LFO’s whose Key Sync is turned OFF will
not be reset even if retriggering occurs.
Priority [Low, High, Last]
Specifies the priority order that will be used when the
number of keys pressed exceeds the maximum
polyphony.
Low: The lowest note will take priority
High: The highest note will take priority
Last: The last-pressed note will take priority
Hold
When this is checked, the note will continue to sound
after the key is released. However, if the EG selected
by “4–1: Amp1,” “Amp2” (normally the Amp EG is
used) has a sustain level of zero, the note will decay
naturally.
1–1d: Scale
Specifies the scale type
Type (Scale Type)
[Equal Temperament…User Octave Scale 15]
Selects the basic scale for the internal tone generator.
The user scales can be specified in Global mode “3–1:
User Scale” (☞page 127 in Parameter Guide).
Equal Temperament
The most widely used scale, consisting of equallyspaced semitone steps.
Pure Major
The major chords of the selected key will be perfectly in tune.
Pure Minor
The minor chords of the selected key will be perfectly in tune.
Arabic
This reproduces a quarter-tone scale of Arabic music.
Pythagorean
A scale based on ancient Greek musical theory, suitable for playing melodies.
Werckmeister (Werkmeister III)
An equal-tempered scale used in the later Baroque
period.
Kirnberger (Kirnberger III)
A scale created in the 18th century, and used mainly
for tuning harpsichords.
Slendro
An Indonesian gamelan scale in which the octave
consists of 5 notes.
If the Key parameter is set to C, use the C, D, F, G,
and A keys. (Other keys will produce the same
pitches as equal temperament.)
Pelog
An Indonesian gamelan scale in which the octave
consists of 7 notes.
If the Key parameter is set to C, use only the white
keys. (The black keys will produce the same pitches
as equal temperament.)
Stretch
This is a tuning used on acoustic pianos.
User All Notes Scale
This is the full-range scale (C-1=G9) that you create in Global mode “3–1b: User All Notes scale”
(☞page 121 in TRITON Parameter Guide).
User Octave Scale 00–15
This is the one-octave scale that you create in Global mode “3–1a: User Octave Scale” (☞page 121
in TRITON Parameter Guide).
Key (Scale Key) [C…B]
Specify the tonic note of the selected scale. This
setting has no effect for Equal Temperament,
Stretch, or User All Note Scale .
If a scale other than equal temperament is
selected, certain combinations of this parameter and the “Key” parameter may cause the
tuning of the base key (for example A=440
Hz) to become incorrect. If this occurs, you
can adjust the “Master Tune” (Global P0:
Basic tab).
Random [0…99]
As this value is increased, the pitch of the note will
become increasingly unpredictable. Normally you will
leave this set at zero.
Adjust this parameter when you wish to simulate
instruments whose pitch is naturally unstable, such as
tape-mechanism organs or acoustic instruments.
13
Page 13
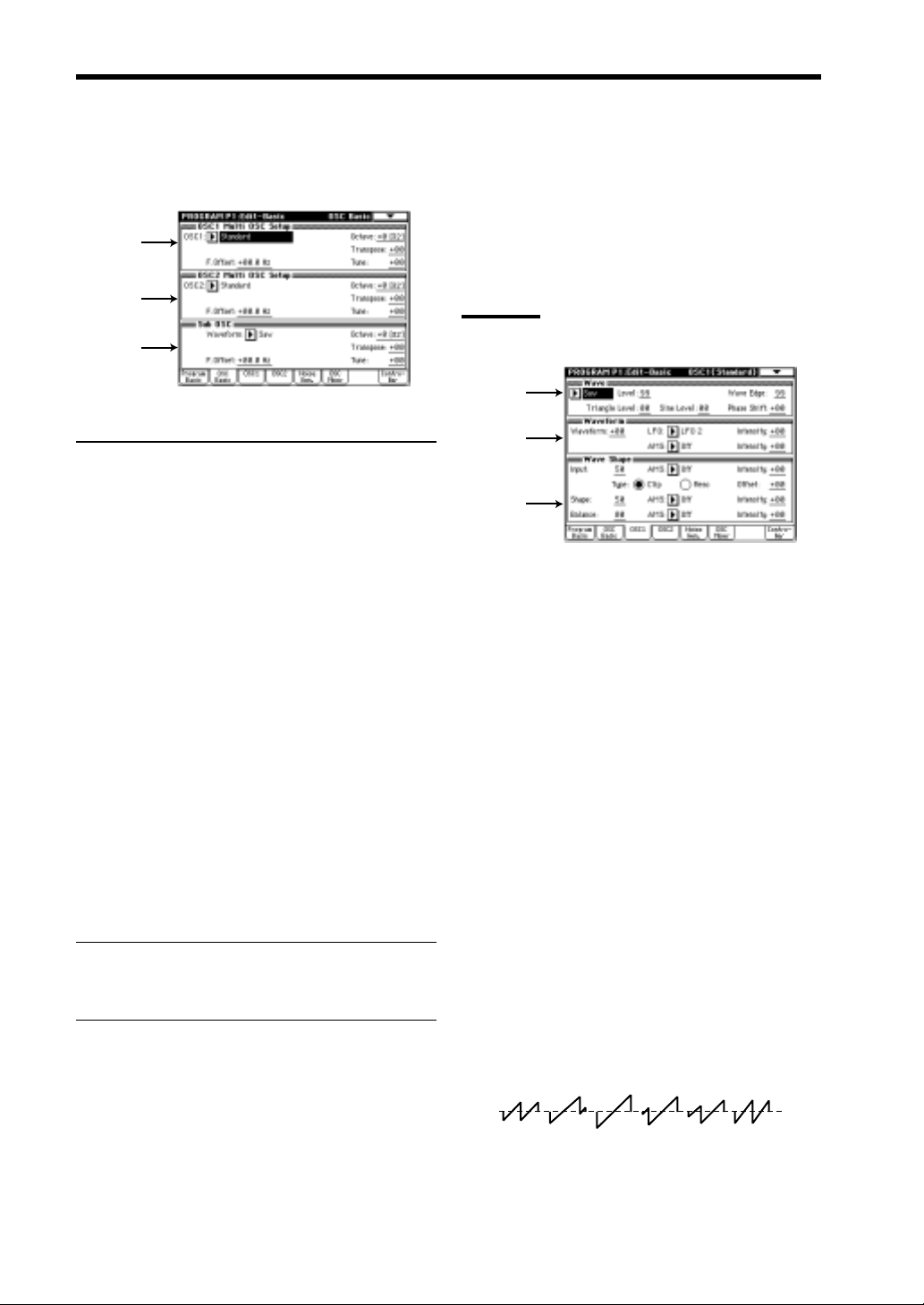
1–2: OSC Basic (Osillator Basic)
1–2a
1–3: OSC1 (Oscillator 1)
Make settings for each oscillator type. The oscillator
type is selected in “1–1a: Mult OSC Setup” or “1–2:
OSC Basic.”
The parameters that are displayed will depend on the
selected oscillator type.
1–2b
1–2c
1–2a: OSC 1 Multi OSC Setup
Specifies the basic pitch of oscillator 1
OSC 1 (Oscillator 1 Type)
[Standard…Bowed String Model]
This shows the oscillator type that was selected in “1–
1a: Multi OSC Setup.” This is linked with the identically-named parameter in “1–1a: Multi OSC Setup.”
Octave [–2[32']…+1[4']]
Specifies the basic pitch of oscillator 1 in steps of an
octave.
32' is two octaves below, 16' is one octave below, 8'
is standard pitch, and 4' is one octave above.
Transpose [–12…+12]
Adjusts the basic pitch specified by “Octave” in
semitone steps.
Tune [–50…+50]
Makes fine adjustments to the pitch in one-cent steps.
F. Offset (Frequency Offset) [–10.0…+10.0]
Makes fine adjustments to the pitch in 0.1 Hz steps.
1–2b: OSC 2 Multi OSC Setup
Selects the oscillator type for oscillator 2.
Standard
1–3a
1–3b
1–3c
This oscillator produces the waveforms used by an
analog synthesizer (sawtooth wave, pulse wave,
triangle wave) and sine wave. Sawtooth wave, pulse
wave and triangle wave waveforms can be modified
using waveform modulation. You can specify either
sawtooth wave or pulse wave as the main waveform,
and mix triangle wave or sine wave with this for
output. The level of these three waveforms can be
adjusted independently.
In addition, wave shaping can be applied to the output
of this oscillator.
Waveform modulation
Pulse width modulation (PWM) on an analog synthesizer produces time-varying change in the pulse width
of a pulse wave. The waveform modulation provided
by the EXB-MOSS option is an extension of this,
which varies not only the pulse width but also the
waveform of a sawtooth wave or triangle wave.
Waveform modulation will affect the various waveforms as follows.
1–2c: Sub OSC
Make basic settings for the sub oscillator.
Parameters other than Waveform are the same as for
oscillator 1.
Waveform [Saw…Sine]
Select the waveform of the sub oscillator.
14
Sawtooth wave
-99 -33 0 33 66 99
Waveform modulation will modify a sawtooth
waveform as shown below, creating time-variant
change in the sound.
Page 14

When modulation is 0, the basic sawtooth waveform
will be produced, and when it is 99, a sawtooth wave
of double the frequency will be produced. If the
modulation value is a negative number, a different
effect will result than with positive settings.
Pulse wave
-98 -33 0 33 66 98
Waveform (pulse width) modulation will modify a
pulse waveform as shown below, creating time-variant
change in the sound. When modulation is 0, a square
wave will be produced, and when it is 99, the pulse
width will be 0, meaning that there will be no sound.
If the modulation value is a negative number, the
results will be inverted.
Triangle wave
Sine Level [0…99]
Specifies the output level of the sine waveform. It will
be output mixed with the main waveform.
Phase Shift (Triangle & Sine Phase Shift)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the phase difference between the main
waveform and the triangle and sine waveforms. (The
triangle and sine waveforms will always be in phase
with each other.)
1–3b: Waveform (Waveform Modulation)
Waveform
[–99…+99]
Specifies the waveform. For the way in which this
value will affect the waveform, refer to the diagrams
shown on the previous page for sawtooth wave, pulse
wave, and triangle wave.
-99 -25 0 25 50 75 99
Waveform modulation will modify a ramp wave as
shown below, creating time-variant change in the
sound. When modulation is 0, a triangle wave will
result, and as the modulation value increases, the
waveform will become a ramp wave (a waveform in
which the slope is broken in two). At a modulation
value of 50, a trapezoidal wave will result, and at a
value of 99 the waveform will once again be a triangle
wave. If the modulation value is a negative number,
the results will be inverted.Compared to sawtooth or
pulse waves, this waveform produces a strong
fundamental with fewer overtones, making it particularly suitable for bass sounds etc.
1–3a: Wave
Main Wave [Saw, Pulse]
Selects the main waveform. Select either Saw
(sawtooth wave) or Pulse (pulse wave).
Level [0…99]
Specifies the output level of the main waveform.
Wave Edge [0…99]
Adjusts the amount of high-range overtones for the
main waveform. As the pitch rises, this effect will
become stronger, and in the low range there will be
little effect. Lower settings of this parameter will
produce a more mellow sound, and in the vicinity of 0
the volume will also decrease.
Triangle Level [0…99]
Specifies the output level of the triangle waveform. It
will be output mixed with the main waveform.
LFO [LFO1…LFO4]
Selects the source LFO for waveform modulation.
LFO settings are made in the “Program P5.”
Intensity (Waveform Modulation LFO Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the waveform
modulation that will be controlled by the LFO
specified in “LFO.”
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Waveform.”
Intensity (Waveform AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the waveform modulation controlled by the “AMS.” For negative settings, the
polarity of the modulation source will be inverted.
1–3c: Wave Shape
Input (Input Level) [0…99]
Specifies the level of the signal that is input from the
standard oscillator to the wave shaping table.
Example of when Input Level is modified (Table Type : Reso)
Output level
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Input.”
Input level
Output waveform
Input Level
=99
Input waveform
Input Level
=75
Input Level
Input Level
=50
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
=25
15
Page 15
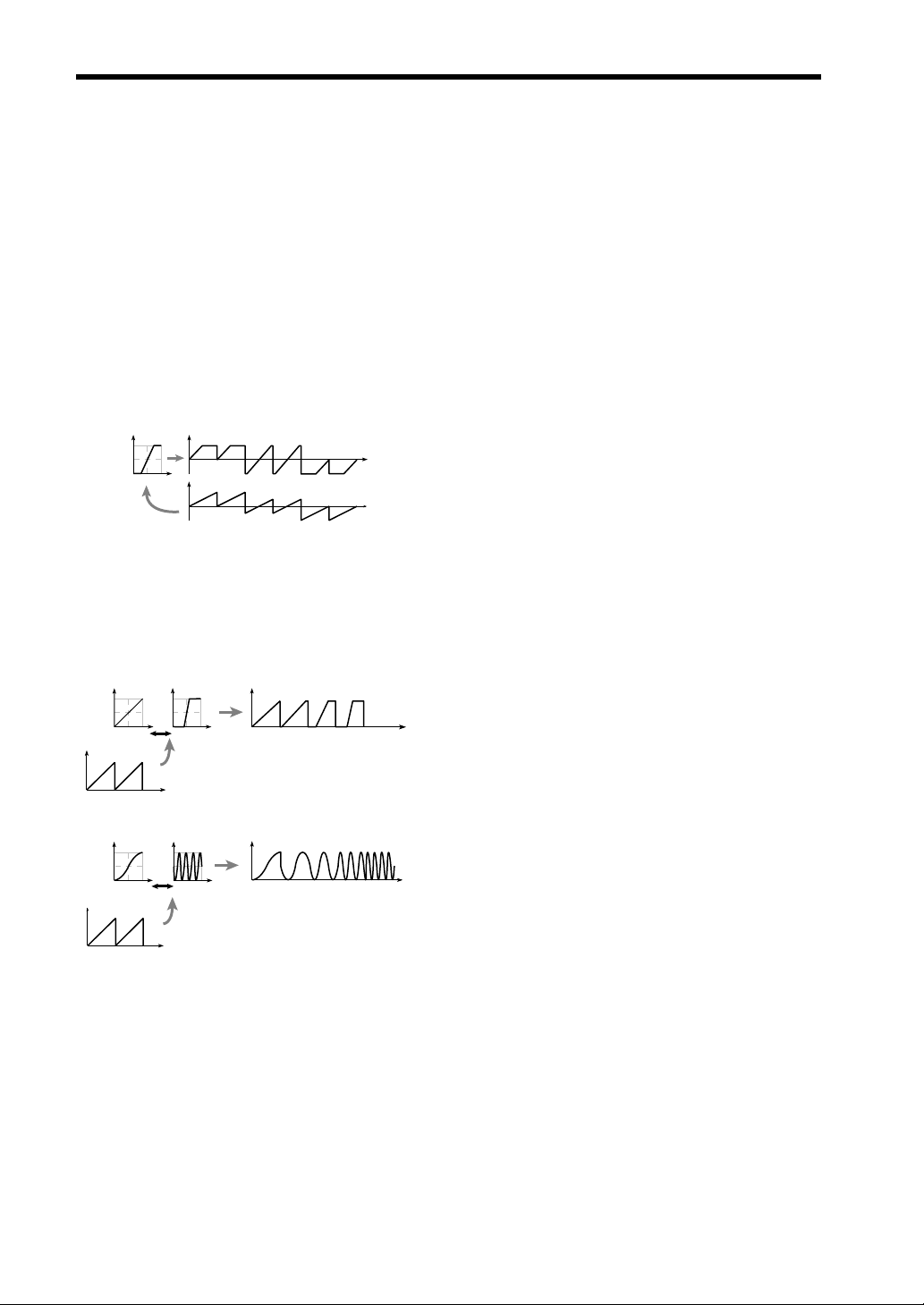
Intensity (Input Level AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the waveform
modulation controlled by the “AMS.”
Type (Wave Shape Table Type) [Clip/Reso]
Use the radio buttons to select the wave shaping
table which will modify the input waveform.
Clip (clip type) and Reso (resonant type) tables will
modify the waveform as shown by the diagrams in
Shape, below.
Offset (Wave Shape Offset) [–99…+99]
Specifies an offset amount that will be added to the
signal specified by “Input.”
Example of when Offset is modified (Table Type: Clip)
Output level
Output waveform
99, it will be only the output of the wave shaping
table.
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Balance.”
Intensity (Balance AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the waveform
modulation controlled by the “AMS.”
Input level
Offset=50 Offset=0 Offset=-50
Input waveform (Input Level fixed)
Shape [0…99]
Specifies the characteristics of the table which will
modify the input waveform. The characteristics of the
table will change as follows.
Shape of the wave shaping table and the Shape parameter
CLIP type
Output level
Shape:0
Waveform
level
Waveform before being input to the table
Resonant type
Output level
Shape:0
Waveform
level
Waveform before being input to the table
Shape:99
Shape:99
Input
level
Output of the clip type table when a sawtooth
waveform is input
Input
level
Output of the resonance type table when
a sawtooth wave is input
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Shape.”
Intensity (Shape AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the waveform
modulation controlled by the “AMS.”
Balance [0…99]
Specifies the balance between the signal that has
passed through the wave shaping table and the output
signal from the standard oscillator. With a setting of
16
Page 16
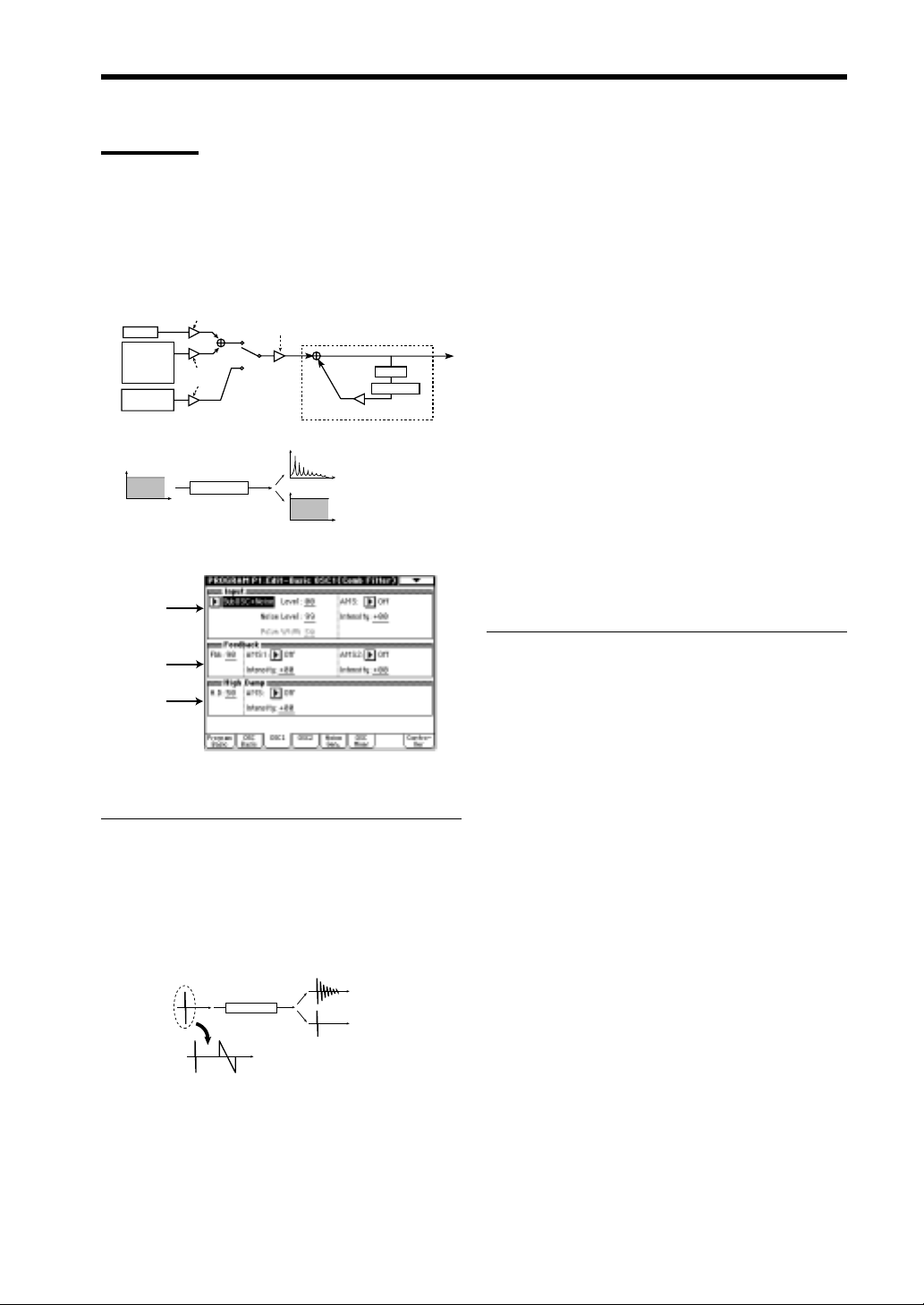
Comb Filter
In this oscillator, the signal from the other oscillator
waveform or the noise generator is sent through a
comb filter, and the feedback level of the comb filter
is varied in order to produce tonal change.
When noise is input, raising the feedback of the comb
filter will gradually change the sound into a pitched
tone.
Comb Oscillator
Example of when noise is input
Level
1–3a: Input
Input
Selects the signal that will be input to the comb filter.
Level (Input Wave Level) [0…99]
Specifies the volume level of the signal that will be
input to the comb filter.
Noise Level
Noise
OSC1/2 or
Sub OSC
Filter1 out
Filter2 out
Pulse Noise
or Impulse
Frequency
Input Level Mod.Source/Intensity
Input Wave
Level
Comb Filter
Feedback>0
Feedback=0
Level
Level
Comb Filter
Delay
High Damp
Comb Filter Feedback
Frequency
As the Feedback value increases,
the sound will become more pitched.
Frequency
1–3a
1–3b
1–3c
[OSC2(1)+Noise, SubOSC+Noise, Filter1+Noise,
Filter2+Noise, Pulse Noise, Impulse]
Example of when an Impulse is input
Time
Pluse
Width=0
Comb Filter
Pluse
Width=99
Feedback>0
Feedback=0
Time
Time
As the Feedback is
increased, the decay
time will become longer.
Time
Noise Level [0…99]
This parameter will be available only if “Input” has
been set to OSC2(1)+Noise, SubOSC+Noise,
Filter1+Noise or Filter2+Noise. It specifies the
volume level of the noise generator output which will
be input to the comb filter.
Pulse Width [0…99]
This parameter will be available only if “Input” has
been set to Pulse Noise or Impluse.
It specifies the length of time that the Pulse Noise or
Impluse will last after being triggered.
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the volume level of the signal being
input to the comb filter.
The volume level is set by the “Level” or the “Noise
Level.”
Intensity (Input Wave Level AMS Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS.”
1–3b: Feedback
Fbk (Feedback) [0…99]
Specifies the amount of feedback for the comb filter.
If this value is high , the resonance of the comb filter
will be high, and the tone will have a clear sense of
pitch. Conversely, if this value is low , the input signal
will be output without change, and if the input signal
is only noise, the output signal will have no sense of
pitch.
AMS1 (Alternate Modulation Source 1)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 1 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Fbk.”
Intensity (Feedback AMS1 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of “AMS1 .”
AMS2 (Alternate Modulation Source 2)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 2 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Fbk.”
Intensity (Feedback AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of “AMS2 .”
17
Page 17

1–3c: High Damp
H. D (High Damp) [0…99]
Specifies the amount of attenuation that will be
applied to the high-frequency component of the
feedback signal within the comb filter.
As this value is increased, the tone will become more
mellow. Conversely, decreasing this value will
produce a brighter tone.
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “H. D.”
Intensity (High Damp AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specify the depth and direction in which “AMS” will
affect high damp.
VPM
The output of a carrier is phase-modulated by a
modulator, and output through wave shape processing.
By controlling the wave shaping parameters and the
feedback gain, tonal changes that are different than
simple phase modulation can be produced.
Carrier Pitch
Modulator Pitch
Modulator
1–3a
1–3b
Modulator Level
(Basic Pitch)
Carrier
Wave Shape Parameter
Wave
Shape
Feedback Gain
Carrier Level
Output
1–3a: Carrier
Wave [Saw, Square, Triangle, Sine]
Selects the carrier waveform.
Level [0…99]
Specifies the output level of the carrier. This will
determine the output level of the VPM oscillator.
AMS1 (Alternate Modulation 1 Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 1 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Level.”
Intensity (Level AMS1 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of “AMS1.”
AMS2 (Alternate Modulation 2 Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 2 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Level.”
Intensity (Level AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of “AMS2.”
Wave Shape [0…99]
Specifies the number of cycle of wave shaping.
As this value is increased, the number of cycles will
increase, causing more overtones to be added to the
high-frequency range of the sound.
18
Page 18

Table valiation
Wave Shape:0 Wave Shape:99
Type (Wave Shap Type) [1, 2]
1: The signal after wave shaping will be output
without further change. If “Shape” is set to the
minimum value, the phase modulated signal will be
output essentially without change.
2: A rounded waveform will be obtained regardless of
the “Shape” value.
AMS1 (Alternate Modulation Source 1)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 1 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Wave Shape” value.
Intensity (Shape AMS1 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of “AMS1.”
AMS2 (Alternate Modulation Source 2)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 2 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Wave Shape” value.
Intensity (Level AMS1 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS1.”
AMS2 (Alternate Modulation Source 2)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 2 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Level.”
Intensity (Level AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS2.”
Frequency Coarse [0.5, 1…16]
Specifies a multiplication factor which will be applied
to the pitch of the modulator, relative to the “1–3a:
Carrier” setting.
Fine [–50…+50]
Makes fine adjustments to the pitch of the modulator.
AMS1 (Alternate Modulation Source 1)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 1 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the pitch of the modulator.
Intensity (Frequncy AMS1 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS1.”
Intensity (Shape AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of “AMS2.”
Feedback [0…99]
Specifies the amount of the output after wave shaping
that will be fed back to the carrier.
1–3b: Modulator
Wave
[Saw, Square, Triangle, Sine, OSC2(1), Sub OSC,
Filter1, Filter2]
Select the waveform of the modulator.
This selects the other oscillator or sub oscillator etc.
If you set this to OSC2(1) , SubOSC , Filter 1 , or
Filter 2 , the Frequency Coarse and following
settings will not be available.
Level [0…99]
Specifies the output level of the modulator.
This value will determine the amount of modulation
that is applied to the “1–3a: Carrier” setting.
AMS1 (Alternate Modulation Source 1)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 1 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Level.”
AMS2 (Alternate Modulation Source 2)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 2 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the pitch of the modulator.
Intensity (Frequncy AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS2.”
19
Page 19

Resonance
This oscillator produces a wide range of tonal change
by allowing you to specify the cutoff frequency and
resonance of four band pass filters (BPF ).
You can select one of the following sources to be the
input for the filters: the output of the other oscillator,
the sub-oscillator, the output of the noise generator, or
the output of filter 1 or filter 2.
OSC 1/2
Sub OSC
Noise Generator
Filter1 out
Filter2 out
Input Level
Input Select
BPF1
Resonance1
BPF2
1–3a
1–3b
1–3c
1–3a: Input
Input [OSC 2(1), Sub OSC, Noise, Filter1, Filter2]
Selects the signal that will be input to the four band
bass filters.
If you select Resonance for OSC 1 and 2 in
“1–2a: Multi Oscillator Synthesis Setup,” and
select the other oscillator as the input for each,
the result will be unstable — the sound may be
non-reproduceable, or you may hear no sound
at all.
Level [0…99]
Specifies the level of the signal that is input to the
four band pass filters.
AMS1 (Alternate Modulation Source 1)
Selects a modulation source 1 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Level.”
Intensity (Level AMS1 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS1.”
Level1
Coarse1
BPF3
BPF4
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
AMS2 (Alternate Modulation Source 2)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 2 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Level.”
Intensity (Level AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS2.”
1–3b: BPF Parameters
Here, you can make settings for each band pass filter 1–4.
Level [0…99]
Specifies the output level.
Coarse [1…16]
Specifies the harmonic (overtone) of the oscillator
pitch at which the center frequency of the filter will be
located. You can specify from the first to the 16th
harmonic.
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Coarse.”
Int (BPF Frequency AMS Intensity) [–15…+15]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
AMS. Positive (+) settings will allow the Coarse
value to be increased, and negative (–) settings will
allow the Coarse value to be decreased. At this time,
the center frequency of band pass filter 1 will change
in steps of harmonics, creating the impression that the
pitch is changing step-wise.
Fine [–99…+99]
Makes fine adjustments to the center frequency of
band pass filter 1 specified by the Coarse parameter.
Reso (Resonance) [0…99]
Specifies the resonance. Increasing this value will
produce a stronger effect.
1–3c: Resonance Modulation
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the resonance that was specified for
each band pass filter.
Intensity (Resonance AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS.”
20
Page 20

Ring Modulation
This multiplies the modulator and carrier and outputs
the signal produced. One of four types of waveform
can be selected as the carrier.
Since the result will be a metallic sound with little
sense of pitch, this is suitable for producing sound
effects. The Ring Modulation oscillator contains an
internal carrier oscillator. The output of the other
oscillator etc. can be selected as the modulator.
By modifying the pitch of the oscillator, you can
produce characteristic ring modulation effects.
AMS1 (Alternate Modulation Source 1)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 1 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Depth.”
Intensity (Modulation Depth AMS1 Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS1.”
AMS2 (Alternate Modulation Source 2)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 2 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Depth.”
1–3a
1–3b
1–3a: Wave
Input [OSC 2(1), Sub OSC, Noise, Filter1, Filter2]
Specifies the modulator.
If Ring Modulation is selected for both OSC 1
and 2, and the input of the other is selected for
each, some parameter settings may produce no
sound.
Carrier [Saw, Square, Triangle, Sine]
Specifies the carrier waveform.
Wave Edge [0…99]
Specifies the amount of high frequency harmonics for
the carrier waveform. As this value is decreased, the
sound will have less high-frequency harmonics, and as
it approaches 0 the volume will also decrease.
Intensity (Modulation Depth AMS2 Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS2.”
Type [1, 2]
Selects the modulation type. The two types differ in
the tone of the high range. Type 2 will produce a
brighter sound than type 1.
1–3b: Modulation Depth
Depth [0…99]
Specifies the depth of modulation. At a setting of 0,
the carrier waveform will be output without change.
21
Page 21

Cross Modulation
This uses a modulator to frequency-modulate a carrier.
You can select one of four waveforms as the carrier.
In general, a pitch envelope is applied to the modulator. A carrier oscillator is built-in to the Cross
Modulation OSC. You can select the output of the
other oscillator etc. as the modulator.
By modifying the pitch of the modulator oscillator,
you can produce characteristic cross-modulation
effects.
1–3a
1–3b
1–3a: Wave
AMS2 (Alternate Modulation Source 2)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 2 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Depth.”
Intensity (Modulation Depth AMS2 Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS2.”
Input [OSC2(1), Sub OSC, Noise, Filter1, Filter2]
Specifies the modulator.
Carrier [Saw, Square, Triangle, Sine]
Specifies the carrier waveform.
Wave Edge [0…99]
Specifies the amount of high frequency harmonics for
the carrier waveform. As this value is decreased, the
sound will have less high-frequency harmonics, and as
it approaches 0 the volume will also decrease.
1–3b: Modulation Depth
Depth [0…99]
Specifies the depth of modulation. At a setting of 0,
the carrier waveform will be output without change.
AMS1 (Alternate Modulation Source 1)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 1 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “ Depth.”
Intensity (Modulation Depth AMS1 Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS1.”
22
Page 22

Sync Modulation
This uses the modulator as the master waveform and
the carrier as the slave waveform (which will be
synchronized to the master).
When the master waveform begins a new cycle (i.e.,
the instant that it passes the zero point going from
negative to positive), the phase of the slave waveform
is reset to 0, causing it to begin a new cycle.
Sync Modulation
Modulator Wave
(Master)
Carrier Wave
(Slave)
1–3a
Organ Model
This is an oscillator used to produce organ-type
sounds. The oscillator simulates three drawbars
similar to electric organs of the past.
You can specify the footage [Harmo] and waveform
setting for each drawbar, allowing a wide range of
sounds to be created.
Drawbar3
Drawbar2
Drawbar1
Harmonics
(Pitch)
1–3a
Wave
Sine1 or Sine2
/Sine3/Triangle
Precussion
Level
Percussion Level
Precussion
Decay/Level Mod.
1–3a: Wave
Input [OSC2(1), Sub OSC, Noise, Filter1, Filter2]
Specifies the master waveform (modulator).
Slave [Saw, Square, Triangle, Sine]
Specifies the slave waveform.
Wave Edge [0…99]
Specifies the amount of high frequency harmonics for
the slave waveform. As this value is decreased, the
sound will have less high-frequency harmonics, and as
it approaches 0 the volume will also decrease.
1–3b
1–3a: Tone Generator
Drawbar1:
Wave [Sine 1, Sine 2, Sine 3, Triangle]
Specifies the waveform for drawbar 1. Sine 1 contains
only the fundamental (i.e., a pure sine wave). Sine 2
and Sine 3 are waveforms which contain the first two
and the first three harmonics respectively.
Coarse (Harmonics Coarse) [1(16’)…16(1’)]
Specifies the pitch of drawbar 1, relative to one octave
below the oscillator pitch.
Fine (Harmonics Coarse Fine) [–99…+99]
Makes fine adjustments to the pitch of drawbar 1.
Level [0…99]
Specifies the volume level of drawbar 1.
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the “Level” of drawbar 1.
23
Page 23

Intensity (Level AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS1.”
Percussion [0…99]
Specifies the volume level of the percussion effect for
drawbar 1.
Drawbar 2:
Drawbar 3:
The parameters are structured identically to those of
“1–3a: Drawbar 1.”
E. Piano Model
This oscillator simulates an electric piano.
There are four groups of parameters: Hammer (which
specifies how the shape and motion of the hammer
will affect tonal change and attack noise), Tone
Generator (which vibrates in response to being struck
by the hammer), Pickup (which specifies the tonal
change that occurs when the vibration of the tone
generator is converted into an electrical signal), and
Low EQ (which is a shelving-type low EQ to adjust
the low range).
Level AMS (Level Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the percussion level of each drawbar.
Intensity (Level AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“Level AMS” on the percussion level.
Trigger [Single/Multi]
Use the radio buttons to specify how the percussion
effect will be triggered.
With a setting of Single, the percussion effect will
apply to the first-played note from a condition of no
sound.
With a setting of Multi, the percussion effect will
apply to each note that is played.
Decay [0…99]
Specifies the decay length of the percussion. As this
value is increased the decay time will become longer.
Pickup
Pickup Location
to Low EQ
Tone Generator
Hammer
1–3a
1–3b
1–3c
1–3d
1–3e
1–3a: Hammer
Force [0…99]
Specifies the “Strength” with which the hammer
strikes the tone generator. Higher settings will
produce a brighter sound.
24
Force Velocity Curve [OFF, 0…99]
Specifies how changes in velocity will affect “Force.”
As this value is increased, velocity will have a
greater effect on “Force,” allowing more dynamic
tonal change to be produced. With a setting of OFF,
the “Force” will be constant.
Width (Hammer Width) [0…99]
Simulates the shape of the hammer. As this value is
increased, the width of the hammer will become
narrower, and the sound of the tone generator and
hammer noise will become sharper.
Click Noise Level [0…99]
Specifies the volume of the hammer noise that occurs
at the attack.
Page 24

1–3b: Tone Generator
The Decay and Release that you specify here will
control the output level of the oscillator. In order for
these settings to have an effect, they must be set
longer than the decay and release of the EG which you
are using for the Amp.
Decay [0…99]
Specifies the decay time of the tone generator.
Release [0…99]
Specifies the release time of the tone generator.
1–3c: Overtone
Level [0…99]
Specifies the volume of the higher overtones that are
produced when the tone generator vibrates.
Frequency [0…99]
Specifies the frequency of the overtones.
Decay [0…99]
Specifies the decay time of the overtone volume.
1–3d: Pickup
Brass Model
This oscillator is a physical model which simulates lipreed instruments such as a trumpet or trombone.
By using key velocity or modulation wheel to modulate
the Pressure (the force of breath blown into the mouthpiece) you can produce performance expressions that are
very similar to those of an actual lip-reed instrument.
The parameters are as follows: Inst Type determines the
model which simulates the bore length and shape of the
instrument, Breath Pressure indicates the force of breath
that is blown into the mouthpiece, Lip Character
produces the tonal changes that result from lip position or
tension, Bell Character produces the tonal changes that
result from the shape of the end of the bore, and Peaking
EQ performs a final tonal adjustment.
Signal Flow
Brass Model
Brass Model
Lip (Character)
Specify tonal change produced by lip position
Pressure
{
Noise
Peaking EQ
Inst Type
Select a model which simulates
the bore length and shape of
various instruments
Specify the force of breath that is blown into the mouthpiece
Specify the amount of breath noise
Strength
Bell
Specify the shape
of the end of the bore
Location [0…99]
Specifies the location of the pickup in relation to the
tone generator. With low settings, the pickup will be
placed in the center of the vertical vibration of the
tone generator, causing the second partial to be
emphasized and the fundamental to be less audible.
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Location.”
Intensity (Pickup Location AMS Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of “AMS.”
1–3e: Low EQ
Makes settings for a Low EQ (shelving type) that will
adjust the output signal.
Frequency [0…49]
Specifies the cutoff frequency of the Low EQ (shelving
type) that will be applied to the output signal.
Gain [–18…+18]
Specifies the gain of the Low EQ.
This oscillator allows you to choose from two types of pitch
bending: jump bending using a mode jump as on a trumpet
(by varying the bore length), and smooth bending produced
by sliding the length of the bore as on a trombone.
For some parameter settings, the pitch may not
change according to the notes that are played on
the keyboard. In some cases, high-pitched notes
may have a lower volume, or may not sound at all.
1–3a
1–3b
1–3c
1–3d
1–3e
1–3a: Inst Type
Inst Type
[Brass 1, Brass 2, Brass 3, Horn 1, Horn 2, Reed Brass]
Selects the instrument type which will determine the
bore length and shape of the simulated instrument.
25
Page 25

Jump Bend:
JS(+X) (Joystick +X)
Specifies how the pitch will change when the joystick is
moved in the +X direction (toward the right).
If this is checked, the pitch will rise by in steps by
changing the resonance of the bore, as on a trumpet.
If this is unchecked, the pitch will rise smoothly, as
on most synthesizers.
JS(-X) (Joystick -X)
Specifies how the pitch will change when the joystick is
moved in the –X direction (toward the left).
If Jump Bend (+X) and Jump Bend (–X) are
checked, notes may not sound depending on the
position of the joystick and the pitch range setting.
For details on setting the pitch range of the joystick,
refer to “2–4a: Picth Bend.”
1–3b: Breath Pressure
EG [EG 1…EG 4, Amp EG]
Selects the EG which will control pressure.
For details on the settings for each EG, refer to “Program P6”
for EG 1–4, and “4–3: Amp EG” for Amp EG.
this uses the signal from the noise generator, the filter
of the noise generator can be used to modify the tone
of the noise.
Strength [0…99]
Adjusts the tone. Higher settings of this value will
produce a overdriven sound.
1–3c: Lip Character
Lip [0…99]
Specifies the tonal change that is produced by lip
position and tension. Higher settings of this value will
produce a harder (more firmly blown) sound. Lower
settings will produce a softer tone.
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Lip.”
Intensity (Lip Character AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of “AMS.”
1–3d: Bell Character
Intensity (Pressure EG Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that the
“EG” will have on the pressure.
AMS1 (Alternate Modulation Source 1)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 1 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control pressure. If you select After Touch,
pressing down on the keyboard will produce the effect
of the instrument being blown strongly. If you select
Joy Stick(X), rotating the Joy Stick in the + direction
will produce this effect. In this case, setting “Intensity
(Pressure EG Intensity)” to 0 will allow you to
completely control the breath pressure by operating
the specified controller.
Intensity (Pressure AMS1 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the change in
pressure controlled by “AMS1.”
AMS2 (Alternate Modulation Source 2)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 2 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control pressure.
Intensity (Pressure AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the change in
pressure controlled by “AMS2.”
Tone [0…99]
Specifies the tone of the bell. As this value is increased, the low frequency portion will disappear,
producing a less solid tone.
Resonance [0…99]
Specifies the level at which the frequency region in
the area of the “Tone” will be boosted. As this value
is increased, the resonance effect will become
stronger.
1–3e: Peaking EQ
Frequency [0…49]
Specifies the center frequency of the frequency range
that will be boosted or attenuated by the Peaking EQ.
Increasing this value will raise the center frequency.
Q[0…29]
Specifies the width of the Peaking EQ frequency
band. Increasing this value will narrow the frequency
band that is boosted or attenuated.
Gain [–18…+18]
Specifies the amount by which the area specified by
“Frequency” and “Q” will be boosted or attenuated.
Breath Noise [0…99]
Specifies the volume level of the breath noise. Since
26
Page 26

Reed Model
This oscillator is a physical model which simulates
woodwind reed instruments such as a saxophone or oboe.
By using key velocity or the modulation wheel to control
Pressure (the strength with which the reed is blown), you
can use performance expressions that are very close to
those of an actual woodwind instrument. Also, by
modulating the characteristics of the reed, you can
produce tonal changes that correspond with the way in
which a reed is blown.
Signal Flow
Reed Model
Bell Character
Peaking EQ
Wave Shape
JS(-X) (Joystick -X)
Specifies how the pitch will change when the joystick is
moved in the –X direction (toward the left).
If Jump Bend (+X) and Jump Bend (–X) are
checked, notes may not sound depending on
the position of the joystick and the pitch range
setting.
For details on setting the pitch range of the
joystick, refer to “1–2c: Pich Bend.”
1–3b: Breath Pressure
Reed Model
Reed Character
Specify the vibrational
characteristics of the reed
Presure Specify the force of the breath that is blown into the reed
{
Noise Specify the amount of breath noise
Inst Type
Select a model to specify the bore length
and shape of the instrument to be simulated
1–3a
1–3b
1–3c
1–3d
1–3e
1–3f
1–3a: Inst Type
Inst Type [Hard Sax 1...Reed Synth]
Selects the type of instrument whose bore shape and
reed characteristics will be simulated.
Hard Sax 1, Hard Sax 2, Hard Sax 3, Soft Sax
1, Soft Sax 2, Double Reed 1, Double Reed 2,
Bassoon, Clarinet, Flute 1, Flute 2, Pan Flute,
Ocarina, Shakuhachi, Harmonica 1, Harmonica
2, Reed Synth
Jump Bend:
JS(+X) (Joystick +X)
Specifies how the pitch will change when the joystick
is moved in the +X direction (toward the right).
If this is checked, the pitch will rise in steps by
changing the resonance of the bore, as on a flute.
If this is unchecked, the pitch will rise smoothly, as
on most synthesizers.
EG [EG 1…EG 4, AmpEG]
Selects the EG which will control pressure.
For details on the settings for each EG, refer to
“Program P6” for EG 1–4, and “4–3: Amp EG” for
Amp EG.
Intensity (Pressure EG Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that the
EG will have on the pressure.
AMS1 (Alternate Modulation Source 1)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 1 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control pressure. If you select After Touch,
pressing down on the keyboard will produce the effect
of the instrument being blown strongly. If you select
Joy Stick (X), moving the joy stick toward the right
will produce this effect.
Intensity (Pressure AMS1 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the change in
pressure controlled by AMS1.
AMS2 (Alternate Modulation Source 2)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 2 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control pressure.
Intensity (Pressure AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the change in
pressure controlled by AMS2.
Breath Noise [0…99]
Specifies the volume level of the breath noise.
Since this uses the signal from the noise generator, the
filter of the noise generator can be used to modify the
tone of the noise.
27
Page 27

1–3c: Reed Character
1–3f: Peaking EQ
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual) that
will modulate the characteristics of the reed.
Intensity (Reed AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth of the modulation effect that
“AMS” will have on the reed.
1–3d: Bell Character
Tone [0…99]
Specifies the tone of the bell. As this value is increased, the low frequency portion will disappear,
producing a less solid tone.
Reso [0…99]
Specifies the level at which the frequency region in
the area of the “Tone” will be boosted. As this value
is increased, the resonance effect will become stronger.
1–3e: Wave Shape
Type (Wave Shape Table Type) [Clip/Reso]
Use the radio buttons to select the wave shaping
table which will modify the input waveform. For the
way in which the table will modify the waveform,
refer to the Wave Shape diagram shown in Standard
(☞page 16 of this manual).
Frequency [0…49]
Specifies the center frequency of the range that will be
boosted or attenuated by the Peaking EQ. Increasing
this value will raise the center frequency.
Q[0…29]
Specifies the width of the Peaking EQ frequency
band. Increasing this value will narrow the frequency
band that is boosted or attenuated.
Gain [–18…+18]
Specifies the amount by which the range specified by
“Frequency” and “Q” will be boosted or attenuated.
Offset [–99…+99]
Specifies the offset value that will be added to the
Reed OSC signal that is input to wave shaping.
Shape [0…99]
Specifies the character of the table that will shape the
input waveform. For details on how the waveform will
change, refer to the “Shape” diagram (☞page 16 of
this manual) for the Standard OSC.
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Shape.”
Intensity (Shape AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of “AMS.”
28
Page 28

Plucked String Model
This oscillator is a physical model which simulates
plucked string instruments such as a guitar or bass
guitar. You can specify aspects of the model such as
the attack waveform that is produced when the string
is plucked by a pick or finger, the characteristics of
the string, the location of the pickup, etc.
Signal Flow
String Model
String Model
Parameters relating to the attack waveform
Attack Level Specify the strength of playing (the level of the attack waveform).
Noise Specify the level and tone of the noise included in the attack waveform.
Attack Curve Specify the envelope of the attack waveform.
Bridge Bridge
String Position
Specify the location
at which the string is struck.
1–3a
1–3c
Pickup
Harmonics Position Specify the string location to be pressed to play harmonics
Harmonics Mod.Source / Mod.Int. Specify the controller which will control the
harmonics effect, and the depth of control.
Low EQ & Low Boost
Delay/Release
Specify the ratio of the wave transmitted along the string
which is reflected back from the bridge (decay/release time).
Parameters relating to the characteristics of the string
Damping Specify the high frequency attenuation of the
wave transmitted along the string. To simulate muted
playing techniques, control this parameter.
Dispersion Specify tonal change caused by
inharmonicity of the higher partials
Noise Level [0…99]
Specifies the level of the noise component that is
included in the attack waveform. As this value is
increased, a greater portion of noise will be included
in the attack, and the sound will be brighter with more
overtones. The noise signal used here is taken from
the output of the noise generator.
Velocity (Noise Level Velocity Control)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
velocity will have on Noise Level. For the way in
which the effect occurs, refer to “Velocity (Attack
Level Velosity Control).”
1–3b: Attack Curve
Up (Curre Up) [0…99]
Specifies the steepness of the rising edge of the attack
waveform.When the rising or falling edge is steep, the
tone will be harder.
Envelope of the attack waveform
Volume level
1–3b
1–3d
1–3e
1–3f
1–3a: Attack
Attack Level [0…99]
Specifies the force with which the string is plucked.
Velocity (Attack Level Velocity Control) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
velocity will have on “Attack Level.” The effect will
be as shown in the following diagram.
Parameter value
+
1
0
+99
Velocity value
–
–99
127
Curve Up Curve Down
Velocity (Curve Up Velocity Control) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
velocity will have on “Up.” For the way in which the
effect occurs, refer to “Velocity (Attack Level Velosity
Control).”
Down (Curre Down) [0…99]
Specifies the steepness of the falling edge of the attack
waveform.
Velocity (Curve Down Velocity Control)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
velocity will have on “Curve Down.” For the way in
which the effect occurs, refer to “Velocity (Attack
Level Velosity Control).”
1–3c: String
Picking Point [0…99]
Specifies the location at which the string will be
plucked. A setting of 0 is the end of the string, 50 is
the middle of the string, and 99 is the other end of the
string.
29
Page 29

AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Picking Point.”
Intensity (Picking Point AMS Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS.”
Damp [0…99]
Specifies the amount of high-frequency attenuation
that will be produced by the characteristics of the
string and by how the string is pressed.
As this value is increased, the high-frequency
components of the vibration in the string will be
attenuated (dampened) more strongly, producing a
darker sound. In general, this parameter should be set
to a higher value to simulate instruments which use
soft strings or which have no frets, and to a lower
value to simulate instruments which use hard strings
or which have frets.
KTr (Damp Keyboard Track) [–99…+99]
Specifies how the Damp amount will be affected by
the keyboard location.
With positive (+) settings, the Damp value will
increase as you play notes above C4.
With negative (–) settings, the Damp will decrease as
you play notes above C4.
+50
0
Damp
99
50
0
+99 +50
-99
C-1 C4 C9
when Damp=50
Damp
+99 +50
99
75
0
-50
0
C-1
when Damp=75
0
-50
-99
C9
C4
Damp
99
25
0
-50
-99
C-1 C4 C9
when Damp=25
+99
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Damp.”
Intensity (Damp AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
“AMS” will have.
Decay [0…99]
Specifies the decay time over which the sound will
decay if you continue pressing a note. Higher settings
of this value will produce a longer decay time.
Depending on the settings of “4–3: Amp EG”,
the setting you make here may not have
audible results. If you raise the EG break level
and sustain level, it will be easier to hear the
result of this setting.
KTr (Decay Keyboard Track) [–99…+99]
Specifies how the “Decay” amount will be affected by
the keyboard location.
With positive (+) settings, the decay will become
faster as you play notes above C4. With negative (–)
settings, it will become slower.
Decay
99
25
0
C-1 C4 C9
-99
+99
-50
Decay
99
+50
50
0
+99 +50
-99
0
C-1 C4 C9
when Decay=50 when Decay=75when Decay=25
Decay
+99 +50
99
75
0
-50
0
C-1
0
-50
-99
C9
C4
Release [0…99]
Specifies the length of time over which the sound will
decay after you release the note. Higher settings of
this value will produce a longer release time.
Depending on the settings of “4–3: Amp EG”,
the setting you make here may not have
audible results. You may need to raise the EG
release level, it will be easier to hear the result
of this setting.
Dispersion [0…99]
Specifies the inharmonicity of the higher partials
relative to the fundamental. With a value of 0, the
partials will be located at integer (whole number)
multiples of the fundamental. As this value is
increased, the partials will move further away from
integer multiple locations. In general, thin and flexible
strings can be simulated by a low “Dispersion” value,
and thick and stiff strings can be simulated by a high
“Dispersion” value.
If this value is raised excessively, the pitch
may become unstable.
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Dispersion.”
Intensity (Dispersion AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS.”
1–3d: Harmonics
Point [0…99]
Specifies the location at which the string will be
pressed to play harmonics.
30
Page 30

Ctrl (Control) [Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the harmonics effect.
Intensity (Harmonics Control Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the control that
“Ctrl” will have on the harmonics effect.
When making the Position setting, you must
assign Control to a controller other than OFF,
and raise the Intensity value. The decay time
of the harmonics effect will differ depending
on the keyboard location that you play.
1–3e: Pickup
Pickup
If this is checked, the sound will be passed through a
simulated pickup. If this is not checked, the sound
will remain unchanged.
Location, AMS, and Intensity can be set when
Pickup has been checked.
Location [0…99]
Adjusts the change in tone that results from differences in pickup location.
Bowed String Model
This oscillator is a physical model which simulates the
sound of a bowed string instrument such as a violin or
cello. By controlling the bowing speed and the bowing
pressure, you can create performance expressions that
are very close to those of an actual bowed string
instrument.
Bowed String Model
Bridge Reflection
Position
1–3a
1–3b
1–3c
1–3d
Peaking EQ
Bow
Pressure
String vibration
Bowed String Model
String
Bow Speed
Bridge Reflection
Parameters related to the string
String Damp
Dispersion
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Pickup.”
Intensity (Pickup Location AMS Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS.”
1–3f: Low EQ
Frequency [0…49]
Specifies the cutoff frequency of the Low EQ.
Gain [–18…+18]
Specifies the gain of the Low EQ.
Low Boost [0…99]
Specifies how the low frequency range will be
emphasized. Raising this value will cause the low
frequency range to be emphasized more strongly.
1–3a: Bow Speed
EG [EG 1…EG 4, AmpEG]
Selects the EG which will control bowing speed (the
speed at which the bow moves across the string).
Int (Speed Modulation EG Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of “EG”
With negative (–) settings, the direction of the bow
speed will be inverted.
AMS1 (Alternate Modulation Source 1)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 1 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control bowing speed.
Instead of using an EG to modify the bowing speed,
you can use the Ribbon Controller or Joy Stick to
simulate bowing without using an EG.
Int (Speed AMS1 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS1.”
AMS2 (Alternate Modulation Source 2)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 2 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control bowing speed.
31
Page 31

Int (Speed AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS2.”
Differential
If this is not checked, the value produced by EG,
AMS1 and AMS2 will be used as the bowing speed. If
you wish to use EG to control the bowing speed, leave
this item un-checked.
If this is checked, the rate of change of EG, AMS1 and
AMS2 will be used as the bowing speed.
• Using the ribbon controller to control bowing speed
As an example, we will assume that you have set
AMS1 to Ribbon (X). In order to control bowing
speed using the ribbon controller alone, raise the Int.
(Speed AMS1 Intensity) value, and set Int. (Speed
Modulation EG Intensity) to 0. Check Differential.
When you are pressing the ribbon controller, the
bowing speed will be zero, so there will be no sound.
As you slide your finger toward the right over the
ribbon controller, the speed at which your finger
moves will be the bowing speed, and sound will be
produced. As you slide your finger to left and right,
the bowing speed will change from positive →zero→
negative→ zero→positive, allowing you to produce
performance expressions that are very similar to those
of actually moving a bow back and forth.
Rosin [0…99]
Specifies the coefficient of static friction between the
bow and the string. (This corresponds to the amount of
rosin on the bow.)
Higher values will increase the friction between the
bow and string. When this value is in the region of 0,
it will be difficult for playing strength to be transmitted to the string.
1–3c: String
Bowing Point [0…99]
Specifies the location at which the bow contacts the
string. A setting of 0 is the end of the string, 50 is near
the middle, and 99 is at the other end.
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Bowing Point.”
Changing the location at which the string is bowed
will also change the overtone structure.
Intensity (Bowing Point AMS Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS.”
Damp [0…99]
Specifies how the high frequency components will be
attenuated by the characteristics of the string and by
the way in which the string is pressed onto the
fingerboard of the violin or cello.
As this value is increased, the high frequency
components of the wave transmitted along the string
will be attenuated more greatly, producing a darker
sound. In general, you should use higher values to
simulate instruments which have flexible strings or
unfretted instruments, and lower values to simulate
instruments with stiff strings or fretted instruments.
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Damp.”
1–3b: Bow Pressure
EG [EG 1…EG 4, AmpEG]
Selects the EG which will control the pressure of the
bow on the string (bow pressure).
Int (Pressure EG Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that the
“EG” will have on bow pressure.
If this value is low, the bow will rest lightly on the
string.
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control bow pressure.
Int (Pressure AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth of the effect produced by “AMS.”
32
Intensity (Damp AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS.”
Damp KTr Key (Damp Keyboard Track Key)
[C–1…G9]
Specifies the key above and below which keyboard
tracking will begin to apply to the “Damp” effect.
You can also input a value by playing a note
on the keyboard while you hold down the
[ENTER] key.
Ramp Low [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction in which the “Damp”
amount will change for notes below the “Damp KTr
Key.” Positive (+) settings will cause “Damp” to
increase for notes below the “Damp KTr Key.”
Negative (–) settings will cause “Damp” to decrease
for notes below the “Damp KTr Key.”
Page 32

Ramp High [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction in which the “Damp”
amount will change for notes above the “Damp KTr
Key.” Positive (+) settings will cause “Damp” to
increase for notes above the “Damp KTr Key.”
Negative (–) settings will cause “Damping” to
decrease for notes above the “Damping KTr Key.”
Gain [–18…+18]
Specifies the gain by which the peaking EQ will boost
or attenuate.
1–4: OSC2 (Oscillator 2)
OSC2 parameters have the same structure as OSC1
parameters. Refer to “1–3: OSC 1.”
Dispersion [0…99]
Specifies the inharmonicity of the higher partials
relative to the fundamental. With a value of 0, the
partials will be located at integer (whole number)x
multiples of the fundamental. As this value is increased, the partials will move further away from
integer multiple locations. In general, thin and flexible
strings can be simulated by a low “Dispersion” value,
and thick and stiff strings can be simulated by a high
“Dispersion” value.
If this value is raised excessively, the pitch
may become unstable.
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Dispersion.”
Intensity (Dispersion AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of “AMS.”
Bridge Reflection [0…99]
Specifies the amount of the wave that will be reflected
at the end of the string. Higher values will make the
notes sound more easily. With a setting of 0 there will
be no reflection at all.
1–5: Noise Generator
Make settings for the noise generator.
The noise generator produces white noise. The noise
signal is passed through a dedicated filter, and is then
mixed with the oscillator 1, 2, and sub oscillator signals
by the mixer section. (Refer to 1–6: OSC Mixer.)
Thru
Low Pass
Noise Generator
Input Trim
Cutoff Frequency
1–5a
1–5b
High Pass
Band Pass
Noise Filter
Filter Type
Resonance
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Bridge Reflection.”
Intensity (Bridge Reflection AMS Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of “AMS.”
1–3d: Peaking EQ
Frequency [0…49]
Specifies the center frequency at which the peaking
EQ will boost (attenuate) the sound.
Q[0…29]
Specifies the width of the region that will be boosted
(attenuated) by the peaking EQ. With a setting of 0, a
wide region will be affected. With a setting of 29,
only a narrow region close to the center frequency will
be boosted (attenuated).
1–5a: Noise Generator
Filter Type [Thru, Low Pass, High Pass, Band Pass]
Selects the type of filter that will be applied to the
output of the noise generator.
If Thru is selected, the parameter settings described
below will not be available.
Input Trim [0…99]
Specifies the input level to the dedicated noise filter.
Frequency (Cutoff Frequency) [0…99]
Specifies the cutoff frequency of the noise signal
filter. For the characteristics of each filter type, refer
to “3–1:Filter1” (☞page 38 of this manual).
Resonance [0…99]
This boosts the frequency region specified by the
“Cutoff Frequency” to add character to the sound.
33
Page 33

Since the filter characteristics differ from the filter
type of the “3–1: Filter 1 ,” “3–3: Filter 2” the
resulting effect will be different even if “Filter Type,”
“Frequency” and “Resonance” settings are identical.
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “output level.”
1–5b: Frequency Modulation
AMS1 (Alternate Modulation Source 1)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 1 (☞ p.48 of this manual)
that will control the “Frequency.”
Intensity (Cutoff Frequency AMS1 Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS1.”
AMS2 (Alternate Modulation Source 2)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 2 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the “Frequency.”
Intensity (Cutoff Frequency AMS2 Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS2.”
1–6: OSC Mixer
The mixer allows you to set the levels at which the
five signals (OSC 1, OSC 2, Sub OSC, Noise Generator, Feedback) will be combined into the two mixer
outputs. You can also select a modulation source to
control each level, and specify its intensity.
Intensity (Level AMS Intensity) [–99...+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS.”
With positive (+) settings, higher values of the
modulation source will increase the “output level.”
With negative (–) settings, lower values of the
modulation source will increase the “output level.” If
EG or LFO has been selected as the “AMS”, positive
(+) settings will cause the original phase of the EG or
LFO to be used, and negative (–) settings will invert
the phase.
OSC2 (OSC2 Output Level)
These parameters adjust the level at which the
oscillator 2 signal is output from mixer output 1, and
specify a modulation source that will control this
level.
Sub OSC
These parameters adjust the level at which the sub
oscillator signal output is output from mixer output 1,
and specify a modulation source that will control this
level.
Noise
These parameters adjust the level at which the output
of the noise generator is output from mixer output 1,
and specify a modulation source that will control this
level.
1–6a
1–6b
1–6a: Mixer1
These parameters adjust the level at which the oscillator
1 signal is output from mixer output 1, and specify a
modulation source that will control this level.
OSC1 (OSC1 Output Level) [00...99]
Specifies the signal level that will be output to mixer
output 1.
34
Feedback
These parameters adjust the level at which the
feedback from the amp section is output from mixer
output 1, and specify a modulation source that will
control this level.
Raising the Feedback level excessively may
cause the sound to distort.
1–6b: Mixer2
These parameters adjust the level at which the
oscillator 1 signal is output from mixer output 2, and
specify a modulation source that will control this
level.
Refer to the above explanation of “1–6a: Mixer 1.”
Page 34

1–7: Contoller Setup
1–7a
1–7b
1-7a: Panel Switch Assign
Assign the function of the front panel [SW1] and
[SW2] keys.
☞Refer to TRITON Parameter Guide p.217 “SW1,
SW2 Assign List.”
Since the [SW1] and [SW2] settings of the program
assigned to each timbre are not used by a combination,
they must be set here again.
☞ Refer to TRITON Parameter Guide p.8 “Panel
Switch Assign” (Program P1: 1–4a).
SW1 (SW1 Assign)
SW1 Mode [Toggle, Momentary]
SW2 (SW2 Assign)
SW2 Mode [Toggle, Momentary]
[Off, ..., After Touch Lock]
[Off, ..., After Touch Lock]
1-7b: Realtime Contol Knobs B-Assign
Here you can assign the B-mode functions (mainly
various types of control change) for the front panel
REALTIME CONTROLS [1]–[4] knobs. The
functions you select here will operate when you move
the corresponding knob of the REALTIME CONTROLS [1]–[4] knobs when B-mode is selected.
☞ Refer to TRITON Parameter Guide p.218
“Realtime Control Knobs B-Assign List.”
Knob 1-B [Off, ..., MIDI CC #00...CC #95]
Knob 2-B [Off, ..., MIDI CC #00...CC #95]
Knob 3-B [Off, ..., MIDI CC #00...CC #95]
Knob 4-B [Off, ..., MIDI CC #00...CC #95]
35
Page 35

Program P2: Edit-Pitch
2–1b: Pitch Modulation
Specifies the pitch Modulation.
2-1: OSC1 P. Mod
(Oscillator 1 Pitch Modulation)
2–1a
2–1b
2–1a: Pitch Slope
Specifies how pitch will change in relation to the
keyboard (key.)
Center Key [C–1…G9]
Specifies the key at which Lower/Higher keyboard
tracking will begin to apply.
You can also input a value by playing a note
on the keyboard while you hold down the
[ENTER] key.
Ramp Low [–1.00…+2.00]
Specifies the depth and direction of the pitch change
that will occur for notes below the “Center Key.”
Ramp High [–1.00…+2.00]
Specifies the depth and direction of the pitch change
that will occur for notes above the Center Key.
When Low Slope and High Slope are set to +2.0,
playing one octave upward from the Center Key will
cause the pitch to rise two octaves.
With a setting of –1.0, playing one octave upward will
cause the pitch to fall one octave. With a setting of
0.0, the notes in the respective areas will produce the
same pitch as the Center Key. To play pitches
normally, set this parameter to +1.0.
Pitch
C9
+2.0
1.0
+1.0
AMS1 (Alternate Modulation Source 1)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 1 (☞p.48 of this manual)
which will modify the pitch (e.g., apply vibrato).
Intensity (Pitch AMS1 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the pitch change
that will be controlled by “AMS1.”
AMS(AMS1 Intensity Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Specifies the controller (☞p.48 of this manual) that
will control the “Intensity (Pitch AMS1 Intensity).”
Intensity (AMS1 Int AMS Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth of the pitch modulation effect
controlled by “AMS1.”
AMS2 (Alternate Modulation Source 2)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 2 (☞p.48 of this manual)
which will modify the pitch (e.g., apply vibrato).
Intensity (Pitch AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth of the pitch modulation effect
controlled by “AMS2.”
2–2: OSC2 P.Mod
(Oscillator 2 Pitch Modulation)
2–3: SubOSC P.Mod
(Sub Oscillator Pitch Modulation)
OSC2 P.Mod and SubOSC P.Mod, have the same
parameter as OSC 1. Refer to “2–1:
OSC1 P. Mod
”
2–4: Common P.Mod
2–4a
2–4b
2–4c
36
C-1
C-1 C4 C9
Center Key
0.0
Key
Page 36

2–4a: Pitch Bend
Specifies the width of pitch change that will occur
when the joystick is moved to left and right.
JS(+X) (Joystick Intensity +X) [–60…+24]
Specifies the amount and direction of pitch change (in
semitone units) that will occur when the joystick is
moved to the right.
With positive (+) settings the pitch will rise, and with
negative (-) settings the pitch will fall. A setting of 12
will produce one octave of change.
Step (Joystick Step +X)
[Continuous, 1/8, 1/4, 1/2, 1…12]
Specifies how the pitch will change when the joystick
is moved to the right.
Continuous: Smooth change.
1/8: Change in 1/8 semitone steps.
1/4: Change in 1/4 semitone steps.
1/2: Change in 1/2 semitone steps.
1...12: Change in steps of the specified number of
semitones (up to 1 octave).
JS(–X) (Joystick Intensity –X) [–60…+24]
Specifies the amount and direction of pitch change (in
semitone units) that will occur when the joystick is
moved to the left.
2–4c: Portamento
These settings specify how portamento will be
applied. (Portamento creates a smooth change in pitch
from one note to the next.)
Enable
Check this when you wish to use portamento.
Fingered
Check this when you want to apply portamento only
when a note is pressed while continuing to hold the
previous note.
Time [0…99]
Specifies the portamento time. Higher values will
cause the pitch to change more slowly.
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Time.”
Intensity (Portamento Time AMS Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the dipth and direction in which the
portamento time will be controlled by the “AMS .”
Step (Joystick Step –X)
[Continuous, 1/8, 1/4, 1/2, 1…12]
Specifies how the pitch will change when the joystick
is moved to the left.
Refer to Step (Joystick Step +X).
If the Step (Joystick Step +X) or Step (Joystick Step –X) settings are greater than the
settings for JS (+X) and JS (–X), the pitch will
not change.
2–4b: Common Pitch Modulation
Creates time-varying changes in the pitch of all
oscillators (oscillators 1 and 2, and the sub oscillator).
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects the modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the pitch of all oscillators (oscillators
1 and 2, and the sub oscillator).
Intensity (Common Pitch AMS Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect produced by AMS.
37
Page 37

Program P3: Edit-Filter
Here, you can make settings for one of the two multimode filters.
3–1: Filter 1
Each multi-mode filter can be set to one of five filter
types.
Input Trim
3–1a
3–1b
3–1c
3–1d
Cutoff Frequency
Multimode Filter
Resonance
Low Pass
High Pass
Band Pass
Band Reject
Dual BPF
Filter Type
Filter Types and Cutoff Frequency
Low Pass Filter (Low Pass)
frequency
Cutoff Frequency
High Pass Filter (High Pass)
Cutoff
Frequency
frequency
frequency
frequency
Cutoff
Frequency B
Cutoff Frequency
Band Pass Filter (Band Pass)
Cutoff Frequency
Band Reject Filter (Band Reject)
Dual Band Pass Filter (Dual BPF)
Cutoff
Frequency A
A low pass filter is the most
commonly-used type of filter, and
passes the range of frequencies that
lie below the cutoff frequency, and
cuts the high range. Cutting the higher
partials will cause a bright sound to
become darker (more mellow).
A high pass filter passes the range of
frequencies that lie above the cutoff
frequency, and cuts the low range.
This type of filter is used when you
wish to make the sound thinner.
However, raising the cutoff frequency
excessively will drastically reduce the
volume.
A band pass filter passes the range of
frequencies in the vicinity of the cutoff
frequency, and cuts the ranges above
and below. This type of filter is used
when you wish to emphasize a
particular portion of the sound.
A band reject filter cuts only the
range in the vicinity of the cutoff
frequency, and passes the rest
of the sound. This type of filter
gives a unique character to the
sound.
The dual band pass filter places
two band pass filters in parallel.
It allows you to simulate sounds
such as human voice and the
frequency
body resonances of a violin or
guitar.
3–1a: Routing (Filter Routing)
Routing [Serial 1/Serial 2/Parallel]
Use the radio buttons to select the way in which
filters 1 and 2 will be combined.
Filter2:
Link to Filter 1
If this is checked, Filter 2 will be linked to Filter 1,
and the following settings will be the same as the
settings of Filter 1.
If this is not checked, the following parameters can
be set for Filter 2.
3–1b: Filter Type
Filter Type
[Low Pass(A), High Pass(A), Band Pass(A), Band
Reject(A), Dual BPF(A/B)]
Selects the filter type.
When Dual BPF(A/B) is selected, the “3–1d: Filter B”
parameters can also be set.
A Trim [0…99]
Specifies the level of the input to filter A.
If this value is raised, the sound may become
distorted if the resonance setting is high, etc.
B Trim [0…99]
Specifies the level of the input to filter B.
If this value is raised, the sound may become
distorted if the resonance setting is high, etc.
3–1c: Filter A
Frequency (Cutoff Frequency) [0…99]
Specifies the cutoff frequency of filter 1.
As this value is increased, the cutoff frequency will rise.
Since the Band Pass(A) and Dual BPF(A/B) filter
types use filters with differing characteristics, their
actual cutoff frequency may differ even if their
settings are identical.
EG (Cutoff Frequency Modulation EG)
[EG1…EG4, AmpEG]
Selects the EG that will create time-varying change in
the cutoff frequency of filter 1.
38
Page 38

Intensity (Cutoff Frequency Mod. EG Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the control that
“EG (Cutoff Frequency Modulation EG)” will have on
the cutoff frequency. With positive (+) settings of this
parameter, the tone will become brighter when the
various EG levels rise into the + area (the setting of the
“Frequency” will be reached when the EG levels are at
0), and darker when the EG levels fall into the – area.
With negative (–) settings of this parameter, the tonal
change will take place in the opposite direction.
Resonance [0…99]
This setting emphasizes the overtones in the region of
the “Frequency” to add character to the sound. Higher
values will produce a stronger effect. With high
settings of resonance, the output signal of the filter
may distort. If this occurs, reduce the “A Trim”
setting.
With the Dual BPF(A/B) filter type, the overtones in
the vicinity of each cutoff frequency will be affected
in the same way as by a Band Pass(A).
The effect of resonance
Low Pass
High Pass
Band Pass
3-2: Filter1 Mod. (Filter 1 Modulation)
3–2a
3–2b
3–2a: FilterA/B Keyboard Track
Keyboard tracking settings specify how the cutoff
frequency of filter 1 will be varied according to
keyboard position.
Filter A:
Key Low [C-1…G9]
Specifies the key at which Lower keyboard tracking
will begin.
Key High [C-1…G9]
Specifies the key at which Higher keyboard tracking
will begin.
Band Reject
Low resonance value High resonance value
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the amount of resonance.
Intensity (Resonance AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
“AMS” will have on the amount of resonance.
3-1d: Filter B
These parameters will be available if Dual BPF (A/B)
was selected as the Type in “3–1b: Filter Type.”
For details on each parameter, refer to “3–1c: Filter
A.” The EG and AMS are set in “3–1c: Filter A.
You can also input a value by playing a note
on the keyboard while you hold down the
[ENTER] key.
Ramp Low [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of cutoff frequency
change that will occur below the “Key Low.”
With a setting of –50, the change will match the
change in pitch.
Ramp High [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of cutoff frequency
change that will occur above the “Key High.”
With a setting of +50, the change will match the
change in pitch.
Cutoff
frequency
-50
Ramp> 0
0
-99
C-1 C4 C9
+99
+50
0
Ramp<0
39
Page 39

Filter B:
Here you can adjust the settings for Filter B. These
parameters have the same structure as the “Filter A”
parameters.
3-2b: Filter A/B Modulation
Program P4: Edit-Amp
Here, you can make volume-related settings.
There are two independent amps, and the signals
which are input to each amp are determined by the
setting of “3–1a: Routing” (☞p.47 of this manual).
Filter A:
AMS1 (Alternate Modulation Source 1)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 1 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Frequency.”
Intensity (Cutoff Frequency AMS1 Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
“AMS1” will have on the cutoff frequency.
AMS2 (Alternate Modulation Source 2)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 2 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control “Frequency.”
Intensity (Cutoff Frequency AMS2 Intensity)
[–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
“AMS2” will have on the cutoff frequency.
Filter B:
Adjust the “Intensity” of “AMS1” and “AMS2”
specified for “Filter A.”
3–3: Filter2
For details on the parameters, refer to “3–1: Filter.”
3–4: Filter2 Mod. (Filter 2 Modulation)
For details on the parameters, refer to “3–2: Filter 1
Mod.”
4–1: Amp1 Level (Amplifier 1 Level)
4–1a
4–1b
4–1a: Amp Level
Amp Level [0…99]
Specifies the volume level of amp 1. The input signal
to amp 1 is determined by the “3–1a:Routing” setting
EG (Amplitude Modulation EG)
[EG1…EG4, AmpEG]
Selects the EG that will create time-variant change in
the volume level of amp 1. For the settings of each
EG, refer to “4–3: Amp EG” , “Program P6.”
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the volume level of amp 1.
40
Intensity (Amplitude AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS” on the volume level.
4–1b: Keyboard Track
Key Low [C-1…G9]
Specifies the key at which Lower keyboard tracking
will begin.
Key High [C-1…G9]
Specifies the key at which Higher keyboard tracking
will begin.
Page 40

You can also input a value by playing a note
on the keyboard while you hold down the
[ENTER] key.
Ramp Low [–99…+99]
Specifies the way in which keyboard tracking will
affect the volume of notes below the “Key Low.”
Ramp High [–99…+99]
Specifies the way in which keyboard tracking will
affect the volume of notes below the “Key High.”
Volume level
Ramp> 0
0
+99
+50
0
Time-variant change in volume created by the amp EG
Attack level Sustain level
Volume
Note-on
Attack
time
Break
level
Decay
time
Slope
time
Note-off
Release
time
4–3a: Level (Amp EG Level)
Attack (Attack Level) [0…99]
Specifies the volume that will be reached after the
Attack Time has elapsed.
Time
-50
C-1
-99
C4
Ramp<0
C9
If Ramp Low or Ramp High are set to
positive (+) settings, you will need to lower
the “4–1a: Amp Level” Amplitude value.
4–2: Amp2 Level (Amplifier 2 Level)
Here you can adjust the settings for Amp 2. These
parameters have the same structure as the “4–1a: Amp
1” parameters.
4–3: Amp EG
(Amplifier Envelope Generator)
4–3a
4–3b
4–3c
4–3d
Break (Break Level) [0…99]
Specifies the volume level that will be reached after
the Decay Time has elapsed.
Sustain (Sustain Level) [0…99]
Specifies the volume level that will be reached after
the Slope Time has elapsed.
4–3b: Time (Amp EG Time)
Attack (Attack Time) [0…99]
Specifies the time from note-on (when a note is
played) until the volume reaches the attack level.
With a value of 0, the volume will change instantly.
With a value of 99, the volume will change slowly.
Decay (Decay Time) [0…99]
Specifies the time from when the attack time ends
until the break level is reached.
Slope (Slope Time) [0…99]
Specifies the time from when the decay time ends
until the sustain level is reached.
Release (Release Time) [0…99]
Specifies the time from note-off (when a note is
released) until the volume falls to zero.
Here, you can make settings for the Amp EG. The
Amp EG lets you specify how the sound will change
over time. Since the Amp EG can also be used as a
general-purpose controller, it can create time-variant
change in parameters other than volume.
4–3c: Level Modulation
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the level of the Amp EG.
Intensity (EG Level AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
“AMS” will have on the level of the Amp EG.
41
Page 41

Velocity Control [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
velocity will have on the level of the amp EG.
4–4: Output Level / Pan
Amp1 EG changes (level) (AMS=Velocity, Intensity=+value)
Note-on
Note-off
When keyboard is
played softly with a
Sustain of 0, and Attack
and Break set to “+”
(the settings of 4-3a:
Level)
Note-on
Note-off
When keyboard is
played strongly with
each Level set to “+”
Note-on
Note-off
When keyboard is
played strongly with
each Level set to “-”
4–3d: Time Modulation
AMS1 (Alternate Modulation Source 1)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 1 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the Amp EG times.
Intensity (EG Time AMS1 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
“AMS1” will have on the Amp EG times.
AMS2 (Alternate Modulation Source 2)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 2 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the Amp EG times.
At (Attack Time AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Dc (Decay Time AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Sl (Slope Time AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Rl (Release Time AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
“AMS2” will have on each EG time.
4–4a
4–4b
4–4a: Output Level
Output Level [0…127]
Specifies the output level following the amp.
4-4b: Pan
Pan [L000…C064…R127]
Set the pan (stereo location) of oscillator 1.
L001 is far left, C064 is center, and R127 is far right.
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects the modulation source (☞p.36 of this manual)
that will move the panning of amp 1 relative to the
Pan setting.
Intensity (Panpot AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect of
“AMS” on the panning.
Amp EG changes (time) (AMS=Velocity, Intensity=+value)
Note-on
Note-off
When keyboard is
played softly with At,
Dc, Sl, and Rl set to “+”
The settings of 4-3d:
AMS2
Note-on
Note-off
When keyboard is
played strongly with
At, Dc, Sl, and Rl
set to “+”
Note-on
When keyboard is
played strongly with
At, Dc, Sl, and Rl
set to “-”
42
Note-off
Page 42

Program P5: Edit-Common LFO
Frequency [0…199]
Specifies the frequency of the LFO.
This section provides four LFOs (Low Frequency
Oscillators). These LFOs can be used as modulation
sources for parameters of other sections, to create
cyclic changes in the sound.
5–1: LFO 1
5–1a
5–1b
5–1c
5–1a: LFO1
Waveform [Triangle 0…Exponential Saw Down]
Settings for the general-purpose LFOs
Triangle 0
Triangle 90
Triangle Random
When Key Sync=ON, the
starting phase will vary
randomly.
Sine
Saw Up 0
Saw Up 180
Saw Down 180
Square
Random-S/H
Amplitude and the duration at
which each level is held will both
change randomly (sample & hold).
Random-Vector
1/2 cycle
Random 2 changes in a
straight line toward a value
which is determined
randomly every 1/2 cycle.
Step Triangle-4
Step Saw-4
Step Saw-6
Exponential Triangle
Exponential Saw Up
Exponential Saw Down
Offset [–50…+50]
Specifies the center value of the LFO waveform.
Offset = 0
The parameter value
being modulated
LFO movement determined
by Modulation Intensity
Offset = 50
The parameter value
being modulated
LFO movement determined
by Modulation Intensity
Offset = -50
The parameter value
being modulated
LFO movement determined
by Modulation Intensity
Amplitude AMS (Alternate Modulation Source 1)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the amplitude of the LFO waveform.
Intensity (Amplitude AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
“AMS” will have on the amplitude of the LFO
waveform.
Key Sync [Off/by Timbre/by Voice]
Use the radio buttons to select the key sync setting
(i.e., whether or not the phase of the LFO waveform
will be returned to its initial state when a note-on
occurs).
Off: The LFO will operate regardless of note-on.
by Timbre: Key sync will occur for the LFOs of all
voices at the time of the first note-on that
occurs in a state when no keys are on.
by Voice: Key sync will occur independently for the
individual LFO of the voice for which note-on
occurred.
Key Sync = byTimbre / byVoice
Saw Down 0
Step Triangle-6
Note-On
Key Sync = Off
Note-On
Note-On
Note-On
43
Page 43

Fade [0…99]
Specifies the time over which the amplitude of the
LFO will increase from 0 until it reaches the maximum value.
5–1b: Frequency Modulation
You can use two alternate modulation sources to
control the frequency of the LFO.
AMS1 (Alternate Modulation Source 1)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Select a modulation source 1 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the LFO frequency.
Intensity (Frequency AMS1 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
“AMS1” will have on the “Frequency” value.
AMS2 (Alternate Modulation Source 2)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 2 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the LFO frequency.
Intensity (Frequency AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
“AMS2” will have on the “Frequency” value.
5–2: LFO 2
5–3: LFO 3
5–4: LFO 4
LFO 2, LFO 3, and LFO 4 have the same parameter as
LFO 1. Refer to “5–1: LFO 1 ”
5–1c: Frequency MIDI/Tempo Sync.
MIDI/Tempo Sync.
Checked: The LFO frequency will synchronize to the
tempo (MIDI Clock). In this case, the settings of “5–
1a: Frequency” and “5–1b: Frequency Modulation”
will have no effect.
Base Note [ ]
Times [01...16]
If “MIDI/Tempo Sync.” is checked, these parameters
specify the “Base Note” note value and a multiple
“Times” relative to the “ (tempo).” These parameters
will determine the frequency of the OSC1 LFO1. For
example if “Base Note” is (quarter note) and
“Times” is 04, the LFO will cycle once every four
beats.
Even if you change the “ (Tempo)” of the arpeggiator
or sequencer, the LFO will always cycle once every
four beats.
If the Global mode parameter “1–1a: MIDI
Clock” (☞ Parameter Guide p.118) is set to
Internal, the LFO will synchronize to the
tempo specified by the program. If it is set to
External MIDI or External PC I/F, the LFO
will synchronize to the MIDI Clock messages
received from an external MIDI device.
44
Page 44

Program P6: Edit-Common EG
6–1b: Time (EG Time)
This section provides four general purpose EGs
(envelope generators). The four EGs can be used as
modulation sources for the parameters of other
sections to create time-variant change in the sound.
Slope
time
Note-off
Release
time
Time
+99
-99
Break
level
Decay
time
Sustain level
Attack level
Note-on
Start
level
0
Attack
time
6–1: EG 1
6–1a
6–1b
6–1c
Attack (Attack Time) [0…99]
Specifies the time from note-on (when a note is
played) until the value reaches the attack level. With a
value of 0, the value will change instantly. With a
value of 99, the value will change slowly.
Decay (Decay Time) [0…99]
Specifies the time from when the attack time ends
until the Break Level is reached.
Slope (Slope Time) [0…99]
Specifies the time from when the decay time ends
until the Sustain Level is reached.
Release (Slope Time) [0…99]
Specifies the time from note-off (when a note is
released) until the Release Level is reached.
6–1c: Level Modulation
AMS (Alternate Modulation Source)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the level of EG1.
6–1d
Intensity (EG Level AMS Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
“AMS” will have on the EG levels.
6–1a: Level (EG Level)
Start (Start Level) [–99…+99]
Specifies the value at the time of note-on.
Attack (Attack Level) [–99…+99]
Specifies the value that will be reached after the
Attack Time has elapsed.
Break (Break Level) [–99…+99]
Specifies the value that will be reached after the
Decay Time has elapsed.
Sustain (Sustain Level) [–99…+99]
Specifies the value that will be reached after the Slope
Time has elapsed.
Release (Release Level) [–99…+99]
Specifies the value that will be reached after the
Release Time has elapsed.
Velocity Control [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
velocity will have on the EG levels.
EG changes (level) (AMS=Velocity, Intensity=+value)
Note-on
Note-off
When keyboard is
played softly with St,
At, and Br set to “+”
(the settings of 6-1a:
Level)
Note-on
Note-off
When keyboard is
played strongly with
St, At and Br set to “+”
Note-on
Note-off
When keyboard is
played strongly with
St, At and Br set to “-”
6–1d: Time Modulation
AMS1 (Alternate Modulation Source 1)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 1 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the EG1 times.
Intensity (EG Time AMS1 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
“AMS1” will have on the EG times.
45
Page 45

AMS2 (Alternate Modulation Source 2)
[Off…MIDI:CC#83]
Selects a modulation source 2 (☞p.48 of this manual)
that will control the EG1 times.
At (Attack Time AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Dc (Decay Time AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Sl (Slope Time AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Rl (Release Time AMS2 Intensity) [–99…+99]
Specifies the depth and direction of the effect that
“AMS2” will have on each EG time.
EG changes (time) (AMS2=Velocity, Intensity=+value)
Note-on
Note-off
Note-on
Note-off
Note-on
Note-off
Program P7: Edit-Arpeggiator
Here you can make arpeggiator-related settings.
For details on the parameters etc., refer to TRITON
Parameter Guide p.22, “Program P7.”
Program P8: Edit-Insert Effect
Here, you can make settings for the insertion effects.
For details on the parameters etc., refer to TRITON
Parameter Guide p.24, “Program P8.”
Program P9: Edit-Master Effect
When keyboard is
played softly with At,
Dc, Sl, and Rl set to “+”
(The settings of 6-1d:
AMS2)
When keyboard is
played strongly with At,
Dc, Sl, and Rl set to “+”
When keyboard is
played strongly with At,
Dc, Sl, and Rl set to “-”
6–2: EG 2
6–3: EG 3
6–4: EG 4
EG 2, EG 3 and EG 4 have the same parameters as EG
1. Refer to “6–1: EG 1.”
Here, you can make settings for the master effects.
For details on the parameters etc., refer to TRITON
Parameter Guide p.27 “Program Edit P9.”
46
Page 46

Combination mode
Insertion/master effect routing and individual audio
output routing for a timbre is set in the Program P8:
Routing tab. Refer to “Multi-timbral settings” in this
manual.
Combination P4: MOSS Setup
Here you can specify how bank F programs will be sounded.
These settings have no effect on bank A–E or
G programs.
4–3: MOSS Setup
Specify the number of voices that will be used by
bank F programs, and how they will be routed through
effects and the individual audio outputs.
The Timbre 1–8 you select here does not have
to be using a bank F program.
The actual levels of send 1 and 2 for a timbre
using a bank A–E or G program is determined
by multiplying the timbre setting by the send
level of the program, but for timbres that use a
bank F program, the send level setting of the
timbre will be the actual level.
Voice Allocation Reserve (Total Max:6voices)
[0 ... 6]
For each timbre, specify the number of voices for
when a bank F program is selected. Make settings so
that the total for all timbres does not exceed six
voices.
If this is set to 0, a bank F program selected for that
timbre will not sound. When using the EXB-MOSS
multi-timbrally, refer to “Multi-timbral settings.”
When you change the bank/program of a
timbre to change from a bank A–E or G
program to a bank F program, it will sound
according to these settings. Timbres that are
set to 0 will not sound if they are switched to a
bank F program. Before you select a bank F
program, set this parameter appropriately.
MOSS BUS Select Reference
[Timbre1 ... Timbre8]
Specify the insertion/master effect routing and
individual audio output routing for all timbres that use
bank F programs. The settings of the timbre you select
here will determine the insertion/master effect and
individual audio output routing of these timbres.
(They cannot be set independently.)
47
Page 47

Appendices
Cautions when using bank F
Sound production when changing
programs
If you change bank F programs while sound is being
produced, the bank F program will stop sounding. The
newly selected program will sound at the next note-on.
MIDI Program Change reception
Depending on the oscillator type that is used by a
program, a certain interval of time may be required
from when a program change is received until the
bank F program actually changes. When changing
programs, please allow a sufficient time interval
between the program change and the note-on.
About noise
The inter-relation between effect settings etc. and the
oscillator parameters of the program may cause noise
to appear in the sound under some conditions. Also,
playing the program immediately after selecting it
(within one second) may cause noise to be mixed with
the output sound.
If you are using bank F programs in multiple timbres
When playing multi-timbrally and a bank F program is
being sounded, selecting a bank F program for the
timbre number prior to that timbre number will cause
noise to be heard in the currently-sounding bank F
program.
Data dump compatibility
Bank F programs are not compatible with the programs of the Prophecy, Z1, TRINITY V3, or TRINITY MOSS-TRI.
AffixtheSondius-XGlabel
Affix the included label to the right side of the front
panel. ☞Refer to the following diagram
4mm
Modulation Source List
Off
EG 1
EG 2
EG 3
EG 4
Amp EG
LFO 1
LFO 2
LFO 3
LFO 4
Portamento
Note No. Linear
Note No. Exp.
Note Split High
Note Split Low
Velocity Soft
Velocity Med.
Velocity Hard
After Touch
JS X
JS +Y: CC#01
JS -Y: CC#02
JS +Y & AT/2*
JS -Y & AT/2*
Pedal: CC#04
Ribbon: CC#16
Ribbon +X
Ribbon -X
Slider: CC#18
KnobMod1: #17
KnobMod2: #19
KnobMod3: #20
KnobMod4: #21
KnobMod1 [+]
KnobMod2 [+]
KnobMod3 [+]
KnobMod4 [+]
Damper: #64
SW 1: CC#80
SW 2: CC#81
Foot SW: #82
MIDI: CC#83
* AT/2 is an aftertouch effect that is one half of After
Touch.
48
Page 48

Voice Name List
Combination (MOSS.PCG)
# Name Arp.SWPattern A Run Mod.SW1 Knob1 Knob3
Category Pattern B Run Mod.SW2 Knob2 Knob4
B000 Forest Piano Off P001: DOWN On Octave Down F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Keyboard P000: UP On Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon F/A Decay (CC#75) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B001 !! MOSSPOWER !! On U153: Drum'n'Bass 1 On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Rhythmic Pattern U043: Trance Bass Riff On Portamento SW (CC#65) F/A Decay (CC#75) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B002 Eternal Partners Off U013: BalladPicking GT On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Volume (CC#07) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Guitar/Plucked P000: UP Off Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Expression (CC#11) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B003 Dirty Moss Sax Off U165: Smooth Hop On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
LeadSplits P000: UP Off Lock Ribbon Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B004 Water Pad Off P000: UP On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Volume (CC#07) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
MotionSynth P000: UP Off Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B005 Intimate Orch Off U029: Arco Arpeggio On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Orchestral P001: DOWN On Lock JS(-Y) F/A Decay (CC#75) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B006 RETRO Rocket Spl On P004: RANDOM On Portamento SW (CC#65) F/A Decay (CC#75) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
LeadSplits U095: Retro Pattern On Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B007 MossTrumpets Cut Off U068: 7-tone Ostinato On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
BrassReed P000: UP Off Octave Down F/A Release (CC#72) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B008 4'5' Splitmoss Off U145: 8 Beat On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
BassSplits U151: Latin-drums On Mod.SW2 (CC#81) F/A Attack (CC#73) F/A Decay (CC#75)
B009 Telegraph Unison On U147: Shuffle 2 On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Rhythmic Pattern U162: House 2 On Octave Down Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B010 Pure Ac.Guitar Off U102: ONCE! On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Guitar/Plucked P000: UP Off Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Volume (CC#07) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B011 Cyber Sly Heart On U150: Bossa Nova On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Filter Resonance (CC#71) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Complex & SE U155: Drum'n'Bass 3 On Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B012 Winter Bells Off P001: DOWN On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Bell/Mallet/Perc P000: UP On Lock JS(-Y) F/A Decay (CC#75) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B013 Trance Leader Off U118: Techno Riff 7 On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Synth P000: UP Off Portamento SW (CC#65) F/A Sustain (CC#70) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B014 Sweep & Cool Off U150: Bossa Nova On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Keyboard U164: New Disco 2 On Mod.SW2 (CC#81) Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B015 Moss Stencil Off U109: Up uP UP Up uP On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Pads U107: 8th Chunk On Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B016 Gaterhythm On U158: Drum'n'Bass 6 On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Decay (CC#75) Filter EG Int. (CC#79)
Rhythmic Pattern U043: Trance Bass Riff On Mod.SW2 (CC#81) Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B017 UnisonMoss SYNC Off U148: Jazz 1 On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Synth U060: Crazy Bee On Octave Down Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B018 Metallic Clavi Off U125: Trance Riff 1 On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) F/A Sustain (CC#70)
Keyboard P000: UP Off Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon F/A Decay (CC#75) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B019 Moss Soprano SP Off U164: New Disco 2 On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
LeadSplits U107: 8th Chunk On Lock Ribbon Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B020 Topper Split Off U051: Old Dance Bass 2 On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
BassSplits P000: UP Off Lock JS(-Y) F/A Decay (CC#75) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B021 Talkabout On U145: 8 Beat On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Complex & SE U151: Latin-drums On Mod.SW2 (CC#81) Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B022 Flute Moss Split Off U165: Smooth Hop On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
LeadSplits U034: TechnoBass Riff2 On Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B023 DigiStrat Guitar Off U016: Soul Strum GT On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Guitar/Plucked P000: UP Off Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon F/A Decay (CC#75) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B024 120 To Sync On U145: 8 Beat On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Rhythmic Pattern P000: UP Off Mod.SW2 (CC#81) Filter Resonance (CC#71) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B025 BIG Synth Saws Off U125: Trance Riff 1 On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) F/A Sustain (CC#70)
Synth P000: UP Off Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon F/A Decay (CC#75) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B026 Sleepy Bells Off U143: Penta-Fall On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Bell/Mallet/Perc P000: UP Off Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon F/A Decay (CC#75) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B027 Wurlysizer ArpSW On P000: UP On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Keyboard P000: UP Off Mod.SW2 (CC#81) Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B028 Moss Brass Split Off U175: BD/HH/SD 16ths On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
BrassReed U054: Walkin' Bass On Mod.SW2 (CC#81) F/A Release (CC#72) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
49
Page 49

# Name Arp.SWPattern A Run Mod.SW1 Knob1 Knob3
Category Pattern B Run Mod.SW2 Knob2 Knob4
B029 Soul-DrumOnKnob1 Off U144: 1Note Repeat-Lo On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
LeadSplits U166: HipHop 1 On Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B030 Geronimoss On U145: 8 Beat On Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Rhythmic Pattern P000: UP Off Mod.SW2 (CC#81) Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B031 Moss Power Split Off U030: DanceBass Riff 1 On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
BassSplits P000: UP Off Mod.SW2 (CC#81) F/A Release (CC#72) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B032 Bright Moss Off U155: Drum'n'Bass 3 On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Mod.SW2 (CC#81) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Keyboard U035: TechnoBass Riff3 On Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B033 Tell me Thelma On U146: Shuffle 1 On Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Mod.SW2 (CC#81)
Rhythmic Pattern U165: Smooth Hop On Mod.SW2 (CC#81) Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B034 SquareTubeSea Off U109: Up uP UP Up uP On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Pads P002: ALTERNATE1 On Mod.SW2 (CC#81) Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B035 Moss Sax Split On P000: UP On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Filter Cutoff (CC#74) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
LeadSplits U144: 1Note Repeat-Lo On Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B036 System Start-Up Off P000: UP Off Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) F/A Sustain (CC#70)
MotionSynth P000: UP Off Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon F/A Decay (CC#75) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B037 AwesomeStringPad Off U029: Arco Arpeggio On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Strings U022: Piano Arpeggio 1 Off Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon F/A Decay (CC#75) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B038 CyberSynthBass Off U123: Echo Riff On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Synth P000: UP Off Portamento SW (CC#65) Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B039 Moss BRASS Sect Off U149: Jazz 2 On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Filter Cutoff (CC#74) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
BrassReed U152: Heavy Rock On Mod.SW2 (CC#81) F/A Release (CC#72) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B040 Z-Lead Moss Off U147: Shuffle 2 On Octave Down Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Synth U162: House 2 On Mod.SW2 (CC#81) Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B041 Moss Srave On U112: Techno Riff 1 On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Rhythmic Pattern U175: BD/HH/SD 16ths On Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B042 NewTouchGuitar Off U093: Bossa Arpeggio On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Guitar/Plucked U004: Guitar Strum 5 On Lock JS(-Y) Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B043 *Water Exchange* On U109: Up uP UP Up uP On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Filter Cutoff (CC#74)
MotionSynth U109: Up uP UP Up uP Off Lock JS(-Y) F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B044 Crystal Bells Off P000: UP On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Bell/Mallet/Perc P001: DOWN On Mod.SW2 (CC#81) F/A Decay (CC#75) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B045 1+3 Splitmoss Off U145: 8 Beat On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
BassSplits U151: Latin-drums On Mod.SW2 (CC#81) F/A Attack (CC#73) F/A Decay (CC#75)
B046 Cutt Da Clav Off U046: Euro Bass On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Keyboard P000: UP Off Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B047 Calm Move On P000: UP On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Mod.SW2 (CC#81) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
MotionSynth P002: ALTERNATE1 On Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B048 Moss Stamina Off U175: BD/HH/SD 16ths On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Rhythmic Pattern P000: UP Off Mod.SW2 (CC#81) Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B049 Palawaters On U144: 1Note Repeat-Lo On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
MotionSynth P000: UP Off Mod.SW2 (CC#81) Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B050 Nu Gtr Pad ArpSw Off P000: UP On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Guitar/Plucked P000: UP Off Mod.SW2 (CC#81) Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B051 UnisonMoss ST On U071: 5-tone Trance 1 On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Synth U062: Stepping Note On Octave Down Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B052 Session Split Off U146: Shuffle 1 On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
BassSplits U150: Bossa Nova On Lock JS(-Y) Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B053 MosStrings ArpSW On U144: 1Note Repeat-Lo On Lock Ribbon Filter Cutoff (CC#74) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Strings P000: UP Off Lock JS(-Y) Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B054 FluteInAmbySauce On U144: 1Note Repeat-Lo On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
LeadSplits P000: UP Off Mod.SW2 (CC#81) Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B055 Windy Guitar On P004: RANDOM On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Guitar/Plucked U102: ONCE! On Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B056 3FingerGateGame On U150: Bossa Nova On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) F/A Decay (CC#75)
Rhythmic Pattern U033: TechnoBass Riff1 On Mod.SW2 (CC#81) Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B057 NakedClav->ArpOn Off P000: UP On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Synth P000: UP Off Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
Filter Resonance(CC#71)
50
Page 50

# Name Arp.SWPattern A Run Mod.SW1 Knob1 Knob3
Category Pattern B Run Mod.SW2 Knob2 Knob4
B058 Little Angels Off P004: RANDOM On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Bell/Mallet/Perc P000: UP Off Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B059 Moss of the Tyne Off U150: Bossa Nova On Octave Down Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Keyboard P000: UP Off Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B060 Violins & Reeds Off P002: ALTERNATE1 On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Orchestral U028: String Melody On Lock Ribbon F/A Decay (CC#75) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B061 SynMoss 01 Off U155: Drum'n'Bass 3 On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
LeadSplits U170: Acid Drum On Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B062 Moss Split Synth Off U169: Bigbeats 2 On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Synth P000: UP Off Lock JS(-Y) & Ribbon F/A Attack (CC#73) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
B063 Superunison On U145: 8 Beat On Mod.SW1 (CC#80) Knob Mod.1 (CC#17) Knob Mod.3 (CC#20)
Rhythmic Pattern U151: Latin-drums On Mod.SW2 (CC#81) Knob Mod.2 (CC#19) Knob Mod.4 (CC#21)
* Combination Bank A and B064–B127 is same as the preloaded data of the TRITON.
51
Page 51

Programs (MOSS.PCG)
Bank F
# Name Category
F000 War Birds FastSynth Off U048: TEKNO stutter Standard OSC Standard OSC
F001 Palawan MotionSynth Off U083: Echo Chords 3 Resonance OSC Organ Model
F002 Whirly E.P. Keyboard Off U035: TechnoBass Riff3 Electric Piano Model Electric Piano Model
F003 Death Lead LeadSynth Off U048: TEKNO stutter Standard OSC Standard OSC
F004 Zoop 1 Drums On U045: Funky Tekno Bass Standard OSC VPM OSC
F005 Neo Clav Keyboard Off U021: Funk Bass/Guitar Plucked String Model
F006 Rich Strings Strings Off U130: Mallet Roller Comb Filter OSC Standard OSC
F007 Speed Comp MotionSynth On U032: DanceBass Riff 3 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F008 Phat Bass Bass/Synth Bass Off U042: Dance Bass+Comp Standard OSC Standard OSC
F009 Square Hollow SlowSynth Off U039: Open Funk Bass 1 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F010 Frequency Lead LeadSynth Off U124: Random Techno Standard OSC Standard OSC
F011 Techno Sequence MotionSynth Off U014: BalladPicking2GT Sync OSC Standard OSC
F012 Blue Guitar Guitar/Plucked Off U008: Guitar Picking Plucked String Model
F013 Garage Choir Vocal/Airy Off U113: Techno Riff 2 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F014 Bold Trumpet Brass Off U060: Crazy bee Brass Model
F015 Forest SE Off U109: Up uP UP Up uP Reed Model
F016 Sweepy Sawz FastSynth Off U134: CrazyComputer 3 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F017 Night Lights MotionSynth On U048: TEKNO stutter Organ Model VPM OSC
F018 Tine Piano Keyboard Off U081: Echo Chords 1 VPM OSC VPM OSC
F019 Sync Comp LeadSynth Off U078: 5-tone Vel Trip Sync OSC Standard OSC
F020 Dream Bell Bell/Mallet Off P001: DOWN VPM OSC Organ Model
F021 SinglePerc Organ Organ Off U051: Old Dance Bass 2 Organ Model Organ Model
F022 Blue Sax Woodwind/Reed Off U079: 5-tone Vel Trip Reed Model
F023 Vowel Phase Mod FastSynth Off U031: DanceBass Riff 2 VPM OSC Comb Filter OSC
F024 Dyna Slap Bass Bass/Synth Bass Off U055: Funk Bass Plucked String Model
F025 Wave Drum Drums On U177: Percussion Plucked String Model
F026 Sub Lead LeadSynth Off U124: Random Techno Standard OSC Standard OSC
F027 Ocean Calm SlowSynth Off U073: 5-tone Trance 3 Organ Model Organ Model
F028 Metallic Bell Bell/Mallet Off U132: CrazyComputer 1 VPM OSC VPM OSC
F029 Male Ahhs Vocal/Airy Off U041: Gated Dance Bass Standard OSC Standard OSC
F030 Hard Flute Woodwind/Reed Off U081: Echo Chords 1 Reed Model
F031 Dimension SE Off U076: 2-tone Vel Trip VPM OSC Resonance OSC
F032 Arena Monster FastSynth Off U071: 5-tone Trance 1 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F033 Butterfly Pad MotionSynth On U079: 5-tone Vel Trip Sync OSC Standard OSC
F034 Tremolo Synth FastSynth Off U085: Dance Comp 1 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F035 Analog Lead LeadSynth Off U126: Trance Riff 2 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F036 Zoop 2 Drums Off U033: TechnoBass Riff1 VPM OSC VPM OSC
F037 Comb Clav Keyboard Off U071: 5-tone Trance 1 Comb Filter OSC Standard OSC
F038 Dream Strings Strings Off U141: Cresc/Decresc Standard OSC Standard OSC
F039 Zipperling LeadSynth Off U036: Tribal Bass VPM OSC Standard OSC
F040 Dirty Old Man MotionSynth On U065: Gated Pattern 1 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F041 BPF Sweep MotionSynth Off P004: RANDOM Standard OSC Standard OSC
F042 Digi Morphious MotionSynth On U123: Echo Riff Standard OSC Standard OSC
F043 Techno S&H Pad MotionSynth On U112: Techno Riff 1 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F044 Psychedelic Gtr. Guitar/Plucked Off U012: CountryPickng2GT Plucked String Model
F045 Stream Pad SlowSynth Off U140: Trickle Standard OSC Organ Model
F046 Zee Solo Violin Strings Off U014: BalladPicking2GT Bowed String Model
F047 Aliens Chitchat SE Off U042: Dance Bass+Comp Bowed String Model
F048 Giant REZ Sweep MotionSynth Off U075: 2-tone Vel Trip Standard OSC Standard OSC
F049 ** ACID Rain ** MotionSynth On U035: TechnoBass Riff3 Comb Filter OSC Standard OSC
F050 Percussive Ring FastSynth Off U097: Staccato Tech Ring Modulation OSC VPM OSC
F051 Light Brass Lead FastSynth Off U077: 4-tone Vel Trip Standard OSC Standard OSC
F052 Bali Bells Bell/Mallet Off U130: Mallet Roller Plucked String Model
F053 Digital Dulcimer Guitar/Plucked On P004: RANDOM Plucked String Model
F054 Soprano Sax Woodwind/Reed Off U123: Echo Riff Reed Model
F055 Moving Picture MotionSynth Off U052: Stagger Bass Standard OSC Standard OSC
Arp.SW
Arpeggio Pattern OSC1 Type OSC2 Type
52
Page 52

# Name Category
F056 Touch FingerBass Bass/Synth Bass Off U050: Old Dance Bass 1 Plucked String Model
F057 Rhythmic Seq MotionSynth On U042: Dance Bass+Comp Standard OSC Resonance OSC
F058 mini Lead LeadSynth Off U062: Stepping Note Standard OSC Standard OSC
F059 Osiris FastSynth Off U112: Techno Riff 1 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F060 Reso Bell Bell/Mallet On U094: Kalimba groove Comb Filter OSC Resonance OSC
F061 Portamento Pad MotionSynth Off U140: Trickle Standard OSC Standard OSC
F062 Analog Brass FastSynth Off U096: Stab Rhythm Standard OSC Standard OSC
F063 LFO gating MotionSynth Off U058: Syncopation Standard OSC Standard OSC
F064 Full Synth FastSynth Off U073: 5-tone Trance 3 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F065 Motion Comb MotionSynth Off U131: Comb & Pipe Ring Modulation OSC Comb Filter OSC
F066 Direct E.P. Keyboard Off U062: Stepping Note VPM OSC Electric Piano Model
F067 Morph 3003 Dist Bass/Synth Bass On U125: Trance Riff 1 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F068 Zoop 3 Drums Off P004: RANDOM VPM OSC Ring Modulation OSC
F069 Prophetic Pulse FastSynth Off U072: 5-tone Trance 2 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F070 Huge Strings Strings Off P004: RANDOM Comb Filter OSC Standard OSC
F071 Rubbery Comp FastSynth Off U066: Gated Pattern 2 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F072 Dark Pop Bass Bass/Synth Bass Off U031: DanceBass Riff 2 VPM OSC VPM OSC
F073 Soft Pad SlowSynth Off U130: Mallet Roller Standard OSC Standard OSC
F074 Emmer's Sun Syn FastSynth Off U037: Acid Bass Riff Standard OSC Standard OSC
F075 Victory Pad MotionSynth Off U111: Random Up Standard OSC Cross Modulation OSC
F076 Nylon Acoustic Guitar/Plucked Off U008: Guitar Picking Plucked String Model
F077 AEIOU Choir Vocal/Airy Off U078: 5-tone Vel Trip Standard OSC Organ Model
F078 Bold Trombone Brass Off U091: House Organ Brass Model
F079
TREXvsHELICOPTER
F080 Golden Synth FastSynth Off U030: DanceBass Riff 1 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F081 Vision Makers MotionSynth Off U062: Stepping Note Standard OSC Sync OSC
F082 Dyna Expressive Keyboard Off U025: Piano Comp 2 Electric Piano Model Electric Piano Model
F083 Deep Sync Lead LeadSynth Off P000: UP Sync OSC Standard OSC
F084 U.K. Synth Bell FastSynth Off U128: Quarks Standard OSC Standard OSC
F085 Pipe Organ Full Organ Off U137: Step Saw Down Organ Model Organ Model
F086 Dirty Sax Woodwind/Reed Off U042: Dance Bass+Comp Reed Model
F087 Flute Moss SlowSynth Off P004: RANDOM Reed Model
F088 Freaky Rez Bass Bass/Synth Bass Off U037: Acid Bass Riff Plucked String Model
F089 Noise Virus SE On U059: Happy Dog Standard OSC Comb Filter OSC
F090 Phunk Rez Lead LeadSynth Off U028: String Melody Standard OSC Standard OSC
F091 Comb Flute Pad FastSynth Off U073: 5-tone Trance 3 Comb Filter OSC Standard OSC
F092 Water Bell Bell/Mallet Off P004: RANDOM Resonance OSC Resonance OSC
F093 'n'Bass Bass/Synth Bass Off U034: TechnoBass Riff2 Standard OSC VPM OSC
F094 Cave Flute Woodwind/Reed Off U044: TB Bass Drone Reed Model
F095 Cyber Zone SE Off U102: ONCE! VPM OSC Resonance OSC
F096 HiPass Stuff FastSynth Off P003: ALTERNATE2 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F097 Sunflower MotionSynth Off P001: DOWN Resonance OSC Comb Filter OSC
F098 Brass Ensemble FastSynth Off U101: Vice Squad VPM OSC VPM OSC
F099 Unison PWM LeadSynth Off P001: DOWN Standard OSC Standard OSC
F100 This is Zee One! MotionSynth On U087: Flashin' Arp Resonance OSC Standard OSC
F101 Analog Comb FastSynth Off U063: Trance Comp Comb Filter OSC Comb Filter OSC
F102 Antique Strings Strings Off U137: Step Saw Down Standard OSC Standard OSC
F103 1000 Knives LeadSynth Off U031: DanceBass Riff 2 Standard OSC Ring Modulation OSC
F104 Deep Top Bass Bass/Synth Bass Off U134: CrazyComputer 3 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F105 Pad Rize MotionSynth Off U141: Cresc/Decresc Comb Filter OSC Standard OSC
F106 Light Res Synth FastSynth On U097: Staccato Tech Standard OSC Standard OSC
F107 Resomotor MotionSynth Off P004: RANDOM Resonance OSC Comb Filter OSC
F108 Dirty Strato Gtr Guitar/Plucked Off U013: BalladPicking GT Plucked String Model
F109 Female Voice Vocal/Airy Off U059: Happy Dog Standard OSC Organ Model
F110 Saw Horn FastSynth Off P003: ALTERNATE2 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F111 Mad Scientist SE Off P000: UP VPM OSC Standard OSC
SE Off U100: Exressive Triad Reed Model
Arp.SW
Arpeggio Pattern OSC1 Type OSC2 Type
53
Page 53

# Name Category
F112 Rezzit Oiid FastSynth Off U112: Techno Riff 1 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F113 Harbinger MotionSynth Off U134: CrazyComputer 3 Resonance OSC Comb Filter OSC
F114 Misty Synth FastSynth Off U091: House Organ Organ Model Organ Model
F115 Soft Syn Brass FastSynth Off U126: Trance Riff 2 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F116 Science Laws MotionSynth On P004: RANDOM Ring Modulation OSC Sync OSC
F117 Rockin Bee! Organ Off U031: DanceBass Riff 2 Organ Model Organ Model
F118 Hybrid Hardsyn FastSynth Off U129: Speed Sequence VPM OSC Standard OSC
F119 Inner Space MotionSynth On U044: TB Bass Drone Standard OSC Organ Model
F120 E.&Syn Bass Bass/Synth Bass Off U043: Trance Bass Riff Plucked String Model
F121 Noise Burst Drums Off U164: New Disco 2 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F122 Rezo Bass Bass/Synth Bass Off U038: Hip Hop Bass1 Standard OSC Standard OSC
F123 Ground Synth FastSynth Off P004: RANDOM Standard OSC Standard OSC
F124 Grand image Pad FastSynth Off U036: Tribal Bass Standard OSC Standard OSC
F125 Big Bass Bass/Synth Bass Off U041: Gated Dance Bass Standard OSC Standard OSC
F126 Laughter SE Off U125: Trance Riff 1 Reed Model
F127 ANALOG INIT FastSynth Off U064: Trance Comp-Maj Standard OSC Standard OSC
Arp.SW
Arpeggio Pattern OSC1 Type OSC2 Type
54
 Loading...
Loading...