Konica 7115-18 Service Manual 7115020e
MECHANICAL/
ELECTRICAL

CONTENTS
1. CROSS SECTIONAL VIEW ............................................................................M-1
2. COPY PROCESS ............................................................................................M-2
3. DRIVE SYSTEM ..............................................................................................M-4
4. SEQUENTIAL EXPLANATION ................. ..................................... ..................M-5
5. WATCHDOG FUNCTION (CPU OVERRUN MONITOR) ................................M-6
5-1. Watchdog Function Post-Processing .......................................................M-6
6. IMAGE STABILIZATION SYSTEM .................................................................. M-7
7. IMAGING UNIT (I/U) ........................................................................................M-8
7-1. Imaging Unit (IU) Drive Mechanism .........................................................M-9
8. PC DRUM SECTION .......................................................................................M-10
8-1. PC Drum Drive Mechanism .....................................................................M-10
8-2. Grounding of the PC Drum .................................................... ......... .... .. ...M-11
9. PC DRUM CHARGING SECTION ...................................................................M-12
10. IMAGE READING SECTION ...........................................................................M-13
10-1.Image Processi ng Pr o cess ......................................................................M-14
10-2.Exposure Components Section ...............................................................M-15
10-3.Scanner and Mirrors Carriage Movement Mechanism ............................M-16
(1) Scanner Movement Mechanism ......................................................M-16
(2) 2nd/3rd Mirrors Carriage Movement Mechanism ............................M-16
10-4.Scanner Motor Drive Control ......... ..........................................................M-17
11. MEMORY STORAGE IMAGE PROCESSING SYSTEM ............. ....................M-18
11-1.Laser Exposure Process .........................................................................M-19
12. DEVELOPING UNIT SECTION . ......................................................................M-20
12-1.Developing Unit Drive Mechanism ..........................................................M-21
12-2.Sleeve/Magnet Roller ............................................................................. .M-22
12-3.Developing Bi a s ..................................................................... ..................M-22
12-4.ATDC Sensor ..........................................................................................M-23
(1) ATDC Sensor Automatic Adjustment .............................................. M-23
12-5.Toner Replenishing Mechanism .... ..........................................................M-24
12-6.Toner Replenishing Control .....................................................................M-25
12-7.T/C Recovery Mode .................................................................................M-26
12-8.Toner Bottle Home Position Detection Mechanism .................................M-27
13. PAPER TAKE UP/FEED SECTION .................................................................M-28
13-1.Drawer In Position Detection ................................................................... M-29
13-2.Paper Empty Detection Mechanism ........................................................M-29
13-3.Paper Lifting Plate ...................................................................................M-30
13-4.Universal Tray Paper Size Detection Mechanism ...................................M-30
13-5.Paper Take Up Mechanism .....................................................................M-32
(1) Paper Separating Mechanism .........................................................M-32
13-6.Paper Take Up Control ............................................................................M-33
(1) Paper Take Up Retry Control ..........................................................M-33
14. MANUAL BYPASS SECTION .........................................................................M-34
14-1.Paper Take Up Drive Mechanism ............................................................M-34
14-2.Paper Detection Mechanism ...................................................................M-34
14-3.Manual Feed Take Up Control ................................................................M-35
15. MULTIPLE BYPASS SECTION .......................................................................M-36
ii

15-1.Paper Take Up Drive Mechanism ............................................................M-36
15-2.Paper Take-Up Mechanism .....................................................................M-37
15-3.Paper Empty Detection Mechanism ........................................................M-38
15-4.Paper Take Up Control ............................................................................M-38
15-5.Paper Take Up Retry Control ..................................................................M-39
16. IMAGE TRANSFER AND PAPER SEPARATION SECTION ..........................M-40
17. PC DRUM CLEANING SECTION ....................................................................M-41
18. MAIN ERASE SECTION ..................................................................................M-42
19. FUSING UNIT SECTION ................................................................................. M-43
19-1.Fusing Unit Drive Mechanism ..................................................................M-44
19-2.Fusing Rollers Pressure Mechanism .......................................................M-44
19-3.Fusing Temperature Control ....................................................................M-45
19-4.CPM Control ............................................................................................M-45
20. JOB TRAY (IT-102): Option .............................................................................M-46
20-1.Tray Selecting Mechanism ......................................................................M-47
20-2.Tray-Full Detecting Mechanism ............................................................... M-48
20-3.Job Tray Paper Detecting Mechanism ....................................................M-48
21. S HI FTIN G UNIT (IS-101) : Option ....................................................................M-49
21-1.Exit Position Shifting Mechanism ............................................................M-50
22. OTHER MECHANISM .....................................................................................M-52
22-1.Cooling Mechanism .. ...............................................................................M-52
(1) Power Supply Section Cooling Mechanism .....................................M-52
(2) Fusing Section Cooling Mechanism ................................................M-53
iii
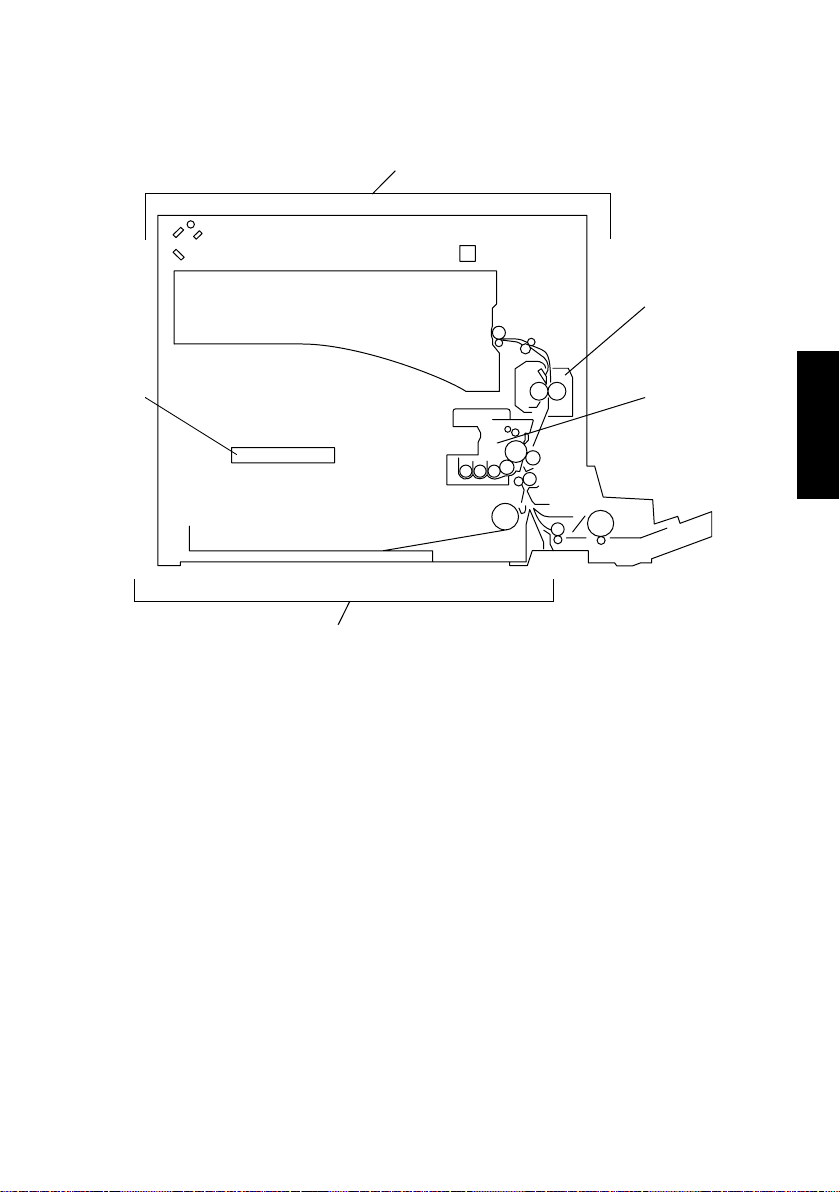
1. CROSS SECTIONAL VIEW
1
2
5
1. IR Section
2. Fusing Unit
3. Imaging Unit
3
4
4. Paper Take-Up/Feed Section
5. PH Section
4021M001AA
M-1
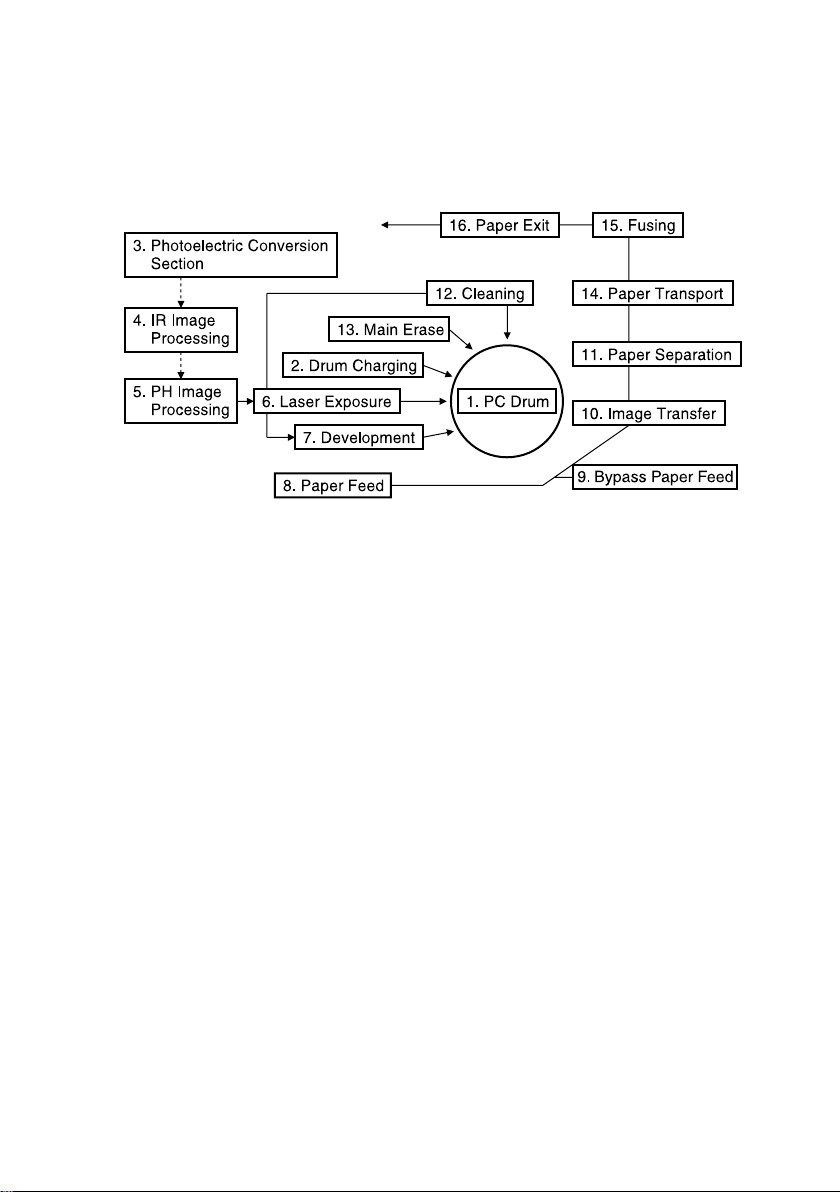
2. COPY PROCESS
4021M065CB
1. PC Drum
• Used as the medium on which a visible developed image of the original is formed.
2. Drum Charging
• A uniform negative DC charge is deposited across the entire surface of the PC Drum.
3. Photoelectric Conversion
• CCD converts the image data represented by light reflected off the original to a corresponding electrical signal which, in turn, is output to IR image-processing section.
4. IR Image-Processing
• The electrical signal is converted to an 8-bit digital image signal (A/D conversion) which,
in turn, goes through appropriate correction before being output to the PH Image Processing.
5. PH Image Processing
• After going through corrections, the digital image signal is converted to a corresponding
electrical signal (D/A conversion) that controls the intensity of the light from the laser
diode.
6. Laser Exposure
• The laser beam strikes the surface of the PC Drum, forming an electrostatic latent image.
7. Developing
• Toner negatively charged in the Developer Mixing Chamber is attracted onto the electrostatic latent image changing it to a visible, developed image.
• An AC/DC negative bias voltage is applied to the Sleeve/Magnet Roller to prevent toner
from being attracted onto those areas of the PC Drum which correspond to the background areas of the original.
8. Paper Feed
• Paper is fed from the drawer.
M-2

9. Bypass Paper Feed
• Feeds paper from the Manual Bypass Tray, one piece at a time.
• The optional Multiple Bypass Tray (MT-102), when mounted on the machine, permits
continuous paper feeding.
10. Image Transfer
• A DC positive charge is applied to the Image Transfer Roller to transfer the visible image
on the surface of the PC Drum onto the paper.Paper Separation.
11. Paper Separation
• The PC Drum Paper Separator Fingers remove paper from the surface of the PC Drum.
• The Charge Neutralizing Plate neutralizes any charge left on the paper.
12. Cleaning
• Residual toner on the surface of the PC Drum is scraped off.
• The toner is then recycled back to the Developing Unit.
13. Main Erase
• Light is directed to the surface of the PC Drum to neutralize any surface potential remaining there after cleaning.
14. Paper Transport
• The paper is fed to the Fusing Unit.
15.Fusing
• The developed image is permanently fused to the paper by a combination of heat and
pressure applied by the Right and Left Fusing Rollers.
16. Paper Exit
• The paper is fed out onto the Exit Tray.
• When the optional Job Tray (IT-102) is mounted, the specific tray into which paper is fed
is selected according to the application mode.
• The optional Shifting Unit (IS-101), when mounted, permits different finishing functions
set on the machine (Non-Sort, and Sort) .
M-3
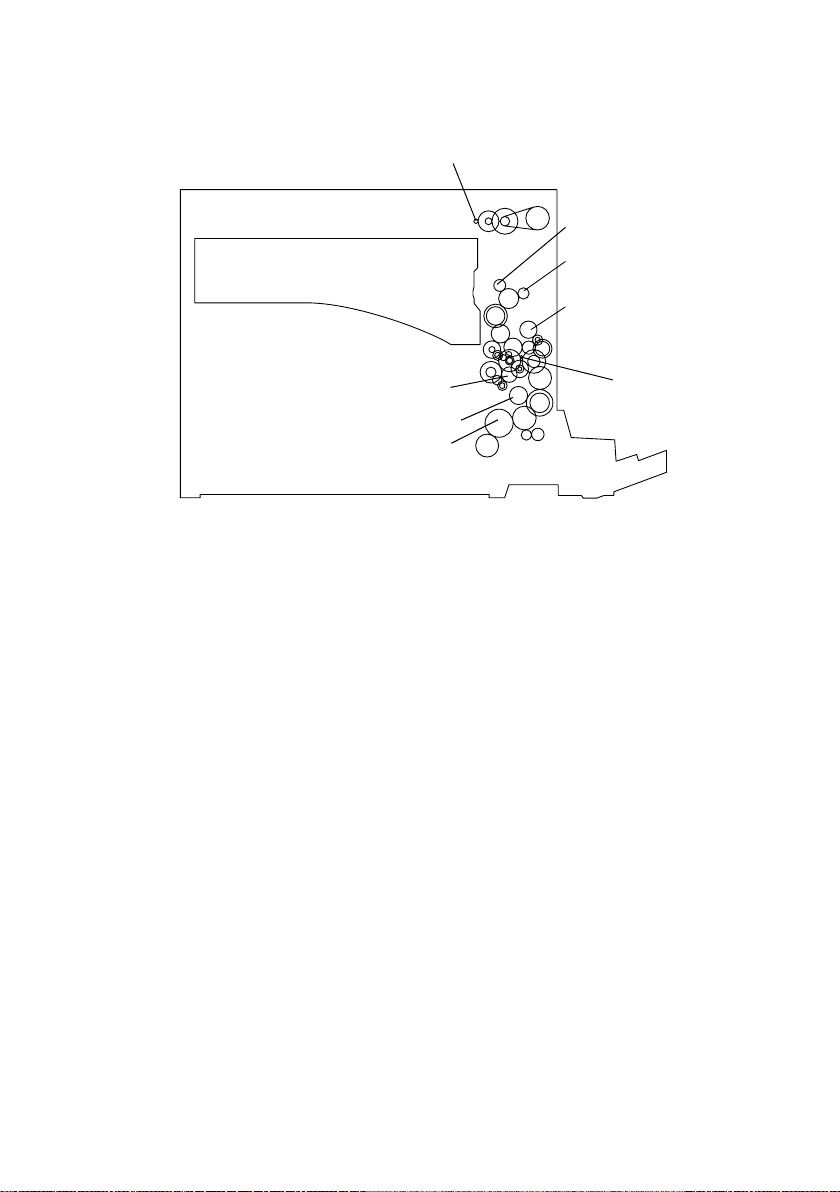
3. DRIVE SYSTEM
1
Paper Exit Roller Gear
Transport Roller Gear
Fusing Roller Gear
1. Scanner Motor M5
2. Main Motor M1
PC Drum
Synchronizing Roller Clutch
Paper Take-Up Roller Gear
2
4021M003AA
M-4
4. SEQUENTIAL EXPLANATION
4021M510CA
Power Switch ON Start Key ON
Polygon Motor M2
Predrive
150 ˚C Warm-up completed
Exposure Lamp LA2
Main Motor M1
Paper Take-Up Solenoid SL1
Synchronizing Roller Sensor PC1
Synchronizing Roller Clutch CL1
Developing Bias (VB) DC
Developing Bias (VB) AC
Image Transfer Bias (+)
Image Transfer Bias (–)
Exit Paper Sensor PC3
M-5
Full speed
Full speed
Speed reduction
Speed reduction
Power Supply Cooling
Fan Motor M4
Fusing Cooling Fan
Motor M3

5. WATCHDOG FUNCTION (CPU OVERRUN MONITOR)
• The watchdog function, or CPU overrun monitor function, monitors whether any of the
CPUs mounted in the copier overruns.
• If the function detects that a CPU overruns, the copier automatically resets the CPU,
thereby restarting the logic circuit and mechanism.
5-1. Watc hdog Function Post-Processing
The following processing is performed if a faulty condition is detected in the CPU.
When the copier CPU is found faulty:
• All CPUs are reset and the system is restarted.
• If the CPU is found faulty during a copy cycle, the system attempts to feed all sheets of
paper out of the copier before restarting. (If paper is left inside the copier, the copier
detects it as a misfeed as it is restarted.)
M-6
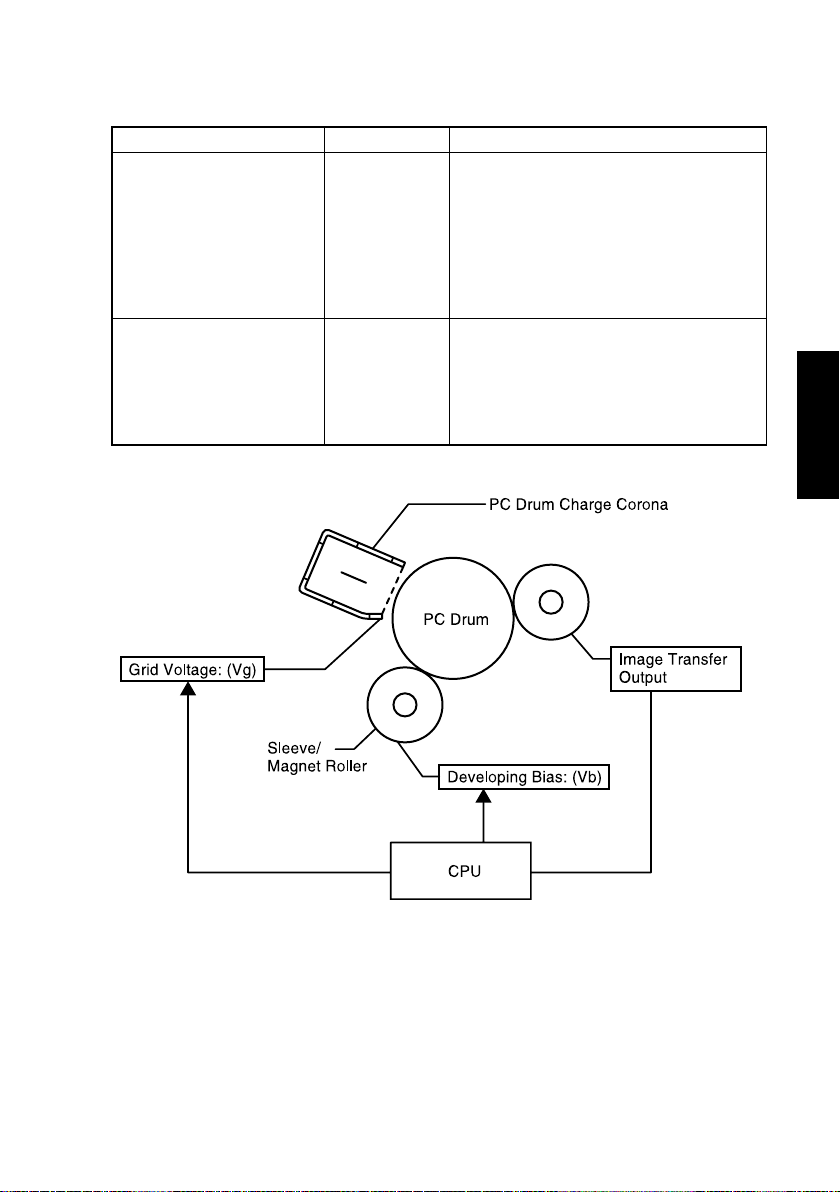
6. IMAGE STABILIZATION SYSTEM
The following image stabilization controls are provided to ensure stabilized copy image.
Purpose Means Control
The Vg/Vb control voltage is varied to bring
Vg/Vb to an appropriate level according to
the following settings.
To stabilize image density. Vg/Vb control
To stabilize image transfer.
Image transfer
output control
• Tech. Rep. Choice: ID Adjustment
• Tech. Rep. Choice: VG Adjustment
• User's Choice: Print Density
• IU Life Counter
• Paper type
The image transfer output is varied to bring
the image transfer current to an appropriate
level according to the following conditions.
• Paper type
• Paper width
• B/W ratio of image
M-7
4021M066CA
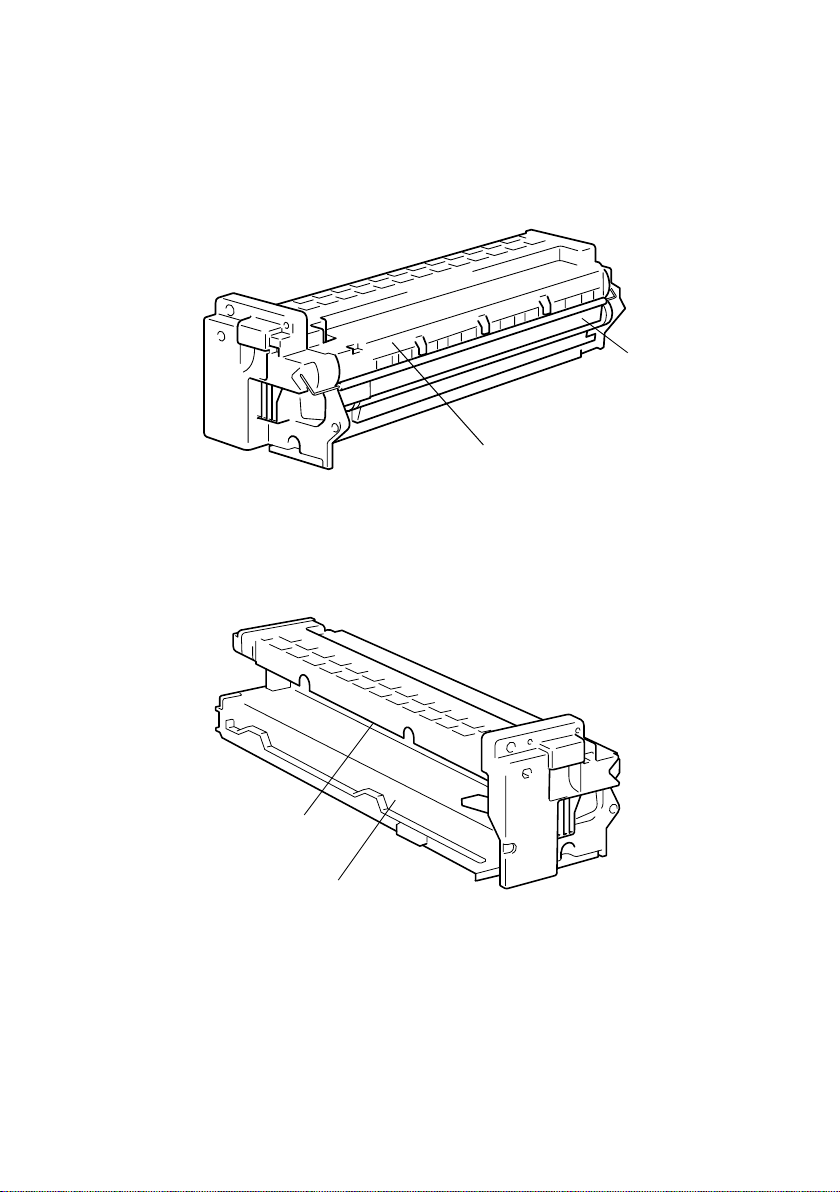
7. IMAGING UNIT (I/U)
• The IU integrates the PC Drum, Developing Unit, PC Drum Charge Corona, and the PC
Drum Cleaning Mechanism, all in one body.
PC Drum
PC Drum Cleaning Mechanism
4021M006AB
PC Drum Charge Corona
Developing Unit
4021M007AB
M-8
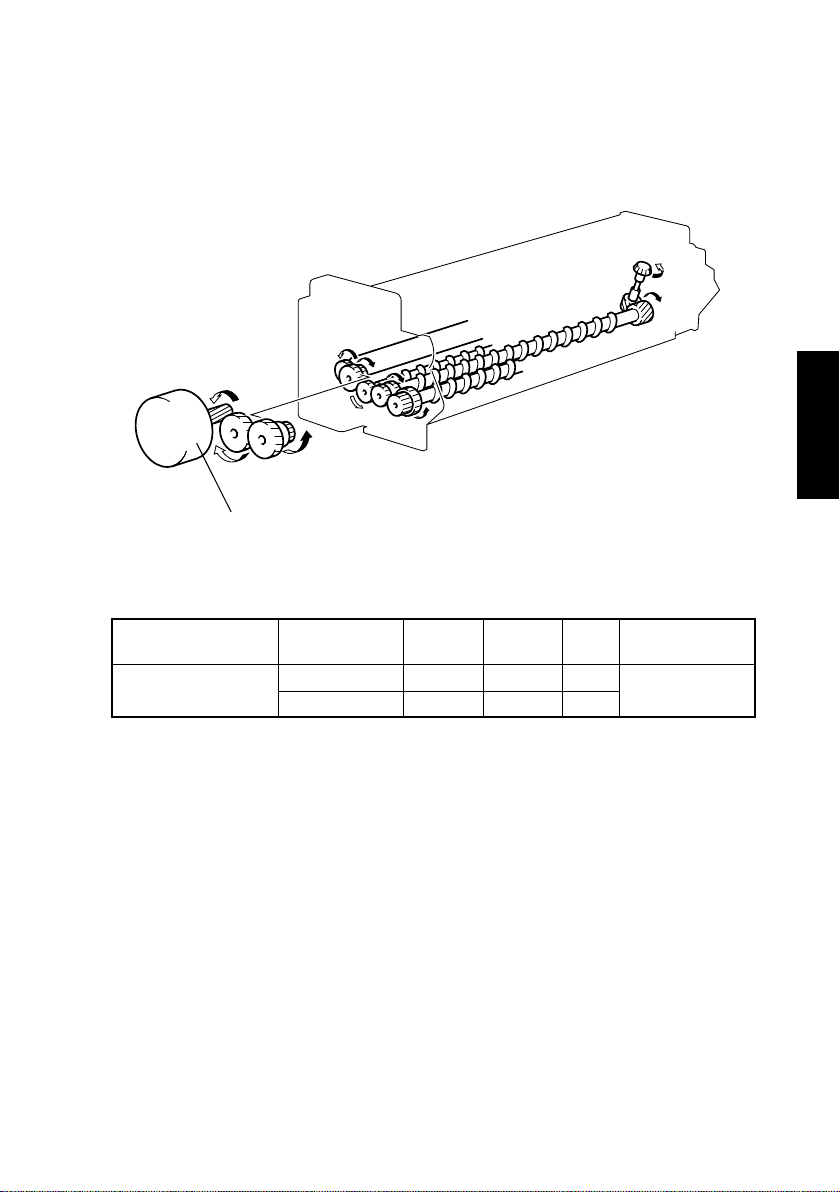
7-1. Imaging Unit (IU) Drive Mechanism
• The IU is driven by the Main Motor.
Main Motor M1
4021M008AB
Elevtrical Component Control Signal
M1
PWB-A PJ7A-5 L L H
PWB-A PJ7A-7 H L H
Forward
Rotation
M-9
Backward
Rotation
OFF Wiring Diagram
17-G
8. PC DRUM SECTION
• The PC Drum consists of layers of semiconductive materials placed on an aluminum
alloy base, on which an electrostatic latent image is formed.
PC Drum
(PC Drum Cross-Section)
Charge Transport Layer
Charge Generation Layer
1167M007AA
8-1. PC Drum Drive Mechanism
• The PC Drum is rotated by drive from a motor.
PC Drum
Aluminum Base
1139M007AA
Main Motor M1
Elevtrical Component Control Signal
M1
PWB-A PJ7A- 5 L H
PWB-A PJ7A- 7 H H
Forward
Rotation
M-10
4021M009AA
OFF Wiring Diagram
17-G
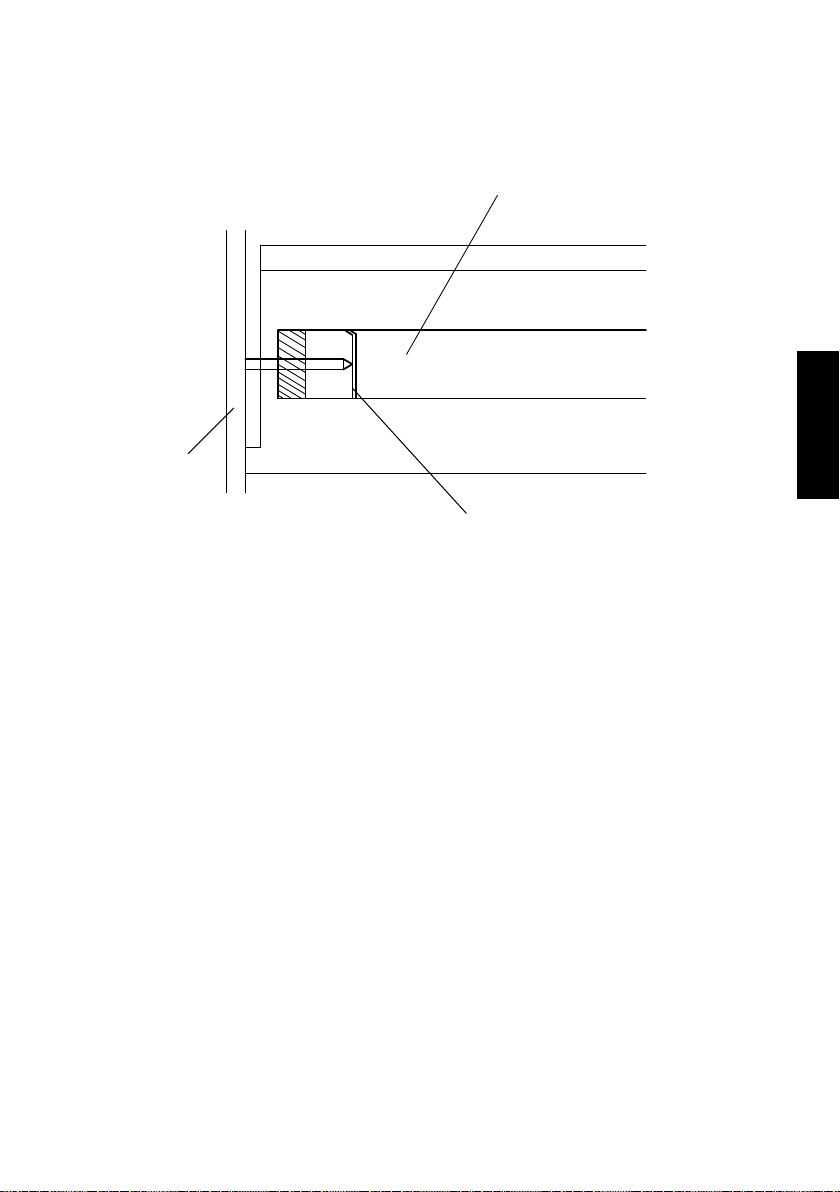
8-2. Grounding of the PC Drum
• The potential on the surface of the PC Drum exposed to the light is grounded to the
frame.
PC Drum
Frame
Ground Plate
4021M010AA
M-11
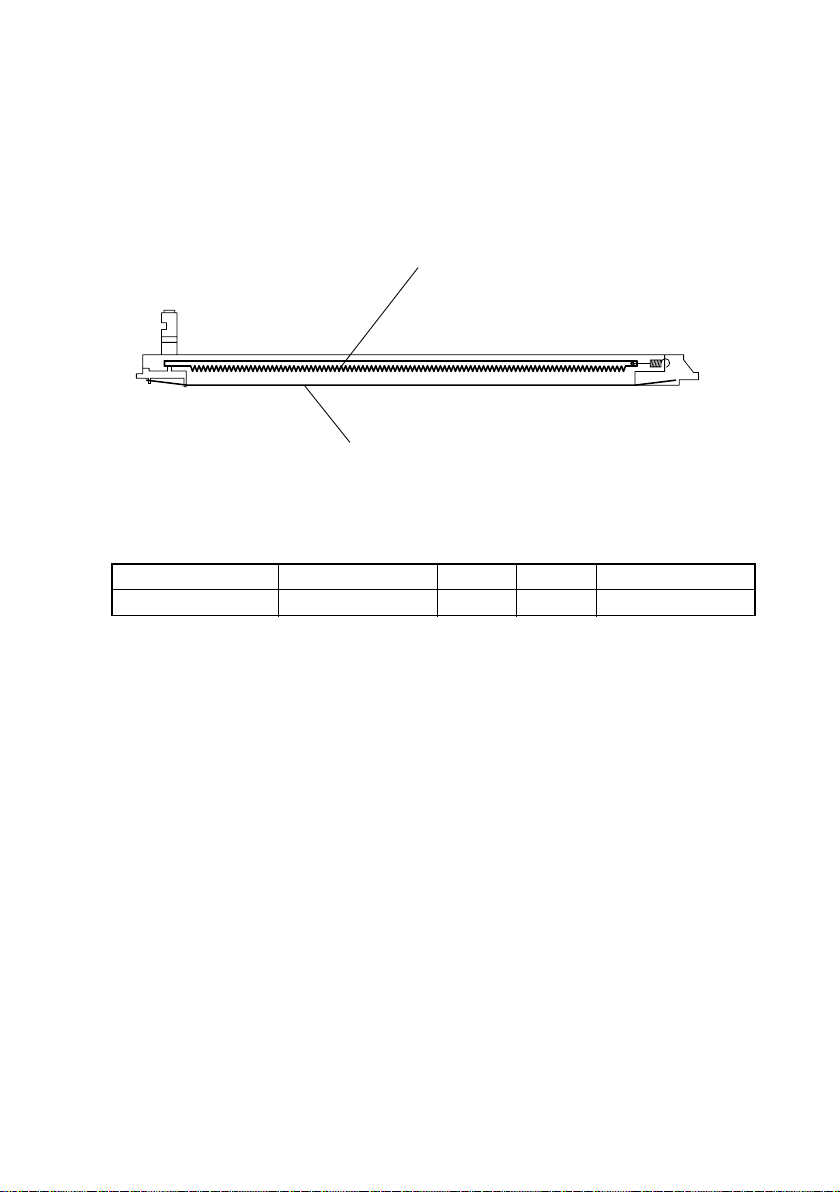
9. PC DRUM CHARGING SECTION
• The PC Drum Charge Corona has a scorotron grid to deposit a charge evenly across the
surface of the PC Drum.
• The corona unit has a comb electrode that discharges only toward the grid mesh, thus
minimizing the amount of ozone produced.
Comb Electrobe
Grid Mesh
Elevtrical Component Control Signal ON OFF Wiring Diagram
HV1 PWB-A PJ8A-8 L H 5-C
4021M011AA
M-12

10. IMAGE READING SECTION
6
5
1. Scanner /Motor M5
2. CCD Board PWB-J
3. Size Reset Switch S10
1
4. Scanner
5. 2nd/3rd Mirrors Carriage
6. Scanner Home Position Sensor PC6
2
3
4
4021M012AB
M-13

10-1. Image Processing Process
1. Photoelectric Conversion
• Light reflected off the original is read by the CCD Sensor which converts the data to a
corresponding analog signal.
2. Analog-to-Digital Conversion
• The analog signal output from the CCD Sensor is converted to a corresponding 8-bit digital signal.
3. Shading Correction
• An error is corrected that occurs due to variations in sensitivity of each CCD chip and the
light distribution varying along the length of the Exposure Lamp.
• The data obtained through actually illuminating the shading sheet with the Exposure
Lamp is compared with the shading sheet reading reference value (white = max. data
value) to make the necessary correction.
4. Zoom Processing
• The synchronous timing of the input data (read) and output data (read) is varied to
decrease (reduction) or increase (enlargement) the number of data readings, thereby
reducing or enlarging the image in the main scanning direction.
5. Data is sent to the PH.
M-14
 Loading...
Loading...