Konica 7920 Wiring Diagram 7920020e
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
MECHANICAL/
ELECTRICAL

FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
CONTENTS
1. CROSS-SECTIONAL VIEW ............................................................................M-1
2. COPY PROCESS ............................................................................................M-2
3. DRIVE SYSTEM .............................................................................................. M-4
4. OPERATING SEQUENCE ......................................................................... .....M-5
5. CONTROL BLOCK DIAGRAM ........................................................................M-7
6. LOCATIONS OF TERMINALS ................................................ ........................M-8
7. IMAGE STABILIZATION SYSTEM .................................................................. M-10
7-1. AIDC Detection ......................................................................... ...............M-11
7-2. Image Stabilization System Control .........................................................M-12
(1) AIDC Sensor LED Intensity Control .................................................M-14
(2) Background Margin Control .............................................................M-14
(3) Max. Density Control ...................... .................................................M-14
(4)γ Correction Control ...................... ...................................................M-14
8. PC DRUM ........................................................................................................ M-15
8-1. PC Drum Drive Mechanism .....................................................................M-15
8-2. Grounding of the PC Drum ............................................................. .... .... .M-15
9. PC DRUM CHARGE CORONA .......................................................................M-16
10. IMAGE READER (IR) SECTION .....................................................................M-17
10-1.IR Image Processing ...............................................................................M-18
10-2.CCD Sensor ......... .......................... ..................................... ....................M-27
10-3.Exposure Components Section ...............................................................M-28
10-4.Exposure Lamp Contr o l ...........................................................................M-29
10-5.Scanner and 2nd/3rd Mirrors Carriage Movement
Mechanism ..............................................................................................M-30
(1) Scanner Movement Mechanism ......................................................M-30
(2) 2nd/3rd Mirrors Carriage Movement Mechanism ............................M-30
10-6.Scanner Motor Drive Control ...................................................................M-31
11. ORIGINAL SIZE DETECTING SECTION ........................................................M-32
11-1.Original Size Detecting Method ...............................................................M-32
11-2.Locations of Original Size Detecting Sensors .........................................M-33
11-3.Determining the Or ig in a l Size ..................................................................M-34
11-4.Original Size Detection Timing ................................................................M-36
12. PRINTER SECTION .................. ...................................... ................................M-37
12-1.Printer Section Image Processing Block Diagram ...................................M-38
13. IMAGING UNIT ................................................................................................M-42
13-1.Control of Detection of New Imaging Unit ............................................... M-43
13-2.Imaging Unit Drive Mechanism ................................................................M-43
13-3.Sleeve/Magnet Roller ..............................................................................M-45
13-4.Doctor Blade ............................................................................................M-45
13-5.Developing Bias and ATDC Bias ............................... .... .... .... ......... .... .... .M-46
13-6.ATDC Sensor ................................... .......................................................M-47
(1) ATDC Sensor (Y, M, C) ...................................................................M-47
(2) ATDC Sensor (Bk) ................................ ...........................................M-47
13-7.Toner Replenishing Control .....................................................................M-48
13-8.Toner Supply Port Covering/Uncovering Mechanism ..............................M-48
14. TONER HOPPER ............................................................................................M-49
i

FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
14-1.Toner Replenishing Mechanism ..............................................................M-50
14-2.Toner Empty Detection Control ...............................................................M-52
15. PAPER TAKE-UP SECTION ...........................................................................M-53
15-1.Drawer-in-Position Detecting Mechanism . ..............................................M-53
15-2.Drawer Paper Empty Detecting Mechanism ............................................M-54
15-3.Drawer Paper Near Empty Detecting Mechanism ...................................M-54
15-4.Paper Supply Level LED Display .............................................................M-55
15-5.Paper Size Detecting System ..................................................................M-56
15-6.Paper Type Setting ..................................................................................M-58
15-7.Drawer Paper Take-Up Mechanism ........................................................M-59
15-8.Double Feed Control ...............................................................................M-60
16. MANUAL BYPASS PAPER TAKE-UP SECTION ............................................ M-61
16-1.Manual Bypass Paper Take-Up Detecting Mechanism ...........................M-62
17. SYNCHRONIZING ROLLERS .........................................................................M-63
17-1.Paper Dust Remover ..................... ..........................................................M-63
17-2.Synchronizing Roller Drive Mechanism ...................................................M-64
17-3.OHP Detecting Mechanism .....................................................................M-65
18. IMAGE TRANSFER SECTION ........................................................................M-66
18-1.Transfer Belt Unit Drive Mechanism ........................................................M-67
18-2.Color Shift Detection .................. ..............................................................M-68
18-3.Color Shift Corre ction ..............................................................................M-69
(1) Outline of Color Shift Detection .............................................. .........M-69
18-4.1st Image Transfer Roller Pressure/Retraction Mechanism ....................M-70
18-5.Pressure Position Changing Mechanism . ................................................M-72
18-6.Retraction Mecha nism .............................................................................M-73
18-7.Backup Mechanism .................................................................................M-74
18-8.2nd Image Transfer Roller Pressure/Retraction Mechanism ...................M-75
18-9.AIDC Sensor Shutter Mechanism ............................................................M-76
18-10.Paper Charge Neutralization .................................................................M-77
18-11.Transfer Belt Paper Separator Fingers ..................................................M-77
18-12.Transfer Belt Cleaning Mechanism .......................................................M-78
18-13.2nd Image Transfer Roller Cleaning Mechanism ..................................M-78
18-14.Waste Toner Collecting Mechanism ............................................... ...... .M-79
18-15.Waste Toner Near Full and Full Detecting Mechanism .........................M-80
18-16.Image Transfer ATVC Control ...............................................................M-82
18-17.Detection of a New Transfer Belt Unit ....................... ............................M-84
19. MAIN ERASE LAMP ........................................................................................M-84
20. PC DRUM CLEANING UNIT ...........................................................................M-85
20-1.Cleaning Mechanism ...............................................................................M-85
21. FUSING SECTION .......................................................................................... M-86
21-1.Fusing Section Drive Mechanism ............................................................M-87
21-2.Fusing Speed Control ..............................................................................M-87
21-3.Fusing Roller Stabilized Rotation Control ................................................M-88
21-4.Lower Fusing Roller Pressure/Retraction Mechanism ............................M-89
21-5.Fusing Unit Cleaning Mechanism ............................................................M-91
(1) Fusing Oil Application Mechanism ..................................................M-91
(2) Oil Coating Roller ............................................................................M-91
ii

FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
(3) Web Take-Up Mechanism ...............................................................M-92
(4) Web Slack Take-Up Control ............................................................M-92
21-6.Fusing Web Near Empty and Empty Detection .......................................M-93
21-7.New Fusing-Related Pa rts Detection ......................................................M-93
21-8.Fusing Temperature Control ....................................................................M-94
22. OTHER MECHANISMS ...................................................................................M-96
22-1.Memory Backup .................................. ......................... ............................M-96
22-2.Flash Memory ..........................................................................................M-96
22-3.Expanded Memory ..................................................................................M-97
22-4.Temperature/Humidity Sensor ................................................................. M-98
22-5.Copier Interior Cooling Mechanism .........................................................M-99
(1) IR Section Cooling Mechanism .......................................................M-99
(2) Fusing Section Cooling Mechanism ................................................M-99
(3) Power Supply Section Cooling Mechanism .....................................M-100
22-6.PC Drum Charge Corona Ozone Removal Mechanism ..........................M-100
iii
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
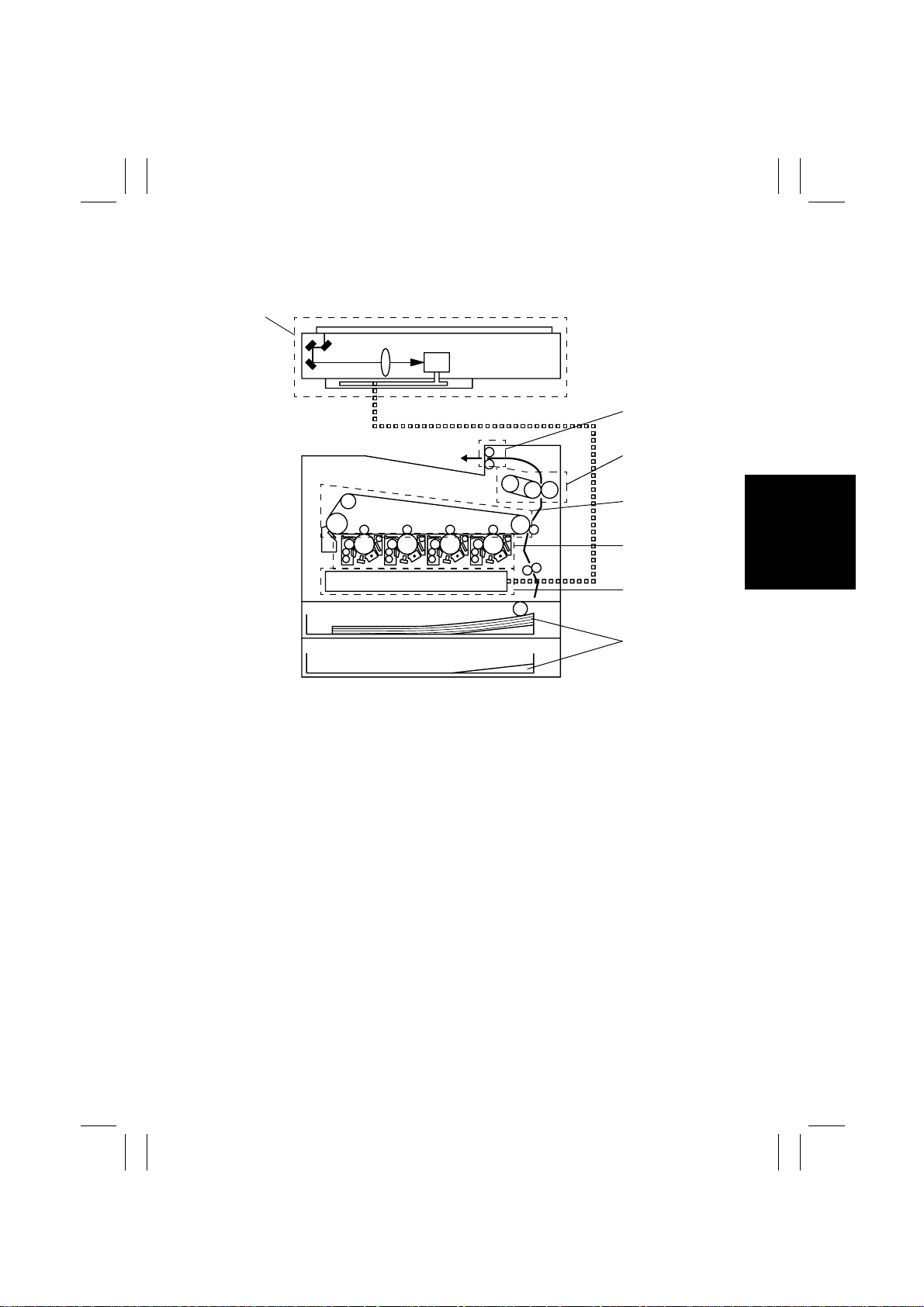
1. CROSS-SECTIONAL VIEW
1
2
3
4
5
6
1. IR Section
2. Exit Section
3. Fusing Section
4. Transfer Belt Unit
7
4004M001AA
5. Imaging Unit
6. LED Drive
7. Drawers
M-1
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
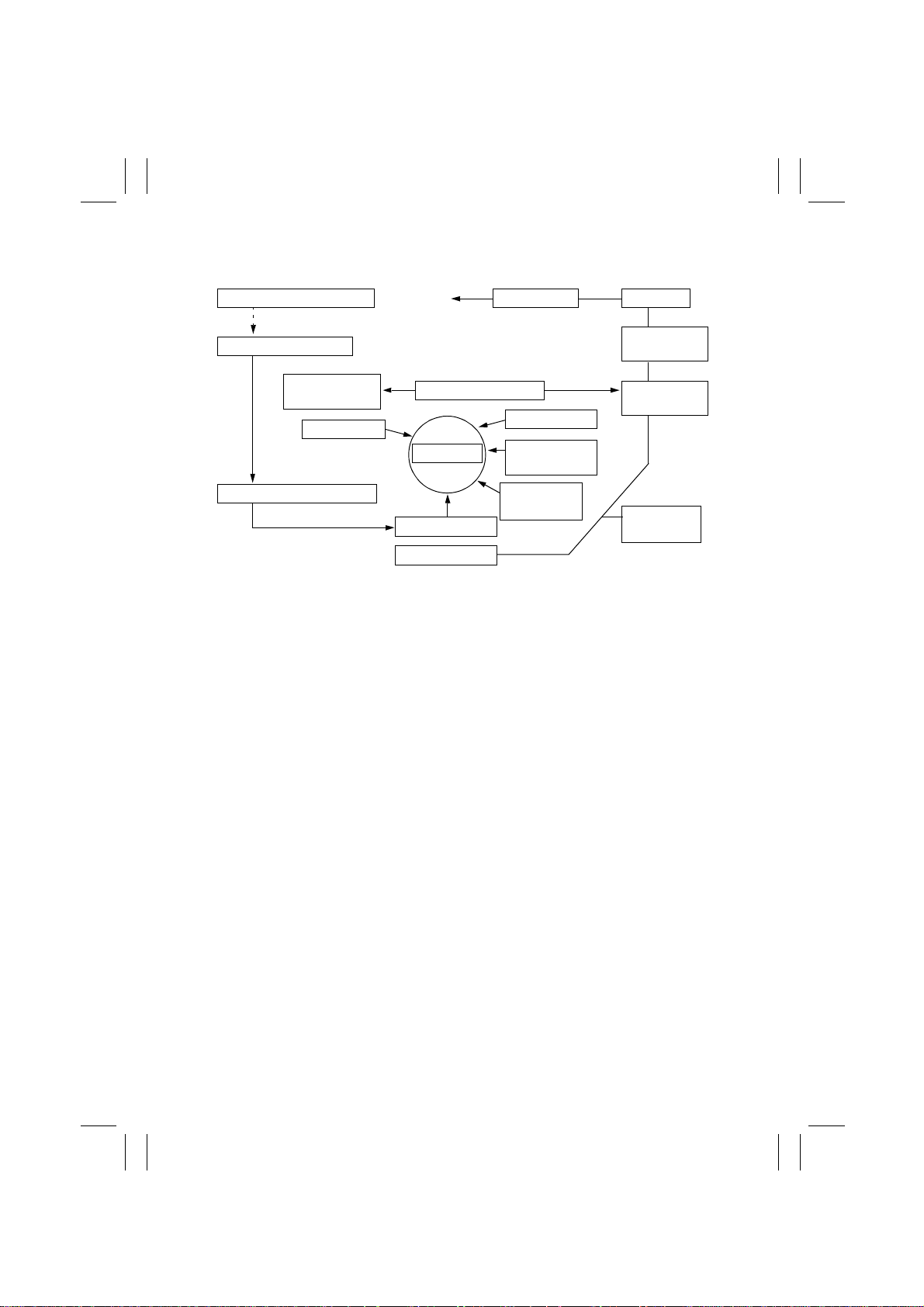
2. COPY PROCESS
3. Photoelectric Conversion
4. IR Image Processing
13. Transfer Belt
Cleaning
7. Developing
5. Printer Image Processing
1. PC Drum
• Changes the image of the original projected onto the surface of the PC Drum to an electrostatic latent image.
2. PC Drum Charging
• Deposits a negative DC charge across the entire surface of the PC Drum.
3. Photoelectric Conversion
• The light reflected off the surface of the original undergoes color separation through the
color filters (R, G, and B) and then the CCD converts it to a corresponding electrical signal and outputs the signal to the IR Image Processing Unit.
10. 1st Image Transfer
1.
PC Drum
6. LED Exposure
8. Paper Feeding
17. Paper Exit 16. Fusing
12. Paper
Separation
11. 2nd Image
14. Main Erase
15. PC Drum
Cleaning
2. PC Drum
Charging
Transfer
9. Manual
Bypass
4. IR Image Processing
• The electrical signal is converted to 8-bit digital image signals. After making some corrections, the Image Processing Unit outputs video signals (C, M, Y, and Bk) to the Printer
Image Processing Unit.
5. Printer Image Processing
• The video signals (C, M, Y, and Bk) output from the IR Image Processing Unit go through
some corrections. Following digital-to-analog conversion, these signals are then used
for the control of the intensity level of the LED.
6. LED Exposure
• LED light illuminates the surface of the PC Drum to form an electrostatic latent image.
7. Developing
• The toner, agitated and negatively charged in the developing unit of each color, is
attracted onto the electrostatic latent image formed on the surface of the PC Drum,
changing it to a visible, developed image.
• AC and DC negative bias voltages are applied to the Sleeve/Magnet Roller to prevent
toner from being attracted to the background area.
M-2

FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
8. Paper Feeding
• Paper is fed from each drawer.
9. Manual Bypass
• Paper is fed from the Manual Bypass Table.
10. 1st Image Transfer
• A DC positive voltage is applied to the backside of the Transfer Belt so that the visible,
developed image formed on each of the four PC Drums (Y, M, C, and Bk) is transferred
to the surface of the Transfer Belt.
11. 2nd Image Transfer
• A DC positive voltage is applied to the backside of the paper so that the visible image on
the surface of the Transfer Belt is transferred to the paper.
12. Paper Separation
• The Transfer Belt Paper Separator Fingers separate the paper properly from the Transfer Belt.
13. Transfer Belt Cleaning
• The residual toner left on the surface of the Transfer Belt is scraped off.
14. Main Erase
• Light from the Main Erase Lamp neutralizes any surface potential remaining on the surface of each PC Drum.
15. PC Drum Cleaning
• The Cleaning Blade scrapes off the residual toner left on the surface of the PC Drum.
16.Fusing
• The Upper and Lower Fusing Rollers apply heat and pressure to the paper so that the
four different color layers of toner lying on the surface of the paper are mixed and fused
together, as well as being fixed collectively to the paper.
17. Paper Exit
• Feeds the paper out of the copier onto the Paper Exit Tray.
M-3
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
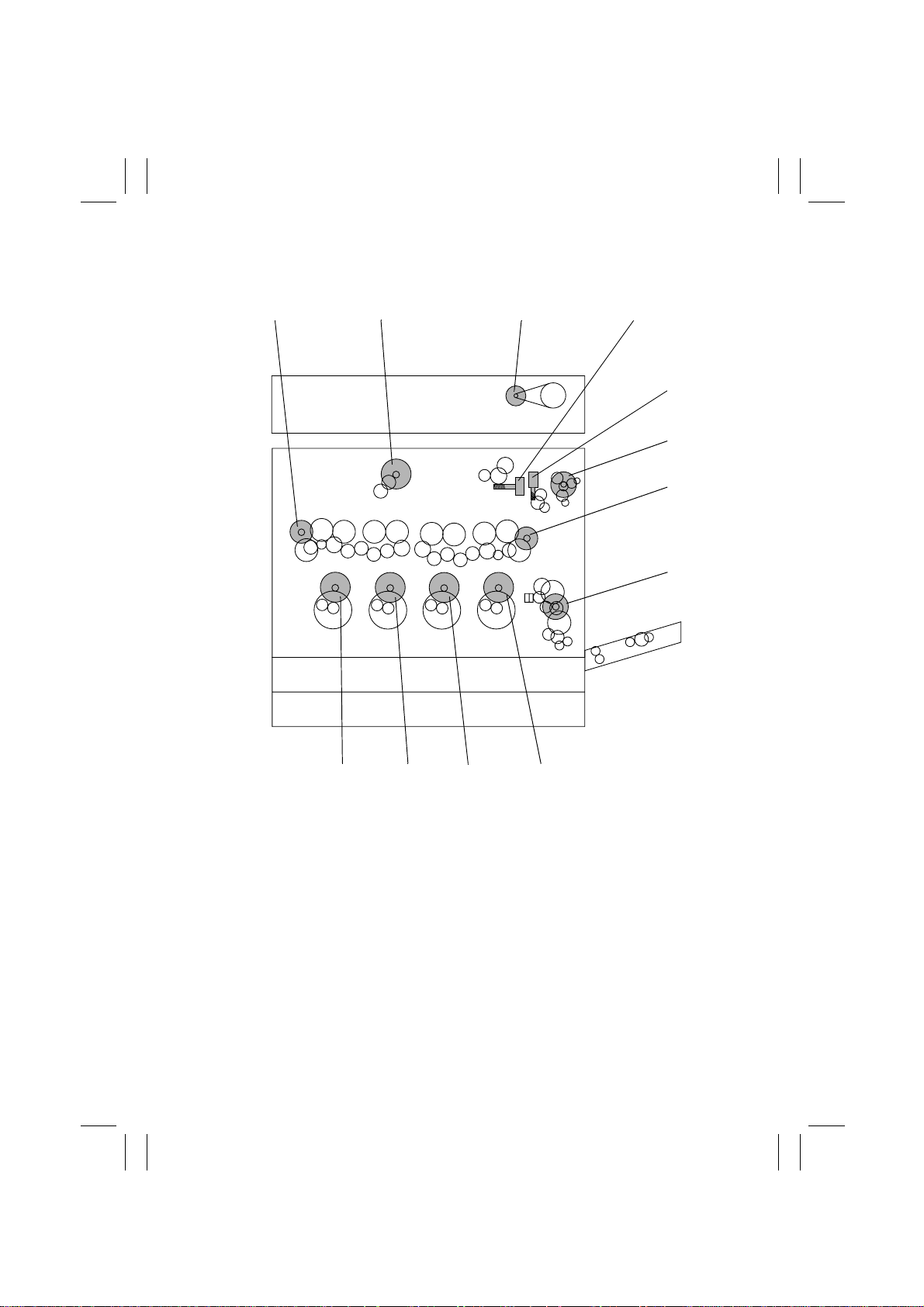
3. DRIVE SYSTEM
12 3 4
5
6
7
8
1. Toner Replenishing Motor Y/M (M10)
2. 1st Image Transfer Pressure/Retraction
Motor (M11)
3. Scanner Motor (M1)
4. Cleaning Web Drive Motor (M5)
5. Fusing Pressure/Retraction Motor (M8)
6. Fusing Drive Motor (M14)
M-4
4004M521AA
101112
7. Toner Replenishing Motor C/Bk (M9)
8. Main Motor (M13)
9. Imaging Unit Motor Bk (M18)
10. Imaging Unit Motor C (M17)
11. Imaging Unit Motor M (M16)
12. Imaging Unit Motor Y (M15)
9

FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
4. OPERATING SEQUENCE
• When Power Switch is Turned ON
Power Switch ON
Full-speed rotation
Power Supply Cooling
Fan Motor (M21)
Ozone Ventilation
Fan Motor (M22)
Fusing Cooling Fan Motor 1 (M23)
Fusing Cooling Fan Motor 2 (M24)
Original Glass Cooling
Fan Motor (M2)
IR Cooling Fan Motor 1 (M3)
IR Cooling Fan Motor 2 (M4)
Heating Roller Heater Lamp 1
Lower Fusing Roller Heater Lamp
Fusing Pressure/Retraction
Motor (M8)
Fusing Drive Motor (M14)
In synchronism with the timing
at which Scanner Motor is energized
Retracted
Half-speed rotation
Pressed
Temperature
control
Retracted
Exposure Lamp (LA1)
Scanner Motor (M1)
Main Motor (M13)
1st Image Transfer Pressure
/Retraction Motor (M11)
2nd Image Transfer Pressure
/Retraction Clutch (CL15)
2nd Image Transfer Bias (HV2)
Pressed
Retracted
Retracted
Pressed
Retracted
4004M062CA
M-5

FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
• When Start key is Turned ON
Start key ON
Full-speed rotation
Power Supply Cooling
Fan Motor (M21)
Ozone Ventilation Fan Motor (M22)
Fusing Cooling Fan Motor 1 (M23)
Fusing Cooling Fan Motor 2 (M24)
Original Glass Cooling
Fan Motor (M2)
IR Cooling Fan Motor 1 (M3)
IR Cooling Fan Motor 2 (M4)
Exposure Lamp (LA1)
Scanner Motor (M1)
Developing Bias (HV3)
Imaging Unit Motors
(M15, M16, M17, M18)
Main Erase Lamps
Y, M, C, Bk
PC Drum Charge Bias (HV1)
Developing Clutches
(CL11, CL12, CL13, CL14)
Main Motor (M13)
1st Drawer Paper Take-Up
Clutch (CL1)
Manual Feed Paper Take-Up
Clutch (CL3)
Synchronizing Roller Sensor (PC17)
Synchronizing Roller Clutch (CL21)
1st Image Transfer Pressure
/Retraction Motor (M11)
2nd Image Transfer Pressure
/Retraction Clutch (CL15)
1st Image Transfer Bias (HV2)
2nd Image Transfer Bias (HV2)
Fusing Pressure
/Retraction Motor (M8)
Fusing Drive Motor (M14)
Half-speed rotation
End of job
4004M553BA
Exit Sensor (PC10)
4004M063CA
M-6
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
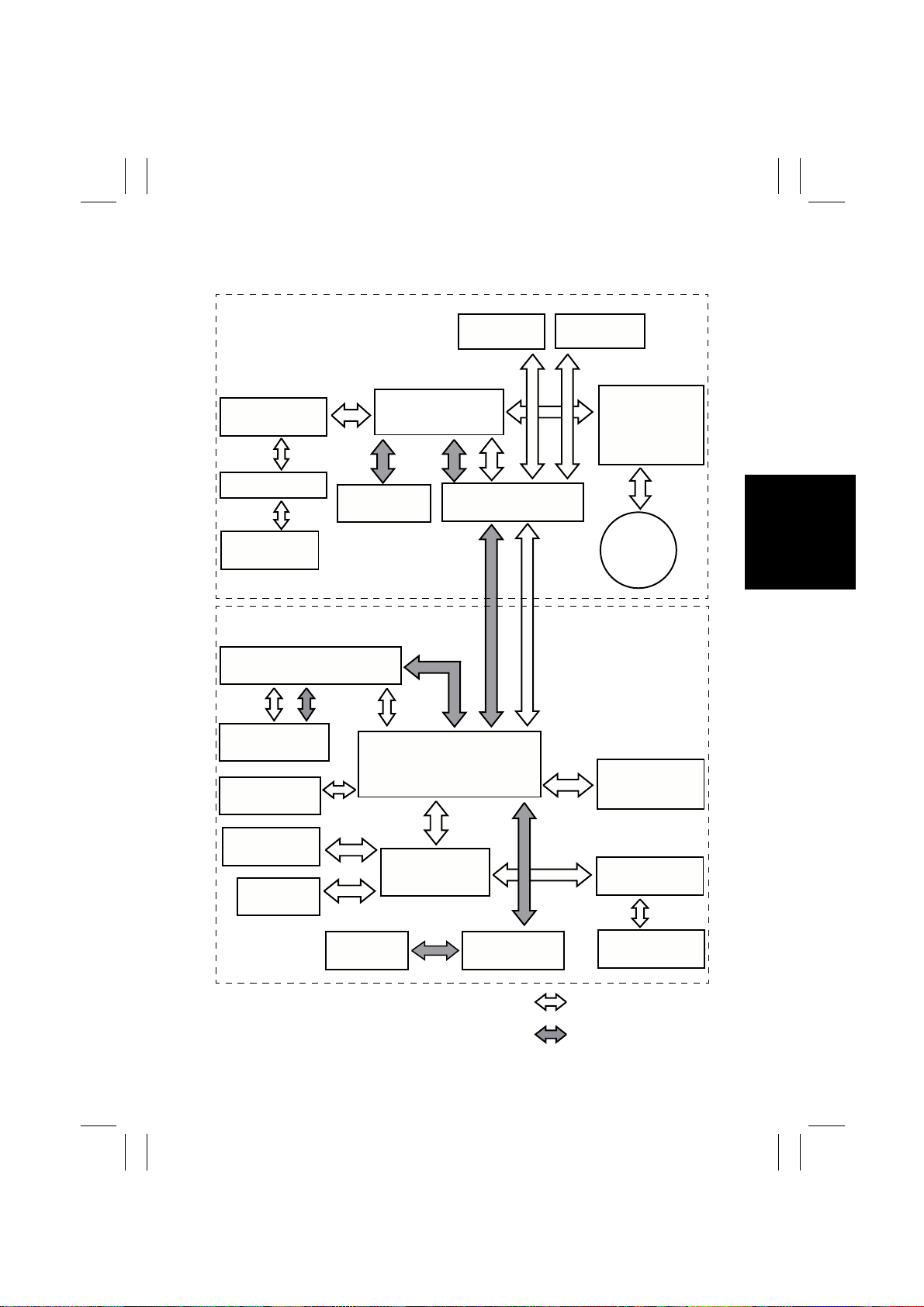
5. CONTROL BL OCK DIAGRAM
IR
DF-331
Control Panel
(UN1)
DC Power Supply 2 (PU2)
Flat Cable
Exposure Lamp
(LA1)
Engine
Controller I/F
Controller
DC Power Supply 1 (PU1)
AD-231
Finishing
Option
Image Processing
Board (PWB-C)
CCD Sensor
Board (PWB-A)
PIC Board (PWB-PIC)
Master Board
(PWB-I)
Scanner Motor
Drive Board
(PWB-IC)
IR PRIF Board
(PWB-D)
Scanner
Motor
(M1)
MSC Board
(PWB-H)
4004M553BA
Control Board
(PWB-A)
LED Units (Y,
M, C, Bk)
M-7
LED Board
(PWB-LK)
Paper Source
Option
Control System Line
Image Bus Line
4004M567AA
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
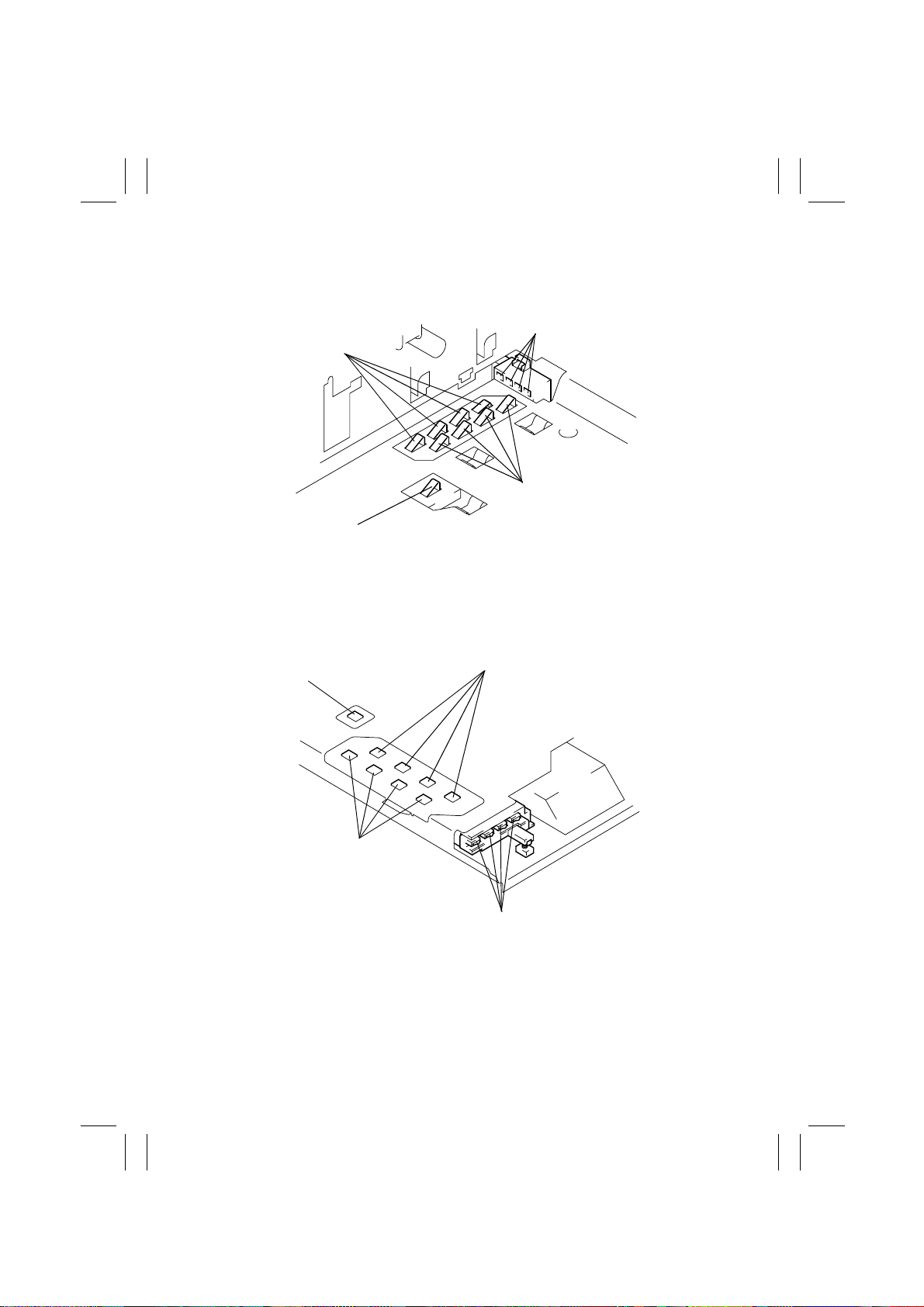
6. LOCATIONS OF TERMINALS
• Inside the Copier (under LED Unit)
Developing Bias: Y, M, C,
and Bk from left to right
Grid Voltage: Y, M, C, and
Bk from left to righ t
PC Drum Charge Output: Bk,
C, M, and Y from left to right
• Back of LED Unit
ATDC Bias
Developing Bias: Y, M, C,
and Bk from left to right
ATDC Bias
4004M579AA
Grid Voltage: Y, M, C, and
Bk from left to right
4004M580AA
PC Drum Charge Output: Bk,
C, M, and Y from left to right
M-8
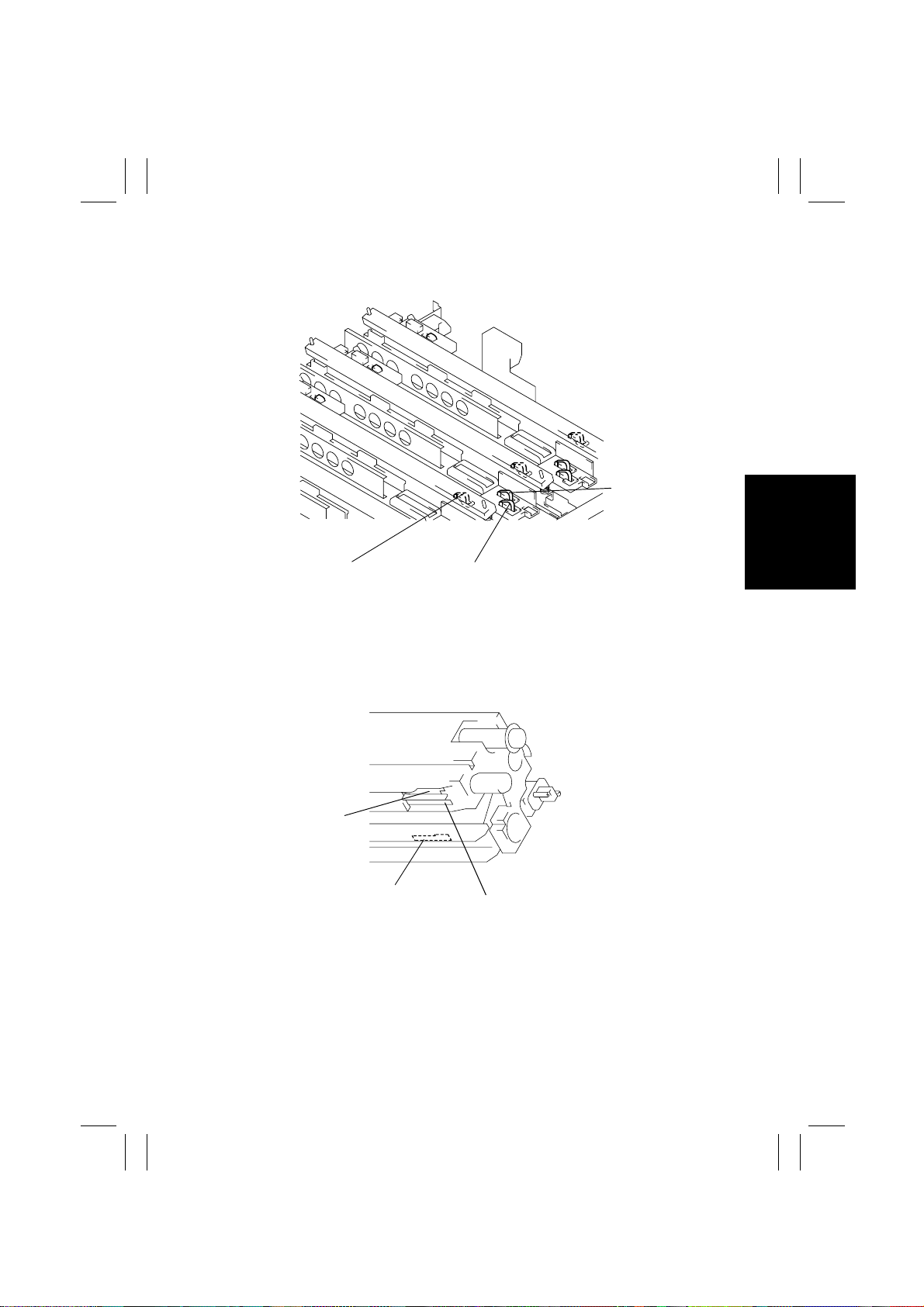
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
• LED Unit
Front
Developing Bias:
Y, M, C, and Bk
from right to left
Grid Voltage: Y, M,
C, and Bk from
right to left
PC Drum Charge
Output: Y, M, C,
and Bk from right
to left
4004M582AA
• Imaging Unit
Grid Voltage
Developing Bias
Rear
4004M581AA
PC Drum Charge
Output
M-9
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
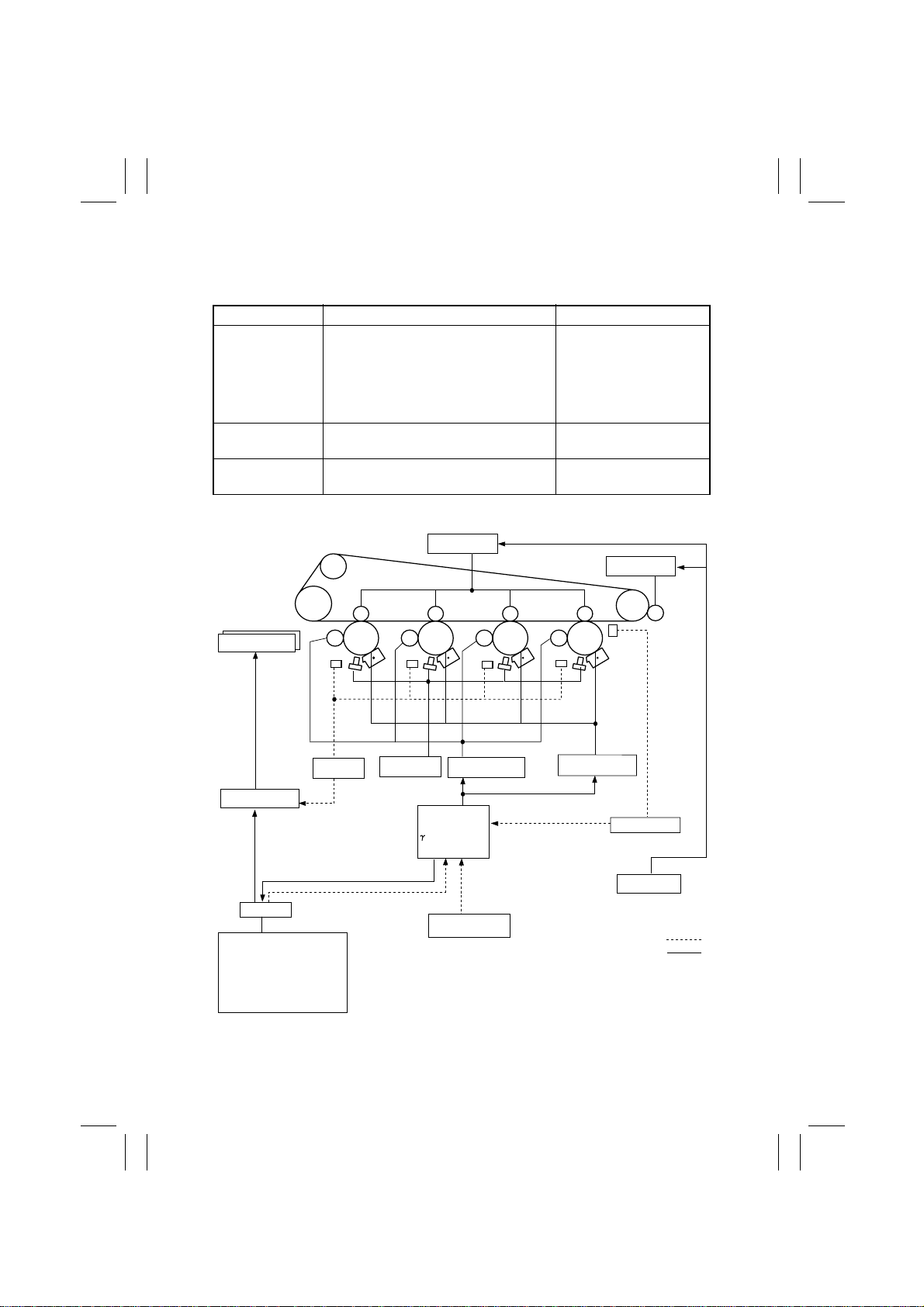
7. IMAGE STABILIZATION SYSTEM
• The copier provides the image stabilization control as detailed below to ensure stabilized
copy image.
Purpose Means Control (Sensor)
• To stabilize
image density
• To stabilize gradation
• To stabilize
toner density
• To stabilize
image transfer
✽
An explanation is given of the control for each section.
• Background margin control
• AIDC intensity control
• Max. density control
✽
Registration control (Color Shift Cor-
• AIDC Sensor
• Temperature/Humidity
Sensor
rection)
•γ correction control
✽
ATDC control (Y, M, C, Bk) • ATDC Sensor
✽
Image transfer output control • Temperature/Humidity
Sensor
1st Image
Transfer Roller
2nd Image
Transfer Roller
Toner Replenishing
Motor
ATDC Sensor
Toner Replenishing
Control
OUT/IN
. To be set on control panel
PRT Max Density
PRT Highlight
Background Voltage Margin
ATDC Level Setting
AE Adjust
ATDC Toner Supply
PC Drum
Y
Registration
Control
PC Drum
MCBk
Image Density
Gradation Control
Correction Data
AIDC Table
Temperature
/Humidity Sensor
PC Drum
Developing Bias
Vb
PC Drum
Grid Voltage Vg
AIDC Sensor
Transfer ATVC
Control
IN
OUT
4004M064CA
M-10
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
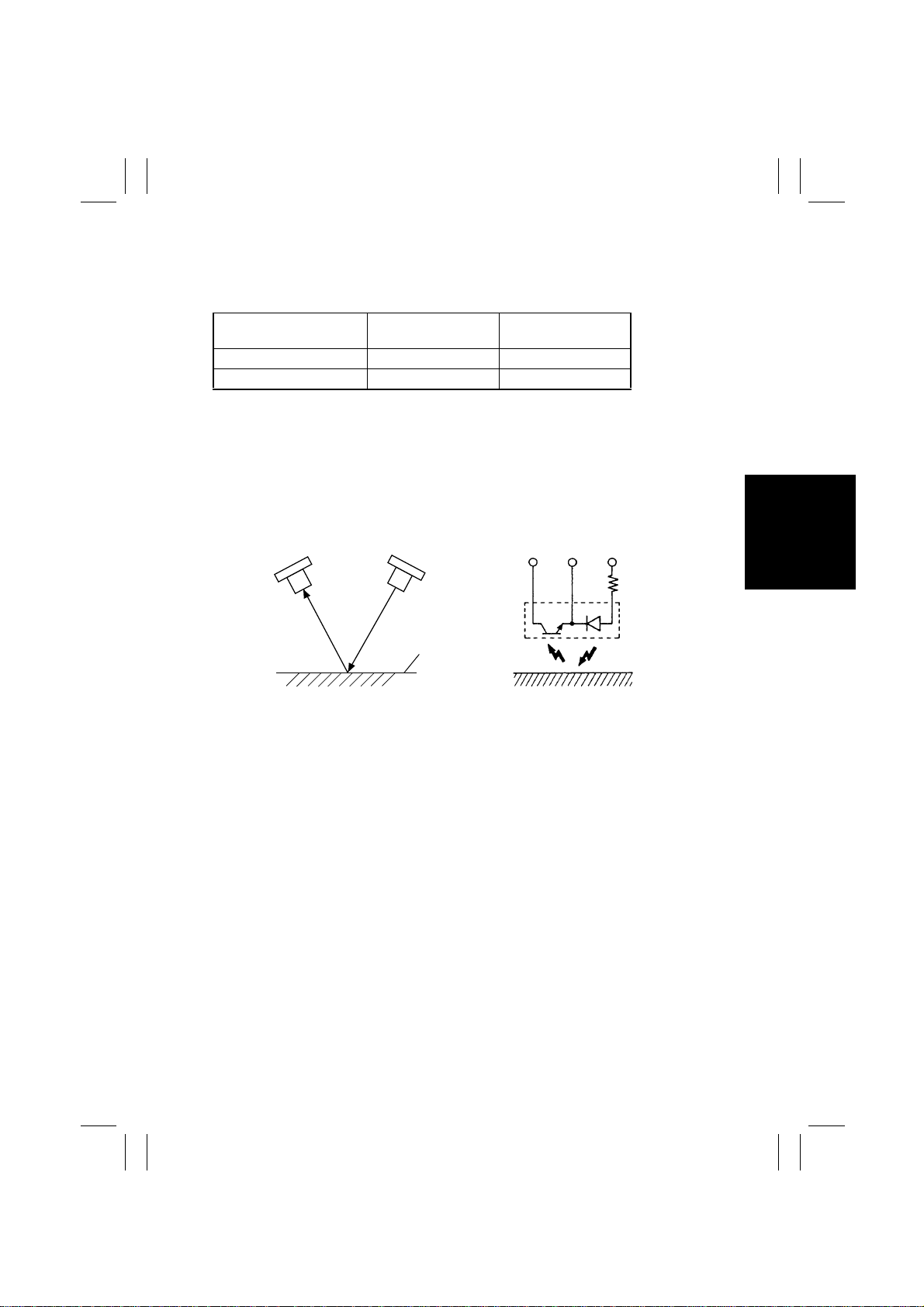
7-1. AIDC Detection
• Patterns are produced on the Transfer Belt and AIDC Sensors detect the amount of
toner sticking to the patterns.
Amount of Toner Sticking
Large Low Small
Small High Great
1. The light-emitting diode emits infrared rays illuminating the toner pattern on the Trans-
fer Belt.
2. The photoreceiver detects the intensity of the infrared light reflected off the toner pat-
tern on the Transfer Belt.
3. A voltage corresponding to the intensity of the reflected light is output to the PIC Board.
Photoreceiver
Intensity of Light
Reflected
LED
Transfer Belt
4004M532AA 1136M068AA
Output
Power SourceGNDOutput
M-11
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
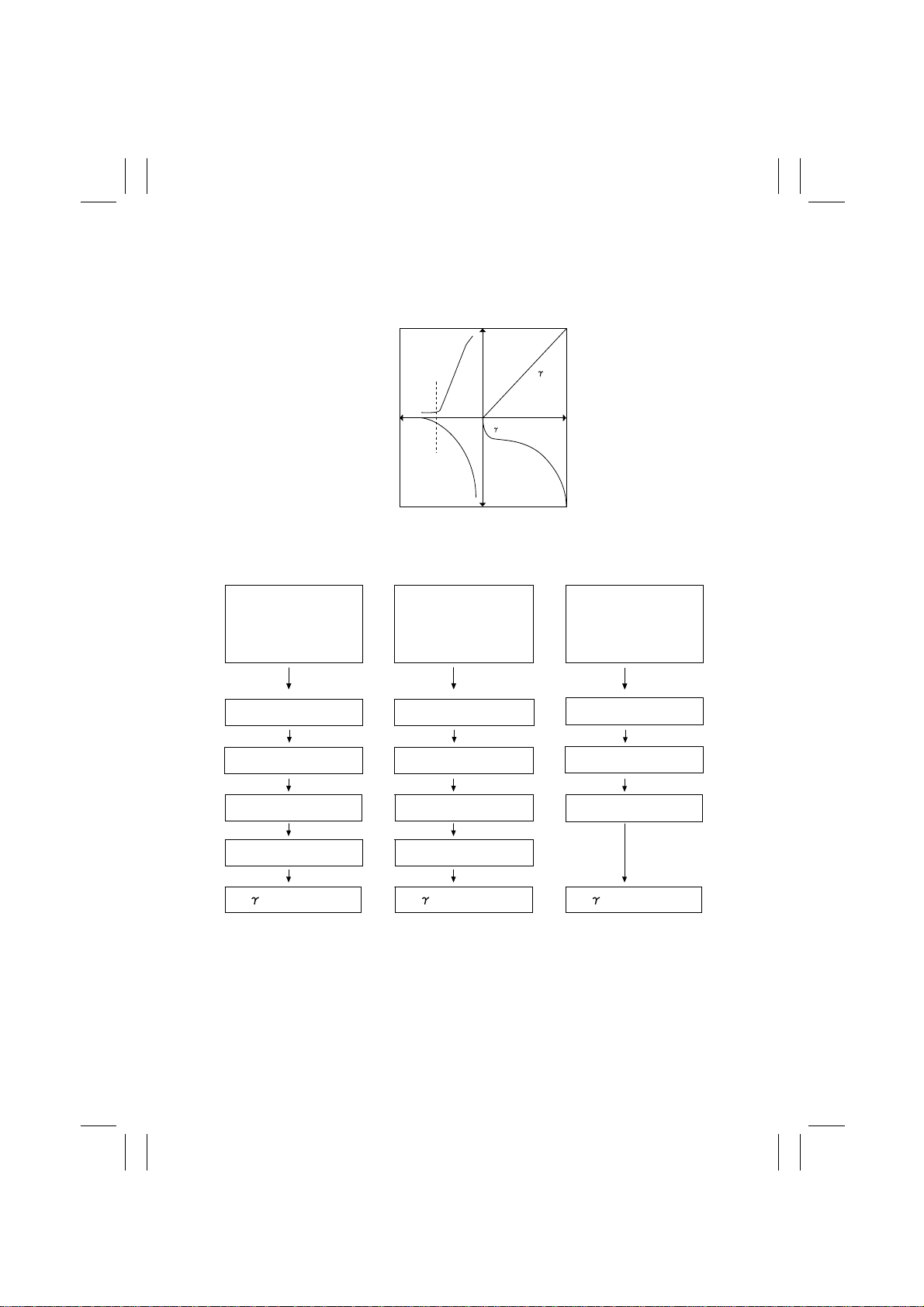
7-2. Image Stabilization System Control
• The copier uses the data obtained through AIDC detection to perform various operations,
thereby finding the optimum γ correction exposure curve for image stabilization control.
Sensitometry
Reversal Developing
Characteristics
ID (Image Density)
VB
Image Density
Characteristics
= 1
• Operation Flow
• A new IU is detected
A new Transfer Belt
•
Unit detected
• Reset + Stabilizer
Mode
(1) AIDC intensity control
(2) Background margin
control
(3) Max. density
control 1
Registration control
Transfer Belt
Surface Potential
Image Input
Correction Curve
PC Drum Light
Decay Curve
LED Light Intensity
•
Power Switch is turned ON
•
Left Door is opened
LED Illumination
Characteristics
Data
4004M065CA
• Multi-print cycle 1*
•
Stabilizer
and closed
•
Front Door is opened
and closed
(1) AIDC intensity control (1) AIDC intensity control
(2) Background margin
control
(3) Max. density
control 2
(2) Background margin
control
(3) Max. density
control 2
Registration control
(4) correction control
✽
Multi-print cycle 1: If the copier has 20 or more pages to be printed as it completes print-
(4) correction control
(4) correction control
4004M066CA
ing 100 pages after the last image stabilization sequence, it suspends that particular print
cycle and, instead, initiates an image stabilizer sequence. As it completes the image stabilization sequence, the machine resumes the suspended print cycle.
M-12
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
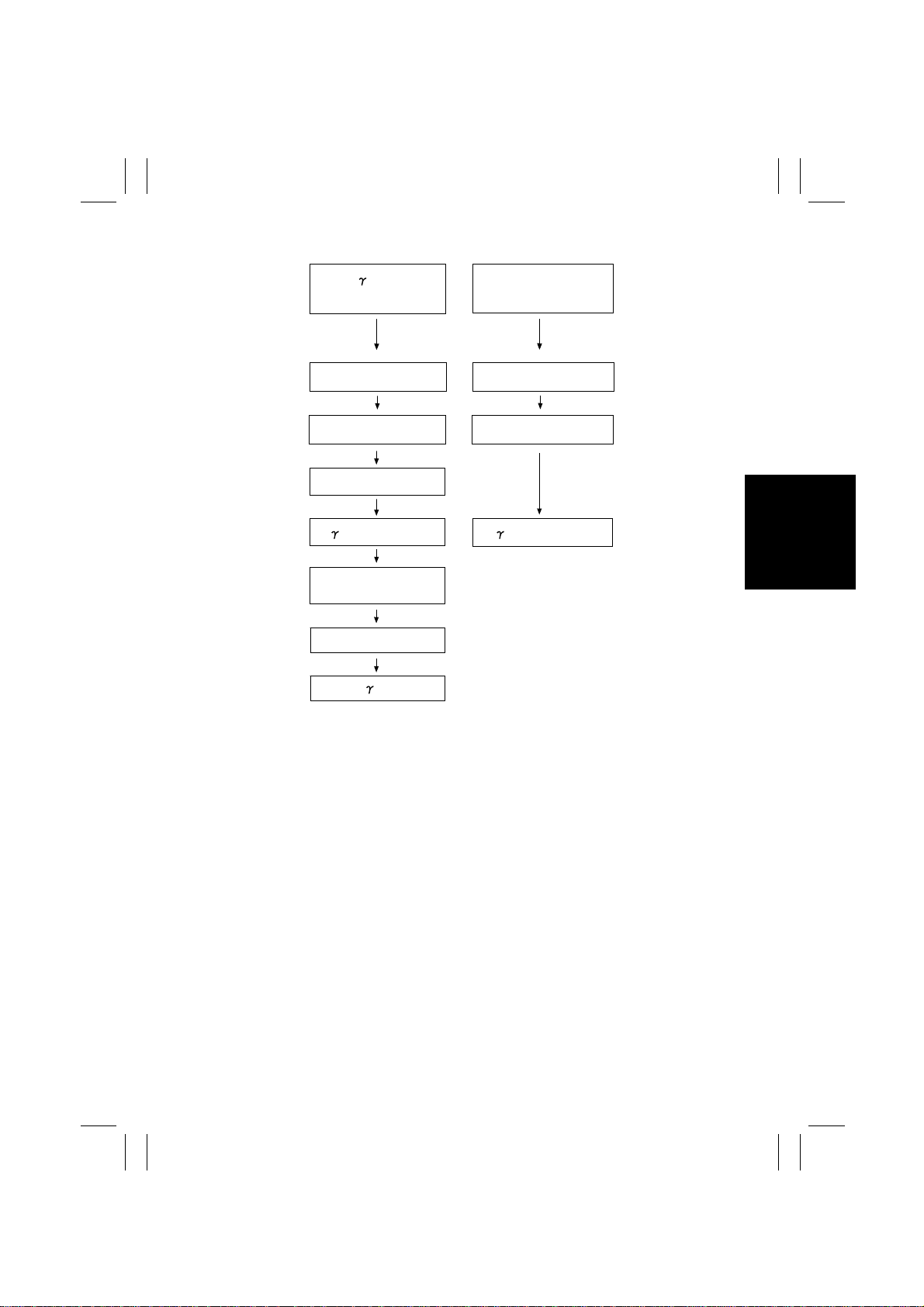
• During
automatic adjustment
(1) AIDC intensity
control
(2) Background
margin control
(3) Max. density
control 2
(4) correction control
Test pattern print
CCD reading
Another correction
✽
Multi-print cycle 2: If the copier has less than 20 pages to be printed as it completes printing 100 pages after the last image stabilization sequence, it continues running that particular print cycle until it is completed before initiating an image stabilizer sequence.
• Multi-print cycle 2
(1) AIDC intensity
control
(2) Background
margin control
(4) correction control
4004M080CA
M-13

FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
(1) AIDC Sensor LED Intensity Control
• Controls changes in characteristics due to change with time and contamination of the
AIDC Sensor, and part-to-part variations in the sensors, and change of environment.
Control Provided:
1. Adjusts the intensity (current value) of the LED on the surface of the Transfer Belt, on
which no toner sticks.
(2) Background Margin Control
• Corrects changes in charging efficiency as a result of a deteriorated PC Drum and environmental condition changes.
• Controls the PC Drum Charge Corona grid voltage so that the background margin
becomes 100 V.
Control Provided:
1. Determines the PC Drum Charge Corona grid voltage based on the information provided by various sensors, system speed, and the target surface potential.
Target surface potential V0 (V) = Required developing bias voltage Vb (V) - 100 V
(3) Max. Density Control
• Adjusts the developing bias (Vb) to control changes in the solid density resulting from
variations in developing characteristics and LED intensity, variations in sensitivity of the
PC Drum, and changes in the environment, durability, and the amount of charge in toner.
Control Provided:
1. Produces patterns on the surface of the Transfer Belt and lets the AIDC Sensor detect
the amount of toner sticking to them.
2. Selects the correction data appropriate for each color based on the correction data
with four different levels for each color.
3. Computes from the detected data the developing bias and grid voltage values that
result in the maximum density and stores the values in memory.
(4)γ Correction Control
• Adjusts the LED intensity to correct changes in gradation characteristics to a linear one.
The changes in gradation characteristics are caused by variations in the PC Drum sensitivity and developing characteristics and changes with time and in environment.
Control Provided:
1. Produces patterns on the surface of the Transfer Belt and lets the AIDC Sensor detect
the amount of toner sticking to them.
2. According to the density measurements of different gradation levels, γ correction data
is computed and the optimum LED intensity is set for each gradation level.
M-14
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
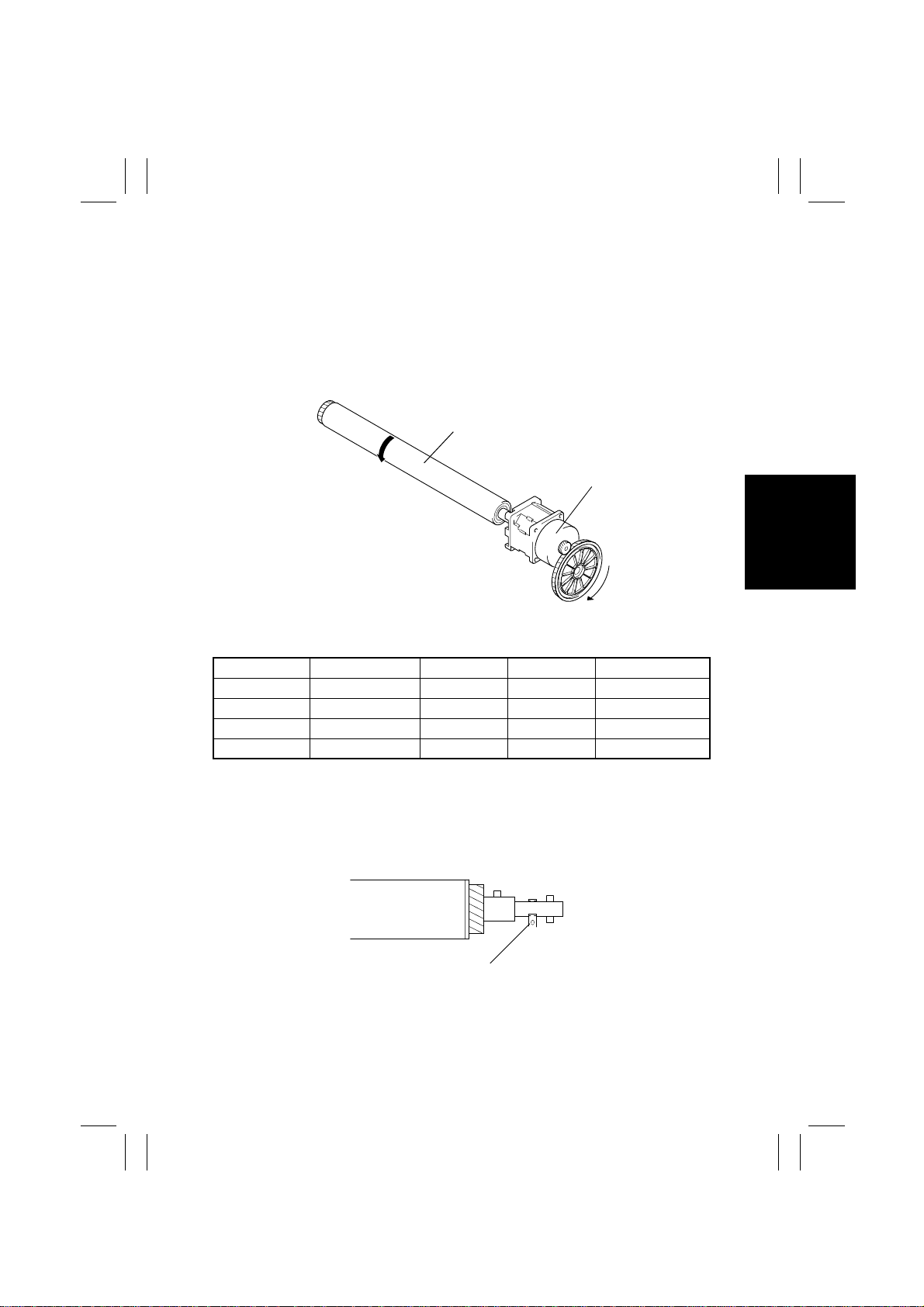
8. PC DRUM
8-1. PC Drum Drive Mechanism
• A motor is used to turn the PC Drum of each color.
• It is a planet motor capable of transmitting highly accurate drive and preventing pitch
noise.
• The motor employs planet rollers that transmit drive through friction to decelerate its
speed, which means that it produces no noise or uneven rotation.
PC Drum
Imaging Unit Motor Y/M/C/Bk
(M15/16/17/18)
4004M002AA
Controlled Part Control Signal Energized Deenergized WIRING DIAGRAM
M15 Y PJ12I-4A L H 15-B
M16 M PJ12I-8A L H 17-B
M17 C PJ12I-4B L H 16-C
M18 Bk PJ12I-8B L H 17-D
8-2. Grounding of the PC Drum
• The potential on the surface of the PC Drum exposed to the LED is grounded to the
frame.
Front
Ground Plate
4004M003AA
M-15

FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
9. PC DRUM CHARGE CORONA
• The PC Drum Charge Corona generates corona emission to deposit a charge evenly
across the surface of the PC Drum through a grid mesh.
• It has a comb electrode, which ensures that a charge is concentrated on the grid mesh,
thus reducing the amount of ozone produced.
• The grid voltage applied to the grid mesh is generated by the Constant-Voltage Circuit in
High Voltage Unit 1.
• The constant voltage of High Voltage Unit 1 is determined through image stabilization
control.
PC Drum Charge Corona
Grid Mesh
PC Drum
PC Drum Charger
4004M023AA
Control Signal ON OFF WIRI N G DIAGRA M
PJ9I-6 (Y) L H
PJ9I-8 (M) L H
PJ9I-10 (C) L H
PJ9I-12 (Bk) L H
22-C
M-16
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
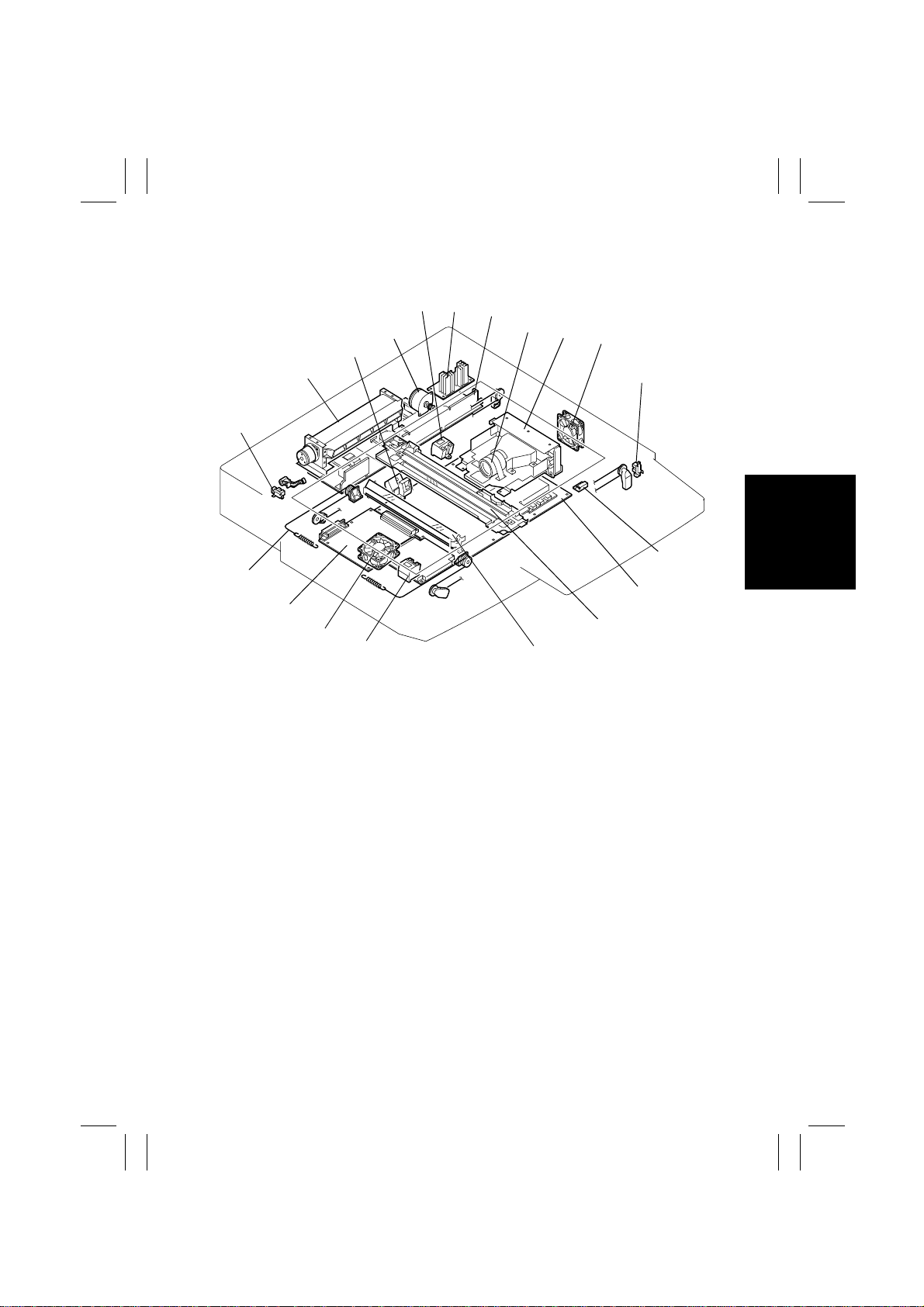
10. IMAGE READER (IR) SECTION
6
5
4
3
2
1
19
18
17
16
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
4004M005AA
1. Original Cover Detecting Sensor PC25
2. Original Glass Cooling Fan Motor M2
3. Original Size Detecting Sensor FD1
PC30
4. Scanner Motor M1
5. Original Size Detecting Sensor FD2
PC31
6. Scanner Motor Drive Board PWB-IC
7. DC Power Supply 2 PU2
8. Lens
9. CCD Sensor Board PWB-A
10. IR Cooling Fan Motor 2 M4
M-17
11. Scanner Home Sensor PC24
12. Size Reset Switch S10
13. Image Processing Board PWB-C
14. Scanner
15. 2nd/3rd Mirror
16. Original Size Detecting Sensor CD1
PC32
17. IR Cooling Fan Motor 1 M3
18. IR PRIF Board PWB-D
19. Cable
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
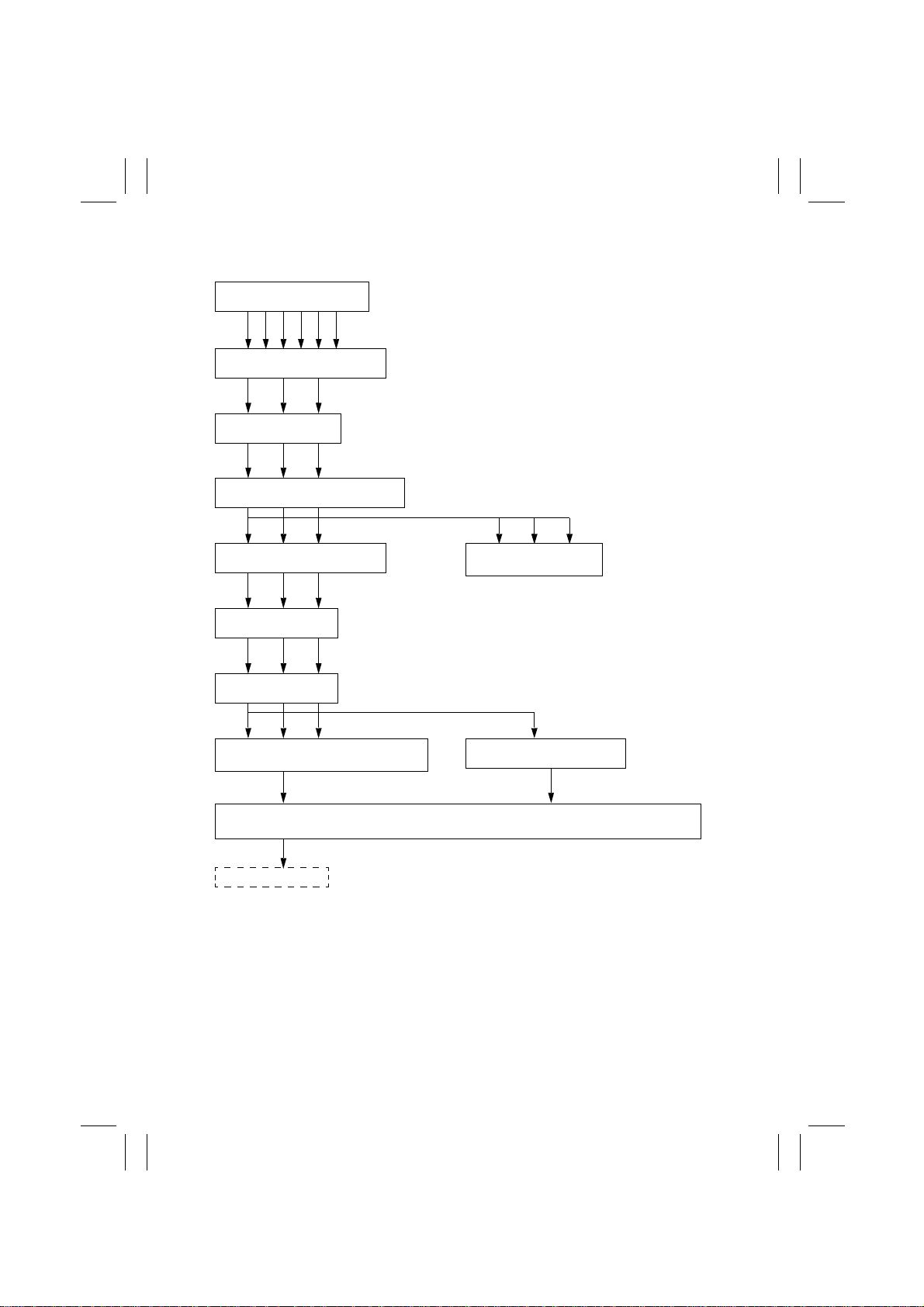
10-1. IR Image Processing
1. Photoelectric Conversion
2. Analog-to-Digital Conversion
3. Shading Correction
4. Line-to-Line Variation Correction
5. Zoom/Movement Processing
7. Image Data Editing
8. AE Processing
10. Color Correction (Reflection/Density
Conversion, Masking, UCR/BP)
11. Miscellaneous Processing (Improved Reproduction of Black Characters, Edge Emphasis, edge
expansion, Smoothing, Color Balance, Gamma (
To Printer (PIC Board)
6. Histogram Making
(ACS/AE Processing)
9. Image Area Discrimination
) Correction)
γ
M-18
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
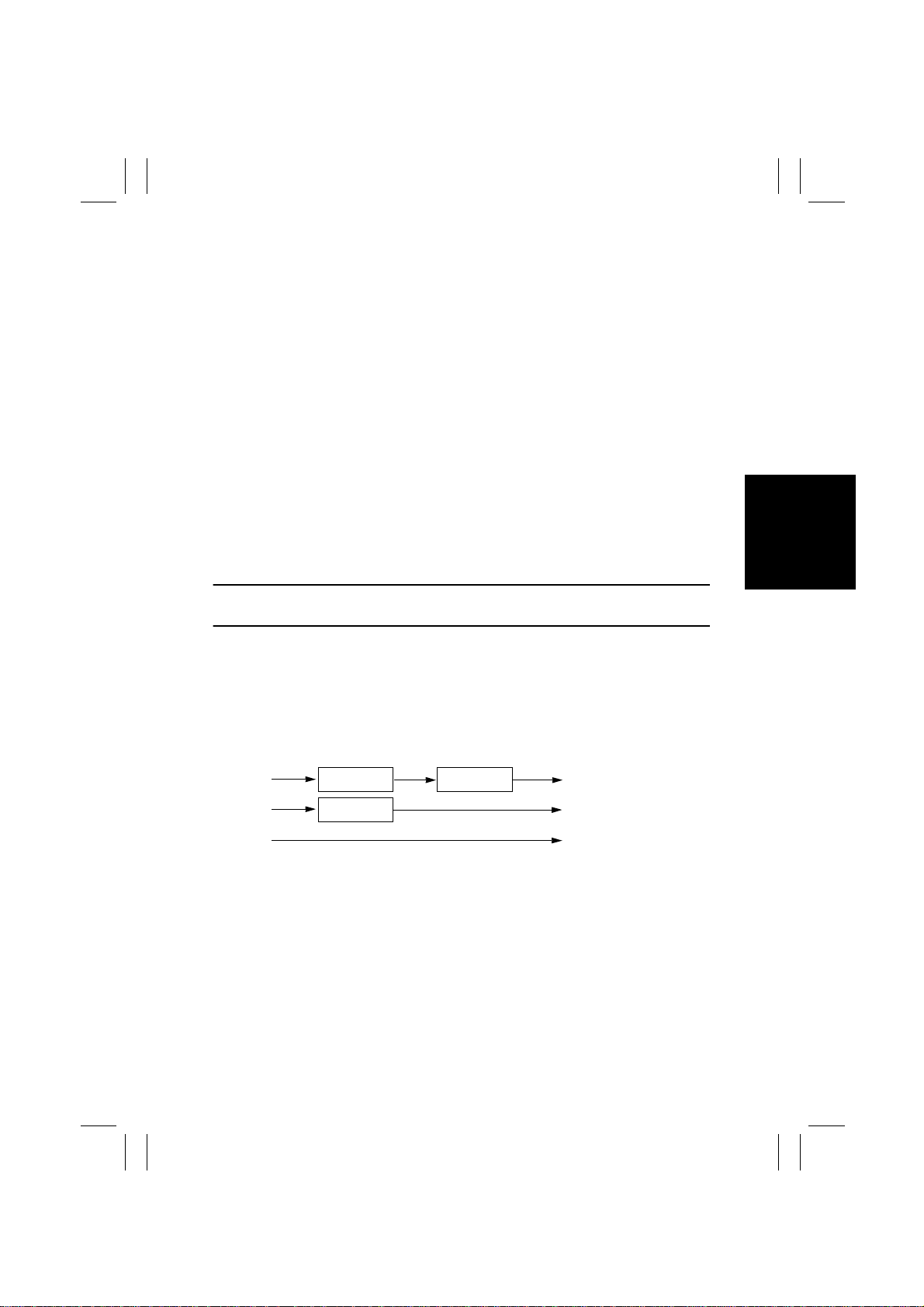
1. Photoelectric Conversion
• A reduction-type color CCD Sensor is used.
• The R, G, and B chips of the CCD Sensor read the light reflected off the original and convert the optical data into a corresponding analog electric signal.
• To make data processing faster, data transfer and output are done through two channels, one for even-numbered pixels and the other for odd-numbered pixels.
2. Analog-to-Digital Conversion
• The odd and even analog signals output from the CCD Sensor are converted
ital signals which are then synthesized.
3. Shading Correction
• An error is corrected that occurs due to variations in sensitivity of each CCD chip and the
light distribution varying along the length of Exposure Lamp.
Operation:
A. Before the start of each copy cycle, light from Exposure Lamp strikes the shading sheet
and the CCD Sensor reads the light reflected off this sheet.
B. This reading is compared with the shading sheet reading reference value (white refer-
ence value = max. value of image data) to determine the correction value for each pixel.
C. When the image is scanned, each pixel data is corrected with the above correction
value.
To prevent adverse effects on the image due to dust on the white plate (shading sheet), a
correction is made based on the readings taken of multiple lines.
to 8-bit dig-
4. Line-to-Line Variation Correction
• The R, G, and B chips of the CCD Sensor are placed so that there is a gap of 4 lines in
the sub-scanning direction between the two adjacent chips (R → G → B). This results in a
deviation in the scanning position of the original. (The slower the scanning speed, the
greater the amount of deviation.)
• A memory called FIFO
timing for R and G data to match it with that for B data.
R data FIFO FIFO Output
G data FIFO Output
B data Output
✽
FIFO (first-in-first-out): Data is output in the same order as it is input.
✽
is used to compensate for this deviation. It retards the output
M-19
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
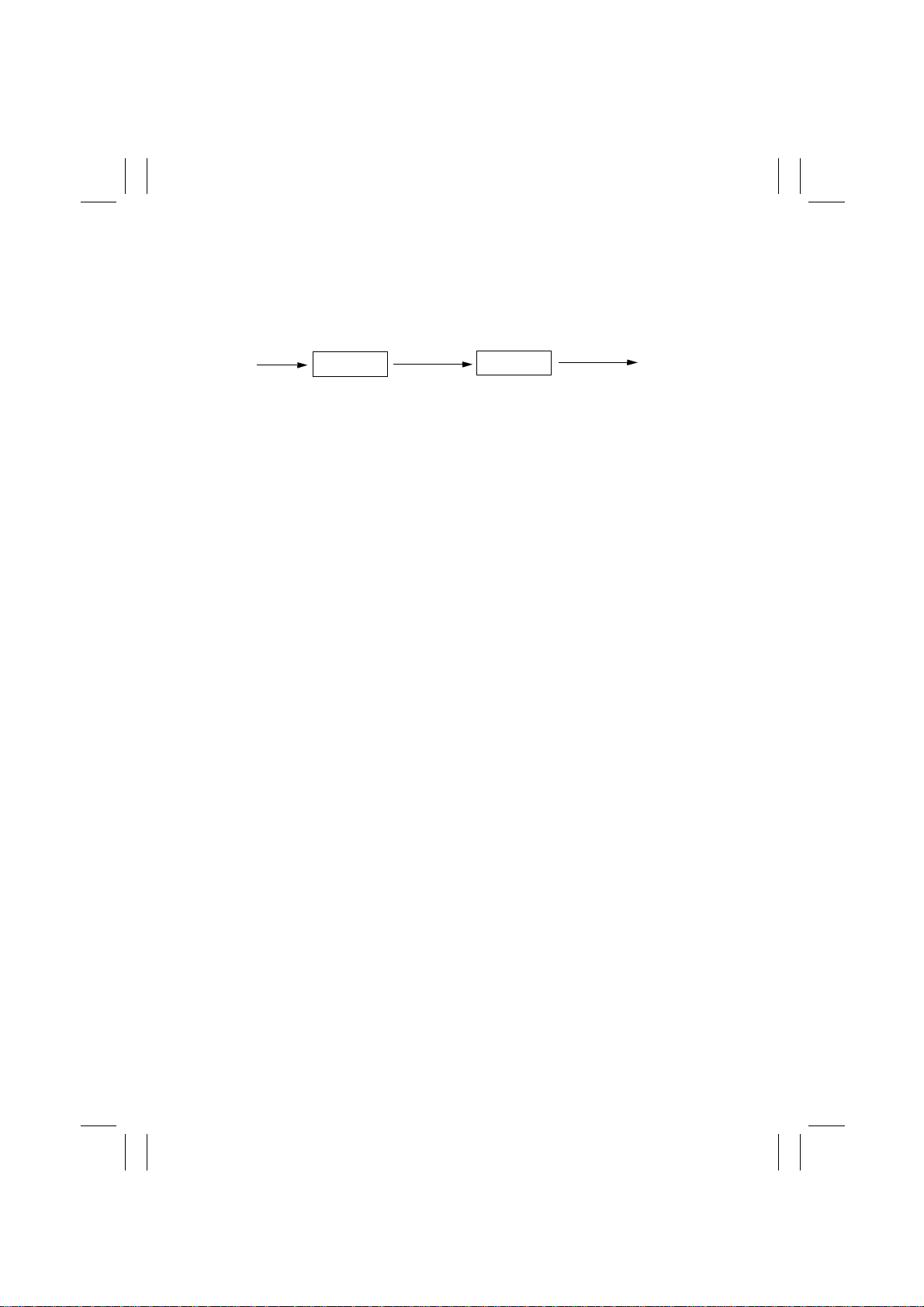
5. Zoom/Movement Processing
• The image is edited according to the editing features selected on the control panel
(enlargement/reduction, Image Monitor)
• Two memories (FIFOs) are used to edit the image as required.
FIFO
Zoom
• The synchronous timing of the input data (read) and output data (read) is varied to
decrease (reduction) or increase (enlargement) the number of data readings, thereby
reducing or enlarging the image in the main scanning direction.
• The image is reduced or enlarged in the sub-scanning direction by varying the speed at
which the Scanner moves.
Image Monitor
• The input data (read) stored in the memory is output (read) several times.
Input
(Write)
FIFO
Output
(Read)
M-20
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
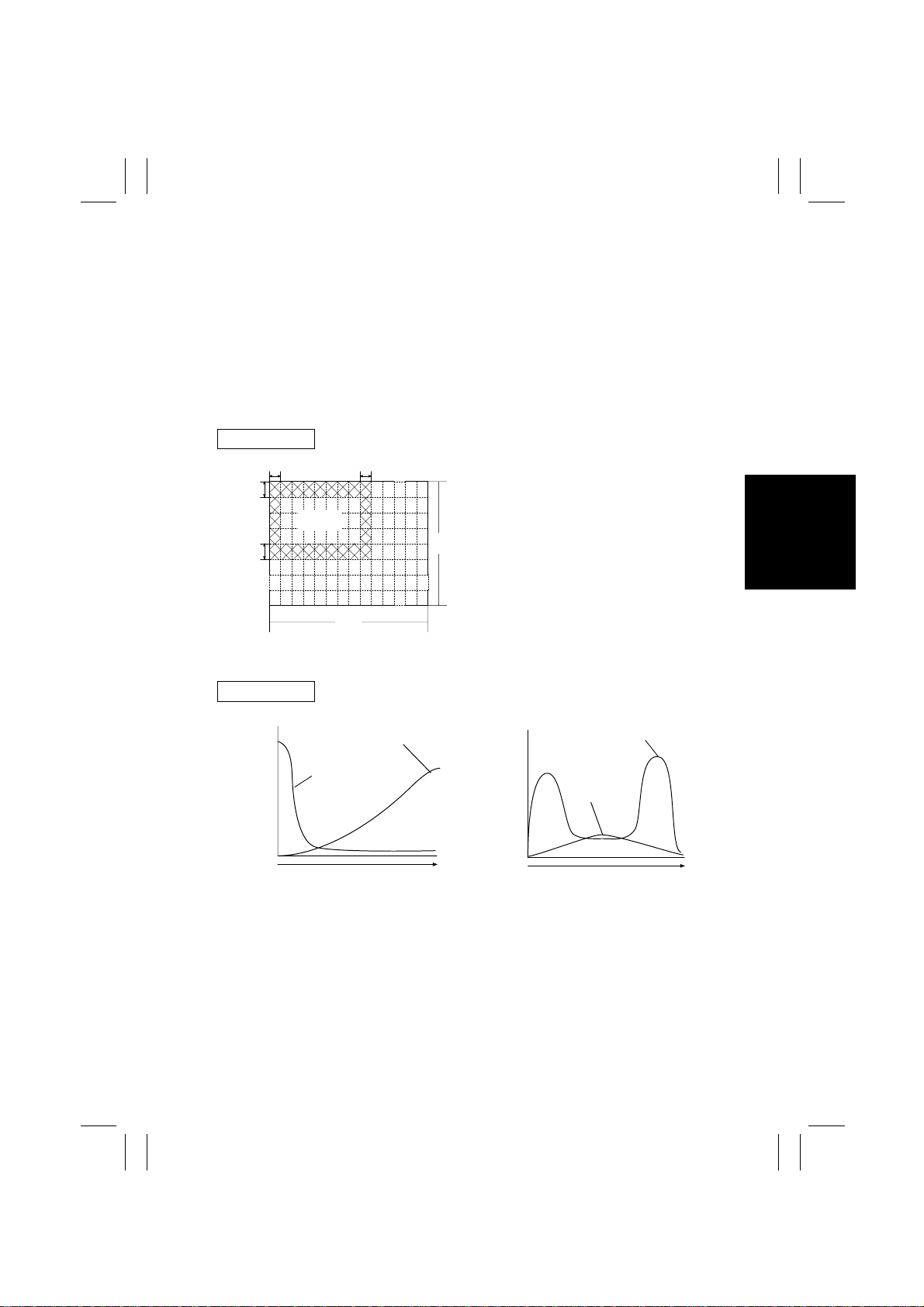
6. Histogram Making
• The scanning area is divided into multiple blocks.
• The image data of the original (excluding the edges) is sampled during the prescan after
the shading correction.
• A histogram is then generated of lightness by saturation.
• The number of color dots in each block is counted.
• The results of the counting are then used to determine whether each block on the original
(excluding the edges) is colored or monochrome.
• Based on the results of the color/monochrome evaluation made of each block, the copier
determines whether the entire original is colored or monochrome (ACS, or Auto Color
Selection).
Block Division
Edge Edge
Edge
Original
Edge
CD
FD
1154M076AA
Histogram
Frequency
Colored
Frequency
Monochrome
Monochrome
Colored
Lightness
4004M600AA
Low High
Saturation
1154M077AA
CD
Dark Light
7. Image Data Editing
• R, G, and B data are converted to V (value), Cr, and Cb (color component) for color
adjustments (saturation, lightness, and hue).
M-21

FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
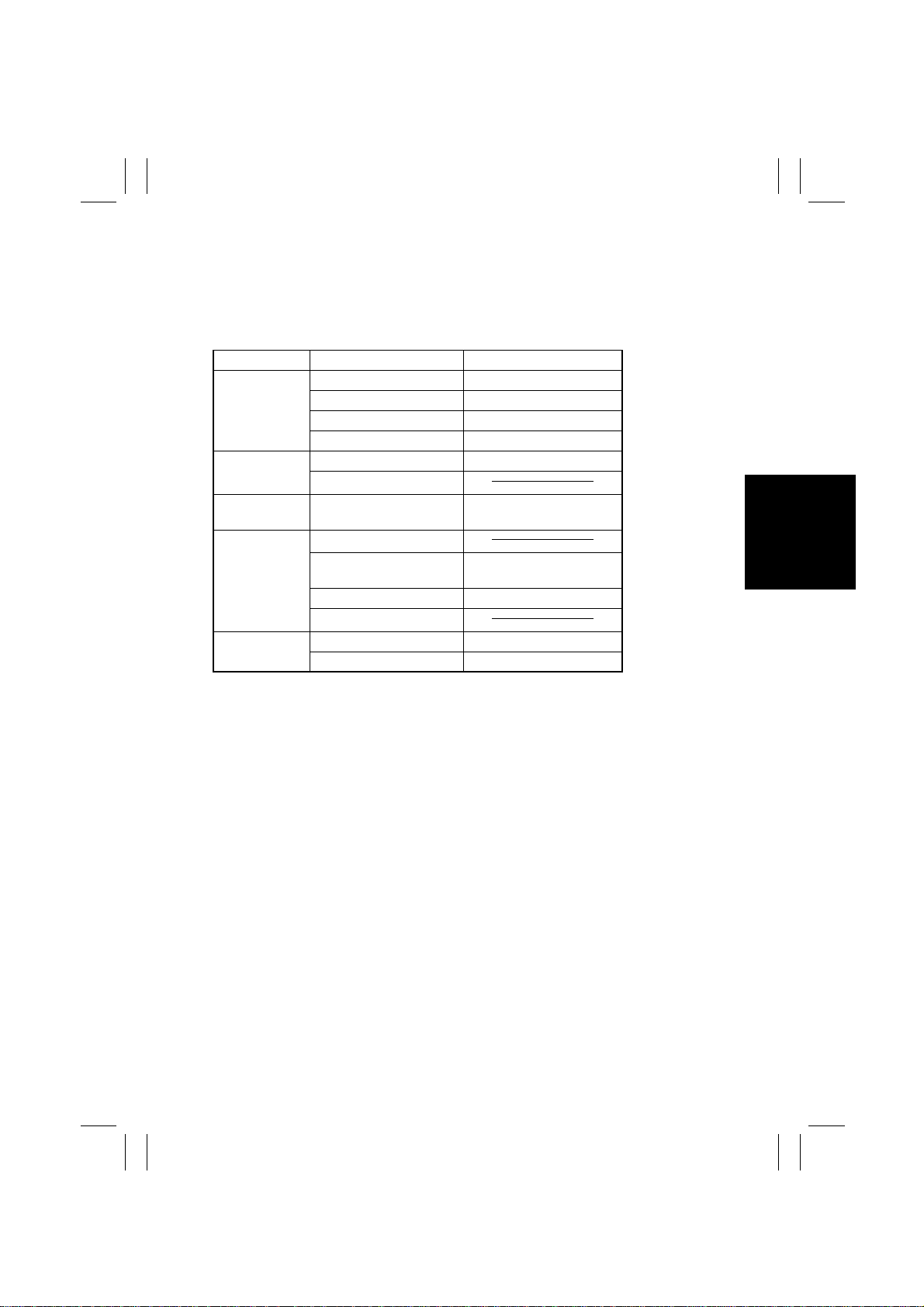
8. AE Processing
Histogram Making
• Lightness data readings are tallied up for each four gradation levels using the image data
sampled through “Histogram Making.”
• The lightness data readings tallied up for each four gradation levels are totaled to generate one lightness histogram (for AE processing).
AE Level Evaluation
• From the histogram with lightness blocked into four gradation levels, the local maximum
value of each block (the gradation level with the greatest frequency in each block) is
extracted.
• Calculation is made to determine if there is any gradation level extracted, the sum of frequency of ±8 gradation levels of which accounts for a given level or more of the sum of
frequency of the entire original. (Processing is done in the order of the gradation level of
higher lightness).
• If there is, the AE level (local minimum value) is determined according to the lightness
frequency at that local maximum value.
• If not, the AE level is determined according to the original mode.
• The AE processing table is determined based on the AE level.
• Background processing (AE processing) is performed as the AE processing table is
determined.
Lightness Histogram
Frequency
Monochrome
Color
4 gradation levels
Local maximum value
Low Lightness High
1154M080AB
M-22
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
9. Image Area Discrimination
• The image areas (color edge area, black edge area, dot area, continuous gradation area)
are discriminated to optimize edge emphasis, smoothing and other processing just right
for the image.
• Either edge emphasis or smoothing is selected according to the results of image area
discrimination.
Original Mode Original Area Smoothing/Edge Emphasis
Text & Photo
mode
Photo Image
mode
Printed Image
mode
Text mode Dot area
Map mode
Dot area Smoothing processing
Black edge area Edge emphasis
Color edge area Edge emphasis
Continuous gradation area Smoothing processing
Edge area Weak edge emphasis
Continuous gradation area
Dot area Smoothing processing
Black edge area BP amount 100 % (printed
with Bk toner only)
Color edge area Edge emphasis
Continuous gradation area
Edge area Strong edge emphasis
Continuous gradation area Smoothing processing
M-23
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
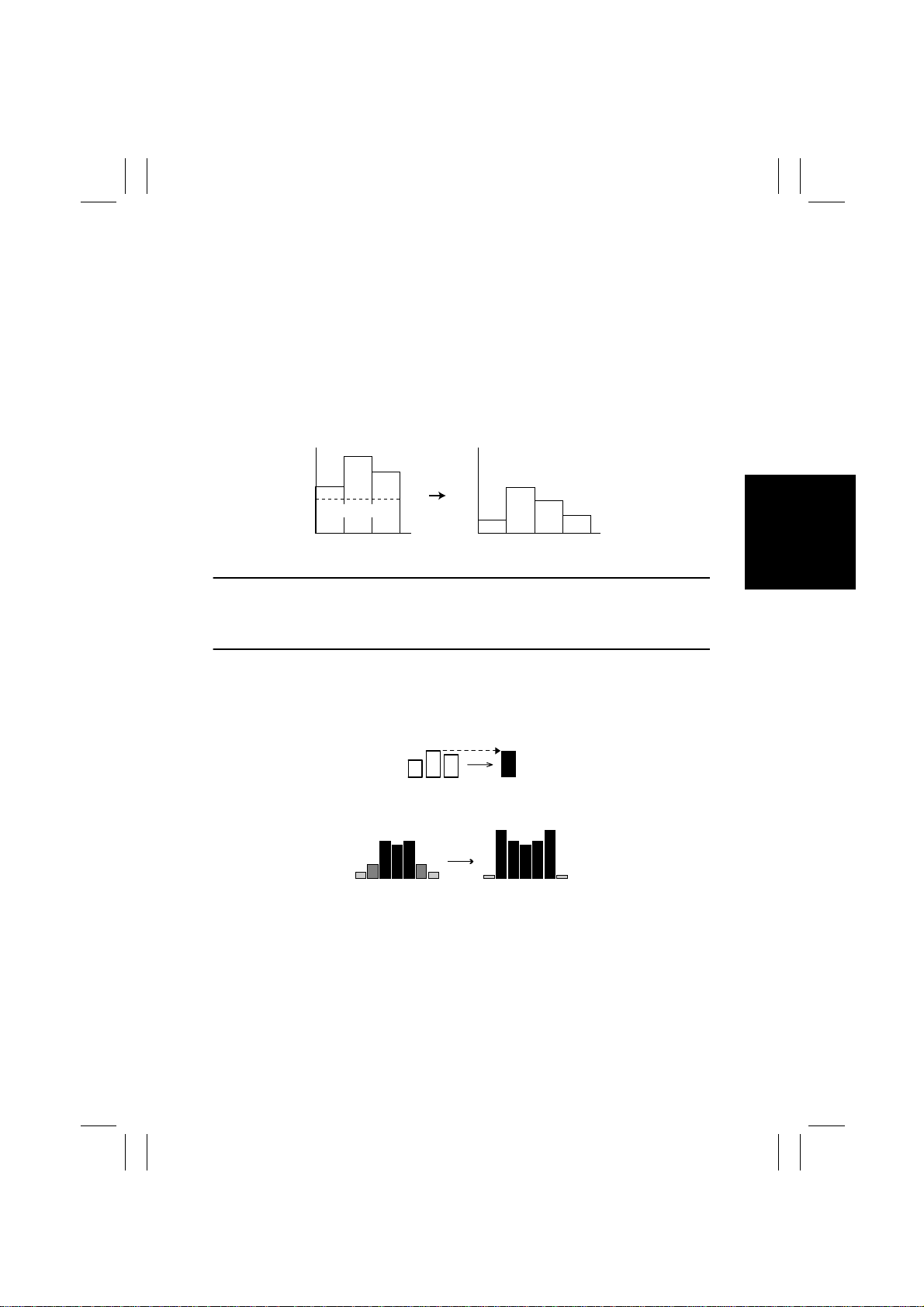
10. Color Correction
Reflection/Density Conversion
• Color reproduction faithful to the original is not possible if the original reflection data (R,
G, B) obtained through the CCD Sensor is converted to the complementary color data for
developing.
Example: White
Reflection
Factor
255
RGB
0
Becoming Black
255
CMY
0
1144M178CA
• The R, G, and B data are therefore input to the LOG table shown below to convert to the
density data (DR, DG, and DB).
Example : White
Reflection
Factor
RGB
255
0
225
DR
DG
DB
255
LOG Table
DR DG DB
0
RGB
225
0
Becoming WhiteDensity
255
CMY
0
1179M051CA
M-24
FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
01.02.09
Masking
• Considering the spectral transmission characteristics of the R, G, and B filters of the
CCD Sensor and the spectral reflection characteristics of the toner, the image data is
corrected and the DR, DG, and DB data are replaced with C, M, and Y data, thereby
enabling color reproduction faithful to the original.
UCR and BP
• In UCR, or Under Color Removal, the C, M, and Y data required for color reproduction
areas are retained, while the C, M, and Y data of gray areas are removed.
• With BP, or Black Paint, a certain ratio of the gray area is replaced with Bk data, the ratio
varying depending on the saturation of the color.
255
M
Y
C
UCR
0
255
M
Y
C
0
BK
1179M602AB
• Because of the spectral reflection characteristics of the toner, simply placing C, M, and Y
toner one on top of the other does not make a pure black.
• If C, M, and Y toner are put together to create a color close to black, it results in an
increased amount of toner sticking, meaning that more toner scatters and is consumed.
11. Miscellaneous Processing
<Improved reproduction of black characters>
• The Bk data for black characters is replaced with MAX (DR, DG, DB) data, which
improves reproduction of black fine lines, realizing reproduction of black characters that
do not depend on line width very much.
DR DG DB
1154M020AA
Edge Emphasis
• The number of data readings on the edges of the image is increased to make the outline
of the image sharper as it appears on the copy.
1144G04MBA
• The amount of edge emphasis is obtained in directions of 0°, 90°, 45°, and -45° and is
determined using the greatest value obtained.
M-25

FrameMaker Ver5.5E(PC) 7915/7920 MECHANICAL/ELECTRICAL
255
128
0
128 255
Output
Input
Sharper
Softer
01.02.09
Edge Expansion
• Edge emphasis produces a difference in contrast between the edge and center of text.
This processing expands edges toward the inner side and identifies them as a new edge.
4004M524AA
Smoothing
• The noise components contained in the image data are removed to smooth the data.
Noise
1144G05MBA
Density Adjustment and Color Balance
• Density adjustment is made by changing the angle of the γ curve that represents the relation between the input and output of the image data.
• Color balance is adjusted by changing the angle of the γ curve for each color.
255
Higher
Output
128
Density
0
128 255
Input
Lower
Density
curve
1179M052CB
Gamma (γ) Correction
• The type of γ curve is changed to make the image brighter or darker, or sharper or softer.
255
Darker
Output
128
Brighter
0
128 255
Input
1179M053CB 1179M054CB
M-26
 Loading...
Loading...