Page 1

Titrimetric Determination of Hypo Index, Thiosulfate, and Sulfite in EASTMAN Color Films,
Process ECN-2 Fixer
ECN-0002/1
Process ECN-2 ECP-2D VNF-1/LC RVNP
Formulas F-34a/F-34aR — — —
INTRODUCTION
This method describes the titrimetric determination of hypo
index (total reductants), thiosulfate, and sulfite in
EASTMAN Color Films, Process ECN-2, fixers. It is
recommended that these determinations be carried out by a
potentiometric titrimetric approach, using an auto-titrator.
However, for those unable to use instrumentation, the
manual titrimetric technique, using the visual starch
indicator, is included.
For the potentiometric measurement, a Metrohm
Potentiograph, Model E536 or equivalent should be us ed.
The potentiometric titration requires a platinum indicator
electrode and a double-junction reference electrode.
The Hypo Index (HI) or total reductants of a fixer is
defined as the millilitres of 0.1 N iodine consumed by the
thiosulfate and sulfite combined (reaction 1 & 2), in a
specified volume of fixer. The fixer is added to an excess of
iodine (liberated from the reaction of potassium iodate and
potassium iodide under acidic conditions - reaction 3). The
unreacted iodine is titrated either potentiometrically or
visually with standardized sodium thiosulfate from the
appropriate capacity burette. The difference between the
blank titration and the sample titration represents the
milliequivalents of iodine consumed by the sample.
Dividing the milliequivalents of iodine by 0.1 meq/mL
yields the HI of the sample. Hypo index is reported in the
terms of HI(1), mL which is the millilitres of 0.1000 N I
consumed by 1.0 mL of sample.
2
The thiosulfate is determined by the visual titration by
adjusting the pH of a sample aliquot to 8.5. At this pH, the
sulfite rapidly forms the stable sulfite - formaldeh yde
adduct. Upon acidification, which prevents the adduct from
reacting with iodine, the thiosulfate from the sample is
titrated with standardized iodine reagent to a starch end
point.
The sulfite content is calculated by subtracting the
milliequivalents of iodine consumed by the thiosulfate from
the milliequivalents of iodine consumed by the thiosulfate
and sulfite. The sulfite is reported as sodium sulfite.
Use of this method requires handling potentially
hazardous chemicals. Consult the Material Safety Data
Sheet for each chemical before use. MSDS’s are available
from your chemical supplier.
PRECISION AND BIAS
Repeatability
To obtain the repeatability data, a single skilled analyst
performed five (5) replicates on each of the following
solutions (this procedure was done by both potentiometric
and visual end point detection):
a. A “fresh” EASTMAN Color Films, Process ECN-2,
Fixer prepared with all components at their respective
aim concentrations in a working tank.
b. A “seasoned” EASTMAN Color Films, Process ECN-2,
Fixer analyzed as received at 125.67 g/L thios ulfate ion
and 28.92 g/L sodium sulfite.
c. The same “seasoned” solution as in number b, above,
reanalyzed after making standard additions of
37.850 g/L thiosulfate ion and 8.415 g/L sodium sulfite.
2 S
=
+ I2 → 2I- + S4O
2O3
=
6
(reaction 1)
Reproducibility
Three EASTMAN Color Films, Process ECN-2, Fixer
=
+ I2 + H2O → SO
HSO
3
=
+ 2I- + 3H
4
+
(reaction 2)
samples were analyzed by four analysts, each us ing different
titration stations, on two different days. Each analyst
analyzed each sample by both the potentiometric and the
-
+ 5I- + 6H+ → 3I2 + 3H2O (reaction 3)
IO
3
visual end point technique. Duplicate analyses were
performed on each sample, on each of the two days. These
samples were:
Na
adding 6 percent formaldehyd e to a second sample aliquo t in
reagent water. Under these conditions, the sulfite in the
sample forms a formaldehyde bisulfite complex (reaction 4).
This sample is then added to an excess of acidified iodine.
The unreacted iodine is titrated either potentiometrically
with standardized sodium thiosulfate from a 50-mL capacity
burette. The difference between the blank titration and the
sample titration represents the milliequivalents of iodine
consumed by the thiosulfate in the sample. The thiosulfate is
expressed as g/L thiosulfate ion (S
+ HCHO + H2O → CH3(OH) SO3Na + NaOH (reaction 4)
2SO3
The thiosulfate is determined potentiometrically by
=
).
2O3
a. a “fresh” tank solution prepared at 109.212 g/L
thiosulfate ion and 21.335 g/L sodium sulfite.
b. an EASTMAN Color Films, Process ECN-2 “seasoned”
tank fixer sample analyzed, as received, in the same
manner as the “fresh” fixer.
c. the same (as in number b, above) EASTMAN Color
Films, Proces s EC N -2 “seasoned” tank fixer sample
reanalyzed in the same manner as the “fresh” fixer, after
standard additions of thiosulfate and su lfite were mad e.
The “seasoned” sample of EASTMAN Color Films,
Process ECN-2 fixer, analyzed to be 115.17 g/L
thiosulfate ion and 15.69 g/L sodium sulfite. Standard
Processing KODAK Motion Picture Films, Module 3, Analytical Procedures • H24.03 1
Page 2
additions of 34.57 g/L thiosulfate ion and 5.444 g/L
sodium sulfite were made to that “seasoned” sample.
POTENTIOMETRIC TITRATION STATISTICS
Repeatability Standard Deviation, 1sr & 95 Percent Confidence Estimate (not including bias)
Repeatability standard deviation is an estimate of the
variability one trained analyst should be able to obtain under
favorable conditions (analyzing a sample, with one
instrument, within one day).
The 95 percent confidence estimate (calculated using the
repeatability standard deviation) around a single test will
include the mean value 95 percent of the time.
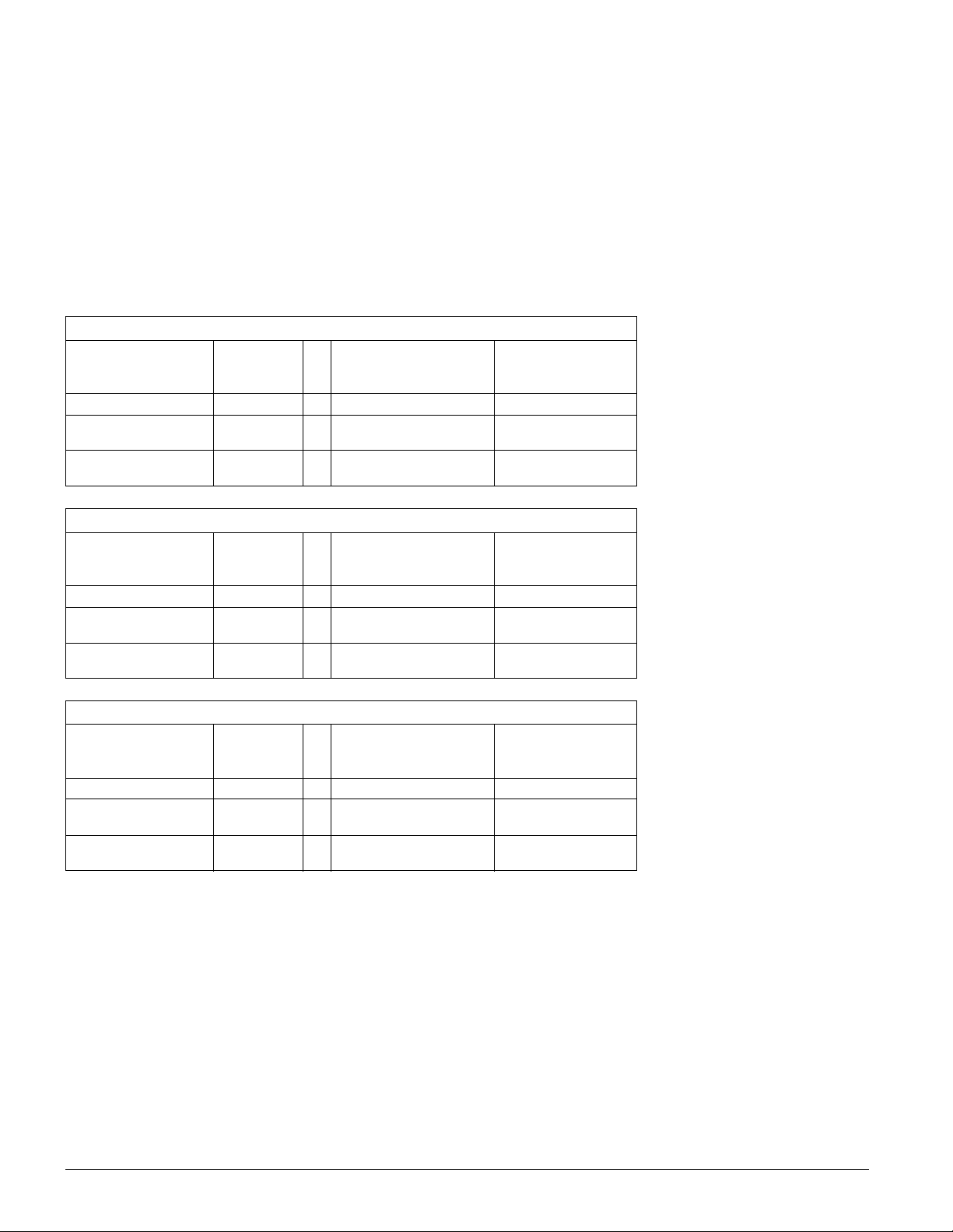
HYPO INDEX (1 mL)
Samples
(Process ECN-2 Fixer)
“Fresh” at “Aim” 10.02 5 0.086 ± 0.24
“Seasoned”, As
Received
“Seasoned” with
Standard Addition
Mean Level
(mL 0.1 N I
15.80 5 0.073 ± 0.20
19.38 5 0.14 ± 0.39
(N)
)
2
Repeatability
Standard Deviation, 1S
(mL 0.1 N I2)
Confidence Estimate
r
95 Percent
(mL 0.1 N I
)
2
THIOSULFATE
Samples
(Process ECN-2 Fixer)
“Fresh” at “Aim” 81.18 5 0.67 ± 1.9
“Seasoned”, As
Received
“Seasoned” with
Standard Addition
Samples
(Process ECN-2 Fixer)
“Fresh” at “Aim” 17.55 5 0.69 ± 1.9
“Seasoned”, As
Received
“Seasoned” with
Standard Addition
Mean Level
(g/L S
2O3
125.67 5 0.47 ± 1.3
153.79 5 0.60 ± 1.7
Mean Level
(g/L Na
28.92 5 0.65 ± 1.8
35.69 5 1.18 ± 3.3
2SO3
=
)
)
(N)
SULFITE
(N)
Repeatability
Standard Deviation, 1S
(g/L S2O
Repeatability
Standard Deviation, 1S
(g/L Na2SO3)
=
)
3
Confidence Estimate
r
Confidence Estimate
r
Bias
Bias is a statistically significant deviation of the mean from
the known mix level at a 95 percent confidence level. It is
determined for “fresh” samples only. Bias is not determined
for “seasoned” samples, since the component concentration
level was not determined independently of the test method.
A statistically significant bias for thiosulfate of
(-1.09 percent) was found for a “fresh” tank Process ECN-2
Fixer sample. The biases fo r Hypo Index and Sodi um Sulfite
were not statistically significant. However, the bias for
thiosulfate was judged not to be practically significant.
95 Percent
(g/L S
2O3
95 Percent
(g/L Na
2SO3
=
)
)
2 Processing KODAK Motion Picture Films, Module 3, Analytical Procedures • H24.03
Page 3
Recovery
Recovery is used instead of bias for “seasoned” samples, since the
component concentration level was not determined independently of
the test method. It is defined as the calculated mean for the
“seasoned” sample with a standard addition of the component minus
the mean for the “seasoned” sample, divi ded by the actual am ount of
the standard addition. It is expressed as a percentage. The table below
shows whether or not a recovery is statistically or practically different
from 100 percent.
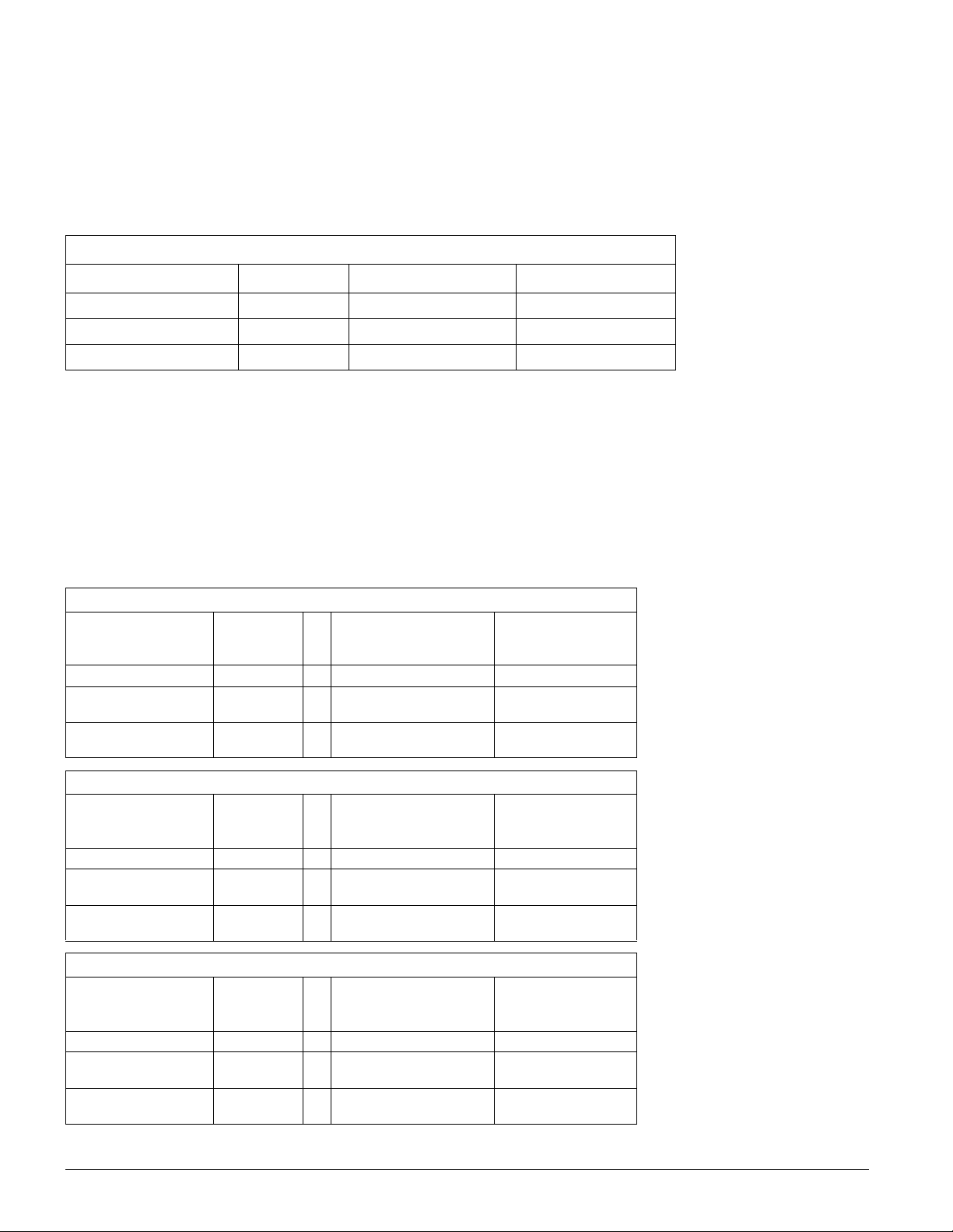
POTENTIOMETRIC RECOVER Y, Process ECN-2
Analyte Recovery Value Statistically Significant Practically Significant
Hypo Index (1 mL) 76% Yes No
Thiosulfate (S
Sodium Sulfite (Na
=
)74% Yes No
2O3
) 80.4% No No
2SO3
Reliability
Customer Standard Deviation, 1s
& 95 Percent
c
Confidence Estimate (not including bias)
The customer standard deviation is an estimate of the variability a
customer could expect when submitting a sample to any
Photoprocessing Quality Services laboratory, where any trained
analyst could test the sample using any instrument on any day.
The 95 percent confidence estimate (calculated using the customer
standard deviation) around a single test result will include the mean
value 95 percent of the time.
HYPO INDEX
Samples (Process
ECN-2 Fixer)
Mean Level
(mL 0.1 N I
(N)
Reproducibility
2
(mL 0.1 N I2)
Standard Deviation, 1S
)
c
95 Percent
Confidence Estimate
(mL 0.1 N I
“Fresh” at “Aim” 12.88 16 0.25 ± 0.54
“Seasoned”, As
Received
“Seasoned” with
Standard Addition
12.73 16 0.13 ± 0.27
15.83 16 0.16 ± 0.33
THIOSULFATE
Samples (Process
ECN-2 Fixer)
Mean Level
(g/L S
2O3
(N)
Reproducibility
=
)
Standard Deviation, 1S
(g/L S2O
=
)
3
c
95 Percent
Confidence Estimate
(g/L S
“Fresh” at “Aim” 108.14 16 0.94 ± 2.00
“Seasoned”, As
Received
“Seasoned” with
Standard Addition
Samples (Process
ECN-2 Fixer)
114.86 16 0.73 ± 1.56
142.23 16 0.78 ± 1.67
)
2SO3
Reproducibility
(g/L Na2SO3)
Confidence Estimate
c
(g/L Na
Mean Level
(g/L Na
2SO3
SULFITE (Na
(N)
Standard Deviation, 1S
)
95 Percent
“Fresh” at “Aim” 20.79 15 0.59 ± 1.26
“Seasoned”, As
Received
“Seasoned” with
Standard Addition
15.70 16 0.68 ± 1.4 5
19.85 16 0.76 ± 1.6 3
2O3
2SO3
)
2
=
)
)
Processing KODAK Motion Picture Films, Module 3, Analytical Procedures 3
Page 4

VISUAL TITRATION STATISTICS
Repeatability Standard Deviation, 1sr and
95 Percent Confidence Estimate
Repeatability standard deviation is an estimate of the
variability one trained analyst should be able to obtain under
favorable conditions (analyzing a sample, with one
instrument, within one day).
HYPO INDEX (3.0 mL)
Samples (Process
ECN-2 Fixer)
Mean Level
(mL 0.1 N I
)
2
“Fresh” at “Aim” 29.42 5 0.089 ± 0.25
“Seasoned”, As
Received
“Seasoned” with
Standard Addition
47.29 5 0.060 ± 0.17
57.65 5 0.084 ± 0.23
THIOSULFATE (S
Samples (Process
ECN-2 Fixer)
Mean Level
(g/L S
2O3
=
)
“Fresh” at “Aim” 81.37 5 0.10 ± 0.28
“Seasoned”, As
Received
“Seasoned” with
Standard Addition
125.29 5 0.24 ± 0.67
155.73 5 0.19 ± 0.53
Repeatability Standard
(N)
Deviation, 1S
(mL 0.1 N I2)
2O3
Repeatability Standard
(N)
Deviation, 1S
(g/L S2O
r
=
)
r
=
)
3
Confidence Estimate
Confidence Estimate
95 Percent
(mL 0.1 N I
95 Percent
(g/L S
2O3
)
2
=
)
)
2SO3
Deviation, 1S
(g/L Na2SO3)
r
Confidence Estimate
Samples (Process
ECN-2 Fixer)
Mean Level
(g/L Na
2SO3
SULFITE (Na
Repeatability Standard
(N)
)
“Fresh” at “Aim” 16.08 5 0.18 ± 0.50
“Seasoned”, As
Received
“Seasoned” with
Standard Addition
28.93 5 0.24 ± 0.67
33.43 5 0.31 ± 0.86
Bias
Bias is a statistically significant deviation of the mean from
the known mix level at a 95 percent confidence level. It is
determined for “fresh” samples only. Bias is not determined
for “seasoned” samples, since the component concentration
level was not determined independently of the test method.
Statistically significant biases were found for hypo index,
thiosulfate, and sodium sulfite (see the table below) for a
“fresh” tank Process ECN-2 Fixer sample. How ever, the
individual biases for hypo index, thiosulfate, or sodium
Hypo Index
(mL 0.1 N I
Thiosulfate
(g/L S
Sodium Sulfite
(Na
sulfite were judged not to be practically significant.
95 Percent
(g/L Na
Analyte
2
=
)
2O3
)
2SO3
)
2SO3
Bias
(Measurement Unit of Analyte)
)
– 0.82 – 2.71%
– 0.696 – 0.85%
– 1.322 – 7.6%
Bias
(%)
4 Processing KODAK Motion Picture Films, Module 3, A nalytical Procedures
Page 5

Recovery
Recovery is used instead of bias for “seasoned” samples, since the
component concentration level was not determined independently of
the test method. It is defined as the calculated mean for the
“seasoned” sample with a standard addition of the component minus
the mean for the “seasoned” sample, divi ded by the actual am ount of
the standard addition. It is expressed as a percentage. The table below
show whether or not a recovery is statistically or practically
significant from 100 percent.
VISUAL RECOVERY, Process ECN-2
Analyte Recovery Value Statistically Significant Practically Significant
Hypo Index (1 mL) 73.3% Yes No
Thiosulfate (S
Sodium Sulfite (Na
=
) 80.4% Yes No
2O3
) 53.4% Yes No
2SO3
Customer Standard Deviation, 1s
& 95 Percent
c
Confidence Estimate (not including bias)
The customer standard deviation (1s
) is an estimate of the variability
c
a customer could expect when submitting a sample to any
Photoprocessing Quality Services laboratory, where any trained
analyst could test the sample using any instrument on any day.
The 95 percent confidence estimate (calculated using the customer
standard deviation) around a single test result will include the mean
value 95 percent of the time.
HYPO INDEX (1.0 mL)
Samples (Process
ECN-2 Fixer)
Mean Level
(mL 0.1 N I
(N)
)
2
“Fresh” at “Aim” 12.97 16 0.18 ± 0.39
“Seasoned”, As
Received
“Seasoned” with
Standard Addition
12.70 16 0.15 ± 0.31
15.93 16 0.20 ± 0.43
THIOSULFATE (S
Samples (Process
ECN-2 Fixer)
Mean Level
(g/L S
2O3
(N)
=
)
“Fresh” at “Aim” 107.95 16 0.93 ± 1.99
“Seasoned”, As
Received
“Seasoned” with
Standard Addition
114.95 16 0.97 ± 2.06
142.59 16 1.07 ± 2.28
Reproducibility
Standard Deviation, 1S
(mL 0.1 N I2)
=
)
2O3
Reproducibility
Standard Deviation, 1S
(g/L S2O
=
)
3
Confidence Estimate
c
Confidence Estimate
c
95 Percent
(mL 0.1 N I
95 Percent
(g/L S
2O3
)
2
=
)
)
2SO3
Reproducibility
(g/L Na2SO3)
95 Percent
Confidence Estimate
c
(g/L Na
2SO3
)
Samples (Process
ECN-2 Fixer)
Mean Level
(g/L Na
2SO3
SULFITE (Na
(N)
Standard Deviation, 1S
)
“Fresh” at “Aim” 21.17 16 1.18 ± 2.52
“Seasoned”, As
Received
“Seasoned” with
Standard Addition
15.46 16 1.14 ± 2.4 3
20.23 16 1.58 ± 3.3 8
Processing KODAK Motion Picture Films, Module 3, Analytical Procedures 5
Page 6

APPARATUS
All volumetric glassware should meet all “Class A”
specifications, as defined by American Society for Testing
and Materials (ASTM) Standards E 287, E 288, and E 969,
unless othe rwise stated.
For Potentiometric Titration:
• Metrohm Potentiograph, Model E536 or equivalent
titrator
• Metrohm Model 665 Dosimat with a 50-mL burette size
(no substitution)
• Electrodes:
Indicator electro d e =
Reference electrode =
Platinum inlay (i.e., Beckman
Model 39273 or equivalent)
Double-junction (i.e. , Orion
900200 or equivalent) (10%
outer filling solution)
KNO
3
For Visual Titration:
• Burette, Class A, 50 mL capacity, Teflon stopcock
• Magnetic Stirrer
REAGENTS
Use ACS Reagent Grade reagents unless otherwise
specified.
• Potassium Iodate, KIO
decimal places
• Acetic Acid, CH
• Potassium Iodide, KI (0.6 M)
• Sodium Thiosulfate, Na
four decimal places
• Formaldehyde (6%), pH 3.9
• Starch Indicator
• Phenolphth alein Indicat or
• Sodium Hydroxide, NaOH (1.0 N)
• Sulfuric Acid, H
• Iodine, I
(0.1 N) - standardized to four decimal places
2
• Water, Type I Reagent – This method was developed, an d
the resulting statistical data were obtained using reagent
water equivalent to or purer than Type I Grade, as defined
in ASTM Standard D 1193. Other grades of water, e.g.,
reverse osmosis (RO), demineralized, or distilled water,
may give equivalent results, but the effects of water
quality on method performance have not been studied.
(0.1 N), - standardized to four
3
COOH (2.0 N)
3
(0.1 N) - standardized to
2S2O3
(1.0 N)
2SO4
PROCEDURE
For Potentiometric Titration
A. Hypo Index (HI) or Total Reductants
1. To a 400-mL beaker with a magnetic stir-bar, add
100 mL reagent water.
2. Pipette 40.0 mL (use a 20-mL pipette, twice) of
standardized 0.1 N potassium iodate into the 400-mL
beaker.
3. While stirring, add 10 mL of 2.0 N acetic acid and
25 mL of 0.6 M potassium iodide (KI) to the 400-mL
beaker.
4. With continued stirring, immediately pipette 1.0 mL
of sample near the surface of the liquid. Rinse the
sides of the beaker with reagent water.
5. Titrate with standardized 0.1 N sodium thiosulfate on
an E536 Metrohm Potentiograph or equivalent titrator.
If using an E536, titrate the solution from step 4, using
the following parameters:
Rate = 10 min/100% vol
Auto Control = OFF
Mode = mV/pH
Range = 500 mV
Burette Size = 50 mL
Indicator Electrode = Platinum inlay or platinum
wire (i.e., Beckman Model
39273)
Reference Electrode = Double-junction reference
(i.e., Orion Model 90-02)
6. Determine the volume of 0.1 N sodium thiosulfate at
the end point using concentric arcs (see Universal
Method ULM-0003-01, Pot e ntiometric Titrations for
Photoprocessing Solutions, or subsequent revision).
7. Run a blank (do steps 1–6, but omit the addition of the
sample in step 4).
6 Processing KODAK Motion Picture Films, Module 3, Analytical Procedures • H24.03
Page 7

B. Thiosulfate Determination
1. Sample Pretreatment:
a. To a 250-mL beaker with a magnetic stir-bar,
add 75 mL of reagent water.
b. Pipette 2.0 mL of sample into the 250-mL
beaker.
c. Add 5 mL of 6% formaldehyde (pH 3.9) to the
beaker.
d. Start stirring the contents of the 250-mL beaker,
set and start a timer for 2 minutes of stirring.
2. Titration of Sample:
a. Into a 400-mL beaker with a magnetic stir-bar,
pipette 40.0 mL of standardized 0.1 N
potassium iodate while the timer from step 1.d.
is running.
b. While stirring, add 10 mL of 2.0 N acetic acid to
the 400-mL beaker (continue stirring through
step 2e.).
c. When the timer goes off, add 25 mL of 0.6 M KI
to the 400-mL beaker.
d. Immediately after the 0.6 M KI has been added,
add the solution in the 250-mL beaker, from
step 1, Sample Pretreatment:, to the 400-mL
beaker.
e. Rinse the 250-mL beaker three times with
reagent water and add the rinses to the 400-mL
beaker.
f. Titrate the contents of the 400-mL beaker with
standardized 0.1 N sodium thiosulfate on an
E536 Metrohm Potentiograph or equival ent
titrator. If using a Metrohm E536, titrate the
solution from step 2e. using the parameters
found in step 5 of the Hypo Index (HI) or Total
Reductants procedure.
g. Determine the volume of 0.1 N sodium
thiosulfate at the end point using concentric arcs
(see Universal Method ULM-0003-01,
Potentiometric Titrations for Photoprocessing
Solutions, or any subsequent revision.
3. Run a blank, following all the steps in 1 and 2 above,
except omit the addition of sample in step 1b.
C. Sulfite
1. Sulfite is a calculated value and requires no additional
measurement.
For Visual Titration
A. Hypo Index (HI) or Total Reductants
Treatment and Titration of Sample:
1. Pipette (wipe before leveling) 40.0 mL of standardized
0.1 N potassium iodate solution into a 250-mL conical
flask containing a magnetic stir bar.
2. Add 10 mL of 2.0 N acetic acid solution from a tip-up
(or equivalent) pipette.
3. Stir the solution with a magnetic stirrer and add 25 mL
of 0.6 M potassium iodide solution from a tip-up
pipette.
4. Immediately pipette (wipe) 1.0 mL of the fixer sample
into the 250-mL flask while the solution is stirring
(hold the tip of the pipette against the wall of the flask
and as close to the surface of the stirring solution as
possible while the sample is draining but do not
immerse the tip of the pipette in the stirring solution).
5. Titrate with standardized 0.1 N sodium thiosulfate
solution to a light yellow color.
6. Add 5 mL of the starch indicator, from a tip-up pipette
and continue the titration until the blue color just
disappears for 15 seconds.
7. Run a blank (do steps 1–6, but omit the addition of the
sample in step 4).
B. Thiosulfate (Hypo)
1. Treatment of the Sample:
a. Pipette 2.0 mL of the fixer sample into a 250-mL
conical flask containing a magnetic stir bar.
b. Add 5 mL of formalin from a tip-up pipette.
c. Add 3 or 4 drops of phenolphthalein indicator to
the flask.
• If the solution is pink, titrate with 1.0 N
sulfuric acid to colorless.
• If the solution is colorless, titrate with 1.0 N
sodium hydroxide to the first light pink
color.
d. Let the solution stand for 2 minutes.
e. Add 10 mL of 2.0 N acetic acid from a tip-up
pipette.
2. Titration with Iodine:
a. Add, from a tip-up pipette, 5 mL of the starch
indicator to the conical flask.
b. Titrate with standardized 0.1 N iodine solution
to the first distinct blue color that persists for
15 seconds.
C. Sulfite
1. Sulfite is a calculated value and requires no additional
measurement.
Processing KODAK Motion Picture Films, Module 3, Analytical Procedures • H24.03 7
Page 8

CALCULATIONS
For Potentiometric Titration
A. Hypo Index (HI) or Total Reductants:
HI (1), mL =
(mL Blank A – mL Sample A) (N Na
0.1000 N Na
2S2O3
2S2O3
Where:
HI (1), mL = mL of 0.1000 N I2 consumed by 1.0 mL
mL Blank A = millilitres of titrant at the end point of the
mL Sample A = millilitres of titrant at the end point of the
N Na
2S2O3
0.1000 = nominal value for the normali t y of the titrant ,
B. Thiosulfate (S2O
2O3
=
g/L S
sample
blank titration of potentiometric Procedure A.
sample titration of po t entiomet ric
Procedure A.
= normality of the titrant (meq/mL)
in meq/mL
=
):
3
(mL Blank B – mL Sample B)(N Na
=
sample size (10 00)
2S2O3
Where:
mL Blank B = millilitres of titrant at the end point of the
mL Sample B = millilitres of titrant at the end point of the
N Na
2S2O3
112.13 = equivalent weight of thiosulfate expressed in
1000 = conversion factor of milligrams to grams
1000 = conversion factor of millilitres to litres
sample size = sample size used in po te nt i om et ric
blank titration of potentiometric Procedure B
sample titration of po t entiomet ric
Procedure B.
= normality of the titrant (meq/mL)
mg/meq
Procedure B (2.0 mL)
)
)(112.13)(1000)
C. Sodium Sulfite (Na2SO3):
mL Blank A – mL Sample A = D mL A
mL Blank B – mL Sample B = D mL B
g/L Na
2SO3
[(D mL A)(2.0) – (D mL B)](N Na
=
sample size (1000)
2S2O3
)(63.02)(1000)
Where:
N Na
sample size = sample size used in po te nt i om et ric
= normality of the titrant
2S2O3
2.0 = conversion of hypo index to 2.0 m L sample
size
63.02 = equivalent weight of sodium sulfite in mg/
meq
1000 = conversion factor of milligrams to grams
Procedure B (2.0 mL)
1000 = conversion factor of millilitres to litres
8 Processing KODAK Motion Picture Films, Module 3, Analytical Procedures • H24.03
Page 9

Example Potentiometric Calculations:
Titration mL 0.1 N Na2S2O3 Titrant
Blank A = 40.50
Sample A = 21.85
Blank B = 40.55
Sample B = 19.80
Hypo Index (HI) or Total Reductants:
HI (1), mL =
(40.50 – 21.85)(0.098 9)
= 18.4 mL 0.1000 N I
Thiosulfate (S
g/L S2O
2O3
(40.55 – 19.80)(0.0989)(112.13)(1000)
=
=
3
= 57.5 g/ L
Sodium Sulfite (Na
2SO3
=
= 51.4 g/ L
g/L Na
0.1000
2
=
):
(2.0)(1000)
):
2SO3
[(40.50 – 21.85)(2.0) – (40.55 – 19. 80)](0.0989)(63.02)(1000)
(2.0)(1000)
Processing KODAK Motion Picture Films, Module 3, Analytical Procedures • H24.03 9
Page 10

For Visual Titration
A. Hypo Index (HI) or Total Reductants:
HI (1), mL =
(mL Blank A – mL Sample A) (N Na
0.1000 N Na
2S2O3
2S2O3
Where:
HI (1), mL = mL of 0.1000 N I2 consumed by 1.0 mL
mL Blank A = millilitres of titrant at the end point of the
mL Sample A = millilitres of titrant at the end point of the
N Na
2S2O3
0.1000 = nominal value for the normali t y of the titrant ,
B. Thiosulfate (S2O
2O3
=
g/L S
sample
blank visual titration, Procedure A.
sample visual titration, Proc edu re A.
= normality of the titrant (meq/mL)
in meq/mL
=
):
3
)(N I2)[eq. wt. S2O
(mL I
=
2
=
](1000)
3
(mL Sample size)(1000)
Where:
[eq. wt. S
mL I2= millilitres of iodine titrant measur ed at th e
N I
2O3
1000 = factors to convert mg/mL to g/L
visual end point
= normality of the titrant (meq/mL)
2
=
] = equivalent weight of thiosulfate expressed
in mg/meq (112.13)
)
C. Sodium Sulfite (Na2SO3):
g/L Na
2SO3
[(HI)(N* I
=
)(3)] – [(mL I2)(N I2)](eq. wt. S2O
2
(mL Sample size)(1000)
Where:
HI = mL of 0.1000 N I2 consumed by 1.0 mL
sample
= nominal 0.1000 nor m ality of iodine used in
N* I
2
the Hypo Index calculation (meq/mL)
3 = conversion of Hypo Index to a 3.0 mL
sample size
= millilitres of iodine titrant measured at the
mL I
2
visual end point, Procedure B
= normality of the iodine titrant (meq/mL) used
N I
2
in Procedure B, visual end point
=
eq. wt. S
mL Sample = sample size used in Procedure B, visual end
= equivalent weight of thiosulfate expressed in
2O3
mg/meq (112.13)
point
1000 = convers ion factors fo r milligrams to grams
and milliliters to liters
=
)(1000)
3
10 Processing KODAK Motion Picture Films, Module 3, Analytical Procedures • H24.03
 Loading...
Loading...