Kenwood TK-80 Service Manual

Document Copyrights
Copyright 2006 by Kenwood Corporation. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced, translated, distributed, or transmitted in any
form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, for
any purpose without the prior written permission of Kenwood.
Disclaimer
While every precaution has been taken in the preparation of this manual, Kenwood
assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions. Neither is any liability assumed for
damages resulting from the use of the information contained herein. Kenwood reserves
the right to make changes to any products herein at any time for improvement purposes.

HF SSB RADIOTELEPHONE
TK-80
SERVICE MANUAL
© 2006-4 PRINTED IN JAPAN
B51-8758-00 (N) PDF
Foot
(J02-0475-05) x 4
Knob (Main dial)
(K29-5080-13)
Knob (VOL, SQL, CLA)
(K29-4973-04) x 3
CONTENTS
Panel assy
(A62-0668-03)
GENERAL ................................................... 2
REALIGNMENT .......................................... 2
INSTALLATION .......................................... 8
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION ........................... 10
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA ....................... 21
COMPONENTS DESCRIPTION ............... 26
PARTS LIST .............................................. 30
EXPLODED VIEW..................................... 45
PACKING .................................................. 46
ADJUSTMENT ......................................... 47
TERMINAL FUNCTION ............................ 55
LEVEL DIAGRAM ..................................... 59
PC BOARD
LCD ASSY (B38-0739-15)..................... 62
FINAL UNIT (X45-3520-21) .................. 64
CONTROL UNIT (X53-3570-21) ........... 68
TX-RX UNIT (X57-4660-21) ................. 72
INTERCONNECTION DIAGRAM ............. 76
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
LCD ASSY (B38-0739-15)..................... 78
FINAL UNIT (X45-3520-21) .................. 80
CONTROL UNIT (X53-3570-21) ........... 82
TX-RX UNIT (X57-4660-21): TX-RX .... 84
TX-RX UNIT (X57-4660-21): PLL ......... 88
BLOCK DIAGRAM .................................... 90
KAT-2
KPE-1 (Selective Call Kit) ...................... 104
SPECIFICATIONS .................. BACK COVER
(Internal Automatic Antenna Tuner)....
92
TK-80
GENERAL / REALIGNMENT
INTRODUCTION
SCOPE OF THIS MANUAL
This manual is intended for use by experienced techni-
cians familiar with similar types of commercial grade commu-
nications equipment. It contains all required service informa-
tion for the equipment and is current as of the publication
date. Changes which may occur after publication are covered
by either Service Bulletins or Manual Revisions, which are
issued as required.
ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS
When ordering replacement parts or equipment informa-
tion, the full part identification number should be included.
This applies to all parts: components, kits, or chassis. If the
part number is not known, include the chassis or kit number
of which it is a part, and a sufficient description of the re-
quired component for proper identification.
PERSONAL SAFETY
The following precautions are recommended for personal
safety:
• DO NOT transmit until all RF connectors are verified to be
secure and any open connectors are properly terminated.
•SHUT OFF and DO NOT operate this equipment near elec-
trical blasting caps or in an explosive atmosphere.
• This equipment should be serviced only by qualified tech-
nicians.
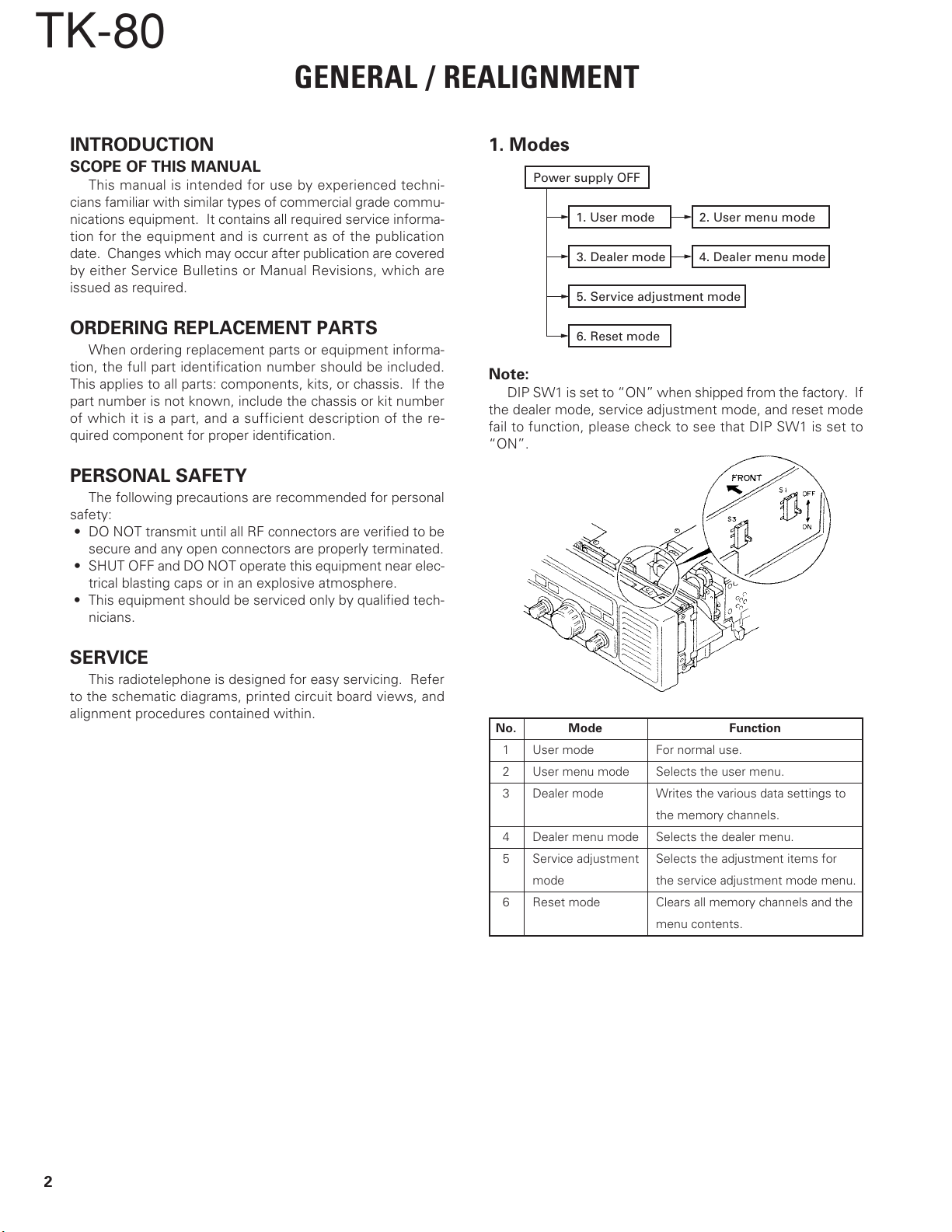
1. Modes
Power supply OFF
1. User mode
3. Dealer mode
5. Service adjustment mode
6. Reset mode
Note:
DIP SW1 is set to “ON” when shipped from the factory. If
the dealer mode, service adjustment mode, and reset mode
fail to function, please check to see that DIP SW1 is set to
“ON”.
2. User menu mode
4. Dealer menu mode
SERVICE
This radiotelephone is designed for easy servicing. Refer
to the schematic diagrams, printed circuit board views, and
alignment procedures contained within.
No. Mode Function
1 User mode For normal use.
2 User menu mode Selects the user menu.
3 Dealer mode Writes the various data settings to
the memory channels.
4 Dealer menu mode Selects the dealer menu.
5 Service adjustment Selects the adjustment items for
mode the service adjustment mode menu.
6 Reset mode Clears all memory channels and the
menu contents.
2
REALIGNMENT
TK-80
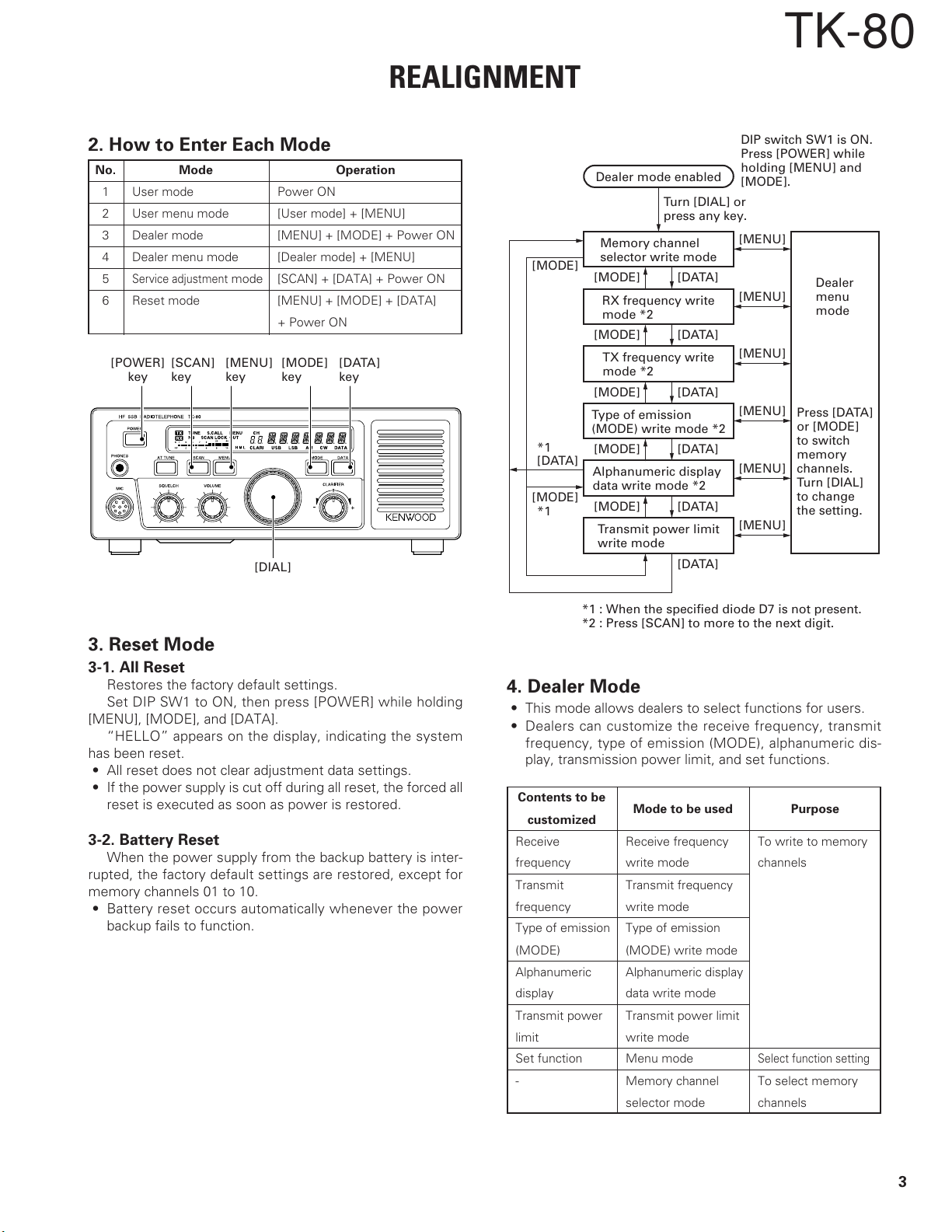
2. How to Enter Each Mode
No. Mode Operation
1 User mode Power ON
2 User menu mode [User mode] + [MENU]
3 Dealer mode [MENU] + [MODE] + Power ON
4 Dealer menu mode [Dealer mode] + [MENU]
5
Service adjustment
6 Reset mode [MENU] + [MODE] + [DATA]
[POWER]
key
[SCAN]
key
mode [SCAN] + [DATA] + Power ON
+ Power ON
[MENU]
key
[DIAL]
[MODE]
key
[DATA]
key
[MODE]
*1
[DATA]
[MODE]
*1
Dealer mode enabled
Turn [DIAL] or
press any key.
Memory channel
selector write mode
[MODE]
RX frequency write
mode *2
TX frequency write
mode *2
Type of emission
(MODE) write mode *2
Alphanumeric display
data write mode *2
[MODE]
Transmit power limit
write mode
[DATA]
[DATA][MODE]
[DATA][MODE]
[DATA][MODE]
[DATA]
[DATA]
DIP switch SW1 is ON.
Press [POWER] while
holding [MENU] and
[MODE].
[MENU]
[MENU]
[MENU]
[MENU]
[MENU]
[MENU]
Dealer
menu
mode
Press [DATA]
or [MODE]
to switch
memory
channels.
Turn [DIAL]
to change
the setting.
3. Reset Mode
3-1. All Reset
Restores the factory default settings.
Set DIP SW1 to ON, then press [POWER] while holding
[MENU], [MODE], and [DATA].
“HELLO” appears on the display, indicating the system
has been reset.
• All reset does not clear adjustment data settings.
• If the power supply is cut off during all reset, the forced all
reset is executed as soon as power is restored.
3-2. Battery Reset
When the power supply from the backup battery is inter-
rupted, the factory default settings are restored, except for
memory channels 01 to 10.
• Battery reset occurs automatically whenever the power
backup fails to function.
*1 : When the specified diode D7 is not present.
*2 : Press [SCAN] to more to the next digit.
4. Dealer Mode
• This mode allows dealers to select functions for users.
• Dealers can customize the receive frequency, transmit
frequency, type of emission (MODE), alphanumeric dis-
play, transmission power limit, and set functions.
Contents to be
customized
Receive Receive frequency To write to memory
frequency write mode channels
Transmit Transmit frequency
frequency write mode
Type of emission Type of emission
(MODE) (MODE) write mode
Alphanumeric Alphanumeric display
display data write mode
Transmit power Transmit power limit
limit write mode
Set function Menu mode
- Memory channel To select memory
Mode to be used Purpose
Select function setting
selector mode channels
3
TK-80
REALIGNMENT
4-1. Procedure ( ): Initial value
1) Press [POWER] while holding [MENU] and [MODE].
Dealer mode display
Turn [DIAL] or press any key, and enter Memory channel
selector mode.
■ Memory channel selector mode (01)
This mode is for selector memory channels when writing
frequency and other information to memory channels.
Second time: 01 USB only. The others are blank.
1) When [DIAL] is turned, channels, including those not en-
tered in memories, are switched continuously.
01 02 79 80...
2) Pressing [DATA] enables the receive frequency write
mode.
■ Receive frequency write mode (00.000.00)
This mode is for writing receive frequencies to memory
channels. The frequency is set in single digits starting from
the 10MHz to the 10Hz digit. The 1Hz digit is defaulted to
“0”.
1) Turning the [DIAL] changes the digit to its minimum fre-
quency setting.
2) When the setting of one digit is completed, press [SCAN]
to move to the next digit. Digits are set in order from the
10MHz digit to the 10Hz digit. (When setting the 10Hz
digit, for example, the display shows the previously en-
tered digits: 12.345.56)
3) Pressing [DATA] enables the transmit frequency write
mode.
• If the transmit frequency happens to be the default setting
(00.000.00), when writing the receive frequency is com-
pleted, the receive frequency setting is automatically writ-
ten to the transmit frequency memory channel as well.
• Leading zeros are not suppressed in the frequency dis-
play.
■ Transmit frequency write mode (00.000.00)
This mode is for writing transmit frequencies to the
memory channels. The frequency is set in single digits start-
ing from the 10MHz digit to the 10Hz digit. The 1Hz digit is
defaulted to “0”.
1) Turning the [DIAL] changes the digit to its minimum fre-
quency setting.
2) When the setting of one digit is completed, press [SCAN]
to move to the next digit. Digits are set in order from the
10MHz digit to the 10Hz digit.
3) Pressing [DATA] enables the type of emission (MODE)
write mode. (When setting the 10Hz digit, for example,
the display shows the previously entered digits:
12.345.56)
4) When wishing to use the memory channel as a receive-
only channel, set all digits to “0”, then press [DATA] to
enable the type of emission (MODE) write mode.
Note:
• Setting begins from the 10MHz digit when the transmit
frequency write mode is first enabled.
• The set frequencies are checked to confirm they are
within the specified transmit frequency range.
• Setting all digits to “0” changes the memory channel to a
receive-only channel.
• In the transmit frequency write mode, the digit being set
flashes as it displays the frequency.
• Leading zeros are not suppressed in the frequency dis-
play.
■ Type of emission (MODE) write mode (USB)
This mode is used to write the type of emission to the
memory channel.
Note:
• Setting begins from the 10MHz digit when the receive fre-
quency write mode is first enabled.
• The set frequencies are checked to confirm they are
within the specified receive frequency range.
• Setting all digits to “0” initializes the memory channel.
• In the receive frequency write mode, the digit being set
flashes as it displays the frequency.
4
1) Turning the [DIAL] triggers a display that scrolls continu-
ously in the following order:
USB LSB AM CW
2) Pressing [DATA] enables the alphanumeric display data
write mode.

REALIGNMENT
TK-80
■ Alphanumeric display data write mode (Blank)
This mode is used to write alphanumeric display data (up
to 7 digits) to the memory channels.
1) Turning the [DIAL] triggers a display that scrolls continu-
ously in the following order:
Blank A B Z 14 types of symbols...
910...
Blank H P X , * 7
AIQY-08
BJRZ/19
CKS$=2
DLT1/1 @ 3
EMU< \ 4
FNV>_ 5
GOW+ # 6
2) Digits are set starting from the left side. Pressing [SCAN]
moves the cursor one digit position to the right.
3) Pressing [DATA] changes control to the:
• Transmit power limit write mode (when specified diode
D7 is installed)
• Memory channel selector mode (when specified diode D7
is not installed)
■ Transmit power limit write mode (100W)
This mode is used to write the transmit power limit to the
memory channel.
1) Turning the [DIAL] triggers a display that scrolls continu-
ously in the following order:
MAXIMUM (100W)
2) Press [DATA] to enable the memory channel switching
mode.
HIGH (50W)
MEDIUM (25W)LOW (15W)
5. Dealer Menu Mode
This mode is used to select functions the dealer sets for
the user.
5-1. Selecting the dealer menu mode
Press [MENU] while in the dealer mode’s memory chan-
nel selector mode or any of its write modes.
5-2. Menu number selection
To select menu numbers, press the [DATA] or [MODE]
keys.
5-3. Selecting the setting contents
To change menu settings, turn the [DIAL].
Note:
• Menu numbers are designed to scroll in order continu-
ously.
• Menu items are designed to scroll in order continuously.
• If the menu is scrolling, turn the [DIAL] to display the item,
then select the desired setting.
• The selective call ON/OFF status and any memory code
setting changes from the User menu mode will be re-
flected in the Dealer menu’s settings.
Menu Content
00 VFO transmit power and receive-only setting
01 MIC gain H/L setting
02 CW/selective call IF filter attachment
03 DATA (AFSK) IF filter attachment
04 AIP ON/OFF
05 AUX ON/OFF
06 Scan speed setting
07 BC AM 1/9kHz steps
08 Clarifier 10/1Hz steps
09 VOX ON/OFF
10 CW delay time setting (full/semi break-in setting)
11 CW sidetone/pitch frequency setting
12 Power setting (H, M, L) display ON/OFF
13 Channel number display ON/OFF
14 DATA mode AFSK/FSK setting
15 DATA (FSK) IF filter selection
16 FSK shift width setting
17 FSK key polarity setting
18 FSK H/L tone setting
19 FSK reverse setting
20 SCAN SW actuation enable/disable
21 MENU SW actuation enable/disable
22 MODE SW actuation enable/disable
23 DATA SW actuation enable/disable
30 Selective call ON/OFF
31 ID (own unit) code setting
5
TK-80
REALIGNMENT
Menu Content
32 Squelch opening time (unmute time) setting
33 Memory code A setting (call ID)
34 Memory code B setting (call ID)
35 Memory code C setting (call ID)
36 Memory code D setting (call ID)
37 Memory code A setting (character)
38 Memory code B setting (character)
39 Memory code C setting (character)
40 Memory code D setting (character)
41 User manu memory code setting ON/OFF
42 ID delay time setting
6. Transfer Mode
This mode is used to copy the memory and menu data
from one TK-80 unit to one or more others to create
“TRANS”.
6-1. Procedure
1) Connect a cross cable (E30-3232-05) to the ACC1 connec-
tors on two TK-80 units, as shown in the figure.
2) Turn on the power of the unit receiving the data.
3) Enable the Dealer mode in the unit to be transferred, then
press [DATA].
As the unit enters the Dealer mode, it automatically de-
tects the connected second TK-80 unit, displays “TRANS”
and begins the transferring transmission.
4) When transferring ends normally, the first TK-80 returns
to the Dealer mode which is then shown on its display.
7. VFO Functions
Dip SW3 is set to ON when shipped from the factory.
Should the VFO mode fail to function, please check to see
that Dip SW3 is set to ON.
7-1. Procedure
1) Press [MENU] to enable the user Menu mode.
2) Press [DATA] or [MODE] to select No. 00.
3) Use [DIAL] to switch the memory to VFO.
4) Press [MENU] to select VFO.
7-2. Description
1) [DIAL] changes from selecting memory channels to se-
lecting VFO frequencies.
2) [SCAN] changes to selecting the step frequency and the
F. LOCK function.
Pressing [SCAN] scrolls through the settings in the follow-
ing order:
10Hz → F. LOCK → 100kHz → 1kHz → 10Hz
Turning the [DIAL] after changing the step frequency
rounds the lower digit off to “0”.
3) When in the user Menu mode, memory channel frequen-
cies and type of emissions (MODE) are set in the VFO at
the point control is switched from Memory to VFO.
4) [DIAL] and [MENU] are disabled during F. LOCK.
5) Even if AT tuning is established during VFO, the changing
of the frequency automatically credits the state of AT
through.
Note:
• Transfer is not possible when the destination diode (D8,
D9, D10, D15) setting of the two units differ.
• Transfer is not possible when neither of the two units is
equipped with transmit power setting diode (D7).
6
8. Personal Computer Interface
In addition to commands (in the instruction manual) made
available to users, the SR (system reset) command is made
available only to dealers.
Note:
• SRP1 = Reset the user menu
SRP2 = Reset all
• The reset user Menu command resets all menu settings
to the factory defaults.

REALIGNMENT
TK-80
9. User Menu Mode
This mode enables users to select various settings to suit
their individual needs. The items that can be modified are
listed below:
Menu Content
00 VFO/M
01 Transmit power switching
02 NB ON/OFF
03 Display switching frequency/alphanumeric
04 LOCK OUT ON/OFF
05 Scan busy stop switching TO/CO/OFF
06 Selective call ON/OFF
07 ID (own unit) code display
08 Memory code A setting (call ID)
09 Memory code B setting (call ID)
10 Memory code C setting (call ID)
11 Memory code D setting (call ID)
12 Memory code A setting (character)
13 Memory code B setting (character)
14 Memory code C setting (character)
15 Memory code D setting (character)
9-1. Selecting settings
• Begin by pressing [MENU] to display the User menu.
• Press [MODE] or [DATA] to select the desired item num-
ber.
• Use [DIAL] to change the setting.
• Press [MENU] once more to complete the change.
Note:
• Menu numbers are designed to scroll in order continu-
ously.
• Menu items are designed to scroll in order continuously.
• Menu item number “00” can only be set when DIP SW3 is
set to ON.
• Menu item numbers 08 to 15 can only be set when the
user memory code setting in the Dealer menu mode is set
to ON.
• Menu item numbers 01 and 04 represent the channels
prior to entering the user menu mode.
• If a Selective call kit is not installed, setting item number 06
(user’s own office code) to ON will only produce on the
display. The selective call mode will not be enabled.
• Switching the [MENU] key ON/OFF can be inhibited from
the Dealer menu mode.
7
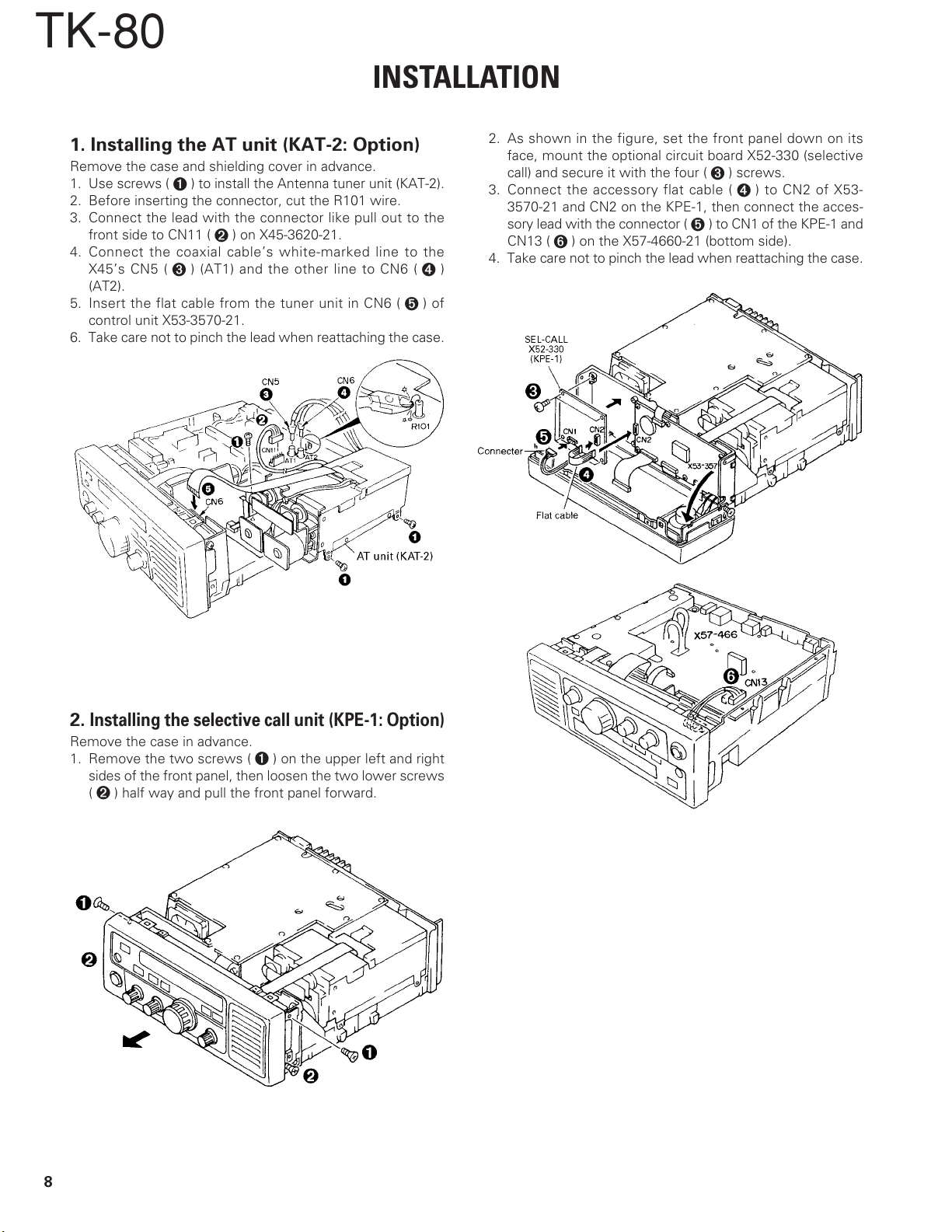
TK-80
INSTALLATION
1. Installing the AT unit (KAT-2: Option)
Remove the case and shielding cover in advance.
1. Use screws (➊) to install the Antenna tuner unit (KAT-2).
2. Before inserting the connector, cut the R101 wire.
3. Connect the lead with the connector like pull out to the
front side to CN11 (➋) on X45-3620-21.
4. Connect the coaxial cable’s white-marked line to the
X45’s CN5 (➌) (AT1) and the other line to CN6 (➍)
(AT2).
5. Insert the flat cable from the tuner unit in CN6 (➎) of
control unit X53-3570-21.
6. Take care not to pinch the lead when reattaching the case.
2. As shown in the figure, set the front panel down on its
face, mount the optional circuit board X52-330 (selective
call) and secure it with the four (➌) screws.
3. Connect the accessory flat cable (➍) to CN2 of X53-
3570-21 and CN2 on the KPE-1, then connect the acces-
sory lead with the connector (➎) to CN1 of the KPE-1 and
CN13 (➏) on the X57-4660-21 (bottom side).
4. Take care not to pinch the lead when reattaching the case.
2.
Installing the selective call unit (KPE-1: Option)
Remove the case in advance.
1. Remove the two screws (➊) on the upper left and right
sides of the front panel, then loosen the two lower screws
(➋) half way and pull the front panel forward.
8
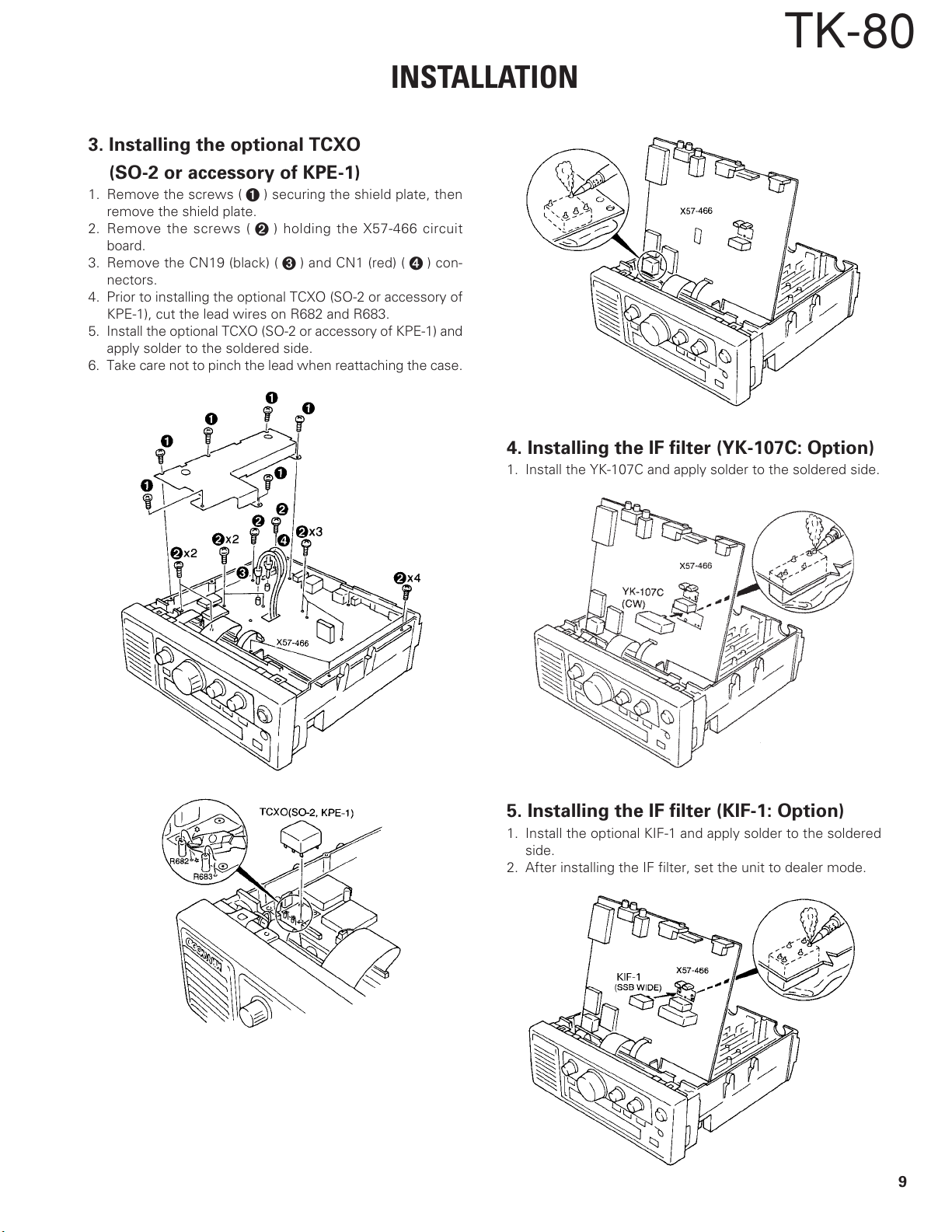
INSTALLATION
3. Installing the optional TCXO
(SO-2 or accessory of KPE-1)
1. Remove the screws (➊) securing the shield plate, then
remove the shield plate.
2. Remove the screws (➋) holding the X57-466 circuit
board.
3. Remove the CN19 (black) (
nectors.
4. Prior to installing the optional TCXO (SO-2 or accessory of
KPE-1), cut the lead wires on R682 and R683.
5. Install the optional TCXO (SO-2 or accessory of KPE-1) and
apply solder to the soldered side.
6. Take care not to pinch the lead when reattaching the case.
) and CN1 (red) (➍) con-
➌
TK-80
4. Installing the IF filter (YK-107C: Option)
1. Install the YK-107C and apply solder to the soldered side.
5. Installing the IF filter (KIF-1: Option)
1. Install the optional KIF-1 and apply solder to the soldered
side.
2. After installing the IF filter, set the unit to dealer mode.
9
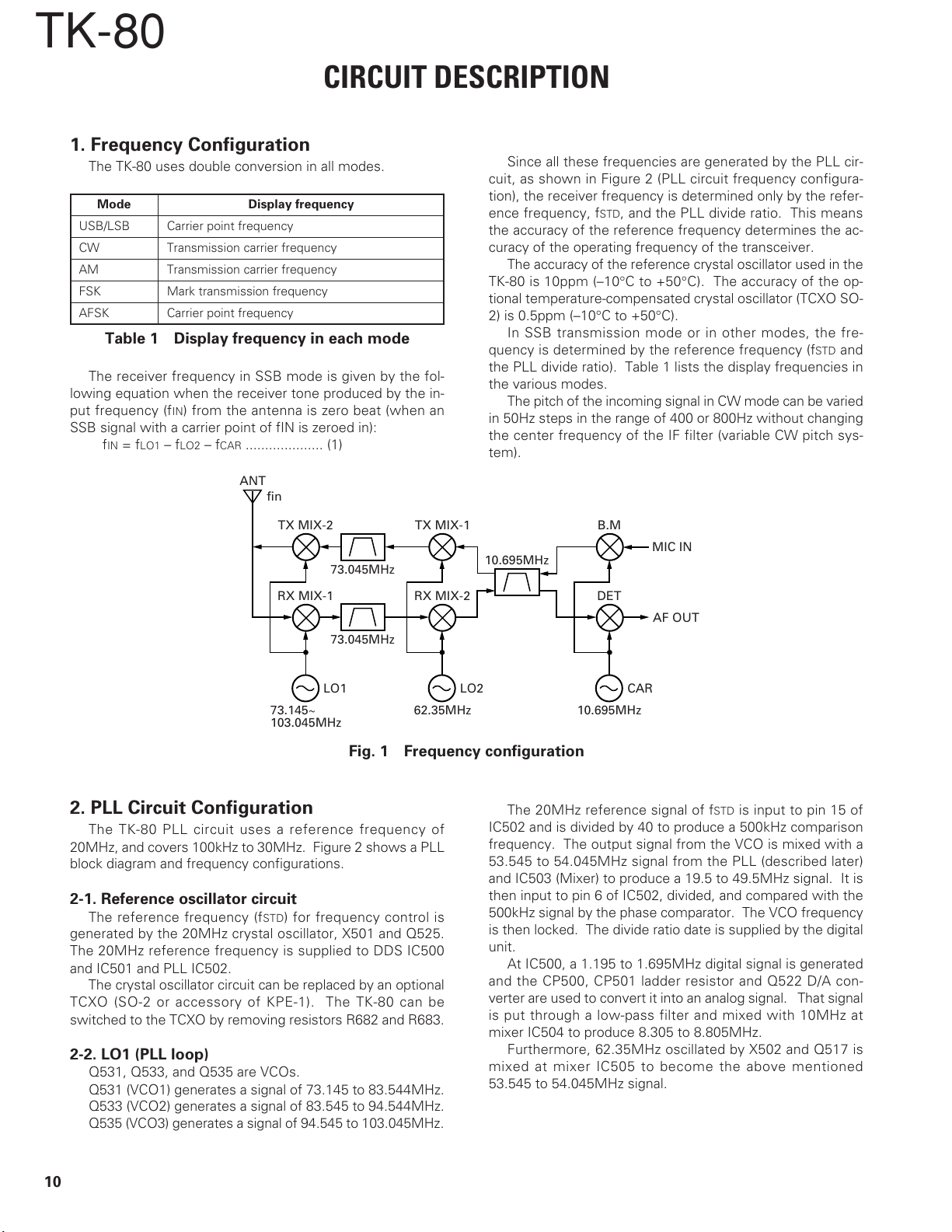
TK-80
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
1. Frequency Configuration
The TK-80 uses double conversion in all modes.
Mode Display frequency
USB/LSB Carrier point frequency
CW Transmission carrier frequency
AM Transmission carrier frequency
FSK Mark transmission frequency
AFSK Carrier point frequency
Table 1 Display frequency in each mode
The receiver frequency in SSB mode is given by the fol-
lowing equation when the receiver tone produced by the in-
put frequency (fIN) from the antenna is zero beat (when an
SSB signal with a carrier point of fIN is zeroed in):
IN = fLO1 – fLO2 – fCAR .................... (1)
f
ANT
fin
Since all these frequencies are generated by the PLL cir-
cuit, as shown in Figure 2 (PLL circuit frequency configura-
tion), the receiver frequency is determined only by the refer-
ence frequency, fSTD, and the PLL divide ratio. This means
the accuracy of the reference frequency determines the ac-
curacy of the operating frequency of the transceiver.
The accuracy of the reference crystal oscillator used in the
TK-80 is 10ppm (–10°C to +50°C). The accuracy of the op-
tional temperature-compensated crystal oscillator (TCXO SO-
2) is 0.5ppm (–10°C to +50°C).
In SSB transmission mode or in other modes, the fre-
quency is determined by the reference frequency (fSTD and
the PLL divide ratio). Table 1 lists the display frequencies in
the various modes.
The pitch of the incoming signal in CW mode can be varied
in 50Hz steps in the range of 400 or 800Hz without changing
the center frequency of the IF filter (variable CW pitch sys-
tem).
TX MIX-2
RX MIX-1
LO1 LO2 CAR
73.145~
103.045MHz
73.045MHz
73.045MHz
TX MIX-1
RX MIX-2
62.35MHz 10.695MHz
Fig. 1 Frequency configuration
2. PLL Circuit Configuration
The TK-80 PLL circuit uses a reference frequency of
20MHz, and covers 100kHz to 30MHz. Figure 2 shows a PLL
block diagram and frequency configurations.
2-1. Reference oscillator circuit
The reference frequency (fSTD) for frequency control is
generated by the 20MHz crystal oscillator, X501 and Q525.
The 20MHz reference frequency is supplied to DDS IC500
and IC501 and PLL IC502.
The crystal oscillator circuit can be replaced by an optional
TCXO (SO-2 or accessory of KPE-1). The TK-80 can be
switched to the TCXO by removing resistors R682 and R683.
2-2. LO1 (PLL loop)
Q531, Q533, and Q535 are VCOs.
Q531 (VCO1) generates a signal of 73.145 to 83.544MHz.
Q533 (VCO2) generates a signal of 83.545 to 94.544MHz.
Q535 (VCO3) generates a signal of 94.545 to 103.045MHz.
B.M
MIC IN
10.695MHz
DET
AF OUT
The 20MHz reference signal of fSTD is input to pin 15 of
IC502 and is divided by 40 to produce a 500kHz comparison
frequency. The output signal from the VCO is mixed with a
53.545 to 54.045MHz signal from the PLL (described later)
and IC503 (Mixer) to produce a 19.5 to 49.5MHz signal. It is
then input to pin 6 of IC502, divided, and compared with the
500kHz signal by the phase comparator. The VCO frequency
is then locked. The divide ratio date is supplied by the digital
unit.
At IC500, a 1.195 to 1.695MHz digital signal is generated
and the CP500, CP501 ladder resistor and Q522 D/A con-
verter are used to convert it into an analog signal. That signal
is put through a low-pass filter and mixed with 10MHz at
mixer IC504 to produce 8.305 to 8.805MHz.
Furthermore, 62.35MHz oscillated by X502 and Q517 is
mixed at mixer IC505 to become the above mentioned
53.545 to 54.045MHz signal.
10
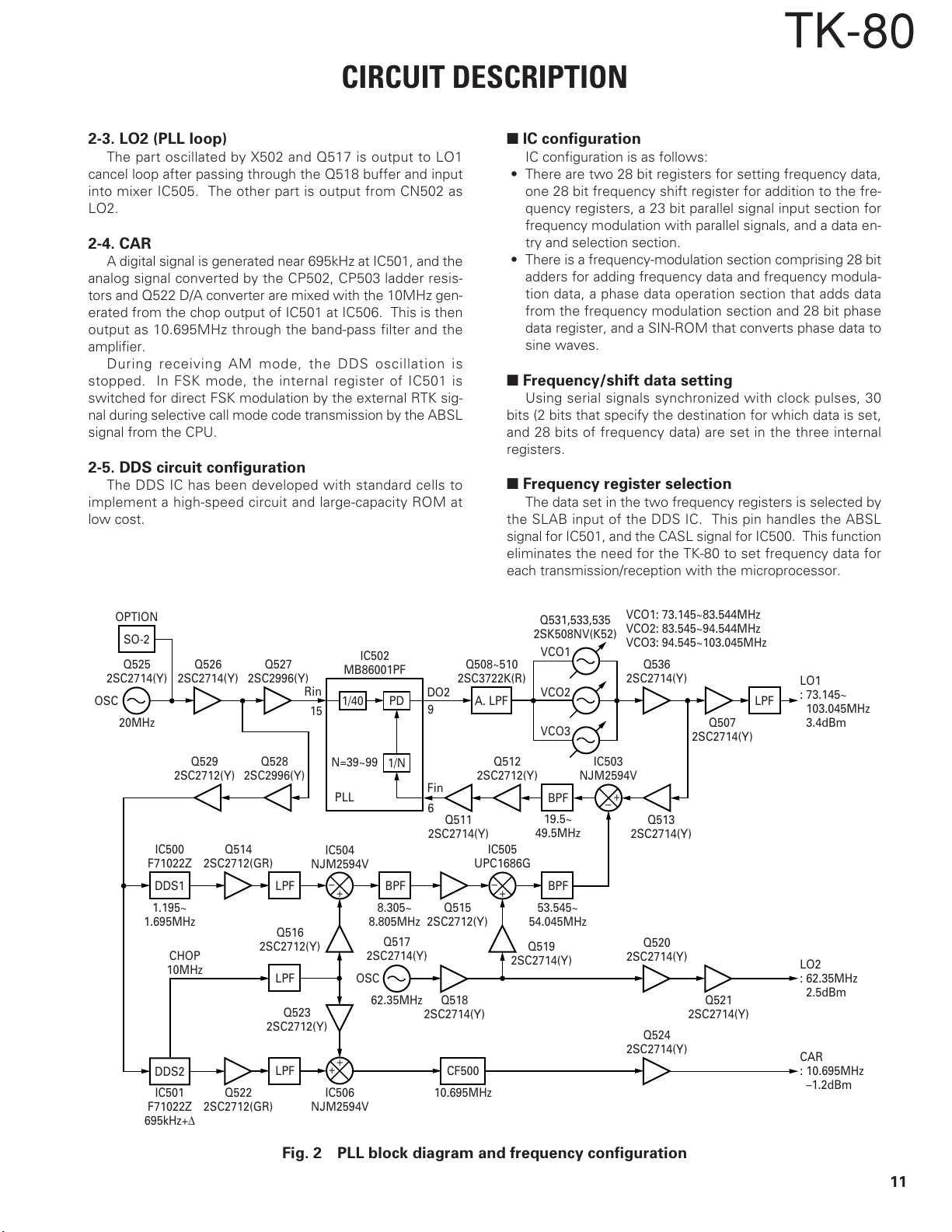
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
TK-80
2-3. LO2 (PLL loop)
The part oscillated by X502 and Q517 is output to LO1
cancel loop after passing through the Q518 buffer and input
into mixer IC505. The other part is output from CN502 as
LO2.
2-4. CAR
A digital signal is generated near 695kHz at IC501, and the
analog signal converted by the CP502, CP503 ladder resis-
tors and Q522 D/A converter are mixed with the 10MHz gen-
erated from the chop output of IC501 at IC506. This is then
output as 10.695MHz through the band-pass filter and the
amplifier.
During receiving AM mode, the DDS oscillation is
stopped. In FSK mode, the internal register of IC501 is
switched for direct FSK modulation by the external RTK sig-
nal during selective call mode code transmission by the ABSL
signal from the CPU.
2-5. DDS circuit configuration
The DDS IC has been developed with standard cells to
implement a high-speed circuit and large-capacity ROM at
low cost.
■ IC configuration
IC configuration is as follows:
• There are two 28 bit registers for setting frequency data,
one 28 bit frequency shift register for addition to the fre-
quency registers, a 23 bit parallel signal input section for
frequency modulation with parallel signals, and a data en-
try and selection section.
• There is a frequency-modulation section comprising 28 bit
adders for adding frequency data and frequency modula-
tion data, a phase data operation section that adds data
from the frequency modulation section and 28 bit phase
data register, and a SIN-ROM that converts phase data to
sine waves.
■ Frequency/shift data setting
Using serial signals synchronized with clock pulses, 30
bits (2 bits that specify the destination for which data is set,
and 28 bits of frequency data) are set in the three internal
registers.
■ Frequency register selection
The data set in the two frequency registers is selected by
the SLAB input of the DDS IC. This pin handles the ABSL
signal for IC501, and the CASL signal for IC500. This function
eliminates the need for the TK-80 to set frequency data for
each transmission/reception with the microprocessor.
OPTION
SO-2
Q525
2SC2714(Y)
OSC
20MHz
2SC2714(Y)
2SC2712(Y)
IC500
F71022Z
1.195~
1.695MHz
CHOP
10MHz
DDS2
IC501
F71022Z
695kHz+∆
Q526
Q529
Q514
2SC2712(GR)
Q522
2SC2712(GR)
Q527
2SC2996(Y)
Q528
2SC2996(Y)
LPF
Q516
2SC2712(Y)
LPF
Q523
2SC2712(Y)
LPF
MB86001PF
Rin
1/40 PD
15
N=39~99
PLL
IC504
NJM2594V
–
+
+
+
IC506
NJM2594V
IC502
1/N
BPFDDS1
8.305~
8.805MHz
Q517
2SC2714(Y)
OSC
62.35MHz
Q508~510
2SC3722K(R)
DO2
9
Fin
6
2SC2714(Y)
2SC2712(Y)
2SC2714(Y)
A. LPF
2SC2712(Y)
Q511
UPC1686G
Q515
Q518
CF500
10.695MHz
Q512
IC505
–
+
2SC2714(Y)
Q531,533,535
2SK508NV(K52)
VCO1
VCO2
VCO3
IC503
NJM2594V
BPF
19.5~
49.5MHz
BPF
53.545~
54.045MHz
Q519
VCO1: 73.145~83.544MHz
VCO2: 83.545~94.544MHz
VCO3: 94.545~103.045MHz
Q536
2SC2714(Y)
Q507
2SC2714(Y)
+
–
Q513
2SC2714(Y)
Q520
2SC2714(Y)
Q521
2SC2714(Y)
Q524
2SC2714(Y)
LPF
LO1
: 73.145~
103.045MHz
3.4dBm
LO2
: 62.35MHz
2.5dBm
CAR
: 10.695MHz
–1.2dBm
Fig. 2 PLL block diagram and frequency configuration
11
TK-80
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
■ Frequency data selection
The SPSL input of the DDS IC selects whether to use the
data in the internal frequency shift register or the data from
the parallel input as frequency modulation data.
■ Frequency modulation
The MDEN input of the DDS IC enables or disables fre-
quency modulation. When frequency modulation is enabled,
frequency data is added, and the result is input to the phase
data operation section.
■ Phase data operation
The target frequency phase data is output by accumulat-
ing 28 bit frequency data in the 28-bit phase accumulator.
FOUT = Fs/228 x Dsum
Fs: DDS IC input frequency/2
Dsum: Frequency data + Frequency modulation data
25
is set for Dsum when 1/8 Fs is output, the phase data
If 2
must be increased by π/8.
So far, 28 bit absolute value operation has been used, but
a 28 bit signed operation can also be used, assuming that the
MSB is a sign. If complement data of 8000000 to FFFFFFFF
(hex) is set, the phase moves in the negative direction for
positive data.
■ SIN-ROM
Phase data from the phase data operation section is con-
verted to sine wave data of 0000 to FFFF (hex) in 16 bit offset
binary format (Fig. 3).
28
2π = 2
FFFFH
25
π/8 = 2
7π/8 = –2
25
0000H
Fig. 3
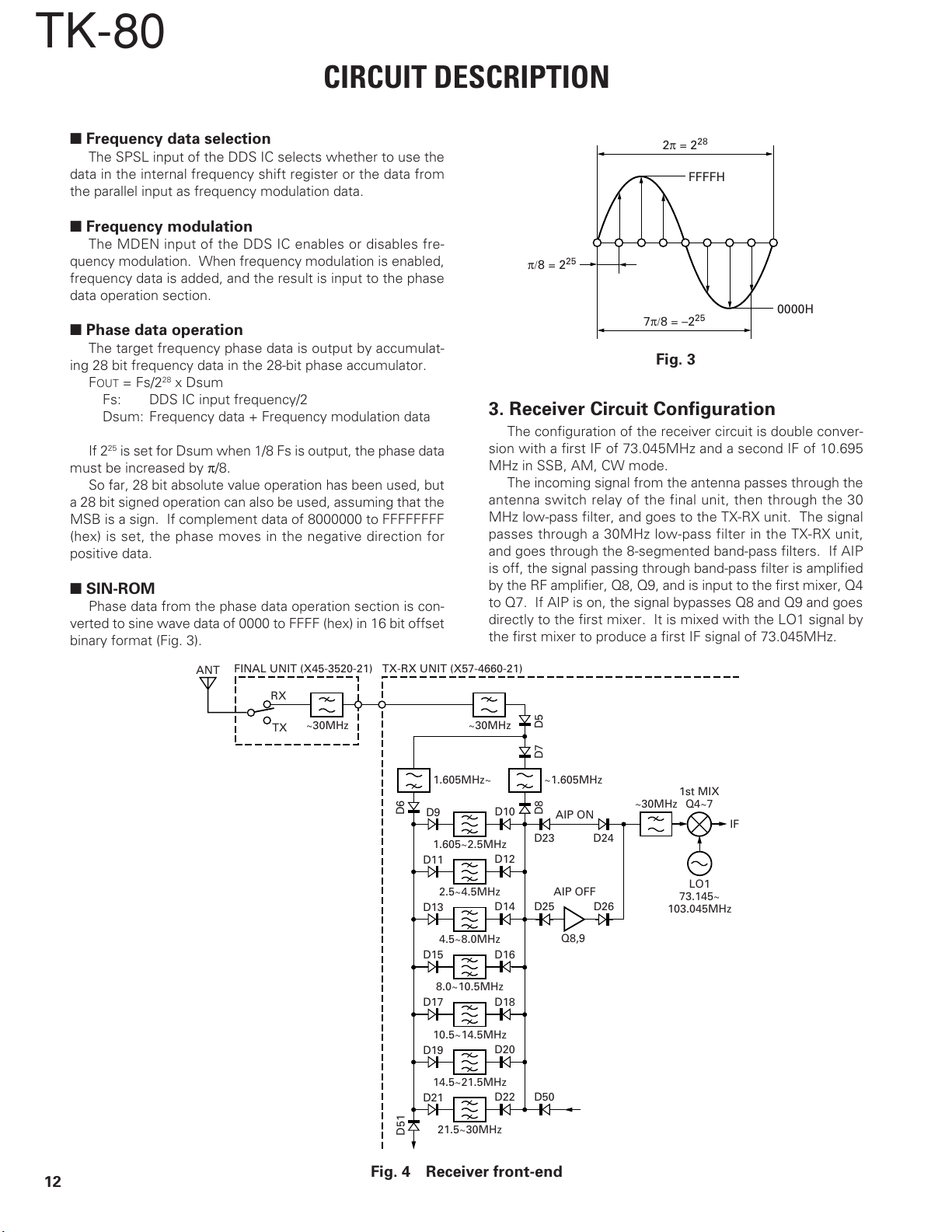
3. Receiver Circuit Configuration
The configuration of the receiver circuit is double conver-
sion with a first IF of 73.045MHz and a second IF of 10.695
MHz in SSB, AM, CW mode.
The incoming signal from the antenna passes through the
antenna switch relay of the final unit, then through the 30
MHz low-pass filter, and goes to the TX-RX unit. The signal
passes through a 30MHz low-pass filter in the TX-RX unit,
and goes through the 8-segmented band-pass filters. If AIP
is off, the signal passing through band-pass filter is amplified
by the RF amplifier, Q8, Q9, and is input to the first mixer, Q4
to Q7. If AIP is on, the signal bypasses Q8 and Q9 and goes
directly to the first mixer. It is mixed with the LO1 signal by
the first mixer to produce a first IF signal of 73.045MHz.
FINAL UNIT (X45-3520-21) TX-RX UNIT (X57-4660-21)
ANT
RX
~30MHz
TX
1.605MHz~ ~1.605MHz
D6
D9
1.605~2.5MHz
D11
D13
D15
D17
10.5~14.5MHz
D19
14.5~21.5MHz
D21
~30MHz
2.5~4.5MHz
4.5~8.0MHz
8.0~10.5MHz
D10
D23 D24
D12
D25 D26
D14
D16
D18
D20
D22 D50
D8 D5D7
AIP ON
AIP OFF
Q8,9
~30MHz
1st MIX
Q4~7
IF
LO1
73.145~
103.045MHz
12
21.5~30MHz
D51
Fig. 4 Receiver front-end
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
TK-80
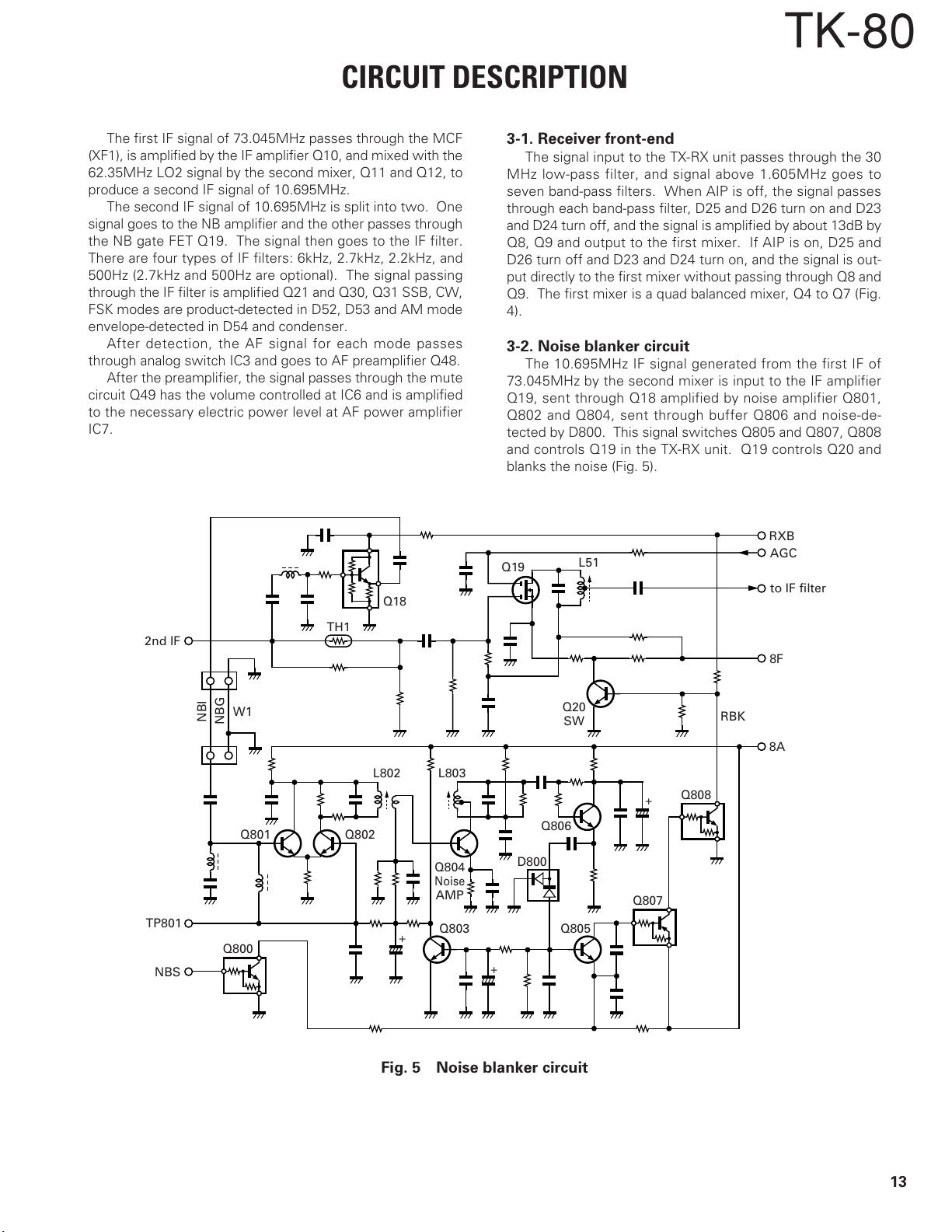
The first IF signal of 73.045MHz passes through the MCF
(XF1), is amplified by the IF amplifier Q10, and mixed with the
62.35MHz LO2 signal by the second mixer, Q11 and Q12, to
produce a second IF signal of 10.695MHz.
The second IF signal of 10.695MHz is split into two. One
signal goes to the NB amplifier and the other passes through
the NB gate FET Q19. The signal then goes to the IF filter.
There are four types of IF filters: 6kHz, 2.7kHz, 2.2kHz, and
500Hz (2.7kHz and 500Hz are optional). The signal passing
through the IF filter is amplified Q21 and Q30, Q31 SSB, CW,
FSK modes are product-detected in D52, D53 and AM mode
envelope-detected in D54 and condenser.
After detection, the AF signal for each mode passes
through analog switch IC3 and goes to AF preamplifier Q48.
After the preamplifier, the signal passes through the mute
circuit Q49 has the volume controlled at IC6 and is amplified
to the necessary electric power level at AF power amplifier
IC7.
Q18
TH1
2nd IF
3-1. Receiver front-end
The signal input to the TX-RX unit passes through the 30
MHz low-pass filter, and signal above 1.605MHz goes to
seven band-pass filters. When AIP is off, the signal passes
through each band-pass filter, D25 and D26 turn on and D23
and D24 turn off, and the signal is amplified by about 13dB by
Q8, Q9 and output to the first mixer. If AIP is on, D25 and
D26 turn off and D23 and D24 turn on, and the signal is out-
put directly to the first mixer without passing through Q8 and
Q9. The first mixer is a quad balanced mixer, Q4 to Q7 (Fig.
4).
3-2. Noise blanker circuit
The 10.695MHz IF signal generated from the first IF of
73.045MHz by the second mixer is input to the IF amplifier
Q19, sent through Q18 amplified by noise amplifier Q801,
Q802 and Q804, sent through buffer Q806 and noise-de-
tected by D800. This signal switches Q805 and Q807, Q808
and controls Q19 in the TX-RX unit. Q19 controls Q20 and
blanks the noise (Fig. 5).
RXB
Q19
L51
AGC
to IF filter
8F
TP801
NBS
NBI
W1
NBG
Q801
Q800
L802 L803
Q802
Q804
Noise
AMP
Q803 Q805
+
+
Fig. 5 Noise blanker circuit
D800
Q806
Q20
SW
+
Q807
RBK
8A
Q808
13
TK-80
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
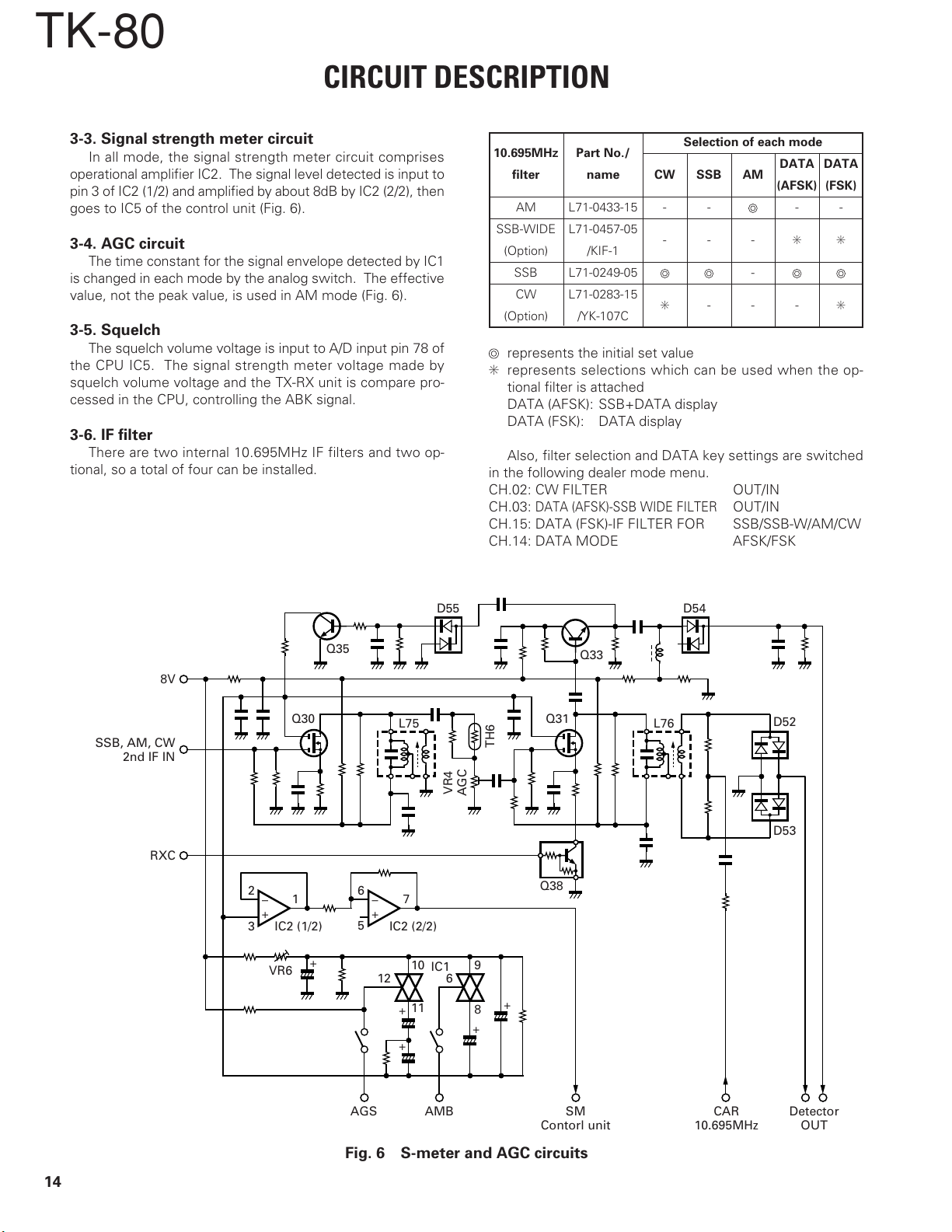
3-3. Signal strength meter circuit
In all mode, the signal strength meter circuit comprises
operational amplifier IC2. The signal level detected is input to
pin 3 of IC2 (1/2) and amplified by about 8dB by IC2 (2/2), then
goes to IC5 of the control unit (Fig. 6).
3-4. AGC circuit
The time constant for the signal envelope detected by IC1
is changed in each mode by the analog switch. The effective
value, not the peak value, is used in AM mode (Fig. 6).
3-5. Squelch
The squelch volume voltage is input to A/D input pin 78 of
the CPU IC5. The signal strength meter voltage made by
squelch volume voltage and the TX-RX unit is compare pro-
cessed in the CPU, controlling the ABK signal.
3-6. IF filter
There are two internal 10.695MHz IF filters and two op-
tional, so a total of four can be installed.
10.695MHz Part No./
filter name CW SSB AM
AM L71-0433-15 - - --
SSB-WIDE L71-0457-05
(Option) /KIF-1
SSB L71-0249-05 -
CW L71-0283-15
(Option) /YK-107C
Selection of each mode
DATA DATA
(AFSK) (FSK)
---✳✳
✳ ---✳
represents the initial set value
✳ represents selections which can be used when the op-
tional filter is attached
DATA (AFSK): SSB+DATA display
DATA (FSK): DATA display
Also, filter selection and DATA key settings are switched
in the following dealer mode menu.
CH.02: CW FILTER OUT/IN
CH.03:
DATA (AFSK)-SSB WIDE FILTER
OUT/IN
CH.15: DATA (FSK)-IF FILTER FOR SSB/SSB-W/AM/CW
CH.14: DATA MODE AFSK/FSK
8V
SSB, AM, CW
2nd IF IN
RXC
Q35
Q30
2
17
–
+
3
IC2 (1/2) IC2 (2/2)
+
VR6
L75
6
–
+
5
12 6
+
+
10
11
D55 D54
Q33
IC1
VR4
AGC
9
8
+
Q31
TH6
Q38
+
L76
D52
D53
14
AGS AMB SM
Contorl unit
Fig. 6 S-meter and AGC circuits
CAR
10.695MHz
Detector
OUT

CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
TK-80
Item Rating
Center frequency (fo) 73.045MHz
Pass bandwidth ±7.5kHz or more at 3dB
Attenuation bandwidth ± 30kHz or less at 20dB
Ripple 1dB or less
Insertion loss 2dB or less
Guaranteed attenuation 40dB or more at fo–910kHz
Terminal impedance 2kΩ± 10% // L type
Temperature range –30°C~+70°C
Table 2 MCF (XF1) (L71-0432-05)
Item Rating
Nominal center frequency (fo) 10.695MHz
Pass bandwidth 6kHz or more at 6dB
Attenuation bandwidth 40kHz or less at 60dB
Ripple 2dB or less
Insertion loss 3dB or less
Guaranteed attenuation 60dB or more within fo±1MHz
Terminal impedance 1.2kΩ± 10% // 6pF± 10%
Table 3 MCF (XF3) (L71-0433-15)
Item Rating
Nominal center frequency (fo) 10.695MHz
Center frequency deviation Within ±200Hz at 6dB
Pass bandwidth and Width 2.75kHz or more at 6dB
Attenuation bandwidth ± 2.2kHz or less at 20dB
±3.1kHz or less at 60dB
Ripple 2dB or less
Insertion loss 6dB or less
Terminal impedance 1.2kΩ± 5% // 8pF± 10%
Temperature range –10°C~+60°C
Table 4 MCF (L71-0457-05) KIF-1: SSB WIDE (Option)
Item Rating
Nominal center frequency (fo) 10.695MHz
Center frequency deviation Within ±200Hz at 6dB
Pass bandwidth and 2.2kHz or more at 6dB
Attenuation bandwidth ± 1.5kHz or less at 20dB
±2.4kHz or less at 60dB
Ripple 2dB or less
Insertion loss 5dB or less
Guaranteed attenuation 60dB or more within fo±40kHz
Terminal impedance 1.2kΩ± 5% // 6pF± 5%
Table 5 MCF (XF2) (L71-0249-05)
Item Rating
Nominal center frequency (fo) 10.695MHz
Center frequency deviation Within ±80Hz (25°C, 6dB)
Pass bandwidth 500Hz or more (6dB)
Insertion loss 5dB±2dB
Terminal impedance 1200Ω // 6pF
Table 6 MCF (L71-0283-15) YK-107C: CW (Option)
4. Transmitter Circuit Configuration
The audio signal from the microphone enters CN 12 of the
TX-RX unit. The signal then goes to IC9, the microphone
amplifier. After amplifying part of IC9’s output at Q54, it is
detected by D59 and applied to the ALC terminal of IC9. The
signal gain is properly adjusted by the D/A converter IC13 and
passes through analog switch IC8, is amplified by Q50. The
amplified signal is balance-modulated with the CAR signal
(10.695MHz) input from CN9 by IC4 passed through Q51,
and sent to the crystal filter passing through the filter, is am-
plified by Q24. The signal is CAR level adjusted by the D48
pin diode, and input to the mixer.
The 62.35MHz LO2 signal from the PLL unit is input from
CN3 of the TX-RX unit, and mixed with the 10.695MHz signal
which CAR level adjusted amplified by Q25 and Q26 to pro-
duce a 73.045MHz signal. The LO1 signal from the PLL unit
is input from CN2 of the TX-RX unit, and mixed with the
73.045MHz signal passes through LC three-stage filter by
Q27 and Q28 to generate the desired signal. The signal
passes through the band-pass filter and is amplified by Q29
to produce the drive output, which goes to the final unit from
CN19.
The signal is amplified to about 100W by Q1, Q2, Q3 and
Q5, Q6. Harmonic components are attenuated by the filter
unit and the signal is output from the antenna connector.
In AM mode, the signal is generated by unbalancing the
carrier of SSB balance modulator IC4.
In CW mode, the signal is input to IC5 of the control unit.
The sidetone monitor signal is generated by IC5, and ampli-
fied by audio amplifier Q79 and IC7, and output from the
speaker. The CW control signal is output from IC5 of the
control unit, and input to CN14 of the TX-RX unit to switch
Q25 and Q26 and generate the CW signal.
4-1. ALC circuit
The forward wave voltage detected in the final unit passes
through CN15 in the TX-RX unit, its level is potential dividing
and it is applied to the differential amplifier comprising Q60
and Q61. When VSF is applied to the base of Q60, the emit-
ter voltage of Q60 and Q61 increases and the current flowing
through the base of Q61 decreases; thus the collector volt-
age rises. When this voltage exceeds the emitter voltage of
Q62 (about 1.8V) plus V
through the base of Q62 and the collector voltage drops.
ALC time constants C and R are connected to this collector.
The collector voltage change is shifted by Q64 and D68
(3.6V), and matched with the voltage for keying by Q65 and
D69 to generate the ALC voltage. This ALC voltage activates
ALC by lowering the second gate voltage of Q24 of the TX-RX
unit (Fig. 7).
BE (about 0.6V), the current flows
15
TK-80
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
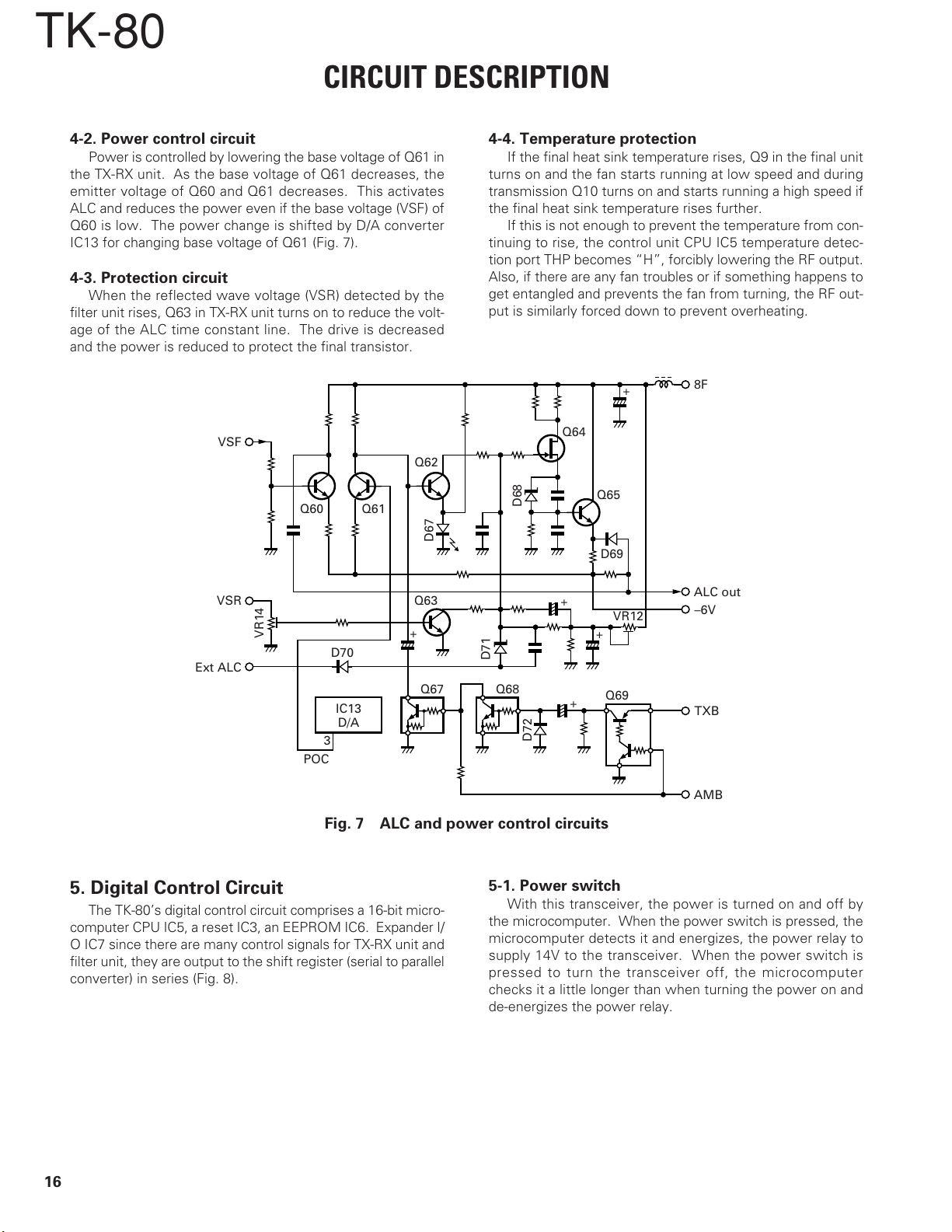
4-2. Power control circuit
Power is controlled by lowering the base voltage of Q61 in
the TX-RX unit. As the base voltage of Q61 decreases, the
emitter voltage of Q60 and Q61 decreases. This activates
ALC and reduces the power even if the base voltage (VSF) of
Q60 is low. The power change is shifted by D/A converter
IC13 for changing base voltage of Q61 (Fig. 7).
4-3. Protection circuit
When the reflected wave voltage (VSR) detected by the
filter unit rises, Q63 in TX-RX unit turns on to reduce the volt-
age of the ALC time constant line. The drive is decreased
and the power is reduced to protect the final transistor.
VSF
Q62
Q60 Q61
D67
4-4. Temperature protection
If the final heat sink temperature rises, Q9 in the final unit
turns on and the fan starts running at low speed and during
transmission Q10 turns on and starts running a high speed if
the final heat sink temperature rises further.
If this is not enough to prevent the temperature from con-
tinuing to rise, the control unit CPU IC5 temperature detec-
tion port THP becomes “H”, forcibly lowering the RF output.
Also, if there are any fan troubles or if something happens to
get entangled and prevents the fan from turning, the RF out-
put is similarly forced down to prevent overheating.
8F
D68
+
Q64
Q65
D69
VSR
VR14
D70
Ext ALC
IC13
D/A
3
POC
Q63
+
Q67 Q68
Fig. 7 ALC and power control circuits
5. Digital Control Circuit
The TK-80’s digital control circuit comprises a 16-bit micro-
computer CPU IC5, a reset IC3, an EEPROM IC6. Expander I/
O IC7 since there are many control signals for TX-RX unit and
filter unit, they are output to the shift register (serial to parallel
converter) in series (Fig. 8).
ALC out
–6V
TXB
AMB
D71
D72
+
VR12
+
Q69
+
5-1. Power switch
With this transceiver, the power is turned on and off by
the microcomputer. When the power switch is pressed, the
microcomputer detects it and energizes, the power relay to
supply 14V to the transceiver. When the power switch is
pressed to turn the transceiver off, the microcomputer
checks it a little longer than when turning the power on and
de-energizes the power relay.
16
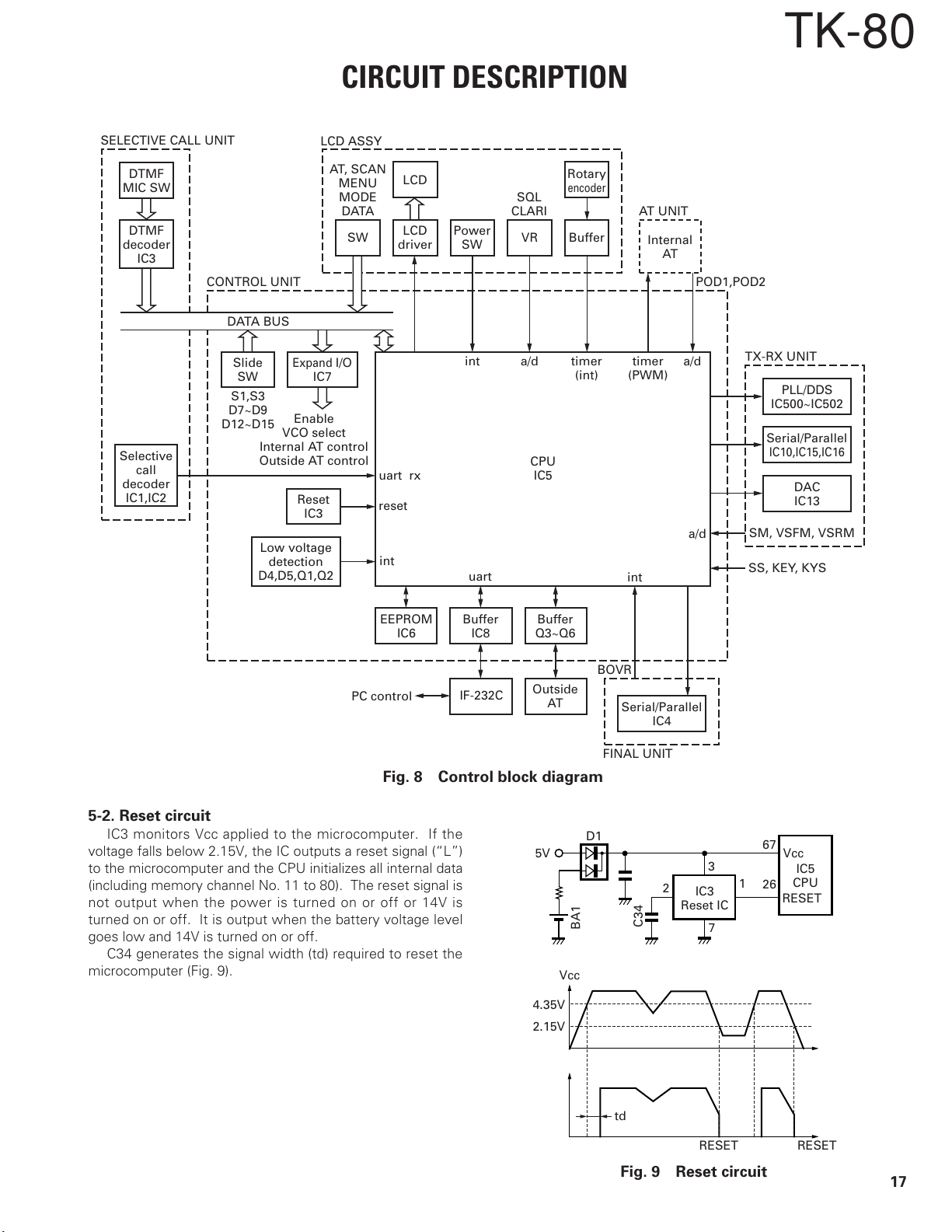
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
TK-80
SELECTIVE CALL UNIT
DTMF
MIC SW
DTMF
decoder
IC3
CONTROL UNIT
D12~D15
Selective
call
decoder
IC1,IC2
DATA BUS
Slide
SW
S1,S3
D7~D9
Expand
Enable
VCO select
Internal AT control
Outside AT control
Low voltage
detection
D4,D5,Q1,Q2
LCD ASSY
IC7
Reset
IC3
AT, SCAN
MENU
MODE
DATA
SW
I/O
LCD
LCD
driver
uart rx
reset
int
SQL
CLARI
Power
SW
int a/d a/dtimer
uart
VR Buffer
CPU
IC5
Rotary
encoder
(int)
AT UNIT
Internal
timer
(PWM)
int
AT
POD1,POD2
a/d
TX-RX UNIT
PLL/DDS
IC500~IC502
Serial/Parallel
IC10,IC15,IC16
DAC
IC13
SM, VSFM, VSRM
SS, KEY, KYS
EEPROM
IC6
PC control
Fig. 8 Control block diagram
5-2. Reset circuit
IC3 monitors Vcc applied to the microcomputer. If the
voltage falls below 2.15V, the IC outputs a reset signal (“L”)
to the microcomputer and the CPU initializes all internal data
(including memory channel No. 11 to 80). The reset signal is
not output when the power is turned on or off or 14V is
turned on or off. It is output when the battery voltage level
goes low and 14V is turned on or off.
C34 generates the signal width (td) required to reset the
microcomputer (Fig. 9).
Buffer
IC8
IF-232C
Buffer
Q3~Q6
Outside
AT
5V
Vcc
4.35V
2.15V
BOVR
FINAL UNIT
D1
BA1
Serial/Parallel
IC4
2
Reset IC
C34
IC3
67
3
7
Vcc
IC5
26
CPU
RESET
1
td
RESET RESET
Fig. 9 Reset circuit
17
TK-80
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
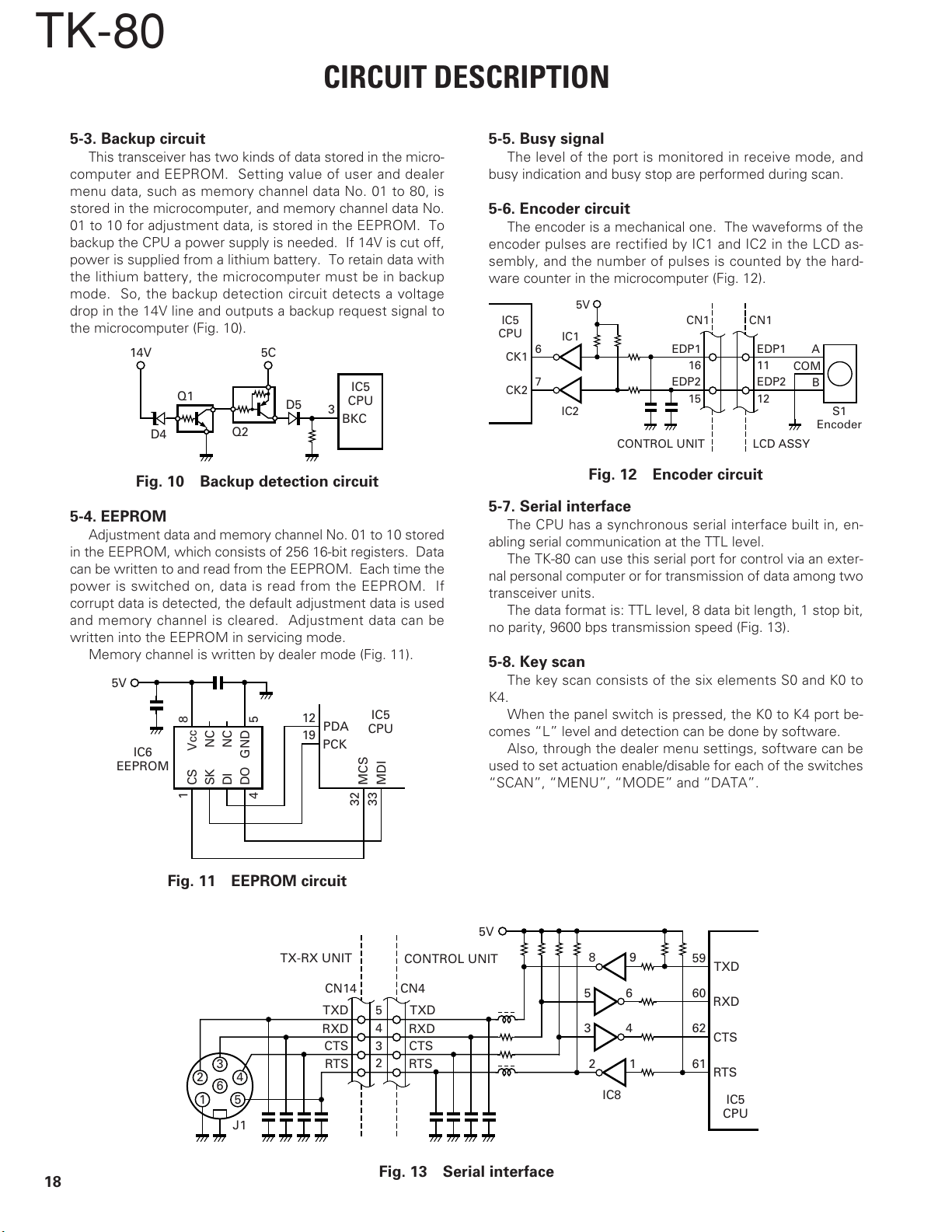
5-3. Backup circuit
This transceiver has two kinds of data stored in the micro-
computer and EEPROM. Setting value of user and dealer
menu data, such as memory channel data No. 01 to 80, is
stored in the microcomputer, and memory channel data No.
01 to 10 for adjustment data, is stored in the EEPROM. To
backup the CPU a power supply is needed. If 14V is cut off,
power is supplied from a lithium battery. To retain data with
the lithium battery, the microcomputer must be in backup
mode. So, the backup detection circuit detects a voltage
drop in the 14V line and outputs a backup request signal to
the microcomputer (Fig. 10).
5C14V
IC5
CPU
3
BKC
D4
Q1
D5
Q2
Fig. 10 Backup detection circuit
5-4. EEPROM
Adjustment data and memory channel No. 01 to 10 stored
in the EEPROM, which consists of 256 16-bit registers. Data
can be written to and read from the EEPROM. Each time the
power is switched on, data is read from the EEPROM. If
corrupt data is detected, the default adjustment data is used
and memory channel is cleared. Adjustment data can be
written into the EEPROM in servicing mode.
Memory channel is written by dealer mode (Fig. 11).
5V
32
IC5
CPU
MCS
33
MDI
IC6
EEPROM
81
Vcc
CSSKDI
12
NC
NC
GND
DO
19
45
PDA
PCK
5-5. Busy signal
The level of the port is monitored in receive mode, and
busy indication and busy stop are performed during scan.
5-6. Encoder circuit
The encoder is a mechanical one. The waveforms of the
encoder pulses are rectified by IC1 and IC2 in the LCD as-
sembly, and the number of pulses is counted by the hard-
ware counter in the microcomputer (Fig. 12).
5V
IC5
CPU
CK1
CK2
IC1
6
7
IC2
CONTROL UNIT LCD ASSY
CN1
EDP1
16
EDP2
15
CN1
EDP1
11
EDP2
12
A
COM
B
S1
Encoder
Fig. 12 Encoder circuit
5-7. Serial interface
The CPU has a synchronous serial interface built in, en-
abling serial communication at the TTL level.
The TK-80 can use this serial port for control via an exter-
nal personal computer or for transmission of data among two
transceiver units.
The data format is: TTL level, 8 data bit length, 1 stop bit,
no parity, 9600 bps transmission speed (Fig. 13).
5-8. Key scan
The key scan consists of the six elements S0 and K0 to
K4.
When the panel switch is pressed, the K0 to K4 port be-
comes “L” level and detection can be done by software.
Also, through the dealer menu settings, software can be
used to set actuation enable/disable for each of the switches
“SCAN”, “MENU”, “MODE” and “DATA”.
18
Fig. 11 EEPROM circuit
TX-RX UNIT
TXD
RXD
CTS
3
6
1 5
42
J1
RTS
5V
CONTROL UNIT
CN4CN14
TXD
5
4
RXD
3
CTS
2
RTS
Fig. 13 Serial interface
98
5
6
4
3
21
IC8
59
60
62
61
TXD
RXD
CTS
RTS
IC5
CPU
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
TK-80
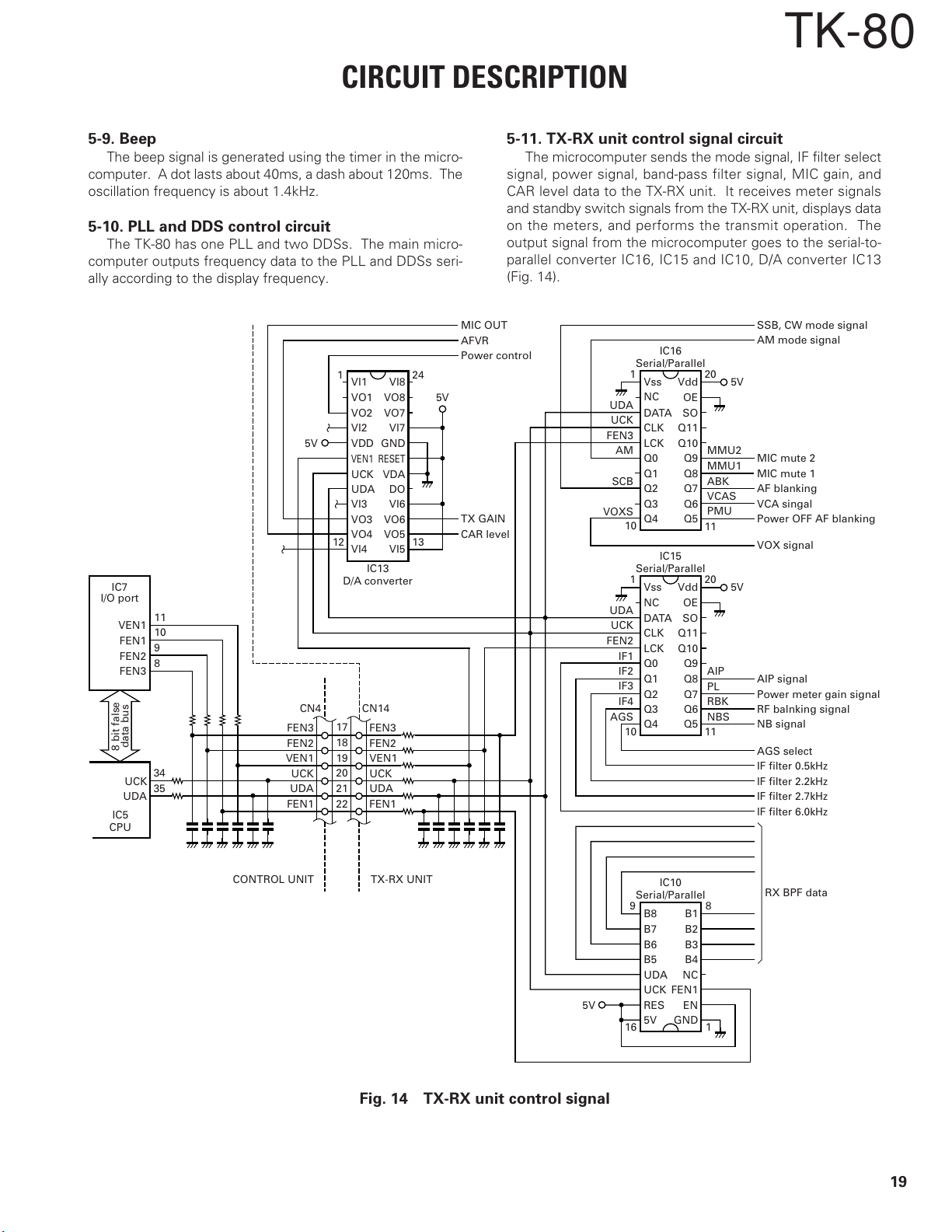
5-9. Beep
The beep signal is generated using the timer in the micro-
computer. A dot lasts about 40ms, a dash about 120ms. The
oscillation frequency is about 1.4kHz.
5-10. PLL and DDS control circuit
The TK-80 has one PLL and two DDSs. The main micro-
computer outputs frequency data to the PLL and DDSs seri-
ally according to the display frequency.
IC7
I/O port
VEN1
FEN1
FEN2
FEN3
8 bit false
UCK
UDA
IC5
CPU
11
10
9
8
data bus
34
35
5V
FEN3
FEN2
VEN1
UCK
UDA
FEN1
1
VI1
VO1
VO2
VI2
VDD
VEN1
UCK
UDA
VI3
VO3
VO4
12 13
VI4
D/A converter
CN14CN4
17
18
19
20
21
22
RESET
IC13
FEN3
FEN2
VEN1
UCK
UDA
FEN1
VI8
VO8
VO7
VI7
GND
VDA
DO
VI6
VO6
VO5
VI5
24
5V
5-11. TX-RX unit control signal circuit
The microcomputer sends the mode signal, IF filter select
signal, power signal, band-pass filter signal, MIC gain, and
CAR level data to the TX-RX unit. It receives meter signals
and standby switch signals from the TX-RX unit, displays data
on the meters, and performs the transmit operation. The
output signal from the microcomputer goes to the serial-to-
parallel converter IC16, IC15 and IC10, D/A converter IC13
(Fig. 14).
MIC OUT
AFVR
Power control
TX GAIN
CAR level
UDA
UCK
FEN3
AM
SCB
VOXS
10
UDA
UCK
FEN2
IF1
IF2
IF3
IF4
AGS
10
IC16
Serial/Parallel
1
Vss
Vdd
NC
DATA
CLK
Q11
LCK
Q10
Q0
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
IC15
Serial/Parallel
1
Vss
Vdd
NC
DATA
CLK
Q11
LCK
Q10
Q0
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
OE
SO
Q9
Q8
Q7
Q6
Q5
OE
SO
Q9
Q8
Q7
Q6
Q5
20
MMU2
MMU1
ABK
VCAS
PMU
11
20
AIP
PL
RBK
NBS
11
SSB, CW mode signal
AM mode signal
5V
MIC mute 2
MIC mute 1
AF blanking
VCA singal
Power OFF AF blanking
VOX signal
5V
AIP signal
Power meter gain signal
RF balnking signal
NB signal
AGS select
IF filter 0.5kHz
IF filter 2.2kHz
IF filter 2.7kHz
IF filter 6.0kHz
TX-RX UNITCONTROL UNIT
5V
Fig. 14 TX-RX unit control signal
IC10
Serial/Parallel
98
B8
B1
B7
B2
B6
B3
B5
B4
UDA
NC
UCK
FEN1
RES
EN
5V
16
GND
1
RX BPF data
19
TK-80
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
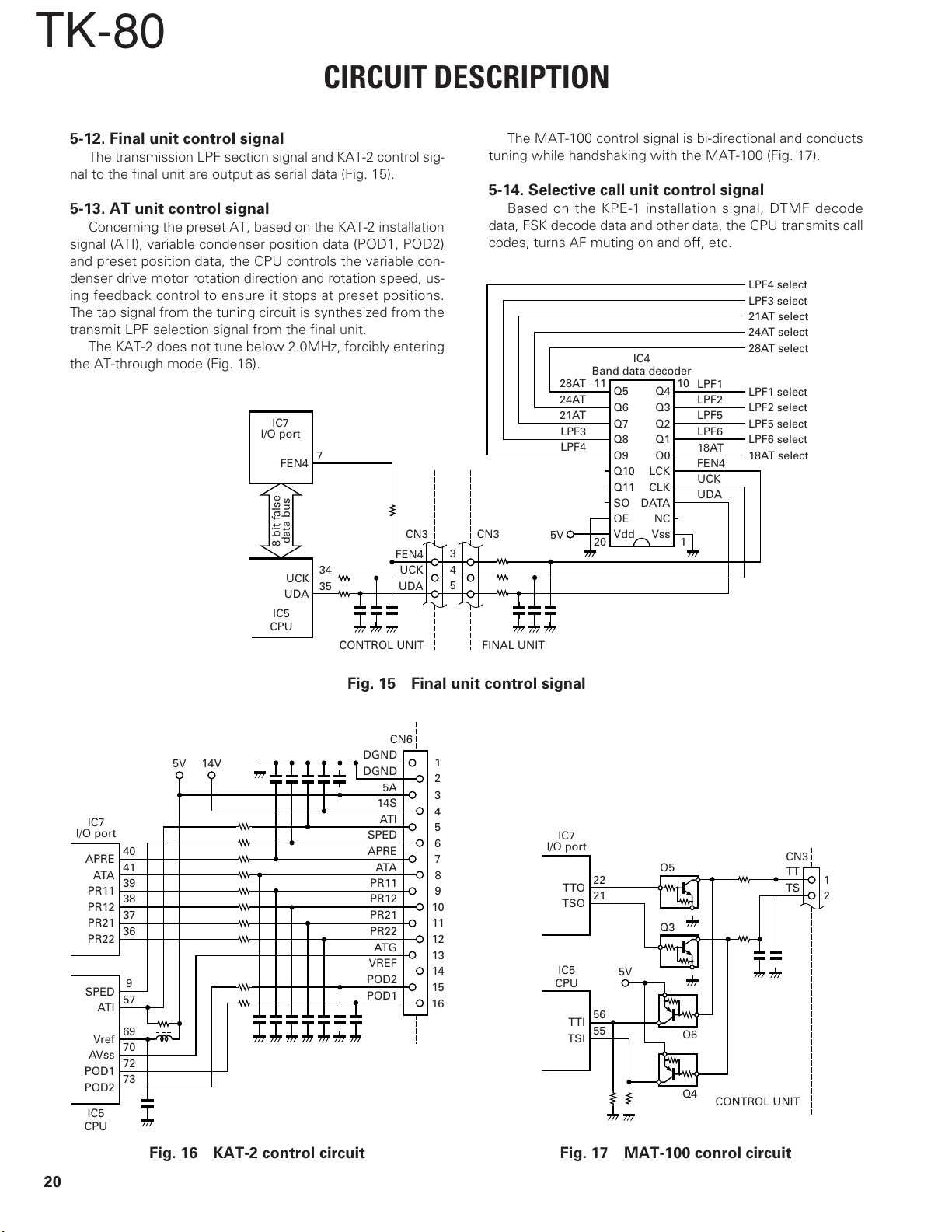
5-12. Final unit control signal
The transmission LPF section signal and KAT-2 control sig-
nal to the final unit are output as serial data (Fig. 15).
5-13. AT unit control signal
Concerning the preset AT, based on the KAT-2 installation
signal (ATI), variable condenser position data (POD1, POD2)
and preset position data, the CPU controls the variable con-
denser drive motor rotation direction and rotation speed, us-
ing feedback control to ensure it stops at preset positions.
The tap signal from the tuning circuit is synthesized from the
transmit LPF selection signal from the final unit.
The KAT-2 does not tune below 2.0MHz, forcibly entering
the AT-through mode (Fig. 16).
IC7
I/O port
7
FEN4
data bus
8 bit false
UCK
UDA
IC5
CPU
34
35
FEN4
UCK
UDA
The MAT-100 control signal is bi-directional and conducts
tuning while handshaking with the MAT-100 (Fig. 17).
5-14. Selective call unit control signal
Based on the KPE-1 installation signal, DTMF decode
data, FSK decode data and other data, the CPU transmits call
codes, turns AF muting on and off, etc.
LPF4 select
LPF3 select
21AT select
24AT select
IC4
Band data decoder
11
28AT
24AT
21AT
LPF3
LPF4
CN3CN3
3
4
5
FINAL UNITCONTROL UNIT
5V
20
Q5
Q6
Q7
Q8
Q9
Q10
Q11
SO
OE
Vdd
Q4
Q3
Q2
Q1
Q0
LCK
CLK
DATA
NC
Vss
10
LPF1
LPF2
LPF5
LPF6
18AT
FEN4
UCK
UDA
1
28AT select
LPF1 select
LPF2 select
LPF5 select
LPF6 select
18AT select
IC7
I/O port
APRE
ATA
PR11
PR12
PR21
PR22
SPED
ATI
Vref
AVss
POD1
POD2
IC5
CPU
40
41
39
38
37
36
57
69
70
72
73
Fig. 15 Final unit control signal
CN6
5V 14V
9
DGND
DGND
5A
14S
ATI
SPED
APRE
ATA
PR11
PR12
PR21
PR22
ATG
VREF
POD2
POD1
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
IC7
I/O port
TTO
TSO
IC5
CPU
TTI
TSI
22
21
56
55
5V
Q5
Q3
Q6
Q4
CONTROL UNIT
CN3
TT
TS
1
2
20
Fig. 16 KAT-2 control circuit Fig. 17 MAT-100 conrol circuit
TK-80
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA
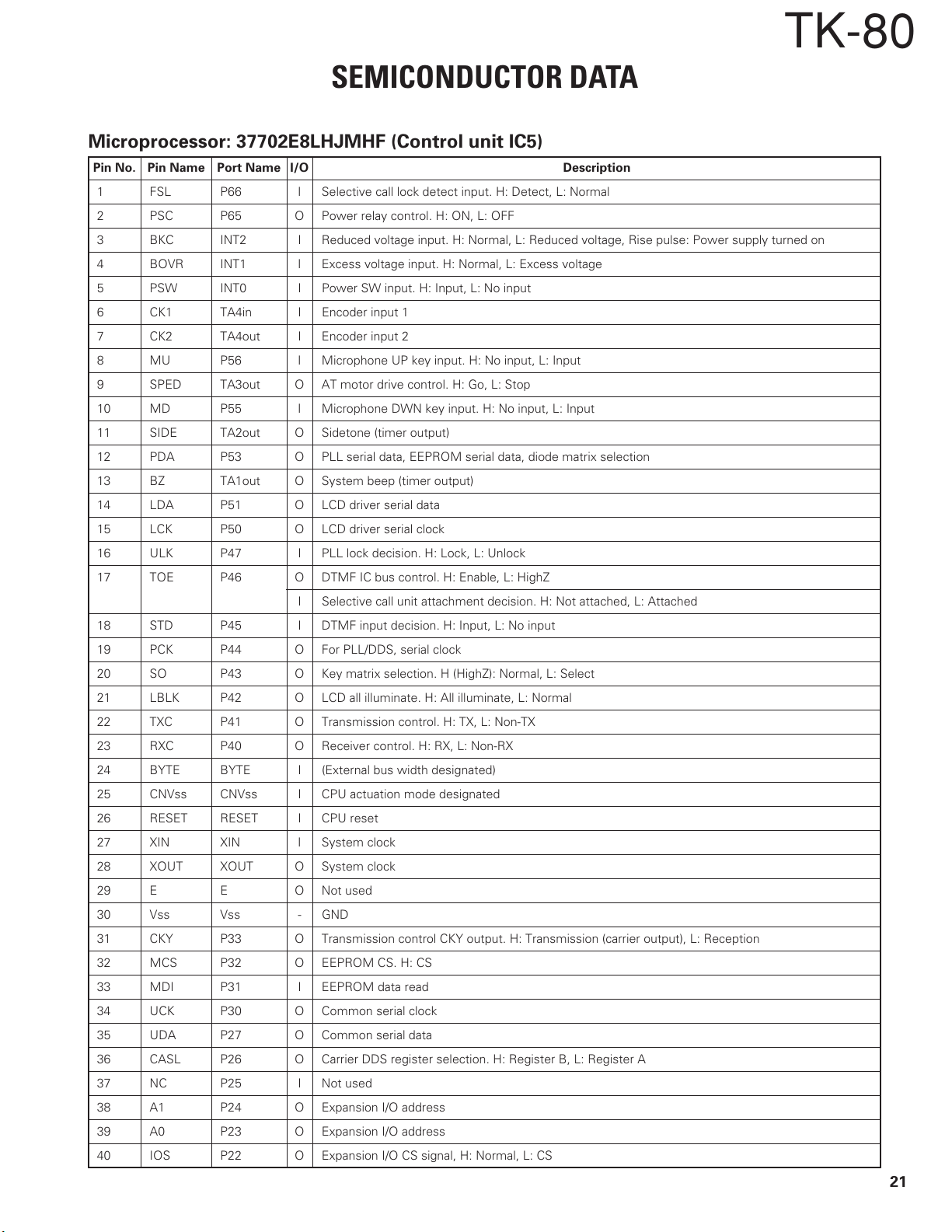
Microprocessor: 37702E8LHJMHF (Control unit IC5)
Pin No. Pin Name Port Name I/O Description
1 FSL P66 I Selective call lock detect input. H: Detect, L: Normal
2 PSC P65 O Power relay control. H: ON, L: OFF
3 BKC INT2 I Reduced voltage input. H: Normal, L: Reduced voltage, Rise pulse: Power supply turned on
4 BOVR INT1 I Excess voltage input. H: Normal, L: Excess voltage
5 PSW INT0 I Power SW input. H: Input, L: No input
6 CK1 TA4in I Encoder input 1
7 CK2 TA4out I Encoder input 2
8MU P56 I Microphone UP key input. H: No input, L: Input
9 SPED TA3out O AT motor drive control. H: Go, L: Stop
10 MD P55 I Microphone DWN key input. H: No input, L: Input
11 SIDE TA2out O Sidetone (timer output)
12 PDA P53 O PLL serial data, EEPROM serial data, diode matrix selection
13 BZ TA1out O System beep (timer output)
14 LDA P51 O LCD driver serial data
15 LCK P50 O LCD driver serial clock
16 ULK P47 I PLL lock decision. H: Lock, L: Unlock
17 TOE P46 O DTMF IC bus control. H: Enable, L: HighZ
I Selective call unit attachment decision. H: Not attached, L: Attached
18 STD P45 I DTMF input decision. H: Input, L: No input
19 PCK P44 O For PLL/DDS, serial clock
20 SO P43 O Key matrix selection. H (HighZ): Normal, L: Select
21 LBLK P42 O LCD all illuminate. H: All illuminate, L: Normal
22 TXC P41 O Transmission control. H: TX, L: Non-TX
23 RXC P40 O Receiver control. H: RX, L: Non-RX
24 BYTE BYTE I (External bus width designated)
25 CNVss CNVss I CPU actuation mode designated
26 RESET RESET I CPU reset
27 XIN XIN I System clock
28 XOUT XOUT O System clock
29 E E O Not used
30 Vss Vss - GND
31 CKY P33 O Transmission control CKY output. H: Transmission (carrier output), L: Reception
32 MCS P32 O EEPROM CS. H: CS
33 MDI P31 I EEPROM data read
34 UCK P30 O Common serial clock
35 UDA P27 O Common serial data
36 CASL P26 O Carrier DDS register selection. H: Register B, L: Register A
37 NC P25 I Not used
38 A1 P24 O Expansion I/O address
39 A0 P23 O Expansion I/O address
40 IOS P22 O Expansion I/O CS signal, H: Normal, L: CS
21
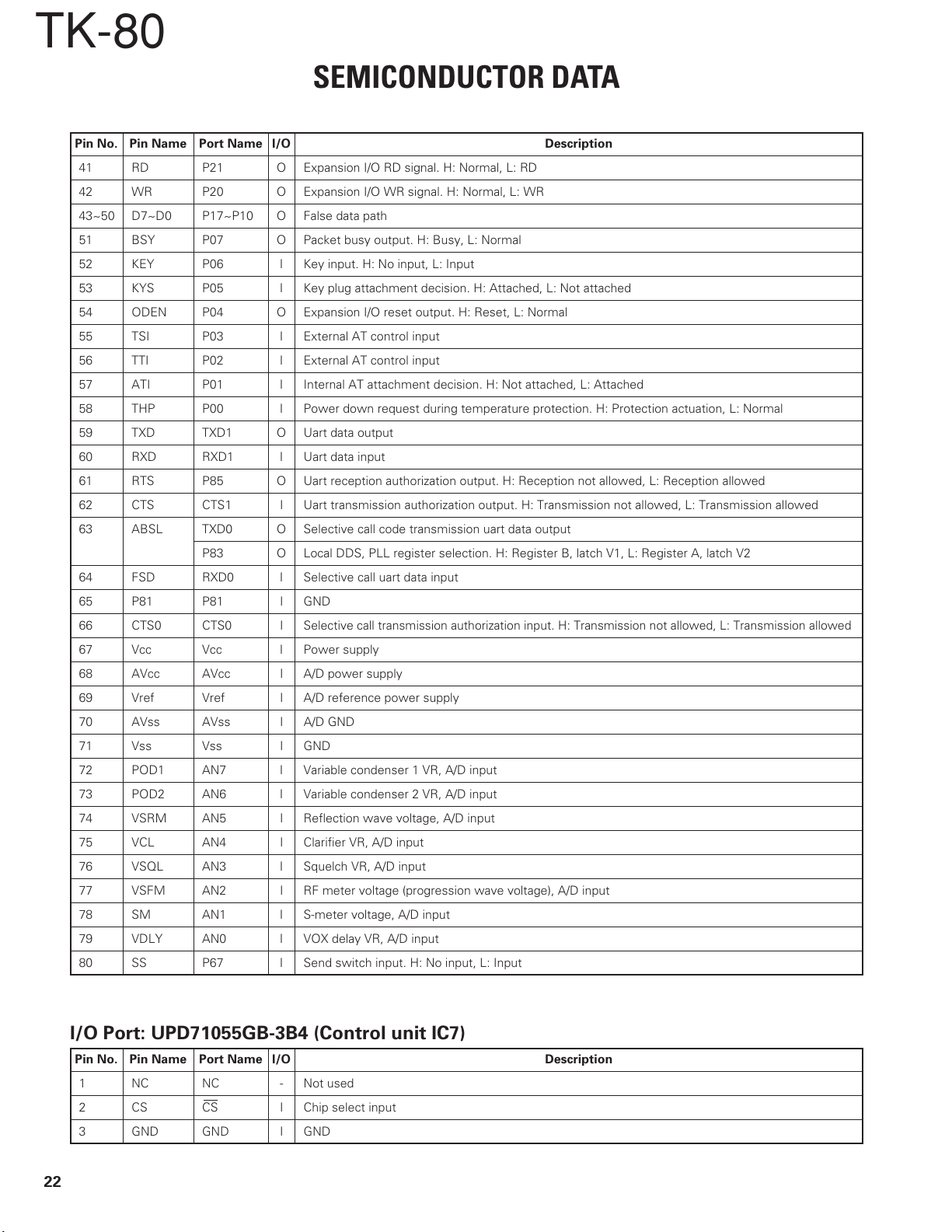
TK-80
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA
Pin No. Pin Name Port Name I/O Description
41 RD P21 O Expansion I/O RD signal. H: Normal, L: RD
42 WR P20 O Expansion I/O WR signal. H: Normal, L: WR
43~50 D7~D0 P17~P10 O False data path
51 BSY P07 O Packet busy output. H: Busy, L: Normal
52 KEY P06 I Key input. H: No input, L: Input
53 KYS P05 I Key plug attachment decision. H: Attached, L: Not attached
54 ODEN P04 O Expansion I/O reset output. H: Reset, L: Normal
55 TSI P03 I External AT control input
56 TTI P02 I External AT control input
57 ATI P01 I Internal AT attachment decision. H: Not attached, L: Attached
58 THP P00 I Power down request during temperature protection. H: Protection actuation, L: Normal
59 TXD TXD1 O Uart data output
60 RXD RXD1 I Uart data input
61 RTS P85 O Uart reception authorization output. H: Reception not allowed, L: Reception allowed
62 CTS CTS1 I Uart transmission authorization output. H: Transmission not allowed, L: Transmission allowed
63 ABSL TXD0 O Selective call code transmission uart data output
P83 O Local DDS, PLL register selection. H: Register B, latch V1, L: Register A, latch V2
64 FSD RXD0 I Selective call uart data input
65 P81 P81 I GND
66 CTS0 CTS0 I
67 Vcc Vcc I Power supply
68 AVcc AVcc I A/D power supply
69 Vref Vref I A/D reference power supply
70 AVss AVss I A/D GND
71 Vss Vss I GND
72 POD1 AN7 I Variable condenser 1 VR, A/D input
73 POD2 AN6 I Variable condenser 2 VR, A/D input
74 VSRM AN5 I Reflection wave voltage, A/D input
75 VCL AN4 I Clarifier VR, A/D input
76 VSQL AN3 I Squelch VR, A/D input
77 VSFM AN2 I RF meter voltage (progression wave voltage), A/D input
78 SM AN1 I S-meter voltage, A/D input
79 VDLY AN0 I VOX delay VR, A/D input
80 SS P67 I Send switch input. H: No input, L: Input
Selective call transmission authorization input. H: Transmission not allowed, L: Transmission allowed
I/O Port: UPD71055GB-3B4 (Control unit IC7)
Pin No. Pin Name Port Name I/O Description
1NCNC-Not used
2CSCSIChip select input
3 GND GND I GND
22
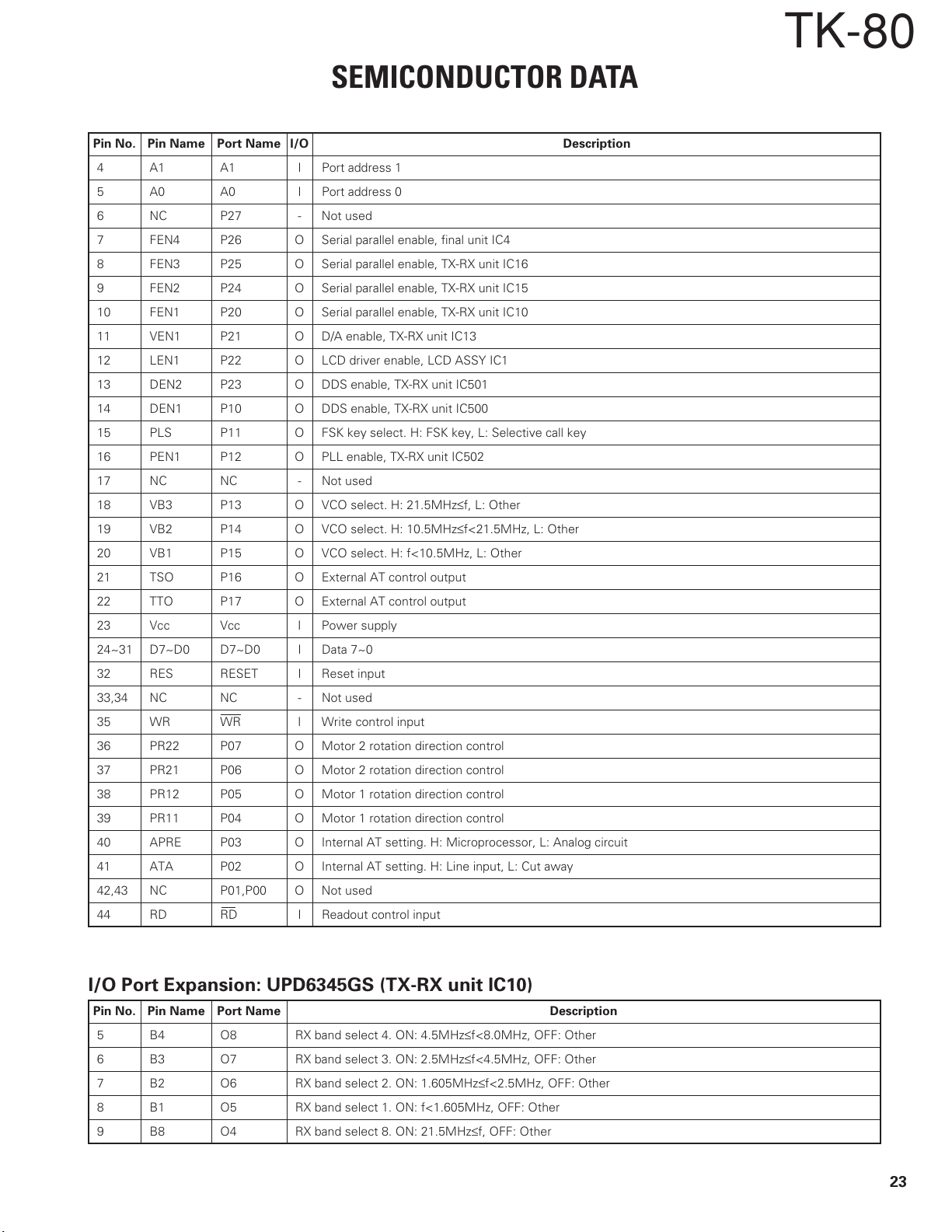
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA
Pin No. Pin Name Port Name I/O Description
4A1A1IPort address 1
5A0A0IPort address 0
6NC P27 - Not used
7FEN4 P26 O Serial parallel enable, final unit IC4
8FEN3 P25 O Serial parallel enable, TX-RX unit IC16
9FEN2 P24 O Serial parallel enable, TX-RX unit IC15
10 FEN1 P20 O Serial parallel enable, TX-RX unit IC10
11 VEN1 P21 O D/A enable, TX-RX unit IC13
12 LEN1 P22 O LCD driver enable, LCD ASSY IC1
13 DEN2 P23 O DDS enable, TX-RX unit IC501
14 DEN1 P10 O DDS enable, TX-RX unit IC500
15 PLS P11 O FSK key select. H: FSK key, L: Selective call key
16 PEN1 P12 O PLL enable, TX-RX unit IC502
17 NC NC - Not used
18 VB3 P13 O VCO select. H: 21.5MHz≤f, L: Other
19 VB2 P14 O VCO select. H: 10.5MHz≤f<21.5MHz, L: Other
20 VB1 P15 O VCO select. H: f<10.5MHz, L: Other
21 TSO P16 O External AT control output
22 TTO P17 O External AT control output
23 Vcc Vcc I Power supply
24~31 D7~D0 D7~D0 I Data 7~0
32 RES RESET I Reset input
33,34 NC NC - Not used
35 WR WR I Write control input
36 PR22 P07 O Motor 2 rotation direction control
37 PR21 P06 O Motor 2 rotation direction control
38 PR12 P05 O Motor 1 rotation direction control
39 PR11 P04 O Motor 1 rotation direction control
40 APRE P03 O Internal AT setting. H: Microprocessor, L: Analog circuit
41 ATA P02 O Internal AT setting. H: Line input, L: Cut away
42,43 NC P01,P00 O Not used
44 RD RD I Readout control input
TK-80
I/O Port Expansion: UPD6345GS (TX-RX unit IC10)
Pin No. Pin Name Port Name Description
5B4O8 RX band select 4. ON: 4.5MHz≤f<8.0MHz, OFF: Other
6B3O7 RX band select 3. ON: 2.5MHz≤f<4.5MHz, OFF: Other
7B2O6 RX band select 2. ON: 1.605MHz≤f<2.5MHz, OFF: Other
8B1O5 RX band select 1. ON: f<1.605MHz, OFF: Other
9B8O4 RX band select 8. ON: 21.5MHz≤f, OFF: Other
23
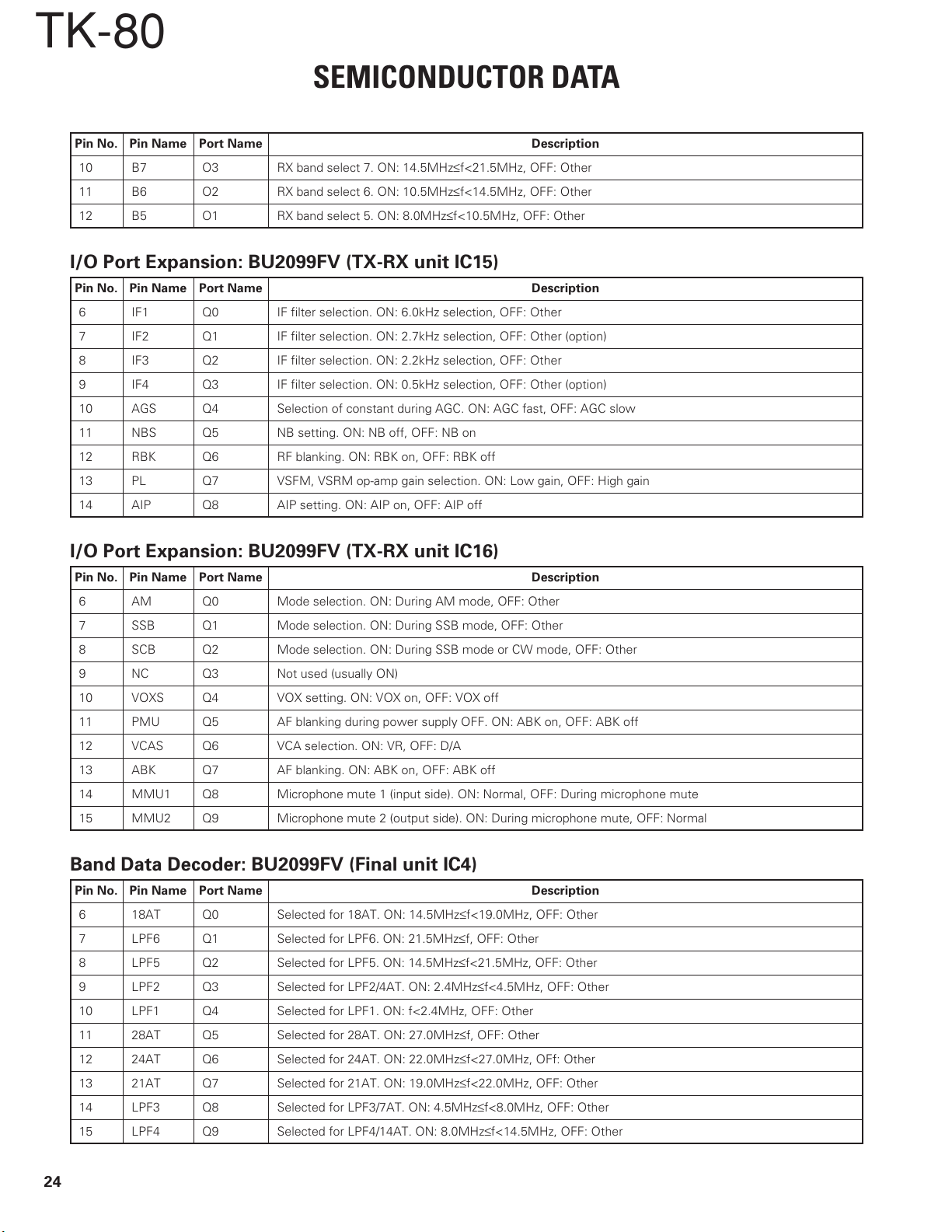
TK-80
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA
Pin No. Pin Name Port Name Description
10 B7 O3 RX band select 7. ON: 14.5MHz≤f<21.5MHz, OFF: Other
11 B6 O2 RX band select 6. ON: 10.5MHz≤f<14.5MHz, OFF: Other
12 B5 O1 RX band select 5. ON: 8.0MHz≤f<10.5MHz, OFF: Other
I/O Port Expansion: BU2099FV (TX-RX unit IC15)
Pin No. Pin Name Port Name Description
6 IF1 Q0 IF filter selection. ON: 6.0kHz selection, OFF: Other
7 IF2 Q1 IF filter selection. ON: 2.7kHz selection, OFF: Other (option)
8 IF3 Q2 IF filter selection. ON: 2.2kHz selection, OFF: Other
9 IF4 Q3 IF filter selection. ON: 0.5kHz selection, OFF: Other (option)
10 AGS Q4 Selection of constant during AGC. ON: AGC fast, OFF: AGC slow
11 NBS Q5 NB setting. ON: NB off, OFF: NB on
12 RBK Q6 RF blanking. ON: RBK on, OFF: RBK off
13 PL Q7 VSFM, VSRM op-amp gain selection. ON: Low gain, OFF: High gain
14 AIP Q8 AIP setting. ON: AIP on, OFF: AIP off
I/O Port Expansion: BU2099FV (TX-RX unit IC16)
Pin No. Pin Name Port Name Description
6AMQ0 Mode selection. ON: During AM mode, OFF: Other
7 SSB Q1 Mode selection. ON: During SSB mode, OFF: Other
8 SCB Q2 Mode selection. ON: During SSB mode or CW mode, OFF: Other
9NCQ3 Not used (usually ON)
10 VOXS Q4 VOX setting. ON: VOX on, OFF: VOX off
11 PMU Q5 AF blanking during power supply OFF. ON: ABK on, OFF: ABK off
12 VCAS Q6 VCA selection. ON: VR, OFF: D/A
13 ABK Q7 AF blanking. ON: ABK on, OFF: ABK off
14 MMU1 Q8 Microphone mute 1 (input side). ON: Normal, OFF: During microphone mute
15 MMU2 Q9 Microphone mute 2 (output side). ON: During microphone mute, OFF: Normal
Band Data Decoder: BU2099FV (Final unit IC4)
Pin No. Pin Name Port Name Description
6 18AT Q0 Selected for 18AT. ON: 14.5MHz≤f<19.0MHz, OFF: Other
7 LPF6 Q1 Selected for LPF6. ON: 21.5MHz≤f, OFF: Other
8 LPF5 Q2 Selected for LPF5. ON: 14.5MHz≤f<21.5MHz, OFF: Other
9 LPF2 Q3 Selected for LPF2/4AT. ON: 2.4MHz≤f<4.5MHz, OFF: Other
10 LPF1 Q4 Selected for LPF1. ON: f<2.4MHz, OFF: Other
11 28AT Q5 Selected for 28AT. ON: 27.0MHz≤f, OFF: Other
12 24AT Q6 Selected for 24AT. ON: 22.0MHz≤f<27.0MHz, OFf: Other
13 21AT Q7 Selected for 21AT. ON: 19.0MHz≤f<22.0MHz, OFF: Other
14 LPF3 Q8 Selected for LPF3/7AT. ON: 4.5MHz≤f<8.0MHz, OFF: Other
15 LPF4 Q9 Selected for LPF4/14AT. ON: 8.0MHz≤f<14.5MHz, OFF: Other
24
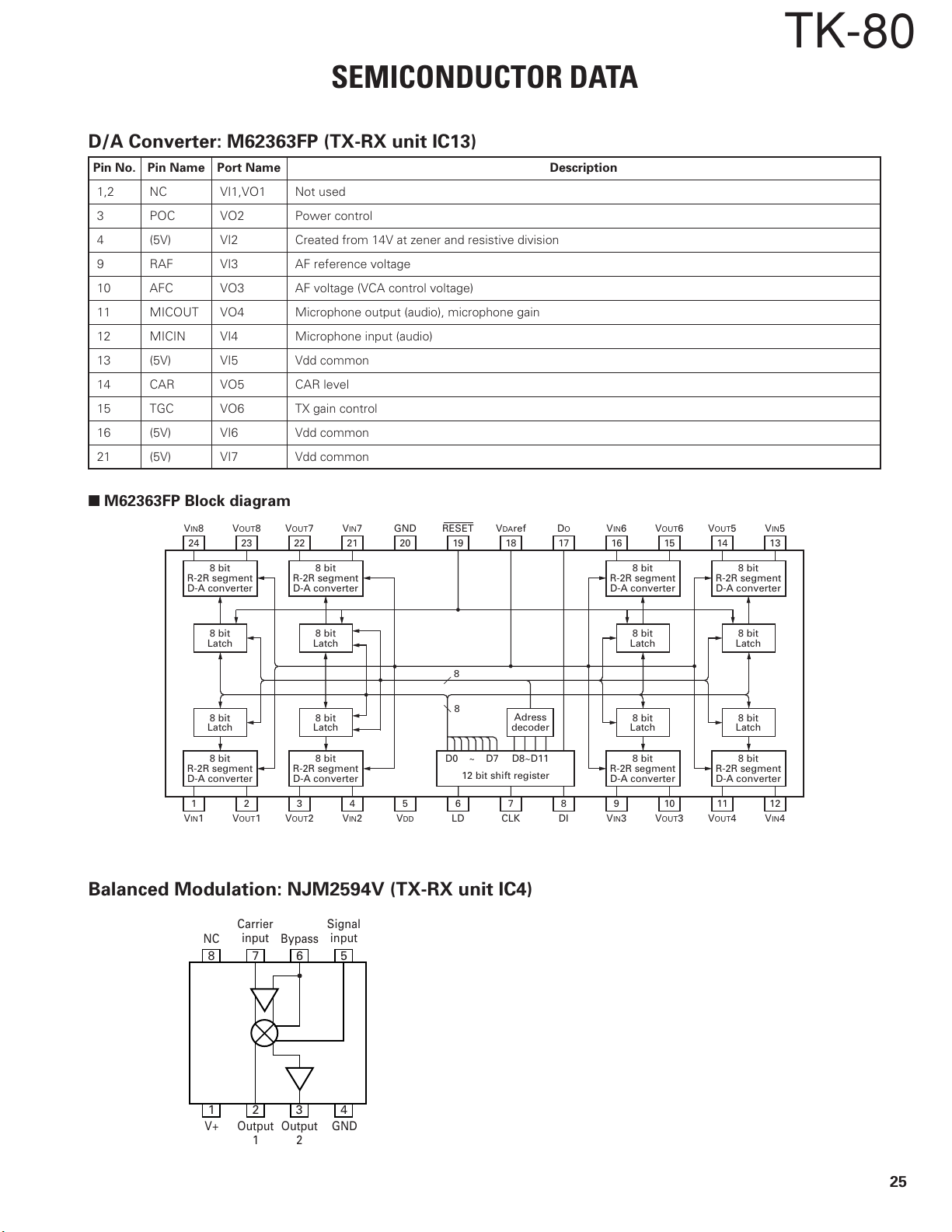
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA
D/A Converter: M62363FP (TX-RX unit IC13)
Pin No. Pin Name Port Name Description
1,2 NC VI1,VO1 Not used
3 POC VO2 Power control
4 (5V) VI2 Created from 14V at zener and resistive division
9 RAF VI3 AF reference voltage
10 AFC VO3 AF voltage (VCA control voltage)
11 MICOUT VO4 Microphone output (audio), microphone gain
12 MICIN VI4 Microphone input (audio)
13 (5V) VI5 Vdd common
14 CAR VO5 CAR level
15 TGC VO6 TX gain control
16 (5V) VI6 Vdd common
21 (5V) VI7 Vdd common
TK-80
■ M62363FP Block diagram
IN8
V
24
R-2R segment
D-A converter
R-2R segment
D-A converter
1
V
IN1
8 bit
8 bit
Latch
8 bit
Latch
8 bit
V
V
OUT8
23
2
OUT1
OUT7
V
22
8 bit
R-2R segment
D-A converter
8 bit
Latch
8 bit
Latch
8 bit
R-2R segment
D-A converter
3
V
OUT2
IN7
V
V
GND19RESET18V
21
4
IN2
V
20
5
DD
8
8
D0 ~ D7 D8~D11
6
LD
DAref
Adress
decoder
12 bit shift register
7
CLK
Balanced Modulation: NJM2594V (TX-RX unit IC4)
Carrier
input
NC Bypass
8
7 6 5
Signal
input
O
D
17
8
DI
IN6
V
16
8 bit
R-2R segment
D-A converter
8 bit
Latch
8 bit
Latch
8 bit
R-2R segment
D-A converter
9
V
IN3
V
V
OUT6
15
10
OUT3
OUT5
V
14
8 bit
R-2R segment
D-A converter
8 bit
Latch
8 bit
Latch
8 bit
R-2R segment
D-A converter
11
V
OUT4
IN5
V
13
12
V
IN4
1234
V+ Output1Output2GND
25
TK-80
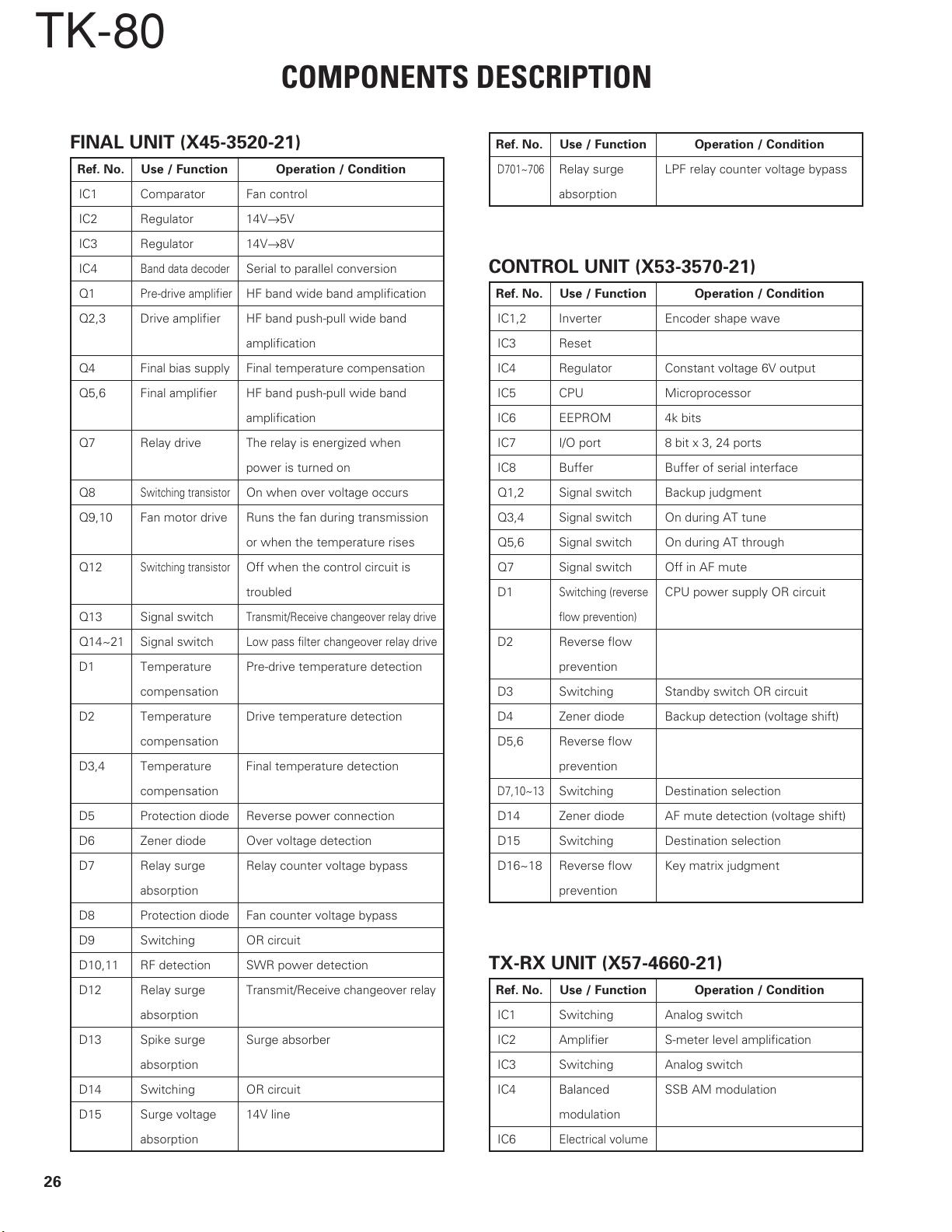
COMPONENTS DESCRIPTION
FINAL UNIT (X45-3520-21)
Ref. No. Use / Function Operation / Condition
IC1 Comparator Fan control
IC2 Regulator 14V→5V
IC3 Regulator 14V→8V
IC4
Q1
Q2,3 Drive amplifier HF band push-pull wide band
Q4
Q5,6 Final amplifier HF band push-pull wide band
Q7 Relay drive The relay is energized when
Q8
Q9,10 Fan motor drive Runs the fan during transmission
Q12
Q13 Signal switch
Q14~21 Signal switch
D1 Temperature Pre-drive temperature detection
D2 Temperature Drive temperature detection
D3,4 Temperature Final temperature detection
D5
D6 Zener diode Over voltage detection
D7 Relay surge Relay counter voltage bypass
D8
D9 Switching OR circuit
D10,11 RF detection SWR power detection
D12 Relay surge
D13 Spike surge Surge absorber
D14 Switching OR circuit
D15 Surge voltage 14V line
Band data decoder
Pre-drive amplifier
Final bias supply
Switching transistor
Switching transistor
compensation
compensation
compensation
Protection diode
absorption
Protection diode
absorption
absorption
absorption
Serial to parallel conversion
HF band wide band amplification
amplification
Final temperature compensation
amplification
power is turned on
On when over voltage occurs
or when the temperature rises
Off when the control circuit is
troubled
Transmit/Receive changeover relay drive
Low pass filter changeover relay drive
Reverse power connection
Fan counter voltage bypass
Transmit/Receive changeover relay
Ref. No. Use / Function Operation / Condition
D701~706
Relay surge LPF relay counter voltage bypass
absorption
CONTROL UNIT (X53-3570-21)
Ref. No. Use / Function Operation / Condition
IC1,2 Inverter Encoder shape wave
IC3 Reset
IC4 Regulator Constant voltage 6V output
IC5 CPU Microprocessor
IC6 EEPROM 4k bits
IC7 I/O port 8 bit x 3, 24 ports
IC8 Buffer Buffer of serial interface
Q1,2 Signal switch Backup judgment
Q3,4 Signal switch On during AT tune
Q5,6 Signal switch On during AT through
Q7 Signal switch Off in AF mute
D1
D2 Reverse flow
D3 Switching Standby switch OR circuit
D4 Zener diode Backup detection (voltage shift)
D5,6 Reverse flow
D7,10~13
D14 Zener diode AF mute detection (voltage shift)
D15 Switching Destination selection
D16~18 Reverse flow Key matrix judgment
Switching (reverse
flow prevention)
prevention
prevention
Switching Destination selection
prevention
CPU power supply OR circuit
TX-RX UNIT (X57-4660-21)
Ref. No. Use / Function Operation / Condition
IC1 Switching Analog switch
IC2 Amplifier S-meter level amplification
IC3 Switching Analog switch
IC4 Balanced SSB AM modulation
modulation
IC6
Electrical volume
26
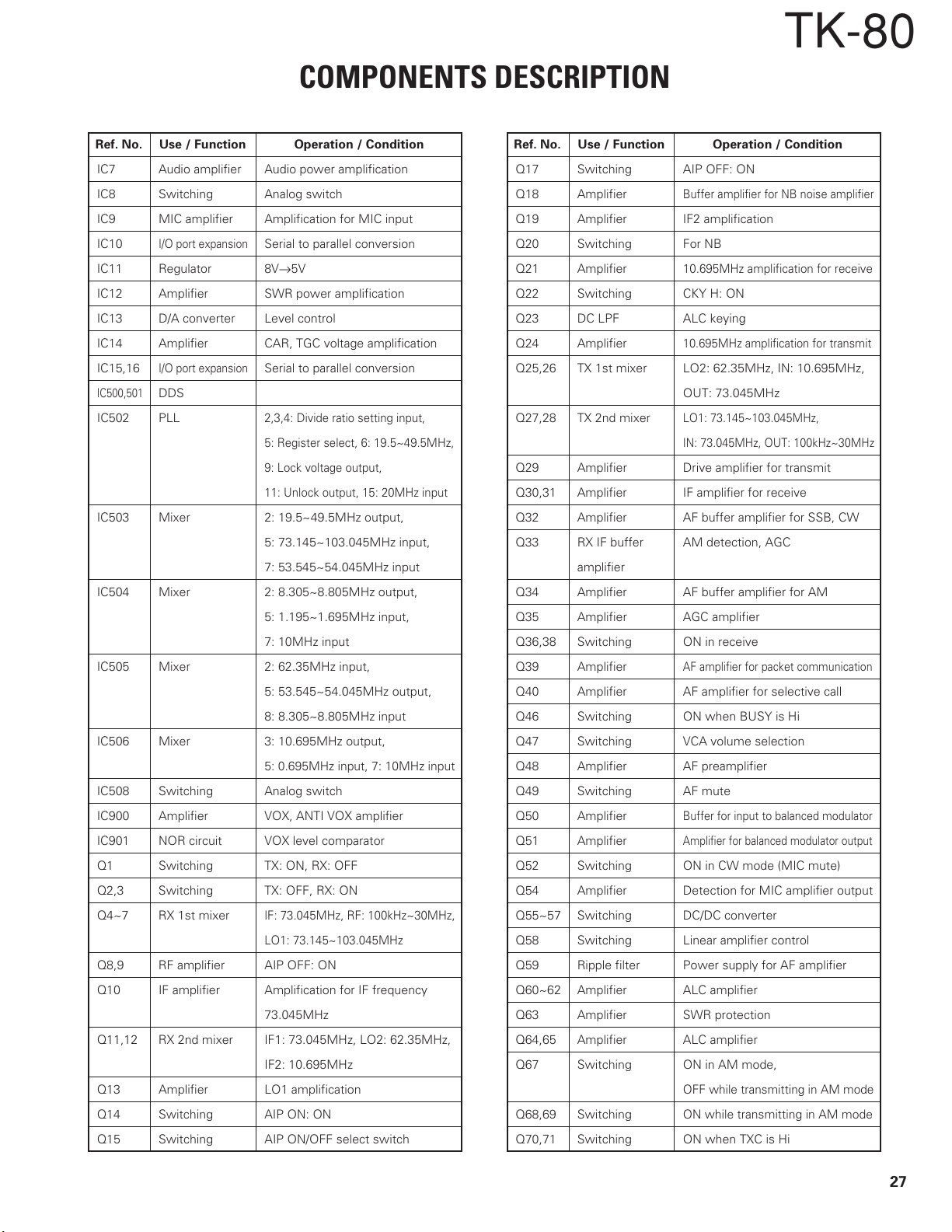
COMPONENTS DESCRIPTION
TK-80
Ref. No. Use / Function Operation / Condition
IC7 Audio amplifier Audio power amplification
IC8 Switching Analog switch
IC9 MIC amplifier Amplification for MIC input
IC10
IC11 Regulator 8V→5V
IC12 Amplifier SWR power amplification
IC13 D/A converter Level control
IC14 Amplifier CAR, TGC voltage amplification
IC15,16
IC500,501
IC502 PLL
IC503 Mixer 2: 19.5~49.5MHz output,
IC504 Mixer 2: 8.305~8.805MHz output,
IC505 Mixer 2: 62.35MHz input,
IC506 Mixer 3: 10.695MHz output,
IC508 Switching Analog switch
IC900 Amplifier VOX, ANTI VOX amplifier
IC901 NOR circuit VOX level comparator
Q1 Switching TX: ON, RX: OFF
Q2,3 Switching TX: OFF, RX: ON
Q4~7 RX 1st mixer
Q8,9 RF amplifier AIP OFF: ON
Q10 IF amplifier Amplification for IF frequency
Q11,12 RX 2nd mixer IF1: 73.045MHz, LO2: 62.35MHz,
Q13 Amplifier LO1 amplification
Q14 Switching AIP ON: ON
Q15 Switching AIP ON/OFF select switch
I/O port expansion
I/O port expansion
DDS
Serial to parallel conversion
Serial to parallel conversion
2,3,4: Divide ratio setting input,
5: Register select, 6: 19.5~49.5MHz,
9: Lock voltage output,
11: Unlock output, 15: 20MHz input
5: 73.145~103.045MHz input,
7: 53.545~54.045MHz input
5: 1.195~1.695MHz input,
7: 10MHz input
5: 53.545~54.045MHz output,
8: 8.305~8.805MHz input
5: 0.695MHz input, 7: 10MHz input
I
F: 73.045MHz, RF: 100kHz~30MHz,
LO1: 73.145~103.045MHz
73.045MHz
IF2: 10.695MHz
Ref. No. Use / Function Operation / Condition
Q17 Switching AIP OFF: ON
Q18 Amplifier
Q19 Amplifier IF2 amplification
Q20 Switching For NB
Q21 Amplifier
Q22 Switching CKY H: ON
Q23 DC LPF ALC keying
Q24 Amplifier
Q25,26 TX 1st mixer LO2: 62.35MHz, IN: 10.695MHz,
Q27,28 TX 2nd mixer
Q29 Amplifier Drive amplifier for transmit
Q30,31 Amplifier IF amplifier for receive
Q32 Amplifier AF buffer amplifier for SSB, CW
Q33 RX IF buffer AM detection, AGC
amplifier
Q34 Amplifier AF buffer amplifier for AM
Q35 Amplifier AGC amplifier
Q36,38 Switching ON in receive
Q39 Amplifier
Q40 Amplifier AF amplifier for selective call
Q46 Switching ON when BUSY is Hi
Q47 Switching VCA volume selection
Q48 Amplifier AF preamplifier
Q49 Switching AF mute
Q50 Amplifier
Q51 Amplifier
Q52 Switching ON in CW mode (MIC mute)
Q54 Amplifier Detection for MIC amplifier output
Q55~57 Switching DC/DC converter
Q58 Switching Linear amplifier control
Q59 Ripple filter Power supply for AF amplifier
Q60~62 Amplifier ALC amplifier
Q63 Amplifier SWR protection
Q64,65 Amplifier ALC amplifier
Q67 Switching ON in AM mode,
Q68,69 Switching
Q70,71 Switching ON when TXC is Hi
Buffer amplifier for NB noise amplifier
10.695MHz amplification for receive
10.695MHz amplification for transmit
OUT: 73.045MHz
LO1: 73.145~103.045MHz,
IN: 73.045MHz, OUT: 100kHz~30MHz
AF amplifier for packet communication
Buffer for input to balanced modulator
Amplifier for balanced modulator output
OFF while transmitting in AM mode
ON while transmitting in AM mode
27
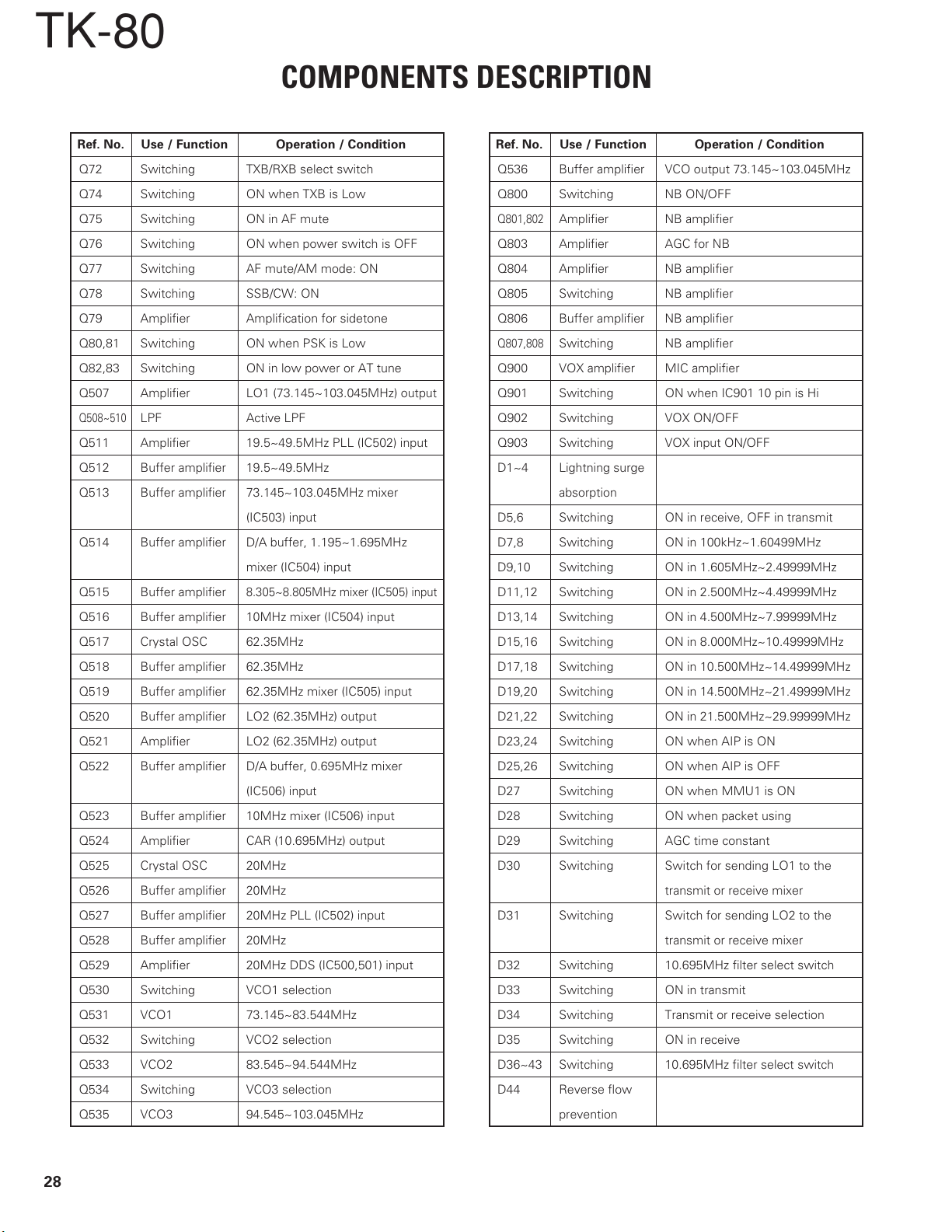
TK-80
COMPONENTS DESCRIPTION
Ref. No. Use / Function Operation / Condition
Q72 Switching TXB/RXB select switch
Q74 Switching ON when TXB is Low
Q75 Switching ON in AF mute
Q76 Switching ON when power switch is OFF
Q77 Switching AF mute/AM mode: ON
Q78 Switching SSB/CW: ON
Q79 Amplifier Amplification for sidetone
Q80,81 Switching ON when PSK is Low
Q82,83 Switching ON in low power or AT tune
Q507 Amplifier LO1 (73.145~103.045MHz) output
Q508~510
Q511 Amplifier 19.5~49.5MHz PLL (IC502) input
Q512 Buffer amplifier 19.5~49.5MHz
Q513 Buffer amplifier 73.145~103.045MHz mixer
Q514 Buffer amplifier D/A buffer, 1.195~1.695MHz
Q515 Buffer amplifier
Q516 Buffer amplifier 10MHz mixer (IC504) input
Q517 Crystal OSC 62.35MHz
Q518 Buffer amplifier 62.35MHz
Q519 Buffer amplifier 62.35MHz mixer (IC505) input
Q520 Buffer amplifier LO2 (62.35MHz) output
Q521 Amplifier LO2 (62.35MHz) output
Q522 Buffer amplifier D/A buffer, 0.695MHz mixer
Q523 Buffer amplifier 10MHz mixer (IC506) input
Q524 Amplifier CAR (10.695MHz) output
Q525 Crystal OSC 20MHz
Q526 Buffer amplifier 20MHz
Q527 Buffer amplifier 20MHz PLL (IC502) input
Q528 Buffer amplifier 20MHz
Q529 Amplifier 20MHz DDS (IC500,501) input
Q530 Switching VCO1 selection
Q531 VCO1 73.145~83.544MHz
Q532 Switching VCO2 selection
Q533 VCO2 83.545~94.544MHz
Q534 Switching VCO3 selection
Q535 VCO3 94.545~103.045MHz
LPF Active LPF
(IC503) input
mixer (IC504) input
8.305~8.805MHz mixer (IC505) input
(IC506) input
Ref. No. Use / Function Operation / Condition
Q536 Buffer amplifier VCO output 73.145~103.045MHz
Q800 Switching NB ON/OFF
Q801,802
Q803 Amplifier AGC for NB
Q804 Amplifier NB amplifier
Q805 Switching NB amplifier
Q806 Buffer amplifier NB amplifier
Q807,808
Q900 VOX amplifier MIC amplifier
Q901 Switching ON when IC901 10 pin is Hi
Q902 Switching VOX ON/OFF
Q903 Switching VOX input ON/OFF
D1~4 Lightning surge
D5,6 Switching ON in receive, OFF in transmit
D7,8 Switching ON in 100kHz~1.60499MHz
D9,10 Switching ON in 1.605MHz~2.49999MHz
D11,12 Switching ON in 2.500MHz~4.49999MHz
D13,14 Switching ON in 4.500MHz~7.99999MHz
D15,16 Switching ON in 8.000MHz~10.49999MHz
D17,18 Switching ON in 10.500MHz~14.49999MHz
D19,20 Switching ON in 14.500MHz~21.49999MHz
D21,22 Switching ON in 21.500MHz~29.99999MHz
D23,24 Switching ON when AIP is ON
D25,26 Switching ON when AIP is OFF
D27 Switching ON when MMU1 is ON
D28 Switching ON when packet using
D29 Switching AGC time constant
D30 Switching Switch for sending LO1 to the
D31 Switching Switch for sending LO2 to the
D32 Switching 10.695MHz filter select switch
D33 Switching ON in transmit
D34 Switching Transmit or receive selection
D35 Switching ON in receive
D36~43 Switching 10.695MHz filter select switch
D44 Reverse flow
Amplifier NB amplifier
Switching NB amplifier
absorption
transmit or receive mixer
transmit or receive mixer
prevention
28
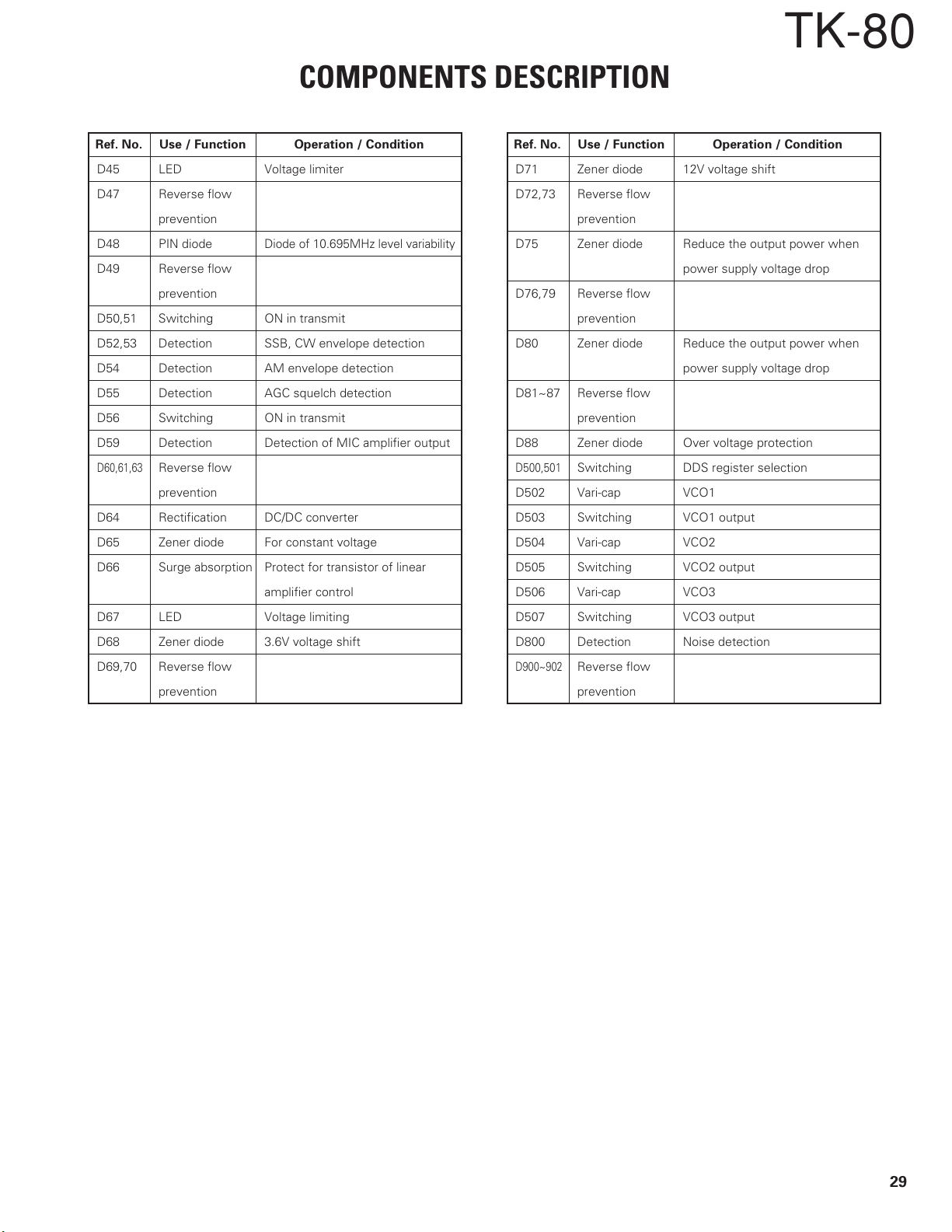
COMPONENTS DESCRIPTION
TK-80
Ref. No. Use / Function Operation / Condition
D45 LED Voltage limiter
D47 Reverse flow
prevention
D48 PIN diode
D49 Reverse flow
prevention
D50,51 Switching ON in transmit
D52,53 Detection SSB, CW envelope detection
D54 Detection AM envelope detection
D55 Detection AGC squelch detection
D56 Switching ON in transmit
D59 Detection Detection of MIC amplifier output
D60,61,63
D64 Rectification DC/DC converter
D65 Zener diode For constant voltage
D66 Surge absorption Protect for transistor of linear
D67 LED Voltage limiting
D68 Zener diode 3.6V voltage shift
D69,70 Reverse flow
Reverse flow
prevention
prevention
Diode of 10.695MHz level variability
amplifier control
Ref. No. Use / Function Operation / Condition
D71 Zener diode 12V voltage shift
D72,73 Reverse flow
prevention
D75 Zener diode Reduce the output power when
power supply voltage drop
D76,79 Reverse flow
prevention
D80 Zener diode Reduce the output power when
power supply voltage drop
D81~87 Reverse flow
prevention
D88 Zener diode Over voltage protection
D500,501
D502 Vari-cap VCO1
D503 Switching VCO1 output
D504 Vari-cap VCO2
D505 Switching VCO2 output
D506 Vari-cap VCO3
D507 Switching VCO3 output
D800 Detection Noise detection
D900~902
Switching DDS register selection
Reverse flow
prevention
29
 Loading...
Loading...