Page 1

®
NOVAJET®
500/630/700 SERIES
COLOR INKJET
PRINTER
SER VICE MANUAL
Part Number 213526-01
Page 2

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Copyright © 1999-2002 Eastman Kodak Company. All
rights reserved.
KODAK, ENCAD and NovaJet are trademarks of
Eastman Kodak Company.
Other trademarks and registered trademarks are the
property of their respective owners.
Except as provided below, no p art of this manual may be
copied or distributed, transmitted, transcribed, stored in
a retrieval system, or translated in any human or computing language, in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechanical, magnetic or otherwise, or disclosed to a
third party without the express written permission of
Encad, Inc., 6059 Cornerstone Court West, San Diego,
CA 92121, U.S.A.
Certain manuals developed by Encad are in an electronic
format to be distributed on CDs or over the internet. The
registered user of an Encad product whose manual is
distributed in this fashion may print one copy for their
personal use only .
Printing history
1st Edition Rev A May 1999
2st Edition Rev B October 2001
ii
Page 3

FCC Statement (U.S.A.)
The United States Federal Communications Commision has specified
that the following notice be brought to the attention of the users of the
NOVAJET 500, 630 or 700 series printers.
FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISION RADIO AND TELEVISION INTERFERENCE FOR CLASS B DEVICE
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
User Instructions:
If the equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on,
the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the
following measures:
NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from
that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for
help.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by ENCAD, Inc. could
void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
v
Page 4

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
for NovaJet 736 and 750
FCC Statement (U.S.A.)
The United States Federal Communications Commision has specified that
the following notice be brought to the attention of the users of the
NOVAJET 736 or 750 printers.
FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISION RADIO AND TELEVISION
INTERFERENCE FOR CLASS A DEVICE
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
class A digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits
are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance
with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
User Instructions:
If the equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on,
the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the
following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from
that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for
help.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by ENCAD, Inc. could
void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
vi
Page 5

VDE Statement
Hiermit wird bescheinigt, daß der NOVAJET 500/630/700 in
Übereinstimmung mit den Bestimmungen der BMPT-AmstbIVfg 234/1991
funkentstört ist. Der vorschriftsmäßige Betrieb mancher Geräte (z.B.
Meßsender) kann allerdings gewissen Einschränkungen unterliegen.
Beachten Sie deshalb die Hinweise in der Bedienungsanleitung.
Dem Zentralamt für Zulassungen im Fernmeldewesen würde dan
Inverkehrbringen dieses Gerätes angezeigt und die Berechtigung zur
Überprüfung der Serie auf die Einhaltung der Bestimmungen
eingeräumt.
ENCAD, Inc. U.S.A
NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
vii
Page 6

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Material Safety Data Sheet
ENCAD QIS (Quality Imaging Supplies) ink is nonhazardous, requiring no
special disposal handling. It can be harmful if swallowed and should be
kept away from children.
To obtain a Material Safety Data Sheet, contact ENCAD, Inc. at:
6059 Cornerstone Court West
San Diego, CA 92121-3734
(619) 452-4350
International users should contact their local dealer or distributor.
viii
Page 7

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
WARRANTY OR DAMAGE CLAIMS
United States
ENCAD®, Inc., warrants its printers ("PRODUCT") to be free from defects in workmanship
and materials for a period of one year from the date of purchase. In order to submit a
Warranty claim, please contact the ENCAD Help Desk at (619) 452-4350.
ENCAD reserves the right to make changes or improvements to Products, without incurring
any obligation to similarly alter Products previously purchased.
Buyer's sole and exclusive rights pursuant to this Warranty shall be for the repair or
replacement of defective Product. ENCAD specifically disclaims any and all other warranties, expressed or implied, including but not limited to, implied warranties of merchantability
and fitness for a particular purpose. In no event shall ENCAD be liable for any loss of
profit or other commercial damages, special, incidental or consequential damages, or any
other damages or claims, whatsoever.
This Warranty gives Buyer specific legal rights, and Buyer may also have other rights that
vary from state to state.
This Warranty applies only to printers purchased from ENCAD, or authorized ENCAD
distributors or dealers. The intent of this Warranty is to repair or replace defective Products subjected to normal wear and tear, when operated according to ENCAD instructions.
This Warranty does not cover damage to the Product resulting from the following:
• Accident or negligence.
• Unauthorized modification of the Product.
• Adverse environmental conditions.
• Service of the Product by other than an ENCAD authorized service provider.
• Unauthorized or improper use, including but not limited to:
– Use in applications for which the Product was not designed.
– Using cartridges or ink other than those supplied by ENCAD or authorized
ENCAD resellers.
– Using media other than that supplied by ENCAD or authorized ENCAD
resellers.
– Lubricating any part of the printer.
Internationally: Contact your dealer or distributor for warranty information.
ix
Page 8

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 General Description ............................................................ 1-1
Introduction ...............................................................................................................1-1
Overview ................................................................................................................... 1-3
Related Publications .......................................................................................... 1-3
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Sensitivity ................................................................. 1-3
Warnings, Cautions and Notes ................................................................................. 1-4
Printer Specifications ................................................................................................ 1-5
Contents of this Service Manual ................................................................................1-6
Technical Support ..................................................................................................... 1-8
Chapter 2 Theory of Operation ............................................................ 2-1
Introduction ............................................................................................................... 2-1
NovaJet 500/630/700 Printers General Block Diagram .............................................. 2-1
Paper (Media) Axis Drive .......................................................................................... 2-3
The Carriage Axis Drive............................................................................................. 2-4
Media Feed and Take-Up System ............................................................................. 2-5
Main Printed Wiring Assembly (MPWA) ................................................................... 2-6
Microprocessor .................................................................................................. 2-7
Gate Array ......................................................................................................... 2-7
Memory Circuits ................................................................................................. 2-8
Flash EEPROM ........................................................................................... 2-8
DRAM .......................................................................................................... 2-9
Serial EEPROM ......................................................................................... 2-10
Stepper Motor Controller................................................................................... 2-10
Servo Motor Controller ...................................................................................... 2-12
Interface Circuits: Serial & Parallel ................................................................... 2-14
Carriage Assembly Circuits .................................................................................... 2-15
Control Panel .......................................................................................................... 2-16
Power Supply ......................................................................................................... 2-17
Beeper and Fans .................................................................................................... 2-17
Chapter 3 Maintenance ........................................................................ 3-1
Introduction ............................................................................................................... 3-1
Scheduled Maintenance ........................................................................................... 3-1
Cleaning Procedures .......................................................................................... 3-2
External Cleaning .........................................................................................3-2
x
Page 9

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Table of Contents (cont)
Chapter 3 Maintenance (cont)
Service Station Cleaning .............................................................................. 3-2
Slide Shaft Cleaning..................................................................................... 3-3
Linear Encoder Strip Cleaning ...................................................................... 3-4
Cartridge Jet Area & Dimples Cleaning ........................................................ 3-5
Flex Cable Contact Cleaning ........................................................................3-6
Clean and Inspect Stepper Motor Gears....................................................... 3-7
Clean and Inspect MPWA ............................................................................ 3-7
Clean and Inspect Carriage Assembly ......................................................... 3-8
Reseat Connectors on MPWA and Carriage Board .............................................3-8
Replace Carriage Bushings .............................................................................. 3-11
Servo Motor Winding Resistance Check ................................................................. 3-12
Stepper Motor Winding Resistance Check .............................................................. 3-13
Power Feed and Take-Up Motor Winding Resistance Check ................................... 3-14
Banding: Hardware vs Software ............................................................................... 3-15
Common Banding Causes ......................................................................... 3-16
Alignments/Adjustments ......................................................................................... 3-18
Slide Shaft Profile Adjustment .......................................................................... 3-18
Head Height Alignment Procedure .................................................................... 3-22
Color Calibration ............................................................................................... 3-26
Deadband Alignments ...................................................................................... 3-29
Deadband Alignment (for 500 Series) ......................................................... 3-32
Color Deadband Alignment (for 630/700) .................................................... 3-33
Paper Axis Calibration ...................................................................................... 3-35
Diagnostics Menu ................................................................................................... 3-37
Limited Access Menu ............................................................................................. 3-40
Firmware Download/Upgrading for the PC ............................................................... 3-41
Firmware Download/Upgrading for the MAC ............................................................ 3-42
Internal Cabling and Signal Flow Diagrams ............................................................. 3-44
Chapter 4 Troubleshooting .................................................................. 4-1
Introduction ............................................................................................................... 4-1
No Power ........................................................................................................... 4-1
Initialization Failure............................................................................................. 4-2
Media Does Not Move ........................................................................................ 4-2
Internal ERROR “Carriage Axis Failure” .............................................................. 4-3
xi
Page 10

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Table of Contents (cont)
Chapter 4 Troubleshooting (cont)
Internal ERROR “Encoder Sensor Failure” .......................................................... 4-5
Internal ERROR “Paper Sensor Failure” .............................................................. 4-5
Internal ERROR “Auto-Sensor Failure” ................................................................4-6
Internal ERROR “MPCB Failure” ......................................................................... 4-6
Unrecognized Cartridges Error ............................................................................ 4-6
Image Skews or Moves ...................................................................................... 4-7
Does Not Print.................................................................................................... 4-7
Ink Cartridge Misfiring ......................................................................................... 4-7
Paper Skewing ................................................................................................... 4-9
Printer Output is Banding (Horizontal) ................................................................ 4-9
Printer Output is Banding (Vertical) .................................................................. 4-11
Printer Output is Banding (Horizontally and Vertically)...................................... 4-11
Keypad Locked-Up or Not Functioning Properly ............................................... 4-11
Noisy Operation ............................................................................................... 4-12
Line Quality Degraded ...................................................................................... 4-13
Fan Does Not Power Up ................................................................................... 4-14
Media Take-Up Motor Not Operating, Sensor Works ........................................ 4-14
Media Feed Motor Not Operating, Sensor Works ............................................. 4-15
Media Feed and Take-Up Motors Not Operating, Both Sensors Working .......... 4-15
Media Feed or Take-Up Sensor(s) Not Operating .............................................. 4-15
Initialization Troubleshooting (500 Series) ............................................................... 4-18
Initialization Troubleshooting (630/700 Series) .........................................................4-20
Chapter 5 Assembly\Disassembly ...................................................... 5-1
Introduction ............................................................................................................... 5-1
Remove the Left, Top, and Right Covers .................................................................... 5-2
Install the Left, Top, and Right Covers ....................................................................... 5-6
Remove the Keypad and Display .............................................................................. 5-7
Install the Keypad and Display.................................................................................. 5-9
Remove Extra Memory (SIMM) ............................................................................... 5-10
Install Extra Memory (SIMM) .................................................................................. 5-11
Remove the MPCB (Main Printed Circuit Board) ..................................................... 5-11
Install the MPCB .................................................................................................... 5-14
Remove Power Supply, Cooling Fan, and AC Entry Module .................................... 5-15
Install the Power Supply, Cooling Fan, and AC Entry Module ................................. 5-17
xii
Page 11

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Table of Contents (cont)
Chapter 5 Assembly/Disassembly (cont)
Remove Servo Motor ............................................................................................... 5-18
Install Servo Motor .................................................................................................. 5-20
Remove the Ink Delivery System .............................................................................5-21
Install the Ink Delivery System................................................................................ 5-23
Remove the Carriage Assembly, Carriage Belt, and the Frame Tensioner................ 5-24
Install the Carriage Assembly, Carriage Belt, and the Frame Tensioner .................. 5-27
Remove the Carriage PCB ...................................................................................... 5-29
Install the Carriage PCB ......................................................................................... 5-31
Remove the Paper Sensor or the Encoder Sensor .................................................. 5-31
Install the Paper Sensor or the Encoder Sensor...................................................... 5-33
Replacing the Carriage Bushings ............................................................................ 5-34
Remove the Service Station .................................................................................... 5-36
Install the Service Station ....................................................................................... 5-36
Remove the Trailing Cable Assembly ...................................................................... 5-37
Install the Trailing Cable Assembly ......................................................................... 5-37
Remove the Stabilizer Bracket and Encoder Strip ...................................................5-38
Install the Stabilizer Bracket and Encoder Strip ...................................................... 5-40
Remove the Y-Arm Assembly, Pinch Rollers, Slide Shaft, and Auto-Load Sensor ... 5-40
Install the Y-Arm Assembly, Pinch Rollers, Slide Shaft, and Auto-Load Sensor ...... 5-43
Remove the Lower Roller Assembly, Stepper Motor and Vacuum Fan ..................... 5-44
Install the Lower Roller Assembly, Stepper Motor and Vacuum Fan ........................ 5-47
Remove the Media Take-Up and Feed Sensor Brackets and Sensors ..................... 5-50
Install the Media Take-Up and Feed Sensor Brackets and Sensors ........................ 5-52
Remove the Media Take-Up and Feed Motors ......................................................... 5-52
Install the Media Take-Up and Feed Motors ............................................................ 5-54
Remove the Media Drying Fans .............................................................................. 5-54
Install the Media Drying Fans ................................................................................. 5-55
Remove the Thermal Dryer Assembly (NovaJet 750) ............................................... 5-56
Install the Thermal Dryer Assembly (NovaJet 750) .................................................. 5-57
Chapter 6 Parts List .............................................................................. 6-1
xiii
Page 12

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
List of Illustrations
Figure Page
Chapter 1 General Description
1-1. NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Inkjet Printers ..................................................... 1-1
Chapter 2 Theory of Operation
2-1. General Block Diagram ................................................................................... 2-2
2-2. Paper (Media) Axis Drive ................................................................................. 2-3
2-3. Carriage Axis Drive ..........................................................................................2-4
2-4. Power Feed and Take-Up System ................................................................... 2-5
2-5. Main Printed Wiring Assembly ........................................................................2-6
2-6. Gate Array ...................................................................................................... 2-7
2-7. Stepper Motor Controller ............................................................................... 2-10
2-8. Servo Motor Controller ................................................................................... 2-12
2-9. Quadrature Signal Generation ....................................................................... 2-13
2-10. Interface Circuits ........................................................................................... 2-14
2-11. Carriage Assembly Circuits........................................................................... 2-15
2-12. Main Menu .................................................................................................... 2-16
Chapter 3 Maintenance
3-1. Encoder Strip Cleaning ................................................................................... 3-5
3-2. Cartridge Dimple Region ..................................................................................3-5
3-3. Flex Cable Contacts ....................................................................................... 3-6
3-4. MPWA Connection Locations ......................................................................... 3-9
3-5. Carriage PWA Connection Locations ............................................................ 3-10
3-6. Ribbon Connector Locking Mechanism ......................................................... 3-11
3-7. Servo Motor ................................................................................................... 3-12
3-8. Stepper Motor ............................................................................................... 3-13
3-9. Power Feed and Take-Up Motor .................................................................... 3-14
3-10. Examples of Banding .................................................................................... 3-15
3-11. Dial Gauge Micrometer Assembly ................................................................. 3-19
3-12. Measurement Positions for Slide Shaft .......................................................... 3-20
3-13. Slide Shaft Profile Adjustment ....................................................................... 3-21
3-14. Carrier Head Height Tolerance ....................................................................... 3-22
3-15. Setting Up Tools from Height Gauge Kit ........................................................ 3-22
3-16. Zeroing the Micrometer Gauge ...................................................................... 3-23
xiv
Page 13

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
List of Illustrations (cont)
Figure Page
Chapter 3 Maintenance (cont)
3-17. Test Cartridge Installed .................................................................................. 3-23
3-18. Support Bracket Placement .......................................................................... 3-24
3-19. Color Calibration ............................................................................................ 3-26
3-20. Utility Menu................................................................................................... 3-27
3-21. Color Calib Menu........................................................................................... 3-28
3-22. Cyan Vertical Options Menu.......................................................................... 3-28
3-23. Slow Deadband ............................................................................................. 3-29
3-24. Service Menu ................................................................................................ 3-30
3-25. Calibration (Deadband) Menu (500 Series)..................................................... 3-31
3-26. Calibration (Deadband) Menu (630/700 Series) .............................................. 3-31
3-27. Calibration Menu ........................................................................................... 3-33
3-28. Color Db Menu .............................................................................................. 3-34
3-29. Paper Axis Test ............................................................................................ 3-36
3-30. Diagnostics Menu ......................................................................................... 3-37
3-31. Accessory Menu ........................................................................................... 3-37
3-32. NVRAM Clear and Clock Reset Menu ........................................................... 3-40
3-33. MPWA Connections Diagram........................................................................ 3-45
3-34. Carriage PWA Connections Diagram............................................................. 3-46
3-35. Leg Harness Connections Diagram ............................................................... 3-47
3-36. Leg Harness Connections Diagram (750) ...................................................... 3-48
Chapter 4 Troubleshooting
4-1. Carriage Board LED D2 Location for NJ 500 Series ....................................... 4-19
4-2. Carriage Board LED D2 and D5 Location for NJ 630/700 Series .................... 4-21
Chapter 5 Assembly/Disassembly
5-1. Right Cover Assembly Removal/Installation ..................................................... 5-3
5-2. Left Cover Assembly Removal/Installation ....................................................... 5-4
5-3. Left Cover Assembly Removal/Installation (NovaJet 750) ................................. 5-5
5-4. Keypad and Display Removal/Installation ........................................................ 5-8
5-5. Keypad and Display Grounding Connection .....................................................5-9
5-6. Extra Memory (SIMM) Removal/Installation ................................................... 5-10
5-7. MPCB Removal ............................................................................................. 5-13
5-8. Power Supply Removal ................................................................................. 5-16
xv
Page 14

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
List of Illustrations (cont)
Figure Page
Chapter 5 Assembly/Disassembly (cont)
5-9. Cooling Fan/AC Entry Module Removal ......................................................... 5-17
5-10. Slacken Carriage Belt ................................................................................... 5-19
5-11. Chain Support Bracket Removal .................................................................... 5-22
5-12. Cariage Cover Removal ................................................................................. 5-22
5-13. Chain Support Bracket Adjustment ............................................................... 5-24
5-14. Strain Relief Removal/Installation .................................................................. 5-25
5-15. Frame Tensioner ........................................................................................... 5-26
5-16. Carriage Belt Clamp ...................................................................................... 5-26
5-17. Carriage PCB Removal/Installation ................................................................ 5-30
5-18. Paper and Encoder Sensor Removal ............................................................. 5-32
5-19. Paper and Encoder Sensor Installation .......................................................... 5-33
5-20. Carriage Bushing Removal ............................................................................ 5-35
5-21. Carriage Bushing Installation ......................................................................... 5-35
5-22. Service Station Removal ................................................................................ 5-36
5-23. Stabilizer Bracket Installation/Removal .......................................................... 5-39
5-24. Y-Arm Installation/Removal ........................................................................... 5-41
5-25. Pinch Roller .................................................................................................. 5-42
5-26. Stepper Motor Removal/Installation ............................................................... 5-47
5-27. Inside Platen, Right Side ............................................................................... 5-49
5-28. Media Take-Up and Feed Sensor Removal .................................................... 5-51
5-29. Media Take-Up and Feed Motor Removal ...................................................... 5-53
5-30. Inner Platen Assembly/Disassembly ............................................................. 5-57
Chapter 6 Parts List
6-1. Left Side Parts Breakdown .............................................................................. 6-3
6-2. Left Side Parts Breakdown (NovaJet 750) ........................................................ 6-5
6-3. Platen and Above Parts Breakdown ................................................................ 6-7
6-4. Right Side Parts Breakdown ........................................................................... 6-9
6-5. Right Side Parts Breakdown (NovaJet 750) ................................................... 6-11
6-6. Inner Platen Parts Breakdown ....................................................................... 6-13
6-7. Carriage Assembly Parts Breakdown ............................................................ 6-15
6-8. Carriage Cover Parts Breakdown ................................................................... 6-17
6-9. Service Station Parts Breakdown .................................................................. 6-19
6-10. Power Feed and Take-Up Parts Breakdown ................................................... 6-21
xvi
Page 15

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
List of Tables
Table Page
Chapter 1 General Description
Chapter 2 Theory of Operation
Chapter 3 Maintenance
3-1. MPWA Connections Table .............................................................................. 3-9
3-2. Carriage PWA Connections Table ................................................................. 3-10
Chapter 4 Troubleshooting
4-1. Troubleshooting Table ......................................................................................4-1
Chapter 5 Assembly/Disassembly
Chapter 6 Parts List
xvii
Page 16

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
This Page Intentionally Left Blank
xviii
Page 17
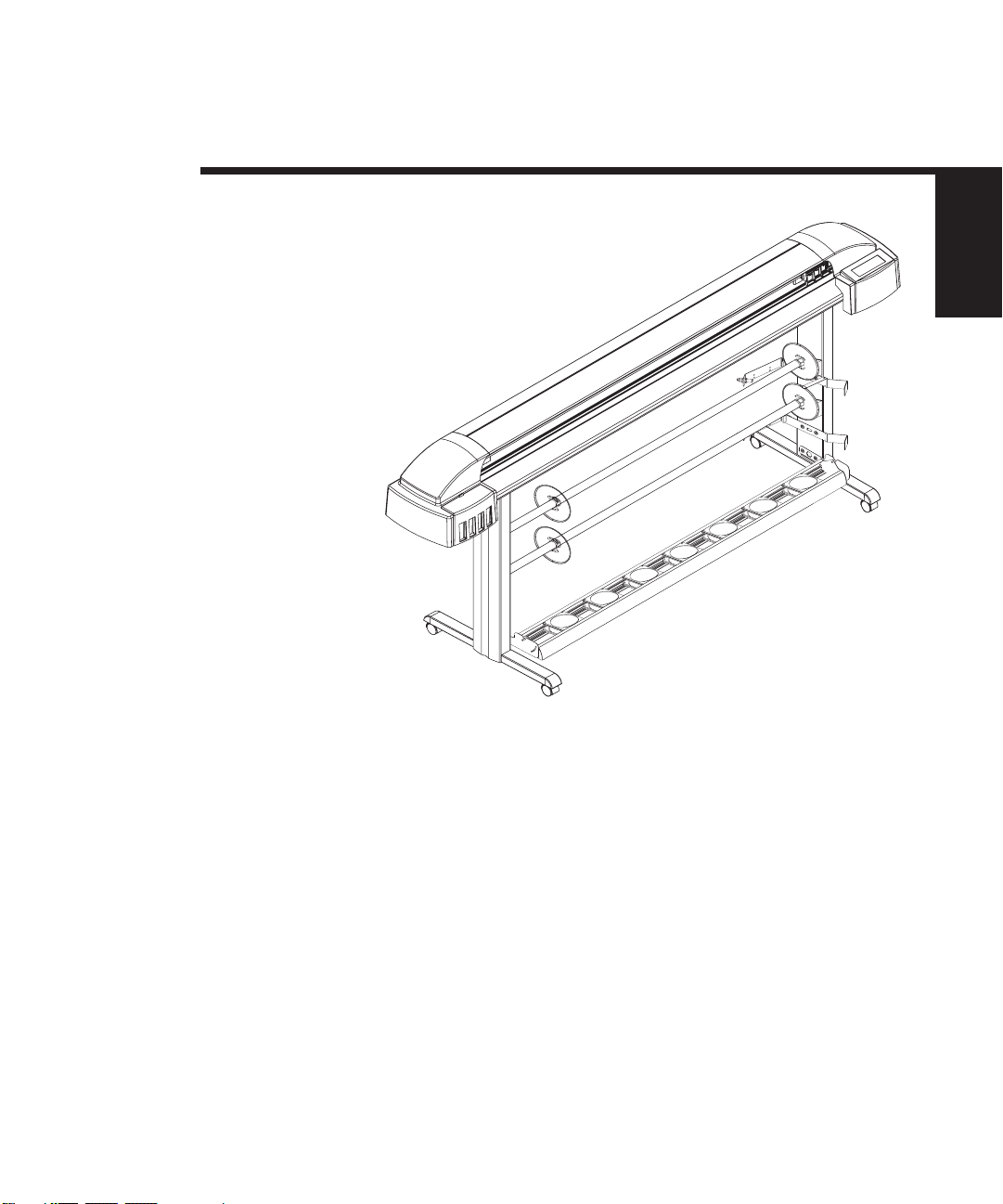
General Description
1
DESCRIPTION
GENERAL
Introduction
This manual provides service information for the ENCAD®, Inc.
NovaJet® 500, NovaJet 630 and the NovaJet 700 Series of Color
Inkjet Printers. The NovaJet 500 series includes the NovaJet 500 and
NovaJet 505 printers. The NovaJet 700 series includes the NovaJet
700, NovaJet 736 and NovaJet 750 printers. All three NovaJet 500/
630/700 printer series comes in two sizes: a 42 inch model and a 60 inch
model. The NovaJet 736 printer comes only as a 36 inch model.
The service manual is written for service personnel who possess analog
and digital circuitry experience. Chapter 2, Theory of Operation, should
Figure 1-1. NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Inkjet Printers.
1-1
Page 18

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
be read and thoroughly understood before troubleshooting/calibrating
the printers.
The printers support pre-cut and roll media. Media size is automatically determined and hardclip limits are set accordingly. Pre-cut media
uses different maximum plotting areas than roll media. See the Printer
Specifications in the User Guide for more details on the media size
printable area.
Both RS-422 serial and Centronics parallel connections are provided to
interface with the host computer. For proper operations, the NovaJet
750 must be connected to a 100BaseT network print server. Commands
sent from the host computer can be in several forms including HP-GL/
2, HP-RTL and EN RTL formats.
Drivers are supplied to support Windows-based PC’s (3.XX, 95/98, and
NT) as well as Macintosh and Power PC computers.
These printers expand upon ENCAD’s tradition of delivering fast, highquality color or monochrome graphics for a variety of applications.
ENCAD has made significant advances in designing these printers to
respond to and anticipate our customers’ needs. Principal features are
summarized below.
Locally or Remotely Configured via Host Computer
Powered Media Take-Up and Feed System (700 series only)
Powered Feed Roll and Take-Up Basket (500 & 630 series)
Optional Powered Take-Up Roll System (500 & 630 series)
Media Drying System (optional on the 500 & 630 series)
Thermal Media Drying System (NovaJet 750)
Quick Ink Changeover
Self-Aligning Pinch Rollers
PowerPC 33 MHz Microprocessor
8 User Configurable Settings
104 Jet Ink Cartridges (500 series)
208 Jet Ink Cartridges (630 & 700 series)
Ink Priming System
4 500ml Ink Reservoirs (8 for the NovaJet 750)
Smart Cartridges
Odometer Function
Improved Septum Connector Design
1-2 General Description
Page 19

Overview
Related Publications
NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Printers draw according to instructions issued from a “host” computer. Every printer is engineered to understand a specific set of
instructions and to execute each instruction in a precise manner. In
addition, most printers are designed to execute predetermined
characters automatically without a specific line-by-line instruction
from the program. These characters are part of the printer’s permanent memory.
The following publication contains additional information which may
be useful in servicing the ENCAD, Inc. NovaJet 500/630/700
Series Color Inkjet Printers:
• ENCAD NovaJet 500/630/700 Quick Start Guide,
P/N 212528-04
• ENCAD NovaJet System CD-ROM,
P/N 212532-02
DESCRIPTION
GENERAL
Copies of these and other ENCAD, Inc. publications may be obtained by contacting your nearest authorized ENCAD, Inc. dealer or
by contacting ENCAD’s Technical Support and Service Department.
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Sensitivity
All PWAs (Printed Wiring Assemblies) associated with the NovaJet
500/630/700 series printers have components sensitive to ESD
(electrostatic discharge). Care must be taken to avoid damage to any
of the components by following current ESD handling procedures and
practices.
Always use an approved ESD grounding strap when handling or
working with PWAs.
General Description 1-3
Page 20
NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Warnings, Cautions and Notes
Warnings, cautions and notes are used when additional information,
instructions or care should be observed. In this manual warnings,
cautions and notes precede the text to which each applies. The definition of each is provided below.
WARNINGS - Warnings are used to stress that the following steps or
procedures has the potential to cause serious harm or death to service
personnel. Extreme care should be observed when following the procedures and to exercise standard safety procedures. They are indicated
by:
WARNING
Followed by a paragraph describing the concern.
CAUTIONS - Cautions depict that the following steps or procedures can
cause damage to the equipment if not properly followed. Extreme care
should be observed when following the procedures and to exercise
standard safety procedures. They are indicated by:
CAUTION
Followed by a paragraph describing the concern.
NOTES - Notes are placed before a procedure to inform the service
personnel of specific details to improve quality, to give reminders of
interrelated parts and to provide other helpful information. They are
indicated by:
NOTE
Followed by a paragraph describing the concern.
1-4 General Description
Page 21

Printer Specifications
The specifications and performance characteristics of the NovaJet
500/630/700 Series Color Inkjet Printers are as follows:
NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
DESCRIPTION
GENERAL
Max Printing Area:
42 inch 60 inch
Norm 40.8” 58.8”
1.04m 1.49m
Extend 41.61” 59.61”
1.06m 1.51m
Language Emulation:
HP-RTL
EN RTL
HP GL/2
Buffer:
32 MB installed (630/700)
8 MB installed (500 series)
upgradeable to 128 MB
Power Requirements:
Input Voltage:
90-264 VAC
48-63 Hz
Output Power:
20 W idle
140 W typical
215 W maximum
Resolution:
630/700 series
600x600 dpi or
300x300 dpi, addressable
500 series
300x300 dpi
Baud Rates:
9600, 19200, 38400
Accuracy:
+/- 0.2% line length using
ROLL feed and 4 mil
drafting matte film
Interface:
Centronics parallel
(IEEE 1284)
RS-422 serial
Network Option: via
10/100BaseT, 10Base2
Print Server
Certifications:
Safety
CSA, CSE/NRTL
(equivalent to UL1950)
TUV GS
EN 50 082-1
EN 60 950
UL1950
NOM-019-SCFI-1993
IEC 950
AS/NZS 3260
EMI
FCC Class A, B
CSA C108.8
EN 55 022 Class A, B
CE Mark
CISPR 22- Class A, B
AS/NZS 3548
General Description 1-5
Page 22

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Environment:
Operating:
59° to 95° F
(15° to 35° C)
10% to 70% RH
non-condensing
Storage:
-5° to 140° F
(-21° to 60° C)
5% to 80% RH
non-condensing
Contents of this Service Manual
Figures are used in this manual to clarify procedures. They are for
illustrative purposes only and may not necessarily be drawn to scale.
Material in this manual may be repeated in various chapters so that
each chapter can “stand alone”. This allows information to be located
without having to refer back and forth between chapters.
Weight:
60” 88 lbs 135 lbs (boxed)
42” 72 lbs 117 lbs (boxed)
Dimensions:
Height 44” (1.12m)
Width 77” (1.96m)
42 inch
95” (2.41m)
60 inch
Depth 28” (0.71m)
Figures and tables are easily located and cross-referenced, and are listed
in the front of the manual under List of Illustrations and List of Tables.
This manual is divided into six chapters as:
Chapter 1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION - Contains a general
description of the ENCAD NovaJet 500/630/700 printers.
This includes printer specifications, and related materials.
Also included is a description of the use of Warnings,
Cautions and Notes as used in this manual and chapter
contents.
1-6 General Description
Page 23

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Chapter 2 THEORY OF OPERATION - Functional
descriptions of the overall printer and major assemblies
are contained in this chapter.
Chapter 3 MAINTENANCE - This chapter covers the
scheduled maintenance, cleaning procedures and
alignment/adjustments recommended to perform on the
printers. Diagnostics and a signal flow diagram are also
listed.
Chapter 4 TROUBLESHOOTING - A table containing
problems that could occur and possible causes and repairs
is found in this chapter. This table is not intended to be a
complete listing of troubleshooting procedures. It will
isolate the problem down to the lowest replacable
assembly. If the problem happens to be the wiring
between assemblies, standard troubleshooting techniques
will have to be implemented to correct the problem.
Chapter 5 ASSEMBLY/DISASSEMBLY - Contains detailed
procedures to remove and replace printer parts and
assemblies.
DESCRIPTION
GENERAL
Chapter 6 PARTS LIST - Contains a complete listing of all
field replacable parts and assemblies for the NovaJet 500/
630/700 Color Inkjet Printers. Illustrated parts
breakdown drawings are included to help clarify and
identify parts for ordering. Special kits and adjustment
jigs may also be required.
ORIENTATION - Instructions in this manual are based on the
assumption that the service person is facing the front of the printer.
References to top view, back view, and so forth are consistent with
this engineering standard. References to the X Axis and Y Axis
(Paper Axis and Carriage Axis, respectively) follow the standard of
AutoCAD™ absolute coordinates: up and down for X, left to right for
Y.
General Description 1-7
Page 24

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Technical Support
ENCAD offers full technical support and service for its various products. If you are unable to find the answer to your question in either the
User’s Guide, Service Manual, or other related publications, check out
ENCAD’s Knowledge Base located on ENCAD’s website support:
ENCAD Website: http://www.encad.com
Additional information is available though our Technical Support and
Service Department’s Help Desk.
ENCAD, Inc.
Technical Support & Service Dept.
6059 Cornerstone Court West
San Diego, CA 92121
Help Desk Telephone: (858) 452-4350 or
Help Desk FAX: (858) 558-4672
(877) ENCAD-TS (362-2387)
International users contact your local ENCAD service provider. See
details on your ENCAD registration card.
1-8 General Description
Page 25

Theory of Operation
Introduction
This chapter explains the mechanical and electrical theory of operation
of the ENCAD NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Color Inkjet printers.
The NovaJet 500/630/700 Series is a PowerPC 33MHz microprocessorbased digital printer that receives plotting instructions from a host
computer through either the RS-422 serial interface or the Centronics
parallel interface.
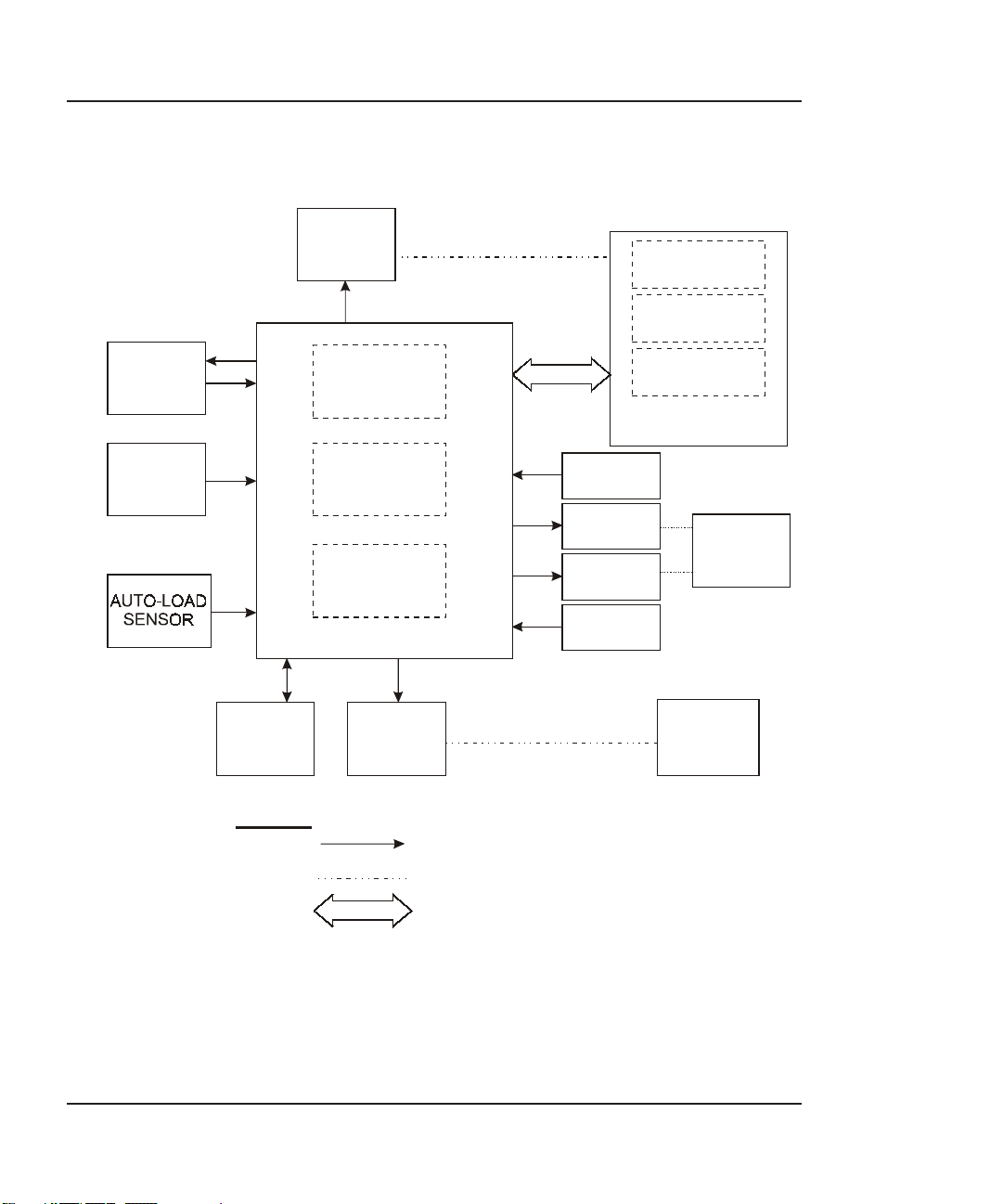
NovaJet 500/630/700 Printers General Block Diagram
Figure 2-1 illustrates the major functional areas of the printers.
The NovaJet 500/630/700 Series printers consist of three mechanical
assemblies:
1. Paper (Media) Axis Drive
2
OPERATION
THEORY OF
2. Carriage Axis Drive
3. Media Feed and Take-Up System
(Mechanical Take-Up system is optional on the 500 & 630
printers.)
and four main electrical assemblies:
1. MPCB (Main Printed Circuit Board)
2. Carriage Assembly
3. Control Panel
4. Power Supply
2-1
Page 26
NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
CONTROL
PAN EL
POWER
SUPPLY
PRINT
SERVER
SERVO
MOTOR
MICRO-
PROCESSOR
GATE
ARRAY
MEMORY
CIRCUITS
MPWA
STEPPER
MOTOR
CARRIAGE AXIS DRIVE
PAPER AXIS DRIVE
FEED
SENSOR
FEED
MOTOR
TAK E-U P
MOTOR
TAK E-U P
SENSOR
PAPER
SENSOR
ENCODER
SENSOR
CARRIAGE
PCB
CARRIAGE
ASSEMBLY
MEDIA
LOWER
DRIVE
ASSEMBLY
LEGEND
ELECTRICAL CONNECTION
MECHANICAL CONNECTION
MAIN DATA BUS
Figure 2-1. General Block Diagram.
2-2 Theory of Operation
Page 27
NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
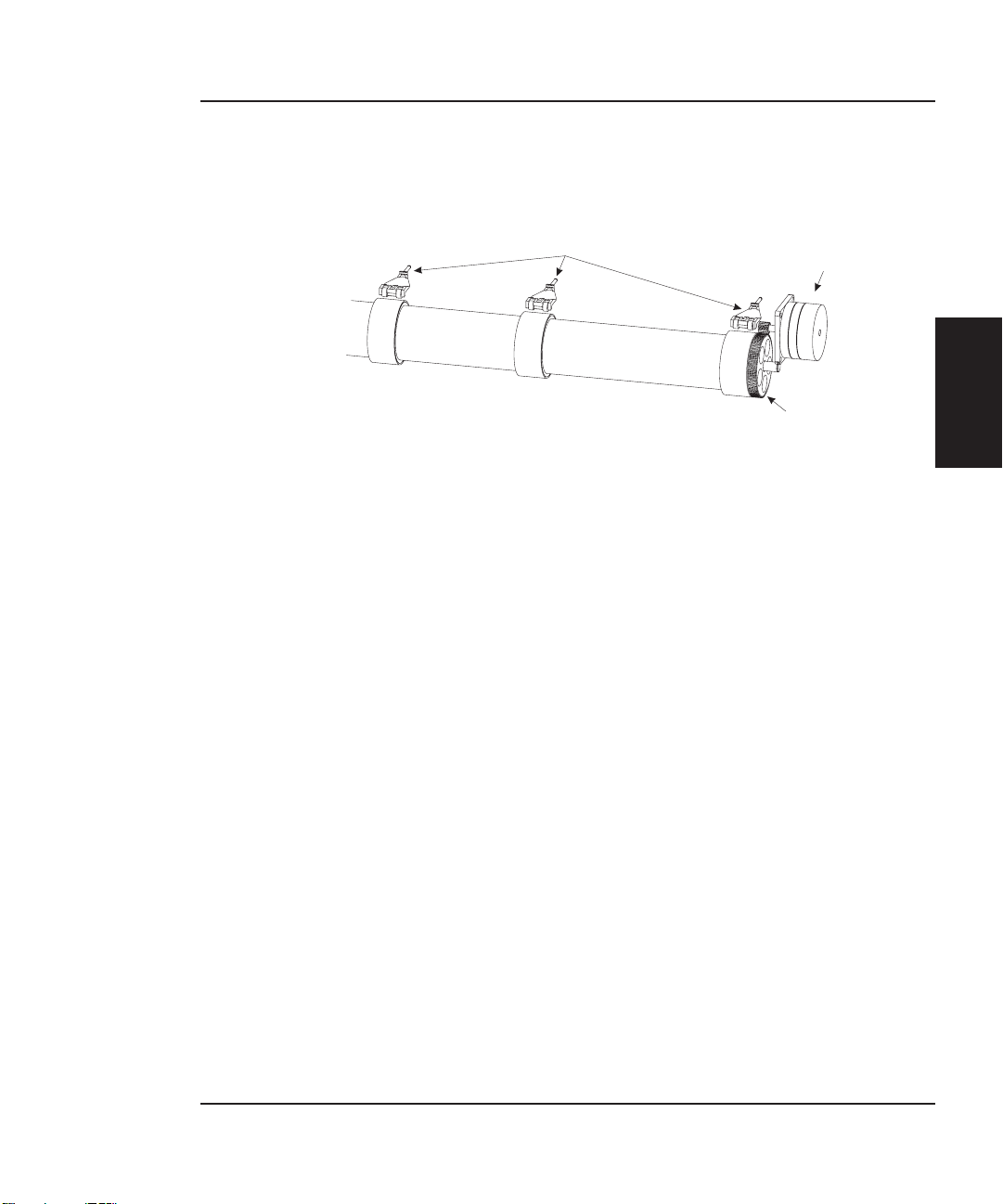
Paper (Media) Axis Drive
PINCH ROLLERS
STEPPER MOTOR
LOWER ROLLER SHAFT ASSY
REDUCTION GEAR
Figure 2-2. Paper (Media) Axis Drive.
The Paper (Media) Axis Drive moves the plotting media in a direction
perpendicular to the length of the printer. This friction drive utilizes a
micro-step drive technology and consists of a stepper motor, reduction
gears, lower drive shaft assembly, and pinch rollers. This can be seen
in Figure 2-2.
The micro-step technology associated with the stepper motor gives the
capability of a resolution up to 9600 dpi.
The reduction gear meshes the stepper motor to the lower drive shaft
assembly which allows the media to advance or retract. The purpose of
the pinch rollers is to apply pressure to the media onto the drive shaft
assembly to reduce the chance of slipping.
OPERATION
THEORY OF
Misaligned pinch wheels is a main cause of skewing of the media. For
that reason the NovaJet 500/630/700 Series was designed with self
aligning pinch rollers. As the media is fed forward, the rollers are
aligned correctly. However, these pinch rollers will not stay aligned
while the media is being fed backwards.
Theory of Operation 2-3
Page 28
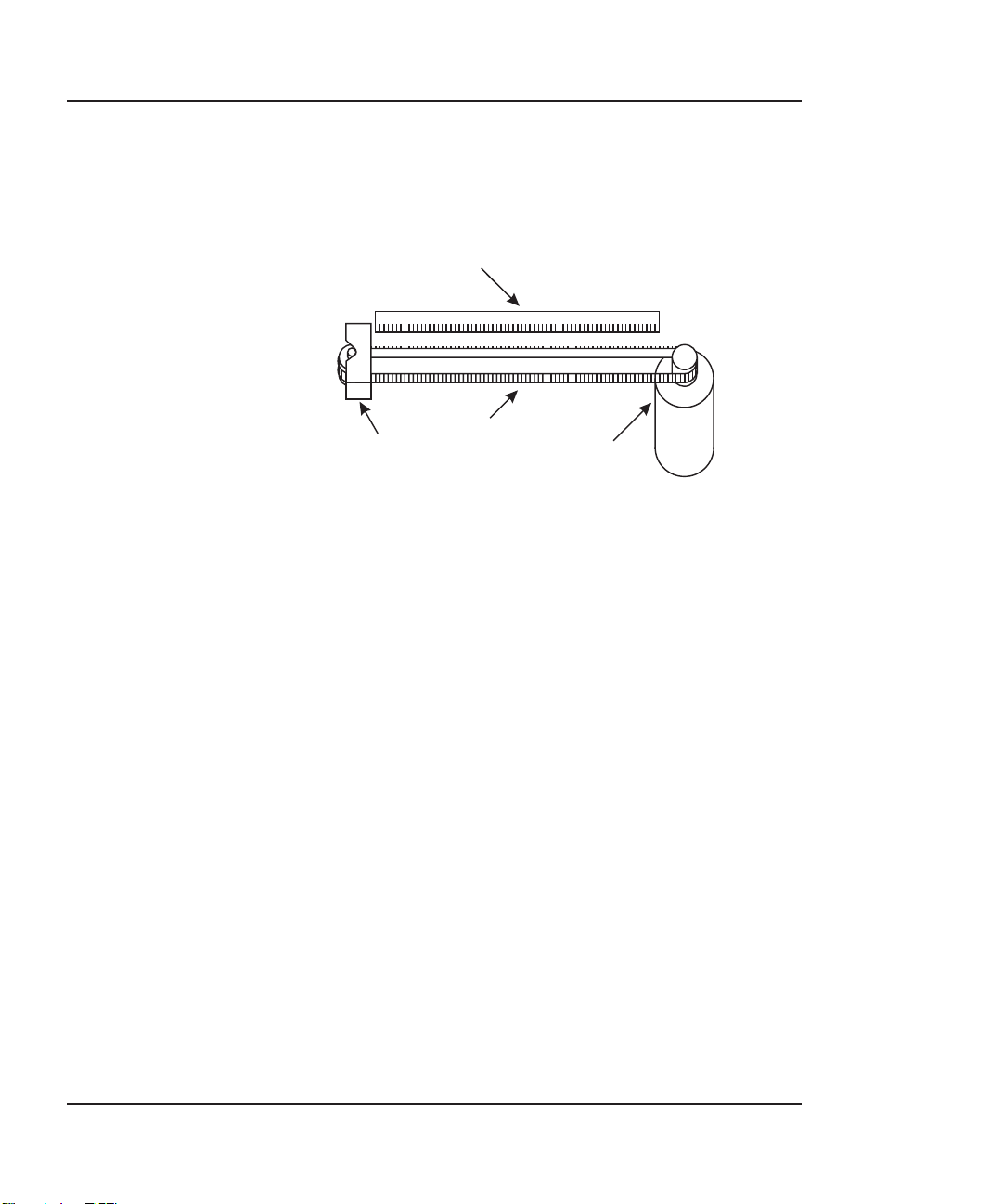
NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
The Carriage Axis Drive
ENCODER STRIP
TENSIONING
ASSY
Figure 2-3. Carriage Axis Drive.
The Carriage Axis Drive moves the printer’s carriage assembly along
the length of the printer. The drive consists of a servo motor, linear
encoder strip, drive belt, and tensioning assembly. These items are
illustrated in Figure 2-3.
The servo motor, drive belt, and tensioning assembly are the components that actually drive the carriage assembly. The servo motor drives
the belt back and forth allowing the attached carriage assembly to be
repositioned as required. The tensioning assembly is spring controlled
and allows the proper amount of tension on the belt.
The linear optical encoder strip is used to obtain the printers accuracy
along the axis of the printer. It is made with 150 parallel lines per inch
etched into it. By utilizing two optical encoder sensors that are slightly
offset from each other, and reading the leading and trailing edges of the
lines, a resolution of 600 dpi can be obtained.
The stepper and servo motors are controlled from the main printed
wiring assembly (MPWA) by the microprocessor.
SERVO
MOTOR
BELT
2-4 Theory of Operation
Page 29
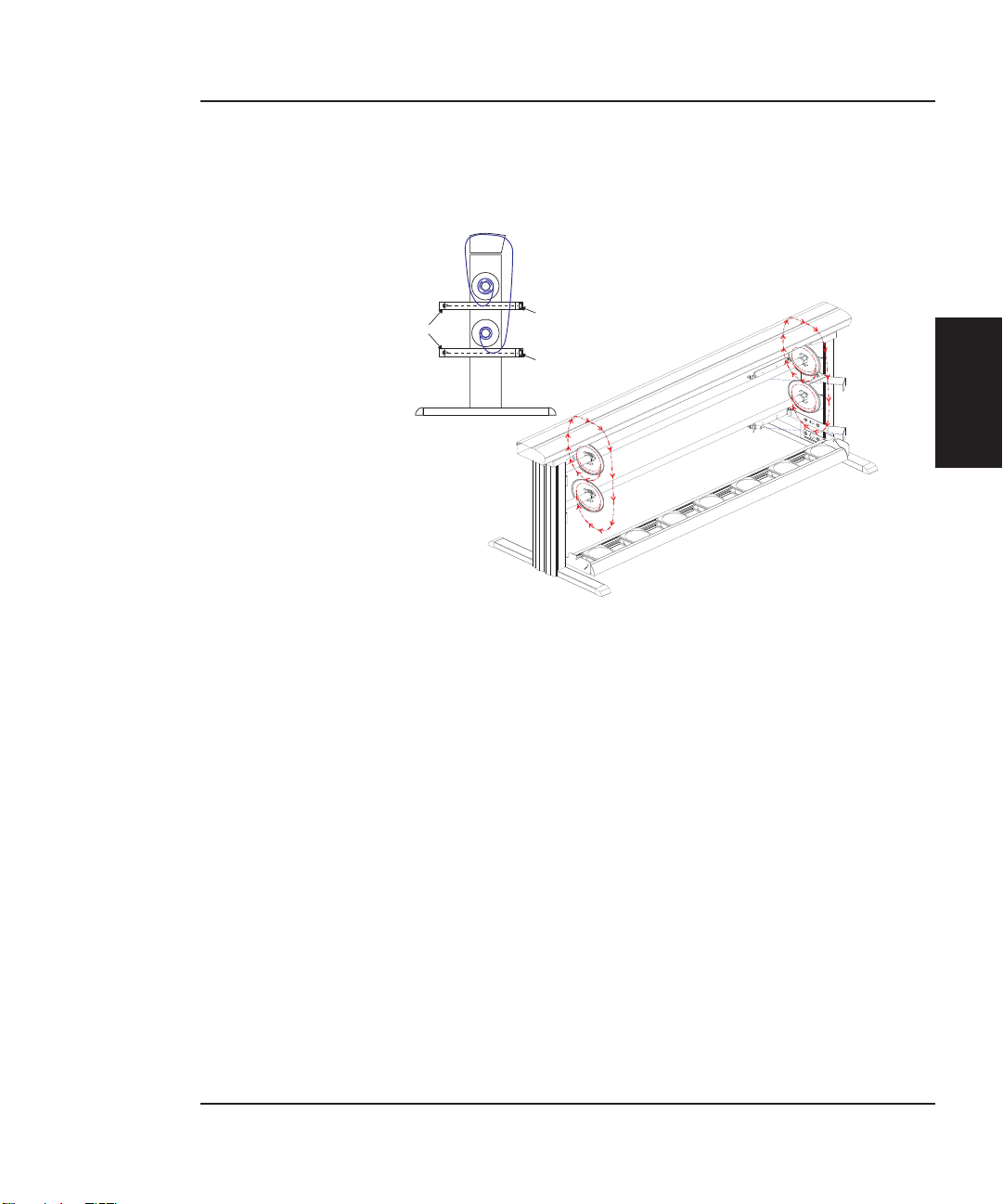
NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Media Feed and Take-Up System
SENSORS
REFLECTOR
REFLECTOR
Figure 2-4. Power Feed and Take-Up System.
The media feed and take-up system comprises of two optical sensors,
two dc motors and a dryer assembly. See Figure 2-4. The NovaJet
750 uses a thermal drying system while all other models use a blower
drying system as shown above.
Motors are used to advance the media feed roll and the media take-up
roll dependant upon the signals they receive from the MPWA. The
MPWA generates the control signals for the motors from the information it receives from the media feed and take-up sensors. The MPWA
also controls the dryer assembly. It activates only the fans required to
cover the width of the loaded media. The fan assembly also contains an
interlock circuit.
OPERATION
THEORY OF
The optical sensors are designed to inform the MPWA when there is not
a proper amount of slack in the media by sensing the ‘curl’ of the media
at the bottom of its loop. This method is used so that all approved forms
of media (including transparent backlit media) is able to take advantage
of the power feed and take-up system.
Theory of Operation 2-5
Page 30
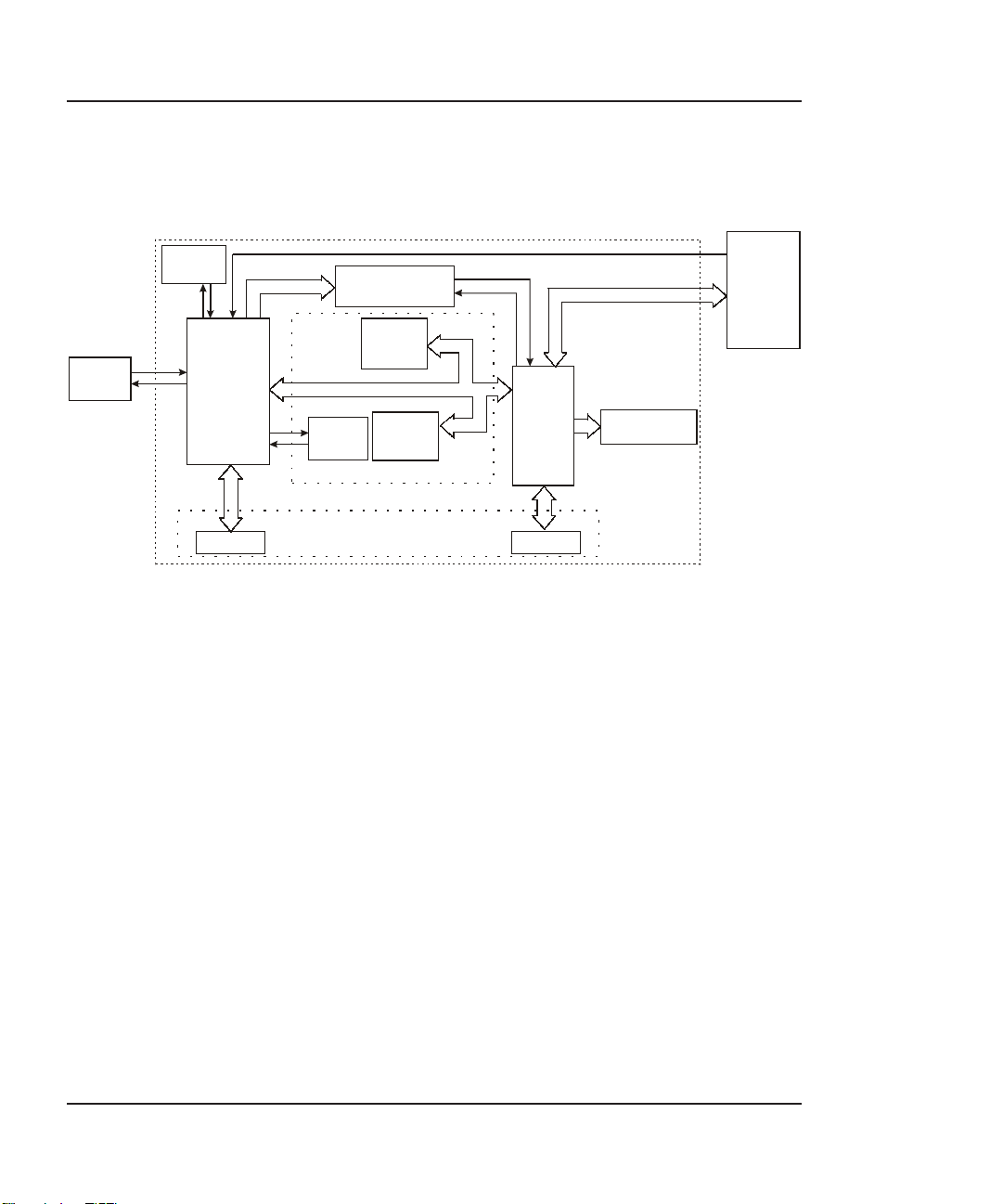
NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Main Printed Wiring Assembly (MPWA)
CRYSTAL
CONTROL
PANEL
X1
MICRO-
PROCESSOR
(CPU)
STEPPER MOTOR
CONTROLLER
FLASH
EEPROM
DATA BUS
SERIAL
EEPROM
DYNAMIC
RAM
(SIMM)
MEMORY CIRCUITS
GATE
ARRAY
SERVO MOTOR
CONTROLLER
CARRIAGE
PWA
SERIAL
INTERFACE CIRCUITS
PARAL LEL
Figure 2-5. Main Printed Wiring Assembly.
The Main Printed Wiring Assembly (MPWA) consists of six functional
areas:
1. Microprocessor (CPU)
2. Gate Array
3. Memory Circuits
4. Stepper Motor Controller
5. Servo Motor Controller
6. Interface Circuits: Serial & Parallel
2-6 Theory of Operation
Page 31

Microprocessor
The microprocessor (an IBM PowerPC) is the central processor unit
which supervises system functions, executes the printer firmware,
manipulates data, and controls input/output data busses. It has two
built-in serial ports, a two channel DMA (Direct Memory Access)
controller, a timer module, clock generator, and an on-board chip
select generator. One serial port connects to the Mini-DIN connector
which can be used to communicate with the host computer; the other
serial port interfaces to the Control Panel. One DMA channel supplies data to the gate array for jet firing; the other DMA channel is
used to receive data through the parallel port via the gate array, or
the serial port when using a high speed serial mode. One timer
generates a servo interrupt every millisecond; the other is used for
timing the Stepper Motor.
A divide-by-two circuit generates the 33MHz system clock from a
66MHz crystal reference (X1).
The chip select generator is programmed to generate chip selects at
the appropriate addresses, with the appropriate data size (byte, word)
and with the appropriate number of wait states.
NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
OPERATION
THEORY OF
Gate Array
PAR A LLEL
PORT
GATE
ARRAY
STATIC
RAM
Figure 2-6. Gate Array.
SERVO
CONTROLLER
TO
CARRIAGE
PWA
Theory of Operation 2-7
Page 32

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
The gate array contains the hardware logic for jet firing, monitoring
changes in the Carriage Assembly position, controlling DMA through
the parallel port, and generating the PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
waveforms for the servo controller.
The gate array is a Xilinx device. It is a static RAM-based field programmable gate array. This means that the logic that it implements is
determined by configuration information in an internal RAM storage
area. Each time power is turned on, this information must be downloaded from the system EEROM. This type of gate array allows for the
flexibility of upgrading the logic by simply downloading the new system
software.
Memory Circuits
Memory is used to retain large amounts of information. This information is stored in the device memory in the form of binary bits.
Printer memory consists of Flash EEPROM, DRAM, and EEPROM.
Maximum installable memory is as follows:
DRAM = 128 MB
Flash EEPROM = 1 MB
Serial EEPROM = 1KB
Flash EEPROM
Flash EEPROM is Electrically Erasable, Programmable, Read Only
Memory used to store instructions and data constants which the
microprocessor can access and interpret, with no loss of information
when power is off.
2-8 Theory of Operation
Page 33

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
The system firmware is stored in Flash EEPROM. The Flash
EEPROM allows the firmware to be upgraded by downloading the files
containing the new firmware. It can be erased and reprogrammed
more than 10,000 times. The term “Flash” means that bytes cannot be
individually erased. A block or the whole device is erased at the same
time and the block or whole device is then reprogrammed.
The normal method of downloading new firmware is to send the unit
the files containing the code using either the GO.EXE utility or printing the file to the unit. This requires using an appropriate host utility
and can be done through the serial port (for Macintosh users) or the
parallel port (for PC users). See Firmware Downloading in Chapter 3
for the procedures.
DRAM
DRAM is Dynamic Random Access Memory which provides temporary
storage of the microprocessor calculation and input/output data. It is
also a faster type of memory then the Flash EEPROM. That’s why the
printer control program is also copied from the Flash EEPROM to
RAM, where it can be executed faster.
OPERATION
THEORY OF
The printer also has two 72-pin 32-bit SIMM sockets for DRAM. The
printer is supplied with a SIMM installed on the MPWA. The SIMM
size for the 500 series is 8 Megabyte and for the 630/700 series is 32
Megabyte. The following SIMM sizes are supported: 4MB (1Mx32),
8MB (2Mx32), 16MB (4Mx32), 32MB (8Mx32) and 64MB (16Mx32.)
The SIMMs must have a minimum operating speed of 70ns, and
conform to JEDEC Standard 21-D release 4 or later. Remove the Right
Cover to install additional memory (see Chapter 5 for installation
procedures.) Care must be taken when choosing a SIMM module for
the printer. Not all SIMM’s on the market today will work on the
printer. It has to do with the “presence detect” signals on pins 67 and
68 of the SIMM’s. Not all SIMM manufacturers use these signals, so
they disable them.
Theory of Operation 2-9
Page 34

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Serial EEPROM
Serial EEPROM is an Electrically Erasable, Programmable, Read Only
Memory which provides storage for calibration constants and user
configuration data entered from the host computer.
An 8K bit serial nonvolatile EEPROM stores calibration and configuration information. It retains data while the unit is off.
Stepper Motor Controller
DATA BUS
WAVEFORM
GENERATOR
COMPARATOR
DRIVER
CURRENT
SENSE
STEPPER
MOTOR
Figure 2-7. Stepper Motor Controller.
The media is driven by a Stepper Motor, which drives the media in a
direction perpendicular to the width of the printer. The media in the
printer can advance forward and backward, depending upon the commands which the Stepper Motor receives from the microprocessor.
The Stepper Motor Controller contains two identical circuits, one for
each winding of the stepper motor. The circuit is a combination of two
simpler types of circuits and can be thought of as a variation of either
one.
A waveform generator receives digital data from the CPU and generates
a sine wave output. This signal is fed into a comparator circuit that is
measuring the current through the winding of the stepper motor. If the
current is too low, a pulse of 24V is generated. When the current goes
above the output of the waveform generator, the pulse turns off. Every
time the output of the waveform generator is changed by the microprocessor, the motor moves 1 “micro-step”.
2-10 Theory of Operation
Page 35

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Each circuit contains four main functions (see Figure 2-7):
1. Reference waveform generator
The microprocessor uses a D/A (digital to analog) converter to set
the desired level for the current in the stepper motor winding. The
output of the D/A converter varies in time to create a reference
waveform. This reference waveform is centered around 10V.
2. Motor current sense
The voltage across a series current sense resistor is measured and
level shifted so that it is centered around 5V.
3. Comparator
This portion divides the output of the reference waveform generator
by two and compares it to the output of the motor current sensor.
Logic inside the gate array generates the control signals for the
power driver that applies voltage across the motor winding in order
to make the actual current match the reference waveform.
OPERATION
THEORY OF
4. Power driver
An H-bridge allows the supply voltage to be applied across the
winding in either polarity used to drive the current level to the
desired value.
Theory of Operation 2-11
Page 36

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Servo Motor Controller
GATE
ARRAY
MOTOR
DRIVER
MAIN PWA
SERVO
CONNECTOR
CARRIAGE
CONNECTOR
SERVO
MOTOR
ENCODER
CARRIAGE
Figure 2-8. Servo Motor Controller.
The Carriage Assembly is driven by the Servo Motor. The speed of the
Carriage Assembly is controlled by varying the duty cycle of the signal
applied to the controller. The microprocessor checks the position of the
Carriage Assembly approximately 1,000 times per second (during the
servo interrupt). It then updates the PWM (pulse width modulator)
register in the gate array which sets the duty cycle to make adjustments to the Carriage Assembly speed. A linear optical encoder is used
to monitor the Carriage Assembly position.
The optical encoder strip runs the length of the Stabilizer Bracket and
contains 150 lines and spaces per inch. Thus there are 300 edges per
inch. The detector circuit actually consists of two optical edge detectors.
They are separated from each other by one half the width of one of the
optical lines on the encoder strip. This allows 4 evenly spaced pulses to
be developed for each line on the encoder strip. This is known as quadrature signals. It gives an effective resolution of 600 lines per inch. See
figure 2-9 for a graphical representation of quadrature signals. For 300
dpi resolution, one of the detectors is not used.
2-12 Theory of Operation
Page 37

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
DETECTOR 2
DETECTOR 1
ENCODER STRIP
OUTPUT OF DETECTOR 1
OUTPUT OF DETECTOR 2
COMPOSITE TRANSITION-TRIGGERED OUTPUT OF BOTH DETECTORS
OPERATION
THEORY OF
4 OUTPUT PULSES
PER OPTICAL LINE
Figure 2-9. Quadrature Signal Generation.
The direction that the Carriage Assembly is moving is known based
upon the state of one detector’s output and the direction of the transition
of the other detector’s output.
A hardware counter in the gate array increments as the Carriage
Assembly moves left and decrements as the Carriage Assembly moves
right. The hardware counter is only eight bits wide, so it cannot store a
value large enough to represent an absolute Carriage Assembly position.
Instead, it is read during the servo interrupt and its value compared
with that from the previous interrupt. This difference is used to update
the absolute position value in the software.
Theory of Operation 2-13
Page 38

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Interface Circuits: Serial & Parallel
SERIAL
CONNECTOR
TRANSCEIVER
MICRO-
PROCESSOR
GATE
ARRAY
PARALLEL
CONNECTOR
Figure 2-10. Interface Circuits.
Data from the host computer is received either through the Centronics
parallel port or the serial port. The gate array provides the control
signals for DMA transfers from the parallel port to DRAM.
The serial port is designed primarily to interface to a Macintosh®
computer. It has an eight pin Mini-DIN connector. The data (TXD,
RXD) signals meet RS-422 electrical specifications, and the control
signal (DTRCLK) meets the RS-423 electrical specifications.
Due to the data flow speed limitations of using the serial interface with
a Macintosh computer system ENCAD does not recommend using this
port for production usage with the new printers. Hesitation may result
if using this port and that can degrade the quality of the output print.
Possible solutions for the Macintosh computer user include using a
print server device with an established network or installing a parallel
port add-on card in the computer to interface with the printer.
The serial port is still required to download new firmware to the printer
with a Macintosh computer.
The serial port is compatible with RS-422 devices when an appropriate
adapter cable is used. This cable is available from ENCAD.
The NovaJet 750 printer ships with a high speed print server that
attaches to the parallal port for network compatibility.
2-14 Theory of Operation
Page 39

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Carriage Assembly Circuits
OPTICAL ENCODER
TRAILING
CABLE
CONNECTION
FROM
MPWA
TRAILING
CABLE
CARRIAGE
PWA
INKJET
DRIVERS
CARRIAGE ASSEMBLY
Figure 2-11. Carriage Assembly Circuits.
The Carriage Assembly contains:
1) Carriage PWA
2) Optical Sensors
3) Paper Sensor
4) Inkjet Cartridges
OPTICAL SENSOR
PAPER SENSOR
CARTRIDGE 1
CARTRIDGE 2
CARTRIDGE 3
CARTRIDGE 4
OPERATION
THEORY OF
The Carriage PWA contains the logic and drive circuitry for the firing of
the inkjet cartridges. It also establishes an interface path for the optical
sensor and paper sensor to communicate with the MPWA.
The optical sensors receive their inputs from the optical encoder strip
and sends this data to the MPWA. The MPWA uses this information to
determine the horizontal position of the carriage assembly so that
accurate printing can be established.
Theory of Operation 2-15
Page 40

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
The paper sensor circuitry senses for the presence of loaded media. It
does this automatically during the start-up and load sequences. It also
constantly monitors the media during printing to determine if the
media has run out.
If no paper is sensed, the paper sensor sends this information to the
MPWA, which immediately begins an ‘out of paper’ subroutine. This
subroutine stops the printer from printing until more media is loaded.
The sensor also checks for the size of the media loaded so it can determine the proper printing parameters.
Control Panel
The Control Panel is located on the right side of the printer and consists
of 8 variable-action control buttons and an LCD graphics display. The
control buttons are assigned to different functions and are dependant
upon the selections that were previously selected. There are four buttons
on the left of the display and four buttons on the right, with the display
showing up to eight possible selections.
Load Media
Cut
Pause
Reset
Figure 2-12 shows the control panel after the printer has been turned on
and completed the start up process. As seen in the figure, the control
buttons are assigned to the corresponding command that is displayed
closest to the physical location of the button.
2-16 Theory of Operation
Feed Media Menu
*
Setup Menu
Figure 2-12. Main Menu.
Utility Menu
Page 41

Power Supply
An internal UL recognized switching power module supplies power for
the NovaJet 500/630/700 Series printers. It provides a constant
24VDC output from input voltage in the 90-132 VAC and 180-246 VAC
ranges. A power switch turns the power on and off. The 24VDC is
applied to the MPWA where it is further regulated and separated into
24VDC, 13VDC, and 5VDC. The 24V supply is used for: the stepper
controller (which advances the paper); the servo controller (which
moves the Carriage); and power to fire the inkjets. The 5V supply
powers the logic circuits.
The power supply is fused using a 6.3A 250V fast blow type fuse.
The outputs share a common ground which is isolated from earth
ground with in the supply itself. Earth ground and DC ground are
connected external of the power supply.
The power supply will shut down under overload/short circuit conditions on any output over the full range of input voltage. Overvoltage
protection is 20%-30% above nominal for the 24V output.
NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
OPERATION
THEORY OF
Beeper and Fans
The beeper contains built-in driver circuitry so that it beeps under
firmware control. The beeper alerts the user to error conditions.
There exists three types of fans that can be on the NovaJet 500/630/
700 series printers.
A single fan, located behind (below for the NovaJet 750) the power
supply, is used for cooling the power supply. Air blows over the power
supply and the heated air is forced out of the printer.
A fan is located inside the platen with its fan vent seen from under
the platen on the right side of the printer. This fan provides suction
on the platen bed and holds the paper (media) flat during the printing
process. The 60 inch model has an additional suction fan located near
the center of the printer inside the platen.
Theory of Operation 2-17
Page 42

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
On the NovaJet 500/505/630/700 printers a media drying fan assembly
is attached to the lower part of the printer legs that is used to speed up
the drying time of the ink that is deposited onto the media. This is to
ensure that the ink is completely dry before the media is rolled onto the
take-up reel. The 42 inch model has five drying fans, while the 60 inch
version has seven.
The drying fan assembly has been designed to keep power consumption
down to a minimum by only activating the amount of fans that are
required to dry the size of media that is loaded on the printer.
The fans will not actually engage until a print command is first established. This commmand can be from a sent print job or any onboard
commands that require printing to complete that function. The fans
will automatically shutdown approximately 20 minutes after the print
is complete.
The drying assembly can also be disabled through the printers firmware
via the control panel.
This drying fan assembly is part of the mechanical take-up system that
is optional on the NovaJet 500 and 630 series printers.
On the NovaJet 750 printers a thermal media drying assembly is used
instead of the fan assembly as on the other models. It accepts control
commands from the MPWA that turns the heating elements on and off.
It also has two fans located underneath the plenum to push the heated/
unheated air out of the holes facing the platen to dry the media. The
drying assembly can be operated with or without the heating elements
being turned on.
2-18 Theory of Operation
Page 43

Maintenance
Introduction
This chapter contains general maintenance and cleaning instructions
for the NovaJet 500/630/700 printers.
Scheduled Maintenance
Scheduled maintenance consists of a list of checks that are planned to
be performed on a regular basis or when conditions warrant it.
3
Scheduled maintenance can be thought of as preventive maintenance
since its purpose is to prolong the life of the printer. It is not intended
to repair or isolate an existing problem, though it can sometimes be
helpful in detecting a condition due to a weakened component that has
not yet completely failed.
Below is a list of scheduled maintenance checks and their recommended periodicity.
Clean external areas: as required
Clean service station: 20-30 plot hours
Clean cartridge jet area & dimples: 50-60 plot hours
Clean slide shaft: 75-100 plot hours
Clean encoder strip: 75-100 plot hours
Clean flex cable contacts: 75-100 plot hours
Clean Y-Arm surface: 75-100 plot hours
Clean cutter groove: 75-100 plot hours
Clean pinch/lower roller: 75-100 plot hours
Clean platen vacuum holes: 100-125 plot hours
Clean dryer plenum (body) - NJ 750 only: 100-125 plot hours
Clean paper sensor: as required
Clean and inspect motor gears: annually
Clean and inspect MPWA: annually
Clean and inspect carriage assembly: annually
Reseat connectors on MPWA: annually
Reseat connectors on carriage board: annually
Replace carriage bushings: 3000 plot hours
MAINTENANCE
3-1
Page 44

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Cleaning Procedures
Always turn the printer OFF, remove the power cord and
the interface cable before cleaning the printer. An electrical shock hazard may be present if these procedures are
not followed.
External Cleaning
Do not use abrasive cleansers of any sort on the surfaces
of the printer. Damage to the surface may result.
WARNING
CAUTION
The exterior surfaces of the printer may be cleaned with a soft cloth
which has been dampened. For more persistent stains, a small amount
of liquid detergent or NovaKlean™ may be used. Cleaning intervals are
determined by the environment in which the printer is used.
Service Station Cleaning
Ink and dust may build up on the service station, resulting in contamination which may smear the prints. The service station is cleaned as
follows:
1. Turn the printer OFF. Disconnect the power cord and interface
2. Raise the printer lid.
3. Carefully move the carriage toward the center of the printer.
3-2 Maintenance
cable.
Page 45

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
4. Using a cotton swab dampened with water, wipe the seals and
the rubber wiper in the service station until no more ink
residue or dust can be removed.
5. With a dry swab, wipe all moisture from the seals and wipers.
6. Close the lid and reconnect the power cord and interface cable.
7. If the service station is filling with ink or very dirty it can be
removed and rinsed under warm water. To remove, pull the
tab on the right side of the service station and lift out. Wash,
dry thoroughly and replace by placing the left side in first then
pushing down on the right side until the tab locks it in place.
Slide Shaft Cleaning
CAUTION
Use only NovaKlean™ or isopropyl alcohol on the slide
shaft of the printer. Damage to the stainless steel slide
shaft may result if cleaned with water and not completely
dried off.
Printer problems can be caused by an accumulation of dirt or other
contamination on the slide shaft. This contamination may lead to drag
on the carriage. Extreme drag results in a “carriage axis failure” fault
and will stop the carriage motion. These problems may be eliminated
by maintaining and cleaning the slide shaft at intervals determined by
the environmental conditions. Do not use any lubrication.
To clean the slide shaft:
1. Turn the printer OFF. Disconnect the power cord and
interface cable.
2. Raise the printer lid.
MAINTENANCE
3. Moisten a clean cloth or paper wipe with NovaKlean™.
Maintenance 3-3
Page 46

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
4. Wipe the length of the slide shaft with the moistened cloth or
wipe.
5. Manually move the carriage assembly from side to side.
6. Wipe the shaft again to remove any deposits left from the
carriage.
7. Close the cover and reconnect the power cord and interface
cable, turn the printer ON and perform the PRIME procedure.
Be sure that the carriage moves freely on the slide shaft.
Linear Encoder Strip Cleaning
Clean the linear encoder strip every 75 - 100 plot hours (every 50 plot
hours if GO ink is being used) or as necessary to remove any buildup of
debris. NovaKlean™ followed by isopropyl alcohol should be used. You
may notice that it tends to fog the encoder strip; however, no detrimental effect has been observed in the field.
To clean the Encoder Strip:
1. Disconnect the power cord and interface cable.
2. Slightly dampen a cotton swab with NovaKlean™ and wipe
3. Slightly dampen a cotton swab with isopropyl alcohol and wipe
4. Reconnect the power cord and interface cable.
3-4 Maintenance
along the length of the encoder strip on both sides.
along the length of the encoder strip on both sides. This is
necessary to remove any possible residue that may have been
left from the NovaKlean™ solution.
Page 47

ENCODER STRIP
NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
COTTON SWAB
Figure 3-1. Encoder Strip Cleaning.
Cartridge Jet Area & Dimples Cleaning
CARTRIDGE
DIMPLE
AREA
MAINTENANCE
Figure 3-2. Cartridge Dimple Region.
Maintenance 3-5
Page 48

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
The cartridge dimple area can easily be contaminated by oils and dirt on
fingers and hands or ink spilled onto them. This causes the cartridges
to not receive some of the electrical signals for a proper firing of the jets.
This can be seen as a misfiring of the cartridge.
Care should be used when handling the cartridges. Avoid
touching the cartridges on the dimple area or on the inkjet
holes on the bottom. The oils and dirt on fingers and
hands can contaminate the area and result in misfiring
of the inkjets.
Clean the cartridge dimple area by gently dabbing the area with a lint
free cloth or cotton swab saturated with NovaKlean™.
Be sure to clean the yellow cartridge because it is not readily apparent
that it is dirty. The yellow ink is hard to see and could be overlooked.
Follow this up by gently dabbing the jet plate area on the bottom of the
cartridge.
NOTE
Flex Cable Contact Cleaning
3-6 Maintenance
Flex Cable
Contacts
Figure 3-3. Flex Cable Contacts.
Page 49

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Cleaning the flex cable contact area is very important due to the ease
of which this area can become dirty. The flex for the yellow cartridge
is deceiving because it is not readily apparent that it is dirty. This
also causes the cartridges to not receive all of the electrical signals for
a proper firing of the jets. This can be seen as a misfiring of the
cartridge.
NOTE
Care should be used when handling the flex cable contact area. Avoid touching the contact area because the
oils on your skin can contaminate the area and result
in misfiring of the inkjets.
Clean the flex cable contacts by gently dabbing the area with a cotton
swab soaked with NovaKlean™.
Clean and Inspect Stepper Motor Gears
The stepper motor gears can become dirty and after time if not
cleaned up, it could cause wide banding in the print. This will reduce
the quality of the intended output. Clean the motor gears with a stiff
brush to knock off any debris. A cotton swab soaked NovaKlean™
can be used to remove any ink that may have accumulated on the
gears.
Clean and Inspect MPWA
Foreign material on the MPWA could short out electrical signals
being developed on the MPWA and cause erroneous prints or even
damage to the MPWA. All electrical circuits should be free of foreign
material, especially those materials with conductive properties.
Clean the MPWA by blowing the objects away or gently brush them
aside with a soft brush if required.
Inspect the MPWA for any damage to the board, connections, or any
of the components on the board. Replace board if inspection reveals
any damage or flaws that could effect the function of the MPWA.
MAINTENANCE
Maintenance 3-7
Page 50

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Clean and Inspect Carriage Assembly
Foreign material on the carriage assembly could short out signals being
developed on the carriage assembly and cause erroneous prints or even
damage to the carriage assembly. A very common problem is where ink
has been spilled onto the carriage assembly. All electrical circuits
should be free of foreign material, especially those with conductive
properties.
Clean the carriage assembly by blowing the objects away or gently
brush them aside with a soft brush if required. Be careful not to let
anything to fall into the printer as you clean or it could cause a new
problem later.
Inspect the carriage assembly for any damage to the boards, connections, or any of the components on the assembly.
Reseat Connectors on MPWA and Carriage Board
Many problems can be corrected simply by removing and reseating
connections found in circuit assemblies. This process helps to clean the
contacts and can dissipate any static electrical charges that might have
developed.
3-8 Maintenance
CAUTION
Integrated circuits may become weakened or damaged by
electrical discharge. Do not touch or work near integrated
circuits without wearing an ESD wrist strap.
CAUTION
Ribbon connectors can be easily damaged if incorrectly
handled. Observe extreme caution when handling the
ribbon connectors to avoid damage.
Page 51

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
J9
J8
J1
J7
J15
J2
J15
J12
J3
J13
J4
J5
J6
J15
Figure 3-4. Main PWA Connection Locations.
MAINTENANCE
J15
Table 3-1. Main PWA Connections.
J1 Stepper Motor J10 not used
J2 Servo Motor J11 not used
J3 Leg Harness J12 Display Data
J4 AutoLoad Sensor J13 Keypad
J5 Vacuum Fan #1 J14 Serial I/O Port
J6 Vacuum Fan #2 J15 Power Supply
J7 Trailing Cable J16 not used
J8 Power Supply Cooling Fan J17 SIMM Sot
J9 Parallel I/O Port J18 SIMM Slot
Maintenance 3-9
Page 52

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
J5
J2
J1
J4
J3
Figure 3-5. Carriage PWA Connection Locations.
Table 3-2. Carriage PWA Connections.
J1 Black Drivers J5 Encoder Sensor
J2 Cyan Drivers J6 Trailing Cable
J3 Magenta Drivers J7 Paper Sensor
J4 Yellow Drivers
3-10 Maintenance
J6
J7
Page 53

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Figures 3-4 and 3-5 shows the locations of all the connectors on the
MPWA and carriage board respectively. To remove the ribbon cables
from their connectors, lift the connector’s ribbon locking mechanism as
shown in figure 3-6. To reattach, depress the locking mechanism back
into the locking position after inserting the ribbon cable end.
RIBBON
LOCKING
MECHANISM
UNLOCKED
LOCKED
MAINTENANCE
CONNECTOR
ASSEMBLY
Figure 3-6. Ribbon Connector Locking Mechanism.
Replace Carriage Bushings
The carriage bushings are rated for approximately 1500 hours of
operational usage. Many factors including, but not limited to, hours/
day used, cleanliness of the slide shaft and general ambient environment make it impossible to calculate the average time that the carriage
bushings to last.
If not replaced, the wear on the bushings can result in erratic carriage
motion and/or carriage axis failures. It can even cause the cartridge
head height to become uneven.
To replace the carriage bushings, follow the procedures for Carriage
Bushing Replacement found in Chapter 5.
Maintenance 3-11
Page 54

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Servo Motor Winding Resistance Check
Figure 3-7. Servo Motor.
1. Disconnect the servo motor connection from J2 on the MPWA.
2. Using a standard ohmmeter or multimeter, connect the meter
leads to the two wires going to the motor.
3. While manually rotating the servo motor, monitor the readings
on the meter. The acceptable range is 6-30 ohms. Typically,
the reading is 7-11 ohms.
4. If the measurement is found to be unsatisfactory, replace the
servo motor.
3-12 Maintenance
Page 55

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Stepper Motor Winding Resistance Check
7.2-8.0
RED
WIRE
Figure 3-8. Stepper Motor.
7.2-8.0
ohms
ohms
MAINTENANCE
1. Disconnect the stepper motor connection from J1 on the MPWA.
2. Using a standard ohmmeter or multimeter, measure between
pins 1 (red wire) and 3.
3. The reading should indicate 7.2-8.0 ohms.
4. Continue by measuring between pins 4 and 6.
5. Reading should also indicate 7.2-8.0 ohms.
6. If either measurement is out of tolerance, replace the stepper
motor.
Maintenance 3-13
Page 56

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Power Feed and Take-Up Motor Winding
Resistance Check
Figure 3-9. Power Feed and Take-Up Motor.
1. Remove the feed and/or take-up roll from the printer.
2. Using Phillips screwdriver, remove the four screws that secure
the cradle idler from the right leg.
3. Ease the cradle idler off of the leg enough to disconnect the
motor wires from the leg harness.
4. Using a standard ohmmeter or multimeter, measure between
the + and - connections on the motor. While manually rotating
the servo motor, monitor the readings on the meter. The
acceptable range is 25-40 ohms. Typically, the reading is 29-36
ohms.
5. If the measurement is found to be unsatisfactory, replace the
motor.
6. Perform the same procedure on the remaining motor.
3-14 Maintenance
Page 57

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Banding: Hardware vs Software
The technician must be able to identify whether the banding that is
being observed is related to either a hardware or a software problem.
The two examples in Figure 3-10 represent classic types of hardware
and software banding errors.
HARDWARE SOFTWARE
Figure 3-10. Examples of Banding.
Hardware banding is usually characterized by consistent banding
strips as shown. It signifies a slippage in the media’s normal movement that is possibly due to the stepper motor, lower drive shaft
assembly, pinch rollers, or the rollguides on the back of the printer.
All these possible faulty areas deal with a rotational movement that, if
faulty, will generate a consistent banding pattern. The MPWA and
Carriage PWA can also cause this type of error to incur.
Software banding is characterized by inconsistent banding lines.
These banding lines are generated by the software when the application incorrectly interprets the media advancing/ink firing sequence of
the expected print file. Because it is not directly tied to a mechanical
movement, the bands become inconsistent in both frequency and
duration. The possible causes are the printer driver, the original
software package, or the RIP, if one is used. To eliminate the chance
that it is the printer driver:
1) Remove any RIP or network systems and connect the printer
directly to the computer.
MAINTENANCE
2) Print a test file approved by ENCAD that uses only the
printer driver software and the ENCAD printer.
Maintenance 3-15
Page 58

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
If the test file prints correctly, the problem lies in either the software
package that generated the print or the RIP, if used.
A simple test to determine if the banding is caused by the computer/
RIP/application or the printer is to rotate the image 90 degrees and see
if the banding rotates or remains in the same orientation as the previous print. If the banding does not rotate, then look for causes in the
printer. If the banding does rotate with the image, then look for causes
in the computer/RIP or application.
Common Banding Causes
1. Uneven drying. Adjust the drying time to compensate for varying
ink percentages and media types. Dry time values range from
10 seconds to 60 minutes. This is especially important in higher
humidity environments.
2. The RIP (Raster Image Processor) and print cycles. We
recommend printing to a file first and then queuing the file to
the printer to avoid the RIP and print cycle delays that can
cause banding while printing.
3. Uneven inkjet kogation (partial clogging or orifice restriction) on
4. Lower quality print modes normally cause slight bands, to avoid
5. Air bubbles in the ink delivery system. This indicates a loss of
6. Improper priming. The lower secondary chamber within the
3-16 Maintenance
the inkjet cartridge head nozzles. Run the 100% color test and
re-prime or replace the cartridge if necessary.
this banding, switch to 4-pass or 6-pass printing modes.
negative pressure within the ink cartridge or ink delivery
system, check all quick release fittings and connections for
possible leaks and ensure that the cartridge is primed properly.
cartridge may de-prime and then temporarily recover after
entering the service station causing a momentary color drop out
in the print if the cartridge is improperly primed. Please
reference Technical Bulletin #97 for a more detailed
explaination and the corrective priming procedures.
Page 59

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
7. A flow restriction in the ink delivery system or ink starvation
in the cartridge. Ink starvation in the cartridge can be caused
by a broken valve in a quick release fitting or pinched tube in
the ink supply lines of the tubing/chain assembly. Check the
ink delivery system for any flow restrictions by disconnecting
the ink cartridge needle from the cartridge in question, raise
the tip of the needle and observe the rate that the ink flows
back into the reservoir. The ink should take approximately 1
inch per second to clear the 3.5 inch cartridge tubing between
the cartridge and the first quick release fitting (flowing back
toward the reservoir), if it takes longer than this, you may
need to replace a defective quick release fitting (near the
cartridge or the reservoir) or tubing/chain assembly.
8. Wiping during a print can sometimes cause a band of lighter
density color in the image. Auto wipe may need to be
temporarily turned off to prevent banding.
9. Operator intervention. If someone lifts up the media on the
take-up side of the printer while it is printing, it can cause
momentary banding in the print. Lifting up the media while
printing changes the inkjet head-to-media distance and will
effect the printed dot size and placement of the ink droplets.
10. Cartridge failures can cause banding — electrical cartridge
failures and partial clogging of the inkjets can produce
banding. With Inkjet Detection and Compensation
technology, electrical cartridge failures and clogging can be
corrected for up to 20 failures per cartridge with minimal
degradation of the output.
11. Media width variations causing the media to drag on the
media guides can cause banding. Check the edges of the
media for evidence of media drag and edge anomalies.
12. Lower quality dithering. Select the highest quality dithering
pattern in the printer driver. i.e. stochastic dithering.
13. Deadband and cartridge calibrations. If the deadband
calibration is off, or the cartridge calibration is off, it can
effect banding. Also, if one color seems to be causing the
banding — shifting the color calibration of that color +/-1 unit
may help.
MAINTENANCE
Maintenance 3-17
Page 60

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
14. Inkjet sputter. If the cartridge heater is set too high, inkjet
sputter may occur causing intermittent white spots throughout
the print.
15. Improper grounding or earthing. An improper A/C outlet power
ground may cause banding due to excessive noise on the line
between the neutral and ground. Ensure the outlet has a clean
zero ground potential with minimal noise between the neutral
and ground.
16. Static electricity. Using certain types of media (i.e. polyesterbased media), static electricity buildup within the media roll
may effect the un-roll resistance and cause momentary banding
to occur. However this has not been tested.
17. Data corruption may also effect banding. If you are using a
parallel cable that is too long or improperly shielded, the data
being sent to the printer may get corrupted and cause artifacts
in the print.
18. Overlapping images of different types on the same print may
create color bands between the images at the overlaps (i.e. RGB
images with CMYK images).
Alignments/Adjustments
The ENCAD NovaJet 500/630/700 printers are designed with a
minimum of maintenance requirements in mind. Calibrations include:
color calibration, deadband alignment, and X-axis calibration. The
mechanical adjustment requirements include the slide shaft profile and
cartridge head height adjustments. They do not require any electrical
alignments.
Slide Shaft Profile Adjustment
The NovaJet 500/630/700 printers Slide Shaft height is factory set and
is firmly mounted on the outer sides and only has adjustments in the
middle portion of the shaft, to remove any bowing of the shaft’s profile.
The following procedure is to ensure that the Slide Shaft is relatively
perpendicular to the surface of the Platen and to remove any bowing
that may be present in the shaft’s profile.
3-18 Maintenance
Page 61

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
The Slide Shaft is set to 1.418” (36cm) from the top of the Slide Shaft to
the Platen surface for the NovaJet 500, 630 and 700 series printers.
The normal operating range for the height of the Slide Shaft is between
1.390” (35.3cm) to 1.440” (36.6cm).
The NovaJet 505 Slide Shaft is set to 1.478” (37.5cm) from the top of
the Slide Shaft to the Platen surface. The normal operating range for
this height of the Slide Shaft is between 1.471” (37.4cm) to 1.483”
(37.4cm).
You will need the following:
· Height Gauge Kit Assembly
· 1/4" open and box end wrench (.110” thick)
Height Gauge (Alignment) Kit Contents are:
Dial Gauge Micrometer
Modified Novajet Cartridge for newer products
Modified Novajet 4/Pro/Pro 50 Cartridge - Not Used
Platen/Carriage Shaft Mounting Block
Calibration Jo Block (1.434”) - Not used
Plastic Gauge Card (0.011”) - Not used
There are two basic measurements that are to be made using
this kit (ensure power is off prior to performing these procedures):
1. Slide Shaft Profile Adjustment
2. Carriage (Cartridge) Head Height Setting
1. Connect the dial gauge micrometer to the Shaft mounting
block as shown in Figure 3-11.
ZERO
GAUGE
TIGHTEN SET
SCREW (NOT
SHOWN)
SHAFT
MOUNTING
BLOCK
MAINTENANCE
Figure 3-11. Dial Gauge Micrometer Assembly.
Maintenance 3-19
Page 62

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
2. Place gauge against left side of shaft assembly allowing
micrometer tip to rest directly on top of shaft. See Figure 3-12.
Zero the gauge (this is to become the reference point).
MEASURE
FIRST
Figure 3-12. Measurement Positions for Slide Shaft.
3. Measure the right side (next to media alignment mark.) and
note the difference. Divide this amount by two.
4. Measure just off the center of the slide shaft and adjust the
center turnbuckle with an open ended wrench if required, for
the average value (the value found in step 3.) See Figure 3-13.
MEASURE
LAST
ADJUST IF
NECESSARY
MEASURE
SECOND
NOTE
The NovaJet 500/630/700 60 inch models have two turn-
buckles, so both of these need to be adjusted together for
the center position.
3-20 Maintenance
Page 63

THESE ARE THE TURNBUCKLE
SCREWS. POSITION GAUGE
IN BETWEEN THE SCREWS
AND AS CLOSE TO CENTER
AS POSSIBLE.
NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
THIS IS THE INNER SCREW.
POSITION GAUGE DIRECTLY
IN FRONT OF IT.
Figure 3-13. Slide Shaft Profile Adjustment.
For example: If the Left = 0, Right = +0.004”, then the center should
be adjusted to + 0.002”. This will ensure a smooth plane of
travel for the carriage assembly. There are no adjustments
on either end of the shaft in all models.
MAINTENANCE
Maintenance 3-21
Page 64

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Head Height Alignment Procedure
Perform this procedure only when the encoder strip stabilizer has been
removed from the Y-Arm or whenever the alignment is in question.
The head height alignment procedure is to ensure that the correct
amount of distance exists between the cartridge jet plate and the Platen.
See Figure 3-14.
HEAD HEIGHT
Figure 3-14. Carriage Head Height Tolerance.
CARTRIDGE
JET PLATE
PLATEN
1. Remove the lid and the right cover of the printer. See Chapter 5
for procedures.
2. Obtain the 3 tools (Micrometer Dial Gauge, Test Cartridge, and
Measuring Tip Extender) from the Height Gauge Kit. Assemble
the tools as shown in Figure 3-15.
SPIN HEAD ON
MICROMETER GAUGE
TO FACE BACKWARDS
TIGHTEN SET
SCREWS
ENSURE TIP EXTENDS
BELOW CARTRIDGE
1/4" (6mm)
MICROMETER
DIAL GAUGE
TEST CARTRIDGE
MEASURING
TIP EXTENDER
Figure 3-15. Setting Up Tools from Height Gauge Kit.
3-22 Maintenance
Page 65

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
3. Place the test cartridge upright on a flat surface and ‘zero’ the
gauge by loosening the knob near the top and turning the dial
until the needle is at the ‘0’ position on the dial. Tighten the
knob. See Figure 3-16.
0
ZERO
GAUGE
ENSURE PRESSURE IS
PLACED ON THE REAR
OF THE CARTRIDGE
Figure 3-16. Zeroing the Micrometer Gauge.
4. Remove the Cyan ink cartridge. Snap the test cartridge with
the micrometer gauge into the position vacated by the Cyan
ink cartridge. See Figure 3-17. Ensure that the micrometer
can be read from the BACK of the printer.
MAINTENANCE
Figure 3-17. Test Cartridge Installed.
Maintenance 3-23
Page 66

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
5. Remove the hardware securing the support bracket of the ink
delivery system to the chain support. Move the support bracket
towards the center of the printer until the larger holes on the
support bracket line up with the holes on the chain support.
See Figure 3-18.
Figure 3-18. Support Bracket Placement.
6. Slightly loosen the screws located on the back of the Y-arm that
secures the stabilizer to the Y-arm.
CAUTION
7. While lifting up the measuring tip of the micrometer, slide the
8. Move the left end of the stabilizer bracket until the reading
3-24 Maintenance
Damage may occur to the micrometer
gauge if the Carriage is moved without
lifting up on the measuring tip. This action could also take the micrometer out
of alignment and foul the results of the
alignment.
Carriage to the left side of the stabilizer. Position it as close to
the screw as possible and drop the measuring tip onto the
platen. Do this a couple of times to ensure an accurate reading.
below is observed. Read only the RED numbers on the
micrometer gauge.
For NovaJet 500, 630 or 700 printers adjust for a reading of 67
+/- 3. This equates to a head height of 0.075”.
For the NovaJet 505 printer adjust for a reading of 17 +/- 3.
Page 67

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
CAUTION
Use extreme care when performing this
calibration on the NovaJet 505 printers.
The actual head height that is to be
achieved is 0.125” +/- 0.003”. The reading will only be correct if the gage rotated
one complete turn before stopping at 17.
If the head is adjusted for 0.025” instead
of 0.125” head strikes and quality issues
will be apparent.
NOTE
The actual measurement is different than the true head
height due to the fact that the test cartridge does not contain a jet plate assembly. A difference had to be calculated to compensate for the lack of a jet plate assembly on
the test cartridge.
MAINTENANCE
9. Tighten the screw on the left side of the stabilizer.
10. While lifting up the measuring tip of the micrometer, slide the
Carriage to the right until the next stabilizer screw is lined up.
Position it as close to the screw as possible and drop the
measuring tip onto the platen. Do this a couple of times to
ensure an accurate reading.
11. Move the left end of the stabilizer bracket until a correct
reading is observed. Read only the RED numbers on the
micrometer gauge.
12. Tighten the screw on the stabilizer that is next to the Carriage.
13. Continue performing steps 10 through 12 until all four of the
stabilizer screws have been adjusted.
Maintenance 3-25
Page 68

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
14. Reposition the Carriage to all of the adjustment positions and
verify that the measurements are correct.
15. Perform steps 6 through 14 as many times as necessary to
correctly accomplish this adjustment.
16. Install the ink delivery system support bracket following the
procedures located in Chapter 5.
Color Calibration
This procedure describes how to check that the cartridges are properly
aligned for color plotting and should be followed each time the ink
cartridges are installed. Figure 3-18 is a representation of how a color
calibration looks when printed.
Y
M
COLOR VERTICAL HEAD-TO-HEAD CALIBRATION
-6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4
COLOR HORIZONTAL HEAD-TO-HEAD CALIBRATION
Current Heads (Y, M, C)
Figure 3-19. Color Calibration.
C
C
M
Y
56
3-26 Maintenance
Page 69

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
The “Current Heads (Y, M, C)” view represents the alignment of the
heads as they are currently entered. This is just an overview of all
heads and how they are aligned. Do not attempt to align the heads
using this view.
The “Color Horizontal Head-to-Head Calibration” checks the alignment
of the nozzles horizontally and allows corrections when required. Just
enter the value below the set of lines that are correctly aligned. Be
careful that you are aligning the correct color by observing the C (cyan),
M (magenta), and Y (yellow) on the right side of the plot.
The “Color Vertical Head-to-Head Calibration” checks the alignment of
the nozzles vertically and allows corrections when required. Just enter
the value below the set of lines that are correctly aligned. Be careful
that you are aligning the correct color by observing the C (cyan), M
(magenta), and Y (yellow) on the right side of the plot.
To perform the Color Calibration:
1. Select “Utility Menu” from the Main Menu. This brings up the
Utility Menu as shown in Figure 3-19.
MAINTENANCE
Prime
Access Cartridge
Color Calib Menu
Calibration Menu
Figure 3-20. Utility Menu.
*
Display Settings
Print Settings
Service Menu
Exit
Maintenance 3-27
Page 70

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
2. From the Utility Menu, select “Color Calib Menu”. This brings
up the color calibration menu and it looks like Figure 3-20.
Cyan Vertical
Magenta Vertical
Yellow Vertical
Calib Print Test
Figure 3-21. Color Calib Menu.
3. Select “Calib Print Test” to print the color calibration plot as
shown in Figure 3-18.
4. When the plot is complete, select “Cyan Vertical” at the Color
Calib Menu. This brings up the options menu for the cyan
vertical adjustment as shown in Figure 3-21.
Cyan Vertical
Next Option
*
*
Cyan Horizontal
Magenta Horizontal
Yellow Horizontal
Exit
Cancel
5. Observe the plot and using either “Prev Option” or “Next
3-28 Maintenance
<>
selected
Prev Option
Figure 3-22. Cyan Vertical Options Menu.
Option”, rotate through the selections until the one that best
aligns the cyan color on the plot is selected. Press “Ok” to
accept the selection and return to the Color Calib Menu.
Ok
Page 71

6. Continue until all six calibrations on the Color Calib Menu have
been accomplished.
Deadband Alignments
Deadband calibration compensates for minute differences created when
bidirectional printing is used. Unidirectional printing is not affected by
deadband. There are four types of deadband tests:
Deadband
Slow Deadband
All Lines Tests
Single Line Test
Figure 3-23. Slow Deadband.
NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
MAINTENANCE
Figure 3-22 shows what the display will look like when printing the
slow deadband test if it is out of alignment. A correctly aligned printer
will appear as if there is only a series of vertical lines printed. No
difference between the top and bottom set of lines to the center set of
lines would be appearant.
The SLOW DEADBAND calibration is a precision test that checks the
firing time of the jets as related to the forward and reverse direction.
Allowable values for the Slow Deadband calibration is -2, -1, 0, 1 and 2.
The Single Line Test and All Line Test are variations of the deadband
test except they print longer lines so that long time integration of the
deadband calibration can be observed. The Single Line Test prints only
one line at a time while the All Line Test prints all lines at the same
time. These tests were designed primarily to be used in manufactoring
only.
The deadband test on a NovaJet 500 series printer will look like the
display in Figure 3-22 and the procedures to adjust the values are in the
following section.
Maintenance 3-29
Page 72

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Allowable values for the Deadband calibration on the 500 series printers
is from 0 to 120.
The deadband test on a NovaJet 630 or 700 series printer will print a
display similiar to Figure 3-22 but will print the pattern for each of the
four colors. This is just a visual check of the color deadband alignment.
No adjustments can be made for this test. To make adjustments, if
needed, see the Color Deadband Calibration section.
Allowable values for the Color Deadband calibrations on the 630/700
series printers is from 0 to 120 but the actual value used by the printer
will only accept certain numbers. The real value used by the printer
will be the closest of 12, 20, 28, 36, 44, 52, 60, 68, 76, 84, 92 or 100.
To perform the Slow Deadband Alignment
1. Select “Utility Menu” from the Main Menu. This brings up the
Utility Menu as shown in Figure 3-19.
2. Select the “Service Menu” from the Utility Menu. This brings
up the Service Menu as shown in Figure 3-23.
3. Select the “Calibration Menu” from the Service Menu.
4. The Calibration Menu is shown in Figure 3-24 for the 500 series
3-30 Maintenance
Calibration Menu
Diagnostics Menu
Figure 3-24. Service Menu.
and Figure 3-25 for the 630/700 series and is where the
deadband tests are performed. Select “Slow Db Test” to run the
slow deadband test.
*
Cartridge Info.
About
Test Print
Exit
Page 73

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Deadband Test
Slow Db Test
Single Line Test
All Lines Test
Figure 3-25. Calibration (Deadband) Menu (500 Series).
Deadband Test
Slow Db Test
Figure 3-26. Calibration (Deadband) Menu (630/700 Series).
Single Line Test
All Lines Test
*
*
Deadband
Slow Deadband
Exit
Slow Deadband
Exit
MAINTENANCE
5. When the plot is complete, select “Slow Deadband” at the
Calibration Menu. This brings up the options menu for the
slow deadband adjustment. This menu is similiar to the
menu depicted in Figure 3-21.
6. Observe the plot and using either “Prev Option” or “Next
Option”, rotate through the selections until the value you
want is selected. Press “Ok” to accept the selection and
return to the Calibration Menu.
7. Continue performing steps 4 through 6 until the slow
deadband adjustment is correct.
Maintenance 3-31
Page 74

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Deadband Alignment (for 500 Series)
The deadband alignment is necessary to ensure that the output images
are being produced with the highest quality standards available while
using the ENCAD printer in a bidirectional mode.
This adjustment helps to compensate for any deviations that may have
become apparent due to the carriage speed and/or the type of media
loaded. Precise calculations are being performed to time the release of
the ink drop so that they land on the media at the correct location.
Differences in media thickness make the distance that the ink has to
fall vary and this variable needs to be compensated for in the calculations.
To perform the Deadband Alignment for the 500 Series printers
1. Select “Utility Menu” from the Main Menu. This brings up the
Utility Menu as shown in Figure 3-19.
2. Select the “Service Menu” from the Utility Menu. This brings
up the Service Menu as shown in Figure 3-23.
3. Select the “Calibration Menu” from the Service Menu.
4. The Calibration Menu is shown in Figure 3-24 and is where the
5. When the plot is complete, select “Deadband” at the Calibration
6. Observe the plot and using either “Prev Option” or “Next
7. Continue performing steps 4 through 6 until the slow deadband
3-32 Maintenance
deadband test is performed for the 500 series printers. Select
“Deadband Test” to run the deadband test.
Menu. This brings up the options menu for the deadband
adjustment. This menu is similiar to the menu depicted in
Figure 3-21.
Option”, rotate through the selections until the value you want
is selected. Press “Ok” to accept the selection and return to the
Calibration Menu.
adjustment is correct.
Page 75

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Color Deadband Alignment (for 630/700 Series)
The color deadband alignments are necessary to ensure that the output
images are being produced with the highest quality standards available
while using the ENCAD printer in a bidirectional mode.
These adjustments help to compensate for any deviations that may have
become apparent due to the carriage speed and/or the type of media
loaded. Precise calculations are being performed to time the release of
the ink drop so that they land on the media at the correct location.
Differences in media thickness make the distance that the ink has to
fall vary and this variable needs to be compensated for in the calculations.
To perform the Color Deadband Alignments for the 630/700 Series
1. Select “Utility Menu” from the Main Menu. This brings up the
Utility Menu as shown in Figure 3-19.
MAINTENANCE
2. Select the “Calibration Menu” from the Utility Menu. This
brings up the Calibration Menu as shown in Figure 3-26.
Use Calib XY
Paper Axis Test
Color Db Menu
Figure 3-27. Calibration Menu.
3. Select the “Color Db Menu” from the Calibration Menu.
4. The Color Db Menu is shown in Figure 3-27 and is where the
color deadband test is performed.
*
Open Jet Menu
Paper Axis
Exit
Maintenance 3-33
Page 76

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Black Deadband
Cyan Deadband
Magenta Deadband
Yellow Deadband
Figure 3-28. Color Db Menu.
Select “Color Db Test” to run the color deadband test.
The test consists of 12 default calibration settings. When the
test is run it will print out a pattern of 5 calibration lines for
each of the 12 settings. It will print this pattern in black first,
followed by cyan, magenta and then yellow. Also printed will be
the current settings for each of the four colors as well as the
slow deadband setting.
5. When the plot is complete, select “Black Deadband” at the Color
Db Menu. This brings up the options menu for the black
deadband adjustment. This menu is similiar to the menu
depicted in Figure 3-21.
*
Color Db Test
Exit
3-34 Maintenance
NOTE
The only acceptable values for the color deadband
adjustments are 12, 20, 28, 36, 44, 52, 60, 68, 76,
84, 92 and 100. Any other value entered will appear to be accepted because it will be displayed in
the current settings section the next time this
test is run. In actuality, the system will default
to the closest allowable setting as listed above.
Page 77

6. Observe the plot and using either “Prev Option” or “Next
Option”, rotate through the selections until one that seems
closer to the correct value is selected. Press “Ok” to accept the
selection and return to the Color Db Menu.
7. Continue performing steps 4 through 6 until the all color
deadband adjustments are correct.
Paper Axis Calibration
The paper axis calibration procedure ensures that the processing that
drives the stepper motor is correct to minimize line length accuracy
errors.
NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
To perform the paper axis procedure:
1. Select “Utility Menu” from the Main Menu. This brings up the
Utility Menu as shown in Figure 3-19.
2. From the Utility Menu, select “Calibration Menu”. This brings
up the Calibration Menu as shown in Figure 3-26.
3. From the Calibration Menu, select “Use Calib XY.” Ensure that
Use Calib XY is set to ON and press “Ok.” This allows the
printer to store the data that is entered in step 7.
4. From the Calibration Menu, select “Paper Axis Test”. This runs
the paper axis test which prints out two “T” figures that are
mirrored from each other and about 33” apart. See Figure 3-28.
MAINTENANCE
Maintenance 3-35
Page 78

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Figure 3-29. Paper Axis Test.
5. With a precision drafters measuring stick, measure the exact
distance from each of the “T” intersections.
33"
6. Select “Paper Axis” at the Calibration Menu. This brings up
7. Using either “Prev Option” or “Next Option”, rotate through the
3-36 Maintenance
the options menu for the paper axis adjustment. This menu is
similiar to the menu depicted in Figure 3-21.
selections until the exact value of the measurement found in
step 5 is selected. Press “Ok” to accept the selection and return
to the Calibration Menu.
Page 79

Diagnostics Menu
The Diagnostics Menu is located in the Service Menu (shown in
Figure 3-23) and is seen in Figure 3-29.
NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Servo PWM Test
Servo Cycle Test
Accessory Menu
Figure 3-30. Diagnostics Menu.
All tests under the Diagnostics Menu should be performed by
competent technicians only. The types of tests that can be performed are: Servo PWM Test, Servo Cycle Test, Carriage Test, Color
Test, Continuous Test, Fan #1 Test, Fan #2 Test and Legs Test.
The Fan #1 Test, Fan #2 Test and Legs Test are located in the
Accessory Menu as shown in Figure 3-30.
Fan#1Test
*
*
Carriage Test
Color Test
Continuous Test
Exit
MAINTENANCE
Fan#2Test
Legs Test
Figure 3-31. Accessory Menu.
Exit
Maintenance 3-37
Page 80

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Servo PWM Test - Monitors the PWM (pulse width modulation)
signal applied to the servo motor from the driver on the MPCB
to check the amount of force required to move the Carriage.
The test performs three complete cycles of the carriage
assembly and lists the average PWM, the maximum PWM, and
the position of the carriage where the maximum PWM occured.
Servo Cycle Test - Tests the servo motor by moving the carriage
back and forth across the slide shaft. The number of cycles is
selectable and the available options are:
10
100
1,000
10,000
100,000
1,000,000.
Carriage Test - Prints 5 sets of 3 parallel lines to test the vibration
characteristics of the carriage assembly.
Color Test - The Color Test prints a wide swath of each color (total
of four) to test for banding. The test is selectable in the amount
of ink that is to be printed. The available are: 10%, 25%, 35%,
50%, 65%, 75%, and 100%.
Continuous Test - The Continuous Test sends the printer into a test
loop that will perform a series of tests continuously. Powering
down and restarting the printer is the only way of exiting this
test loop.
3-38 Maintenance
Page 81

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
The Continuous Test will first prime the cartridges,
followed by a serial port test, parallel port test, a fast
deadband display and a color calibration display.
The deadband and color calibration displays are used only
as a visual inspection of the operating condition of the
printer. No adjustments can be performed while in the
Continuous Test mode.
A loopback Test Cable is required to correctly accomplish
the serial and parallel port tests. Install both ends of the
Loopback Cable before running this test. The Loopback Test
Cable is listed in Chapter 6.
After completing the deadband display, the test will begin
again with the prime and continue until power is removed.
Fan #1 and Fan #2 Tests - Tests the operation of the fans on the
printer. Fan #1 Test (while depressed) turns on the power
supply cooling fan and the suction fan inside the platen on
the right side of the printer. Fan #2 Test (while depressed)
turns on the suction fan inside the platen near the center of
the printer. The 42 inch printer does not have this second
suction fan, therefore, the Fan #2 Test is disabled.
Legs Test - Tests the condition of the leg harness connections
and the components of the power feed and take-up system.
MAINTENANCE
Maintenance 3-39
Page 82

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Limited Access Menu
A menu that is not accessable to the operators can be activated in the
Service Menu as shown in Figure 3-31. Press the lower left button in
the Service Menu to bring up the Code Menu. The code to be entered to
bring up the hidden menu is “16753.”
Calibration Menu
Diagnostics Menu
PRESS
*
Code 1
Code 2
Code 3
Code 4
ENTER "16753" TO GET...
Clear NVRAM
Clock Reset
*
About
Exit
Code 5
Code 6
Code 7
Exit
*
Exit
3-40 Maintenance
Figure 3-32. NVRAM Clear and Clock Reset Menu.
Page 83

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
This menu allows the technician to clear the NVRAM and to reset the
system clock.
Clear NVRAM - Clearing the NVRAM is required anytime that a
MPWA is to be permanently removed from a printer. The NVRAM is
a section of nonvolatile memory that stores printer size information.
The MPWA is the identical for both printers but it will have to learn
which size printer it is installed in. Clearing the NVRAM allows the
MPWA to relearn which size printer it is reinstalled into.
Clearing the NVRAM also resets all values to their default settings,
including the clock. After clearing the NVRAM, all user settings and
electrical calibrations will be lost and needs to be performed again.
Clock Reset - Resets the system clock to “000.” This procedure should
only be accomplished when refurbishing a MPWA and installing it
into another printer.
Firmware Download/Upgrading for the PC
The normal method of downloading new firmware is to send the file as
if it was a standard print job.
To perform the firmware download, follow the steps listed below:
1. Power OFF printer, wait 15 seconds.
2. Connect parallel printer cable between the printer and PC.
3. Turn the printer ON.
4. Obtain the latest firmware for your NovaJet 500, 505, 630,
700, 736 or 750 printer. Save both of the files to the same
directory on the hard drive. Double click on XXXX.EXE file to
inflate the compressed files. The file name might be different
then listed above.
5. Go to a DOS environment and from within that same
directory type: GO XXXX.ROM and press Enter. The
firmware is sent to the printer as an ordinary print job.
MAINTENANCE
Maintenance 3-41
Page 84

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
For NT3.5x or NT4.0 systems click on “Start” - “Programs”, “Command Prompt.” At the “dos” prompt go to
the location of the .ROM (i.e.: if the .ROM file is on a
floppy disk, type A: and press Enter.
Then type: PRINT /D:LPT1 A:\XXXX.ROM and
press Enter.
6. Wait approximately 20 to 40 seconds later until you hear a
SINGLE beep, indicating the download was successful. You may
encounter a set of double beeps shortly after sending the
firmware file, but you must wait until you hear the SINGLE
beep.
7. After hearing the single beep, remove power from printer for 1520 seconds. Apply power to the printer. The printer should
initialize properly. Verify firmware revision by sequencing
through Utility Menu - Service Menu - About menu.
Verify firmware has been incorporated.
NOTE
8. If the firmware download is not successful you may hear more
than 1 beep or complete silence. Check parallel port connections
and return to step 5.
Firmware Download/Upgrading for the MAC
The normal method of downloading new firmware is to send the file as if
it was a standard print job.
1. Power OFF printer, wait 15 seconds.
2. Connect an Image Writer II cable between the printer and
MAC.
3. Turn the printer ON.
3-42 Maintenance
Page 85

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
4. Obtain the latest firmware revision, unpack the file and
launch the “XXX Firmware Utility.” File names may be
different then that listed above.
Click on “File”
Click on “Preferences”
Select the appropriate port that your printer is connected to
(either Modem or Printer.)
Drag and Drop the XXXX.ROM file (or the latest version)
into the “Spool Folder”.
Wait approximately 20 to 40 seconds later until you hear a
SINGLE beep, indicating the download was successful. You
may encounter a set of double beeps shortly after sending
the firmware file, but you must wait until you hear the
SINGLE beep.
5. After hearing the single beep, remove power from printer for
15-20 seconds. Apply power to the printer. The printer
should initialize properly. Verify firmware revision by
sequencing through Utility Menu - Service Menu -
About menu. Verify firmware has been incorporated.
If the firmware download is not successful you may hear
more than 1 beep or complete silence. Check port
connections and return to step 4.
MAINTENANCE
Maintenance 3-43
Page 86

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Internal Cabling and Signal Flow Diagrams
Figures 3-32 through 3-34 are schematics of the major components and
the cabling associated between them. The diagrams depicts component
boards or assemblies, jack connections, cables, and signal flow. It is to
be used by the technician as an additional aid in troubleshooting and
improve understanding of the printers theory of operation.
Figure 3-32 shows all cable connections to the MPWA and the power
supply. Figure 3-33 shows all cable connections to the carriage PWA
and Figure 3-34 shows all connections of the leg harness assembly.
3-44 Maintenance
Page 87

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
J1
1
J7
TRAILING
STEPPER
2
3
CABLE
MOTOR
4
5
1
J8
+24V
0V/+24V
COOLING
LEG HARNESS
ENABLE
J4
MAIN
LOAD
SENSOR
+5V
GND
1
2
CIRCUIT
PRINTED
SENSOR OUT
3
4
BOARD
J5
FAN 1
VACUUM
+24V
0V/+24V
1
2
FAN 2
VACUUM
+24V
0V/+24V
J6
1
2
3
3
SERVO
MOTOR
J2
6
1
J3
2
3
MAINTENANCE
2
J9
FAN
PARALLEL
J12
J13
J14
SERIAL
KEYPAD
DISPLAY
J15
P2
1
GND
+24V
1
2
2
3
GND
GND
3
4
4
SWITCHING
1
2
P1
LINE
NEUT
AC INPUT
& PWR SWITCH
Figure 3-33. MPWA Connections Diagram.
Maintenance 3-45
SUPPLY
POWER
3
GND
Page 88

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
1
2
3
4
5
CART COM
3
4
+5V
5
EXB
6
EXA
6
TRAILING CABLE
J7
+24V
+24V
CART COM
J1
1
2
7
CART COM
7
8
CLK+
8
MAIN
BOARD
CIRCUIT
PRINTED
21
22
23
24
25
23
+24V
CART COM
24
25
26
+24V
26
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
+5V
CART COM
HEAD STROBE
18
19
DAN
PSIN/PWM
21
22
20
CART COM
CLK-
GND
DATA 1-
DATA 1+
9
10
11
12
13
DATA 2+
14
DATA 2-
CART COM
15
16
LATCH
17
3-46 Maintenance
PCB
CARRIAGE
1
2
3
J2
J1
EXA
GND
1
2
OPTICAL
ENCODER
4
EXB
+5V
3
4
SENSOR
1
2
3
4
J4
YELLOW
J5
MAGENTA
J3
PSIN
+5V
+5V
GND
J1
1
2
3
4
PCB
PAPER
SENSE
J7
J6
CYAN
BLACK
DRIVERS
CARTRIDGE
Figure 3-34. Carriage PWA Connections Diagram.
Page 89

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
LEG HARNESS
PLATEN HARNESS
J3
1
1
+24V
FEED SENSOR
1
DRYER FAN 1
FEED SENSOR
2
3
4
2
3
4
GND
+24V
2
3
TAKE-UP SENSOR
5
5
GND
TAKE-UP SENSOR
4
5
DRYER FAN 6
DRYER FAN 3
DRYER FAN 2
DRYER FAN 5
DRYER FAN 4
DRYER FAN 7
MAINTENANCE
ASSEMBLY
16
16
N.C.
16
17
17
+24V
DRYING FAN 1
17
18
18
18
DRYER FAN
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
DRYING FAN 7
DRYING FAN 5
DRYING FAN 3
DRYING FAN 6
DRYING FAN 4
DRYING FAN 2
N.C.
N.C.
21
19
22
20
23
24
25
26
FEED MOTOR
TAKE-UP MOTOR
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
FEED RTN
FEED PWR
TAKE-UP RTN
TAKE-UP PWR
N.C.
6
7
8
9
10
11
FAN INTLK
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
12
13
14
15
MAIN
BOARD
CIRCUIT
PRINTED
Figure 3-35. Leg Harness Connections Diagram.
Maintenance 3-47
Page 90

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
DRYER
THERMAL
SUBA SSE MBLY
3
J1
SUPPLY SENSOR
TAKE -U P SENSOR
LEG HAR NESS
PLATEN HARNESS
123456789
123456789
GND
+24V
+24V
SUPPLY SENSOR
TAKE-UP SENSOR
123456789
J6
SUPPLY MOTOR
GND
SUPPLY RTN
+5V DRYER
+24V SUPPLY PWR
+24V TAKE-UP PWR
71121114
TAKE-UP MOTOR
1011121314151617181920212223242526
1011121314151617181920212223242526
TAKE-UP RTN
DRYER GND
DRYER +24V
1011121314151617181920
DRYER FAN 1
DRYER FAN 8
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
13
DRYER FAN 7
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
2122232425
N.C.
N.C.
26
Figure 3-36. Leg Harness Connections Diagram (750).
3-48 Maintenance
MAIN
WIRING
PRINTED
ASSEMBLY
Page 91

Troubleshooting
Introduction
Chapter 4, Troubleshooting consists of a table that is intended to aide
the technician in troubleshooting the Novajet 500/630/700 Series
printers. This table addresses symptoms with their possible causes
and solutions.
Basic troubleshooting skills will be required to perform the symptom
identification, troubleshooting, fault isolation, and repair of the printer
when using this table.
Ensure that all applicable software diagnostic tests have been properly
executed, all visual indications (including LED status) have been
observed, and all applicable pushbuttons have been depressed to obtain
a complete list of symptoms to be applied to the table below.
Use the table in conjunction with Chapter 3, Maintenance, whenever
the table prompts you for additional information. This information
may be in the form of an illustration, additional data, or a procedure
that needs to be performed.
4
SHOOTING
TROUBLE-
Table 4-1. Troubleshooting Table.
Symptoms Possible cause Solution
No Power
• printer not ON depress power
switch
• faulty power replace power cord
cord
• AC input not replace AC entry
present at power module
supply
4-1
Page 92

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Table 4-1. Troubleshooting Table (cont).
Symptoms Possible cause Solution
No Power (cont) • DC output replace power
Initialization Failure
voltage not supply
present (see
Figure 3-32 for
pin-out)
• DC voltage replace MPCB
present at MPCB
• SIMM unseated, reseat or replace
defective or missing SIMM
• faulty take up or replace motor
feed motor (if
installed)
Media Does Not Move
4-2 Troubleshooting
• faulty leg harness disconnect at J3 on
cable MPCB to test,
replace as necessary
• power supply replace power
defective supply
• trailing cable replace trailing
defective cable
• perform Stepper replace stepper
Motor Winding motor if out of
Resistance check tolerance
• rough motion bad bearings while spinning replace stepper
stepper motor motor
Page 93

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Table 4-1. Troubleshooting Table (cont).
Symptoms Possible cause Solution
Media Does Not • paper sensor replace paper
Move (cont) not responding sensor
• media control driver corrupted -
switches are reload printer
operating correctly driver
• firmware reload firmware
corrupted
• bad MPCB replace MPCB
• ESD discharge ensure that all ESD
components are
properly installed
then replace MPCB
Internal ERROR “Carriage Axis Failure”
• dirty (or perform Slide Shaft
lubricated) slide Cleaning procedure
shaft
SHOOTING
TROUBLE-
• perform Servo replace servo motor
Motor Winding
Resistance check
• check servo bad bearings -
motor for smooth replace servo motor
movement
• obstruction in remove obstruction
path of carriage
(may or may not
be visible)
Troubleshooting 4-3
Page 94

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Table 4-1. Troubleshooting Table (cont).
Symptoms Possible cause Solution
Internal ERROR • dirty encoder perform Encoder
“Carriage Axis strip Strip Cleaning
Failure” (cont) procedure
• dirt under the remove carriage
carriage bushings bushings and clean
• damaged replace encoder
encoder strip strip
• bad encoder replace encoder
sensor sensor
• worn carriage replace carriage
bushings bushings
• loose trailing remove power and
cable connections reseat trailing cable
connections at the
MPCB and the
carriage assembly
4-4 Troubleshooting
• cutter assembly replace cutter
malfunction assembly
• damaged 1) check idler/
carriage drive tension assembly
belt system
2) check carriage
belt
• faulty trailing replace trailing
cable cable
Page 95

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Table 4-1. Troubleshooting Table (cont).
Symptoms Possible cause Solution
Internal ERROR “Encoder Sensor Failure”
• encoder sensor reseat encoder
cable unseated sensor cable
• bad encoder replace encoder
sensor sensor
Internal ERROR “Paper Sensor Failure”
• servo motor reattach connections
and vaccuum fan correctly (use Figure
connections to 3-4 for reference)
MPCB are switched
• paper sensor reseat paper
cable unseated sensor cable
• bad trailing cable replace trailing cable
SHOOTING
TROUBLE-
• bad paper replace paper
sensor sensor
• servo motor check servo motor
disconnected connections
• trailing cable reseat trailing cable
connection is
faulty
Troubleshooting 4-5
Page 96

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Table 4-1. Troubleshooting Table (cont).
Symptoms Possible cause Solution
Internal ERROR “Auto-Sensor Failure”
Internal ERROR “MPCB Failure”
Unrecognized Cartridges Error
•auto-sensor reseat autocable unseated sensor cable
• bad auto- replace autosensor sensor
• bad MPCB replace MPCB
• faulty connection check cartridges
of cartridge ID
chip to flex cable
4-6 Troubleshooting
• wrong cartridges check cartridges
installed
• carriage flex check flex driver
cable disconnected cable connections
• trailing cable reseat trailing
connections cable
• faulty trailing replace trailing
cable cable
• faulty carriage replace carriage
PCB PCB
Page 97

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Table 4-1. Troubleshooting Table (cont).
Symptoms Possible cause Solution
Image Skews or Moves
• dirty encoder clean encoder
strip strip (top and
bottom)
Does Not Print
• bad connection reseat cable
between computer connections on
and printer computer and
printer
• firmware is refresh EEPROM
corrupted firmware with new
download
• faulty quad flex replace quad flex
cable cable or complete
carriage assembly
• bad MPCB replace MPCB
SHOOTING
TROUBLE-
Ink Cartridge Misfiring
• cartridge low on refill or replace
ink cartridge
• firing rate set adjust firing rate
too fast lower (optimum
is 5)
Troubleshooting 4-7
Page 98

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Table 4-1. Troubleshooting Table (cont).
Symptoms Possible cause Solution
Ink Cartridge • ink drop out lower ink pre-heat
Misfiring (cont) (ink starvation settings
resembling
intermittent
banding)
• flex contacts 1) perform Flex
dirty or damaged Cable Contact
Cleaning
procedures
2) replace carriage
assembly
• cartridge dimple 1) perform
area dirty or Cartridge Dimple
damaged Cleaning procedure
2) replace cartridge
• cartridge not reseat cartridge
seated correctly
• bad cartridge replace cartridge
• service station 1) perform Service
dirty or not Station Cleaning
properly sealing procedures
cartridge jet area
2) replace seal on
service station
• bad carriage replace carriage
assembly assembly
• bad MPCB replace MPCB
4-8 Troubleshooting
Page 99

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Table 4-1. Troubleshooting Table (cont).
Symptoms Possible cause Solution
Paper Skewing
• paper guides not install paper
installed guides
• stepper motor perform Clean and
gearing dirty or Inspect Stepper
damaged Motor Gears
procedure
• lower roller tighten screws
loose securing lower roller
Printer Output is Banding (Horizontal)
• if banding is 1) inspect and/or
consistent replace stepper
motor (perform
Stepper Motor
Winding Resistance
Check)
SHOOTING
TROUBLE-
2) inspect and/or
replace stepper
motor gears and/or
lower roller
assembly
3) replace MPCB
• check amount replace or refill
of ink in cartridges cartridges
• cartridges need perform Prime
to be primed
Troubleshooting 4-9
Page 100

NovaJet 500/630/700 Series Service Manual
Table 4-1. Troubleshooting Table (cont).
Symptoms Possible cause Solution
Printer Output is • color calibration perform Color
Banding (Horizontal) required Calibration
(cont)
• paper axis perform Paper Axis
calibration Test Calibration
required
• faulty or corrupt reload firmware
firmware
• cartridge dimple 1) perform
area dirty or Cartridge Dimple
damaged Cleaning procedure
2) replace cartridge
• flex cable 1) perform Flex
contacts dirty or Cable Contact
damaged Cleaning
4-10 Troubleshooting
2) replace carriage
assembly
• carriage check carriage
assembly assembly for proper
obstructed movement along
Y-arm
• carriage belt is reinstall, check
loose, too tight, tension assembly,
worn, or damaged and/or replace belt
• carriage bushings replace bushings
worn or damaged
• corrupted clear NVRAM
NVRAM
 Loading...
Loading...